Page 1

VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation
Instructions
MS-VMA1615, MS-VMA1626, MS-VMA1628, MS-VMA1630
(barcode for factory use only)
Part No. 24-10143-217, Rev. J
Issued April 2018
Refer to the QuickLIT website for the most up-to-date version of this document.
Applications
The VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 programmable digital
controllers are designed for VAV applications that
communicate through the BACnet® MS/TP or N2
protocol. These VMA controllers feature combinations of
an integral digital pressure sensor (DPT), a damper
actuator, and a 32-bit microprocessor. The VMA1626 has
an actuator but does not contain a DPT. The VMA1628
model has a DPT but does not contain an actuator. The
controllers' small package size facilitates quick field
installation and efficient use of space without
compromising high-tech control performance. These VMA
controllers connect easily to the wired and wireless
network sensors for zone and discharge air temperature
sensing.
Switchable Communications
Protocols
The Metasys® system FEC Family Controllers and
network sensors communicate using either the standard
BACnet protocol, based on the ANSI/ASHRAE 135-2008,
or the BACnet/IP protocol. The BACnet protocol is a
standard for ANSI, ASHRAE, and the International
Standards Organization (ISO) for building controls.
The N2-capable FEC Family Controllers can be used as
functional replacements for legacy N2 controllers. The
N2-capable FEC Family Controllers:
• have the input and output (I/O) quantities and
characteristics of the FEC Family Controllers
• must be programmed with CCT, which has similar,
but not identical programming capabilities as
HVACPro, GX9100, GPL, and other legacy tools
• support SA Bus devices
• support WRZ wireless sensors from the controller
using the WRZ-7860 receiver (most models)
• are available in Buy American versions (most models)
The N2-capable FEC family controllers:
• do not support Zone Bus (for example, TMZ sensors
and M100 actuators) or XT-Bus (System 91) devices
(for example, XT, XTM, and XP modules)
• do not support a wireless connection to the N2 bus
• do not support NxE passthrough
North American Emissions
Compliance
FEC, VMA16, VMA18, and most IOM field controllers are
BTL-listed as BACnet Application Specific Controllers
(B-ASCs). FAC field controllers and the VMA1930 Field
Controller are BTL-listed as BACnet Advanced Application
Controllers (B-AACs).
Release 10.1 and later of the Controller Configuration
Tool (CCT) can be used to switch the Field Bus
communications protocol in supported FEC, FAC and
VMA controllers to be either the standard BACnet MS/TP
or the N2 protocol. All new controllers use either BACnet
MS/TP as the default communications protocol, or
BACnet/IP. Switchable communications protocols in the
MS/TP models provide a cost-effective upgrade and
modernization path for customers with existing N2
controllers.
United States
This equipment has been tested and found to comply
with the limits for a Class A digital device pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful
interference when this equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction
manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a
residential area may cause harmful interference, in which
case the users will be required to correct the interference
at their own expense.
1VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 2
Canada
This Class (A) digital apparatus meets all the
requirements of the Canadian Interference-Causing
Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la Classe (A) respecte toutes
les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel brouilleur
du Canada.
Installation
Observe these guidelines when installing a
VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 controller:
• Transport the VMA controller in the original container
to minimize vibration and shock damage to the VMA
controller.
• Do not drop the VMA controller or subject it to physical
shock.
Parts Included
• one VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 controller with
removable SA bus and power terminal blocks
• one installation instructions sheet
• one self-drilling No. 10 x 25 mm (1 in.) screw
Materials and Special Tools Needed
• several 6 mm (1/4 in.) female spade terminals for
input and output wiring, and crimping tool for spade
mounted terminal blocks
• small, straight-blade screwdriver for securing wires
in the terminal blocks
• 8 mm (5/16 in.) wrench or 10 mm (3/8 in.) 12-point
socket to tighten the square coupler bolt
• several shims or washers to mount the VMA
• power screwdriver, 100 mm (4 in.) extension socket,
punch, drill, and 3.5 mm (9/64 in.) drill bits to mount
the VMA
• pliers to open and close the damper
• required length of 3.97 mm (5/32 in.) ID pneumatic
tubing and barbed fittings
Mounting
Observe these guidelines when mounting a VMA:
Important: When the air supply to the VAV box is below
10°C (50°F), make sure that any
condensation on the VAV box, particularly
on the damper shaft, does not enter the
VMA electronics. Mount the VMA vertically
above the damper shaft to allow any shaft
condensation to fall away from the VMA.
Additional measures may be required in
some installations.
• Ensure that the mounting surface can support the
VMA and any user-supplied enclosure.
• Mount the VMA on a hard, even surface whenever
possible.
• Use shims or washers to mount the VMA securely
and evenly on the mounting surface.
• Mount the VMA in an area free of corrosive vapors
that matches the ambient conditions specified in the
Technical Specifications section.
• Provide sufficient space around the VMA for cable
and wire connections and adequate ventilation
through the controller (at least 50 mm [2 in.] on the
top, bottom, sides, and front of the controllers).
• Do not mount the VMA in areas where
electromagnetic emissions from other devices or
wiring can interfere with controller communication.
• Avoid mounting the VMA on surfaces with excessive
vibration.
• When using the VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 to replace
a VMA1610 or VMA1620 controller, plug the unused
open hole in the duct work from the original VMA
mounting if possible. Plug the hole using the sheet
metal screw from the original installation (preferred
option).
On panel or enclosure mount applications, observe these
additional guidelines:
• Do not install the VMA in an airtight enclosure.
• Mount the VMA so that the enclosure walls do not
obstruct cover removal or ventilation through the
controller.
• Mount the VMA so that the power transformer and
other devices do not radiate excessive heat to the
controller.
To mount the VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 controllers:
1. Set all the switches on the field controller to their
known settings.
2. Place the VMA controller in the proper mounting
position on the damper shaft so that the wiring
2VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 3
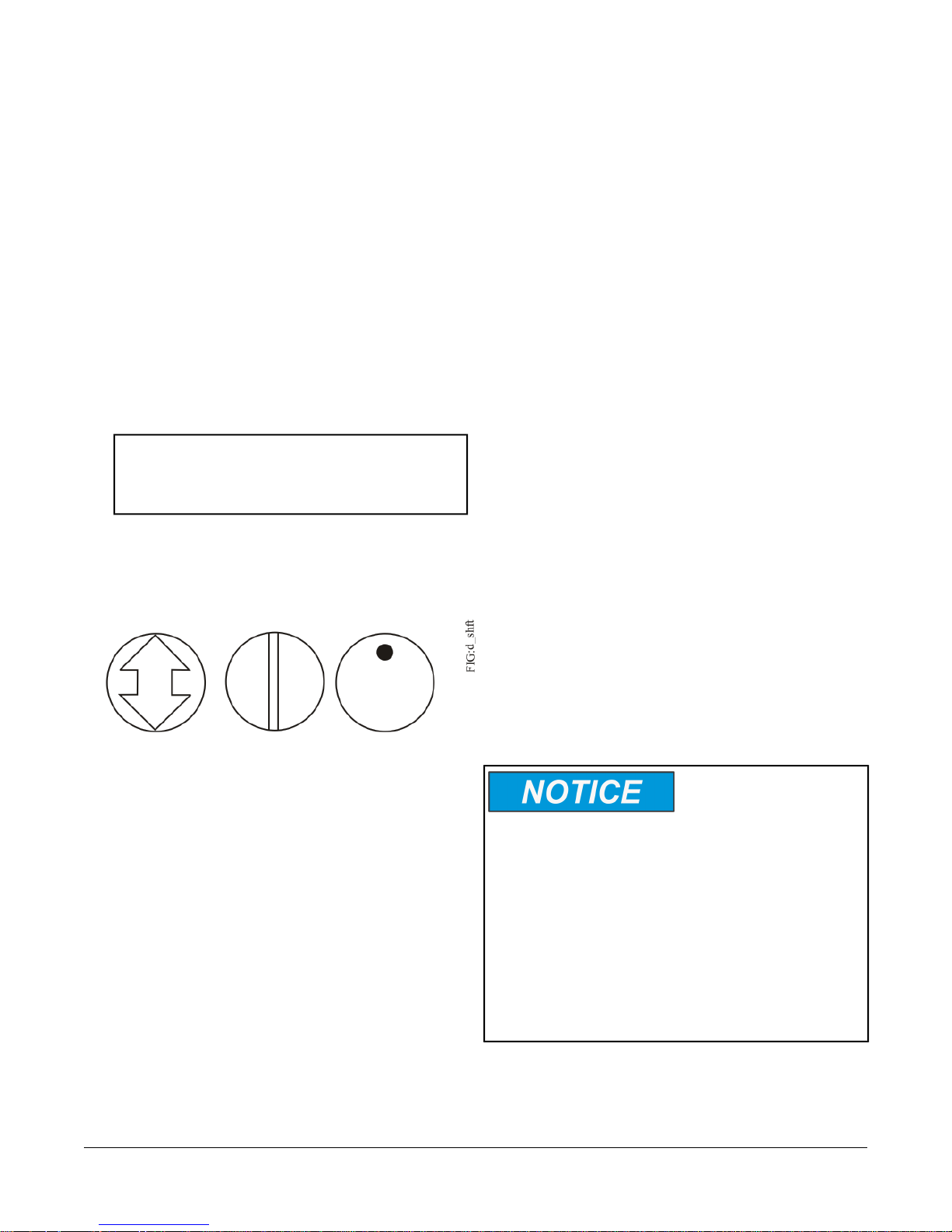
connections are easily accessible. Make sure the
VMA controller base is parallel to the VAV box
(perpendicular to the damper shaft). If needed, use
a spacer to offset tipping of the VMA controller
caused by the shaft bushings.
Note: Use the alignment marks to center the captive
spacer to ensure sufficient VMA movement
in either direction.
3. Secure the self-drilling No.10 screw through the
captive spacer (Figure 2) with a power screwdriver
and 100mm (4in.) extension socket. Otherwise, use
a punch to mark the position of the shoulder washer,
and then drill a hole into the VAV box using a 3.5mm
(9/64in.) drill bit. Insert the mounting screw and
tighten against the spacer. For the VMA1628 models,
use the additional 1.25 inch screw to mount to one
of the two holes provided near the actuator opening
(see Figure 2) to mount the controller.
Important: Do not overtighten the screw, or the
threads may strip. If mounting to the
VAV box, make sure the screws do not
interfere with damper blade movement.
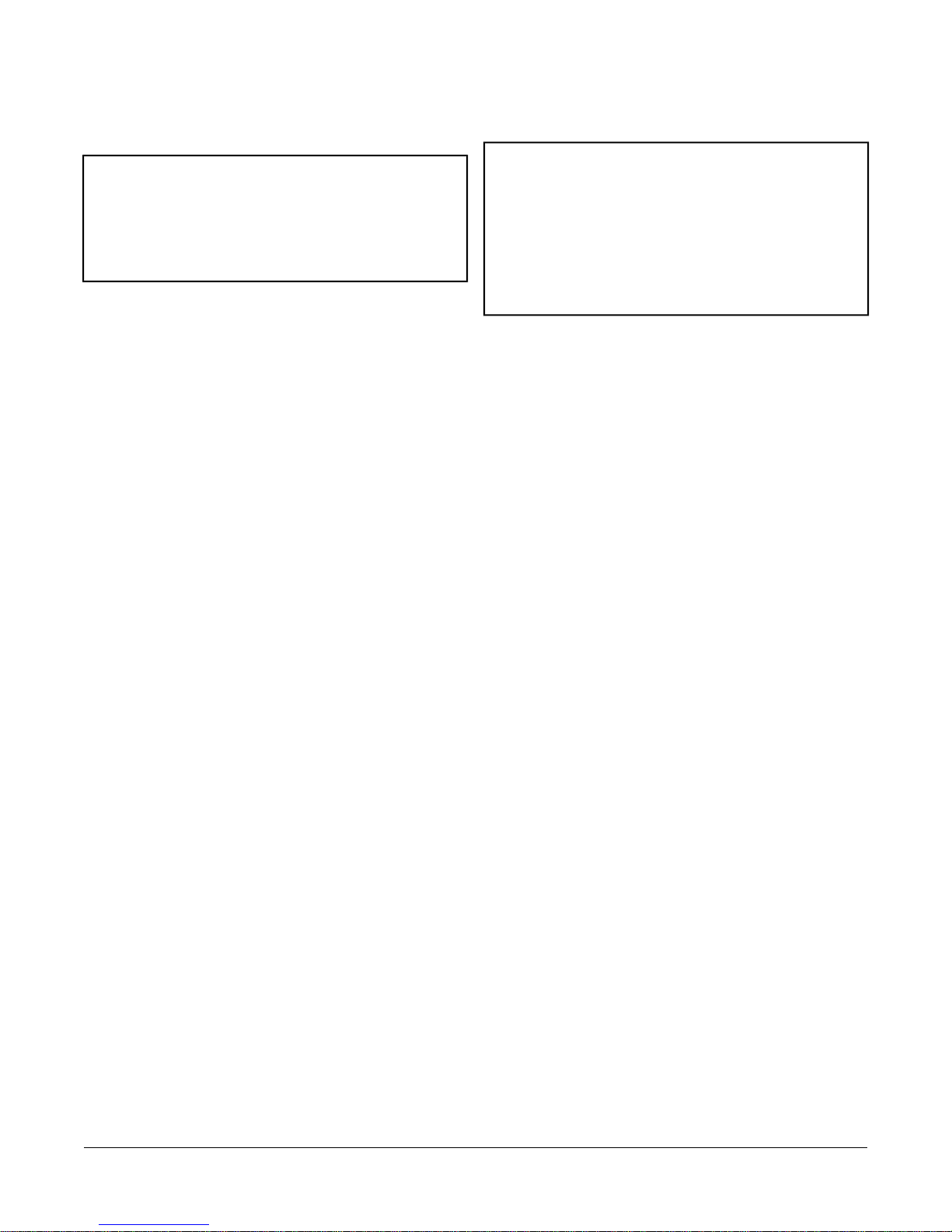
4. Locate the damper position using the typical marking
on the end of the damper shaft as shown in the figure
below.
Figure 1: Typical Damper End Shaft Icons
5. Note the direction, clockwise (CW) or
counterclockwise (CCW), required to close the
damper. Grasp the damper shaft firmly with pliers,
and either manually close the damper for 90° boxes
or manually open the damper for 45° or 60° boxes.
6. Push down and hold the Manual Override button
(Figure 2) and turn the VMA controller coupler until
it contacts the mechanical end-stop at either the
full-closed (90° boxes) or full-open (45° and 60°
boxes) position.
7. If the damper for a 90° box closes CCW, rotate the
coupler to the CCW mechanical limit. If the damper
for a 90° box closes CW, rotate the coupler to the
CW mechanical limit. The open end-stop is
automatically set for 90° boxes.
For 45° and 60° boxes, hard stops must be provided
at both full-closed and full-open damper positions.
By installing the VMA controller at the full-open
position, the VMA controller provides the open stop
for 45° and 60° boxes. The closed damper seal
provides the full-closed stop.
8. All models are compact in size and are easily
installed on VAV boxes. The VMA1615/1626/1630
models have either a round shaft up to 13 mm in
diameter or a 10 mm square shaft. Tighten the
square coupler bolt to the shaft using an 8 mm (5/16
in.) wrench or 10 mm (3/8 in.) 12-point socket.
Tighten to 10.5 to 11.5 N·m (95 to 105 lb·in).
9. Skip this step if you are installing the VMA1626
model. Loop the pneumatic tubing (supplied by field
personnel) to include a trap for condensation. Attach
the needed length of tubing (supplied and installed
by field personnel) to the dual port fitting on the VMA
controller and the other ends of the tubing to the
pressure transducer in the VAV box application
(Figure 2).
Note: The VMA uses a digital non-flow pressure
sensor (all models except the VMA1626) with
bidirectional flow operation, which allows you
to connect the high- and low-pressure DP
tubes to either barbed fitting on the VMA
controller. You do not need to make a specific
high- or low-side connection when you attach
the tubing to the barbed fittings on the VMA.
10. Push the Manual Override button, and turn the
actuator coupling manually to ensure that the
actuator can rotate from full-closed to full-open
positions without binding.
11. Complete the mounting by rotating the damper to
the full-open position.
Risk of Property Damage. Rotate the damper to the
full-open position before starting the air handler. Failure
to rotate the damper to the full-open position may result
in damage to the VAV box or ductwork when the air
handler is started.
Risque de dégâts matériels. Faire pivoter le registre
pour le placer en position d'ouverture complète avant
de démarrer l'unité de traitement d'air. Le non-respect
de cette directive risque d'endommager le caisson de
l'unité à volume d'air variable (VAV) ou le réseau de
conduites au démarrage de l'unité de traitement d'air.
3VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 4
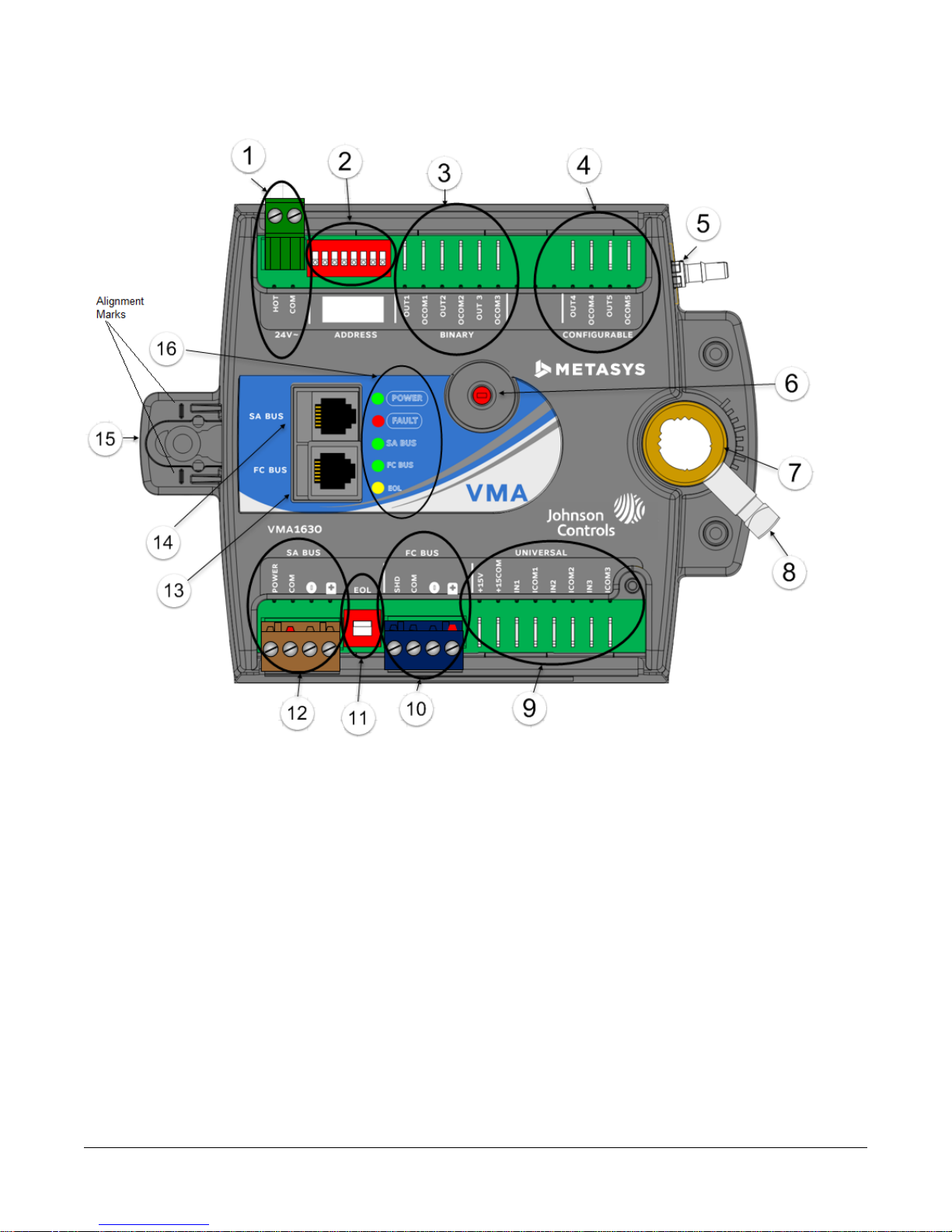
Figure 2: VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 Controller Wiring Terminations and Physical Features (VMA1630 Model
Shown)
4VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 5
Table 1: VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 Feature Callout Numbers and Descriptions
Physical Features: Description and ReferencesCallout
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
13
14
15
16
24 VAC, Class 2 Supply Power Terminal Block (see Supply Power Terminal Block)
Device Address DIP Switch Block (see Setting the Device Address)
Binary Outputs, 24 VAC Triacs (see Table 3)
Configurable Outputs: Voltage Analog Output (0–10 VDC) and Binary Output (24 VAC Triac)
(VMA1630, 1626, and 1628 (see Table 3)
Dual Port Fitting (see Figure 2)
Manual Override Button (see Mounting)
Coupler Bolt (see Mounting)
Controller Coupler (see Mounting)
Universal Input: Voltage Analog Input (0–10 VDC)
Resistive Analog Inputs (0–600k ohm) (see Table 3):
0–2k Potentiometer
RTD: 1k Nickel, 1k Platinum, or A99B SI
NTC: 10K Type L (10K Johnson Controls Type II is equivalent to Type L) or 2.252K Type II
Dry Contact Binary Input
FC Bus Terminal Block. May also be used for N2 connections. See FC Bus Terminal Block (Or
N2 Protocol As Required).
EOL (End-of-Line) Switch (see Setting the EOL Switch)
SA Bus Terminal Block12
Modular Port (FC Bus) RJ-12 6-Pin Modular Jack (see Modular Ports)
Modular Port (SA Bus) RJ-12 6-Pin Modular Jack (see Modular Ports)
Captive Spacer and Screw (see Figure 2)
LED Status Indicators (see Table 9)
5VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 6
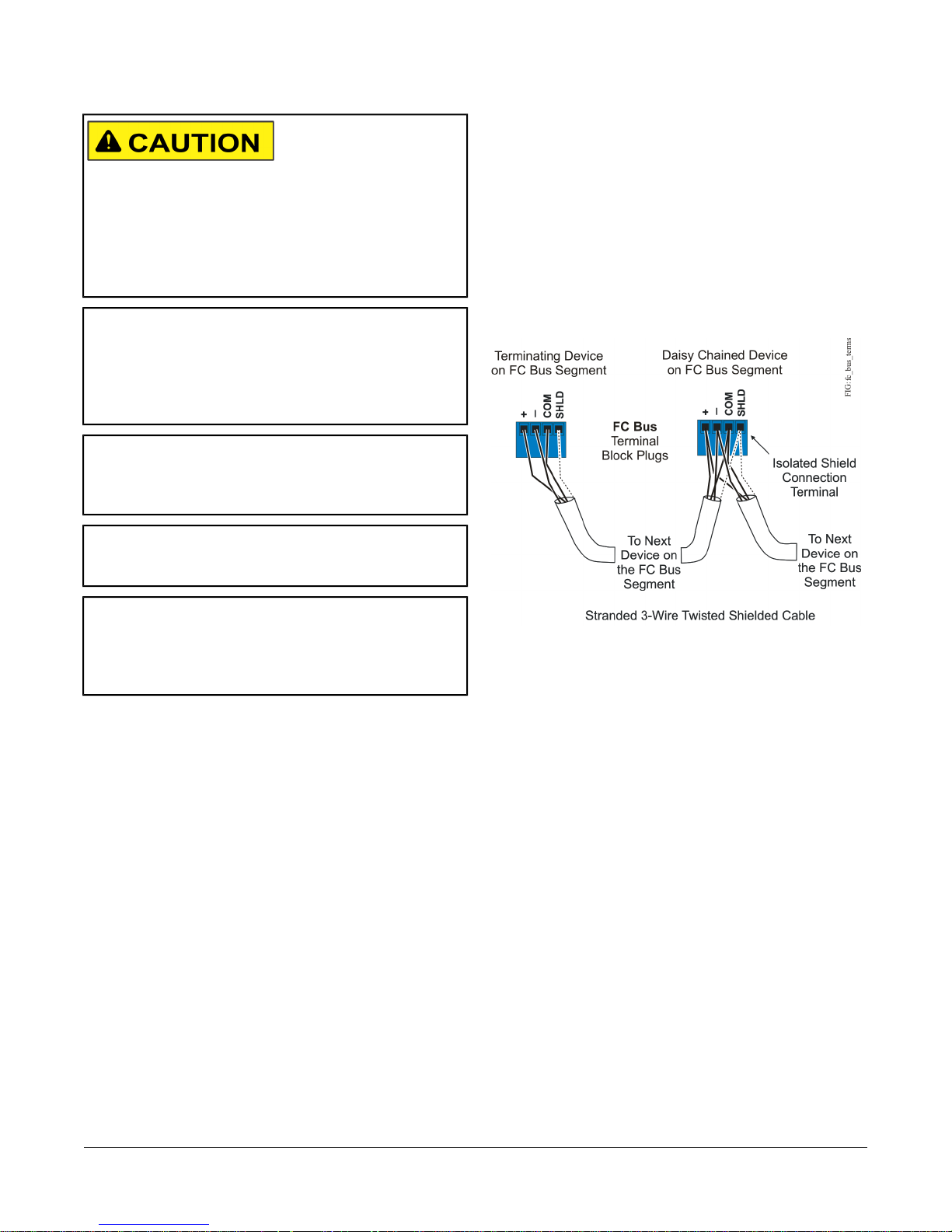
Wiring
Risk of Electric Shock. Disconnect the power supply
before making electrical connections to avoid electric
shock.
Risque de décharge électrique. Débrancher
l'alimentation avant de réaliser tout raccordement
électrique afin d'éviter tout risque de décharge électrique.
FC Bus Terminal Block (Or N2 Protocol As
Required)
The FC Bus terminal block is a blue, removable,
4-terminal plug that fits into a board-mounted jack.
Wire the removable FC Bus terminal block plugs on the
VMA and other controllers in a daisy-chain configuration
using 3-wire twisted, shielded cable as shown in Figure
3. See Table 5 for more information.
Important: Do not connect supply power to the
controller before finishing wiring and
checking all wiring connections. Short
circuits or improperly connected wires can
result in damage to the controller and void
any warranty.
Important: Do not exceed the controller electrical
ratings. Exceeding controller electrical
ratings can result in permanent damage to
the controller and void any warranty.
Important: Use copper conductors only. Make all wiring
in accordance with local, national, and
regional regulations.
Important: Electrostatic discharge can damage
controller components. Use proper
electrostatic discharge precautions during
installation, setup, and servicing to avoid
damaging the controller.
For detailed information on configuring and wiring an
Master-Slave/Token-Passing (MS/TP) Bus, Field
Controller (FC), or Sensor/Actuator (SA) Bus, refer to the
MS/TP Communications Bus Technical Bulletin
(LIT-12011034).
VMA Terminals and Bus Ports
See for input and output terminal and bus port locations
on the VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 controllers. Observe
the following guidelines when wiring a VMA controller.
Figure 3: FC Bus Terminal Block Wiring
Note: The Shield terminal (SHLD) on the FC Bus
terminal block is isolated and can be used to
connect the cable shields on the bus (Figure 3).
SA Bus Terminal Block
The SA Bus terminal block is a brown, removable,
4-terminal plug with +15 VDC that fits into a
board-mounted jack.
Wire the removable SA Bus terminal block plugs on the
VMA and other SA Bus devices in a daisy-chain
configuration using 4-wire twisted, shielded cable as
shown in Figure 4. See Table 5 for more information.
Input and Output Terminals
The input spade terminals are located on the side of the
VMA near the FC Bus terminal block. The output spade
terminals are located on the opposite side of the controller
near the power supply terminal block. See Table 3 for
more information.
6VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 7
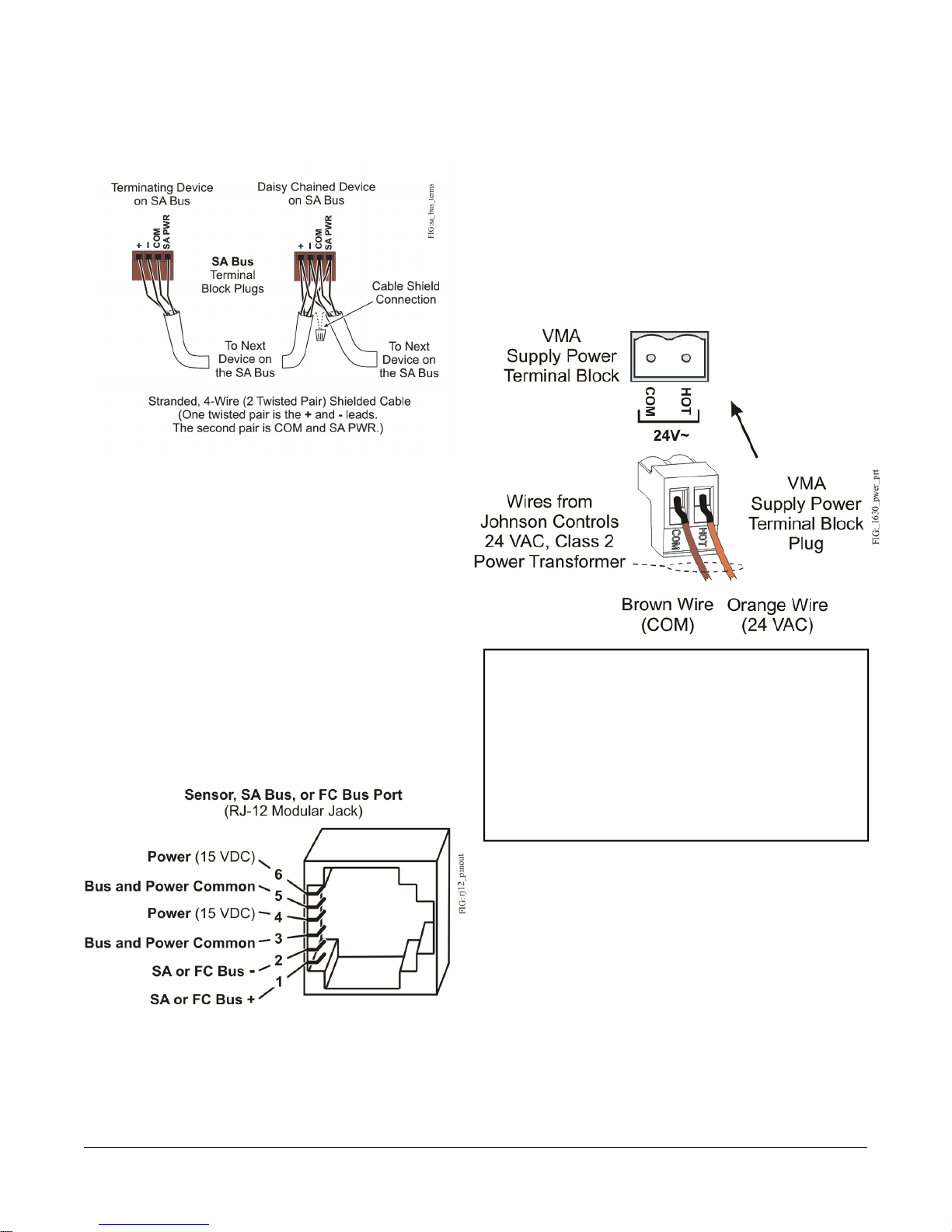
Figure 4: SA Bus Terminal Block Wiring
Modular Ports
The modular and FC Bus ports on the face of the VMA
(Figure 2) are RJ-12 (6-position) modular jacks as shown
in Figure 5.
Supply Power Terminal Block
The 24 VAC supply power terminal block is a gray,
removable, 2-terminal plug that fits into a board-mounted
jack on the upper left of the VMA controller.
Wire the 24 VAC supply power wires from the transformer
to the HOT and COM terminals on the terminal plug as
shown in Figure 6. See Table 5 for more information.
Figure 6: 24 VAC Supply Power Terminal Block Wiring
The modular SA Bus port provides a connection for the
Wireless Commissioning Converter (BTCVT), VAV
Balancing Tool, DIS1710 Local Controller Display,
WRZ78xx Series One-to-One Wireless Transmitter, and
NS Series sensors. The modular FC Bus port provides
a connection for the Wireless Commissioning Converter
and the ZFR/ZFR Pro Wireless Router.
Figure 5: Pin Number Assignments for Sensor (SA
Bus and FC Bus) Ports on VMA1615/1626/1628/1630
Controllers
Note: Do not use the modular SA Bus port and the
terminal block SA Bus simultaneously. Only use
one of these connections at a time.
Important: Exercise caution while rewiring the power
plug when replacing a VMA1610 or
VMA1620 controller. The supply power
terminal on a new VMA is a two-position
terminal block (Figure 6). A VMA1610 or
VMA1620 controller uses a three-position
terminal block, and the center position is
not used. Stray wire strands may make
contact and cause a short circuit across the
24 VAC power supply.
The supply power wire colors may be different on
transformers from other manufacturers. Refer to the
transformer manufacturer’s instructions and the project
installation drawings for wiring details.
7VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 8

Important: Connect 24 VAC supply power to the VMA
and all other network devices so that
transformer phasing is uniform across the
network devices. Powering network devices
with uniform 24 VAC supply power phasing
reduces noise, interference, and ground
loop problems. The VMA does not require
an earth ground connection. However, when
grounding the secondary of the 24 VAC
transformer is required, only one connection
to ground should be made near the
transformer. See the following figure.
Figure 7: Transformer Grounding
Risk of Property Damage: Do not apply power to the
system before checking all wiring connections. Improper
wiring of this terminal may cause a short circuit across
the 24 VAC power supply on -1 VMA models. A short
circuit may result in a tripped circuit breaker or blown
fuse. If using a transformer with a built-in fuse, the
transformer may need to be replaced.
Risque de dommages matériels: Ne mettez pas
l’appareil sous tension avant d’avoir vérifié toutes les
connexions du câblage. Le câblage inadéquat de cette
borne peut causer un court-circuit sur l’alimentation
électrique de 24 V c.a. des -1 VMA modèles. Un
court-circuit peut causer le déclenchement du disjoncteur
ou le grillage d’un fusible. Si vous utilisez un
transformateur avec un fusible intégré, vous pourriez
devoir remplacer le transformateur.
To wire the VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 controller:
Setting the Device Address.) Also, activate the
end-of-line (EOL) switch if necessary.
5. Connect the VMA controller to 24 VAC, Class 2
power.
Note: If you are using the VMA1615/1626/1628/1630
controller with the Wireless Field Bus System,
refer to the WNC1800/ZFR182x Pro Series
Wireless Field Bus System Bulletin
(LIT-12012320) or the ZFR1800 Series Wireless
Field Bus System Bulletin (LIT-12011336)
VMA Terminal Functions, Ratings,
Requirements, and Wiring Guidelines
Input and Output Wiring Guidelines
Table 3 provides information about the functions, ratings,
and requirements for the VMA input and output terminals,
and Table 4 provides guidelines for wire sizes and cable
lengths.
In addition to the wiring guidelines in Table 3, observe
these guidelines when wiring VMA inputs and outputs:
• Run all low-voltage wiring and cables separate from
high-voltage wiring.
• All input and output cables, regardless of wire size or
number of wires, should consist of twisted, insulated,
and stranded copper wires.
• Shielded cable is not required for input or output
cables but is recommended for input and output
cables that are exposed to high electromagnetic or
radio frequency noise.
• Cable runs of less than 30 m (100 ft) typically do not
require an offset in the input/output software setup.
• Cable runs over 30 m (100 ft) may require an offset
in the input/output software setup.
Maximum Cable Length versus Load Current
Use Figure 8 to estimate the maximum cable length
relative to the wire size and the load current (in mA) when
wiring inputs and outputs.
1. Terminate wiring according the appropriate figure in
Termination Diagrams.
2. Wire network sensors and other devices to the VMA's
SA Bus.
3. Wire the FC Bus in a daisy chain.
4. Ensure that the VMA’s device address DIP switches
are set to the appropriate device address. (See
8VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 9

FC and SA Bus and Supply Power Wiring
Guidelines
Table 5 provides information about terminal block
functions, ratings, and requirements.
Table 5 also provides wire size, cable type, and cable
length guidelines for wiring the VMA communication
buses and supply power.
In addition to the guidelines in Table 5, observe these
guidelines when wiring the SA/FC Buses and supply
power:
• Run all low-voltage wiring and cables separate from
high-voltage wiring.
• All FC and SA Bus cables, regardless of wire size,
should be twisted, insulated, stranded copper wire.
• Shielded cable is strongly recommended for all FC
and SA Bus cables.
•
Refer to the MS/TP Communications Bus Technical
Bulletin (LIT-12011670) for detailed information
regarding wire size and cable length requirements for
the FC and SA Buses.
Termination Diagrams
A set of Johnson Controls® termination diagrams provides details for wiring inputs and outputs to the controllers.
See the figures in this section for the applicable termination diagrams.
Table 2: Termination Details
Type of Field
Device
External Source
Input/Output
UIVoltage Input -
Termination DiagramsType of
Internal Source
(Self-Powered)
Sensor
UIVoltage Input -
UIVoltage Input
UITemperature
9VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 10

Table 2: Termination Details
Type of Field
Device
Actuator (External
Source)
Actuator (Internal
Source)
Input/Output
UIDry Contact
CO0–10 VDC Output to
CO0–10 VDC Output to
Termination DiagramsType of
Output (Switch
Low, External
Source)
to Actuator (Switch
Low, External
Source)
(Voltage)
CO24 VAC Triac
Note: Applies to CO4 and CO5.
COIncremental Control
Note: Applies to CO4 and CO5.
COAnalog Output
10VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 11

Table 2: Termination Details
Type of Field
Device
to Actuator (Switch
Low, Internally
Sourced)
Output (Switch
Low, Internally
Sourced)
Phone Jack (Fixed
Address = 199)
Input/Output
BOIncremental Control
BO24 VAC Binary
SA BusNetwork Stat with
Termination DiagramsType of
Note: Applies to BO3 (for VMA 1630 only), BO1, and BO2.
Terminals
Addressable
Terminals (Fixed
Address = 199)
SA BusNetwork Stat with
SA BusNetwork Stat with
11VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 12

Table 3: I/O Terminal Blocks, Functions, Ratings, Requirements, and Cables
Terminal Block Label
Function, Ratings, and RequirementsTerminal
Labels
15 VDC Power Source for active (3-wire) input
devices connected to the Universal INn terminals.
Provides 35 mA total current.
Analog Input - Voltage Mode (0–10 VDC)
10 VDC maximum input voltage
Internal 75k ohm Pulldown
Analog Input - Resistive Mode (0–600k ohm)
Internal 12 V, 15k ohm pull up
Qualified Sensors: 0–2k potentiometer,
RTD (1k Nickel [Johnson Controls sensor],
1k Platinum, and A99B Silicon Temperature
Sensor)
Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) Sensor
10K Type L (10K Johnson Controls Type II is
equivalent to Type L) or 2.252K Type II
Binary Input - Dry Contact Maintained Mode
1 second minimum pulse width
Internal 12 V, 15k ohm pull up
Universal Input Common for all Universal IN
terminals
Note: All Universal ICOMn terminals are
isolated from all other commons on the
-0 models. The -1 model ICOMn
terminals are isolated from FC BUS
COM terminals only.
Binary Output - 24 VAC Triac (Internal Power)
Sources internal 24 VAC power (24~ HOT)
Binary Output - 24 VAC Triac (Internal Power)
Connects OCOMn to 24~ COM when activated.
Internal Power Source:
30 VAC maximum voltage to load
0.5 A maximum output current
1.3 A at 25% duty cycle
40 mA minimum load current
(Inputs)
BINARY
(Outputs)
+15 VUNIVERSAL
INn
ICOMn
OUTn
OCOMn
To Determine Wire Size
and Maximum Cable
Length
Same as (Universal) INn.
Note: Use 3-wire cable for
See Guideline A in Table 4.
See Guideline A in Table 4.
See Guideline A in Table 4.
Same as (Universal) INn.
See Guideline C in Table 4.
See Guideline C in Table 4.
1
devices that source
power from the +15 V
terminal.
12VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 13

Table 3: I/O Terminal Blocks, Functions, Ratings, Requirements, and Cables
Terminal Block Label
Function, Ratings, and RequirementsTerminal
Labels
CONFIGURABLE
(Outputs)
OUTn
OCOMn
Analog Output - Voltage Mode (0–10 VDC)
10 VDC maximum output voltage
10 mA maximum output current
External 1k to 50k ohm load required
Binary Output 24 VAC Triac
Connects OUT to OCOM when activated.
External Power Source:
30 VAC maximum voltage to load
0.5 A maximum output current
1.3 A at 25% duty cycle
40 mA minimum load current
Analog Output Signal Common: All
Configurable Outputs defined as Analog Outputs
share a common, which is isolated from all other
commons except the Binary Input common.
Binary Output Signal Common: All
Configurable Outputs defined as Binary Outputs
are isolated from all other commons, including
other Configurable Output commons.
To Determine Wire Size
and Maximum Cable
Length
See Guideline A in Table 4.
See Guideline C in Table 4.
Same as (Configurable) OUTn.
1
1
Table 4 defines cable length guidelines for the various wire sizes that may be used for input and output wiring.
Table 4: Cable Length Guidelines for Recommended Wire Sizes
Wire Size/Gauge and TypeGuideline
AssumptionsMaximum Cable Length
and Type
457 m (1,500 ft) twisted wire1.0 mm (18 AWG) stranded copperA
297 m (975 ft) twisted wire0.8 mm (20 AWG) stranded copper
297 m (975 ft) twisted wire
183 m (600 ft) twisted wire0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded copper
183 m (600 ft) twisted wire
107 m (350 ft) twisted wire0.5mm (24 AWG) stranded copper
107 m (350 ft) twisted wire
229 m (750 ft) twisted wire1.0 mm (18 AWG) stranded copperB
137 m (450 ft) twisted wire0.8 mm (20 AWG) stranded copper
297 m (975 ft) twisted wire
91 m (300 ft) twisted wire0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded copper
183 m (600 ft) twisted wire
61 m (200 ft) twisted wire0.5 mm (24 AWG) stranded copper
107 m (350 ft) twisted wire
C
See Figure 8 to select wire
size/gauge.
Use stranded copper wire.
See Figure 8 to determine
cable length.
Use twisted wire cable.
100 mV maximum voltage drop
Depending on the cable length
and the connected input or
output device, you may have to
define an offset in the setup
software for the input or output
point.
100 mV maximum voltage drop
Depending on the cable length
and the connected input or
output device, you may have to
define an offset in the setup
software for the input or output
point.
N/A
13VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 14

Figure 8: Maximum Wire Length by Current and Wire Size
Table 5: Communication Bus and Supply Power Terminal Blocks, Functions, Ratings, Requirements, and
Cables
Terminal LabelsTerminal Block/Port Label
Function, Electrical
Recommended Cable Type
Ratings/Requirements
FC BUS
SA BUS
FC BUS
2
FC Bus Communications+
-
COM
Signal Reference (Common) for bus
communications
SHLD
Isolated terminal (optional shield drain
connection)
2
SA Bus Communications+
-
COM
SA Bus Signal Reference and 15 VDC
Common
SA PWR
15 VDC Supply Power for Devices on
the SA Bus
2
FC BUS
RJ-12 6-Position Modular Port
provides FC Bus Communications
FC Bus provides 15 VDC Power for:
• Wireless Bluetooth®
Commissioning Converter
• Wireless ZigBee® Field Bus
Router
0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded, 3-wire
twisted, shielded cable
recommended
0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded, 4-wire
(2 twisted-pairs), shielded cable
recommended
Note: The + and - wires are one
twisted pair, and the COM
and SA PWR wires are the
second twisted pair.
24 AWG 3-pair CAT 3 Cable
<30.5m (100 ft)
1
14VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 15

Table 5: Communication Bus and Supply Power Terminal Blocks, Functions, Ratings, Requirements, and
Cables
Terminal LabelsTerminal Block/Port Label
Function, Electrical
Recommended Cable Type
Ratings/Requirements
SA BUS
2
SA BUS
HOT24~
COM
RJ-12 6-Position Modular Port
provides SA Bus Communications
SA Bus provides 15 VDC Power for:
• NS Series Sensors
• Wireless ZigBee WRZ-78xx
Series One-to-One Wireless
Receiver
• Wireless Bluetooth
Commissioning Converter
(BTCVT)
• DIS1710 Local Controller Display
• VAV Balancing Tool
24 VAC Power Supply - Hot
Supplies 20–30 VAC (Nominal
24VAC)
24 VAC Power Supply Common
The -0 models isolate this terminal
from all other commons.
The -1 models only isolate this
terminal from the FC bus common.
24 AWG 3-pair CAT 3 Cable
<30.5m (100 ft)
0.8 mm to 1.0 mm
(20 to 18 AWG) 2-wire
1
1
See Table 4 to determine wire size and cable lengths for cables other than the recommended cables.
2 The SA Bus and FC Bus wiring recommendations in this table are for MS/TP Bus communications at 38.4k baud. For more
information, refer to the MS/TP Communications Bus Technical Bulletin (LIT-12011034).
Setup and Adjustments
Important: Electrostatic discharge can damage
controller components. Use proper
electrostatic discharge precautions during
installation, setup, and servicing to avoid
damaging the controller.
Setting the Device Address
Metasys® field controllers are master devices on
BACnet®MSTP (SA or FC) Buses. Before operating field
controllers on a bus, you must set a valid and unique
device address for each controller on the bus.
Set a field controller’s device address by setting the
positions of the switches on the Device Address DIP
switch block at the top of the controller (Figure 2). Device
addresses 4 through 127 are the valid addresses for
these controllers.
The DIP switch block (Figure 9) has eight switches
numbered 128, 64, 32, 16, 8, 4, 2, and 1. Switches 64
through 1 are device address switches. Switch 128 is a
mode switch that enables a field controller to operate on
a ZFR /ZFR Pro Series Wireless Field Bus. Switch 128
must be set to OFF for all hard-wired SA and FC Bus
applications. Set Switch 128 to ON for wireless FC Bus
applications only.
Figure 9: Device Address Switches Set to 21
15VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 16

Note: Metasys field controllers ship with Switch 128 ON
and the remaining address switches OFF. This
renders the controllers wired slave devices, which
do not interfere on MSTP Buses and do not
interfere with bus operation. Set a valid and
unique device address on the controller before
applying power to the controller on the bus.
To set the device addresses on a Metasys field controller:
1. Set all of the switches on the field controller’s device
address DIP switch block (128 through 1) to OFF.
2. Set one or more of the seven address switches (64
through 1) to ON, so that the sum of the switch
numbers set to ON equals the intended device
address. See Table 6 and Table 7 for valid field
controller addresses.
Set the highest number switch that is less than or
equal to the intended device address to ON. Then
continue setting lower numbered switches until the
total equals the intended address. For example, if the
intended device address is 21, set Switch 16 to ON
first, then set Switch 4 ON, followed by Switch 1
(16+4+1=21). See Figure 9.
3. Set Switch 128 to ON only for controllers on a ZFR
/ZFR Pro Series Wireless Field Bus application. For
all hard-wired SA and FC Bus applications, ensure
that Switch 128 is set to OFF.
Note: Do not connect a wirelessly enabled field
controller to a wired FC Bus.
Refer to the WNC1800/ZFR182x Pro Series Wireless
Field Bus System Technical Bulletin (LIT-12012356)
or the ZFR1800 Series Wireless Field Bus System
Technical Bulletin (LIT-12011295) for more
information on device addresses in wireless
applications.
4. Set a unique and sequential device address for each
of the field controllers connected on the SA or FC
Bus, starting with device address 4.
Table 6 and Table 7 show and describe the valid FC Bus
and SA Bus device addresses for Johnson Controls
MSTP communications bus applications.
Table 6: FC Bus Device Address Descriptions
Address DescriptionDevice
Address
0
(Switch 128
OFF)
1 to 3
(Switch 128
OFF)
4 to 127
(Switch 128
OFF)
Reserved for FC Bus Supervisory Controller
(not valid for field controllers).
Reserved for peripheral devices (not valid for
field controllers).
Valid for MSTP Master field controllers on a
hard-wired SA Bus or FC Bus.
Table 7: Wireless Field Bus Device Address
Address DescriptionDevice
Address
0 to 3
(Switch 128
ON)
4 to 127
(Switch 128
ON)
Reserved addresses for wired slave devices
(not valid for field controllers).
Note: Metasyscontrollers ship with 128 ON
and the remaining address switches
OFF, rendering the controllers wired
slave devices, which do not operate
on Metasys field buses.
Valid for MSTP Master field controllers on
wireless FC Buses only.
Note: Do not connect a Metasys controller
with these device addresses to an
active wired SA or FC Bus. When a
controller with one of these device
address is connected to a wired field
bus, the field bus is rendered
inoperable until the controller is
disconnected or Switch 128 is set to
OFF.
To ensure the best bus performance, set sequential
device addresses with no gaps in the device address
range (4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and so on). The field controllers
do not need to be physically connected on the bus in
their numerical device address order.
5. Write each field controller’s device address on the
white label below the DIP switch block on the
controller’s cover.
Refer to the MSTP Communications Bus Technical
Bulletin (LIT-12011034) for more information on field
controller device addresses and how to set them on
MSTP Buses.
Setting the N2 Controller Address to
be Greater than 127
N2-configured controllers support the full range of
possible N2 device addresses provided by the N2 protocol
standard (1-255). However, these controllers require
special configuration for addresses above 127.
Use the following instructions for controller addresses
greater than 127.
16VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 17

Notes:
• Prior to performing this procedure, be sure the
controller has been converted from BACnet to N2
protocol first. Refer to the Modernization Guide for
Legacy N2 Controllers (LIT-12012005) for more
information.
• This special configuration is required because
controller addresses above 127 were originally
intended for use with the Wireless Field Bus system.
1. Disconnect the 24 VAC supply from the controller.
2. Remove the FC Bus connector from the controller.
3. Set the address switch set to the desired N2 address.
4. Set the address switch segment labeled 128 to OFF.
5. Reconnect the 24 VAC supply to the controller.
6. Using an SA bus connection, download the firmware
and controller application file. The download process
asks to confirm switching the communication protocol
to N2.
7. Click OK.
8. After the download is finished, disconnect the 24
VAC supply to the controller.
9. Set the address switch segment labeled 128 to ON.
10. Reattach the FC Bus connector to the controller.
11. Reconnect the 24 VAC supply to the controller.
Setting the EOL Switch
Each field controller has an EOL switch, which, when set
to ON (up), sets the field controller as a terminating device
on the bus. See Figure 2 for the EOL switch location on
the field controller. The default EOL switch position is
OFF (down). The amber EOL LED illuminates to show
the EOL is active.
Figure 10: EOL Switch Positions
To set the EOL switch on a field controller:
1. Determine the physical location of the controller on
the SA or FC Bus.
2. Determine if the controller must be set as a
terminating device on the bus.
Note: The EOL termination rules for SA Buses and
FC Buses are different. Refer to the MSTP
Communications Bus Technical Bulletin
(LIT-12011034) for detailed information
regarding EOL termination rules and EOL
switch settings on SA and FC Buses.
3. If the controller is a terminating device on the FC Bus,
set the EOL switch to ON. If the controller is not a
terminating device on the bus, set the EOL switch to
OFF.
Note: When the EOL switch is set to ON, the LED
light on the face of the controller is illuminated.
Commissioning
Use the following procedure to commission the
VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 controller:
1. Download the control application to the VMA controller
using the Controller Configuration Tool (CCT). Refer
to the Controller Tool Help (LIT-12011147).
2. Commission the VAV Box. Refer to the Controller
Tool Help (LIT-12011147).
3. Perform airflow balancing on the VAV box. Refer to
the VAV Balancing Tool Technical Bulletin
(LIT-12011087).
4. Perform commissioning checkout procedures. Refer
to the Controller Tool Help (LIT-12011147).
The CCT connects to the VMA through a laptop computer
using different connection options: the Wireless
Commissioning Converter, or the wired BACnet Ethernet
to MS/TP Router can be used when using the BACnet
MS/TP protocol. When the controller is configured to use
the N2 protocol, you must use the Commissioning
Converter at the SA bus. Wireless connections are not
supported in N2 mode. These connection options require
additional hardware listed in Table 10.
Repair Information
If the VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 controller fails to operate
within its specifications, replace the unit. For a
replacement unit, contact the nearest Johnson Controls
representative.
Troubleshooting
Table 9 provides LED status indicator information for
troubleshooting the VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 controller.
17VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 18

Table 8 provides some additional troubleshooting
information for possible problems.
Note: If you experience short circuits in the 24 VAC
power supply causing protective devices such as
breakers or fuses to trip, make sure that the power
connections on the VMA are not reversed. The
most common cause of this problem is when the
24 VAC power supply on the VMA is reversed but
not reversed on a connected secondary device.
Improper wiring of this power terminal may cause
a short circuit across the 24 VAC power supply
on -1 models.
18VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 19

Table 8: Troubleshooting
VerificationCorrectionPossible CauseProblem
Transformer has trippedPower at Primary of
Transformer, 0V at
Secondary
Controller is Off 1.1.1. Disconnect the
secondary of the 24
VAC transformer
Ensure polarity of ~24 V COM /
ICOM / + 15VCOM/SA BUS
COM on the controller, auxiliary
devices and I/O is the same.
Transformer is shorted
2. 24VAC powered sensor is not
wired with the same polarity as
the controller
Breaker/Fuse has tripped.Power at Primary of
Transformer, 24 V at
Secondary, 0V at
Fuse/Breaker.
2. Use an ohm-meter to
measure between ~24 V
HOT and COM; there
should be no short
circuit.
2. Ensure OUT1-OUT3 terminals
of binary outputs are not
connected to ~24 VAC COM,
verify that OCOM1-OCOM3 are
not connected to ~24 VAC HOT
(these terminals are internally
sourced).
3. SA bus device is not wired with
the same polarity as the
controller
Note: Note that some
installations require
the secondary of the
Transformer to be
Earth Grounded. If
this is the case,
verify that the Earth
Ground connection
is valid and not
shared between
multiple pieces of
equipment.
3. Verify the short circuit has been
resolved with an ohm-meter.
4. Reset the breaker/fuse or
replace the transformer.
Note: When replacing the
transformer, it is
recommended to replace
with a model that utilizes a
resettable circuit breaker. A
circuit breaker makes
solving wiring problems
easier.
Ensure polarities of ~24 V
COM/OCOM match and that the
connected end device uses the
same polarity.
Power polarity mismatch between
connected device and configurable
output
Output is in protection
mode - a state the analog
portion of the configurable
output goes into when it
detects a wiring problem.
The analog output is set
to 0% regardless of the
command whenever a
wiring fault is detected.
0–10 V output is set
to 10–100%, but 0 V
is at output terminals
Configurable output
- analog mode is
invalid.
1. Measure the output and
verify that it matches the
command.
2. Disconnect the
connected device and
verify the commanded
value is present.
Connect OCOM terminal of the
configurable output to the common
of the connected end device.
OCOM terminal is not connectedCommon Reference is
incorrect
0–10V output has an
undesirable offset of
up to 1 V
19VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 20

Table 9: VMA Controller Status LEDs
On SteadyGreenPOWER
Off SteadyRedFAULT
Blink - 2 HzGreenFC BUS
Blink - 2 HzGreenSA BUS
OffAmberEOL
Descriptions of LED StatesNormal StateLED ColorLED Label
Off Steady = No power
On Steady = Power is supplied by primary voltage
Blink - 2 Hz = Download or startup in progress, not ready for normal
operation, SA Bus devices offline (such as netsensors)
Rapid blink = SA Bus communications issue
Off Steady = No faults
On Steady = Device fault or no application loaded
Blink - 2 Hz = Data transmission (normal communication)
Off Steady = No data transmission (auto baud in progress)
On Steady = communication lost, waiting to join communication
ring
Blink - 2 Hz = Data transmission (normal communication)
Off Steady = No data transmission (N/A - auto baud not supported)
On Steady = Communication lost; waiting to join communication
ring
On Steady = EOL is active
Off Steady = EOL is not active
Accessories
Use Table 10 to order accessories.
Table 10: VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 Controller Accessories (Order Separately)
DescriptionProduct Code Number
IOM Series Controllers
Mobile Access Portal
(MAP) Gateway
MS-BTCVTCBL-700
Y64T15-0
Y65A13-0
Y65T42-0
Y65T31-0
Refer to the Metasys®System Field Equipment Controllers and Related Products Product Bulletin
(LIT-12011042) for a complete list of available IOM Series Controllers.
Refer to the Mobile Access Portal Gateway Catalog Page (LIT-1900869) to identify the appropriate
product for your region.
Local Controller DisplayMS-DIS1710-0
Cable Replacement Set for the MS-BTCVT-1 or the NS-ATV7003-0; includes One 1.5 m (5 ft)
Retractable Cable
Transformer, 120/208/240 VAC Primary to 24 VAC Secondary, 92 VA, Foot Mount, 72.2 cm (30
in.), Primary Leads and 76.2 cm (30 in.) Secondary Leads, Class 2
Transformer, 120 VAC Primary to 24 VAC Secondary, 40 VA, Foot Mount (Y65AS), 20.32 cm (8
in.), Primary Leads and 76.2 cm (30 in.) Secondary Leads, Class 2
Transformer, 120/208/240 VAC Primary to 24 VAC Secondary, 40 VA, Hub Mount (Y65SP+),
20.32 cm (8 in.), Primary Leads and Secondary Screw Terminals, Class 2
Transformer, 120/208/240 VAC Primary to 24 VAC Secondary, 40 VA, Foot Mount (Y65AR+),
20.32 cm (8 in.), Primary Leads and Secondary Screw Terminals, Class 2
2-position Screw Terminal that plugs onto VMA Output Point Spade LugsAP-TBK1002-0
3-position Screw Terminal that plugs onto VMA Output Point Spade LugsAP-TBK1003-0
Replacement MS/TP SA Bus Terminal, 4-Position Connector, Brown, Bulk Pack of 10AP-TBK4SA-0
Replacement MS/TP FC Bus Terminal, 4-Position Connector, Blue, Bulk Pack of 10AP-TBK4FC-0
Replacement Power Terminal, 2-Position Connector, Gray, Bulk Pack of 10AP-TBK2PW-0
20VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 21

Table 10: VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 Controller Accessories (Order Separately)
DescriptionProduct Code Number
Cable adapter for connection to 8-pin TE-6700 Series sensorsAS-CBLTSTAT-0
F-1000-325
F-1000-326
Replacement Barbed Fitting for use on VMA1615, VMA1630, and VMA1832 for Connecting
Tubing, Bulk Pack of 10
Flexible Tubing Extension with Barbed Fitting for VMA1615, VMA1630, and VMA1832, 35.56 cm
(14 in.) Length, Bulk Pack of 20
VMA Actuator Assembly Gearbox Replacement KitMS-VMAACT-701
Portable BACnet/IP to MS/TP RouterTL-BRTRP-0
Technical Specifications
Table 11: VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 Controllers
Product Code Numbers
Protocol
Engines
Supply Voltage
Power Consumption
Ambient Conditions
Terminations
Controller Addressing
for BACnet MSTP
for N2
MS-VMA1615-x: 32-bit, Integrated VAV Controller/Actuator/Pressure Sensor - DPT, 3 UI and 2 BO,
24VAC, FC and SA Bus
MS-VMA1626-x: 32-bit, Integrated VAV Controller/Actuator (No Pressure Sensor - DPT); 3 UI, 3
BO, and 2 CO; 24VAC; FC and SA Bus
MS-VMA1628-x: 32-bit, Integrated VAV Controller/(No Actuator) Pressure Sensor - DPT; 3 UI, 3
BO, and 2 CO; 24VAC; FC and SA Bus
MS-VMA1630-x: 32-bit, Integrated VAV Controller/Actuator/Pressure Sensor - DPT; 3 UI, 3 BO, and
2 CO; 24VAC; FC and SA Bus
BACnet MSTP, N2Communications
All Model types. Some NIE models support MS/TP and N2 devices. Refer to the Network Engines
Product Bulletin (LIT-12012138) for details.
24 VAC (nominal, 20 VAC minimum/30 VAC maximum), 50/60 Hz, Power Supply Class 2 (North
America), Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) (Europe)
10 VA typical, 14 VA maximum
Note: The VA rating does not include any power supplied to the peripheral devices connected to
Binary Outputs (BOs) or Configurable Outputs (COs), which can consume up to 12 VA for
each BO or CO, for a possible total consumption of an additional 60 VA (maximum).
Operating: 0 to 50°C (32 to 122°F)
Storage: -40 to 70°C (-40 to 158°F)
Inputs/Outputs: 6.3 mm (1/4 in.) Spade Lugs
FC Bus, SA Bus, and Supply Power: 4-Wire and 2-Wire Pluggable Screw Terminal Blocks
FC and SA Bus Modular Ports: RJ-12 6-Pin Modular Jacks
DIP switch set; valid field controller device addresses 4–127
(Device addresses 0–3 and 128–255 are reserved and not valid field controller addresses.)
DIP switch set; valid field controller device addresses 1–255Controller Addressing
21VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 22

Table 11: VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 Controllers
1
Communications Bus
RS-485: selectable between BACnet MSTP or N2
FC Bus: 0.6 mm (22 AWG) standard 3-wire, twisted, shielded cable recommended between the
supervisory controller and field controller
10/100 Mbps; 8-pin RJ-45 connector
SA Bus: 0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded, 4-wire (2-twisted pairs) shielded cable recommended from
the VMA controller for network sensors and other sensor/actuator devices; includes a terminal to
source 15 VDC supply power from VMA to SA Bus devices
RX630 32-bit Renesas microcontrollerProcessor
1 MB flash memory and 512 KB RAMMemory
1
Universal Input
Mode/Configurable
Output Mode Accuracy
Air Pressure Differential
Sensor
Dimensions
(Height x Width x Depth)
Compliance
UI Analog Input Mode: 15-bit resolution on UIs
CO Analog Output Mode (VMA1626/1628/VMA1630 only): 0–10 VDC ± 200 mV
Range: -1.5 in. to 1.5 in. W.C.
Performance Characteristics:
Accuracy: ±1.3% Full Span Maximum2(±0.039 in. W.C.)
Typical accuracy at zero (null) pressure is ±0.02 in. W.C.3(if provided)
4 N·m (35 lb·in) minimum shaft length = 44 mm (1-3/4 in.) (if provided)Actuator Rating
Mounts to damper shaft using single set screw and to duct with single mounting screwMounting
165 x 125 x 73 mm (6.5 x 4.92 x 2.9 in.)
Center of Output Hub to Center of Captive Spacer: 135 mm (5-5/16 in.)
0.65 kg (1.45 lb)Weight
United States:
UL Listed, File E107041, CCN PAZX, UL 916, Energy Management Equipment; Suitable for use in
other environmental air space (plenums) in accordance with Section 300.22(C) of the National Electric
Code.
FCC Compliant to CFR47, Part 15, Subpart B, Class A.
Canada:
UL Listed, File E107041, CCN PAZX7, CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 205, Signal Equipment.
Industry Canada Compliant, ICES-003
Europe:
CE Mark – Johnson Controls declares that this product is in compliance with the essential
requirements and other relevant provisions of the EMC Directive.
Australia and New Zealand:
RCM Mark, Australia/NZ Emissions Compliant.
BACnet International
BACnet Testing Laboratories (BTL) Protocol Revision 12 Listed BACnet Advanced Application
Controller (B-AAC)
1
For more information, refer to the MS/TP Communications Bus Technical Bulletin (LIT-12011034)
2 Combined error due to offset, non-linearity, and temperature variation.
3 Includes error due to non-linearity.
22VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
Page 23

The performance specifications are nominal and conform to acceptable industry standard. For application at conditions
beyond these specifications, consult the local Johnson Controls office. Johnson Controls shall not be liable for
damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products.
APAC Single Point of Contact:NA/SA Single Point of Contact:European Single Point of Contact:
JOHNSON CONTROLS
WESTENDHOF 3
45143 ESSEN
GERMANY
JOHNSON CONTROLS
507 E MICHIGAN ST
MILWAUKEE WI 53202
USA
JOHNSON CONTROLS
C/O CONTROLS PRODUCT MANAGEMENT
NO. 22 BLOCK D NEW DISTRICT
WUXI JIANGSU PROVINCE 214142
CHINA
507 E. Michigan Street, Milwaukee, WI 53202
Building Technologies & Solutions
Johnson Controls® is a registered trademark of Johnson Controls.
All other marks herein are the marks of their respective owners.© 2018 Johnson Controls
www.johnsoncontrols.comPublished in U.S.A.
23VMA1615/1626/1628/1630 VAV Controllers Installation Instructions
 Loading...
Loading...