
HiQnet Third Party
Programmer
Documentation
Protocol Specification
System Development and Integration Group
19th February 2013
© HARMAN

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Abstract
This document describes the formatting and methods available for third-party
programmers to control HiQnet Devices.
For BSS Soundweb London devices you should refer to the BSS Soundweb
London Third Party Control Document available from the BSS Audio website.
Limited warranty
No warranties: Harman expressly disclaims any warranty for the 'HiQnet Third
Party Programmer Documentation'. The 'HiQnet Third Party Programmer
Documentation‟ and any related documentation is provided 'as is' without
warranty of any kind, either express or implied, including, without limitation, the
implied warranties or merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, or noninfringement. The entire risk arising out of use or performance of the 'HiQnet
Third Party Programmer Documentation' remains with you.
No Liability for damages: In no event shall Harman or its suppliers be liable for
any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of
business profits, business interruption, loss of business information, or any other
pecuniary loss) arising out of the use of, misuse of, or inability to use this Harman
product, even if Harman has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
Because some states/jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of
liability for consequential or incidental damages, the above limitation may not
apply to you.
Harman
8760 South Sandy Parkway
Sandy, Utah 84070
Phone +1 (801) 568-7660
Fax +1 (801) 568-7662
International fax +1 (801) 568-7583
Revision 2.2 February 2013
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 1 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Table of Contents
1 OVERVIEW ......................................................................................................... 6
1.1 References ....................................................................................................... 6
1.2 Scope................................................................................................................ 6
2 HIQNET PRODUCT ARCHITECTURE ...................................................................... 7
2.1 Device ............................................................................................................... 8
2.2 Virtual Device ................................................................................................... 8
2.3 Virtual Device Attributes ................................................................................... 8
2.4 Device Manager Virtual Device ........................................................................ 8
2.5 Object ............................................................................................................... 9
2.6 Parameter ......................................................................................................... 9
2.6.1 Parameter Attributes ................................................................................ 9
2.7 HiQnet Addressing ......................................................................................... 11
2.7.1 HiQnet Device Address ......................................................................... 12
2.7.2 Virtual Device Address .......................................................................... 13
2.7.3 Object Address ...................................................................................... 14
2.7.4 Source & Destination Addresses in Messages...................................... 14
2.7.5 Parameter Index .................................................................................... 15
2.7.6 Parameter Range .................................................................................. 15
2.8 Alternate methods of finding a HiQnet address. ............................................ 16
2.8.1 Copy HiQnet Information ....................................................................... 16
2.8.2 Finding an Address using the Custom Panels and the Properties
Window ............................................................................................. 17
3 HIQNET MESSAGE FORMAT .............................................................................. 22
3.1 Header ............................................................................................................ 22
3.1.1 Version ................................................................................................... 23
3.1.2 Header Length ....................................................................................... 23
3.1.3 Message Length .................................................................................... 23
3.1.4 Source Address ..................................................................................... 23
3.1.5 Destination Address ............................................................................... 23
3.1.6 Message ID ............................................................................................ 24
3.1.7 Flags ...................................................................................................... 24
3.1.8 Hop Count .............................................................................................. 24
3.1.9 Sequence Number ................................................................................. 24
3.2 Types of Messages ........................................................................................ 24
3.2.1 Request Acknowledgement Message ................................................... 24
3.2.2 Acknowledge Message Flag .................................................................. 25
3.2.3 Information Message Flag ..................................................................... 25
3.2.4 Error Message Flag ............................................................................... 25
3.2.5 Guaranteed Message Flag .................................................................... 25
3.2.6 Multi-part Message Flag ........................................................................ 26
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 2 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
3.3 Device Level Methods .................................................................................... 27
3.3.1 Get Attributes ......................................................................................... 27
3.3.2 GetVDList............................................................................................... 28
3.3.3 Store ...................................................................................................... 29
3.3.4 Recall ..................................................................................................... 31
3.3.5 Recall Action Determines Type of Data Affected .................................. 31
3.3.6 Locate .................................................................................................... 32
3.3.7 Locate Message .................................................................................... 32
3.4 Event Log ....................................................................................................... 33
3.4.1 Event Log Data ...................................................................................... 33
3.4.2 Requesting Event Log Client Subscriptions .......................................... 35
3.4.3 Request Event Log ................................................................................ 38
3.4.4 Request Event Log INFORMATION (response):................................... 39
3.5 Introduction to Parameters ............................................................................. 41
3.5.1 Data Type Definition .............................................................................. 41
3.5.2 Sensor/Non-Sensor ............................................................................... 42
3.6 MultiParamSet ................................................................................................ 42
3.7 MultiParamGet ................................................................................................ 42
3.7.1 INFORMATION: ..................................................................................... 43
3.8 MultiParamSubscribe ..................................................................................... 44
3.9 MultiParamUnsubscribe ................................................................................. 45
3.10 MultiObjectParamSet.................................................................................... 46
3.11 ParamSetPercent ......................................................................................... 46
3.11.1 ParamSetPercent Message ................................................................. 48
3.12 ParamSubscribePercent .............................................................................. 49
3.12.1 ParamSubscribePercent Message ...................................................... 50
4 HIQNET NETWORK MODEL ................................................................................ 51
4.1 Routing Layer ................................................................................................. 51
4.1.1 Routing Layer Introduction ..................................................................... 51
4.1.2 Transmitting Messages .......................................................................... 52
4.1.3 Datagram Service .................................................................................. 52
4.1.4 DiscoInfo ................................................................................................ 53
4.1.5 NetworkInfo ............................................................................................ 54
4.1.6 Device Arrival “Announce” ..................................................................... 54
4.1.7 Device Departure “Goodbye” ................................................................. 55
4.2 Device Discovery on Demand ........................................................................ 55
4.2.1 Searching for a Device .......................................................................... 56
4.2.2 Keep Alive/Device Departure................................................................. 56
4.3 Table of Routing Layer Message IDs ............................................................. 58
4.3.1 DiscoInfo ................................................................................................ 58
4.3.2 GetNetworkInfo ...................................................................................... 59
4.3.3 Request Address ................................................................................... 60
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 3 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
4.3.4 AddressUsed ......................................................................................... 60
4.3.5 SetAddress ............................................................................................ 61
4.3.6 Goodbye ................................................................................................ 61
4.3.7 Hello Query ............................................................................................ 62
4.3.8 Hello Info ................................................................................................ 63
4.4 Packet Service Layers .................................................................................... 63
4.5 TCP/IP Packet Service ................................................................................... 63
4.5.1 Reliable (TCP) Packet Service .............................................................. 64
4.5.2 Datagram (UDP) Packet Service ........................................................... 64
4.5.3 NetworkInfo ............................................................................................ 64
4.5.4 Gateway ................................................................................................. 65
4.5.5 Use Case – Closed loop control of a HiQnet product via TCP/IP –
addressing already fixed. .................................................................. 65
4.5.6 Use Case – Open Loop control of a HiQnet product via UDP ............... 66
5 HIQNET STRING SETTINGS ................................................................................ 67
6 RS232 PACKET SERVICE .................................................................................. 69
6.1 Getting Started/Basic Command Structure .................................................... 69
6.1.1 Baud Rate .............................................................................................. 70
6.1.2 Big Endian.............................................................................................. 70
6.1.3 Data Types............................................................................................. 70
6.1.4 Resync Request / Resync Acknowledge ............................................... 70
6.1.5 Ping ........................................................................................................ 70
6.1.6 Resync_Acknowledge Byte ................................................................... 71
6.1.7 Frame Start Bytes .................................................................................. 71
6.1.8 Basic Command Structure (Unacknowledged – Open Loop) ................ 71
6.1.9 Number Parameters .............................................................................. 72
6.1.10 Parameter_ID ....................................................................................... 72
6.1.11 Data_Type............................................................................................ 72
6.1.12 Parameter_Val ..................................................................................... 72
6.1.13 CCIT checksum ................................................................................... 72
6.2 Setting Up and Maintaining a Communication Connection ............................ 73
6.2.1 Guaranteed Acknowledgement ............................................................. 77
6.2.2 Resync ................................................................................................... 77
6.3 Recall 0x0125 (Message ID) .......................................................................... 77
6.4 Calculating Checksums .................................................................................. 78
6.4.1 How to calculate a checksum using code for the Harman HiQnet
Device: .............................................................................................. 78
6.4.2 Serial String Method .............................................................................. 80
6.5 Feedback ........................................................................................................ 80
6.5.1 ParameterSubscribeAll .......................................................................... 81
6.5.2 ParameterUnSubscribeAll ..................................................................... 82
7 SESSIONS ................................ ................................................................ ........ 85
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 4 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
7.1 Starting a Session .......................................................................................... 85
7.2 Detecting a Session Break ............................................................................. 85
7.3 Characteristics of a Session ........................................................................... 86
7.4 Sessions Use Cases ...................................................................................... 87
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 5 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
1 Overview
1.1 References
1.2 Scope
This document provides the publicly available means for controlling HiQnet
products. Included are the following:
HiQnet product architecture
All formatting of messages
Network specific information for implemented transports
Open-loop and closed loop control methodologies
Examples utilizing System Architect to facilitate message formation
Although examples are given using specific Devices, detailed documentation is
not provided for every HiQnet Device. Instead, methods of using System
Architect to glean that information are provided. It is assumed that readers are
familiar with System Architect, the basics of Ethernet networking, and RS232.
Note that it is not intended that third-party control Devices implement all of the
methods detailed in this document. It is assumed that in most cases only a subset
of these messages will be implemented. Some of the information presented is for
explanatory reasons only, such that a person desiring to control a HiQnet Device
may understand the underlying behavior. Lastly, control of USB products is
beyond the scope of this document.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 6 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Node
Virtual Device (Node Manager)
Param
Param
Param
Object
Object
Param
Param
Param
Object
Param
Param
Param
Virtual Device
Param
Param
Param
Param
Param
2 HiQnet Product Architecture
It is important to have a basic knowledge of how HiQnet products are developed.
We envisage HiQnet as more than just a networking protocol. Our goal is to
develop a system solution for all Harman Pro networked products. To facilitate
that end, we have designed a common model or architecture for all products that
will be developed under HiQnet. This common product architecture is then
reflected as a messaging system that enables communication between products.
Finally, HiQnet also consists of reference designs on common physical networks.
The HiQnet messaging protocol was designed to be transport independent, it
requires only certain network services.
The HiQnet product is modeled with a multi-tiered approach. The top level that
usually represents the product itself is called a Device. The Device must contain
at least one Virtual Device, the first of which acts as a Device Manager. Each
Virtual Device can contain Objects and/or Parameters. Objects themselves can
contain other Objects or Parameters. A Parameter contains the state of a single
controllable variable. Below we will define each of these terms in detail.
At every level in the hierarchy there are also attributes. Attributes are member
variables that contain useful data about the containing Virtual Device, Object, or
Parameter. For instance, one Object attribute is the Object Name. In the case of
parameters, attributes are used to hold the parameter's max and min values.
Attributes can either be STATIC, Instance, or Instance+Dynamic. STATIC
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 7 of 91
attributes are the same value across all Devices that are the same
manufacturer/model. Attributes that are denoted Instance indicates that the Device
upon powerup sets the value of the attribute. Attributes that are denoted
Instance+Dynamic are those that are set on Instantiation and can change during
the life of the item.

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Virtual Devices, Objects, and Parameters all have a unique Class ID and Class
Name. Either the Class Name or ID can be used to uniquely identify the HiQnet
item and allow the designer to know key information about the item. For example,
from the Class ID of an Object, the designer knows the number, type, and order of
Parameters in the object. From the Parameter Class ID, the designer knows the
data type and max/min.
It is important to note that there is no distinction in HiQnet between elements used
for signal processing such as a Parametric EQ, control elements such as a
mechanical fader, or sensor elements such as an output meter. Even global items
such as passwords and MIDI channels can and should be put inside the basic
HiQnet model. By viewing everything as a parameter, Object, or Virtual Device,
the same mechanisms for subscriptions and control can be universally applied
across the product.
2.1 Device
Device designates the Device or product itself. Devices are comprised of Virtual
Devices.
2.2 Virtual Device
The Virtual Device is a collection of Objects, parameters and attributes that make
up a useful unit. They offer the designers a convenient method of segmenting the
product. As an example, if you examine the structure of the dbx 4800 in the
System Explorer you will see that they have separated the product into two
sections, one for all the processing objects that can change with presets changes
and the other for the global utility section. At a glance it is very easy to
distinguish which parameters will be affected by a preset change.
2.3 Virtual Device Attributes
All Virtual Devices have the following Attributes:
AttributeID Attribute Data Type
0 Class Name STRING Static
1 Name String STRING Instance + Dynamic
2.4 Device Manager Virtual Device
Every product contains at least one Virtual Device, the Device Manager. Some
products such as the Crown UPS3 have been architected with only the Minimum
Device Manager Virtual Device.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 8 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
2.4.1.1 Device Manager Attributes
All Device managers Virtual Devices have the following Attributes:
Attribute ID Attribute Data Type
0 Class Name STRING Static
1 Name String STRING Instance + Dynamic
2 Flags UWORD Instance
3 Serial Number BLOCK Instance
4 Software Version STRING Instance
2.5 Object
A HiQnet Object is a collection of parameters grouped together for convenience.
An example would be an EQ object or compressor object. Objects can contain
other objects so for example a channel object could be comprised of a gain and an
EQ object.
2.6 Parameter
Within the HiQnet model, the smallest modifiable parameter in a product is held
within the parameter. Examples of parameters include the variables of an audio
object, like frequency and the position of a fader on a control surface. Simple
products like a wall controller may contain only several parameters, while others
such as a mixing console may contain hundreds of thousands. Typical operations
on parameters include „set‟ a variable and „get‟ a variable; these could translate to
setting the frequency of an EQ and getting a delay time for display.
The HiQnet protocol supports several different data types including Unsigned
Byte, Float, String, etc. It is important when you are sending a message to a
HiQnet Device that you use the appropriate data format.
2.6.1 Parameter Attributes
Attribute ID Attribute Name Data Type Category
0 Data Type See Definition Static
1 Name String STRING Instance+Dynamic
2 Minimum Value Data Type Instance
3 Maximum Value Data Type Instance
4 Control Law Static
5 Flags UWORD Static
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 9 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
2.6.1.1 Minimum Value
Minimum Value is specified in the Parameter‟s Data Type. See section 2.7.6 for
an explanation on how to retrieve the minimum value of a parameter.
2.6.1.2 Maximum Value
Maximum Value is specified in the Parameter‟s Data Type except for the BLOCK
and STRING types, which will use a UWORD for its maximum. In the case of a
block, the maximum value specifies the maximum size that the variable length
block can be in bytes. In the case of a string, the maximum value also specifies
storage, which is twice the number of characters including the NULL because
strings are encoded with Unicode. See section 2.7.6 for an explanation on how to
retrieve the maximum value of a parameter.
2.6.1.3 Control Law
The processing object uses a control law to recommend how it would like to be
controlled. For example, a Parameter for frequency may want to be logarithmic, a
gain SV may want to be logarithmic with extra resolution around 0 dB.
If you have a Parameter that can take on any floating-point value between the
Minimum and Maximum, you still want to specify the control law to give a good
look and feel to the user. For example, in the case of a frequency variable, it is
often desirable that when the user turns an encoder or pushes the <up> control on
a spinner that the next value be logarithmically spaced from the previous value.
The control law may also be used to specify the granularity that a Parameter can
accept. For example, a gain Parameter may have a maximum resolution of .1 dB.
This control law is not needed in the case of an enumerated Parameter, as all steps
are known.
2.6.1.4 Flags
Bits 0, 2, and 3 are reserved. Bit 1 is the Sensor Attribute.
0 = Non-Sensor
1 = Sensor
This attribute is used in subscriptions to automatically set the type of subscription
to periodic or on change. Examples of sensor Parameters include output meters,
threshold meters, or power amp temperature. Non-sensor Parameters are things
like frequency or MIDI channel.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 10 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
HiQnet Addressing
HiQnet
Devices
Address
16 bits
Parameter
Index
16 Bits
VD
Address
8 Bits
Object Address
24 Bits
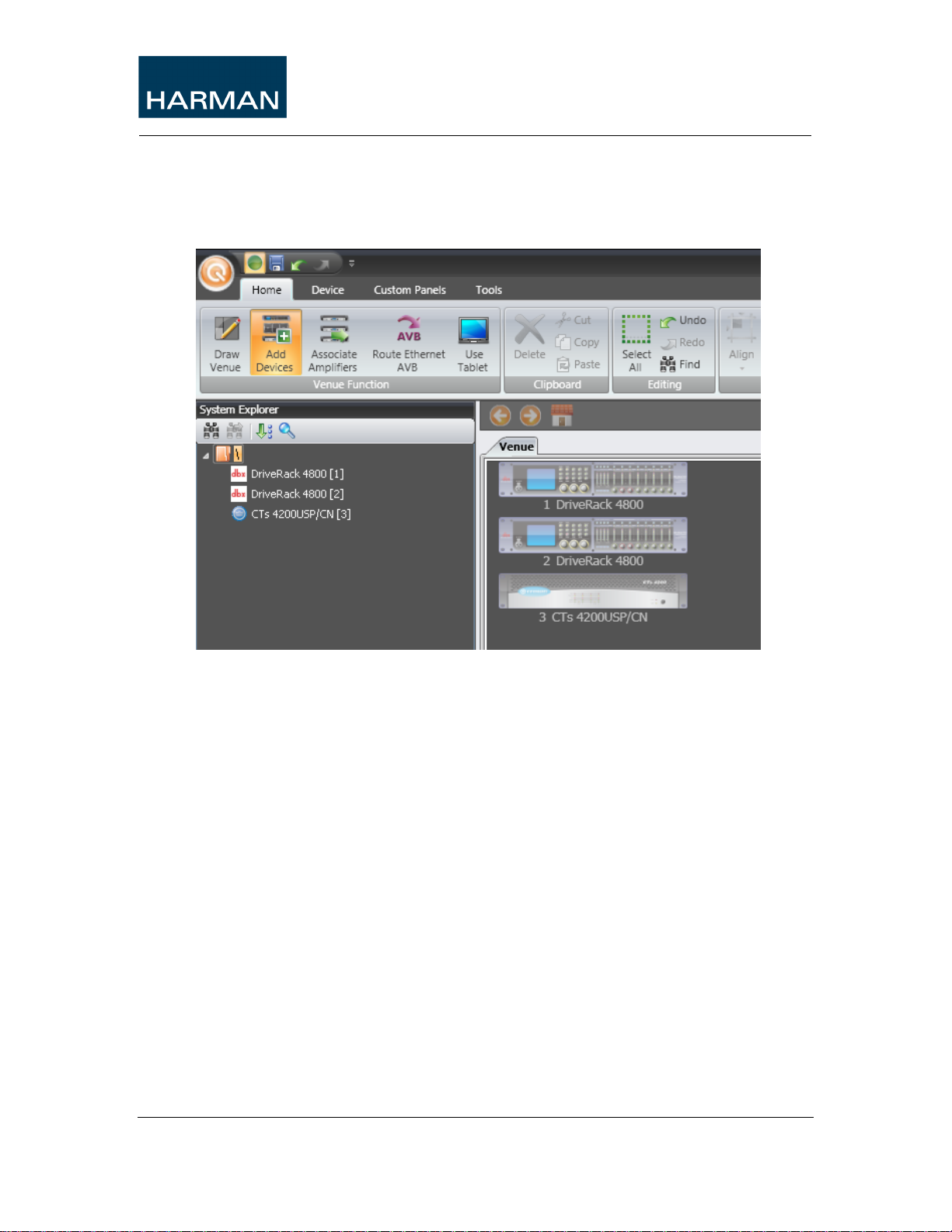
2.7 HiQnet Addressing
Addressing in HiQnet is split up into three main sections, a 16 bit HiQnet Device
address, a 32 bit field that designates the Virtual Device and Object and finally a
parameter Address that designates the correct parameter within the Object. The
System Explorer in System Architect always shows any of these addresses with a
trailing number enclosed in „[ ]‟.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 11 of 91
HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
2.7.1 HiQnet Device Address
The HiQnet Device address is often referred to as the HiQnet address in System
Architect. In the below example, the three Devices are addressed 1, 2 and 3.
These addresses are shown in the System Explorer and the Venue View.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 12 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
2.7.2 Virtual Device Address
The Virtual Device and Object Addresses comprise a 32 bit number, segmented
into an eight bit Virtual Device and a 24 bit Object address. Using the dbx 4800
as an example, you see that the default configuration shows three Virtual Devices,
the Device Manager(Shown with the Device Name “DriveRack 4800”), the
Processing Object Virtual Device(shown with the preset name of “Wide Open”)
and the Utilities Virtual Device. These have the Virtual Device Addresses of 0, 1,
and 2 respectively.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 13 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
2.7.3 Object Address
The Object Address in the System explorer is broken into its three eight-bit
sections. For example, the first Input Mixer Object in the DriveRack 4800 is
addressed [3.2.0]. The second mixer is addressed [3.2.1]. The Object Address will
be unique within that Virtual Device.
The fully qualified 48 bit address of the first mixer then is
[3(Device).0(VD).3.2.0(Object)]
2.7.4 Source & Destination Addresses in Messages
Some messages are specific as to the kind of HiQnet „item‟ they may originate
from or can be sent to. An example is clearer – the SetAttribute message may be
sent by a Device Manager Virtual Device, a Virtual Device or an Object. This
asymmetry in permissible Source and Destination addresses is documented using
the following convention:
„DEVICE‟ is a placeholder for any Device Address.
„VD‟ is a placeholder for any Virtual Device Address.
„OBJECT‟ is a placeholder for any Object Address.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 14 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
2.7.5 Parameter Index
The Parameter Index uniquely identifies the parameter within an Object.
Continuing with the example 4800, you will see that the Input Mixer has four
parameters: Source Select[0], Input Gain[1], Pink Noise On/Off[2], and Pink
Noise Gain[3].
2.7.6 Parameter Range
The range of a parameter can be found in the SetSV message string that is
copied to the clipboard. In the HiQnet String Settings in the options, “Use
Placeholder for Parameter Value” should be enabled (see section 5). Rightclick on a control on a panel and choose “Copy HiQnet Parameter String”.
Paste in to a program such as notepad to find the SetSV message string and
which includes the range of the parameter.
02,19,00,00,00,22,00,33,00,00,00,00,00,01,11,06,11,00,01,
00,00,20,05,00,00,00,01,00,01,06,[Float (20 -
20000)]:XX,XX,XX,XX
The value where the XX‟s are are where the value should be inserted.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 15 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
2.8 Alternate methods of finding a HiQnet address.
Sometimes it can be difficult to find exactly the correct parameter you need
within the System Explorer. There are two other good ways to find the addresses
you need.
2.8.1 Copy HiQnet Information
The simplest method to find the HiQnet address of an object is to locate the
object on a panel, right-click the object, and choose “Copy HiQnet
Information”. The figure below shows the right-click context menu when a
PEQ is right-clicked on an dbx SC 32.
You can then paste the HiQnet Information in to a program like Notepad
which will give you
Name(type of object): 6-band PEQ
Node: (Hex):0x01, (Decimal):1
VD: (Hex):0x11, (Decimal):17
ObjectID: (Hex):0x061100, (Decimal):6.17.0
This provides you with the node address, virtual device address, and object
address. Combined these give you the overall HiQnet address of the object.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 16 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
2.8.2 Finding an Address using the Custom Panels and the
Properties Window
The simplest way to find an address when you don‟t know it is to find the
parameter you want to control on a factory panel and then drag it to a custom
panel. In this example, to get the address for a gain in the input module of the
Crown 4200.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 17 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
1) Start a new custom panel by going to the Custom Panel tab and selecting
“Create”
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 18 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
2) Now open the Channel 1 Source selector factory panel.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 19 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
3) Next, holding down the <Control> key, drag the “Routed” fader to the
new custom panel
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 20 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
4) Right Click on the Control to access the Parameter Address Editor
5) The full address is now visible in the Parameter Address Window. In this
example, this is HiQnet Address 3, Virtual Device 0, Object Address
[5.40.1] and Parameter Index 0.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 21 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0xXX
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xXXXXXXXX
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0xXXXX
FLAGS
UWORD
0x0000
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
0x01
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
0x0001
ERROR CODE
UWORD
0x02
ERROR STRING
STRING
“The Error Message”
START SEQ. NO.
UWORD
0x02
BYTES REMAINING
ULONG
0xXXXXXXXX
SESSION NUMBER
UWORD
0xXXXX
3 HiQnet Message Format
The following section lists the detailed message formats for the common HiQnet
messages. See section 3.4.1 for an explanation of the datatypes and how they are
stored.
3.1 Header
This is the common header for HiQnet messages. The first field is for HiQnet
message version. The current HiQnet version is 0x02, please use this as the
default.
Optional „Error‟ header (FLAGS=0x0008):
Optional „Multi-part‟ header (FLAGS=0x0040):
Optional „Session Number‟ header (FLAGS=0x0100):
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 22 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
When using multiple header extensions in a single packet they must be added to
the end of the header in the same order as they are listed above.
A Device will send an error header back as a reply to a received message with a
header extension it does not understand. Older Devices do not support sessions,
for example. Some newer Devices require sessions always. Other Devices will
support sessions, but allow session-less communication. So always start a session
with a Hello(Query) with a session number, and if the Device replies with a
Hello(Error) header, then proceed with session-less communication with that
Device.
If an error message is returned in response to a Hello message, a
MultiParamGet(NumParams=0) message will be used for backward
compatibility in order to start Keep Alives.
See the sessions section.
Messages may originate from anywhere in the hierarchy –
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT.
3.1.1 Version
The Version Number indicates the revision number of the entire protocol; it is not
used for differentiating between revisions of individual messages. HiQnet is
currently at revision 2. Devices that communicate with HiQnet version 1.0
include the dbx ZonePro family. All others use version 2.0.
3.1.2 Header Length
The Header Length is the size in bytes of the entire message header, including any
additional headers such as 'Error' or 'Multi-part'.
3.1.3 Message Length
The Message Length is the size in bytes of the entire message - from the
„Version‟ field through to the last byte of the payload.
3.1.4 Source Address
The Source Address specifies the HiQnet address where the message has come
from; this is often used by the recipient for sending back reply messages.
3.1.5 Destination Address
The Destination Address specifies where the message is to be delivered to.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 23 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Bit 15:
Reserved
Bit 14:
Reserved
Bit 13:
Reserved
Bit 12:
Reserved
Bit 11:
Reserved
Bit 10:
Reserved
Bit 9:
Reserved
Bit 8:
Session
Number
(header
extension)
Bit 7:
Reserved
Bit 6:
Multi-part
message
(header
extension)
Bit 5:
Guaranteed
Bit 4:
Reserved
Bit 3:
Error
(header
extension)
Bit 2:
Information
Bit 1:
Acknowledge-
ment
Bit 0:
Request
Acknowledge-
ment
3.1.6 Message ID
The Message ID is a unique identifier that indicates the method that the
destination Device must perform. If there is a payload, it is usually specific to the
type of method indicated by the Message ID. Product-specific IDs may also exist
and will be documented appropriately.
3.1.7 Flags
The Flags denote what kinds of options are active when set to „1‟ and are
allocated in the following manner:
Bit 5 must be set for any applications using TCP/IP only on the network
interface. This will ensure that any messages are sent guaranteed (TCP rather
than UDP).
3.1.8 Hop Count
The Hop Count denotes the number of network hops that a message has traversed
and is used to stop broadcast loops. This field should generally be defaulted to
0x05.
3.1.9 Sequence Number
The Sequence number is used to uniquely identify each HiQnet message leaving a
Device. This is primarily used for diagnostic purposes. The sequence number
starts at 0 on power-up and increments for each successive message the Routing
Layer sends to the Packet Layer. The Sequence Number rolls over at the top of its
range.
3.2 Types of Messages
3.2.1 Request Acknowledgement Message
The ReqAck flag is used to provide a message level service that can be used by
the sender to know when the recipient of the message has carried out the specified
action. When the message sender sets the ReqAck flag, the message recipient,
upon performing the specified action, will send back the same message to the
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 24 of 91
sender with the ReqAck flag cleared and the Ack flag set. This provides a

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
valuable mechanism because the Ack is not sent upon receipt of the message
which would mean “I have received your request;” instead by sending the Ack
upon performing the action this literally means “I have done it.” If the original
message had any data in its payload, that data is not sent back with the
acknowledge message. This mechanism can be used to key actions such as the
sending of the next message only once the recipient has serviced the first
message.
3.2.2 Acknowledge Message Flag
As specified above, a message with the Ack bit set means I have performed the
requested action.
3.2.3 Information Message Flag
The Information flag is normally used to denote a response to a request. Instead of
defining a new message ID for the reply to each request, we have decided to
encode the reply ID using the Information flag. For example, the response to a
Get message is also a Get with the Information flag set and the corresponding data
appended in the payload. Note that the Information and Ack flags may be used
together. If you receive a Get message with the ReqAck flag set, then your
response would be a Get with the Ack and Information flags sent and any
corresponding payload appended to the end.
The Info flag is also used to indicate unsolicited informational messages (a
message that is neither a request nor a response to a request). Again, the
Information flag simply means the message is not a request!
3.2.4 Error Message Flag
In the case of an error in a received message, the „error‟ flag must be set and an
error code and error string appended to the end of the message header. The
original message is then returned to the sender.
3.2.5 Guaranteed Message Flag
When set, the „guaranteed‟ flag indicates the message must be transmitted on a
network service with guaranteed delivery. A cleared flag denotes a preference for
the message to be sent via an unreliable, datagram service. In this latter case, the
Routing Layer may in some circumstances (such as proxy) choose to send the
message via the guaranteed service instead.
1 – Guaranteed
0 – Unreliable datagram
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 25 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
3.2.6 Multi-part Message Flag
When set, this flag indicates the message is part of a multi-part message sequence
and the message header is extended by the addition of the „Multi-part‟ header.
1 – Multi-part message
0 – Single-part message
Many Devices will not be able to send a single message large enough to contain
all the data they wish to transmit (such as the data set required for a preset
change). For this reason, we provide a means of sending multi-part messages
where the payload is spread over a number of messages, which together form all
the data required for a single method.
The algorithm for multi-part messages is as follows:
1. Preparing the first multi-part message header
a) Set the „Multi-part‟ flag.
b) Copy the „Sequence Number‟ to the „Start Sequence No.‟
c) Set „Bytes Remaining‟ to be the data outstanding, including this data.
- this is the total size of the payload, not including headers
d) Transmit the first message.
2. Preparing the remaining multi-part message headers
a) Set the „Multi-part‟ flag.
b) Set the „Start Sequence No.‟ to that used in the first multi-part message.
c) Set 'Bytes Remaining' to be the data outstanding, including this data.
- does not include the previous messages' payload sizes
d) Transmit the current message. This is the last message when 'Bytes
Remaining' is equal to this message's payload.
Destination knows when the last message is being received because the „Bytes
Remaining‟ in the last message's multi-part header is the same as the size of the
payload in the last message.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 26 of 91
HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
GetAttributes
0x010D
Gets ‘n’ attribute values from Object
or VD
GetVDList
0x011A
Gets list of Virtual Devices in a Device
Store
0x0124
Stores local performance data
Recall
0x0125
Recalls local or venue-wide
performance data
Locate
0x0129
Requests a Device to identify itself to
the customer
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x010D
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
NoOfAttributes
UWORD
0x0003
AID
UWORD
0x0000
AID
UWORD
0x0001
AID
UWORD
0x0002
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x010D
FLAGS
UWORD
3.3 Device Level Methods
METHOD NAME MESSAGE ID PURPOSE
3.3.1 Get Attributes
INFORMATION (response to message):
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 27 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
NoOfAttributes
UWORD
0x0003
AID
UWORD
Zero-based Attribute ID (AID)
Data type
UBYTE
Enumerated Data Type of Attribute
Value
‘N’ bytes
Value of Attribute
AID
UWORD
Zero-based Attribute ID (AID)
Data type
UBYTE
Enumerated Data Type of Attribute
Value
‘N’ bytes
Value of Attribute
AID
UWORD
Zero-based Attribute ID (AID)
Data type
UBYTE
Enumerated Data Type of Attribute
Value
‘N’ bytes
Value of Attribute
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xFFFF00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x011A
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Workgroup Path
STRING
Workgroup asked to respond
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x011A
3.3.2 GetVDList
INFORMATION (response):
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 28 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Workgroup Path
STRING
Workgroup that is replying
NumVDs
UWORD
0x0004
VDAddress
UBYTE
0
VDClassID
UWORD
Class Of Device Manager
VDAddress
UBYTE
VDClassID
UWORD
VDAddress
UBYTE
VDClassID
UWORD
VDAddress
UBYTE
VDClassID
UWORD
3.3.3 Store
The Store method saves various types of performance data into non-volatile local
storage such as FLASH.
UBYTE ubyStoreAction
UWORD uwStoreNumber
STRING strWorkgroup
UBYTE ubyScope
The „Store Action‟ determines the type of data affected:
0 – Parameters (parameters only)
1 – Subscriptions (Subscriptions only)
2 – Scenes (1 to N PARAM + Subscriptions)
3 – Snapshots (All PARAMs + Subscriptions)
4 – Presets (Config + Snapshot)
The uwStoreNumber parameter identifies a local storage space and undergoes no
translation or mapping to another value.
The strWorkgroup parameter is not used and should be set to 0.
The ubyScope parameter is reserved for future definition.
Devices that are unable to perform the store operation will return an error.
5 – Venue
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 29 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVD000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0124
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Store Action
UBYTE
Store Number
UWORD
Workgroup Path
STRING
Not Used – Set Length to 0.
Scope
UBYTE
Reserved for Automation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVD000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0124
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Store Action
UBYTE
Store Number
UWORD
Workgroup Path
STRING
Not Used – Set Length to 0.
Scope
UBYTE
Reserved for Automation
The Store(info) message allows a Device to indicate to a subscribed Device that a
storage location has been modified. The source of the data stored into non-volatile
storage is not inferred. The payload indicates the storage location that has been
modified.
Store(info) allows synchronization between multiple System Architects
subscribed to a Device whenever a change in the configuration state occurs.
INFORMATION:
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 30 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVD000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0125
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Recall Action
UBYTE
Recall Number
UWORD
Workgroup Path
STRING
Workgroup doing Recall Venue
Scope
UBYTE
Reserved for Automation
3.3.4 Recall
Activates various kinds of performance data.
3.3.5 Recall Action Determines Type of Data Affected
Recall Action
0 – Parameters (parameters only)
1 – Subscriptions (Subscriptions only)
2 – Scenes (1 to N PARAM + Subscriptions)
3 – Snapshots (All PARAMs + Subscriptions)
4 – Presets (Config + Snapshot)
5 – Venue
For actions 0 to 4, Recall Number identifies a local storage space and undergoes
no translation or mapping to another value.
For action 5, Recall Number identifies a „venue recall number‟, which each
Device translates into a „local recall‟ and „local action‟ via the „Venue Table'.
The Venue Table for Devices can be examined and modified through System
Architect. See the Tools/Venue Recall button on the ribbon.
Some Devices are not required to do anything for a specific „Recall Number‟;
these may enter the enumerated value „No Action‟ in their Venue Table.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 31 of 91
The Workgroup Path indicates which Devices are to respond to a „venue recall‟.
Devices that are outside of the specified workgroup will take no action. For all
other recall actions this parameter is not used and should be set to 0.

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0xXX
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xXXXXXXXX
SRC
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0129
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
The Scope parameter is reserved for future definition.
Devices that are unable to perform the requested recall will return an error. See
the Event Log section for the format of the Event Log Subscription Information
message that is sent from Devices when an errors occur.
3.3.6 Locate
The „locate‟ method requests that the receiver makes itself „visible‟ to the
customer by flashing its „Locate LEDs‟. If available, these are typically located on
the hardware panel of the product.
The locate method is compulsory for Device Manager Virtual Devices. Virtual
Devices and Objects may optionally choose to support it.
The method has a single parameter:
UWORD uwTime - Locate time in milliseconds
0x0000 – Turn off locate LEDs
0xFFFF - Turn on locate LEDs.
Time periods between 0x0001 and 0xFFFE indicate a period of time during which
the locate LEDs must flash. After the time period is completed the LEDs must be
turned off.
The locate method will flash the LEDs at a rate of 2Hz. This allows the „locate‟
signal to be differentiated from product-specific flashes which may be active on
the same LED (some products only have one LED).
3.3.7 Locate Message
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 32 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Payload…
Time
UWORD
Locate time in milliseconds
HiQnet Serial Number
BLOCK
Serial number of Device to be located
3.4 Event Log
Each HiQnet Device has an Event Log. Items reported into the Event Log such as
protocol errors or product-specific errors can be transmitted onto the network. If
you subscribe to Device foo’s Event Log and Device bar sends foo a malformed
packet, because you are subscribed to foo’s Event Log, foo will send you an event
log message telling you it has received a bad message from Device bar.
3.4.1 Event Log Data
3.4.1.1 Category
Category identifies a sub-system within the product into which associated Event
IDs are grouped. There may be no more than 32 event categories, those already
declared as are follows:
0 – Unassigned
1 – Application
2 – Configuration
3 – Audio Network
4 – Control Network
5 – Vendor Network
6 – Startup
7 – DSP
8 – Miscellaneous
9 – Control Logic
10 – Foreign Protocol
11 – Digital I/O
12 – Unassigned
13 – Unassigned
14 – Control Surface
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 33 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Event ID
Possible causes
0x0001 – Invalid Version
The version number in the HiQnet header is unknown.
0x0002 – Invalid Length
The header length specified in the packet is wrong.
There are not enough bytes in packet payload to hold
message type.
0x0003 – Invalid Virtual Device
Tried to Create VD on an invalid VD.
Set/Get/Subscribe/Attributes referenced an invalid
VD.
0x0004 – Invalid Object
Set/Get/Subscription referenced an invalid object.
0x0005 – Invalid Parameter
Set/Get/Subscribe/Attributes referenced an invalid
Parameter.
0x0006 – Invalid Message ID
Received a message with an unknown Message ID.
0x0007 – Invalid Value
Tried to set an attribute with a value that is out of
range.
Referenced an invalid scene number, or encountered
an invalid scene “data” length.
Referenced an invalid preset number.
15 – 31 Unassigned
The Category is represented in some messages by an enumerated UWORD and in
others as a ULONG bit-field.
3.4.1.2 Event ID
The Event ID identifies the actual event that triggered a log entry. These are held
within a zero based enumeration with the range of a UWORD. The Event ID may
be „overloaded‟ across event categories; that is to say, an Event ID such as zero
may mean „Device Started‟ within one Category and „Preset Recalled‟ in another.
The Event ID range is divided into two sections:
0x0000 – 0x7FFF Global Event IDs common across all products
0x8000 – 0xFFFF Custom Event IDs specific to a Device Manager Class ID
3.4.1.3 Event ID Definitions
The Global Event IDs for each category are given below:
Control Network Event IDs
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 34 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
0x0008 – Resource Unavailable
Running out of internal software resources.
Device is in a state where it cannot process the
current request (flashing, configuration, etc).
Cannot set Device ID, subscription, Parameter value,
or the configuration is locked.
0x0009 – Unsupported
Received a message that is considered obsolete.
Trying to flash a Device that does not support flashing.
Trying to add unsupported or invalid (to long)
attribute types.
0x000A – Invalid Virtual Device Class
Referenced an invalid VD Class.
0x000B – Invalid Object Class
Referenced an invalid Object Class.
0x000C – Invalid Parameter Class
Referenced an invalid Parameter Class.
0x000D – Invalid Attribute ID
Get/Set referenced an invalid Attribute ID.
0x000E – Invalid DataType
Set referenced an invalid data type (class).
0x000F – Invalid Configuration
Began creating a new VD and never finished.
Lost connection while creating a new VD.
Trying to configure a Device that is “owned” by a
different Device.
0x0010 – Flash Error
An error was encountered during the requested flash
operation.
0x0011 – Not a Router
Another Device has requested a guaranteed delivery
connection through this Device to a third Device, and
this Device is not a router.
3.4.2 Requesting Event Log Client Subscriptions
A client requests an event log subscription by sending a
SubscribeEventLogError! Reference source not found. message to the Device
Manager Virtual Device of the Device it is interested in receiving events from.
The „Category Filter‟ indicates which categories of event the client wishes to hear
about.
The category is a field of type ULONG, a „1‟ indicates a subscription; „0‟ means
no action (it does not mean unsubscribe). Each category is represented by a bit in
the ULONG. The same client may subscribe multiple times to the same Device.
The server receiving the SubscribeEventLog message will perform an OR
operation on the current filter settings and the ones in the message payload; the
result will be the actual categories subscribed to:
Current Filter Settings: 00000000000000000000000100010011
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 35 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Payload Filters: 00000000000000010000001000010000
Resulting Subscription: 00000000000000010000001100010011
The „Max Data Size‟ allows the client a chance to limit the size of any „additional
data‟ sent to it as part of an event log entry. It is the server‟s responsibility to
ensure this data is not larger than the figure specified by the client.
3.4.2.1 Sending Subscribed Events
Once an event log subscription is activated, the server will send the client a
RequestLogInfo(I) message. Typically, there will be one message per event, but
the server is able to package multiple events per message and so the client must
be able to handle a message containing multiple events.
3.4.2.2 Cancelling Client Subscriptions
A client may cancel a category of event log subscription by sending the server an
"Unsubscribe Event Log" message. The „Category‟ in the payload specifies the
category of events the client is unsubscribing from; this may be a single category
or multiple categories.
Event Log subscriptions, along with all other types of subscriptions, are
automatically cancelled if you send the Device a Goodbye message.
A „1‟ bit represents „unsubscribe‟, a „0‟ represents „do nothing‟.
For example:
Current Filter Settings: 00000000000000010000001100010011
Payload Filters: 00000000000000000000000000000011
Resulting Subscription: 00000000000000010000001100010000
3.4.2.3 Protocol Errors
A Protocol error is a special kind of event which occurs when a Device receives a
HiQnet message it cannot service. This may be for any number of reasons but
usually because the message is incorrectly formatted, addressed to the wrong
destination, or contains out of range parameter data. All HiQnet Devices must be
able to generate and handle error messages.
The error must be reported back to the message sender by returning a HiQnet
„error‟ message. The error message contains both an error code and a networkbyte-ordered Unicode string representation of the error which may be used by a
technician for diagnosing the fault. The protocol error codes which may be used
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 36 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0115
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Max Data Size
UWORD
Max size of ‘Additional Data’ in any
RequestEventLog(I) message
Category Filter
ULONG
in the message are the same as the Event IDs enumerated in the „Control
Network‟ category of the Event Logging section.
Unlike event logging, when a protocol error occurs, the error message is always
returned to the sender, regardless of any event log settings.
3.4.2.4 Subscribe Event Log Messages
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 37 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x012B
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Category
ULONG
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x012C
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
3.4.2.5 Unsubscribe Event Log
3.4.3 Request Event Log
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 38 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x012C
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
No Of Entries
UWORD
Number of entries in log
Category
UWORD
Enumerated Category event falls in
Event ID
UWORD
Enumerated ID of this event
Priority
UBYTE
3 enumerated priority levels
Sequence Number
ULONG
Incrementing event instance counter
Time
STRING
HH:MM:SS
Date
STRING
YEAR-MO-DA
Information
STRING
Description of event
Additional Data
BLOCK
Application specific extra data
Category
UWORD
Enumerated Category event falls in
Event ID
UWORD
Enumerated ID of this event
Priority
UBYTE
3 enumerated priority levels
Sequence Number
ULONG
Incrementing event instance counter
Time
STRING
23:16:23
Date
STRING
2004-12-15
Information
STRING
Description of event
Additional Data
BLOCK
Application specific extra data
3.4.4 Request Event Log INFORMATION (response):
3.4.4.1 Priority
The Priority field allows events in the Event Log to be assigned one of three
levels of importance, these are enumerated as follows:
The Priority is represented by a UBYTE.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 39 of 91
0 - Fault
1 - Warning
2 - Information

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
3.4.4.2 Sequence Number
The Sequence Number denotes the order that events occurred in. This field is
important for products that do not have a real time clock with which to generate
the time and date fields of the event log. The sequence number starts at 0 the first
time the unit is powered on and continues to increment by one for each generated
event. The sequence number must be preserved in non-volatile storage so that it
persists across power cycles and firmware upgrades.
The Sequence Number is a ULONG.
3.4.4.3 Time
Time represents when the event was generated and logged. The format is 24 hour
clock, with two digits for hours, minutes & seconds separated by a colon For
example:
17:25:47
The Time is transported via the STRING data-type.
3.4.4.4 Date
Date represents the day the event was generated and logged. The format is year,
month & day separated by hyphens. For example:
2004-12-13
The Date is transported via the STRING data-type.
3.4.4.5 Information
This is a string giving any additional information about the event. The data-type is
STRING.
3.4.4.6 Additional Data
Additional Data is a BLOCK field for events which carry event-specific data.
This could for example, be a copy of a HiQnet message which when processed
triggered an internal error within a Device. The format and purpose of the data
may also be event-specific, it is not required that the recipient should necessarily
be able to understand or want to use the extra data.
The maximum size of this data is a decision left open to the product designer.
However, the product must be able to truncate the data to the maximum size
requested by a client that subscribed to the event log.
If an event does not carry additional data then the length of the BLOCK must be
set to 0.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 40 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Name
‘C’ Declaration
Range
Bytes
Enum
eratio
n
BYTE
Char
-128 to 127
1
0
UBYTE
unsigned char
0 to 255
1
1
WORD
Short
-32768 to 32767
2
2
UWORD
unsigned short
0 to 65535
2
3
LONG
Long
-2147,483648 to
2147,483647
4
4
ULONG
unsigned long
0 to 4,294,967,926
4
5
FLOAT32
Float
As IEEE-754
4 6 FLOAT64
Double
As IEEE-754
8
7
BLOCK
N/A
0 to 65535 bytes
N/A
8
STRING
N/A
0 to 32767 chars
N/A
9
LONG64
N/A
Very Big
8
10
ULONG6
N/A
Huge
8
11
3.5 Introduction to Parameters
3.5.1 Data Type Definition
A small set of data types are used in HiQnet to represent parameter values. All
parameters must use one of the following data types:
The format for BLOCK is a variable length of memory that may be used for any
kind of data. The first two bytes are a UWORD that contains the size of the block
in bytes not including the UWORD itself. The maximum size of the BLOCK is
constrained to 65536 bytes. Because blocks can be used to represent any kind of
structured data, it is assumed that the sending and receiving sides know how to
format the data.
Strings are Unicode and stored using the String data type. Like BLOCK, the
actual string data is prefixed with a UWORD count indicating the length of the
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 41 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0100
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
NumParam
UWORD
3
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_DataType
UBYTE
Value
‘N’ bytes
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_DataType
UBYTE
Value
‘N’ bytes
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_DataType
UBYTE
Value
‘N’ bytes
string in bytes. Strings sent over the network are to include the NULL character at
the end of the string. Because we are using Unicode, the length used in the String
format is 2 * (strlen + 1). For example: for the string “Hello World,” the count
will be 24. Note, strings are network-byte-ordered Unicode while on the wire.
3.5.2 Sensor/Non-Sensor
Sensor parameters are those that update periodically such as a meter. Non-sensors
are normal parameters that update only when changed. Examples of non-sensors
include Frequency or Gain.
3.6 MultiParamSet
Set „NumParam‟ parameters values within an object or Virtual Device.
„Param_ID‟ specifies the particular parameter to set. The payload example below
shows an array of three Parameters.
3.7 MultiParamGet
Get „NumParam‟ parameters values within an object or Virtual Device.
„Param_ID‟ specifies the particular parameter to get.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 42 of 91
HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0103
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
NumParam
UWORD
0x0003
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_ID
UWORD
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0103
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
NumParam
UWORD
0x0003
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_DataType
UBYTE
Param_Value
‘N’ bytes
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_DataType
UBYTE
Param_Value
‘N’ bytes
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_DataType
UBYTE
Param_Value
‘N’ bytes
3.7.1 INFORMATION:
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 43 of 91
HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x010F
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
No of Subscriptions
UWORD
2
Publisher Param_ID
UWORD
Subscription Type
UBYTE
0 – Set to 0
Subscriber Address
HIQNETADDR
Subscriber Param_ID
UWORD
Reserved
UBYTE
0 – Reserved
Reserved
UWORD
0 – Reserved
Sensor Rate
UWORD
Period in milliseconds
Publisher Param_ID
UWORD
Subscription Type
UBYTE
0 – Set to 0
Subscriber Address
HIQNETADDR
Subscriber Param_ID
UWORD
Reserved
UBYTE
0 – Reserved
Reserved
UWORD
0 - Reserved
Sensor Rate
UWORD
Period in milliseconds
3.8 MultiParamSubscribe
Subscriptions are used so that the client may be automatically notified when a
parameter has been changed. Because the HiQnet model is a peer-to-peer model,
you may specify the receiving destination parameter. This might be useful when
your controller only has a few parameters in it that you want to map across the
network.
The sensor rate is the fastest that the client wishes to receive updates for sensor
parameters. Based on workload, the server may choose to send the updates
slower. The sensor rate is ignored for non-sensor parameters.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 44 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0112
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Subscriber Address
HIQNETADDR
Number of Subscriptions
UWORD
2
Publisher Param_ID
UWORD
Subscriber Param_ID
UWORD
Publisher Param_ID
UWORD
Subscriber Param_ID
UWORD
3.9 MultiParamUnsubscribe
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 45 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0101
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Num_Objects
UWORD
0x0002
Object_Dest
ULONG
0xXXXXXXXX
Num_Params
UWORD
0x0002
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_DataType
UBYTE
Value
‘N’ bytes
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_DataType
UBYTE
Value
‘N’ bytes
Object_Dest
ULONG
0xXXXXXXXX
Num_Params
UWORD
0x0001
Param_ID
UWORD
Param_DataType
UBYTE
Value
‘N’ bytes
3.10 MultiObjectParamSet
Certain devices may respond to a MultiParamSubscribe message with a
MultiObjectParamSet message. This message encodes parameter values from
different objects. The example below shows two objects, the first with two
parameters and the second object with one parameter.
3.11 ParamSetPercent
ParamSetPercent sets the value of a parameter using a Percentage Value. Unlike
ParamSetPercent allows simple control of any parameter without the need to
provide control law conversions or format the value in the native format required
by the parameter Class ID. Indeed, when using ParamSetPercent, no prior
knowledge of the parameter‟s attributes are required because the burden of
dealing with Data Type formatting, range limiting and control law conversions are
off-loaded from the controller to the controlled.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 46 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Let‟s compare controlling a parameter with ParamSet and ParamSetPercent.
Suppose you wanted to perform a ParamSet on a Param with a Class ID of
ClassPeqFreq and the following attributes:
ParamClass ParamClassPeqFreq
Data_Type ULONG
Max 20000
Min 20
Control Primitive LOG
The attributes state that the Param is a frequency value in the range 20Hz to
20,000Hz and stored in a ULONG. The Control Primitive recommends a
logarithmic mapping between the surface control and the Param. This ensures that
adequate resolution is given at the bottom end and the control has a good feel to
the user when they adjust the frequency.
ParamSetPercent requires no prior knowledge of the parameter‟s attributes. A
control surface wishing to set the value just sends down a percentage value
between 0 and 100%. The ParamSetPercent method will take care of everything –
even the logarithmic Control Primitive.
ParamSet, in contrast, requires that the frequency value sent to the parameter be
formatted in the manner dictated by the parameter‟s Class ID – a ULONG in the
range 20 to 20,000. Further to that, the Control Primitive recommends a LOG
conversion; the control surface wishing to do this would need to provide a
translation from the linear units that an encoder or fader outputs into the log curve
requested by the parameter. Of course prior to this, the control surface must have
had prior knowledge of the parameter‟s Class ID or had issued a query for the
attributes.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 47 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0102
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
NumPARAM
UWORD
0x0003
PARAM_ID
UWORD
PARAM_Value
UWORD
1.15 signed fixed point
PARAM_ID
UWORD
PARAM_Value
UWORD
1.15 signed fixed point
PARAM_ID
UWORD
PARAM_Value
UWORD
1.15 signed fixed point
7 01236 4599101112131415
Sign Bit
Fractional Part
The Percentage Value is encoded as a UWORD in 1.15 fixed-point format:
In 1.15 format, bit 15 is used to indicate the sign and the remaining bits 0 to 14
are used to represent the fractional part of the number. 0x8000 represents –1.0 and
0x7fff represents1.0 – 1/32768. The method uses an implicit scale factor of 100%,
so 0x8000 = -100% and 0x7FFF = approximately 100%.
3.11.1 ParamSetPercent Message
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 48 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
3.12 ParamSubscribePercent
The ParamSubscribePercent method sets up a percentage-subscription. It
functions pretty much the same way as MultiParamSubscribe, except
subscriptions are sent out using the ParamSetPercent message, rather than
MultiParamSet.
UWORD uwPublisherParamID
UBYTE ubySubscriptionType
HIQNETADDR hiqSubscriberAddress
UWORD uwSubscriberParamID
UBYTE ubyMode
UWORD uwModeParamID
UWORD uwSensorRate
uwPublisherParamID – Param being subscribed to
ubySubscriptionType – Set to zero
hiqSubscriberAddress – Object to send the subscription to
uwSubscriberParamID – Param to send subscription to
ubyMode – Sets display mode for Parameter
uwModeParamID – Subscriber Param to receive the „ubyMode‟
uwSensorRate – Period rate in ms for sending sensor Params
The ParamSubscribePercent method is invoked by a subscriber to request that the
publisher send the subscriber the value of a Param whenever it has been changed
by a third party; this is the subscription. The Param being subscribed to is
specified by the PublisherParamID parameter. Where the subscription is for a
sensor Param, the subscribed Param value will actually be sent out on a periodic
basis, whether it has changed value or not. The subscriber can request a specific
rate via the SensorRate parameter. Whenever the Param value, is transmitted to
the subscriber, the message is sent to the location the subscriber requested; the
hiqSubscriberAddress and uwSubscriberParamID.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 49 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0111
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
No of Subscriptions
UWORD
2
Publisher ParamID
UWORD
Subscription Type
UBYTE
0 – Set to 0
Subscriber Address
HIQNETADDR
Subscriber Param_ID
UWORD
Reserved
UBYTE
0 – Not Used
Reserved
UWORD
0
Sensor Rate
UWORD
Period in milliseconds
Publisher ParamID
UWORD
Subscription Type
UBYTE
0 – Set to 0
Subscriber Address
HIQNETADDR
Subscriber ParamID
UWORD
Reserved
UBYTE
0 – Not Used
Reserved
UWORD
0
Sensor Rate
UWORD
Period in milliseconds
3.12.1 ParamSubscribePercent Message
This message shares the same payload as the MultiParamSubscribe message.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 50 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
RS485
Datalink
Layer
RS232
Datalink
Layer
Reliability
Layer
Application Layer (Product-specific code)
USB Datalink Layer
Message Layer
TCP (Transport Layer)
Routing Layer
Packet
Layer
Reliability
Layer
Reliability
Layer
Packet
Layer
Packet
Layer
Translation
Layer
...
...
...
...
Packet Layer
IP (Network Layer)
Ethernet
Datalink Layer
Network
Layer
Network
Layer
4 HiQnet Network Model
The HiQnet architecture is transport agnostic. Each network type has a common
layering structure as shown above. Message layer functions have been defined
above; we now dive into the routing and transport layers.
4.1 Routing Layer
4.1.1 Routing Layer Introduction
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 51 of 91
The Routing Layer in HiQnet performs two main functions – the abstraction of
different networking architectures, and the routing of messages between them.
The goal of abstraction is to isolate the Application Layer code from the differing
characteristics of the underlying protocols and Physical Layers. The Application
Layer code need not know that a particular Device is on TCP/IP or Token Bus, or
Ethernet or RS485; it just needs to know that the Device can be communicated
with over a standard interface. The Routing Layer takes care of locating the
Device and sending messages to it over the appropriate network. In this function,

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
the Routing Layer may also be queried by the Application Layer code for network
specific information; this can be useful for monitoring purposes or when a user
wants direct control over specific settings such as the IP address of a Device.
The second main function of the Routing Layer is to route messages across
different Packet Service Layers. A product may serve as a bridge onto a different
network type or a router between similar network types. Messages are received in
on one Packet Service Layer, and in the Routing Layer passed up to the Message
Layer service if the message is for this Device, or onto another Packet Service
Layer if the message is actually for a different Device.
The Routing Layer‟s routing function is not to be confused with any routing that
may occur within a protocol‟s Network Layer. The former routes a HiQnet
message across a variety of Network Protocols and physical media, whilst the
latter typically only routes a datagram within a specific Network Protocol.
4.1.2 Transmitting Messages
The Routing Layer offers two services for transmitting messages, Datagram and
Guaranteed. The service used to convey a message across the network is
determined by the „Guaranteed‟ flag in the HiQnet Message Header.
With some messages, in some circumstances, the Routing Layer will choose to
override the service specified in the message header and send the message out on
a different service.
4.1.3 Datagram Service
The Datagram service provides a fast connectionless means of transmitting
messages to either unicast or broadcast addresses. The service does not guarantee
delivery nor protect against duplicate, missing, or out of sequence messages.
Typically, this service is used for locating other Devices on the network (Device
Discovery) and for transmission of sensor/meter data.
4.1.3.1 Guaranteed Service
The Guaranteed service provides a reliable, connection-oriented means of
transmitting messages to unicast addresses. The service will guarantee delivery
and protect against duplicate, missing, or out of sequence messages. Typically,
this service is used for all HiQnet messages except those that are more
appropriately sent via the Datagram service.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 52 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
4.1.3.2 HiQnet Device Addressing
All products need a HiQnet Device Address prior to initiating or receiving
messages across a network. This can be obtained either by „address negotiation‟
or by hard coding. Devices that have negotiated for their initial address must also
be ready to accept an address received via a message from the network.
It is strongly recommended that devices in the HiQnet system have their node
addresses fixed.
4.1.3.3 Negotiating a HiQnet Address
The Device as initially shipped (or factory reset) will see that its HiQnet Address
is zero, so it will set its HiQnet Address to a number between 1 and 65535 and
use broadcast messages to "negotiate" its address with other Devices already on
the network. After that process settles down, the HiQnet Address will be fixed at
that chosen number. Devices never re-negotiate their HiQnet Addresses once they
are non-zero.
The SetAddress message is normally used to set the Device to a specific non-zero
HiQnet Address so that it makes sense and fits into a user's specific numbering
scheme.
4.1.4 DiscoInfo
The DiscoInfo message is central to all Routing Layer activities. For this reason,
we introduce the message early because a basic grasp of its various forms and
uses is essential to understanding almost any aspect of the Routing Layer.
The DiscoInfo message is used to:
Announce the arrival of a Device on the network.
Search for other Devices on the network.
Exchange routing information between Devices.
Keep a network connection Alive
The DiscoInfo message takes two forms, the Query and Info; these are often
referred to as DiscoInfo(Q) & DiscoInfo(I). The Q indicates that the „Info‟ bit in
the Message Header flags field is zero, the I indicates that the „Info‟ bit is set to
one. The payload is the same for both forms of message, and their usage is now
explained in more detail.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 53 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
4.1.4.1 Query
DiscoInfo(Q) is a Get type message which serves two purposes. The primary
purpose is to find a Device on the network; the secondary purpose is to pass onto
the receiving Devices some additional information about the sender.
4.1.4.2 Info
DiscoInfo(I) is a message which may be a reply to a DiscoInfo(Q), or it may be
sent as an informational message. Either way, the primary purpose is to convey
routing information about the sender to the recipient.
4.1.5 NetworkInfo
The Routing Layer has a number of sub-systems that rely on the exchange of
Network-specific information. Within this document, for the purposes of clarity,
this information is referred to generically as „NetworkInfo‟. There is a
NetworkInfo structure for each type of Protocol/Physical media combination. The
Packet Layer is responsible for providing a NetworkInfo structure representing
each of its particular network interfaces. In implementation terms, this is the
means by which the Routing Layer achieves its aim of abstracting different
network architectures. By grouping differences together within a common
structure supplied by the Packet Layer we are able to design and implement the
Routing Layer in a generic manner.
The NetworkInfo structure forms a part of the DiscoInfo message payload and
this is the means by which each Routing Layer communicates network-specific
information between Devices.
So that the Routing Layer may identify what kind of NetworkInfo structure is
attached to a DiscoInfo payload, each type of NetworkInfo is identified via an
enumerated UBYTE. This is called the NetworkID and is enumerated as follows:
1 – TCP/IP
2 – Reserved
3 – Reserved
4 – RS232
4.1.6 Device Arrival “Announce”
A Device will announce its arrival by transmitting 5 DiscoInfo(I) messages on to
the network at regular 2 second intervals. Prior to transmitting, the Device must
pause for a random period of between 0 and 2 seconds.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 54 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
HiQnet Address Negotiation will have been completed before the Device Arrival
procedure executes.
4.1.7 Device Departure “Goodbye”
A Device which has power-fail detection (or can be manually shutdown as in the
case of closing a GUI), must notify other Devices it is communicating with of its
departure from the network via a „Goodbye‟ message. The Goodbye allows the
remaining Devices to free any resources associated with the departing Device
without having to wait for their Keep timeouts to activate the cleanup. In some
situations, such as restarting the Device, this also allows the network to be rediscovered more quickly.
A Goodbye is NOT sent when a Keep Alive timeout occurs.
The closing Device must unicast the Goodbye message to each Device within its
Routing Table which has a Keep Alive active. After this point the Device is
assumed to be unavailable and not able to receive or send messages. The only
way the Device may re-enter the network, is to follow the same procedure as for a
newly connected Device.
4.2 Device Discovery on Demand
Device Discovery is the name given to locating a specific Device on the HiQnet
network. In doing this, the Routing Layer makes use of the lower layers in the
HiQnet model services supplied by the underlying layers in the HiQnet model
(e.g. TCP/IP on an Ethernet network, Token Network Services on a 485 bus) to
determine the presence of HiQnet compatible Devices residing on a given
network interface. The purpose of this level of discovery is to discover the
network information necessary to address a Device at a particular HiQnet address.
Each Network Interface must be able to specify the HiQnet Device Address that it
can be found on and the Network Address of the Network Interface. A Network
interface may be found on only one Device, but a Device can have more than one
Network Interface. Some types of Network Interface include Ethernet, 485 Token
bus, 232 Full Duplex, etc.
The Device Discovery Algorithm is used when a Device wishes to transmit a
message to another Device, for which it has no available route. This „demand
driven‟ approach minimizes the size of the routing table by only requesting routes
for those Devices that need to be contacted.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 55 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
4.2.1 Searching for a Device
This section illustrates the steps required to search for a specific Device on the
network. The Device to search for is identified by its HiQnet Destination Address;
if the Broadcast HiQnet Address is used then the search returns ALL Devices
presently on the network – including those Devices which mistakenly have a
HiQnet address of zero.
1. Search the Routing Table for a route to the required Device. If a route
already exists (the Device Address searched for matches a Device Address
in the table), use it.
2. If no route exists, network-broadcast on the datagram service a
DiscoInfo(Q) message specifying the requested Device in the „HiQnet
Device‟ field.
3. Wait three seconds for a DiscoInfo(I) message(s) to arrive with the HiQnet
Device address which matches that requested in step 2. If the correct
message does not arrive, repeat from step 2 for a maximum of three
attempts. If after three attempts the no matching response has been
received, exit with a „not found‟ error.
4. If a DiscoInfo(I) message is received from the Device being searched for,
create a new entry in the Routing Table using the following information
extracted from the message:
Device Address
Serial Number
Cost
Max Message Size
Network Address
The remaining item, the Interface is expected to be supplied by the Routing Layer
itself – it must know which interface the DiscoInfo(I) came in on.
If the search specified the HiQnet broadcast address, many DiscoInfo(I) messages
may arrive in return to the DiscoInfo(I).
4.2.2 Keep Alive/Device Departure
Having found a Device and established a means of communication with it, the
Routing Layer becomes responsible for tracking the Device‟s continued
participation in the network. If, for whatever reason the Device should become
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 56 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
un-contactable, it is the responsibility of the Routing Layer to notify the
Application Layer that the Device has become unavailable. The „keep alive‟
mechanism is the means by which the continued presence of a Device is checked
and monitored.
We strongly advise the use of a guaranteed service (where available) for Keep
Alive.
4.2.2.1 When to initiate Keep Alive
Keep Alives are only triggered by the Hello/Hello(info) messages
4.2.2.2 Keep Alive Period
The Keep Alive Period (KAP) determines the maximum period of inactivity
allowed on a route before it is „timed-out‟ and deemed invalid. A source Device
specifies the KAP it requires of the destination by placing it in all the DiscoInfo
messages it sends.
The Keep Alive Period is specified in milliseconds and has a DataType of
UWORD. The minimum permissible period is 250ms. Normally the KAP is 10
seconds (10000ms).
4.2.2.3 Guaranteed
For each guaranteed connection (such as TCP), a Device must transmit a
DiscoInfo(I) message „KAP‟ milliseconds after it last transmitted a DiscoInfo(I)
or Application Layer message. The period „KAP‟ is the „Keep Alive Period‟ that
was specified in the latest DiscoInfo message received from the source Device.
The destination Device shall time-out a route when it has received no messages
within the timeframe of the Keep Alive Period.
If the connection is terminated to save resources, the keep alive must transfer to
the Datagram service. If at a later time, the guaranteed connection is reestablished the keep alive must move back to guaranteed service.
4.2.2.4 Datagram
For each discovered route that uses the datagram service exclusively (such as
UDP), a Device will unicast a DiscoInfo(I) to the destination „KAP‟ milliseconds
after it last transmitted a DiscoInfo(I) or Application Layer message.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 57 of 91
HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
DiscoInfo
0x0000
Locates Devices and exchanges routing
information
Reserved
0x0001
Reserved
GetNetworkInfo
0x0002
Gets information on network interfaces
Reserved
0x0003
Reserved
RequestAddress
0x0004
Requests the use of a specific HiQnet Address
AddressUsed
0x0005
Notifies that an HiQnet Address is in use
SetAddress
0x0006
Sets an address (HiQnet & Network)
Goodbye
0x0007
Notifies receiver that the sender is shutting down
Hello
0x0008
Open a session between two HiQnet Devices
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0000
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
HiQnet Device
UWORD
Device address of sender
Cost
UBYTE
Aggregated cost of route back to src
Serial Number
BLOCK
Sender’s HiQnet Serial Number
Max Message Size
ULONG
Max Msg size sender can handle
Keep Alive Period
UWORD
Keep Alive rate in ms
NetworkID
UBYTE
NetworkInfo
Network specific
Network specific info of sender
4.3 Table of Routing Layer Message IDs
4.3.1 DiscoInfo
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 58 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0002
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Serial Number
BLOCK
Destination’s Serial Number
VERSION
UBYTE
2
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
25
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0002
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Serial Number
BLOCK
Destination’s Serial Number
Number of Interfaces
UWORD
2
Max Message Size
ULONG
Max for size Device/interface
NetworkID
UBYTE
NetworkInfo
Network specific
Network info of Sender
Max Message Size
ULONG
Max for size Device/interface
NetworkID
UBYTE
NetworkInfo
Network specific
Network info of Sender
4.3.2 GetNetworkInfo
INFORMATION MESSAGE:
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 59 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0x000000000000
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xFFFF00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0004
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
HiQnet Device Address
UWORD
0xNNNN
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xFFFF00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0004
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
4.3.3 Request Address
4.3.4 AddressUsed
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 60 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0006
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Serial Number
BLOCK
128-bit GUID
New Device Address
UWORD
0xNNNN
NetworkID
UBYTE
NetworkInfo
Network specific
Network specific info of sender
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0007
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Device Address
UWORD
0xNNNN
4.3.5 SetAddress
4.3.6 Goodbye
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 61 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xNNNN00000000
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xNNNN00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0008
FLAGS
UWORD
0x0020 (GUARANTEED)
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Note, no header extension yet
Session Number
UWORD
0xNNNN (not equal to zero)
This Device's newly-invented
session number
FLAG mask
UWORD
0xXXXX
4.3.7 Hello Query
See the Sessions chapter discussion. A Hello(Query) does not yet have a header
extension, but the answering Hello(Info) does.
After bootup, a Device will generate a random session number between 1 and
65535. Then, for each new session until the next bootup, the Device will
increment the session number. This avoids accidentally using the same session
number for two consecutive sessions in case of session breakage.
The Hello and Hello(info) message payloads also contain a mask to indicate the
supported header flags.
The minimum support for the flag mask is: 0x01FF (see the Flags chart)
Bit 0 – Request Acknowledgement
Bit 1 – Acknowledgement
Bit 2 – Information
Bit 3 – Error
Bit 4 – Reserved
Bit 5 – Guaranteed
Bit 6 – Multi-part message
Bit 7 – Reserved
Bit 8 – Session Header Extension
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 62 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xNNNN00000000
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xNNNN00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0008
FLAGS
UWORD
0x0124 (100100100)
SESSION+GUARANTEED+INFORMAT
ION
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
SESSION NUMBER
UWORD
0xNNNN (not equal to zero) The
DEST Device's session number;
remote Device
Payload…
Session Number
UWORD
0xNNNN (not equal to zero)
This Device's newly-invented
session number; the SOURCE
Device
FLAG mask
UWORD
0xXXXX
4.3.8 Hello Info
After a session has been established between two Devices, each Device will put
the OTHER Device's session number in all message header extensions before
sending the message to the other Device. Each Device will check all received
messages, and ensure the SESSION NUMBER in the Header Extension matches
its own local session number that it generated for this session.
4.4 Packet Service Layers
The Packet Service Layer interfaces to the Routing layer above and the Reliability
Layer below. The function of the Packet Service Layer is to provide a means of
sending and receiving single HiQnet messages to and from the underlying
network architecture. For example, a Routing Layer may sit upon two Packet
Service Layers, one for TCP/IP and another for RS485.
4.5 TCP/IP Packet Service
HiQnet defines a method for packing multiple messages into a single UDP packet.
TCP/IP based Devices making use of UDP must adhere to this standard to ensure
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 63 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
MacAddr
6 bytes
MAC address
DHCP/AutoIP
UBYTE
1 = DHCP/AutoIP 0 = Static Addr
IPAddr
ULONG
IP address
SubnetMask
ULONG
Subnet mask
Gateway
ULONG
Gateway address
interoperability across TCP/IP based products. Since TCP is stream-based there is
no similar requirement for that protocol.
4.5.1 Reliable (TCP) Packet Service
TCP is a stream-based mechanism, accessed usually via a sockets interface. To
minimize overhead, the programmer may wish to aggregate several messages into
a single buffer (aka packet) and present them to the TCP socket in one hit; this is
an implementation choice for the programmer.
The IANA designation for HiQnet is „HiQnet-port 3804/tcp Harman HiQnet
Port‟.
4.5.2 Datagram (UDP) Packet Service
In HiQnet, a sender has the ability to put several messages together into a UDP
packet and send them. The receiver is expected to have the ability to separate out
these into distinct messages as long as the maximum buffer size on the receiver
has not been exceeded.
The IANA designation for HiQnet is „HiQnet-port 3804/udp Harman HiQnet
Port‟
4.5.3 NetworkInfo
This section describes the „NetworkInfo‟ structure for an IPv4 based Packet
Layer. The Routing Layer relies on the NetworkInfo to describe each network
interface it is bound to. This structure is appended to every DiscoInfo message the
Routing Layer sends out and the information contained within used by each
recipient Device to build its Routing Table. Some GUIs may also display this
information to the user.
In a multi-homed Device, there will be one NetworkInfo structure for each and
every network interface. The NetworkInfo contains the following information:
4.5.3.1 MAC Address
The MAC Address uniquely identifies the network interface associated with the
message payload. On Devices with a single interface, this parameter could be
considered redundant since the Serial Number is typically sent within a message
and is constructed from the Device‟s MAC address. However, on Devices with
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 64 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
multiple interfaces, a message may originate from any one of the secondary
interfaces and this MAC address allows the recipient to identify each of them.
4.5.3.2 DHCP Flag
The Routing Layer does not explicitly use the DHCP flag, but this information is
exchanged between Devices for informational purposes where there is a
requirement to show a map of the network, a GUI for example. One exception to
this is the „SetAddress‟ message, which uses the NetworkInfo block to „set‟
whether the Device uses DHCP to obtain an IP address.
4.5.3.3 IP Address
The IP Address identifies the network address of the interface a message came
from. In many cases this will be the same as the source address presented by the
receiving interface. However, when a Device is acting as a proxy for others, this
address will differ to the source presented by the receiving interface. In terms of
implementation, the safest approach is to use this IP Address when it is supplied
in preference to the source address.
4.5.3.4 Subnet Mask
The Routing Layer uses this information to help determine whether it may unicast
to another Device.
4.5.4 Gateway
The Routing Layer does not explicitly use the Gateway parameter, this is
exchanged between Devices for informational purposes where displaying this
information could be useful.
4.5.5 Use Case – Closed loop control of a HiQnet product via
TCP/IP – addressing already fixed.
Suppose you desire to control a HiQnet product via TCP/IP. The Devices all have
their IP addresses and HiQnet addresses already fixed. Assume we have a thirdparty control Device (CD) that wants to control a level in a HiQnet product (HP).
In this case, use the following steps
1. Upon booting of the control Device (CD), it will broadcast on port 3804 a
DiscoAnnounce
2. To find the route to the HP, CD will IP broadcast a DiscoQuery with the
HiQnet address of CD in the payload.
3. HP replies with a DiscoInfo – giving CD the route information required
for HP to open a TCP/IP connection to CD
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 65 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
4. HP opens a TCP connection to CD on port 3804 and then sends a Hello to
start Keep Alives
5. CD replies back with a HelloInfo
6. HP sends a ParamSubscribe message to CD
7. CD replies with an ParamSet(I) message, synchronizing the value to HP
8. HP is now ready to send ParamSet messages to CD. If any other party
changes the parameter in question, then HP will automatically receive the
change. If HP would like to get a notification that CD has actually
changed the Param, then all ParamSet messages should set the Ack flag.
9. Periodically HP and CD will exchange Keep Alives via TCP based on the
original specified rate.
4.5.6 Use Case – Open Loop control of a HiQnet product via UDP
Suppose you desire to control a HiQnet product via UDP. The Devices all have
their IP addresses and HiQnet addresses already fixed. Assume we have a thirdparty control Device (CD) that wants to control a level in a HiQnet product (HP).
In this case, use the following steps
1. Upon booting of the control Device (CD), it will broadcast on port 3804 a
DiscoAnnounce
2. To find the route to the HP, CD will IP broadcast a DiscoQuery with the
HiQnet address of CD in the payload.
3. HP replies with a DiscoInfo – giving CD the route information required
for HP to transmit to CD
4. HP is now ready to send ParamSet messages to CD via UDP
5. Session numbers, Hello(Q/I) and Goobye are not used
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 66 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
5 HiQnet String Settings
System Architect has the ability to copy HiQnet strings to the clipboard to
make it easy to use these strings in your control application. The format of the
string that is copied to the clipboard can be customized to meet your needs
and these settings are configured from the HiQnet string settings options.
Make sure that “Enable HiQnet String Visibility” is checked. This turns on the
feature.
If you are controlling the HiQnet device via IP (Ethernet), then select IP. If
you are using serial then select RS232. There are some subtle differences in
the strings that are created by System Architect between IP and RS232.
Depending on how you need the strings formatted, choose either decimal or
hexadecimal, and use the Custom Formatting section to customize further.
Pre-defined custom formatting can be selected by choosing AMX or Crestron
from the “Format” drop down list.
The Source Address is the address of your device. This is the address that the
HiQnet device will reply to.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 67 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Enable “Use Placeholder for Parameter Value” if the HiQnet message string
should include placeholders for the parameter value instead of the current
value for the parameter. See section 2.7.6
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 68 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
6 RS232 Packet Service
This section is outlined as follows:
Introduction
Section 1 – Getting Started/Basic Command Structure
Section 2 – Setting Up and Maintaining a Communication Connection
Section 3 – Generating Command Strings via the Network Trace Window
Using the MultiParameterSet message. Router example.
Section 4 – Calculating Checksums
Section 5 – Feedback
Introduction
The purpose of this section is to show how to connect to a HiQnet Device
product, generate and format command strings, calculate a checksum, and
receive feedback using the Harman HiQnet Device protocol. This quick guide
is for developers who want to rapidly achieve communications with a HiQnet
Device using an open loop approach. While a closed loop driver would be
desired, some developers may choose to implement an open loop driver. This
document will assist developing an open loop driver to control most aspects of
a HiQnet Device.
Throughout this section specific reference of Object IDs, Parameter IDs, and
Parameter Values are shown. These specific references originate from a dbx
SC. The same principles are used for any HiQnet device.
6.1 Getting Started/Basic Command Structure
This section is for RS232 only, all messages and examples have RS232
formatting included.
IP Connections
All information contained for RS232 Packet Service Connections is valid
for TCP/IP connections except that no FS, FC, or checksum characters are
transmitted within a command. Also, the TCP/IP connection also does not
need any PING, ACK/NAK, RESYNC/RESYNC_ACK, or Guaranteed ACK
because UDP and TCP have their own link layer. The IP port is 3804.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 69 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
6.1.1 Baud Rate
dbx HiQnet Devices are fixed at: 57.6 kbps, 8N1.
6.1.2 Big Endian
Multi Byte data types are sent Big Endian, which means they are send most
significant byte first. If a 16 bit word 0x1234 is sent, it is presented to the
transmit register as 0x12 first then 0x34.
6.1.3 Data Types
UBYTE 8 bits unsigned 0 - 255
UWORD 16 bits unsigned 0 - 65535
ULONG 32 bits unsigned 0 - 4294967295
6.1.4 Resync Request / Resync Acknowledge
The communications protocol uses special characters to synchronize both
ends of the serial connection and to keep the connection open. To synchronize
the serial drivers, Resysnc Request and Resync Acknowledge are used.
Resynch_Request 0xFF
Resysnc_Acknowledge 0xF0
Since these characters are not accepted from the rest of the protocol, the
resynch procedure will issue a string of Resync_Request and
Resync_Acknowledge bytes to flush the receiving state machine. To
synchronize with a HiQnet Device send 16 Resynch_Request and 261
Resysnc_Acknowledge bytes.
6.1.5 Ping
To maintain a connection, a PING byte lets the other side know that you are
still connected.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 70 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Frame Start
UBYTE
0x64
Frame Count
UBYTE
0x00
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
Length of entire packet (not
including FS FC, or CS bytes)
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
Ping 0xF0 0x8C
If a message has not been sent within the last second, send a PING. A timeout
of 2.5 seconds will result in the HiQnet Device attempting a resync (0xFF‟s,
0xF0s).
6.1.6 Resync_Acknowledge Byte
Send this byte at the beginning of every command. This byte will keep the
HiQnet Device from attempting a resync when using open-loop
implementation.
Sync 0xF0
6.1.7 Frame Start Bytes
To indicate the start of a frame, two bytes are used. The frame bytes will
always precede a Message Header.
Frame_Start 0x64
Frame_Count 0x00, or 0x01-0xFF
For an open loop implementation, use a Frame_Count of 0x00. This indicates
to the receiver that it need not acknowledge the receipt of the message.
6.1.8 Basic Command Structure (Unacknowledged – Open Loop)
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 71 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICEVDOBJECT
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
Specific type of command
issued
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
(Payload)
Checksum
UBYTE
CCITT-8 (over FS, FC, Header,
Payload)
6.1.9 Number Parameters
How many Parameters are being changed within one Frame.
6.1.10 Parameter_ID
Each control inside an object is assigned a particular Parameter (state
variable) ID. For example, the fader inside a mixer, a particular source inside
a router, or a mute button.
6.1.11 Data_Type
Data types held by the Parameter_Val
Data_Type = 1 for a single unsigned byte of range 0 to 255 (i.e. a Mute
button, or Route) Data_Type = 3 for two unsigned bytes of range 0 to 65535
(i.e. a fader)
6.1.12 Parameter_Val
This variable holds the value of the Parameter_ID in question. For example, if
a Router is the object we want to control, the Parameter_Val will be a single
byte of a value 0(NONE), 1 (Source 1), 2 (Source 2), etc. The Parameter_Val
for a fader within a Mixer object consists of 4 bytes and will hold a float value
between –inf – 20dB].
6.1.13 CCIT checksum
The CCIT checksum is an 8 bit CRC byte used to validate the Header and
Payload. This byte can be calculated by initializing the checksum byte to
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 72 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
0xFF and passing each byte though the following calculation. The
Network_CCITT_8_Table is included in the Appendix.
UCHAR update_bcc(UCHAR current_bcc, UCHAR new_byte)
{
return Network_CCITT_8_Table[current_bcc ^ new_byte];
}
The checksum is calculated on all bytes in the Frame, Header, and Payload.
See Calculating Checksum section for detailed information concerning
checksum calculations.
6.2 Setting Up and Maintaining a Communication
Connection
In order to send commands to a Harman HiQnet Device unit from a 3rd party
controller, a connection should be kept alive by the continuous sending and
receiving of specific commands. There are two different levels of “keep-alive”
or “heartbeat” commands that should be continuously exchanged. The first is
a Ping designed to keep the transmission layer connection open. This is done
by sending a 0xF0 0x8C every 1 second. The HiQnet Device will respond
with a 0x8C. If the user desires to only send commands and not receive any
feedback from the HiQnet Device, then only this connection must be
maintained If the 3rd party controller is not capable of parsing commands,
storing independent variables, or receiving commands, then the user may send
pre-formed commands with a 0xF0 preceding all commands. This will open a
connection just long enough for the HiQnet Device to accept a command.
Setting the protocol to RS232 in the HiQnet String Settings (see section will
automatically prefix the message string copied to the clipboard with the
necessary 0xF0.
The second is a Disco command and it is designed to keep a
connection open at the Protocol layer. If a user wants to receive feedback from
the HiQnet Device, a Disco must be sent from the 3rd party controller at least
every 10 seconds to keep this connection open. To initiate a connection with
the HiQnet Device, a Disco Broadcast should be sent. Any HiQnet Device
Devices on this connection will answer back.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 73 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Frame Start
UBYTE
0x64
Frame Count
UBYTE
0x00
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0000 DiscoInfo
FLAGS
UWORD
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
HiQnet Device
UWORD
Device address of sender
Cost
UBYTE
Aggregated cost of route back to src
Serial Number
BLOCK
Sender’s HiQnet Serial Number
Max Message Size
ULONG
Max Msg size sender can handle
Keep Alive Period
UWORD
Keep Alive rate in ms
NetworkID
UBYTE
0x04
NetworkInfo
Network specific
RS232 NetworkInfo as below
Checksum
UBYTE
CCITT-8 (over FS, FC, Header,
Payload)
COM ID
UBYTE
Com Port Identifier
Baud Rate
ULONG
Bits per second, 9600, 57600
Parity
UBYTE
0 – None
1 – Odd
2 – Even
3 – Mark
4 – Space
The Disco Broadcast command:
RS232 NetworkInfo is as follows:
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 74 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Stop Bits
UBYTE
0 – 1 Bits
1 – 1.5 Bits
2 – 2 Bits
Data Bits
UBYTE
Number of bits for data, typically 4-9
Flow Control
UBYTE
0 – None
1 – Hardware
2 – XON/OFF
Frame Start
UBYTE
0x64
Frame Count
UBYTE
0x00
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
Typical values used in the RS232 NetworkInfo are:
Baud Rate = 57600
Parity = 0
Stop Bits = 1
Data Bits = 8
Flow Control = 0
When using the serial port it is suggested that the Source Node (3rd Party
Device) address 0x00 0x33. So the actual command sent out the serial port is:
0xF0 0x64 0x00 0x02 0x19 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x3E 0x00 0x33 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0xFF
0xFF 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x20 0x05 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x33 0x01 0x00
0x10 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0xFD 0x01 0x02 0x03
0x04 0x00 0x00 0x27 0x10 0x4E 0x20 0x04 0x00 0x00 0x00 0xE1 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x08
0x00 0x(checksum byte)
The HiQnet Device will respond to this Disco message with its address
(node). Parse this incoming message in order to get the HiQnet Device‟s
address. Once the address is found you must reply to all incoming Disco
messages (send at least every 10 seconds whether a Disco is received or not)
or the connection will be shut down. The reply is the same message as the
broadcast command, but with the HiQnet Device‟s address inserted in place of
the 0xFF 0xFF. The incoming Disco message will be:
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 75 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0xNNNNNNNN
SOURCE ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
DEST. ADDRESS
HIQNETADDR
0xDEVICE00000000
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0000 DiscoInfo
FLAGS
UWORD
0x0024 (Guaranteed Info)
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Payload…
Node
UWORD
Node address of sender
Cost
UBYTE
Aggregated cost of route
back to source
Serial Number
BLOCK
Sender’s Serial Number
Max Message Size
ULONG
Max Msg size sender can
handle
NetworkID
UBYTE
Network type of sender
0x01 = TCP/IP
0x04 = RS232
NetworkInfo
Network specific
Network specific info of
sender
Checksum
UBYTE
CCITT-8 (over FS, FC, Header,
Payload)
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 76 of 91
It will be assumed that in this example if the dbx node address is 0x00 0x20
(decimal 32).
0x64 0x00 0x02 0x19 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x3E 0x00 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x33
0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x24 0x05 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x20 0x64 0x00 0x10
0x59 0x22 0xF0 0xAA 0x2A 0x0C 0x11 0xDE 0xBE 0x67 0x00 0x0F 0xD7 0x00 0xC0
0x1B 0x00 0x00 0x07 0xD0 0x27 0x10 0x04 0x01 0x00 0x00 0xE1 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x08
0x00 0x0B(checksum)
So the 3rd party controller needs to send the following command for every
incoming Disco (send at least every 10 seconds whether a Disco is received or
not):
0xF0 0x64 0x00 0x02 0x19 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x3E 0x00 0x33 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x20 0x05 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x33 0x01 0x00
0x10 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0xFD 0x01 0x02 0x03
0x04 0x00 0x00 0x27 0x10 0x4E 0x20 0x04 0x00 0x00 0x00 0xE1 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x08
0x00 0x5F(checksum byte)

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Frame Start
UBYTE
0x64
Frame Count
UBYTE
0x00
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0x000000xx
SRC
UWORD:ULONG
0xNODEVDOBJECT
DEST
UWORD:ULONG
0xNODEVDOBJECT
Once these two “heartbeats” are being continuously exchanged, the
connection is open and the 3rd party controller can send and receive
commands as necessary.
6.2.1 Guaranteed Acknowledgement
Every command that is sent or received starts with the 0xFS 0xFC start
frame bytes. If the Frame Count (second byte) is anything besides a 0x00,
then it is a guaranteed service message and a 0xA5 must be sent to
acknowledge this message has been received. The HiQnet Device will try and
initiate a re-sync if it doesn‟t receive the 0xA5 Ack for every guaranteed
message sent. The user may send a 0xA5 after every received message if the
user doesn‟t want to deal with guaranteed service requirements.
6.2.2 Resync
The HiQnet Device will send at least 261 0xFF‟s if it believes it is out of
sync with the controller. The HiQnet Device will not accept any serial
commands in this state. This happens when the 0xF0 0x8C heartbeat or the
Disco commands, is not being sent at required intervals. This will also happen
if a 0xA5 is not received for each guaranteed packet sent.
6.3 Recall 0x0125 (Message ID)
HiQnet devices support recalling preset data. The most common preset to
recall is the scene. To change a scene on a HiQnet Device, issue a recall scene
command (Preset type = 2). If you are using subscriptions, the changed
parameter values will come back to you in multiParameterset messages.
The Workgroup Path and Scope
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 77 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
MESSAGE ID
UWORD
0x0125
Flags
UWORD
0x0000
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
(Payload)
Recall Action
UBYTE
Scene type 2 for Scene, 3 for
Device preset, 5 for Venue
preset
Recall Number
[UWORD]
Scene to load, 0 (default), 1,
2, 3…
Workgroup Path
STRING
0x00 0x02 0x00 0x00
(Reserved)
Scope
UBYTE
0x00 (Reserved)
Checksum
UBYTE
CCITT-8 (over FS, FC, Header,
Payload)
Here is an example for recalling Device Preset 1.
0xF0 0x64 0x00 0x02 0x19 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x21 0x00 0x33 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00
0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x01 0x25 0x00 0x20 0x05 0x00 0x00 0x03 0x00 0x01 0x00
0x02 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x01 (checksum byte)
6.4 Calculating Checksums
This document will show two ways of calculating checksums. The first
method is using code to perform the checksum operations systematically. The
second method is using a Microsoft Excel Spreadsheet and manually entering
commands into the spreadsheet. The spreadsheet will then calculate the
checksum.
6.4.1 How to calculate a checksum using code for the Harman
HiQnet Device:
//shown in AMX Netlinx syntax
//CCIT copied from “Full Duplex Data Link Specification .PDF”
//$ = hex
CHAR CCIT[] = {$5E,$BC,$E2,$61,$3F,$DD,$83,$C2,$9C,$7E,$20,$A3,$FD,$1F,$41,
$9D,$C3,$21,$7F,$FC,$A2,$40,$1E,$5F,$01,$E3,$BD,$3E,$60,$82,$DC,
$23,$7D,$9F,$C1,$42,$1C,$FE,$A0,$E1,$BF,$5D,$03,$80,$DE,$3C,$62,
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 78 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
//COMMAND COPIED FROM System Architect String Export
CHAR DBX[] =
$BE,$E0,$02,$5C,$DF,$81,$63,$3D,$7C,$22,$C0,$9E,$1D,$43,$A1,$FF,
$46,$18,$FA,$A4,$27,$79,$9B,$C5,$84,$DA,$38,$66,$E5,$BB,$59,$07,
$DB,$85,$67,$39,$BA,$E4,$06,$58,$19,$47,$A5,$FB,$78,$26,$C4,$9A,
$65,$3B,$D9,$87,$04,$5A,$B8,$E6,$A7,$F9,$1B,$45,$C6,$98,$7A,$24,
$F8,$A6,$44,$1A,$99,$C7,$25,$7B,$3A,$64,$86,$D8,$5B,$05,$E7,$B9,
$8C,$D2,$30,$6E,$ED,$B3,$51,$0F,$4E,$10,$F2,$AC,$2F,$71,$93,$CD,
$11,$4F,$AD,$F3,$70,$2E,$CC,$92,$D3,$8D,$6F,$31,$B2,$EC,$0E,$50,
$AF,$F1,$13,$4D,$CE,$90,$72,$2C,$6D,$33,$D1,$8F,$0C,$52,$B0,$EE,
$32,$6C,$8E,$D0,$53,$0D,$EF,$B1,$F0,$AE,$4C,$12,$91,$CF,$2D,$73,
$CA,$94,$76,$28,$AB,$F5,$17,$49,$08,$56,$B4,$EA,$69,$37,$D5,$8B,
$57,$09,$EB,$B5,$36,$68,$8A,$D4,$95,$CB,$29,$77,$F4,$AA,$48,$16,
$E9,$B7,$55,$0B,$88,$D6,$34,$6A,$2B,$75,$97,$C9,$4A,$14,$F6,$A8,
$74,$2A,$C8,$96,$15,$4B,$A9,$F7,$B6,$E8,$0A,$54,$D7,$89,$6B,$35};
{$64,$00,$02,$19,$00,$00,$00,$1F,$00,$33,$01,$01,$01,$00,$00,$20,$01,$01,$01,$00,$01,$00,$02,$20
,$05,$00,$00,$00,$01,$00,$02,$01,$01};
BUTTON_EVENT[dvTP,65]
{
PUSH:
{
LOCAL_VAR CHAR BCC; //CHECKSUM
LOCAL_VAR INTEGER I; //LOOP COUNTER
BCC = $FF; //INITIALIZE CHECKSUM
FOR (I = 1; I<= LENGTH_ARRAY(DBX);I++)
{
BCC = CCIT[(BCC BXOR DBX[I])]; //bitwise XOR each element of command
}
}
}
Checksum (BCC) is $08 for the DBX[] command stated in the example;
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 79 of 91
HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Frame Start
UBYTE
0x64
Frame Count
UBYTE
0x00
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0x000000xx <xx is variable>
SRC
UWORD:ULONG
0xNODEVDOBJECT
DEST
UWORD:ULONG
0xNODEVDOBJECT
MSG_ID
UWORD
0x0113
FLAGS
UWORD
0x0000
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
( Payload)
Subscriber Address
Subscription Type
Sensor Rate
Subscription Flags
UWORD:ULONG
UBYTE
UWORD
UWORD
0xNODEVDOBJECT
0-ALL, 1 –Non-Sensor, 2Sensor
Period in milliseconds
Bit 0 – ‘1’ Send initial
updates
Checksum
UBYTE
CCITT-8 (over FS, FC, Header,
Payload)
6.4.2 Serial String Method
The System Architect String Export will calculate and append the proper
checksum to every message desired. This tool is useful for checking the
validity of the 3rd party controller checksum method..
6.5 Feedback
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 80 of 91
The HiQnet Device utilizes a command called „subscribe‟ to manage all
feedback traffic. Once a subscribe command has been issued, the HiQnet
Device will send a string containing the current state of the Parameter (or
Parameter‟s) every time the Parameter changes value. This will allow a 3rd
party controller to get Parameter updates when a user changes values via the
front panel, HiQnet Device GUI, or from another 3rd party controller. The
HiQnet Device will continue to send feedback until a „unsubscribe‟ command
is issued, or until the unit loses power.

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
6.5.1 ParameterSubscribeAll
This message is used to subscribe to every State Variable under an Object or
Virtual Device. If this message is sent to a Mixer Object, then a feedback
string will be generated if a user changes any values within that particular
Mixer Object.
The ParameterSubscribeAll command:
Sample String: Subscribing to Router on a SC32 (source address 0x0033, dest
address 0x0020):
0x64 0x00 0x02 0x19 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x24 0x00 0x33 0x01 0x01 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x20
0x01 0x01 0x01 0x00 0x01 0x13 0x02 0x20 0x05 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x33 0x00 0x00 0x00
0x00 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x01 0xF9
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 81 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Frame Start
UBYTE
0x64
Frame Count
UBYTE
0x00
VERSION
UBYTE
0x02
HEADER LENGTH
UBYTE
0x19
MESSAGE LENGTH
ULONG
0x000000xx <xx is variable>
SRC
UWORD:ULONG
0xNODEVDOBJECT
DEST
UWORD:ULONG
0xNODEVDOBJECT
MSG_ID
UWORD
0x0114
FLAGS
UWORD
0x0000
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Subscription Type
UBYTE
0-ALL, 1 –Non-Sensor, 2Sensor
Checksum
UBYTE
CCITT-8 (over FS, FC, Header,
Payload)
6.5.2 ParameterUnSubscribeAll
This message is used to unsubscribe to every State Variable under an Object
or Virtual Device.
The ParameterUnSubscribeAll command:
Sample String: UnSubscribing to Router on a SC32 (source address 0x0033,
dest address 0x0020):
0x64 0x00 0x02 0x19 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x20 0x00 0x33 0x01 0x01 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x20
0x01 0x01 0x01 0x00 0x01 0x14 0x02 0x20 0x05 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x33 0x00 0x00 0x00
0x00 0x01 0x49
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 82 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
SRC
UWORD:ULONG
0xNODEVDOBJECT
DEST
UWORD:ULONG
0xNODEVDOBJECT
MSG_ID
UWORD
0x0114
FLAGS
UWORD
0x0000
HOP COUNT
UBYTE
SEQUENCE NUMBER
UWORD
Subscription Type
UBYTE
0-ALL, 1 –Non-Sensor, 2Sensor
Checksum
UBYTE
CCITT-8 (over FS, FC, Header,
Payload)
Note: If the HiQnet Device issues a resync request that means the connection
has been shut down, and all Parameter‟s will need to be re-subscribed. All
Parameter‟s will need to be subscribed to whenever the AC power is lost to
the HiQnet Device unit.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 83 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Appendix
IP Connections
All information contained above for Section 6 RS232 connections is valid
for TCP/IP connections except that no FS, FC, or checksum characters are
transmitted within a command. Also, the TCP/IP connection also does not
need any PING, ACK/NAK, RESYNC/RESYNC_ACK, or Guaranteed ACK
because UDP and TCP have their own link layer. The IP port is 3804.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 84 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
7 Sessions
For third party control sessions are optional.
Communication between HiQnet Devices is predicated on the history of messages
having already been sent. Subscriptions need to be established before subscription
values can be sent. After a configuration has been described to another Device,
this configuration is expected to persist. Session IDs ensure that communication
with a particular Device ID has not been broken and that the Device has not
rebooted and re-presented before Keep Alive Period has elapsed.
It is possible that Devices can reboot and present themselves within a Keep Alive
Period. This raises the possibility that messages intended for a previous boot cycle
may be delivered to a Device on its next boot cycle. This is undesirable.
Putting the session number in the header of a HiQnet message allows the
detection of a break in a HiQnet session. If the session number does not match the
session number expected a session break is detected and coherency between the
two Devices is assumed to be lost.
7.1 Starting a Session
A session is opened between two HiQnet Devices with an exchange of
Hello(Query)/Hello(Info) messages. When a Hello arrives, the payload contains
the session number(A) that sending Device has generated for this session. The
response to a Hello(Query) is a Hello(Info) with a payload containing the session
number(B) the answering Device has generated for this session. In the header
extension of the Hello(Info) is the original session number(A).
Once session numbers are exchanged, any message can be guaranteed to be
within the session only if session numbers are checked on a frame per frame
basis. Each Device expects to see its own session number in the header extension
portion of the header of every message it receives.
7.2 Detecting a Session Break
A session number is created to be associated with the destination Device. The
session numbers are transmitted through Hello/Hello(info) messages, creating a
pair of session numbers identifying the session. Purging of messages for previous
sessions is performed when a new session number is presented in either a new
Hello or Hello(info) message or a conflicting session number is found in a HiQnet
Header. Keep Alive is triggered.
Associating a session number with a HiQnet Device ID allows a remote Device to
determine when a new instance of a Device is presented. Specifying a session
number in the HiQnet header allows a session break to be detected. Incoming
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 85 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
messages intended for the broken session are discarded, as are outgoing messages
intended for the broken session.
7.3 Characteristics of a Session
The following list represents characteristics of a session:
Hello/Goodbye messages are bookends for a HiQnet session.
If a Hello or Hello(info) message arrives while a session is currently open
to the same Node ID, the current session is closed, and the new session
supersedes.
Hello and Hello(info) messages will trigger Keep Alives.
Each live session between two Devices has a unique pair of session
numbers for those Devices. If a session with a remote Device is closed and
reopened a new unique session number is used.
After booting, the first session number shall be random (not the same
session number as on the previous boot cycle).
If a session number is indicated in the HiQnet Header Flags field, the
session number in the header extension is checked against the session
number that was generated locally when the session was started with the
remote Device. If the session number in the header does not match the
session number that the remote Device is echoing back, the incoming
message is blocked. An error message is sent to the Device that sent the
invalid session number.
A goodbye message is sent to a Device that sends an invalid session
number in the header extension causing it to be destroyed on the remote
Device. No session number is allowed to be in the header of this goodbye,
since no session exists for this remote Device ID.
If a Goodbye is sent on an open session, the session number is included in
the header extension.
On a Keep Alive timeout, the current session is closed. No Goodbye is
sent. Nor is any other message.
If an error message is returned in response to a Hello message, a
MultiParamGet(NumParams=0) message will be used for backward
compatibility in order to start Keep Alives.
Hello/Hello(info) must use guaranteed delivery service. The GUAR bit in
the Flags field must be set to 1.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 86 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Session Number Sequence NULL case
with Socket Cycling
Node 1 session = 3456
(node2SN = 2345)
For some reason, TCP socket
is closed.
MultiSvSet Accepted
(Session still open)
Hello(node2 SN=2345)
MultiSvSet1(SN=3456)
Node 2 session = 2345
(node1 sn = 3456)
MultiSvSet4 generated
Hello-info(node1 SN=3456)
MultiSvSet2(SN=3456)
MultiSvSet3(SN=3456)
MultiSvSet4(SN=3456)
SYN
ACK
SYN/ACK
Disco(R)
Disco(I)
Node 1 Node 2
(Configuration State Syncronization)
FIN
FIN/ACK
Time
Null case: socket cycling has no effect
on HiQnet sessions
7.4 Sessions Use Cases
In the following use cases, "Node" means "HiQnet Device." "MultSVSet" means
"MultiParamSet."
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 87 of 91
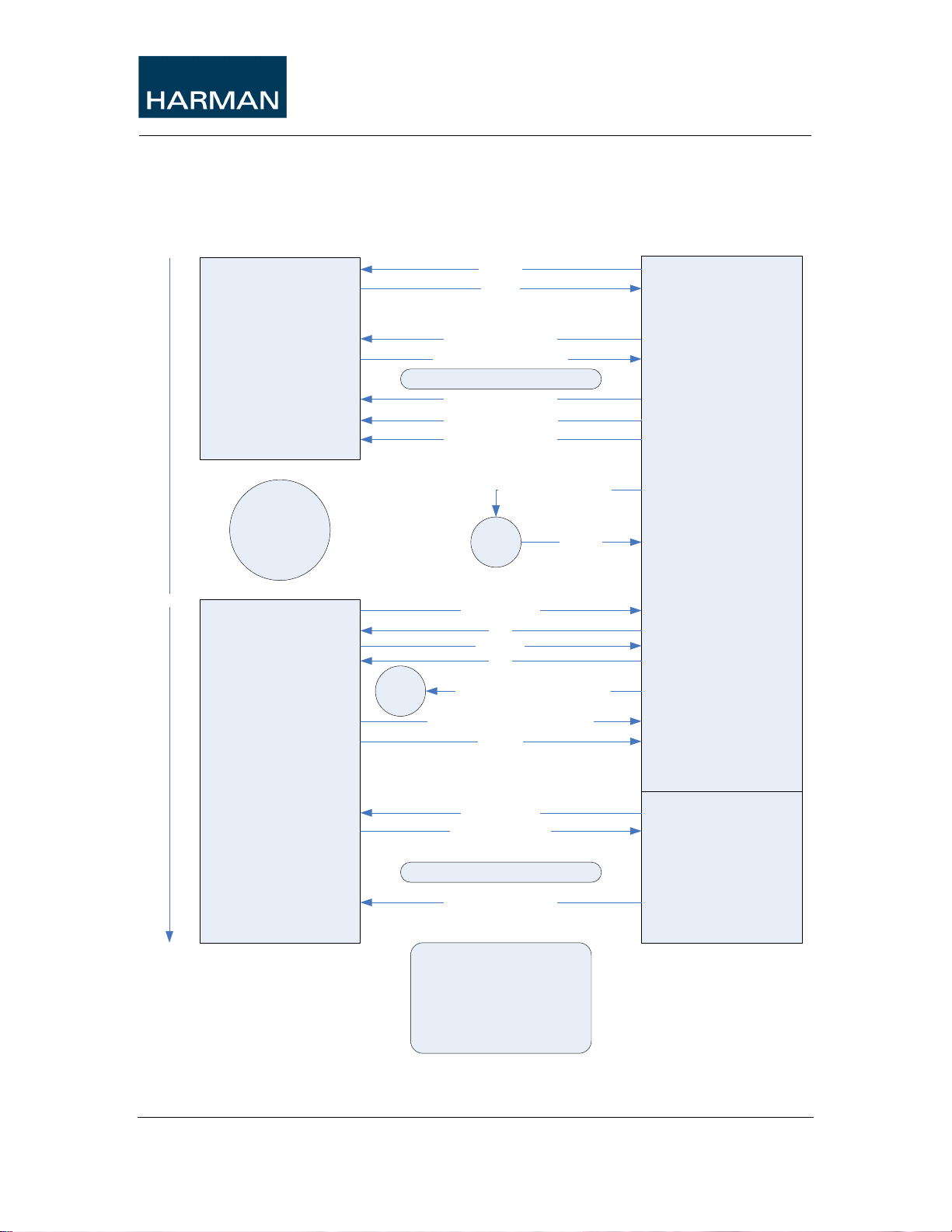
HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Session Number
Reboot Sequence
Node 1 session = 3456
(node2SN = 2345)
Reboot!
TCP fail
Keep for
later
Hello(node2 SN=2345)
MultiSvSet1(SN=3456)
Node 2 session = 2345
(node1 sn = 3456)
MultiSvSet4 still queued
Node 2 session
2345->3456 is destroyed
(no session exists for
Node 2 to talk on)
Node 1 session = 3457
(Node2 SN = 2346)
Hello-info(node1 SN=3456)
MultiSvSet2(SN=3456)
MultiSvSet3(SN=3456)
MultiSvSet4(SN=3456)
!Ses
sion
Block
No
ACK
Resend MultiSvSet4(SN=3456)
SYN
ACK
SYN/ACK
Disco(Q)
Disco(I)
Node 2 session = 2346
(node1 sn = 3457)
Hello(SN=2346)
Hello-info(SN=3457)
Node 1 Node 2
(Configuration State Resync)
(Configuration State Syncronization)
Time
Devices remain coherent,
Messages intended for a previous
sessions are rejected
Error Message sent to Node2
Goodbye destroys the old session
And triggers a new session to be
created
Disco(Anounce)
Goodbye
MultiSvSet4(ERROR !no session)
MultiSvSet5(SN=3457)
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 88 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
Session Number
Reboot Sequence 2
Node 1 session = 3456
(node2 session = 2345)
Reboot!
Hello(node2 SN=3456)
MultiSvSet1(SN=2345)
Node 2 session = 2345
(node1 session = 3456)
Node 2 session
2345->3456 is destroyed
Node 1 session = 3457
(Node2 session = 2346)
Hello-info(node1 SN=2345)
MultiSvSet2(SN=2345)
MultiSvSet3(SN=2345)
Disco(Q)
Disco(I)
Node 2 session = 2346
(node1 session = 3457)
Node 1 Node 2
(Configuration State Syncronization)
Time
Devices remain coherent
Hello message triggers the end
of a session opened by a
previous instance
Disco(Q)
Disco(I)
Hello(node2 SN=3457)
Hello-info(node1 SN=2346)
(Configuration State Syncronization)
MultiSvSet4(SN=2346)
When conflicting session 3457 is presented by node 1, no error is generated. The new
session supersedes the old session.
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 89 of 91

HiQnet Third Party Programmer Documentation
END OF DOCUMENT
© HARMAN 19 February 2013
Page 90 of 91
 Loading...
Loading...