Intel WPC2011NA - Pro/wireless 2011 Pccard Wireless Nic, PRO/Wireless 2011 Product Reference Manual
Page 1

Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011
LAN PC Card
Product Reference Guide
July 2000
Page 2

Copyright
Copyright © 2000, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
Intel Corporation, 5200 N.E. Elam Young Parkway, Hillsboro, OR 97124-6497
This manual as well as the software described in it is furnished under license and may only be used or copied in
accordance with the terms of the license. The information in this manual is furnished for informational use only, is subject
to change without notice, and should not be construed as a commitment by Intel Corporation. Intel Corporation assumes
no responsibility or liability for any errors or inaccuracies that may appear in this document or any software that may be
provided in association with this document.
Except as permitted by such license, no part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted in any form or by any means without the express written consent of Intel Corporation.
* Other product and corporate names may be trademarks of other companies and are used only for explanation and to
the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
Patents
This product is covered by one or more of the following U.S. and foreign Patents:
U.S. Patent No.
I4,387,297; 4,460,120; 4,496,831; 4,593,186; 4,603,262; 4,607,156; 4,652,750; 4,673,805; 4,736,095;
4,758,717; 4,816,660; 4,845,350; 4,896,026; 4,897,532; 4,923,281; 4,933,538; 4,992,717; 5,015,833;
5,017,765; 5,021,641; 5,029,183; 5,047,617; 5,103,461; 5,113,445; 5,130,520; 5,140,144; 5,142,550;
5,149,950; 5,157,687; 5,168,148; 5,168,149; 5,180,904; 5,216,232; 5,229,591; 5,230,088; 5,235,167;
5,243,655; 5,247,162; 5,250,791; 5,250,792; 5,260,553; 5,262,627; 5,262,628; 5,266,787; 5,278,398;
5,280,162; 5,280,163; 5,280,164; 5,280,498; 5,304,786; 5,304,788; 5,306,900; 5,321,246; 5,324,924;
5,337,361; 5,367,151; 5,373,148; 5,378,882; 5,396,053; 5,396,055; 5,399,846; 5,408,081; 5,410,139;
5,410,140; 5,412,198; 5,418,812; 5,420,411; 5,436,440; 5,444,231; 5,449,891; 5,449,893; 5,468,949;
5,471,042; 5,478,998; 5,479,000; 5,479,002; 5,479,441; 5,504,322; 5,519,577; 5,528,621; 5,532,469;
5,543,610; 5,545,889; 5,552,592; 5,557,093; 5,578,810; 5,581,070; 5,589,679; 5,589,680; 5,608,202;
5,612,531; 5,619,028; 5,627,359; 5,637,852; 5,664,229; 5,668,803; 5,675,139; 5,693,929; 5,698,835;
5,705,800; 5,714,746; 5,723,851; 5,734,152; 5,734,153; 5,742,043; 5,745,794; 5,754,587; 5,762,516;
5,763,863; 5,767,500; 5,789,728; 5,789,731; 5,808,287; 5,811,785; 5,811,787; 5,815,811; 5,821,519;
5,821,520; 5,823,812; 5,828,050; 5,850,078; 5,861,615; 5,874,720; 5,875,415; 5,900,617; 5,902,989;
5,907,146; 5,912,450; 5,914,478; 5,917,173; 5,920,059; 5,923,025; 5,929,420; 5,945,658; 5,945,659;
5,946,194; 5,959,285; 6,002,918; D305,885; D341,584; D344,501; D359,483; D362,453; D363,700;
D363,918; D370,478; D383,124; D391,250; D405,077; D406,581; D414,171; D414,172; D419,548
Invention No. 55,358; 62,539; 69,060; 69,187 (Taiwan); No. 1,601,796; 1,907,875; 1,955,269 (Japan);
European Patent 367,299; 414,281; 367,300; 367,298; UK 2,072,832; France 81/03938; Italy 1,138,713
A28555-01
Revision A
ii Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 3

About This Document
Reference Documents
This Reference Guide refers to the following documents:
Part Number Document Title
A28551-01
A28553-01
A28557-01
Conventions
Keystrokes are indicated as follows:
ENTER identifies a key.
FUNC, CTRL, C identifies a key sequence. Press and release each key
Press
A+B press the indicated keys simultaneously.
Hold A+B press and hold the indicated keys while performing or
®
PRO/Wireless 2011Access Point Product
Intel
Reference Guide
®
Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011LAN Utilities User Guide
®
PRO/Wireless 2011Site Survey
Intel
in turn.
waiting for another function. Used in combination
with another keystroke.
Typeface conventions used include:
<angles> indicates mandatory parameters in a given syntax.
[brackets] for command line, indicates available parameters;
in configuration files brackets act as separators
for options.
GUI Screen text indicates the control name in a GUI-based
application.
Italics indicates the first use of a term, book title, or menu.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide iii
Page 4
‘single quotes’ indicates the exact setting for a parameter.
Screen
indicates monitor screen dialog. Also indicates
user input.
A screen is the hardware device on which
data appears.
A display is data arranged on a screen.
Terminal
URL
indicates text shown on a terminal screen.
indicates Uniform Resource Locator. Click the URL to
launch browser.
This document uses the following icons for certain conditions or types
of information:
Indicates tips or special requirements.
Indicates conditions that can cause equipment damage
or data loss.
Indicates a potentially dangerous condition or
procedure that only Intel-trained personnel should
attempt to correct or perform.
iv Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 5

Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction.....................................................1
Chapter 2 About the Intel® PRO/Wireless
2011LAN Adapter
2.1 MU Mode ......................................................4
2.2 11 Mbps Operation ........................................4
2.3 Mobile IP........................................................ 5
2.4 Power Management ........................................6
2.5 Card and Socket Services ................................6
2.6 Intel
LED Descriptions...................................................7
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter
Chapter 3 Hardware Installation....................................9
3.1 Preparation ....................................................9
3.2 Installing the PC Card ...................................10
Chapter 4 Installing and Configuring the
Windows 95/98 Driver................................13
4.1 Installing the Intel
LAN Driver in Windows 95 ..................................13
4.2 Installing the Intel
LAN Driver in Windows 98 ..................................15
®
4.3 Intel
LAN Adapter Configuration for
Windows 95/98 .................................................17
PRO/Wireless 2011
..........................................3
®
PRO/Wireless 2011
®
PRO/Wireless 2011
Chapter 5 Installing and Configuring the
Windows NT Driver......................................19
®
5.1 New Intel
Adapter Installation.............................................20
5.2 Intel
Configuration for Windows NT ............................22
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide v
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter
Page 6

Chapter 6 Installing and Configuring the
Driver in Windows 2000
6.1 Configuring the Intel
2011 LAN Adapter for Windows 2000..................26
.............................23
®
PRO/Wireless
Chapter 7 Verifying the Firmware Version.................29
Appendix A Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA) .. A-1
A.1 Installing NCPA .......................................... A-1
A.2 Using NCPA............................................... A-2
A.2.1 Mobile Unit Property Page .................. A-4
A.2.2 Power Property Page .......................... A-6
A.2.3 Mobile IP Property Page...................... A-7
A.2.4 Encryption Property Page.................... A-9
A.2.5 WLAN Adapter Property Page ........... A-12
Appendix B WLAN Adapter Specifications.................. B-1
Appendix C Troubleshooting ......................................... C-1
C.1 Windows 95/98 Troubleshooting Tips ..........C-1
C.2 Windows NT 4.0 Troubleshooting ................ C-3
C.2.1 Useful Tool for Windows NT
Troubleshooting .........................................C-4
C.2.2 Windows NT Errors............................ C-5
C.3 Windows 2000 Troubleshooting Tips............ C-7
Appendix D Customer Support......................................D-1
D.1 Intel Automated Customer Support ..............D-1
D.2 Software License Agreement........................ D-3
D.3 Limited Lifetime Hardware Warranty ............ D-5
Appendix E Regulatory Compliance................................E-1
Index............................................................................... Index-1
vi Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 7

Chapter 1 Introduction
The Intel® Wireless LAN PC Card is a direct-sequence
(DS) product. The Intel
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN is a
spread spectrum network operating between 2.4 and
2.5 GHz. Spread spectrum communication provides a
high-capacity network within large or small
®
environments. Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN products
provide a high-capacity network using multiple access
points within large or small environments.
®
• Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN bridging
architecture allows communication between wired
network devices and mobile devices.
®
• Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN supports the IEEE
802.11 specification. This open architecture allows
devices to communicate with wireless devices from
other manufacturers.
®
• Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN allows mobile
devices to roam throughout large facilities while
remaining connected to the LAN.
®
• Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN allows protocol
firmware upgrades while devices remain
operational.
®
• Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN antenna diversity
feature alternates between antennas with the best
reception, increasing overall performance.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 1
Page 8

Introduction
2 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 9

Chapter 2 About the Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011
LAN Adapter
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter allows PC
Card equipped host systems to configure, connect to
and establish a wireless network.
Features Include:
• Low-power operation for battery-powered devices
with PC Card slots
• Standard NDIS (Network Driver Interface
Specification)
• Windows 95, 98, NT 4.0 and 2000
driver support
• Card and Socket Services support
• Plug and Play support
• Power management [Continuously Aware Mode
(CAM) and Power Save Polling (PSP)].
®
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 3
Page 10

About the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter
2.1 MU Mode
In the Mobile Unit (MU) mode, the WLAN adapter
connects to an access point (AP) or another WLAN
installed system. MU mode allows the device to roam
freely between AP cells in the network. MUs appear as
network nodes to other devices.
2.2 11 Mbps Operation
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter supports an
11 Mbps data rate. The adapter can default to a 5.5,
2 or 1 Mbps data rate when unable to establish an
11 Mbps association.
The following factors can dynamically alter the
data rate:
• signal strength between the AP and the MU
• the ratio of good transmitted packets to attempted
• transmitted packets fall below a threshold
• the MU finds a higher transmit rate with another AP
or it encounters an unspecified data rate.
4 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 11
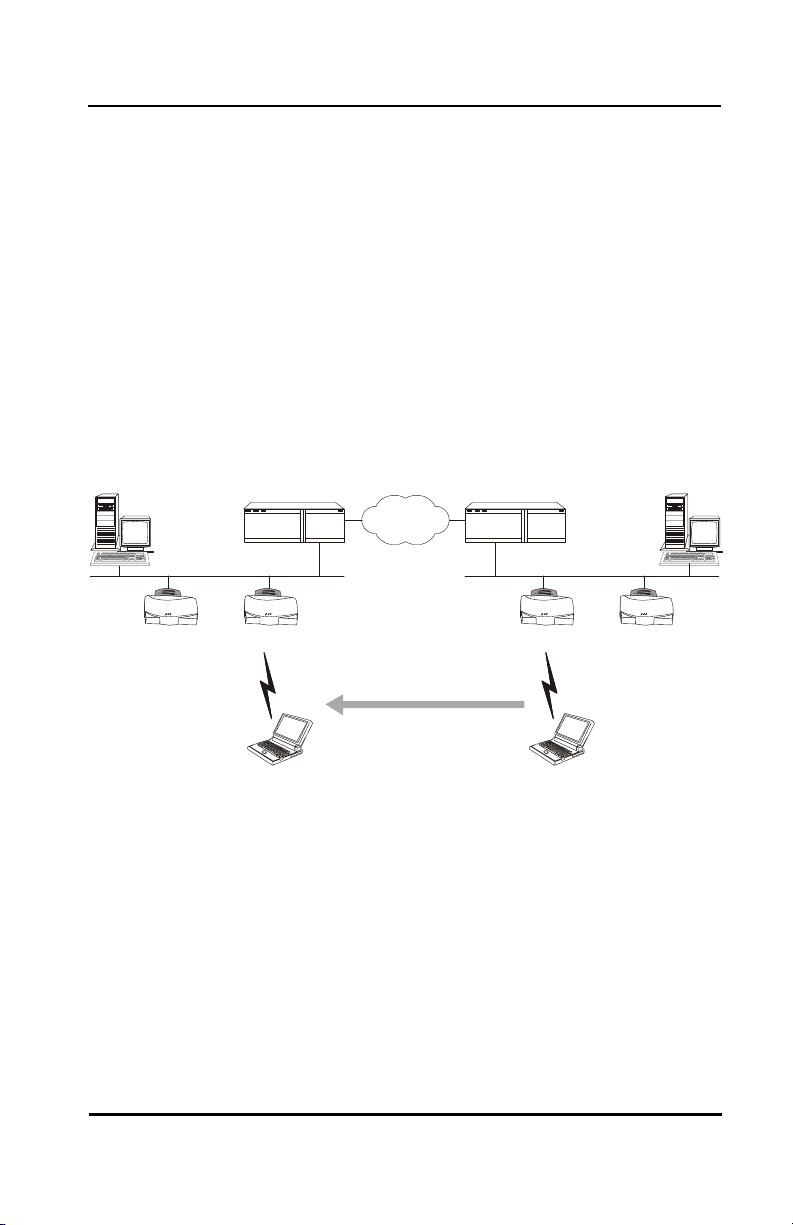
2.3 Mobile IP
Mobile Node
Mobile Node
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter supports
Mobile IP (roaming across routers) when properly
configured to support Mobile IP. The Mobile IP feature
allows Wireless LAN devices to roam across routers.
The MU retains its IP address when configured for
Mobile IP and can:
• move from one IP subnet to another
• move from an Ethernet segment to a wireless LAN
• move from one Ethernet segment to another.
About the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter
Host Router
Ethernet
AP 4
AP 3
Internet
AP 1
HostRouter
Ethernet
AP 2
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 5
Page 12
About the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter
2.4 Power Management
The WLAN adapter supports the Continuously
Aware (CAM) and Power Save Polling (PSP) powermanagement modes. CAM requires the radio to remain
on. Intel does not recommend CAM for battery
powered devices.
PSP mode allows the MU to conserve power by
suspending communication while still associated with
an AP. The AP saves data for transmission to the MU
when it wakes at given intervals. When the adapter
wakes to check for data, it switches back into CAM
until it is ready suspend communications again.
The PSP performance index, which varies from 1 to 5,
allows users to specify how often the MU wakes up to
check for data. PSP performance index 1 provides the
quickest response time (shortest sleep interval), while
PSP performance index 5 provides efficient power
consumption (longest sleep interval).
Use the Intel Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA) or
the Intel WLAN Monitor utility to manually set the PSP
performance index.
2.5 Card and Socket Services
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN supports Card and
Socket services. Card and Socket Service software
packages work with the host computer operating system
enabling the Wireless LAN adapter to interface with
host computer configuration and power management
functions. Card and Socket Service software packages
include SystemSoft and Phoenix.
6 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 13

About the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter
2.6 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
Adapter LED Descriptions
The WLAN adapter LED illuminates during connection
or data transfer to indicate the functional status of
the adapter.
Status Function
Off WLAN adapter radio is disabled
or incapable of transmission
Slow Yellow Flash Adapter associated with an
access point
Rapid Yellow Flash Indicates data traffic between
adapter and access point. The
faster the flash, the more data
traffic on the network.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 7
Page 14

About the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter
8 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 15
Chapter 3 Hardware Installation
Physical installation of the PC Card differs for each
system. Refer to the system manufacturer
documentation for specific information.
3.1 Preparation
Before beginning the installation, verify the hardware
package contains:
®
• Intel
• installation CD and utilities.
Verify the model indicated on the card and packaging
before use. Contact the Intel Support Center if an item is
missing or not functioning.
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 9
Page 16

Hardware Installation
3.2 Installing the PC Card
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN PC Card
installation requires:
• a computer with a Type II PC Card slot
• a CDROM drive
• an available interrupt (IRQ)
• an available I/O port address
• Intel
Installation and removal methods vary for different host
devices. Refer to system documentation for information.
Avoid WLAN adapter contact with liquids or
abrasive materials.
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN driver installation
CDROM.
To install the PC Card:
1. Insert the PC Card into the PC slot. Arrows on the
front of the PC Card indicate the insertion point to
the slot.
2. Slide in the PC Card until it firmly seats.
10 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 17
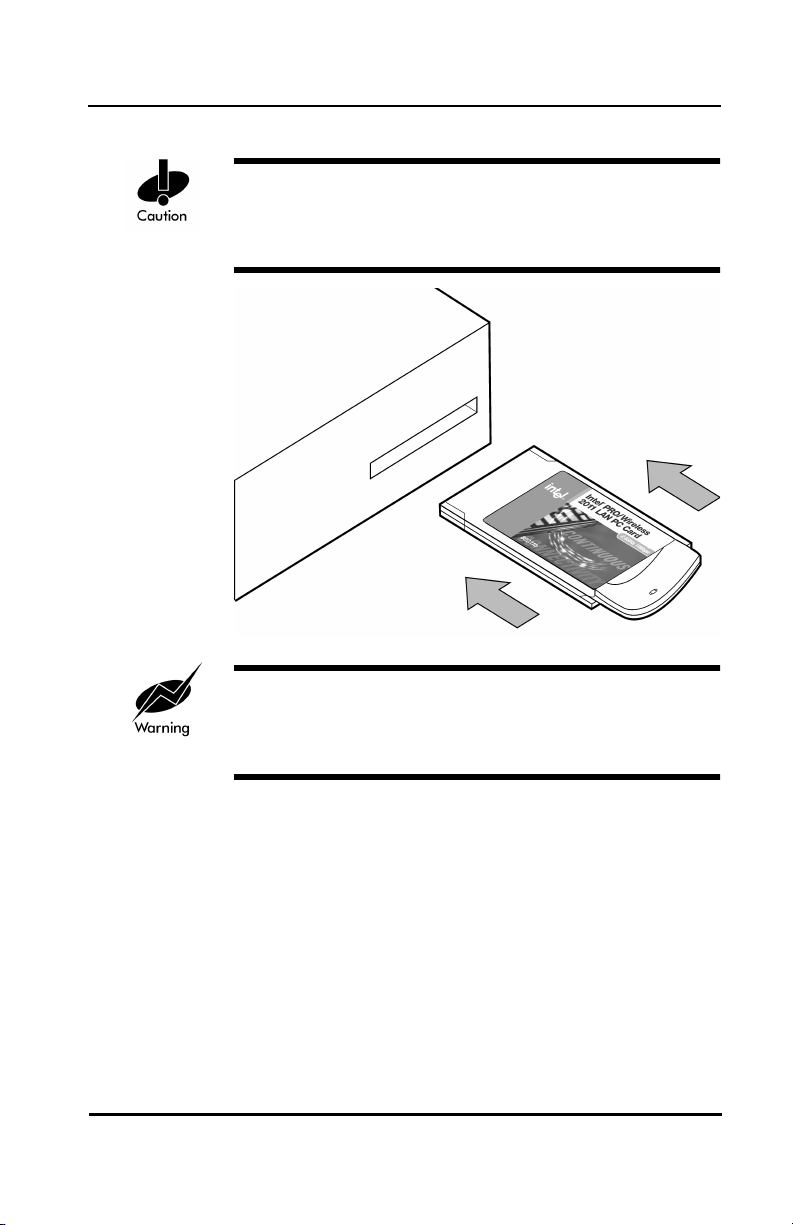
Hardware Installation
Align the card properly when inserting. Insert the card
firmly without forcing. Forcing the card into the slot can
damage the device or the card.
FCC RF exposure requirements state the PC Card
antenna should be positioned so it is at least 5 cm
(2 inches) away from the user.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 11
Page 18

Hardware Installation
12 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 19
Installing and Configuring the Windows 95/98 Driver
Chapter 4 Installing and
Configuring the
Windows 95/98 Driver
4.1 Installing the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Driver in Windows 95
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows driver
ships with the Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
utility on a CDROM. Use NCPA to view and edit WLAN
adapter settings.
Intel recommends updating the Intel® PRO/Wireless
2011 LAN adapter to the latest firmware. After the
driver and Wireless LAN Utilities have been installed,
use the WLAN Update utility to update the firmware in
Windows 95. Refer to the documentation shipped with
the Intel
instructions on using WLAN Update. To download the
latest firmware, go to (http://support.intel.com).
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Utilities for
Before installing the Intel
Windows driver:
• verify the Intel
is installed
• obtain the driver installation CDROM.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 13
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter
Page 20

Installing and Configuring the Windows 95/98 Driver
To install the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN driver for
the first time in Windows 95:
1. Install the Intel
WLAN adapter as described in
Chapter 3.
2. Power up the system.
3. Insert the Intel
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows
driver installation CD.
4. When Windows 95 recognizes the adapter, an
Update Device Driver Wizard dialog box appears
requesting a driver to install. Click Next.
5. Click Finish when Windows displays the
following message:
Windows found the following updated
®
driver for this device: Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011
LAN PC Card.
Complete the installation instructions displayed by
Windows 95.
6. Enter the network ESSID in the Easy Setup window.
Click OK.
7. Click Finish.
8. When prompted, restart the computer.
9. Proceed to 4.3 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
Adapter Configuration for Windows 95/98 on page
17.
14 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 21

4.2 Installing the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Driver in Windows 98
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows driver
ships with the Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
utility on a CDROM. Use NCPA to view and edit WLAN
adapter settings.
Intel recommends updating the WLAN adapter to the
latest firmware. After the driver and Wireless LAN
Utilities have been installed, use the WLAN Update
utility to update the firmware in Windows 98. Refer to
the documentation shipped with the Wireless LAN
Utilities for instructions on using WLAN Update. To
download the latest firmware, go to
(http://support.intel.com).
®
Before installing the Intel
Windows driver:
• verify the WLAN adapter is installed
• obtain the Intel
driver installation CDROM.
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 15
Page 22

Installing and Configuring the Windows 95/98 Driver
To install the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN driver for
the first time in Windows 98:
®
1. Install the Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter
as described in Chapter 3.
2. Power up the system.
3. Insert the Intel
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows
driver installation CD.
4. When Windows 98 recognizes the adapter, the Add
New Hardware Wizard dialog box appears.
Click Next.
5. Select Search for best driver for your device.
Click Next.
6. Specify the location of the driver files.
Click Next.
7. Click Next when Windows locates and displays
the adapter.
The Easy Setup dialog box displays.
8. Enter the network ESSID in the Easy Setup window.
Click OK.
The Add New Hardware Wizard dialog box
displays stating the required software has
been installed.
9. Click Finish.
10. When prompted, restart the computer.
11. Proceed to 4.3 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
Adapter Configuration for Windows 95/98 on page
17.
16 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 23
Installing and Configuring the Windows 95/98 Driver
4.3 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter Configuration for Windows 95/98
To configure the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter
in Windows 95/98:
1. Click Start, select Settings and Control Panel.
2. Select the Network icon and click on the Intel
Wireless LAN PC Card.
3. Select the Properties button.
The Easy Setup dialog box displays.
4. Click the Advanced button to view the default
adapter configuration.
Use the Mobile Unit, Power, Mobile IP, Encryption
and WLAN Adapter tabs to view or adjust the
adapter configuration settings.
®
For information on using the NCPA utility to configure
®
Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter properties, refer
to Appendix A.
5. Exit and save the configuration settings by
clicking OK or Finish. Select Cancel to use the
default values.
6. Restart the system for the changes to take effect.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 17
Page 24

Installing and Configuring the Windows 95/98 Driver
18 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 25

Installing and Configuring the Windows NT Driver
Chapter 5 Installing and
Configuring the
Windows NT Driver
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows driver
ships with the Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
utility on a CDROM. Use NCPA to view and edit WLAN
adapter settings.
Intel recommends updating the WLAN adapter to the
latest firmware. After the driver and Wireless LAN
Utilities have been installed, use the WLAN Update
utility to update the firmware in Windows NT. Refer to
the documentation shipped with the Wireless LAN
Utilities for instructions on using WLAN Update. To
download the latest firmware, go to
(http://support.intel.com).
Before installing the Intel
Windows NT driver:
• verify the WLAN adapter is installed
• obtain the Intel
driver installation CDROM.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 19
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows
Page 26

Installing and Configuring the Windows NT Driver
5.1 New Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter Installation
To install the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN driver for
the first time in Windows NT:
Verify there is no existing Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011
LAN Windows NT driver in the system. If there is an
existing driver, remove it and complete the instructions
in this section.
If IRQ or I/O conflicts occur during the installation,
configure the IRQ and I/O addresses for available
values. Refer to the Windows NT Diagnostics Tool to
verify the values. Use the NCPA WLAN Adapter page to
set the Interrupt Number, the I/O Port Address and the
Memory Base Address values.
1. Install the WLAN adapter as described in
Chapter 3.
2. Power up the system.
3. Insert the Intel
driver installation CD.
4. Click Start, select Settings and Control Panel.
5. Click on the Network icon and select the Adapters
tab. Click Add.
6. Click Have Disk.
A window appears prompting for the location of the
driver files.
20 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows
Page 27

7. Enter the driver letter assigned to the CD drive.
Click OK.
The Select OEM Option dialog box displays.
8. Select the Intel
®
Wireless LAN PC Card. Click OK.
The Easy Setup dialog box displays.
9. Enter the network ESSID in the Easy Setup dialog
box. Click OK.
The Network dialog box appears.
10. Click Close, and complete the installation
instructions displayed by the Windows
operating system.
11. Reboot the computer when prompted by
Windows NT.
12. Proceed to 5.2 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
Adapter Configuration for Windows NT on page 22.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 21
Page 28

Installing and Configuring the Windows NT Driver
5.2 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter Configuration for Windows NT
To configure the WLAN adapter for Windows NT:
1. Click Start, select Settings and Control Panel.
2. Click on the Network icon.
3. Select the Adapters tab and click on the Intel
Wireless LAN PC Card.
4. Click the Properties button.
The Easy Setup dialog box displays.
5. Click the Advanced button to view the default
adapter configuration.
Use the Mobile Unit, Power, Mobile IP, Encryption
and WLAN Adapter tabs to view or adjust the
adapter configuration settings.
®
For information on using the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011
LAN NCPA utility to configure adapter properties, refer
to Appendix A.
6. Click OK or Close to save the changes to the
adapter configuration and exit the NCPA utility.
Select Cancel to use the default values.
®
7. Remove the Intel
Windows driver installation CD and follow the
remaining instructions.
8. Restart the computer when prompted by
Windows NT.
22 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
Page 29

Installing and Configuring the Driver in Windows 2000
Chapter 6 Installing and
Configuring the Driver in
Windows 2000
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows driver
ships with the Intel Network Control Panel Applet
(NCPA) utility on a CDROM. Use NCPA to view and edit
WLAN adapter settings.
Intel recommends updating the WLAN adapter to the
latest firmware. After the driver and Wireless LAN
Utilities have been installed, use the WLAN Update
utility to update the firmware in Windows 2000. Refer to
the documentation shipped with the Wireless LAN
Utilities for instructions on using WLAN Update. To
download the latest firmware, go to
(http://support.intel.com).
Before installing the Intel
Windows 2000 driver:
• verify the WLAN adapter is installed
• obtain the Intel
driver installation CDROM.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 23
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows
Page 30

Installing and Configuring the Driver in Windows 2000
To install the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN driver for
the first time in Windows 2000:
1. Install the WLAN adapter as described in
Chapter 3.
2. Power up the system.
3. Insert the Intel
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Windows
driver installation CD.
4. When the Found New Hardware Wizard dialog
box displays, click Next.
5. When Windows 2000 recognizes the adapter,
the Found New Hardware Wizard dialog box
displays again.
6. Select the Search for a suitable driver for my
device button. Click Next.
7. Specify the location of the driver files.
Click Next.
8. Click Next when a message displays stating
Windows has found the required device driver.
The Microsoft Digital Signature Not Found dialog
box could appear at this point in the installation.
A Microsoft digital signature is not required for the
driver installation. Click Ye s to continue with the
driver installation
A progress bar displays showing the progress of the
driver file download.
When the driver download is complete, the Easy
Setup dialog box displays.
24 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 31

Installing and Configuring the Driver in Windows 2000
9. Enter the network ESSID in the Easy Setup window.
Click OK.
The Found New Hardware Wizard dialog box
displays again stating Windows has finished
installing the software required for this device.
10. Click Finish.
11. Restart the computer for the changes to take effect.
12. Proceed to 6.1 Configuring the Intel® PRO/Wireless
2011 LAN Adapter for Windows 2000 on page 26.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 25
Page 32

Installing and Configuring the Driver in Windows 2000
6.1 Configuring the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN Adapter for Windows 2000
To configure the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter
for 2000:
1. Click Start, select Settings and Control Panel.
2. Click on the System icon and select the
Hardware tab.
3. Click on the Device Manager button.
4. Double-click on Network Adapters.
5. Right-click on the Intel
WLAN adapter.
6. Select Properties.
The Intel PC Card Properties dialog box displays.
7. Select the Intel
The NCPA Easy Setup dialog box displays.
8. Select the Advanced button to view the default
adapter configuration.
Use the Mobile Unit, Power, Mobile IP, Encryption
and WLAN Adapter tabs to view or adjust the
adapter configuration settings.
®
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN tab.
For information on using the NCPA utility to configure
adapter properties, refer to Appendix A.
26 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 33

9. Click OK or Close to save the changes to the
adapter configuration and exit the NCPA utility.
Select Cancel to use the default values.
10. Restart the computer when prompted by the
Windows operating system.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 27
Page 34

Installing and Configuring the Driver in Windows 2000
28 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 35

Verifying the Firmware Version
Chapter 7 Verifying the Firmware
Version
Verify the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter
firmware is the most recent version to ensure optimal
functionality. In Windows 95/98, NT 4.0 and 2000,
WLAN adapters use the Wireless LAN Monitor utility to
view driver and firmware revision data. The WLAN
Monitor General properties page allow users to verify
driver firmware version data and view wireless LAN
adapter signal and transmission quality information.
The WLAN Update utility updates the firmware in a PC
Card. Refer to the documentation shipped with the
Wireless LAN Utilities suite for instructions on using
WLAN Update.
The driver and Wireless LAN Utilities installation is
required to run the WLAN Update utility.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide 29
Page 36

Verifying the Firmware Version
30 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 37

Appendix A
Network Control Panel Applet
(NCPA)
A.1 Installing NCPA
NCPA supports Windows 95/98, NT 4.0 and 2000.
The Intel
comes bundled with the Intel
Windows device driver on a CDROM. Use NCPA to
configure the adapter. Complete the driver installation
instructions described in Chapters 4, 5 and 6 for the
Windows 95/98, NT and 2000 operating systems to
install NCPA.
Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA) utility
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide A - 1
Page 38

Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
A.2 Using NCPA
NCPA allows users to view and edit Intel® PRO/Wireless
2011 LAN adapter settings. Access NCPA through the
Windows Network Control Panel. When NCPA is
installed, the applet displays an Easy Setup window
allowing users to set the 802.11 ESSID.
Clicking the Advanced button allows users to view or
edit adapter settings using the Mobile Unit, Power,
Mobile IP, Encryption and WLAN Adapter
property pages.
The Easy Setup window and the five Advanced property
pages can appear different between the Windows 95,
98, NT and 2000 operating systems.
A - 2 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 39

Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
Use the WLAN Adapter property page to create a
NCPA Advanced property pages password dialog box.
The password dialog box displays when the user clicks
the Advanced button on the Easy Setup window. When
enabled, users cannot access the Advanced property
pages without entering the correct password.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide A - 3
Page 40

Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
A.2.1 Mobile Unit Property Page
Use the Mobile Unit property page to configure the
adapter operating mode and ESSID.
Use the Operating Mode pull-down menu to select one
of the following operating modes for the adapter:
ESS (802.11 Station) - Select ESS (802.11 Station)
to enable the MU to transmit and receive data with an
access point. The MU data rate is based on transmit
retries. When a data rate is not achieved the MU
defaults to the next highest selected data rate. ESS
is the MU default mode.
A - 4 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 41

Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
IBSS (802.11 Ad Hoc) - Select IBSS (802.11 Ad Hoc) to
enable MUs to form their own local network where MUs
communicate peer-to-peer without access points. Use
IBSS to create networks where needed within established
cells. In IBSS, MUs take turns generating beacons and
handling probe responses. The MU starting the IBSS
network (the first station transmitting a beacon)
determines the channel and data rate used for the IBSS
network. If a single MU is sending every beacon, there
are no other MUs in the IBSS network and at least one
more MU is needed to communicate peer-to-peer.
Pseudo IBSS (Proprietary Ad Hoc) - Select Pseudo IBSS
when the highest throughput is required in an IBSS
network for testing MUs. Pseudo IBSS does not support
PSP MUs and does not use beacons or authentication.
In Pseudo IBSS mode, each MU is required to be on the
same channel. Pseudo IBSS is not recommended as a
normal operational mode or for MUs operating on
battery power.
Enter an ESSID in the 802.11 ESSID field. The ESSID is
the 802.11 Extended Service Set Identifier. The ESSID is
a 32-character (maximum) string identifying the wireless
local area network. The ESSID assigned to the adapter
is required to match the access point ESSID for the
adapter to communicate with the access point. The
ESSID can also be entered from the Easy Setup window.
Use the Mandatory AP address field to enter the IEEE
MAC address of the access point where the adapter is
required to associate. The adapter associates to only
this access point when communicating on the network.
Enter an access point MAC address to associate to an
access point that has a compatible ESSID.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide A - 5
Page 42

Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
A.2.2 Power Property Page
Use the Power property page to control adapter power
consumption in the ESS and IBSS operating modes.
The adapter has two power consumption modes,
Continuous Access Mode (CAM) and Power Save Poll
(PSP) mode. CAM yields the best performance but uses
the most power. CAM is the preferred mode for systems
running on AC power. PSP saves significant amounts of
power over CAM. PSP is the preferred mode for systems
running on battery power.
Set the slider to the far right to keep the adapter in CAM
or set the slider to a PSP performance index (1 to 5).
Each mode is described underneath the sliding scale.
Disable Power Management in WLAN Monitor to use
the settings in Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA).
Set the adapter power consumption mode and click OK.
A - 6 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 43

A.2.3 Mobile IP Property Page
Use the Mobile IP property page to configure the
adapter to support the roaming across routers function.
Mobile IP enables an MU to communicate with other
hosts using only its home IP address after changing its
point-of-attachment to the internet/intranet.
Select the Enable Mobile IP checkbox to enable
Mobile IP support. Restart the system for the changes
to take effect.
Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
Enter the Home Agent AP Address of an AP on the
home subnet. This enables the MU to register with a
foreign subnet AP and tell the AP where the MU home
AP is located.
Enter a Mobile Home MD5 Key matching the MD5 key
on the AP of the home subnet. Use this password to
protect the registration packets from being tampered
when forwarded to the home agent AP.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide A - 7
Page 44

Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
Use the Registration Timeout pull-down menu to select
a timeout value. When the MU registers with a foreign
subnet AP the registration is required to take place
within the time specified. The default registration time is
60 seconds. If the MU does not register with the foreign
subnet AP within the specified time, the foreign subnet
AP removes the MU from its list of registered MUs.
Use the Delay Time pull-down menu to select the time
an MU waits for a response from a foreign subnet AP
when trying to register with that AP. An Mu attempts to
register with an AP three times before stopping.
A - 8 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 45

A.2.4 Encryption Property Page
Use the Encryption property page for configuring
WLAN adapter Encryption settings. The absence of a
physical connection makes wireless links vulnerable to
information theft. Encryption is an efficient method of
preventing data theft and improving data security.
The firmware supports Open System, 40-bit and
128-bit Encryption algorithms.
Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
Use the Encryption Algorithm pull-down menu to select
the Open System, 40-bit or 128-bit Encryption
algorithm to be used for the adapter. The Open System
algorithm (default setting) does not encrypt packets over
the network. Select Open System to disable Encryption
for the WLAN adapter and allow for the transmission
and receipt of data with no security.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide A - 9
Page 46

Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
An access point and MU are required to use the same
Encryption algorithm to associate and transmit data. If
an access point is set to WEP (Privacy) disabled and an
MU is set to 40-bit or 128-bit, no association takes
place. The same is true if the MU is set for Open System
and the access point is set to 40-bit or 128-bit.
If an access point is set to 40-bit and the MU is set to
128-bit the devices can associate, but no data
transmission can take place between the two devices.
Access Point MU Association
Open Open OK
40 40 OK
128 40 Association, No
Open 40 No Association
Open 128 No Association
40 128 Association, No
40 Open No Association
128 Open No Association
128 128 OK
Status
data transmission
data transmission
When 40-bit Encryption is selected, the user is required
to enter a 10 Hex digit Encryption key. The key can be
entered by spreading the 10 Hex digits between the two
fields provided. Click OK to save and implement the
Encryption key data.
128-bit Encryption is subject to export restrictions. An
access code is required if 128-bit Encryption is selected
and an export restrictions dialog box displays.
Contact Intel Automated Customer Support
(http://support.intel.com) for information on acquiring
an access code for 128-bit Encryption.
A - 10 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 47

Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
If an access code is required, click the Access Code
button to display the Enable 128-bit Encryption dialog
box. Enter the access code in the three fields provided
and click OK. Once the access code is entered, the
Access Code button is no longer displayed on the
Encryption property page and the access code is stored.
Once 128-bit Encryption is enabled, select 128-bit
Encryption from the Encryption Algorithm pull-down
menu. Enter the 26 Hex digit Encryption key by
spreading the 26 Hex digits across the six fields
provided. Click OK to save and implement the
Encryption key data.
Click Reset Keys to clear the entries in the Shared
Encryption Key fields.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide A - 11
Page 48

Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
A.2.5 WLAN Adapter Property Page
Use the WLAN Adapter property page to configure
hardware and radio settings.
Use the Card Type pull-down menu to specify the type
of adapter in the system.
The Interrupt Number, IO Port Address and Memory
Base Address fields are automatically updated.
If resource conflicts exist (on Windows NT systems)
modify these settings to fit system needs.
Select Diversity on if dual antenna support is required.
Diversity improves communication in highly reflective
environments. Do not select Diversity on if a secondary
antenna is not being used. Using diversity in a
single antenna application can cause poor wireless
network performance.
A - 12 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 49

Password Protecting NCPA
NCPA has a password protection feature that can be
turned on and off from the WLAN Adapter property
page. When the NCPA program is initially launched,
the password is off (default).
To create a password for the NCPA Advanced
property pages:
1. Click the Password button from the WLAN Adapter
property page.
The Change Setup Password dialog box displays.
Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
2. Enter the case-sensitive password (10 characters
maximum) in the Current Password field and click
OK.
The NCPA Advanced property pages dialog box is
enabled and now appears when the Advanced
button is clicked from Easy Setup window.
To disable the password dialog box, enter the
current password and leave the New Password and
Confirm New Password fields blank. Click OK.
To change the password, enter the current password
and enter a new password in the New Password
and Confirm New Password fields. Click OK.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide A - 13
Page 50

Network Control Panel Applet (NCPA)
A - 14 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 51

Appendix B
WLAN Adapter Specifications
PC Card Physical
Dimensions
(less antenna)
Weight
(with antenna)
Operating temperature
Humidity 95% maximum non condensing
Cargo/Packaged 6ft(1.8m) drop 5hz vibration Mil-Std 810E
Altitude 15,000 ft. (4.6 km) - Storage 8,000 ft.
Vibration 2 G peak, sine; 0.02 G peak random
Shock 40 G, 11mS, half sine
ESD meets CE-Mark
PCMCIA Compliance Type II, Card and Socket Services
3.3 inches x 2.1 in. x 0.2 inches
(85 mm x 54 mm x 5 mm)
1.6 oz (45.36 g)
32 to 130
(2.4 km) - Operating
(5Hz - 2000Hz)
°F (20 to 70 °C)
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide B-1
Page 52

WLAN Adapter Specifications
Radio
Frequency Range country dependent. Typically 2412 MHz to
2462 MHz
Radio Data Rate 11 Mbps - Optional
5.5 Mbps - Optional
2 Mbps - Optional
1 Mbps - Required
Range open environment over 100 ft (at 11 Mbps).
Typical office or retail environment 30 - 50 ft
(at 11 Mbps).
TX Max. Radiated EIRP US: FCC part 15.247
Europe: ETS 300 320
Japan: RCR STD-33
Modulation Binary GFSK
TX Out-of-Band Emissions US: FCC part 15.247, 15.205, 15.209
Europe: ETS 300 320
Japan: RCR STD-33
B-2 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 53

Appendix C
Troubleshooting
C.1 Windows 95/98 Troubleshooting Tips
Use the tools provided by Windows 95/98 and LAN
analyzers (FTP Software NETXRAY, Novell LAN analyzer)
to diagnose problems. Some common problems
exhibited when the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
adapter has not been properly installed include:
• Windows 95/98 does not recognize the Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter when installed.
– Verify that Windows 95/98 PCMCIA support
is installed.
• The driver fails to load.
– A resource conflict could exist. Use the Device
Manager to resolve resource conflicts.
Select the System applet from the Control Panel.
Select the Device Manager tab.
• The workstation cannot associate to the
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN access point.
Intel
– Verify the adapter ESSID matches the ESSID
of the access point. Refer to the Configuration
section of this document for details.
®
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide C-1
Page 54

Troubleshooting
• Degraded performance from the Intel®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter.
– Verify a secure antenna connection on the
PC Card.
– Verify two antennas remain attached to the
PC Card if Diversity is selected.
• Network drive mappings disappear when the
laptop suspends or the adapter is removed
then reinserted. Windows 95/98 does not
restore Netware network drive mappings under
these conditions.
– Log out and log in again, or restart the
machine to restore the connections.
• Nonfunctioning adapter LEDs.
– Verify that the adapter ESSID matches the
ESSID of the access point.
C-2 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 55

Troubleshooting
C.2 Windows NT 4.0 Troubleshooting
Use the tools provided by Windows NT and LAN
analyzers (FTP Software NETXRAY, Novell LAN analyzer)
to diagnose problems.
• A resource conflict (usually IRQ or I/O base
address) caused the driver not to load.
– Check entries in the System Log to look for the
conflicts.
• Check Service Monitor entries in the System Log to
look for the conflicts.
– Use the Windows NT Diagnostics program to
locate a free resource.
Resource conflicts could exist without an entry in the
event log when another adapter failed to register its
resources. When event log entries do not appear and
the ESSID is set appropriately, try different settings with
the Memory Base Address, Interrupt Number and
IO Port Address parameters.
• No resource conflicts were detected, but the system
does not attach to the network.
– Verify the ESSID of the Intel
2011 LAN adpater matches the ESSID of the
access point. Use NCPA to modify ESSID.
– Verify the Mandatory BSSID setting of the Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter is set to 0 or
matches the BSSID of the access point. Use
NCPA to modify the Mandatory BSSID.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide C-3
®
PRO/Wireless
®
Page 56

Troubleshooting
• A degraded performance from the Intel®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter is detected.
– Verify a secure antenna connection on the
PC Card.
– Verify two antennas remain attached to the
PC Card when Diversity is selected.
• Nonfunctioning adapter LEDs.
– Verify the adapter is selected in the Card Type
field.
– Verify the adapter ESSID matches the ESSID
of the access point.
C.2.1 Useful Tool for Windows NT Troubleshooting
Windows NT Provides an additional tool for analyzing
the network installation and performance.
PCMCIA Applet A Control Panel utility included with
Windows NT 4.0 displays information
®
about the Intel
LAN adapter. If the card is installed,
but does not appear in the display
it is probably defective.
PRO/Wireless 2011
If it appears with an X, it is not
configured properly.
C-4 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 57

C.2.2 Windows NT Errors
When errors occur during driver installation, they
appear in the System Log. Use the Event Viewer
program from the Administrative Tools group to view
the System Log. Locate the WLA11ND4 or Service
Monitor entries. If the driver fails to load, one of the
following messages display in the System Log.
WLA11ND4: Could not allocate the resources necessary for operation.
• The driver could not allocate enough memory for
internal data.
WLA11ND4: Has determined that the adapter is not functioning
properly.
• The driver could not initialize the Intel®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN PC Card. Possible
problems include:
– The PC Card firmware could be corrupted.
Use WLAN Update to verify the firmware status.
– The Intel
could have a hardware problem.
– The PCMCIA controller or host bus adapter is
not opterating properly. Use an alternate
PCMCIA socket.
Troubleshooting
®
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN PC Card
WLA11ND4: Could not find an adapter.
• The driver could not locate an Intel® PRO/Wireless
2011 LAN PC Card in any PCMCIA socket.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide C-5
Page 58

Troubleshooting
– Verify that the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN
PC Card is firmly seated.
WLA11ND4: Could not connect to the interrupt number supplied.
• The driver could not claim the configured interrupt.
– The configured interrupt number could be in
use by another adapter. Choose a different
interrupt number.
WLA11ND4: Does not support the configuration supplied.
• An invalid driver configuration parameter
was specified.
– Use NCPA to view the driver configuration.
Make sure values appear in each data
entry field. If a value is missing, key in or
use the associated list box to select an
appropriate value.
WLA11ND4: A required parameter is missing from the Registry.
• A required configuration parameter was not found
in the system registry.
– Use NCPA to view the driver configuration.
Ensure values appear in each data entry
field. If a value is missing, key in or use
the associated list box to select an
appropriate value.
C-6 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 59

Troubleshooting
C.3 Windows 2000 Troubleshooting Tips
Use the tools provided by Windows 2000 to
diagnose problems.
• The workstation cannot associate to the
®
Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN access point.
– Verify the adapter ESSID matches the ESSID
of the access point. Refer to the Configuration
section of this document for details.
®
• Degraded performance from the Intel
PRO/Wireless 2011 LAN adapter is detected.
– Verify a secure antenna connection on the
PC Card.
– Verify the antennas remain attached to the
PC Card if Diversity is selected.
• Nonfunctioning adapter LEDs.
– Verify that the adapter ESSID matches the
ESSID of the access point.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide C-7
Page 60

Troubleshooting
C-8 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 61

Appendix D
Customer Support
D.1 Intel Automated Customer Support
You can reach Intel automated support services
24 hours a day, every day at no charge. The services
contain the most up-to-date information about Intel
products. You can access installation instructions,
troubleshooting information, and product information.
User Guide on Your Product CDROM
For more information about installing drivers or
troubleshooting other topics, see the online User Guide.
To view the guide, insert the Intel CD in your drive and
wait for the Autorun to display. Click the User Guide
button to view the guide. Note that a web browser is
required to view the guide.
Web and Internet Sites
• Support: http://support.intel.com
• Network Products: http://www.intel.com/network
• Corporate: http://www.intel.com
• Newsgroups:news://cs.intel.com
• FTP Host: download.intel.com
• FTP Directory: /support/network/adapter/
Customer Support Technicians
US and Canada: 1-916-377-7000
(7:00 - 17:00 M-F Pacific Time)
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide D-1
Page 62

Customer Support
Worldwide access: Intel has technical support centers
worldwide. Many of the centers are staffed by
technicians who speak the local languages. For a
list of all Intel support centers, the telephone numbers,
and the times they are open, download document
9089 from one of the automated services.
D.2 Software License Agreement
IMPORTANT - READ BEFORE COPYING, INSTALLING
OR USING.
Do not use or load this software and any associated
materials (collectively, the "Software") until you have
carefully read the following terms and conditions.
By loading or using the Software, you agree to
the terms of this Agreement. If you do not wish to so
agree, do not install or use the Software.
LICENSE. You may copy the Software onto a single
computer for your personal, non-commercial use, and
you may make one back-up copy of the Software,
subject to these conditions:
This Software is licensed for use only in conjunction with
Intel component products. Use of the Software in
conjunction with non-Intel component products is not
licensed hereunder.
You may not copy, modify, rent, sell, distribute or
transfer any part of the Software except as provided in
this Agreement, and you agree to prevent unauthorized
copying of the Software.
You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or
disassemble the Software.
You may not sublicense or permit simultaneous use of
the Software by more than one user.
D-2 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 63

Customer Support
The Software may contain the software or other property
of third party suppliers, some of which may be identified
in, and licensed in accordance with, any enclosed
"license.txt" file or other text or file.
OWNERSHIP OF SOFTWARE AND COPYRIGHTS. Title
to all copies of the Software remains with Intel or its
suppliers. The Software is copyrighted and protected by
the laws of the United States and other countries, and
international treaty provisions. You may not remove any
copyright notices from the Software. Intel may make
changes to the Software, or to items referenced therein,
at any time without notice, but is not obligated to
support or update the Software. Except as otherwise
expressly provided, Intel grants no express or implied
right under Intel patents, copyrights, trademarks, or
other intellectual property rights. You may transfer the
Software only if the recipient agrees to be fully bound by
these terms and if you retain no copies of the Software.
LIMITED MEDIA WARRANTY. If the Software has been
delivered by Intel on physical media, Intel warrants the
media to be free from material physical defects for a
period of ninety (90) days after delivery by Intel. If such
a defect is found, return the media to Intel for
replacement or alternate delivery of the Software as
Intel may select.
EXCLUSION OF OTHER WARRANTIES. EXCEPT AS
PROVIDED ABOVE, THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS
IS" WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND INCLUDING WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY, NON-INFRINGEMENT, OR
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Intel does not warrant or assume responsibility for
the accuracy or completeness of any information,
text, graphics, links or other items contained within
the Software.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide D-3
Page 64

Customer Support
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY. IN NO EVENT SHALL
INTEL OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY
DAMAGES WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION,
OR LOST INFORMATION) ARISING OUT OF THE USE
OF OR INABILITY TO USE THE SOFTWARE, EVEN IF
INTEL HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
SUCH DAMAGES. SOME JURISDICTIONS PROHIBIT
EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR CONSEQUENTIAL OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION
MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU. YOU MAY ALSO HAVE
OTHER LEGAL RIGHTS THAT VARY FROM
JURISDICTION TO JURISDICTION.
TERMINATION OF THIS AGREEMENT. Intel may
terminate this Agreement at any time if you violate
its terms. Upon termination, you will immediately
destroy the Software or return all copies of the
Software to Intel.
APPLICABLE LAWS. Claims arising under this
Agreement shall be governed by the laws of
California, excluding its principles of conflict of laws
and the United Nations Convention on Contracts
for the Sale of Goods. You may not export the
Software in violation of applicable export laws and
regulations. Intel is not obligated under any other
agreements unless they are in writing and signed
by an authorized representative of Intel.
GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS. The Software is
provided with "RESTRICTED RIGHTS." Use, duplication,
or disclosure by the Government is subject to restrictions
as set forth in FAR52.227-14 and DFAR252.227-7013
et seq. or their successors. Use of the Software by the
Government constitutes acknowledgment of Intel’s
proprietary rights therein. Contractor or Manufacturer is
Intel Corporation, 2200 Mission College Blvd., Santa
Clara, CA 95052.
D-4 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 65

Customer Support
D.3 Limited Lifetime Hardware Warranty
Intel warrants to the original owner that the adapter
product delivered in this package will be free from
defects in material and workmanship. This warranty
does not cover the adapter product if it is damaged in
the process of being installed or improperly used.
THE ABOVE WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ANY OTHER
WARRANTY, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR
STATUTORY, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY
WARRANTY OF NONINFRINGEMENT OF
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARISING OUT OF ANY
PROPOSAL, SPECIFICATION, OR SAMPLE.
This warranty does not cover replacement of adapter
products damaged by abuse, accident, misuse, neglect,
alteration, repair, disaster, improper installation, or
improper testing. If the adapter product is found to be
defective, Intel, at its option, will replace or repair the
hardware product at no charge except as set forth
below, or refund your purchase price provided that you
deliver the adapter product along with a Return Material
Authorization (RMA) number (see below), along with
proof of purchase (if not registered), either to the dealer
from whom you purchased it or to Intel with an
explanation of any deficiency. If you ship the adapter
product, you must assume the risk of damage or loss in
transit. You must use the original container (or the
equivalent) and pay the shipping charge.
Intel may replace or repair the adapter product with
either new or reconditioned parts, and any adapter
product, or part thereof replaced by Intel becomes
Intel’s property. Repaired or replaced adapter products
will be returned to you at the same revision level as
received or higher, at Intel’s option. Intel reserves the
right to replace discontinued adapter products with an
equivalent current generation adapter product.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide D-5
Page 66

Customer Support
Returning a defective product
From North America:
Before returning any adapter product, contact
Intel Customer Support and obtain a Return
Material Authorization (RMA) number by
calling +1 916-377-7000.
If the Customer Support Group verifies that the
adapter product is defective, they will have the RMA
department issue you an RMA number to place on
the outer package of the adapter product. Intel
cannot accept any product without an RMA number
on the package.
All other locations:
Return the adapter product to the place of purchase
for a refund or replacement.
Intel Adapter Money-back Guarantee
(North America Only)
Intel wants you to be completely satisfied with the Intel
adapter product that you have purchased. Any time
within ninety (90) days of purchase, you may return
your Intel adapter to the original place of purchase
for a full refund of the purchase price from your
dealer. Resellers and distributors, respectively,
accepting returns and refunding money back to their
customers may return Intel adapters to their original
place of purchase. Intel guarantees that it will accept
returns under this policy and refund the original
purchase price to customers purchasing directly
from Intel.
Limitation of Liability and Remedies
INTEL’S SOLE LIABILITY HEREUNDER SHALL BE LIMITED
TO DIRECT, OBJECTIVELY MEASURABLE DAMAGES. IN
NO EVENT SHALL INTEL HAVE ANY LIABILITY FOR ANY
INDIRECT OR SPECULATIVE DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
D-6 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 67

Customer Support
WITHOUT LIMITING THE FOREGOING,
CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL, AND SPECIAL
DAMAGES) INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
INFRINGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY,
REPROCUREMENT COSTS, LOSS OF USE, BUSINESS
INTERRUPTIONS, LOSS OF GOODWILL, AND LOSS
OF PROFITS, WHETHER ANY SUCH DAMAGES ARISE
OUT OF CONTRACT NEGLIGENCE, TORT, OR UNDER
ANY WARRANTY, IRRESPECTIVE OF WHETHER INTEL
HAS ADVANCE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF ANY
SUCH DAMAGES. NOTWITHSTANDING THE
FOREGOING, INTEL’S TOTAL LIABILITY FOR ALL
CLAIMS UNDER THIS AGREEMENT SHALL NOT
EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT. THESE
LIMITATIONS ON POTENTIAL LIABILITIES WERE AN
ESSENTIAL ELEMENT IN SETTING THE PRODUCT
PRICE. INTEL NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES
ANYONE TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER LIABILITIES.
Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of
incidental or consequential damages, so the above
limitations may not apply to you.
Critical Control Applications: Intel specifically disclaims
liability for use of the adapter product in critical control
applications (including, for example only, safety or
health care control systems, nuclear energy control
systems, or air or ground traffic control systems) by
Licensee or Sublicensees, and such use is entirely at the
user’s risk. Licensee agrees to defend, indemnify, and
hold Intel harmless from and against any and all claims
arising out of use of the adapter product in such
applications by Licensee or Sublicensees.
Software: Software provided with the adapter product is
not covered under the hardware warranty described
above. See the applicable software license agreement
which shipped with the adapter product for details on
any software warranty.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide D-7
Page 68

Customer Support
D-8 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 69

Appendix E
Regulatory Compliance
To comply with U.S. and international regulatory
requirements, the following information has been
included. The document applies to the complete line
of Intel products. Some of the labels shown, and
statements applicable to other devices might not apply
to all products.
Radio Frequency Interference Requirements
This device has been tested and found to comply with
the limits for a Class A digital device pursuant to Part 15
of the Federal Communications Commissions Rules and
Regulation. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is
likely to cause harmful interference in which case the
user will be required to correct the interference at his
own expense.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide E-1
Page 70

Regulatory Compliance
However, there is no guarantee that interference will
not occur in a particular installation. If the equipment
does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the
equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to
try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
• Re-orient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment
and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit
different from that which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV
technician for help.
Radio Frequency Interference Requirements - Canada
This Class A digital apparatus meets the requirements
of the Canadian Interference-Causing Equipment
Regulations.
CE Marking & European Union Compliance
Products intended for sale within the European
Union are marked with the CEMark which
indicates compliance to applicable Directives
and European Normes (EN), as follows.
Amendments to these Directives or ENs are
included: Normes (EN), as follows.
Applicable Directives:
• Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive
89/336/EEC
• Low Voltage Directive 73/23/EEC
E-2 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 71

Applicable Standards:
• EN 55 022 - Limits and Methods of Measurement
of Radio Interference Characteristics of Information
technology Equipment
• EN 50 082-1 - Electromagnetic Compatibility Generic Immunity Standard, Part 1: Residential,
commercial, Light Industry
• IEC 801.2 - Electromagnetic Compatibility for
Industrial Process Measurement and Control
Equipment Part 2: Electrostatic
Discharge Requirements
• IEC 801.3 - Electromagnetic Compatibility for
Industrial Process Measurement and Control
Equipment Part 3: Radiated Electromagnetic
Field Requirements
• IEC 801.4 - Electromagnetic Compatibility for
Industrial Process Measurement and Control
Equipment Part 4: Electrical Fast
Transients Requirements
Regulatory Compliance
• EN 60 950 + Amd 1 + Amd 2 - Safety of
Information Technology Equipment Including
Electrical Business Equipment
• EN 60 825-1 (EN 60 825) - Safety of Devices
Containing Lasers
RF Devices
Intel RF products are designed to be compliant with the
rules and regulations in the locations into which they are
sold and will be labeled as required. The majority of
Intel’s RF devices are type approved and do not require
the user to obtain license or authorization before using
the equipment. Any changes or modifications to Intel
equipment not expressly approved by Intel could void
the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide E-3
Page 72

Regulatory Compliance
Telephone Devices (Modems)
United States
If this product contains an internal modem it is
compliant with Part 68 of the Federal Communications
Commission Rules and Regulations and there will be a
label on the product showing the FCC ID Number and
the REN, Ringer Equivalence Number. The REN is used
to determine the quantity of devices which maybe
connected to the telephone line. Excessive RENs on the
telephone line may result in the device not ringing in
response to an incoming call. In most but not all areas,
the sum of the RENs should not exceed 5.0. To be
certain of the number of devices that may be connected
to the line, as determined by the total number of RENs,
contact the telephone company to determine the
maximum REN for the calling area.
If the modem causes harm to the telephone network,
the telephone company will notify you in advance;
however, if advance notice is not practical, you will be
notified as soon as possible. Also, you will be advised of
your right to file a complaint with the FCC if you believe
it is necessary.
The telephone company may make changes in its
facilities, equipment, operations or procedures that
could affect the operation of the modem. If this happens
the telephone company will provide advance notice so
you may make any necessary modifications to maintain
uninterrupted service.
Canada
If this product contains an internal modem it is
compliant with CS-03 of Industry Canada and there will
be a Canadian certification number (CANADA:
on a label on the outside of the product. This
certification means that the equipment meets certain
E-4 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
)
Page 73
Regulatory Compliance
telecommunications network protective, operational
and safety requirements. The Department does
not guarantee the equipment will operate to the
user’s satisfaction.
Before installing this equipment, users should ensure
that it is permissible to be connected to the facilities of
the local telecommunications company. The equipment
must also be installed using an acceptable method of
connection. In some cases, the company’s inside wiring
associated with a single-line, individual service maybe
extended by means of a certified convector assembly
(telephone extension cord). The customer should be
aware that compliance with the above conditions may
not prevent degradation of service in some situations.
Repairs to certified equipment should be made by an
authorized Canadian maintenance facility designated
by the supplier. Any repairs or alterations made by the
user to this equipment, or equipment malfunctions, may
give the telecommunications company cause to request
the user to disconnect the equipment.
User should ensure for their own protection that the
electrical ground connections of the power utility,
telephone lines and internal metallic water pipe system,
if present, are connected together. This precaution may
be particularly important in rural areas.
User should not attempt to make such connections
themselves, but should contact the appropriate electric
inspection authority, or electrician, as appropriate.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide E-5
Page 74

Regulatory Compliance
The Load Number (LN) assigned to each terminal
device denotes the percentage of the total load to be
connected to the telephone loop which is used by the
device, to prevent overloading. The termination of a
loop may consist of any combination of devices, subject
only to the requirement that the total of the Load
Numbers of all devices not exceed 100.
The Load Number is located on a label on the product.
Si ce produit contient un intérieur modem duquel est
conformité avec le code CS-03 de l'industrie canadien
alors il aura un numéro de la certification canadienne
(CANADA:______ ) sur l'étiquette afficheé au produit.
L'étiquette d'Industrie Canada a identifiée le matériel
homologué. Cette étiquette a certifiée que le matériel
est conformé aux certaines normes de protection,
d'exploitation et de sécurité des réseaux de
télécommunications. Toutefois, le Ministère n'assure pas
que le matériel fonctionnera à la satisfaction de
l'utilisateur.
Avant d'installer ce matériel, l'utilisateur doit assurer
qu'il soit permis de raccorder aux installations de
l'entreprise télécommunications locales. Le matériel doit
être également installé au suivant d'une méthode de
raccordement. Dans certains cas, les fils intérieurs de
l'entreprises utilisés pour un service individuel à la ligne
unique peuvent être prolongés au moyen d'un dispositif
de raccordement homologué (cordon rallongé
téléphonique interne). L'abonné ne doit pas oublier qu'il
est possible que la conformité aux conditions énoncées
ci-dessus n'empêchent pas la dégradation du service
dans les certaines situations. Actuellement, les
entreprises de télécommunication ne permettent pas
que l'on raccorde leur matériels à des jacks d'abonnés,
sauf dans les cas précis et prévus pas les tarrifs
particuliers de ces entreprises.
E-6 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 75

Regulatory Compliance
Les réparations de matériel homologué doivent être
effectuées par un centre d'entretien canadien autorisé
par le fournisseur. La compagnie de
télécommunications peut demander à l'utilisateur de
débrancher un appareil à la suite des réparations ou
des modifications effectuées par l'utilisateur, ou à cause
des mauvais fonctionnement.
Pour sa propre protection, l'utilisateur doit assurer que
tous les fils de mise à terre de la source d'énergie
électrique, lignes téléphoniques et les canalisations
d'eau métalliques, s'il y en a, soient raccordés
ensemble. Cette précaution est particulièrement
importante dans les regions rurales.
AVERTISSEMENT: L'utilisateur ne doit pas tenter de faire
ces raccordements lui-même; il doit avoir recours aux
services d' électronician.
L'indice de charge (IC) assigné à chaque dispositif
terminal indique, pour éviter toute surcharge, le
pourcentage de la charge totale qui peut être rac-cordé
au circuit téléphonique bouclé d' utiliser par ce
dispositif. La terminasion du circuit bouclé peut être
constituée de n'importe quelle combinaison de
dispositifs, pourvu que la somme des indices de charge
dans l'ensemble des dispositifs ne dépassent pas 100.
L'indice de charge se trouve sur le produit.
Laser Devices
Intel products using lasers comply with US
21CFR1040.10, Subchapter J and IEC825/EN 60 825
(or IEC825-1/EN 60 825-1, depending on the date of
manufacture). The laser classification is marked one of
the labels on the product.
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide E-7
Page 76

Regulatory Compliance
Class 1 Laser devices are not considered to be
hazardous when used for their intended purpose. The
following statement is required to comply with US and
international regulations:
Use of controls, adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified herein may result
in hazardous visible or invisible laser light exposure.
Class 2 laser scanners use a low power, visible light
diode. As with any very bright light source, such as the
sun, the user should avoid staring directly into the light
beam. Momentary exposure to a Class 2 laser is not
known to be harmful.
E-8 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 77

Index
Numerics
11 Mbps Operation 4
NCPA A-1
WLAN property page A-12
A
access point
A-2
11 Mbps operation 4
2.4 and 2.5 GHz 1
CAM 6
direct-sequence 1
Mobile IP 5
MU mode 4
power management 6
PSP 6
roaming 4
signal strength 4
adapter LED 7
antenna
diversity 1
FCC requirements 11
features 1
PC card 10
WLAN property page A-12
C
CAM (Continuously Aware Mode)
power management 6
Configuring 26
CSS (Card and Socket Services)
wireless LAN 6
D
data rate 4
11 Mbps association 4
11 Mbps operation 4
CAM 6
NCPA A-1
PSP 6
WLAN property page A-12
direct-sequence
data rate 4
driver configuration 13
Windows 2000 23
Windows 95 13, 17
Windows 98 17
Windows NT 22, 26
driver installation 13
firmware update 13
Windows 2000 23
Windows 95 13
Windows 98 15
Windows NT 19
E
Encryption
64-bit A-10
open systems A-9
Encryption property page A-9
configure A-9
ESSID A-2
easy setup A-2
edit A-2
Mobile Unit properties A-4
NCPA A-1, A-6
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide Index-1
Page 78

F
FCC requirements 11
Features 3
firmware 29
update 29
verification 29
Windows 2000 23
Windows 95 13
Windows 98 15
Windows NT 19
WLAN Monitor 29
WLAN Update 29
H
hardware installation 9
PC card 10
preparation 9
Windows NT driver 19, 23
I
IEEE 802.11 1
installation
card and socket services 6
firmware 29
hardware 9
NCPA A-1
PC card 10
power management 6
preparation 9
Windows 95 driver 13
Windows NT driver 19
Intel 17, 22
Intel Web site 13, 15, 19, 23
L
LED 7
M
Mobile IP (Internet Protocol)
Mobile IP property page A-7
roaming 5
roaming across routers 5
Mobile IP property page A-7
configure A-7
mobile unit property page A-4
MU (Mobile Unit)
11 Mbps Operation 4
CAM 6
card and socket services 6
firmware 29
hardware installation 9
Mobile IP 5
MU Mode 4
NCPA A-1
operation 4
PC card installation 10
power management 6
PSP 6
roaming 4
roaming across routers 5
MU Mode 4
Index-2 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 79

N
NCPA
802.11 ESSID A-2
Encryption property page A-9
installing A-1
Mobile IP property page A-7
Mobile Unit properties A-4
password A-13
Power property page A-6
tools and utilities A-2
using A-2
Windows 2000 installation 23
Windows 95/98 configuration
17
Windows NT configuration
22, 26
WLAN property page A-12
Network adapter configuration
Windows 95 17
Windows NT 22, 26
P
PC card
11 Mbps data rate 4
about 3
alignment 11
CAM 6
driver 13
features 3
firmware 29
installation 9
installation requirements 10
LED descriptions 7
Mobile IP 5
MU mode 4
power management 6
PSP 6
Windows 2000 23
Windows 95 13
Windows 98 15
Windows NT 19
power management
CAM 6
PSP 6
PSP (Power Save Polling)
power management 6
R
roaming
Mobile IP 5
roaming across routers 5
S
system documentation 10
T
tools and utilities
NCPA A-2
Toubleshooting
Windows 98 C-1
Troubleshooting C-1
adapter LEDs C-2
ESSID C-3
NT driver C-5
PC Card C-2
Windows 2000 C-7
Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide Index-3
Page 80

Windows 95 C-1
Windows NT 4.0 C-3
Windows NT Errors C-5
U
Using NCPA A-2
utilities
NCPA A-1
WLAN Update 13, 29
W
Windows 13, 15, 19, 23
Windows 2000 23
Configuring 23
Installing 23
Windows 95
configuration 17
driver installation 13
Windows 98
configuration 17
Windows NT
configuration 22, 26
driver installation 19, 23
wireless LAN local area network)
CSS 6
WLAN adapter page A-12
Index-4 Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide
Page 81

Wireless LAN Adapter Product Reference Guide Index-5
 Loading...
Loading...