Page 1

Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300
Series
Specification Update
- on 45 nm Process in the 775-land LGA Package
January 2012
Reference Number: 309007-011
Page 2

Legal Lines and Disclaimers
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS
PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER,
AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING T O SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCT S INCLUDING
LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELA TING T O FITNES S FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANT ABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY
PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving,
life sustaining, critical control or safety systems, or in nuclear facility applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.” Intel
reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoev er for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future
changes to them.
The processor may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published
specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Δ
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each processor
family, not across different processor families. See http://www.intel.com/products/processor_number for details. Over time
processor numbers will increment based on changes in clock, speed, cache, or other features, and increments are not intended to
represent proportional or quantitative increases in any particular feature. Current roadmap processor number progression is not
necessarily representative of future roadmaps. See www.intel.com/products/processor_number for details.
®
Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT) requires a computer system with Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel®
Intel
Virtualization Technology (Intel
processor, chipset, BIOS, Authenticated Code Modules and an Intel TXT-compatible measured launched environment (MLE). The
MLE could consist of a virtual machine monitor, an OS or an application. In addition, Intel TXT requires the system to contain a TPM
v1.2, as defined by the Trusted Computing Group and specific software for some uses. For more information, see http://
®
VT-x) and Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)), a Intel TXT-enabled
www.intel.com/technology/security
®
Virtualization Technology requires a computer system with an enabled Intel® processor, BIOS, virtual machine monitor
Intel
(VMM) and, for some uses, certain computer system software enabled for it. Functionality, performance or other benefits will vary
depending on hardware and software configur ations and may re quire a BIOS update. S oftware applicatio ns may not be compatible
with all operating systems. Please check with your application vendor.
®
Turbo Boost Technology requires a PC with a processor with Intel Turbo Boost Technology capability. Intel Turbo Boost
* Intel
Technology performance varies depending on hardware, software and overall system configuration. Check with your PC
manufacturer on whether your system delivers Intel Turbo Boost Technology. For more information, see http://www.intel.com/
technology/turboboost
®
Intel
Hyper-threading Technology requires a computer system with a processor supporting HT Technology and an HT Techn olog yenabled chipset, BIOS, and operating system. Performance will vary depending on the specific hardware and software you use. F or
more information including details on which processors support HT Technology, see http://www.intel.com/info/hyperthreading.
64-bit computing on Intel architecture requires a computer system with a processor, chipset, BIOS, operating system, device
drivers and applications enabled for Intel
configurations. Consult with your system vendor for more information.
®
64 architecture. Performance will vary depending on your hardware and software
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature may be obtained
by visiting Intel's website at http://www.intel.com.
Intel, Intel Core, Celeron, Pentium, Intel Xeon, Intel Atom, Intel SpeedStep, and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered
trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2012, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
2 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specifcation Update January 2012
Page 3

Contents
Revision History .................................................................................................................5
Preface...............................................................................................................................6
Summary Tables of Changes.............................................................................................8
Identification Information..................................................................................................14
Component Identification Information...............................................................................15
Errata................................................................................................................................17
Specification Changes......................................................................................................40
Specification Clarifications ...............................................................................................41
Documentation Changes..................................................................................................42
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 3
Specifcation Update January 2012
Page 4

4 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specifcation Update January 2012
Page 5

Revision History
Version Description Date
-001 Initial release January 2008
-002 Added Erratum AAA52 February 1, 2008
-003
-004
-005 Added Errata AAA58-AAA60 July 2008
-006 Added Errata AAA61-AAA62 August 2008
-007
-008 Updated Component Identification section with L3360 processor info February 2009
-009 Updated Component Identification section with X3380 processor info March 2, 2009
-010 Updated Erratum AAA1 March 11, 2009
-011
Added Errata AAA53-AAA54
Updated Erratum AAA18
Added Errata AAA55-AAA57
Added Spec Clarification AAA1
Added Errata AAA63-AAA75
Updated Erratum table with M0/R0/E0 info
Updated Component Information Table
Added Erratum AAA76
Added Erratum AAA77
February 13, 2008
May 2008
January 2009
January 2012
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 5
Specification Update January 2012
Page 6
Preface
This document is an update to the specifications contained in the documents listed in
the following Affected Documents/Related Documents table. It is a compilation of
device and document errata and specification clarifications and changes, and is
intended for hardware system manufacturers and for software developers of
applications, operating system, and tools.
Information types defined in the Nomenclature section of this document are
consolidated into this update document and are no longer published in other
documents. This document may also contain information that has not been previously
published.
Affected Documents
®
Intel
Xeon® Processor 3300 Series Datasheet 319005
Related Documents
®
Intel
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual Volume 1:
Basic Architecture
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual Volume 2A:
Intel
Instruction Set Reference Manual A–M
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual Volume 2B:
Intel
Instruction Set Reference Manual, N–Z
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual Volume 3A:
Intel
System Programming Guide
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual Volume 3B:
Intel
System Programming Guide
Document Title Document Number
Document Title Document Location
http://www.intel.com/products/
processor/manuals/index.htm
Nomenclature
S-Spec Number is a five-digit code used to identify products. Products are
differentiated by their unique characteristics (for example, core speed, L2 cache size,
package type, and so forth) as described in the processor identification information
table. Care should be taken to read all notes associated with each S-Spec number
Errata are design defects or errors. Errata may cause the processor’s behavior to
deviate from published specifications. Hardware and software designed to be used with
any given stepping must assume that all errata documented for that stepping are
present on all devices.
Specification Changes are modifications to the current published specifications.
These changes will be incorporated in the next release of the specifications.
Specification Clarifications describe a specification in greater detail or further
highlight a specification’s impact to a complex design situation. These clarifications will
be incorporated in the next release of the specifications.
6 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 7

Documentation Changes include typos, errors, or omissions from the current
published specifications. These changes will be incorporated in the next release of the
specifications.
Note: Errata remain in the specification update throughout the product’s life cycle, or until a
particular stepping is no longer commercially available. Under these circumstances,
errata removed from the specification update are archived and available upon request.
Specification changes, specification clarifications and documentation changes are
removed from the specification update when the appropriate changes are made to the
appropriate product specification or user documentation (datasheets, manuals, and so
forth).
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 7
Specification Update January 2012
Page 8

Summary Tables of Changes
The following table indicates the Specification Changes, Errata, Specification
Clarifications or Documentation Changes, which apply to the listed MCH steppings.
Intel intends to fix some of the errata in a future stepping of the component, and to
account for the other outstanding issues through documentation or Specification
Changes as noted. This table uses the following notations:
Codes Used in Summary Table
Stepping
X: Erratum, Specification Change or Clarification that
(No mark) or (Blank Box): This erratum is fixed in listed stepping or specification
Status
Doc: Document change or update that will be implemented.
Plan Fix: This erratum may be fixed in a future stepping of the
Fixed: This erratum has been previously fixed.
No Fix: There are no plans to fix this erratum.
Row
Shaded: This item is either new or modified from the previous version of the
Item Numbering
Each Specification Update item is prefixed with a capital letter to distinguish the
product. The key below details the letters that are used in Intel’s microprocessor
specification updates:
applies to this stepping.
change does not apply to listed stepping.
product.
document.
A = Intel® Xeon® processor 7000 sequence
C = Intel® Celeron® processor
D = Intel® Xeon® processor 2.80 GHz
E = Intel® Pentium® III processor
F = Intel® Pentium® processor Extreme Edition and Intel® Pentium® D
processor
I = Intel® Xeon® processor 5000 series
J = 64-bit Intel® Xeon® processor MP with 1 MB L2 cache
K = Mobile Intel® Pentium® III processor
8 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 9

L = Intel® Celeron® D processor
M = Mobile Intel® Celeron® processor
N = Intel® Pentium® 4 processor
O = Intel® Xeon® processor MP
P = Intel ® Xeon® processor
Q = Mobile Intel® Pentium® 4 processor supporting Hyper-Th reading technology
on 90-nm process technology
R = Intel® Pentium® 4 processor on 90 nm process
S = 64-bit Intel® Xeon® processor with 800 MHz system bus (1 MB and 2 MB L2
cache versions)
T = Mobile Intel® Pentium® 4 processor-M
U = 64-bit Intel® Xeon® processor MP with up to 8MB L3 cache
V = Mobile Intel® Celeron® processor on .13 micron process in Micro-FCPGA
package
W= Intel® Celeron® M processor
X = Intel® Pentium® M processor on 90nm process with 2-MB L2 cache and
Intel® processor A100 and A110 with 512-KB L2 cache
Y = Intel® Pentium® M processor
Z = Mobile Intel® Pentium® 4 processor with 533 MHz system bus
AA = Intel® Pentium® D processor 900 sequence and Intel® Pentium® processor
Extreme Edition 955, 965
AB = Intel® Pentium® 4 processor 6x1 sequence
AC = Intel® Celeron® processor in 478 pin package
AD = Intel® Celeron® D processor on 65 nm processor
AE = Intel® Core™ Duo processor and Intel® Core™ Solo processor on 65 nm
process
AF = Intel® Xeon® processor LV
AG = Intel® Xeon® processor 5100 series
AH = Intel® Core™ 2 Duo/Solo processor for Intel® Centrino® Duo processor
technology
AI = Intel® Core™ 2 Extreme processor X6800 and Intel® Core™ 2 Duo desktop
processor E6000 and E4000 sequence
AJ = Intel® Xeon® processor 5300 series
AK = Intel® Core™2 Extreme quad-core processor QX6000 sequence and Intel®
Core™ 2 Quad processor Q6000 sequence
AL = Intel® Xeon® processor 7100 series
AM= Intel® Celeron® processor 400 sequence
AN = Intel® Pentium® dual-core processor
AO = Intel® Xeon® processor 3200 series
AP = Intel® Xeon® processor 3000 series
AQ = Intel® Pentium® dual-core desktop processor E2000 sequence
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 9
Specification Update January 2012
Page 10
AR = Intel® Celeron® processor 500 series
AS = Intel® Xeon® processor 7200, 7300 series
AT = Intel® Celeron® processor 200 series
AV = Intel® Core™ 2 Extreme Processor QX9650 Intel® Core™ 2 Extreme
Processor QX9650 and Intel® Core™ 2 Quad Processor Q9000 Series
AW = Intel® Core™ 2 Duo desktop processor E8000 and E7000 series
AX = Intel® Xeon® processor 5400 series
AY = Intel® Xeon® processor 5200 series
AAA = Intel® Xeon® processor 3300 series
AAB = Intel® Xeon® processor 3100 series
AAC= Intel® Celeron® dual-core processor E1000 series
The Specification Updates for the Pentium® processor, Pentium® Pro processor, and
other Intel products do not use this convention.
Table 1. Errata (Sheet 1 of 4)
NO C0 M0 C1 M1 E0 R0 Plan ERRATA
AAA1 XX X X X X No Fix
AAA2 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA3 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA4 X X X X X X No Fix Non-Temporal Data Store May be Observed in Wrong Program Order
AAA5 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA6 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA7 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA8 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA9 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA10XXX XXXNo FixPerformance Monitoring Event MISALIGN_MEM_REF May Over Count
AAA11XXX XXXNo FixThe Processor May Report a #TS Instead of a #GP Fault
AAA12XXX XXXNo FixCode Segment limit violation may occur on 4 Gigabyte limit check
AAA13XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA14XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA15XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA16XXX XXXNo Fix
EFLAGS Discrepancy on a Page Fault After a Multiprocessor TLB
Shootdown
EFLAGS Discrepancy on Page Fault After a Translation Change
INVLPG Operation for Large (2M/4M) Pages May be Incomplete
Under Certain Conditions
Store to WT Memory Data May be Seen in Wrong Order by Two
Subsequent Loads
Page Access Bit May be Set Prior to Signaling a Code Segment Limit
Fault
Updating Code Page Directory Attributes without TLB Invalidation
May Result in Improper Handling of Code #PF
Storage of PEBS Record Delayed Following Execution of MOV SS or
STI
Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX May Not
Count Some Transitions
A REP STOS/MOVS to a MONITOR/MWAIT Address Range May
Prevent Triggering of the Monitoring Hardware
A Write to an APIC Register Sometimes May Appear to Have Not
Occurred
Last Branch Records (LBR) Updates May be Incorrect after a Task
Switch
REP MOVS/STOS Executing with Fast Strings Enabled and Crossing
Page Boundaries with Inconsistent Memory Types may use an
Incorrect Data Size or Lead to Memory-Ordering Violations.
Upper 32 bits of ‘From’ Address Reported thr ough B T Ms or B TSs May
be Incorrect
10 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 11
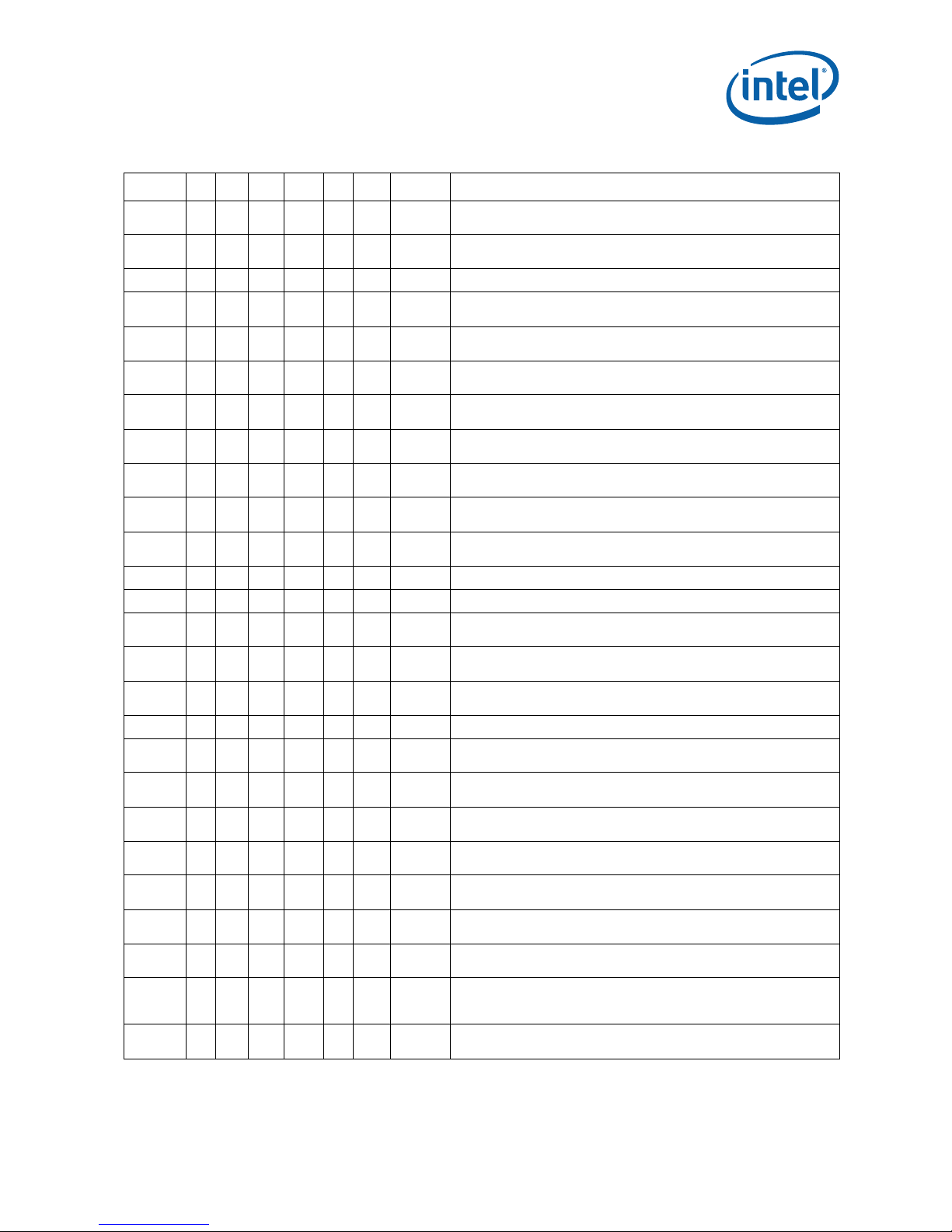
Table 1. Errata (Sheet 2 of 4)
NO C0 M0 C1 M1 E0 R0 Plan ERRATA
AAA17 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA18 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA19 X X X X X X No Fix Store Ordering May be Incorrect between WC and WP Memory Types
AAA20 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA21 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA22 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA23 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA24 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA25 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA26 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA27 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA28 X X X X X X No Fix INIT Does Not Clear Global Entries in the TLB
AAA29 X X X X X X No Fix Split Locked Stores May not Trigger the Monitoring Hardware
AAA30 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA31 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA32 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA33 X X X X X X No Fix An Asynchronous MCE During a Far Transfer May Corrupt ESP
AAA34 X X X X X X Plan Fix
AAA35 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA36 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA37 X X X X Fixed
AAA38 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA39 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA40 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA41 X X X X Fixed
AAA42 X X X X X X No Fix
Address Reported by Machine-Check Architecture (MCA) on Singlebit L2 ECC Errors May be Incorrect
Code Segment Limit/Canonical Faults on RSM May be Serviced
before Higher Priority Interrupts/Exceptions
EFLAGS, CR0, CR4 and the EXF4 Signal May be Incorrect after
Shutdown
Premature Execution of a Load Operation Prior to Exception Handler
Invocation
Performance Monitoring Events for Retired Instructions (C0H) May
Not Be Accurate
Returning to Real Mode from SMM with EFLAGS.VM Set May Result in
Unpredictable System Behavior
CMPSB, LODSB, or SCASB in 64-bit Mode with Count Greater or
Equal to 248 May Terminate Early
Writing the Local Vector Table (LVT) when an Interrupt is Pending
May Cause an Unexpected Interrupt
Pending x87 FPU Exceptions (#MF) Following STI May Be Serviced
Before Higher Priority Interrupts
VERW/VERR/LSL/LAR Instructions May Unexpectedly Update the
Last Exception Record (LER ) MSR
Programming the Digital Thermal Sensor (D TS) Threshold May Cause
Unexpected Thermal Interrupts
Writing Shared Unaligned Data that Crosses a Cache Line without
Proper Semaphores or Barriers May Expose a Memory Ordering Issue
General Protection (#GP) Fault May Not Be Signaled on Data
Segment Limit Violation above 4-G Limit
CPUID Reports Architectural Performance Monitoring Version 2 is
Supported, When Only Version 1 Capabilities are Available
B0-B3 Bits in DR6 May Not be Properly Cleared Af ter Code
Breakpoint
An xTPR Update Transaction Cycle, if Enabled, May be Issued to the
FSB after the Processor has Issued a Stop-Grant Special Cycle
Performance Monitoring Event IA32_FIXED_CTR2 May Not Function
Properly when Max Ratio is a Non-Integer Core-to-Bus Ratio
Instruction Fetch May Cause a Liv elock During Snoop s of the L1 Data
Cache
Use of Memory Aliasing with Inconsistent Memory T yp e may Cause a
System Hang or a Machine Check Exception
A WB Store Following a REP STOS/MOVS or FXSAVE May Lead to
Memory-Ordering Violations
VM Exit with Exit Reason “TPR Below Th reshold” Can Cause the
Blocking by MOV/POP SS and Blocking by STI Bits to be Cleared in
the Guest Interruptibility-State Field
Using Memory Type Aliasing with cacheable and WC Memory Types
May Lead to Memory Ordering Violations
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 11
Specification Update January 2012
Page 12
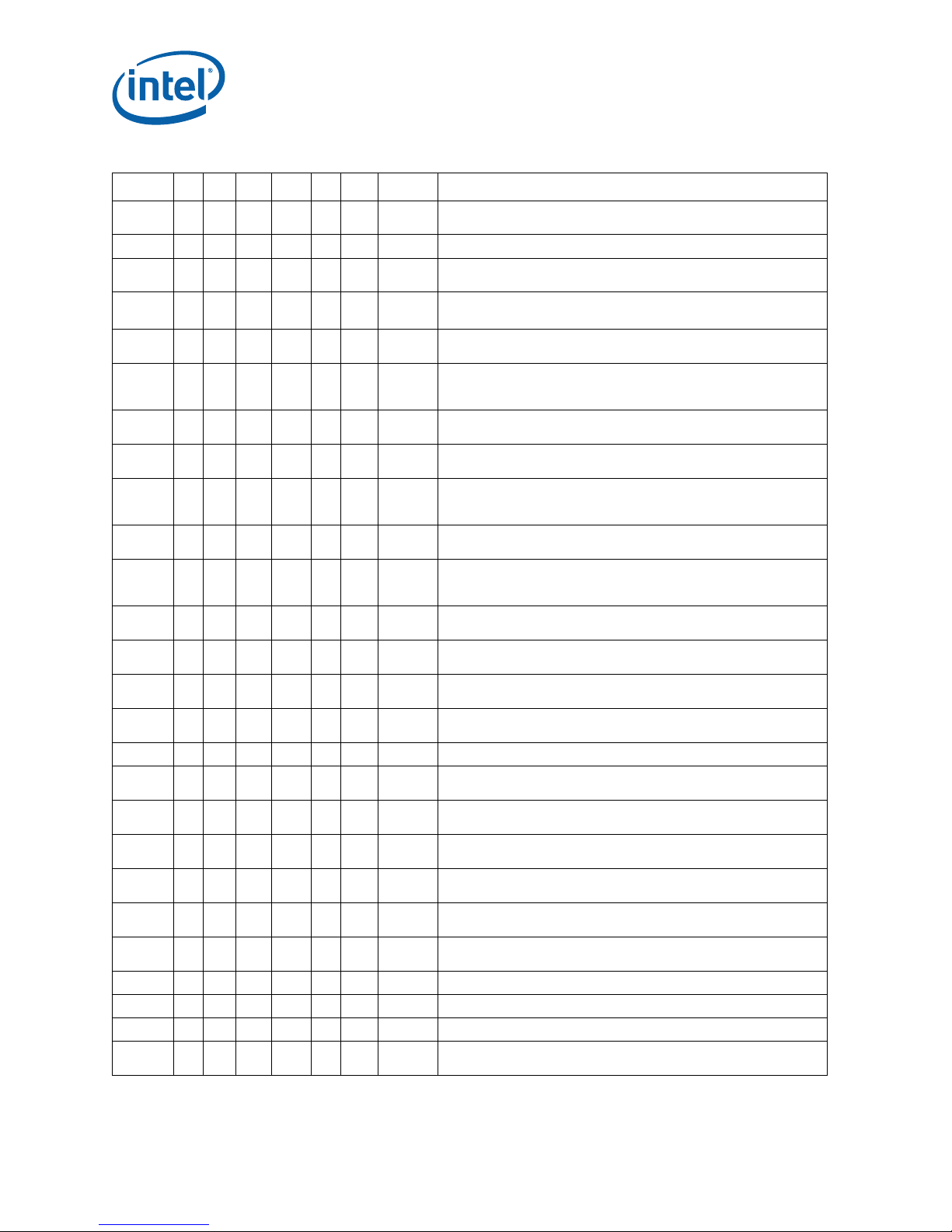
Table 1. Errata (Sheet 3 of 4)
NO C0 M0 C1 M1 E0 R0 Plan ERRATA
AAA43XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA44 X X X X Fixed NMIs May Not Be Blocked by a VM-Entry Failure
AAA45 X X X X Fixed
AAA46 X X X X Fixed
AAA47 X X X X Fixed
AAA48XXX XXXPlan Fix
AAA49 X X X X Fixed
AAA50XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA51XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA52XXX XXXPlan Fix
AAA53XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA54XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA55XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA56XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA57XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA58XXX XXXPlan FixPSI# Signal Asserted During Reset
AAA59XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA60XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA61XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA62XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA63XXX XXXNo Fix
AAA64 X X No Fix
AAA65 X X No Fix VM Entry May Use Wrong Address to Access Virtual-APIC Page
AAA66 X X No Fix XRSTORE Instruction May Cause Extra Memory Reads
AAA67 X X Plan Fix CPUID Instruction May Return Incorrect Brand String
AAA68 X X No Fix
VM Exit Caused by a SIPI Results in Zero to be Saved to the Guest
RIP Field in the VMCS
Partial Streaming Load Instruction Sequence May Cause the
Processor to Hang
Self/Cross Modifying Code May Not be Detected or May Cause a
Machine Check Exception
Data TLB Eviction Condition in the Middle of a Cacheline Split Load
Operation May Cause the Processor to Hang
Update of Read/Write (R/W) or User/Super visor (U/S) or Presen t (P)
Bits without TLB Shootdown May Cause Unexpected Processor
Behavior
RSM Instruction Execution under Certain Conditions May Cause
Processor Hang or Unexpected Instruction Execution Results
Benign Exception after a Double Fault May Not Cause a Triple Fault
Shutdown
LER MSRs May be Incorrectly UpdatedThe LER (Last Exception
Record) MSRs, MSR_LER_FROM_LIP (1DDH) and MSR_LER_TO_LIP
(1DEH) may contain incorrect values after any of the following:
Short Nested Loops That Span Multiple 16-Byte Boundaries May
Cause a Machine Check Exception or a System Hang
An Enabled Debug Breakpoint or Single Step Trap May Be T aken after
MOV SS/POP SS Instruction if it is Followed by an Instruction That
Signals a Floating Point Exception
IA32_MC1_STATUS MSR Bit[60] Does Not Reflect Machine Check
Error Reporting Enable Correctly
A VM Exit Due to a Fault While Delivering a Software Interrupt May
Save Incorrect Data into the VMCS
A VM Exit Occurring in IA-32e Mode May Not Produce a VMX Abort
When Expected
IRET under Certain Conditions May Cause an Unexpected Alignment
Check Exception
Thermal Interrupts are Dropped During and While Exiting Deep
Power Down State
VM Entry May Fail When Attempting to Set
IA32_DEBUGCTL.FREEZE_WHILE_SMM_EN
Corruption of CS Segment Register During RSM While Transitioning
From Real Mode to Protected Mode
LBR, BTS, BTM May Report a Wrong Address when an Exception/
Interrupt Occurs in 64-bit Mode
Memory Ordering Violation With Stores/Loads Crossing a Cacheline
Boundary
Processor May Hold-off / Delay a PECI Transaction Longer than
Specified by the PECI Protocol
Global Instruction TLB Entries May Not be Invalidat ed on a VM Exit or
VM Entry
12 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 13
Table 1. Errata (Sheet 4 of 4)
NO C0 M0 C1 M1 E0 R0 Plan ERRATA
AAA69 X X No Fix
AAA70 X X No Fix
AAA71 X X No Fix INIT Incorrectly Resets IA32_LSTAR MSR
AAA72 X X No Fix
AAA73 X X No Fix
AAA74 X X No Fix Store Ordering Violation When Using XSAVE
AAA75 X X Plan Fix
AAA76 X X X X X X No Fix
AAA77 X X X X X X No Fix Intel® Trusted Execution Technology ACM Revocation
Number SPECIFICATION CHANGES
- There are no Specification Changes in this Specification Update revision.
Number SPECIFICATION CLARIFICATIONS
- There are no Specification Clarifications in this Specification Update revision.
When Intel® Deep Power-Down State is Being Used,
IA32_FIXED_CTR2 May Return Incorrect Cycle Counts
Enabling PECI via the PECI_CTL MSR Does Not Enable PECI and May
Corrupt the CPUID Feature Flags
The XRSTOR Instruction May Fail to Cause a General-Protection
Exception
The XSAVE Instruction May Erroneously Set Reserved Bits in the
XSTATE_BV Field
Unsynchronized Cross-Modifying Code Operations Can Cause
Unexpected Instruction Execution Results
A 64-bit Register IP-relative Instruction May Return Unexpected
Results
Number DOCUMENTATION CHANGES
- There are no Documentation Changes in this Specification Update revision.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 13
Specification Update January 2012
Page 14

Identification Information
ATPO
S/N
INTEL ©'06 3300
INTEL® XEON®
SLxxx [COO]
2.83GHZ/2M/1333/05
[FPO]
M
e
4
Figure 1. Processor Package Example
14 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 15

Component Identification
Information
The Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series can be identified by the following values:
Reserved
31:28 27:20 19:16 15:14 13:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
Extended
Family
00000000b 0001b 00b 0110b 0111b XXXXb
1
Extended
2
Model
Reserved
Processor
3
Type
Family
Code
4
Model
Number
5
Stepping
6
ID
When EAX is initialized to a value of 1, the CPUID instruction returns the Extended
Family, Extended Model, Type, Family, Model and Stepping value in the EAX register.
Note that the EDX processor signature value after reset is equivalent to the processor
signature output value in the EAX register.
Notes:
1. The Extended Family, bits [27:20] are used in conjunction with the Family Code,
specified in bits [11:8], to indicate whether the processor belongs to the Intel386,
Intel486, Pentium, Pentium Pro, Pentium 4, Intel® Core
TM
, or Enhanced Intel®
CoreTM processor family.
2. The Extended Model, bits [19:16] in conjunction with the Model Number, specified
in bits [7:4], are used to identify the model of the processor within the processor’s
family.
3. The Processor Type , spec ified in bits [1 3:12] indicates whether the processor is an
original OEM processor or a Dual CPU Socket system.
4. The Family Code corresponds to bits [11:8] of the EDX register after RESET, bits
[11:8] of the EAX register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the
EAX register, and the generation field of the Device ID register accessible through
Boundary Scan.
5. The Model Number corresponds to bits [7:4] of the EDX register after RESET, bits
[7:4] of the EAX register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX
register, and the model field of the Device ID register accessible through Boundary
Scan.
6. The Stepping ID in bits [3:0] indicates the revision number of that model. See
Table 2, “Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series Identification Information” for the
processor stepping ID number in the CPUID information.
Cache and TLB descriptor parameters are provided in the EAX, EBX, ECX and EDX
registers after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 2 in the EAX register. Refer to
the Intel Processor Identification and the CPUID Instruction Application Note (AP-485)
for further information on the CPUID instruction.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 15
Specification Update January 2012
Page 16

Table 2. Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series Identification Information
S-Spec
Core
Stepping
SLAN5 C0
SLAN7 C0
SLAWZ C1
SLAX2 C1
SLAWF M1
SLB8Y E0
SLB8X E0
SLB8Z E0
SLGPG E0
SLGPF E0
SLB69 R0
SLB6C R0
L2 Cache
Size
(bytes)
12 MB
(2x6 MB)
12 MB
(2x6 MB)
12 MB
(2x6 MB)
12 MB
(2x6 MB)
6 MB
(2x3 MB)
12 MB
(2x6 MB)
12 MB
(2x6 MB)
12 MB
(2x6 MB)
12 MB
(2x6 MB)
12 MB
(2x6 MB)
6 MB
(2x3 MB)
6 MB
(2x3 MB)
Processor
Signature
Processor
Number
10676h X3360
10676h X3350
10676h X3360
10676h X3350
10676h X3320
1067Ah X3350
1067Ah X3360
1067Ah X3370
1067Ah X3380
1067Ah L3360
1067Ah X3320
1067Ah X3330
Speed Core/
Bus
2.83 GHz /
1333 MHz
2.66 GHz /
1333 MHz
2.83 GHz /
1333 MHz
2.66 GHz /
1333 MHz
2.50 GHz /
1333 MHz
2.66 GHz /
1333 MHz
2.83 GHz /
1333 MHz
3.00 GHz / 1333
MHz
3.16 GHz /
1333 MHz
2.83 GHz /
1333 MHz
2.50 GHz /
1333 MHz
2.66 GHz /
1333 MHz
Package Notes
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
775-land LGA
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11, 12, 13
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11, 12, 13
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11, 12, 13
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11, 12, 13
2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,
10, 11, 12, 13, 14
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11, 12, 13
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10, 11, 12, 13
Notes:
1. These processors support the 775_VR_CONFIG_05A specifications.
2. These parts support Intel
3. These parts support Intel
4. These parts support Execute Disable Bit Feature.
5. These parts have PROCHOT# enabled.
6. These parts have THERMTRIP# enabled.
7. These parts support Thermal Monitor 2 (TM2) feature.
8. These parts have PECI enabled.
9. These parts have Enhanced Intel SpeedStep
10. T he se parts have Extended HALT State (C1E) enabled.
11. These parts have Extended Stop Grant State (C 2E) enabled.
12. These parts have Deep Sleep State (C3E) enabled.
13. T he se parts have Deeper Sleep State (C4E) enabled.
®
64.
®
Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT).
®
Technology enabled.
14. These processors support the 775_VR_CONFIG_06A specifications.
16 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 17

Errata
AAA1. EFLAGS Discrepancy on Page Fault After a Translation Change
Problem: This erratum is regarding the case where paging structures are modified to change a
linear address from writable to non-writable without software performing an
appropriate TLB invalidation. When a subsequent access to that address by a specific
instruction (ADD, AND, BTC, B TR, B TS, CMPXCHG, DEC, INC, NEG, NOT, OR, ROL/ROR,
SAL/SAR/SHL/SHR, SHLD, SHRD, SUB , XOR, an d XADD) causes a page fault, the v alue
saved for EFLAGS may incorrectly contain the arithmetic flag values that the EFLAGS
register would have held had the instruction completed without fault. This can occur
even if the fault causes a VM exit or if its delivery causes a nested fault.
Implication: None identified. Although the EFLAGS value sav ed may contain incorrect arithmetic flag
values, Intel has not identified software that is affected by this erratum. This erratum
will have no further effects once the original instruction is restarted because the
instruction will produce the same results as if it had initially completed without a page
fault.
Workaround: If the page fault handler inspects the arithmetic portion of the saved EFLAGS value,
then system software should perform a synchronized paging structure modification and
TLB invalidation.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA2. INVLPG Operation for Large (2M/4M) Pages May be Incomplete Under
Certain Conditions
Problem: The INVLPG instruction may not completely invalidate Translation Look-aside Buffer
(TLB) entries for large pages (2M/4M) when both of the following conditions exist:
• Address range of the page being invalidated spans several Memory Type Range
Registers (MTRRs) with different memory types specified
• INVLPG operation is preceded by a Page Assist Event (Page Fault [#PF] or an
access that results in either A or D bits being set in a Page Table Entry [PTE])
Implication: Stale translations may remain valid in TLB after a PTE update resulting in unpredictable
system behavior. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available
software.
Workaround: Software should ensure that the memory type specified in the MTRRs is the same for
the entire address range of the large page.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA3. Store to WT Memory Data May be Seen in Wrong Order by Two
Subsequent Loads
Problem: When data of Store to WT memory is used by two subsequent loads of one thread and
another thread performs cacheable write to the same address the first load may get the
data from external memory or L2 written by another core, while the second load will
get the data straight from the WT Store.
Implication: Software that uses WB to WT memory aliasing may violate proper store ordering.
Workaround: Do not use WB to WT aliasing.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 17
Specification Update January 2012
Page 18

AAA4. Non-Temporal Data Store May be Observed in Wrong Program Order
Problem: When non-temporal data is accessed by multiple read operations in one thread while
another thread performs a cacheable write operation to the same address, the data
stored may be observed in wrong program order (that is, later load operations may
read older data).
Implication: Software that uses non-temporal data without proper serialization before accessing the
non-temporal data may observe data in wrong program order.
Workaround: Software that conforms to the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer's
Manual, Volume 3A, section “Buffering of Write Combining Memory Locations” will
operate correctly.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA5. Page Access Bit May be Set Prior to Signaling a Code Segment Limit
Fault
Problem: If code segment limit is set close to the end of a code page, then due to this erratum
the memory page Access bit (A bit) may be set for the subsequent page prior to
general protection fault on code segment limit.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, a non-accessed page which is present in memory and
follows a page that contains the code segment limit may be tagged as accessed.
Workaround: Erratum can be avoided by placing a guard page (non-present or non-executable page)
as the last page of the segment or after the page that includes the code segment limit.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA6. Updating Code Page Directory Attributes without TLB Invalidation May
Result in Improper Handling of Code #PF
Problem: Code #PF (Page Fault exception) is normally handled in lower priority order relative to
both code #DB (Debug Exception) and code Segment Limit Violation #GP (General
Protection Fault). Due to this erratum, code #PF may be handled incorrectly, if all of
the following conditions are met:
• A PDE (Page Directory Entry) is modified without invalidating the corresponding
TLB (Translation Look-aside Buffer) entry
• Code execution transitions to a different code page such that both
— The target linear address corresponds to the modified PDE
— The PTE (Page T able Entry) for the target linear address has an A (Accessed) bit
that is clear
• One of the following simultaneous exception conditions is present following the
code transition
— Code #DB and code #PF
— Code Segment Limit Violation #GP and code #PF
Implication: Software may observe either incorrect processing of code #PF before code Segment
Limit Violation #GP or processing of code #PF in lieu of code #DB.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA7. Storage of PEBS Record Delayed Following Execution of MOV SS or STI
Problem: When a performance monitoring counter is configured for PEBS (Precise Event Based
Sampling), overflow of the counter results in storage of a PEBS record in the PEBS
18 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 19

buffer. The information in the PEBS record represents the state of the next instruction
to be executed following the counter overflow. Due to this erratum, if the counter
overflow occurs after executio n of eithe r MOV SS or STI, storage of the PEBS record is
delayed by one instruction.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, software may observe storage of the PEBS record being
delayed by one instruction following execution of MOV SS or STI. The state information
in the PEBS record will also reflect the one instruction delay.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA8. Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX May Not
Count Some Transitions
Problem: Performance Monitor Event FP_MMX_TRANS_T O_MMX (Event CCH, Umask 01H) coun ts
transitions from x87 Floating Point (FP) to MMX™ instructions. Due to this erratum, if
only a small number of MMX instructions (including EMMS) are executed immediately
after the last FP instruction, a FP to MMX transition may not be counted.
Implication: The count value for Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX may be
lower than expected. The degree of undercounting is dependent on the occurrences of
the erratum condition while the counter is active. Intel has not observed this erratum
with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA9. A REP STOS/MOVS to a MONITOR/MWAIT Address Range May Prevent
Triggering of the Monitoring Hardware
Problem: The MONITOR instruction is used to arm the address monitoring hardware for the
subsequent MWAIT instruction. The hardware is triggered on subsequent memory
store operations to the monitored address range. Due to this erratum, REP STOS/
MOVS fast string operations to the monitored address range may prevent the actual
triggering store to be propagated to the monitoring hardware.
Implication: A logical processor executing an MWAIT instruction may not immediately continue
program execution if a REP STOS/MOVS targets the monitored address range.
Workaround: Software can avoid this erratum by not using REP STOS/MOVS store operations within
the monitored address range.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA10. Performance Monitoring Event MISALIGN_MEM_REF May Over Count
Problem: Performance monitoring event MISALIGN_MEM_REF (05H) is used to count the number
of memory accesses that cross an 8-byte boundary and are blocked until retirement.
Due to this erratum, the performance monitoring event MISALIGN_MEM_REF also
counts other memory accesses.
Implication: The performance monitoring event MISALIGN_MEM_REF may over count. The extent of
the over counting depends on the number of memory accesses retiring while the
counter is active.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 19
Specification Update January 2012
Page 20

AAA11. The Processor May Report a #TS Instead of a #GP Fault
Problem: A jump to a busy TSS (Task-State Segment) may cause a #TS (invalid TSS exception)
instead of a #GP fault (general protection exception).
Implication: Operation systems that access a busy TSS may get invalid TSS fault instead of a #GP
fault. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA12. Code Segment limit violation may occur on 4 Gigabyte limit check
Problem: Code Segment limit violation may occur on 4 Gigabyte limit check when the code
streamwraps around in a way that one instruction ends at the last byte of the segment
and the next instruction begins at 0x0.
Implication: This is a rare condition that may result in a system hang. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software, or system.
Workaround: Avoid code that wraps around segment limit.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA13. A Write to an APIC Register Sometimes May Appear to Have Not
Occurred
Problem: With respect to the retirement of instructions, stores to the uncacheable memory-
based APIC register space are handled in a non-synchronized way. For example if an
instruction that masks the interrupt flag, for example, CLI is executed soon after an
uncacheable write to the Task Priority Register (TPR) that lowers the APIC priority, the
interrupt masking operation may take effect before the actual priority has been
lowered. This may cause interrupts whose priority is lower than the initial TPR, but
higher than the final TPR, to not be serviced until the interrupt enabled flag is finally
set, that is, by STI instruction. Interrupts will remain pending and are not lost.
Implication: In this example the processor may allow interrupts to be accepted but may delay their
service.
Workaround: This non-synchronization can be avoided by issuing an APIC register read after the
APIC register write. This will force the store to the APIC register before any subsequent
instructions are executed. No commercial operating system is known to be impacted by
this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA14. Last Branch Records (LBR) Updates May be Incorrect after a Task
Switch
Problem: A Task-State Segment (TSS) task switch may incorrectly set the LBR_FROM value to
the LBR_TO value.
Implication: The LBR_FROM will have the incorrect address of the Branch Instruction.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA15. REP MOVS/STOS Executing with Fast Strings Enabled and Crossing
Page Boundaries with Inconsistent Memory Types may use an
Incorrect Data Size or Lead to Memory-Ordering Violations.
Problem: Under certain conditions as described in the Software Developers Manual section “Out-
of-Order Stores For String Operations in Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6 Family
20 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 21

Processors” the processor performs REP MOVS or REP STOS as fast strings. Due to this
erratum fast string REP MOVS/REP STOS instructions that cross page boundaries from
WB/WC memory types to UC/WP/WT memory types, may start using an incorrect data
size or may observe memory ordering violations.
Implication: Upon crossing the page boundary the following may occur, dependent on the new page
memory type:
• UC the data size of each write will now always be 8 bytes, as opposed to the
original data size.
• WP the data size of each write will now always be 8 bytes, as opposed to the
original data size and there may be a memory ordering violation.
• WT there may be a memory ordering violation.
Workaround: Software should avoid crossing page boundaries from WB or WC memory type to UC,
WP or WT memory type within a single REP MOVS or REP STOS instruction that will
execute with fast strings enabled.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA16. Upper 32 bits of ‘From’ Address Reported through BTMs or BTSs May
be Incorrect
Problem: When a far transfer switches the processor from 32-bit mode to IA-32e mode, the
upper 32 bits of the ‘From’ (source) addresses reported through the BTMs (Branch
Trace Messages) or BTSs (Branch Trace Stores) may be incorrect.
Implication: The upper 32 bits of the ‘From’ address debug information reported through BTMs or
BTSs may be incorrect during this transition.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA17. Address Reported by Machine-Check Architecture (MCA) on Single-bit
L2 ECC Errors May be Incorrect
Problem: When correctable Single-bit ECC errors occur in the L2 cache, the address is logged in
the MCA address register (MCi_ADDR). Under some scenarios, the address reported
may be incorrect.
Implication: Software should not rely on the value reported in MCi_ADDR, for Single-bit L2 ECC
errors.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA18. Code Segment Limit/Canonical Faults on RSM May be Serviced before
Higher Priority Interrupts/Exceptions
Problem: Normally, when the processor encounters a Segment Limit or Canonical Fault due to
code execution, a #GP (General Protection Exception) fault is generated after all higher
priority Interrupts and exceptions are serviced. Due to this erratum, if RSM (Resume
from System Management Mode) returns to execution flow that results in a Code
Segment Limit or Canonical Fault, the #GP fault may be serviced before a higher
priority Interrupt or Exception (for example, NMI (Non-Maskable Interrupt), Debug
break(#DB), Machine Check (#MC), and so forth).
Implication: Operating systems may observe a #GP fault being serviced before higher priority
Interrupts and Exceptions. Intel has not observed this erratum on any commercially
available software.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 21
Specification Update January 2012
Page 22

Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA19. Store Ordering May be Incorrect between WC and WP Memory Types
Problem: According to Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel Architecture Software Developer's Manual,
Volume 3A "Methods of Caching Available", WP (Write Protected) stores should drain
the WC (Write Combining) buffers in the same way as UC (Uncacheable) memory type
stores do. Due to this erratum, WP stores may not drain the WC buffers.
Implication: Memory ordering may be violated between WC and WP stores.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA20. EFLAGS, CR0, CR4 and the EXF4 Signal May be Incorrect after
Shutdown
Problem: When the processor is going into shutdown due to an RSM inconsistency failure,
EFLAGS, CR0 and CR4 may be incorrect. In addition the EXF4 signal may still be
asserted. This may be observed if the processor is taken out of shutdown by NMI#.
Implication: A processor that has been taken out of shutdown may have an incorrect EFLAGS, CR0
and CR4. In addition the EXF4 signal may still be asserted.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA21. Premature Execution of a Load Operation Prior to Exception Handler
Invocation
Problem: If any of the below circumstances occur, it is possible that the load portion of the
instruction will have executed before the exception handler is entered.
1. If an instruction that performs a memory load causes a code segment limit
violation.
2. If a waiting X87 floating-point (FP) instruction or MMX™ technology (MMX)
instruction that performs a memory load has a floating-point exception pending.
3. If an MMX or SSE/SSE2/SSE3/SSSE3 extensions (SSE) instruction that perfor ms a
memory load and has either CR0.EM=1 (Emulation bit set), or a floating-point Topof-Stack (FP TOS) not equal to 0, or a DNA exception pending.
Implication: In normal code execution where the target of the load operation is to write back
memory there is no impact from the load being prematurely executed, or from the
restart and subsequent re-execution of that instruction by the exception handler. If the
target of the load is to uncached memory that has a system side-effect, restarting the
instruction may cause unexpected system behavior due to the repetition of the sideeffect. Particularly, while CR0.TS [bit 3] is set, a MOVD/MOVQ with MMX/XMM register
operands may issue a memory load before getting the DNA exception.
Workaround: Code which performs loads from memory that has side-effects can effectively
workaround this behavior by using simple integer-based load instructions when
accessing side-effect memory and by ensuring that all code is written such that a code
segment limit violation cannot occur as a part of reading from side-effect memory.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
22 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 23

AAA22. Performance Monitoring Events for Retired Instructions (C0H) May
Not Be Accurate
Problem: The INST_RETIRED performance monitor may miscount retired instructions as follows:
• R epeat string and repeat I/O operations are not counted when a hardware interrupt
is received during or after the last iteration of the repeat flow.
• VMLAUNCH and VMRESUME instructions are not counted.
• HLT and MWAIT instructions are not counted. The following instructions, if
executed during HLT or MWAIT events, are also not counted:
a. RSM from a C-state SMI during an MWAIT instruction.
b. RSM from an SMI during a HLT instruction.
Implication: There may be a smaller than expected value in the INST_RETIRED performance
monitoring counter. The extent to which this value is smaller than expected is
determined by the frequency of the above cases.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA23. Returning to Real Mode from SMM with EFLAGS.VM Set May Result in
Unpredictable System Behavior
Problem: Returning back from SMM mode into real mode while EFLAGS.VM is set in SMRAM may
result in unpredictable system behavior.
Implication: If SMM software changes the values of the EFLAGS.VM in SMRAM, it may result in
unpredictable system behavior. Intel has not observed this behavior in commercially
available software.
Workaround: SMM software should not change the value of EFLAGS.VM in SMRAM.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA24. CMPSB, LODSB, or SCASB in 64-bit Mode with Count Greater or Equal
to 2
48
May Terminate Early
Problem: In 64-bit Mode CMPSB, LODSB, or SCASB executed with a repeat prefix and count
greater than or equal to 248 may terminate early . Early termination ma y result in one of
the following.
• The last iteration not being executed
• Signaling of a canonical limit fault (#GP) on the last iteration
Implication: While in 64-bit mode, with count greater or equal to 2
48
, repeat string operations
CMPSB, LODSB or SCASB may terminate without completing the last iteration. Intel
has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
48
Workaround: Do not use repeated string operations with RCX greater than or equal to 2
.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA25. Writing the Local Vector Table (LVT) when an Interrupt is Pending
May Cause an Unexpected Interrupt
Problem: If a local interrupt is pending when the LVT entry is written, an interrupt may be taken
on the new interrupt vector even if the mask bit is set.
Implication: An interrupt may immediately be generated with the new vector when a LVT entry is
written, even if the new LVT entry has the mask bit set. If there is no Interrupt
Service Routine (ISR) set up for that vector the system will GP fault. If the ISR does
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 23
Specification Update January 2012
Page 24

not do an End of Interrupt (EOI) the bit for the vector will be left set in the in-service
register and mask all interrupts at the same or lower priority.
Workaround: Any vector programmed into an LVT entry must have an ISR associated with it, even if
that vector was programmed as masked. This ISR routine must do an EOI to clear any
unexpected interrupts that may occur. The ISR associated with the spurious vector
does not generate an EOI, therefore the spurious vector should not be used when
writing the LVT.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA26. Pending x87 FPU Exceptions (#MF) Following STI May Be Serviced
Before Higher Priority Interrupts
Problem: Interrupts that are pending prior to the execution of the STI (Set Interrupt Flag)
instruction are normally serviced immediately after the instruction following the STI. An
exception to this is if the following instruction triggers a #MF. In this situation, the
interrupt should be serviced before the #MF. Because of this erratum, if following STI,
an instruction that triggers a #MF is executed while STPCLK#, Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep® Technology transitions or Thermal Monitor 1 events occur, the pending
#MF may be serviced before higher priority interrupts.
Implication: Software may observe #MF being serviced before higher priority interrupts.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA27. VERW/VERR/LSL/LAR Instructions May Unexpectedly Update the Last
Exception Record (LER) MSR
Problem: The LER MSR may be unexpectedly updated, if the resultant value of the Zero Flag (ZF)
is zero after executing the following instructions
1. VERR (ZF=0 indicates unsuccessful segment read verification)
2. VERW (ZF=0 indicates unsuccessful segment write verification)
3. LAR (ZF=0 indicates unsuccessful access rights load)
4. LSL (ZF=0 indicates unsuccessful segment limit load)
Implication: The value of the LER MSR may be inaccurate if VERW/VERR/LSL/LAR instructions are
executed after the occurrence of an exception.
Workaround: Software exception handlers that rely on the LER MSR value should read the LER MSR
before executing VERW/VERR/LSL/LAR instructions.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA28. INIT Does Not Clear Global Entries in the TLB
Problem: INIT may not flush a TLB entry when:
• The processor is in protected mode with paging enabled and the page global enable
flag is set (PGE bit of CR4 register)
• G bit for the page table entry is set
• TLB entry is present in TLB when INIT occurs
Implication: Software may encounter unexpected page fault or incorrect address translation due to
a TLB entry erroneously left in TLB after INIT.
24 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 25

Workaround: Write to CR3, CR4 (setting bits PSE, PGE or PAE) or CR0 (setting bits PG or PE)
registers before writing to memory early in BIOS code to clear all the global entries
from TLB.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA29. Split Locked Stores May not Trigger the Monitoring Hardware
Problem: Logical processors normally resume program execution following the MWAIT, when
another logical processor performs a write access to a WB cacheable address within the
address range used to perform the MONITOR operation. Due to this erratum, a logical
processor may not resume execution until the next targeted interrupt event or O/S
timer tick following a locked store that spans across cache lines within the monitored
address range.
Implication: The logical processor that executed the MWAIT instruction may not resume execution
until the next targeted interrupt event or O/S timer tick in the case where the
monitored address is written by a locked store which is split across cache lines.
Workaround: Do not use locked stores that span cache lines in the monitored address range.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA30. Programming the Digital Thermal Sensor (DTS) Threshold May Cause
Unexpected Thermal Interrupts
Problem: Software can enable DTS thermal interrupts by programming the thermal threshold
and setting the respective thermal interrupt enable bit. When programming D T S v alue,
the previous DTS threshold may be crossed. This will generate an unexpected thermal
interrupt.
Implication: Software may observe an unexpected thermal interrupt occur after reprogramming the
thermal threshold.
Workaround: In the ACPI/OS implement a workaround by temporarily disabling the DTS threshold
interrupt before updating the DTS threshold value.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA31. Writing Shared Unaligned Data that Crosses a Cache Line without
Proper Semaphores or Barriers May Expose a Memory Ordering Issue
Problem: Software which is written so that multiple agents can modify the same shared
unaligned memory location at the same time may experience a memory ordering issue
if multiple loads access this shared data shortly thereafter. Exposure to this problem
requires the use of a data write which spans a cache line boundary.
Implication: This erratum may cause loads to be observed out of order. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software or system.
Workaround: Software should ensure at least one of the following is true when modifying shared
data by multiple agents:
• The shared data is aligned
• Proper semaphores or barriers are used in order to prevent concurrent data
accesses.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 25
Specification Update January 2012
Page 26

AAA32. General Protection (#GP) Fault May Not Be Signaled on Data Segment
Limit Violation above 4-G Limit
Problem: In 32-bit mode, memory accesses to flat data segments (base = 00000000h) that
occur above the 4G limit (0ffffffffh) may not signal a #GP fault.
Implication: When such memory accesses occur in 32-bit mode, the system may not issue a #GP
fault.
Workaround: Software should ensure that memory accesses in 32-bit mode do not occur above the
4G limit (0ffffffffh).
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA33. An Asynchronous MCE During a Far Transfer May Corrupt ESP
Problem: If an asynchronous machine check occurs during an interrupt, call through gate, FAR
RET or IRET and in the presence of certain internal conditions, ESP may be corrupted.
Implication: If the MCE (Machine Check Exception) handler is called without a stack switch, then a
triple fault will occur due to the corrupted stack pointer, resulting in a processor
shutdown. If the MCE is called with a stack switch, for example, when the CPL (Current
Privilege Level) was changed or when going through an interrupt task gate, then the
corrupted ESP will be saved on the new stack or in the TSS (Task State Segment), and
will not be used.
Workaround: Use an interrupt task gate for the machine check handler.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA34. CPUID Reports Architectural Performance Monitoring Version 2 is
Supported, When Only Version 1 Capabilities are Available
Problem: CPUID leaf 0Ah reports the architectural performance monitoring version that is
available in EAX[7:0]. Due to this erratum CPUID reports the supported version as 2
instead of 1.
Implication: Software will observe an incorrect version number in CPUID.0Ah.EAX [7:0] in
comparison to which features are actually supported.
Workaround: Software should use the recommended enumeration mechanism described in the
Architectural Performance Monitoring section of the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures
Software Developer's Manual, Volume 3: System Programming Guide.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA35. B0-B3 Bits in DR6 May Not be Properly Cleared After Code Breakpoint
Problem: B0-B3 bits (breakpoint conditions detect flags, bits [3:0]) in DR6 may not be properly
cleared when the following sequence happens:
1. POP instruction to SS (Stack Segment) selector;
2. Next instruction is FP (Floating Point) that gets FP assist followed by code
breakpoint.
Implication: B0-B3 bits in DR6 may not be properly cleared.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
26 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 27

AAA36. An xTPR Update Transaction Cycle, if Enabled, May be Issued to the
FSB after the Processor has Issued a Stop-Grant Special Cycle
Problem: According to the FSB (Front Side Bus) protocol specification, no FSB cycles should be
issued by the processor once a Stop-Grant special cycle has been issued to the bus. If
xTPR update transactions are enabled by clearing the IA32_MISC_ENABLES[bit 23] at
the time of Stop-Clock assertion, an xTPR update transaction cycle may be issued to
the FSB after the processor has issued a Stop Grant Acknowledge transaction.
Implication: When this erratum occurs in systems using C-states C2 (Stop-Grant State) and higher
the result could be a system hang.
Workaround: BIOS must leave the xTPR update transactions disabled (default).
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA37. Performance Monitoring Event IA32_FIXED_CTR2 May Not Function
Properly when Max Ratio is a Non-Integer Core-to-Bus Ratio
Problem: Performance Counter IA32_FIXED_CTR2 (MSR 30BH) event counts CPU reference
clocks when the core is not in a halt state. This event is not affected by core frequency
changes (e.g., P states, TM2 transitions) but counts at the same frequency as the
Time-Stamp Counter IA32_TIME_STAMP_COUNTER (MSR 10H). Due to this erratum,
the IA32_FIXED_CTR2 will not function properly when the non-integer core-to-bus
ratio multiplier feature is used and when a non-zero value is written to IA32_
FIXED_CTR2. Non-integer core-to-bus ratio enables additional operating frequencies.
This feature can be detected by IA32_PLATFORM_ID (MSR 17H) bit [23].
Implication: The Performance Monitoring Event IA32_FIXED_CTR2 may result in an inaccurate
count when the non-integer core-to-bus multiplier feature is used.
Workaround: If writing to IA32_FIXED_CTR2 and using a non-integer core-to-bus ratio multiplier,
always write a zero.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA38. Instruction Fetch May Cause a Livelock During Snoops of the L1 Data
Cache
Problem: A livelock may be observed in rare conditions when instruction fetch causes multiple
level one data cache snoops.
Implication: Due to this erratum, a livelock may occur. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software.
Workaround: It is possible for BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA39. Use of Memory Aliasing with Inconsistent Memory Type may Cause a
System Hang or a Machine Check Exception
Problem: Software that implements memory aliasing by having more than one linear addresses
mapped to the same physical page with different cache types may cause the system to
hang or to report a machine check exception (MCE). This would occur if one of the
addresses is non-cacheable and used in a code segment and the other is a cacheable
address. If the cacheable address finds its way into the instruction cache, and the non-
cacheable address is fetched in the IFU, the processor may invalidate the non-
cacheable address from the fetch unit. Any micro-architectural event that causes
instruction restart will be expecting this instruction to still be in the fetch unit and lack
of it will cause a system hang or an MCE.
Implication: This erratum has not been observed with commercially available software.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 27
Specification Update January 2012
Page 28

Workaround: Although it is possible to have a single physical page mapped by two different linear
addresses with different memory types, Intel has strongly discouraged this practice as
it may lead to undefined results. Software that needs to implement memory aliasing
should manage the memory type consistency.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA40. A WB Store Following a REP STOS/MOVS or FXSAVE May Lead to
Memory-Ordering Violations
Problem: Under certain conditions, as described in the Software Developers Manual section "Out-
of-Order Stores For String Operations in Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6 Family
Processors", the processor may perform REP MOVS or REP STOS as write combining
stores (referred to as “fast strings”) for optimal performance. FXSAVE may also be
internally implemented using write combining stores. Due to this erratum, stores of a
WB (write back) memory type to a cache line previously written by a preceding fast
string/FXSAVE instruction may be observed before string/FXSAVE stores.
Implication: A write-back store may be observed before a previous string or FXSAVE related store.
Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: Software desiring strict ordering of string/FXSAVE operations relative to subsequent
write-back stores should add an MFENCE or SFENCE instruction between the string/
FXSAVE operation and following store-order sensitive code such as that used for
synchronization.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA41. VM Exit with Exit Reason “TPR Below Threshold” Can Cause the
Blocking by MOV/POP SS and Blocking by STI Bits to be Cleared in the
Guest Interruptibility-State Field
Problem: As specified in Section, “VM Exits Induced by the TPR Shadow”, in the Intel® 64 and
IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B, a VM exit occurs
immediately after any VM entry performed with the “use TPR shadow", "activate
secondary controls”, and “virtualize APIC accesses” VM-execution controls all set to 1
and with the value of the TPR shadow (bits 7:4 in byte 80H of the virtual-APIC page)
less than the TPR-threshold VM-execution control field. Due to this erratum, such a VM
exit will clear bit 0 (blocking by STI) and bit 1 (blocking by MOV/POP SS) of the
interruptibility-state field of the guest-state area of the VMCS (bit 0 - blocking by STI
and bit 1 - blocking by MOV/POP SS should be left unmodified).
Implication: Since the STI, MOV SS, and POP SS instructions cannot modify the TPR shadow, bits
1:0 of the interruptibility-state field will usually be zero before any VM entry meeting
the preconditions of this erratum; behavior is correct in this case. However, if VMM
software raises the value of the TPR -threshold VM-ex ecution control field above that of
the TPR shadow while either of those bits is 1, incorrect behavior may result. This may
lead to VMM software prematurely injecting an interrupt into a guest. Intel has not
observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: VMM software raising the value of the TPR-threshold VM-execution control field should
compare it to the TPR shadow. If the threshold value is higher, software should not
perform a VM entry; instead, it could perform the actions that it would normally take in
response to a VM exit with exit reason “TPR below threshold”.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
28 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 29

AAA42. Using Memory Type Aliasing with cacheable and WC Memory Types
May Lead to Memory Ordering Violations
Problem: Memory type aliasing occurs when a single physical page is mapped to two or more
different linear addresses, each with different memory types. Memory type aliasing
with a cacheable memory type and WC (write combining) may cause the processor to
perform incorrect operations leading to memory ordering violations for WC operations.
Implication: Software that uses aliasing between cacheable and WC memory types may observe
memory ordering errors within WC memory operations. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified. Intel does not support the use of cacheable and WC memory type
aliasing, and WC operations are defined as weakly ordered.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA43. VM Exit Caused by a SIPI Results in Zero to be Saved to the Guest RIP
Field in the VMCS
Problem: If a logical processor is in VMX non-root operation and in the wait-for-SIPI state, an
occurrence of a start-up IPI (SIPI) causes a VM exit. Due to this erratum, such VM exits
always save zero into the RIP field of the guest-state area of the virtual-machine
control structure (VMCS) instead of the value of RIP before the SIPI was received.
Implication: In the absence of virtualization, a SIPI received by a logical processor in the wait-for-
SIPI state results in the logical processor starting execution from the vector sent in the
SIPI regardless of the value of RIP before the SIPI was received. A virtual-machine
monitor (VMM) responding to a SIPI-induced VM exit can emulate this behavior
because the SIPI vector is saved in the lower 8 bits of the exit qualification field in the
VMCS. Such a VMM should be unaffected by this erratum. A VMM that does not emulate
this behavior may need to recover the old value of RIP through alternative means. Intel
has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: VMM software that may respond to SIPI-induced VM exits by resuming the interrupt
guest context without emulating the non-virtualized SIPI response should (1) save
from the VMCS (using VMREAD) the value of RIP before any VM entry to the wait-for
SIPI state; and (2) restore to the VMCS (using VMWRITE) that value before the next
VM entry that resumes the guest in any state other than wait-for-SIPI.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA44. NMIs May Not Be Blocked by a VM-Entry Failure
Problem: The Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual Volume 3B:
System Programming Guide, Part 2 specifies that, following a VM-entry failure during
or after loading guest state, “the state of blocking by NMI is what it was before VM
entry.” If non-maskable interrupts (NMIs) are blocked and the “virtual NMIs” VM-
execution control set to 1, this erratum may result in NMIs not being blocked after a
VM-entry failure during or after loading guest state.
Implication: VM-entry failures that cause NMIs to become unblocked may cause the processor to
deliver an NMI to software that is not prepared for it.
Workaround: VMM software should configure the virtual-machine control structure (VMCS) so that
VM-entry failures do not occur.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 29
Specification Update January 2012
Page 30

AAA45. Partial Streaming Load Instruction Sequence May Cause the Processor
to Hang
Problem: Under some rare conditions, when multiple streaming load instructions (MOVNTDQA)
are mixed with non-streaming loads that split across cache lines, the processor may
hang.
Implication: Under the scenario described above, the processor may hang. Intel has not observed
this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum. However,
streaming behavior may be re-enabled by setting bit 5 to 1 of the MSR at address 0x21
for software development or testing purposes. If this bit is changed, then a readmodify-write should be performed to preserve other bits of this MSR. When the
streaming behavior is enabled and using streaming load instructions, always consume
a full cache line worth of data and/or avoid mixing them with non-streaming memory
references. If streaming loads are used to read partial cache lines, and mixed with
non-streaming memory references, use fences to isolate the streaming load operations
from non-streaming memory operations.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA46. Self/Cross Modifying Code May Not be Detected or May Cause a
Machine Check Exception
Problem: If instructions from at least three different ways in the same instruction cache set exist
in the pipeline combined with some rare internal state, self-modifying code (SMC) or
cross-modifying code may not be detected and/or handled.
Implication: An instruction that should be overwritten by another instruction while in the processor
pipeline may not be detected/modified, and could retire without detection.
Alternatively the instruction may cause a Machine Check Exception. Intel has not
observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA47. Data TLB Eviction Condition in the Middle of a Cacheline Split Load
Operation May Cause the Processor to Hang
Problem: If the TLB translation gets evicted while completing a cacheline split load operation,
under rare scenarios the processor may hang.
Implication: The cacheline split load operation may not be able to complete normally, and the
machine may hang and generate Machine Check Exception. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA48. Update of Read/Write (R/W) or User/Supervisor (U/S) or Present (P)
Bits without TLB Shootdown May Cause Unexpected Processor
Behavior
Problem: Updating a page table entry by changing R/W, U/S or P bits, even when transitioning
these bits from 0 to 1, without keeping the affected linear address range coherent with
all TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffers) and paging-structures caches in the processor,
in conjunction with a complex sequence of internal processor microarchitectural events
and store operations, may lead to unexpected processor behavior.
30 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 31

Implication: This erratum may lead to livelock, shutdown or other unexpected processor behavior.
Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA49. RSM Instruction Execution under Certain Conditions May Cause
Processor Hang or Unexpected Instruction Execution Results
Problem: RSM instruction execution, under certain conditions triggered by a complex sequence of
internal processor micro-architectural events, may lead to processor hang, or
unexpected instruction execution results.
Implication: In the above sequence, the processor may live lock or hang, or RSM instruction may
restart the interrupted processor context through a nondeterministic EIP offset in the
code segment, resulting in unexpected instruction execution, unexpected exceptions or
system hang. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available
software.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA50. Benign Exception after a Double Fault May Not Cause a Triple Fault
Shutdown
Problem: According to the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Volume 3A, “Exception and Interrupt Reference”, if another exception occurs while
attempting to call the double-fault handler, the processor enters shutdown mode.
However due to this erratum, only Contributory Exceptions and Page Faults will cause a
triple fault shutdown, whereas a benign exception may not.
Implication: If a benign exception occurs while attempting to call the double-fault handler, the
processor may hang or may handle the benign exception. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA51. LER MSRs May be Incorrectly UpdatedThe LER (Last Exception Record)
MSRs, MSR_LER_FROM_LIP (1DDH) and MSR_LER_TO_LIP (1DEH)
may contain incorrect values after any of the following:
• Either STPCLK#, NMI (NonMaskable Interrupt) or external interrupts
• CMP or TEST instructions with an uncacheable memory operand followed by a
conditional jump
• STI/POP SS/MOV S S instructions followed by CMP or TEST instructions and then by
a conditional jump
Implication: When the conditions for this erratum occur, the value of the LER MSRs may be
incorrectly updated.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA52. Short Nested Loops That Span Multiple 16-Byte Boundaries May Cause
a Machine Check Exception or a System Hang
Problem: Under a rare set of timing conditions and address alignment of instructions in a short
nested loop sequence, software that contains multiple conditional jump instructions
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 31
Specification Update January 2012
Page 32

and spans multiple 16-byte boundaries, may cause a machine check exception or a
system hang.
Implication: Due to this erratum, a machine check exception or a system hang may occur.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA53. An Enabled Debug Breakpoint or Single Step Trap May Be Taken after
MOV SS/POP SS Instruction if it is Followed by an Instruction That
Signals a Floating Point Exception
Problem: A MOV SS/POP SS instruction should inhibit all interrupts including debug breakpoints
until after execution of the following instruction. This is intended to allow the sequential
execution of MOV SS/POP SS and MOV [r/e]SP, [r/e]BP instructions without having an
invalid stack during interrupt handling. However, an enabled debug breakpoint or single
step trap may be taken after MOV SS/POP SS if this instruction is followed by an
instruction that signals a floating point exception rather than a MOV [r/e]SP, [r/e]BP
instruction. This results in a debug exception being signaled on an unexpected
instruction boundary since the MOV SS/POP SS and the following instruction should be
executed atomically.
Implication: This can result in incorrect signaling of a debug exception and possibly a mismatched
Stack Segment and Stack Pointer. If MOV SS/POP SS is not followed by a MOV [r/e]SP,
[r/e]BP, there may be a mismatched Stack Segment and Stack Pointer on any
exception. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available
software, or system.
Workaround: As recommended in the IA32 Intel® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual, the use
of MOV SS/POP SS in conjunction with MOV [r/e]SP, [r/e]BP will avoid the failure since
the MOV [r/e]SP, [r/e]BP will not generate a floating point exception. Developers of
debug tools should be aware of the potential incorrect debug event signaling created by
this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA54. IA32_MC1_STATUS MSR Bit[60] Does Not Reflect Machine Check Error
Reporting Enable Correctly
Problem: IA32_MC1_STATUS MSR (405H) bit[60] (EN- Error Enabled) is supposed to indicate
whether the enable bit in the IA32_MC1_CTL MSR (404H) was set at the time of the
last update to the IA32_MC1_STATUS MSR. Due to this erratum, IA32_MC1_STATUS
MSR bit[60] instead reports the current value of the IA32_MC1_CTL MSR enable bit.
Implication: IA32_MC1_STATUS MSR bit [60] may not reflect the correct state of the enable bit in
the IA32_MC1_CTL MSR at the time of the last update.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA55. A VM Exit Due to a Fault While Delivering a Software Interrupt May
Save Incorrect Data into the VMCS
Problem: If a fault occurs during delivery of a software interrupt (INTn) in virtual-8086 mode
when virtual mode extensions are in effect and that fault causes a VM exit, incorrect
data may be saved into the VMCS. Specifically, information about the software
interrupt may not be reported in the IDT-vectoring information field. In addition, the
interruptibility-state field may indicate blocking by STI or by MOV SS if such blocking
were in effect before execution of the INTn instruction or before execution of the VM-
entry instruction that injected the software interrupt.
32 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 33

Implication: In general, VMM software that follows the guidelines given in the section “Handling VM
Exits Due to Exceptions” of Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s
Manual Volume 3B: System Programming Guide should not be affected. If the erratum
improperly causes indication of blocking by STI or by MOV SS, the ability of a VMM to
inject an interrupt may be delayed by one instruction.
Workaround: VMM software should follow the guidelines given in the section “Handling VM Exits Due
to Exceptions” of Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual
Volume 3B: System Programming Guide.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA56. A VM Exit Occurring in IA-32e Mode May Not Produce a VMX Abort
When Expected
Problem: If a VM exit occurs while the processor is in IA-32e mode and the “host address-space
size” VM-exit control is 0, a VMX abort should occur. Due to this erratum, the expected
VMX aborts may not occur and instead the VM Exit will occur normally. The conditions
required to observe this erratum are a VM entry that returns from SMM with the “IA32e guest” VM-entry control set to 1 in the SMM VMCS and the “host address-space
size” VM-exit control cleared to 0 in the executive VMCS.
Implication: A VM Exit will occur when a VMX Abort was expected.
Workaround: An SMM VMM should always set the “IA-32e guest” VM-entry control in the SMM VMCS
to be the value that was in the LMA bit (IA32_EFER.LMA.LMA[bit 10]) in the IA32_EFER
MSR (C0000080H) at the time of the last SMM VM exit. If this guideline is followed,
that value will be 1 only if the “host address-space size” VM-exit control is 1 in the
executive VMCS.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA57. IRET under Certain Conditions May Cause an Unexpected Alignment
Check Exception
Problem: In IA-32e mode, it is possible to get an Alignment Check Exception (#AC) on the IRET
instruction even though alignment checks were disabled at the start of the IRET. This
can only occur if the IRET instruction is returning from CPL3 code to CPL3 code. IRETs
from CPL0/1/2 are not affected. This erratum can occur if the EFLAGS value on the
stack has the AC flag set, and the interrupt handler's stack is misaligned. In IA-32e
mode, RSP is aligned to a 16-byte boundary before pushing the stack frame.
Implication: In IA-32e mode, under the conditions given above, an IRET can get a #AC even if
alignment checks are disabled at the start of the IRET. This erratum can only be
observed with a software generated stack frame.
Workaround: Software should not generate misaligned stack frames for use with IRET.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA58. PSI# Signal Asserted During Reset
Problem: Power Status Indicator (PSI) is a feature that, when available, may be used to enable
voltage regulator power savings while idle and in the Deeper Sleep State (C4 state).
Under proper operation the processor will assert the PSI# signal to indicate that the
voltage regulator can enter a higher efficiency mode of operation. The processor will
incorrectly assert the PSI# signal while the RESET# signal is asserted. This PSI#
assertion will extend beyond the deassertion of the RESET# signal for a short duration
(maximum of one millisecond).
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 33
Specification Update January 2012
Page 34

Implication: When this erratum occurs on a platform designed to support PSI, the voltage regulator
will transition to mode of operation that may not be capable of supplying the necessary
voltage and current required by the processor.
Workaround: Do not use PSI# signal without blocking the assertion during the error period as
specified from RESET# assertion to a maximum of 1ms from the deasserted edge.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA59. Thermal Interrupts are Dropped During and While Exiting Deep Power
Down State
Problem: Thermal interrupts are ignored while the processor is in Deep Power Down State as
well as during a small window of time while exiting from Deep Power Down State.
During this window, if the PROCHOT signal is driven or the internal value of the sensor
reaches the programmed thermal trip point, then the associated thermal interrupt may
be lost.
Implication: In the event of a thermal event while a processor is waking up from Deep Power Down
State, the processor will initiate an appropriate throttle response. However, the
associated thermal interrupt generated may be lost.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA60. VM Entry May Fail When Attempting to Set
IA32_DEBUGCTL.FREEZE_WHILE_SMM_EN
Problem: If bit 14 (FREEZE_WHILE_SMM_EN) is set in the IA32_DEBUGCTL field in the guest-
state area of the VMCS, VM entry may fail as described in Section “VM-Entry Failures
During or After Loading Guest State” of Intel
Developer’s Manual Volume 3B: System Programming Guide, Part 2. (The exit reason
will be 80000021H and the exit qualification will be zero.) Note that the
FREEZE_WHILE_SMM_EN bit in the guest IA32_DEBUGCTL field may be set due to a
VMWRITE to that field or due to a VM exit that occurs while
IA32_DEBUGCTL.FREEZE_WHILE_SMM_EN=1.
Implication: A VMM will not be able to properly virtualize a guest using the FREEZE_WHILE_SMM
feature.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum. Alternatively, the
following software workaround may be used. If a VMM wants to use the
FREEZE_WHILE_SMM feature, it can configure an entry in the VM-entry MSR-load area
for the IA32_DEBUGCTL MSR (1D9H); the value in the entry should set the
FREEZE_WHILE_SMM_EN bit. In addition, the VMM should use VMWRITE to clear the
FREEZE_WHILE_SMM_EN bit in the guest IA32_DEBUGCTL field before every VM entry.
(It is necessary to do this before every VM entry because each VM exit will save that bit
as 1.) This workaround prevents the VM-entry failure and sets the
FREEZE_WHILE_SMM_EN bit in the IA32_DEBUGCTL MSR.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software
AAA61. Corruption of CS Segment Register During RSM While Transitioning
From Real Mode to Protected Mode
Problem: During the transition from real mode to protected mode, if an SMI (System
Management Interrupt) occurs between the MOV to CR0 that sets PE (Protection
Enable, bit 0) and the first far JMP, the subsequent RSM (Resume from System
Management Mode) may cause the lower two bits of CS segment register to be
corrupted.
34 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 35

Implication: The corruption of the bottom two bits of the CS segment register will have no impact
unless software explicitly examines the CS segment register between enabling
protected mode and the first far JMP. Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software
Developer’s Manual Volume 3A: System Programming Guide, Part 1, in the section
titled "Switching to Protected Mode” recommends the far JMP immediately follows the
write to CR0 to enable protected mode. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA62. LBR, BTS, BTM May Report a Wrong Address when an Exception/
Interrupt Occurs in 64-bit Mode
Problem: An exception/interrupt event should be transparent to the LBR (Last Branch Record),
BTS (Branch Trace Store) and BTM (Branch Trace Message) mechanisms. However,
during a specific boundary condition where the exception/interrupt occurs right after
the execution of an instruction at the lower canonical boundary (0x00007FFFFFFFFFFF)
in 64-bit mode, the LBR return registers will save a wrong return address with bits 63
to 48 incorrectly sign extended to all 1’s. Subsequent BTS and BTM operations which
report the LBR will also be incorrect.
Implication: LBR, BTS and BTM may report incorrect information in the event of an exception/
interrupt.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA63. Memory Ordering Violation With Stores/Loads Crossing a Cacheline
Boundary
Problem: When two logical processors are accessing the same data that is crossing a cacheline
boundary without serialization, with a specific set of processor internal conditions, it is
possible to have an ordering violation between memory store and load operations.
Implication: Due to this erratum, proper load/store ordering may not be followed when multiple
logical processors are accessing the same data that crosses a cacheline boundary
without serialization.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA64. Processor May Hold-off / Delay a PECI Transaction Longer than
Specified by the PECI Protocol
Problem: PECI (Platform Environment Control Interface) transactions may be held off longer than
the PECI protocol hold-off limit while the processor is exiting C-states. This may occur if
STPCLK# has been asserted by the system, the beginning of a PECI message coincides
with a C-state transition, and the processor is executing a long instruction flow. Note
that the processor can still complete the PECI transaction if the host chooses to process
the remainder of the message.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor may violate the PECI hold-off protocol.
Workaround: PECI hosts can choose to either complete or not complete PECI transactions when the
processor goes beyond the hold-off limit. The processor generates the PECI hold-off
indication by keeping the PECI bus high when the PECI host sends the first bit of the
address timing negotiation phase. If the PECI host does not choose to complete the
transaction, it should consider the transaction a failure and retry 1ms after the
processor deactivates the hold-off indication.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 35
Specification Update January 2012
Page 36

Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA65. VM Entry May Use Wrong Address to Access Virtual-APIC Page
Problem: When XFEATURE_ENABLED_MASK register (XCR0) bit 1 (SSE) is 1, a VM entry
executed with the “use TPR shadow” VM-execution control set to 1 may use the wrong
address to access data on the virtual-APIC page.
Implication: An affected VM entry may exhibit the following behaviors: (1) it may use wrong areas
of the virtual-APIC page to determine whether VM entry fails or whether it induces a VM
exit due to the TPR threshold; or (2) it may clear wrong areas of the virtual-APIC page.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA66. XRSTORE Instruction May Cause Extra Memory Reads
Problem: An XRSTOR instruction will cause non-speculative accesses to XSAVE memory area
locations containing the FCW/FSW and FOP/FTW Floating Point (FP) registers even
though the 64-bit restore mask specified in the EDX:EAX register pair does not indicate
to restore the x87 FPU state.
Implication: Page faults, data breakpoint triggers, etc. may occur due to the unexpected non-
speculative accesses to these memory locations.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA67. CPUID Instruction May Return Incorrect Brand String
Problem: When a CPUID instruction is executed with EAX = 8000_0002H, 8000_0003H, or
8000_0004H, the returned EAX, EBX, ECX, and/or EDX values may be incorrect.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the processor may report an incorrect brand string.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA68. Global Instruction TLB Entries May Not be Invalidated on a VM Exit or
VM Entry
Problem: If a VMM is using global page entries (CR4.PGE is enabled and any present page-
directories or page-table entries are marked global), then on a VM entry, the
instruction TLB (Translation Lookaside Buffer) entries caching global page translations
of the VMM may not be invalidated. In addition, if a guest is using global page entries,
then on a VM exit, the instruction TLB entries caching global page translations of the
guest may not be invalidated.
Implication: Stale global instruction linear to physical page translations may be used by a VMM after
a VM exit or a guest after a VM entry.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA69. When Intel® Deep Power-Down State is Being Used,
IA32_FIXED_CTR2 May Return Incorrect Cycle Counts
Problem: When the processor is operating at an N/2 core to front side bus ratio, after exiting
Deep Power-Down State, the internal increment value for IA32_FIXED_CTR2 (Fixed
Function Performance Counter 2, 30BH) will not take into account the half ratio setting.
36 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 37

Implication: Due to this erratum, IA32_FIXED_CTR2 MSR will not return reliable counts after
returning from an Intel Deep Power-Down State.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA70. Enabling PECI via the PECI_CTL MSR Does Not Enable PECI and May
Corrupt the CPUID Feature Flags
Problem: Writing PECI_CTL MSR (Platform Environment Control Interface Control Register) will
not update the PECI_CTL MSR (5A0H), instead it will write to the VMM Feature Flag
Mask MSR (CPUID_FEATURE_MASK1, 478H).
Implication: Due to this erratum, PECI (Platform Environment Control Interface) will not be enabled
as expected by the software. In addition, due to this erratum, processor features
reported in ECX following execution of leaf 1 of CPUID (EAX=1) may be
masked. Software utilizing CPUID leaf 1 to verify processor capabilities may not work
as intended.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum. Do not initialize
PECI before processor update is loaded. Also, load processor update as soon as
possible after RESET as documented in the RS – Wolfdale Processor Family BIOS
Writers Guide, Section 14.8.3 Bootstrap Processor Initialization Requirements.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA71. INIT Incorrectly Resets IA32_LSTAR MSR
Problem: In response to an INIT reset initiated either via the INIT# pin or an IPI (Inter Processor
Interrupt), the processor should leave MSR values unchanged. Due to this erratum
IA32_LSTAR MSR (C0000082H), which is used by the iA32e SYSCALL instruction, is
being cleared by an INIT reset.
Implication: If software programs a value in IA32_LSTAR to be used by the SYSCALL instruction and
the processor subsequently receives an INIT reset, the SYSCALL instructions will not
behave as intended. Intel has not observed this erratum in any commercially available
software.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA72. The XRSTOR Instruction May Fail to Cause a General-Protection
Exception
Problem: The XFEATURE_ENABLED_MASK register (XCR0) bits [63:9] are reserved and must be
0; consequently , the XRST OR instruction should cause a general-protection exception if
any of the corresponding bits in the XSTATE_BV field in the header of the XSAVE/
XRSTOR area is set to 1. Due to this erratum, a logical processor may fail to cause such
an exception if one or more of these reserved bits are set to 1.
Implication: Software may not operate correctly if it relies on the XRSTOR instruction to cause a
general-protection excepti on when an y of the bits [63 :9] in the XS TATE_BV field in the
header of the XSAVE/XRSTOR area is set to 1.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 37
Specification Update January 2012
Page 38

AAA73. The XSAVE Instruction May Erroneously Set Reserved Bits in the
XSTATE_BV Field
Problem: XFEATURE_ENABLED_MASK bits [63:9] of register (XCR0) are reserved and must be 0;
consequently the XSAVE instruction should not modify the corresponding bits of the
XSTATE_BV field in the header of the XSAVE/XRSTOR area. Due to this erratum, a
logical processor may erroneously write 1 to one or more of these reserved bits.
Implication: Software may not operate correctly if it relies on the XSAVE instruction not to modify
bits [63:9] of the XSTATE_BV field in the header of the XSAVE/XRSTOR area.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA74. Store Ordering Violation When Using XSAVE
Problem: The store operations done as part of the XSA VE in struction ma y cause a store ordering
violation with older store operations. The store operations done to save the processor
context in the XSAVE instruction flow , when XSAVE is used to store only the SSE
context, may appear to execute before the completion of older store operations.
Implication: Execution of the stores in XSAVE, when XSAVE is used to store SSE context only, may
not follow program order and may execute before older stores. Intel has not observed
this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA75. Unsynchronized Cross-Modifying Code Operations Can Caus e
Unexpected Instruction Execution Results
Problem: The act of one processor, or system bus master, writing data into a currently executing
code segment of a second processor with the intent of having the second processor
execute that data as code is called cross-modifying code (XMC). XMC that does not
force the second processor to execute a synchronizing instruction, prior to execution of
the new code, is called unsynchronized XMC.
Implication: Software using unsynchronized XMC to modify the instruction byte stream of a
processor can see unexpected or unpredictable execution behavior from the processor
that is executing the modified code.
Workaround: In this case, the phrase "unexpected or unpredictable execution behavior"
encompasses the generation of most of the exceptions listed in the Intel Architecture
Software Developer's Manual Volume 3: System Programming Guide, including a
General Protection Fault (GPF) or other unexpected behaviors. In the event that
unpredictable execution causes a GPF the application executing the unsynchronized
XMC operation would be terminated by the operating system.
In order to avoid this erratum, programmers should use the XMC synchronization
algorithm as detailed in the Intel Architecture Software Developer's Manual Volume 3:
System Programming Guide, Section: Handling Self- and Cross-Modifying Code.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA76. A 64-bit Register IP-relative Instruction May Return Unexpected
Results
Problem: Under an unlikely and complex sequence of conditions in 64-bit mode, a register IP-
relative instruction result may be incorrect.
38 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 39

Implication: A register IP-relative instruction result may be incorrect and could cause software to
read from or write to an incorrect memory location. This may result in an unexpected
page fault or unpredictable system behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAA77. Intel® Trusted Execution Technology ACM Revocation
Problem: SINIT ACM Q45_Q43_SINIT_19.BIN or earlier are revoked and will not launch with new
processor configuration information.
Implication: Due to this erratum, SINIT ACM Q45_Q43_SINIT_19.BIN and earlier will be revoked.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum. All Intel® TXT
enabled software must use SINIT ACM Q45_Q43_SINIT_51.BIN or later .
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 39
Specification Update January 2012
Page 40

Specification Changes
The Specification Changes listed in this section apply to the following documents:
®
•Intel
• Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual volumes 1, 2A, 2B ,
All Specification Changes will be incorporated into a future version of the appropriate
processor documentation.
Xeon® Processor 3300 Series Datasheet
3A, and 3B
§
40 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
Page 41

Specification Clarifications
The Specification Clarifications listed in this section apply to the following documents:
®
•Intel
• Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual volumes 1, 2A, 2B,
All Specification Clarifications will be incorporated into a future version of the
appropriate processor documentation.
AAA1. Clarification of TRANSLATION LOOKASIDE BUFFERS (TLBS)
Invalidation
Section 10.9 INVALIDATING THE TRANSLATION LOOKASIDE BUFFERS (TLBS) of the
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer's Manual, Volume 3A: System
Programming Guide will be modified to include the presence of page table structure
caches, such as the page directory cache, which Intel processors implement. This
information is needed to aid operating systems in managing page table structure
invalidations properly.
Intel will update the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer's Manual,
Volume 3A: System Programming Guide in the coming months. Until that time, an
application note, TLBs, Paging-Structure Caches, and Their Invalidation (http://
www.intel.com/products/processor/manuals/index.htm), is available which provides
more information on the paging structure caches and TLB invalidation.
Xeon® Processor 3300 Series Datasheet
3A, and 3B
In rare instances, improper TLB invalidation may result in unpredictable system
behavior, such as system hangs or incorrect data. Developers of operating systems
should take this documentation into account when designing TLB invalidation
algorithms. For the processors affected, Intel has provided a recommended update to
system and BIOS vendors to incorporate into their BIOS to resolve this issue.
Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series 41
Specification Update January 2012
Page 42

Documentation Changes
The Documentation Changes listed in this section apply to the following documents:
®
•Intel
All Documentation Changes will be incorporated into a future version of the appropriate
processor documentation.
Xeon® Processor 3300 Series Datasheet
Note: Documentation changes for Intel
Manual volumes 1, 2A, 2B, 3A, and 3B will be posted in a separate document Intel
and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual Documentation Changes. Follow
the link below to become familiar with this file.
http://www.intel.com/design/processor/specupdt/252046.htm
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s
§
®
64
42 Intel® Xeon® Processor 3300 Series
Specification Update January 2012
 Loading...
Loading...