Page 1

SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Order Number: A09429-003
A Guide for Technically Qualified Assemblers of Intel® Identified Subassemblies/Products
Page 2

Disclaimer
Intel Corporation (Intel) mak es no warranty of any kind with regard t o this material, includi ng, but not limited to, the im pl i ed
warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Int el as sumes no responsibility for any errors t hat may
appear in this document. Intel makes no commitm ent to update nor to keep current the inform ation contained in this
document. No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without prior wri t ten
consent of Intel.
®
An Intel
product, when used in accordance wi th its associated doc um entation, is "Year 2000 Capable" when, upon
installation, it accurately stores, di splays, processes , provides, and/or receives dat e data from, into, and between the
twentieth and twenty-first centuries, includi ng l eap year calculations, provi ded that all other technology used i n combination
with said product properly exchanges date data with it.
†
Third party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright © 1998-2000 Intel Corporation.
Page 3

Contents
Part I: User’s Guide........................................................................................................ 11
1 Baseboard Description
Baseboard Features........................................................................................................... 13
Baseboard Connector and Component Locations...................................................... 14
Processor........................................................................................................................... 15
Memory..............................................................................................................................16
Peripherals......................................................................................................................... 18
Super I/O Chip (SIO)................................................................................................. 18
Add-in Board Slots ............................................................................................................. 18
DesotoE2 Hot-Plug PCI Controller ..................................................................................... 19
IDE Interface...................................................................................................................... 19
USB Interface..................................................................................................................... 20
Network Interface Controller (NIC) ..................................................................................... 20
Video.................................................................................................................................. 20
SCSI Controller .................................................................................................................. 21
IDE Controller..................................................................................................................... 22
Keyboard and Mouse......................................................................................................... 22
Server Management........................................................................................................... 23
Baseboard Management Controller (BMC)................................................................ 23
System Security.................................................................................................................24
Software Locks via the SSU or BIOS Setup............................................................... 24
2 Configuration Software and Utilities
Hot Keys............................................................................................................................. 28
Power-On Self Test (POST)............................................................................................... 28
Using BIOS Setup.............................................................................................................. 29
Record Setup Settings............................................................................................... 29
If Setup is Not Accessible.......................................................................................... 29
Starting Setup............................................................................................................ 29
Setup Menus ............................................................................................................. 30
Main Menu................................................................................................................. 31
Advanced Menu......................................................................................................... 33
Security Menu............................................................................................................ 39
Server Menu.............................................................................................................. 40
Boot Menu................................................................................................................. 42
Exit Menu................................................................................................................... 43
Changing the Boot Device Priority Temporarily.................................................................. 44
Changing the Boot Device Priority Permanently................................................................. 44
Running the SCSI
When to Run the SCSI
Running the SCSI
Configuring the Adaptec AIC-7880 SCSI Adapter...................................................... 46
Configuring the Adaptec AIC-7899 SCSI Adapter...................................................... 46
Select
Utility........................................................................................... 45
Select
Select
Utility........................................................................... 45
Utility................................................................................... 45
iii
Page 4

Using the System Setup Utility (SSU)................................................................................. 47
When to Run the SSU ............................................................................................... 47
What You Need to Do................................................................................................ 48
Running the SSU Remotely....................................................................................... 48
Creating SSU Diskettes............................................................................................. 48
Running the SSU....................................................................................................... 49
Direct Platform Control (DPC) Console.............................................................................. 49
DPC Console Modes of Operation............................................................................. 50
Running the DPC Console......................................................................................... 50
FRU and SDR Load Utility.................................................................................................. 51
What You Need to Do................................................................................................ 51
How You Use the FRUSDR Load Utility..................................................................... 51
Cleaning Up and Exiting ............................................................................................ 53
Upgrading the BIOS........................................................................................................... 53
Preparing for the Upgrade......................................................................................... 53
Upgrading the BIOS................................................................................................... 54
Recovering the BIOS................................................................................................. 55
Changing the BIOS Language................................................................................... 55
Using the Firmware Update Utility...................................................................................... 56
Running the Firmware Update Utility ......................................................................... 56
Part II: Service Technician’s Guide ........................................................................... 57
3 Removing and Installing Baseboard Components.......................................... 59
Tools and Supplies Needed................................................................................................ 59
Safety: Before You Work with the Baseboard.................................................................... 59
Warnings and Cautions...................................................................................................... 59
Memory..............................................................................................................................61
Removing the Memory Module.................................................................................. 61
Installing the Memory Module.................................................................................... 62
Removing DIMMs...................................................................................................... 62
Installing DIMMs........................................................................................................ 62
Processors......................................................................................................................... 63
Removing a Processor .............................................................................................. 64
Installing a Processor ................................................................................................ 65
Removing Processor Retention Mechanisms ............................................................ 65
Installing Processor Retention Mechanisms.............................................................. 65
Installing Processor Handles ..................................................................................... 65
Installing Processor Heatsinks................................................................................... 66
Voltage Regulator Modules (VRMs) ................................................................................... 66
Removing a VRM....................................................................................................... 67
Installing a VRM......................................................................................................... 67
Replacing the Backup Battery ............................................................................................ 68
Add-in Boards.....................................................................................................................69
Removing a 32-bit, 33 MHz Half-Length PCI Add-in Board........................................ 70
Installing a 32-bit, 33 MHz Half-Length PCI Add-in Board.......................................... 70
Removing a 64-bit, 66/33 MHz Hot-Plug PCI Add-in Board....................................... 71
Installing a 64-bit, 66/33 MHz Hot-Plug PCI Add-in Board......................................... 72
iv SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 5

ICMB Card.........................................................................................................................73
Installing an ICMB Card............................................................................................. 74
Removing an ICMB Card........................................................................................... 75
4 Solving Problems
Boot Issues........................................................................................................................77
Issue 1: My server will not power on......................................................................... 77
Issue 2: Upon boot, my server starts beeping........................................................... 78
Issue 3: My HDD lights went on, I heard t he dr ives spin up, and my
floppy drive light turned on – but I’m not seeing video................................. 78
Issue 4: I’m installing adapters in my powered-down system, and my
system boots up when I install a PCI adapter!............................................. 79
Issue 5: My system boots up automatically when I power on my power-strip ........... 80
Issue 6: The boot up process takes too long............................................................. 80
Issue 7: I put one processor in my system but it doesn’t boot................................... 81
Other Issues....................................................................................................................... 82
Issue 8: Some of my hard drives show up during POST and some don’t.................. 82
Issue 9: My hard drives don’t show up under Windows NT....................................... 83
Checking Field Replaceable Units (FRU) with the Diagnostic Wizard................................. 84
Starting the Service Partition & Test Menu................................................................ 84
Running Tests ........................................................................................................... 85
5 Technical Reference
Connectors......................................................................................................................... 90
Power Distribution Board Interface Connectors (J9B1, J9D1, J9B2).......................... 92
Front Panel Interface (J9E3)...................................................................................... 94
Hot-Plug PCI Indicator Board Interface (J3D1).......................................................... 96
Memory Module Interface (J6F1)............................................................................... 97
Processor Module Connector (J7A1, J7B1, J7C1, J7D1)........................................... 99
Processor Termination, Regulation, and Power....................................................... 102
Termination Card..................................................................................................... 103
Server Monitor Module Connector (J7H1)................................................................ 103
SM Bus Connector (J9E4)....................................................................................... 104
ICMB Connector (J1D2) .......................................................................................... 105
2
Auxiliary I
Baseboard Fan Connectors (J3C1, J3A1, J4A1, J4C1)........................................... 105
Internal USB Header (J1B3).................................................................................... 106
Internal Disk Drive LED Connection......................................................................... 106
Baseboard Jumpers......................................................................................................... 107
Changing Jumper Settings....................................................................................... 108
CMOS Clear Jumper ............................................................................................... 109
Password Clear Jumper........................................................................................... 110
Recovery Boot Jumper............................................................................................ 110
Interrupts.......................................................................................................................... 111
Video Modes.................................................................................................................... 112
C Connector (J9E4)................................................................................ 105
Contents v
Page 6

A Equipment Log and Configuration Worksheets
Equipment Log ........................................................................................................ 113
Configuration Worksheets........................................................................................ 115
Power Configuration Worksheet.............................................................................. 115
SSU Worksheets..................................................................................................... 115
B Regulatory Specifications
Environmental Specifications and Regulatory Compliance............................................... 125
Environmental Specifications................................................................................... 125
Regulatory Compliance............................................................................................ 125
Installation Instructions ..................................................................................................... 126
Ensure EMC Compliance......................................................................................... 126
Ensure Host Computer and Accessory Module Certifications.................................. 127
Prevent Power Supply Overload.............................................................................. 127
Place Battery Marking on Computer........................................................................ 128
Use Only for Intended Applications.......................................................................... 128
Installation Precautions .................................................................................................... 128
C Warnings
WARNING: English (US)................................................................................................. 129
AVERTISSEMENT: Français........................................................................................... 129
WARNUNG: Deutsch ...................................................................................................... 129
AVVERTENZE: Italiano................................................................................................... 130
ADVERTENCIAS: Español.............................................................................................. 130
Index.................................................................................................................................... 131
Figures
1. Baseboard Connector and Component Locations..................................................... 14
2. Memory Module DIMM Installation Sequence............................................................ 16
3. Memory Module DIMM Installation Sequence............................................................ 61
4. Installing DIMMs: Orientation of DIMM in a Memory Module..................................... 63
5. Processor Orientation and Components.................................................................... 64
6. Installing a VRM ........................................................................................................ 67
7. Example of a Front Hot-Plug Retention Mechanism.................................................. 69
8. ICMB Card................................................................................................................. 73
9. Section of ICMB Internal Cable.................................................................................. 74
10. Example of an ICMB Card Attached to a Chassis...................................................... 74
11. Internal Cable Attached to the ICMB Card................................................................. 75
12. External Cable Attached to the Card ......................................................................... 75
13. Detailed Diagram of Connector Locations ................................................................. 90
14. SKA4 Configuration Jumpers................................................................................... 107
Tables
1. Baseboard Features.................................................................................................. 13
2. SKA4 Pentium Xeon Processor Family Support Matrix.............................................. 15
3. Slot State Indicators .................................................................................................. 19
4. Software Security Features....................................................................................... 25
vi SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 7

5. Configuration Utilities................................................................................................. 27
6. Hot Keys.................................................................................................................... 28
7. Main Menu................................................................................................................. 31
8. Primary IDE Master and Slave Submenu.................................................................. 32
9. Processor Settings Submenu .................................................................................... 32
10. Advanced Menu......................................................................................................... 33
11. Embedded Video Controller Submenu....................................................................... 33
12. Embedded Legacy SCSI Submenu........................................................................... 33
13. Embedded Dual Ultra 160 SCSI Submenu................................................................ 34
14. Embedded NIC Submenu.......................................................................................... 34
15. PCI Device, Slot 1 Submenu..................................................................................... 34
16. PCI Device, Slot 2 Submenu..................................................................................... 35
17. PCI Device, Slot 3 Submenu..................................................................................... 35
18. PCI Device, Slot 4 Submenu..................................................................................... 35
19. PCI Device, Slot 5 Submenu..................................................................................... 36
20. PCI Device, Slot 6 Submenu..................................................................................... 36
21. PCI Device, Slot 7 Submenu..................................................................................... 36
22. PCI Device, Slot 8 Submenu..................................................................................... 37
23. Hot-Plug PCI Control Submenu................................................................................. 37
24. Integrated Peripheral Configuration Submenu........................................................... 37
25. Advanced Chipset Control Submenu......................................................................... 38
26. Security Menu............................................................................................................ 39
27. Server Menu.............................................................................................................. 40
28. System Management Submenu................................................................................. 40
29. Console Redirection Submenu.................................................................................. 41
30. EMP Configuration Submenu.................................................................................... 41
31. PEP Management Submenu ..................................................................................... 42
32. Boot Menu................................................................................................................. 42
33. Boot Device Priority Submenu................................................................................... 42
34. Hard Drive Submenu................................................................................................. 43
35. Removable Devices Selection Submenu................................................................... 43
36. Exit Menu.................................................................................................................. 43
37. Navigation Keys......................................................................................................... 45
38. Main Menu................................................................................................................. 46
39. Exit Menu.................................................................................................................. 46
40. Main Menu................................................................................................................. 46
41. Menu for each SCSI Channel.................................................................................... 46
42. Exit Menu.................................................................................................................. 47
43. Command Line Format.............................................................................................. 51
44. VRM/Processor Power Sequence ............................................................................. 66
45. Processor/VRM Population Sequencing.................................................................... 66
46. Standard BIOS Port-80 Codes................................................................................... 78
47. Recovery BIOS Port-80 Codes .................................................................................. 78
48. Main Power Connector A (J9B1) ............................................................................... 92
49. Main Power Connector B (J9D1)............................................................................... 93
50. Auxiliary Power Connector (J9B2)............................................................................. 93
51. Front Panel Connector (J9E3)................................................................................... 94
52. Hot-Plug Indicator Board Connector Pin Out (J3D1).................................................. 96
Contents vii
Page 8

53. Memory Module Interface.......................................................................................... 97
54. Processor Card Connector Pin Out (J7A1, J7B1, J7C1, J7D1).................................. 99
55. Processor VRM Connectors (J2A2, J2B1, J2C1): Add-in VRM Connector
Pin Listing.............................................................................................................. 102
56. Server Monitor Module Connector Pin Out.............................................................. 103
57. SM Bus Connector (J9E4)....................................................................................... 104
58. ICMB Connector (J1D2).......................................................................................... 105
59. IMB Connector Pin out (J8F1)................................................................................. 105
60. Processor Fan Connector #1 (J3C1)....................................................................... 105
61. Processor Fan Connector #2 (J3A1) ....................................................................... 106
62. Processor Fan Connector #3 (J4A1) ....................................................................... 106
63. Processor Fan Connector #4 (J4C1)....................................................................... 106
64. Internal USB Connector (J1B3)............................................................................... 106
65. Internal USB Connector (J1B3)............................................................................... 106
66. Configuration Jumper Settings................................................................................. 107
67. Configuration of Jumpers......................................................................................... 108
68. Beep Codes............................................................................................................. 111
69. Interrupt Definitions................................................................................................. 111
70. Standard VGA Modes.............................................................................................. 112
71. Equipment Log........................................................................................................ 113
72. Devices Worksheet 1............................................................................................... 115
73. Systems Group Worksheet 2................................................................................... 115
74. On-board Disk Controllers Worksheet 3.................................................................. 115
75. Onboard Communications Devices Worksheet 4..................................................... 116
76. Diskette Drive Subsystems Group Worksheet 5...................................................... 116
77. IDE Subsystem Group Worksheet 6........................................................................ 116
78. On-Board PCI Devices Group Worksheet 7............................................................. 116
79. Multiboot Group Worksheet 8.................................................................................. 117
80. Security Subsystems Worksheet 9.......................................................................... 117
81. Main Menu Worksheet 10........................................................................................ 119
82. Primary Master and Slave Submenu Worksheet 11 ................................................ 119
83. Processor Settings Submenu Worksheet 12 ........................................................... 119
84. Advanced Menu Worksheet 13................................................................................ 119
85. Embedded Video Controller Submenu Worksheet 14.............................................. 120
86. Embedded Legacy SCSI Submenu Worksheet 15 .................................................. 120
87. Embedded Dual Ultra 160 SCSI Submenu Worksheet 16....................................... 120
88. Embedded NIC Submenu Worksheet 17................................................................. 120
89. PCI Device, Slot 1 Submenu Worksheet 18............................................................ 120
90. PCI Device, Slot 2 Submenu Worksheet 19............................................................ 120
91. PCI Device, Slot 3 Submenu Worksheet 20............................................................ 120
92. PCI Device, Slot 4 Submenu Worksheet 21............................................................ 120
93. PCI Device, Slot 5 Submenu Worksheet 22............................................................ 121
94. PCI Device, Slot 6 Submenu Worksheet 23............................................................ 121
95. PCI Device, Slot 7 Submenu Worksheet 24............................................................ 121
96. PCI Device, Slot 8 Submenu Worksheet 25............................................................ 121
97. Hot-Plug PCI Control Submenu Worksheet 26........................................................ 121
98. Integrated Peripheral Configuration Submenu Worksheet 27.................................. 121
99. Advanced Chipset Control Submenu Worksheet 28................................................ 122
viii SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 9

100. Security Menu Worksheet 29................................................................................... 122
101. Server Menu Worksheet 30..................................................................................... 122
102. System Management Submenu Worksheet 31........................................................ 122
103. Console Redirection Submenu Worksheet 32......................................................... 123
104. EMP Configuration Submenu Worksheet 33............................................................ 123
105. PEP Management Submenu Worksheet 34 ............................................................ 123
106. Boot Menu Worksheet 35........................................................................................ 123
107. Boot Priority Submenu Worksheet 36 ...................................................................... 123
108. Hard Drive Submenu Worksheet 37........................................................................ 123
109. Removable Devices Selection Submenu Worksheet 38.......................................... 124
110. Safety Regulations .................................................................................................. 125
111. Verification to EMC Regulations.............................................................................. 125
Contents ix
Page 10

x SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 11

Part I: User’s Guide
1 Baseboard Description
2 Configuration Software and Utilities
11
Page 12

12 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 13
1 Baseboard Description
Baseboard Features
Table 1. Baseboard Features
Feature Description
Processor Installed: Up to four Intel® Pentium® III Xeon™ processors, packaged in single
edge contact (S.E.C.) cartridges and installed in 330-pin SC330.1 compliant
edge connectors, operating at 1.8 V to 3.5 V. The baseboard’s voltage regulator
is automatically programmed by the processor’s VID pins to provide the required
voltage. The baseboard includes connectors for three 8.3-compliant plug-in
voltage-regulator modules (VRM).
Memory, dynamic
random access (DRAM)
Video memory (DRAM) Installed: 2 MB of video memory.
PCI Segment A bus
PCI Segment B bus
PCI Segment C bus
PCI Bus Master IDE
Interface
USB Interface The baseboard provides a dual external USB connector and one internally
Server Management Thermal/voltage monitoring and error handling.
Graphics ATI Rage IIc VGA Graphics Accelerator, along with video SGRAM and support
SCSI Two embedded SCSI controllers:
System I/O PS/2†-compatible keyboard and mouse ports, 6-pin DIN.
Form Factor Form-factor, 16 × 13 inches, ATX-style backpanel I/O.
Single plug-in module containing 64/72-bit four-way-interleaved pathway to main
memory supporting SDRAM.
Installed: 256 MB to 16 GB of error correcting code (ECC) memory. A minimum
of four DIMMs must be installed.
PCI-A—Two full length connectors and one embedded device:
• Two 184-pin, 3.3 V keyed, 64-bit PCI expansion connectors (66/33 MHz).
• One DesotoE2 Hot-Plug PCI controller.
PCI-B—Four full length connectors and two embedded devices:
• One Adaptec
• Four 184-pin, 5 V keyed, 64-bit PCI expansion connectors (33 MHz).
• One DesotoE2 Hot-Plug PCI controller.
PCI-C—Two half length connectors and several embedded devices:
• Two 120-pin, 32-bit PCI expansion connectors (33 MHz).
• OSB4 I/O APIC.
• PCI network interface controller.
• ATI Rage
• PCI narrow/wide Adaptec AIC-7880 Ultra SCSI controller.
The baseboard supports Ultra DMA33 Synchronous Direct Memory Access
(DMA) mode transfers.
accessible header.
Front panel controls and indicators (LEDs).
circuitry for an embedded SVGA video subsystem.
Adaptec AIC-7899 SCSI Controller—Dual Channel Wide Ultra/Ultra II/Ultra
160/M SCSI controller.
Adaptec AIC-7880 SCSI Controller—PCI narrow/wide Ultra SCSI controller.
Advanced parallel port, supporting Enhanced Parallel Port (EPP) levels 1.7 and
1.9, ECP, compatible 25-pin.
VGA video port, 15-pin.
Two serial ports, 9-pin (serial port A is the top connector).
†
AIC-7899 dual channel SCSI-3 Ultra 160/m SCSI controller.
†
IIc video controller.
13
Page 14
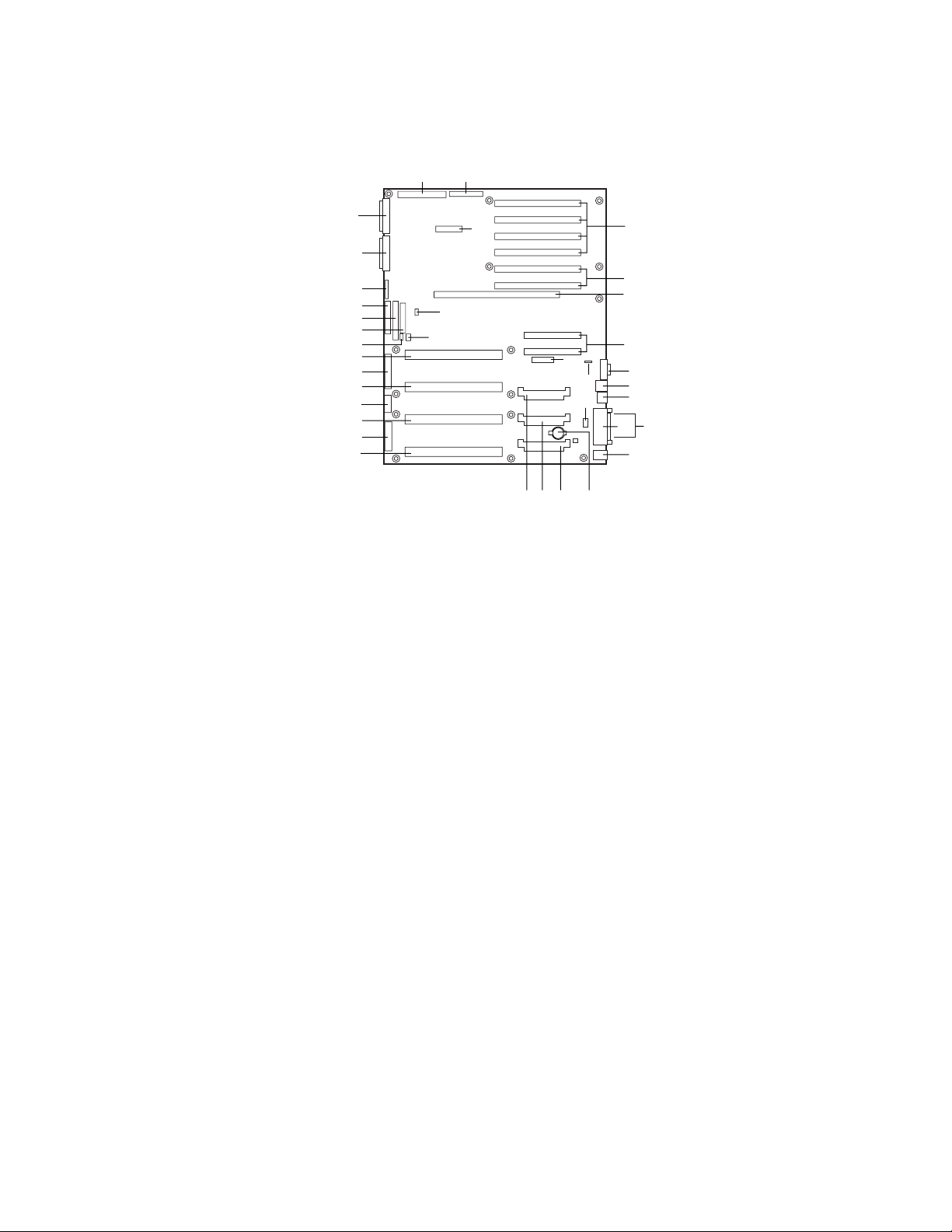
Baseboard Connect or and Component Locations
A B
Z
Y
X
W
V
U
T
AA
S
BB
R
CC
Q
DD
C
D
E
F
H
FFEE
GG
G
I
JJ
I I
J
HH
K
L
M
N
P
OM09918
O
Figure 1. Baseboard Connector and Component Locations
A. Legacy Narrow SCSI B. Legacy Wide SCSI
C. SMM Connector D. IMB Connector
E. HDD Activity F. HPIB Connector
G. ICMB Connector H. Internal USB Connector
I. Lithium Battery J. Memory Module Connector
K. Video Connector L. USB, External Connector
M. Network Connector N. Parallel Connector
O. COM1, COM2 Connector P. Keyboard/Mouse
Q. Main Power 1 R. Auxiliary Power
S. Main Power 2 T. SMBus
U. Front Panel V. IDE Connector
W. Floppy Connector X. Configuration Jumpers
Y. Ultra 160 SCSI A Z. Ultra 160 SCSI BA. Legacy
Narrow SCSI
AA. Processor #1 BB. Processor #2
CC. Processor #3 DD. Processor #4
EE. Voltage Regulator Module (VRM)
Connector #2
GG. Voltage Regulator Module (VRM)
Connector #4
II. 64-bit, 66/33 MHz Hot-Plug PCI
Slots
FF. Voltage Regulator Module (VRM)
Connector #3
HH. 32-bit, 33 MHz Half-length PCI
Slots
JJ. 64-bit, 33 MHz Hot-Plug PCI Slots
14 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 15

CAUTION
Lithium Battery: See "Replacing the Backup Battery" on page 68 of this
product guide for instructions on replacing and disposing of the Lithium
Battery.
Processor
Each Intel Pentium III Xeon processor is packaged in a single edge contact (S.E.C.) cartridge. The
cartridge includes the processor core with an integrated 32 KB primary (L1) cache, the secondary
(L2) cache, a thermal plate, and a plastic cover.
The processor core and L2 cache components are on a pre-assembled printed circuit board,
approximately 5 inches by 6 inches. The L2 cache and processor core L1 cache interface use a
private bus isolated from the processor host bus. The L2 cache bus operates at the processor core
frequency.
Each S.E.C. cartridge connects to the baseboard through a 330-pin SC330.1 compliant edge
connector. A retention module attached to the baseboard secures the cartridge. Depending on
configuration, the system supports one to four processors.
The processor external interface is MP-ready and operates at 100 MHz. The processor contains a
local Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (APIC) unit for interrupt handling in
multiprocessor (MP) and uniprocessor (UP) environments.
Table 2. SKA4 Pentium Xeon Processor Family Support Matrix
Name Frequency Cache Size Support (Y/N)
Pentium II Xeon processor 400 MHz, 450 MHz 512k, 1M, 2M No
Pentium III Xeon processor 500 MHz
550 MHz
Pentium III Xeon processor 600 MHz + 256k No
2.8 V Pentium III Xeon processor 600 MHz + 1M, 2M Yes
5/12 V Pentium III Xeon processor 600 MHz + 1M, 2M No
512k, 1M, 2M Yes
The L2 cache is located on the substrate of the S.E.C. cartridge. The cache:
• Is offered in 512 KB, 1 MB, and 2 MB configurations
• Has ECC
• Operates at the full core clock rate
Baseboard Description 15
Page 16
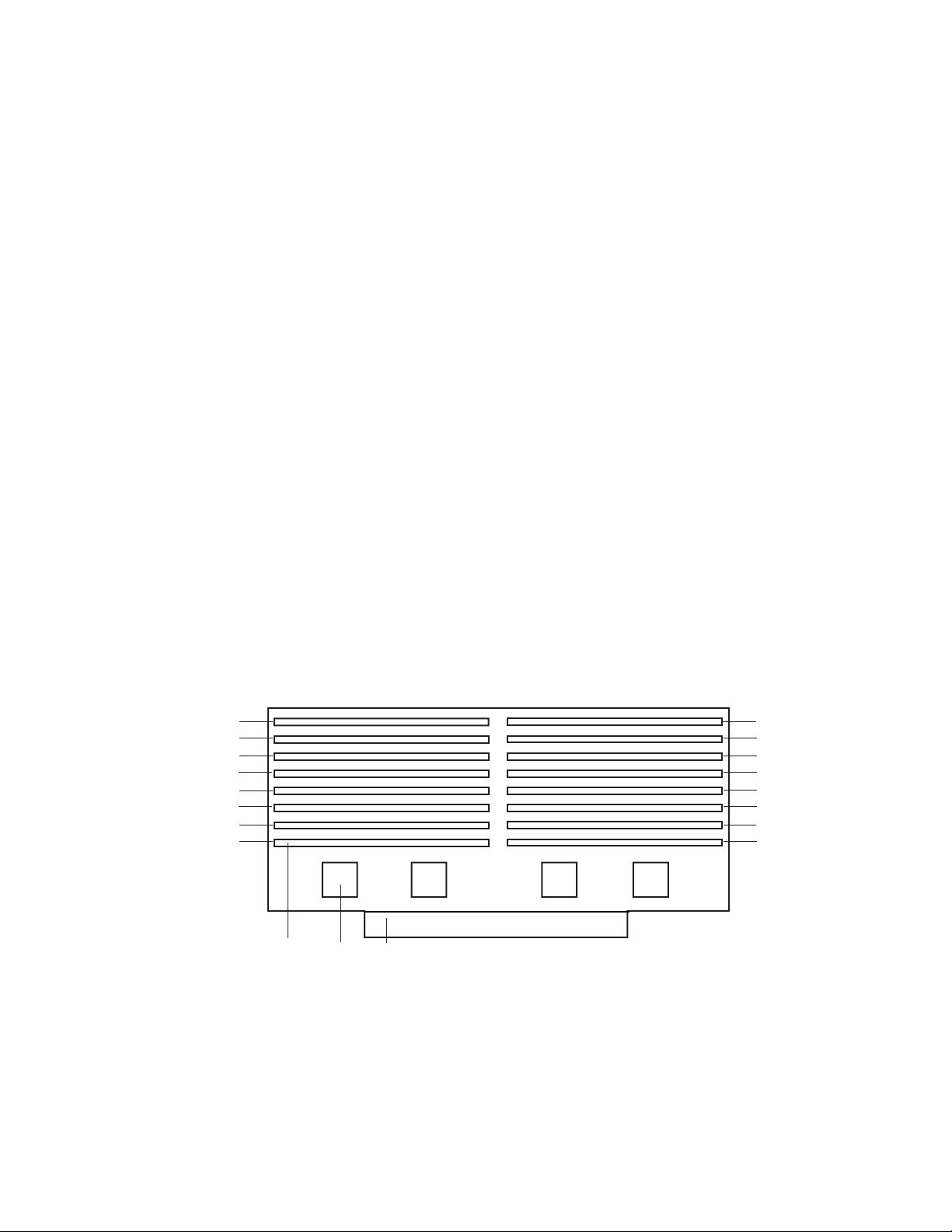
Memory
Main memory resides on an add-in board, called a memory module, designed for the SKA4
baseboard. The memory module contains slots for 16 DIMMs, each of which must be at least
64 MB, and is attached to the baseboard through a 330-pin connector, called the Memory
Expansion Card Connector (MECC). The memory module supports PC-100 compliant registered
ECC SDRAM memory modules. The ECC used for the memory module is capable of correcting
single-bit errors (SBEs) and detecting 100 percent of double-bit errors over one code word. Nibble
error detection is also provided.
System memory begins at address 0 and is continuous (flat addressing) up to the maximum amount
of DRAM installed (exception: system memory is noncontiguous in the ranges defined as memory
holes using configuration registers). The system supports both base (conventional) and extended
memory.
• Base memory is located at addresses 00000h to 9FFFFh (the first 1 MB).
• Extended memory begins at address 0100000h (1 MB) and extends to 3FFFFFFFFh (16 GB),
which is the limit of supported addressable memory. The top of physical memory is a
maximum of 16 GB (to 3FFFFFFFFh).
Memory amounts from 256 MB to 16 GB of DIMM are supported, with a 64/72-bit
four-way-interleaved pathway to main memory, which is also located on the module. Therefore,
data transfers between MADPs and DIMMs is in four-way interleave fashion. Each of the four
DIMMs must be populated in a bank. The 16 slots are divided into four banks of four slots each.
They are labeled A through D. Bank A contains DIMM sockets A1, A2, A3, and A4. Banks B, C,
and D each contain 4 DIMM sockets and are named in the same fashion. There are silk screens on
the module next to each DIMM socket to label its bank number. For the best thermal results,
populate the banks from A to D. For example, populate bank A and then bank B. For best
performance results, populate adjacent banks. For example, populate bank A and then bank C.
A3
C3
B3 B4
D3
A1
C1
B1
D1
XY
Figure 2. Memory Module DIMM Installation Sequence
Z
X. One of sixteen DIMM sockets
Y. One of four Memory Address Data Paths (MADP)
Z. Memory Expansion Card Connector (MECC)
A4
C4
D4
A2
C2
B2
D2
OM09919
16 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 17

Each slot is identified by another notation. Sockets A1 through A4 are identified as J1 through J4
respectively. Sockets B1 through B4 are identified as J5 through J8. Sockets C1 through C4 are
identified as J9 through J12. Sockets D1 through D4 are identified as J13 through J16.
NOTE
✏
Based on the chipset, addressable memory can be extended to 16 GB.
However, some server systems are not thermally configured to support all
16 GB. Consult the documentation accompanying your server system to
determine the maximum memory configuration of your server system.
Some operating systems and application programs use base memory while others use both
conventional and extended memory. Examples are
†
• Base memory: Microsoft MS-DOS
†
UNIX
• Conventional and extended memory: IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows NT, and various UNIX
MS-DOS does not use extended memory; however, some MS-DOS utility programs like RAM
disks, disk caches, print spoolers, and windowing environments use extended memory for better
performance.
The BIOS automatically detects, sizes, and initializes the memory array, depending on the type,
size, and speed of the installed DIMMs, and reports memory size and allocation to the system via
configuration registers.
, IBM OS/2†, Microsoft Windows NT†, and various
✏
NOTE
DIMM sizes and compatibility: Use DIMMs that have been tested for
compatibility with the baseboard. For a list of approved DIMMs, see the
SKA4 Memory Qualification List. The document can be found on
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SKA4/compat.htm.
Baseboard Description 17
Page 18

Peripherals
Super I/O Chip (SIO)
The National† PC97317VUL Super I/O Plug and Play Compatible with ACPI Compliant
Controller/Extender device supports two serial ports, one parallel port, diskette drive, and
PS/2-compatible keyboard and mouse. The system provides the connector interface for each port.
Serial Ports
Both serial ports can be relocated. Each serial port can be set to one of four different COMx ports,
and each can be enabled separately. When disabled, serial port interrupts are available to add-in
boards.
Parallel Port
The SKA4 baseboard provides a 25-pin Parallel Port connector. The SIO provides an IEEE
1284-compliant 25-pin bi-directional parallel port. BIOS programming of the SIO registers enable
the parallel port, and determine the port address and interrupt. When disabled, the interrupt is
available to add-in cards.
Add-in Board Slots
The baseboard has eight slots for PCI add-in boards supported by three PCI bus segments called
PCI-A, PCI-B, and PCI-C. There are two on PCI-A, four on PCI-B, and two on PCI-C. PCI-C
supports half-length boards (5.6" to 6.3") only; the other slots support full-length boards.
The two slots for the PCI bus segment PCI-C consume a maximum of 375 mA of standby current
on a 3.3V AUX power line. The remaining six slots do not have any 3.3V Aux capabilities.
Both PCI segments A and B allow you to add, remove, or replace PCI add-in boards installed in
their slots without interrupting normal operation or powering down the system. To use this PCI
Hot-Plug (PHP) feature, a server system requires PCI Hot-Plug software and PCI Hot-Plug capable
add-in boards. PCI Hot-Plug software usually is a driver loaded for a specific operating system.
Each Hot-Plug PCI slot has two LEDs. The green LED indicates the state of power on each slot.
The amber LED indicates an error condition with that slot.
18 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 19

The table below summarizes typical LED states that you may encounter during a system’s
operation.
Table 3. Slot State Indicators
LED State Status
Green On
Amber Off
Green On
Amber On
Green Off
Amber On
Green blinking
Amber Off
Off The slot is powered off.
The slot is on and functioning normally.
The slot is on and the card requires attention.
The slot is off and the card in the slot requires attention.
Slot power is transition from either ON to OFF or OFF to ON.
PCI features include:
• 33 or 66 MHz bus speed
• 32-bit or 64-bit memory addressing
• 3.3V or 5V signaling environment
• Independent bus structure supports transfers up to 1.2 GB/sec
• 8-, 16-, 32-, or 64-bit data transfers
• Plug and Play ready
• Parity enabled
DesotoE2 Hot-Plug PCI Controller
The DesotoE2 Hot-Plug PCI controller is a 32-bit PCI bus agent that operates at either 33 or
66 MHz. The PCI controller manages PHP functionality for the PCI segment it resides on. There
is a DesotoE2 controller on PCI segments A and B. The DesotoE2 PHP controller is:
• ACPI compliant
†
• Compatible with Compaq’s
PHP controller design
• Supports either a 3.3 V or 5 V PCI bus
The DesotoE2 is responsible for:
• Managing power application and removal to individual slots
• Properly resetting newly-added PCI boards prior to bringing the board online
• Managing connection and disconnection of the PCI signals between the P CI bus and the add-
in board
• Managing seamless addition and removal of individual PCI add-in boards without impacting
bus functionality
IDE Interface
The Open South Bridge (OSB4) acts as a PCI-based fast IDE controller. The controller supports
programmed I/O and bus master transfers. While the OSB4 supports two IDE channels, the SKA4
baseboard uses only the primary IDE channel and provides a single 40 pin IDE connector.
Baseboard Description 19
Page 20

USB Interface
The SKA4 baseboard provides a dual external USB connector for the back panel of a server
system. The connector is defined by the USB Specification, Revision 1.0. Both ports function
identically with the same bandwidth. The SKA4 baseboard also provides a proprietary internal
USB header.
Network Interface Controller (NIC)
The SKA4 baseboard supports a 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX network subsystem based on the
®
82559 Fast Ethernet Multifunction PCI/CARDBus controller. The Intel 82559 controller is
Intel
a highly integrated PCI LAN controller in a 196-pin Ball Grid Array (BGA) supporting 10 or
100 Mbps fast Ethernet networks.
Supported network features include:
• Glueless 32-bit PCI Bus Master Interface compatible with the PCI Local bus Specification
• 82596-like chained memory structure with improved dynamic transmit chaining for enhanced
performance
• Programmable transmit threshold for improved bus utilization
• Early receive interrupt for concurrent processing of receive data
• On-chip counters for network management
• Auto-detect and auto-switching for 10 or 100 Mbps network speeds
• Support for both 10 and 100 Mbps networks
• Integrated physical interface to TX magnetics
• The magnetics component terminates the 100BASE-TX connector interface and a flash device
stores the network ID
Video
The SKA4 baseboard provides an ATI Rage IIc VGA Graphics Accelerator, along with video
Synchronous Graphics RAM (SGRAM) and support circuitry for an embedded Super VGA
(SVGA) video subsystem. The ATI Rage IIc chip contains an SVGA video controller, clock
generator, BitBLT engine, and a RAM digital-to-analog Converter (RAMDAC) in a 208-pin
PQFP. One 256K x 32 SGRAM chip provides 2 MB of 10-ns video memory. The baseboard does
not support adding video memory to the system. The SVGA subsystem supports a variety of
modes, up to 1600 x 1200 resolution, or up to 16.7 M colors.
The SVGA subsystem also supports analog VGA monitors, single- and multi-frequency, interlaced
and non-interlaced, up to 100 Hz vertical retrace frequency. The SKA4 baseboard provides a
standard 15-pin VGA connector and video blanking logic for server management console
redirection support.
Depending on the environment, the controller displays up to 16.7 M colors in some video
resolutions.
20 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 21

SCSI Controller
The baseboard includes two SCSI controllers. A dual function SCSI controller
(Adaptec AIC-7899) is on the PCI-B bus, and a PCI wide SCSI controller (Adaptec AIC-7880) is
on the PCI-C bus.
The Adaptec AIC-7899 SCSI controller contains two independent SCSI controllers that share a
single PCI bus master interface as a multifunction device, packaged in a 352-pin ball grid array
(BGA). Internally, each controller is identical, capable of operations using either 16-bit SE or Low
Voltage Differential (LVD) SCSI providing 40 MBps (Ultra-wide SE), 80 MBps (Ultra 2), or
160 MBps (Ultra 160/m).
In the SKA4 implementation, both controller A and controller B attach to a 68-pin 16-bit
differential SCSI connector LVD interface. Each controller has its own set of PCI configuration
registers and SCSI I/O registers. As a PCI bus master, the AIC-7899 controller supports burst data
transfers on PCI up to the maximum rate of 266 MBps using on-chip buffers.
The AIC-7880 controller contains a single SCSI controller with full-featured PCI bus master
interface in a 160-pin Plastic Quad Flat Pack (PQFP). The controller supports either 8- or 16-bit
Fast SCSI providing 10 MBps or 20 MBps (Fast-10) throughput, or Fast-20 SCSI that can burst
data at 20 MBps or 40 MBps. As a PCI 2.1 bus master, the AIC-7880 controller supports burst
data transfers on PCI up to the maximum rate of 133 MBps using the on-chip 256-byte FIFO.
The SKA4 AIC-7880 implementation offers 8-bit or 16-bit SCSI connectors and operation at data
transfer rates of 10, 20, or 40 MBps. The AIC-7880 controller also offers active negation outputs,
controls for external differential transceivers, a disk activity output, and a SCSI terminator powerdown control. Active negation outputs reduce the chance of data errors by actively driving both
polarities of the SCSI bus, avoiding indeterminate voltage levels and common-mode noise on long
cable runs. The SCSI output drivers can directly drive a 48-mA single-ended SCSI bus with no
additional drivers. The SCSI segment can support up to 15 devices.
The AIC-7880 controller can be used as an 8-bit controller via the narrow, 50-pin connector and as
a 16-bit controller via the wide, 68-pin connector. As a result, the AIC-7880 controller is not
always at one end of the SCSI bus, and termination is controlled through some simple circuitry.
The circuitry senses whether there is a device attached through the narrow 50-pin connector or the
wide 68-pin connector. When there are devices off both connectors, the termination is on for the
upper 8 bits of data and the parity bit associated with these data lines. All other signals are not
terminated on board and are terminated by the devices attached through the connector. When there
is a device on only one connector (either wide or narrow), all on-board termination is on.
Baseboard Description 21
Page 22

IDE Controller
IDE is a 16-bit interface for intelligent disk drives with AT† disk controller electronics onboard.
The Open South Bridge (OSB4) acts as a PCI-based fast IDE controller. The device controls:
• PIO and IDE DMA/bus master operations
• Mode 4 timings
• Transfer rates up to 33 MB/sec
• Ultra DMA 33 capacity
• Buffering for PCI/IDE burst transfers
• Master/slave IDE mode
• Up to two drives for one IDE channel
NOTE
✏
18-inch maximum length of IDE cable: An IDE signal cable can be
connected up to the IDE connector on the baseboard. However, the
maximum length of the cable is 18 inches. The cable supports up to two
devices, one at the end of the cable and the other six inches from the end.
Keyboard and Mouse
The PS/2-compatible keyboard and mouse connectors are mounted in a single-stacked housing
with the mouse connector over the keyboard. External to the system, they appear as two
connectors.
The user can plug in the keyboard and mouse to either connector before powering up the system.
BIOS detects these and configures the keyboard controller accordingly.
®
The keyboard controller is functionally compatible with the Intel
system can be locked automatically if no keyboard or mouse activity occurs for a predefined length
of time, if specified through the SSU. Once the inactivity (lockout) timer has expired, the
keyboard and mouse do not respond until the previously stored password is entered.
8042A microcontroller. The
22 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 23

Server Management
Server management features are implemented using one microcontroller called the Baseboard
Management Controller (BMC).
Baseboard Management Controller (BMC)
The BMC and associated circuitry are powered from 5V_Standby, which remains active when
system power is switched off. The BMC is IPMI 1.0 compliant.
The primary function of the BMC is to autonomously monitor system platform management events
and log their occurrence in the nonvolatile System Event Log (SEL). The BMC is compliant to the
Intelligent Platform Management Interface Specification, Version 1.0. These events include
overtemperature and overvoltage conditions, fan failure, or chassis intrusion. While monitoring,
the BMC maintains the nonvolatile Sensor Data Record Repository (SDRR), from which run-time
information can be retrieved. The BMC provides an interface to SDRR information, so software
running on the server can poll and retrieve the current status of the platform. A shared register
interface is defined for this purpose.
Field service personnel can retrieve SEL contents after system failure for analysis by using system
®
management tools like Intel
Platform control (DPC). Because 5V_Standby provides power the BMC, SEL (and SDRR)
information is also available via the interperipheral management bus (IPMB). During monitoring,
the BMC performs the following functions:
• Baseboard temperature and voltage monitoring
• Processor presence monitoring and FRB control
• Baseboard fan failure detection and indicator control
• SEL interface management
• Sensor Data Record Repository (SDRR) interface management
• SDR/SEL timestamp clock
• Baseboard Field Replaceable Unit (FRU) information interface
• System management watchdog timer
• SMI/NMI Status Monitor
• Front panel NMI handling
• Event receiver
• IPMB Management Controller Initialization Agent
• Secure mode control, front panel lock/unlock initiation, and video blank and diskette write
protect monitoring and control
• ACPI Support
• Direct Platform Control (DPC) support
• Platform Event Paging (PEP) / Platform Event Filtering (PEF)
• Power distribution board monitoring
• Speaker beep capability. When the system is powered up, this capability is used to indicate
conditions such as "empty processor slot"
• Pentium III Xeon processor SEEPROM interface for Processor Information ROM (PIROM)
and Scratch EEPROM access
LANDesk® Server Manager, Intel Server Control (ISC), or Direct
Baseboard Description 23
Page 24

• Processor temperature monitoring
• Hot-Plug PCI slot status reporting
• Processor bus speed setting
• Chassis fan failure light control
• Chassis power fault light control
• Chassis power light control
System Security
To help prevent unauthorized entry or use of the system, the system includes a three-position key
lock/switch to permit selected access to drive bays (position is communicated to BMC). The
system also includes server management software that monitors the chassis intrusion switch.
Software Locks via the SSU or BIOS Setup
The SSU provides a number of security features to prevent unauthorized or accidental access to the
system. Once the security measures are enabled, access to the system is allowed only after the user
enters the correct password(s). For example, the SSU allows:
• Enable the keyboard lockout timer so the server requires a password to reactivate the keyboard
and mouse after a specified time-out period of 1 to 120 minutes
• Set and enable administrator and user passwords
• Set secure mode to prevent keyboard or mouse input and to prevent use of the front panel reset
and power switches
• Activate a hot key combination to enter secure mode quickly
• Disable writing to the diskette drive when secure mode is set
Using Passwords
If a user password is set and enabled, but an administrator password is not set, a user password
must be entered to boot the system and run the SSU.
If both a user and administrator password is set:
• Enter either one to boot the server and enable the keyboard and mouse
• Enter the administrator password to access the SSU or BIOS Setup to change the system
configuration
Secure Mode
Configure and enable the secure boot mode by using the SSU. When secure mode is in effect,
• The system can boot and the operating system runs, but the user password must be entered for
a user to use the keyboard or mouse
• The system cannot be turned off or reset from the front panel switches
Secure mode has no effect on functions enabled via the Server Manager Module or power control
via the real-time clock (RTC).
24 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 25
Taking the system out of secure mode does not change the state of system power. That is, if you
press and release the power switch while secure mode is in effect, the system will not power off
when secure mode is later removed. However, if the front panel power switch remains depressed
when secure mode is removed, the system will power off.
Summary of Software Security Features
Table 4 lists the software security features and describes what protection each offers. In general,
to enable or set the features listed here, the SSU must be run and configured with the Security
Menu (described in this manual on page 39.) The table also refers to other SSU menus and to the
Setup utility. For greater detail, see Chapter 2, beginning on page 27.
Table 4. Software Security Features
Feature Description
Secure mode
Disable writing to diskette In secure mode, the server will not boot from or write to a diskette unless a
Disable the power and
reset buttons
Set a time out period so
that keyboard and mouse
input are not accepted
Also, screen can be
blanked, and writes to
diskette can be inhibited
How to enter secure mode:
• Setting and enabling passwords automatically places the system in secure
mode.
• If a hot key combination is set (through the SSU or Setup), the system can be
secured simply by pressing the key combination. This means that the user
does not have to wait for the inactivity time-out period.
When the system is in secure mode:
• The server can boot and run the operating system, but mouse and keyboard
input is not accepted until the user password is entered.
• At boot time, if a CD is detected in the CD-ROM drive or a diskette in drive A,
the system prompts for a password. When the password is entered, the
server boots from CD or diskette and disables the secure mode.
• If there is no CD in the CD-ROM drive or diskette in drive A, the server boots
from drive C and automatically goes into secure mode. All enabled secure
mode features go into effect at boot time.
To leave secure mode, enter the correct password(s).
password is entered. To set this feature, use the SSU Secur ity Subsystem
Group.
To write protect access to diskette whether the server is in secure mode or not,
use the Setup main menu, Floppy Options, and specify Floppy Access as
read only.
Power and reset buttons are always disabled when the server is in secure mode.
Specify and enable an inactivity time out period of from 1 to 120 minutes.
If no keyboard or mouse action occurs for the specified period, attempted
keyboard and mouse input will not be accepted.
The monitor display will go blank, and the diskette drive will be write protected
(if these security features are enabled through Setup or the SSU and using
onboard video).
To resume activity, enter the user password.
continued
Baseboard Description 25
Page 26

Table 4. Software Security Features (continued)
Feature Description
Control acce ss to using
the SSU: set
administrative password
Control acce ss to the
system other than SSU:
set user password
Boot without keyboard The system can boot with or without a keyboard. During POST, before the
Specify the boot
sequence
To control access to setting or changing the system configuration, set an
administrative password and enable it through Setup or the SSU.
If both the administrative and user passwords are enabled, either can be used to
boot the server or enable the keyboard and/or mouse, but only the
administrative password will allow Setup and the SSU to be changed.
To disable a password, change it to a blank entry or press CTRL-D in the
Change Password menu of the Administrative Password Option menu found in
the Security Subsystem Group.
If you cannot access Setup or the SSU to clear the password, change the Clear
Password jumper. See "CMOS Clear Jumper" on page 109.
To control access to usin g the system, se t a user passwo rd and enable it
through Setup or the SSU.
To disable a password, change it to a blank entry or press CTRL-D in the
Change Password menu of the User Password Option menu found in the
Security Su bsystem Group.
If you cannot access Setup or the SSU to clear the password, change the Clear
Password jumper. See "CMOS Clear Jumper" on page 109.
system complet es the boot sequence, the BIOS automatically detects and tests
the keyboard if it is present and displays a message. There is no entry in the
SSU to enable or disable a keyboard.
The sequence specified on the menu in the SSU MultiBoot Group will determine
the boot order. If secure mode is enabled (a user password is set), then the
user is prompted for a password before the server fully boots. If secure mode is
enabled and the “Secure Boot Mode” option is also enabled, the server fully
boots but requires a password before accepting any keyboard or mouse input.
26 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 27
2 Configuration Software and Utilities
This chapter describes the Power-On Self Test (POST) and system configuration utilities. The
table below briefly describes the utilities.
Table 5. Configuration Utilities
Utility Description and brief procedure Page
BIOS Setup If the system does not have a diskette drive, or the drive is
disabled or misconfigured, use Setup to enable it.
Or, you can move the CMOS jumper on the system board from the
default setting (Protect CMOS memory) to the Clear setting; this
will allow most system configurations to boot. For the procedure to
do this, see “CMOS Clear Jumper” on page 109.
Changing Boot Device
Priority
SCSI
Select
Utility Use to configure the SCSI controllers in the system. 45
Adaptec SCSI Utility Use to configure or view the settings of the SCSI host adapters
Server Setup Utility (SSU) Use for extended system configuration of onboard resources and
Direct Platform Control
(DPC) Console
FRUSDR Load Utility Use to update the Field Replacement Unit (FRU), Sensor Data
BIOS Update Utility Use to update the BIOS or recover from a corrupted BIOS update. 53
Firmware Update Utility Use to update BMC flash ROM. 56
Use this option to change the boot device priority temporarily or
permanently.
and onboard SCSI devices in the system.
add-in boards, viewing the system event log (SEL), setting boot
device pri ority, or setting system security options.
The SSU can be run from either the configuration software CD or
from a set of bootable diskettes. You can create the diskettes from
the CD.
Information entered via the SSU overrides information entered via
Setup.
Use to access and monitor the server remotely. 49
Record (SDR), and Desktop Management Interface (DMI) flash
components.
29
44
46
47
51
27
Page 28

Hot Keys
Use the keyboard’s numeric pad to enter numbers and symbols.
Table 6. Hot Keys
To do this: Press these keys
Clear memory and reload the operating
systemthis is a system reset.
Secure your system immediately. <Ctrl+Alt>+hot key (Set yo ur hot key combination
Enter the Adaptec SCSI Utility during BIOS POST. <Ctrl+A>
Enter BIOS Setup during BIOS POST. F2
Abort memory test during BIOS POST. ESC (Press while BIOS is updating memory size on
<Ctrl+Alt+Del>
with the SSU or Setup.)
screen.)
Power-On Self Test (POST)
Each time you turn on the system, the BIOS begins execution of the Power-On Self Test (POST).
POST discovers, configures, and tests the processors, memory, keyboard, and most installed
peripheral devices. The length of time needed to test memory depends on the amount of memory
installed. POST is stored in flash memory.
1. Turn on your video monitor and system. After a few seconds, POST begins to run and a splash
screen is displayed.
2. While the splash screen is displayed, you can either
• press <F2> to enter the BIOS Setup (see "Using BIOS Setup" on page 29)
OR
• press <Esc> to change the boot device priority for this boot only (see "Changing the Boot
Device Priority Temporarily" on page 44).
3. After pressing <F2> or <Esc> during POST, you can press <Ctrl+A> to run the SCSISelect
Utility. For more information, see "Running the SCSISelect Utility" on page 45.
4. If you do not press <F2> or <Esc> and do NOT have a device with an operating system
loaded, the boot process continues and the system beeps once. The following message is
displayed:
Operating System not found
5. At this time, pressing any key causes the system to attempt a reboot. The system searches all
removable devices in the order defined by the boot priority.
6. If you want to boot from a hard drive loaded with an operating system, make sure that the hard
drive is installed and push the Reset button on the front panel.
28 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 29

Using BIOS Setup
This section describes the BIOS Setup options. Use Setup to change the system configuration
defaults. You can run Setup with or without an operating system being present. Setup stores most
of the configuration values in battery-backed CMOS; the rest of the values are stored in flash
memory. The values take effect when the system is booted. POST uses these values to configure
the hardware; if the values and the actual hardware do not agree, POST generates an error
message. You must run Setup to specify the correct configuration.
†
Run Setup: Run Setup to modify any standard PC-AT
• Select diskette drive
• Select parallel port
• Select serial port
• Set time/date (to be stored in RTC)
• Configure hard drive(s)
• Specify boot device sequence
• Enable SCSI BIOS
Run SSU, not Setup: Run the SSU instead of Setup to do the following:
• Enter or change information about a board
• Alter system resources (e.g., interrupts, memory addresses, I/O assignments) to user-selected
choices instead of choices selected by the BIOS resource manager
baseboard feature such as:
Record Setup Set tings
If the default values ever need to be restored (after a CMOS clear, for example), Setup must be run
again. Referring to the worksheets could make the task easier.
If Setup is Not Accessible
If the diskette drive is misconfigured and you cannot use Setup to correct the problem, you might
need to clear CMOS memory. You must open the system, change a jumper setting, use Setup to
check and set diskette drive options, and change the jumper back. For a step-by-step procedure,
see “CMOS Clear Jumper” on page 109.
Starting Setup
Setup can be entered under several conditions:
• When you turn on the system, after POST completes the memory test.
• When you reboot the system by pressing <Ctrl+Alt+Del> while at the DOS operating system
prompt.
• When you have moved the CMOS jumper on the baseboard to the “Clear CMOS” position
(enabled); for a step-by-step procedure, see “CMOS Clear Jumper” on page 109.
In the three conditions listed above, the following prompt is displayed:
Press <F2> to enter SETUP
Configuration Software and Utilities 29
Page 30

In a fourth condition, when CMOS/NVRAM has been corrupted, these other prompts are
displayed, but not the <F2> prompt:
Warning: cmos checksum invalid
Warning: cmos time and date not set
In this condition, the BIOS loads default values for CMOS and attempts to boot.
Setup Menus
Setup has six major menus and several submenus:
1. Main Menu
• Primary IDE Master and Slave Adapters
• Processor Settings Information
2. Advanced Menu
• PCI Configuration
Embedded Video Controller
Embedded Legacy SCSI
Embedded Dual Ultra 160 SCSI
Embedded NIC
PCI Devices, Slots 1 - 8
Hot-Plug PCI Control
• Integrated Peripheral Configuration
• Advanced Chipset Control
3. Security Menu
• Passwords
• Lockout features
4. Server Menu
• System Management
• Console Redirection
• EMP Configuration
• PEP Management
5. Boot Menu
• Boot Device Priority
• Hard Drive
• Removable Devices Selections
6. Exit Menu
30 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 31

Navigation
To: Press:
Get general help <F1> or <Alt+H>
Move between menus ← →
Go to the previous item ↑
Go to the next Item ↓
Change the value of an item + or Select an item or display a submenu <Enter>
Leave a submenu or exit Setup <Esc>
Reset to Setup defaults <F9>
Save and exit Setup <F10>
Display
When you see this: What it means:
On screen, an option is shown but you cannot
select it or move to that field.
On screen, the phrase Press Enter appears next
to the option.
You cannot change or configure the option in that
menu screen for one of the following reasons:
• The option is auto-configured or auto-detected.
• You must use a different Setup screen to change it.
• You must use the SSU.
Press <Enter> to display a submenu that is either a
separate full-screen menu or a pop-up menu with one
or more choices.
The rest of this section lists the features that display onscreen after you press <F2> to enter Setup.
Not all of the option choices are described, because (1) a few are not user-selectable but are
displayed for your information, and (2) many of the choices are relatively self-explanatory.
Main Menu
Table 7 lists the selections you can make on the Main Menu itself. Use the submenus for other
selections. Default values are in bold.
Table 7. Main Menu
Feature Choices Description
System Time HH:MM:SS Sets the system time.
System Date MM/DD/YYYY Sets the system date .
Legacy Diskette A: Disabled
1.44/1.25 MB 3½"
2.88 MB 3½"
Legacy Diskette B:
Primary IDE Master N/A Enters submenu.
Primary IDE Slave N/A Enters submenu.
Processor Settings N/A Enters submenu.
Language
Disabled
1.44/1.25 MB 3½"
2.88 MB 3½"
English (US)
French
Spanish
German
Italian
Japanese (Kanji)
Selects the diskette type.
Selects the diskette type.
Selects which language BIOS displays.
NOTE
✏
Serial redirection does
not work with Kanji.
Configuration Software and Utilities 31
Page 32

Primary IDE Master and Slave Submenu
In the following table, the features other than “Type” appear only for Type Auto if a drive is
detected.
Table 8. Primary IDE Master and Slave Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Type User
Auto
CD-ROM
ATAPI Removable
Multi-Sector
Transfers
LBA Mode
Control
32 Bit I/O
Transfer Mode
Ultra DMA Mode
Disabled
2, 4, 8, or 16 sectors
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Standard
Fast PIO 1
Fast PIO 2
Fast PIO 3/DMA 1
Fast PIO 4/DMA 2
Disabled
Enabled
User allows the manual entry of all fields described below.
Auto allo ws the system to at tempt auto-detection of the drive
type.
CD-ROM allows the manual entry of fields described below.
Determines the number of sectors per block for multisector
transfers.
For Type Auto, this field is informational only.
For Type Auto, this field is informational only.
Enabling allows 32-bit IDE data transfers.
For Type Auto, this field is informational only.
Selects the method for moving data to and from the drive.
For Type Auto, this field is informational only.
For use with Ultra DMA drives. Ultra DMA is disabled by
default to work around a chipset erratum.
For Type Auto, this field is informational only.
Processor Settings Submenu
Table 9. Processor Settings Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Processor Rete st
Processor Serial Number
Memory Cache
Measured Processor Speed N/A Reports the speed of Processor 1.
Processor 1 CPU ID N/A Reports Stepping for Processor 1.
Processor 1 L2 Cache Size N/A Reports L2 Cache Size for Processor 1. This feature is
Processor 2 CPU ID N/A Reports Stepping for Processor 2.
Processor 2 L2 Cache Size N/A Reports L2 Cache Size for Processor 2. This feature is
Processor 3 CPU ID N/A Reports Stepping for Processor 3.
Processor 3 L2 Cache Size N/A Reports L2 Cache Size for Processor 3. This feature is
Processor 4 CPU ID N/A Reports Stepping for Processor 4.
Processor 4 L2 Cache Size N/A Reports L2 Cache Size for Processor 4. This feature is
No
Yes
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Select yes for the BIOS to clear historical processor status
and retest all processors on the next boot.
If enabled, the system records the serial number of each
processor.
Controls cacheability. For debug purposes only.
hidden if processor 1 is absent or disabled.
hidden if processor 2 is absent or disabled.
hidden if processor 3 is absent or disabled.
hidden if processor 4 is absent or disabled.
32 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 33

Advanced Menu
You can make the following selections on the Advanced Menu itself. Use the submenus for the
three other selections that appear on the Advanced Menu.
Table 10. Advanced Menu
Feature Choices Description
PCI Configuration N/A Enters submenu.
Integrated Peripheral
Configuration
Advanced Chipset Control N/A Enters submenu.
Reset Configuration Data
Enable Sleep Button
System Wakeup Feature Enabled
Delay on Option ROMs Enabled
PCI Configuration Submenu
N/A Enters submenu.
No
Yes
Yes
No
Disabled
Disabled
Select Yes to clear the system configuration d ata during
next boot. System automatically resets to No in next boot.
If Yes, the ACPI sleep button is activated.
If enabled, the system will be powered up upon receiving a
LAN wakeup event, ring on COM1/COM2, or PME interrupt
from a PCI board.
Enables a short delay after an Option ROM scan.
The PCI Configuration submenu contains selections that access other submenus.
Embedded Video Controller Submenu
Table 11. Embedded Video Controller Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Embedded Video
Controller
Enabled
Disabled
Enables the embedded video controller.
Embedded Legacy SCSI Submenu
Table 12. Embedded Legacy SCSI Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Embedded Legacy
SCSI
Option ROM Scan
Latency Timer Default
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
020h
040h
060h
080h
0A0h
0C0h
0E0h
Enables or disables embedded legacy SCSI controller
hardware.
Initializes the device expansion ROM on the device.
Minimum guaranteed time, in units of PCI bus clocks, that a
device can be master on a PCI bus. Typically, option ROM
code overwrites the value set by the BIOS.
Configuration Software and Utilities 33
Page 34

Embedded Dual Ultra 160 SCSI Submenu
Table 13. Embedded Dual Ultra 160 SCSI Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Embedded Legacy
SCSI
Option ROM Scan
Latency Timer Default
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
020h
040h
060h
080h
0A0h
0C0h
0E0h
Embedded NIC Submenu
Table 14. Embedded NIC Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Embedded NIC
Enabled
Disabled
Enables or disables embedded legacy SCSI controller
hardware.
Initializes the device expansion ROM on the device.
Minimum guaranteed time, in units of PCI bus clocks, that a
device can be master on a PCI bus. Typically, option ROM
code overwrites the value set by the BIOS.
If enabled, the system uses the embedded NIC.
PCI Device, Slot 1
Table 15. PCI Device, Slot 1 Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Option ROM Scan
Enable Master
Latency Timer Default
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
020h
040h
060h
080h
0A0h
0C0h
0E0h
Initializes device expansion ROM.
Enables the selected device as a PCI bus master.
Minimum guaranteed time, in units of PCI bus clocks, that a
device can be master on a PCI bus. Typically, option ROM
code overwrites the value set by the BIOS.
34 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 35

PCI Device, Slot 2
Table 16. PCI Device, Slot 2 Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Option ROM Scan
Enable Master
Latency Timer Default
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
020h
040h
060h
080h
0A0h
0C0h
0E0h
PCI Device, Slot 3
Table 17. PCI Device, Slot 3 Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Option ROM Scan
Enable Master
Latency Timer Default
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
020h
040h
060h
080h
0A0h
0C0h
0E0h
Initializes device expansion ROM.
Enables the selected device as a PCI bus master.
Minimum guaranteed time, in units of PCI bus clocks, that a
device can be master on a PCI bus. Typically, option ROM
code overwrites the value set by the BIOS.
Initializes device expansion ROM.
Enables the selected device as a PCI bus master.
Minimum guaranteed time, in units of PCI bus clocks, that a
device can be master on a PCI bus. Typically, option ROM
code overwrites the value set by the BIOS.
PCI Device, Slot 4
Table 18. PCI Device, Slot 4 Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Option ROM Scan
Enable Master
Latency Timer Default
Configuration Software and Utilities 35
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
020h
040h
060h
080h
0A0h
0C0h
0E0h
Initializes device expansion ROM.
Enables the selected device as a PCI bus master.
Minimum guaranteed time, in units of PCI bus clocks, that a
device can be master on a PCI bus. Typically, option ROM
code overwrites the value set by the BIOS.
Page 36

PCI Device, Slot 5
Table 19. PCI Device, Slot 5 Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Option ROM Scan
Enable Master
Latency Timer Default
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
020h
040h
060h
080h
0A0h
0C0h
0E0h
PCI Device, Slot 6
Table 20. PCI Device, Slot 6 Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Option ROM Scan
Enable Master
Latency Timer Default
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
020h
040h
060h
080h
0A0h
0C0h
0E0h
Initializes device expansion ROM.
Enables the selected device as a PCI bus master.
Minimum guaranteed time, in units of PCI bus clocks, that a
device can be master on a PCI bus. Typically, option ROM
code overwrites the value set by the BIOS.
Initializes device expansion ROM.
Enables the selected device as a PCI bus master.
Minimum guaranteed time, in units of PCI bus clocks, that a
device can be master on a PCI bus. Typically, option ROM
code overwrites the value set by the BIOS.
PCI Device, Slot 7
Table 21. PCI Device, Slot 7 Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Option ROM Scan
Enable Master
Latency Timer Default
36 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
020h
040h
060h
080h
0A0h
0C0h
0E0h
Initializes device expansion ROM.
Enables the selected device as a PCI bus master.
Minimum guaranteed time, in units of PCI bus clocks, that a
device can be master on a PCI bus. Typically, option ROM
code overwrites the value set by the BIOS.
Page 37

PCI Device, Slot 8
Table 22. PCI Device, Slot 8 Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Option ROM Scan
Enable Master
Latency Timer Default
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
020h
040h
060h
080h
0A0h
0C0h
0E0h
Hot-Plug PCI Control Submenu
Table 23. Hot-Plug PCI Control Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Hot-Plug PCI BIOS
Support
Resource Padding
Level
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
Minimum
Maximum
Initializes device expansion ROM.
Enables the selected device as a PCI bus master.
Minimum guaranteed time, in units of PCI bus clocks, that a
device can be master on a PCI bus. Typically, option ROM
code overwrites the value set by the BIOS.
If enabled, the system uses resource padding and the HotPlug resource table.
Determines amount of resources used by each Hot-Plug
PCI slot.
Empty Bus Default
Speed
33 MHtz
66 MHtz
Unoccupied bus default speed.
Integrated Peripheral Configuration Submenu
Table 24. Integrated Peripheral Configuration Submenu
Feature Choices Description
COM1: Disabled
Enabled
Auto
OS Controlled
Base I/O Address
Interrupt
COM2: Disabled
3F8h
2F8h
3E8h
2E8h
IRQ 4
IRQ 3
Enabled
Auto
OS Controlled
If set to "Auto", BIOS configures the port.
If set to "OS Controlled", the OS configures the port.
Selects the base I/O address for COM port A.
Selects the IRQ for COM port A.
If set to "Auto", BIOS configures the port.
If set to "OS Controlled", the OS configures the port.
continued
Configuration Software and Utilities 37
Page 38

Table 24. Integrated Peripheral Configuration Submenu (continued)
Feature Choices Description
Base I/O Address 3F8h
2F8h
3E8h
2E8h
Interrupt IRQ 4
IRQ 3
Parallel Port Disabled
Enabled
Auto
OS Controlled
Mode Output only
Bi-Directional
EPP
ECP
Base I/O Address
Interrupt IRQ 5
DMA Channel DMA 1
Floppy Disk Controller
378
278
IRQ 7
DMA 3
Enabled
Disabled
Selects the base I/O address for COM port B.
Selects the interrupt for COM port B.
If set to "Auto", BIOS configures the port.
If set to "OS Controlled", the OS configures the port.
Selects mode for parallel port.
Selects the base I/O address for parallel port.
Selects the interrupt for parallel port.
Selects the DMA channel for parallel port.
If enabled, the system enables the floppy disk
controller.
Advanced Chipset Control Submenu
Table 25. Advanced Chipset Control Submenu
Feature Option Description
Base RAM Step
Extended RAM Step
Remap Memory Enable
1 MB
1 KB
Every location
1 MB
1 KB
Every location
No Memory Test
Disable
Selects the size of step to use during Base RAM tests.
Selects the size of the step to use during Extended
RAM tests.
Enables or disables remapping some amount of
memory lost to PCI devices. This is an advanced
feature. Consult the technical product specification
before changing this option.
38 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 39

Security Menu
You can make the following selections on the Security Menu. Enabling the Supervisor Password
field requires a password for entering Setup. The passwords are not case sensitive.
Table 26. Security Menu
Feature Choices Description
User Password is
Administrator Password is
Set User Password Press Enter When the <Enter> key is pressed, the user is prompted for a
Set Administrative Password Press Enter When the <Enter> key is pressed, the user is prompted for a
Password on Boot
Fixed Disk Boot Sector
Secure Mode Timer Disabled
Secure Mode Hot Key
(Ctrl-Alt- )
Secure Mode Boot
Video Blanking
Floppy Write Protect
Clear
Set
Clear
Set
Disabled
Enabled
Normal
Write Protect
1, 2, 5, 10,
or 20 min
1 or 2 hr
[ ]
[A, B, ..., Z]
[0-9]
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Status only; user cannot modify. Once set, this can be
disabled by setting it to a null string or by clearing password
jumper on baseboard (see “Password Clear Jumper,”
page 110).
Status only; user cannot modify. Once set, this can be
disabled by setting it to a null string or by clearing
password jumper on baseboard (see “Password Clear
Jumper” page 110).
password; press ESC key to abort. Once set, this can be
disabled by setting it to a null string or by clearing password
jumper on baseboard (see “Password Clear Jumper”
page 110).
password; press ESC key to abort. Once set, this can be
disabled by setting it to a null string or by clearing password
jumper on baseboard (see “Password Clear Jumper”
page 110).
If enabled and the user password is set, the system
prompts the user for a password before the system boots.
Write-protects boot sector on hard disk to protect against
viruses.
Period of keyboard or PS/2 mouse inactivity specified for
secure mode to activate. A password is required for
secure mode to function. Cannot be enabled unless at
least one password is enabled.
Key assigned to invoke the secure mode feature. Cannot
be enabled unless at least one password is enabled. Can
be disabled by entering a new key followed by a
backspace or by entering <Delete>.
System boots in secure mode. The user must enter a
password to unlock the system. Cannot be enabled unless
at least one password is enabled.
Blank video when secure mode is activated. The user
must enter a password to un lock the system. Cannot be
enabled unless at least one password is enabled.
When secure mode is activated, the diskette drive is write
protected. The user must enter a password to re-enable
diskette writes. Cannot be enabled unless at least one
password is enabled.
Configuration Software and Utilities 39
Page 40

Server Menu
Table 27. Server Menu
Feature Choices Description
System Management N/A Enters submenu.
Console Redirection N/A Enters submenu.
EMP Configuration N/A Enters submenu.
PEP Management N/A Enters submenu.
Service Boot Enable
Service Partition Type [0-999]
System Event Logging Disabled
Clear Event Log
Assert NMI on PERR
Assert NMI on SERR Disabled
FRB-2 CPU Policy
Disable
Enabled
No
Yes
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
Disable BSP
Do not disable
BSP
Enabled forces BIOS and BMC to log system events.
If Yes, the System Event log is cleared.
If enabled, PCI bus parity error (PERR) is enabled and is
routed to NMI.
If enabled, PCI bus system error (SERR) is enabled and
is routed to NMI.
What action to take when FRB-2 occurs.
System Management Submenu
Table 28. System Management Submenu
Feature Choices Description
Board Part Number N/A Information field only
Board Serial Number N/A Information field only
System Part Number N/A Information field only
System Serial Number N/A Information field only
Chassis Part Number N/A Information field only
Chassis Serial Number N/A Information field only
BMC Revision N/A Information field only
Primary HSBP Revision N/A Information field only
40 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 41

Console Redirection Submenu
Table 29. Console Redirection Submenu
Feature Choices Description
COM Port Address:
Redirection
disabled
IRQ # 3 or 4 When Console Redirection is enabled, this displays the IRQ
Baud Rate 9600
Flow Control No flow control
Disabled
3F8
2F8
3E8
19.2k
38.4k
115.2k
CTS/RTS
XON/XOFF
CTS/RTS + CD
EMP Configuration Submenu
When enabled, Console Redirection uses the I/O port specified.
When disabled, Console Redirection is completely disabled.
assigned per the address chosen in the COM Port Address field.
When Console Redirection is enabled, use the baud rate
specified.
When the Direct Platform Control (DPC) shares the COM port as
console redirection, the baud rate must be set to 19.2k to match
DPC baud rate, unless the autobaud feature is used.
None disallows flow control.
CTS/RTS is hardware based flow control.
XON/XOFF is software flow control.
CTS/RTS +CD is hardware based plus carrier-detect flow control.
When DPC is sharing the Comm port as Console Redirection, the
flow control must be set to XON/XOFF or XON/XOFF+CD
depending on whether a modem is used.
Table 30. EMP Configuration Submenu
Feature Choices Description
EMP Password
Switch
EMP ESC
Sequence
EMP Hang-up Line
String
Modem Init String
EMP Access Mode
EMP Restricted
Mode Access
EMP Direct
Connect/Modem
Mode
System Phone
Number
Disabled
Enabled
+++ or other
text
ATH or other
text
ATE1Q0V1X4&
D0S0=0 or
other text
Pre-Boot Only
Always
Active
Disabled
Disabled
Enabled
Direct Connect
Modem Mode
[Phone number] Phone number of system you are dialing into.
Enabled/Disables EMP password.
Escape string for the modem EMP port.
Hang-up string for the modem EMP port.
20 characters to set up the modem.
Establishes EMP access mode.
Enables/Disables EMP Restricted Mode Access.
Establishes connection for EMP port.
Configuration Software and Utilities 41
Page 42

PEP Management Submenu
Table 31. PEP Management Submenu
Feature Choices Description
PEP Filter Events N/A Enters Submenu with a single feature listed. If the feature is
enabled, all triggers for PEP are enabled.
PEP Enable Enable
Disable
PEP Blackout
Period
PEP Page String [Phone number]
Send Test Page
[0 – 255]
<Enter>
Enables PEP.
Time in minutes between consecutive pages. Entering 0
disables paging.
Press <Enter> to send a test page.
Boot Menu
You can make the following selections on the Boot Menu itself.
Table 32. Boot Menu
Feature Choices Description
Boot-Time Diagnostic Screen
Boot Device Priority N/A Enters submenu.
Hard Drive N/A Enters submenu.
Removable Devices N/A Enters submenu.
Maximum number of I2O Drives
Disabled
Enabled
1
4
If Enabled, system displays the diagnostic screen
during the boot process.
Selects the maximum number of I2O drives assigned
a DOS drive letter.
Boot Device Priority Submenu
Use the up- or down-arrow keys to select a device. Press the <+> or <-> keys to move the device
higher or lower in the boot priority list.
Table 33. Boot Device Priority Submenu
Boot Priority Device Description
1. Removable Devices Attempts to boot from a removable media device.
2. Hard Drive Attempts to boot from a hard drive device.
3. ATAPI CD-ROM Drive Attempts to boot from an ATAPI CD-ROM drive.
4. Intel UND1, PXE-2.0 Wired for Management WFM 2.0 Specification.
42 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 43

Hard Drive Submenu
For options on this menu, use the up or down arrow keys to select a device. Press the <+> or <->
keys to move the device higher or lower in the boot priority list.
Table 34. Hard Drive Submenu
Option Description
1. Drive #1 (or actual drive string)
2. Other bootable cards
(additional entries for each drive that
has a PnP header)
Other bootable cards cover all the boot devices that are not
reported to the system BIOS through BIOS Boot Specification
mechanisms. It may or may not be bootable, and may not
correspond to any device.
Removable Devices Selection Submenu
For options on this menu, use the up or down arrow keys to select a device.
Table 35. Removable Devices Selection Submenu
Feature Option Description
Lists Bootable Removable devices in
the system.
+/- This list includes legacy 1.44 MB floppy drives and
120 MB floppy drives.
Exit Menu
You can make the following selections on the Exit Menu. Select an option using the up or down
arrow keys. Press <Enter> to run the option. Pressing <Esc> does not exit this menu. You must
select one of the items from the menu or menu bar to exit.
Table 36. Exit Menu
Choices Description
Exit Saving Changes Exits and saves changes to CMOS.
Exit Discarding Changes Exits without saving changes to CMOS. User is prompted if any of
the Setup fields were modified.
Load Setup Defaults Loads default values for all Setup data.
Save Custom Defaults Loads settings from custom defaults.
Discard Changes Reads previous values of all Setup data from CMOS.
Save Changes Saves Setup data to CMOS.
Configuration Software and Utilities 43
Page 44

Changing the Boot Device Priority Temporarily
During POST, you can change the boot device priority for the current boot process. The changes
made during this instruction set are not retained for the next boot process.
1. Boot the server.
2. At any time during POST, press <Esc>. When POST completes, a pop-up Boot menu is
displayed.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight the device you want the server system to boot from first. For
example, if you want the server system to boot from the CD-ROM first, you select "CD-ROM
Drive."
NOTE
✏
One of the selections on the pop-up Boot menu is "Enter Setup". Selecting
this option brings you into the BIOS setup. For more information about the
BIOS setup, see "Using BIOS Setup" on page 29.
4. Press <Enter>.
5. The bootup process continues. When finished, a system prompt is displayed.
Changing the Boot Device Priority Permanently
You can change the boot device permanently. Until you change the boot device priority again via
this instruction set, the boot device priority does not change.
1. Quickly press the <F2> key. A prompt may or may not appear. After a few bootup tests
complete, the main BIOS Setup screen appears.
2. From the Setup screen, select Boot Menu. Press <Enter>.
3. Select Boot Device Priority, and press <Enter>.
4. In the Boot Device Priority screen, use the up- or down-arrow keys to select "ATAPI
CD-ROM Drive", or the appropriate SCSI CD-ROM drive, then press the <+> key to move it
to the top of the list.
5. Now set the second boot device to Diskette Drive and the third boot device to Hard Drive.
6. Press the <F10> key to save your changes and exit Setup.
7. When the Exit prompt appears, press <Enter> again.
8. The bootup process continues. When finished, an operating system prompt is displayed.
9. Make sure the CD is in the drive, and boot the server.
44 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 45

Running the SCSI
Each host adapter includes an onboard SCSISelect configuration utility that allows you to
configure/view the settings of the host adapters and devices in the server.
After pressing <F2> or <Esc> during POST, the splash screen is replaced by text.
The system first finds the Adaptec AIC-7880 SCSI host adapter and displays the message
Adaptec AIC-7880 SCSI BIOS V x.xxx where x.xxx is the version number of the SCSISelect
utility. Pressing <Ctrl+A> at this time allows you to configure the Adaptec AIC-7880 SCSI host
adapter.
If you do not press <Ctrl+A>, the system finds the Adaptec AIC-7899 SCSI host adapter and
displays the message
of the SCSISelect utility. Pressing <Ctrl+A> at this time allows you to configure the Adaptec
AIC-7899 SCSI host adapter.
Once you enter the configuration menus for one of the host adapters, you cannot switch to the
other adapter. For example, once you press <Ctrl+A> to configure the Adaptec AIC-7899 SCSI
host adapter, you have to reboot the system to configure the Adaptec AIC-7880 SCSI host adapter.
Select
Adaptec AIC-7899 SCSI BIOS V x.xxx where x.xxx is the version number
Utility
When to Run the SCSI
Use the SCSISelect utility to
• change default values
• check and/or change SCSI device settings that may conflict with those of other devices in the
server
• do a low-level format on SCSI devices installed in the server
Running the SCSI
1. When this message appears on the video monitor:
<<<Press <Ctrl><A> for SCSISelect(TM) Utility!>>>
2. Press <Ctrl+A> to run the utility. When the main menu for the host adapter appears, choose
the adapter that you want to configure—each SCSI bus accepts up to 15 devices.
Use the following keys to navigate through the menus and submenus.
Table 37. Navigation Keys
Press To
ESC Exit the utility
Enter Select an option
↑ Return to a previous option
↓ Move to the next option
F5 Switch between color and monochrome
F6 Reset to host adapter defaults
Select
Select
Utility
Utility
Configuration Software and Utilities 45
Page 46

Configuring the Adaptec AIC-7880 SCSI Adapter
The following menu is displayed when you configure the Adaptec AIC-7880 SCSI adapter.
Table 38. Main Menu
Host Adapter Option Comment
AIC-7880 Ultra/Ultra W
at Bus:Device 00:01h
Configure/View Host
Adapter Settings
SCSI Disk Utilities Press <Enter> to view the SCSI Disk Utilities Menu.
Press <Enter> to view the Configuration Menu.
Make a selection and press <Enter>.
When you are finished, press <Esc> and make your selection from the following menu.
Table 39. Exit Menu
Feature Option Comment
Exit Utility? Yes
No
When you finish configuring your SCSI devices, select Yes and press <Enter>.
When this message appears:
Please press any key to reboot
Press any key, and your server will reboot.
Configuring the Adaptec AIC-7899 SCSI Adapter
The Adaptec AIC-7880 SCSI adapter has two busses. Select the bus from the following menu.
Table 40. Main Menu
Menu Item Options
You have an AIC-7899 adapter in your system. Move
the cursor to the bus:device:channel of the one to be
configured and press <Enter>.
<F5> - Toggle color/monochrome
Bus:Device:Channel
01:06:A
01:06:B
After selecting the bus, the following menu is displayed.
Table 41. Menu for each SCSI Channel
Host Adapter Option Comment
AIC-7899 at
Bus:Device:Channel
01:06:A (or 01:06:B)
Configure/View Host
Adapter Settings
SCSI Disk Utilities Press <Enter> to view the SCSI Disk Utilities
Press <Enter> to view the Configuration Menu.
Menu. This menu allows you to format hard
disks and/or verify disk media.
46 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 47

When you are finished, press <Esc> and make your selection from the following menu.
Table 42. Exit Menu
Feature Option Comment
Exit Utility? Yes
No
When you finish configuring your SCSI devices, press <Esc>. Then select Yes
and press <Enter>. When this message appears:
Please press any key to reboot
Press any key, and the server reboots.
Using the System Setup Utility (SSU)
The SSU is on the configuration software CD shipped with the server. The SSU provides a
graphical user interface (GUI) over an extensible framework for server configuration. The
SSU framework supports the following functions and capabilities:
• Assigns resources to baseboard devices and add-in boards before loading the operating system
• Specifies the boot device order and system security options
• Permits viewing and clearing of the system event log (SEL)
• Permits viewing of the system FRU and SDRs
• Allows troubleshooting of the server when the operating system is not operational
• Provides a system-level view of the server’s I/O devices
When to Run the SSU
The SSU is a DOS-based utility that supports extended system configuration operations for
onboard resources and add-in boards. Use the SSU to:
• Add and remove boards affecting the assignment of resources (ports, memory, IRQs, DMA)
• Modify the server’s boot device order or security settings
• Change the server configuration settings
• Save the server configuration
• View or clear the SEL
• View FRU information
• View the SDR table
The SSU is PCI 2.1 compliant and uses the information entered and provided by configuration
registers, flash memory to specify a system configuration. The SSU then writes the configuration
information to flash memory.
The SSU stores configuration values in flash memory. These values take effect when the server is
booted. POST checks the values against the actual hardware configuration; if the values do not
agree, POST generates an error message. You must then run the SSU to specify the correct
configuration before the server boots.
The SSU always includes a checksum with the configuration data so the BIOS can detect any
potential data corruption before the actual hardware configuration takes place.
Configuration Software and Utilities 47
Page 48

What You Need to Do
Run the SSU directly from the configuration software CD after you have installed a CD-ROM
drive, or from a set of diskettes.
If you choose to run the SSU from diskettes, create the SSU diskettes from the CD by following
the instructions in "Creating SSU Diskettes" on page 48.
If the diskette drive is disabled or improperly configured, use the flash-resident Setup utility to
enable it to use the SSU. If necessary, disable the drive after exiting the SSU. Information entered
using the SSU overrides any entered using Setup.
Running the SSU Remotely
Running the SSU remotely requires a remote server with a LANDesk Server Monitor Module 2
(SMM2) card and a local system with Remote Control software available.
When running the SSU remotely, the client SSU (CSSU) runs on the remote server. The CSSU
controls the local server and uses the local server’s SSU software.
The SMM2 card provides video memory, keyboard, and mouse redirection support for the remote
server. The Remote Control console of the local system displays and sends video memory and
user input to the remote server through either a modem or an Ethernet link. Because the CSSU
runs exclusively on the remote server, any files required for the CSSU to run must be available on
the remote server (on removable or non-removable media).
If the local system is connected to the remote server through a network or modem, you can see the
console of the local system, control the mouse, and control the keyboard from the remote server.
For more information, see the documentation accompanying your SMM2 card.
Creating SSU Diskette s
When creating SSU diskettes, the system copies the SSU from the CD to the diskettes.
1. Make sure that the CD-ROM is the first bootable device for the system.
2. Place the CD in the CD-ROM drive and boot the system.
3. Use the arrow keys to highlight "Create Diskettes" and press <Enter>.
4. Make sure "Create Disk Sets by Device/Function" is highlighted and press <Enter>.
5. Make sure "System Setup Utility" is highlighted and press <Enter>.
6. The software prompts you to insert a blank diskette. Insert the diskette in the floppy drive.
7. After the system formats the diskette, remove it from the drive and label it "SSU Disk 1".
8. The software prompts you to insert another blank diskette. Insert the diskette in the floppy
drive.
9. After the system creates the diskette, remove it from the drive and label it "SSU Disk 2".
48 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 49

Running the SSU
You can run the SSU from diskettes, a hard drive, or a CD-ROM drive.
Running the SSU from Diskettes
For best results, Intel recommends that you execute the SSU from diskettes. Place the bootable
diskette in the floppy drive. Typically, the floppy drive is recognized by the system as drive A. If
the system is not set to boot from the floppy drive, change the boot priority. For more information,
see "Changing the Boot Device Priority Permanently" on page 44. After making sure that the
system boots from the floppy drive, restart the system.
Once the system boots, a virtual drive is created. The System Setup Utility files are copied to the
virtual drive and invoked.
Running the SSU from a CD
You can also run the SSU from a CD. Place the CD in the CD-ROM drive. If the system is not set
to boot from the CD-ROM drive, change the boot priority. For more information, see "Changing
the Boot Device Priority Permanently" on page 44. After making sure that the system boots from
the CD-ROM drive, restart the system. Run the file SSU.BAT.
Running the SSU from a Hard Drive
First, install the SSU software to the hard drive. To install the SSU software on the hard drive,
insert either the diskette or CD into the floppy drive or CD-ROM drive respectively. Run the
excitable file called SSIOMAGE.EXE. If you are using diskettes, the executable file is on disk 1.
When prompted, insert disk 2.
Lastly, run the file SSU.BAT on the hard disk. Note that the SSU does not function properly in a
DOS window under another operating system.
Direct Platform Control (DPC) Console
Direct Platform Control (DPC) Console is an application that provides a user interface to the
emergency management port (EMP). The EMP allows remote system management.
DPC console runs on a client workstation. It communicates with a server by
• A Windows† 98/NT compatible modem.
• An RS-232 connection to the server COM2 port.
DPC Console is independent of the server operating system.
Even when the server is powered off, you can use DPC Console to verify the state of a server or
diagnose a problem with the server hardware. DPC console features allows you to:
• Establish or end a connection to a remote server.
• Apply power to a remote server.
• Remove power from a remote server.
• Reset a remote server to either EMP mode or Re-direct Mode.
Configuration Software and Utilities 49
Page 50

• Retrieve and display:
System Event Log (SEL) entries for information about recent server activities, such as
from processors or fans.
Sensor Data Records (SDR) entries for information about sensor characteristics.
Field Replaceable Unit (FRU) inventories of the hardware components on the server.
Current Remote Sensor Access (RSA) information.
• Maintain a Phonebook for remote connection management.
• Run Remote Diagnostics.
• Transfer file to and from a server.
• Reboot to the service partition to get access to run DOS-based utilities on the server.
DPC Console Modes of Opera tion
There are three modes DPC console modes of operation:
• EMP mode. The default mode. DPC console features are accessed using the DPC console
window menus and/or toolbar.
• Re-direct mode. Active when the server is running BIOS console redirection. In this mode,
the DPC console launches a separate window. The window operates as an ANSI terminal and
communicates with the server through the port. Character-based commands you type in the
DPC Console are sent directly to the server, and the DPC Console displays the text that would
normally be displayed on the server console.
To use this mode, you must configure the Console Redirection option of BIOS setup for Redirect mode. If the redirection window does not display information, the Console Redirection
is not correctly configured or enabled, the EMP is disabled in BIOS setup, or the server is in
protected mode. For DPC to function, the server must NOT be in graphics mode.
If the DPC console fails to connect in EMP within 10 seconds and the server can operate in
Re-direct mode, a prompt is displayed with the option to switch to Re-direct mode.
• Service Partition mode. Entered when the server reboots from the service partition and the
DPC Console has successfully connected to the server through a modem. This mode allows
running of DOS-based programs that are stored on the service partition and transferring of
files.
Running the DPC Console
For more information about setting up and running the DPC Console, see the document named
"ENUDPCUG.pdf". This document is in the Manuals\SrvMgmt directory on the server software
kit accompanying the SKA4 baseboard.
50 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 51

FRU and SDR Load Utility
The Field Replacement Unit (FRU) and Sensor Data Record (SDR) load utility is a DOS-based
program used to update the server management subsystem’s product level FRU, SDR, and the
Desktop Management Interface (DMI) nonvolatile storage components (EEPROMs). The utility:
• Discovers the product configuration based on instructions in a master configuration file
• Displays the FRU information
• Updates the EEPROM associated with the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) that
holds the SDR and FRU area
• Updates the DMI FRU area located in the BIOS nonvolatile storage device
• Generically handles FRU devices that might not be associated with the BMC
What You Need to Do
Run the utility either directly from the configuration software CD or from diskettes created from
the CD.
If you run the FRUSDR Load Utility from a diskette, copy the utility from the CD. Follow the
instructions in the included README.TXT file.
If the diskette drive is disabled, or improperly configured, use BIOS Setup to enable it. If
necessary, disable the drive after you are done with the FRUSDR utility.
How You Use the FRUSDR Load Utility
The utility:
• Is compatible with ROM-DOS Ver. 6.22, MS-DOS Ver. 6.22, and later versions
• Accepts CFG, SDR, and FRU load files (the executable file for the utility is frusdr.exe)
• Requires the following supporting files
one or more .fru files describing the system’s field replaceable units
a .cfg file describing the system configuration
an .sdr file describing the sensors in the system
Command Line Format
The basic command line format is
frusdr [-?] [-h] [-d {dmi, fru, sdr}] [-cfg filename.cfg] [-fru filename.fru]
Table 43. Command Line Format
Command Description
-? or -h Displays usage information
-d {dmi, fru, sdr} Displays requested area only
-cfg filename.cfg Uses custom CFG file
-p Pause between blocks of dat a
Configuration Software and Utilities 51
Page 52

Parsing the Command Line
The FRUSDR load utility allows only one command line function at a time. A command line
function can consist of two parameters. Example: -cfg filename.cfg. Invalid parameters cause an
error message and exit the program. You can use either a slash (/) or a minus sign (-) to specify
command line options. The -p and flags can be used in conjunction with any of the other options.
Displaying a Given Area
When the utility is run with the -d DMI, -d FRU, or -d SDR command line flag, information about
each area is read from memory and printed on the screen. Each area represents one sensor for each
instrumented device in the server. If the given display function fails because of an inability to
parse the data present or a hardware failure, the utility displays an error message and exits.
Using Specified CFG File
The utility can be run with the command line parameter of -cfg filename.cfg. The filename can be
any DOS-accepted, eight-character filename string. The utility loads the specified CFG file and
uses the entries in that file to probe the hardware and to select the proper SDRs to load into
nonvolatile storage.
Displaying Utility Title and Version
The utility displays its title
:
FRU & SDR Load Utility, Version Y.Y, Revision X.XX where Y.Y is the version number and
X.XX is the revision number for the utility.
Configuration File
The configuration file is in ASCII text. The utility executes commands formed by the strings
present in the configuration file. These commands cause the utility to run tasks needed to load the
proper SDRs into the nonvolatile storage of the BMC and possibly generic FRU devices. Some of
the commands may be interactive and require you to make a choice.
Prompting for Product Level FRU Information
Through the use of a configuration file, the utility might prompt you for FRU information.
Filtering Records From the SDR File
The MASTER.SDR file has all the possible SDRs for the system. These records might need to be
filtered based on the current product configuration. The configuration file directs the filtering of
the SDRs.
Updating the SDR Nonvolatile Storage Area
After the utility validates the header area of the supplied SDR file, it updates the SDR repository
area. Before programming, the utility clears the SDR repository area. The utility filters all tagged
SDRs depending on the product configuration set in the configuration file. Nontagged SDRs are
automatically programmed. The utility also copies all written SDRs to the SDR.TMP file; it
contains an image of what was loaded. The TMP file is also useful for debugging the server.
52 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 53

Updating FRU Nonvolatile Storage Area
After the configuration is determined, the utility updates the FRU nonvolatile storage area. First it
verifies the common header area and checksum from the specified FRU file. The internal use area
is read out of the specified .FRU file and is programmed into the nonvolatile storage. The chassis
area is read out of the specified .FRU file. Finally, it reads the product area out of the specified
FRU file, then the area is programmed into the FRU nonvolatile storage. All areas are also written
to the FRU.TMP file.
Updating DMI FRU Nonvolatil e St orage Area
After programming the BMC FRU area, the utility programs chassis, board, and product
FRU information to the DMI fields, if the DMI flag follows each FRUAREA command in the
configuration file.
Cleaning Up and Exiting
If an update was successfully performed, the utility displays a single message and then exits.
If the utility fails, it immediately exits with an error message and exit code.
Upgrading the BIOS
Preparing for the Upgr ade
Before upgrading the BIOS, prepare for the upgrade by recording the current BIOS settings,
obtaining the upgrade utility, and making a copy of the current BIOS.
Recording the Current BIOS Settings
1. Boot the computer and press <F2> when you see the splash screen.
2. Write down the current settings in the BIOS Setup program.
NOTE
✏
If you are not familiar with BIOS settings for the system, make sure you
complete step two. You need these settings to configure your computer at
the end of the procedure.
Obtaining the Upgrade Utility
Upgrade to a new version of the BIOS using the new BIOS files and the BIOS upgrade utility,
iFLASH.EXE. Obtain the BIOS upgrade file and the iFLASH.EXE utility from the Intel World
Wide Web site:
http://www.intel.com
Configuration Software and Utilities 53
Page 54

NOTE
✏
Please review the instructions distributed with the upgrade utility before
attempting a BIOS upgrade.
This upgrade utility allows you to upgrade the BIOS in flash memory. The following steps explain
how to upgrade the BIOS.
Creating a Bootable Diskette
1. Use a Microsoft DOS system to create the diskette.
2. Insert a diskette in drive A.
3. At the C:\ prompt, for an unformatted diskette, type:
format a:/s
or, for a formatted diskette, type:
sys a:
4. Press <Enter>
Creating the BIOS Upgrade Diskette
The BIOS upgrade file is a compressed self-extracting archive that contains the files you need to
upgrade the BIOS.
1. Copy the BIOS upgrade file to a temporary directory on the hard disk.
2. From the C:\ prompt, change to the temporary directory.
3. To extract the file, type the name of the BIOS upgrade file, for example:
10006BI1.EXE
4. Press <Enter>. The extracted file contains the following files:
LICENSE.TXT
README.TXT
BIOS.EXE
5. Read the LICENSE.TXT file, which contains the software license agreement, and the
README.TXT file, which contains the instructions for the BIOS upgrade.
6. Insert the bootable diskette into drive A.
7. To extract the BIOS.EXE file to the diskette, change to the temporary directory that holds the
BIOS.EXE file and type:
BIOS A:
8. Press <Enter>.
9. The diskette now holds the BIOS upgrade and recovery files.
Upgrading the BIOS
1. Boot the computer with the floppy disk in drive A.
2. Press <1> and <Enter>.
3. When the utility is done updating the BIOS, the system reboots automatically. Remove the
floppy from the floppy drive.
54 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 55

4. Press <F2> while the splash screen is displayed to enter the BIOS Setup program.
5. Load the Setup program defaults. To load the defaults, press <F9>. To accept the defaults,
press <Enter>.
6. Clear the CMOS. See "CMOS Clear Jumper" on page 109.
7. Turn off the computer and reboot.
8. If you need to change the BIOS settings, press <F2> while the splash screen is displayed to
enter the Setup program.
Recovering the BIOS
It is unlikely that anything will interrupt the BIOS upgrade; however, if an interruption occurs, the
BIOS could be damaged. The following steps explain how to recover the BIOS if an upgrade fails.
The following procedure use recovery mode for the Setup program.
NOTE
✏
Because of the small amount of code available in the nonerasable boot block
area, there is no video support. You will not see anything on the screen
during the procedure. Monitor the procedure by listening to the speaker and
looking at the floppy drive LED.
1. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer.
2. Remove the computer cover.
3. Locate jumper block J9F2.
4. Move the Recovery Boot jumper from pins 9-10 to pins 10-11. See "Recovery Boot Jumper"
on page 110.
5. Insert the bootable BIOS upgrade floppy disk into floppy drive A.
6. Replace the cover, turn on the computer, and allow it to boot. The recovery process will take a
few minutes.
7. Listen to the speaker.
8. Two beeps indicate successful BIOS recovery.
9. A series of continuous beeps indicates failed BIOS recovery.
10. If recovery fails, return to step 1 and repeat the recovery process.
11. If recovery is successful, turn off the computer. Remove the computer cover and continue
with the following steps.
12. Move the Recovery Boot jumper back to pins 9-10.
13. Replace the computer cover.
14. Follow the instructions for "Upgrading the BIOS" on page 53.
Changing the BIOS Language
You can use the BIOS upgrade utility to change the language BIOS displays. Use a bootable
diskette containing the Intel flash utility and language files (see page 54). See "Using BIOS
Setup" on page 29.
Configuration Software and Utilities 55
Page 56

Using the Firmware Update Utility
The Firmware Update Utility is a DOS-based program used to update the BMC’s firmware code.
You need to run the utility only if new firmware code is necessary.
Running the Firmware Update Utility
1. Create a DOS-bootable diskette. The version of DOS must be 6.0 or higher.
2. Place the firmware update utility (FWUPDATE.EXE) and the *.hex file on the diskette. Make
a note of the *.hex file name, because you will need it later.
3. Insert the diskette into the drive and boot to it.
4. At the DOS prompt, run the executable file (FWUPDATE.EXE).
5. The utility displays a menu screen. Select “Upload Flash.”
6. The utility asks for a file name. Enter the name of the *.hex file.
7. The program will load the file and then ask if it should upload boot code. Press “N” to
continue.
8. The program next asks if it should upload operational code. Press “Y” to continue. The
process of uploading operational code takes a few minutes.
9. Once the operational code has been updated and verified, press any key to continue. Then
press <ESC> to exit the program.
10. Shut the system down and remove any diskettes in the system.
11. Disconnect the AC power cord from the system and wait 60 seconds.
12. Reconnect the AC power cord and power up the system.
56 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 57

Part II: Service Technician’s Guide
3 Removing and Installing Baseboard Components
4 Solving Problems
5 Technical Reference
A Equipment Log and Configuration Worksheets
B Regulatory Specifications
C Warnings
57
Page 58

58 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 59

3 Removing and Installing Baseboard
Components
Tools and Supplies Needed
• Phillips (cross-head) screwdriver (#1 and #2 bit).
• Phillips (cross-head) screwdriver with a long blade (#1 and #2 bit).
• Jumper removal tool or needle-nosed pliers.
• Antistatic wrist strap and conductive foam pad (recommended).
• Pen or pencil.
• Equipment log: as you integrate new parts into the system, add information about them to
your equipment log (page 113.) Record the model and serial number of the system, all
installed options, and any other pertinent information specific to the system. You will need
this information when running the SSU.
Safety: Before You Work with the Baseboard
Before working with the baseboard, provide some electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection by
wearing an antistatic wrist strap attached to chassis ground of the system—any unpainted metal
surface. Turn off the system by using the power on/off switch on the front panel AND unplug all
AC power cords.
✏ NOTE
Hot-Plug PCI add-in boards: If you are only removing and/or installing
Hot-Plug PCI add-in board, you do not need to turn off the system.
Warnings and Cautions
These warnings and cautions apply whenever you work with the SKA4 baseboard. Only a
technically qualified person should integrate and configure the system.
✏ NOTE
Hot-Plug PCI add-in boards: If you are only removing and/or installing
Hot-Plug PCI add-in boards, you do not need to turn off the system and the
warnings pertaining to turning off the system do not apply.
59
Page 60

WARNINGS
System power on/off: The on/off button (a convex button) on the
front panel DOES NOT turn off the system AC power. To remove
power from system, you must unplug the AC power cords from the wall
outlet or the system.
Hazardous conditions, devices, and cables: Hazardous electrical
conditions may be present on power, telephone, and communication
cables. Turn off the system and disconnect the power cords,
telecommunications systems, networks, and modems attached to the
system before opening it. Otherwise, personal injury or equipment
damage can result.
CAUTIONS
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) and ESD protect i on: ESD can
damage disk drives, boards, and other parts. We recommend that you do all
procedures in this chapter only at an ESD-protected workstation. If one is
not available, provide some ESD protection by wearing an antistatic wrist
strap attached to chassis groundany unpainted metal surfaceon your
system when handling parts.
ESD and handling boards: Always handle boards carefully. They can
be extremely sensitive to ESD. Hold boards only by their edges. After
removing a board from its protective wrapper or from the system, place it
component-side UP on a grounded, static-free surface. If you place the
baseboard on a conductive surface, the battery leads may short out. If they
do, this will result in a loss of CMOS data and will drain the battery. Use a
conductive foam pad if available but NOT the board wrapper. Do not slide
board over any surface.
Chassis covers, proper cooling, and airflow : For proper cooling and
airflow, always install the chassis access covers before turning on the
system. Operating the system without this cover in place can damage
system parts.
Installing or removing jumpers: A jumper is a small, plastic-encased
conductor that slips over two jumper pins. Newer jumpers have a small tab
on top that you can grip with your fingertips or with a pair of fine, needlenosed pliers. If your jumpers do not have such a tab, take care when using
needle-nosed pliers to remove or install a jumper; grip the narrow sides of
the jumper with the pliers, never the wide sides. Gripping the wide sides can
damage the contacts inside the jumper, causing intermittent problems with
the function controlled by that jumper. Take care to gently grip, but not
squeeze, with the pliers or other tool you use to remove a jumper; you might
bend or break the stake pins on the board.
60 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 61

Memory
Memory amounts from 256 MB to 16 GB of DIMM are supported, with a 64/72-bit
four-way-interleaved pathway to main memory, which is also located on the module. Therefore,
data transfers between MADPs and DIMMs is in four-way interleave fashion. Each of the four
DIMMs must be populated in a bank. The 16 slots are divided into four banks of four slots each.
They are labeled A through D. Bank A contains DIMM sockets A1, A2, A3, and A4. Banks B, C,
and D each contain 4 DIMM sockets and are named in the same fashion. There are silk screens on
the module next to each DIMM socket to label its bank number. DIMM banks do not have to be
filled in any order, but for best thermal results, you should populate them from A to D. If only one
DIMM bank is used, use bank A first, and then B, C, and D.
A3
C3
B3 B4
D3
A1
C1
B1
D1
XY
Figure 3. Memory Module DIMM Installation Sequence
Z
X. One of sixteen DIMM sockets
Y. One of four Memory Address Data Paths (MADP)
Z. Memory Expansion Card Connector (MECC)
Removing the Memory Module
See “Memory” on page 16 for memory size and requirements. The memory module is located on
the baseboard as shown in Figure 1 on page 14. The DIMM locations are shown in Figure 3.
A4
C4
D4
A2
C2
B2
D2
OM09919
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter.
2. Remove the memory module from the baseboard:
• Pull the module upward slightly to disengage it from the baseboard connector.
• Slide the module straight up and away from the baseboard until it clears the guide rails.
• Place the module component-side up on a nonconductive, static-free surface.
Removing and Installing Baseboard Components 61
Page 62

Installing the Memory Module
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter.
2. Holding the memory module by its edges, align the module so its edge engages the guide rails
at the back and front of the electronics bay.
CAUTION
The memory module is held in place by the 330-pin connector on the
baseboard, the guide rails in the center of the electronics bay. You must
support the module until it is fully seated in the connector.
3. Push the memory module toward the baseboard until it fully engages the connector on the
baseboard.
Removing DIMMs
CAUTION
Use extreme care when removing a DIMM. Too much pressure can damage
the socket slot. Apply only enough pressure on the plastic ejector levers to
release the DIMM.
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter.
2. Remove the memory module and place it component-side up on a nonconductive, static-free
surface. See “Removing the Memory Module” on page 61.
3. Gently push the plastic ejector levers down. The DIMM is ejected from its socket.
4. Hold the DIMM only by its edges, being careful not to touch its components or gold edge
connectors. Carefully lift it away from the socket and store it in an antistatic package.
5. Repeat to remove other DIMMs as necessary.
Installing DIMMs
CAUTIONS
Use extreme care when installing a DIMM. Applying too much pressure can
damage the socket. DIMMs are keyed and can be inserted in only one way.
Mixing dissimilar metals might cause memory failures later, resulting in
data corruption. Install DIMMs with gold-plated edge connectors only in
gold-plated sockets.
NOTE
✏
DIMM slots on the memory module must be installed only in certain
configurations. See “Memory” on page 16 for requirements.
62 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 63

1. Holding the DIMM only by its edges, remove it from its antistatic package.
2. Orient the DIMM so that the two notches in the bottom edge of the DIMM align with the
keyed socket on the memory module. See Figure 4.
OM09920
Figure 4. Installing DIMMs: Orientation of DIMM in a Memory Module
3. Insert the bottom edge of the DIMM into the socket, then press down firmly on the DIMM
until it seats correctly.
4. Gently push the plastic ejector levers on the socket ends to the upright position.
5. Repeat the steps to install each DIMM.
Processors
CAUTIONS
Processor must be appropriate: You might damage the system if you
install a processor that is inappropriate for your system. Make sure your
system can handle the thermal and power conditions of the newer, faster
processor. For exact information about processor interchangeability, contact
your customer service representative.
ESD and handling processors: Reduce the risk of electrostatic
discharge (ESD) damage to the processor by doing the following: (1) Touch
the metal chassis before touching the processor or baseboard. Keep part of
your body in contact with the metal chassis to dissipate the static charge
while handling the processor. (2) Avoid moving around unnecessarily.
Removing and Installing Baseboard Components 63
Page 64

A processor has the following components.
G
J
L
Figure 5. Processor Orientation and Components
A. Processor 1
B. Processor 2
C. Processor 3
D. Processor 4
E. Screws (2) at the top of the processor
F. Clip on processor handle
G. Processor handle
H. Termination Module
I. Processor Heat Sink
J. Processor retention mechanism
K. Screws (2) for retention module guide rails
L. Note the handle/screw orientation for each
processor pair
D
C
B
A
E
F
I
K
H
OM09921
Removing a Processor
See Figure 5.
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter and the additional
cautions given here.
2. Remove the two screws that secure the handle to the processor.
3. Pull firmly and straight up on either side of the processor handle.
4. Put the processor on a piece of conductive foam and store it in an antistatic package.
64 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 65

Installing a Processor
See Figure 5.
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter and the additional
cautions on page 63.
2. Remove the new processor from its antistatic package and place it on a grounded, static-free
surface or conductive foam pad.
3. Attach the processor handle to the processor. For more information, see "Installing Processor
Handles" on page 65.
4. If necessary, attach the heatsink to the processor. For more information, see "Installing
Processor Heatsinks" on page 66.
5. Orient the processor correctly in the chassis. See Figure 5 and Figure 1.
6. Slide the processor into the guides on each side of the processor slot and press the processor
downward firmly into the baseboard connector.
7. Insert and tighten two screws at the top of the processor handle.
Removing Processor Retention Mechanisms
See Figure 5.
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter and the additional
cautions on page 63.
2. Make sure that the processor has been removed from the baseboard. To remove the processor,
see "Removing a Processor" on page 64.
3. With a long bladed screwdriver, remove the two screws at the base of the processor retention
mechanism.
4. Remove the retention mechanism from the baseboard.
Installing Processor Retention Mechanisms
See Figure 5.
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter and the additional
cautions on page 63.
2. With a long bladed screwdriver, tighten the two screws at the base of the processor retention
mechanism.
Installing Processor Handles
Depending on your configuration, the handles for the processor might not be attached to the
processor. In this case, you must attach a handle to each processor.
See Figure 5.
1. Orient the handle as shown in the Figure 5.
2. Press the handle into the processor until the handle snaps into place.
Removing and Installing Baseboard Components 65
Page 66

Installing Processor Heatsinks
See Figure 5.
Depending on your configuration, the heatsink for each processor might not be attached. In this
case, you must attach one heatsink to each processor. If you are working with a processor
terminator module, you do not install a heatsink.
1. Remove the heatsink from its protective cover.
2. Pull the tab on the bottom of the heatsink to remove the blue plastic film and expose the square
of adhesive thermal grease that will help attach the heatsink to the processor.
3. Orient the heatsink on the correct side of the processor. For correct orientation, see Figure 5.
4. Because of the adhesive grease on the heatsink, be careful to orient the heatsink properly
before placing it against the processor.
5. Attach the heatsink to the processor with five 6-32 X 3/8 screws, and tighten to 8-10 inchpounds.
Voltage Regulator Modules (VRMs)
Up to seven voltage regulator modules provide power for processors. Table 44 shows this
relationship.
Table 44. VRM/Processor Power Sequence
VRM # VRM provides power for Description
1 (Embedded) Processor #1 Processor core power only
2 (Embedded) Processor #1 GLT (FSB reference)
3 (Embedded) Processor #1 and #2 L2 cache power only
4 (Embedded) Processor #3 and #4 L2 cache power only
#2 Connector Processor #2 Processor core power only
#3 Connector Processor #3 Processor core power only
#4 Connector Processor #4 Processor core power only
VRMs 1 through 4 are embedded in the SKA4 baseboard. Additional VRMs plug into connectors
2 though 4 on the baseboard. You must use a specific number and connector population sequence
of VRMs for each combination of processors and termination boards. Table 45 lists the required
number and location of VRMs for each potential processor. Figure 1 on page 14 shows this
information graphically.
Table 45. Processor/VRM Population Sequencing
If you have a processor in connector # VRM in connector #
1 None. All required VRMs are embedded in the
SKA4 baseboard.
1 and 2 2
1, 2, and 3 3
1, 2, 3, and 4 4
66 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 67

Removing a VRM
CAUTIONS
VRM must be appropriate: You might damage the system if you install
a VRM that is inappropriate for your system. For exact information about
VRM and processor interchangeability, contact your customer service
representative.
ESD and handling processors: Reduce the risk of electrostatic
discharge (ESD) damage to the VRM by doing the following: (1) Touch the
metal chassis before touching the VRM or baseboard. Keep part of your
body in contact with the metal chassis to dissipate the static charge while
handling the VRM. (2) Avoid moving around unnecessarily.
To decide what VRM you need to remove, see Figure 1 on page 14.
1. Using a small flat-bladed screwdriver, push the plastic ejector levers on each end of the
connector away from the VRM to eject it out of the connector.
2. Pull VRM straight up and out of the baseboard.
3. Place the VRM on a nonconductive, static-free surface, or store it in an antistatic protective
wrapper.
Installing a VRM
To decide what VRM you need to install, see Figure 1 on page 14.
1. Remove the VRM from its protective package.
2. Orient the VRM within the VRM connector correctly. See Figure 6 on page 67.
3. Carefully insert the VRM in the connector on the baseboard. Make sure you do not bend the
connector pins.
4. Push down firmly on both ends of the VRM until the ejector levers of the connector snap into
place, locking the VRM in the connector.
5. Make sure that the ejector levers are firmly in place. If not, use a screwdriver to push them
into place.
A
C
B
OM09922
Figure 6. Installing a VRM
A. VRM
B. VRM connector on baseboard
C. Ejector lever
Removing and Installing Baseboard Components 67
Page 68

Replacing the Backup Battery
The lithium battery on the baseboard powers the real-time clock (RTC) for three to four years in
the absence of power. When the battery weakens, it loses voltage and the system settings stored in
CMOS RAM in the RTC (e.g., the date and time) may be wrong. Contact your customer service
representative or dealer for a list of approved devices.
WARNING
If the system has been running, any installed processor and heat sink on
the processor board(s) will be hot. To avoid the possibility of a burn, be
careful when removing or installing baseboard components that are
located near processors.
The following warning and translations are required by specific certifying agencies to be printed
immediately adjacent to the procedure for removing the RTC.
WARNING
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with
the same or equivalent type recommended by the equipment
manufacturer. Discard used batteries according to manufacturer’s
instructions.
ADVARSEL!
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering. Udskiftning
må kun ske med batteri af samme fabrikat og type. Levér det brugte
batteri tilbage til leverandøren.
ADVARSEL
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosjonsfare. Ved utskifting benyttes kun batteri
som anbefalt av apparatfabrikanten. Brukt batteri returneres
apparatleverandøren.
VARNING
Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte. Använd samma batterityp eller
en ekvivalent typ som rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren. Kassera
använt batteri enligt fabrikantens instruktion.
VAROITUS
Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu. Vaihda paristo
ainoastaan laitevalmistajan suosittelemaan tyyppiin. Hävitä käytetty
paristo valmistajan ohjeiden mukaisesti.
68 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 69

Note the location of the lithium battery in Figure 1 on page 14.
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter and the additional
warning given on page 68.
2. Remove the VRMs in VRM connectors 3 and 4. For more information, see "Removing a
VRM" on page 67.
3. Insert the tip of a small flat-bladed screwdriver or equivalent under the plastic tab on the
snap-on plastic retainer.
4. Gently push down on the screwdriver to lift the battery.
5. Remove the battery from its socket.
6. Dispose of the battery according to local ordinance.
7. Remove the new lithium battery from its package and, being careful to observe the correct
polarity, insert it in the battery socket.
Add-in Boards
Figure 1 on page 14 identifies the add-in board locations. The SKA4 baseboard contains eight PCI
slots. There are
• Two 32-bit, 33 MHz half-length PCI slots
• Two 64-bit, 66/33 MHz Hot-Plug PCI slots
• Four 64-bit, 33 MHz Hot-Plug PCI slots
Typically, the Hot-Plug PCI add-in boards are held in the Hot-Plug slots by a front and rear HotPlug retention mechanism.
A
B
Figure 7. Example of a Front Hot-Plug Retention Mechanism
A. Green and Amber LEDs
B. Press here on the inside of the chassis and then rotate to
release the PCI board
C. PHP Retention Mechanism from the outside of the chassis
D. HW push-button
C
D
OM09943
Removing and Installing Baseboard Components 69
Page 70

Removing a 32-bit, 33 MHz Half-Length PCI Add-in Board
WARNING
If the system has been running, any installed PCI add-in board on the
processor board(s) will be hot. To avoid the possibility of a burn, be
careful when removing or installing baseboard components that are
located near processors.
System power on/off: The on/off button on the front panel DOES
NOT turn off the system AC power. To remove power from system, you
must unplug the AC power cords from the wall outlet or the system.
CAUTION
Slot covers must be installed on all vacant expansion slots. This
maintains the electromagnetic emissions characteristics of the system and
ensures proper cooling of system components.
The add-in boards for the half-length 33 MHz PCI slots are NOT Hot-Pluggable. In other words,
you must turn off the AC power to the system first before installing boards at these locations.
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter.
2. Disconnect any cables attached to the PCI board you are removing.
3. Remove and save the screw that attaches the existing board retaining bracket to the chassis.
4. Holding the board by its top edge or upper corners, carefully pull it out. Do not scrape the
board against other components.
5. Store board in an antistatic protective wrapper.
6. If you are not reinstalling a board in the same slot, install a slot cover over the vacant slot. The
tapered foot of the cover must fit into the mating slot in the expansion slot frame.
7. Use the screw removed earlier to fasten the new board to the chassis. Tighten the screw firmly
(6.0 inch-pounds).
Installing a 32-bit, 33 MHz Half-Length PCI Add-in Board
WARNING
If the system has been running, any installed PCI add-in board(s) will
be hot. To avoid the possibility of a burn, be careful when removing or
installing baseboard components that are located near processors.
System power on/off: The on/off button on the front panel DOES
NOT turn off the system AC power. To remove power from system, you
must unplug the AC power cords from the wall outlet or the system.
70 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 71

CAUTIONS
Do not overload baseboard: Do not overload the baseboard by installing
add-in boards that draw excessive current.
ESD and handling boards: Add-in boards can be extremely sensitive to
ESD and always require careful handling. After removing the board from its
protective wrapper or from the baseboard, place it component-side up on a
grounded, static-free surface or conductive foam pad—if available. Do not
slide the board over any surface.
1. Remove add-in board from its protective wrapper. Be careful not to touch the components or
gold edge connectors. Place board component-side up on an antistatic surface.
2. Record the serial number of the add-in board in your equipment log.
3. Set jumpers or switches on the PCI board according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
4. Remove and save the screw that attaches the existing board or expansion slot cover to the
chassis.
5. Remove and save the expansion slot cover.
6. Hold the add-in board by its top edge or upper corners. Firmly press it into an expansion slot
on the baseboard. The tapered foot of the board-retaining bracket must fit into the mating slot
in the expansion slot frame. Install a PCI board component-side DOWN.
7. Use the screw removed earlier to fasten the new board-retaining bracket to the chassis.
Tighten the screw firmly (6.0 inch-pounds). Attach cables if necessary.
Removing a 64-bit, 66/33 MHz Hot-Plug PCI Add-in Board
WARNING
If the system has been running, any installed PCI board on the
processor board(s) will be hot. To avoid the possibility of a burn, be
careful when removing or installing baseboard components that are
located near processors.
CAUTION
Slot covers must be installed on all vacant expansion slots. This
maintains the electromagnetic emissions characteristics of the system and
ensures proper cooling of system components.
See Figure 7 on page 69.
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter.
2. Make sure that the slot is powered off. If the slot is powered on, turn the power to the slot off
through the PCI Hot-Plug application on your system. If the system has a HW push-button,
press it to turn the power to the slot off.
3. Disconnect any cables attached to the board you are removing.
4. If there is a front and rear Hot-Plug retention mechanism, release it.
Removing and Installing Baseboard Components 71
Page 72

5. Remove the PCI board by pulling straight up.
6. Store board in an antistatic protective wrapper.
7. If you are not reinstalling a board in the same slot, install a slot cover over the vacant slot. The
tapered foot of the cover must fit into the mating slot in the expansion slot frame.
Installing a 64-bit, 66/33 MHz Hot-Plug PCI Add-in Board
WARNING
If the system has been running, any installed PCI add-in board on the
processor board(s) will be hot. To avoid the possibility of a burn, be
careful when removing or installing baseboard components that are
located near processors.
CAUTIONS
Do not overload baseboard: Do not overload the baseboard by installing
add-in boards that draw excessive current.
ESD and handling boards: Add-in boards can be extremely sensitive to
ESD and always require careful handling. After removing the board from its
protective wrapper or from the baseboard, place it component-side up on a
grounded, static-free surface or conductive foam pad—if available. Do not
slide the board over any surface.
1. If necessary, expose the SKA4 baseboard by removing the access covers and foam cover. For
instructions on how to remove access covers for your system, see the product guide
accompanying your system.
2. Remove add-in board from its protective wrapper. Be careful not to touch the components or
gold edge connectors. Place board component-side up on an antistatic surface.
3. Record the serial number of the add-in board in your equipment log.
4. Make sure that the slot is powered off. Power off the add-in board through the PCI Hot-Plug
application on your system, or through a HW push-button (if available).
5. Set jumpers or switches on the board according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
6. If necessary, remove and save the expansion slot cover.
7. Hold the add-in board by its top edge or upper corners. Firmly press it into an expansion slot
on the baseboard. The tapered foot of the board-retaining bracket must fit into the mating slot
in the expansion slot frame. Install a PCI board component-side DOWN.
8. If there is a front and rear Hot-Plug retention mechanism, engage it.
9. Use the screw removed earlier to fasten the new board to the chassis. Tighten the screw firmly
(6.0 inch-pounds).
10. Attach cables if necessary.
11. Power on the add-in board through the PCI Hot-Plug application on your system, or through a
HW push-button (if available).
72 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 73

ICMB Card
The ICMB card allows two servers to communicate through a serial connection. An ICMB card is
installed in each server; the cards are connected through a serial cable.
Establishing communication between servers using the ICMB card is a two-step process. First,
install the ICMB card in each server. Lastly, make sure that the software required for the card is in
place. Software for the ICMB card includes firmware on the card and software already included in
the ISC software. ISC software is included in the server software kit accompanying the SKA4
baseboard.
This product guide does not discuss the software for the ICMB card. However, this product guide
does provide instructions for removing and installing ICMB hardware.
Figure 8 is a drawing of the ICMB card.
C
A
B
OM09923
Figure 8. ICMB Card
A filler panel is attached to the ICMB card with two screws. The screws are noted by "A" and the
card is noted by "C" in Figure 8. The panel, noted by "B", is identical to any filler panel for a PCI
add-in board. You attach the filler panel to the rear of a chassis in the same way as you would
attach a PCI add-in board.
Removing and Installing Baseboard Components 73
Page 74

Installing an ICMB Card
1. Remove the ICMB card and internal cable. The cable is noted by "A" in Figure 9.
A
OM09926
Figure 9. Section of ICMB Internal Cable
2. Designate a PCI slot for the ICMB card. The card does not plug into the connector on the
baseboard, but does use the opening at the rear of the chassis.
3. Secure the filler panel to the chassis. On most systems, you use one screw. The screw is noted
by "A" in Figure 10.
A
OM09927
Figure 10. Example of an ICMB Card Attached to a Chassis
74 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 75

4. Attach the internal cable to the internal connector on the ICMB card. The internal cable
connection to the card is noted by "A" in Figure 11.
A
OM09928
Figure 11. Internal Cable Attached to the ICMB Card
5. Connect the other end of the cable to the ICMB connector on the baseboard. The location of
the connector is shown in Figure 1 on page 14.
6. The ICMB kit contains an external cable. The cable attaches to the card’s external connector.
The external cable connection to the card is noted by "A" in Figure 12.
A
OM09929
Figure 12. External Cable Attached to the Card
Removing an ICMB Card
1. Disconnect the internal and external cables from the card and the baseboard.
2. Remove the screw securing the card to the chassis. The screw is noted by "A" in Figure 10 on
page 74.
3. Remove the ICMB card from the server.
Removing and Installing Baseboard Components 75
Page 76

76 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 77

4 Solving Problems
This chapter helps you identify and solve problems that might occur while you are using the
system.
In the event you encounter an issue with your SKA4 baseboard, this chapter helps you trouble
shoot and identify possible problem areas. In some cases, you are directed to contact your
customer service representative.
Boot Issues
Issue 1: My server will not power on
Check for the following possibilities:
• Is the server AC power cord securely plugged into the power supply?
• Is the server plugged into a “powered on” power strip?
• Some ATX power supplies have a power switch on the back of the power supply next to the
fan, is it switched on?
• Is the front panel power switch cable properly connected to the front panel header pins on the
baseboard located at J9E3, pins 2 and 16?
• If you are using a SSI compliant power supply, make sure the proper power supply connector
is attached to the auxiliary signal connector. SSI power supplies require a 3-volt sense signal
to properly power on and have a special 5 pin by 2 row connector for that purpose. If that
connector is available with your power supply, make sure it is firmly seated in the Auxiliary
Signal connector located at J9B2 on the baseboard.
• Remove all add-in cards and see if the server boots using just the on-board components. If
successful, add the cards back in one at a time with a reboot in between to see if you can
pinpoint a suspect card.
• Remove the processor and terminator card and reseat them.
• Remove and reseat the memory modules. Try using memory modules from a known working
server system. Memory must be used in fours.
Though it is unlikely that a server will not boot, there are many reasons why it may not boot. If
you are unable to resolve this issue, please fill out the included customer support form and call
your customer support representative. Please note the answers to the following questions below.
• What memory is being used? Is it on the tested memory list? Contact your customer service
representative for the latest tested memory list.
• What chassis and power supply is being used?
• If you are using a chassis with front panel lights, are there any front panel lights on?
• Is the power supply fan spinning?
• Does the system beep? See issue 2.
• Please note what is displayed on the monitor or any sounds emanating from the server system.
77
Page 78

Issue 2: Upon boot, my ser ver starts bee ping
Most likely, these beeps are what are known as “beep codes.” They identify system events in case
video fails to display. The following list is an excerpt of available beep codes. Contact your
customer service representative for a complete list of beep codes.
Table 46. Standard BIOS Port-80 Codes
CP Beeps Reason
xx 1-1-1-1 There are no processors present in the system, or the processor s are so
incompatible that the system BIOS cannot be run (like mismatched cache
voltages).
16 1-2-2-3 BIOS ROM checksum.
20 1-3-1-1 Test DRAM refresh.
22 1-3-1-3 Test 8742 Keyboard Controller.
28 1-3-3-1 Autosize DRAM, system BIOS stops execution here if the BIOS does not detect
any usable memory DIMMs.
2C 1-3-4-1 Base RAM failure, BIOS stops execution here if entire memory is bad.
46 2-1-2-3 Check ROM copyright notice.
58 2-2-3-1 Test for unexpected interrupts.
98 1-2 Search for option ROMs. One long, two short beeps on checksum failure.
B4 1 One short beep before boot.
Table 47. Recovery BIOS Port-80 Codes
CP Beeps Reason
xx 1-1-1-1 There are no processors present in the system, or the processors are so
incompatible that the system BIOS cannot be run (like mismatched cache
voltages).
Issue 3: My HDD lights went on, I heard the drives spin up, and
my floppy drive light turned on – but I’m not seeing
video
Check the following:
• Remove all add-in cards and retry booting with just the on-board components. If successful,
try adding the add-in boards one at a time with a reboot in between to try and pinpoint a
suspect card.
• Remove and reseat memory modules. Try using memory from a known working system.
• Remove and reseat processor and terminator card.
• If you are using a switch box to share a monitor between multiple servers, ensure you are
switched to the proper server.
78 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 79

If you are still unable to get a video image, please fill out the included customer support form and
call your customer support representative. Please note the answers to the following questions
below.
• What memory is being used? Is it on the tested memory list? Contact your customer service
representative for the latest tested memory list.
• What chassis and power supply is being used?
• If the chassis has front panel lights, are there any front panel lights on?
• Is the power supply fan spinning?
• Does the system beep? See issue 2.
• Please note any sounds emanating from the server system.
• If you are using a third party video adapter, please have manufacturer and model number
ready.
Issue 4: I’m installing adapters in my powered-down system, and
my system boots up when I install a PCI adapter!
Server management features require full time “standby” power. This means that power is still
provided to parts of the system even if the user has turned the system “off” via the front panel
power switch.
Additionally, there are signals in the PCI connectors that tell the system to boot (normally used by
server management adapters/NICs). Plugging in the adapter with AC power still applied can cause
false signals to be transmitted commanding the system to boot. Before removing the cover to your
chassis, you should always
• Turn off the server via the front panel power switch.
• Unplug the AC cord from the back.
Also, see issue 5. If your server is booting automatically, but the conditions specified here or in
issue 5 do not match, please fill out the included customer support form and call your customer
service representative. Please pay special attention to the following information:
• What BIOS do you have loaded on the system? (The latest tested BIOS is posted to the Intel
Customer Support Website)
• What is the PBA number of the baseboard? (The PBA number is located on a white label near
the edge of the board and is printed in the following format: PBA xxxxxx-xxx)
• What memory is being used? Is it on the tested memory list? Contact your customer service
representative for the latest tested memory list.
• What chassis and power supply is being used?
Solving Problems 79
Page 80

Issue 5: My system boots up automatically when I power on my
power-strip
Some server systems save the “last known power state” since the last AC power connection. If
you remove AC power before powering down the system via the front panel power switch, your
system will automatically attempt to come back to the “on” state it was in once you restore AC
power.
• Please keep in mind that unplugging the system or flipping a switch on the power strip both
remove AC power.
• Follow the correct A/C removal sequence: Press the front panel button, then remove the A/C
power cord.
Allowing your system to fully power up and then power down the system using the front panel
power switch should correct this problem. If it does not, refer to issue 3. If neither of these
options fix your problem, fill out the attached customer support form and call your customer
support representative. Please have the following information available:
• What BIOS do you have loaded on the system? (the latest tested BIOS is posted to the Intel
Customer Support Website)
• What is the PBA number of the baseboard? (The PBA number is located on a white label near
the edge of the board and is printed in the following format: PBA xxxxxx-xxx)
• What memory is being used? Is it on the tested memory list? Contact your customer service
representative for the latest tested memory list.
• What chassis and power supply is being used?
Issue 6: The boot up process takes too long
What most people typically consider “booting” actually involves multiple phases:
• BIOS Power-On Self Test (POST): This includes the memory count and the keyboard/mouse
and IDE drive check.
• Option-ROM loading: Each device may load a portion of its operating code or “option ROM”
into memory. This is what the user may see as the messages that come up identifying the
add-in device such as a SCSI card ROM.
• Operating system boot: During this time, the operating system takes control of the server and
performs whatever checks & setups are necessary for operation. An example of this is the
Windows NT “blue boot screen.”
A slow-down at any of these three points can produce what users perceive as a “slow boot.” The
following is a list of items that can produce a slower boot:
• Large memory configurations. Large memory installations can take 1-2 minutes to check.
Extended memory test can be disabled in BIOS setup to speed up the boot process when
performing service which requires multiple reboots, however this memory test should be
enabled for normal system operation.
• Multiple SCSI adapters. SCSI adapters take time to load their option ROMs and execute their
code that scans for drives.
80 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 81

• Numerous SCSI devices. SCSI device adapters, like many other adapters, have option ROMs
that must be loaded into memory. Detection & option ROM loading takes additional time.
• Numerous other adapters. Many adapters have a option ROM which takes time to load into
memory.
If your system does not have any of these items and you still experience an extended boot time,
please fill out the included customer support form and call your customer support representative.
Please pay special attention to the following information:
• Amount of memory in the system.
• What memory is being used? Is it on the tested memory list? Contact your customer service
representative for the latest tested memory list.
• Number and type of adapters in the system (manufacturer and model number).
• The number and type of hard drives in the system (manufacturer and model number).
Issue 7: I put one processor in my system but it doesn’t boot
Check the following:
• Is the processor a 100 MHz system bus or 133 MHz system bus processor? The SKA4 server
board only supports Intel Pentium III processors designed for the100 MHz system bus.
• Is the processor in the primary processor slot? Refer to the configuration label or the
Technical Product Specification for details on which slot is the primary.
• Does the secondary processor slot contain a terminator card? The Pentium III processor
architecture requires non-populated processor slots to be terminated. Without proper
termination, the signals do not maintain their electrical integrity & may cause errors. Some
server products prevent boot up if they do not detect a terminator card.
• Are the processor and terminator card firmly seated? The retention mechanisms designed to
hold the processor and term card firmly in place. Ensure the processor and termination card
have “snapped” into the retention mechanism.
• Does the system beep? Refer to issue 2.
If you are still having no-boot issues, please fill out the included customer support form and call
your customer support representative. Have the following information ready:
• Does the system beep? What beep code is it giving?
• Does the system show video?
• What memory is being used? Is it on the tested memory list? Contact your customer service
representative for the latest tested memory list.
• What error does the system give if any?
• What add-in adapters are installed in your system? (manufacturer and model number)
• Chassis and power supply manufacturer and model number.
Solving Problems 81
Page 82

Other Issues
Issue 8: Some of my hard drives show up during POST and
some don’t
Check on the following:
• Are you using third party SCSI adapters? System memory limitations limit the number & size
of option ROMs in the system. If you place too many adapters or adapters that take up too
much space in memory, they may not install and show the hard drives connected to them.
• If you disconnect your hard drives from the third party adapter and connect them to the on-
board adapter, do they show up?
• Verify that pin 1 on the data cable is connected to pin 1 on the device. In most cases, if you
orient the data cable so that the colored stripe on the cable is pointing towards the power
connector on the device, you will have proper orientation.
• Verify that the device power cable is firmly connected.
• Are your hard drives properly terminated? If you are using Ultra 2 or Ultra 160 drives without
a hot-swap backplane, a terminator needs to be placed in the last connector on the SCSI cable.
Ultra 2/Ultra 160 devices do not provide their own termination logic like Ultra Wide devices
did.
• Check your SCSI ID numbers. SCSI devices must have their own unique ID on the SCSI bus.
This number is set automatically when using an Intel SCSI hot-swap backplane, but must be
set with jumpers on the device when using a SCSI cable. ID number should be set starting at 0
and must be set lower than 8 if the drive is to be booted from.
If your hard drives still do not show, please fill out the included customer support form and call
your customer support representative. Please pay special attention to the following information:
• What add-in adapters do you have in your system (manufacturer and model number)?
• What types of hard drives are in the system (manufacturer and model number)?
• If you are using a SCSI cable to attach your drives, what kind of terminator do you have at the
end of the cable? (manufacturer and type e.g. ultra 160)
• What are the SCSI IDs of the devices on your SCSI bus?
• How many SCSI channels are you using?
• Are you using a hot-swap backplane with your third party adapter?
• What memory is being used? Is it on the tested memory list? Contact your customer service
representative for the latest tested memory list.
82 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 83

Issue 9: My hard drives don’t show up under Windows NT
Verify that all your drives are detected during POST (see issue 8). IDE devices will be identified
and listed on the screen by the server board BIOS and SCSI drives will be identified and listed on
the screen by the SCSI BIOS.
Windows NT 4.0 does not ship with the latest drivers for some SCSI controllers. Because of this,
Windows NT installation must be directed to the proper drivers during installation. To do this, you
must press the F6 key during installation start up at the sight of the first “installation blue screen.”
This will allow you to skip auto-detection and manually install a driver. The other way to perform
a manual install is to use the three boot floppies. When asked to perform an auto detection of mass
storage devices or do it manually, choose to do it manually and you will be asked to choose from a
list or provide the driver from a floppy. If you are unsure about what you should choose from the
list, contact your customer service representative.
If your system can still not see the onboard adapter or your hard drives, please fill out the included
customer support form and call your customer support representative. Please pay special attention
to the following information:
• Does the SCSI controller identify itself during POST?
• Can you see the drives being identified at POST either by the system BIOS or the SCSI BIOS?
(You should see the manufacturer’s name and drive type during the Adaptec SCSI scan).
• If you are using a SCSI cable to attach your drives, what kind of terminator do you have at the
end of the cable? (manufacturer and type e.g. ultra 160)
• What memory is being used? Is it on the tested memory list? Contact your customer service
representative for the latest tested memory list.
Solving Problems 83
Page 84

Checking Field Replaceable Units (FRU) with the Diagnostic Wizard
The Diagnostic Wizard is a suite of test utilities that check the functionality of Field Replaceable
Units (FRU). First, the wizard displays a list of test modules to choose from. After completing the
tests, the selected test modules return either a PASS or FAIL status on tested components. To run
the Diagnostic Wizard, run it from the Service Partition installed on the system. For instructions
on setting up the service partition, see the Installation Guide for the Intel Server Control.
Starting the Ser vice Partition & Test Menu
The Diagnostic Wizard may be started remotely, or you can do the following to work locally:
1. Power on your system. If it is currently running, restart using the method recommended by
your operating system vendor. For example, in MS-DOS you press <Ctrl+Alt+Del>.
2. When your screen displays the message
F2 to enter setup
3. Press <F2>.
4. Once System Setup is started, use the arrow keys to highlight the Advanced menu.
5. Highlight Server Management and press <Enter>.
6. Highlight Service Boot and press <Enter>.
7. A menu is displayed. Highlight Enable and press <Enter>.
8. Press <F10> to save and exit setup.
9. Press Y to confirm saving current settings.
10. The system restarts to a ROM-DOS prompt. At this point, you can execute any software
installed on your Service Partition from the command line, or you can run the Diagnostic
Wizard as instructed below.
NOTE
✏
The option in System Setup to perform a Service Boot is a flag only. As soon as you save and exit
setup, it is reset to disable. The next reboot returns you to the operating system or boot manager.
Therefore, to reboot to the service partition, you must follow the steps above every time.
11. To open the Diagnostic Wizard test selection menu, type
testmenu and press <Enter>.
84 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 85

Running Tests
NOTE
✏
The test modules included with your Server Software Kit CD are specifically designed to run on
the server system you purchased from Intel. Running the tests on any other platform results in the
following error message.
This Motherboard is not supported by this test.
Press any key to exit.
After displaying this message, the program terminates.
Test Menu
The Test Menu displays a list of tests that you can run. Use your keyboard cursor (arrow) keys to
highlight the desired test and press <Enter> to execute it.
SAMPLE SCREEN DISPLAY
H820diag Version 1.0 ©Copyright 1999 Intel Corp. All Rights Reserved.
Server Diagnostic Options
Quick Test
Comprehensive Test
Comprehensive Test with continuous looping
Highlight selection using Cursor UP/DOWN and press ENTER
Solving Problems 85
Page 86

System Configuration Check
Before executing the tests, the system hardware is scanned and a message is displayed for
confirmation. Before continuing with the tests, check the accuracy of the scan. Once you are sure
that the system has successfully scanned the system hardware, press <Enter>.
To cancel press <Ctrl + Break>. A message is displayed and instructs you to check all hardware
and cable connections before returning to the test menu.
SAMPLE SCREEN DISPLAY
DiagWiz Test Configuration
Base Memory Size: 640KB
CPU Type: Pentium® III Processor
CPU Speed: 550MHz
CPU SMP #0: Present
CPU SMP #1: Present
Keyboard Type: 101-Key
Mouse: Enabled
RTC RAM Size: 128
Number of SCSI
Channels:
COM2 at Port Address: 2F8 is enabled
LPT1: 0x378
Floppy Cfg. Drive A: 1.44MB (3.5 inch)
Hard Drive 0: Cylinders: 531 Heads: 255 Sectors:65 Total Size:
Video Subsystem: Rage IIC, 1024K video RAM
External Cache Size: 512KB
Memory Size: 128MB
2
4157MB
If the above configuration is correct, press <Enter> to continue
or press <Ctrl + Break> to quit.
86 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 87

Test Results
Once the tests have ran, a summary is displayed showing the status of each test. If an FRU passed
the test, the text PASSED in green letters is displayed. If an FRU failed the test, the text FAILED
in red letters is displayed.
The report is broken down by FRU. Each section contains the status of every test run for one FRU.
The text for an FRU is red even if just one test fails. The specific tests that failed are indicated
below it in the report. Also be aware that the failure of some tests may effect the passing or
failing of subsequent tests. If all the tests for an individual FRU pass, the FRU is displayed in
Green.
SAMPLE SCREEN DISPLAY
CPU FRU PASSED
MATH_COPROCESSOR PASSED
CPU PASSED
SMP_PROCESSOR_0 PASSED
MEMORY FRU PASSED
MEMORY PASSED
STRESS PASSED
HARD DISK FRU PASSED
HARD DISK 0 PASSED
HARD DISK 1 PASSED
Solving Problems 87
Page 88

88 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 89

5 Technical Reference
This section includes:
• Connectors’ pinouts and baseboard locations
• Information on baseboard jumpers
• Baseboard interrupts
• Video modes
89
Page 90

Connectors
The following figure shows connector locations on the baseboard. This section provides pin
information about the connectors.
HH
GG
FF
EE
DD
CC
BB
AA
C
A
B
E
D
F
31
G
3
H
1
I
J
3
K
B1
L
M
N
O
P
Q
11
R
S
Z
Y
X
VW
OM09924
Figure 13. Detailed Diagram of Connector Locations
90 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
T
U
Page 91

Item Connector Description Item Connector Description
A. J1A1 Keyboard and Mouse
Connector
B. J1B3 Internal USB S. J9G1 Jumper Block
C. J2B1 VRM Connector #3 T. J9G2 Ultra 160 Wide SCSI Channel B
J2A2 VRM Connector #4 (VRM
above)
J2C1 VRM Connector #2 (VRM
below)
D. J3C1 Fan Connector #1 W. J7H1 SMM Feature Connector
E. J4C1 Fan Connector #4 X. J6J1 Legacy Wide SCSI
F. J3A1 Fan Connector #2 Y. J6F1 Memory Expansion Card
G. J4A1 Fan Connector #3 Z. (Top to
H. (Top to
bottom)
J7A1 Processor Connector #4 J4G1 PCI Slot #4 P64-A2
J7B1 Processor Connector #3 J4G2 PCI Slot #5 P64-B1
J7C1 Processor Connector #2 J4H1 PCI Slot #6 P64-B2
J7D1 Processor Connector #1 J4H2 PCI Slot #7 P64-B3
I. J9B2 Auxiliary Power
Connector
J. (Top to
bottom)
J9B1 Main Power Connector A BB. J2D1 PCI Slot #1 P32-C2
J9D1 Main Power Connector B CC. J3D1 Hot Plug Indicator Board
K. J9E1 IDE Activity Input
Connector
L. J9E4 SMBus Connector EE. J1D1 Video
M. J9E5 IDE Connector FF. J1C2 USB
N. J9E6 Floppy Connector GG. J1C1 NIC
O. J9E3 Front Panel Connector HH. (Top to
P. J8F1 IMB Connector J1A2 Serial Port A
Q. J9F1 Jumper Block J1B2 Parallel Port
R. J9F2 Jumper Block
U. J9H1 Ultra 160 Wide SCSI Channel A
V. J7J1 Legacy Narrow SCSI Connector
Connector
bottom)
J4F1 PCI Slot #3 P64-A1
J4J1 PCI Slot #8 P64-B4
AA. J2E1 PCI Slot #2 P32-C1
Connector (HPIB)
DD. J1D2 ICMB Connector
bottom)
J1B1 Serial Port B
Technical Reference 91
Page 92

Power Distribution Board Interface Connectors (J9B1, J9D1, J9B2)
The SKA4 Baseboard receives its main power through two primary and one auxiliary power
connectors. The two main power connectors are identified as J9B1 and J9D1. The auxiliary
power connector, identified as J9B2, provides a power subsystem communication path, control
signals, power supply sense connections and other miscellaneous signals defined in the table
below.
Table 48. Main Power Connector A (J9B1)
Current Carrying
Pin Signal Type*
1 12V power 6 Amps Power supply 12V
2 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
3 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
4 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
5 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
6 VCC power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V
7 VCC power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V
8 VCC power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V
9 VCC power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V
10 VCC power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V
11 SB5V power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V standby
12 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
13 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
14 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
15 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
16 VCC power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V
17 VCC power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V
18 VCC power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V
19 VCC power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V
20 VCC power 6 Amps Power Supply 5V
* Type (in, out, in/out, power, ground) is from the perspective of the baseboard.
Capability Description
92 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 93

Table 49. Main Power Connector B (J9D1)
Current Carrying
Pin Signal Type*
1 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
2 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
3 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
4 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
5 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
6 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
7 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
8 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
9 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
10 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
11 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
12 12V power 6 Amps Power Supply 12V
13 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
14 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
15 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
16 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
17 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
18 VCC3 power 6 Amps Power supply 3.3V
19 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
20 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
21 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
22 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
23 Ground ground 6 Amps Ground return connection
24 12V power 6 Amps Power Supply 12V
* Type (in, out, in/out, power, ground) is from the perspective of the baseboard.
Capability Description
Table 50. Auxiliary Power Connector (J9B2)
Current Carrying
Pin Signal Type*
1 Ground ground Ground return connection
2 5V Sense out N/A Sense line feedback to power supply
3 3.3V Sense out N/A Sense line feedback to power supply
4 BMC FAN SPD CTL out N/A
5 SM PRI 5VSB SCL in/out N/A Server Management I2C bus - clock
6 SM PRI 5VSB SDA in/out N/A Server Management I2C bus - data
7 Ground ground Ground return connection
8 PWRGD PS in N/A Signal from power subsystem indicating
Technical Reference 93
Capability Description
power is stable
continued
Page 94

Table 50. Auxiliary Power Connector (J9B2) (continued)
Current Carrying
Pin Signal Type*
9 PS PWR ON_L out N/A Control signal from baseboard to power
10 Ground ground Ground return connection
11 -12V power Power Supply negative 12V
12 Key N/A
13 12V power Power Supply 12V
14 Ground ground Ground return connection
* Type (in, out, in/out, power, ground) is from the perspective of the baseboard.
Capability Description
supply
Front Panel Interface (J9E3)
The front panel attaches to a 30-pin header on the baseboard. The header contains reset, NMI,
sleep, and power control buttons, LED indicators, and an IPMB connection. The table below
summarizes the front panel signal pins, including the signal mnemonic, name, and brief
description.
Table 51. Front Panel Connector (J9E3)
Pin Signal Type* Description
1 SPKR_FP out SPEAKER DATA for the front panel/chassis mounted
speaker.
2 GROUND ground GROUND is the power supply ground.
3 CHASSIS_INTRUSION in CHASSIS INTRUSION is connected to the BMC and
indicates that the chassis has been opened.
CHASSIS_INTRUSION is pulled high to +5 V standby on the
baseboard.
4 FP_HD_ACT* out HARD DRIVE ACTIVITY indicates there is activity on one of
the hard disk controllers in the system.
5 +5V power +5 V is the 5 volt power supply.
6 FP_SLP_BTN* in FRONT PANEL SLEEP is connected to the BMC and causes
the system to be put to sleep if supported by the operating
system. FP_SLP_BTN* is pulled high to +5 V on the
baseboard and is intended to be connected to a momentary-
contact push button (connected to GROUND when pushed)
on the system front.
7 COOL_FLT_LED* out COOLING FAULT LED indicates that either a fan failure has
occurred or the system is approaching an over-temperature
situation. COOL_FLT_LED* is an output of the BMC.
8 PWR_LED* out POWER PRESENT LED.
9 PWR_FLT_LED* out SYSTEM FAULT indicates that either a power fault or SCSI
drive failure has occurred in th e system.
10 GROUND ground GROUND is the power supply ground.
11 SM_IMB_SDA in/out I2C DATA is the data signal for the Intelligent Platform
Management Bus.
continued
94 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 95

Table 51. Front Panel Connector (J9E3) (continued)
Pin Signal Type* Description
12 FP_NMI_BTN* in FRONT PANEL NMI is connected to a BMC input port,
allowing the front panel to generate an NMI. FP_NMI_BTN*
is pulled high to +5 V on the baseboard and is intended to be
connected to a momentary-contact push button (connected to
GROUND when pushed) on the system front panel.
13 SM_IMB_SCL in/out I2C CLOCK is the clock signal for the Intelligent Platform
Management Bus.
14 FP_RST_BTN* in FRONT PANEL RESET is connected to the BMC. A hard
resent occurs and all baseboard devices, except for the BMC
are reset. FP_RST_BTN* is pulled high to +5V on the
baseboard, and is intended to be connected to a momentary-
contact push button (connected to GROUND when pushed)
on the system front panel.
15 +5V standby power +5 V STANDBY is the standby 5 volt power supply.
16 FP_PWR_BTN* in FRONT PANEL POWER CONTROL is connected to the
BMC and causes the power to toggle (on → off, or off → on).
FP_PWR_BTN* is pulled high to +5 V standby on the
baseboard and is intended to be connected to a momentary-
contact push button (connected to GROUND when pushed)
on the system front panel.
17 SM_FP_ISOL in SM_FP_ISOL, when asserted, isolates the front panel SM
bus.
18 GROUND ground GROUND is the power supply ground.
19 FAN_TACH(0) in FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the
FAN speed.
20 FAN_TACH(1) in FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the
FAN speed.
21 FAN_TACH(2) in FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the
FAN speed.
22 FAN_TACH(3) in FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the
FAN speed.
23 FAN_TACH(4) in FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the
FAN speed.
24 FAN_TACH(5) in FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the
FAN speed.
25 FAN_TACH(6) in FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the
FAN speed.
26 FAN_TACH(7) in FAN_TACH signal is connected to the BMC to monitor the
FAN speed.
27 RJ45_ACTLED_R in NIC activity LED.
28 reserved - Reserved.
29 SM_PRI_SCL in/out I2C CLOCK is the clock signal for the Primary Private Bus.
30 SM_PRI_SDA in/out I2C DATA is the data signal for the Primary Private Bus.
* Type (in, out, in/out, power, ground) is from the perspective of the baseboard.
Technical Reference 95
Page 96

Hot-Plug PCI Indicator Board Interface (J3D1)
The Hot-Plug PCI Indicator Board (HPIB) contains the necessary LEDs and pushbutton switches
to help the user run PCI Hot-Plug (PHP) operations.
To indicate slot status, each PHP slot contains a green LED and amber LED. The actual
interpretation of the LEDs depends on the operating system running on the system.
Each PHP slot also has a momentary pushbutton switch. When you push this button, the SKA4
baseboard notifies the operating system that a PHP operation on the respective slot is requested. If
PHP operation is supported by the operating system, the user momentarily presses the switch and
then waits for the operating system to signal via the LEDs that the PHP slot has been disabled.
The user can then perform the desired PHP operation on the slot, such as replacing, removing, or
adding a PCI adapter. When the user wants the operating system to enable and initialize the PHP
slot, the user momentarily presses the switch again.
This (Active Low) pushbutton switch for the respective slot is routed to the PRSNT1# input to the
PCI Hot-Plug Controller (PHPC). This switch should not be confused with slot-interlock switches,
which are used in conjunction with mechanical lever designs to prevent access to an energized
PHP slot. The slot interlock inputs into the PHPC are permanently pulled down to ground and are
not accessible through the Hot-Plug PCI Indicator Board interface.
NOTE
✏
The HW push button is located on the Hot-Plug Indicator board. Do not use
this button to turn power on and off to the PCI slot. In some instances,
pushing this button interrupts normal operation of the operating system.
Instead, turn power off using a Hot-Plug PCI application.
The Hot-Plug PCI Indicator Board interface contains the necessary signals to drive the LEDs and
receive the pushbutton signals.
A 20-pin connector is provided on the baseboard for connection to the external HPIB. The pin out
for this connector is given in the table below.
Table 52. Hot-Plug Indicator Board Connector Pin Out (J3D1)
Connector contact Signal Name Connector contact Signal Name
1 Vcc 2 GROUND
3 P64_A_SWITCH<0> 4 P64_A_GRN_LED<1>
5 P64_A_AMB_LED<0> 6 P64_A_SWITCH<1>
7 P64_A_GRN_LED<1> 8 P64_A_AMB_LED<1>
9 P64_B_SWITCH<0> 10 P64_A_GRN_LED<0>
11 P64_B_AMB_LED<0> 12 P64_B_SWITCH<1>
13 P64_B_GRN_LED<1> 14 P64_A_AMB_LED<1>
15 P64_B_SWITCH<2> 16 P64_A_GRN_LED<2>
17 P64_A_AMB_LED<2> 18 P64_B_SWITCH<3>
19 P64_A_GRN_LED<3> 20 P64_A_AMB_LED<3>
96 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 97

Memory Module Interface (J6F1)
Table 53. Memory Module Interface
Pin** Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
A001 GND B001 PIN_B1 A084 GND B084 MAA9
A002 GND B002 VCC3 A085 MAA10 B085 VCC3
A003 GND B003 SYNTH_OUT_MADPCLK A086 MAA11 B086 MAA12
A004 GND B004 VCC3 A087 GND B087 MAA13
A005 ASCLK B005 VCC3 A088 MAA14 B088 VCC3
A006 CMD0 B006 ASDATA A089 MCD_MUXSEL B089 VCC3
A007 GND B007 CMD16 A090 GND B090 VCC3
A008 CMD1 B008 VCC3 A091 BSCLK B091 VCC3
A009 CMD2 B009 CMD3 A092 MECC12 B092 BSDATA
A010 GND B010 CMD19 A093 GND B093 MECC14
A011 CMD17 B011 VCC3 A094 MECC13 B094 VCC3
A012 CMD4 B012 CMD20 A095 MECC15 B095 CMD97
A013 GND B013 CMD6 A096 GND B096 CMD96
A014 CMD18 B014 VCC3 A097 CMD112 B097 VCC3
A015 CMD5 B015 CMD21 A098 CMD113 B098 CMD98
A016 GND B016 CMD23 A099 GND B099 CMD99
A017 CMD8 B017 VCC3 A100 CMD114 B100 VCC3
A018 CMD7 B018 CMD22 A101 CMD100 B101 CMD116
A019 GND B019 CMD9 A102 GND B102 CMD115
A020 CMD25 B020 VCC3 A103 CMD101 B103 VCC3
A021 CMD26 B021 CMD24 A104 CMD117 B104 CMD102
A022 GND B022 CMD10 A105 GND B105 CMD103
A023 CMD12 B023 VCC3 A106 CMD118 B106 VCC3
A024 CMD28 B024 CMD11 A107 CMD119 B107 CMD104
A025 GND B025 CMD27 A108 GND B108 CMD120
A026 CMD29 B026 VCC3 A109 CMD105 B109 VCC3
A027 CMD14 B027 CMD30 A110 CMD121 B110 CMD106
A028 GND B028 CMD13 A111 GND B111 CMD107
A029 CMD15 B029 VCC3 A112 CMD122 B112 VCC3
A030 CMD31 B030 MECC0 A113 CMD123 B113 CMD108
A031 GND B031 MECC1 A114 GND B114 CMD124
A032 MECC2 B032 VCC3 A115 CMD109 B115 VCC3
A033 MECC3 B033 CKE_0 A116 CMD125 B116 CMD110
A034 GND B034 0_RAS A117 GND B117 CMD126
A035 0_WE* B035 VCC3 A118 GND B118 VCC3
A036 0_CAS B036 0_CS0 A119 GND B119 VCC3
A037 GND B037 0_CS1 A120 CMD111 B120 VCC3
continued
Technical Reference 97
Page 98

Table 53. Memory Module Interface (continued)
Pin** Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
A038 0_CS2 B038 VCC3 A121 CMD127 B121 CKE_1
A039 0_CS3 B039 0_MCDOE* A122 GND B122 1_RAS
A040 GND B040 MEMPRSNT A123 1_WE* B123 VCC3
A041 0_MCDSEL* B041 VCC3 A124 1_CAS B124 1_CS0
A042 GND B042 TMD0 A125 GND B125 1_CS1
A043 GND B043 VCC3 A126 1_CS2 B126 VCC3
A044 CMD34 B044 VCC3 A127 1_CS3 B127 1_MCDOE*
A045 CMD50 B045 CMD49 A128 GND B128 1_MCDSEL*
A046 GND B046 CMD54 A129 CMD80 B129 VCC3
A047 CMD52 B047 VCC3 A130 MECC8 B130 MECC10
A048 CMD51 B048 CMD33 A131 GND B131 CMD64
A049 GND B049 CMD32 A132 CMD81 B132 VCC3
A050 CMD40 B050 VCC3 A133 MECC9 B133 MECC11
A051 CMD38 B051 CMD53 A134 GND B134 CMD65
A052 GND B052 CMD36 A135 CMD66 B135 VCC3
A053 CMD35 B053 VCC3 A136 CMD82 B136 CMD85
A054 CMD42 B054 CMD58 A137 GND B137 CMD67
A055 GND B055 CMD39 A138 CMD83 B138 VCC3
A056 GND B056 VCC3 A139 CMD84 B139 CMD68
A057 GND B057 VCC3 A140 GND B140 CMD71
A058 CMD55 B058 VCC3 A141 CMD87 B141 VCC3
A059 CMD37 B059 CMD43 A142 CMD70 B142 CMD86
A060 GND B060 CMD57 A143 GND B143 CMD69
A061 CMD56 B061 VCC3 A144 CMD73 B144 VCC3
A062 CMD62 B062 CMD63 A145 CMD89 B145 CMD72
A063 GND B063 CMD61 A146 GND B146 CMD88
A064 CMD44 B064 VCC3 A147 CMD76 B147 VCC3
A065 CMD60 B065 CMD41 A148 CMD92 B148 CMD75
A066 GND B066 MECC6 A149 GND B149 CMD91
A067 CMD47 B067 VCC3 A150 CMD74 B150 VCC3
A068 CMD48 B068 CMD59 A151 CMD90 B151 CMD78
A069 GND B069 CMD45 A152 GND B152 CMD77
A070 CMD46 B070 VCC3 A153 CMD94 B153 VCC3
A071 MECC7 B071 MECC4 A154 CMD93 B154 CMD79
A072 GND B072 MECC5 A155 GND B155 CMD95
A073 GND B073 VCC3 A156 GND B156 VCC3
A074 MADPCLK_FB_DLY B074 VCC3 A157 GND B157 VCC3
continued
98 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
Page 99

Table 53. Memory Module Interface (continued)
Pin** Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
A075 GND B075 BCLK_MADP_OUT A158 GND B158 VCC3
A076 MAA0 B076 VCC3 A159 GND B159 VCC3
A077 MAA1 B077 VCC3 A160 GND B160 VCC3
A078 GND B078 SDRDCLK_HE_DLY A161 GND B161 VCC3
A079 MAA2 B079 VCC3 A162 GND B162 RESERVED162
A080 MAA3 B080 MAA4 A163 GND B163 VCC
A081 GND B081 MAA5 A164 GND B164 VCC
A082 MAA6 B082 VCC3 A165 PIN_A165 B165 VCC
A083 MAA7 B083 MAA8 A166 NC B166 NC
* Signal active low.
** Pins are numbered with respect to the module edge connector. Axx signals appear on the front
(processor side) of the processor card.
Processor Module Connector (J7A1, J7B1, J7C1, J7D1)
Table 54. Processor Card Connector Pin Out (J7A1, J7B1, J7C1, J7D1)
Pin** Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
A001 RESERVED (nc) B001 PWR_EN1 A084 GND B084 RESERVED (nc)
A002 VCC_TAP B002 VCCP A085 D11* B085 VCCP
A003 RESERVED (nc) B003 OCVR_OK* A086 D10* B086 D17*
A004 GND B004 TEST_VSS_B4 A087 GND B087 D15*
A005 VTT B005 VCCP A088 D14* B088 VCCP
A006 VTT B006 VTT A089 D9* B089 D12*
A007 SELFSB1 B007 VTT A090 GND B090 D7*
A008 RESERVED_A8 B008 VCCP A091 D8* B091 VCCP
A009 RESERVED_A9 B009 RESERVED (nc) A092 D5* B092 D6*
A010 GND B010 FLUSH* A093 GND B093 D4*
A011 TEST_GND (pd) B011 VCCP A 094 D3* B094 VCCP
A012 IERR* B012 SMI* A095 D1* B095 D2*
A013 GND B013 INIT* A096 GND B096 D0*
A014 A20M* B014 VCCP A097 BCLK B097 VCCP
A015 FERR* B015 STPCLK* A098 TEST_VSS
(pd)
A016 GND B016 TCK A 099 GND B099 FRCERR
A017 IGNNE* B017 VCCP A100 BERR* B100 VCCP
A018 TDI B018 SLP* A101 A33* B101 A35*
A019 GND B019 TMS A 102 GND B102 A32*
A020 TDO B020 VCCP A103 A34* B 103 VCCP
A021 PWRGOOD B021 TRST* A104 A30* B104 A29*
A022 GND B022 RESERVED (nc) A105 GND B105 A26*
B098 RESET*
continued
Technical Reference 99
Page 100

Table 54. Processor Card Connector Pin Out (J7A1, J7B1, J7C1, J7D1) (continued)
Pin** Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
A023 TEST_25 (pu)
A024 THERMTRIP* B024 RESERVED (nc) A107 A27* B107 A24*
A025 GND B025 RESERVED (nc) A108 GND B108 A28*
A026 OCRV_EN B026 VCCP A109 A22* B109 VCCL2
A027 INTR B027 TEST_VCCP
A028 GND B028 NMI A111 GND B111 A21*
A029 PICD0 B029 VCCP A112 A19* B112 VCCL2
A030 PREQ* B030 PICCLK A113 A18* B113 A25*
A031 GND B031 PICD1 A114 GND B114 A15*
A032 BP3* B032 VCCP A115 A16* B115 VCC_L2
A033 BMP0* B033 BP2* A116 A13* B116 A17*
A034 GND B034 RESERVED (nc) A117 GND B117 A11*
A035 BINIT* B035 VCCP A118 A14* B118 VCC_L2
A036 DEP0* B036 PRDY* A119 GND B119 A12*
A037 VSS B037 BPM1* A120 A10* B120 VCCL2
A038 DEP1* B038 VCCP A121 A5* B121 A8*
A039 DEP3* B039 DEP2* A122 GND B122 A7*
A040 GND B040 DEP4* A123 A9* B123 VCCL2
A041 DEP5* B041 VCCP A124 A4* B124 A3*
A042 DEP6* B042 DEP7* A125 GND B125 A6*
A043 GND B043 D62* A126 RESERVED
A044 D61* B044 VCCP A127 BNR* B127 AERR*
A045 D55* B045 D58* A128 GND B128 REQ0*
A046 GND B046 D63* A129 BPRI* B129 VCCL2
A047 D60* B047 VCCP A130 TRDY* B130 REQ1*
A048 D53* B048 D56* A131 GND B131 REQ4*
A049 GND B049 D50* A132 DEFER* B132 VCCL2
A050 D57* B050 VCCP A133 REQ2* B133 LOCK*
A051 D46* B051 D54* A134 GND B134 DRDY*
A052 GND B052 D59* A135 REQ3* B135 VCCL2
A053 D49* B053 VCCP A136 HITM* B136 RS0*
A054 D51* B054 D48* A137 GND B137 HIT*
A055 GND B055 D52* A138 DBSY* B138 VCCL2
A056 CPU_SENSE B056 VCCP A139 RS1* B139 RS2*
A057 GND B057 L2_SENSE A140 GND B140 RP*
A058 D42* B058 VCCP A141 BR2* B141 VCCL2
A059 D45* B059 D41* A142 BR0* B142 BR3*
A060 GND B060 D47* A143 GND B143 BR1*
***
B023 VCCP A106 A31* B106 VCCL2
A110 A23* B110 A20*
(pu)
B126 VCCL2
(nc)
continued
100 SKA4 Baseboard Product Guide
 Loading...
Loading...