Page 1

M4-CGM General Purpose Application
Controllers Installation Guide
Part No. 24-10143-01698 Rev. B
2019-10-18
Application
The CGM09090 General Purpose Application MS/
TP Controller (CGM) are equipment controllers
that run pre-engineered and user-programmable
applications, and provides the inputs and outputs
required to monitor and control a wide variety of
HVAC and other facility equipment. CGM controllers
operate on an RS-485 BACnet® MS/TP Bus as
BACnet Advanced Application Controllers (B-AACs)
and integrate into Johnson Controls® and thirdparty BACnet systems.
CGM equipment controllers include an integral realtime clock, which enables the controllers to monitor
and control schedules, calendars, and trends, and
operate for extended periods of time as stand-alone
controllers when offline from the Metasys® system
network.
Communications Protocols
The CGM controllers can communicate using BACnet
MS/TP, N2, or wireless Zigbee®. By default, the
CGM controllers communicate using the BACnet
MS/TP protocol. The BACnet protocol is a standard
for ANSI, ASHRAE, and the International Standards
Organization (ISO) for building controls.
The CGM controllers can be used as functional
replacements for legacy N2 controllers. The N2capable MS/TP equipment controller models
provide a cost-effective upgrade and modernization
path for customers with existing N2 controllers.
For installation and commissioning support,
and tips for efficient and safe replacement,
refer to the Modernization Guide for Legacy N2
Controllers (LIT-12012005) and the controllerspecific documentation. For information about
mapping N2 Objects in controllers with switchable
communications protocols, refer to the N2
Compatibility Options chapter of the Controller Tool
Help (LIT-12011147).
To configure CGM controllers to communicate using
the N2 communications protocol, see Configuring
N2 communications.
The CGM controller can also be installed in a
wireless application using aZFR/ZFR Pro Wireless
Field Bus Router. To configure these controllers to
communicate using the wireless communications
protocol, see Configuring wireless communications.
North American Emissions Compliance
United States
This equipment has been tested and found to
comply with the limits for a Class A digital device
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when this equipment
is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area
may cause harmful interference, in which case the
users will be required to correct the interference at
their own expense.
Canada
This Class (A) digital apparatus meets all the
requirements of the Canadian InterferenceCausing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la Classe (A) respecte
toutes les exigences du Règlement sur le matériel
brouilleur du Canada.
Installation
Observe the following guidelines when installing a
CGM Controller:
• To minimize vibration and shock damage to the
controller, transport the controller in the original
container.
• Verify that all parts shipped with the controller.
• Do not drop the controller or subject it to physical
shock.
*241014301698B*
(For factory use only)
M4-CGM09090
Page 2
Parts included
• One CGM controller with removable terminal
blocks (Input/Output, Power, FC, and SA bus are
removable)
• One installation instructions sheet
Materials and special tools needed
• Three fasteners appropriate for the mounting
surface (M4 screws or #8 screws)
• One 20 cm (8 in.) or longer piece of 35 mm DIN
rail and appropriate hardware for DIN rail mount
(only)
• Small straight-blade screwdriver for securing
wires in the terminal blocks
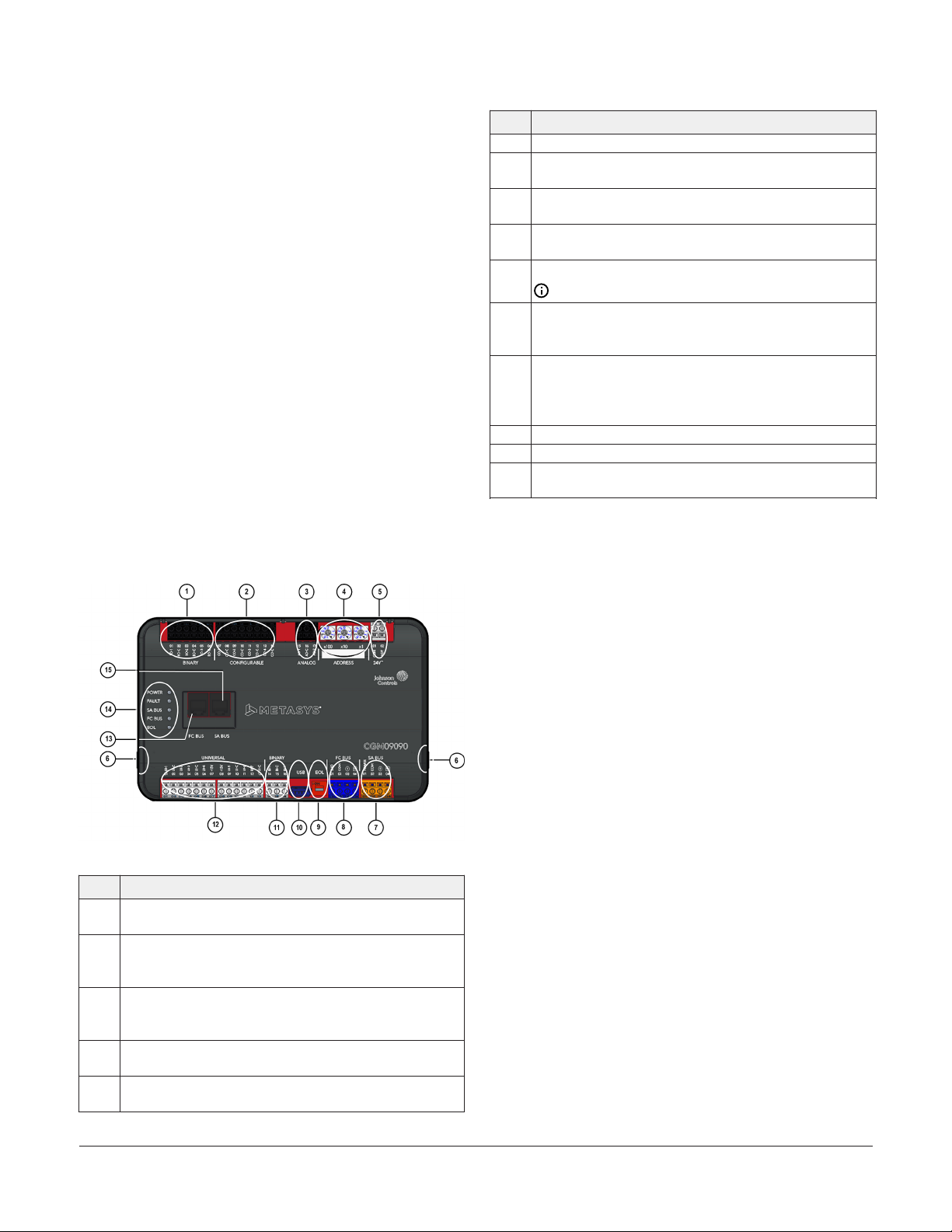
CGM09090 physical features
The following figure displays the physical features
of the CGM controllers, and the accompanying table
provides a description of the physical features and a
reference to further information where required.
Table 1: CGM09090 physical features
Physical Feature: Description and References
6 Cover Lift Tab (see Removing the controller cover)
Sensor Actuator (SA) Bus Terminal Block: Orange terminal
7
(see SA bus terminal block)
Field Controller (FC) Bus Terminal Block: Blue terminal
8
(see FC bus terminal block (or N2 protocol as required))
End-of-Line (EOL) Switch (see Setting the End-of-Line
9
(EOL) switch)
Universal Serial Bus (USB) 2.0 host type A Port
10
11
12
13 FC Bus Port RJ-12 6-pin Modular Jack (see FC bus port)
14 LED Status Indicators (see Table 11)
15
Note: The USB feature is not currently supported.
Binary Input (BI) Terminal Block: White terminals; dry
Contact Maintained or Pulse Counter/Accumulator Mode
(see Table 5)
Universal Inputs (UI) Terminal Block: White terminals; can
be defined as Voltage Analog Input (0-10 VDC), Current
Analog Input (4-20 mA), Resistive Analog Inputs (0-600k
ohm), or Dry Contact Binary Input (see Table 5)
Sensor (SA Bus) Port: RJ-12 6-Pin Modular Jack (see SA Bus
port)
Mounting
Figure 1: CGM09090 Physical Features
Table 1: CGM09090 physical features
Physical Feature: Description and References
Binary Outputs (BO) Terminal Block: Black terminals; 24
1
VAC Triac (see Table 5)
Configurable Outputs (CO) Terminal Block: Black
2
terminals; can be defined as Voltage Analog Output (0-10
VDC) or Binary Output (24 VAC Triac) (see Table 5)
Analog Output (AO) Terminal Block: Black terminals;
3
can be defined as Voltage Analog Output (0-10 VDC) or
Current Analog Output (4-20 mA) (see Table 5)
Device Address Rotary Switch Block: Decimal Addressing
4
(see Setting the device address)
Supply Power Terminal Block: Gray terminals; 24 VAC,
5
Class 2 (see Supply power terminal block)
Observe the following guidelines when mounting a
CGM controller:
• Ensure the mounting surface can support the
controller, DIN rail, and any user-supplied
enclosure.
• Mount the controller horizontally on 35 mm DIN
rail whenever possible.
• Mount the controller in the proper mounting
position.
• Mount the controller on a hard, even surface
whenever possible in wall-mount applications.
• Use shims or washers to mount the controller
securely and evenly on the mounting surface.
• Mount the controller in an area free of corrosive
vapors and observe the Ambient Conditions
requirements in Table 14.
• Provide for sufficient space around the controller
for cable and wire connections for easy cover
removal and good ventilation through the
controller (50 mm [2 in.] minimum on the top,
bottom, and front of the controller).
• Do not mount the controller on surfaces prone to
vibration, such as duct work.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide2
Page 3
• Do not mount the controller in areas where
electromagnetic emissions from other
devices or wiring can interfere with controller
communication.
On panel or enclosure mount applications, observe
the following additional guidelines :
• Mount the controller so that the enclosure walls
do not obstruct cover removal or ventilation
through the controller.
• Mount the controller so that the power
transformer and other devices do not radiate
excessive heat to the controller.
• Do not install the controller in an airtight
enclosure.
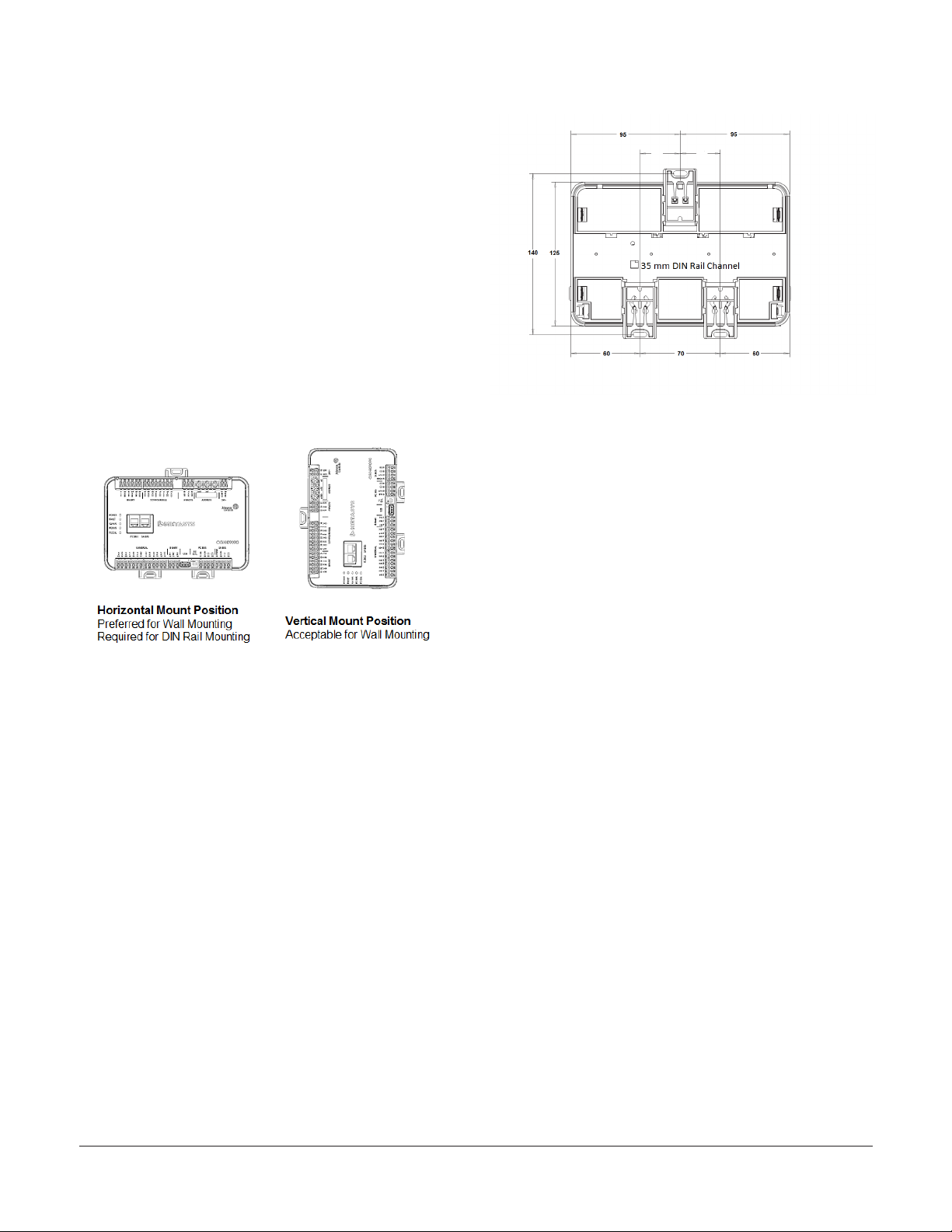
Figure 2: Controller mounting position
Figure 3: Back of controller
DIN rail mount applications
To mount a CGM controller horizontally on a 35
mm DIN rail (recommended method), complete the
following steps:
1. Securely mount a 20 cm (8 in.) or longer section
of 35 mm DIN rail horizontal and centered in the
desired space so that the controller mounts in
the horizontal position.
Mounting features and dimensions
See the Figure 3 for mounting dimensions in
millimeters. Figure 3 also illustrates the DIN rail
channel and the mounting clips in an extended
position.
2. Pull the two bottom mounting clips outward
from the controller to the extended position
(Figure 3).
3. Hang the controller on the DIN rail by the hooks
at the top of the (DIN rail) channel on the back
of the controller (Figure 3), and position the
controller snugly against the DIN rail.
4. Push the bottom mounting clips inward (up) to
secure the controller on the DIN rail.
To remove the controller from the DIN rail, pull the
bottom mounting clips out to the extended position
and carefully lift the controller off the DIN rail.
Wall mount applications
To mount a CGM controller directly on a wall or
other flat vertical surface, complete the following
steps:
1. Pull the two bottom mounting clips outward
and ensure they are locked in the extended
position as shown in Figure 3.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 3
Page 4
2. Mark the mounting hole locations on the wall
using the dimensions in one of the mount
positions shown in Figure 2. Or hold the
controller up to the wall or surface in a proper
mount position and mark the hole locations
through the mounting clips.
3. Drill holes in the wall or surface at the marked
locations, and insert appropriate wall anchors in
the holes (if necessary).
ATTENTION
Mise En Garde: Risque de dégâts matériels:
Ne pas mettre le système sous tension avant d'avoir
vérifié tous les raccords de câblage. Des fils formant un court-circuit ou connectés de façon incorrecte risquent d'endommager irrémédiablement
l'équipement.
4. Hold the controller in place, and insert the
screws through the mounting clips and into the
holes (or anchors). Carefully tighten all of the
screws.
Important: Do not over-tighten the mounting
screws. Over-tightening the screws may
damage the mounting clips.
Wiring
Observe the following guidelines when wiring a CGM
controller:
CAUTION
Risk of Electric Shock:
Disconnect the power supply before making electrical
connections to avoid electric shock.
ATTENTION
Mise En Garde: Risque de décharge électrique:
Débrancher l'alimentation avant de réaliser tout raccordement électrique afin d'éviter tout risque de
décharge électrique.
CAUTION
Risk of Property Damage:
Do not apply power to the system before checking all
wiring connections. Short circuited or improperly connected wires may result in permanent damage to the
equipment.
Important: Do not exceed the controller
electrical ratings. Exceeding controller electrical
ratings can result in permanent damage to the
controller and void any warranty.
Important: Use copper conductors only. Make
all wiring in accordance with local, national, and
regional regulations.
Important: Electrostatic discharge can damage
controller components. Use proper electrostatic
discharge precautions during installation,
setup, and servicing to avoid damaging the
controller.
For detailed information about configuring and
wiring an MS/TP Bus, FC bus, and SA bus, refer to
the MS/TP Communications Bus Technical Bulletin
(LIT-12011034). For detailed information about wiring
an N2 network, refer to the N2 Communications Bus
Technical Bulletin (LIT-636018).
Terminal blocks and bus ports
See CGM09090 physical features for terminal block
and bus port locations on the CGM controller.
Observe the following guidelines when wiring a CGM
controller.
Input and Output terminal blocks
On the CGM controller models, the input and
output terminal blocks are removable. All of the
input terminal blocks are mounted on the bottom
of the controller, and the output terminal blocks
are mounted on the top of the controller. For
information about removing a terminal block, see
Removing a terminal block. For more information
about I/O terminal functions, requirements, and
ratings, see Terminal wiring guidelines, functions,
ratings, and requirements.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide4
Page 5
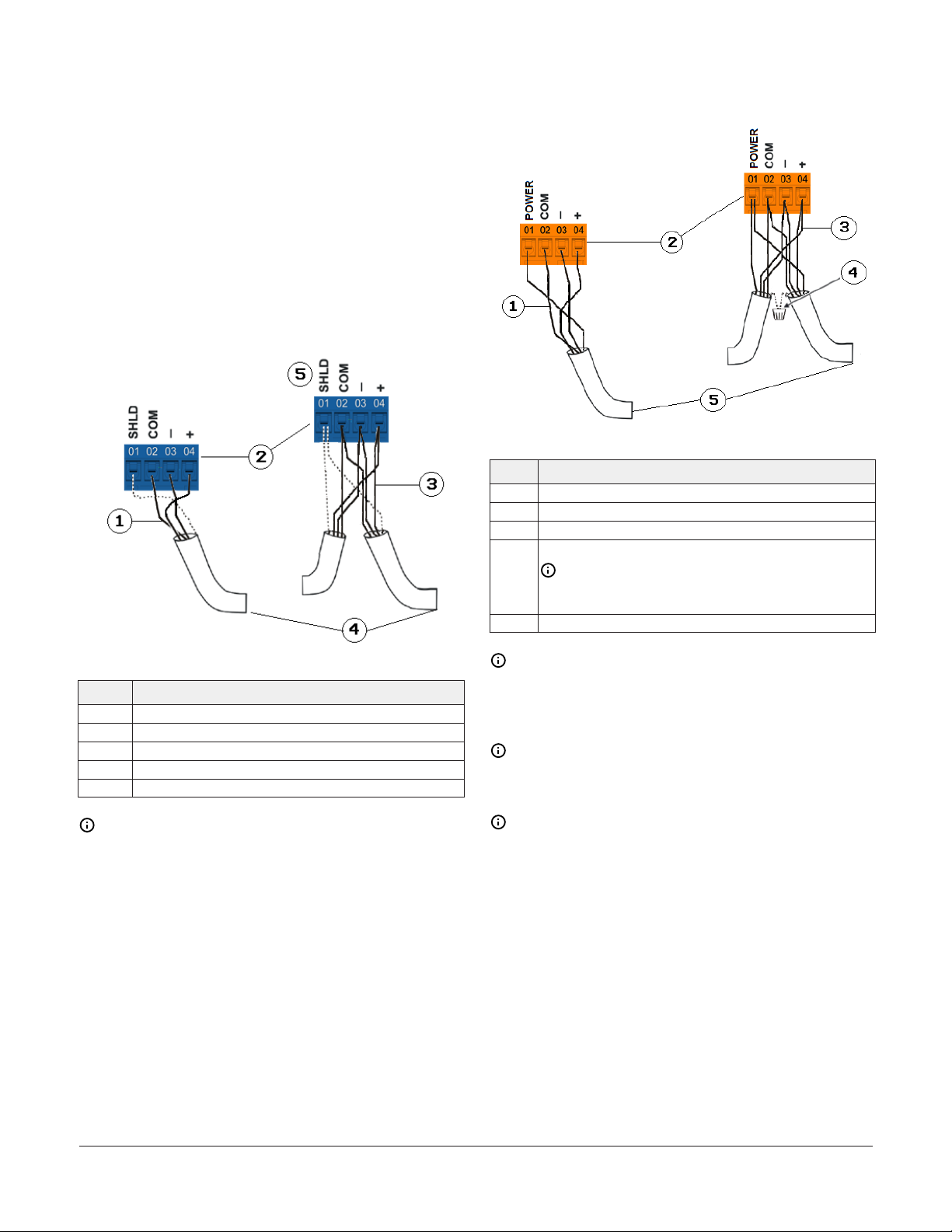
FC bus terminal block (or N2 protocol as required)
The FC bus terminal block is a blue, removable, 4terminal plug that fits into a board-mounted pin
header.
Use a 3-wire twisted, shielded cable, as shown in
Figure 4, to wire the removable FC bus terminal
block plugs on the controller, and other controllers,
in a daisy-chain configuration. For more information
about FC Bus terminal functions, requirements, and
ratings, see Table 7.
Figure 4: FC Bus terminal block wiring
Figure 5: SA Bus Terminal Block Wiring
Table 3: SA bus configuration
Description
1 Wiring for a terminating device on SA bus
2 SA bus terminal block plugs
3 Wiring for a daisy chained device on SA bus
Cable shield connection
4
5 Connects to the next device on the SA bus
Note: Connect the shields to ensure they are
continuous the entire length with only one ground
location.
Table 2: FC bus configuration
Description
1 Wiring for a terminating device on the FC bus
2 FC bus terminal block plugs
3 Wiring for a daisy-chained device on an FC bus segment
4 Connects to the next device on the FC bus
5 Isolated Shield connection terminal
Note: The FC bus Shield (SHLD) terminal is
isolated and can be used to connect (daisy
chain) the shields for FC bus wiring.
SA bus terminal block
The SA Bus terminal block is an orange, removable,
4-terminal plug that fits into a board-mounted jack.
Use a 4-wire twisted, shielded cable, as shown in
Figure 5, to wire the removable SA Bus terminal
block plugs on the controller, and other SA bus
devices, in a daisy-chain configuration. See
Terminal wiring guidelines, functions, ratings, and
requirements for more information.
Note: The POWER terminal supplies 15 VDC.
The POWER terminal can be used to connect
(daisy chain) the 15 VDC power leads on the SA
bus.
Note: Do not use the modular SA Bus port and
the terminal block SA Bus simultaneously. Only
use one of these connections at a time.
Note: The CGM controller is the EOL for the SA
Bus.
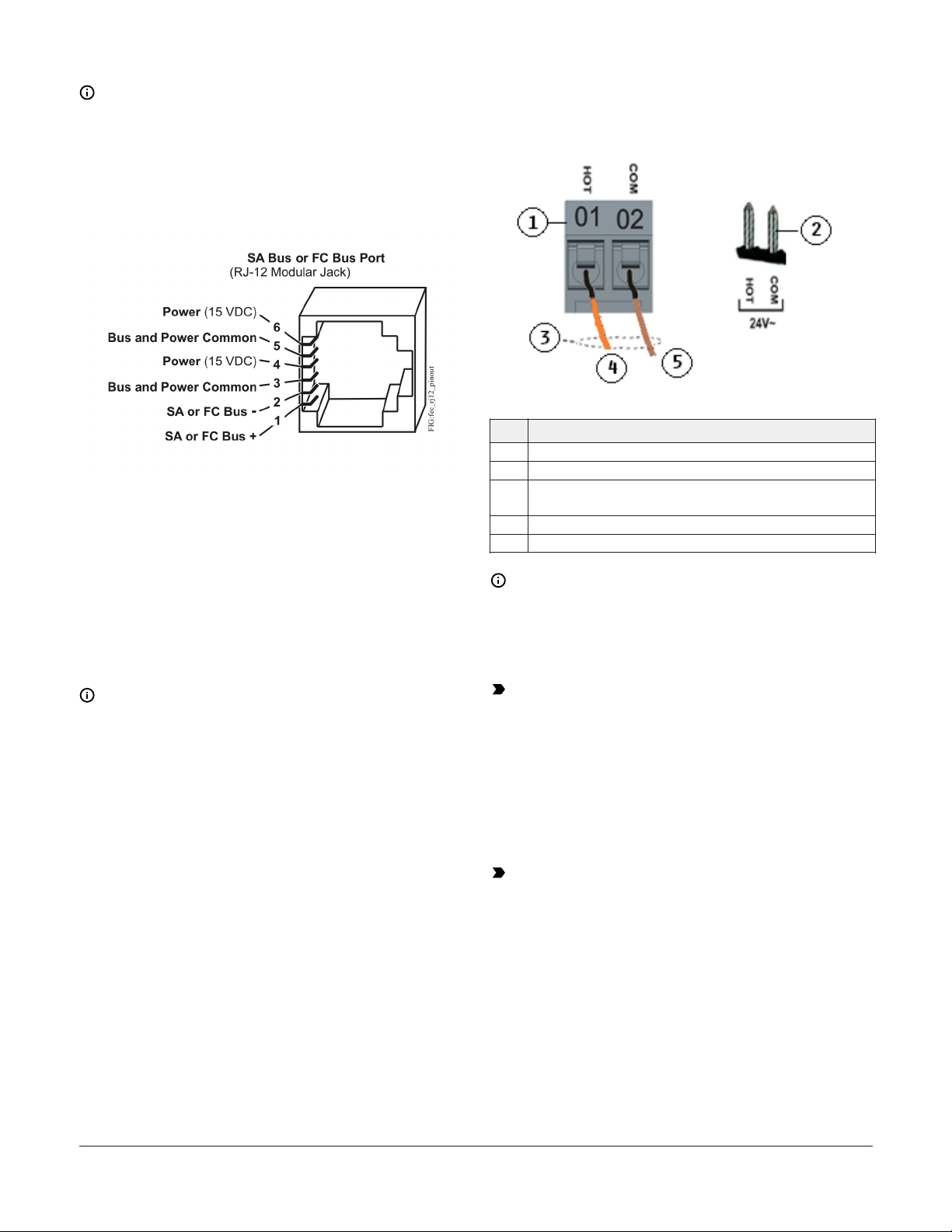
FC bus port
The FC bus port on the front of the controller is
an RJ-12, 6-position modular jack that provides
a connection for the Mobile Access Portal (MAP)
Gateway, or the ZFR/ZFR Pro Wireless Field Bus
Router.
The FC bus port is connected internally to the FC bus
terminal block. See Table 7 for more information.
The FC bus port pin assignment is shown in Figure 6.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 5
Page 6
Note: The MAP Gateway serves as a
replacement for the BTCVT, which is no longer
available for purchase, but continues to be
supported.
Figure 6: Pin number assignments for FC bus and
SA bus ports on equipment controllers
SA Bus port
The Sensor (SA Bus) port on the front of the
controller is an RJ-12, 6-position modular jack that
provides a connection for the MAP Gateway, BTCVT,
the VAV Balancing Tool, the DIS1710 local controller
display, specified network sensors, or other SA
Bus devices with RJ-12 plugs. When the CGM is
configured for N2 network communication, you
must download and commission the controller using
the SA Bus port.
Note: The MAP Gateway serves as a
replacement for the BTCVT, which is no longer
available for purchase, but continues to be
supported.
The Sensor port is connected internally to the SA bus
terminal block. See Table 7 for more information.
The Sensor port pin assignment is shown in Figure 6.
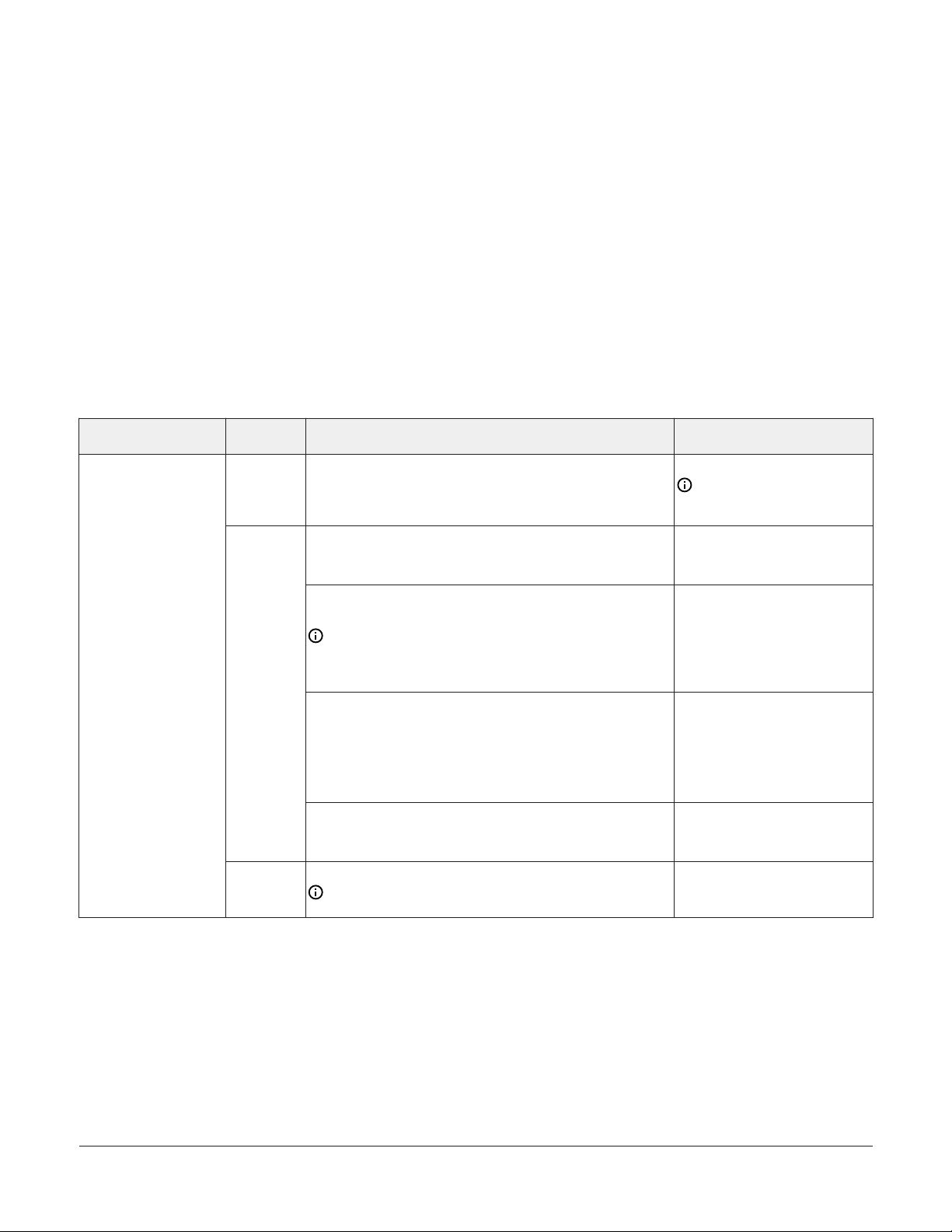
Supply power terminal block
The 24 VAC supply power terminal block is a gray,
removable, 2-pin terminal plug that fits into a boardmounted jack on the top right of the controller.
Wire the 24 VAC supply power wires from the
transformer to the HOT and COM terminals on
the terminal plug as shown in Figure 7. For more
information about the Supply Power Terminal Block,
see Table 7.
Figure 7: 24 VAC supply power terminal block
wiring
Table 4: Supply power terminal block wiring
Description
1 Supply power terminal block
2 Supply power terminal header
Wires from Johnson Controls 24 VAC, class 2 power
3
transformer
4 24 VAC (Orange wire)
5 COM (Brown wire)
Note: The supply power wire colors may
be different on transformers from other
manufacturers. Refer to the transformer
manufacturer’s instructions and the project
installation drawings for wiring details.
Important: Connect 24 VAC supply power
to the equipment controller and all other
network devices so that transformer phasing is
uniform across the network devices. Powering
network devices with uniform 24 VAC supply
power phasing reduces noise, interference,
and ground loop problems. The equipment
controller does not require an earth ground
connection.
Important: Power wires must be less than 30
meters between controller and transformer
Terminal wiring guidelines, functions, ratings, and requirements
This section provides further guidelines on input and
output wiring, maximum cable length versus load
current, and SA Bus and supply power wiring.
For information about removing a terminal block
from the controller, see Removing a terminal block.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide6
Page 7
Input and Output wiring guidelines
• All input and output cables, regardless of wire size
or number of wires, should consist of stranded,
Table 5 provides information and guidelines about
the functions, ratings, and requirements for the
controller input and output terminals, and Table 6
also references guidelines for determining proper
insulated, and twisted copper wires.
• Shielded cable is not required for input or output
cables.
wire sizes and cable lengths.
In addition to the wiring guidelines in Table 5,
observe these guidelines when wiring controller
inputs and outputs:
• Run all low-voltage wiring and cables separate
from high-voltage wiring.
• Shielded cable is recommended for input
and output cables that are exposed to high
electromagnetic or radio frequency noise.
• Inputs/outputs with cables less than 30 m (100 ft)
typically do not require an offset in the software
setup. Cable runs over 30 m (100 ft) may require
an offset in the input/output software setup.
I/O terminal blocks, ratings and requirements
Table 5: I/O terminal blocks, functions, ratings, requirements, and cables
Terminal Block label
UNIVERSAL
(Inputs)
Terminal
label
+15 V
INn
ICOMn
Function, ratings, requirements
15 VDC Power Source for active (3-wire) input devices
connected to the Universal INn terminals.
Provides 100 mA total current
Analog Input - Voltage Mode (0–10 VDC)
10 VDC maximum input voltage
Internal 10k ohm Pull-down
Analog Input - Current Mode (4–20 mA)
Internal 100 ohm load impedance
Note: Current loop jumpers are fail-safe to maintain a
closed 4 to 20 mA current loop, even when the power to
the controller is interrupted or off. See UI current loop
jumpers.
Analog Input - Resistive Mode (0–600k ohm)
Internal 12 V. 15k ohm pull up
Qualified Sensors: 0-2k ohm potentiometer, RTD (1k Nickel
[Johnson Controls® sensor], 1k Platinum, and A99B Silicon
Temperature Sensor) Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC)
Sensor
Binary Input - Dry Contact Maintained Mode
1 second minimum pulse width
Internal 12 V. 15k ohm pull up
Universal Input Common for all Universal Input terminals
Note: All Universal ICOMn terminals share a common,
which is isolated from all other commons.
Determine wire size and
maximum cable length
Same as (Universal) INn
Note: Use 3-wire cable for
devices that source power
from the +15V terminal.
See Guideline A in Table 6
See Guideline B in Table 6.
See Guideline A in Table 6.
See Guideline A in Table 6.
Same as (Universal) INn
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 7
Page 8
Table 5: I/O terminal blocks, functions, ratings, requirements, and cables
Terminal Block label
BINARY
(Inputs)
CONFIGURABLE
(Outputs)
ANALOG
(Outputs)
Terminal
label
INn
ICOMn
OUTn
OCOMn
OUTn
OCOMn
Function, ratings, requirements
Binary Input - Dry Contact Maintained Mode
0.01 second minimum pulse width
Internal 18 V. 3k ohm pull up
Binary Input - Pulse Counter/Accumulator Mode
0.01 second minimum pulse width
(50 Hz at 50% duty cycle)
Internal 18 V. 3k ohm pull up
Binary Input Common for all Binary Input (IN) terminals
Note: All Binary ICOMn terminals share a common,
which is isolated from all other commons, except the
Configurable Output (CO) common (OCOMn) when the
CO is defined as an Analog Output.
Analog Output - Voltage Mode (0–10 VDC)
10 VDC maximum output voltage
10 mA maximum output current
Required an external load of 1,000 ohm or more.
Binary Output - 24 VAC Triac (External Power Source only)
Connects OUTn to OCOMn when activated.
External Power Source Requirements:
30 VAC maximum output voltage
0.5 A maximum output current
1.3 A at 25% duty cycle
Maximum 6 cycles/hour with M9220BGx-3
40 mA minimum load current
Analog Output Signal Common All Configurable Outputs
(COs) defined as Analog Outputs (AOs) share a common,
which is isolated from all other commons except the Binary
Input common.
Binary Output Signal Common All Configurable Outputs
(COs) defined as Binary Outputs are isolated from all other
commons, including other CO commons.
Analog Output - Voltage Mode (0–10 VDC)
10 VDC maximum output voltage
10 mA maximum output current
Required an external load of 1,000 ohm or more.
Note: The Analog Output (AO) operates in the Voltage
Mode when connected to devices with impedances
greater than 1,000 ohm. Devices that drop below 1,000
ohm may not operate as intended for Voltage Mode
applications.
Analog Output - Current Mode (4–20 mA)
Requires and external load between 0 and 300 ohm.
Note: The Analog Output (AO) operates in the Current
Mode when connected to devices with impedances less
than 300 ohm. Devices with impedances greater than
300 may not operate as intended for Current Mode
applications.
Analog Output Signal Common for all Analog OUT terminals.
Note: All Analog Output Common terminals (OCOMn)
share a common, which is isolated from all other
commons.
Determine wire size and
maximum cable length
See Guideline A in Table 6.
See Guideline A in Table 6.
See Guideline C in Table 6.
Same as (Configurable) OUTn.
See Guideline C in Table 6.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide8
Page 9

Table 5: I/O terminal blocks, functions, ratings, requirements, and cables
Terminal Block label
BINARY
(Output)
Terminal
label
OUTn
OCOMn
Function, ratings, requirements
Binary Output - 24 VAC Triac (External Power Source)
Connects OUTn to OCOMn when activated.
External Power Source Requirements:
30 VAC maximum output voltage
0.5 A maximum output current
1.3 A at 25% duty cycle
Maximum 6 cycles/hour with M9220BGx-3
40 mA minimum load current
Binary Output Common (for OUTn terminal)
Note: Each Binary Output Common terminal (OCOMn) is
isolated from all other commons, including other Binary
Output Common terminals.
Determine wire size and
maximum cable length
See Guideline C in Table 6.
Cable and wire length guidelines
Table 6 defines cable length guidelines for the various wire sizes that may be used for wiring low-voltage
(<30 V) input and outputs. The required wire sizes and lengths for high-voltage (>30 V) Relay Outputs are
determined by the load connected to the relay, and local, national or regional electrical codes.
Table 6: Cable length guidelines
Guideline Wire size/Gauge and type
1.0 mm (18 AWG) stranded copper 457 m (1,500 ft) twisted wire
0.8 mm (20 AWG) stranded copper
297 m (975 ft) twisted wire
A
B
C
0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded copper
183 m (600 ft) twisted wire
0.5mm (24 AWG) stranded copper
107 m (350 ft) twisted wire
1.0 mm (18 AWG) stranded copper 229 m (750 ft) twisted wire
0.8 mm (20 AWG) stranded copper
297 m (975 ft) twisted wire
0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded copper
183 m (600 ft) twisted wire
0.5 mm (24 AWG) stranded copper
107 m (350 ft) twisted wire
See Figure 8 to select wire size/
gauge.
Use stranded copper wire.
Maximum cable length and
type
297 m (975 ft) twisted wire
183 m (600 ft) twisted wire
107 m (350 ft) twisted wire
137 m (450 ft) twisted wire
91 m (300 ft) twisted wire
61 m (200 ft) twisted wire
See Figure 8 to determine cable
length.
Use twisted wire cable.
Assumptions
100 mV maximum voltage drop
Depending on the cable length
and the connected input or
output device, you may have
to define an offset in the setup
software for the input or output
point.
100 mV maximum voltage drop
Depending on the cable length
and the connected input or
output device, you may have
to define an offset in the setup
software for the input or output
point.
N/A
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 9
Page 10

Maximum cable length versus load current
Use the following figure to estimate the maximum
cable length relative to the wire size and the load
current (in mA) when wiring inputs and outputs.
Figure 8: Maximum wire length for low-voltage (<30 V) Inputs and Outputs by current and wire size
Note: Figure 8 applies to low-voltage (<30 V)
inputs and outputs only.
Communications bus and supply power wiring guidelines
Table 7 provides information about the functions,
ratings, and requirements for the communication
bus and supply power terminals. The table also
provides guidelines for wire sizes, cable types,
and cable lengths for wiring the controller's
communication buses and supply power.
Important: Refer to the N2 Modernization Guide
for Legacy N2 Controllers (LIT-12012005) for
guidelines when you use this device on an N2
bus.
In addition to the guidelines in Table 7, observe the
following guidelines when you wire an FC or SA bus
and the 24 VAC supply power:
• Run all low-voltage wiring and cables separate
from high-voltage wiring.
• All FC and SA bus cables, regardless of wire size,
should be twisted, insulated, stranded copper
wire.
• Shielded cable is strongly recommended for all FC
and SA bus cables.
• Refer to the MS/TP Communications Bus
Technical Bulletin (LIT-12011034) for detailed
information regarding wire size and cable length
requirements for FC and SA buses.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide10
Page 11

Communications bus and supply power terminal blocks, ratings, and requirements
Table 7: Communications bus and supply power terminal blocks, functions, ratings, requirements, and
cables
Terminal block/
Port label
22
FC BUS
FC BUS (Port)
2
SA BUS
SA BUS (Port)
24~
1 See Input and Output wiring guidelines to determine wire size and cable lengths for cables other than the recommended cables.
2 The FC bus and SA bus wiring recommendations in this table are for MS/TP Bus communications at 38.4k baud. For more
information, refer to the MS/TP Communications Bus Technical Bulletin (LIT-12011034).
3 The MAP Gateway serves as a replacement for the BTCVT, which is no longer available for purchase, but continues to be supported.
Terminal
labels
+
-
Function, electrical ratings/Requirements
FC Bus Communications
COM Signal Reference (Common) for Bus communications
SHLD Isolated terminal
RJ-12 6-Position Modular Connector provides:
FC Bus Communications
2
FC Bus
FC Bus Signal Reference and 15 VDC Common
15 VDC, 180 mA, Power for Bluetooth Commissioning
Converter (BTCVT) or ZFR or ZFR Pro Wireless Router
+
-
SA Bus Communications
COM SA Bus Signal Reference and 15 VDC Common
SA PWR
15 VDC Supply Power for Devices on the SA Bus
(Maximum total current draw for SA Bus is 240 mA.)
RJ-12 6-Position Modular Connector provides:
2
SA BUS
SA Bus Communications
SA Bus Signal Reference and 15 VDC Common
15 VDC Power for devices on the SA bus and BTCVT
HOT
24 VAC Power Supply - Hot
Supplies 20–30 VAC (Nominal 24 VAC)
24 VAC Power Supply Common (Isolated from all other
COM
Common terminals on controller)
14 VA
Recommended cable type
11
0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded, 3-wire
twisted, shielded cable recommended
Bluetooth Commissioning Converter
retractable cable or 24 AWG 3-pair
CAT 3 Cable <30.5 m (100 ft)
33
0.6 mm (22 AWG) stranded, 4-wire
(2 twisted-pairs), shielded cable
recommended.
Note: The + and - wire are one
twisted pair, and the COM and
SA PWR are the second twisted
pair of wires.
24 AWG 3-pair CAT3 cable <30.5 m
(100 ft)
0.8 mm to 1.0 mm
(18 AWG) 2-wire
< 30 m (100 ft)
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 11
Page 12

Termination diagrams
A set of Johnson Controls termination diagrams provides details for wiring inputs and outputs to the
controllers. See the figures in this section for the applicable termination diagrams.
Table 8: Termination details
Type of field
device
Type of Input/
Output
Termination diagrams
Temperature
Sensor
Voltage Input External Source
Voltage Input Internal Source
UI
UI
UI
Voltage Input
(Self-Powered)
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide12
UI
Page 13

Table 8: Termination details
Type of field
device
Current Input External Source
(Isolated)
Current Input Internal Source (2wire)
Type of Input/
Output
UI
UI
Termination diagrams
Current Input Internal Source (3
wire)
Current Input External Source (in
Loop)
Feedback from
EPP-1000
UI
UI
UI
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 13
Page 14

Table 8: Termination details
Type of field
device
Type of Input/
Output
Termination diagrams
Dry Contact
(Binary Input)
0–10 VDC Output
to Actuator
(External Source)
0–10 VDC Output
to Actuator
(Internal Source)
UI or BI
AO
AO
Current Output AO
24 VAC Triac
Output (Switch
Low, External
Source)
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide14
AO
Page 15

Table 8: Termination details
Type of field
device
Type of Input/
Output
Termination diagrams
Analog Output
(Current)
4–20 mA Output to
Actuator
4–20 mA Output to
Actuator
AO
AO
AO
Incremental
Control to
Actuator (Switch
Low, Externally
Sourced)
24 VAC Binary
Output (Switch
Low, Externally
Sourced)
BO
BO
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 15
Page 16

Table 8: Termination details
Type of field
device
24 VAC Binary
Output (Switch
High, Externally
Sourced)
Incremental
Control to
Actuator (Switch
High, Externally
Sourced)
Type of Input/
Output
BO
BO
Termination diagrams
Network Stat with
Phone Jack (Fixed
Address = 199)
Network Stat
with Terminals
Addressable
SA Bus
Note: The bottom jack (J2) on the TE-700 and TE-6x00 Series Sensors is not usable as a zone
bus or an SAB connection.
SA Bus
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide16
Page 17

Table 8: Termination details
Type of field
device
Network Stat with
Terminals (Fixed
Address = 199)
Type of Input/
Output
SA Bus
Termination diagrams
Setup and adjustments
Important: Electrostatic discharge can
damage controller components. Use proper
electrostatic discharge precautions during
installation, setup, and servicing to avoid
damaging the controller.
Configuring N2 communications
N2-capable controllers support the full range of
possible N2 device addresses provided by the N2
protocol standard (1-254).
To configure a controller to communicate using the
N2 protocol, complete the following steps:
1. Disconnect the 24 VAC supply from the
controller.
2. Set the address switches to the desired N2
address. For details about setting a device
address, see Setting the device address.
3. Reconnect the 24 VAC supply to the controller.
1. Disconnect the 24 VAC supply from the
controller.
2. Set the address switches to the desired BACnet
MS/TP address. For details about setting a
device address, see Setting the device address.
3. Reconnect the 24 VAC supply to the controller.
4. Using an SA Bus connection, download a
controller application file configured for BACnet
MS/TP to the controller.
Configuring wireless communications
To configure a controller for use with the ZFR/ZFR
Pro Series Wireless Field Bus system, complete the
following steps:
1. Disconnect the 24 VAC supply from the
controller.
4. Using an SA bus connection, download the
firmware and controller application file
configured for N2 to the controller.
Switching the Communications Protocol from N2 to MS/TP
For N2 sites that are converting to BACnet MS/TP,
you can switch the communications protocol of N2configured MS/TP controllers back to BACnet MS/TP.
To switch the CGM controller operating in N2
mode back into BACnet MS/TP mode, complete the
following steps:
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 17
2. Wire the input/output terminals and SA bus.
Note: In wireless network applications, do not
connect any wires to the FC bus terminal block.
(Connect the FC/SA terminal block on an IOM
to an SA bus only.)
3. Important: Before the CGM controller is
powered on, connect the ZFR/ZFR Pro Wireless
Field Bus Router to the FC bus port (RJ-12
modular jack) on the front of the controller.
Page 18

4. Ensure that the controller's rotary switches are
set to the correct device address. For details
about setting a device address, see Setting the
device address.
5. Reconnect the 24 VAC supply to the controller.
For more information about the ZFR Pro Wireless
Field Bus system, refer to the WNC1800/ZFR182x
Pro Series Wireless Field Bus System Product Bulletin
(LIT-12012320).
For more information about the ZFR 1800 Wireless
Field Bus system, refer to the ZFR1800 Series Wireless
Field Bus System Product Bulletin (LIT-12011336).
Setting the device address
switches are set to 1 2 3, designating this
controller's device address as 123.
Figure 9: Device address rotary switch block
Metasys equipment controllers are master devices
on MS/TP (FC or SA) buses. Before you operate
controllers on a bus, you must set a valid and
unique device address for each controller on the
bus. You set the CGM device address by setting the
positions of the Device Address rotary switches at
the top of the controller.
The following table describes the valid rotary
switch device addresses for communications bus
applications.
Table 9: Switch device addresses
FC Bus Communication
Mode
Wired MS/TP
communication
Zigbee wireless
communication
N2 communication
Valid Device Address Range
4-127
Note: Addresses 0-3 are
reserved and not for use on
equipment controllers.
4-127
Note: Addresses 0-3 are
reserved and not for use on
equipment controllers.
1-254
Note: Addresses 0 and 255 are
reserved and not for use on
equipment controllers.
Note: The controller auto-detects if the
communication protocol is wired MS/TP, Zigbee
Wireless, or N2 on the FC Bus.
The device address must match the device
address defined in the Controller Configuration
Tool (CCT) under Define Hardware > Network
Settings.
To set the device addresses on CGM controllers,
complete the following steps:
1. Set a unique and sequential device address for
each of the equipment controllers connected
on the FC or SA Bus, starting with device
address 4.
2. To ensure the best bus performance, set
sequential device addresses with no gaps in
the device address range (4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, and
so on). The equipment controllers do not need
to be physically connected on the bus in their
numerical device address order.
3. Write each controller's device address on the
white label below the device address rotary
switch block on the controller's cover.
Refer to the MS/TP Communications Bus Technical Bul-
letin (LIT-12011034) for more information about controller device addresses and how to set them on
MS/TP buses.
The device address is a decimal address that is
set using three rotary switches. The numbers
are ordered from left to right, most significant
bit (MSB) to least significant bit (LSB) when the
controller is oriented as shown in CGM09090
physical features. In the following figure, the
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide18
Removing a terminal block
To remove the terminal block from the circuit board,
complete the following steps:
Note: You need a flat blade screwdriver to
remove the terminal block.
Page 19

1. To prevent any possibility of damage from an
accidental short, remove power from the
controller.
2. Underneath the terminal block, in the small gap
between the bottom of the terminal block and
the circuit board, insert the flat blade of the
screwdriver.
1. Place your fingertips under the two cover lift
tabs (CGM09090 physical features) on the sides
of the housing cover and gently pry the top of
the cover away from the base to release the
cover from the two upper latches.
2. Pivot the top of the cover further to release it
from the lower two latches.
Figure 10: Terminal block
3. To detach the left-hand side of the terminal
block, position the flat blade underneath the
terminal block to the left, and push down the
screwdriver handle. When you do this, you are
using the screwdriver as a lever to pry up the
terminal block.
4. To detach the right-hand side of the terminal
block, position the flat blade underneath the
terminal block to the right, and push down the
screwdriver handle.
5. If necessary, repeat steps 3 and 4 until the
terminal block is removed.
Removing the controller cover
Important: Electrostatic discharge can
damage controller components. Use proper
electrostatic discharge precautions during
installation, setup, and servicing to avoid
damaging the controller.
3. Replace the cover by placing it squarely over
the base, and then gently and evenly push the
cover on to the latches until they snap into the
latched position.
Cover removed, EOL switch, and current jumpers
Figure 11: CGM with cover removed showing EOL
switch and jumper positions
Setting the End-of-Line (EOL) switch
Important: Disconnect all power sources
to the controller before removing cover and
changing the position of any jumper or the EOL
switch on the controller. Failure to disconnect
power before changing a jumper or EOL switch
position can result in damage to the controller
and void any warranties.
The controller cover is held in place by four
plastic latches that extend from the base and
snap into slots on the inside of the housing
cover.
To remove the controller cover, complete the
following steps:
Each CGM controller has an EOL switch, which, when
set to ON (up), sets the controller as a terminating
device on the bus. See Figure 11 for the EOL switch
location. The default EOL switch position is OFF
(down).
Figure 12: End-of-Line switch positions
To set the EOL switch on a controller, complete the
following steps:
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 19
Page 20

1. Determine the physical location of the
controller on the FC bus.
2. Determine if the controller must be set as a
terminating device on the bus.
Note: For detailed information about EOL
termination rules and EOL switch settings on
FC buses, refer to the MS/TP Communications
Bus Technical Bulletin (LIT-12011034).
3. If the controller is a terminating device on
the FC bus, set the EOL switch to ON. If the
controller is not a terminating device on the
bus, set the EOL switch to Off.
When a controller is connected to power with its
EOL switch set to ON, the amber EOL LED on the
controller cover is illuminated.
Figure 13: Exchange enable and default settings
Setting the current loop jumper to the Enabled
position, (Figure 13) connects an internal 100 ohm
resistor across the UI terminals, which maintains the
4-20 mA current loop circuit even when power to the
controller is interrupted or off.
Important: Current Loop jumpers must be in
the Disabled (default) position for all UIs that
are not set up to operate as 4-20 mA analog
inputs.
Setting the input jumpers
CAUTION
Risk of Electric Shock:
Disconnect supply power to the field controller before
attempting to adjust the Binary Output Source Power
Selection Jumpers. Failure to disconnect the supply
power may result in electric shock.
ATTENTION
Mise En Garde: Risque de décharge électrique:
Débrancher l'alimentation de l'controller avant tout
réglage du Binary Output Source Power Selection
Jumpers. Le non-respect de cette précaution risque
de provoquer une décharge électrique.
UI current loop jumpers
The following table identifies the current loop
switches associated with each UI on the CGM
controller.
Table 10: CGM UI Inputs and jumper labels
Universal Input
label
IN1 J13
IN2 J14
IN3 J15
IN4 J16
IN5 J17
IN6 J18
IN7 J19
Jumper label on circuit board
Setting up a local display
CGM models do not have an integral display, but
can be connected to a DIS1710 Local Controller
Display. For detailed information about setting
up and operating a remotely connected DIS1710
display, refer to the DIS1710 Local Controller Display
Technical Bulletin (LIT-12011270) .
Input/Output Wiring Validation
The UI current loop fail-safe jumpers are on the
circuit board under the controller cover near the UI
terminals (Figure 11). When a UI is defined (in the
system software) as a 4-20 mA Analog Input and the
UI’s current loop jumper is in the Disabled (default)
position (Figure 13), the internal 100 ohm load
resister is disconnected and the 4-20mA current
loop is open.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide20
The CGM controllers ship with a default state that
can assist in validating the wiring of the input and
output terminals prior to download of an application
file. When the controller is powered on in this state,
the Fault LED will flash in a pattern of two quick
blinks and then a long pause (see Table 11).
To make use of this feature, ensure the rotary
switches are set to the desired address and wire the
input and output terminals. Apply power to the CGM
Page 21

controller and connect to the device with either a
MAP Gateway or MS-DIS1710-0 Local Display to view
the points in the controller. The CGM controller will
report an Operational status even though there is
no true application loaded. CCT will not be able to
commission or upload the device as a result until
a true application is downloaded. The application
name displayed will be the address of the controller
followed by the model of the controller and “Default
State”.
For example, a CGM09090 controller whose rotary
switches are set to 8 would have the default state
application name of “8-CGM09090 Default State”.
The default state creates I/O points for all
connections on the input and output terminals.
It assumes all Universal Inputs (UIs) are Nickel
temperature sensors. All Configurable Outputs
(COs) are treated as Binary Outputs (BOs) with an
initial value of 0. The default state also takes input
from a Network Sensor at address 199. If there is
no connected Network Sensor, the startup of this
default state will be delayed by 30 seconds as the
controller attempts to establish connection with the
sensor.
Commissioning equipment controllers
You commission MS/TP equipment controllers with
the CCT software using either MAP Gateway , a
BTCVT, a ZFR wireless dongle, or in passthrough
mode when connected to an NAE or NCE. For
detailed information about commissioning
field controllers, refer to Controller Tool Help
(LIT-12011147).
Note: You can use the Bluetooth connection
to Transfer to Computer (Upload) and
commission the controller, but you cannot use
the Bluetooth connection to Transfer to Device
(Download).
Note: The MAP Gateway serves as a
replacement for the BTCVT, which is no longer
available for purchase, but continues to be
supported.
Troubleshooting equipment controllers
Observe the Status LEDs on the front of the
equipment controller. Table 11 provides LED
status indicator information for troubleshooting
the controller. To troubleshoot an integral or
local controller display, refer to the DIS1710 Local
Controller Display Technical Bulletin (LIT-12011666).
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 21
Page 22

LED status and states
Table 11: Status LEDs and description of LED states
LED label LED color Normal LED state Description of LED states
Off Steady = No Supply Power or the controller’s polyswitch/resettable fuse is
POWER Green On Steady
FAULT Red Off Steady
SA BUS Green Blink - 2 Hz
FC BUS Green Blink - 2 Hz
Off (Except on
EOL Amber
terminating
devices)
open. Check Output wiring for short circuits and cycle power to controller.
On Steady = Power Connected
2 blinks followed by long pause = Controller powered on in default state. For more
information about this default state, see Input/Output Wiring Validation.
Off Steady = No Faults
On Steady = Device Fault; no application loaded; Main Code download required, if
controller is in Boot mode, or a firmware mismatch exists between the CGM and
the ZFR1811 Wireless Field Bus Router.
Blink - 2 Hz = Download or Startup in progress, not ready for normal operation
Rapid blink = SA Bus communications issue
Blink - 2 Hz = Data Transmission (normal communication)
Off Steady = No Data Transmission (N/A - auto baud not supported)
On Steady = Communication lost, waiting to join communication ring
Blink - 2 Hz = Data Transmission (normal communication)
Off Steady = No Data Transmission (auto baud in progress)
On Steady = Communication lost, waiting to join communication ring
On Steady = EOL switch in ON position
Off Steady = EOL switch in Off position
Repair information
If an equipment controller fails to operate within
its specifications, replace the controller. For a
replacement controller, contact your Johnson
Controls representative.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide22
Page 23

Ordering information and accessories
The following tables provide the product code number and description for the CGM models and accessories.
Table 12: CGM Series ordering information
Product code number Description
General Purpose Application Controller
M4-CGM09090-0
Table 13: CGM Controller accessories (order separately)
Product Code Number Description
IOM Series Controllers
TL-CCT-0
MS-FCP-0
Mobile Access Portal (MAP) Gateway
MS-DIS1710-0 Local Controller Display
NS Series Network Sensors
AS-CBLTSTAT-0 Cable adapter for connection to 8-pin TE-6700 Series sensors
NS-WALLPLATE-0 Network Sensor Wall Plate
WRZ Series Wireless Room Sensors
WRZ-7860-0
WRZ-SST-120
WNC1800/ZFR182x Pro Wireless Field Bus System
ZFR1800 Series Wireless Field Bus System
ZFR-USBHA-0
Y64T15-0
Y65A13-0
Y65T31-0
Y65T42-0
Includes: MS/TP (and N2) communication; 18 points (7 UI, 2 BI, 4 CO, 2 AO, 3 BO); real-time clock; 32-bit
microprocessor; 24VAC input
Refer to the Metasys® System Field Equipment Controllers and Related Products
Product Bulletin (LIT-12011042) for a complete list of available IOM Series
Controllers.
License enabling Metasys Controller Configuration Tool (CCT) software for one
user
License enabling Metasys Equipment Controller Firmware Package Files required
for CCT
Refer to the Mobile Access Portal Gateway Catalog Page (LIT-1900869) to identify the
appropriate product for your region.
Note: The MAP Gateway serves as a replacement for the BTCVT, which is no
longer available for purchase, but continues to be supported.
Refer to the NS Series Network Sensors Product Bulletin (LIT-12011574) for specific
sensor model descriptions.
Refer to the WRZ Series Wireless Room Sensors Product Bulletin (LIT-12000653) for
specific sensor model descriptions.
Refer to the WRZ-7860 Receiver for One-to-One Wireless Room Sensing Product
Bulletin (LIT-12011640) for a list of available products.
Refer to the WRZ-SST-120 Wireless Sensing System Tool Installation Instructions
(LIT-24-10563-55) for usage instructions.
Refer to the WNC1800/ZFR182x Pro Series Wireless Field Bus System Product Bulletin
(LIT-12012320) for a list of available products.
Refer to the ZFR1800 Series Wireless Field Bus System Product Bulletin (LIT-12011336)
for a list of available products.
ZFR USB Dongle provides a wireless connection through CCT to allow wireless
commissioning of the wirelessly enabled CGM, CVM, FAC, FEC, VMA16, and IOM
controllers. It also allows use of the ZFR Checkout Tool (ZCT) in CCT.
Note: The ZFR-USBHA-0 replaces the IA OEM DAUBI_2400 ZFR USB dongle.
For additional information about the ZFR-USBHA-0 ZFR dongle, refer to the
ZCT Checkout Tool Help LIT-12012292 or the WNC1800_ZFR182x Pro Series
Wireless Field Bus System Technical Bulletin (LIT-12012356).
Transformer, 120/208/240 VAC Primary to 24 VAC Secondary, 92 VA, Foot Mount,
72.2 cm (30 in.), Primary Leads and 76.2 cm (30 in.) Secondary Leads, Class 2
Transformer, 120 VAC Primary to 24 VAC Secondary, 40 VA, Foot Mount (Y65AS),
20.32 cm (8 in.), Primary Leads and 76.2 cm (30 in.) Secondary Leads, Class 2
Transformer, 120/208/240 VAC Primary to 24 VAC Secondary, 40 VA, Foot Mount
(Y65AR+), 20.32 cm (8 in.), Primary Leads and Secondary Screw Terminals, Class 2
Transformer, 120/208/240 VAC Primary to 24 VAC Secondary, 40 VA, Hub Mount
(Y65SP+), 20.32 cm (8 in.), Primary Leads and Secondary Screw Terminals, Class 2
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 23
Page 24

Table 13: CGM Controller accessories (order separately)
Product Code Number Description
The Field Inspection Tool or (FIT) is a portable handheld device with a user
interface that is used to test and troubleshoot the BACnet protocol MS/TP RS-485
communications bus that connects supervisory controllers and equipment
MS-FIT100-0
TL-BRTRP-0 Portable BACnet/IP to MS/TP Router
controllers to field point interfaces.
The FIT can be used to check out the wiring of the MS/TP RS-485 bus as well
as verify proper communications of supervisory controllers and equipment
controllers connected to the bus. The FIT can be used on both the FC Bus and SA
Bus.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide24
Page 25

Technical specifications
Table 14: Technical specifications
M4-CGM09090-0 General Purpose Application Controller
Product Code Numbers
Power Requirement
Power Consumption
Power Source
Ambient Conditions
Network Engines All network engine model types
Communications Protocol
Device Addressing for BACnet MS/TP Decimal address set via three rotary switches; valid controller device addresses 4-127
Device Addressing for N2 Decimal address set via three rotary switches: valid controller device addresses 1-254
Communications Bus
Processor RX64M Renesas® 32-Bit microcontroller
Memory 16 MB flash memory and 8 MB SDRAM
Real-Time Clock Backup Power Supply
Input and Output Capabilities
Universal Input (UI) Resolution/ Analog
Output (AO) Accuracy
Terminations
Mounting
Housing
Dimensions (Height x Width x Depth)
Weight 0.5 kg (1.1 lb)
Includes: MS/TP (and N2) communication; 18 points (7 UI, 2 BI, 4 CO, 2 AO, 3 BO); realtime clock; 32-bit microprocessor; 24VAC input
24 VAC (nominal, 20 VAC minimum/30 VAC maximum), 50/60 Hz, Power Supply Class 2
(North America), Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV) (Europe)
14 VA maximum
Note: The USB feature is not currently supported.
Note: The VA rating does not include any power supplied to the peripheral devices
connected to Binary Outputs (BOs) or Configurable Outputs (COs), which can
consume up to 12 VA for each BO or CO; for a possible total consumption of an
additional 84 VA (maximum).
+15 VDC power source terminals provide 100 mA total current. Quantity 2 located in
Universal IN terminals - for active (3-wire) input devices
Operating: 0°C to 50°C (32°F to 122°F); 10% to 90% RH noncondensing
Storage: -40°C to 80°C (-40°F to 176°F); 5% to 95% RH noncondensing
BACnet MS/TP; N2. Wireless also supported (at FC Bus and for Sensors) with additional
hardware.
BACnet MS/TP (default); N2
3-wire FC Bus between the supervisory controller and equipment controllers
4-wire SA Bus between equipment controller, network sensors and other sensor/actuator
devices, includes a lead to source 15 VDC supply power (from equipment controller) to
bus devices.
Super capacitor maintains power to the onboard real-time clock for a minimum of 72
hours when supply power to the controller is disconnected.
Universal Inputs: Defined as 0–10 VDC, 4–20 mA, 0–600k ohms, or Binary Dry Contact
Binary Inputs: Defined as Dry Contact Maintained or Pulse Counter/Accumulator Mode
Configurable Outputs Defined as 0-10 VDC or 24 VAC Triac BO
Analog Outputs: Defined as 0–10 VDC or 4–20 mA
Binary Outputs: Defined as 24 VAC Triac (external power source only)
Input: 24-bit Analog to Digital converter
Output: +/- 200 mV accuracy in 0–10 VDC applications
Input/Output: Pluggable Screw Terminal Blocks
SA/FC Bus and Supply Power: 4-Wire and 2-Wire Pluggable Screw Terminal Blocks
SA/FC Bus Port: RJ-12 6-Pin Modular Jacks
Horizontal on single 35 mm DIN rail mount (recommended), or screw mount on flat
surface with three integral mounting clips on controller
Enclosure material: ABS and polycarbonate UL94 5VB; Self-extinguishing
Protection Class: IP20 (IEC529)
150 mm x 190 mm x 44.5 mm (5-7/8 in. x 7-1/2 in. x 2-1/8 in.) including terminals and
mounting clips
Note: Mounting space requires an additional 50 mm (2 in.) space on top,
bottom, and front face of controller for easy cover removal, ventilation, and wire
terminations.
M4-CGM General Purpose Application Controllers Installation Guide 25
Page 26

Table 14: Technical specifications
United States: UL Listed, File E107041, CCN PAZX, UL 916, Energy Management
Equipment
Compliance
FCC Compliant to CFR47, Part 15, Subpart B, Class A
Canada: UL Listed, File E107041, CCN PAZX7 CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 205, Signal Equipment
Industry Canada Compliant, ICES-003
Europe: Johnson Controls declares that this product is in compliance with the essential
requirements and other relevant provisions of the EMC Directive nd RoHS Directive.
Australia and New Zealand: RCM Mark, Australia/NZ Emissions Compliant
BACnet International: BACnet Testing Laboratories™ (BTL) Protocol Revision 15 Listed
and Certified BACnet Advanced Application Controller (B-AAC), based on ANSI/ASHRAE
135-2016
The performance specifications are nominal and conform to acceptable industry standard. For application at
conditions beyond these specifications, consult the local Johnson Controls office. Johnson Controls shall not be
liable for damages resulting from misapplication or misuse of its products.
Product warranty
This product is covered by a limited
warranty, details of which can be found at
www.johnsoncontrols.com/buildingswarranty.
Single point of contact
APAC Europe NA/SA
JOHNSON CONTROLS
C/O CONTROLS PRODUCT
MANAGEMENT
NO. 32 CHANGJIJANG RD NEW
DISTRICT
WUXI JIANGSU PROVINCE 214028
CHINA
JOHNSON CONTROLS
WESTENDHOF 3
45143 ESSEN
GERMANY
JOHNSON CONTROLS
507 E MICHIGAN ST
MILWAUKEE WI 53202
USA
For more contact information, refer to
www.johnsoncontrols.com/locations.
© 2019 Johnson Controls. All rights reserved. All specifications and other information shown were current as of document revision and
are subject to change without notice.
www.johnsoncontrols.com
 Loading...
Loading...