Intel SAI2 - Ss3/le Dual Fcpga Max-4GB Atx2pci-64 4pci-32 Vid Lan 133mhz, SAI2 Specification
Page 1

SAI2 Server Board
Technical Product Specification
Revision 1.0
November 2001
Enterprise Platforms and Services Marketing
Page 2

Revision History SAI2 Server Board TPS
Revision History
Date Revision
Number
November 2001 1.0 Initial Release.
Modifications
ii
Revision 1.0
Page 3

SAI2 Server Board TPS Disclaimers
Disclaimers
Information in this document is pr ovided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express
or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual propert y rig ht s is granted by this
document. Except as provided in Intel's Terms and Condit ions of Sale for such products, Intel
assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating t o
sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to fit ness for a particular
purpose, merchantability, or inf ringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property
right. Intel products ar e not intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining
applications. Intel may make changes t o specifications and product descriptions at any time,
without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characterist ics of any features or instructions
marked "reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no
responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
The SAI2 Server Board may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause
the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errat a ar e available
on request.
Intel, Pentium, Itanium , and Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
*Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of ot hers.
Copyright © Intel Corporation 2001.
Revision 1.0
iii
Page 4

Table of Contents SAI2 Server Board TPS
Table of Contents
1. Introduction........................................................................................................................ 1
1.1 Purpose.........................................................................................................................1
1.2 Audience....................................................................................................................... 1
1.3 SAI2 Server Board Feature Overview............................................................................1
1.4 SAI2 Server Board Block Diagram ................................................................................ 2
2. SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview....................................................................... 3
2.1 Intel® Pentium® III Processor Subsystem..................................................................... 3
2.1.1 Supported Processor Types .................................................................................... 3
2.1.2 Dual Processor Operation........................................................................................ 3
2.1.3 PGA370 Socket....................................................................................................... 4
2.1.4 Processor Bus Termination / Regulation / Power..................................................... 4
2.1.5 APIC Bus................................................................................................................. 4
2.1.6 Boxed Processors.................................................................................................... 4
2.2 ServerWorks ServerSet III LE Chipset.......................................................................... 5
2.3 Memory......................................................................................................................... 5
2.4 PCI I/O Subsystem........................................................................................................ 6
2.4.1 64-bit / 66 MHz PCI Subsystem............................................................................... 6
2.4.2 32-bit/33 MHz PCI Subsystem................................................................................. 6
2.5 Chipset Support Components.....................................................................................12
2.5.1 Legacy I/O (Super I/O) National* PC87417............................................................ 12
2.5.2 BIOS Flash............................................................................................................ 13
2.5.3 External Device Connectors................................................................................... 13
2.6 Interrupt Routing ......................................................................................................... 13
2.6.1 Default I/O APIC.................................................................................................... 14
2.6.2 Extended I/O APIC................................................................................................14
2.6.3 PCI IDs.................................................................................................................. 17
2.6.4 Relationship between PCI IRQ and PCI Device..................................................... 17
2.7 ACPI............................................................................................................................18
2.8 AC Link Mode.............................................................................................................. 18
2.9 Wake On LAN Function .............................................................................................. 18
3. Basic Input Output System (BIOS)................................................................................. 19
iv
Revision 1.0
Page 5

SAI2 Server Board TPS Table of Contents
3.1 BIOS Overview............................................................................................................ 19
3.1.1 System BIOS......................................................................................................... 20
3.1.2 Flash Update Utility................................................................................................ 20
3.2 Setup Utility................................................................................................................. 21
3.2.1 Configuration Utilities Overview............................................................................. 21
3.2.2 Setup Utility Operation........................................................................................... 21
3.3 CMOS Memory Definition............................................................................................ 32
3.4 CMOS Default Override...............................................................................................32
3.5 Flash Update Utility..................................................................................................... 33
3.5.1 Loading the System BIOS......................................................................................33
3.5.2 Customization........................................................................................................ 34
3.5.3 Language Area...................................................................................................... 37
3.5.4 Recovery Mode...................................................................................................... 37
3.6 Error Messages and Error Codes................................................................................ 38
3.6.1 POST Codes ......................................................................................................... 38
3.6.2 POST Error Codes and Messages.........................................................................42
3.7 Identifying BIOS Revision Level .................................................................................. 44
3.7.1 BIOS Revision Level Identification......................................................................... 44
4. Jumpers and Connectors................................................................................................ 45
4.1 SAI2 Server Board Jumper and Connector Locations................................................. 45
4.2 Jumper Blocks............................................................................................................. 47
4.2.1 Setting CMOS/Password Clear Jumper Block (JP5) .............................................. 47
4.3 Connectors.................................................................................................................. 49
4.3.1 Main Power Connector (ATX1).............................................................................. 49
4.3.2 I2C Connector (J13)............................................................................................... 49
4.3.3 System Fan Connectors (J8, J11, J7, J14)............................................................ 50
4.3.4 Processor Fan Connectors (J10, J9) ..................................................................... 50
4.3.5 HDD LED (J12)...................................................................................................... 50
4.3.6 Diskette Drive Connector (FDD) ............................................................................ 51
4.3.7 SVGA Video Port (VGA1)...................................................................................... 51
4.3.8 Keyboard (KB) and Mouse (MS) Connectors......................................................... 52
4.3.9 Parallel Port (LPT1)............................................................................................... 52
4.3.10 Serial Ports COM1 and COM2............................................................................. 52
4.3.11 RJ-45 LAN Connector (J2)................................................................................... 53
Revision 1.0
v
Page 6

Table of Contents SAI2 Server Board TPS
4.3.12 USB Connectors (J2)........................................................................................... 53
4.3.13 IDE Connectors (PRI_IDE, SEC_IDE) ................................................................. 53
4.3.14 32-Bit PCI Connectors.........................................................................................54
4.3.15 64-Bit PCI Connectors.........................................................................................55
4.3.16 Front Panel 24-pin Connector Pinout (FRONT_PANEL_HDR)............................. 56
5. Hardware Monitoring....................................................................................................... 57
6. Baseboard Specifications............................................................................................... 59
6.1 Estimated Baseboard MTBF....................................................................................... 59
6.2 Absolute Maximum Ratings......................................................................................... 60
6.3 Calculated Power Consumption .................................................................................. 60
6.4 Measured Power Consumption ................................................................................... 61
7. Regulatory and Integration Information......................................................................... 62
7.1 Regulatory Compliance............................................................................................... 62
7.2 Installation Instructions ................................................................................................ 63
7.2.1 Ensure EMC.......................................................................................................... 63
7.2.2 Ensure Host Computer and Accessory Module Certifications................................ 63
7.2.3 Prevent Power Supply Overload............................................................................ 64
7.2.4 Place Battery Marking on Computer...................................................................... 64
7.2.5 Use Only for Intended Applications........................................................................ 65
7.2.6 Installation Precautions.......................................................................................... 65
Glossary..................................................................................................................................... I
Reference Documents ............................................................................................................ III
Index.........................................................................................................................................IV
vi
Revision 1.0
Page 7

SAI2 Server Board TPS List of Figures
List of Figures
Figure 1. SAI2 Server Board Block Diagram.............................................................................. 2
Figure 2. Embedded NIC PCI Signals........................................................................................ 7
Figure 3. Video Controller PCI Signals....................................................................................... 9
Figure 4. SAI2 Baseboard Interrupt Routing Diagram (PIC Mode)........................................... 15
Figure 5. SAI2 Baseboard Interrupt Routing Diagram (Symmetric Mode) ................................ 16
Figure 6. SAI2 Server Board Jumper and Connector Locations............................................... 45
Figure 7. I/O Back Panel Connectors....................................................................................... 46
Revision 1.0
vii
Page 8

List of Tables SAI2 Server Board TPS
List of Tables
Table 1. SAI2 Server Board Supported Processors ................................................................... 3
Table 2. Video Controller Supported PCI Commands ................................................................ 9
Table 3. Standard VGA Modes.................................................................................................10
Table 4. SAI2 PCI IDs.............................................................................................................. 17
Table 5. SAI2 Relationship between PCI IRQ and PCI Device................................................. 17
Table 6. Setup Utility Screen.................................................................................................... 21
Table 7. Main Menu Selections................................................................................................ 23
Table 8. Primary/Secondary Master and Slave Adapters Submenu Selections........................ 24
Table 9. Advanced Menu Selections........................................................................................ 25
Table 10. Advanced Submenu Selections................................................................................ 25
Table 11. Memory Reconfiguration Submenu Selections......................................................... 26
Table 12. CPU Reconfiguration Submenu Selections .............................................................. 26
Table 13. Peripheral Configuration Submenu Selections ......................................................... 27
Table 14. PCI Device Submenu Selections.............................................................................. 28
Table 15. Option ROM Submenu Selections............................................................................ 28
Table 16. Numlock Submenu Selections.................................................................................. 29
Table 17. Security Menu Selections......................................................................................... 29
Table 18. Secure Mode Submenu Selections........................................................................... 30
Table 19. Server Menu Selections............................................................................................ 30
Table 20. Wake On Events Submenu Selections..................................................................... 31
Table 21. Boot Device Priority Selections................................................................................. 31
Table 22. Hard Drive Selections............................................................................................... 31
Table 23. Removable Devices Selections................................................................................ 32
Table 24. Exit Menu Selections................................................................................................ 32
Table 25. User Binary Area Scan Point Definitions...................................................................36
Table 26. Format of the User Binary Information Structure...................................................... 36
Table 27. Port-80h Code Definition.......................................................................................... 38
Table 28. Standard BIOS Port-80 Codes................................................................................. 38
Table 29. Recovery BIOS Port-80 Codes................................................................................. 41
Table 30. POST Error Messages and Codes........................................................................... 42
Table 31. POST Error Conditions and Beep Codes ................................................................. 43
viii
Revision 1.0
Page 9

SAI2 Server Board TPS List of Tables
Table 32. Jumper Block JP5 Settings....................................................................................... 47
Table 33. Main Power Connector Pinout.................................................................................. 49
Table 34. I2C Connector Pinout................................................................................................ 49
Table 35. Board Fan Connector Pinout.................................................................................... 50
Table 36. Processor Fan Connector Pinout.............................................................................. 50
Table 37. HDD LED Pinout....................................................................................................... 50
Table 38. Diskette Drive Connector Pinout............................................................................... 51
Table 39. Video Port Connector Pinout.................................................................................... 51
Table 40. Keyboard and Mouse Connector Pinout................................................................... 52
Table 41. Parallel Port Connector Pinout ................................................................................. 52
Table 42. Serial Ports COM1 and COM2 Connector Pinouts................................................... 52
Table 43. RJ-45 LAN Connector Signals.................................................................................. 53
Table 44. USB Connectors....................................................................................................... 53
Table 45. IDE Connector Pinout............................................................................................... 53
Table 46. 32-Bit PCI Connector Pinout.....................................................................................54
Table 47. 64-Bit PCI Connctor Pinout.......................................................................................55
Table 48. Front Panel 24-pin Connector Pinout........................................................................56
Table 49. Estimated MTBF Calculated Numbers for SAI2/SC5100.......................................... 59
Table 50. Absolute Maximum Ratings...................................................................................... 60
Table 51. SAI2 Server Board Calculated Power Consumption................................................. 60
Table 52. SAI2 Server Board Measured Power Consumption.................................................. 61
Table 53. Safety Regulations................................................................................................... 62
Table 54. EMC Regulations...................................................................................................... 62
Revision 1.0
ix
Page 10

List of Tables SAI2 Server Board TPS
< This page intentionally left blank. >
x
Revision 1.0
Page 11

SAI2 Server Board TPS Introduction
1. Introduction
1.1 Purpose
This document provides an architectural overview of the SAI2 server boar d, including the board
layout of major components and connectors, and an overview of the server boar d’s feature set.
1.2 Audience
This document for technical per sonnel who want a technical overview of the SAI2 server board.
Familiarity with the personal computer, Intel server ar chitecture and the Peripheral Component
Interconnect (PCI) local bus architecture is assumed.
1.3 SAI2 Server Board Feature Overview
The SAI2 server board provides the following f eat ur es:
• Dual Intel® Pentium® III processor support
- Support for one or two identical Intel Pentium III processors for the PGA370 socket,
which utilizes the Flip Chip Pin Grid Array (FC-PGA) pack age
- Two embedded Voltage Regulating Modules (VRM) for suppor t of both primary and
secondary processors
• ServerWorks* ServerSet* III LE chipset
- 133-MHz Front Side Bus (FSB) Capability
- CNB30LE North Bridge
- CSB5 South Bridge
• Support for four 3.3-V, registered ECC SDRAM DIMMs that are compliant with the
JEDEC PC133 specification
- Support for DIMM sizes 64 MB to 1 GB. Four DIMM slots allow a maxiumum
installed memory of 4 GB
- ECC single-bit correction, and m ultiple-bit detection
• 64-bit, 66-MHz, 3.3-V keyed PCI segment with two expansion connectors
- Two 64-bit, 66-MHz, 3.3-V keyed PCI expansion slots
• 32-bit, 33-MHz, 5-V keyed PCI segment with four expansion connector s and t hr ee
embedded devices
- Four 32-bit, 33-MHz, 5-V keyed PCI expansion slots
- CSB5 South Bridge, which provides Integrated Device Electronics (IDE) and
Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller functions
- Integrated on-board Intel® EtherExpress™ PRO100+ 10/100 meg abit PCI Ethernet
controller (Intel® 82559) with an RJ-45 Ethernet connect or
- Integrated on-board AT I* Rage XL video controller with 8 MB of on-board VRAM
video memory
Revision 1.0
1
Page 12
Introduction SAI2 Server Board TPS
• Compatibility bus segment with two embedded devices
- Super I/O Controller (PC87417) that provides all PC-compatible I/O (floppy, parallel,
serial, keyboard, mouse, and Real-Tim e Clock)
- 4 megabit Flash device for system BIOS
• Dual Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports
• Two IDE connectors
• Flash BIOS support for all of the above
• ATX board form factor
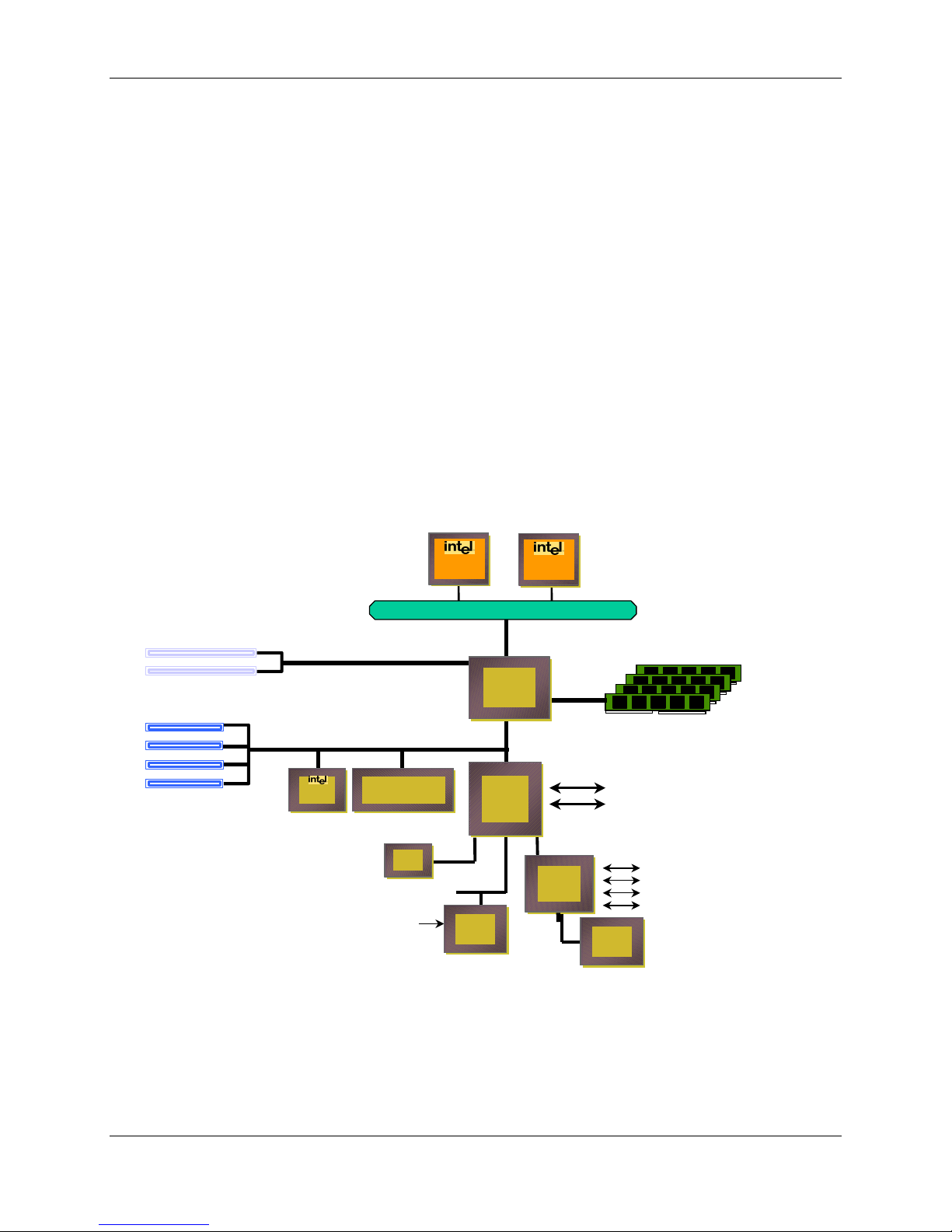
1.4 SAI2 Server Board Block Diagram
The SAI2 server board off er s a “ flat” design, with the processors and mem or y subsystems
residing on the board. The following figure shows the major funct ional blocks of the SAI2 server
board. The following section describes the major components of the server board.
SAI2 Server Board Block Diagram
SAI2 Server Board Block Diagram
2x 64bit/66MHz PCI Slots
4x 32bi t/33MHz PCI Slot s
8255982559
10/100 NIC
PCI (64/66)
PCI (32/33)
ATI RAGE* XL
ATI RAGE* XL
8MB RAM
8MB RAM
Flash
Flash
BIOS
BIOS
Temp
Voltage
FAN
FCPGA
FCPGA
Tualatin
Tualatin
FCPGA
FCPGA
Tualatin
Tualatin
133MHz System Bus
MCH
LE-T
CSB5
LPC
Super
SM-BUS
HW
HW
Monitor
Monitor
Super
I/O
I/O
X-BUS
Up to 4GB ECC Memory (4 DIMMs)
PC133 Buffered SDRAM
2x IDE (Ultra -ATA/100)
2x USB
Floppy
Keyboard, Mouse
Serial Ports
Parallel Port
NvRAM
NvRAM
(32KB)
(32KB)
Figure 1. SAI2 Server Board Block Diagram
2
Revision 1.0
Page 13
SAI2 Server Board TPS SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview
2. SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview
The architecture of the SAI2 server board is based on a design that supports dual-processor
operation with Intel Pentium III processors and the ServerWorks ServerSet III LE chipset.
The SAI2 server contains embedded devices for video, Network I nt erface Card (NIC), and IDE.
The SAI2 server board also provides support for basic monitoring hardware, and interrupt
control that supports dual-processor and PC/ AT compatible operation.
The section provides an overview of the following SAI2 subsystems:
• Pentium III processor subsystem
• SeverWorks* ServerSet* III LE chipset
• Memory
• PCI subsystem
• Chipset support components
2.1 Intel® Pentium® III Processor Subsystem
The SAI2 server board is designed to accommodate one or two Intel Pentium III processors for
the PGA370 socket. The Pentium III processor for the PGA370 socket uses the same core and
offers the same performance as the Intel Pentium III processor for the SC242 connector, but
utilizes a FC-PGA. This package utilizes the sam e 370- pin zero- inser t ion force socket
(PGA370) used by the Intel® Celeron™ processor.
2.1.1 Supported Processor Types
The table below summarizes the processors that are planned f or the SAI2 server board:
Table 1. SAI2 Server Board Supported Processors
Speed FSB Frequency Cache Size
1.00 GHz 133 MHz 256K
1.13 GHz 133 MHz 512K
1.26 GHz 133 MHz 512K
2.1.2 Dual Processor Operation
The Pentium III processor interface is designed to be multi-processor ready. Each processor
contains a local Intel
handling. W hen two processors are installed, both processors must be of identical revision,
core voltage, and bus/core speeds.
®
Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller (APIC) section f or interrupt
Revision 1.0
3
Page 14

SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview SAI2 Server Board TPS
2.1.3 PGA370 Socket
The SAI2 server board provides two PGA370 sockets. These ar e 370- pin zero- insertion force
(ZIF) sockets into which a FC-PGA package t echnology processor plugs.
2.1.4 Processor Bus Termination / Regulation / Power
The termination circuitry required by the Intel Pentium III processor bus signaling environment,
and the circuitry to set the AGTL/ AGTL+ reference voltage, ar e im plem ented directly on the
processor. The SAI2 server board provides VRM 8.5 compliant DC-t o- DC convert ers to provide
processor power, Voltage Controlled Current Plane ( VCCP) , at each PGA370 socket. The
server board provides embedded VRMs for both the primary and secondary processors.
Additional termination is provided on the SAI2 server board f or terminator-less operation when
only one processor is installed.
2.1.5 APIC Bus
Interrupt notificat ion and generation for the processors is done using an independent path
between local APICs in each processor and the I/O APIC located in the CSB5 South Bridge
component.
2.1.6 Boxed Processors
The Intel Pentium III processor for the PGA370 socket is offered as an Intel boxed processor.
Intel boxed processors are intended for system integrators who build systems from a server
board and standard components.
2.1.6.1 Boxed Processor Fan Heatsinks
The boxed Pentium III processor for the PGA370 socket will be supplied with an unattached fan
heatsink that has an integrat ed clip. Clearance is required around the fan heat sink to ensure
unimpeded airflow for proper cooling . Note that the airflow of t he fan heatsink is into the center
and out of the sides of the fan heatsink. The boxed processor therm al solut ion m ust be installed
by a system integrator to secure the ther mal cooling solution to the processor aft er it is installed
in the 370-pin ZIF socket.
The boxed processor’s fan heatsink req uires a +12-V power supply. A fan power cable is
attached to the fan and connects to pr ocessor fan headers on the SAI2 server board.
The boxed processor fan heatsink will keep the pr ocessor cor e at the recommended junction
temperature, as long as airflow through the fan heatsink is unimpeded. It is recommended that
the air temperature entering the fan inlet be below 45 °C (measured at 0.3 inches above the fan
hub).
4
Revision 1.0
Page 15

SAI2 Server Board TPS SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview
2.2 ServerWorks ServerSet III LE Chipset
The ServerWorks ServerSet III LE chipset provides an integrated I/O bridge and memory
controller and a flexible I/O subsystem core (PCI), targeted for multiprocessor systems and
standard high-volume servers that are based on the Intel Pentium III processor. The
ServerWorks ServerSet III LE chipset consists of two components:
• CNB30LE North Bridge
The CNB30LE North Bridge is responsible f or accepting access requests fr om the host
(processor) bus and for directing those accesses to memory or to one of the PCI buses.
The CNB30LE North Bridge monitor s t he host bus, examining addresses for each
request. Accesses may be directed to a memory req uest queue for subsequent
forwarding to the memory subsystem, or t o an outbound request queue for subsequent
forwarding to one of the PCI buses.
The CNB30LE North Bridge is responsible for controlling data transfers to and from the
memory. The CNB30LE North Bridg e pr ovides the int erface for both the 64-b it , 66-MHz,
Revision 2.2-compliant PCI bus and the 32-bit, 33-MHz, Revision 2.2-compliant PCI bus.
The CNB30LE North Bridge is both a mast er and target on both PCI buses.
• CSB5 South Bridge
The CSB5 South Bridge controller has several component s. It can be both a master and
a target on the 32-bit, 33- MHz PCI bus. The CSB5 Sout h Bridge also includes a USB
controller and an IDE controller. T he CSB5 South Bridge is responsible for many of the
power management functions, with Advanced Config ur ation and Power Interface (ACPI)
control registers built in. The CSB5 South Bridge provides a number of In finiband pins.
2.3 Memory
The SAI2 server board contains four 168- pin DI MM sockets. Memory is partitioned as four
banks of registered SDRAM DIMMs, each of which provides 72 bits of single interleaved
memory (64-bit main memory plus ECC).
The SAI2 server board supports up to four 3.3-V, registered ECC SDRAM DIMMs that are
compliant with the JEDEC PC133 specification. A wide range of DIMM sizes are supported,
including 64 MB, 128 MB, 256 MB, 512 MB, and 1-GB DIMMs. The minimum supported
memory configuration is 64 MB using one DIMM. The maximum configurable memory size is
4 GB using four DIMMs.
Note: Neither PC100 DIMMs nor non-ECC DIMMs can be used.
DIMMs may be installed in one, two, three, or four DIMM slots and must be populated starting
with the lowest numbered slot and filling the slots in consecutive order . Em pty memory slots
between DIMMs are not supported. Although the SAI2 server board architect u r e allows the user
to mix various sizes of DIMMS, Intel recommends that module and DRAM vendors not be
mixed in the same server system.
Revision 1.0
5
Page 16

SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview SAI2 Server Board TPS
System memory begins at address 0 and is continuous (f lat addressing) up to the maximum
amount of DRAM installed (exception: system memory is noncontiguous in the ranges defined
as memory holes using configuration r egisters). The server board supports bot h base
(conventional) and extended memory.
2.4 PCI I/O Subsystem
The expansion capabilities of the SAI2 server board meet t he needs of file and application
servers for high performance I/O by providing two PCI bus segments in the form of one 64-bit /
66-MHz bus segment and one 32-bit / 33-MHz bus segment. Each of the PCI buses comply
with Revision 2.2 of the PCI Local Bus Specification.
2.4.1 64-bit / 66 MHz PCI Subsystem
The 64-bit, 66-MHz, 3.3-V keyed PCI segm ent includes two 64-bit, 66-MHz, 3.3-V keyed PCI
expansion slots that can support 66-MHz, 64/32-bit cards or 33-MHz, 64/32-bit cards.
64-bit PCI features include:
• Bus speed up to 66 MHz
• 3.3-V signaling environment
• Burst transfers up to a peak of 528 MB per second (MBps)
• 8-, 16-, 32-, or 64-bit dat a t ransfers
• Plug-and-Play ready
• Parity enabled
2.4.2 32-bit/33 MHz PCI Subsystem
The 32-bit, 33-MHz, 5-V keyed PCI includes the following embedded devices and connector s :
• Four 32-bit, 33-MHz, 5-V keyed PCI expansion slots
• Integrated Intel
(Intel® 82559)
• Integrated ATI Rage* XL video controller with 8 MB of on-board SGRAM
• CSB5 South Bridge I/O APIC, PCI-to- Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) bridge, IDE
controller, USB controller, and power management.
32-bit PCI features include:
• Bus speed up to 33 MHz
• 5-V signaling environment
• Burst transfers up to a peak of 132 MBps
• 8-, 16-, or 32-bit data tr ansfers
• Plug-and-Play ready
• Parity enabled
®
EtherExpress™ PRO100+ 10/100 megabit PCI Ethernet controller
6
Revision 1.0
Page 17
SAI2 Server Board TPS SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview
2.4.2.1 Network Interface Controll er ( NI C)
The SAI2 server board includes a 10Base-T / 100Base-TX network controller that is based on
the Intel
predecessor (Intel
®
82559 Fast Ethernet PCI Bus Controller. This device is similar in architecture to its
®
82558). No external devices are required to implement an embedded
network subsystem, other than TX / RX magnetics, two status Light Emit ting Diodes (LEDs), and
a connector.
Status LEDs are included on the external NIC connector. The SAI2 server board provides the
ability to disable the embedded NIC in the BIOS Setup opt ion. When disabled it is not visible to
the operating system.
The 82559 is a highly integrated PCI Local Ar ea Net work (LAN) controller for 10 or 100 Mbps
Fast Ethernet networks. As a PCI bus master , the 82559 can burst data at up to 132 MBps.
This high-perform ance bus master interface can eliminate t he int ermediate copy step in RX/TX
frame copies, resulting in faster frame processing.
The network operating system communicates with the 82559 using a memory-mapped I/O
interface, PCI interr upt connected directly to the CSB5, and two large receive and transm it
FIFOs. The receive and transmit FIFO s pr event dat a overr uns or under runs while waiting for
access to the PCI bus, and also enable back-to-back frame transmission within the minimum
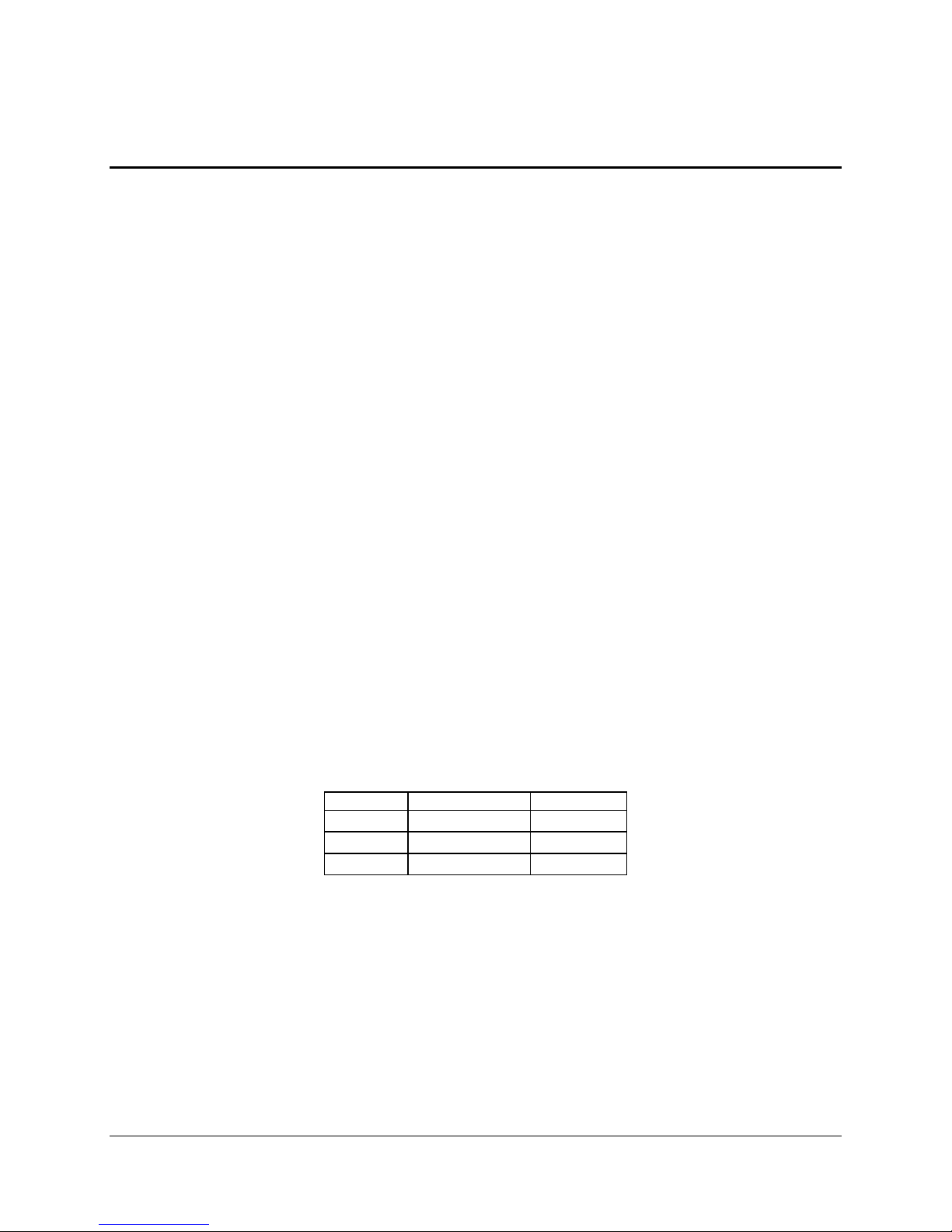
960ns inter-frame spacing. The figure below shows the PCI signals supported by the 82559:
AD[31::0]
C/BE[3::0]_L
PAR
FRAME_L
TRDY_L
IRDY_L
STOP_L
i82559 NIC
DEVSEL_L
IDSEL
REQ_L
GNT_L
PCI_CLK
RST_L
PERR_L
SERR_L
PCI_INT_L
Revision 1.0
Figure 2. Embedded NIC PCI Signals
7
Page 18

SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview SAI2 Server Board TPS
2.4.2.1.1 Supported Network Features
The 82559 contains an IEEE MII compliant interf ace t o the components necessary to
implement an IEEE 802.3 100Base TX net work connect ion. The SAI2 supports the following
features of the 82559 cont r oller :
• Glueless 32-bit PCI Bus Master Interf ace ( Dir ect Drive of Bus), compatible with PCI Bus
Specification, revision 2.1 / 2.2
• Chained memory structure, with improved dynamic transmit chaining for enhanced
performance
• Programmable transmit t h r eshold for improved bus utilization
• Early receive interrupt for concurrent processing of receive data
• On-chip counters for network management
• Autodetect and autoswitching for 10 or 100 Mbps network speeds
• Support for both 10 Mbps and 100 Mbps networks, full or half duplex-capable, with
back-to-back transmit at 100 Mbps
• Integrated physical interface to TX magnetics
• The magnetics component term inat es t he 100Base- TX connector interface. A flash
device stores the network ID.
• Support for Wake-on-LAN (WOL)
2.4.2.2 Video Controller
The SAI2 server board includes an ATI Rage XL video controller, 8 MB video SDRAM, and
support circuitry for an embedded SVG A video subsystem. The Rage XL, 64-bit VGA Gr aphics
Accelerator contains a SVGA video controller, clock generator, BitBLT engine, and RAMDAC.
One 2M x 32 SDRAM chip provides 8 MB of 7ns video memory.
The SVGA subsystem supports a variety of modes: up to 1600 X 1200 resolution for CRT
displays and up to 1024 X 768 resolution for TFT displays, and up to 16.7 million colors. It also
supports analog VGA monitors, single- and multi-freq uency, int er laced and non- int er laced, up
to 100 Hz vertical refresh frequency. The SAI2 server board provides a standard 15-pin VGA
connector.
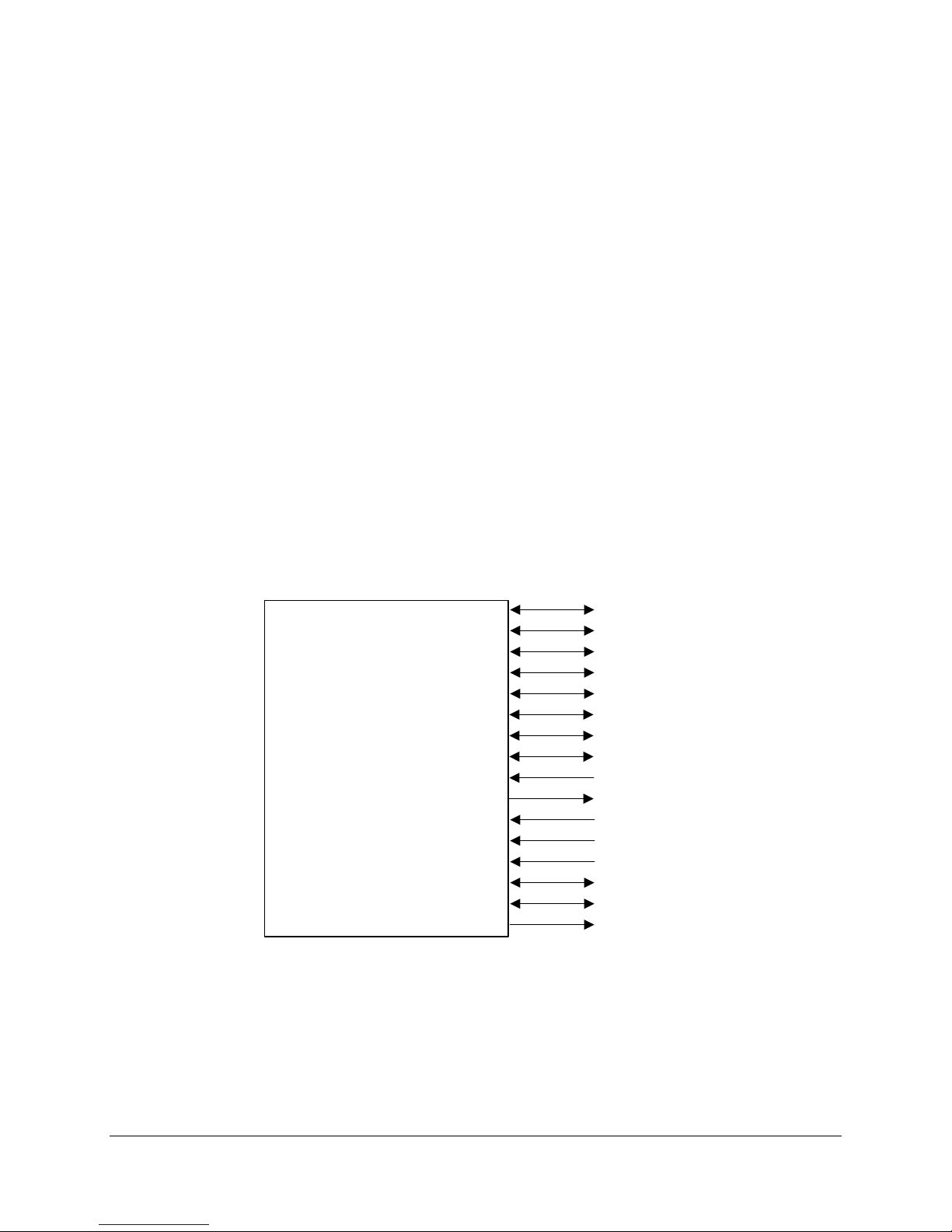
2.4.2.2.1 Video Controller PCI Signals
The Rage XL supports a minimal set of 32-bit PCI signals because it never acts as a PCI
master. As a PCI slave, the device requires no arbitration or interrupts.
8
Revision 1.0
Page 19
SAI2 Server Board TPS SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview
AD[3 1::0 ]
C/BE [ 3::0]_L
PAR
FRAME_L
TRDY_L
IRD Y _ L
STOP_L
Rage XL
DEVSEL_L
IDSEL
Figure 3. Video Controller PCI Signals
2.4.2.2.2 Video Controller PCI Commands
The Rage XL supports the following PCI commands:
Table 2. Video Controller Supported PCI Commands
Rage XL Support
C/BE[3::0]_L Command Type Target Master
0000 Interrupt Acknowledge No No
0001 Special Cycle No No
0010 I/O Read Yes No
0011 I/O Write Yes No
0100 Reserved No No
0101 Reserved No No
0110 Memory Read Yes No
0111 Memory Write Yes No
1000 Reserved No No
1001 Reserved No No
1010 Configuration Read Yes No
1011 Configuration Write Yes No
1100 Memory Read Multiple No No
1101 Dual Address Cycle No No
1110 Memory Read Line No No
1111 Memory Write and Invalidate No No
PCI_CLK
RST_L
PERR_L
SERR_L
PCI_ INT _L
Revision 1.0
9
Page 20

SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview SAI2 Server Board TPS
2.4.2.2.3 Video Modes
The Rage XL supports all standard IBM* VGA modes. The following tables show the standard
resolutions that this implementation suppor ts, including the number of color s and t he refresh rate.
Table 3. Standard VGA Modes
Resolution Refresh Rate (Hz) Colors
640x480 100 256
800x600 100 256
1024x768 100 256
1280x1024 72 256
1600x1200 85 256
640x480 100 65K
800x600 100 65K
1024x768 100 65K
640x480 100 16.7 M
800x600 100 16.7 M
2.4.2.3 CSB5 South Bridge
The CSB5 South Bridge is a PCI device that provides mult iple PCI functions in a single
package: PCI-to- ISA bridge, PCI IDE interface, PCI USB controller, and power managem ent
controller. Each function within the CSB5 South Br idge has its own set of configuration
registers. Once configured, each appears to the system as a distinct hardware controller
sharing the same PCI bus interface.
On the SAI2 baseboard, the primar y role of the CSB5 South Bridge is to provide the g ateway to
all PC-compatible I/O devices and features. The SAI2 server board uses the following CSB5
South Bridge features:
• PCI interface
• IDE interface
• USB interface
• PC-compatible timer/counters and Dir ect Memory Access (DMA) controllers
• Baseboard Plug-and-Play support
• General purpose I/O
• Power management
• APIC and 82C59 interrupt controller
• Host interface for AT compatible signaling
• Internal only ISA bus (no ISA expansion connectors) bridge for communication with
Super I/O, and BIOS flash
The following sections describe each supported f eature as used on the SAI2 server board.
10
Revision 1.0
Page 21

SAI2 Server Board TPS SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview
2.4.2.3.1 PCI Interface
The CSB5 South Bridge fully implements a 32-bit PCI master/slave interface, in accordance
with Revision 2.2 of the PCI Local Bus Specification. On the SAI 2 ser ver boar d, the PCI
interface operates at 33 MHz, using the 5V-signaling environment.
2.4.2.3.2 PCI Bus Master IDE Interface
The CSB5 South Bridge acts as a PCI-based enhanced IDE 32-bit interface controller for
intelligent disk drives that have disk cont r oller electronics on-board. The server board includes
two IDE connectors, each featuring 40 pins ( 2 x 20) t hat suppor t a master and a slave device.
The IDE controller provides support for an internally mounted CD-ROM.
The IDE controller has the following features:
• Programmed Input/Output (PIO) and DMA transfer modes
• Up to PIO Mode 4 , DMA Mode 4, and Ultra DMA Mode 5 timings
• Transfer rates up to 100 MBps
• Buffering for PCI/IDE burst transfers
• Master/slave IDE mode
• Support for up to two devices per channel
2.4.2.3.3 USB Interface
The CSB5 South Bridge contains a USB controller and USB hub. The USB controller moves
data between main memory and the two USB connectors provided.
The SAI2 server board provides a dual external USB connector interface. Both ports function
identically and with the same bandwidth. The external connector is defined by Revision 1.0 of
the USB Specification.
2.4.2.4 Compatibility Interrupt Control
The CSB5 South Bridge provides the functionality of two 82C59 Programmable Interrupt
Controller (PIC) devices, for I SA- compatible interrupt handling.
2.4.2.5 APIC
The CSB5 South Bridge integrates a 16-entry I/O APIC that is used to distribute 16 PCI interrupts.
It also includes an additional 16-entry I/O APIC for distribution of legacy ISA interrupts.
2.4.2.6 Power Management
One of the embedded funct ions of CSB5 South Bridge is a power management contr oller. The
SAI2 server board uses this to implement ACPI-compliant power management feat ur es. SAI2
supports sleep states s0, s1, s4, and s5.
Revision 1.0
11
Page 22

SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview SAI2 Server Board TPS
2.5 Chi pset Suppor t Components
2.5.1 Legacy I/O (Super I/O) National* PC87417
The National* PC87417 Super I/O Plug-and-Play Compatible with ACPI-Compliant
Controller/Extender is used on the SAI2 server board. This device provides the system with:
• Real-time Clock (RTC)
• Two serial ports
• One parallel port
• Floppy disk controller (FDC)
• PS/2-compatible keyboard and mouse controller
• General purpose I/O pins
• Plug-and-Play functions
• A power management controller
The SAI2 server board provides the connector interface for the floppy, dual serial por t s , par allel
port, PS/2 mouse and the PS/2 keyboard. Upon reset, the Super I/O (SIO) reads the values on
strapping pins to determine the boot- up addr ess configuration.
2.5.1.1 Serial Ports
Two 9-pin connectors in D-Sub housing are provided for ser ial por t 1 and serial port 2. Both
ports are compatible with 16550A and 16450 modes, and both are re-locat able. Each serial port
can be set to one of four different COM-x ports, and each can be enabled separately. When
enabled, each port can be programmed t o generate edge- or level-sensitive interrupts. When
disabled, serial port interrupts are available to add-in car ds.
2.5.1.2 Parallel Port
The SAI2 baseboard provides a 25-pin parallel port connector . The SIO provides an IEEE
1284-compliant 25-pin bi-directional parallel port . BIOS programming of the SIO registers
enables the parallel port and determines the port addr ess and int errupt. W hen disabled, the
interrupt is available to add-in cards.
2.5.1.3 Floppy Port
The FDC in the SIO is functionally compat ible with floppy disk controllers CMOS 765B and
82077AA. The baseboard provides the 24-MHz clock, termination resist ors, and chip selects. All
other FDC functions are integrated into the SIO, including analog data separator and 16-byte
FIFO.
2.5.1.4 Keyboard and Mouse Connectors
The keyboard controller is functionally compatible with the 8042A. The keyboard and mouse
connectors are PS/2-compatible.
12
Revision 1.0
Page 23

SAI2 Server Board TPS SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview
2.5.1.5 Real-time Clock
The PC87417 contains an MC146818-compatible real-time clock with external bat t er y back up.
The device also contains 242 bytes of general purpose batt er y-backed CMOS RAM. The realtime clock provides system clock and calendar information stored in non-volatile memory.
2.5.1.6 Plug-and-Play Functions / ISA Data Transfers
The PC87417 contains all signals for I SA com pat ible interrupts and DMA channels. This ISA
subsystem transfers all SIO peripheral control data to the CSB5 South Bridge as well via the
LPC bus interface. The SIO also suppor t s an X-Bus interface that provides control, data and
address signals to and from t he RAS NVRAM device.
2.5.1.7 Power Management Controller
The PC87417 component contains functionality that allows various events to allow the poweron and power-off of the system. This can be from PCI Power Management Events or the front
panel. This circuitry is powered from stand- by voltage, which is present anytime the system is
plugged into the AC outlet.
2.5.2 BIOS Flash
The SAI2 baseboard incorporates an SST39SF040 Flash RO M component. The SST39SF040
is a high-performance 4 m egabit memory organized as 512K x8 bits in128 4-KB blocks.
The 8-bit flash memory provides 512K x 8 of BIOS and nonvolatile storage space. The flash
device is directly addressed as 8-bit ISA memory and accessed through the CSB5 X-Bus
interface.
2.5.3 External Device Connectors
The external I/O connectors provide support for a PS/2 compatible mouse and keyboard, an
SVGA monitor, two serial port connector s, a parallel port connector, a LAN port, and two USB
connections.
2.6 Interrupt Routing
The SAI2 server board interrupt architecture implements two I/O APICs and two PICs through
the use of the integrat ed com ponents in the CSB5 South Bridge component. The SAI2 server
board interrupt architecture allows first and second PCI interrupts to be mapped t o com patible
interrupts through the PCI Interrupt Address Index Register (I/O Address 0C00h) in the CSB5
South Bridge.
The CSB5 South Bridge uses integr at ed logic to map 16 PCI interrupts to EI SA/ISA. In default
or Extended APIC configurations, each PCI interrupt can be independently routed to one of t he
11 EISA interrupts. The interrupt mapping logic for PCI interrupts is disabled when the make bit
in the corresponding I/O APIC redirection table entry is disabled (clear). This interrupt routing
mechanism allows a clean transition from PIC mode to an APIC during operating system boot.
Revision 1.0
13
Page 24

SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview SAI2 Server Board TPS
2.6.1 Default I/O APIC
The CSB5 South Bridge integrates a 16-entry I/O APIC which is used to distribute 16 PCI
interrupts.
2.6.2 Extended I/O APIC
An additional 16-entry I/O APIC is integrated in the CSB5 South Bridge to distribute EISA/ISA
interrupts. This additional I/O APIC is enabled only when the CSB5 South Bridge is configured
to the Extended APIC configuration.
14
Revision 1.0
Page 25
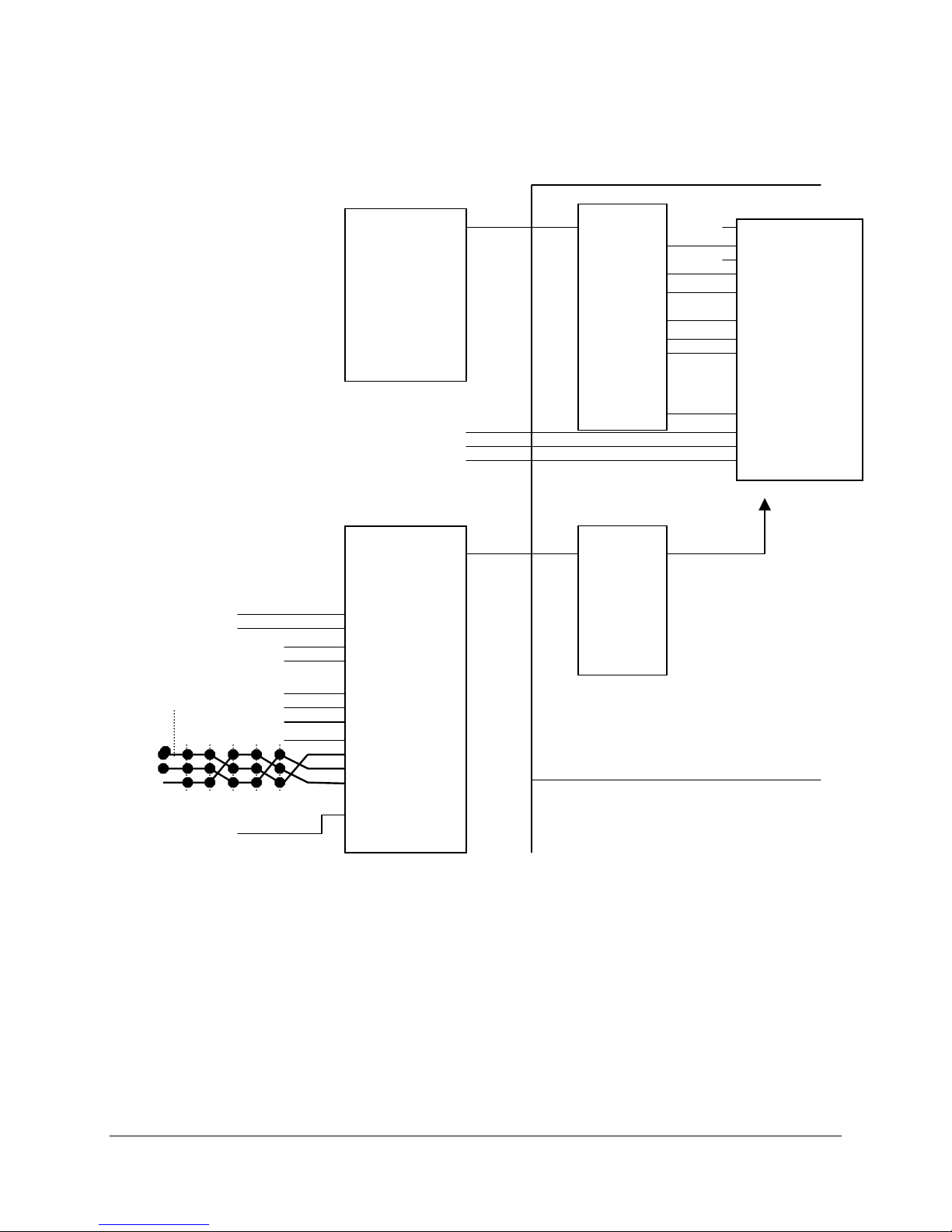
SAI2 Server Board TPS SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview
A
CSB5
PC87417
(Super-I/O)
FERR#
IDE #0
IDE #1
Keyboard
Serial Port2
Serial Port1
FDD
Parallel Port
RTC
Mouse
IRQ 0
IRQ 1
IRQ 2
IRQ 3
IRQ 4
IRQ 5
IRQ 6
IRQ 7
IRQ #8
IRQ 9
IRQ 10
IRQ 11
IRQ 12
IRQ 13 (FERR#)
IRQ 14
IRQ 15
SCAN PIRQ
PCI IRQ to
PIRQ 0
PIRQ 1
LAN
VGA
PCI 3 INT A
PCI 4 INT A
PCI 2 INT A
PCI 5 INT A
PCI 6 INT A
B
PCI 1 INT
C
D
PCI1
PCI3
PCI4
SCI
*1 setting by CSB5 I/O Address C00h Interrupts Address Index Register and I/O
Address C01h Interrupt Redirection
PCI5
PCI6+
PIRQ 2
PIRQ 3
PIRQ 4
PIRQ 5
PIRQ 6
PIRQ 7
PIRQ 8
PIRQ 9
PIRQ 10
PIRQ 11
PIRQ 12
PIRQ 13
PIRQ 14
PIRQ 15
*1
IRQ
Figure 4. SAI2 Baseboard Interrupt Routing Diagram (PIC Mode)
Revision 1.0
15
Page 26

SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview SAI2 Server Board TPS
r
The SAI2 system interrupt rout ing is as follows:
CSB5
Keyboard
Serial Port2
Serial Port1
FDD
Parallel Port
RTC
Mouse
FERRL#
IDE #0
IDE #1
LAN
VGA
PCI 3 INT A
PCI 4 INT A
PCI 2 INT A
PCI 5 INT A
PCI 6 INT A
PCI 1 INT A
PCI 1 PCI 2 PCI 3 PCI 4 PCI 5 PCI 6
Time
Cascade
IRQ 0
IRQ 1
IRQ 2
IRQ 3
IRQ 4
IRQ 5
IRQ 6
IRQ 7
IRQ #8
IRQ 9
IRQ 10
IRQ 11
IRQ 12
IRQ 13 (FERR#)
IRQ 14
IRQ 15
PIRQ0 (16)
PIRQ1 (17)
PIRQ2 (18)
PIRQ3 (19)
PIRQ4 (20)
PIRQ5 (21)
PIRQ6 (22)
PIRQ7 (23)
PIRQ8 (24)
PIRQ9 (25)
PIRQ10 (26)
PIRQ11 (27)
PIRQ12 (28)
PIRQ13 (29)
PIRQ14 (30)
PIRQ15 (31)
SCI
Figure 5. SAI2 Baseboard Interrupt Routing Diagram (Symmetric Mode)
16
Revision 1.0
Page 27

SAI2 Server Board TPS SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview
2.6.3 PCI IDs
The SAI2 server board PCI IDs are def ined as follows:
Table 4. SAI2 PCI IDs
Device Bus Number [23:16] Device Number [15:11] Slot ID Signal
CNB30LE 00h 0000 0b
ATI* Rage XL 00h 0001 0b P32_AD18
Intel 82559 00h 0001 1b P32_AD19
PCI Slot 1 (32bit) 00h 0011 0b P32_AD22
PCI Slot 2 (32bit) 00h 0011 1b P32_AD23
PCI Slot 5 (32bit) 00h 0100 0b P32_AD24
PCI Slot 6 (32bit) 00h 0100 1b P32_AD25
CSB5 00h 0111 1b
PCI Slot 3 (64bit) 01h 0101 0b P64_AD26
PCI Slot 4 (64bit) 01h 0101 1b P64_AD27
Note: Do not change the BUSNUM register (Offset 44h) in the CNB30LE North Bridge from the default
value.
2.6.4 Relationship between PCI IRQ and PCI Device
The relationship between PCI IRQ and PCI devices are defined as follows on the SAI2 server
board:
Table 5. SAI2 Relationship between PCI IRQ and PCI De vice
PCI IRQ PCI Device
PCI IRQ 0
PCI IRQ 1
PCI IRQ 2 Intel 82559
PCI IRQ 3 ATI Rage XL
PCI IRQ 4 PCI Slot 3 (INTA)
PCI IRQ 5 PCI Slot 4 (INTA)
PCI IRQ 6
PCI IRQ 7 PCI Slot 2 (INTA)
PCI IRQ 8 PCI Slot 5 (INTA)
PCI IRQ 9 PCI Slot 6 (INTA)
PCI IRQ 10 PCI Slot 1 (INTA)
PCI IRQ 11 PCI Slot 1 (INTB), PCI Slot 2 (INTB), PCI Slot 3 (INTB), PCI Slot 4 (INTC), PCI Slot 5 (INTC), PCI
Slot 6 (INTD)
PCI IRQ 12 PCI Slot 1 (INTC), PCI Slot 2 (INTC), PCI Slot 3 (INTC), PCI Slot 4 (INTD), PCI Slot 5 (INTD), PCI
Slot 6 (INTB)
PCI IRQ 13 PCI Slot 1 (INTD), PCI Slot 2 (INTD), PCI Slot 3 (INTD), PCI Slot 4 (INTB), PCI Slot 5 (INTB), PCI
Slot 6 (INTC)
Revision 1.0
17
Page 28

SAI2 Server Board Architecture Overview SAI2 Server Board TPS
2.7 ACPI
The Advance Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)-aware operating system can place the
system into a state where the hard drives spin down, the system fans stop, and all pr ocessing is
halted. In this state the power supply is still on and the processors still dissipate some power,
such that the power supply fan and processor fans are st ill r unning.
Note: ACPI requires an operating system that supports this feature.
The ACPI sleep states discussed below are defined as:
• s0: Normal running state.
• s1: Processor sleep state. No content is lost in t his st ate and the processor caches
maintain coherency.
• s4: Hibernate or Save to Disk. The mem ory and machine state are saved to disk.
Pressing the power button or another wakeup event restores t he system st at e from the
disk and resumes normal operation. T his assum es that no hardware changes were
made to the system while it was off.
• s5: Soft off. Only the RTC section of the chip set is r unning in this state.
The SAI2 server board supports sleep states s0, s1, s4, and s5. When the ser ver boar d is
operating in ACPI mode, the operat ing system retains control of the system and the OS policy
determines the entry methods and wake up sources for each sleep st at e – sleep entry and
wake up event capabilities are provided by the hardware but are enabled by the OS.
With future versions of Microsoft* Windows* 9X that support ACPI, the system BI OS supports
only sleep states s0, s1 and s5.
2.8 AC Link Mode
The AC link mode allows the system to monitor it s AC input power so that if AC input power is
lost and then restored, the system retur ns t o one of the following pre-selected settings:
• Power On
• Last State (Factory Default Set ting)
• Stay Off
The AC link mode settings can be chang ed by running the BIOS Setup Utility.
2.9 Wake On LAN Function
The remote power-on function turns on t he system power through a network or modem. If the
system power is set to Off, it can be turned on remotely by sending a specific packet from the
main computer to the remote system.
Note: The standard default value of the remote power-on function is “Disabled”. The Wake-onLAN / Ring function can changed by setting the option to “Enabled” in the BIOS Setup Utility.
18
Revision 1.0
Page 29

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
3. Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
This section describes BIOS embedded soft ware for the SAI2 board set. The BIO S cont ains
standard PC-compatible basic input/output (I/O) services, standard Intel
®
server features, plus
the SAI2 system-specific hardware configuration routines and register default settings,
embedded in Flash read-only memory (ROM). This section also describes BIO S suppor t utilities
(not ROM-resident) that are required for system config ur ation and flash ROM update.
The BIOS is implemented as f irmware that resides in the flash ROM. Support f or applicable
baseboard peripheral devices (SCSI, NIC, and video adapters), which is also loaded into the
baseboard flash ROM, is not specified in this document . Hooks are provided to support adding
BIOS code for these adapters; t he binar ies m ust be obtained from the peripheral device
manufacturers and loaded into the appr opriate locations.
3.1 BIOS Overview
The term BIOS, as used in the context of this section, refers t o t he system BI O S, the BIOS
Setup and option ROMs for on-board peripheral devices that ar e contained in the system flash.
System BIOS controls basic system functionality using st or ed configuration values. The terms
flash ROM, system flash, and BIOS f lash m ay be used inter c hangeably in this section.
The term BIOS Setup refers to the flash ROM-resident set up ut ility that provides the user with
control of config ur at ion values stor ed in battery-backed CMOS configuration RAM. The System
Setup Utility (SSU), which also provides this functionality, is discussed in a separate document.
BIOS Setup is closely tied with the system BIOS and is considered a part of BI O S.
Phoenix* Phlash (PHLASH.EXE) is used to load predefined areas of flash ROM with Setup,
BIOS, and other code/data.
The following is the break-down of the SAI2 product ID string:
• 4-byte board ID, ‘SAI2’
• 1-byte board revision, starting fr om ‘0’
• 3-byte OEM ID, ‘86B’ for standard BIOS
• 4-byte build number
• 1-3 byte describing build type (D for development, A for Alpha, B for Beta, Pxx for
production version xx)
• 6-byte build date in yymmdd format
• 4-bytes time in hhmm format
Revision 1.0
19
Page 30

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
3.1.1 System BIOS
The system BIOS is the core of the flash ROM-resident portion of the BIOS. The system BIOS
provides standard PC-BIOS services and support for some new industry standards, such as the
Advanced Configuration and Power Interf ace Specif ication, Revision 1.0 and Wired For
Management Baseline Specification, Revision 2.0. In addition, the system BI OS supports
certain features that ar e com m on acr oss all the Intel servers. These include:
• Security
• Intel Multi-Processor Specification ( MPS) support
• Server management and error handling
• CMOS configuration RAM management
• OEM customization
• PCI and Plug and Play (PnP) BIOS interface
• Console redirection
• Resource allocation support
BIOS setup is embedded in flash ROM and provides the means to conf igure on-board hardware
devices and add-in cards. For more information, refer to Section 3.2, Set up Utility.
3.1.2 Flash Update Utility
The system BIOS and the setup utility are resident in partitioned flash ROM. The device is incircuit reprogrammable. On the SAI2 platform, 1 MB of flash ROM is provided. The Phoenix
Phlash Utility may be used to reprogram the BI OS operational code located in the flash ROM. A
BIOS image is provided on a diskette in t he form of a binary file t hat is r ead by the Phoenix
Phlash Utility. Baseboard revisions may create hardware incompatibilities and may req u ir e
different BIO S code.
3.1.2.1 System Flash ROM Layout
The flash ROM contains system initialization routines, BIOS strings, BIOS Setup, and run- time
support routines. The exact layout is subject to change, as determined by Intel. A 16-KB user
block is available for user ROM code and another 128-KB block is available for custom logos.
The flash ROM also contains compressed initialization code for on-board peripherals such as
SCSI, NIC, and video controllers. The BIOS image contains all the BIOS component s at
appropriate locations. The Phoenix Phlash Utility can be used to reprogram the BIOS
operational code areas.
At run time, none of the flash blocks are visible at the aliased addresses below 1 MB due to
shadowing. Intel reserves the right to chang e the flash map without notice.
A 64-KB parameter block in the flash ROM is dedicated to storing configur ation data that
controls extended system configuration dat a ( ESCD), OEM configuration areas, etc. The block
is partitioned into separate areas for logically different data. Application software must use
standard advanced programmable interrupts ( API s) to access these areas and may not access
the data directly.
20
Revision 1.0
Page 31

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
3.2 Setup Utility
This section describes the ROM resident setup utility that provides the means to configure the
platform. The set up utility is part of the system BIOS and allows limited cont r ol over on- boar d
resources such as the parallel port and mouse. The following topics are covered below:
• Setup utility operation
• Configuration CMOS RAM definition
• Function of the CMOS clear jumper
3.2.1 Configuration Utilities Overview
Configuration of on-board devices is done using the setup utility that is embedded in f lash
ROM. Setup provides sufficient configuration functionality to boot a system disk ette or
CD-ROM. The System Setup Utility, which is discussed in a separate document, is r eleased on
diskette or CD-ROM. Setup is always provided in flash for basic system configuration.
The configuration ut ilit ies modify CMOS RAM and Non-Volatile Random Access Memory
(NVRAM) under direction of the user. The BIOS POST routines and the BIO S Plug-N-Play
Auto-configuration Manager accomplish the actual hardware configuration. The configuration
utilities always update a checksum for both areas, so that any potential data corruption is
detectable by the BIOS before the hardware configuration takes place. If data is corrupted, the
BIOS requests that the user r econfigure the system and reboot.
3.2.2 Setup Utility Operation
The ROM-resident setup utility config ur es only on-boar d devices. The setup utility screen is
divided into four functional areas. T he t able below describes each area:
Table 6. Setup Utility Screen
Functional Area Description
Keyboard Command Bar Located at the bottom of the screen. This bar displays the keyboard commands
supported by the setup utility.
Menu Selection Bar Located at the top of the screen. Displays the various major menu selections
available to the user. The server setup utility major menus are: Main Menu, Advanced
Menu, Security Menu, System Menu, Boot Menu, and the Exit Menu.
Options Menu Each Option Menu occupies the left and center sections of the screen. Each menu
contains a set of features. Selecting certain features within a major Option Menu
drops you into submenus.
Item Specific Help Screen Located at the right side of the screen is an item-specific Help screen.
3.2.2.1 Entering Setup Utility
During POST operation, the user is prompted to enter Setup using the F2 function key as
follows:
Press <F2> to enter Setup
Revision 1.0
21
Page 32

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
y
After the F2 key is pressed, a few seconds might pass before Setup is entered while POST
finishes test and initialization functions t hat m ust be completed before Setup can be entered.
When Setup is ent er ed, the Main Menu options page is displayed.
3.2.2.2 Keyboard Command Bar
The bottom portion of t he scr een provides a list of commands that are used f or navigating the
Setup utility. These commands are displayed at all times, for every menu and submenu.
Each Setup menu page contains a number of features. Except those used for informative
purposes, each feature is associated with a value field. T his field contains user-selectable
parameters. Depending on the security option chosen and in effect via password, a menu
feature’s value can be changeable or not. If a value is cannot be changed due to insufficient
security privileges or other reasons, the feature’s value field is inaccessible. The Keyboard
Command Bar supports the following:
F1 Help
Enter Execute Command
ESC Exit
↑↑↑↑
↓↓↓↓
←←←← →→→→
F5/– Change Value
F6/+ Change Value
F9 Setup Defaults
Select Item
Select Item
Select Menu
Pressing F1 on any menu invokes the general Help window. This window
describes the Setup key legend. The up arrow, down arrow, Page Up, Page Down,
Home, and End keys scroll the text in this window.
The Enter key is used to activate submenus when the selected feature is a
submenu, or to display a pick list if a selected feature has a value field, or to select
a subfield for multi-valued features like time and date. If a pick list is displayed, the
Enter key will undo the pick list, and allow another selection in the parent menu.
The ESC key provides a mechanism for backing out of any field. This key will undo
the pressing of the Enter key. When the ESC key is pressed while editing any field
or selecting features of a menu, the parent menu is re-entered. When the ESC key
is pressed in any submenu, the parent menu is re-entered. When the ESC key is
pressed in any major menu, the exit confirmation window is displayed and the user
is asked whether changes can be discarded.
The up arrow is used to select the previous value in a pick list, or the previous
feature in a menu item’s option list. The selected item must then be activated by
pressing the Enter key.
The down arrow is used to select the next value in a menu item’s option list, or a
value field’s pick list. The selected item must then be activated by pressing the
Enter key.
The left and right arrow keys are used to move between the major menu pages.
The keys have no affect if a submenu or pick list is displayed.
The minus key and the F5 function key are used to change the value of the current
item to the previous value. These keys scroll through the values in the associated
pick list without displaying the full list.
The plus key and the F6 function key are used to change the value of the current
menu item to the next value. These keys scrolls through the values in the
associated pick list without displaying the full list. On 106-key Japanese
keyboards, the plus key has a different scan code than the plus key on the other
keyboard, but it still has the same effect.
Pressing the F9 key causes the following to appear:
Setup Confirmation
Load default configuration now?
[Yes] [No]
If “Yes” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, all Setup fields are set to their
default values. If “No” is selected and the Enter ke
is pressed, or if the ESC key is
22
Revision 1.0
Page 33

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
pressed, the user is returned to where s/he was before the F9 key was pressed,
without affecting any existing values.
F10 Save and Exit
Pressing F10 causes the following message to appear:
Setup Confirmation
Save Configuration changes and exit now?
[Yes] [NO]
If “Yes” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, all changes are saved and Setup
is exited. If “No” is selected and the Enter key is pressed, or the ESC key is
pressed, the user is returned to where s/he was before the F10 key was pressed,
without affecting any existing values.
3.2.2.3 Menu Selection Bar
The Menu Selection Bar is located at the top of the scr een. It displays the various major menu
selections available to the user:
• Main Menu
• Advanced Menu
• Security Menu
• System Menu
• Boot Menu
• Exit Menu
These and associated submenus are described below.
3.2.2.4 Main Menu Selections
The following tables describe the available functions on t he Main Menu, and associated
submenus. Default values are highlighted.
Table 7. Main Menu Selections
Feature Choices or Display
Only
Processor Type Display only Indicates the processor(s) type installed.
Processor Speed Display only Indicates the processor(s) speed.
Cache RAM Display only Indicates the cache RAM size.
System Memory Display only Indicates the total capacity of the basic memory.
Extended Memory Display only Indicates the total capacity of the extended memory.
Language
System Time HH:MM:SS Sets the system time (hour, minutes, seconds, on 24
English (US)
French
German
Spanish
Italian
Selects which language BIOS displays.
Note: This feature immediately changes to the language
BIOS selected.
hour clock).
Description User
Setting
Revision 1.0
23
Page 34

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
Feature Choices or Display
Only
Syste m Date MM/DD/ YYYY Se ts the system date (month, day, year).
Diskette A Not Installed
1.2 MB 5 ¼”
1.44 / 1.25 MB 3.5"
2.88 MB 3.5”
Diskette B
Hard Disk Pre-Delay
Primary Master Displays IDE device selection. Enters submenu if
Primary Slave Displays IDE device selection. Enters submenu if
Secondary Master Displays IDE device selection. Enters submenu if
Secondary Slave Displays IDE device selection. Enters submenu if
Disabled
1.2 MB 5 ¼”
1.44 / 1.25 MB 3.5"
2.88 MB 3.5”
Disabled
3 Seconds
6 Seconds
9 Seconds
12 Seconds
15 Seconds
21 Seconds
30 Seconds
Selects the diskette type.
Note: 1.25-MB, 3.5-inch references a 1024-byte/sector
Japanese media format. To support this type of media
format requires a 3.5-inch, 3-mode diskette drive.
Selects the diskette type.
Note: 1.25-MB, 3.5-inch references a 1024-byte/sector
Japanese media format. To support this type of media
format requires a 3.5-inch, 3-mode diskette drive.
Delays first access to disk to ensure the disk is
initialized by the BIOS before any accesses.
selected.
selected.
selected.
selected.
Description User
Setting
Table 8. Primary/Secondary Master and Slave Adapters Submenu Selections
Feature Choices or Display Only Description User
Setting
Type
Mult-Sector Transfers
LBA Mode Control
24
Revision 1.0
Auto
None
CD-ROM
ATAPI Removable
IDE Removable
Other ATAPI
User
Disable
2 Sectors
4 Sectors
8 Sectors
16 Sectors
Disabled
Enabled
Select the type of device that is attached to the IDE
channel
If User is selected, the user will need to enter the
parameters of the IDE device (cylinders, heads and
sectors).
Specifies the number of sectors that are transferred
per block during multiple sector transfers.
Enable/Disable Logical Block Addressing instead of
cylinder, head, sector addressing.
Page 35

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
Feature Choices or Display Only Description User
Setting
32 Bit I/O
Transfer Mode
Ultra DMA Mode Disabled
Disabled
Enabled
Standard
Fast PIO 1
Fast PIO 2
Fast PIO 3
Fast PIO 4
FPIO 3/ DMA 1
FPIO 4 / DMA 2
Enabled
Enable/Disable 32-Bit IDE data transfers
Select the method of moving data to and from the hard
drive. (If Type: Auto is select, optimum transfer mode
will be selected)
Enable/Disable Ultra DMA mode (If Type: Auto is
select, optimum transfer mode will be selected)
3.2.2.5 Advanced Menu Selections
The following tables describe the menu options and associat ed subm enus available on the
Advanced Menu. Please note that MPS 1.4 / 1.1 selection is no longer configurable. The BIOS
will always build MPS 1.4 tables.
Table 9. Advanced Menu Selections
Feature Choices or Display
Only
Advanced Refer to Advanced Submenu.
Memory Reconfiguration Refer to Memory Reconfiguration Submenu.
CPU Reconfiguration Refer to CPU Reconfiguration Submenu.
Peripheral Configuration Refer to Peripheral Reconfiguration Submenu.
PCI Device Refer to PCI Device Submenu.
Option ROM Refer to Option ROM Submenu. It Disables/Enables
the Option ROM BIOS on the PCI Bus.
Numlock Refer to Numlock Submenu.
Description User
Table 10. Advanced Submenu Selections
Feature Choices or Display
Installed OS
Reset Configuration Data
Boot-time Diagnostic Screen Enabled
POST Error Pause Enabled
Other
PnP OS
No
Yes
Disabled
Disabled
Only
Selects the type of operating system that will be
used most.
Clears the Extended System Configuration Data if
selected.
Enable/Disable boot-time diagnostic screen. Splash
screen is displayed over the diagnostic screen
when is option is Disabled.
Pauses and displays SETUP entry or resume boot
prompt if error occurs on boot. If disabled, system
always attempts to boot.
Description User
Setting
Setting
Revision 1.0
25
Page 36

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
Table 11. Memory Reconfiguration Submenu Selections
Feature Choices or Display Only Description User
Setting
DIMM Group #1 Status Display only:
Normal
None
Error (DIMM Row Error)
DIMM Group #2 Status Display only:
Normal
None
Error (DIMM Row Error)
DIMM Group #3 Status Display only:
Normal
None
Error (DIMM Row Error)
DIMM Group #4 Status Display only:
Normal
None
Error (DIMM Row Error)
Clears DIMM Errors Press Enter Clears the DIMM group error status information.
DIMM Error Pause Enabled
Disabled
If enabled, the POST operation pauses if a DIMM error
occurs.
Table 12. CPU Reconfiguration Submenu Selections
Feature Choices or Display
Only
CPU #1 Status Display only:
Normal
None
Error (CPU Error)
CPU #2 Status Display only:
Normal
None
Error (CPU Error)
Clear CPU Errors Press Enter Clears CPU error status information.
CPU Error Pause Enabled
Disabled
If enabled, the POST operation pauses if a CPU error occurs.
Description User
Setting
26
Revision 1.0
Page 37

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
Table 13. Peripheral Configuration Submenu Selections
Feature Choices or
Display Only
Serial Port 1: (COM 1) Disabled
3F8, IRQ3
3F8, IRQ4
2F8, IRQ3
2F8, IRQ4
3E8, IRQ3
3E8, IRQ4
2E8, IRQ3
2E8, IRQ4
Auto
Serial Port 2: (COM 2) Disabled
3F8, IRQ3
3F8, IRQ4
2F8, IRQ3
2F8, IRQ4
3E8, IRQ3
3E8, IRQ4
2E8, IRQ3
2E8, IRQ4
Auto
Parallel Port Disabled
378, IRQ5
378, IRQ7
278, IRQ5
278, IRQ7
3BC, IRQ5
3BC, IRQ7
Auto
Parallel Mode Output only
Bi-directional
EPP
ECP, DMA1
ECP, DMA3
Diskette Controller Disabled
Enabled
Mouse Disabled
Enabled
Auto Detect
LAN Controller Disabled
Enabled
VGA Controller Disabled
Enabled
Disables serial port 1 or selects the base address and
interrupt (IRQ) for serial port 1.
Disables serial port 2 or selects the base address and
interrupt (IRQ) for serial port 2.
Disables the parallel port or selects the base address and
interrupt (IRQ) for the Parallel port.
Selects the parallel port operation mode.
Disables/Enables the floppy disk controller.
Disabled prevents any installed PS/2 mouse from
functioning, but frees up IRQ12.
Enabled forces the PS/2 mouse port to be enabled
regardless if a mouse is present.
Auto Detect enables the PS/2 mouse only if present.
Disables/Enables on-board LAN controller.
Disables/Enables on-board Video controller.
Description User
Setting
Revision 1.0
27
Page 38

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
Feature Choices or
Display Only
USB Controller Disabled
Enabled
IDE Controller Disabled
Primary
Secondary
Both
Feature Choices or Display
PCI IRQ1 through PCI
IRQ14
Disabled
Auto Select
IRQ3
IRQ4
IRQ5
IRQ6
IRQ7
IRQ9
IRQ10
IRQ11
IRQ12
Description User
Enables/Disables on-board USB controller.
Enables the integrated local bus IDE adapter.
Table 14. PCI Device Submenu Selections
Description User
Only
Specify which PIC IRQ a certain PCI IRQ maps to.
Setting
Setting
Table 15. Option ROM Submenu Selections
Feature Choices or Display
Only
Onboard LAN
PCI Slot 1
PCI Slot 2
PCI Slot 3
PCI Slot 4
PCI Slot 5
PCI Slot 6
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Disables/Enables option ROM expansion for the on-board LAN
option ROM.
Disables/Enables the expansion of the option ROM for devices in
PCI slot 1
Disables/Enables the expansion of the option ROM for devices in
PCI slot 2
Disables/Enables the expansion of the option ROM for devices in
PCI slot 3
Disables/Enables the expansion of the option ROM for devices in
PCI slot 4
Disables/Enables the expansion of the option ROM for devices in
PCI slot 5
Disables/Enables the expansion of the option ROM for devices in
PCI slot 6
Description User
Setting
28
Revision 1.0
Page 39

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
Table 16. Numlock Submenu Selections
Feature Choices or
Display Only
Numlock Auto
On
Off
Key Click
Keyboard Auto-repeat Rate 2-second
Keyboard Auto-repeat Delay 0.25-second
Disabled
Enabled
6-second
10-second
13.3-second
18.5-second
21.8-second
26.7-second
30-second
0.5-second
0.75-second
1-second
Selects the power-on state for Numlock.
Disables or enables keyclick.
Selects key repeat rate.
Selects delay before key repeat.
3.2.2.6 Security Menu Selections
Description User
Setting
Table 17. Security Menu Selections
Feature Choices or Display
Only
Supervisor Password is Display only:
Clear
User Password is Display only:
Clear
Set Supervisor Password Press Enter Supervisor password controls access to the setup
Set User Password Press Enter When the <Enter> key is pressed, the user is
Password on Boot
Diskette Access
Disabled
Enabled
Everyone
Supervisor
Once set, this can be disabled by setting it to a null
string, or by clearing password jumper on system
board.
Once set, this can be disabled by setting it to a null
string, or by clearing password jumper on system
board
utility.
When the <Enter> key is pressed, the user is
prompted for a password; press ESC key to abort.
Once set, this can be disabled by setting it to a null
string, or by clearing password jumper on system
board.
prompted for a password; press ESC key to abort.
Once set, this can be disabled by setting it to a null
string, or by clearing password jumper on system
board.
Disables or enables password entry on boot.
Controls access to diskette drives.
Description User
Setting
Revision 1.0
29
Page 40

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
Floppy Write Protect
Fixed Disk Boot Sector
Secure Mode See the Secure Mode Submenu below. Submenu
Power Switch Mask Masked
Processor Serial Number
Disabled
Enabled
Normal
Write Protect
Unmasked
Disabled
Enabled
Write protects Floppy drive.
Write protects boot sector on hard disk.
can only be entered if supervisor and user password
is set.
Determines whether power switch will function from
front panel.
Determines whether the processor serial number
feature is enabled or disabled.
Table 18. Secure Mode Submenu Selections
Feature Choices or Display
Secure Mode Timer
Secure Mode HotKey
Secure Mode Boot
Disabled
1 minute
2 minutes
5 minutes
10 minutes
30 minutes
1 hour
2 hours
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Enabled
Only
Period of keyboard and mouse inactivity before secure
mode is activated and a password is required gain
access.
Enables/Disables the ability to lock the system with a
<CTRL>+<ALT> + <key> combination. The key can be
selected and submenu appears when enabled. A
password is required to gain access.
Enables/Disables secure boot. The system will boot as
normal, but a password is required to access the system
using any PS/2 device.
Description User
Setting
3.2.2.7 System Hardware Menu Selections
Feature Choices or Display
Wake On Events See Wake On Events submenu.
AC Link Power On
Last State
Stay Off
Error Log Initialization
30
Revision 1.0
No
Yes
Table 19. Server Menu Selections
Only
Selects power retention mode if AC power is lost a
regained.
Select to clear the system Error Log.
If Clear OK, then display “System Event Log Cleared!”
If Clear failed, then display “System Event Log Not
Cleared!”
Description User
Setting
Page 41

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
Feature Choices or Display
Assert NMI on PERR
Disabled
Enabled
Only
Enables PCI PERR support.
Description User
Setting
Table 20. Wake On Events Submenu Selections
Feature Choices or Display
Wake On LAN Enabled
Disabled
Wake On Ring Enabled
Disabled
Console Connection
Direct
Via Modem
Only
Enables/Disables Wake-on-LAN support.
Enables/Disables Wake-on-Ring support.
Indicate whether the console is connected directly to the
system or if a modem is used to connect.
Description User
Setting
3.2.2.8 Boot Menu Selections
Boot Menu options allow the user to select the boot device. The following table is an example of
a list of devices ordered in priority of the boot invocation. Items can be re-prioritized by using
the up and down arrow keys to select the device. Once the device is selected, use the plus (+)
key to move the device higher in the boot priority list. Use the minus (-) key to move the device
lower in the boot priority list.
Table 21. Boot Device Priority Selections
Device Description User Setting
ATAPI CD-ROM Drive Attempts to boot from an ATAPI CD-ROM drive.
Removable Devices Attempts to boot from a removable device.
Hard Drive Attempts to boot from a hard drive device.
Intel® Boot Agent Version 4.0.17 Attempts to boot from a PXE server.
Table 22. Hard Drive Selections
Boot Priority Device Description User Setting
1
2
3
4 Bootable Add-in Cards
Note:
1. These selections will change depending on the system configuration
AIC-7899,CH B ID 1 1
AIC-7899 CH A, ID 9 1
AIC-7899 CH B, ID 4 1
Select the order in which each drive is attempted to be
used as the boot device.
Revision 1.0
31
Page 42

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
Table 23. Removable Devices Selections
Boot Priority Device Description User Setting
1 Legacy Floppy Drives Select the order in which each removable device is
attempted to be used as the boot device.1
Note:
1. These selections will change depending on the system configuration
3.2.2.9 Exit Menu Selections
The following menu options are available on the Exit menu. Use t he up and down arrow keys to
select an option, and then press the Enter k ey to execute t he opt ion.
Table 24. Exit Menu Selections
Option Description
Save Changes & Exit Exit after writing all modified Setup item values to CMOS.
Exit Without Saving Changes Exit without saving Setup data to CMOS.
Get Default Value Load default values for all Setup items.
Load Previous Value Read previous values of all Setup items from CMOS.
Save Changes Write all Setup item values to CMOS.
3.3 CM OS Memory Definition
Only the BIOS needs to know the CMOS map. The CMOS map is available in the NVRAM.LST
file generated for every BIOS release. The CMOS map is subject to change without notice.
3.4 CM OS Default Override
The BIOS detects the state of the CMOS default switch. If t he switch is set t o “CMOS Clear”
prior to power-on or a hard reset, the BI O S changes the CMOS and NVRAM settings to a
default state. This guarantees the system’s ability to boot from floppy.
Password settings are not aff ect ed by CMOS clear. T he BI O S clear s the ESCD parameter
block and loads a null ESCD image. The boot or der information is also cleared when CMOS is
cleared via jumper.
If the Reset Configuration Data option is enabled in Setup, ESCD data and BIOS Boot
specification data is cleared and reinitialized in next boot.
32
Revision 1.0
Page 43

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
3.5 Flash Update Utility
The BIOS update utility (Phoenix* Phlash.exe) loads a f r esh copy of the BIOS into flash ROM.
The loaded code and data include the following:
• On-board video BIOS and network controller BIOS
• BIOS Setup utility
• User-definable flash area (user binar y area)
• Splash screen
When running Phoenix* Phlash in int er active mode, the user may choose to update a particular
flash area. Updating a f lash area takes a file or series of files from a hard or f loppy disk, and
loads it in the specified area of flash ROM.
Note: The Phoenix Phlash utility must be run without the presence of a 386 protected mode
control program, such as Windows* or EMM386*. Phoenix* Phlash uses the processor’s flat
addressing mode to update the flash par t .
3.5.1 Loading the System BIOS
The BIOS update utility (PHLASH) loads a new copy of the BIOS into Flash ROM. The loaded
code and data include the following:
• On-board Video BIOS
• BIOS Setup Utility
• Quiet Boot Logo Area
When running PHLASH in interactive mode, the user may choose to update a particular Flash
area. Updating a flash area loads a file or a series of files f r om a hard or floppy disk into the
specified area of Flash ROM.
To manually load a portion of the BIOS, t he user must specify which data file(s) to load. The
choices include
• PLATCBLU.BIN
• PLATCXLU.BIN
• PLATCXXX.BIN
• PLATCXLX.BIN
• PLATCXXU.BIN
The last three letters specify the functions to perform dur ing the flash process:
• C = Rewrite BIOS
• B = Rewrite Bootblock
• L = Clear LOGO area
• U = Clear user binary
• X = place holder
Revision 1.0
33
Page 44

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
This file is loaded into the PHLASH prog r am with the / b =<bin file>.
The disk created by the BIOS.EX E pr ogram will automatically run in non-interactive mode:
phlash /s /b=PLATCXLU.BIN
For a complete list of phlash switches, run phlash /h.
Once an update of the system BIOS is complet e, the user is prompted for a reboot. The user
binary area is also updated during a system BIOS update. User binar y can be updated
independently of the system BIOS. CMOS is cleared when the system BIOS is updated.
3.5.2 Customization
The SAI2 BIOS can be customized for pr oduct differentiation. T he extent of customization is
limited to what is stated in this section. Adding an alternative splash screen/logo can change
the BIOS look and feel. Dealer s can m anage dealer-specific hardware, if any, by executing their
own code during POST by using the “User-supplied BIOS Code Support.”
3.5.2.1 User-supplied BIOS Code Support
A 16 KB region of flash ROM is available to store a user binar y. The Phoenix* Phlash utility
allows the dealer or end user to update the user binary region with dealer supplied code and/or
data. At several points throughout POST, control is passed to this user binary. I nt el pr ovides
tools and reference code to help dealers create a user binary. The user binary must adhere to
the following requirements:
• To allow detection by BIOS and protection from run time memory managers, the user
binary must have an option ROM header (i.e., 55AAh, size).
• The system BIOS performs a scan of the user binary area at predefined points dur ing
POST. Mask bits must be set within the user binar y to inform the BIOS which entry
points exist.
• The system state must be preserved by the user binary (all reg ist er s, including extended
and MMX, stack contents, and nonuser binary data space, etc.).
• The user binary code must be relocatable. The user binar y is located within the first
1 MB of memory. The user binary code must not mak e any assumpt ions about the value
of the code segment.
• The user binary code is always executed from RAM and never from flash.
• The user binary must not hook critical int er rupts, must not reprogram the chip set, and
must not take any action that affects the correct functioning of the system BIOS.
• The user binary ROM must be checksummed. The checksum byte must be placed in
the last byte position of the 16K ROM.
The BIOS copies the user binary into system memory bef ore the first scan point. If the user
binary reports that it does not contain run time code, it is located in conventional memory (0-640
KB). Reporting that the user binar y has no run t im e code has t he advantage of not using limited
option ROM space (therefore, more option ROMs may be executed in a large system
34
Revision 1.0
Page 45

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
configuration). I f user binary code is required at run time, it is copied into and executed from
option ROM space (0C8000H – 0E7fffH).
At each scan-point during POST, t he system BI OS determines if the scan-point has a
corresponding user binary entry point to transfer control to the user binary. Presence of a valid
entry point in the user binary is determined by examining the bitmap at byte 4 of the user binary
header; each entry point has a corresponding “presence” bit in this bitmap. If the bit m ap has t he
appropriate bit set, an entry point ID is placed in the “AL” register and execution is passed to
the address computed by (ADR(Byte 5)+5*scan sequence #).
During execution, the user binary may access 11 bytes of extended BIOS data area RAM
(EBDA). The segment of EBDA can be found at address 40:0e. Offset 18h through offset 22h is
available for the user binary. The BIOS also r eser ves eig ht CMOS bits for the user binary.
These bits are in an unchecksummed re gion of CMOS with default values of zero, and will
always be located in the first bank of CMOS. T hese bit s ar e cont iguous, but are not in a fixed
location. Upon entry into the user binary, DX contains a ‘t oken’ that points to the reserved bits.
This token is of the following format:
MSB LSB
15 12 11 0
# of bit available –1 Bit offset from start of CMOS of first bit
The most significant four bits are equal to the num ber of CMOS bits available minus one. This
field is equal to seven, since eight CMOS bits are available. The 12 least significant bits define
the position of the CMOS bit in the real-t im e clock (RTC). This is a bit address rather than a
byte address. The CMOS byte location is 1/8th of the 12-bit num ber, and the remainder is the
starting bit position within that byte. For example, if the 12-bit number is 0109h, user binar y can
use bit 1 of CMOS byte 0108h/8 or 021h. It should be noted that the bits available to the user
binary may span more than one byte of CMOS (i.e., a value of 07084h indicates t hat the upper
nibble of byte 10h and the lower nibble of byte 11h are reserved for the user binary).
The following code fragm ent shows the header and format for a user binary:
db 55h, 0AAh, 20h ; 16KB USER Area
MyCode PROC FAR ; MUST be a FAR procedure
db CBh ; Far return instruction
db 04h ; Bit map to define call points, a 1
; in any bit specifies
; that the BIOS is called at that
; scan point in POST
db CBh ; First transfer address used to
; point to user binary extension
; structure
dw ? ; Word Pointer to extension
; structure
dw 0 ; Reserved
JMP ErrRet ; This is a list of 7 transfer
JMP ErrRet ; bit in the bitmap.
Revision 1.0
; addresses, one for each
35
Page 46

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
; 5 Bytes must be used for each
JMP Start ; JMP to maintain proper offset for
; each entry. Unused entry JMP’s
; should be filled with 5 byte
; filler or JMP to a RETF
JMP ErrRet ;
JMP ErrRet
JMP ErrRet
JMP ErrRet
3.5.2.2 Scan Point Definitions
The table below defines the bitmap for each scan point, indicating when the scan point occurs
and which resources are available (RAM, stack, binary data area, video, and keyboard).
Table 25. User Binary Area Scan Point Definitions
Scan Point Mask RAM/Stack/ Binary
Data Area (BDA)
Near pointer to the user binary extension structure, mask bit is 0
if this structure is not present. Instead of a jump instruction the
scan address (offset 5) contains an 0CB followed by a near
pointer.
Obsolete. No action taken. 02h NA NA
This scan occurs immediately after video initialization. 04h Yes Yes
This scan occurs immediately before video initialization. 08h Yes No
This scan occurs on POST error. On entry, BX contains the
number of the POST error.
This final scan occurs immediately prior to the INT 19 for normal
boot and allows one to completely circumvent the normal INT 19
boot if desired.
This scan occurs immediately before the normal option ROM
scan.
This scan occurs immediately following the option ROM area
scan.
01h Not applicable Not applicable
10h Yes Yes
20h Yes Yes
40h Yes Yes
80h Yes Yes
Video/Keyboard
Table 26. Format of the User Binary Information Structure
Offset Bit Definition
0 Bit 0 = 1 if mandatory user binary, 0 if not mandatory. If a user binary is mandatory, it will always be
executed. If a platform supports a disabling of the user binary scan through Setup, this bit will override
Setup setting.
Bit 1 - 1 if runtime presence required (other than SMM user binary portion, SMM user binary will always be
present in runtime irrespective of setting of this bit).
0, if not required in runtime, and can be discarded at boot time.
Bit 7:2 – reserved for future expansion.
1 - 0fh Reserved for future expansion.
36
Revision 1.0
Page 47

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
If this structure is not present (bit 0 of the scan point struct ur e is not set), the system BIOS
assumes that the user binary is not mandatory (bit 0 in User Binary Information Structur e
assumed cleared), and it is required in r un time (bit 1 in User Binary Information Structure
assumed set).
3.5.2.3 Splash Screen
A 128-KB region of Flash ROM is available to store the alter native logo in compressed format.
The BIOS will contain the standard Intel logo. Using the Phoenix Phlash utility, this region can
be updated with an alternative supplied logo image. The alternative logo must fit within 640 X
480 size. If an alternative logo is flashed into the system, it will override the built in Intel log o .
Intel supplies utilities that will compress and convert a 16 color bit map file into a logo file
suitable for Phoenix Phlash.
3.5.3 Language Area
The system BIOS language area can be updat ed only by updating t he entire BIOS. The SAI2
platform supports Eng lish, Spanish, French, German, and Italian. Intel provides translations for
all the strings in five languages. These languages are selectable using Setup.
3.5.4 Recovery Mode
In the case of a corrupt or an unsuccessful update of the system BIOS, the SAI 2 can boot in
recovery mode. To place SAI2 into recovery mode, move the boot option jumper (jumper block
JP5 pins 9-10) to the recovery boot position. By default and for normal operation, pins 9 and 10
are not jumpered.
Recovery mode requires at least 8 MB of RAM in the first DI MM socket, and dr ive A: mu st be
set up to support a 3.5-inch, 1.44-MB floppy drive. (Note: the system requires 64 MB to boot).
This is the mode of last resort, used only when the main system BIOS will not come up. In
recovery mode operation, PHLASH (in non-interactive mode only) automat ically updates only
the main system BIOS. PHLASH senses that SAI2 is in r ecovery mode and aut om atically
attempts to update the system BIOS
Before powering up the system, the user must obtain a bootable diskette that contains a copy
of the BIOS recovery files. T his is cr eated by running the “crisdisk.bat” from the compressed
recovery file distributed with the BIOS.
Note: During recovery mode, video will not be initialized and many high-pitched beep t ones will
be heard. The entire process takes t wo to four minutes. When the process is completed, the
tones will stop. The user may see a “Checksum error ” on t he first boot after updat ing the BIOS.
This is normal and should correct itself after the firs t boot.
If a failure occurs, it is most likely that of the system BIOS .ROM file is corrupt or missing.
After a successful update, power down the system and remove the j um per from pins 9-10.
Power up the system. Verify that the BIOS version number matches the version of the entire
BIOS used in the original attempt to update.
Revision 1.0
37
Page 48

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
3.6 Error M essages and Error Codes
The system BIOS displays error messages on t he video screen. Before video initialization, beep
codes inform the user of er r or s . POST error codes are logged in t he event log. The BIOS
displays POST error codes on the video monitor.
Following are definitions of POST error codes, POST beep codes, and system error m essages.
3.6.1 POST Codes
After the video adapter has been successfully initialized, the BIOS indicates the current testing
phase during POST by writing a 2-digit hex code to I/O location 80h. If a Port-80h card
(Postcard*) is installed, it displays this 2-digit code on a pair of hex display LEDs.
Table 27. Port-80h Code Definition
Code Meaning
CP Phoenix* checkpoint (port-80) code
The table below contains the port-80 codes displayed during the boot pr ocess. A beep code is a
series of individual beeps on the PC speaker, each of equal length. The following table
describes the error conditions associated with each beep code and the corresponding POST
checkpoint code as seen by a ‘port 80h’ card. For example, if an er ror occurs at checkpoint
22h, a beep code of 1-3-1-1 is generat ed. The “-“ means there is a pause between the
sequence that delimits the sequence.
Some POST codes occur before t he video display being initialized. To assist in determining the
fault, a unique beep-code is derived f rom these checkpoints as follows:
• The 8-bit test point is brok en down to four 2-bit groups.
• Each group is made one-based (1 through 4)
• One to four beeps are generat ed based on each group’s 2-bit pattern.
Example:
Checkpoint 04Bh will be broken down to: 01 00 10 11
The beep code will be: 2 1 3 4
Table 28. Standard BIOS Port-80 Codes
CP Beeps Reason
02 Verify Real Mode
04 Get Processor type
06 Initialize system hardware
08 Initialize chipset registers with initial POST values
09 Set in POST flag
0A Initialize processor registers
0B Enable processor cache
38
Revision 1.0
Page 49

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
CP Beeps Reason
0C Initialize caches to initial POST values
0E Initialize I/O
0F Initialize the local bus IDE
10 Initialize Power Management
11 Load alternate registers with initial POST values
12 Restore processor control word during warm boot
14 Initialize keyboard controller
16 1-2-2-3 BIOS ROM checksum
18 8254 timer initialization
1A 8237 DMA controller initialization
1C Reset Programmable Interrupt Controller
20 1-3-1-1 Test DRAM refresh
22 1-3-1-3 Test 8742 Keyboard Controller
24 Set ES segment register to 4 GB
28 1-3-3-1 Autosize DRAM, system BIOS stops execution here if the BIOS does not detect any usable
memory DIMMs
2A Clear 8 MB base RAM
2C 1-3-4-1 Base RAM failure, BIOS stops execution here if entire memory is bad
32 Test Processor bus-clock frequency
34 Test CMOS
35 RAM Initialize alternate chipset registers
36 Warm start shut down
37 Reinitialize the chipset
38 Shadow system BIOS ROM
39 Reinitialize the cache
3A Autosize cache
3C Configure advanced chipset registers
3D Load alternate registers with CMOS values
40 Set Initial Processor speed new
42 Initialize interrupt vectors
44 Initialize BIOS interrupts
46 2-1-2-3 Check ROM copyright notice
47 Initialize manager for PCI Option ROMs
48 Check video configuration against CMOS
49 Initialize PCI bus and devices
4A Initialize all video adapters in system
4B Display QuietBoot screen
4C Shadow video BIOS ROM
4E Display copyright notice
50 Display Processor type and speed
52 Test keyboard
54 Set key click if enabled
55 USB initialization
56 Enable keyboard
58 2-2-3-1 Test for unexpected interrupts
Revision 1.0
39
Page 50

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
CP Beeps Reason
5A Display prompt "Press F2 to enter SETUP"
5C Test RAM between 512 and 640 k
60 Test extended memory
62 Test extended memory address lines
64 Jump to UserPatch1
66 Configure advanced cache registers
68 Enable external and processor caches
6A Display external cache size
6B Load custom defaults if required
6C Display shadow message
6E Display non-disposable segments
70 Display error messages
72 Check for configuration errors
74 Test real-time clock
76 Check for keyboard errors
7A Test for key lock on
7C Set up hardware interrupt vectors
7D Intelligent system monitoring
7E Test coprocessor if present
82 Detect and install external RS232 ports
85 Initialize PC-compatible PnP ISA devices
86 Re-initialize on board I/O ports
88 Initialize BIOS Data Area
8A Initialize Extended BIOS Data Area
8C Initialize floppy controller
90 Initialize hard disk controller
91 Initialize local bus hard disk controller
92 Jump to UserPatch2
93 Build MPTABLE for multi-processor boards
94 Disable A20 address line
95 Install CD-ROM for boot
96 Clear huge ES segment register
98 1-2 Search for option ROMs. One long, two short beeps on checksum failure
9A Shadow option ROMs
9C Set up Power Management
9E Enable hardware interrupts
A0 Set time of day
A2 Check key lock
A4 Initialize typematic rate
A8 Erase F2 prompt
AA Scan for F2 key stroke
AC Enter SETUP
AE Clear in-POST flag
B0 Check for errors
B2 POST done – prepare to boot Operating System
40
Revision 1.0
Page 51

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
CP Beeps Reason
B4 1 One short beep before boot
B5 Display MultiBoot menu
B6 Check password, password is checked before option ROM scan
B7 ACPI initialization
B8 Clear global descriptor table
BC Clear parity checkers
BE Clear screen (optional)
BF Check virus and backup reminders
C0 Try to boot with INT 19
C8 Forced shutdown
C9 Flash recovery
DO Interrupt handler error
D2 Unknown interrupt error
D4 Pending interrupt error
D6 Initialize option ROM error
D8 Shutdown error
DA Extended Block Move
DC Shutdown 10 error
Table 29. Recovery BIOS Port-80 Codes
CP Beeps Reason
E0 Initialize chip set
E1 Initialize bridge
E2 Initialize processor
E3 Initialize timer
E4 Initialize system I/O
E5 Check forced recovery boot
E6 Validate checksum
E7 Go to BIOS
E8 Initialize processors
E9 Set 4 GB segment limits
EA Perform platform initialization
EB Initialize PIC and DMA
EC Initialize memory type
ED Initialize memory size
EE Shadow boot block
EF Test system memory
F0 Initialize interrupt services
F1 Initialize real time clock
F2 Initialize video
F3 Initialize beeper
F4 Initialize boot
F5 Restore segment limits to 64 KB
Revision 1.0
41
Page 52

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
F6 Boot mini DOS
F7 Boot full DOS
3.6.2 POST Error Codes and Messages
The following table defines POST error codes and their associated messages. T he BIOS
prompts the user to press a key in case of a ser ious er r or . Som e er ror messages are preceded
by the string "Error” to highlight that the system mig ht be malfunctioning. All POST er rors and
warnings are logged in the system event log unless it is full.
Table 30. POST Error Messages and Codes
Code Error Message Failure Description
0200: Failure Fixed Disk hard disk error
0210: Stuck Key Keyboard connection error
0211: Keyboard error Keyboard failure
0212: Keyboard Controller Failed Keyboard Controller Failed
0213: Keyboard locked– Unlock key switch Keyboard locked
0220: Monitor type does not match CMOS– Run SETUP Monitor type does not match CMOS
0230: System RAM Failed at offset System RAM error
Offset address
0231: Shadow RAM Failed at offset Shadow RAM Failed
Offset address
0232: Extend RAM Failed at address line Extended RAM failed
Offset address
0233: Memory type mixing detected Memory type mixing detected
0234: Single – bit ECC error Memory 1 bit error detected
0235: Multiple- bit ECC error Memory multiple-bit error detected
0250: System battery is dead – Replace and run SETUP NVRAM battery dead
0251: System CMOS checksum bad – Default configuration
used
0252: Password checksum bad – Passwords cleared
0260: System timer error System timer error
0270: Real time clock error RTC error
0271: Check date and time setting RTC time setting error
02B0: Diskette drive A error
02B2: Incorrect Drive A type – run SETUP Incorrect Drive A type
02D0: System cache error – Cache disabled Processor cache error
0B00: Rebooted during BIOS boot at Post Code
0B1B: PCI System Error on Bus/Device/Function PCI system error in Bus/device/Function
0B1C: PCI Parity Error in Bus/Device/Function PCI system error in Bus/device/Function
0B50: CPU#1 with error taken offline Failed Processor#1 because an error was
0B51: CPU#2 with error taken offline Failed Processor#2 because an error was
0B5F: Forced to use CPU with error An error detected in the entire processor
0B60: DIMM #1 has been disabled Memory error, memory group #1 failed
CMOS checksum error
detected
detected
42
Revision 1.0
Page 53

SAI2 Server Board TPS Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
Code Error Message Failure Description
0B61: DIMM #2 has been disabled Memory error, memory group #2 failed
0B62: DIMM #3 has been disabled Memory error, memory group #3 failed
0B63: DIMM #4 has been disabled Memory error, memory group #4 failed
0B6F: DIMM with error is enabled An error detected in all the memory
0B70: The error occurred during temperature sensor reading Error while detecting a temperature failure.
0B71: System temperature out of the range Temperature error detected.
0B74: The error occurred during voltage sensor reading Error while detecting voltage
0B75: System voltage out of the range System voltage error
0B7C: The error occurred during redundant power module
confirmation
0BB0: SMBIOS – SROM data read error SROM data read error
0BB1: SMBIOS – SROM data checksum bad Bad checksum of SROM data
0BD0: 1st SMBus device address not acknowledged. Some SMBus device (chip) failed
0BD1: 1st SMBus device Error detected.
0BD2: 1st SMBus timeout.
N/A Expansion ROM not initialized. PCI Expansion ROM card not initialized
N/A Invalid System Configuration Data System configuration data destroyed
N/A System Configuration Data Read Error System configuration data read error
N/A Resource Conflict PCI card resource is not mapped correctly.
N/A System Configuration Data Write error System configuration data write error
N/A Warning: IRQ not configured PCI interrupt is not configured correctly.
8503: Incorrect memory speed in location: XX, XX, … Non-PC133 DIMMs have been installed in slots
The error occurred while retrieving the power
information
XX, XX, …
A beep code is a series of individual beeps on the PC speaker, each of equal length. The
following table describes the error conditions associated with each beep code and the
corresponding POST checkpoint code as seen by a port 80h car d. For example, if an error
occurs at checkpoint 22h, a beep code of 1- 3- 1- 1 is generated.
Table 31. POST Error Conditions and Beep Codes
Beeps Error Cause Recommended Action
1-2-2-3 ROM Checksum Error — Change system board
1-3-1-1 DRAM Refresh Test Error — Change memory DIMM's
1-3-1-3 Keyboard Controller Test Error — Change system board
1-3-3-1 Memory Not Detected No memory.
Can not write to memory
Memory Capacity Check Error No memory.
Can not write to memory
1-3-4-1 DRAM Address Test Error Memory address signal failure Change DIMM or M/B
1-3-4-3 DRAM Test low byte Error Memory data signal failure (low) Change DIMM or M/B
1-4-1-1 DRAM Test high byte Error Memory data signal failure (high) Change DIMM or M/B
1-4-3-3 All Memory Group Errors — —
2-1-2-3 BIOS ROM Copy-Write Test Error Error with Shadow RAM Change system board
2-2-3-1 Unexpected Interrupt Test Error Unexpected interrupt Change CPU or system board
Verify DIMM installation.
Change memory DIMM's
Verify DIMM installation.
Change memory DIMM's
Revision 1.0
43
Page 54

Basic Input Output System (BIOS) SAI2 Server Board TPS
Beeps Error Cause Recommended Action
2-3-1-3 All Memory Group Errors Memory address signal failure Change DIMM or M/B
3-3-1-4 Memory Not Detected — —
1-2 Option ROM Initialization Error Failure to initialize Option ROM
BIOS
1-2 Video configuration fails Failure to initialize VGA BIOS Change option video board or
1-2 OPTION ROM Checksum Error Failure to initialize Option BIOS Change M/B or option board
Change system board or option
board
system board
3.7 Identifying BIOS Revision Level
The following sections provide informat ion t o help identify a system's current BIOS revision
level.
3.7.1 BIOS Revision Level Identification
During system POST, which runs automatically when the system is powered on, the monit or
displays several messages, one of which identifies the BI O S r evision level current ly loaded on
the system (see the following example).
Phoenix BIOS 4.0 Release 6.0.250A
In the example above, BIOS 6.0.250A is the current BIOS revision level loaded on the system.
: Press the Esc key to see the diagnostic messages.
Note
The BIOS revision level stated in the example might not r eflect the actual BIOS setting in
Note:
any particular system.
44
Revision 1.0
Page 55

SAI2 Server Board TPS Jumpers and Connectors
U
4. Jumpers and Connecto rs
4.1 SAI2 Server Board Jumper and Connector Locations
The following figure shows the location of the jumper blocks and connectors on t he SAI 2 Server
board.
B
A
V
T
S
R
Q
C
P
O
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
OM13065
Figure 6. SAI2 Server Board Jumper and Connector Locations
A 33 MHz/32-bit PCI connectors L Secondary processor heat sink fan connector (J9)
B 66 MHz/64-bit PCI connectors M Floppy drive connector (FDD)
C Primary processor connector (CPU1) N Primary IDE connector (PRI_IDE)
D Back panel connectors O Secondary IDE connector (SEC_IDE)
E Primary processor heat sink fan connector (J10) P Fan 3 connector (J8)
F Fan 5 connector (J7) Q Fan 4 connector (J11)
G Fan 6 connector (J14) R CSB5 (South Bridge)
H Main power connector (Main Power) S Front panel connector (FRONT_PANEL_HDR)
I Secondary processor (CPU2) T Configuration jumper block (JP5)
J CNB30LE (North Bridge) U HDD LED (J12)
K DIMM slots (DIMM1 - DIMM4) V Battery
Revision 1.0
45
Page 56

Jumpers and Connectors SAI2 Server Board TPS
The following diagram shows the location of the connectors on the SAI2 server board I/O panel.
1
ON
B
A
C
E
FD
GI
H
OM12377
Figure 7. I/O Back Panel Connectors
A Serial port 1 connector (COM1) F Mouse connector
B Serial port 2 connector (COM2) G SVGA connector
C NMI (Non Maskable Interrupt) switch H Network connector
D Keyboard connector I USB connectors (2)
E Parallel port connector
46
Revision 1.0
Page 57

SAI2 Server Board TPS Jumpers and Connectors
4.2 Jumper Blocks
Jumpers on the JP5 jumper block of the SAI2 server board set the system configuration. The
jumpers are small plastic-encased conductors ( shor t ing plugs) that slip over two jumper pins on
a jumper block.
On the SAI2 server board, the f ollowing j um per blocks are user-config ur able.
• CMOS and Password Clear
• BIOS Recovery
4.2.1 Setting CMOS/Password Clear Jumper Block (JP5)
Setting a jumper on system board jum per block JP5 enables the user to clear the CMOS or to
clear a forgotten password. See the above figure for the location of t he jumper block location.
The following table lists the f actory default settings fo r jumper block JP5, which are indicated in
bold typeface. Procedures for set ting the jumper on the block follow the table.
Table 32. Jumper Block JP5 Settings
Jumper Pin
Numbers
1 - 2 CMOS clear
Closed, Erase Clears CMOS
3 - 4 Password protected
Closed, Disable Disables the password
5 - 6 Reserved
7 - 8 Reserved
9 - 10 BIOS Recovery Boot
Closed, Recovery Boot If this jumper is set, BIOS recovery will be
11 - 12 Spare
Function Jumper Position What it does at system reset
Open, Protect
Open, Normal
Open, Not Used
Open, Not Used
Open, Normal
Closed, Spare
Preserves the contents of CMOS
Preserves the password
No function
No function
BIOS Recovery Boot disabled. Normal
operation.
attempted from a bootable BIOS recovery
floppy diskette.
Provides a spare jumper
4.2.1.1 Clearing and Changing a Password
Clear and change a password as follows.
1. Power off t he system, unplug the power cord, and remove the chassis panel.
2. Use needle-nose pliers or your f ingers to remove the spare jumper f r om pins 11-12 on
jumper block JP5.
3. Reinstall the jumper on pins 3- 4 (Password Disable) of jumper block JP5.
4. Reinstall the chassis panel, plug in the power cord(s), and power on the system.
5. While waiting for POST to complete, press the F2 key to enter BIOS setup.
Revision 1.0
47
Page 58

Jumpers and Connectors SAI2 Server Board TPS
6. This automatically clears all passwords, pr ovided you save and exit the BIOS setup.
7. Power off t he system, unplug the power cord(s), and remove the chassis panel.
8. Remove the Password Disable jumper f r om pins 3- 4 and store the jumper on pins 11-12.
9. Replace the chassis panel, plug in the power cord( s) , and power on the system.
10. To specify a new password run the BIOS Setup Utility as described earlier in this section.
4.2.1.2 Clearing CMOS
Clear CMOS as follows.
1. Power off t he system, unplug the power cord, and remove the chassis panel.
2. Use needle-nose pliers or your f ingers to remove the spare jumper f r om pins 11-12 on
jumper block JP5.
3. Position the jumper over pins 1- 2 on jumper block JP5.
4. Replace the chassis panel, plug in the power cable(s) , and power on the system .
5. After POST completes, power down the system, unplug the power cable(s), and rem ove the
chassis panel.
6. Remove the jumper from pins 1-2 and store the jumper on pins 11- 12.
7. Replace the chassis panel and connect system cables.
8. Power on the system, press F2 at the prom pt to run the BIOS Setup utility, and select “G et
Default Values” at the Exit menu.
4.2.1.3 Perfoming a BIOS Recovery Boot
In the event of BIOS corruption, the following procedure may be used to perfor m a BIOS
recovery.
1. Obtain the BIOS update file package f rom Intel’s http://support.intel.com
web site.
2. A file called “cr isis. zip” is one of the files included with each SAI2 BIOS release f ile
package. Unzip the “crisis.zip” file t o a dir ectory on your hard drive.
3. Obtain a blank formatted floppy diskett e ( t he floppy diskette should not be a bootable DOS
diskette). Insert the blank formatted floppy diskette in the floppy drive.
4. From the MS-DOS* prompt on an MS-DOS system, run the “crisdisk.bat” file from the
directory you created on your hard drive. Follow the instructions on the screen to create the
BIOS recovery floppy diskette.
Note: The BIOS recovery floppy diskette will not be created correctly under the MS-DOS
prompt window of a Windows* operating system. I t is necessar y to use a MS-DOS system
to create the BIOS recovery floppy diskette.
5. Power off t he SAI 2 system , unplug the power cord, and remove the chassis panel.
6. Remove the spare jumper from pins 11-12 on jumper block JP5.
7. Reinstall the jumper on pins 9- 10 (BIOS recovery) of jumper block JP5.
48
Revision 1.0
Page 59

SAI2 Server Board TPS Jumpers and Connectors
8. Insert the BI O S r ecovery f loppy disk et t e into the diskette drive.
9. Reinstall the chassis panel, plug in the power cord(s), and power on the system.
10. The screen will remain blank while the BIOS recovery is performed. A number of beeps will
occur during the BIOS update. The floppy drive access light will not turn off when the BI O S
recovery is completed. Allow four minutes for the BIOS recovery to complete. If a POST
card is installed in a PCI slot during the BIOS recovery, you can tell that the BIOS recovery
is complete when code “EC” is displayed. When t he BIOS recovery is complete, it is safe to
power off the system.
11. Power off the system, unplug the power cord(s), and remove the chassis panel.
12. Remove the BIOS recovery jumper from pins 9-10 and store the jumper on pins 11- 12.
13. Replace the chassis panel, plug in the power cord(s), and power on the system.
14. Perform a CMOS clear following the BIOS recovery.
4.3 Connectors
This section provides pin information about t he connect or s on t he SAI 2 server board.
4.3.1 Main Power Connector (ATX1)
Table 33. Main Power Connector Pinout
Pin Signal Wire color Pin Signal Wire Color
1 +3.3 VDC Orange 13 +3.3 VDC Orange
2 +3.3 VDC Orange 14 -12 VDC Blue
3 COM Black 15 COM Black
4 +5 VDC Red 16 PS-ON_L Green
5 COM Black 17 COM Black
6 +5 VDC Red 18 COM Black
7 COM Black 19 COM Black
8 PWR-OK Grey 20 N.C. N.C.
9 5 VSB Purple 21 +5 VDC Red
10 +12 VDC Yellow 22 +5 VDC Red
11 +12 VDC Yellow 23 +5 VDC Red
12 +3.3 VDC Orange 24 COM Black
4.3.2 I2C Connector (J13)
Table 34. I2C Connector Pinout
Revision 1.0
Pin Signal
1 I2C Data
2 COM
3 I2C Clock
4 Reserved
49
Page 60

Jumpers and Connectors SAI2 Server Board TPS
4.3.3 System Fan Connectors (J8, J11, J7, J14)
• System Fan 3: Fan 3 (J8)
• System Fan 4: Fan 4 (J11)
• System Fan 5: Fan 5 (J7)
• System Fan 6: Fan 6 (J14)
Table 35. Board Fan Connector Pinout
Pin Signal
1 COM
2 PWM
3 Fan Sense
4.3.4 Processor Fan Connectors (J10, J9)
• Primary Processor Fan 1: CPU1_FAN1 (J10)
• Secondary Processor Fan 2: CPU2_FAN2 (J9)
Table 36. Processor Fan Connector Pinout
4.3.5 HDD LED (J12)
Pin Signal
1 COM
2 + 12 VDC
3 Fan Sense
Table 37. HDD LED Pinout
Pin Signal
1 N.C.
2 (+) HDD L E D Anode
3 (+) HDD L E D Anode
4 N.C.
50
Revision 1.0
Page 61

SAI2 Server Board TPS Jumpers and Connectors
4.3.6 Diskette Drive Connector (FDD)
Table 38. Diskette Drive Connector Pinout
Pin Signal Diskette Drive Connector Pin Diagram Pin Signal
1 GND 2 FD_DENSEL
3 GND 4 No Connection
5 Pin
Removed
7 GND 8 FD_INDEX_L
9 GND 10 FD_MON0_L
11 GND 12 FD_SEL1_L
13 GND 14 FD_SEL0_L
15 GND 16 FD_MON1_L
17 GND 18 FD_DIR_L
19 GND 20 FD_STEP_L
21 GND 22 FD_WDATA_L
23 GND 24 FD_WGATE_L
25 GND 26 FD_TRK0_L
27 GND 28 FD_WPT_L
29 GND 30 FD_RDATA_L
31 GND 32 FD_SIDE_L
33 MSENO
2
1 33
6 Reserved
34
34 FD_DCHG_L
4.3.7 SVGA Video Port (VGA1)
Table 39. Video Port Connector Pinout
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Red 9 NC
2 Green 10 GND
3 Blue 11 NC
4 NC 12 DDCDAT
5 GND 13 HSYNC
6 GND 14 VSYNC
7 GND 15 DDCCLK
8 GND
Revision 1.0
51
Page 62

Jumpers and Connectors SAI2 Server Board TPS
4.3.8 Keyboard (KB) and Mouse (MS) Connectors
The keyboard and mouse connectors are functionally equivalent.
Table 40. Keyboard and Mouse Connector Pinout
Pin Keyboard Signal Pin Mouse Signal
1 KEYDAT 1 MSEDAT
2 GND 2 NC
3 GND 3 GND
4 FUSED_VCC (+5 V) 4 FUSED_VCC (+5 V)
5 KEYCLK 5 MSECLK
6 NC 6 NC
4.3.9 Parallel Port (LPT1)
Table 41. Parallel Port Connector Pinout
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 STROBE_L 10 ACK_L
2 Data bit 0 11 Busy
3 Data bit 1 12 PE
4 Data bit 2 13 SLCT
5 Data bit 3 14 AUTO_L
6 Data bit 4 15 ERROR_L
7 Data bit 5 16 INIT_L
8 Data bit 6 17 SLCTIN_L
9 Data bit 7
4.3.10 Serial Ports COM1 and COM2
Table 42. Serial Ports COM1 and COM2 Connector Pinouts
Pin Signal Description
1 DCD Data carrier detected
2 RXD Receive data
3 TXD Transmit data
4 DTR Data terminal ready
5 GND Ground
6 DSR Data set ready
7 RTS Return to send
8 CTS Clear to send
9 RIA Ring indication active
18−25
GND
52
Revision 1.0
Page 63

SAI2 Server Board TPS Jumpers and Connectors
4.3.11 RJ-45 LAN Connector (J2)
Table 43. RJ-45 LAN Connector Signals
Pin Signal Description
1 TX+ Transmit data plus—the positive signal for the TD differential pair contains the serial output data
stream transmitted onto the network
2 TX- Transmit data minus—the negative signal for the TD differential pair contains the same output
as pin 1
3 RX+ Receive data plus—the positive signal for the RD differential pair contains the serial input data
stream received from the network
4 NC
5 NC
6 RX- Receive data minus—the negative signal for the RD differential pair contains the same input as
pin 3
7 NC
8 NC
4.3.12 USB Connectors (J2)
Table 44. USB Connectors
USB 1 Pin Signal USB 2 Pin Signal
1 +5 VDC 1 +5 VDC
2 USB_P1_N 2 USB_P0_N
3 USB_P1_P 3 USB_P0_P
4 GND 4 GND
4.3.13 IDE Connectors (PRI_IDE, SEC_IDE)
If no IDE drives are present, no IDE cable should be connect ed. If a single IDE drive is
installed, it must be connected at the end of the cable.
Table 45. IDE Connector Pinout
Pin Signal IDE Connector Pin Diagram Pin Signal
1 RESET_L 2 GND
3 DD7 4 DD8
5 DD6 6 DD9
7 DD5 8 DD10
9 DD4 10 DD11
11 DD3 12 DD12
13 DD2 14 DD13
15 DD1
2
1
40
39
16 DD14
Revision 1.0
53
Page 64

Jumpers and Connectors SAI2 Server Board TPS
17 DD0 18 DD15
19 GND 20 Keyed
21 IDEDRQ 22 GND
23 DIOW_L 24 GND
25 DIOR_L 26 GND
27 IORDY 28 SPSYNC
29 IDEDAK_L 30 GND
31 IDEIRQ 32 No Connection
33 IDESA1 34 P80_IDE
35 IDESA0 36 IDESA2
37 IDECS0_L 38 IDECS1_L
39 HD_LED
40 GND
4.3.14 32-Bit PCI Connectors
Table 46. 32-Bit PCI Connector Pinout
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
A1 TRST_L B1 -12 V A32 AD16 B32 AD17
A2 +12 V B2 TCK A33 +3.3 V B33 CBE2_L
A3 TMS B3 GND A34 FRAME_L B34 GND
A4 TDI B4 TD0 (NC) A35 GND B35 IRDY_L
A5 +5 V B5 +5 V A36 TRDY_L B36 +3.3 V
A6 INTA_L B6 +5 V A37 GND B37 DEVSEL_L
A7 INTC_L B7 INTB_L A38 STOP_L B38 GND
A8 +5 V B8 INTD_L A39 +3.3 V B39 LOCK_L
A9 Reserved B9 PRSNT1_L A40 SDONE B40 PERR_L
A10 +3.3 V B10 Reserved A41 SBO_L B41 +3.3 V
A11 Reserved B11 PRSNT2_L A42 GND B42 SERR_L
A12 KEY B12 KEY A43 PARITY B43 +3.3 V
A13 KEY B13 KEY A44 AD15 B44 CBE1_L
A14 3.3VSB B14 Reserved A45 +3.3 V B45 AD14
A15 RST_L B15 GND A46 AD13 B46 GND
A16 +3.3 V B16 PCICLK A47 AD11 B47 AD12
A17 GNT_L B17 GND A48 GND B48 AD10
A18 GND B18 REQ_L A49 AD9 B49 GND
A19 PME_L B19 +3.3 V A50 GND B50 GND
A20 AD30 B20 AD31 A51 GND B51 GND
A21 +3.3 V B21 AD29 A52 BE0_L B52 AD8
A22 AD28 B22 GND A53 +3.3 V B53 AD7
A23 AD26 B23 AD27 A54 AD6 B54 +3.3 V
A24 GND B24 AD25 A55 AD4 B55 AD5
A25 AD24 B25 +3.3 V A56 GND B56 AD3
A26 IDSEL B26 CBE3_L A57 AD2 B57 GND
A27 +3.3 V B27 AD23 A58 AD0 B58 AD1
54
Revision 1.0
Page 65

SAI2 Server Board TPS Jumpers and Connectors
A28 AD22 B28 GND A59 +3.3 V B59 +3.3 V
A29 AD20 B29 AD21 A60 REQ64_L B60 ACK64_L
A30 GND B30 AD19 A61 +5 V B61 +5 V
A31 AD18 B31 +3.3 V A62 +5 V B62 +5 V
4.3.15 64-Bit PCI Connectors
Table 47. 64-Bit PCI Connctor Pinout
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
A1 TRST_L B1 -12 V A48 GND B48 AD10
A2 +12 V B2 TCK A49 AD9 B49 M66EN
A3 TMS B3 GND A50 KEY B50 KEY
A4 TDI B4 TD0 (NC) A51 KEY B51 KEY
A5 +5 V B5 +5 V A52 CBE0_L B52 AD8
A6 INTA_L B6 +5 V A53 +3.3 V B53 AD7
A7 INTC_L B7 INTB_L A54 AD6 B54 +3.3 V
A8 +5 V B8 INTD_L A55 AD4 B55 AD5
A9 Reserved B9 PRSNT1_L A56 GND B56 AD3
A10 +5 V B10 Reserved A57 AD2 B57 GND
A11 Reserved B11 PRSNT2_L A58 AD0 B58 AD1
A12 GND B12 GND A59 +5 V B59 +5 V
A13 GND B13 GND A60 REQ64_L B60 ACK64_L
A14 Reserved B14 Reserved A61 +5 V B61 +5 V
A15 RST_L B15 GND A62 +5 V B62 +5 V
A16 +5 V B16 PCICLK A63 GND B63 Reserved
A17 GNT_L B17 GND A64 CBE7_L B64 GND
A18 GND B18 REQ_L A65 CBE5_L B65 CBE6_L
A19 PME_L B19 +5 V A66 +3.3 V B66 CBE4_L
A20 AD30 B20 AD31 A67 Parity B67 GND
A21 +3.3 V B21 AD29 A68 AD62 B68 AD63
A22 AD28 B22 GND A69 GND B69 AD61
A23 AD26 B23 AD27 A70 AD60 B70 +3.3 V
A24 GND B24 AD25 A71 AD58 B71 AD59
A25 AD24 B25 +3.3 V A72 GND B72 AD57
A26 IDSEL B26 CBE3_L A73 AD56 B73 GND
A27 +3.3 V B27 AD23 A74 AD54 B74 AD55
A28 AD22 B28 GND A75 +3.3 V B75 AD53
A29 AD20 B29 AD21 A76 AD52 B76 GND
A30 GND B30 AD19 A77 AD50 B77 AD51
A31 AD18 B31 +3.3 V A78 GND B78 AD49
A32 AD16 B32 AD17 A79 AD48 B79 +3.3 V
A33 +3.3 V B33 CBE2_L A80 AD46 B80 AD47
A34 FRAME_L B34 GND A81 GND B81 AD45
A35 GND B35 IRDY_L A82 AD44 B82 GND
Revision 1.0
55
Page 66

Jumpers and Connectors SAI2 Server Board TPS
Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal Pin Signal
A36 TRDY_L B36 +3.3 V A83 AD42 B83 AD43
A37 GND B37 DEVSEL_L A84 +3.3 V B84 AD41
A38 STOP_L B38 GND A85 AD40 B85 GND
A39 +3.3 V B39 LOCK_L A86 AD38 B86 AD39
A40 SDONE B40 PERR_L A87 GND B87 AD37
A41 SBO_L B41 +3.3 V A88 AD36 B88 +3.3 V
A42 GND B42 SERR_L A89 AD34 B89 AD35
A43 PARITY B43 +3.3 V A90 GND B90 AD33
A44 AD15 B44 CBE1_L A91 AD32 B91 GND
A45 +3.3 V B45 AD14 A92 Reserved B92 Reserved
A46 AD13 B46 GND A93 GND B93 Reserved
A47 AD11 B47 AD12 A94 Reserved B94 GND
4.3.16 Front Panel 24-pin Connector Pinout (FRONT_PANEL_HDR)
Table 48. Front Panel 24-pin Connector Pinout
Pin Description
1 Power LED Anode
2 +5VSB
3 Key
4 Reserved
5 Power LED Cathode
6 Reserved
7 Hard Drive Activity LED Anode
8 Reserved
9 Hard Drive Activity LED Cathode
10 Reserved
11 Power Switch (Low True)
12 NIC Activity L ED Anode
13 Power Switch (GND)
14 NIC Activity LE D Cathode
15 Reset Switch (Low True)
16 SMBus SDA
17 Reset Switch (GND)
18 SMBus SCL
19 ACPI Sleep Switch (Low True)
20 Reserved
21 ACPI Sleep Switch (GND)
22 Reserved
23 NMI to CPU Switch (Low True)
24 Reserved
56
Revision 1.0
Page 67

SAI2 Server Board TPS Hardware Monitoring
5. Hardware Monitoring
The SAI2 server board has an integrated Winbond* Heceta chip that is responsible for
hardware monitoring. Together , the Winbond Heceta chip and t he Winbond Hardware Doctor*
software provide basic server hardware monitoring which alerts a system administr ator if a
hardware problem occurs on an Intel Server Board SAI2-based system. The Winbond
Hardware Doctor software is for use with Windows* 2000 Server and Windows 2000 Advanced
Server* operating systems. Below is a table of monitor ed header s and sensor s on the SAI2
server board.
Item Description
Voltage CPU1 Monitors primary processor voltage.
CPU2 Monitors secondary processor voltage.
VCC3 Monitors VCC3.
VCC Monitors VCC.
+12V Monitors +12V.
VTT Monitors VTT (AGTL bus termination voltage).
2.5V Monitors 2.5V.
5VSB Monitors 5VSB (5V stand-by).
Fan Speed CPU1_FAN Monitors primary processor fan speed.
CPU2_FAN Monitors secondary processor fan speed.
CHASSIS_FAN Monitors chassis fan speed through chassis fan header 3 only.
Temperature CPU2 Monitors primary processor temperature.
CPU1 Monitors secondary processor temperature.
CHASSIS Monitors chassis ambient temperature.
Winbond Hardware Doctor software and a white paper that provides more inform at ion on using
Winbond Hardware Doctor software are available on the Intel
Server Board SAI2 Resource
CD and are also available for download at:
http://www.support.intel.com/support/motherboards/server/SAI2
Revision 1.0
57
Page 68

Hardware Monitoring SAI2 Server Board TPS
Below is a diagram explaining what the W inbond Hecet a chip m onitors on the Intel® SAI2 server
board and how the monitoring is accomplished.
W83782D
PKG Temperature
CPU0 Temperature
CPU1 Temperature
CPU0 VRM
CPU1 VRM
+3.3V
+5V
+12V
VTT
+2.5V
CPU0 FAN
Temperature Sensor (Index 27h)
Temperature Sensor 2 High Byte (Index 50h, Bank 1)
Temperature Sensor 3 High Byte (Index 50h, Bank 2)
VCOREA (Index 20h)
VINR0 (Index 21h)
+3.3VIN (Index 22h)
+5VIN (Index 23h)
+12VIN (Index 24h)
-12VIN (Index 25h)
-5VIN (Index 26h)
FAN1 divisor bit2 (Index 5Dh(Bank0) bit5)
FAN1 divisor bt1 (Index 47h bit5)
FAN1 divisor bit0 (Index 47h bit4)
FAN1
(Index 28h)
SM Bus
CSB5
FAN2 divisor bit2 (Index 5Dh(Bank0) bit6)
CPU1 FAN
Chassis FAN
(for HDD)
58
Revision 1.0
FAN2 divisor bt1 (Index 47h bit7)
FAN2 divisor bit0 (Index 47h bit6)
FAN3 divisor bit2 (Index 5Dh(Bank0) bit7)
FAN3 divisor bt1 (Index 4Bh bit7)
FAN3 divisor bit0 (Index 4Bh bit6)
FAN2
(Index 29h)
FAN3
(Index
Page 69

SAI2 Server Board TPS Baseboard Specifications
6. Baseboard Specifications
This chapter specifies the operational parameters and physical characteristics for the SAI2
server board. This is a board-level specification only. System specifications are beyond the
scope of this document.
6.1 Estimated Baseboard M TBF
The table below shows the estimated MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures) calculated numbers
for the SAI2 server board and the SAI2 ser ver boar d with the SC5100 chassis.
• Mean Time between Interrupts (SAI2 server board alone): 110, 000 hour s
• Mean Time between Interrupts (SAI2 server board with SC5100 chassis): 26,313 hours
• Maximum Operating Temperature: 35 °C
Table 49. Estimated MTBF Calculated Numbers for SAI2/SC5100
Sub Assembly
Description
Baseboard 1
Front panel board
(typ) 1 2,852,904 55 100 100 50 3,566,515 280
Processor 1 1,000,000 55 100 100 50 1,250,000 800
Hard Drive 0 1,000,000 55 100 100 N/A NA NA
PRO 100 B 2 464,382 55 100 100 15 1,680,930 595
IDE CD-ROM (typ) 1 100,000 50 25 5 50 500,000 2,000
Power supply (typ) 1 150,000 50 100 100 50 150,000 6,667
1.44MB 3.5" FDU
(typ) 1 81,000 35 5 1 50 405,000 2,469
32 Meg DIMM (typ) 6 1,358,496 55 100 100 50 283,051 3,533
FAN (typ) 4 612,184 40 100 100 50 96,062 10,410
Sub Assy
Qty
Sub Assy
MTBF
Quote
(hrs)
110,000
Sub
Assu
Temp
Quote (C)
55 100 100 50 125,013 7,999
Sub Assy
Duty
Cycle
Quote (%)
Duty Cycle
as used in
Sys (%)
Sub Assy
temp in
sys (C)
Total Failure Rate (FITs): 38,004
Total Sub
Assy MTBF
(hours)
MTBF (in hours): 26,313
Total Sub
Assy Failure
Rate (FITs)
Revision 1.0
59
Page 70

Baseboard Specifications SAI2 Server Board TPS
6.2 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Operation of the SAI2 server board at conditions beyond those shown in the following table may
cause permanent damage to the system (provided f or stress testing only). Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect system reliability.
Table 50. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature -55 °C to +150 °C
Voltage on any signal with respect to ground
3.3-V Supply Voltage with Respect to ground -0.3 to +3.63 V
5-V Supply Voltage with Respect to ground -0.3 to +5.5 V
Notes:
1. Chassis design must provide proper airflow to avoid exceeding Pentium
2. V
means supply voltage for the device.
DD
0 °C to +55 °C 1
-0.3 V to V
®
III maximum case temperature.
+ 0.3 V 2
DD
6.3 Cal c ul ated Power Consumption
The following table shows the calculated power consumption for each of the power supply
voltage rails for the SAI2 server boar d. These values were calculated using the specifications
for the on-board components and processor s. Assumptions for add-in card power and other
peripherals powered from the server board are included in t he t able. Customers will need to
modify the calculated power consumption numbers based on their ant icipated usage – watts
per PCI slot, etc.
Note: The following numbers are provided as an example. Actual power consumption will vary
depending on the exact SAI2 configurat ion. Refer to the appropriate system chassis document
for more information.
Table 51. SAI2 Server Board Calculated Power Consumption
Device(s) 3.3 V +5 V +12 V -12 V 5-V Standby Total
Server Board
Processors
Memory (Four PC133
Registered GB SDRAM
DIMMs)
PCI Connectors
32-bit PCI slots (10 W per
slot on 5 V)
64-bit PCI slots (10 W per
slot on 3.3 V)
USB (500mA per connector)
Keyboard/Mouse
60
Revision 1.0
2.5 2.5 0.1 0.1 0.5
15
5.6
6.1 8.0 0.2 0.1
1.0
0.5
Page 71

SAI2 Server Board TPS Baseboard Specifications
Device(s) 3.3 V +5 V +12 V -12 V 5-V Standby Total
Fans (Four chassis and two
processor)
Total Current
Total Power
1.94
14.2 27 2.24 0.2 0.5 43.48
46.86 135 26.88 2.4 2.5 213.64
The total power calculation assumes a system configuration containing dual Pentium® III
1.26GHz processors, four 1-G B DI MMs, all PCI slots containing 10-W car ds, two USB devices,
keyboard and mouse, four chassis fans, and two processor fan heat sinks.
6.4 Measured Power Consumption
An SAI2 server board was configured with dual Pentium® III 1.26GHz processors and four 1GB PC133 SDRAM DIMMs.
The system was configured with Microsoft* Windows* 2000 Advanced Server. Test software
utilized during the power consumption measurement consisted of the Hipower* test suite, used
to simulate medium processor activity, and the WinMTA* memory stress test suite, used to
simulate high memory activity.
The SAI2 server board measured power consumption including the memory and processor
power is listed in the following table.
Table 52. SAI2 Server Board Measured Power Consumption
Device(s) 3.3 V +5 V +12 V Total Wattage
Server Board 18.8 54.5 12 85.3
Revision 1.0
61
Page 72

Regulatory and Integration Information SAI2 Server Board TPS
7. Regulatory and Integration Information
7.1 Regulatory Compliance
The SAI2 server board complies with the following safe t y standar d r equirements.
Table 53. Safety Regulations
Regulation Title
UL 1950/CSA950 Bi-National Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment
including Electrical Business Equipment. (USA and Canada)
EN 60950 The Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment including
Electrical Business Equipment. (European Community)
IEC60 950 The Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment including
Electrical Business Equipment. (International)
EMKO-TSE (74-SEC) 207/94 Summary of Nordic deviations to EN 60950. (Norway, Sweden, Denmark,
and Finland)
EU Low Voltage Directive 73/23/ECC Compliance to EU LV Directive via EN60 950 / IEC 60950
The SAI2 server board has been tested and verified to comply with the following EMC
regulations when installed in a compatible Intel host system. For information on Intel compatible
host system(s), refer to Intel’s Server Builder website, or contact your local Intel r epr esentative.
Table 54. EMC Regulations
Regulation Title
FCC – Class A Title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Parts 2 and 15, Subpart B, pertaining to
unintentional radiators. (USA)
ICES-003 – Class A Interference-Causing Equipment Standard, Digital Apparatus, Class A (including
CRC c. 1374) (Canada).
CISPR 22 Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Interference Characteristics of
Information Technology Equipment. (International)
VCCI – Class A Implementation Regulations for Voluntary Control of Radio Interference by Data
Processing Equipment and Electronic Office Machines. (Japan)
EN55022 Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Interference Characteristics of
Information Technology Equipment. (Europe)
EN55024 Generic Immunity Standard; currently compliance is determined via testing to IEC
801-2, -3, and -4. (Europe)
EU EMC Directive
89/336/EEC Compliance to EU EMC Directive via EN55022 & EN55024
BSMI (CNS13438) – Class A Taiwan EMC Regulations based on CISPR 22
C-tick (AS/NZS 3548) Australia & New Zealand EMS Regulations based on CISPR 22
62
Revision 1.0
Page 73

SAI2 Server Board TPS Regulatory and Integration Information
This server board assembly has the following required certification type mark ings:
• UL Joint Recognition Mark: Consists of small c (for Canada) followed by a stylized
backward UR and followed by a small US (USA) (on component side).
• Intel’s UL File Number E139761 (Component side).
• Battery “+” marking: located on the component side of the boar d in close pr oximit y to t he
battery holder.
• CE Mark: (Component side)
• Australian C-Tick Mark: Consists of solid circle with white check mark and supplier code
N232.
• Russian GOST (Open letter “ C” with the let t e r “ P” inside t he “C” and the letter “T” in the
mouth of the “C”.
• Taiwan BSMI Certification mark. Two Chinese characters and an 8 digit number.
7.2 Installation Instructions
CAUTION: Follow these guidelines to meet safety and regulator y requirements when installing
this board assembly.
Read and adhere to these instructions and to the instr uct ions supplied with the host com put er
and associated modules. If the instructions for the host computer are inconsist ent with these
instructions or the instructions for associated modules, contact the supplier’s technical support
to find out how to ensure that the system meets safety and regulatory requirements. I f the
instructions are not followed, the user incr eases safety risk and the possibility of noncompliance
with regional laws and regulations.
7.2.1 Ensure EMC
Before computer integr ation, the host chassis, power supply, and other modules should pass
EMC certification testing.
In the installation instructions for the host chassis, power supply, and other modules, pay close
attention to the following:
• Certifications
• External I/O cable shielding and filtering
• Mounting, grounding, and bonding r equirements
• Keying connectors when mismating of connectors could be hazardous
If the host chassis, power supply, and other modules have not passed applicable EMC
certification testing before integration, EMC testing m ust be conducted on a representative
sample of the newly completed computer.
7.2.2 Ensure Host Computer and Accessory Module Certifications
The host computer and any added subassembly (such as a board or drive assembly, including
internal or external wiring) should be certified for the region(s) where the end product will be
used. Marks on the product are proof of certification. Certification marks are as follows:
Revision 1.0
63
Page 74

Regulatory and Integration Information SAI2 Server Board TPS
7.2.2.1 In Europe
The CE marking sig nifies compliance with all relevant European requirements. If the host
computer does not bear the CE mark ing, obtain a supplier’s Declaration of Conformity to the
appropriate standards required by the Eur opean EMC Directive and Low Voltage Directive.
Other directives, such as the Machinery and Telecommunications Directives, may also apply
depending on the type of product. No regulatory assessment is necessary for low voltage DC
wiring used internally or wiring used externally when provided with appropriate overcurrent
protection. Appropriate protect ion is pr ovided by a maximum 8 Amp cur r ent limiting circuit or a
maximum 5-Amp fuse or positive temper at ur e coefficient (PTC) resist or . This Intel server board
has PTCs on all external ports that provide DC power externally.
7.2.2.2 In the United States
A certification mark by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) such as UL, CSA,
or ETL signifies compliance with saf et y requirements. External wiring must be UL Listed and
suitable for the intended use. Internal wiring must be UL Listed or Recognized and rated f or
applicable voltages and temperatures. T he FCC mark (Class A for comm ercial or industrial only
or Class B for residential) sig nifies compliance with electromagnetic interference requirements.
7.2.2.3 In Canada
A nationally recognized certification mar k such as CSA or cUL signifies compliance with safet y
requirements. No reg ulatory assessment is necessary for low voltage DC wiring used internally
or wiring used externally when provided with appropriate overcurrent protection. Appropriate
protection is provided by a maximum 8 Amp current limiting circuit or a maximum approved
5 Amp fuse or positive temperature coefficient (PTC) resist or . This server board has PTCs on
all external ports that provide DC power externally.
7.2.3 Prevent Power Supply Overload
The power supply output must not be overloaded. To avoid overloading the power supply, the
calculated total current load of all t he modules within the computer should be less than the
maximum output current rating of the power supply. If this is not adhered to, t he power supply
may overheat, catch fire, or damage the insulation that separates hazardous AC line circuitry
from low voltage user accessible circuitry and result in a shock hazard. If the load drawn by a
module cannot be determined by the marking s and instructions supplied with the module,
contact the module supplier’s technical support.
7.2.4 Place Battery Marking on Computer
There is insufficient space on t his ser ver boar d t o pr ovide instr uct ions for replacing and
disposing of the battery. The following warning must be placed permanently and legibly on the
host computer as near as possible to the batter y.
WARNING: Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace with only the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufactur er . Dispose of
used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
64
Revision 1.0
Page 75

SAI2 Server Board TPS Regulatory and Integration Information
7.2.5 Use Only for Intended Applications
This product was evaluated for use in ITE comput er s t hat will be installed in offices, schools,
computer rooms and similar locations. T he suitability of this product for ot her product categories
other than ITE applications, (such as m edical, industrial, alarm systems, and test equipment)
may require further evaluation.
7.2.6 Installation Precautions
During the installation and testing of the board, the user should observe all warnings and
cautions in the installation instructions. T o avoid injur y, be aware of the following:
• Sharp pins on connectors.
• Sharp pins on printed circuit assemblies.
• Rough edges and sharp corners on the chassis.
• Hot components (like processors, voltage regulators, and heat sinks).
• Damage to wires that could cause a short circuit.
• Observe all warnings and cautions that instruct you to refer computer servicing to
qualified technical personnel.
WARNING: Do not open the power supply. There is risk of elect r ic shock and burns from high
voltage and rapid overheating. Refer servicing of the power supply to qualified t echnical
personnel.
Revision 1.0
65
Page 76

Regulatory and Integration Information SAI2 Server Board TPS
This page intentionally left blank
66
Revision 1.0
Page 77

SAI2 Server Board TPS Glossary
Glossary
This appendix contains important terms used in t he pr eceding chapters. For ease of use,
numeric entries are listed first (e.g., “82460GX”) with alpha entr ies following (e.g., “AGP 4x”).
Acronyms are then entered in their respective place, with non-acronyms following.
Term Definition
ACPI Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
API Advanced Programmable Interrupt
APIC Intel Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller
BDA Binary Data Area
BIOS Basic Input Output System
CMOS Complementary Metal-Oxide Semi-Conductor
DIMM Dual In-Line Memory Module
DMA Direct Memory Access
DRAM Dynamic Random Access Memory
EBDA Extended BIOS Data Area
ECC Error Correcting Code
EMP Emergency Management Port
ESCD Extended System Configuration Data
FC-PGA Flip Chip Pin Grid Array
FDC Floppy Disk Controller
FIFO First-In, First-Out
FRB Fault Resilient Booting
FRU Field Replaceable Unit
FSB Front Side Bus
ICH I/O Controller Hub
IDE Integrated Device Electronics
I/O Input / Output
IPMI Intelligent Platform Management Interface
IPMB Intelligent Platform Management Bus
IRQ Interrupt Request
ISA Industry Standard Architecture
LAN Local Area Network
LED Light Emitting Diode
LSB Least Significant Bit
LUN Logical Unit Number
LVD Low Voltage Differential
MP Multiprocessor
MPS Intel Multi-Processor Specification
MSB Most Significant Bit
MTBF Mean Time Between Failures
NIC Network Interface Card
NMI Non-Maskable Interrupt
NRTL Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory
NVRAM Non-Volatile Random Access Memory
Revision 1.0
I
Page 78

Glossary SAI2 Server Board TPS
Term Definition
OEM Original Equipment Manufacturer
OS Operating System
PCI Peripheral Component Interconnect
PIC Programmable Interrupt Controller
PIO Programmed Input/Output
PnP Plug-and-Play
POST Power On Self Test
PTC Positive Temperature Coefficient
PXE Preboot Execution Environment
RAM Random Access Memory
RAMDAC Random Access Memory Digital-to-Analog Converter
ROM Read Only Memory
RTC Real Time Clock
RX A communications abbreviation for receive. Contrast with TX.
SCAM
SDRAM Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory
SDR Sensor Data Record
SCSI Small Computer Systems Interface
SE Single Ended
SEL System Event Log
SGRAM Synchronous Graphics RAM
SIO Super I/O
SMC Satellite Management Controller
SMI Server Management Interrupt
SMM Server Management Module
SSU System Setup Utility
SVGA Super VGA
TX A communications abbreviation for transmit. Contrast with RX.
USB Universal Serial Bus
VCCP Voltage Controlled Current Plane
VRM Voltage Regulating Module
WDT Watchdog Timer
WOL Wake-on-LAN
ZIF Zero Insertion Force
SCSI Configuration Automatically
II
Revision 1.0
Page 79

SAI2 Server Board TPS Reference Documents
Reference Documents
Refer to the following documents for additional inform at ion:
• 5-Volt Flash File (28F008SAx8) Datasheet.
• Advanced Configuration and Power Interf ace Specification, Revision 1.0
• ATI Rage XL Technical Reference Manual.
2
• I
C Bus Specification.
• Intel
• PCI Local Bus Specification, Revision 2.2.
• ServerWorks ServerSet* III LE North Bridge Specification.
• ServerWorks ServerSet* III LE South Bridge Specification.
• USB Specification, Revision 1.0.
• VRM 8.4 DC-DC Converter Specification.
• Wired For Management Baseline Specification, Revision 2.0
82559 Fast Ethernet Multifunction PCI/CardBus Controller Datasheet.
Revision 1.0
III
Page 80

Index SAI2 Server Board TPS
Index
Boot Menu, 21, 23, 31
Bridge, 5
3
32-bit PCI connector pinout, 54
6
64-bit PCI connctor pinout, 55
7
765B, 12
8
8042A, 12
82077AA, 12
82C59, 10, 11
Burst transfers, 6
Bus speed, 6
C
Certification, 63
Chained memory structure, 8
Checksum error, 37
CMOS, 12, 13, 19, 20, 21, 34, 35, 49
CMOS clear, 32, 47, 48
CMOS clear jumper, 21
CMOS map, 32
CNB30LE-T, 1, 5, 17
Configuration, 21, 23, 25, 32
Connector, PCI, 60
Console Redirection, 20
Controller, 7
crisdisk.bat, 37, 48
crisis.zip, 48
CSB5, 1, 4, 5, 6, 10, 11, 13, 14, 17
A
ACPI, 5, 18
Address, 13
Advanced Menu, 21, 23, 25
AIC-7899, 31
APIC, 3, 4, 6, 10, 11, 13, 14
ATI* Rage IIC, 8, 9, 10, 17
ATI* Rage XL video controller, 1
Autodetect, 8
Autoswitching, 8
B
Battery, 63, 64
BIOS, 2, 7, 10, 12, 13, 18, 19, 20, 21, 23, 24, 25, 32,
33, 34, 35, 37, 38, 48, 49
BIOS corruption, 48
BIOS customization, 34
BIOS data area RAM, 35
BIOS language area, 37
BIOS recovery, 47, 48, 49
BIOS recovery diskette, 37
BIOS recovery jumper, 48, 49
BIOS revision level, 44
BIOS Setup, 19, 33
BIOS update, 33
BIOS update file package, 48
BitBLT engine, 8
BMC, 10, 13
Board fan connector pinout, 50
D
DC-to-DC converter, 4
DIMM, 1, 5, 26
DIMM error, 26
DIMM sizes, 5
DIMM slot population, 5
DIMM slots, 1
Diskette drive connector pinout, 51
DMA Mode, 11, 25
E
Early receive interrupt, 8
EBDA, 35
ECC, 1, 5
EISA interrupts, 13
Ethernet, 1, 6, 7
Exit Menu, 21, 23, 32
Expansion connectors, 1, 10
F
Fan, 61
Fan heatsink, 4
FC-PGA, 1, 3, 4
Flash ROM, 13, 33, 37
Flip Chip Pin Grid Array, 1
Form factor, 2
Front panel 24-pin connector pinout, 56
IV
Revision 1.0
Page 81

SAI2 Server Board TPS Index
Front Panel reset, 32
Front Side Bus, 1
H
HDD LED pinout, 50
Hipower* test suite, 61
I
I2C connector pinout, 49
ICH, 7
IDE connector pinout, 53
IDE controller, 5, 6
IDE Controller, 28
®
Intel
82559, 1, 6, 7, 8, 17
Intel® Celeron™ processor, 3
Intel® EtherExpress™ PRO100+, 1, 6
Interrupt Acknowledge, 9
Interrupt generation, 4
Interrupt handling, 3, 11
Interrupt notification, 4
Interrupt routing, 13, 16
ISA, 10, 11, 13, 14
J
JEDEC, 1, 5
K
Keyboard and mouse connector pinout, 52
Keyboard Command Bar, 21, 22
Keyboard connector, 46
Keyed PCI expansion slots, 1, 6
Keyed PCI segment, 1, 6
L
Legacy, 32
Logo, 33
M
MPS, 20, 25
MTBF, 59, I
Multi-Processor Specification, 20
N
Network connector, 46
NMI switch, 46
North Bridge, 1, 5, 17
NVRAM, 21, 32
NVRAM.LST, 32
P
Parallel port connector, 46
Parallel port connector pinout, 52
Password
Change, 47
Disable jumper, 47
Password Clear, 47
Password disable jumper, 48
Password settings, 32
PC87417, 2, 12, 13
PCI IDs, 17
PERR, 54
PGA370, 1, 3, 4
Phlash, 19, 20, 33, 34, 37
PIC, 13
PIO Mode, 11
PLATCBLU.BIN, 33
PLATCXLU.BIN, 33, 34
PLATCXLX.BIN, 33
PLATCXXU.BIN, 33
PLATCXXX. BIN, 33
port 80h, 38, 43
Port 80h, 38
POST, 21, 22, 26, 34, 35, 36, 38
POST card, 49
POST checkpoint code, 38, 43
POST error codes, 42
POST scan-point, 35
Postcard, 38
Power consumption, 60, 61
Power-on Self-Test
See POST, 35, 36
Processor fan connector pinout, 50
Programmable Interrupt Controller, 11
Programmable transmit threshold, 8
PXE, 31
Main Menu, 21, 22, 23
Main power connector pinout, 49
MC146818, 13
Memory, 3, 5, 60
Maximum, 5
Memory Read, 9
Memory reconfiguration, 25
Memory Write, 9
Mouse connector, 46
Revision 1.0
R
RAMDAC, 8
Read Configuration, 9
Real Time Clock
See RTC, 2
Recovery failure, 37
Recovery mode, 37
V
Page 82

Index SAI2 Server Board TPS
Remote power-on, 18
RJ-45 LAN connector signals, 53
RTC, 12, 18, 35
S
S0 sleep state, 18
S1 sleep state, 11, 18
S4 sleep state, 11, 18
S5 sleep state, 11, 18
Safety regulations, 62
SC242, 3
SC242 connector, 3
SCSI, 19
SDRAM, 1, 5, 60, 61
Secure Mode, 30
Security, 20
Security Menu, 21, 23, 29
Serial port 1 connector, 46
Serial port 2 connector, 46
Serial ports COM1 and COM2 connector pinout, 52
SERR, 54
Server Menu, 30
ServerWorks ServerSet III LE chipset, 1, 3, 5
Setup Utility, 18, 19, 33, 48
SGRAM, 1, 6, 8
South Bridge, 1, 6
APIC, 11
Components, 5
EISA/ISA, 14
Features, 10
IDE, 1
Interrupts, 4, 13
PCI, 10, 11, 13, 14
PIC, 11
PNP, 13
Power management controller, 11
USB, 1, 11
SST39SF040, 13
Super I/O Controller, 2
Supervisor, 29
SVGA connector, 46
System initialization routines, 20
System Menu, 21, 23
System Setup Utility, 21
System Setup Utility, 19
T
termination circuitry, 4
Transfer Mode, 25
TX magnetics, 8
U
Ultra DMA Mode, 11
Universal Serial Bus, 60
USB, 60
USB connections, 13
USB connectors, 11, 46, 53
USB controller, 5, 6, 10, 11, 28
USB controller functions, 1
USB devices, 61
USB hub, 11
USB interface, 10, 11
USB ports, 2
User, 29
User Binary, 36
User binary code, 34, 35
User Binary Information Structure, 37
User binary ROM, 34
V
VGA connector, 8
Video BIOS, 33
Video port connector pinout, 51
VRM, 1, 4
W
Wake-on-LAN, 8, 18, 31
Wake-on-Ring, 18
Winbond, 57, 58
WinMTA* memory stress test suite, 61
Write Configuration, 9
Z
VI
Revision 1.0
Zero-insertion force socket, 3, 4
ZIF, 4
ZIF socket, 4
 Loading...
Loading...