PD-93946A
IRFP460P
l Dynamic dv/dt Rating
l Repetitive Avalanche Rated
l Isolated Central Mounting Hole
l Fast Switching
l Ease of Paralleling
l Simple Drive Requirements
l Solder Plated for Reflowing
Description
Third Generation HEXFET®s from International Rectifier
G
HEXFET® Power MOSFET
D
V
= 500V
DSS
R
DS(on)
= 0.27Ω
ID = 20A
S
provide the designer with the best combination of fast
switching, ruggedized device design, low on-resistance
and cost-effectiveness.
The TO-247 package is preferred for commercial-industrial
applications where higher power levels preclude the use
of TO-220 devices. The TO-247 is similar but superior to
the earlier TO-218 package because of its isolated
mounting hole. It also provides greater creepage distance
between pins to meet the requirements of most safety
specifications.
The solder plated version of the TO-247 allows the reflow
TO-247AC
soldering of the package heatsink to a substrate material.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Max. Units
ID @ TC = 25°C Continuous Drain Current, VGS @ 10V 20
ID @ TC = 100°C Continuous Drain Current, VGS @ 10V 13 A
I
DM
PD @TC = 25°C Power Dissipation 280 W
V
GS
E
AS
I
AR
E
AR
dv/dt Peak Diode Recovery dv/dt 3.5 V/ns
T
J
T
STG
Maximum Reflow Temperature 230 (Time above 183 °C
should not exceed 100s) °C
Pulsed Drain Current 80
Linear Derating Factor 2.2 W/°C
Gate-to-Source Voltage ± 20 V
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy 960 mJ
Avalanche Current 20 A
Repetitive Avalanche Energy 28 mJ
Operating Junction and -55 to + 150
Storage Temperature Range
Soldering Temperature, for 10 seconds 300 (1.6mm from case )
Mounting torque, 6-32 or M3 srew 10 lbf•in (1.1N•m)
°C
Thermal Resistance
Parameter Typ. Max. Units
R
θJC
R
θCS
R
θJA
Junction-to-Case ––– 0.45
Case-to-Sink, Flat, Greased Surface 0.24 ––– °C/W
Junction-to-Ambient ––– 40
www.irf.com 1
01/17/01
IRFP460P
Electrical Characteristics @ TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units Conditions
V
(BR)DSS
∆V
(BR)DSS
R
DS(on)
V
GS(th)
g
fs
I
DSS
I
GSS
Q
g
Q
gs
Q
gd
t
d(on)
t
r
t
d(off)
t
f
L
D
L
S
C
iss
C
oss
C
rss
Drain-to-Source Breakdown Voltage 500 ––– ––– VVGS = 0V, ID = 250µA
/∆T
Breakdown Voltage Temp. Coefficient ––– 0.63 ––– V/°C Reference to 25°C, ID = 1mA
J
Static Drain-to-Source On-Resistance ––– ––– 0.27 Ω VGS = 10V, ID = 12A
Gate Threshold Voltage 2.0 ––– 4.0 V VDS = VGS, ID = 250µA
Forward Transconductance 13 ––– ––– SVDS = 50V, ID =12A
Drain-to-Source Leakage Current
––– ––– 25
––– ––– 250 VDS = 400V, VGS = 0V, TJ = 125°C
Gate-to-Source Forward Leakage ––– ––– 100 VGS = 20V
Gate-to-Source Reverse Leakage ––– ––– -100
VDS = 500V, VGS = 0V
µA
nA
VGS =-20V
Total Gate Charge ––– ––– 210 ID = 20A
Gate-to-Source Charge ––– ––– 29 nC VDS = 400V
Gate-to-Drain ("Miller") Charge ––– ––– 110 VGS = 10V, See Fig. 6 and 13
Turn-On Delay Time ––– 18 ––– VDD = 250V
Rise Time ––– 59 ––– ID = 20A
Turn-Off Delay Time ––– 110 ––– RG = 4.3Ω
ns
Fall Time ––– 58 ––– RD = 13Ω,See Fig. 10
5.0
Internal Drain Inductance
Internal Source Inductance ––– –––
––– –––
13
Between lead,
6mm (0.25in.)
nH
from package
and center of die contact
Input Capacitance ––– 4200 ––– VGS = 0V
Output Capacitance ––– 870 ––– VDS = 25V
Reverse Transfer Capacitance ––– 350 ––– pF ƒ = 1.0MHz, See Fig. 5
D
G
S
Source-Drain Ratings and Characteristics
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units Conditions
I
S
I
SM
V
SD
t
rr
Q
rr
t
on
Continuous Source Current MOSFET symbol
(Body Diode)
Pulsed Source Current integral reverse
(Body Diode)
––– –––
––– –––
20
80
showing the
A
p-n junction diode.
G
Diode Forward Voltage ––– ––– 1.8 V TJ = 25°C, IS = 20A, VGS = 0V
Reverse Recovery Time ––– 570 860 ns TJ = 25°C, IF = 20A
Reverse RecoverCharge ––– 5.7 8.6 µC di/dt = 100A/µs
Forward Turn-On Time Intrinsic turn-on time is negligible (turn-on is dominated by LS+LD)
Notes:
Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by
max. junction temperature. ( See fig. 11 )
Starting T
RG = 25Ω, I
= 25°C, L =4.8mH
J
= 20A. (See Figure 12)
AS
I
≤ 20A, di/dt ≤ 160A/µs, V
SD
DD
≤ V
(BR)DSS
TJ ≤ 150°C
Pulse width ≤ 300µs; duty cycle ≤ 2%.
,
2 www.irf.com
D
S
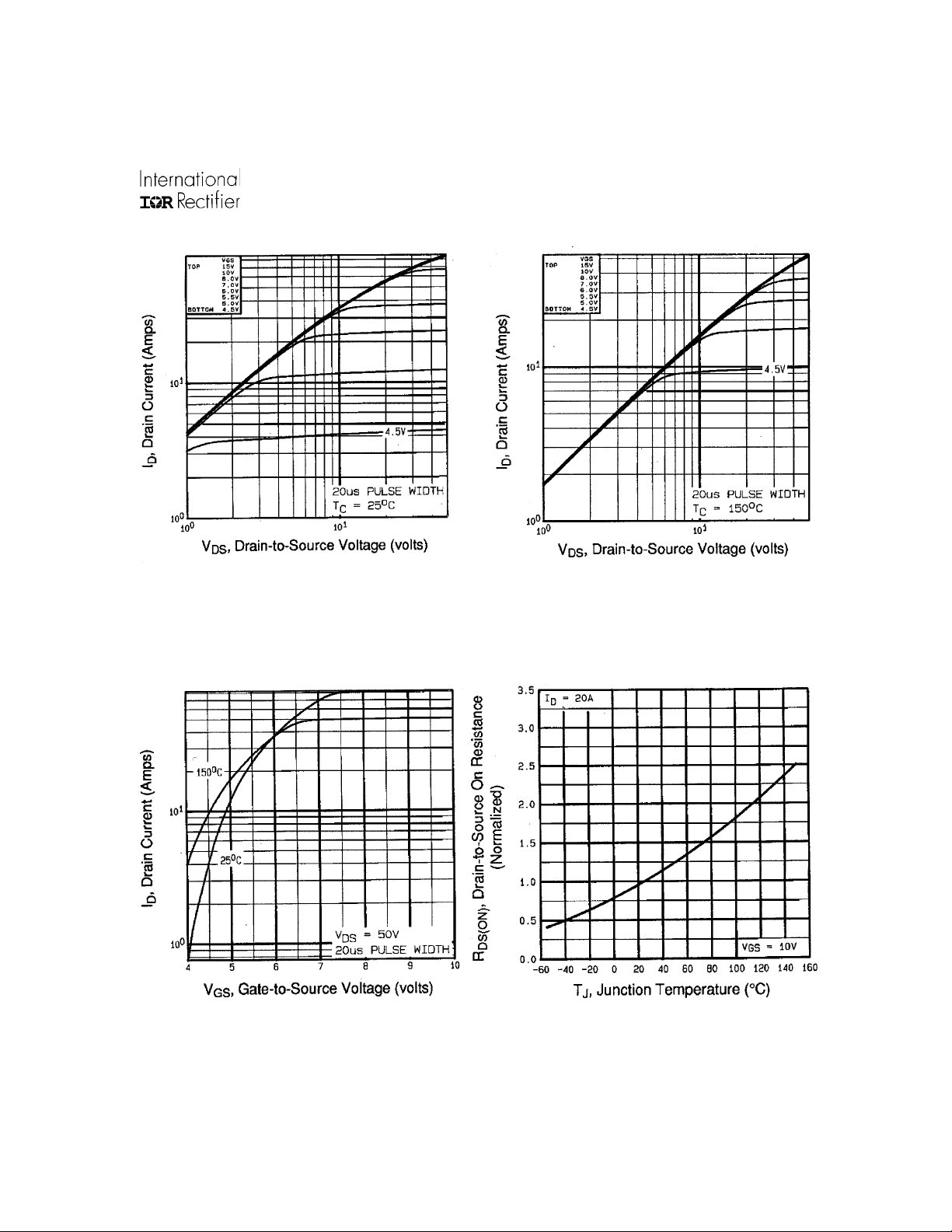
IRFP460P
Fig 1. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 3. Typical Transfer Characteristics Fig 4. Normalized On-Resistance
www.irf.com 3
Fig 2. Typical Output Characteristics
Vs. Temperature
 Loading...
Loading...