Page 1

IF
2
Network Reader
Model 1009FF01
User’s Manual
Page 2

Intermec Technologies Corporation
Worldwide Headquarters
6001 36th Ave.W.
Everett, WA 98203
U.S.A.
www.intermec.com
The information contained herein is provided solely for the purpose of allowing customers to
operate and service Intermec-manufactured equipment and is not to be released, reproduced, or
used for any other purpose without written permission of Intermec Technologies Corporation.
Information and specifications contained in this document are subject to change without prior
noticed and do not represent a commitment on the part of Intermec Technologies Corporation.
© 2011 by Intermec Technologies Corporation. All rights reserved.
The word Intermec, the Intermec logo, Norand, ArciTech, Beverage Routebook, CrossBar,
dcBrowser, Duratherm, EasyADC, EasyCoder, EasySet, Fingerprint, i-gistics, INCA (under license),
Intellitag, Intellitag Gen2, JANUS, LabelShop, MobileLAN, Picolink, Ready-to-Work, RoutePower,
Sabre, ScanPlus, ShopScan, Smart Mobile Computing, SmartSystems, TE 2000, Trakker Antares,
and Vista Powered are either trademarks or registered trademarks of Intermec Technologies
Corporation.
This product includes copyrighted software that is licensed under GPL v2 (www.gnu.org/
licenses/old-licenses/gpl-2.0.html) or LGPL v2.1 (www.gnu.org/licenses/lgpl-2.1.html). You
may obtain the complete Corresponding Source code from Intermec (www.intermec.com) for a
period of three years after Intermec's last shipment of this product. This offer is valid to anyone in
receipt of this information.
There are U.S. and foreign patents as well as U.S. and foreign patents pending.
This product includes cryptographic software written by Eric Young (EAY@cryptsoft.com).
Part of the software embedded in this product is gSOAP software. Portions created by gSOAP are
Copyright (C) 2001-2004 Robert A. van Engelen, Genivia inc. All Rights Reserved.
In no event shall the author be liable for any direct, indirect, incidental, special, exemplary, or
consequential damages (including, but not limited to, procurement of substitute goods or
services; loss of use, data, or profits; or business interruption) however caused and on any theory of
liability, whether in contract, strict liability, or tort (including negligence or otherwise) arising in
any way out of the use of this software, even if advised of the possibility of such damage.
ACE(TM), TAO(TM), CIAO(TM), and CoSMIC(TM) (henceforth referred to as “DOC software”)
are copyrighted by Douglas C. Schmidt and his research group at Washington University,
University of California, Irvine, and Vanderbilt University, Copyright (c) 1993-2006, all rights
reserved.
ii IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 3

Contents
Before You Begin. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Safety Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Global Services and Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Warranty Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . vii
Web Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Telephone Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Service Location Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . viii
Who Should Read This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Related Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ix
Patent Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . x
Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
1
Overview of the IF2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Understanding the LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
About the Intermec Ready-to-Work Indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Understanding the Network and Power Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Understanding the Top Panel Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Communicating with the IF2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Assigning an Initial IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Using the Web Browser Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Saving Configuration Changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Disabling Help in the Web Browser Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Contents
Installing the IF2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Connecting the IF2 to Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Setting the Date and Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Using the IF2 Securely. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Configuring Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2
Configuring Settings for Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Configuring Ethernet Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Configuring Common Network Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Configuring Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Controlling Access Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Setting Up Logins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .26
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual iii
Page 4

Contents
Configuring the IF2 to Use a Password Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Changing the Default Login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Disabling Access Via the Serial Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Managing Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Viewing Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Installing and Uninstalling Certificates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Developing and Using RFID Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3
RFID Applications and the IF2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Using the RFID Resource Kit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Creating RFID Applications for the IF2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Modifying IF4 Applications for Use With the IF2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
About RFID Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Configuring BRI Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Changing BRI Attribute Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
About BRI Attribute Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Tag Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Read Tries. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Write Tries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Lock Tries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Field Separator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
ID Report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
No Tag Report. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Report Timeout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Timeout Configuration Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Select Tries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Unselect Tries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Session. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Initial Q. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Initialization Tries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Schedule Option. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
ID Tries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Antenna Tries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
EPCC1G2 Advance Medium Access Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Dense Reader Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Antenna Field Strength 1 to 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Antenna Sequence: First through Eighth. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Configuring the BRI Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Viewing the BRI Server Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
iv IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 5

Configuring LLRP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
4
Managing the IF2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Using the Device Configuration Web Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Using SmartSystems Foundation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Configuring the IF2 With Intermec Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Opening a Serial or USB Connection to the IF2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Opening a Serial Connection to the IF2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Opening a USB Connection to the IF2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Maintaining the IF2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Viewing the System Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Viewing the About Screen. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Using the LEDs to Locate the IF2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Restoring the IF2 to the Default Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Restoring Default Settings Using the Web Browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .61
Restoring Default Settings Using the Reset Switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Restoring Default Settings Using a Serial Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Rebooting the IF2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Contents
Troubleshooting the IF2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Problems While Working With RFID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Connecting Directly to the RFID Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Problems With Connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
Calling Intermec Product Support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Accessing Intermec Web Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Upgrading Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Configuring the Firmware Upgrade. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Installing the Firmware Upgrade . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Upgrading From the Web Browser Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
Upgrading With SmartSystems Foundation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Using the IF2 GPIO Interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
5
About the GPIO Interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual v
Page 6

Contents
Accessing the Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Using the Input Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
IF2 Powered Input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Isolated Input Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
Open Collector Input Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
Using the Output Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Switching the High Side Using IF2 Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Switching the Low Side Using IF2 Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Switching the High Side Using External Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Driving a DC Relay to Control an AC Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Using the Power Interface. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
A
IF2 Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .82
RFID Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Port Pin Assignments. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
GPIO Port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Serial Ports (COM1). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Ethernet Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
I
vi IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 7

Before You Begin
This section provides you with safety information, technical support
information, and sources for additional product information.
This section provides you with safety information, technical support
information, and sources for additional product information.
Safety Information
Your safety is extremely important. Read and follow all warnings and
cautions in this document before handling and operating Intermec
equipment. You can be seriously injured, and equipment and data can
be damaged if you do not follow the safety warnings and cautions.
This section explains how to identify and understand warnings,
cautions, and notes that are in this document.
A warning alerts you of an operating procedure, practice,
condition, or statement that must be strictly observed to avoid
death or serious injury to the persons working on the equipment.
Before You Begin
A caution alerts you to an operating procedure, practice,
condition, or statement that must be strictly observed to prevent
equipment damage or destruction, or corruption or loss of data.
Note: Notes either provide extra information about a topic or contain
special instructions for handling a particular condition or set of
circumstances.
Global Services and Support
Warranty Information
To understand the warranty for your Intermec product, visit the
Intermec web site at www.intermec.com and click Support >
Returns and Repairs > Warranty.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual vii
Page 8

Before You Begin
Disclaimer of warranties: The sample code included in this document
is presented for reference only. The code does not necessarily
represent complete, tested programs. The code is provided “as is with
all faults.” All warranties are expressly disclaimed, including the
implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular
purpose.
Web Support
Visit the Intermec web site at www.intermec.com to download our
current manuals (in PDF).
Visit the Intermec technical knowledge base (Knowledge Central) at
www.intermec.com and click Support > Knowledge Central to
review technical information or to request technical support for your
Intermec product.
Telephone Support
In the U.S.A. and Canada, call 1-800-755-5505.
Outside the U.S.A. and Canada, contact your local Intermec
representative. To search for your local representative, from the
Intermec web site, click About Us > Contact Us.
Service Location Support
For the most current listing of service locations, go to
www.intermec.com and click Support >Returns and Repairs >
Repair Locations.
For technical support in South Korea, use the after service locations
listed below:
AWOO Systems
102-1304 SK Ventium
522 Dangjung-dong
Gunpo-si, Gyeonggi-do Korea, South 435-776
Contact: Mr. Sinbum Kang
Telephone: +82-31-436-1191
E-mail: mjyun@awoo.co.kr
viii IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 9

IN Information System PTD LTD
6th Floor
Daegu Venture Center Bldg 95
Shinchun 3 Dong
Donggu, Daegu City, Korea
E-mail: jmyou@idif.co.kr or korlim@gw.idif.co.kr
Who Should Read This Manual
This user’s manual is for the person who is responsible for installing,
configuring, and maintaining the IF2 Network Reader.
This manual provides you with information about the features of the
IF2, and how to install, configure, operate, maintain, and
troubleshoot it.
Before you work with the IF2, you should be familiar with your
network and general networking terms, such as IP address. You
should also be familiar with your RFID system.
Related Documents
This is a list of IF2 related documents:
Before You Begin
• Basic Reader Interface Programmer’s Reference Manual
• Device Configuration Web Services Command Reference Manual
• LLRP Programmer’s Reference Manual
The Intermec web site at www.intermec.com contains our
documents (as PDF files) that you can download for free.
To do wnload documents
1 Visit the Intermec web site at www.intermec.com.
2 Click Products tab.
3 Using the Products menu, navigate to your product page. For
example, to find the IF2 RFID reader, click RFID > Network
Readers > IF2.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual ix
Page 10

Before You Begin
Patent Information
Product is covered by one or more of the following patents:
5,414,624; 5,479,160; 5,485,520, 5,504,485; 5,510,795; 5,521,601;
5,528,222; 5,538,803; 5,550,547; 5,552,778; 5,554,974; 5,563,583;
5,565,847; 5,606,322; 5,606,323; 5,635,693; 5,673,037; 5,680,106;
5,682,143; 5,729,201; 5,729,697; 5,736,929; 5,737,710; 5,739,754;
5,763,867; 5,767,789; 5,777,561; 5,786,626; 5,812,065; 5,821,859;
5,825,045; 5,826,328; 5,828,318; 5,828,693; 5,831,532; 5,850,181;
5,850,187; 5,874,902; 5,889,489; 5,909,176; 5,912,632; 5,939,984;
5,942,987; 5,962,837; 5,966,082; 5,972,156; 5,995,006; 5,995,019;
6,028,564; 6,032,127; 6,056,199; 6,078,251; 6,078,259; 6,097,347;
6,100,804; 6,104,281; 6,104,291; 6,109,526; 6,114,962; 6,118,379;
6,121,878; 6,121,880; 6,122,329; 6,130,612; 6,140,146; 6,147,604;
6,147,606; 6,163,260; 6,166,638; 6,172,596; 6,177,872; 6,195,053;
6,201,474; 6,204,765; 6,215,401; 6,215,402; 6,236,223; 6,239,703;
6,243,013; 6,246,326; 6,249,227; 6,259,408; 6,275,157; 6,278,413;
6,280,544; 6,281,794; 6,285,342; 6,286,762; 6,286,763; 6,288,629;
6,294,997; 6,294,998; 6,318,636; 6,320,509; 6,329,915; 6,357,662;
6,360,208; 6,366,260; 6,369,711; 6,371,375; 6,384,712; 6,400,274;
6,404,325; 6,412,086; 6,422,476; 6,429,775; 6,441,740; 6,486,769;
6,501,807; 6,518,885; 6,525,648; 6,529,880; 6,535,108; 6,535,175;
6,566,850; 6,593,845; 6,597,465; 6,608,551; 6,610,379; 6,639,509;
6,645,327; 6,677,852; 6,784,789; 6,794,000; 6,812,841; 6,812,852;
6,816,063; 6,830,181; 6,853,294; 6,859,190; 6,906,615; 6,919,793;
7,039,359; 7,075,413; 7,103,087; 7,121,467; 7,158,046; 7,190,257;
7,298,268; 7,447,251; 7,482,926; 7,486,172; 7,501,932; 7,541,929;
7,564,366; 7,616,094;
There may be other U.S. and foreign patents pending.
x IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 11

1
Getting Started
This chapter introduces the IF2 Network Reader, explains the
ports and LEDs, and explains how the reader fits into your
network. It contains these topics:
• Overview of the IF2
• Communicating with the IF2
• Installing the IF2
• Setting the Date and Time
• Using the IF2 Securely
1
Page 12

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
Container
with RFID tag
RFID
antenna
IF2
Overview of the IF2
The IF2 Network Reader is an RFID reader that provides connectivity
between tag data and an enterprise system.
IF2 Network Reader
Note: The IF2 does not ship with RFID antennas. For more
information on these accessories, contact your Intermec sales
representative.
7
2 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
The reader forwards RFID tag data to the Ethernet network as shown
in the next illustration.
IF2 in a Wired Ethernet Network
Page 13

Understanding the LEDs
PoE
The IF2 has six LEDs that indicate the status of the reader during
operation. Use the next table to identify the LED icons on the front
panel of the IF2.
IF2 LED Descriptions
Icon Name Description
Chapter 1 — Getting Started
Intermec
Ready-to-Work™
indicator
• On when an application is communicating
with the IF2 BRI server or an LLRP client has
connected.
• Blinks when no application is
communicating with the IF2. For more
information, see “About the Intermec
Ready-to-Work Indicator” on page 4.
Power Over
Ethernet
• Green if Power Over Ethernet (POE) is
enabled.
• Red if a fault condition is detected. For
example, if the power converter for POE
does not provide enough power to the IF2,
the POE LED stays red indicating a fault
condition.
Power On when the IF2 has power.
Wired LAN
• Off when there is no Ethernet connectivity.
• On when an Ethernet link is detected.
• Flashes when there is activity on the
Ethernet network.
RFID status
• Green if RF power is being transmitted.
• Red if an antenna fault is detected, or if the
reader cannot output the requested RF
power level.
• Off if RF power is off.
Tag ID Flashes when an RFID tag ID is successfully
read or written to.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 3
Page 14

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
About the Intermec Ready-to-Work Indicator
The blue Ready-to-Work indicator shows when an application is
communicating with the Basic Reader Interface (BRI) server or LLRP
client on the IF2. The next table explains the different states of the
Ready-to-Work indicator.
Ready-to-Work Indicator Status Descriptions
Status Description
Off IF2 does not have power.
Blinking IF2 is initializing and not yet ready to use, or no application is
currently communicating with the IF2 BRI or LLRP server or
LLRP server.
Steady An application is communicating with the BRI server or an
LLRP client has connected to the IF2.
For more information on the BRI server, see “Configuring the BRI
Server” on page 43.
Understanding the Network and Power Ports
The IF2 network and power ports are located under the cable cover.
GPIO
IOIOI
GPIO port
IF2 Network and Power Ports
4 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
DC power port
COM 1
Ethernet port
(high power POE)
Page 15

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
IF2 Port Descriptions
Port Description
GPIO General purpose input/output (GPIO) port that
connects the IF2 to industrial controls such as relays or
indicators.
For more information on the IF2 GPIO interfaces, see
“About the GPIO Interfaces” on page 74.
DC power Connects the reader to a 12 volt DC power source.
COM1 Connects the IF2 to a desktop PC for configuration.
Use an RS-232 null modem cable (P/N 059167).
Ethernet 10BaseT/100BaseTx port that connects the reader to
your Ethernet network. The reader auto-negotiates with
the server to set the best data rate. This port uses MDI/
MDI-X auto-switching so you can connect either a
standard Ethernet cable or a crossover cable.
The Ethernet port also supports POE. To use POE you
need an 802.3at compliant power converter. For more
information, contact your Intermec sales
representative.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 5
Page 16

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
Antenna port
(4 places)
Reset switch
USB service
port
Understanding the Top Panel Ports
The IF2 top panel ports consist of four antenna ports, a reset switch,
and a USB service port.
IF2 Top Panel Ports
The IF2 RFID antenna ports uses Reverse TNC connectors. Make sure
you have appropriate antennas and cables for your IF2. For help,
contact your Intermec sales representative.
Government regulatory agencies require that this RFID reader
uses only approved antennas. Therefore, this reader uses a
custom antenna connector. Do not use antennas not approved
for use with this reader.
6 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 17

Communicating with the IF2
By default, the IF2 is configured to be a DHCP client and accepts
offers from any DHCP server. Therefore, the IF2 will work out of the
box if you connect it to your network and use a DHCP server to assign
it an IP address. In this case, you configure the IF2 using the web
browser interface from a desktop PC. For help, see “Using the Web
Browser Interface” on page 10.
However, if you are not using a DHCP server to assign an IP address,
you use a serial communications program such as HyperTerminal to
assign a static IP address. For help, see the next section, “Assigning an
Initial IP Address.”
After the IF2 has been assigned an IP address, connect it to your
network and then complete the configuration by using a web browser
interface from a desktop PC. For help, see “Using the Web Browser
Interface” on page 10.
Assigning an Initial IP Address
Follow this procedure to assign an initial IP address to the IF2. After
you assign the IP address, connect the IF2 to your network and use
the web browser interface to complete the configuration.
Chapter 1 — Getting Started
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 7
Page 18

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
To assign an initial IP address
1 Open a serial connection to the IF2. For help, see “Opening a
Serial or USB Connection to the IF2” on page 54.
2 Type config and press Enter, and then type config again in
the Password field and press Enter. The IF2 Initial Configuration
screen appears.
3 If DHCP is enabled, press D. DHCP is disabled and the Ethernet
Configuration Options screen appears.
8 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 19

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
4 To set the IP address, press 1 and enter the static IP address in the
entry field.
5 Press Enter. The static IP address is set. If you do not need to set
the subnet mask or IP router values, you can now continue to
configure the IF2 through the web browser interface. For help, see
“Using the Web Browser Interface” on page 10.
If you need to change the values for subnet mask or the IP router,
continue with the next step.
6 To set the subnet mask, press 2 and enter the subnet mask value in
the entry field. Press Enter to save the changes.
To set the IP router address, press 3 and enter the IP router address
in the entry field. Press Enter to save the changes.
7 (Optional) To change the Ethernet link speed, press L and choose
a link speed from the list of options:
Ethernet Link Speed Options
To choose this speed: Press:
Auto detect (default) A
100 Mbps - full duplex 1
100 Mbps - half-duplex 2
10 Mbps - full duplex 3
10 Mbps - half duplex 4
Keep the current selection and close this dialog box Q
8 Press Q to close the Initial Configuration screen.
9 Disconnect the null-modem cable from the IF2.
The IF2 is now ready to be connected to your network. See
“Connecting the IF2 to Your Network” on page 15.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 9
Page 20

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
Using the Web Browser Interface
After the IF2 is assigned an IP address, configure the IF2 using the
web browser interface.
To use the web browser interface, the IF2 must be connected to your
wired network. For help, see “Connecting the IF2 to Your Network”
on page 15.
When using the web browser interface, remember that your session
automatically terminates if you do not use it for 15 minutes.
Note: If you access the Internet using a proxy server, add the IF2 IP
address to your Exceptions list. The Exceptions list contains the
addresses that you do not want to use with a proxy server.
To use the IF2 web browser interface
1 Determine the IP address of the IF2. If a DHCP server assigned the
IP address, you need to get the IP address from that server.
2 Start the web browser.
3 In the browser address field, enter the IP address, and press Enter.
The IF2 login screen appears.
Or, for a secure session, click A secure session is available. The
secure login screen appears.
10 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 21

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
Note: If a security alert message appears:
• Click Yes to continue to the secure login screen.
• Click No to cancel.
• Click View certificate to see the security certificate before
continuing.
IF2 Secure Login Screen
4 If necessary, enter a user name and password. The default user
name is
intermec and the default password is intermec. You can
define the user name and password. For help, see “Setting Up
Logins” on page 26.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 11
Page 22

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
5 Click Login (or Secure Login in the secure login screen). The
Ethernet screen appears and your web browser session is
established.
For help with configuring network settings, see “Configuring
Settings for Your Network” on page 20.
For help with configuring RFID reader settings, see “Configuring
BRI Settings” on page 38.
For more information on other methods for managing the IF2, see
“Managing the IF2” on page 50.
Saving Configuration Changes
After you make configuration changes, click Activate Changes in the
browser window to save your changes and immediately make the
changes active.
Changes are discarded if you click another link in the browser window
without clicking Activate Changes first.
Disabling Help in the Web Browser Interface
By default, the web browser interface shows help text as you move the
cursor over items in each screen. Follow the next procedure to disable
the help text feature.
12 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 23

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
To di sable help text
1 In the web browser interface, click Help in the upper right corner
of the screen.
The Help screen appears.
2 Clear the Enable Help check box.
3 Click Activate Changes to save your changes and immediately
make them active. The Help text is disabled.
Installing the IF2
This section explains how to mount the IF2 to a wall using the IF2
Network Reader Drilling Template Instructions that comes in the box
with the IF2.
The IF2 should be professionally installed. For more
information, contact your local Intermec representative.
To install the IF2
1 Choose a mounting location.
2 Use the IF2 Network Reader Drilling Template Instructions to drill
holes in the mounting location.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 13
Page 24

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
Mounting screw
(4 places)
3 Mount the IF2 using your parts and screws.
Note: The IF2 is certified to an IP53 environmental rating only when
mounted as shown.
The next table includes environmental requirements for the IF2.
Choose a location that meets these requirements.
14 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
IF2 Environmental Requirements
Typ e Minimum Maximum
Operating temperature -20ºC (-4ºF) 50ºC (122ºF)
Storage temperature -30ºC (-22ºF) 70ºC (158ºF)
Humidity (non-condensing) 5% 95%
Page 25

Connecting the IF2 to Your Network
After you place the IF2 in its mounting location, you can connect it to
your network.
To connect the IF2 to your network
1 Install the IF2 in its mounting location. For help, see “Mount the
IF2 using your parts and screws.” on page 14.
2 Attach one to four RFID antennas to the RFID antenna ports,
starting with port 1. For help, see “Understanding the Top Panel
Ports” on page 6.
3 Connect an Ethernet cable to the IF2 Ethernet port.
4 Connect power to the IF2:
• If you are using DC power, connect the DC power cord to a
power source, and to the power port on the IF2.
• If you are using Power Over Ethernet, connect the Ethernet
cable to the Ethernet port, and use an 802.3at compliant power
converter to power the IF2.
When you apply power, the IF2 boots and the green Power LED
turns on.
Chapter 1 — Getting Started
Note: If you are using a DHCP server, make sure the server is
running before you connect power to the IF2.
The IF2 is now ready to communicate with your network. Once the
IF2 has been assigned an IP address (either manually or from your
DHCP server), you can use the web browser interface to complete
configuration. For help, see “Using the Web Browser Interface” on
page 10.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 15
Page 26

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
Setting the Date and Time
After you have installed the IF2, you can set the date and time via the
web browser interface.
To set the date and time
1 Connect to the IF2 via the web browser interface. For help, see
“Using the Web Browser Interface” on page 10.
2 In the web browser screen, click the date and time in the upper
right corner. The Time screen appears.
3 Choose your time zone from the drop-down list and then click
Activate Changes.
4 Enter the current month, day, and year in the entry fields.
5 Enter the current hour, minute, and second in the entry fields.
6 Click Activate Changes. The new time and date are set.
16 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 27

Using the IF2 Securely
To help protect the integrity and security of your data, the IF2
supports a variety of secure access methods:
• You can use a secure web browser session (HTTPS) to access the
IF2. For help, see “Using the Web Browser Interface” on
page 10.
• You can configure and use network security methods, or disable
basic configuration through the serial port. For help, see
“Configuring Security” on page 24.
Chapter 1 — Getting Started
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 17
Page 28

Chapter 1 — Getting Started
18 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 29

2
Configuring Network Settings
This chapter describes how to configure network settings for
the IF2 and includes these topics:
• Configuring Settings for Your Network
• Configuring Security
• Managing Certificates
This chapter assumes that you are familiar with your network,
networking terms, and the type of security implemented by
your network.
19
Page 30

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
Configuring Settings for Your Network
You use the web browser interface to configure network settings. For
more information on using the web browser, see “Using the Web
Browser Interface” on page 10.
This chapter explains how to use the web browser interface to
configure settings for:
• wired Ethernet connections. For help, see the next section,
“Configuring Ethernet Settings.”
• parameters common to the wired connections, such as DNS
addresses and time servers. For help, see “Configuring Common
Network Settings” on page 23.
• network security, such as passwords and access methods. For help,
see “Configuring Security” on page 24.
• certificates. For help, see “Managing Certificates” on page 31.
From a device management standpoint, there are several other
methods you can use to configure network settings, including
Intermec SmartSystems and the Device Configuration web service.
For more information on using these methods to configure the IF2,
see Chapter 4, “Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the
IF2.”
Configuring Ethernet Settings
This section explains how to configure wired Ethernet settings using
the web browser interface.
If you are using a DHCP server, you may not need to configure
Ethernet settings. For more information, contact your network
administrator.
20 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 31

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
To configure Ethernet settings
1 From the menu, click Network Configuration or Ethernet in the
left pane. The Ethernet screen appears.
If DHCP is enabled, you see this screen:
If DHCP is disabled, the current values for IP address, subnet
mask, and router appear in entry fields:
2 Configure the Ethernet settings. For help, see the next table.
Note: Different settings appear in this screen depending on the
current DHCP mode for the IF2.
If you need to configure other network settings such as DNS
addresses and suffixes or a SYSLOG destination, see
“Configuring Common Network Settings” on page 23.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 21
Page 32

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
3 Click Activate Changes to save your changes and immediately
make them active.
Ethernet Settings Descriptions
Parameter Description
Enable DHCP Check this check box if you want the IF2 to get its IP address from a
DHCP server.
If this check box is not checked, you need to specify the IP address,
subnet mask, and IP router for your network.
IP Address IP address of the IF2. The IP address has the form x.x.x.x, where x is a
number from 0 to 255.
If DHCP is enabled, the currently assigned IP address appears in this
field.
If DHCP is disabled, specify the IP address in the entry field.
IP Subnet Subnet mask for this network. The subnet mask has the form x.x.x.x,
where x is a number from 0 to 255.
If DHCP is enabled, the currently assigned subnet mask appears in this
field.
If DHCP is disabled, you may need to specify the subnet mask for the
network.
IP Router (Gateway) IP address of the router. The IP address has the form x.x.x.x, where x is a
number from 0 to 255.
If DHCP is enabled, the currently assigned router address appears in this
field.
If DHCP is disabled, you may need to specify the router address for the
network.
Link Local IP Address IP address of the IF2 is only routable on the local IP subnet. The IF2
auto-negotiates with other devices on its Ethernet segment to obtain a
unique address, so no user configuration of the Link Local IP Address is
necessary. The IF2 will always have a Link Local IP Address, even if
another address is assigned through DHCP or statically via userconfiguration.
IPv6 Autoconfigure Enables IPv6 automatic configuration. Clear this check box to disable
IPv6 auto-configuration on the IF2.
Auto-configuration is enabled by default. If you disable auto-
configuration, you need to specify an IPv6 address, subnet mask, and
router.
IPv6 Address 128-bit IPv6 address for the IF2.
IPv6 Router 128-bit address for the IPv6 router.
22 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 33

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
Configuring Common Network Settings
Common network settings are configuration items that apply to the
IF2 network interface.
This section explains how to use the web browser interface to
configure these common network settings:
• Hostname
• Domain Name Server (DNS) addresses and suffixes
• Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) server addresses 1 and 2.
For information on public NTP servers, see
http://support.ntp.org.
• Local time zone
• SYSLOG destination
To configure common network settings
1 In the menu, click Network Configuration > Common. The
Common screen appears.
2 Configure settings. For help, see the next table.
3 Click Activate Changes to save your changes and immediately
make them active.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 23
Page 34

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
Common Network Settings Descriptions
Parameter Description
Hostname Name for this IF2. The default is “IF2<serial number of the IF2>”.
The hostname can be either a simple hostname, or a qualified domain
name (FQDN). If this IF2 obtains its IP address via DHCP, this parameter
is sent to the DHCP server. If the server supports it, this field is used for
dynamic DNS updates.
DNS Server 1 IP address of a domain name server that the IF2 uses to resolve DNS
names.
DNS Server 2 IP address of a second domain name server that the IF2 uses to resolve
DNS names.
DNS Suffix 1 Primary DNS suffix to be appended to unqualified names.
DNS Suffix 2 Secondary DNS suffix to be appended to unqualified names.
SNTP Server Name 1 DNS name or IP address of an SNTP or NTP server.
SNTP Server Name 2 DNS name or IP address of a second SNTP or NTP server.
Time Zone Time zone for this IF2. Choose the time zone from the drop-down list.
Default is GMT.
For more information, see “Setting the Date and Time” on page 16.
SYSLOG Destination Domain name or IP address of the SYSLOG server.
Configuring Security
Note: Before you configure security settings for this IF2, you should
be familiar with the type of security implemented for your network.
The IF2 supports a variety of security features to help maintain the
integrity of your secure network. You can:
• enable/disable access services.
• change the default user name and password. For help, see “Setting
Up Logins” on page 26.
• use a password server to maintain a list of authorized users who
can configure and manage the IF2. For help, see “Setting Up
Logins” on page 26
24 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 35

• disable serial port access to the IF2. For help, see “Disabling
Access Via the Serial Port” on page 30.
For general information on securely using the IF2, see “Using the IF2
Securely” on page 17.
Controlling Access Services
Access services are the different ways that users can access and
configure the IF2.
You can control how developers access the IF2 by enabling or
disabling these services:
• Web browser interface (secure and non-secure)
• Discovering the IF2 via Bonjour or Universal Plug and Play™
(UPnP) service advertisement (enabled by default)
To enable or disable these services, see the next procedure.
To enable access services
1 From the menu, click Network Configuration > Services. The
Services screen appears.
Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
2 Enable or disable developer access services by checking or clearing
the check boxes, or by choosing options from the drop-down list.
For help, see the next table.
3 Click Activate Changes to save your changes and immediately
make them active.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 25
Page 36

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
Access Services Descriptions
Service Description
Enable Web Server Enables access to the IF2 via the web browser interface.
Select Enable Web Server (Insecure) to allow users to log in using either
a nonsecure (HTTP via port 80) or secure (HTTPS via port 443) web
interface.
Select Enable Web Server (Secure) to allow only the secure web interface
through port 443.
If both web server services are disabled, you can only restore services by:
• the SmartSystems console. For more information about SmartSystems
Foundation, see “Using SmartSystems Foundation” on page 52.
• or by restoring the IF2 to the factory defaults. For more information,
see “Restoring the IF2 to the Default Configuration” on page 60.
Enable Bonjour
Service
Advertisement
Enable UPnP
Discovery
Enables the IF2 to advertise services and be discovered by Bonjour zeroconfiguration networking. Bonjour is enabled by default.
To prevent errors when using Bonjour, make sure the IF2 hostname does
not include spaces. To set the hostname, see “Configuring Common
Network Settings” on page 23.
Enables the IF2 to be discovered by Universal Plug and Play protocols.
UPnP is enabled by default.
Setting Up Logins
To ensure login security for configuring or maintaining the IF2, you
should use a password server or at least change the default user name
and password.
• A password server is typically an embedded authentication server
(EAS) or other RADIUS server. To use a password server, you must
have a password server on the network that contains the user
name/password database. On the IF2, you need to enable RADIUS
for login authorization.
When you attempt to log in to the IF2, you must enter a user name
and password. This login is sent to the RADIUS server, which
compares the login to its list of authorized logins. If a match is
found, you can log in to the IF2 with read/write privileges.
For help, see the next section, “Configuring the IF2 to Use a
Password Server.”
26 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 37
Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
• If you do not want to use a password server, you should change the
default login user name and password, and create a read-only
password. For help, see “Changing the Default Login” on
page 29.
Configuring the IF2 to Use a Password Server
If you use a password server to manage users who log in to this IF2,
you need to tell the IF2 how to communicate with the password server
and then you need to configure the password server.
Note: If errors occur and you cannot log in to the IF2, restore defaults
via a serial connection to reset all passwords to default values. For
help, see “Restoring the IF2 to the Default Configuration” on
page 60.
To configure the IF2 to use a password server
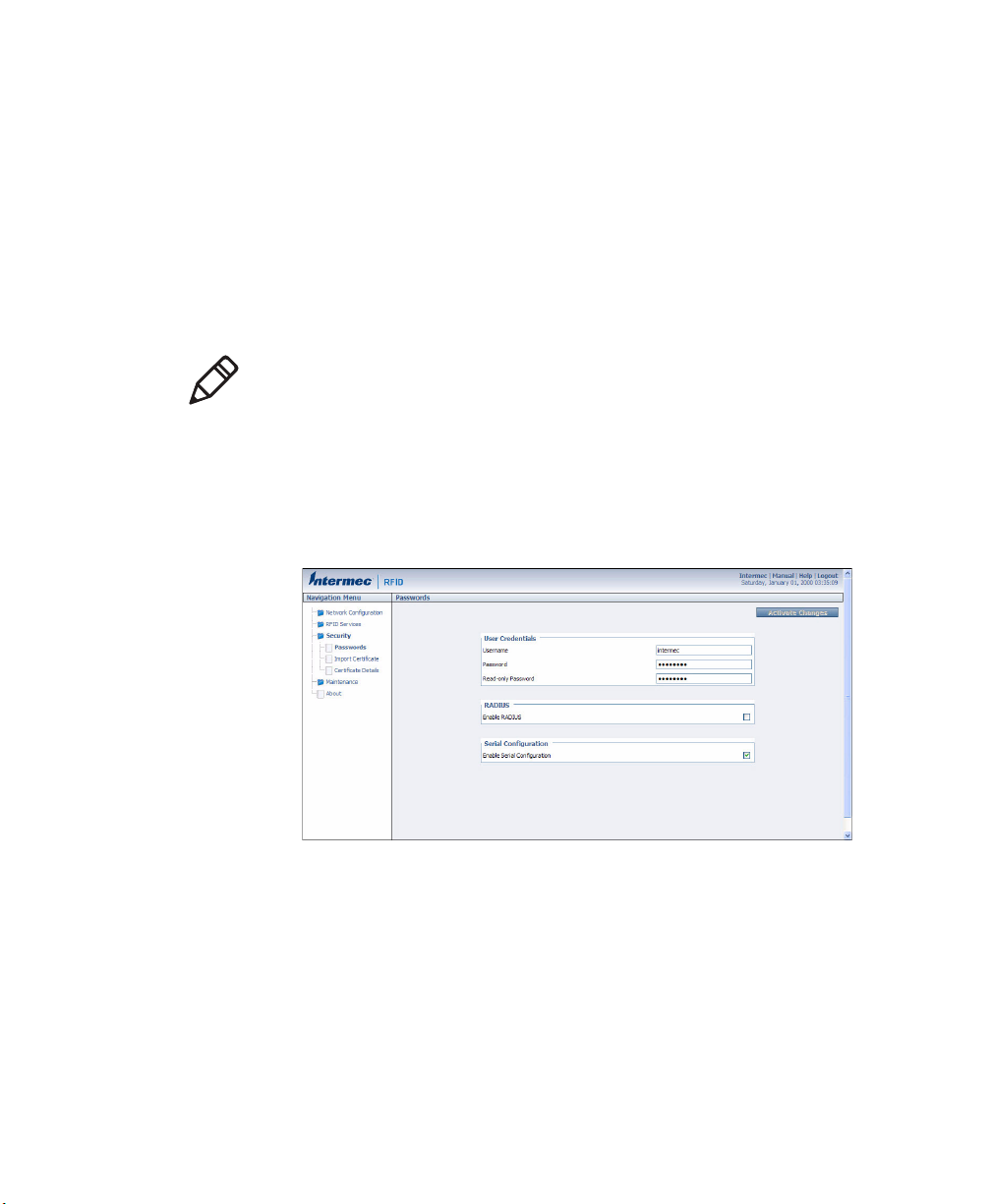
1 From the menu, click Security > Passwords. The Passwords
screen appears.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 27
Page 38

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
2 Check the Enable RADIUS check box. A list of RADIUS
configuration items appears.
3 Configure the settings. For help, see the next table.
4 Click Activate Changes.
5 Configure the password server database. For help, see the
documentation that came with your server.
RADIUS Server Information Descriptions
Typ e Description
Enable RADIUS Enables RADIUS authentication for this IF2.
Primary Radius
Server
Secret Secret key for this RADIUS server.
Port Port number of the primary RADIUS server. Default
Secondary Radius
Server
Secret Secret key for this RADIUS server.
Port Port number of the secondary RADIUS server.
Enable Serial
Configuration
28 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
IP address or DNS name of the RADIUS server. If this
field is blank, the RADIUS client does not use this
entry.
is 1812.
IP address or DNS name of the RADIUS server to use
if there is no response from the primary RADIUS
server.
Default is 1812.
Enable basic network configuration using the serial
or USB port.
Page 39

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
Changing the Default Login
If you are not using a password server to authorize user logins,
Intermec recommends that you change the default user name and
password and create a read-only password.
To set up logins
1 From the main menu, click Security > Passwords. The Passwords
screen appears.
2 Make sure the Enable RADIUS check box is not checked. Clear
this check box if necessary and then click Activate Changes.
3 Configure the parameters. For help, see the next table.
4 Click Activate Changes to save your changes and immediately
make them active.
Password Parameter Descriptions
Parameter Description
Username Enter the user name you need to use to log in to this IF2.
The user name can be from 1 to 32 characters long. You
must always specify a user name. Default is
Password Enter the password you need to use to log in to this IF2.
This password gives you read and write access to the IF2
configuration. The password can be from 8 to 32
characters long. You must always specify a password.
Default is
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 29
intermec.
intermec.
Page 40

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
Password Parameter Descriptions (continued)
Parameter Description
Read-only
Password
Enter the password you need to use to log in to this IF2.
This password gives the user read-only access to the IF2.
This user can view the configuration and execute
diagnostics but cannot perform any tasks that affect IF2
operation, such as changing configuration options or
upgrading firmware. Default is
The read-only password cannot be deleted. To disallow
read-only access, you need to enable RADIUS
authentication. For help, see “Configuring Security” on
page 24.
Disabling Access Via the Serial Port
When serial port access is disabled, you also disable USB access. When
you disable access, you will not be able to configure the IF2 as
described in “Assigning an Initial IP Address” on page 7. You must
use a network application (such as a web browser, SmartSystems
Console, or Device Configuration Web Service application) for all
configuration.
readonly.
To disable serial port access
1 From the menu, click Security > Passwords. The Passwords
screen appears.
2 Clear the Enable Serial Configuration check box.
3 Click Activate Changes to save your changes and immediately
make them active.
30 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 41

Managing Certificates
The default server certificate on the IF2 (ValidForHTTPSOnly)
provides support for secure network applications such as the secure
web browser interface, secure LLRP client connections, and secure
web services. You can use a third-party certificate authority to issue
unique client certificates and a root certificate.
Note: To install or uninstall certificates, you need to access the IF2 via
a secure web browser. For help, see “Using the Web Browser
Interface” on page 10.
Viewing Certificates
You can use the web browser interface to view the certificates loaded
on the IF2.
To view certificates
• From the menu, click Security > Certificate Details. The
Certificate Details screen appears.
Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
The Server Certificate table lists the server certificate that is installed,
and the CA Certificate table lists the trusted CA certificate that is
installed.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 31
Page 42

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
Installing and Uninstalling Certificates
Once you have determined that you need to install or uninstall a
certificate, use this procedure.
Note: If you follow the procedure to uninstall all certificates, you will
lose the unique server certificate and the trusted CA certificate. You
will need to contact your local Intermec representative to purchase
new certificates.
Note: To install or uninstall certificates, you need to access the IF2 via
a secure web browser. For help, see “Using the Web Browser
Interface” on page 10.
To install or uninstall certificates
1 From the main menu, click Security > Import Certificate. The
Import Certificate screen appears.
2 Click Browse and follow the prompts to browse to the location of
the certificate you want to install. Or, enter the path to the
certificate in the Enter or select the name of the certificate file
to import entry field.
Note: If you are not using a secure web browser, you will be
prompted to log in again. Click A secure session is available and
log in to the IF2. If a Security Alert dialog box appears, click Yes
to proceed. Repeat Steps 1 and 2.
3 Click Server Certificate or Trusted CA Certificate.
32 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 43

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
4 (Server Certificate only) In the Enter the associated passphrase
for this certificate field, carefully enter the passphrase for the
certificate.
5 Click Import Certificate. If a Security Alert dialog box appears,
click Yes to proceed.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 33
Page 44

Chapter 2 — Configuring Network Settings
34 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 45

3
Developing and Using RFID Applications
This chapter explains how you can develop and test RFID
applications for the IF2 and includes these topics:
• RFID Applications and the IF2
• Creating RFID Applications for the IF2
• Modifying IF4 Applications for Use With the IF2
• About RFID Services
• Configuring BRI Settings
• Configuring LLRP Settings
This chapter assumes you are familiar with developing
applications and with your RFID system.
35
Page 46

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
RFID Applications and the IF2
Your application communicates with the IF2 through one of two
RFID services:
• the Basic Reader Interface (BRI) server, which controls the reader
by issuing BRI commands. For more information on the BRI
server, see “Configuring the BRI Server” on page 43.
For more information on using BRI, see the Basic Reader Interface
Programmer’s Reference Manual.
• the Low-Level Reader Protocol (LLRP), based on the EPCglobal
standard. For more information on LLRP settings, see
“Configuring LLRP Settings” on page 46.
For more information on LLRP, see the LLRP Programmer’s
Reference Guide.
The application you develop resides on a remote server which
communicates with the IF2. In this case, all processing is performed
by the server.
Using the RFID Resource Kit
The Intermec Developer Library RFID Resource Kit includes Java and
C# tools you can use to develop applications that enable control of
the reader and data management.
The resource kit is available as part of the Intermec Developer Library
(IDL). To learn more about the RFID Resource Kit, go to
www.intermec.com and choose Products > Applications and
Software > Development Library > Developer Resource Kits.
36 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 47

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
Creating RFID Applications for the IF2
An RFID application can communicate directly with the IF2 BRI
Server using the BRI protocol, or it can communicate with the IF2
using the Low-Level-Reader Protocol (LLRP).
Intermec recommends that you write and test your application on a
development workstation (your desktop PC). The application can
access the IF2 BRI interface via TCP on port 2189.
Modifying IF4 Applications for Use With the IF2
If you are using an application that was previously written for the IF4,
you need to modify the application to be compatible with the IF2,
make sure you:
• enable the BRI server on the IF2. For more information, see
“Configuring the BRI Server” on page 43.
• change your application to ignore start-up messages from the
bootloader.
• change your application to not expect the power-up banner
message.
• change your application to handle “EVT:RESET”.
• change your application so that it does not expect BRI attributes
to be non-volatile.
• handle any differences in default settings.
• handle antenna faults.
• handle the “EVT:BRISERVICE NOSESSIONS” event.
While you are making changes to your application, make sure you are
aware that:
• some BRI features may have changed. For example the IF4
supports “read cont” for continuous reads, but the IF2 uses “read
report=no”
• the “facdflt” command has changed in function.
• triggers are non-volatile in the IF2, but are volatile in the IF4.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 37
Page 48

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
• The IF2 is no longer guaranteed to be the only RFID module
resource. The serial connection is one of eight possible
connections.
For more information on BRI, see the Basic Reader Interface
Programmer’s Reference Manual.
About RFID Services
The RFID service sets the protocol your application uses to
communicate with the RFID module. The available services are:
• BRI (Basic Reader Interface) - Intermec proprietary protocol for
controlling the reader. To configure BRI settings, see the next
section.
• LLRP (Low-Level Reader Protocol) - EPCglobal standard for
network interfaces between the RFID reader and its controlling
software. To configure LLRP settings, see “Configuring LLRP
Settings” on page 46.
Configuring BRI Settings
This section explains how to configure BRI settings that control
reader operation and communication with your application.
• To configure BRI attribute settings that control reader operation,
such as read and write tries, tag types, or antenna settings, see the
next section, “Changing BRI Attribute Settings.”
• To configure BRI server settings, which manage how your
application communicates with the reader, see “Configuring the
BRI Server” on page 43.
Changing BRI Attribute Settings
BRI attribute settings control how the IF2 reader module reads tags.
Follow the next procedure to change attribute settings.
Note: The BRI attribute settings in the web interface define the
default BRI attributes when a client initially connects to the BRI. The
settings do not change the attributes of any current BRI sessions.
38 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 49

To change BRI attribute settings
1 From the menu, click RFID Services > BRI > BRI Attributes. The
BRI Attributes screen appears.
2 Change RFID settings as needed. For help, see the next section.
3 Click Activate Changes to save your changes and immediately
make them active.
About BRI Attribute Settings
Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
This section explains the BRI attribute settings that control how the
reader operates. For more information, see the Basic Reader Interface
Programmer’s Reference Manual.
Tag Types
Check the appropriate check boxes to enable RFID operations for
these kinds of tags:
• EPC Class 1 Gen 2 (default)
• Phillips v1.19
• ISO6B/G1
• ISO6B/G2
This setting is equivalent to the TAGTYPE BRI attribute.
Read Tries
Sets the maximum number of times the read algorithm is executed
before a response is returned to a Read command.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 39
Page 50

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
In practice, this is the number of times an identified tag is read until
the Read is successful. Valid range is 1 to 254 (default is 3).
This setting is equivalent to the RDTRIES BRI attribute.
Write Tries
Sets the maximum number of times the write algorithm is executed
before a response is returned to a Write command.
In practice, this is the number of times an identified tag is written to
until the Write is successful. Valid range is 1 to 254 (default is 3).
This setting is equivalent to the WRTRIES BRI attribute.
Lock Tries
Sets the maximum number of times the lock algorithm is executed
before a response is returned to a Lock command. Valid range is 1 to
254 (default is 3).
This setting is equivalent to the LOCKTRIES BRI attribute.
Field Separator
Sets the character to be used for separating fields in tag data. Choose
from space ( ), comma (,), colon (:), semicolon (;), tab, caret (^), or tilde
(~). Default is space.
This setting is equivalent to the FIELDSEP BRI attribute.
ID Report
Enables or disables tag ID reporting after a Read, Write, or Lock
command is executed:
• For ISO tags, the tag identifier corresponds to TAGID.
• For EPC tags, the identifier corresponds to EPCID.
Check the check box to enable tag ID reporting. This setting is
equivalent to the IDREPORT BRI attribute, and is enabled by default.
No Tag Report
Enables or disables a NOTAG message, which is sent when no tags are
found during execution of a Read, Write, or Lock command. Check
the check box to enable the message. This setting is equivalent to the
NOTAGRPT BRI attribute, and is enabled by default.
40 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 51

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
Report Timeout
Sets the timeout (in ms) for delays in tag reporting when the IF2 is in
continuous read mode. Range is 0 (default) to 65534.
Timeout Configuration Mode
Enables a timeout mode. Instead of specifying the number of antenna
or ID tries, you specify an antenna or ID timeout value. If the IF2 does
not find any tags after an antenna or ID try, the reader waits this long
before starting the next antenna or ID try. If you enable timeout
mode, you need to set the ID Timeout and Antenna Timeout values.
This setting is equivalent to the TIMEOUTMODE BRI attribute, and
is disabled by default.
To enable Timeout Configuration mode
1 Check the check box. The screen refreshes. The Antenna Tries
setting is replaced by Antenna Timeout, and the ID Tries setting is
replaced by ID Timeout.
2 Specify the value (in ms) for the antenna or ID timeout in the
entry fields and then click Activate Changes.
For more information on ID Timeout and Antenna Timeout, see
those topics later in this section.
Select Tries
(Not supported by EPCglobal Class 1 Gen 2 tags) Sets the number of
times a group select is attempted. A group select is the command that
starts the identity process. Valid range is 1 (default) to 254.
This setting is equivalent to the SELTRIES BRI attribute.
Unselect Tries
(Not supported by EPCglobal Class 1 Gen 2 tags) Sets the number of
times a group unselect is attempted. Valid range is 1 (default) to 254.
Session
(EPCglobal Class 1 Gen 2 tags only) Sets the command session
parameter to the corresponding EPCglobal Class 1 Gen 2 air protocol
command (default is QueryAdjust).
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 41
Page 52

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
This setting is equivalent to the SESSION BRI attribute. For more
information on this setting, see the EPCglobal Class 1 Gen 2
documentation.
Initial Q
(EPCglobal Class 1 Gen 2 tags only) Sets the initial Q parameter value
used by the Query command. Valid range is 0 to 15 (default is 4). If
you know there is only one tag in the field, set this attribute to 0 for
best performance.
This setting is equivalent to the INITIALQ BRI attribute.
Initialization Tries
Sets the maximum number of times the reader attempts to initialize a
tag. Valid range is 1 (default) to 254.
This setting is equivalent to the INITTRIES BRI attribute.
Schedule Option
Determines how antennas are switched during the inventory process.
This attribute controls the behavior of the inventory scheduling
parameters.
This setting is equivalent to the SCHEDULOPT BRI attribute.
ID Tries
Sets the maximum number of times the reader executes the identify
algorithm before a response is returned to a Read or Write command.
In practice, this is the number of times a tag ID attempt is made for
each antenna being used. Valid range is 1 to 254 (default is 3).
This setting is equivalent to the IDTRIES BRI attribute.
Antenna Tries
Sets the maximum number of ID Tries that the reader executes per
antenna. Valid range is 1 to 254 (default is 3).
This setting is equivalent to the ANTTRIES BRI attribute.
42 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 53

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
EPCC1G2 Advance Medium Access Mode
Selects low-level protocol (such as tari and back-link frequency)
settings. If you are using CAEN tags, you must enable this mode
before the tags can be read.
This setting is equivalent to the EPCC1G2PARAMETERS or
EPCC1G2PARMS BRI attribute.
Dense Reader Mode
Allows the reader to hop between channels within a certain frequency
spectrum to prevent other readers in the area from interfering with
one another.
This setting is equivalent to the DENSEREADERMODE or DRM BRI
attribute.
Antenna Field Strength 1 to 4
Sets the RF power level (in dBm) for each of the 4 antenna ports. Valid
range is 15 to 30. Default is 30. Note that the maximum power level is
dependent on the region that the IF2 is operating in.
Use this setting to attenuate the antenna field strength. In some
situations, full output power can cause unnecessary interference. For
example, if the tag is close to the antenna, full output power might
overload the tag and cause unreliable behavior.
This setting is equivalent to the FIELDSTRENGTH BRI attribute.
Antenna Sequence: First through Eighth
Sets the RFID antenna to be used for each of up to eight tag inventory
operations. Choose any one of the 16 available antennas from the
drop-down list. If more than one antenna is enabled, the antennas fire
in this sequence.
This setting is equivalent to the ANTS BRI attribute.
Configuring the BRI Server
The IF2 BRI server handles communication between your application
and the RFID module. When your application is communicating with
the BRI server, the blue Intermec Ready-To-Work Indicator on the IF2
front panel turns on and stays on. For more information, see “About
the Intermec Ready-to-Work Indicator” on page 4.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 43
Page 54

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
To configure BRI server settings
1 From the menu, click RFID Services > BRI > BRI Server. The BRI
Server screen appears.
2 Change BRI server settings as needed. For help, see the next table.
3 Click Activate Changes to save your changes and immediately
make them active.
BRI Server Parameter Descriptions
Parameter Description
Enable External
BRI Connections
BRI TCP Port Specifies the TCP port used for incoming connections
Enable Logging Enables/disables logging of BRI server events.
Enable BRI on
serial port
Enables/disables external TCP connections to the BRI
server. If this check box is not checked, BRI applications
will not be able to connect to the IF2.
to the BRI server. This port must be unique for all TCP
services running on the IF2. Valid range is 2189 to
65535. Default is 2189.
For more information on logging, see the next section.
Enables/disables sending BRI commands through the
serial port.
Viewing the BRI Server Log
If you enable logging, you can see a list of BRI server events. You can
save the logfile as a .txt file.
44 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 55

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
To enable BRI server logging and view the logfile
1 Enable BRI logging as described in the previous section,
“Configuring the BRI Server” on page 43.
2 In the left navigation list, click RFID Services > BRI > BRI Log.
The BRI Log screen appears with a list of BRI events. For more
information on server events, see the next table, “BRI Event
Descriptions.”
3 To save the log file, click Export log to text file and then choose
File > Save As. Follow the prompts to save the log file to your
desktop PC.
BRI Event Descriptions
Event Name Description
Time/Date Time and date of the event.
Connection Session ID of the client communicating with the BRI server.
Type Message type of the event, generally indicating which system
sent the message:
1 = Command received by BRI server
2 = Response sent by BRI server
3 = BRI server connection message
Message Text of the message, including responses.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 45
Page 56

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
Configuring LLRP Settings
The IF2 supports version 1.0.1 of the EPCglobal Low-Level Reader
Protocol (LLRP), which establishes a specific interface method
between a reader and its corresponding client. Follow the next
procedure to configure LLRP settings.
Note: For information on LLRP, including standards, see
http://www.epcglobalinc.org/standards/llrp. An open source
LLRP Toolkit can be downloaded at http://sourceforge.net/
projects/llrp-toolkit.
To configure LLRP settings
1 From the menu, click RFID Services > LLRP. The LLRP screen
appears.
2 Configure LLRP settings as needed. For help, see the next table.
• To disconnect an existing LLRP connection, click Terminate.
• To connect to a remote LLRP client, enter information in the
Reader-Initiated Connections section, and then click Initiate.
46 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 57

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
3 Click Activate Changes to save your changes and immediately
make them active.
LLRP Settings Descriptions
Setting Description
Secure Server Enable Check this check box to allow connections to the
secure LLRP server on port 5085.
Unsecure Server Enable Check this check box to allow connections to the
unsecure LLRP server on port 5084.
Download Intermec
Extension Definitions
Reader-Initiated
Connections
Click the link to download the Intermec extension
definitions xml file.
For reader-initiated TCP/IP connections to a
remote LLRP client, enter this information:
• Client Address - IP address of the remote LLRP
client.
• TCP Port - Port number for the TCP/IP socket
connection.
• Enable Security (TLS) - Check this check box
to enable Transport Layer Security for this TCP/
IP connection.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 47
Page 58

Chapter 3 — Developing and Using RFID Applications
48 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 59

4
Managing, Troubleshooting, and
Upgrading the IF2
This chapter includes information on managing the IF2 and
includes these topics:
• Managing the IF2
• Using the Device Configuration Web Service
• Using SmartSystems Foundation
• Opening a Serial or USB Connection to the IF2
• Maintaining the IF2
• Troubleshooting the IF2
• Calling Intermec Product Support
• Accessing Intermec Web Pages
• Upgrading Firmware
49
Page 60

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Managing the IF2
There are several methods you can use to manage the IF2. You can use:
• a web browser. For help, see “Using the Web Browser Interface”
on page 10. This manual assumes you are using this method for
all procedures.
• the Device Configuration web service. For help, see the next
section.
• the Intermec SmartSystems Console. For help, see “Using
SmartSystems Foundation” on page 52.
Using the Device Configuration Web Service
The Device Configuration web service provides a way to
programmatically configure the IF2 over your network. This SOAPbased service provides a configuration API that allows you to specify a
variety of network, RFID, and system settings via XML-encoded
messages.
Follow the next procedure to enable the web service or to download
the Device Configuration web service description language (WSDL)
document.
For more information on the Device Configuration web service, see
the Device Configuration Web Service Command Reference Manual.
50 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 61

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
To enable the web service and download the WSDL document
1 From the menu, click Network Configuration > Device
Management. The Device Management screen appears.
By default, Device Configuration web services are enabled for
either secure or insecure connections.
2 To disable web services over a secure connection, clear the Enable
Device Web Services (Secure) check box, and then click Activate
Changes.
To disable web services over an insecure connection, uncheck the
Enable Device Web Services (Insecure) check box, and then
click Activate Changes.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 51
Page 62

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
To download the device configuration WSDL document, click
DeviceConfiguration.wsdl. The document opens in the browser
window.
Using SmartSystems Foundation
The IF2 ships with a SmartSystems™ client, which means you can
manage it from a central host PC using Intermec’s SmartSystems
Foundation. The SmartSystems Console displays all discovered
SmartSystems devices in your network.
For more information on SmartSystems Foundation, go to
www.intermec.com/SmartSystems. For information on using the
SmartSystems Console, in the Console choose SmartSystems > Help.
To use SmartSystems Foundation
1 From the menu, click Network Configuration > Device
Management. The Device Management screen appears.
52 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 63

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
On the IF2, SmartSystems is enabled by default.
2 To automatically connect to the SmartSystems server at boot time,
enter the server address in the SmartSystems Server Address
entry field. After you specify the server address, SmartSystems will
discover the IF2 during the next broadcast interval.
To disable SmartSystems access to the IF2, uncheck the Enable
SmartSystems Access check box.
3 Click Activate Changes to save your settings and immediately
make them active.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 53
Page 64

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Configuring the IF2 With Intermec Settings
In the SmartSystems console, right-click an IF2 and choose Intermec
Settings from the menu. The Intermec Settings window appears.
Intermec Settings: If you use the SmartSystems Console to manage the IF2,
you can use Intermec Settings to configure the IF2.
For help with using Intermec Settings, in the Intermec Settings
browser choose Help > Online Manual.
Opening a Serial or USB Connection to the IF2
You can connect the IF2 to your desktop PC via the serial or USB port
to perform these tasks:
• Assign the IF2 an initial IP address.
• Restore default settings.
• Establish a BRI session.
54 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 65

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Opening a Serial Connection to the IF2
If you are opening a serial connection to the IF2, you need:
• a null-modem cable (P/N 059167).
• a communications program such as HyperTerminal.
Note: If you have Microsoft ActiveSync running on your desktop PC,
disable ActiveSync to make the serial port available.
To connect to the IF2 via the serial port
1 Connect the null-modem cable from the serial port on the IF2 to a
serial port on your PC.
2 Start the communications program and configure the serial port
communications parameters to:
• Bits per second: 115200
• Data bits: 8
• Parity: None
• Stop bit: 1
• Flow control: None
3 Connect the IF2 to power. The IF2 boots as soon as you apply
power. In about a minute, the message “Loading System” appears
as the IF2 initializes, and in another minute or two the login
message appears.
The serial connection is established. From here you can do these
tasks:
• You can assign an initial IP address to the IF2 for
configuration. For help, see “Assigning an Initial IP
Address” on page 7.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 55
Page 66

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
• You can restore default settings. For help, see “To restore
defaults via a serial connection” on page 62.
• You can open a BRI session.
Opening a USB Connection to the IF2
If you are connecting the IF2 using a USB connection, you need:
• a USB cable.
• to create a folder with a gserial.inf and a usbser.sys file.
To connect to the IF2 using the USB port
1 Create a folder to place the gserial.inf and usb.sys file in.
2 Click Start > Programs > Accessories > Notepad.
3 In Notepad, copy and paste the following text:
[Version]
Signature="$Windows NT$"
Class=Ports
ClassGuid={4D36E978-E325-11CE-BFC1-08002BE10318}
Provider=%LINUX%
DriverVer=08/17/2004,0.0.2.0
; Copyright(C)2004 Al Borchers (alborchers@steinerpoint.com)
[Manufacturer]
%LINUX%=GSerialDeviceList
[GSerialDeviceList]
%GSERIAL%=GSerialInstall, USB\VID_0525&PID_A4A7
[DestinationDirs]
DefaultDestDir=10,System32\Drivers
[GSerialInstall]
CopyFiles=GSerialCopyFiles
AddReg=GSerialAddReg
[GSerialCopyFiles]
usbser.sys
[GSerialAddReg]
HKR,,DevLoader,,*ntkern
HKR,,NTMPDriver,,usbser.sys
HKR,,EnumPropPages32,,"MsPorts.dll,SerialPortPropPageProvider"
56 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 67

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
[GSerialInstall.Services]
AddService = usbser,0x0002,GSerialService
[GSerialService]
DisplayName = %GSERIAL_DISPLAY_NAME%
ServiceType = 1 ; SERVICE_KERNEL_DRIVER
StartType = 3 ; SERVICE_DEMAND_START
ErrorControl = 1 ; SERVICE_ERROR_NORMAL
ServiceBinary = %10%\System32\Drivers\usbser.sys
LoadOrderGroup = Base
[Strings]
LINUX = "Linux"
GSERIAL = "Gadget Serial"
GSERIAL_DISPLAY_NAME = "USB Gadget Serial Driver"
4 Click File > Save As.
5 Browse to the folder that you created in Step 1.
6 In the File name: text box, type gserial.inf, and click Save.
7 Browse to the c:\Windows\Driver Cache\i386 directory and locate
the driver.cab file.
8 Open the driver.cab file with a .cab extraction tool and find the
usb.sys file.
9 Copy the usb.sys file to the folder you created in Step 1.
10 Connect the IF2 to your PC using a USB cable. The Found New
Hardware Wizard appears.
11 Select Install from a list or specific location (Advanced), and
click Next.
12 Select Include this location in the search, and enter browse to
the folder you created in Step 1.
13 Click Continue Anyway when the Windows Logo Testing screen
appears. The IF2 is connected by a USB connection. From here you
can do these tasks:
• You can assign an initial IP address to the IF2 for
configuration. For help, see “Assigning an Initial IP
Address” on page 7.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 57
Page 68

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
• You can restore default settings. For help, see “To restore
defaults via a serial connection” on page 62.
• You can open a BRI session.
Maintaining the IF2
The Maintenance menu lets you view IF2 parameters and statistics,
including a list of logged events. You may need this information if you
need to call Intermec Product Support.
Viewing the System Log
The System Log screen shows events that have been logged by the IF2.
To view the System Log screen
1 From the menu, click Maintenance > System Log. The System
Log screen appears. This screen is read-only.
2 To save the list, click Export log to text file. The log is saved as
Syslog.log and appears in the browser window.
3 Choose File > Save As and follow the prompts to save the log file
to your desktop PC.
58 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 69

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Viewing the About Screen
The About screen lists installed software versions, serial numbers, and
other IF2-specific information.
To view the About screen
• From the menu, click About. The About screen appears. This
screen is read-only.
The About screen includes this information:
• Device information: IF2 firmware version, hardware configuration
string, and serial number.
• System information: Available memory, number of running
processes, and amount of time the IF2 has been running.
• RFID Module firmware: Firmware version installed.
• Network interface information.
• Installed subsystems: versions of all currently loaded IF2
subsystems, including Linux.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 59
Page 70

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Using the LEDs to Locate the IF2
You can use the LEDs to help locate a specific IF2 in your location.
To locate a n IF2
• In the About This IF2 RFID Reader screen, click Find This
Device. All of the LEDs except the Power and Wired LAN LEDs
flash. Click Finished Finding This Device to turn off the LEDs.
Restoring the IF2 to the Default Configuration
Note: Restoring default settings as described in this section does not
affect security certificates you have installed.
There are four ways to restore the default configuration on the IF2:
• You can restore default settings from the web browser interface.
For help, see the next section.
• You can restore default settings by pressing the reset switch
located on the top of the IF2.
• You can restore default settings via a serial connection. For help,
see “To restore defaults via a serial connection” on page 62.
• You can restore default settings using the Device Configuration
Web Services. For help, see the Device Configuration Web Services
Command Reference Manual.
60 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 71

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Restoring Default Settings Using the Web Browser
If you are having problems with the IF2, you can use the web browser
interface to restore the default settings to the IF2.
To restore defaults using the web browser
1 From the menu, click Maintenance > Configuration. The
Configuration screen appears and displays all configuration
changes from the factory default settings.
2 Click Restore Defaults. A confirming message appears.
3 Click OK. The IF2 reboots and restores the default configuration.
Or, click Cancel to close the confirming message without
restoring defaults.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 61
Page 72

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Restoring Default Settings Using the Reset Switch
If you are having problems with the IF2, you can press the reset switch
to restore the default settings to the IF2.
To restore defaults via a serial connection
1 Make sure the IF2 is powered on.
2 Using a paper clip, push and hold the reset switch for three
seconds. The LEDs on the IF2 flashes.
Reset switch
3 Release the reset switch. The IF2 reboots and restores the default
configuration.
Restoring Default Settings Using a Serial Connection
If you are having problems with the IF2, you can use a serial
connection to restore the default settings to the IF2.
To restore defaults via a serial connection
1 Open a serial connection to the IF2. For help, see “Opening a
Serial or USB Connection to the IF2” on page 54.
2 In the login field, type restore_defaults and then press
Enter.
3 In the Password field, press Enter. The IF2 reboots and the default
settings are restored.
62 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 73

Rebooting the IF2
You can reboot the IF2 from the web browser interface as described in
the next procedure. For example, you may need to reboot the IF2 to
enable changes in an application.
To reboot the IF2
1 From the menu, click Maintenance > Reboot. The Reboot screen
appears.
2 Click Reboot to reboot the IF2. You need to log in again after the
IF2 reboots.
Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 63
Page 74

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Troubleshooting the IF2
This section includes lists of problems and possible solutions.
Problems While Working With RFID
Many problems you may encounter when working with your RFID
system can be solved by carefully checking the RFID settings and
changing them accordingly. For help, see “About RFID Services” on
page 38.
RFID Problems and Solutions
Problem Solution
The IF2 is unable to read RFID tags,
or seems to read tags slowly or
inconsistently.
The IF2 does not respond to your RFID
application.
Check these conditions:
• Your RFID antennas must be connected correctly to
the IF2 and mounted in optimum locations. Make
sure all antenna connections are tight and that the
cables are in good condition. For help, contact your
Intermec RFID system consultant.
• To maximize IF2 performance, make sure you have
chosen the correct tag types for your application. For
help, see “Configuring BRI Settings” on page 38.
Your application may not be communicating with the
IF2 BRI server.
You may need to change BRI server settings to
communicate with your application. For example, if
your application is running on a desktop PC, you need to
enable external BRI connections to the IF2. For help, see
“Configuring the BRI Server” on page 43.
Connecting Directly to the RFID Module
If your application does not appear to be communicating with the IF2
RFID module, you can use a communications program to verify that
the RFID module is working properly.
You need to know the IF2 IP address to connect directly to the RFID
module. To verify that the RFID reader is reading tags, you need a
known good RFID antenna and at least one good RFID tag.
64 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 75

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
To connect directly to the IF2 RFID module and verify operation
1 Make sure the RFID antenna is connected properly to the IF2.
2 Apply power to the IF2.
3 Use a communications program (such as HyperTerminal) to open
a TCP/IP connection to the IF2 with these parameters:
Parameter Value
IP Address IP address of the IF2
Port 2189
Configure the communications program to echo typed characters
locally and to send line feeds with line ends.
4 Press Enter. The BRI prompt (OK>) appears.
If the prompt does not appear, there may be a problem with the
RFID module or your connection to the module.
5 Type ATTRIB and press Enter. A list of the current settings for the
RFID module appears, indicating that the module is receiving
commands.
If the list does not appear, there may be a problem with the RFID
module.
6 (Optional) To verify that the RFID module is reading tags:
a Place a known good RFID tag within range of the antenna.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 65
Page 76

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
b Type READ and press Enter. The tag ID appears, indicating
that the module is reading tags.
If the tag ID does not appear, there may be a problem with the
RFID module or antenna system.
Problems With Connectivity
When troubleshooting problems with connectivity, make sure you
know and understand these network-specific items:
• TCP/IP settings
• COM port settings for serial connections
You should also make sure all physical network connectors and cables
are in good working order.
Connectivity Problems and Solutions
Problem Solution
You cannot connect to the IF2
using the serial port.
1 Verify that you are using a null-modem cable to connect to
the desktop PC.
2 Verify that you are communicating through the correct
serial port.
3 Verify that your PC is set to 115200, N, 8, 1, no flow
control.
You cannot connect to the IF2
using a web browser.
You cannot load a security
certificate.
You have assigned a static IP
address to the IF2 but cannot
connect to the IF2 over your
network.
66 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
1 Verify that you have the correct IP address for the IF2.
2 If you access the Internet through a proxy server, be sure
you have added the IP address of the IF2 to the Exceptions
list.
You must use a secure web browser connection to load
certificates. For help, see “Using the Web Browser
Interface” on page 10.
Make sure that DHCP is disabled and that your TCP/IP
parameters are set correctly. For help, see “Communicating
with the IF2” on page 7.
Page 77

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Calling Intermec Product Support
You may need to call Intermec Product Support if you have problems
operating the IF2. Before calling, be sure you can answer the following
questions:
• What kind of network are you using?
• What were you doing when the error occurred?
• What error message did you see?
• What is your RFID reader’s serial number?
• Can you reproduce the problem?
• What versions of IF2 and RFID software are you using? For help,
see “Viewing the About Screen” on page 59.
When you have gathered this information, call Intermec Product
Support at 1-800-755-5505.
Accessing Intermec Web Pages
Periodically, IF2 firmware updates can be downloaded from
www.intermec.com.
You can use the IF2 web browser interface to visit
www.intermec.com or to download manuals from Intermec as
described next.
To access Intermec web pages
1 Open a web browser interface to the IF2. For help, see “Using the
Web Browser Interface” on page 10.
2 To go to www.intermec.com, click Intermec in the upper right
corner.
To locate IF2 firmware updates, from the main Intermec web page
choose Support > Downloads and search for IF2.
Or, to download an Intermec product manual, click Manual in
the upper right corner.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 67
Page 78

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Follow the prompts to search for and download manuals or other
documentation.
Upgrading Firmware
Make sure the IF2 is connected to a reliable power source before
you upgrade the firmware. Do not cycle power to the IF2 during
the upgrade. If power is lost during the upgrade, the IF2 may
require factory repair.
This section explains how to configure and install firmware upgrades
on the IF2.
Note: To upgrade the firmware, use only .bin files provided by
Intermec. Be sure to contact your Intermec RFID system consultant
before upgrading. To locate IF2 upgrades, see the previous section,
“Accessing Intermec Web Pages” on page 67.”
To upgrade the firmware
1 Download the Intermec IF2 OS Upgrade Package utility from the
Intermec web site. For help, see the previous section, “Accessing
Intermec Web Pages” on page 67.
2 Run the Upgrade Package utility to configure the firmware
upgrade file. For help, see the next section.
3 Install and run the firmware upgrade file on the IF2. For help, see
“Installing the Firmware Upgrade” on page 70.
68 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 79

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Configuring the Firmware Upgrade
The Upgrade Package installer configures IF2 firmware upgrades. The
configuration you need depends on the method you use to upgrade
the IF2:
• Using the web browser interface.
• Using Intermec SmartSystems Server.
• Using Device Configuration Web Services. For help, see the Device
Configuration Web Services Command Reference Manual.
This section explains how to choose the correct configuration.
To configure the firmware upgrade file
1 Double-click the Upgrade Package utility to run it. The opening
screen appears.
2 Click Next.
3 If you are going to upgrade the IF2 via the web browser interface,
deselect the SmartSystems Upgrade Bundle button and click
Next. The bundle install location screen appears.
If you are going to use Intermec SmartSystems Server to upgrade
the IF2, deselect the Web Upgrade Bundle button and then click
Next. The bundle install location screen appears.
4 Click Next to install the upgrade file at the default location, and
then click Install. The upgrade file is installed.
To choose a different location:
a Click Browse to browse to a different location.
b Double-click a folder to choose the location.
c Click Next.
d Click Install. The file is installed at the new location.
5 Click Finish to close the utility.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 69
Page 80

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
Installing the Firmware Upgrade
This section describes the different methods of how to install and run
the IF2 firmware upgrade.
Upgrading From the Web Browser Interface
You can use the web browser interface to upgrade the firmware on the
IF2.
To upgrade the IF2 using the web browser interface
1 From the menu, click Maintenance > Firmware. The Firmware
screen appears.
2 Click Browse to browse to the location of the upgrade file, and
then double-click the filename. The name of the file appears in the
Enter or select the name of the firmware upgrade file entry
field.
70 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 81

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
3 Click Upgrade IF2 RFID Fixed Reader. The upgrade process
begins and the firmware is transferred to the IF2.
During the upgrade, the web browser interface screen does not
auto-refresh. Click Refresh in the web browser to check the
progress of the upgrade. When the login screen appears, the
upgrade is complete and the IF2 has already rebooted.
Upgrading With SmartSystems Foundation
You can use the SmartSystems server to upgrade the firmware on the
IF2. The server is part of SmartSystems Foundation, which is available
from the Intermec web site.
Before you can upgrade the IF2, you need:
• SmartSystems Foundation. For more information, go to
www.intermec.com/SmartSystems.
• the IF2 upgrade file. For help, see “Configuring the Firmware
Upgrade” on page 69.
To upgrade the IF2 using the SmartSystems Foundation Server
1 Install SmartSystems Foundation on your PC and open the server.
2 Make sure the server and your IF2 are on the same subnet.
3 In the software vault, locate the IF2 upgrade to install.
4 Drag-and-drop the upgrade file onto the IF2 you want to upgrade.
SmartSystems server tells you that it is installing the upgrade on
the IF2.
The SmartSystems server shows the IF2 as being offline until the
reader reboots and reconnects to the system.
Do not cycle power to the IF2 during the upgrade. If power is lost
during the upgrade, the IF2 may require factory repair.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 71
Page 82

Chapter 4 — Managing, Troubleshooting, and Upgrading the IF2
72 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 83

5
Using the IF2 GPIO Interfaces
This chapter explains how to access the IF2 general purpose
input/output (GPIO) interfaces and how to connect industrial
controls such as motion sensors or indicator lamps to the IF2.
This chapter includes the following topics:
• About the GPIO Interfaces
• Accessing the Interfaces
• Using the Input Interfaces
• Using the Output Interfaces
• Using the Power Interface
73
Page 84

Chapter 5 — Using the IF2 GPIO Interfaces
About the GPIO Interfaces
The IF2 has four general purpose input and output (GPIO) interfaces.
You connect external controls such as motion sensors or indicator
lamps to the GPIO interfaces, which can then trigger IF2 operations.
Each interface is electrically isolated from the IF2 and designed for
low voltage DC loads. The IF2 can also supply 12 VDC at 0.5 A to
external devices.
How the inputs and outputs are used depends on the RFID
application software being used in the system. You need to coordinate
input and output control wiring with the software developer.
Accessing the Interfaces
You can access the GPIO interfaces through the IF2 GPIO port. The
port uses a standard 25-pin serial cable. For port pin assignments, see
“Port Pin Assignments” on page 84.
Intermec offers these GPIO accessories:
• The GPIO Terminal Block (P/N 203-726-xxx). Use this accessory
to connect devices to the IF2 GPIO interfaces. The block provides
access to the IF2 GPIO interfaces via standard screw terminals.
• The Light Stack Kit (P/N 203-858-xxx). This 3-color indicator
light and beeper connects directly to the IF2 GPIO port and is
triggered by the output interfaces. The kit includes a connecting
cable.
• The Sensor Kit (P/N 203-859-xxx). This motion sensor connects
directly to the IF2 GPIO port and triggers the input interfaces. The
kit includes a mounting bracket and connecting cable.
• The Light Stack and Sensor Kit (P/N 203-860-xxx). This kit
includes the light stack, a sensor with mounting bracket, and
connecting cable.
For more information on these GPIO accessories, contact your local
Intermec distributor.
74 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 85

Using the Input Interfaces
Each of the four inputs is compatible with input signals of 10 to 36
VDC. Both the high and low signal contacts are exposed and isolated
to 1500 V. Input impedance is 1.8 K ohms minimum.
GPIO Input Signal Descriptions
Signal Description Min. Typical Max.
V
(High) High input voltage 10 V 24 V 36 V
in
V
(Low) Low input voltage -1 V 0 V 1 V
in
In a typical application, the IF2 senses input from an external control
like a switch and then starts a tag read operation.
There are three basic ways to connect input controls to the IF2 input
interfaces:
• Supply the input interface with power from the IF2.
• Isolate the IF2 from the input power source.
Chapter 5 — Using the IF2 GPIO Interfaces
• Use an open collector solid state drive from a remote device to
control the inputs.
For more information, see the next examples.
IF2 Powered Input
This is the simplest way to connect a control to an IF2 input interface.
If the external control device is a switch, you can connect one side of
the switch to an IF2 +Input pin, and the other side of the switch to
one of the +12 VDC sources. Ground the corresponding -Input pin as
shown in the next illustration.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 75
Page 86

Chapter 5 — Using the IF2 GPIO Interfaces
+12V
+Input
- Input
Ground
IF2 Powered Input
Isolated Input Interface
Use this method to minimize noise induced by distance or grounding
characteristics. The isolated input avoids induced noise by referencing
a remote input to chassis return of the IF2. The next illustration
shows how this method is wired.
+Input
External
input
switch
External
input
switch
-
-Input
Twisted
pair
Isolated Input Interface
+
10-48 VDC
Open Collector Input Interface
The input can be connected to an open collector interface of an
external device. This typically implies that the grounds are tied
together for the two systems. The common ground can be a source of
input noise, so you should follow good grounding practices for both
the IF2 and the input device.
In this situation, the IF2 provides power to the pull-up resistor for the
open collector. Connect the +Input pin to the +12 VDC source as
shown in the next illustration.
76 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 87

+12V
+Input
- Input
Ground
Open Collector Input Interface
Using the Output Interfaces
Each IF2 output interface is optically isolated from the IF2, polarized,
and rated for 5 to 48 VDC at 0.25 A. All IF2 outputs include internal
thermal fuses that trip if the load exceeds 0.25 A, and the fuses are
self-recovering once the excessive load is removed. The high and low
contacts are exposed and isolated from ground. Transient
suppression limits output voltage spikes to 65 VDC.
GPIO Output Specifications
Chapter 5 — Using the IF2 GPIO Interfaces
Signal Description Min. Ty pic al Max.
Leakage
current (High)
V
(Low) Switch output on, saturation
sat
Switch output, high leakage
current
voltage with 0.25A load
0 mA 1 mA 10 mA
0V 1V 1.5V
Because the outputs are optically isolated, each one can be configured
to switch the high side or the low side of the load. You can power the
load directly from the IF2 or from an external power supply.
In a typical application, the outputs control indicator lamps that
signal good reads or errors. The basic methods for connecting
external devices to the GPIO outputs include:
• Switching the high side, with the load powered by the IF2
• Switching the low side, with the load powered by the IF2
• Switching the high side, with the load powered externally
• Driving a DC relay that controls an AC load
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 77
Page 88

Chapter 5 — Using the IF2 GPIO Interfaces
These methods are shown in the next examples.
Switching the High Side Using IF2 Power
In this example, an external indicator lamp (0.25 A maximum current)
is connected to the -Output and Ground pins, and the corresponding
+Output pin is connected to the +12 VDC source.
+12V
+Output
External
indicator lamp
0.25A maximum
- Output
Ground
Switching the High Side
Switching the Low Side Using IF2 Power
For low side switching applications, the lamp power is routed to all
the lamps in common and the low side of the load is routed to the
switch.
In this method, connect the external indicator lamp to the +Output
and +12 VDC pins, and short the corresponding -Output pin to
ground as shown.
External
indicator lamp
0.25A maximum
+12V
+Output
- Output
Ground
Switching the Low Side of the Output Load
78 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 89

Chapter 5 — Using the IF2 GPIO Interfaces
External
indicator
lamp
External
power
5-48 VDC
+
-
Ground
+Output
- Output
Switching the High Side Using External Power
To use external power (5 to 48 VDC) to switch the high side, connect
the Ground pin to the ground system of the external power supply,
and connect the positive side of the external supply to the +Output
pin. The external indicator lamp is connected to the corresponding
-Output and Ground pins as shown in the next illustration.
Switching the High Side With External Power
Driving a DC Relay to Control an AC Load
While the IF2 outputs are designed to switch DC loads, they can drive
relays that control AC loads. The next illustration shows how to
connect such a system to an IF2 output.
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 79
Page 90

Chapter 5 — Using the IF2 GPIO Interfaces
AC motor
120-230
VAC
External
relay
+ Output
+ 12V
Ground
- Output
Driving a DC Relay: The external relay provides dry contacts for controlling the
AC motor.
Note: In many installations, the relay and AC wiring must be placed
in an enclosure that meets local fire code regulations.
Using the Power Interface
The IF2 GPIO interface provides 12 VDC at 0.5 A for powering
external inputs and loads, eliminating the need for an external DC
supply and simplifying the system installation.
The GPIO interface power has an internal thermal fuse that trips if
the load exceeds 0.5 A. The fuse is self-recovering once the excessive
load is removed.
The total load on the GPIO interface power must stay within the 0.5A
limit. When you design a system that uses the GPIO interface power,
be sure to complete a power budget assessment to ensure that the
supply is adequate for the system.
If your system needs more than +12 VDC at 0.5 A, you can connect an
external power supply to the +12 V and Ground pins. The external
supply powers the external loads, and that power will be available at
all +12 V pins on the GPIO port.
80 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 91

A
Specifications
This appendix includes physical and electrical specifications
for the IF2 and information about the port pin assignments.
81
Page 92

Appendix A — Specifications
IF2 Specifications
Specifications Values
Height 19.9 cm (7.87 in)
Length 18.8 cm (7.42 in)
Width 4.3 cm (1.7 in)
Weight 1 kg (2.2 lb)
DC electrical rating 12 V +/- 5%, 30 W
Operating temperature -20ºC to +50ºC (-4ºF to +122ºF)
Storage temperature -30ºC to +70ºC (-22ºF to +158ºF)
Humidity
(non-condensing)
Ethernet interfaces 10BaseT/100BaseTx (twisted-pair) with
Ethernet compatibility Ethernet frame types and Ethernet
Ethernet data rate 10 Mbps/100 Mbps
Serial port maximum
data rate
(55 V, 30 W for High Power Over Ethernet)
5% to 95% non-condensing
802.3at High Power Over Ethernet (POE)
addressing
115,200 bps
82 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 93

RFID Specifications
Specifications Values
Protocols Supported EPCglobal Class 1 Gen 2
Frequency Range 865.6 - 867.6 MHz, or 902 - 928 MHz
Output power
865-867 MHz, 900 MHz
Occupied frequency
bandwidth
Tag data rate 32 kbps/320 kbps
Dispatch rates > 200 tags per second
Transmitter type 90% amplitude modulation index
Frequency stability <±100 ppm from -25°C to +55°C
Number of antennas Up to 4, electronically switched
Antenna port isolation 22 dB
Antenna connectors Reverse TNC
Appendix A — Specifications
ISO 18000-6B Generation 1
ISO 18000-6B Generation 2
ATA
Minimum: 1 dBm
Maximum: 30.0 dBm
<250 KHz
(-13°F to 131°F)
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 83
Page 94

Pin 1
Pin 13
Pin 25
Pin 14
Appendix A — Specifications
Port Pin Assignments
GPIO Port
GPIO Port Pin Assignments
Pin Description Active Polarity
1-Input 1 Low-RTN
2-Input 2 Low-RTN
3-Input 3 Low-RTN
4-Input 4 Low-RTN
5Ground
6Ground
7 +Output 1 High (10-48V)
8Ground
9 +Output 2 High (10-48V)
10 Ground
11 +Output 3 High (10-48V)
12 Ground
13 +Output 4 High (10-48V)
14 +Input 1 High (10-48V)
15 +Input 2 High (10-48V)
16 +Input 3 High (10-48V)
17 +Input 4 High (10-48V)
18 12VDC
19 -Output 1 Low-RTN
20 12VDC
21 -Output 2 Low-RTN
22 12VDC
23 -Output 3 Low-RTN
84 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 95

GPIO Port Pin Assignments (continued)
Pin Description Active Polarity
24 12VDC
25 -Output 4 Low-RTN
Serial Ports (COM1)
Pin 9
Serial Port Pin Assignments
Pin Description Active Polarity
1NC
2 Receive data (RXD)
3 Transmit data (TXD)
4NC
5 Signal ground
6NC
7 Request to send (RTS) Low
8Clear to send (CTS)Low
9NC
Appendix A — Specifications
Pin 1
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 85
Page 96

Appendix A — Specifications
Ethernet Port
Pin 1
Ethernet Port Pin Assignments
Pin Description
1 Ethernet TX+/Spare POE return
2 Ethernet TX-/Spare POE return
3 Ethernet RX+/Spare POE 48 VDC
4 Not used/POE 48 VDC
5 Not used/POE 48 VDC
6 Ethernet RX-/Spare POE 48 VDC
7Not used/POE return
8Not used/POE return
86 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 97

I
Index
87
Page 98

Index
A
About screen
AC power port
location
Antenna Tries setting
ANTTRIES equivalent
applications
configuring BRI server
how to develop
using with IF2 36
B
Basic Reader Interface
attribute equivalents for BRI
attributes, changing
described
external connections, enabling
TCP Port setting, for BRI server
blue LED, described
Bonjour service advertisement,
enabling
BRI server
BRI TCP Port
configuring 43
Enable External BRI
Enable Logging 44
log, enabling and viewing
logfile command event
settings, described
using with Intermec Ready-To-
BRI TCP Port setting, for BRI server
44
BRI. See Basic Reader Interface
C
cable access door, removing
Certificate Details screen,
illustrated
certificates
described
installing and uninstalling
viewing
Common Internet File System
shares, enabling
configuring the IF2
59
4
42
42
37
Attribute settings
38
38
44
44
4
26
44
Connections
descriptions
44
45
44
Work indicator
4
31
31
31
23
43
39
44
4
32
BRI server 43
connecting with
communications program
7
default configuration, restoring
60
DHCP settings
DNS settings
Ethernet link speed 8
Ethernet settings
firmware, upgrading
Intermec Settings, using 54
network settings
password server
RFID services
RFID settings
saving changes
security 24
serial port connection
setting IP address, described
SNTP settings 23
SYSLOG destination
user name and password, setting
26
using web browser interface
viewing software versions
web service 50
connecting IF2 to network
D
date and time
setting with web browser
interface
SNTP client settings
default configuration, restoring 60
default login, changing
defaults, restoring
Dense Reader Mode, enabling
DENSEREADERMODEequivalent
43
developing applications
access services, controlling
guidelines
using with IF2
with Intermec RFID Resource
Kit
Device Configuration web service
50
DHCP settings, configuring
diagnostics
BRI server event log, viewing
22
23
20, 23
27
38
38
12
16
60
37
36
36
20
68
54
7
23
10
59
15
23
29
43
25
22
44
88 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
Page 99

Index
events log, viewing
DNS
server IP address, setting
settings, configuring
suffixes, setting
DRM equivalent 43
E
edgeware
updates, locating
electrical specifications 82
Enable DHCP check box
Ethernet
Enable External BRI Connections
Enable Help check box
Enable Logging check box, for BRI
Enable RADIUS check box
Enable Serial Configuration check
Enable Web Server check box
environmental requirements 14
EPCC1G2 Access mode, enabling
EPCC1G2PARAMETERS
EPCC1G2PARMS equivalent
EPCglobal Class 1 Gen 2
tags, choosing in BRI Attribute
Ethernet
IF2 in wired network, illustrated
link speed, configuring 8
port
settings, configuring with web
troubleshooting problems
events log, viewing in Maintenance
external controls, using with IF2
F
Field Separator setting
Field Strength setting
fields, in tags, separating 40
FIELDSEP equivalent
FIELDSTRENGTH equivalent
22
setting
44
server
44
box
30
43
equivalent
settings
2
described
location
pin assignments
menu
4
browser interface
58
58
24
23
24
67
13
28
26
43
43
39
5
86
20
66
74
40
43
40
43
firmware, upgrading
installing upgrade file on IF2
overview 68
upgrade file, configuring
web browser interface
Forced Client Termination 47
front panel ports
accessing
described 5
G
general purpose input/output
accessing
described
inputs, using
isolated input 76
open collector input
output, switching high side
output, switching the high side
output, switching the low side
outputs, using
port location 4
port pin assignments
power, using
powered input 75
relay, driving to control AC load
GPIO. See general purpose input/
H
Help screen, illustrated
help text, in web browser interface
hostname
http
//support.ntp.org
HyperTerminal, using to configure
I
ID Report check box
ID Tries setting
IDREPORT equivalent
IDTRIES equivalent
IF2
applications, developing
connecting to network 15
4
interfaces
74
74
using external power
78
78
79
output interfaces
12
24
IF2
7
68
75
77
80
23
40
42
42
70
69
70
76
79
84
12
40
37
IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual 89
Page 100

Index
connecting with
communications program
7
default configuration, restoring
60
described 2
developer access, controlling
dimensions
environmental requirements,
Ethernet network, described and
firmware, upgrading
installing
locating with LEDs
maintaining
managing
mounting location, choosing 13
overview
rebooting via web browser
related documents, list of
RFID settings, configuring
specifications 82
troubleshooting
using securely
IF61
POE, connecting
indicator lamps, external
using with IF2
Initial Q setting
Initialization Tries setting
initialize tags setting 42
INITIALQ equivalent
INITTRIES equivalent
input interface
isolated
open collector
powered
signal descriptions
installing
IF2
13
RFID antennas
Intermec
manuals, how to download from
Product Support, what to know
Settings, application 54
SmartSystems Foundation
IP address
82
listed
14
illustrated
2
13
58
50
2
interface
63
64
17
74
42
76
76
75
15
web
ix, 67
when calling
68
60
3
42
42
42
75
67
ix
38
52
25
Ethernet
setting with communications
setting with web browser
IPv6 settings
Ethernet
ISO6B tags, choosing
L
LEDs
described
Intermec Ready-To-Work
location
power
RFID Transmit 3
Tag ID
using to locate the IF2
wired LAN 3
Link Local IP Address
LLRP. See Low-Level Reader
location, choosing for IF2
Lock Tries setting
LOCKTRIES equivalent 40
login screen
login, changing default
Low-Level Reader Protocol 46
configuring settings
settings, described
M
maintaining the IF2
Maintenance menu
events log, viewing
locating the IF2
using LEDs to locate the IF2
managing the IF2
defaults, restoring
developer access, controlling
Device Configuration web
firmware, upgrading
methods
security, configuring
SmartSystems Foundation
using securely
manuals, Intermec, how to
motion sensors, external
using with IF2
22
program
interface
22
3
Indicator
3
3
3
Protocol
10
service
50
download from web
7
20
39
3
60
22
13
40
29
46
47
58
58
58
60
60
60
25
50
68
24
52
17
ix, 67
74
90 IF2 Network Reader User’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...