Page 1
product brief
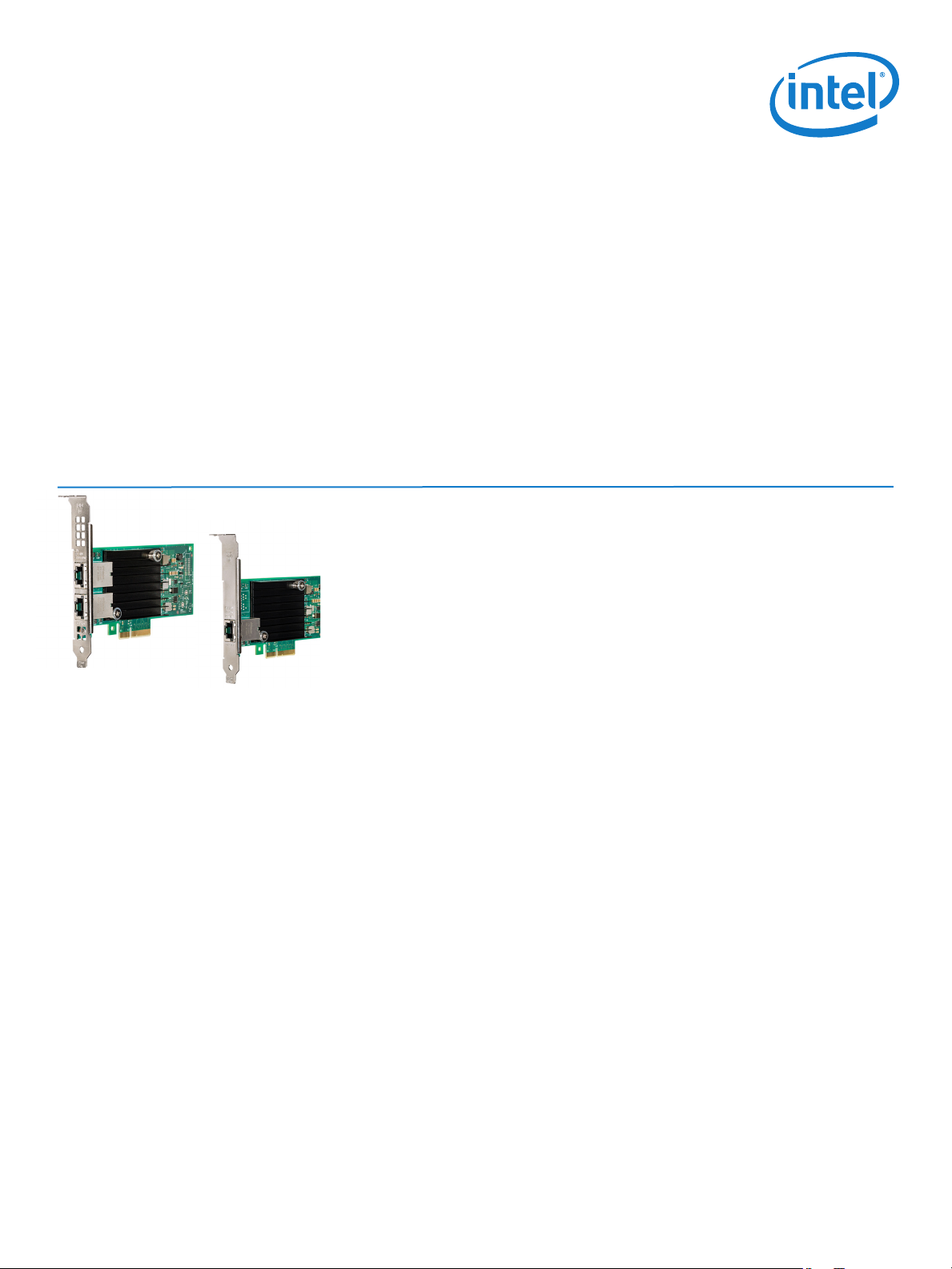
Intel® Ethernet Converged Network
Adapter X550
10GBASE-T Converged Network Adapter (CNA)
Simplies Migration to 10 Gigabit Ethernet (GbE), Provides iSCSI,
FCoE, Virtualization and Flexible Port Partitioning (FPP)
Key Features
• Low cost, low power, 10 GbE
performance for the entire
datacenter.
• Intel’s second generation, single- and
dual-port 10GBASE-T controller with
integrated MAC and PHY.
• Standard CAT 6a cabling with RJ45
connectors.
• Supports NBASE-T* technology (2.5
and 5.0 GbE over CAT 5e)1.
• Backward compatibility with existing
1000BASE-T networks simplies the
transition to 10 GbE.
• PCI Express* (PCIe*) v 3.0 with up to
8.0 G T/s .
• Unied networking delivering LAN,
iSCSI and FCoE in one low-cost CNA.
• Flexible I/O virtualization for port
partitioining and Quality of Service
(QoS) of up to 64 virtual ports.
• Reliable, proven 10 GbE technology
from Intel Corporation.
10 GbE for the Broad Market
The Intel® Ethernet Converged Network
Adapter X550 is the newest innovation
in Intel’s leadership to drive 10 GbE into
the broad server market. This adapter
hosts Intel’s latest Ethernet silicon, the
Intel® Ethernet Controller X550, a low
cost single-chip 10GBASE-T solution
for today’s server platforms.
Simplify the Transition to 10 GbE
With 10GBASE-T, migration to 10 GbE
is dramatically simplied with backward
compatibility for your existing GbE
network infrastructure. Install an X550
adapter into a server and the autonegotiation between 1 GbE and 10
GbE provides the necessary backwards
compatibility that most customers
require for a smooth transition and
easy migration to 10 GbE. When
time and budget allows, 10GBASE-T
switches can be added any time to
experience the full benets of 10 GbE.
10GBASE-T uses the copper twistedpair cables that are very familiar to IT
professionals today. It is all you know
and love about 1000BASE-T. The
knowledge, training, and investment
in BASE-T are preserved. 10GBASE-T
is the easiest and most versatile 10
GbE interface that can be deployed
anywhere in your data center. Its
exible reach from 1 meter to 100
meters supports the latest network
architectures including Top of Rack
(ToR), Middle of Row (MoR), and End of
Row (EoR).
10 GbE Performance at Low Cost
and Low Power
The new Intel® Ethernet Converged
Network Adapter X550 is the lowest
cost way to deploy 10 GbE in your data
center today. The Intel X550 uses low
cost CAT 6 and CAT 6a cabling. Chances
are this cabling already exists in the
data center.
A way for Intel to reduce cost and
power is to integrate components
into a single-chip solution. Why is
integration important? First, integration
translates to lower power. This means
no active heat sink and reduces
the per-port power consumption.
Second, integration also means a
lower cost per port, because two
separate components are not needed.
When cabling is accounted for, cost
eciencies realized from a single part
mean 10GBASE-T is the lowest cost
media to deploy.
With lower cost and power, 10GBASE-T
is ideal for broad deployment.
10GBASE-T is an option for every rack
and tower server in the data center.
The new Intel® Ethernet Converged
Page 2

Product Brief
Intel® Ethernet Converged Network
Adapter X550
Network Connectivity
2
Network Adapter X550 (CNA X550
family) provides bandwidth-intensive
applications with highly aordable
10 GbE network performance and
cost-eective RJ45 connectivity for
distances up to 100 meters.
Exciting New Data Center Models
More than just a 10 times per-port
increase in performance by using the
CNA X550 family versus a standard
1 GbE adapter opens doors for exciting
new usage models, including unied
networking, I/O virtualization, and
exible port partitioning.
A Complete Unified Network
Solution
Converging data and storage onto
one fabric eliminates the need for
multiple adapters and cables per
server. Furthermore, 10 GbE provides
the bandwidth to converge these
multiple fabrics into a single wire. A key
capability that makes all this possible is
trac class separation provided by Data
Center Bridging (DCB). DCB provides a
collection of standards for additional
QoS functionality such as lossless
delivery, congestion notication,
priority-based ow control, and priority
groups. This enables the CNA X550
family to provide a one-wire solution
with virtual pipes for the dierent
classes of trac:
• Data: best eort delivery of standard
LAN trac.
• Storage: NAS or SAN including
lossless FCoE and iSCSI.
• Management: Guaranteed
connectivity of data center IP
management.
Unified Networking Principles
Intel’s unied networking solutions are
built on the principles that have made
us successful in Ethernet:
• Open architecture integrates
networking with the server, enabling
IT managers to reduce complexity and
overhead while enabling a exible and
scalable data center network.
• Intelligent ooads lower cost and
power while delivering the application
performance that customers expect.
• Proven unied networking is built on
trusted Intel Ethernet technology,
enabling customers to deploy FCoE
or iSCSI with the same quality used in
their traditional Ethernet network.
Intel’s unied networking solutions are
enabled through a combination of Intel
Ethernet products along with network
and storage protocols integrated in the
operating systems. This combination
provides proven reliability with
the performance that data center
administrators around the world have
come to expect from Intel.
Best Choice for Server
Virtualization
Virtualization changes server resource
deployment and management by
running multiple applications and
operating systems on a single physical
server.
With Intel® Virtualization Technology
for connectivity (VT-c), the CNA
X550 family delivers outstanding I/O
performance and QoS in virtualized
data centers and cloud environments.
I/O virtualization advances network
connectivity used in today’s servers
to more ecient models by providing
FPP, multiple Tx/Rx queues, Tx queue
rate-limiting, and on-controller
QoS functionality that is useful for
both virtual and non-virtual server
deployments.
The CNA X550 family reduces I/O
bottlenecks by providing intelligent
ooad of networking trac per VM,
enabling near-native performance
and VM scalability. The host-based
virtualization technologies include:
• VMDq for emulated path: NIC-based
VM queue sorting enabling ecient
hypervisor-based switching.
• SR-IOV for direct assignment: NIC-
based isolation and switching for
various virtual station instances
enabling optimal CPU usage in
virtualized environment.
Additionally, the CNA X550 family
provides virtual bridging support that
delivers both host-side and switch-side
control and management of virtualized
I/O as well as the following modes of
virtualized operation:
• VEPA: IEEE 802.1Qbg support for
Virtual Ethernet Port Aggregator.
• VEB: Virtual Ethernet Bridge support
with Intel V T.
Networking Virtualization
Network virtualization is the next big
trend in creating an agile data center.
The X550 CNA family of adapters are
ready to help take you to the next level.
• VXLAN and NVGRE ooads:
These stateless ooads preserve
application performance for overlay
networks. With these ooads it is
possible to distribute network trac
across a CPU core.
• Preserves application performance in
network virtualized environment.
Flexible Port Partitioning (FPP)
By taking advantage of the PCI-SIG*
SR-IOV specication, FPP enables
virtual Ethernet controllers that can be
used by a Linux* host directly and/or
assigned directly to virtual machines
for hypervisor virtual switch bypass.
FPP enables the assignment of up
to 64 Linux host processes or virtual
machines per port to virtual functions.
An administrator can use FPP to control
the partitioning of the bandwidth across
multiple virtual functions. FPP can also
provide balanced QoS by giving each
assigned virtual function equal access
to 10 Gb/s of bandwidth.
The combination of 10 GbE and unied
networking helps organizations
overcome connectivity challenges and
simplify the data center infrastructure.
10 GbE provides a simple, well-
understood fabric for virtualized data
centers, one that helps reduce cost and
complexity as the number of Virtual
Machines (VMs) continue to grow.
Page 3

Product Brief
Intel® Ethernet Converged Network
Adapter X550
Network Connectivity
GENERAL
FEATURES BENEFITS
Intel® Ethernet Converged Network Adapter
• Intel’s second integrated 10GBASE-T MAC/PHY, low-cost solution
X550
Enhanced Low-Profile Solution • Enables higher bandwidth and throughput from standard and low-profile PCIe slots and servers
RJ45 Connections Over CAT 6A Cabling • Ensures compatibility with cable length up to 100 meters
Remote Boot iSCSI and FCoE • Provides centralized Storage Area network (SAN) management at a lower cost than competing
solutions
Support For Most Network Operating Systems
• Enables widespread deployment
(NOS)
RoHS-compliant, Lead-free Technology • Complies with the European Union (EU) directives to reduce the use of hazardous materials
Intel Backing • Backed by an Intel limited lifetime warranty, 90-day money-back guarantee (U.S. and Canada)
and worldwide support
I/O FEATURES FOR MULTI-CORE PROCESSOR SERVERS
FEATURES BENEFITS
MSI-X Support • DMA engine – Enhances data acceleration across the platform (network, chipset, processor),
lowering CPU usage
Low Latency • Based on the sensitivity of the incoming data, the adapter can bypass the automatic moderation
of time intervals between interrupts
Header Splits and Replication in Receive • Helps the software device driver focus on the relevant part of the packet without the need to
parse it
Multiple Queues – 64 Tx and Rx Per Port • Network packet handling without waiting or buffer overflow providing efficient packet
prioritization
Tx/Rx IP, SCTP, TCP, and UDP Checksum
Offloading (IPv4, IPv6) Capabilities
• Lower processor usage
• Checksum and segmentation capability extended to a new standard packet type
Tx TCP Segmentation Offload (IP v4, IPv6) • Increased throughput and lower processor usage
• Compatible with large-send offload feature (in Microsoft Windows* Server operating systems)
IPSec • Offloads IPSec capability onto the adapter instead of sof tware to significantly improve
throughput and CPU usage
Compatible with x4, x8 and x16 Standard and
• Enables each PCIe slot por t to operate without interfering or competing with other PCIe slot port
Low-profile PCIe Slots
Receive and Transmit Side Scaling for Windows
• Enables the direc tion of the interrupts to the processor cores in order to improve CPU use rate
Environment and Scalable I/O for Linux*
Environments (IPv4, IPv6 and TCP/ UDP)
3
SINGLE PORT POWER CONSUMPTION
LINK SPEED AVERAGE POWER (W) MAX POWER (W)
100 Mb/s 3.9 4.5
1 GbE 4.7 5.3
10 GbE 7.4 8.4
* LFM = minimum of 150 LFM under all operating conditions.
DUAL PORT POWER CONSUMPTION
LINK SPEED AVERAGE POWER (W) MAX POWER (W)
100 Mb/s 3.9 4.9
1 GbE 5.5 6.4
10 GbE 11. 2 13.0
Page 4

Product Brief
Intel® Ethernet Converged Network
Adapter X550
Network Connectivity
VIRTUALIZATION FEATURES
FEATURE BENEFIT
Multi-mode I/O Virtualization Operations • Supports two modes of operation of virtualized environments:
– Direct assignment of part of the port resources to dif ferent guest operating systems using the
PCI SIG SR-IOV standard (also known as native mode or pass-through mode)
– Central management of the networking resources by hypervisor (also known as software
switch acceleration mode)
• A hybrid model, where some of the VMs are assigned a dedicated share of the port and the rest
are ser viced by a hypervisor is also supported
VXLAN Stateless Offloads • A framework for overlaying virtualized layer 2 networks over layer 3 networks. VXLAN enables
users to create a logical network for VMs across dif ferent net works
NVGRE Stateless Offloads • Network Virtualization using Generic Routing Encapsulation. The encapsulation of an Ethernet
Layer 2 Frame in IP that enables the creation of virtualized Layer 2 subnets that can span physical
Layer 3 IP networks
Virtual Machine Device Queues (VMDq) • Offloads data sorting from the hypervisor to silicon, improving data throughput and CPU usage
• QoS feature for Tx data by providing round-robin servicing and preventing head-of-line blocking
• Sorting based on MAC addresses and VLAN tags
64 Transmit (Tx) and Recive (Rx) Queue Pairs
Per Port
• Supports VMware* NetQueue and Microsof t* VMQ
• MAC/VLAN filtering for pool selection and either DCB or RSS for the queue in pool selection
FPP – 64 VFs Per Port • VFs appear as Ethernet controllers in Linux operating systems that can be assigned to VMs,
Kernel processes or teamed using the Linux bonding drivers
Support for PCI-SIG SR-IOV Specification • Up to 64 VFs per port
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Support with VLAN Tag
Insertion, Stripping and Packet Filtering for up
to 4096 VLAN tags
• Ability to create multiple VLAN segments
• Filtering packets belonging to certain VLANs
4
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Intel® Ethernet Converged Network Adapter
X550
• Single port:
– X550T1 (single pack)
– X550T1BLK (bulk 5 pack)
• Dual port:
– X550T2 (single pack)
– X550T2BLK (bulk 5 pack)
Connector • RJ45 copper
Cabling Distances • 10GBASE-T:
– 100 m using CAT 6A
– 55 m using CAT 6
• 1000BASE-T:
– 100 m using CAT 5e, CAT6 or CAT 6A
Page 5

Product Brief
Intel® Ethernet Converged Network
Adapter X550
Network Connectivity
SPECIFICATIONS
NETWORK MANAGEMENT
Wired for Management (WfM) Baseline v2.0
Enabled for Servers
DMI 2.0 Support, Windows Management
Instrumentation (WMI) and SNMP
Remote Installation Services (RIS)
PXE 2.0 Enabled Through Boot Read-only
Memory (ROM)
SPECIFICATIONS
ADAPTER PRODUCT FEATURES
Intel® PROSet Utilit y for Easy Configuration and
Management
Intel® Lead-free Technology
Plug and Play Specification Support
Full-height Bracket Installed; Low-profile
Bracket Included in Package
RoHS Compliant
5
SPECIFICATIONS
HARDWARE FEATURES DESCRIPTION
Data rate(s) Support Per Por t • 100 Mb/s, 1 GbE and 10 GbE
Bu s Typ e • PCI Express 3.0 (8.0 GT/s)
Bus Width • x4 lane PCIe, operable in x8 and x16 slots
Interrupt Levels • INTA, MSI, and MSI-X
Hardware Certifications • Class A: USA-FCC; Canada – ICES- 003/NMB- 003, European Union – CE, Japan – VCCI, Taiwan –
BSMI, Korea – MSIP, Australia/New Zealand – RCM, Safety EN/UL and CSA C22. 2 60950-1
Controller/Processor • Intel® Ethernet Controller X550
Page 6

OPERATING SYSTEM/ARCHITECTURE SUPPORT
OPERATING SYSTEM IA32 X64 IPF
Windows 7* SP1 x
Windows 8 x
Win dows 8 .1 x
Windows 10 x
Windows Server* 2008 R2 x
Windows Server 2012 x
Windows Server 2012 R2 x
Windows PE 3.0 (2008 R2 PE) x x
Windows PE 4.0 (2012 PE) x x
Windows PE 5.0 (2012 R2 PE) x x
Linux* Stable Kernel Version 2.6/3.x/4.x x x x
Linux RHEL 6.7 x x
Linux RHEL 7.1 x x
Linux SLES 11 SP4 x x x
Linux SLES 12 x x
FreeBSD* 10.2 x x
UEF I* 2.1 x x
UEFI 2.3 x x
UEFI 2.4 x
VMware* ESXi 5.5 x
VMware ESXi 6.0 x
For more information on the Intel® Ethernet Converged Network Adapter X550, visit www.intel.com/ethernet
1
Featur e to be enabl ed in a post- launch rmwa re release.
No licen se (express o r implied, b y estoppel or o therwis e) to any intelle ctual prop erty rig hts is grant ed by this docu ment.
Intel discl aims all ex press and impli ed warranti es, includin g witho ut limitation , the implied war ranties of mer chantabili ty, tness for a par ticular pur pose, and non- infringement , as well as any w arranty ar ising
from cou rse of per formance, co urse of deal ing, or usag e in trade.
This do cument cont ains inform ation on prod ucts, se rvices an d/or processe s in developm ent. All info rmation pro vided here i s subject to c hange witho ut notice. Con tact your Int el represe ntative to ob tain the
lates t forec ast, sched ule, specic ations and road maps.
The produc ts and servi ces describe d may conta in defects or er rors which may ca use deviatio ns from publish ed specicat ions.
Copies o f document s which have an o rder number a nd are refer enced in this d ocument may b e obtained b y calling 1-8 00-548 -4725 or by vis iting www .intel.co m/design/l iterature .htm.
Intel an d the Intel log o are tradem arks of Intel C orporati on in the U.S. a nd/or other cou ntries.
* Other n ames and br ands may be cla imed as the pr operty o f others.
©
2016 Intel Coprporation
Printed in U SA 06/15/16/LH/DVA Please R ecycle 333525-0 02US
 Loading...
Loading...