Page 1

Intel® Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
®
A Guide for Technically Qualified Assemblers of Intel
Subassemblies/Products
Order Number: A90327-002
Identified
Page 2

Disclaimer
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or
otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in Intel’s Terms and Conditions
of Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating
to sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability,
or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right. Intel products are not designed, intended or
authorized for use in any medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications or for any other application in which the failure of
the Intel product could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Intel may make changes to
specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and
other countries.
†
Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2002, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

Contents
1 Description
Server Board Features ......................................................................................................... 9
Back Panel Connectors ............................................................................................. 10
Server Board Connector and Component Locations .................................................. 11
Processor .................................................................................................................. 12
Memory...................................................................................................................... 12
Add-in Board Connectors ................................................................................................... 13
Video.................................................................................................................................. 13
SCSI Controller .................................................................................................................. 14
Modular RAID Capable PCI-X Slot 6.......................................................................... 14
IDE Controller..................................................................................................................... 14
USB Interface ............................................................................................................ 14
Network Controllers............................................................................................................ 15
Network Teaming Features........................................................................................ 15
Keyboard and Mouse ......................................................................................................... 17
ACPI................................................................................................................................... 17
Security .............................................................................................................................. 17
Security with Mechanical Locks and Monitoring......................................................... 17
Software Locks.......................................................................................................... 18
2 Server Board Installation
Tools and Supplies Needed................................................................................................ 21
Before You Begin ............................................................................................................... 21
Emissions Disclaimer................................................................................................. 21
Safety Cautions ......................................................................................................... 21
Safety and Regulatory Compliance .................................................................................... 22
Minimum Hardware Requirements ..................................................................................... 22
Installation Notes................................................................................................................ 23
Installation Procedures ....................................................................................................... 23
Installing the I/O Gasket and Shield........................................................................... 23
Installing Memory....................................................................................................... 26
Configuring Chassis Standoffs................................................................................... 27
Installing the Server Board......................................................................................... 28
Installing the Processor(s).......................................................................................... 29
Installing the Processor Wind Tunnel......................................................................... 32
Making Connections to the Server Board................................................................... 35
Cable Routing – Intel® SC5200 Base Chassis ........................................................... 36
Cable Routing – Intel SC5200 Hot-Swap, Redundant Power Chassis ....................... 37
Installing the Serial B Cable....................................................................................... 38
Finishing Up............................................................................................................... 39
Getting Started with Intel® Server Management and Intel
®
SMaRT Tool (Optional) ... 40
iii
Page 4

3 Upgrading
Tools and Supplies Needed................................................................................................ 43
Cautions............................................................................................................................. 43
Memory .............................................................................................................................. 44
Processors ......................................................................................................................... 45
Adding or Replacing a Processor............................................................................... 52
Installing the Processor Wind Tunnel......................................................................... 52
Removing a Processor............................................................................................... 52
Replacing the Backup Battery ............................................................................................ 52
4 Configuration Software and Utilities
Hot Keys............................................................................................................................. 55
Power-On Self-Test (POST)............................................................................................... 56
Using BIOS Setup .............................................................................................................. 57
Record Your Setup Settings....................................................................................... 57
If You Cannot Access Setup ...................................................................................... 57
Starting Setup............................................................................................................ 57
Using the System Setup Utility ........................................................................................... 58
Creating SSU Diskettes ............................................................................................. 58
Running the SSU....................................................................................................... 59
Setting Boot Device Priority ....................................................................................... 60
Setting Passwords and Security Options ................................................................... 60
Viewing the System Event Log .................................................................................. 62
Viewing FRU Information ........................................................................................... 62
Viewing Sensor Data Records ................................................................................... 63
Updating System Firmware and BIOS ....................................................................... 63
Saving and Restoring the System Configuration........................................................ 64
Alerting for Platform Events ....................................................................................... 65
Managing the Server Remotely.................................................................................. 67
FRUSDR Load Utility.......................................................................................................... 69
When to Run the FRUSDR Load Utility...................................................................... 69
What You Need to Do................................................................................................ 69
How You Use the FRUSDR Load Utility..................................................................... 70
Upgrading the BIOS ........................................................................................................... 73
Preparing for the Upgrade ......................................................................................... 73
Upgrading the BIOS................................................................................................... 74
Recovering the BIOS ................................................................................................. 75
Changing the BIOS Language ................................................................................... 75
Using the Firmware Update Utility ...................................................................................... 76
Making a BMC Firmware Update Diskette ................................................................. 76
Updating the BMC Firmware...................................................................................... 76
Recovering the BMC Firmware.................................................................................. 77
Updating the FRU/SDR Files.............................................................................................. 77
Making a FRU/SDR File Update Diskette................................................................... 77
Updating the FRU/SDR Files ..................................................................................... 77
Using the Adaptec SCSI Utility ........................................................................................... 78
Running the SCSI Utility ............................................................................................ 78
iv Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 5

5 Solving Problems
Resetting the System ......................................................................................................... 79
Initial System Startup..........................................................................................................79
Checklist.................................................................................................................... 79
Running New Application Software..................................................................................... 80
Checklist.................................................................................................................... 80
After the System Has Been Running Correctly ................................................................... 80
Checklist.................................................................................................................... 80
More Problem Solving Procedures ..................................................................................... 81
Preparing the System for Diagnostic Testing ............................................................. 81
Monitoring POST ....................................................................................................... 81
Verifying Proper Operation of Key System Lights ...................................................... 81
Confirming Loading of the Operating System............................................................. 81
Specific Problems and Corrective Actions .......................................................................... 82
Power Light Does Not Light ....................................................................................... 82
No Characters Appear on Screen.............................................................................. 82
Characters Are Distorted or Incorrect......................................................................... 83
System Cooling Fans Do Not Rotate Properly ........................................................... 83
Diskette Drive Activity Light Does Not Light ............................................................... 84
Hard Disk Drive Activity Light Does Not Light ............................................................ 84
CD-ROM Drive Activity Light Does Not Light ............................................................. 84
Cannot Connect to a Server....................................................................................... 84
Problems with Network .............................................................................................. 85
PCI Installation Tips................................................................................................... 85
Problems with Application Software.................................................................................... 86
Bootable CD-ROM Is Not Detected .................................................................................... 86
6 Getting Help .................................................................................................................. 87
7 Technical Reference
Server Board Jumpers........................................................................................................ 89
Enabling PCI-X on Slot 6 and Disabling On-board SCSI............................................ 90
8 Regulatory and Integration Information
Product Regulatory Compliance ......................................................................................... 91
Product Safety Compliance........................................................................................ 91
Product EMC Compliance.......................................................................................... 91
Product Regulatory Compliance Markings ................................................................. 92
Electromagnetic Compatibility Notices................................................................................ 93
FCC (USA) ................................................................................................................ 93
INDUSTRY CANADA (ICES-003).............................................................................. 94
Europe (CE Declaration of Conformity)...................................................................... 94
Taiwan Declaration of Conformity.............................................................................. 94
Korean RRL Compliance ........................................................................................... 94
Australia / New Zealand............................................................................................. 94
Contents v
Page 6

9 Equipment Log Worksheet
Equipment Log ...................................................................................................................95
Index...................................................................................................................................... 97
Figures
1. Back Panel Connectors............................................................................................... 10
2. Server Board Connector and Component Locations.................................................... 11
3. Attaching the Gasket to the I/O Shield......................................................................... 24
4. Attaching the Label to the I/O Shield ........................................................................... 24
5. Installing the I/O Shield ............................................................................................... 25
6. DIMM Locations .......................................................................................................... 26
7. Installing Memory ........................................................................................................ 27
8. Configuring Chassis Standoffs .................................................................................... 27
9. Placing the Server Board in the Chassis ..................................................................... 28
10. Installing the Retention Brackets................................................................................. 29
11. Opening Socket Lever and Attaching Processor ......................................................... 30
12. Applying Thermal Grease............................................................................................ 31
13. Aligning the Heat Sink................................................................................................. 31
14. Attaching the Heat Sink and Retention Clip................................................................. 32
15. Processor Wind Tunnel Air Flow ................................................................................. 32
16. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Assembly.......................................................................... 33
17. Attaching the Heat Sink Fan to the Air Intake Assembly.............................................. 33
18. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Intake and Exhaust........................................................... 34
19. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Intake and Exhaust........................................................... 34
20. Making Connections to the Server Board .................................................................... 35
21. Routing Cables............................................................................................................ 36
22. Routing the Floppy and USB Cables ........................................................................... 37
23. Routing the Floppy and ICMB Cables ......................................................................... 37
24. Installing the Serial B Cable ........................................................................................ 38
25. Making Back Panel Connections................................................................................. 39
26. Installing Memory ........................................................................................................ 45
27. Installing the Retention Brackets................................................................................. 52
28. Opening Socket Lever and Attaching Processor ......................................................... 52
29. Applying Thermal Grease............................................................................................ 52
30. Aligning the Heat Sink................................................................................................. 52
31. Attaching the Heat Sink and Retention Clip................................................................. 52
32. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Assembly.......................................................................... 52
33. Attaching the Heat Sink Fan to the Air Intake Assembly.............................................. 52
34. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Intake and Exhaust........................................................... 52
35. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Intake and Exhaust........................................................... 52
36. Replacing the Back up Battery .................................................................................... 53
37. Jumper Locations........................................................................................................ 89
vi Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 7

Tables
1. Server Board Features.................................................................................................. 9
2. Video Modes ............................................................................................................... 13
3. Software Security Features ......................................................................................... 19
4. Configuration Utilities .................................................................................................. 55
5. Hot Keys ..................................................................................................................... 55
6. Beep Codes ................................................................................................................ 81
7. Configuration Jumper (CN43)...................................................................................... 89
8. Configuration Jumper (CN27)...................................................................................... 90
9. Configuration Jumper (CN53)...................................................................................... 90
Contents vii
Page 8

viii Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide 9
Page 9
1 Description
Server Board Features
Table 1. Server Board Features
Feature Description
Processor
System Bus Frequency 400 MHz Front Side Bus
Memory (DRAM) Six 72-bit sockets for 184-pin, 200 MHz, 2.5 V, DDR200 or DDR266 compliant,
Video Memory 8 MB SDRAM of video memory
PCI bus • One PCI-X 133 MHz/64-bit 3.3 V full-length expansion slot for an add-in
Graphics Integrated onboard ATI Rage† XL 32-bit SVGA controller
SCSI Adaptec† AIC-7899W dual channel Ultra160 SCSI, supporting onboard Ultra 2
Network Two integrated onboard Network Interface Controllers (NICs):
System I/O • PS/2†-compatible keyboard and mouse ports, 6 pin DIN
Form Factor Server ATX form factor, ATX 2.03 compliant I/O SSI Entry E-Bay 3.0
Up to two 1.8 GHz to 2.4 GHz Intel
support packaged in a 603-pin micro Pin-Grid Array (PGA)
registered, ECC, SDRAM single-sided or double-sided memory
modules (DIMM)
board (see “Enabling PCI-X on Slot 6 and Disabling On-board SCSI” on
page 90)
• Two PCI-X 100 MHz/64-bit full-length expansion slots
• Three standard PCI 33 MHz/32-bit full-length expansion slots for add-in
boards
(LVD) wide, Ultra-wide, and Ultra160 SCSI interfaces
• An Intel® 82550PM single-chip PCI LAN controller for 10Base-T/100BaseTX
Fast Ethernet networks
• An Intel
providing 10/100/1000 Mbps data rates
Two RJ-45 Ethernet connectors at the I/O back panel
• IEEE 1284-compliant, 25-pin, bi-directional parallel port
• VGA video port, 15-pin
• Two serial ports, one 9-pin on the rear I/O and one through a 10-pin header
on the baseboard
• Two RJ-45 Ethernet ports
• Four USB ports, three on the rear I/O and one through a 10-pin header on
the baseboard
®
82544GC single-chip Gigabit Ethernet Controller capable of
®
Xeon™ processors with 512K cache
Page 10

Back Panel Connectors
A
BC E
JK
NIC2
NIC1
(Gbit)
(10/100)
DF
A AC Power* G Video
B USB 1, 2, 3 H NIC2 (Gbit)
C Mouse I NIC1 (10/100)
D Keyboard J ICMB/External SCSI Connector Knockout*
E Parallel Port K Serial B Knockout*
F Serial A
* Intel SC5200 Base chassis shown here. Item may be different on your chassis.
G H
I
OM14358
Figure 1. Back Panel Connectors
10 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 11
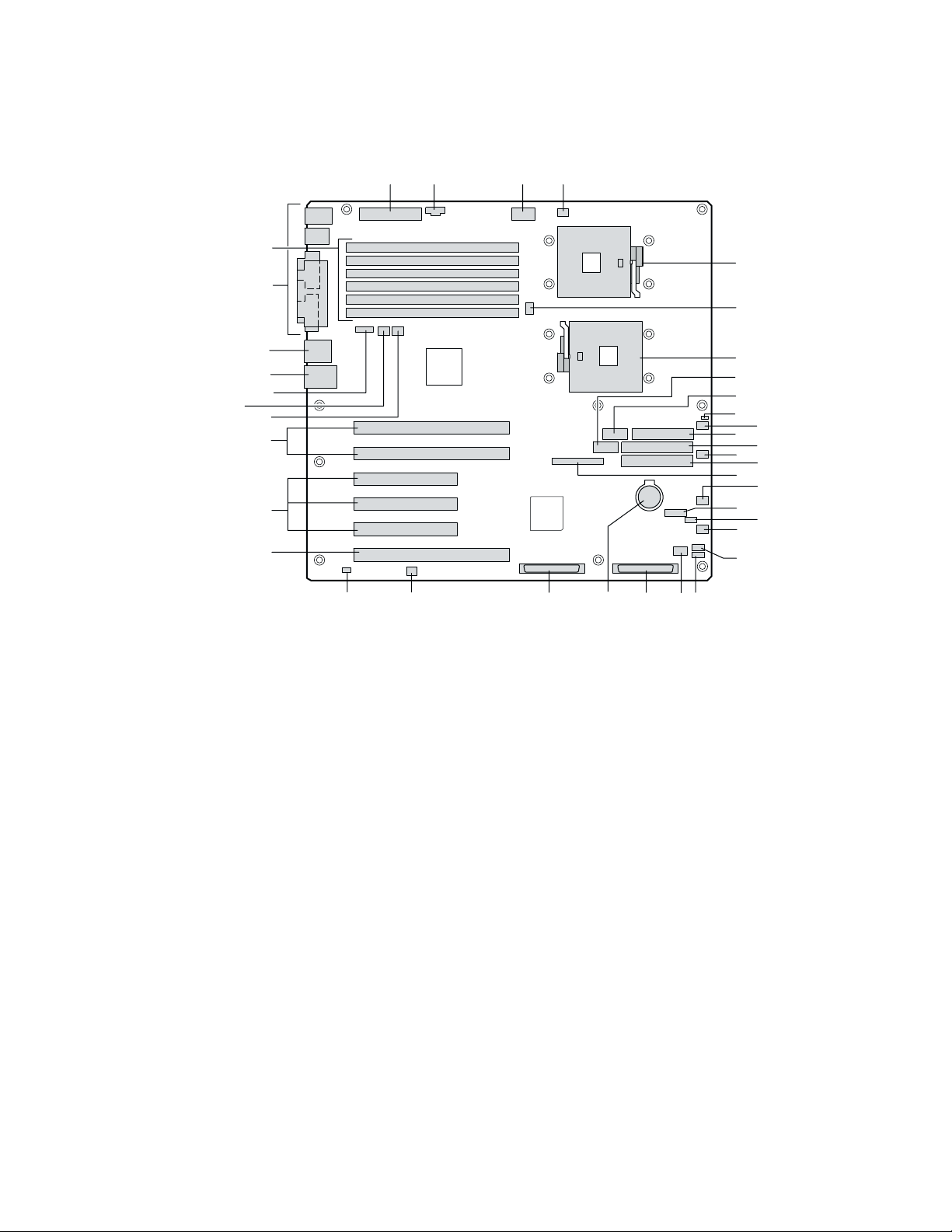
Server Board Connector and Component Locations
II JJ KK
LL
HH
A
GG
B
FF
EE
DD
CC
BB
AA
Z
Y
W
A Primary Processor Socket (CPU1) T LVD SCSI B
B CPU2 Fan U Battery
C Secondary Processor Socket (CPU2) V LVD SCSI A
D Front Panel USB W Jumper block CN53
E Serial B X Chassis Intrusion
F Jumper Block CN27 Y PCI-X 64-bit/133 MHz
G System Fan 5 Z PCI 32-bit/33 MHz
H Floppy disk drive connector AA PCI-X 64-bit/100 MHz
I Secondary IDE BB System Fan 1
J System Fan 6 CC System Fan 2
K Primary IDE DD ICMB
L Front Panel connector EE NIC1 (10/100)
M IPMB FF NIC2 (Gbit)
N Jumper Block CN43 GG System I/O connectors
O System Fan 3 HH DIMMs
P System Fan 4 II Main Power
Q HSBP B JJ Aux Sig
R HSBP A KK +12 V CPU Power
S HDD LED Connector LL CPU1 Fan
RSTUVX
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
OM14357
Figure 2. Server Board Connector and Component Locations
Description 11
Page 12

Processor
The Intel® Server Board SHG2 supports one or two Intel Xeon processors from 1.8 GHz to
2.4 GHz, with 512 KB of L2 advanced transfer cache packaged in a 603-pin micro-PGA (Pin-Grid
Array).
When two processors are installed, both processors must be identical. When only one processor is
installed, the processor must be installed in the CPU1 socket, which is the socket closest to the
corner of the server board.
For a complete list of supported processors, see:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
Memory
The Intel Server Board SHG2 contains six 184-pin DIMM sockets. Memory is partitioned as three
banks. DIMMs must be populated in identical pairs.
The SHG2 server board supports up to six 2.5 V, ECC, DDR 200 or 266-compliant, registered
SDRAM 184-pin gold DIMMs. A wide range of DIMM sizes are supported, including 128 MB,
256 MB, 512 MB, 1 GB, and 2 GB DIMMs. The minimum supported memory configuration is
256 MB, using two identical 128 MB DIMMs. The maximum configurable memory size is 12 GB
using six 2 GB DIMMs.
The SDRAM interface runs at a frequency of 200 MHz; however 266 MHz memory can be used.
The memory controller supports 2-way interleaved SDRAM, memory scrubbing, single-bit error
correction and multiple-bit error detection with Chipkill
continue to run even in the event of a multi-bit SDRAM failure.
Memory can be implemented with either single-sided (one row) or double-sided (two row) DIMMs.
NOTE
✏
Use DIMMs that have been tested for compatibility with the server board.
Contact your sales representative or dealer for a current list of approved
memory modules. Check the Intel Customer Support website for the latest
tested memory list:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
†
capability that allows the system to
12 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 13
Add-in Board Connectors
The server board has the following add-in board connectors:
• Two 184-pin full-length, 3.3 V, PCI-X 64-bit/100 MHz connectors.
• Three 120-pin full-length, 5 V, standard PCI 32-bit/33 MHz connectors.
• One 184-pin full-length, 3.3 V, connector that is capable if PCI-X 64-bit/133 MHz operation.
To enable PCI-X 64-bit/133 MHz operation, you must disable the onboard SCSI controller
using BIOS Setup. See page 57 for more information on using BIOS Setup. The default
operation of this connector (slot 6) is PCI 64-bit/66 MHz operation.
Video
The system has an integrated ATI Rage XL 32-bit high-performance SVGA subsystem that
supports the following:
• BIOS compatibility with all standard VGA modes
• 8 MB of video memory
• Pixel resolutions up to 1600 x 1200 pixels per inch (ppi) in 8/16/24/32 bpp modes under 2D
and up to 1024 x 768 ppi in 8/16/24/32 bpp modes under 3D
• Both CRT and LCD monitors up to 100 Hz vertical refresh rate
Table 2. Video Modes
2D Mode Refresh Rate (Hz)
640x480 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
800x600 60, 70, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1024x768 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1280x1024 43, 60 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1280x1024 70, 72 Supported – Supported Supported
1600x1200 60, 66 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1600x1200 76, 85 Supported Supported Supported –
3D Mode Refresh Rate (Hz) SHG2 3D Mode Video Support with Z Buffer Enabled
640x480 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
800x600 60, 70, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1024x768 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1280x1024 43, 60, 70, 72 Supported Supported – –
1600x1200 60, 66, 76, 85 Supported – – –
3D Mode Refresh Rate (Hz) SHG2 3D Mode Video Support with Z Buffer Disabled
640x480 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
800x600 60, 70, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1024x768 60, 72, 75, 90, 100 Supported Supported Supported Supported
1280x1024 43, 60, 70, 72 Supported Supported Supported –
1600x1200 60, 66, 76, 85 Supported Supported – –
SHG2 2D Mode Video Support
8 bpp 16 bpp 24 bpp 32 bpp
Description 13
Page 14

SCSI Controller
The embedded Adaptec AIC-7899W dual function SCSI controller provides Ultra160 (LVDS),
(Ultra 2), and Ultra wide (SE) SCSI interfaces as two independent PCI functions.
The Intel SHG2 baseboard provides active terminators, termination voltage, resetable fuse, and
protection diode for both SCSI channels.
Modular RAID Capable PCI-X Slot 6
The SHG2 server board supports a modular RAID controller, such as the Intel® RAID Controller
SRCMR, on PCI-X Slot 6. An add-in card installed in this slot leverages the onboard SCSI
controller along with its own built-in intelligence to provide a complete RAID controller subsystem
onboard. If a specified modular RAID card is installed, then SCSI interrupts are routed to the
RAID card instead of the PCI-X interrupt controller effectively hiding the host-based I/O device
from the system. The SHG2 Server Board uses an implementation commonly referred to as
“RAIDIOS” to support this feature.
To use this feature, see “Enabling PCI-X on Slot 6 and Disabling On-board SCSI” on page 90.
For a complete list of qualified add-in cards, see:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
IDE Controller
The system includes a dual-channel enhanced IDE 32-bit interface controller for intelligent disk
drives with disk controller electronics onboard. The controller has two connectors, Primary and
Secondary, located on the system board, each of which supports a master and a slave device.
The device supports:
• PIO, ATA-100 Synchronous DMA, and bus master IDE transfer modes
• Ultra DMA 33/66/100 synchronous DMA transfers
• Master/slave IDE modes
• Up to four devices
USB Interface
The SHG2 Server Board provides three external USB connectors on the rear I/O panel. The
external connectors are defined by the USB Specification, Revision 1.1. One additional USB
connector is supported internally through a 10-pin header on the server board that can be cabled to
a front panel board. All four ports function identically and with the same bandwidth.
14 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 15

Network Controllers
The server board includes two integrated onboard Network Interface Controllers (NICs).
One NIC is a 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX network solution based on the Intel 82550PM single-chip
Fast Ethernet PCI Bus Controller. As a PCI bus master, the controller can burst data at up to
132 MB/s. The controller contains two receive and transmit FIFO buffers that prevent data
overruns or underruns while waiting for access to the PCI bus. The controller has the following:
• 32-bit PCI bus master interface (direct drive of bus), compatible with PCI Bus Specification,
Revision 2.2
• Chained memory structure with improved dynamic transmit chaining for enhanced
performance
• Programmable transmit threshold for improved bus utilization
• Early receive interrupt for concurrent processing of receive data
• On-chip counters for network management
• Auto-detect and auto-switching for 10 or 100 Mbps network speeds
• Support for both 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps networks, capable of full or half duplex, with
back-to-back transmit at 100 Mbps
• Low-power +3.3 V device
• Alert on LAN functionality
The second NIC is an Intel 82544GC Gigabit Ethernet Controller capable of providing
10/100/1000 Mbps data rates. It is a single-chip device containing both the MAC and PHY layer
functions.
The 82544GC utilizes a 64-bit/100 MHz direct interface to the PCI-X bus. It is compliant with the
PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.2. It also supports the PCI-X extension to the PCI Local
Bus, Revision 1.0a.
NOTE
✏
If you install a 32/64-bit, 33/66 MHz PCI card in Add-in card slots 1 or 2,
you will slow the PCI-X bus to the speed of the card you install. This will
also slow the 82455GC’s interface to the PCI-X bus.
Network Teaming Features
The network controller provides several options for increasing throughput and fault tolerance when
running Windows
• Adapter Fault Tolerance (AFT) - provides automatic redundancy for your adapter. If the
primary adapter fails, the secondary takes over. AFT works with any hub or switch.
• Adaptive Load Balancing (ALB) - creates a team of 2 - 4 adapters to increase transmission
throughput. Also includes AFT. Works with any 10Base-TX or 100Base-TX switch.
• Fast EtherChannel
reception throughput. Also includes AFT. Requires an FEC-enabled switch.
†
2000 or NetWare† 6.0 or newer:
†
(FEC) - creates a team of 2, 3, or 4 adapters to increase transmission and
Description 15
Page 16

Adapter Fault Tolerance
Adapter Fault Tolerance (AFT) is a simple, effective, and fail-safe approach to increase the
reliability of server connections. AFT gives you the ability to set up link recovery to the server
adapter in case of a cable, port, or network interface card failure. By assigning two server adapters
as a team, AFT enables you to maintain uninterrupted network performance.
AFT is implemented with two server adapters: a primary adapter and a backup, or secondary,
adapter. During normal operation, the backup will have transmit disabled. If the link to the
primary adapter fails, the link to the backup adapter automatically takes over.
Preferred Primary Adapter
With multiple adapters installed, you can specify one as the Preferred Primary adapter. For
example if you have a server with an Intel
adapter and an Intel
PRO/1000 adapter as the secondary, you would want the PRO/100 Intelligent
PRO/100 Intelligent Server adapter as the primary
Server adapter to be the preferred primary. In this scenario, if the PRO/100 Intelligent Server
adapter fails, the PRO/1000 will take over. Then when the PRO/100 Intelligent Server adapter is
replaced, it will automatically revert to being the primary adapter in the team.
If a Preferred Primary is not selected, the Intel
PROSet II will attempt to select the best adapter
based on adapter model and speed.
Mixed Adapter Teaming
AFT supports up to four PRO/1000 or PRO/100 adapters per team, in any mix.
Adaptive Load Balancing
Adaptive Load Balancing (ALB) is a simple and efficient way to increase your server’s transmit
throughput. With ALB you group server adapters in teams to provide an increased transmit rate (up
to 400 Mbps) using a maximum of four adapters. The ALB software continuously analyzes
transmit loading on each adapter and balances the rate across the adapters as needed. Adapter
teams configured for ALB also provide the benefits of AFT. Receive rates remain at 100 Mbps.
To use ALB, you must have two, three, or four server adapters installed in your server or
workstation and linked to the same network switch.
16 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 17

Keyboard and Mouse
The keyboard/mouse controller is PS/2-compatible. If specified through the System Setup Utility
(SSU), the server may be locked automatically if there is no keyboard or mouse activity for a
predefined length of time. Once the inactivity (lockout) timer has expired, the keyboard and mouse
do not respond until the previously stored password is entered.
ACPI
The SHG2 supports the Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI) as defined by the
ACPI 1.0b. An ACPI-aware operating system can put the system into a sleep state where the hard
drives spin down, the system fans stop, and all processing is halted. However, the power supply
will still be on and the processors will still be dissipating some power, so the power supply fan and
processor fans will still run.
The SHG2 supports sleep states s0, s1, s4, and s5.
• s0: Normal running state.
• s1: Processor sleep state: No context will be lost in this state and the processor caches will
maintain coherency.
• s4: Hibernate or Save to Disk: The memory and machine state are saved to disk. Pressing the
power button or other wakeup event will restore the system state from the disk and resume
normal operation. This assumes that no hardware changes have been made to the system while
it was off.
• s5: Soft off: Only the real time clock (RTC) section of the chipset and the Baseboard
Management Controller (BMC) are running in this state.
CAUTION
The system is off only when the AC power is disconnected.
Security
To help prevent unauthorized entry or use of the server, Intel® Server Management software
monitors the system intrusion switch.
Security with Mechanical Locks and Monitoring
If installed, you can activate the chassis intrusion alarm switch. When the side door is opened, the
switch transmits an alarm signal to the server board, where BMC firmware and server management
software process the signal. The system can be programmed to respond to an intrusion by locking
the keyboard, for example.
Description 17
Page 18

Software Locks
The BIOS Setup and the System Setup Utility (SSU) provide a number of security features to
prevent unauthorized or accidental access to the system. Once the security measures are enabled,
you can access the system only after you enter the correct password(s). For example:
• Enable the keyboard lockout timer so that the server requires a password to reactivate the
keyboard and mouse after a specified time-out period - 1 to 120 minutes.
• Set and enable a supervisor password.
• Set and enable a user password.
• Set secure mode to prevent keyboard or mouse input and to prevent use of the front panel reset
and power switches.
• Activate a hot-key combination to enter secure mode quickly.
• Disable writing to the diskette drive when secure mode is set.
• Disable access to the boot sector of the operating system hard disk drive.
Using Passwords
You can set either the user password, the supervisor password, or both passwords. If only the user
password is set, you:
• Must enter the user password to enter BIOS Setup or the SSU.
• Must enter the user password to boot the server if Password on Boot is enabled in either the
BIOS Setup or SSU.
• Must enter the user password to exit secure mode.
If only the supervisor password is set, you:
• Must enter the supervisor password to enter BIOS Setup or the SSU.
• Must enter the supervisor password to boot the server if Password on Boot is enabled in either
the BIOS Setup or SSU.
• Must enter the supervisor password to exit secure mode.
If both passwords are set, you:
• May enter the user password to enter BIOS Setup or the SSU. However, you will not be able to
change many of the options.
• Must enter the supervisor password if you want to enter BIOS Setup or the SSU and have
access to all of the options.
• May enter either password to boot the server if Password on Boot is enabled in either the BIOS
Setup or SSU.
• May enter either password to exit secure mode.
18 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 19
Secure Mode
Configure and enable the secure boot mode by using the SSU. When secure mode is in effect:
• You can boot the server and the operating system will run, but you must enter the user
password to use the keyboard or mouse.
• You cannot turn off system power or reset the server from the front panel switches.
Secure mode has no effect on functions enabled via the Server Manager Module or power control
via the real time clock.
Taking the server out of secure mode does not change the state of system power. That is, if you
press and release the power switch while secure mode is in effect, the system will not be powered
off when secure mode is later removed. However, if the front panel power switch remains
depressed when secure mode is removed, the server will be powered off.
Summary of Software Security Features
The table below lists the software security features and describes what protection each offers. In
general, to enable or set the features listed here, you must run the SSU and go to the Security
Subsystem Group, menu. The table also refers to other SSU menus and to the BIOS Setup utility.
Table 3. Software Security Features
Feature Description
Secure mode How to enter secure mode:
• Setting and enabling passwords automatically places the system in secure
mode.
• If you set a hot-key combination (through Setup), you can secure the
system simply by pressing the key combination. This means you do not
have to wait for the inactivity time-out period.
When the system is in secure mode:
The server can boot and run the operating system, but mouse and keyboard
input is not accepted until the user password is entered.
At boot time, if a CD is detected in the CD-ROM drive or a diskette in drive A,
the system prompts for a password. When the password is entered, the
server boots from CD or diskette and disables the secure mode.
If there is no CD in the CD-ROM drive or diskette in drive A, the server boots
from drive C and automatically goes into secure mode. All enabled secure
mode features go into effect at boot time.
To leave secure mode: Enter the correct password(s).
Disable writing to diskette In secure mode, the server will not boot from or write to a diskette unless a
password is entered.
To write protect access to diskette whether the server is in secure mode or
not, use the Setup main menu, Floppy Options, and specify Floppy Access as
read only.
continued
Description 19
Page 20
Table 3. Software Security Features (continued)
Feature Description
Set a time-out period so
that keyboard and mouse
input are not accepted
Also, screen can be
blanked, and writes to
diskette can be inhibited
Specify and enable an inactivity time-out period of from 1 to 120 minutes.
If no keyboard or mouse action occurs for the specified period, attempted
keyboard and mouse input will not be accepted.
The monitor display will go blank, and the diskette drive will be write protected
(if these security features are enabled through Setup).
To resume activity: Enter the correct password(s).
Control access to using
the SSU: set supervisor
password
Control access to the
system other than SSU:
set user password
Boot without keyboard The system can boot with or without a keyboard. During POST, before the
Specify the boot sequence The sequence that you specify in Setup will determine the boot order. If
To control access to setting or changing the system configuration, set a
supervisor password and enable it through Setup.
If both the supervisor and user passwords are enabled, either can be used to
boot the server or enable the keyboard and/or mouse, but only the supervisor
password will allow Setup to be changed.
To disable a password, change it to a blank entry or press CTRL-D in the
Change Password menu of the Supervisor Password Option menu found in
the Security Subsystem Group.
To clear the password if you cannot access Setup, change the Clear
Password jumper (see Chapter 7).
To control access to using the system, set a user password and enable it
through Setup.
To disable a password, change it to a blank entry or press CTRL-D in the
Change Password menu of the User Password Option menu found in the
Security Subsystem Group.
To clear the password if you cannot access Setup, change the Clear
Password jumper (see Chapter 7).
system completes the boot sequence, the BIOS automatically detects and
tests the keyboard if it is present and displays a message.
secure mode is enabled (a user password is set), then you will be prompted
for a password before the server fully boots. If secure mode is enabled and
the “Secure Boot Mode” option is also enabled, the server will fully boot but
will require a password before accepting any keyboard or mouse input.
20 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 21

2 Server Board Installation
Tools and Supplies Needed
• Phillips† (cross head) screwdriver (#1 bit and #2 bit)
• Flat blade screwdriver
• Antistatic wrist strap and conductive foam pad (recommended)
Before You Begin
Emissions Disclaimer
To ensure EMC compliance with your local regional rules and regulations, the final configuration
of your end system product may require additional EMC compliance testing. For more
information, please contact your local Intel Representative.
See “Regulatory and Integration Information” on page 91 for product Safety and EMC regulatory
compliance information. This is an FCC Class A device. Integration of it into a Class B chassis
does not result in a Class B device.
Safety Cautions
CAUTIONS
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) & ESD protection: ESD can damage disk
drives, boards, and other parts. We recommend that you perform all
procedures in this chapter only at an ESD workstation. If one is not
available, provide some ESD protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap
attached to chassis groundany unpainted metal surfaceon your server
when handling parts.
ESD and handling boards: Always handle boards carefully. They can be
extremely sensitive to ESD. Hold boards only by their edges. After
removing a board from its protective wrapper or from the server, place the
board component side up on a grounded, static free surface. Use a
conductive foam pad if available but not the board wrapper. Do not slide
board over any surface.
21
Page 22

Safety and Regulatory Compliance
See “Regulatory and Integration Information” on page 91 for product Safety and EMC regulatory
compliance information.
Intended uses: This product was evaluated for use in servers that will be installed in offices,
computer rooms, and similar locations. Other uses require further evaluation.
EMC testing: Before computer integration, make sure that the chassis, power supply, and other
modules have passed EMC testing using a server board with a microprocessor from the same
family (or higher) and operating at the same (or higher) speed as the microprocessor used on this
server board.
Server board diagram label provided: Place the label inside the chassis in an easy-to-see location,
preferably oriented similarly to the server board.
Minimum Hardware Requirements
To avoid integration difficulties and possible board damage, your system must meet the following
minimum requirements.
For more information on supported processors and qualified memory and chassis components, see:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
Processor
A minimum of one 1.8 GHz Intel Xeon processor with 512K cache support packaged in a 603-pin
micro-PGA (Pin-Grid Array).
Memory
Minimum of two 128 MB ECC, DDR 200 or 266-compliant registered SDRAM 184-pin gold
DIMMs. DIMMs must be populated in identical pairs.
Power Supply
Minimum of 450 W with 1.2 A +5 V standby current (in order to support Wake On LAN† (WOL))
and 12+ V CPU power support [ATX], which meets the SSI EPS 12 V specification. You must
provide standby current, or the board will not boot.
For more information on the SSI EPS 12 V specification, see:
http://www.ssiforum.org
22 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 23

Installation Notes
Installation Process Quick Reference
Step Where the information is located
Install the primary processor This guide
Install the secondary processor (optional) This guide
Install memory This guide
Remove the access cover Your chassis manual
Install the I/O shield This guide
Rearrange the standoffs This guide
Install the server board This guide
Connect cables to the server board This guide and your chassis manual
Finish setting up your chassis Your chassis manual
Installation Procedures
Installing the I/O Gasket and Shield
✏ NOTE
An ATX 2.03-compliant I/O shield is provided with the server board. The
shield is required by Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) regulations to
minimize EMI. If the shield does not fit the chassis, obtain a properly sized
shield from the chassis supplier.
The shield fits the rectangular opening in the back of a chassis. The shield has cutouts that match
the I/O ports. Install the shield from inside the chassis.
Server Board installation 23
Page 24
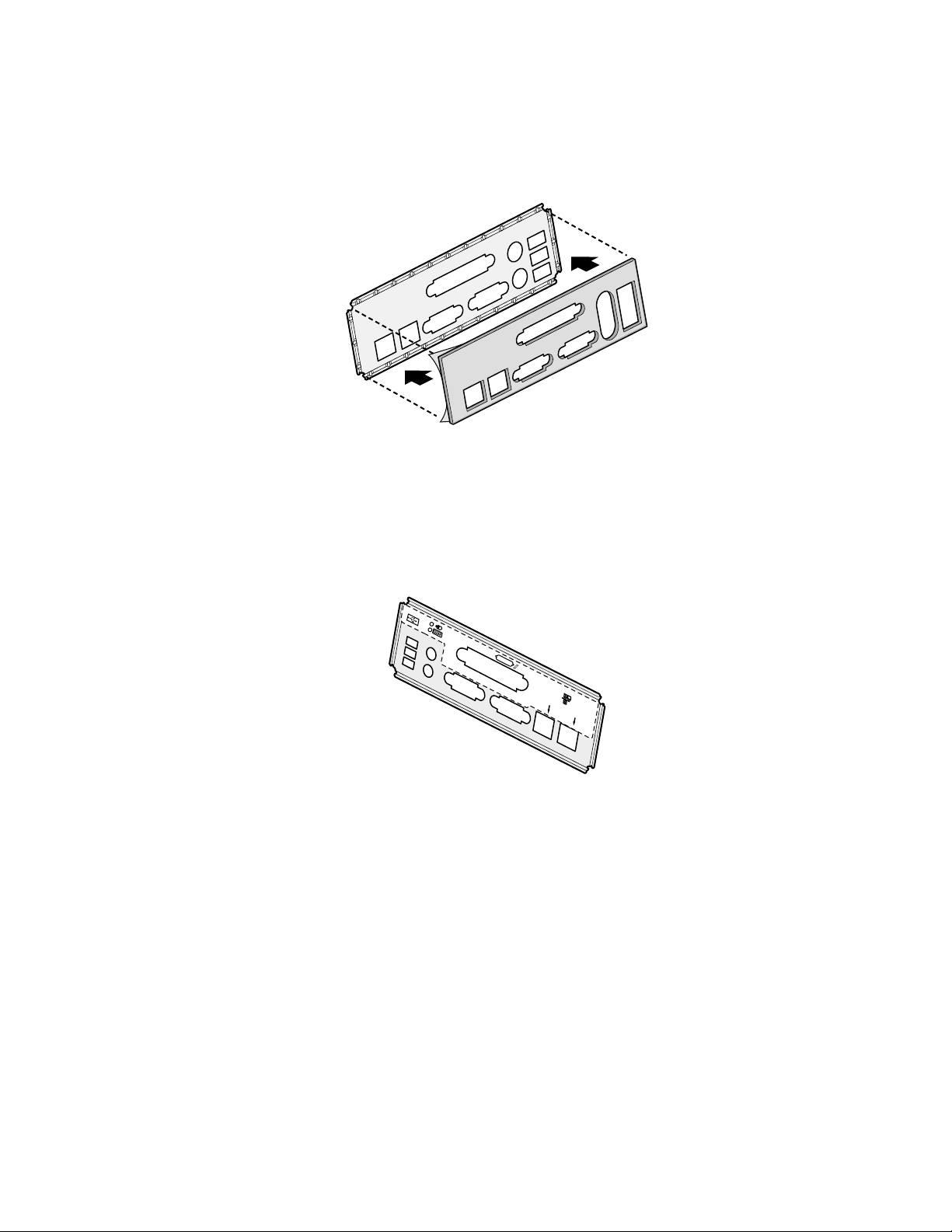
Attaching the Gasket to the I/O Shield
1. Remove the two backing strips from the gasket.
2. Press the gasket onto the inside face of the I/O shield as shown.
Figure 3. Attaching the Gasket to the I/O Shield
Attaching the Label to the I/O Shield
1. Remove the backing from the label included with your server board.
2. Press the label onto the outside face of the I/O shield.
OM14359
U
S
B
1
2
3
M
O
U
S
E
K
Y
B
D
P
A
R
A
L
L
E
L
N
IC
2
(G
b
it)
N
IC
(1
1
0
/1
0
0
)
OM14360
Figure 4. Attaching the Label to the I/O Shield
24 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 25
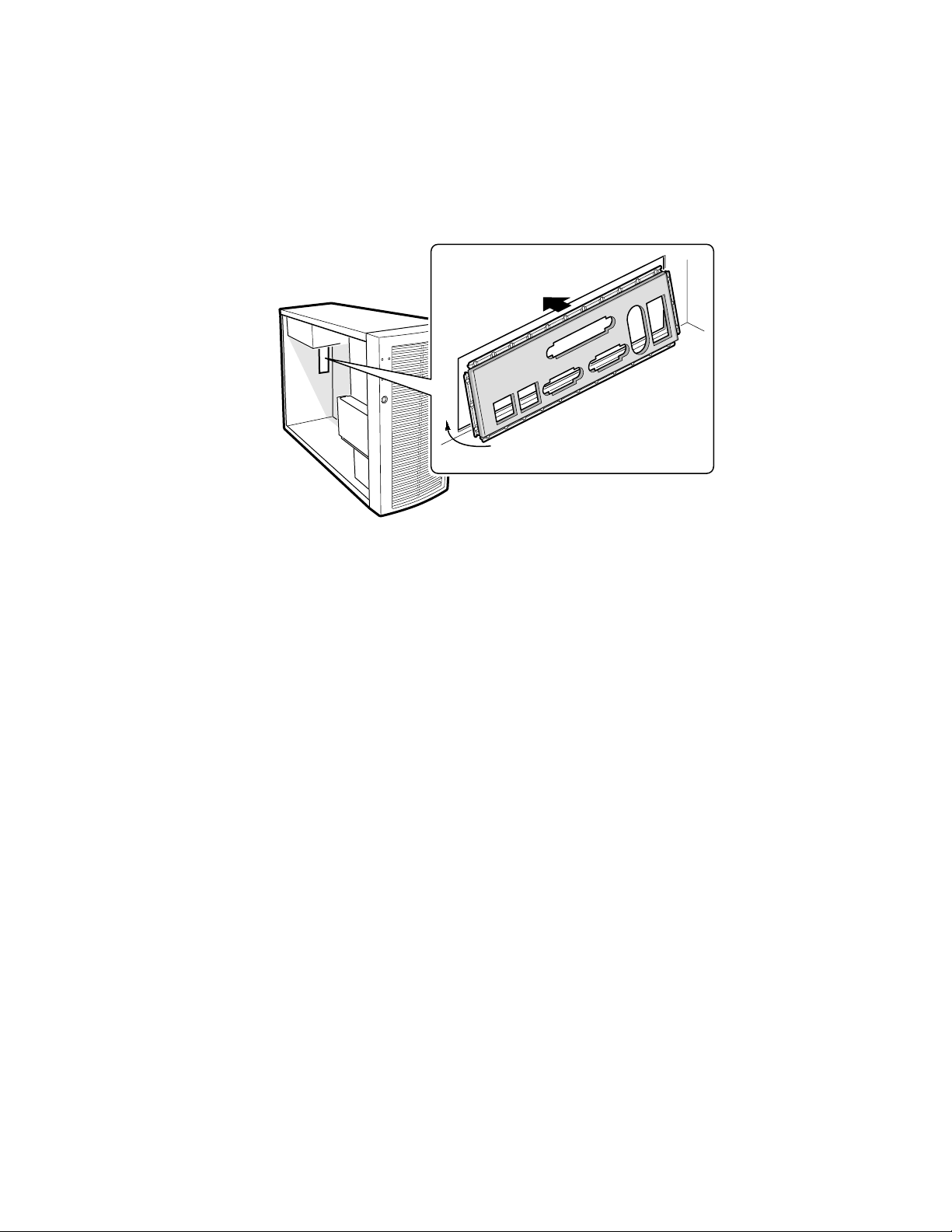
Installing the I/O Shield
1. Position one edge so that the dotted groove is outside the chassis wall, and the lip of the shield
rests on the inner chassis wall.
2. Hold the shield in place, and push it into the opening until it is seated. Make sure the I/O shield
snaps into place all the way around.
OM14361
Figure 5. Installing the I/O Shield
Server Board installation 25
Page 26
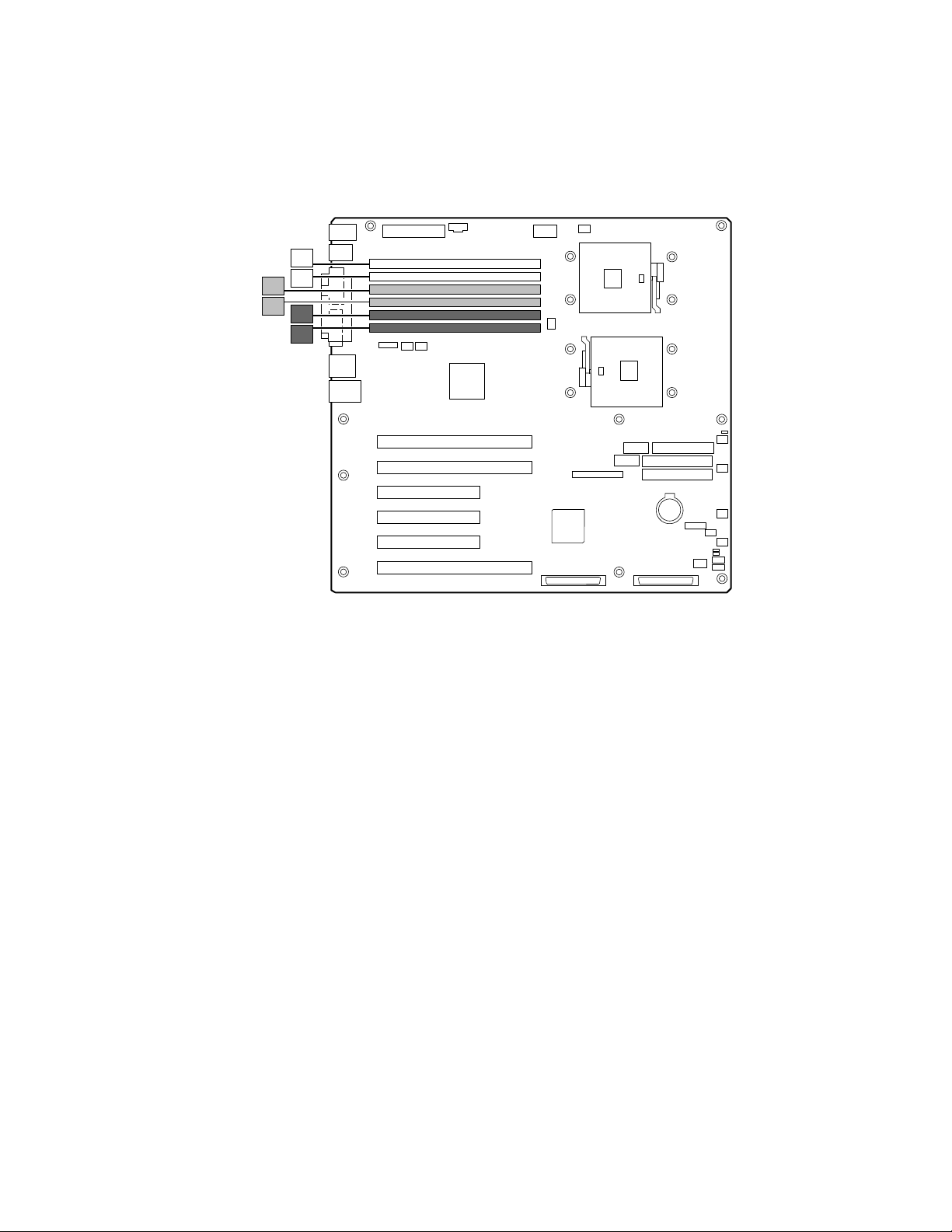
Installing Memory
The SHG2 Server Board contains six 184-pin DIMM sockets. Memory is partitioned as three
banks. DIMMs must be populated in identical pairs.
3B
3A
2B
2A
1B
1A
OM14558
Figure 6. DIMM Locations
The SHG2 server board supports up to six 2.5 V, ECC, DDR 200 or 266-compliant, registered
SDRAM 184-pin gold DIMMs. A wide range of DIMM sizes are supported, including 128 MB,
256 MB, 512 MB, 1 GB, and 2 GB DIMMs. The minimum supported memory configuration is
256 MB, using two identical 128 MB DIMMs. The maximum configurable memory size is 12 GB
using six 2 GB DIMMs.
The SDRAM interface runs at 200 MHz; however 266 MHz memory can be used. The memory
controller supports 2-way interleaved SDRAM, memory scrubbing, single-bit error correction and
multiple-bit error detection with Chipkill capability that allows the system to continue to run even
in the event of a multi-bit SDRAM failure. Memory can be implemented with either single-sided
(one row) or double-sided (two row) DIMMs.
NOTE
✏
Use DIMMs that have been tested for compatibility with the server board.
Contact your sales representative or dealer for a current list of approved
memory modules. Check the Intel Customer Support website for the latest
tested memory list:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
26 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 27
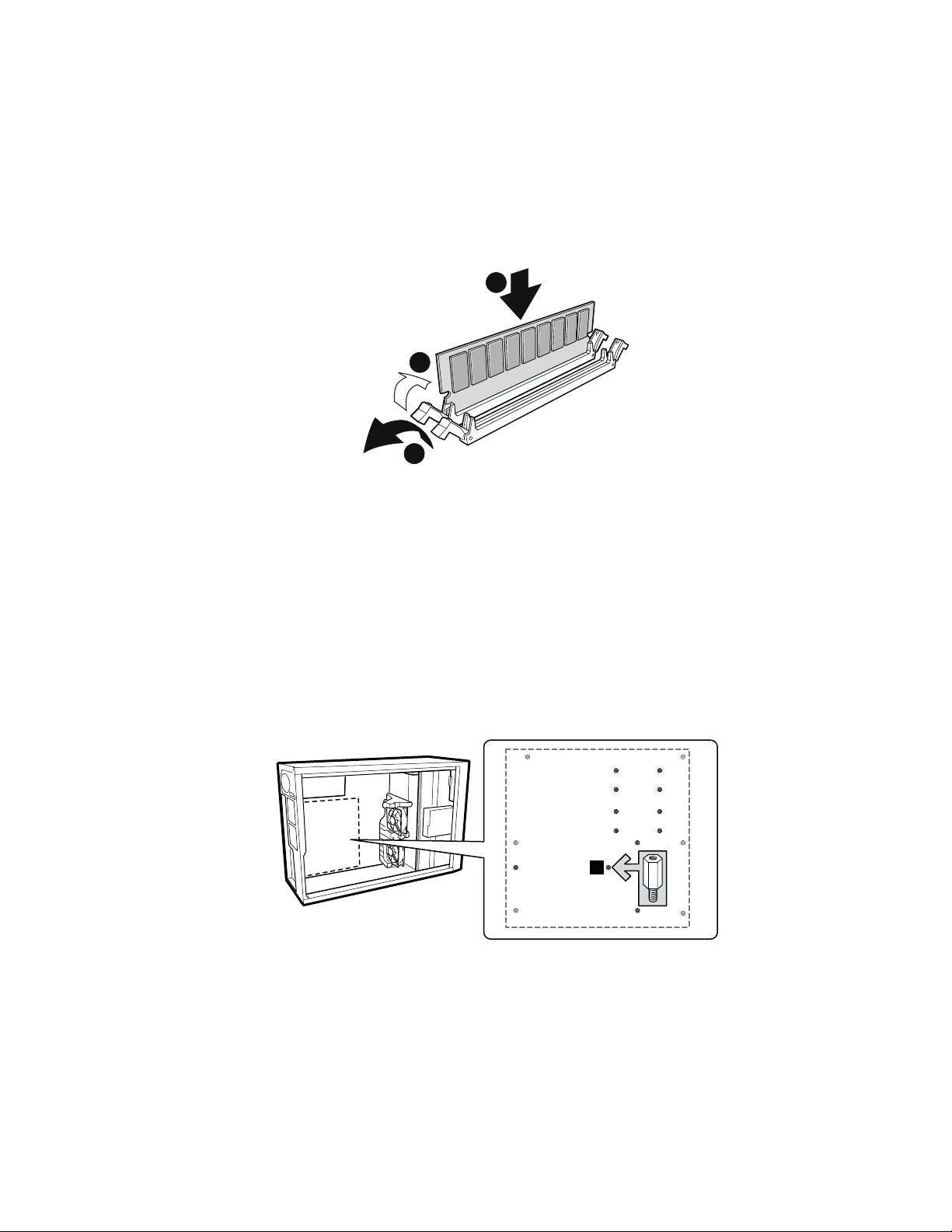
1. If the server board is not already installed in the chassis, remove the server board from its
packaging and place it on a clean ESD protected work surface such as the antistatic plastic
packaging in which the board was shipped.
2. Open both DIMM socket levers.
3. Insert DIMM making sure the connector edge of the DIMM aligns correctly with the slot.
4. Check that socket levers are securely latched. DIMMs must be populated in identical pairs.
2
1A
3
1B
1
OM13205
Figure 7. Installing Memory
Configuring Chassis Standoffs
If your chassis does not have standoffs placed as shown below, you must rearrange them so they
match the holes in the server board. Failure to properly rearrange the metal standoffs may cause the
server board to malfunction and may permanently damage it. Your chassis may be different from
the illustration.
For the Intel SC5200 chassis:
1. Install standoffs in positions 5, 18, S, 19 and in the eight positions marked P. Standoffs are
included with your chassis. Standoff numbering in other chassis may be different.
1
4
5
6
P
P
P
P
18
S
19
Figure 8. Configuring Chassis Standoffs
20
P
P
P
P
23
26
OM14362
Server Board installation 27
Page 28

Installing the Server Board
1. Place the board into the chassis, making sure that the back panel I/O shield openings and
chassis standoffs align correctly.
2. Attach the board with the screws included with your chassis at the ten locations marked below.
For the Intel SC5200 chassis, these screws are packaged in a bag labeled “C.”
1
Figure 9. Placing the Server Board in the Chassis
2
OM14363
28 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 29
Installing the Processor(s)
CAUTIONS
If only one processor is to be used, it must be installed in the Processor
Socket labeled CPU1, which is the socket closest to the corner of the
server board.
If you are adding a second processor to your system, you must verify that the
second processor is identical in speed to the first processor.
This server board has “zero-insertion-force” sockets. If processor does not
drop easily into socket holes, make sure the lever is in the full-upright
position and the processor is oriented properly.
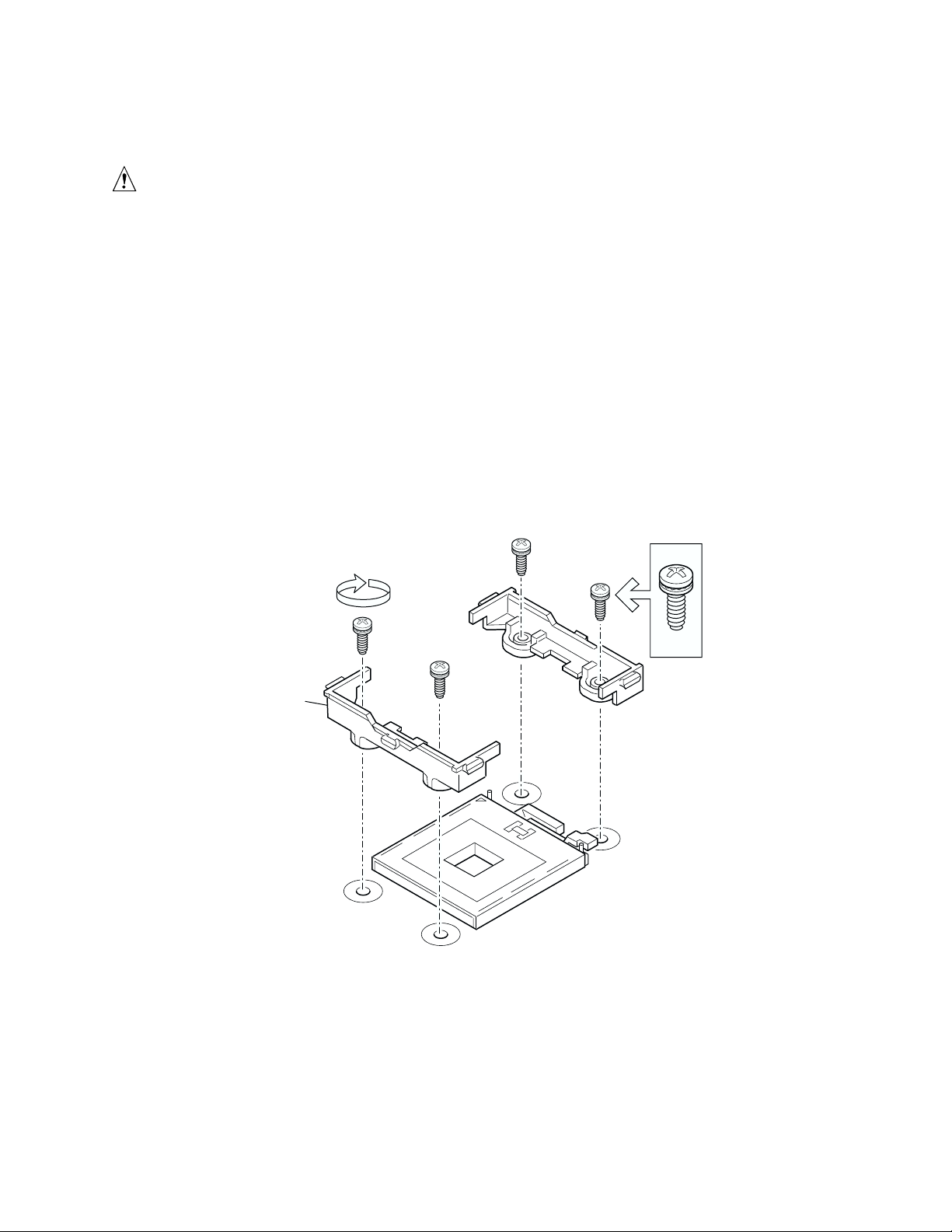
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter and the additional
precautions given here.
2. Install the retention brackets for the primary processor by inserting the retention brackets and
tightening the four retention screws. The primary processor socket is located nearest to the
corner of the server board. If installing a second processor, install the retention brackets for the
secondary processor.
A
A. Heat Sink Retention Bracket
Figure 10. Installing the Retention Brackets
OM14364
Server Board installation 29
Page 30

3. Lift the socket lever on the processor socket labeled CPU1. (If adding a second processor, lift
the socket lever on the processor socket labeled CPU2.)
4. Align the pins of the processor with the socket, and insert the processor into the socket. Lower
the socket lever completely.
NOTE
✏
When installing a second processor, note that the secondary processor socket
is oriented so that the processor pins are rotated 180° relative to the primary
processor socket.
A
B
OM14365
A. Alignment Triangle Mark
B. Alignment Triangle Cutout
Figure 11. Opening Socket Lever and Attaching Processor
30 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 31

5. Apply thermal grease to the processor as shown.
OM14366
Figure 12. Applying Thermal Grease
6. Align the heat sink with the retention brackets and place heat sink on the processor.
OM14367
Figure 13. Aligning the Heat Sink
Server Board installation 31
Page 32
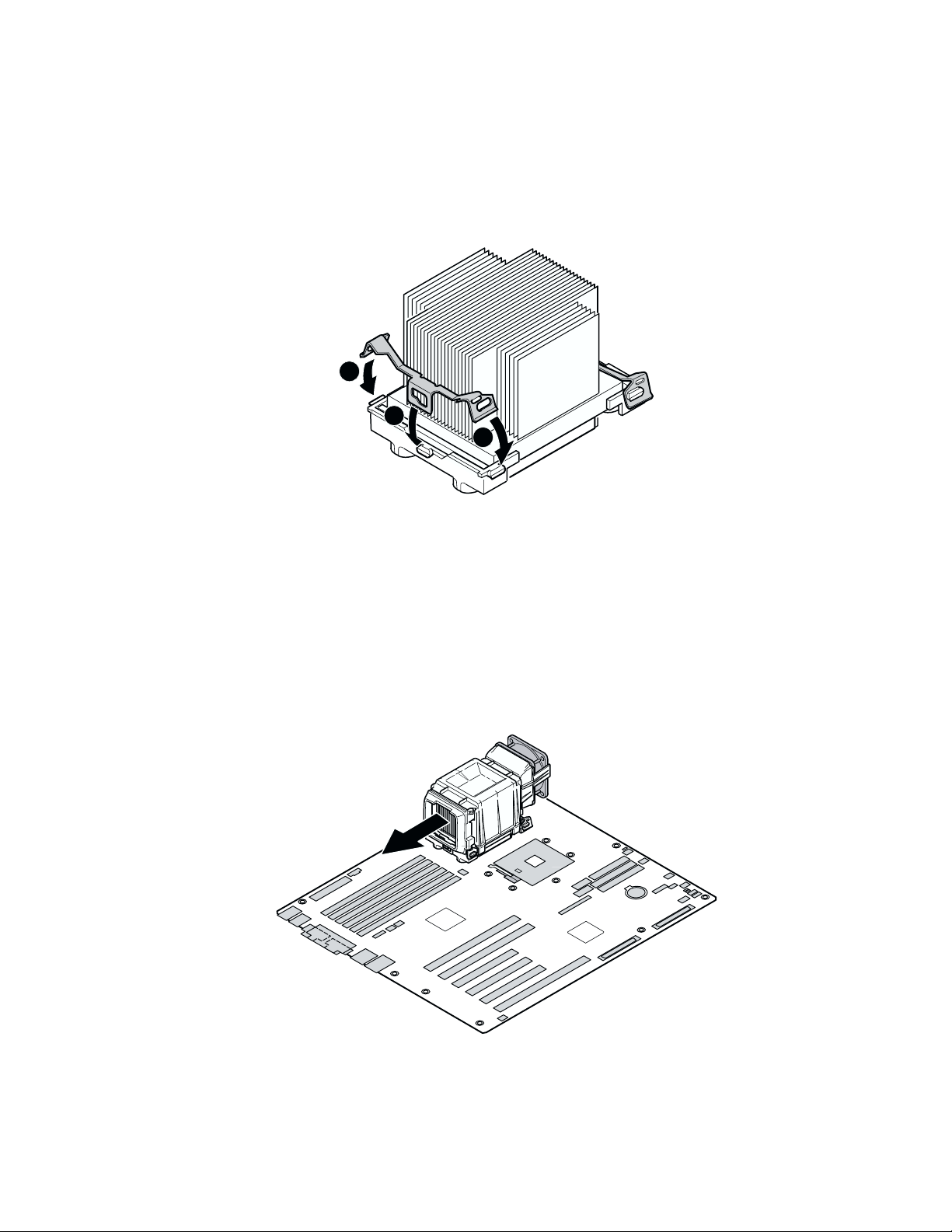
7. Position the retention clip over the plastic tab and engage the retention clip end-slot over the
plastic tab (see 1 in Figure 14). Note that the slot in the clip provides room for side-to-side
motion while engaging the retention clip slots located at each end.
8. Press downward on the retention clip ends over the plastic tabs on the retention bracket (see
2 in Figure 14).
9. Install two retention clips for each processor you install.
2
1
2
OM14368
Figure 14. Attaching the Heat Sink and Retention Clip
Installing the Processor Wind Tunnel
The following instructions apply to the Intel SC5200 Base Server Chassis and reference chassis
installations. If you are installing your server board in the Intel SC5200 Hot-Swap, Redundant
Power Server Chassis, DO NOT install the processor wind tunnel. The ducting in the Intel SC5200
Hot-Swap, Redundant Power Server Chassis eliminates the need for a processor wind tunnel.
Air flow for the processor wind tunnel should be directed toward the rear of the chassis as shown
below.
OM14375
Figure 15. Processor Wind Tunnel Air Flow
32 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 33

1. Install processor wind tunnel center section over the heat sink / processor assembly. Note that
plastic tabs on the wind tunnel center section engage the tabs on the retention clips.
OM14369
Figure 16. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Assembly
2. Attach the processor wind tunnel fan to the wind tunnel air intake assembly as shown. The fan
label must be pointing into the air intake assembly.
Fan label
OM14370
Figure 17. Attaching the Heat Sink Fan to the Air Intake Assembly
CAUTION
To ensure proper system cooling, the heat sink fan must be installed as
shown in Figure 18 and the air intake fan assembly must be attached to the
side of the processor / wind tunnel assembly nearest to the front of the
chassis.
Server Board installation 33
Page 34

3. Attach the air intake fan assembly to the side of the heat sink wind tunnel closest to the front of
the chassis.
a. Press both sides of the air intake section to bend tabs inward (see 1 in Figure 18).
b. Insert tabs into slots on the wind tunnel center section (see 2 in Figure 18).
c. Press the air intake section downward to engage the assembly (see 3 in Figure 18).
2
3
1
Figure 18. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Intake and Exhaust
1
OM14371
4. Attach the air exhaust fan assembly to the heat sink wind tunnel.
a. Press both sides of the air exhaust section to bend tabs inward (see 1 in Figure 19).
b. Insert tabs into slots on the wind tunnel center section (see 2 in Figure 19).
c. Press the air intake section downward to engage the assembly (see 3 in Figure 19).
2
1
3
1
OM14374
Figure 19. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Intake and Exhaust
5. Attach CPU Fan cable(s). See the next section “Making Connections to the Server Board” for
fan connector location information.
34 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 35

Making Connections to the Server Board
II JJ KK
LL
HH
A
GG
B
FF
EE
DD
CC
BB
AA
Z
Y
W
A. Primary Processor Socket (CPU1) T. LVD SCSI B
B. CPU2 Fan U. Battery
C. Secondary Processor Socket (CPU2) V. LVD SCSI A
D. Front Panel USB W. Jumper block CN53
E. Serial B X. Chassis Intrusion
F. Jumper Block CN27 Y. PCI-X 64-bit/133 MHz
G. System Fan 5 Z. PCI 32-bit/33 MHz
H. Floppy disk drive connector AA. PCI-X 64-bit/100 MHz
I. Secondary IDE BB. System Fan 1
J. System Fan 6 CC. System Fan 2
K. Primary IDE DD. ICMB
L. Front Panel connector EE. NIC1 (10/100)
M. IPMB FF. NIC2 (Gbit)
N. Jumper Block CN43 GG. System I/O connectors
O. System Fan 3 HH. DIMMs
P. System Fan 4 II. Main Power
Q. HSBP B JJ. Aux Sig
R. HSBP A KK. +12 V CPU Power
S. HDD LED LL. CPU1 Fan
RSTUVX
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
P
Q
OM14357
Figure 20. Making Connections to the Server Board
Server Board installation 35
Page 36

Intel® SC5200 Base Server Chassis Note
Connect front system fans to the System Fan 3 and System Fan 4 connectors on the server board.
Intel SC5200 Hot-Swap, Redundant Power Server Chassis Note
Be sure to attach system fans to their correspondingly numbered connector on the server board.
System fan numbers can be found on the system fan carrier and on the system fan cables.
Cable Routing – Intel SC5200 Base Chassis
To ensure proper air-flow within the chassis, follow the cable routing guidelines below.
IDE or SCSI Cables
Cables that connect to devices in the lower device bays should be routed around the epac system
fan carrier as shown below.
1. Route cables as shown.
2. Replace the top half of the epac.
Figure 21. Routing Cables
OM14556
36 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 37

Floppy and Front Panel Cables
Route the floppy drive and front panel cables as shown.
A
B
OM14376
A. Front Panel Cable
Figure 22. Routing the Floppy and Front Panel Cables
B. Floppy Diskette Cable
Cable Routing – Intel SC5200 Hot-Swap, Redundant Power Chassis
Route the floppy drive cable and the hot-swap drive bay ICMB cable between the chassis wall and
the hot-swap fan holder as shown below at location A.
A
OM14377
A. Cable Routing Location
Figure 23. Routing the Floppy and ICMB Cables
Server Board installation 37
Page 38

Installing the Serial B Cable
For the Intel SC5200 chassis, you can connect the Serial B serial port cable to either the front (rack
configuration only) or back panels. Connecting it to the back panel is illustrated below.
1. Install the Serial B cable by inserting it into the chassis back panel cutout and attaching it as
shown.
2. Attach the other end to the Serial B connector located on your server baseboard. See “Making
Connections to the Server Board” on page 35 for the Serial B connector location.
A
B
OM14557
A. Chassis Back Panel Cutout
B. Screw
Figure 24. Installing the Serial B Cable
38 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 39

Finishing Up
WARNING
An electrical shock hazard exists if the chassis cover is not replaced
before connecting the chassis AC power.
1. Install the chassis cover according to the instructions for your chassis.
2. See your chassis documentation to complete rack or pedestal installation.
3. Connect the keyboard, mouse and monitor cables to the back panel.
4. Connect the power cable to the back panel and to an AC outlet.
A
BC E
JK
NIC2
NIC1
(Gbit)
(10/100)
DF
A AC Power* G Video
B USB 1,2, 3 H NIC2 (Gbit)
C Mouse I NIC1 (10/100)
D Keyboard J ICMB/External SCSI Connector Knockout*
E Parallel Port K Serial B Knockout*
F Serial A
* Intel SC5200 Base chassis shown here. Item may be different on your chassis.
G H
I
OM14358
Figure 25. Making Back Panel Connections
Server Board installation 39
Page 40

Getting Started with Intel® Server Management and Intel® SMaRT Tool (Optional)
Intel® Server Management and the hard drive Service Partition provide real-time monitoring and
alerting for your SHG2 server hardware, emergency remote management, and remote server setup.
Intel Server Management is implemented by installing it within client-server architecture.
The Service Partition provides you with the ability to remotely access a local partition on the server
and to identify and diagnose server health issues. Remote access is provided through either a
modem or network connection.
To get started with Intel Server Management, install the Service Partition first, then the system’s
operating system, and finally Intel Server Control. The information here describes installation on a
system running a Microsoft Windows operating system.
®
The Intel
tool providing support information to assist with the maintenance and repair of Intel-based server
systems and accessories. SMaRT Tool features visual, step-by-step instructions for replacing parts;
a complete Field Replacement Unit (FRU) database containing part numbers and images; product
spares lists, and worldwide Intel support information.
Intel Server Management provides an interface to the Intel
detection and alerting with interactive maintenance and repair assistance. When Intel Server
Management detects a hardware error and a part needs replacing, SMaRT Tool can be launched
directly from Intel Server Management to locate the correct part information and corresponding
"How to Replace" steps required to quickly get the server back up and running.
Server Maintenance and Reference Training (SMaRT) Tool is an interactive software
®
SMaRT Tool, combining remote error
To activate Intel Server Management’s interface with the Intel SMaRT Tool, both software
programs need to be installed. You can install the software on a server or on a workstation used to
manage the server. The information here describes installation on a system running a Microsoft
Windows operating system. For other operating systems, see the Installation Guide & User Guide
located in the “ISM/Docs” folder on the Intel Server Management CD-ROM. SMaRT Tool and
ISM Console may only be installed on a system running a Microsoft Windows operating system.
Note: Prior to installation, uninstall any previous version of Intel Server Control.
Installing a Service Partition on the Server (Optional)
The Service Partition provides advanced remote management and configuration functionality.
Installing it on a server is optional.
1. Power-on the server, insert the Intel Server Management CD into the CD-ROM drive, and boot
to the CD.
2. Select Utilities > Run Service Partition Administrator > Create Service Partition-first
time.
3. Select an available hard drive. The server will reboot to the CD.
4. Select Format Service Partition and Install Software.
5. Exit the menu. Remove the CD and reboot to install the server operating system. After
installing the operating system, proceed to Installing Intel Server Management.
40 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 41

Installing your Operating System
Install your operating system now.
Installing Intel Server Management
You can install Intel Server Management on a local server or on a remote workstation that is used
to manage a LAN/WAN.
1. Insert the Intel Server Management CD into the system’s CD-ROM.
2. Click Install Server Management.
3. Complete the Registration form and click Submit.
4. Select the applicable system option.
5. Review the Intel Software License Agreement and click Accept.
6. If installing to a local server, click Install Now. If this is a multiple system installation, click
Add to compile a list of systems and then click Install Now.
7. Select Reboot Now or Reboot Later.
8. Remove the Intel Server Management CD.
Server Board installation 41
Page 42

Installing Intel SMaRT Tool
Follow the instructions below to install the Intel Server Maintenance and Reference Training Tool
(SMaRT Tool) on your system.
NOTES
✏
SMaRT Tool may only be installed on a system running a Microsoft
Windows operating system.
To download the SHG2 SC5200 server system module for SMaRT Tool, you
must have Internet access.
1. Insert the Intel Server Board SHG2 Resource CD into the system’s CD-ROM drive.
2. Click on Intel SMaRT Tool in the menu on the left side of the screen.
3. In the green Make a Selection drop-down menu, select SMaRT Tool Install Guide. Print the
Guide, and keep it on hand for reference.
4. Review the SMaRT Tool Install Guide prior to proceeding.
5. In the Make a Selection drop-down menu, select Install SMaRT Tool.
6. Click on the Run Installer icon to launch the SMaRT Tool Setup program.
7. Follow the on-screen installation instructions. Review the Intel Software License Agreement
and click Accept. When installation is complete, launch SMaRT Tool.
8. In SMaRT Tool’s Welcome page, click on Systems.
9. Select Select System > Servers > Xeon > SHG2 SC5200 and then follow the on-screen
instructions to download the SHG2 SC5200 server system module. When download is
complete, SMaRT Tool will restart.
10. Select Systems > Select System > Servers > Xeon > SHG2 SC5200 to access information on
your new server system.
11. You can invoke SMaRT Tool directly from Intel Server Management’s Platform
Instrumentation Control application by clicking on the SMaRT Tool icon, or by selecting
Launch SMaRT Tool from the SMaRT Tool menu. The interface between the two programs
is context-sensitive. To find out more about the integration between Intel SMaRT Tool and
Intel Server Management, please select SMaRT Tool and Server Management in the Make a
Selection drop-down menu.
42 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 43

3 Upgrading
Tools and Supplies Needed
• Phillips (cross head) screwdriver (#1 bit and #2 bit)
• Antistatic wrist strap and conductive foam pad (recommended)
Cautions
These warnings and cautions apply throughout this chapter. Only a technically qualified person
should configure the server board.
CAUTIONS
System power on/off: The power button DOES NOT turn off the system
AC power. To remove power from system, you must unplug the AC power
cord from the wall outlet. Make sure the AC power cord is unplugged before
you open the chassis, add, or remove any components.
Hazardous conditions, devices & cables: Hazardous electrical conditions
may be present on power, telephone, and communication cables. Turn off
the server and disconnect the power cord, telecommunications systems,
networks, and modems attached to the server before opening it. Otherwise,
personal injury or equipment damage can result.
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) & ESD protection: ESD can damage disk
drives, boards, and other parts. We recommend that you perform all
procedures in this chapter only at an ESD workstation. If one is not
available, provide some ESD protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap
attached to chassis groundany unpainted metal surfaceon your server
when handling parts.
ESD and handling boards: Always handle boards carefully. They can be
extremely sensitive to ESD. Hold boards only by their edges. After
removing a board from its protective wrapper or from the server, place the
board component side up on a grounded, static free surface. Use a
conductive foam pad if available but not the board wrapper. Do not slide
board over any surface.
43
Page 44

Installing or removing jumpers: A jumper is a small plastic encased
conductor that slips over two jumper pins. Some jumpers have a small tab on
top that you can grip with your fingertips or with a pair of fine needle nosed
pliers. If your jumpers do not have such a tab, take care when using needle
nosed pliers to remove or install a jumper; grip the narrow sides of the
jumper with the pliers, never the wide sides. Gripping the wide sides can
damage the contacts inside the jumper, causing intermittent problems with
the function controlled by that jumper. Take care to grip with, but not
squeeze, the pliers or other tool you use to remove a jumper, or you may
bend or break the stake pins on the board.
Memory
The SHG2 Server Board contains six 184-pin DIMM sockets. Memory is partitioned as three
banks. DIMMs must be populated in identical pairs.
The SHG2 server board supports up to six 2.5 V, ECC, DDR 200 or 266-compliant, registered
SDRAM 184-pin gold DIMMs. A wide range of DIMM sizes are supported, including 128 MB,
256 MB, 512 MB, 1 GB, and 2 GB DIMMs. The minimum supported memory configuration is
256 MB, using two identical 128 MB DIMMs. The maximum configurable memory size is 12 GB
using six 2 GB DIMMs.
The SDRAM interface runs at 200 MHz; however 266 MHz memory can be used. The memory
controller supports 2-way interleaved SDRAM, memory scrubbing, single-bit error correction and
multiple-bit error detection with Chipkill capability that allows the system to continue to run even
in the event of a multi-bit SDRAM failure. Memory can be implemented with either single-sided
(one row) or double-sided (two row) DIMMs.
✏
NOTE
Use DIMMs that have been tested for compatibility with the server board.
Contact your sales representative or dealer for a current list of approved
memory modules. Check the Intel Customer Support website for the latest
tested memory list:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
44 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 45

1. Open both DIMM socket levers.
2. Insert DIMM making sure the connector edge of the DIMM aligns correctly with the slot.
3. Check that socket levers are securely latched. DIMMs must be populated in identical pairs.
2
1A
3
1B
1
OM13205
Figure 26. Installing Memory
Processors
WARNING
If the server has been running, any installed processor and heat sink on
the processor board(s) will be hot. To avoid the possibility of a burn, be
careful when removing or installing server board components that are
located near processors.
CAUTIONS
Adding a second processor: If you are adding a second processor to your
system, you must verify that the second processor is identical to the first
processor.
Processor upgrades must be appropriate: You may damage the server if
you install a processor that is inappropriate for your server. Make sure your
server can handle a newer, faster processor (thermal and power
considerations). For exact information about processor interchangeability,
contact your customer service representative or visit the Intel Customer
Support website:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
ESD and handling processors: Reduce the risk of electrostatic discharge
(ESD) damage to the processor by doing the following: (1) Touch the metal
chassis before touching the processor or server board. Keep part of your
body in contact with the metal chassis to dissipate the static charge while
handling the processor. (2) Avoid moving around unnecessarily.
Upgrading 45
Page 46

Adding or Replacing a Processor
If you are adding a second processor to your system, the second processor must be identical in
speed with the first processor.
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter and the additional
cautions given here.
2. Remove power from your system by unplugging the AC power cord.
3. Remove the side cover (see your system or chassis documentation for instructions).
4. Install the retention brackets for the primary processor by inserting the retention brackets (A)
and tightening the four retention screws. The primary processor socket is located nearest to the
corner of the server board. If installing a second processor, install the retention brackets for the
secondary processor.
A
Figure 27. Installing the Retention Brackets
OM14364
46 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 47

5. Lift the socket lever on the processor socket labeled CPU1. (If adding a second processor, lift
the socket lever on the processor socket labeled CPU2.)
6. Align the pins of the processor with the socket, and insert the processor into the socket. Lower
the socket lever completely.
NOTE
✏
When installing a second processor, note that the secondary processor socket
is oriented so that the processor pins are rotated 180° relative to the primary
processor socket.
A
B
OM14365
C. Alignment Triangle Mark
D. Alignment Triangle Cutout
Figure 28. Opening Socket Lever and Attaching Processor
Upgrading 47
Page 48

7. Apply thermal grease to the processor as shown.
OM14366
Figure 29. Applying Thermal Grease
8. Align the heat sink with the retention brackets and place heat sink on the processor.
OM14367
Figure 30. Aligning the Heat Sink
48 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 49

9. Position the retention clip over the plastic tab and engage the retention clip end-slot over the
plastic tab (see 1 in Figure 31). Note that the slot in the clip provides room for side-to-side
motion while engaging the retention clip slots located at each end.
10. Press downward on the retention clip ends over the plastic tabs on the retention bracket (see 2
in Figure 31).
11. Install two retention clips on each processor you install.
2
1
2
OM14368
Figure 31. Attaching the Heat Sink and Retention Clip
Installing the Processor Wind Tunnel
The following instructions apply to the Intel SC5200 Base Server Chassis and reference chassis
installations. If you are installing your server board in the Intel SC5200 Hot-Swap, Redundant
Power Server Chassis, DO NOT install the processor wind tunnel. The ducting in the Intel SC5200
Hot-Swap, Redundant Power Server Chassis eliminates the need for a processor wind tunnel.
1. Install processor wind tunnel center section over the heat sink / processor assembly. Note that
plastic tabs engage the tabs on the retention clips.
OM14369
Figure 32. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Assembly
Upgrading 49
Page 50

2. Attach the processor wind tunnel fan to the wind tunnel air intake assembly as shown. The fan
label must be pointing into the air intake assembly.
Fan label
OM14370
Figure 33. Attaching the Heat Sink Fan to the Air Intake Assembly
CAUTION
To ensure proper system cooling, the heat sink fan must be installed as
shown in Figure 34 and the air intake fan assembly must be attached to the
side of the processor / wind tunnel assembly nearest to the front of the
chassis.
50 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 51

3. Attach the air intake fan assembly to the side of the heat sink wind tunnel closest to the front of
the chassis.
a. Press both sides of the air intake section to bend tabs inward (see 1 in Figure 34).
b. Insert tabs into slots on the wind tunnel center section (see 2 in Figure 34).
c. Press the air intake section downward to engage the assembly (see 3 in Figure 34).
2
3
1
Figure 34. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Intake and Exhaust
1
OM14371
4. Attach the air exhaust fan assembly to the heat sink wind tunnel.
a. Press both sides of the air exhaust section to bend tabs inward (see 1 in Figure 35).
b. Insert tabs into slots on the wind tunnel center section (see 2 in Figure 35).
c. Press the air intake section downward to engage the assembly (see 3 in Figure 35).
2
1
3
1
OM14374
Figure 35. Attaching the Wind Tunnel Intake and Exhaust
5. Attach CPU Fan cable(s). See “Making Connections to the Server Board” on page 35 for fan
connector location information.
Upgrading 51
Page 52

Removing a Processor
1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter and the additional
cautions given here.
2. Unplug the heat sink fan.
3. Detach the processor wind tunnel, if attached to the heat sink.
4. Detach the heat sink clip from the processor socket. See the documentation that shipped with
your processor for more detail.
5. Remove the heat sink from the processor.
6. Raise the locking bar on the socket.
7. Remove the processor from the socket.
Replacing the Backup Battery
The lithium battery on the server board powers the RTC for up to 10 years in the absence of power.
When the battery starts to weaken, it loses voltage, and the server settings stored in CMOS RAM in
the RTC (for example, the date and time) may be wrong. Contact your customer service
representative or dealer for a list of approved devices.
WARNING
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with
the same or equivalent type recommended by the equipment
manufacturer. Discard used batteries according to manufacturer’s
instructions.
ADVARSEL!
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering. Udskiftning
må kun ske med batteri af samme fabrikat og type. Levér det brugte
batteri tilbage til leverandøren.
ADVARSEL
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosjonsfare. Ved utskifting benyttes kun batteri
som anbefalt av apparatfabrikanten. Brukt batteri returneres
apparatleverandøren.
VARNING
Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte. Använd samma batterityp eller
en ekvivalent typ som rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren. Kassera
använt batteri enligt fabrikantens instruktion.
VAROITUS
Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu. Vaihda paristo
ainoastaan laitevalmistajan suosittelemaan tyyppiin. Hävitä käytetty
paristo valmistajan ohjeiden mukaisesti.
52 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 53

1. Observe the safety and ESD precautions at the beginning of this chapter.
2. Open the chassis.
3. Insert the tip of a small flat-blade screwdriver, or equivalent, under the tab in the plastic
retainer. Gently push down on the screwdriver to lift the battery.
4. Remove the battery from its socket.
5. Dispose of the battery according to local ordinance.
6. Remove the new lithium battery from its package, and, being careful to observe the correct
polarity, insert it in the battery socket.
7. Close the chassis.
8. Run BIOS Setup to restore the configuration settings to the RTC.
Figure 36. Replacing the Back up Battery
OM14372
Upgrading 53
Page 54

54 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide 55
Page 55

4 Configuration Software and Utilities
This chapter describes the Power-On Self-Test (POST) and server configuration utilities. The table
below briefly describes the utilities.
Table 4. Configuration Utilities
Utility Description Page
BIOS Setup Used for modifying server board set features, including setting time,
date, and system passwords; setting the boot device priority;
configuring the diskette drive and serial ports; and enabling the SCSI
BIOS and system management features.
System Setup Utility
(SSU)
FRUSDR Load Utility Used for updating the Field Replacement Unit (FRU), Sensor Data
BIOS Upgrade Utility Used to upgrade the BIOS. 73
Firmware Update Utility Used to update the Firmware. 76
Adaptec SCSI Utility Used to configure or view the settings of the SCSI host adapters and
Used for viewing and clearing the system event log, viewing the
system management FRU information, or viewing the system
management SDR repository.
Record (SDR), and SM BIOS (SMB) flash components.
onboard SCSI devices in the server.
57
58
69
78
Hot Keys
Use the keyboard’s numeric pad to enter numbers and symbols.
Table 5. Hot Keys
To do this: Press these keys
Clear memory and reload the operating
system - this is a system reset.
Secure your system immediately. <Ctrl+Alt>+hot key (Set your hot key combination with Setup.)
<Ctrl+Alt+Del>
Page 56

Power-On Self-Test (POST)
Each time you turn on the system, POST starts running. POST checks the server board, processor,
memory, keyboard, and most installed peripheral devices. During the memory test, POST displays
the amount of memory that it is able to access and test. The length of time needed to test memory
depends on the amount of memory installed. POST is stored in flash memory.
1. Turn on your video monitor and server. After a few seconds POST begins to run.
2. After the memory test, these screen prompts and messages appear:
Press <F2> to enter SETUP
3. If you do not press <F2> and do NOT have a device with an operating system loaded, the
above message remains for a few seconds while the boot process continues, and the system
beeps once. Then this message appears:
Operating system not found
If you do not press <F2> and DO have an operating system loaded, the boot process continues,
and this message appears:
Press <Ctrl><A> to enter SCSI Utility
4. Press <Ctrl+A> if there are SCSI devices installed. When the utility opens, follow the
displayed instructions to configure the onboard SCSI host adapter settings and to run the
SCSI utilities. Also see “Using the Adaptec SCSI Utility” on page 78. If you do not enter the
SCSI utility, the boot process continues.
5. Press <Esc> during POST to pop up a boot menu when POST finishes. From this menu you
can choose the boot device or enter BIOS Setup.
After POST completes, the system beeps once.
What appears on the screen after this depends on whether you have an operating system loaded and
if so, which one.
If the system halts before POST completes running, it emits a beep code indicating a fatal system
error that requires immediate attention. If POST can display a message on the video display screen,
it causes the speaker to beep twice as the message appears.
Note the screen display and write down the beep code you hear; this information is useful for your
service representative. For a listing of beep codes and error messages that POST can generate, see
the “Monitoring POST” on page 81.
56 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 57

Using BIOS Setup
This section describes the BIOS Setup options. Use Setup to change the server configuration
defaults. You can run Setup with or without an operating system being present. Setup stores most
of the configuration values in battery backed CMOS; the rest of the values are stored in flash
memory. The values take effect when you boot the server. POST uses these values to configure
the hardware; if the values and the actual hardware do not agree, POST generates an error message.
You must then run Setup to specify the correct configuration.
Record Your Setup Settings
Record your setup settings on a worksheet. If the default values ever need to be restored (after a
CMOS clear, for example), you must run Setup again. Referring to the worksheet could make your
task easier.
If You Cannot Access Setup
If the diskette drive is misconfigured so that you cannot access it to run a utility from a diskette,
you may need to clear CMOS memory. You will need to open the server, change a jumper setting,
use Setup to check and set diskette drive options, and change the jumper back. For a step-by-step
procedure, see Chapter 5, under the heading, “CMOS Jumper.”
Starting Setup
You can enter and start Setup under several conditions:
• When you turn on the server, after POST completes the memory test
• When you reboot the server by pressing <Ctrl+Alt+Del> while at the DOS operating system
prompt
• When you have moved the CMOS jumper on the server board to the “Clear CMOS” position
(enabled); for the procedure, see “Server Board Jumpers” on Page 89.
In the three conditions listed above, after rebooting, you will see this prompt:
Press <F2> to enter SETUP
NOTE
✏
If the BIOS setup option “POST Diagnostic Screen” is enabled (Default),
you will not see the message “Press <F2> to enter SETUP.” This message is
hidden by the Manufacturer’s Splash screen. To see the message, press the
<ESC> key while the splash screen is displayed. This will temporarily
disable the splash screen allowing you to see the message.
In a fourth condition, when CMOS/NVRAM has been corrupted, you will see other prompts but not
the <F2> prompt:
Warning: cmos checksum invalid
Warning: cmos time and date not set
In this condition, the BIOS will load default values for CMOS and attempt to boot.
Configuration Software and Utilities 57
Page 58

Using the System Setup Utility
The System Setup Utility (SSU) is located on the Intel Server Board SHG2 Resource CD-ROM
shipped with the server.
Run the System Setup Utility to:
• Set boot device priority
• Set passwords and security options
• View system events
• View FRU information
• View sensor data records
• Update system firmware and BIOS
• Save and restore the system configuration
• Set up the server to send alerts for platform events
• Set up the server for remote management
You can specify the boot device sequence and set up system passwords and security options using
either the System Setup Utility or BIOS Setup (page 57). Both utilities access the same stored
configuration data for these items, and the result of making a change to these settings using either
utility is identical.
The SSU consists of a collection of task-oriented modules plugged into a common framework
called the Application Framework (AF). The Application Framework provides a launching point
for individual tasks and a location for setting customization information.
Creating SSU Diskettes
You can run the SSU directly from the Utilities menu of the System Resource CD-ROM, from a set
of DOS diskettes, or from the service partition of the hard disk.
If you choose to run the SSU from a set of DOS diskettes, you must create the SSU diskettes from
the Resource CD-ROM as follows:
1. Boot to the System Resource CD-ROM.
2. Choose Create Diskettes > Create Diskettes by Device/Function > System Setup Utility.
3. Follow the instructions displayed.
Alternatively, if you have a workstation with the Microsoft Windows operating system, you can
insert the CD into that system and create the diskettes on that system.
58 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 59

Running the SSU
When the SSU starts in the default local execution mode, the SSU accepts input from the keyboard
or mouse. The SSU presents a VGA-based GUI on the primary monitor.
If you run the SSU from read-only media, such as the CD-ROM, you cannot save user preference
settings (such as screen colors).
The SSU supports ROM-DOS version 6.22. The SSU will not operate from a “DOS box” running
under an operating system such as Windows.
To start the SSU:
1. Start the SSU using one of the following methods:
From diskettes: Insert the first SSU diskette in drive A and boot the server from the
diskette. You are prompted to insert the second diskette. After loading completes the SSU
starts automatically.
From the System Resource or ISM CD-ROM: Boot the server to the System Resource
CD and start the SSU from the Utilities menu.
From the Service Partition: Boot the server to the Service Partition and execute the
following DOS commands:
C:\> cd ssu
C:\SSU> ssu.bat
2. The mouse driver loads if it is available; press Enter to continue.
3. When the SSU title appears on the screen, press Enter to continue.
Working with the GUI
You can access features of the GUI using the mouse or keyboard:
• Mouse—Click once to choose menu items and buttons or to select items in a list, such as the
Available Tasks list. To run a list item, such as one of from the Available Tasks list, select the
item and click OK or double-click the item.
• Keyboard—Use the tab and arrow keys to highlight buttons and press the spacebar or <Enter>
to execute. You can also execute a menu or button by using the <Alt> key in combination with
the underlined letter in the name of the menu or button.
You can have more than one task open at the same time, although some tasks might require
complete control to avoid possible conflicts. The tasks achieve complete control by keeping the
task as the center of operation until you close the task window.
The SSU has a build-in help system, which you access by clicking a Help button or choosing the
Help menu.
Configuration Software and Utilities 59
Page 60

Customizing the SSU Interface
The SSU lets you customize your interface using the Preferences section of the main window. The
SSU sets these preferences and saves them in the AF.INI file so that they take effect the next time
you start the SSU. There are four user customizable settings:
• Color - lets you change the default colors associated with different items on the screen using
predefined color combinations. The color changes take effect immediately.
• Mode - lets you set the desired expertise level: novice, intermediate, or expert.
The expertise level determines which tasks are visible in the Available Tasks section and which
actions each task performs. For a new mode setting to take effect, you must exit the SSU and
restart it.
• Language - lets you change the text in the SSU to the appropriate language. For a new
language setting to take effect, you must exit the SSU and restart it.
• Other - lets you show or hide the status bar at the bottom of the SSU main window. The
change takes effect immediately.
NOTE
✏
If you run the SSU from read-only media (CD-ROM, for example), these
preferences are lost when you exit the SSU.
Exiting the SSU
Exiting the SSU closes all SSU windows.
Setting Boot Device Priority
To change the boot priority of a device:
1. From the SSU Main window, choose Boot Devices.
2. In the Multiboot Options Add-in window, select a device.
3. Click the Move Up button to move it up in the list. Click the Move Down button to move it
down.
Setting Passwords and Security Options
You can set a user password and an admin password. On some systems, you must set an admin
password before you can set a user password. On other systems, the passwords are independent.
You can set the same passwords and security options by using BIOS Setup (page 57).
60 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 61

Setting the Admin Password
The Admin Password button lets you set or change the admin password used by both the SSU and
the system BIOS. This option is not available if both an admin and a user password are set and you
entered only the user password when you started the SSU. All changes to the admin password take
effect immediately.
To change or clear the administrator password:
1. From the SSU Main window, choose Security.
2. Click the Admin Password button.
3. If you are changing passwords, enter the old password.
4. Enter the new password (or leave blank to clear).
5. Confirm the password by entering it again (or leave blank to clear).
6. Click OK to save the password and return to the Security window.
Setting the User Password
The User Password button lets you set or change the user password used by both the SSU and the
system BIOS. All changes to the user password take effect immediately.
To change or clear the user password:
1. From the SSU Main window, choose Security.
2. Click the User Password button.
3. If you are changing passwords, enter the old password in the first box.
4. Enter the new password (or leave blank to clear).
5. Confirm the password by entering it again (or leave blank to clear).
6. Click OK to save the password and return to the Security window.
Setting Security Options
For a description of security features, see page 19.
To set the security options:
1. In the Security window, click the Options button.
2. For each option, select the desired setting from the list. The options are:
• Security Hot Key: The key combination that can be used to put the server into secure
mode.
• Secure Mode Timer: If no keyboard or mouse activity occurs during the chosen time
interval, the server enters secure mode.
• Secure Mode Boot: Enable forces the server to boot directly into secure mode.
• Video Blanking: Enable turns off the video when the server is in secure mode.
• Floppy Write: Enable prevents writing to the diskette drive while the server is in secure
mode.
• Power Switch Inhibit: Enable prevents the power and reset buttons from functioning
when the server is in secure mode. Disable allows the power and reset buttons to function
normally when the server is in secure mode.
3. Click Save to save the settings and return to the Security window.
Configuration Software and Utilities 61
Page 62

Viewing the System Event Log
To view the System Event Log (SEL):
1. From the SSU Main window, choose SEL Manager.
When you start the SEL Manager, it automatically loads the current list of events from
non-volatile memory.
2. Use the <F4> and <F5> keys to scroll the window contents to the left and right to view all of
the columns.
3. Use the File and SEL menu items to work with the SEL information:
• Open: Views data from a previously saved SEL file.
• Save As: Saves the currently loaded SEL data to a file.
• Properties: Displays information about the SEL.
• Clear SEL: Clears the SEL data from the nonvolatile storage area.
• Reload: Refreshes the display by reading the current SEL entries from the server.
• Sort By: Sorts the displayed events by event number, time stamp, sensor type and number,
event description, or event generator ID.
Viewing FRU Information
To view the Field Replaceable Unit (FRU) information:
1. From the SSU Main window, choose FRU Manager.
When you start the FRU Manager, it automatically loads the current list of events from
non-volatile memory.
The FRU Manager window has a navigation pane on the left that displays, in a tree format,
the inventory of components in the server. The tree has three categories: Chassis, Board,
and Product. Clicking on a category expands or collapses a list of components for that
category. Clicking on an individual component displays the FRU information for that
component in the presentation pane in the upper right. The description pane in the lower
right displays a description of the currently selected FRU area.
2. Use the <F4> and <F5> keys to scroll the window contents to the left and right to view all of
the columns.
3. Use the File and FRU menu items to work with the FRU information:
• Open: Views data from a previously saved FRU file.
• Save As: Saves the currently loaded FRU data to a file.
• Properties: Displays the number of FRU devices in the system and the number being
displayed. Only FRU devices with valid FRU areas are displayed.
• Reload: Refreshes the display by reading the current FRU entries from the server.
62 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 63

Viewing Sensor Data Records
To view the Sensor Data Records (SDR):
1. From the SSU Main window, choose SDR Manager.
When you start the SDR Manager, it automatically loads the SDR entries from non-volatile
memory.
The SDR Manager window has a navigation pane on the left that displays, in a tree format,
the sensor data records. The tree has categories for each type of record. Clicking on a
category expands or collapses a list of SDRs for that category. Clicking on an individual
SDR displays the information for that SDR in the presentation pane in the upper right. The
description pane in the lower right displays a description of the currently selected
SDR type.
2. Use the <F4> and <F5> keys to scroll the window contents to the left and right to view all of
the columns.
3. Use the File and SDR menu items to work with the SDR information:
• Open: Views data from a previously saved SDR file.
• Save As: Saves the currently loaded SDR data to a file.
• Properties: Displays information about the SDR, including IPMI version, number of SDR
entries, time stamps for changes to the SDR information, and free space remaining.
• Reload: Refreshes the display by reading the SDR data from the server.
Updating System Firmware and BIOS
Using the SSU, you can update the BIOS, update the firmware, and verify the firmware.
Procedures for each are given below. You can also update the BIOS and firmware without using
the SSU (see page 74). You can download the updates from the Intel support website:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
Updating the BIOS
To update the BIOS:
1. Download the update from the Intel support website.
2. From the SSU Main window, choose System Update. (System Update is available only in
Expert mode.)
When you start System Update, it automatically displays the current revision information for
the system firmware and BIOS.
3. From the File menu, choose Load and choose a .uif or .bio file to use for the update.
4. Click the Update button to update the BIOS.
Configuration Software and Utilities 63
Page 64

Updating the Firmware
To update the system firmware:
1. Download the update from the Intel support website.
2. From the SSU Main window, choose System Update. (System Update is available only in
Expert mode.)
3. When you start System Update, it automatically displays the current revision information for
the system firmware and BIOS.
4. From the File menu, choose Load and choose a .uif or .hex file to use for the update.
5. Click the Update button to perform the update.
Verifying the Firmware
To compare the system firmware in nonvolatile memory with a firmware file:
1. Download the update from the Intel support website.
2. From the SSU Main window, choose System Update. (System Update is available only in
Expert mode.)
When you start System Update, it automatically displays the current revision information for
the system firmware and BIOS.
3. From the File menu, choose Load and choose a .hex file to use for the update.
4. Click the Verify button to compare the firmware code in nonvolatile storage with the
selected file.
Saving and Restoring the System Configuration
Using the SSU, you can save the following configuration information to a file:
• Platform type, BIOS revision, and firmware revision
• CMOS settings
• Extended system configuration data (ESCD)
• Settings for the emergency management port (EMP), platform event paging (PEP), and BMC
LAN alerts
Data is saved from all sources. There is no way to choose only certain pieces of configuration data
to save. You can also restore the information from a saved configuration file.
NOTE
✏
BIOS passwords are stored in the file. Restoring a configuration can change
passwords on a server. EMP and LAN passwords are not stored in the file.
Saving a Configuration
To save the system configuration:
1. From the SSU Main window, choose Config Save/Restore. (Configuration Save/Restore is
available only in Expert mode.)
2. Click Save To File and specify a filename and location.
64 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 65

Restoring a Configuration
To restore the system configuration from a file:
1. From the SSU Main window, choose Config Save/Restore. (Configuration Save/Restore is
available only in Expert mode.)
2. Click Restore from File and specify a filename and location.
The CSR reads the platform type, BIOS revision, and firmware revision from the file and compares
that information with the same information retrieved from the server. If the two do not match, an
error message is displayed and the restore operation aborts. If they do match, the CSR restores the
configuration data to the server. It prompts you to reboot the server for the new settings to
take effect.
Alerting for Platform Events
You can set up the server to alert you when various events occur. Alerts can be delivered either as
telephone pages, over the LAN, or by email.
Setting Up Email Alerts
You can receive email alerts for any of the same events supported by LAN alert or Platform Events
Paging. Unlike LAN Alert and Platform Events Paging that can be configured using the SSU, you
must use the Intel Server Management Platform Interface Control (PIC) software to configure an
email address to receive alerts.
For more information on installing Intel Server Management (ISM) software, see page 40. For
more information on configuring email alerts using the PIC, see the Installation & User Guide
located on the ISM CD-ROM.
Setting Up Paging Alerts
To set up the server to send alerts as telephone pages:
1. Install an external modem on the Emergency Management Port (COM2).
2. From the SSU Main window, choose Platform Event Manager (PEM).
3. In the PEM window, click Configure EMP.
4. In the corresponding boxes, enter the following command strings for the modem attached to the
EMP port:
• ESC Sequence: the escape sequence. This string is sent to the modem before sending
command strings. The maximum string length is five characters; longer strings are
truncated.
• Hangup String: hang up or drop the connection. The EMP automatically sends an
<ENTER> character following this string. The maximum string length is eight characters;
longer strings are truncated.
• Modem Dial Command: the command to dial a phone number. This string is sent to the
modem before sending the paging string.
• Modem Init String: the initialization string for the modem. This string is sent every time
the EMP initializes. The maximum length for the string is determined at run-time from
firmware. You will be notified if the string is truncated. Following a save, the actual string
saved is displayed in the edit box.
Configuration Software and Utilities 65
Page 66

5. Click Save to save the changes.
6. Click Close to return to the PEM window.
7. In the PEM window, click Configure PEP.
8. Select the Enable PEP check box.
9. In the Blackout Period box, enter the minimum time, in minutes, between successive pages.
The valid range is [0 - 255] where 0 disables the blackout period. Setting a blackout period can
save you from being flooded with repeat pages. After you receive a PEP page, no additional
pages are sent by PEP for the duration of the blackout period.
10. In the Paging String box, enter the phone number to dial for the page and the message you
want sent with the page. The maximum length for the paging string is determined at run-time
from firmware. You will be notified if the string is truncated. Following a save, the actual
string saved is displayed in the edit box.
11. From the Options menu, choose Configure Event Actions.
12. In the Platform Event Paging Actions window, move the events that you want to generate an
alert to the Enabled column and move all other events to the disabled column using the
following buttons:
• >>: Moves all events from the enabled list to the disabled list.
• >: Moves the selected event from the enabled list to the disabled list.
• <: Moves the selected event from the disabled list to enabled the list.
• <<: Moves all events from the disabled list to the enabled list.
13. Click Save to save the changes.
14. Click Close to return to the PEP Configuration window.
15. To send a test page to verify that you have correctly configured PEP, from the Options menu,
choose Send Alert.
16. Click Save to save the configuration.
17. Click Close to return to the Platform Event Manager window.
Setting Up LAN Alerts
To set up the server to send alerts over the LAN:
1. Configure the remote system to receive alerts. For more information, see the documentation
for Intel Server Management software.
2. From the SSU Main window, choose Platform Event Manager (PEM).
3. In the PEM window, click Configure LAN.
4. Select the Enable LAN Alerts check box.
5. (Optional) In the SNMP Community String box, enter a string for the community field in the
Header section of the SNMP trap sent for an alert. The string must be from 5 to 16 characters.
The default string is public.
6. In the IP Setup box, choose either:
• DHCP: the IP address for the server is automatically assigned by the DHCP (dynamic host
control protocol) server on the network. The Host, Gateway, and Subnet Mask boxes in the
dialog are ignored.
• Static: assign the IP address for the server using the Host, Gateway, and Subnet Mask
boxes in the dialog.
66 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 67

7. If you chose Static IP Setup in the previous step, fill in the IP addressing boxes:
• Host IP Address: the IP address of this server.
• Gateway IP Address: the IP address of the router for this server.
• Subnet Mask: the IP address for the server’s subnet. The server uses this to decide if the
alert destination is on the same subnet.
8. In the Alert IP Address box, fill in the IP address of the system you want to receive alerts from
this server. If you want the alert to be broadcast to an entire subnet, enter the IP address for the
subnet.
9. From the Options menu, choose Configure Event Actions.
10. In the BMC LAN Alerting Actions window, move the events that you want to generate an alert
to the Enabled column and move all other events to the disabled column using the following
buttons:
• >>: Moves all events from the enabled list to the disabled list.
• >: Moves the selected event from the enabled list to the disabled list.
• <: Moves the selected event from the disabled list to enabled the list.
• <<: Moves all events from the disabled list to the enabled list.
11. Click Save to save the changes.
12. Click Close to return to the BMC LAN Configuration window.
13. To send a test alert to verify that you have correctly configured BMC LAN alerts, from the
Options menu, choose Send Alert.
14. Click Save to save the changes.
15. Click Close to return to the PEM window.
Managing the Server Remotely
You can set up the server to so that you can connect to it from a remote client system to perform
management tasks. You can make the connection over a LAN or by using a modem or direct serial
cable to the Emergency Management Port (EMP). Instructions for setting up the server for remote
LAN and serial/modem access are given below.
Setting Up Remote LAN Access
To configure remote LAN access:
1. From the SSU Main window, choose Platform Event Manager (PEM).
2. In the PEM window, click Configure LAN.
3. If you want to require a password for remote access, enter the password in the Enter New
Password box and in the Verify New Password box. Passwords can be from 1 to 16
characters long, using any ASCII character in the range [32-126]. To clear the passwords,
leave both boxes blank. (You can also clear the password by choose the menu Options > Clear
LAN Password.)
4. From the LAN Access Mode list, select the remote access mode:
• Full Access: a remote system can initiate a LAN connection regardless of the state or
health of the server.
Configuration Software and Utilities 67
Page 68

• Restricted: a remote system can initiate a LAN connection, but cannot perform control
operations such as power down, reset, or front panel NMI.
• Disabled: remote systems are not allowed to initiate LAN connections.
5. In the IP Setup box, choose either:
• DHCP: the IP address for the server is automatically assigned by the DHCP (dynamic host
control protocol) server on the network. The Host, Gateway, and Subnet Mask boxes in the
dialog are ignored.
• Static: assign the IP address for the server using the Host, Gateway, and Subnet Mask
boxes in the dialog.
6. If you chose Static IP Setup in the previous step, fill in the IP addressing boxes:
• Host IP Address: the IP address of this server.
• Gateway IP Address: the IP address of the router for this server.
• Subnet Mask: the IP address for the server’s subnet. The server uses this to decide if the
alert destination is on the same subnet.
7. Click Save to save the changes.
8. Click Close to return to the PEM window.
Setting Up Remote Modem or Serial Access
To configure remote modem or serial access:
1. From the SSU Main window, choose Platform Event Manager (PEM).
2. In the PEM window, click Configure EMP.
3. If you want to require a password for remote access, enter the password in the Enter New
Password box and in the Verify New Password box. Passwords can be from 1 to 16
characters long, using any ASCII character in the range [32-126]. To clear the passwords,
leave both boxes blank. (You can also clear the password by choose the menu Options > Clear
LAN Password.)
4. In the Modem Ring Time box, enter the number of 500ms intervals that the BMC should wait
before taking control of the COM2 port and answering an incoming call. A value greater than
zero gives the BIOS time to answer before the BMC takes control. A value of zero causes the
BMC to answer immediately. The maximum value, 63, tells the BMC to ignore the call.
Modem Ring Time applies only to Preboot access mode and is ignored for other access modes.
5. In the System Phone Number box, enter the number for the phone line connected to the
modem on the EMP.
6. From the Access Mode list, choose the remote access mode:
• Always Active: the EMP is available at any time.
• Preboot: the EMP is available only when the server is powered down or is in the running
POST during startup.
• Disabled: remote systems are not allowed to initiate connections.
7. From the Restricted Mode list, choose either:
• Enabled: a remote system can initiate a connection, but cannot perform control operations
such as power down, reset, or front panel NMI.
• Disabled: the remote system has full control of the server.
68 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 69

8. From the Connection Mode list, choose either:
• Direct Connect: the COM2 port on the server is connected by a serial cable to the remote
system.
• Modem Connect: the COM2 port on the server is connected to a modem.
9. Click Save to save the changes.
10. Click Close to return to the PEM window.
FRUSDR Load Utility
The Field Replacement Unit (FRU) and Sensor Data Record (SDR) Load Utility is a DOS-based
program used to update the server management subsystem’s product level FRU, SDR, and the
SM BIOS (SMB) nonvolatile storage components (EEPROMs). The load utility
• Discovers the product configuration based on instructions in a master configuration file
• Displays the FRU information
• Updates the nonvolatile storage device (EEPROM) associated with the Baseboard Management
Controller (BMC) that holds the SDR and FRU area
• Updates the SMB area located in the BIOS nonvolatile storage device
• Generically handles FRU devices that may not be associated with the BMC
When to Run the FRUSDR Load Utility
You should run the FRUSDR Load Utility each time you upgrade or replace the hardware in your
server, excluding add-in boards, hard drives, and RAM. For example, if you replace an array of
fans, you need to run the utility. It programs the sensors that need to be monitored for server
management.
Because the firmware must reload to properly initialize the sensors after programming, turn the
server off and remove the AC power cords from the server. Wait approximately 30 seconds, and
reconnect the power cords.
What You Need to Do
The FRUSDR Load Utility may be run directly from the Configuration Software CD or from a
diskette you create from the CD. It can be extracted from the CD by booting to the CD and
selecting “Make Diskettes” or by inserting the CD into a PC running Windows 95 or later and
selecting the “Utilities” section.
NOTE
✏
If your diskette drive is disabled, or improperly configured, you must use
BIOS Setup to enable it. If necessary, you can disable the drive after you are
done with the FRUSDR utility.
Configuration Software and Utilities 69
Page 70

How You Use the FRUSDR Load Utility
This utility is compatible with ROM-DOS Ver. 6.22, MS-DOS
†
Ver. 6.22, and later versions. The
utility accepts CFG, SDR and FRU load files. The executable file for the utility is frusdr.exe. The
utility requires the following supporting files:
• One or more .fru files describing the system’s field replaceable units
• A .cfg file describing the system configuration
• A .sdr file describing the sensors in the system
Command Line Format
The basic command line format is
frusdr [/?] [/h] [/d {smb, fru, sdr}] [/cfg filename.cfg] /p
Command Description
frusdr Is the name of the utility
/? or /h Displays usage information
/d {smb, fru, sdr} Only displays requested area
/cfg filename.cfg Uses custom CFG file
/p Pause between blocks of data
Parsing the Command Line
The FRUSDR Load Utility allows only one command line function at a time. A command line
function may consist of two parameters; for example, cfg filename.cfg. Any invalid parameters
result in displaying an error message and exiting the program. You can use either a slash (/) or a
minus sign (-) to specify command line options. The /p flag may be used in conjunction with any
of the other options.
Displaying Usage Information
When the utility is run with the /? or /h command line flags, the following message is displayed:
FRU & SDR Load Utility Version X.XX
Usage: frusdr Is the name of the utility.
/? Or /h Displays usage information.
/d {smb,fru,sdr} Only displays requested area.
/cfg filename.cfg Uses custom CFG file.
/p Pause between blocks of data.
Displaying a Given Area
When the utility is run with the /d SMB, /d FRU, or /d SDR command line flag, the indicated area
is displayed. Each area represents a sensor; one sensor for each instrumented device in the server.
If the given display function fails because of an inability to parse the data present or a hardware
failure, the utility displays an error message and exits.
70 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 71

Displaying SM BIOS Area
The SM BIOS area is displayed in ASCII format when the field is ASCII or as a number when the
field is a number. Each SM BIOS area displayed is headed with the SM BIOS area designated
name. Each field has a field name header followed by the field in ASCII or as a number.
Displaying FRU Area
The FRU area is displayed in ASCII format when the field is ASCII or as a number when the field
is a number. Each FRU area displayed is headed with the FRU area designated name. Each field
has a field name header followed by the field in ASCII or as a number. The Board, Chassis, and
Product FRU areas end with an END OF FIELDS CODE that indicates there is no more data in this
area. The Internal Use area is displayed in hex format, 16 bytes per line.
Displaying SDR Area
The SDR nonvolatile storage area is displayed in the following hex format. The data is separated
by a Sensor Record Number X header, where X is the number of that sensor record in the
SDR area. The next line after the header is the sensor record data in hex format delineated by
spaces. Each line holds up to 16 bytes. The data on each line is followed by the same data in
ASCII format; nonprintable characters are substituted by a period (.).
Using Specified CFG File
The utility can be run with the command line parameter of -cfg filename.cfg. The filename can be
any DOS accepted, eight-character filename string. The utility loads the specified CFG file and
uses the entries in the configuration file to probe the hardware and to select the proper SDRs to load
into nonvolatile storage.
Displaying Utility Title and Version
The utility displays its title:
FRU & SDR Load Utility, Version X.XX
Where X.XX is the revision number for the utility.
Configuration File
The configuration file is in ASCII text. The utility executes commands formed by the strings
present in the configuration file. These commands cause the utility to perform various tasks needed
to ultimately load the proper SDRs into the nonvolatile storage of the BMC and possibly generic
FRU devices. Some of the commands may be interactive and require you to make a choice.
Prompting for Product Level FRU Information
Through the use of a Configuration File, the utility may prompt you for FRU information.
Filtering Sensor Data Record From the SDR File
The MASTER.SDR file has all the possible SDRs for the system. These records may need to be
filtered based on the current product configuration. The configuration file directs the filtering of
the SDRs.
Configuration Software and Utilities 71
Page 72

Updating the SDR Nonvolatile Storage Area
After the utility validates the header area of the supplied SDR file, it updates the SDR repository
area. Before programming, the utility clears the SDR repository area. The SDR file is loaded via
the .cfg File. Then the utility filters all tagged SDRs depending on the product configuration set in
the Configuration File. Nontagged SDRs are automatically programmed. The utility also copies all
written SDRs to the SDR.TMP file. It contains an image of what was loaded, and the TMP file is
also useful for debugging the server.
Updating FRU Nonvolatile Storage Area
After the configuration is determined, the utility updates the FRU nonvolatile storage area. First it
verifies the Common Header area and checksum from the specified FRU file. The Internal Use
Area is read out of the specified .FRU file and is programmed into the nonvolatile storage. The
Chassis, Board, Product and MultiRecord areas are read out of the specified .FRU file, if they exist,
then those areas are programmed into the FRU nonvolatile storage. All the areas are also written to
the FRU.TMP file, which is useful for debugging the server.
Updating SMB FRU Nonvolatile Storage Area
After programming the BMC FRU area, the corresponding SMB fields are automatically updated
when the server is re-booted.
Cleaning Up and Exiting
If an update was successfully performed, the utility displays an appropriate message and then exits
with a DOS exit code of zero.
If the utility fails, it immediately exits with an error message and a non-zero DOS exit code.
72 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 73

Upgrading the BIOS
Preparing for the Upgrade
Before you upgrade the BIOS, prepare for the upgrade by recording the current BIOS settings,
obtaining the upgrade utility, and making a copy of the current BIOS.
Recording the Current BIOS Settings
1. Boot the computer and press <F2> when you see the message:
Press <F2> to enter SETUP
2. Write down the current settings in the BIOS Setup program.
NOTE
✏
Do not skip step 2. You will need these settings to configure your computer
at the end of the procedure.
Obtaining the Upgrade Utility
You can upgrade to a new version of the BIOS using the new BIOS files and the BIOS upgrade
utility, iFLASH.EXE. You can obtain the BIOS upgrade file and the iFLASH.EXE utility through
your computer supplier or from the Intel Customer Support website:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
NOTE
✏
Please review the instructions distributed with the upgrade utility before
attempting a BIOS upgrade.
This upgrade utility allows you to:
• Upgrade the BIOS in flash memory
• Update the language section of the BIOS
The following steps explain how to upgrade the BIOS.
Creating a Bootable Diskette
1. Use a DOS system to create the diskette or boot the server to the System Resource CD and
“Quit to DOS”.
2. Insert a diskette in diskette drive A.
3. At the C:\ prompt, for an unformatted diskette, type:
format a:/s
or, for a formatted diskette, type:
sys a:
4. Press <Enter>
Configuration Software and Utilities 73
Page 74

Creating the BIOS Upgrade Diskette
The BIOS upgrade file is a compressed self-extracting archive that contains the files you need to
upgrade the BIOS.
1. Insert the bootable diskette into the diskette drive.
2. Extract the contents of the BIOS.EXE file onto the bootable diskette. To do this, read the
instructions distributed with the BIOS package.
Upgrading the BIOS
1. Place the bootable diskette containing the BIOS update files into the diskette drive of your
system. Boot the system with the diskette is in the drive.
2. At this point you have a choice of two options. Press 1 and ENTER to automatically update
the system BIOS. This will update the system BIOS and reset the system. Press 2 and ENTER
to update the User Binary and reset the system.
3. Wait while the BIOS files are updated. Do not power down the system during the BIOS update
process! The system will reset automatically when the BIOS update process is completed.
Remove the diskette from the diskette drive.
4. Check to make sure the BIOS version displayed during POST is the new version as the system
reboots.
5. Enter Setup by pressing the F2 key during boot. Once in Setup, press F9 and ENTER to set
the parameters back to default values.
6. Re-enter the values you wrote down at the beginning of this process. Press F10 and ENTER to
exit BIOS Setup and Save Changes.
7. If you do not set the CMOS values back to defaults using the F9 key, the system may function
erratically.
✏
NOTE
You may encounter a CMOS Checksum error or other problem after reboot.
Try shutting down the system and booting up again. CMOS checksum errors
require that you enter Setup, check your settings, save your settings, and exit
Setup.
74 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 75

Recovering the BIOS
It is unlikely that anything will interrupt the BIOS upgrade; however, if an interruption occurs, the
BIOS could be damaged. The following steps explain how to recover the BIOS if an upgrade fails.
In the event of BIOS corruption, the following procedure may be used to perform a BIOS
recovery boot.
1. Prepare a bootable floppy diskette containing the BIOS recovery files for the SHG2 server
board obtained from Intel’s web sites.
2. Power off the system, unplug the power cord, and remove the chassis cover.
3. Add a jumper on CN43 pins 9-10 (BIOS recovery).
4. Insert the BIOS Recovery floppy diskette into the disk drive.
5. Reinstall the chassis’ cover, plug in the power cord(s), and power on the system.
6. The screen will remain blank while the BIOS Recovery is performed. At the end of the BIOS
Recovery, two high-pitched beeps will sound and the floppy drive access light will turn off.
The BIOS Recovery may take several minutes to complete. When the BIOS Recovery is
complete, it is safe to power off the system.
7. Power off the system, unplug the power cord(s), and remove the chassis cover.
8. Remove the BIOS Recovery jumper from CN43 pins 9-10.
9. Replace the chassis’ cover, plug in the power cord(s), and power on the system.
Changing the BIOS Language
You can use the BIOS upgrade utility to change the language the BIOS uses for messages and the
Setup program. Use a bootable diskette containing the Intel flash utility and language files.
1. Boot the computer with the bootable diskette in drive A. The BIOS upgrade utility screen
appears.
2. Select
3. Select
4. Select drive A and use the arrow keys to select the correct
Update Flash Memory From a File.
Update Language Set. Press <Enter>.
.lng file. Press <Enter>.
5. When the utility asks for confirmation that you want to flash the new language into memory,
select
Continue with Programming. Press <Enter>.
6. When the utility displays the message
upgrade is complete, remove the diskette. Press
<Enter>.
7. The computer will reboot and the changes will take effect.
Configuration Software and Utilities 75
Page 76

Using the Firmware Update Utility
The Firmware Update Utility is a DOS-based program used to update the Baseboard Management
Controller’s firmware code. You only need to run the Firmware Update Utility if new firmware
code becomes necessary or the firmware becomes corrupted. It is highly recommended that you
also update the FRU/SDR files at the same time that you update the BMC Firmware.
You can obtain the latest version of the firmware update file from the Intel Customer Support
website:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
Making a BMC Firmware Update Diskette
1. Place a formatted diskette into the diskette drive.
2. Extract the contents of the SHG2 firmware file onto the diskette.
Making the Update Diskette Bootable
1. Use a DOS system to create the diskette or boot the server to the System Resource CD and
“Quit to DOS”.
2. Insert the update diskette into diskette drive A.
At the C:\ prompt, type:
sys a:
3. Press
<Enter>
Updating the BMC Firmware
In the event of a release of an updated BMC Firmware, the following procedure may be used to
update the firmware.
NOTE
✏
These instructions for BMC Update are a general guideline. Please follow
the specific instructions described in the release notes.
1. Prepare a bootable floppy diskette containing the updated BMC firmware files for the
SHG2 Server Board obtained from:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
2. Insert the BMC Firmware floppy diskette into the disk drive.
3. Reboot the system. BMC Firmware update occurs automatically and may take several minutes
to complete. When the BMC Firmware update is complete, it is safe to power off the system.
4. Power off the system and remove the power cord for 30 seconds.
5. Connect the power cord and power on the system.
76 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 77

Recovering the BMC Firmware
In the event of BMC Firmware corruption, the following procedure may be used to perform a
BMC Firmware recovery boot.
1. Prepare a bootable floppy diskette containing the updated BMC firmware files for the
SHG2 Server Board obtained from Intel’s Customer Support web site.
2. Power off the system, unplug the power cord, and remove the chassis cover.
3. Add a jumper on CN47 pins 1-2 (BMC Force Update).
4. Insert the BMC Firmware floppy diskette into the disk drive.
5. Reinstall the chassis’ cover, plug in the power cord(s), and power on the system.
BMC Firmware update occurs automatically and may take several minutes to complete. When
the BMC Firmware update is complete, it is safe to power off the system.
6. Power off the system, unplug the power cord(s), and remove the chassis’ cover.
7. Remove the BMC Force Update jumper from CN47 pins 1-2. Place it on pins 11-12 of jumper
CN 43 for future use.
8. Replace the chassis’ cover and plug in the power cord(s).
9. Wait 30 seconds after connecting the power cord in order to allow the BMC firmware to load.
10. Power on the system.
Updating the FRU/SDR Files
You can obtain the latest version of the FRU/SDR update files from the Intel Customer Support
website:
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
Making a FRU/SDR File Update Diskette
1. Place a formatted diskette in the diskette drive.
2. Extract the contents of the SHG2 FRU/SDR file onto the diskette.
Making the Update Diskette Bootable
1. Use a DOS or Windows 95 system to create the bootable diskette.
2. Insert a diskette in diskette drive A.
At the C:\ prompt, type:
sys a:
3. Press <Enter>
Updating the FRU/SDR Files
1. Place the diskette containing the FRU/SDR update files into the diskette drive of your system.
Boot the system while the diskette is in the drive.
2. Follow the instructions that appear on the screen.
Configuration Software and Utilities 77
Page 78

Using the Adaptec SCSI Utility
The Adaptec SCSI utility detects the SCSI host adapters on the server board. The utility runs out of
BIOS and is used to:
• Change default values
• Check and/or change SCSI device settings that may conflict with those of other devices in the
server
Running the SCSI Utility
1. When this message appears on the video monitor:
Press Ctrl-A to run SCSI Utility...
2. Press <Ctrl+A> to run this utility. When it appears, choose the host adapter that you want to
configure.
78 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 79

5 Solving Problems
This chapter helps you identify and solve problems that might occur while you are using the
system.
Resetting the System
To do this: Press:
Soft boot reset, which clears system memory and reloads the operating system. <Ctrl+Alt+Del>
Clear system memory, restart POST, and reload the operating system. Reset button
Cold boot reset. Turn the system power off and then on. This clears system memory,
restarts POST, reloads the operating system, and halts power to all peripherals.
Initial System Startup
Problems that occur at initial system startup are usually caused by incorrect installation or
configuration. Hardware failure is a less frequent cause.
Checklist
q Are the power supplies turned on? Check the switches on the back of the chassis.
q Are all cables correctly connected and secured?
q Are the processors fully seated in their slots on the server board?
q Are all add-in PCI boards fully seated in their slots on the server board?
q Are all jumper settings on the server board correct?
q Are all jumper and switch settings on add-in boards and peripheral devices correct? To check
these settings, refer to the manufacturer’s documentation that comes with them. If applicable,
ensure that there are no conflicts—for example, two add-in boards sharing the same interrupt.
q Are all DIMMs installed correctly?
q Are all peripheral devices installed correctly?
q If the system has a hard disk drive, is it properly formatted or configured?
q Are all device drivers properly installed?
q Are the configuration settings made in BIOS Setup correct?
q Is the operating system properly loaded? Refer to the operating system documentation.
q Did you press the system power on/off switch on the front panel to turn the server on (power on
light should be lit)?
q Is the system power cord properly connected to the system and plugged into a
NEMA 5-15R outlet for 100-120 V∼ or a NEMA 6-15R outlet for 200-240 V∼?
q Is AC power available at the wall outlet?
q Are all integrated components from the tested components lists? Check the tested memory, and
chassis lists, as well as the supported hardware and operating system list on the Intel Customer
Support website.
Power off/on
79
Page 80

Running New Application Software
Problems that occur when you run new application software are usually related to the software.
Faulty equipment is much less likely, especially if other software runs correctly.
Checklist
q Does the system meet the minimum hardware requirements for the software? See the software
documentation.
q Is the software an authorized copy? If not, get one; unauthorized copies often do not work.
q If you are running the software from a diskette, is it a good copy?
q If you are running the software from a CD-ROM disk, is the disk scratched or dirty?
q If you are running the software from a hard disk drive, is the software correctly installed? Were
all necessary procedures followed and files installed?
q Are the correct device drivers installed?
q Is the software correctly configured for the system?
q Are you using the software correctly?
If the problems persist, contact the software vendor’s customer service representative.
After the System Has Been Running Correctly
Problems that occur after the system hardware and software have been running correctly may
indicate equipment failure. Many situations that are easy to correct, however, can also cause such
problems.
Checklist
q If you are running the software from a diskette, try a new copy of the software.
q If you are running the software from a CD-ROM disk, try a different disk to see if the problem
occurs on all disks.
q If you are running the software from a hard disk drive, try running it from a diskette. If the
software runs correctly, there may be a problem with the copy on the hard disk drive. Reinstall
the software on the hard disk, and try running it again. Make sure all necessary files are
installed.
q If the problems are intermittent, there may be a loose cable, dirt in the keyboard (if keyboard
input is incorrect), a marginal power supply, or other random component failures.
q If you suspect that a transient voltage spike, power outage, or brownout might have occurred,
reload the software and try running it again. (Symptoms of voltage spikes include a flickering
video display, unexpected system reboots, and the system not responding to user commands.)
NOTE
✏
Random errors in data files: If you are getting random errors in your data
files, they may be getting corrupted by voltage spikes on your power line. If
you are experiencing any of the above symptoms that might indicate voltage
spikes on the power line, you may want to install a surge suppressor between
the power outlet and the system power cord.
80 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 81

More Problem Solving Procedures
This section provides a more detailed approach to identifying a problem and locating its source.
Preparing the System for Diagnostic Testing
CAUTION
Turn off devices before disconnecting cables: Before disconnecting any
peripheral cables from the system, turn off the system and any external
peripheral devices. Failure to do so can cause permanent damage to the
system and/or the peripheral devices.
1. Turn off the system and all external peripheral devices. Disconnect all of them from the
system, except the keyboard and video monitor.
2. Make sure the system power cord is plugged into a properly grounded AC outlet.
3. Make sure your video display monitor and keyboard are correctly connected to the system.
Turn on the video monitor. Set its brightness and contrast controls to at least two thirds of their
maximum ranges (see the documentation supplied with your video display monitor).
4. If the operating system normally loads from the hard disk drive, make sure there is no diskette
in drive A. Otherwise, place a diskette containing the operating system files in drive A.
5. Turn on the system. If the power LED does not light, see “Power Light Does Not Light” on
page 82.
Monitoring POST
The server may start to beep while booting. These beeps identify system events. The following
gives a description of possible beep codes.
Table 6. Beep Codes
Beep Code Description
1 One short beep before boot (this is normal, not an error)
1-2 Search for option ROMs. One long, two short beeps on checksum failure
1-2-2-3 BIOS ROM checksum
1-3-1-1 Test DRAM refresh
1-3-1-3 Test 8742 Keyboard Controller
1-3-3-1 Auto size DRAM, system BIOS stops execution here if the BIOS does not detect any usable
memory DIMMs
1-3-4-1 Base RAM failure; BIOS stops execution here if entire memory is bad
2-1-2-3 Check ROM copyright notice
2-2-3-1 Test for unexpected interrupts
For additional information regarding monitoring POST, see Chapter 4.
Solving Problems 81
Page 82

Verifying Proper Operation of Key System Lights
As POST determines the system configuration, it tests for the presence of each mass storage device
installed in the system. As each device is checked, its activity light should turn on briefly. Check
for the following:
q Does the diskette drive activity light turn on briefly? If not, see “Diskette Drive Activity Light
Does Not Light” on page 84.
q If a second diskette drive is installed, does its activity light turn on briefly? If not, see “Diskette
Drive Activity Light Does Not Light” on page 84.
Confirming Loading of the Operating System
Once the system boots up, the operating system prompt appears on the screen. The prompt varies
according to the operating system. If the operating system prompt does not appear, see “Initial
System Startup” on page 79.
Specific Problems and Corrective Actions
This section provides possible solutions for these specific problems:
• Power light does not light
• There is no beep or an incorrect beep pattern
• No characters appear on screen
• Characters on the screen appear distorted or incorrect
• System cooling fans do not rotate
• Diskette drive activity light does not light
• CD-ROM drive activity light does not light
• There are problems with application software
• The bootable CD-ROM is not detected
Try the solutions in the order given. If you cannot correct the problem, contact your service
representative or authorized dealer for help.
Power Light Does Not Light
Check the following:
q Is the system operating normally? If so, the power LED may be defective or the cable from the
front panel to the server board is loose.
q Are there other problems with the system? If so, check the items listed under “System Cooling
Fans Do Not Rotate Properly”.
If all items are correct and problems persist, contact your service representative or authorized dealer
for help.
82 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 83

No Characters Appear on Screen
Check the following:
q Is the keyboard functioning? Check to see that the “Num Lock” light is functioning.
q Is the video monitor plugged in and turned on?
q Are the brightness and contrast controls on the video monitor properly adjusted?
q Are the video monitor switch settings correct?
q Is the video monitor signal cable properly installed?
q Is the onboard video controller enabled?
If you are using an add-in video controller board, do the following:
1. Verify that the video controller board is fully seated in the server board connector.
2. Reboot the system for changes to take effect.
3. If there are still no characters on the screen after you reboot the system and POST emits a beep
code, write down the beep code you hear. This information is useful for your service
representative.
4. If you do not receive a beep code and characters do not appear, the video display monitor or
video controller may have failed. Contact your service representative or authorized dealer
for help.
Characters Are Distorted or Incorrect
Check the following:
q Are the brightness and contrast controls properly adjusted on the video monitor? See the
manufacturer’s documentation.
q Are the video monitor signal and power cables properly installed?
If the problem persists, the video monitor may be faulty or it may be the incorrect type. Contact
your service representative or authorized dealer for help.
Solving Problems 83
Page 84

System Cooling Fans Do Not Rotate Properly
If the system cooling fans are not operating properly, system components could be damaged.
Check the following:
q Is AC power available at the wall outlet?
q Is the system power cord properly connected to the system and the wall outlet?
q Did you press the power button?
q Is the power on light lit?
q Have any of the fan motors stopped (use the server management subsystem to check the fan
status)?
q Are the fan power connectors properly connected to the server board?
q Is the cable from the front panel board connected to the server board?
q Are the power supply cables properly connected to the server board?
q Are there any shorted wires caused by pinched cables or power connector plugs forced into
power connector sockets the wrong way?
If the switches and connections are correct and AC power is available at the wall outlet, contact
your service representative or authorized dealer for help.
Diskette Drive Activity Light Does Not Light
Check the following:
q Are the diskette drive’s power and signal cables properly installed?
q Are all relevant switches and jumpers on the diskette drive set correctly?
q Is the diskette drive properly configured?
q Is the diskette drive activity light always on? If so, the signal cable may be plugged in
incorrectly.
If you are using the onboard diskette controller, use the Setup Utility to make sure that “Onboard
Floppy” is set to “Enabled”. If you are using an add-in diskette controller, make sure that
“Onboard Floppy” is set to “Disabled”.
If the problem persists, there may be a problem with the diskette drive, server board, or drive signal
cable. Contact your service representative or authorized dealer for help.
Hard Disk Drive Activity Light Does Not Light
The hard disk drive activity light is not connected to the SHG2 server board.
84 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 85

CD-ROM Drive Activity Light Does Not Light
Check the following:
q Are the CD-ROM drive’s power and signal cables properly installed?
q Are all relevant switches and jumpers on the drive set correctly?
q Is the drive properly configured?
q Is the onboard IDE controller enabled?
Cannot Connect to a Server
q Make sure you are using the drivers that are shipped on the system Configuration Software CD
for the onboard network controller.
q Make sure the driver is loaded and the protocols are bound.
q Make sure the network cable is securely attached to the connector at the system back panel. If
the cable is attached but the problem persists, try a different cable.
q Make sure the hub port is configured for the same duplex mode as the network controller.
q Check with your LAN administrator about the correct networking software that needs to be
installed.
q If you are directly connecting two servers (no hub), you will need a crossover cable (see your
hub documentation for more information on crossover cables).
q Check the network controller LEDs that are visible through an opening at the system
back panel.
Problems with Network
The server hangs when the drivers are loaded.
q Change the PCI BIOS interrupt settings. Try the “PCI Installation Tips” below.
Diagnostics pass, but the connection fails.
q Make sure the network cable is securely attached.
q Make sure you specify the correct frame type in your NET.CFG file.
The controller stopped working when an add-in adapter was installed.
q Make sure the cable is connected to the port from the onboard network controller.
q Make sure your PCI BIOS is current. Try the “PCI Installation Tips” below.
q Make sure the other adapter supports shared interrupts. Also, make sure your operating system
supports shared interrupts.
q Try reseating the add in adapter.
The add-in adapter stopped working without apparent cause.
q Try reseating the adapter first; then try a different slot if necessary.
q The network driver files may be corrupt or deleted. Delete and then reinstall the drivers.
q Run the diagnostics.
Solving Problems 85
Page 86

PCI Installation Tips
Some common PCI tips are listed here.
q Certain drivers may require interrupts that are not shared with other PCI drivers. The SSU can
be used to adjust the interrupt numbers for PCI devices. For certain drivers, it may be
necessary to alter settings so that interrupts are not shared.
Problems with Application Software
If you have problems with application software, do the following:
q Verify that the software is properly configured for the system. See the software installation and
operation documentation for instructions on setting up and using the software.
q Try a different copy of the software to see if the problem is with the copy you are using.
q Make sure all cables are installed correctly.
q Verify that the server board jumpers are set correctly. See Chapter 5.
q If other software runs correctly on the system, contact your vendor about the failing software.
If the problem persists, contact the software vendor’s customer service representative for help.
Bootable CD-ROM Is Not Detected
Check the following:
q Is the BIOS set to allow the CD-ROM to be the first bootable device?
86 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 87

6 Getting Help
World Wide Web
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SHG2
Telephone
All calls are billed US $25.00 per incident, levied in local currency at the applicable credit card
exchange rate plus applicable taxes.
In U.S. and Canada 1-800-404-2284
In Europe
UK 0870 6072439
France 01 41 918529
Germany 069 9509 6099
Italy 02 696 33276
Spain 91 377 8166
In Asia-Pacific region
Australia 1800 649931
Hong Kong 852 2 844 4456
Korea 822 767 2595
PRC 800 820 1100
Singapore 65 831-1311
Taiwan 2 2718 9915
India 0006517-2-830 3634
In Japan
0120-868686 (Domestic)
In Latin America
Brazil 0021-0811-408-5540
Mexico 001-800-628-8686
Colombia 980-9-122-118
Costa Rica 0-800-011-0395
Panama 001-800-628-8686
Chile 800-532-992
Miami 1-800-621-8423
Finland 9 693 79297
Denmark 38 487077
Norway 23 1620 50
Sweden 08 445 1251
Holland 020 487 4562
Indonesian 001-803 65 7249
Malaysia 1-800 80 1390
New Zealand 0800 444 365
Pakistan 632 6368415
Philippines 1-800 1 651 0117
Thailand 001-800 6310003
Vietnam 632 6368416
81-298-47-0800 (outside country)
Ecuador 999-119, 800-628-8686 (via AT&T)
Guatemala 99-99-190, 800-628-8686 (via AT&T)
Venezuela 800-11-120, 800-628-8686 (via AT&T)
Argentina 001-800-222-1001, 800-628-8686 (via AT&T)
Paraguay 008-11, 800-628-8686 (via AT&T)
Peru 0-800-50000, 800-628-8686 (via AT&T)
Uruguay 000-410, 800-628-8686 (via AT&T)
87
Page 88

88 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide 89
Page 89

7 Technical Reference
Server Board Jumpers
2
1
4
3
CN53
11
12
12
3
1
3
7109
5
CN43
8
2
4
6
4
CN27
OM14373
Figure 37. Jumper Locations
Table 7. Configuration Jumper (CN43)
Jumper Name Pins What it does at system reset
CMOS clear 1-2 If these pins are jumpered, the CMOS settings will be cleared on the next
reset. These pins should not be jumpered for normal operation.
Password Clear 3-4 If these pins are jumpered, the password will be cleared on the next reset.
These pins should not be jumpered for normal operation.
Reserved 5-6 Reserved. These pins should not be jumpered for normal operation.
Reserved 7-8 Reserved. These pins should not be jumpered for normal operation.
BIOS Recovery 9-10 If these pins are jumpered, the BIOS will attempt a recovery boot, loading
BIOS code from a floppy diskette into the Flash device. This is typically
used when the BIOS code has been corrupted. These pins should not be
jumpered for normal operation.
SPARE 11-12 SPARE jumper.
Page 90

Table 8. Configuration Jumper (CN27)
Jumper Name Pins What it does at system reset
BIOS Write Protect 1-2 If these pins are jumpered, write protect is disabled allowing the BIOS boot
block to be updated. This feature is used in the rare case that a BIOS
update requires a BIOS boot block update as well. These pins should not
be jumpered for normal operation.
BMC Write Protect 3-4 If these pins are jumpered, write protect is disabled allowing the BMC boot
block to be updated. This feature is used in the rare case that a BIOS
update requires a BMC boot block update as well. These pins should not
be jumpered for normal operation.
Table 9. Configuration Jumper (CN53)
Jumper Name Pins What it does at system reset
PCIX1 DIS 1-2 Placing a jumper on pins 1-2 disables the 133 MHz PCI-X mode for the
CIOBX2 primary channel and forces the bus to run 66 MHz PCI. The
primary channel consists of Slot 1, Slot 2 and Gbit.
In the default configuration, pins 1-2 are not jumpered therefore the
primary channel is configured for 133 MHz PCI-X.
PCIX2 DIS
3-4 Placing a jumper on pins 3-4 disables the PCI-X mode for the CIOBX2
secondary channel and forces the bus to run 66 MHz PCI. The secondary
channel consists of Slot 6 and the on-board SCSI.
In the default configuration, pins 3-4 are jumpered therefore the secondary
channel is configured for 66 MHz PCI and on-board SCSI is enabled.
Enabling PCI-X on Slot 6 and Disabling On-board SCSI
NOTE
✏
Enabling the 133 MHz PCI-X on Slot 6 disables the on-board SCSI.
To enable the 133 MHz PCI-X on Slot 6, follow these instructions:
1. Enter BIOS setup.
2. While in BIOS setup, remove the jumper from CN53 pins 3-4.
3. In BIOS setup disable the on-board SCSI.
4. Select Save & Exit BIOS setup.
5. While the system is posting, shutdown the system by pushing the front panel power button.
6. While the system in off, plug a PCI-X card into Slot 6.
7. Push the front panel power button to power up the system.
8. Slot 6 is now 133 MHz PCI-X capable.
90 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 91

8 Regulatory and Integration Information
Product Regulatory Compliance
Product Safety Compliance
The SHG2 complies with the following safety requirements:
• UL 1950 - CSA 950 (US/Canada)
• EN 60 950 (European Union)
• IEC60 950 (International)
• CE – Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC) (European Union)
• EMKO-TSE (74-SEC) 207/94 (Nordics)
• GOST R 50377-92 (Russia)
Product EMC Compliance
The SHG2 has been has been tested and verified to comply with the following electromagnetic
compatibility (EMC) regulations when installed a compatible Intel host system. For information on
compatible host system(s) refer to Intel’s Server Builder website or contact your local Intel
representative.
• FCC (Class A Verification) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (USA)
• ICES-003 (Class A) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Canada)
• CISPR 22, 3
• EN55022 (Class A) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (European Union)
• EN55024 (Immunity) (European Union)
• CE – EMC Directive (89/336/EEC) (European Union)
• VCCI (Class A) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Japan)
• AS/NZS 3548 (Class A) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Australia / New Zealand)
• RRL (Class A) Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Korea)
• BSMI (Class A) Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Taiwan)
• GOST R 29216-91 (Class A) Radiated & Conducted Emissions (Russia)
• GOST R 50628-95 (Immunity) (Russia)
rd
Edition (Class A) – Radiated & Conducted Emissions (International)
91
Page 92

Product Regulatory Compliance Markings
This product is marked with the following Product Certification Markings:
UL Recognition Mark
CE Mark
Russian GOST Mark
Australian C-Tick Mark
BSMI DOC Marking
BSMI EMC Warning
RRL MIC Mark
92 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 93

Electromagnetic Compatibility Notices
FCC (USA)
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
For questions related to the EMC performance of this product, contact:
Intel Corporation
5200 N.E. Elam Young Parkway
Hillsboro, OR 97124
1-800-628-8686
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit other than the one to which the receiver is
connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the grantee of this device could void the
user’s authority to operate the equipment.
the modified product.
Only peripherals (computer input/output devices, terminals, printers, etc.) that comply with
FCC Class A or B limits may be attached to this computer product. Operation with noncompliant
peripherals is likely to result in interference to radio and TV reception.
All cables used to connect to peripherals must be shielded and grounded. Operation with cables,
connected to peripherals, that are not shielded and grounded may result in interference to radio and
TV reception.
The customer is responsible for ensuring compliance of
Regulatory and Integration Information 93
Page 94

INDUSTRY CANADA (ICES-003)
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class A limits for radio noise emissions from digital
apparatus set out in the interference-causing equipment standard entitled: “Digital Apparatus,”
ICES-003 of the Canadian Department of Communications.
Cet appareil numérique respecte les limites bruits radioélectriques applicables aux appareils
numériques de Classe A prescrites dans la norme sur le material brouilleur: “Apparelis
Numériques”, NMB-003 édictee par le Ministre Canadian des Communications.
Europe (CE Declaration of Conformity)
This product has been tested in accordance too, and complies with the Low Voltage Directive
(73/23/EEC) and EMC Directive (89/336/EEC). The product has been marked with the CE Mark
to illustrate its compliance.
Taiwan Declaration of Conformity
This product has been tested and complies with CNS13438. The product has been marked with the
BSMI DOC mark to illustrate compliance.
Korean RRL Compliance
This product has been tested and complies with MIC Notices No. 1997-41 and 1997-42. The
product has been marked with the MIC logo to illustrate compliance.
The English translation for the above is as follows:
1. Type of Equipment (Model Name): SHG2
2. Certification No.: Contact Intel Representative
3. Name of Certification Recipient: Intel
4. Date of Manufacturer: Marked on Product
5. Manufacturer / Nation : Intel
Australia / New Zealand
This product has been tested and complies with AS/NZS 3548. The product has been marked with
the C-Tick mark to illustrate compliance.
94 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 95

9 Equipment Log Worksheet
Equipment Log
Use the blank equipment log provided here to record information about your system. You will
need some of this information when you run the SSU.
Item
System
Server Board
Primary Processor Speed
and Cache
Secondary Processor Speed
and Cache
Video Display
Keyboard
Mouse
Diskette Drive A
Diskette Drive B
Tape Drive
CD-ROM Drive
Hard Disk Drive 1
Hard Disk Drive 2
Hard Disk Drive 3
Hard Disk Drive 4
Hard Disk Drive 5
Manufacturer Name and
Model Number
Serial Number
Date Installed
continued
95
Page 96

Equipment Log (continued)
Item
Manufacturer Name and
Model Number
Serial Number
Date Installed
96 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 97

Index
A
Adapter Fault Tolerance, 15, 16
Adaptive Load Balancing, 15, 16
Add-in boards
add-in board connectors, 13
PCI-X, 13
administrative password, 18
limiting access to SCU, 20
AFT. See Adapter Fault Tolerance
ALB. See Adaptive Load Balancing
audible beep error codes, 56
B
Back Panel Connectors, 10
battery
disposing of safely, 52
installing, 53
removing, 52
beep codes, 56
BIOS
changing the language, 75
recovering, 75
updates, 63
upgrading, 73
boot sequence
booting without keyboard, 20
setting in Setup, 20
bootable media, required by POST, 56
booting cold, 79
booting the server, boot device priority, 60
C
Caution
avoid damaging jumpers when changing,
44
avoid touching processor pins, 45, 52
selecting correct processor, 45, 52
controller, video, 13
CMOS
clear to reconfigure diskette drive, 57
saving and restoring, 64
CN42 pins, 75
configuration, limiting access to system with
administrative password, 20
configuring server board jumpers
location on server board, 87, 89
configuring system
SCU, 55
Setup, 55
Connector, USB, 14
controller
keyboard/mouse, 17
network, 9, 15
SCSI, 14
video, 9
IDE, 14
Memory, 12, 26, 44, 45
D
diagnostics, preparing system for testing, 81
DIMM, 12, 26, 44, 45
diskette
enabling/disabling floppy writes, 19
no booting in secure mode without
password, 19
reconfiguring if cannot enter Setup, 57
running SCU from, 56
E
email alerts, 65
emergency management port, 65, 68
equipment log, 95
ESD
add-in boards, 21, 43
avoiding damage to product, 21, 43
do not touch processor pins, 45, 52
Index 97
Page 98

F
fan, heat sink, disconnecting, 46, 52
Fast EtherChannel, 15
feature summary
back panel connectors, 10
board, 9
FEC. See Fast EtherChannel
field replaceable units, viewing, 62
Firmware Update Utility, 76
firmware updates, 63
form factor, 9
FRUSDR load utility, 55, 69
when to run, 69
G-J
GUI, working with, 59
heat sink, fan, 46, 52
hot key option, quick reference, 55
I/O
PCI expansion slots, 9
ports provided, 9
IDE, feature summary, 13
IDE controller, 14
intrusion detection, 17
jumpers, do not damage when changing, 44
K-L
keyboard
compatibility, 17
lockout timer, seting in SCU, 17
LAN alerts, 66
LAN remote access, 67
language, changing in BIOS, 75
lithium backup battery
disposing of safely, 52
installing, 53
removing, 52
M-N
memory
amount tested, POST, 56
capacity, 9
DIMM requirements, 12, 15, 26, 30, 44,
45, 47, 52
video amount, 9
what type to install, 9
modem remote access, 68
Modular RAID, 14
mouse
compatibility, 17
inactivity timer, 17
network, controller, 9, 15
Network Teaming, 15
P
password, 18, 60
administrative, 18
administrator, 18
entering to unblank screen, 20
user, 18
using to reactivate keyboard/mouse, 20
using to reactivate keyboard/mouse, 17
PCI
embedded devices, 9
expansion slots, 9
platform event management, 65, 67
platform event paging, 65
POST
bootable media required, 56
memory, amount tested, 56
problems
after running new application software, 80
after system has been running correctly,
80
application software, 86
bootable CD-ROM not detected, 86
cannot connect to network server, 84
CD-ROM drive activity light, 84
confirm OS loading, 81
diskette drive light, 84
hard drive light, 84
initial system startup, 79
network, 85
no characters on screen, 82
PCI installation tips, 85
power light, 82
preparing system for diagnostic testing, 81
random error in data files, 80
screen characters incorrect, 83
system cooling fans do not rotate, 83
system lights, 81
98 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
Page 99

processor, 52
adding, 46
removing, 46, 52
selecting the correct processor, 45, 52
wind tunnel installation, 49
R
RAIDIOS, 14
real time clock, running SCU to configure
settings, 53
remote access, 67, 68
reset system, 55, 79
S
SCSI controller, 14
SCU
administrative password limits access to,
20
changing configuration, 55
inactivity (lockout) timer, 17
software locking feature, 18
secure mode, 19
affects boot sequence, 20
enter by setting passwords, 19
no booting from diskette without
password, 19
using hot keys to enter, 55
security, 17, 19
alarm switches, 17
boot sequence, 20
enabling/disabling floppy writes, 19
locking mouse, keyboard with timer, 17,
20
password, 20
secure mode, 19
secure mode, setting in SCU, 19
software lock, SCU, 18
unattended start, 20
using hot key combination, 55
video blanking, 20
security options, setting, 61
sensor data records, viewing, 63
serial remote access, 68
server board
component locations, figure, 11
configurations, 87, 89
server management, intrusion detection, 17
Setup
cannot enter, need to reconfigure diskette,
57
changing configuration, 55
description, 57
recording settings, 57
soft boot, 79
software updates, 63
SSU
Configuration Save/Restore, 64
creating diskettes, 58
customizing the interface, 60
FRU Manager, 62
Multiboot Options, 60
Passwords, 60
Platform Event Manager, 65, 67
running, 59
SDR Manager, 63
SEL Manager, 62
System Update, 63
switches,
alarm, 17
DC power, 79
reset, 79
System Configuration Utility. See SCU
system event log, viewing, 62
T-U
timer
keyboard or mouse inactive, 17
lockout (inactivity), setting in SCU, 17
upgrade Flash utility, 73
user password, 18
limit access to using system, 20
utilities
Firmware update, 76
FRUSDR load, 55
SCSI, 55
SCU, 55
Setup, 55, 57
Utilities, FRUSDR load utility, 69
Index 99
Page 100

V-W
video
blanking for security, 20
memory, 9
video controller, 9, 13
Warning
components may be hot, 45, 52
dispose of lithium battery safely, 52
ESD can damage product, 21, 43
write to diskette, disabling, 19
100 Intel Server Board SHG2 Product Guide
 Loading...
Loading...