Intel P4208IP4LHGC, P4216IP4LHJC, P4216IP4LHKC, P4224IP4LHKC, P4308IP4LHGC Technical Product Specification
...Page 1

Intel® Server System P4000IP and
Revision 1.0
February, 2012
Enterprise Platforms and Services Marketing
Intel® Workstation System
P4000CR Family
Technical Product Specification
Intel reference number G38159-001
Page 2

Revision History Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Date
Revision
Number
Modifications
February, 2012
1.0
Initial release.
Revision History
Disclaimers
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express
or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this
document. Except as provided in Intel®'s Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel®
assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to
sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular
purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property
right. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining
applications. Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time,
without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions
marked “reserved” or “undefined”. Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no
responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
This document contains information on products in the design phase of development. Do not
finalize a design with this information. Revised information will be published when the product is
available. Verify with your local sales office that you have the latest datasheet before finalizing a
design.
The Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Familymay contain
design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from
published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Intel Corporation server baseboards contain a number of high-density VLSI and power delivery
components that need adequate airflow to cool. Intel‟s own chassis are designed and tested to
meet the intended thermal requirements of these components when the fully integrated system
is used together. It is the responsibility of the system integrator that chooses not to use Intel
developed server building blocks to consult vendor datasheets and operating parameters to
determine the amount of air flow required for their specific application and environmental
conditions. Intel Corporation cannot be held responsible if components fail or the server board
does not operate correctly when used outside any of their published operating or non-operating
limits.
Intel, Pentium, Itanium, and Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation.
*Other brands and names may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © Intel Corporation 2012
ii Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 3

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS Table of Contents
iii
Table of Contents
1. Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview ....................... 1
1.1 Intergrated System family overview ........................................................................ 1
1.1.1 Intel® Server System P4208IP4LHGC View ........................................................... 6
1.1.2 Intel® Server System P4216IP4LHJC View ............................................................ 7
1.1.3 Intel® Server System P4216IP4LHKC View ............................................................ 8
1.1.4 Intel® Server System P4224IP4LHKC View ............................................................ 9
1.1.5 Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHGC View ......................................................... 10
1.1.6 Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHJC(L) View ...................................................... 11
1.1.7 Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHKC View .......................................................... 12
1.1.8 Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFGN View ............................................... 13
1.1.9 Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFJN(L) View ............................................ 14
1.1.10 Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFKN View ................................................ 15
1.2 Chassis dimensions ............................................................................................. 16
1.3 Front control panel feature Overview ................................................................... 16
1.3.1 Front Control Panel LED/Button Functionality ...................................................... 16
1.3.2 Front Control Panel LED Status ........................................................................... 18
1.4 Back panel feature Overveiw ............................................................................... 19
1.5 Hot swap Hard Drivers and front panel options .................................................... 20
1.6 Chassis Security .................................................................................................. 20
1.7 Front Bezel Features ............................................................................................ 21
2. System Power Sub-system ................................ .............................................................. 23
2.1 750-W Power Supply ........................................................................................... 23
2.1.1 Mechanical Overview ........................................................................................... 23
2.1.2 AC Input Requirements ........................................................................................ 25
2.1.3 Efficiency.............................................................................................................. 28
2.1.4 DC Output Specification ....................................................................................... 28
2.1.5 Protection Circuits ................................................................................................ 32
2.1.6 Control and Indicator Functions............................................................................ 33
2.1.7 Thermal CLST ...................................................................................................... 35
2.1.8 Power Supply Diagnostic “Black Box” .................................................................. 35
2.1.9 Firmware Uploader ............................................................................................... 36
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 4

Table of Contents Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
2.2 1200-W Power Supply ......................................................................................... 36
2.2.1 Mechanical Overview ........................................................................................... 36
2.2.2 AC Input Requirements ........................................................................................ 39
2.2.3 Efficiency.............................................................................................................. 41
2.2.4 DC Output Specification ....................................................................................... 41
2.2.5 Protection Circuits ................................................................................................ 45
2.2.6 Control and Indicator Functions............................................................................ 46
2.2.7 Thermal CLST ...................................................................................................... 49
2.2.8 Power Supply Diagnostic “Black Box” .................................................................. 49
2.2.9 Firmware Update .................................................................................................. 49
2.3 1600-W Power Supply ......................................................................................... 49
2.3.1 Mechanical Overview ........................................................................................... 49
2.3.2 AC Input Requirements ........................................................................................ 52
2.3.3 Efficiency.............................................................................................................. 54
2.3.4 DC Output Specification ....................................................................................... 55
2.3.5 Protection Circuits ................................................................................................ 59
2.3.6 Control and Indicator Functions............................................................................ 60
2.3.7 Thermal CLST ...................................................................................................... 62
2.3.8 Power Supply Diagnostic “Black Box” .................................................................. 62
2.3.9 Firmware Update .................................................................................................. 63
2.4 Higer Current Power Common Redundant Power Distribution Board (PDB) ........ 63
2.4.1 Mechanical Overview ........................................................................................... 64
2.4.2 DC Output Specification ....................................................................................... 65
2.4.3 Protection Circuits ................................................................................................ 75
2.4.4 PWOK (Power OK) Signal ................................................................................... 76
2.4.5 PSON Signal ........................................................................................................ 76
2.4.6 PMBus ................................................................................................................. 77
3. Thermal Management ....................................................................................................... 78
3.1 Thermal Operation and Configuration Requirements ........................................... 78
3.2 Thermal Management Overview .......................................................................... 78
3.3 System Fan Configuration .................................................................................... 78
3.3.1 Non-Redundant Cooling Solution ......................................................................... 79
3.3.2 Redundant Cooling Solution ................................................................................. 79
3.4 Fan Control .......................................................................................................... 80
iv Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 5

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS Table of Contents
v
3.5 Fan Header Connector Descriptions .................................................................... 80
4. Storage and Peripheral Drive Bays ................................................................................. 81
4.1 2.5‟„ Hard Disk Drive Support ............................................................................... 81
4.1.1 2.5'' Drive Hot-Swap Backplane Overview ............................................................ 82
4.1.2 Cypress* CY8C22545 Enclosure Management Controller .................................... 83
4.2 3.5'' Hard Disk Drive Support ............................................................................... 84
4.2.1 3.5'' Drive Hot-Swap Backplane Overview ............................................................ 85
4.2.2 Cypress* CY8C22545 Enclosure Management Controller .................................... 87
4.3 SAS Expander Card Option ................................................................................. 87
4.3.1 Protocol Support .................................................................................................. 90
4.3.2 SAS Expander Features ....................................................................................... 90
4.4 Optical Drive Support ........................................................................................... 90
4.5 Low Profile eUSB SSD Support ........................................................................... 91
5. Reliability and Availability................................................................................................ 92
5.1 Mean Time between Failure ................................................................................. 92
6. Environmental Limits ....................................................................................................... 95
6.1 System Environment Limits .................................................................................. 95
6.2 System Environmental Testing ............................................................................. 95
Appendix A: Integration and Usage Tips ............................................................................... 97
Glossary .................................................................................................................................. 98
Reference Documents .......................................................................................................... 100
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 6

List of Figures Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
List of Figures
Figure 1. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4208IP4LHGC ................................... 6
Figure 2. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4216IP4LHJC .................................... 7
Figure 3. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4216IP4LHKC ................................... 8
Figure 4. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4224IP4LHKC ................................... 9
Figure 5. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHGC ................................. 10
Figure 6. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHJC .................................. 11
Figure 7. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHKC ................................. 12
Figure 8. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFGN ....................... 13
Figure 9. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFJN ........................ 14
Figure 10. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFKN ..................... 15
Figure 11. Front Control Panel LED/Button Arragement ........................................................... 16
Figure 12. Back panel feature ................................................................................................... 19
Figure 13. Hot-Swap Hard Disk Drive Cage .............................................................................. 20
Figure 14. Front Closed Chassis View for Fixed Hard Drives Configuration .............................. 21
Figure 15. Front Closed Chassis View for Hot-swap Hard Drives Configuration ....................... 21
Figure 16. 750-W Power Supply Outline Drawing ..................................................................... 23
Figure 17. Differential Noise test setup ..................................................................................... 31
Figure 18. Turn On/Off Timing (Power Supply Signals) ............................................................ 32
Figure 19. PSON# Required Signal Characteristic .................................................................... 34
Figure 20. Power Supply Outline Drawing ................................................................................. 36
Figure 21. Differential Noise test setup ..................................................................................... 44
Figure 22. PSON# Required Signal Characteristic .................................................................... 47
Figure 23. PWOK Circuit Requirement ..................................................................................... 48
Figure 24. Power Supply Outline Drawing ................................................................................. 50
Figure 25 Differential Noise test setup ...................................................................................... 57
Figure 26 Turn On/Off Timing (Power Supply Signals) ............................................................. 59
Figure 27. PSON# Required Signal Characteristic .................................................................... 61
Figure 28. PWOK Circuit Requirement ..................................................................................... 62
Figure 30. Outline Drawing ....................................................................................................... 64
Figure 30. Airflow Diagram........................................................................................................ 65
Figure 31. Differential Noise test setup ..................................................................................... 74
vi Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 7

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS List of Figures
vii
Figure 32. Fixed Fans in Intel® Workstation System P4000CR ................................................. 79
Figure 33. Hot-swap Fans in Intel® Server System P4000IP ..................................................... 80
Figure 34. 2.5'' Hard Disk Drive Cage ....................................................................................... 81
Figure 35. 2.5'' Hard Disk Drive Support - LED Status .............................................................. 82
Figure 36. 2.5'' Backplane, Front Side ...................................................................................... 82
Figure 37. 2.5'' Backplane, Back Side ....................................................................................... 83
Figure 38. 3.5'' Hard Disk Drive Cage ....................................................................................... 84
Figure 39. 3.5'' Hard Disk Drive Support - LED Status .............................................................. 84
Figure 40. 3.5'' Backplane, Front Side ...................................................................................... 85
Figure 41. 2.5'' Backplane, Back Side ....................................................................................... 86
Figure 42. Internal SAS Expander Installation ........................................................................... 87
Figure 43. Internal 24-Port SAS Expander Card ....................................................................... 87
Figure 44. 24-Port Expander SAS Connector/Drive Identification Block Diagram ..................... 88
Figure 45. Internal 36-Port SAS Expander Card ....................................................................... 88
Figure 46. 36-Port Expander SAS Connector/Drive Identification Block Diagram ..................... 88
Figure 47. Optical Drive ............................................................................................................ 90
Figure 48. eUSB SSD Support .................................................................................................. 91
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 8

List of Tables Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
List of Tables
Table 1. Intel® Server System P4000IP Hot-Swap 3.5 HDDs and Non-HDD configuration base
feature .................................................................................................................................. 3
Table 2. Intel® Server System P4000IP Hot-Swap 2.5 HDDs configuration base feature ............ 4
Table 3. Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Fixed 3.5 HDDs configuration base feature ........ 4
Table 4. Power/Sleep LED Functional States............................................................................ 17
Table 5. Front Control Panel LED Status .................................................................................. 18
Table 6. DC Output Connector .................................................................................................. 23
Table 7. LED Characteristics .................................................................................................... 24
Table 8. Power Supply LED Functionality ................................................................................. 24
Table 9. Environmental Requirements ...................................................................................... 25
Table 10. Power Factor Requirements for Computer Servers ................................................... 26
Table 11. AC Input Voltage Range ........................................................................................... 26
Table 12. AC Line Holdup Time ................................................................................................ 26
Table 13. AC Line Sag Transient Performance ......................................................................... 27
Table 14. AC Line Surge Transient Performance ...................................................................... 27
Table 15. Silver Efficiency Requirement ................................................................................... 28
Table 16. Minimum Load Ratings .............................................................................................. 28
Table 17. Voltage Regulation Limits .......................................................................................... 29
Table 18. Transient Load Requirements ................................................................................... 29
Table 19. Capacitive Loading Conditions .................................................................................. 29
Table 20. Ripples and Noise ..................................................................................................... 30
Table 21. Timing Requirements ................................................................................................ 31
Table 22. Over Current Protection ............................................................................................ 33
Table 23. Over Voltage Protection (OVP) Limits for 750W PSU ............................................... 33
Table 24. PSON# Signal Characteristic .................................................................................... 33
Table 25. PWOK Signal Characteristics.................................................................................... 34
Table 26. SMBAlert# Signal Characteristics .............................................................................. 35
Table 27. DC Output Connector ................................................................................................ 37
Table 28. LED Characteristics .................................................................................................. 38
Table 29. LED Status ................................................................................................................ 38
Table 30. Environmental Requirements .................................................................................... 38
Table 31. AC Input Voltage Range ........................................................................................... 39
viii Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 9

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS List of Tables
ix
Table 32. AC Line Sag Transient Performance ......................................................................... 41
Table 33. AC Line Surge Transient Performance ...................................................................... 41
Table 34. Platinum Efficiency Requirement............................................................................... 41
Table 35. Minimum Load Ratings .............................................................................................. 42
Table 36. Voltage Regulation Limits .......................................................................................... 42
Table 37. Transient Load Requirements ................................................................................... 43
Table 38.Capacitive Loading Conditions ................................................................................... 43
Table 39. Ripples and Noise ..................................................................................................... 44
Table 40. Timing Requirements ................................................................................................ 45
Table 41. Over Current Protection ............................................................................................ 46
Table 42. Over Voltage Protection (OVP) Limits for 1200W PSU ............................................. 46
Table 43. PSON# Signal Characteristic .................................................................................... 46
Table 44. PWOK Signal Characteristics.................................................................................... 47
Table 45. SMBAlert# Signal Characteristics .............................................................................. 48
Table 46. DC Output Connector ................................................................................................ 50
Table 47. LED Characteristics .................................................................................................. 51
Table 48. LED Indicator States ................................................................................................. 51
Table 49 Environmental Requirements ..................................................................................... 52
Table 50 Environmental Requirements ..................................................................................... 52
Table 51 AC Input Voltage Range ............................................................................................ 53
Table 52. AC Line Holdup Time ................................................................................................ 53
Table 53 AC Line Sag Transient Performance .......................................................................... 54
Table 54 AC Line Surge Transient Performance ....................................................................... 54
Table 55 Platinum Efficiency Requirement................................................................................ 54
Table 56 Minimum Load Ratings ............................................................................................... 55
Table 57 Voltage Regulation Limits ........................................................................................... 55
Table 58. Transient Load Requirements ................................................................................... 55
Table 59. Capacitive Loading Conditions .................................................................................. 56
Table 60. Ripples and Noise ..................................................................................................... 57
Table 61. Timing Requirements ................................................................................................ 58
Table 62 Over Current Protection ............................................................................................. 59
Table 63. Over Voltage Protection (OVP) Limits for 1600W PSU ............................................. 60
Table 64 PSON# Signal Characteristic ..................................................................................... 60
Table 65 PWOK Signal Characteristics..................................................................................... 61
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 10

List of Tables Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Table 66 SMBAlert# Signal Characteristics .............................................................................. 62
Table 67. Thermal Requirements .............................................................................................. 65
Table 68. Input Connector and Pin Assignment Diagrams ........................................................ 66
Table 69. PDB Cable Length .................................................................................................... 66
Table 70. P1 Baseboard Power Connector ............................................................................... 67
Table 71. P0 Processor Power Connector ................................................................................ 68
Table 72. P1 Processor Power Connector ................................................................................ 68
Table 73. Power Signal Connector ............................................................................................ 68
Table 74. P12 12V connectors .................................................................................................. 69
Table 75. P13 - P16 12V connectors ........................................................................................ 69
Table 76. P8, P9, P10, P11 Legacy Peripheral Power Connectors ........................................... 69
Table 77. P7Legacy Peripheral Power Connectors ................................................................... 69
Table 78. SATA Peripheral Power Connectors ......................................................................... 69
Table 79. Remote Sense Connection Points ............................................................................. 70
Table 80. Remote Sense Requirements ................................................................................... 70
Table 81. 12V Rail Distribution .................................................................................................. 71
Table 82. Hard Drive 12V rail configuration options .................................................................. 72
Table 83. DC/DC Converters Load Ratings .............................................................................. 72
Table 84. 5VSB Loading ........................................................................................................... 72
Table 85. Voltage Regulation Limits .......................................................................................... 73
Table 86. Transient Load Requirements ................................................................................... 73
Table 87. Capacitive Loading Conditions .................................................................................. 73
Table 88. Ripple and Noise ....................................................................................................... 74
Table 89. Output Voltage Timing .............................................................................................. 74
Table 90. PDB Over Current Protection Limits/240VA Protection ............................................. 76
Table 91. Over Voltage Protection (OVP) Limits ....................................................................... 76
Table 92. System PWOK Requirements ................................................................................... 76
Table 93. PDB addressing ........................................................................................................ 77
Table 94. 2.5'' Hard Disk Drive Status LED States .................................................................... 82
Table 95. 2.5'' Hard Disk Drive Activity LED States ................................................................... 82
Table 96. 3.5'' Hard Disk Drive Status LED States .................................................................... 84
Table 97. 3.5'' Hard Disk Drive Activity LED States ................................................................... 85
Table 98. Calculated Mean Time Between Failure .................................................................... 92
Table 99. System Environment Limits Summary ....................................................................... 95
x Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 11

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS List of Tables
xi
<This page is intentionally left blank.>
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 12

Page 13

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
1
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
1. Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel®
Workstation System Overview
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System is 4U pedestal, 27'' length server
chassis that is designed to support Intel® Server Board S2600IP and Intel® Workstation Board
W2600CR. This chapter provides a high-level overview of the chassis features. Greater detail
for each major chassis component or feature is provided in the following chapters.
1.1 Intergrated System family overview
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System make extensive use of tool-less
hardware features and, depending on configuration and upgrade features, provides redundant
power supply, redundant cooling and hot swappable hard drives capability. Intel® Server
System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System comes with the following configuration:
Your Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFJN(L) ships with the following items:
One Intel® Workstation Board W2600CR2(L)
One CRPS 1200W power supply, installed in the chassis
One fixed system CPU zone fan, installed in the chassis
One fixed system PCI zone fan, installed in the chassis
Four fixed HDD carrier tray, installed in the chassis
Front panel, installed in the chassis
Front Bezel for fixed hard drive, EMI shield, 5.25'' bay filler
Pre-routing cables
Two heat sinks
Your Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFGN ships with the following items:
One Intel® Worstation Board W2600CR2
One CRPS 750W power supply, installed in the chassis
One fixed system CPU zone fan, installed in the chassis
One fixed system PCI zone fan, installed in the chassis
Four fixed HDD carrier tray, installed in the chassis
Front panel, installed in the chassis
Front Bezel for fixed hard drive, EMI shield, 5.25'' bay filler
Pre-routing cables
Two heat sinks
Your Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFKN ships with the following items:
One Intel® Workstation Board W2600CR2
One CRPS 1600W power supply, installed in the chassis
One fixed system CPU zone fan, installed in the chassis
One fixed system PCI zone fan, installed in the chassis
Four fixed HDD carrier tray, installed in the chassis
Front panel, installed in the chassis
Front Bezel for fixed hard drive, EMI shield, 5.25'' bay filler
Pre-routing cables
Two heat sinks
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 14

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
Your Intel® Server System P4216IP4LHJC ships with the following items:
One Intel® Server Board S2600IP4
Two CRPS 1200W power supply, installed in the chassis
Five hot-swap redundant system fans, installed in the chassis
16*2.5'' hot-swap HDD cage with sixteen 2.5 HDD carrier, installed in the chassis
Front panel, installed in the chassis
Front Bezel for hot-swap hard drive, EMI shield, 5.25'' bay filler
Pre-routing cables
Two heat sinks
Your Intel® Server System P4208IP4LHGC ships with the following items:
One Intel® Server Board S2600IP4
Two CRPS 750W power supply, installed in the chassis
Five hot-swap redundant system fans, installed in the chassis
8*2.5'' hot-swap HDD cage with eight 2.5 HDD carrier, installed in the chassis
Front panel, installed in the chassis
Front Bezel for hot-swap hard drive, EMI shield, 5.25'' bay filler
Pre-routing cables
Two heat sinks
Your Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHJC(L) ships with the following items:
One Intel® Server Board S2600IP4 (L)
Two CRPS 1200W power supply, installed in the chassis
Five hot-swap redundant system fans, installed in the chassis
8*3.5'' hot-swap HDD cage with eight 3.5 HDD carrier, installed in the chassis
Front panel, installed in the chassis
Front Bezel for hot-swap hard drive, EMI shield, 5.25'' bay filler
Pre-routing cables
Two heat sinks
Your Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHGC ships with the following items:
One Intel® Server Board S2600IP
Two CRPS 750W power supply, installed in the chassis
Five hot-swap redundant system fans, installed in the chassis
8*3.5'' hot-swap HDD cage with eight 3.5 HDD carrier, installed in the chassis
Front panel, installed in the chassis
Front Bezel for hot-swap hard drive, EMI shield, 5.25'' bay filler
Pre-routing cables
Two heat sinks
Your Intel® Server System P4224IP4LHKC ships with the following items:
One Intel® Server Board S2600IP
Two CRPS 1600W power supply, installed in the chassis
Five hot-swap redundant system fans, installed in the chassis
24*2.5'' hot-swap HDD cage with twenty four 2.5 HDD carrier, installed in the chassis
Front panel, installed in the chassis
Front Bezel for hot-swap hard drive, EMI shield, 5.25'' bay filler
Pre-routing cables
Two heat sinks
2 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 15
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
3
Feature
P4308IP4LHGC
P4308IP4LHJC (L)
P4308IP4LHKC
Dimensions
438mm high
173mm wide
697mm deep
Hard Drives
8*3.5 hot-swap driver cage
Peripherals
Three multi-mount 5.25'' peripheral bays
Control Panel
(dependent on
option selected)
Front Panel
Intel® Local Control Panel (Optional)
LEDs and displays
(dependent on
option selected)
With Front Panel
o NIC1 Activity
o NIC2 Activity
o NIC3 Activity
o NIC4 Activity
o Power/Sleep
o System Status
o System Chassis Identification
o Hard Drive Activity
Power Supply
Two hot-swap 750W
common redundant power
supply
Two hot-swap 1200W common
redundant power supply
Two hot-swap 1600W
common redundant power
supply
Fans
Five hot-swap system fans
USB 2.0
Two front panel USB ports with Front Panel
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
Your Intel® Server System P4216IP4LHKC ships with the following items:
One Intel® Server Board S2600IP
Two CRPS 1600W power supply, installed in the chassis
Five hot-swap redundant system fans, installed in the chassis
16*2.5'' hot-swap HDD cage with sixteen 2.5 HDD carrier, installed in the chassis
Front panel, installed in the chassis
Front Bezel for hot-swap hard drive, EMI shield, 5.25'' bay filler
Pre-routing cables
Two heat sinks
Your Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHKC ships with the following items:
One Intel® Server Board S2600IP
Two CRPS 1600W power supply, installed in the chassis
Five hot-swap redundant system fans, installed in the chassis
8*3.5'' hot-swap HDD cage with eight 3.5 HDD carrier, installed in the chassis
Front panel, installed in the chassis
Front Bezel for hot-swap hard drive, EMI shield, 5.25'' bay filler
Pre-routing cables
Two heat sinks
The following table summarizes the features for all System combinations:
Table 1. Intel® Server System P4000IP Hot-Swap 3.5 HDDs and Non-HDD configuration base
feature
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 16
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Feature
P4308IP4LHGC
P4308IP4LHJC (L)
P4308IP4LHKC
Four Back panel USB ports
Video
One rear panel video port
Feature
P4208IP4LHGC
P4216IP4LHJC
P4216IP4LHKC
P4224IP4LHKC
Dimensions
438mm high
173mm wide
697mm deep
Hard Drives
One 8x2.5'' Hot-
swap HDD cage
support up to
8x2.5'' hot-swap
HDDs
Two 8x2.5'' Hot-
swap HDD cage
support up to
16x2.5'' hot-swap
HDDs
Two 8x2.5'' Hot-
swap HDD cage
support up to
16x2.5'' hot-swap
HDDs
Three 8x2.5'' Hot-
swap HDD cage
support up to
24x2.5'' hot-swap
HDDs
Peripherals
Three multi-mount 5.25'' peripheral bays
one multi-mount
5.25'' peripheral
bays
Control Panel
(dependent on
option selected)
Front Panel
Intel® Local Control Panel (Optional)
LEDs and displays
(dependent on
option selected)
With Front Panel
o NIC1 Activity
o NIC2 Activity
o NIC3 Activity
o NIC4 Activity
o Power/Sleep
o System Status
o System Chassis Identification
o Hard Drive Activity
Power Supply
Two hot-swap 750W
common redundant
power supply
Two hot-swap
1200W common
redundant power
supply
Two hot-swap
1600W common
redundant power
supply
Two hot-swap
1600W common
redundant power
supply
Fans
Five hot-swap system fans
USB 2.0
Two front panel USB ports with Front Panel
Four Back panel USB ports (depending on server/workstation board)
Video
One rear panel video port
Feature
P4304CR2LFGN
P4304CR2LFJN(L)
P4304CR2LFKN
Dimensions
17.2 inches high
6.8 inches wide
25 inches deep (without bezel: 24.5 inches)
Hard Drives
Four Fixed 3.5'' HDDs tray
Peripherals
Three multi-mount 5.25 peripheral bays
Control Panel
(dependent on
Front Panel
Intel® Local Control Panel (Optional)
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
Table 2. Intel® Server System P4000IP Hot-Swap 2.5 HDDs configuration base feature
Table 3. Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Fixed 3.5 HDDs configuration base feature
4 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 17
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
5
Feature
P4304CR2LFGN
P4304CR2LFJN(L)
P4304CR2LFKN
option selected)
LEDs and displays
(dependent on
option selected)
With Front Panel
o NIC1 Activity
o NIC2 Activity
o NIC3 Activity (no functional)
o NIC4 Activity (no functional)
o Power/Sleep
o System Status
o System Chassis Identification
o Hard Drive Activity
Power Supply
Two hot-swap 750W common
redundant power supply
Two hot-swap 1200W
common redundant power
supply
Two hot-swap 1600W
common redundant power
supply
Fans
One fixed system CPU zone fan
One fixed system PCI zone fan
USB 2.0 and USB
3.0
Two front panel USB ports with Front Panel
Two Back panel USB ports
Two Back panel USB 3.0 ports
Video
One onboard internal video header
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 18
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
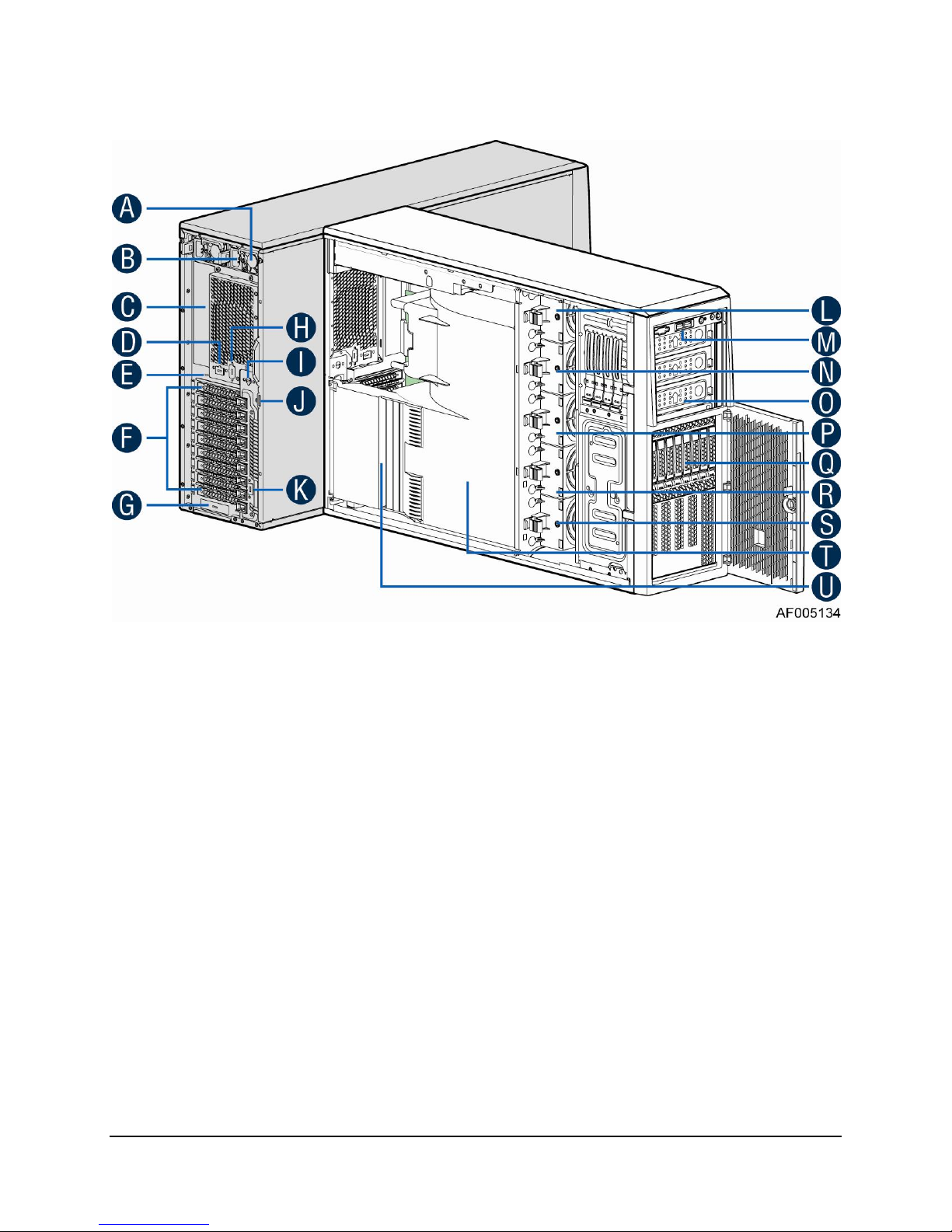
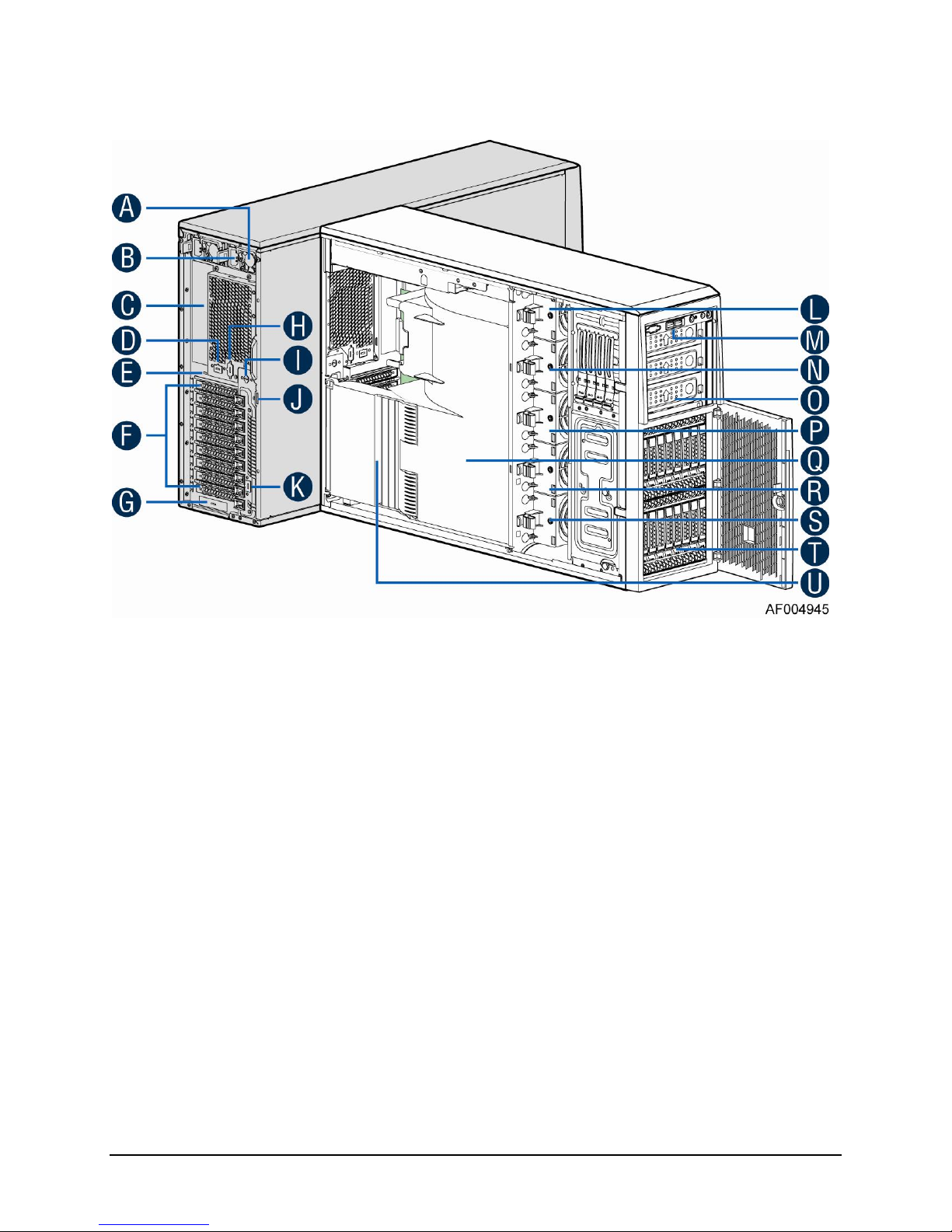
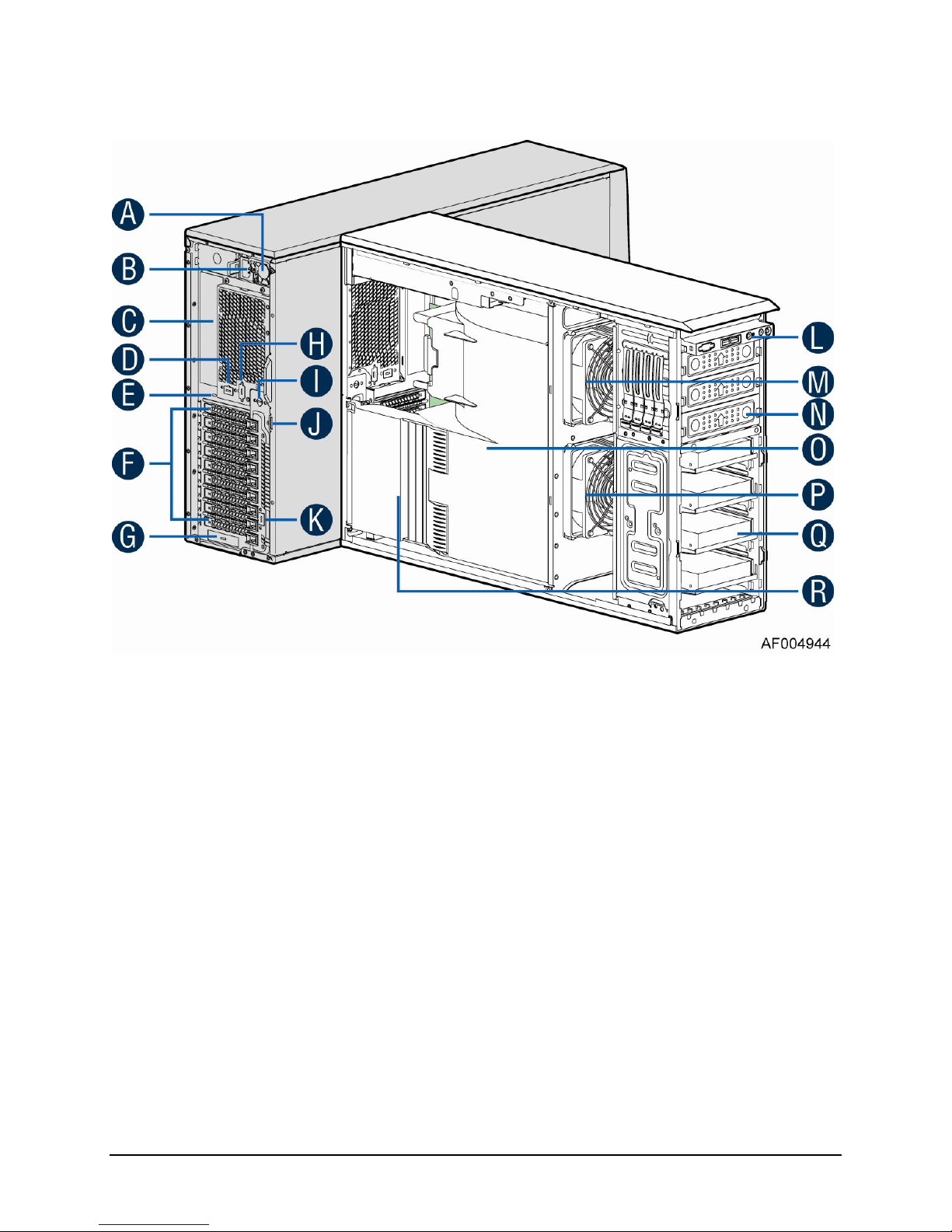
1.1.1 Intel® Server System P4208IP4LHGC View
A. 750W CRPS Power supply
B. AC Input Power connecotor
C. I/O ports
D. Serial port knockout
E. A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
F. PCI Add-in card slot covers
G. IO module slot cover
H. Alternate knockout
I. Opening for SPDIF cable
J. Padlock loop
K. RMM4 knockout
L. Hot swap system fan 5
M. Front panel
N. Hot swap system fan 4
O. 5.25'' peripheral bays
P. Hot swap system fan 3
Q. One 8x2.5'' Hot-swap HDD Cage
R. Hot swap system fan 2
S. Hot swap system fan 1
T. Air duck
U. PCI card retainer
Figure 1. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4208IP4LHGC
6 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 19
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
7
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
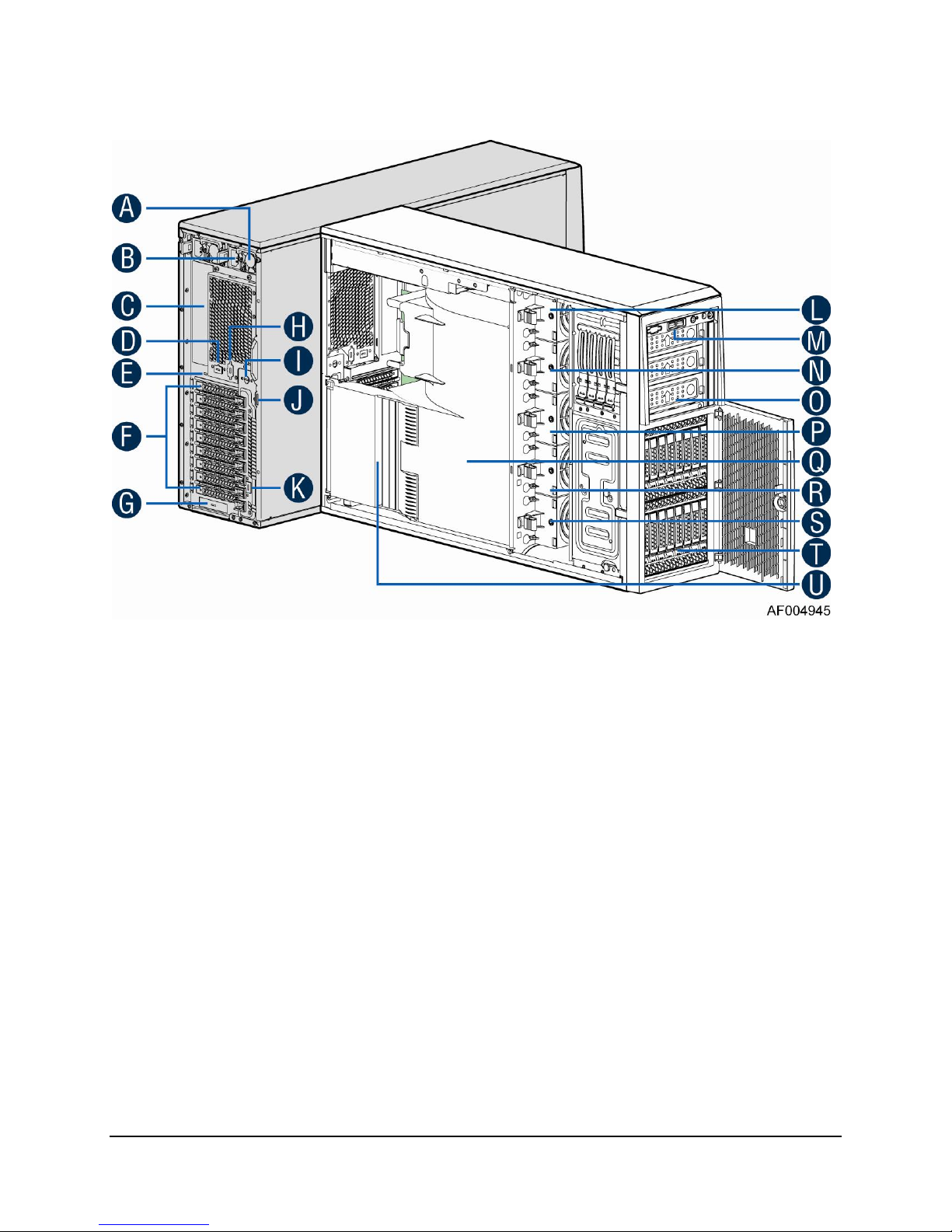
1.1.2 Intel® Server System P4216IP4LHJC View
A. 1200W CRPS Power supply
B. AC Input Power connecotor
C. I/O ports
D. Serial port knockout
E. A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
F. PCI Add-in card slot covers
G. IO module slot cover
H. Alternate knockout
I. Opening for SPDIF cable
J. Padlock loop
K. RMM4 knockout
L. Hot swap system fan 5
M. Front panel
N. Hot swap system fan 4
O. 5.25'' peripheral bays
P. Hot swap system fan 3
Q. Air duck
R. Hot swap system fan 2
S. Hot swap system fan 1
T. Two 8x2.5'' Hot-swap HDD Cage
U. PCI card retainer
Figure 2. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4216IP4LHJC
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 20
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
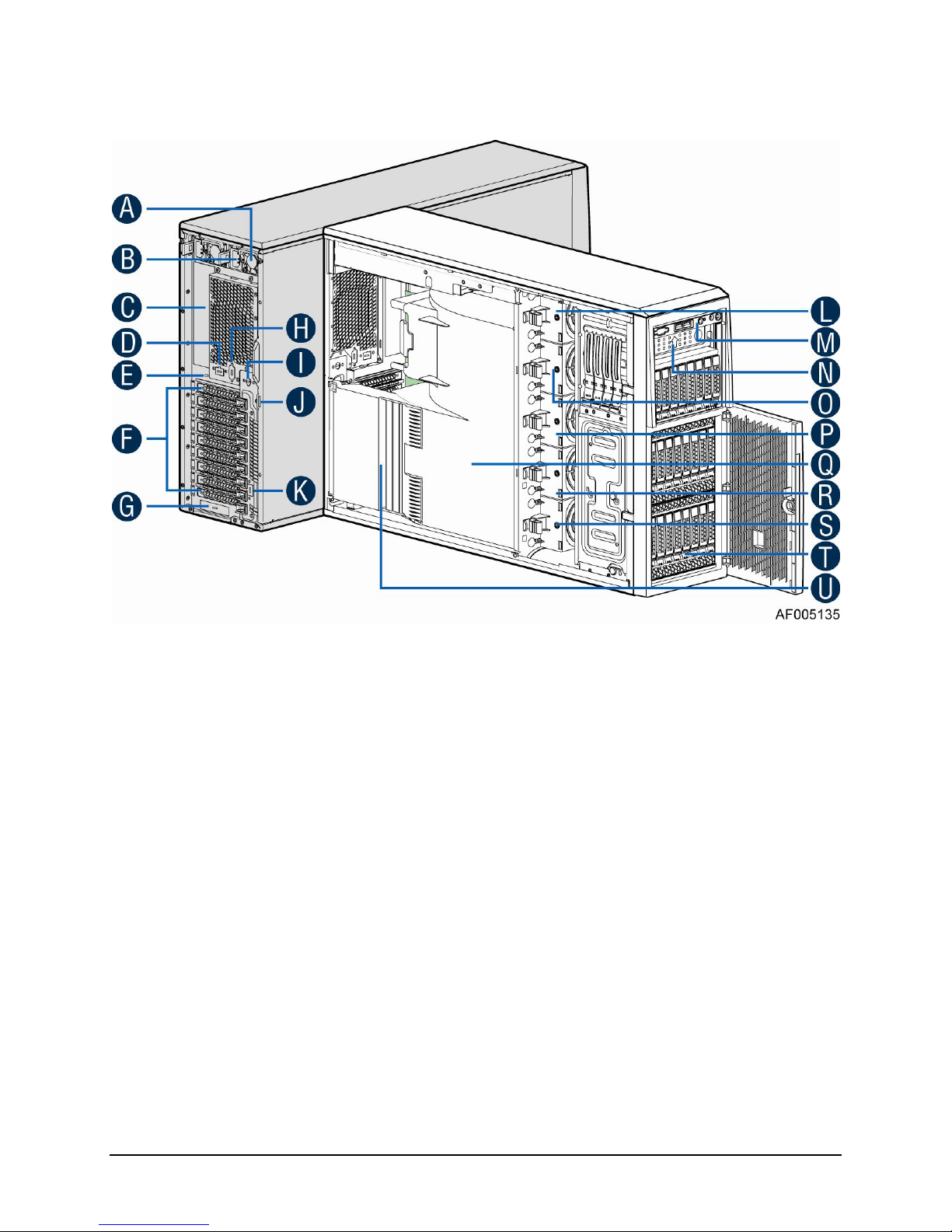
1.1.3 Intel® Server System P4216IP4LHKC View
A. 1600W CRPS Power supply
B. AC Input Power connecotor
C. I/O ports
D. Serial port knockout
E. A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
F. PCI Add-in card slot covers
G. IO module slot cover
H. Alternate knockout
I. Opening for SPDIF cable
J. Padlock loop
K. RMM4 knockout
L. Hot swap system fan 5
M. Front panel
N. Hot swap system fan 4
O. 5.25'' peripheral bays
P. Hot swap system fan 3
Q. Air duck
R. Hot swap system fan 2
S. Hot swap system fan 1
T. Two 8x2.5'' Hot-swap HDD Cage
U. PCI card retainer
Figure 3. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4216IP4LHKC
8 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 21
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
9
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
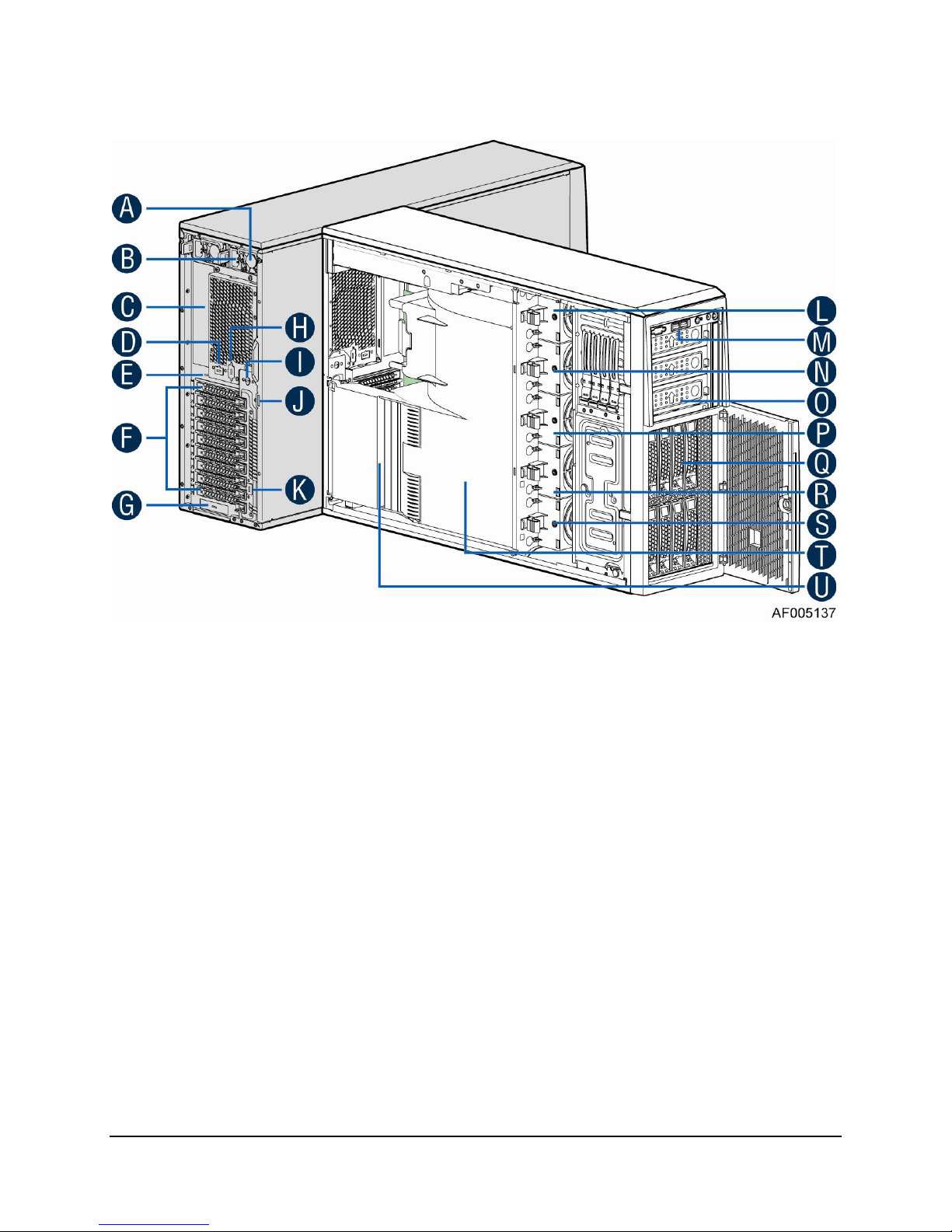
1.1.4 Intel® Server System P4224IP4LHKC View
A. 1600W CRPS Power supply
B. AC Input Power connecotor
C. I/O ports
D. Serial port knockout
E. A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
F. PCI Add-in card slot covers
G. IO module slot cover
H. Alternate knockout
I. Opening for SPDIF cable
J. Padlock loop
K. RMM4 knockout
L. Hot swap system fan 5
M. Front panel
N. 5.25'' peripheral bays
O. Hot swap system fan 4
P. Hot swap system fan 3
Q. Air duck
R. Hot swap system fan 2
S. Hot swap system fan 1
T. Three 8x2.5'' Hot-swap HDD Cage
U. PCI card retainer
Figure 4. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4224IP4LHKC
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 22
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
1.1.5 Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHGC View
A. 750W CRPS Power supply
B. AC Input Power connecotor
C. I/O ports
D. Serial port knockout
E. A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
F. PCI Add-in card slot covers
G. IO module slot cover
H. Alternate knockout
I. Opening for SPDIF cable
J. Padlock loop
K. RMM4 knockout
L. Hot swap system fan 5
M. Front panel
N. Hot swap system fan 4
O. 5.25'' peripheral bays
P. Hot swap system fan 3
Q. One 8x3.5'' Hot-swap HDD Cage
R. Hot swap system fan 2
S. Hot swap system fan 1
T. Air duck
U. PCI card retainer
Figure 5. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHGC
10 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 23
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
11
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
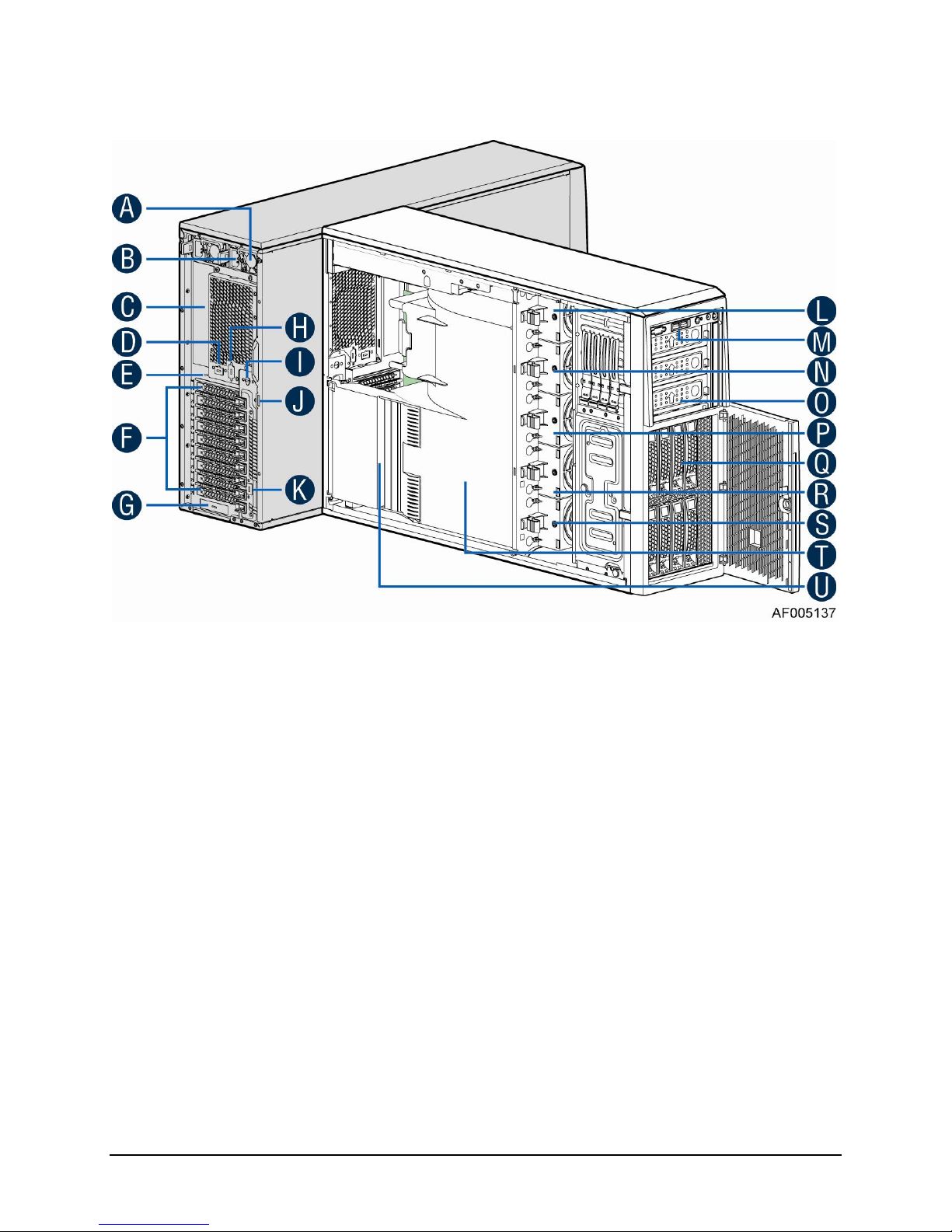
1.1.6 Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHJC(L) View
A. 1200W CRPS Power supply
B. AC Input Power connecotor
C. I/O ports
D. Serial port knockout
E. A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
F. PCI Add-in card slot covers
G. IO module slot cover
H. Alternate knockout
I. Opening for SPDIF cable
J. Padlock loop
K. RMM4 knockout
L. Hot swap system fan 5
M. Front panel
N. Hot swap system fan 4
O. 5.25'' peripheral bays
P. Hot swap system fan 3
Q. One 8x3.5'' Hot-swap HDD Cage
R. Hot swap system fan 2
S. Hot swap system fan 1
T. Air duck
U. PCI card retainer
Figure 6. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHJC
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 24
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
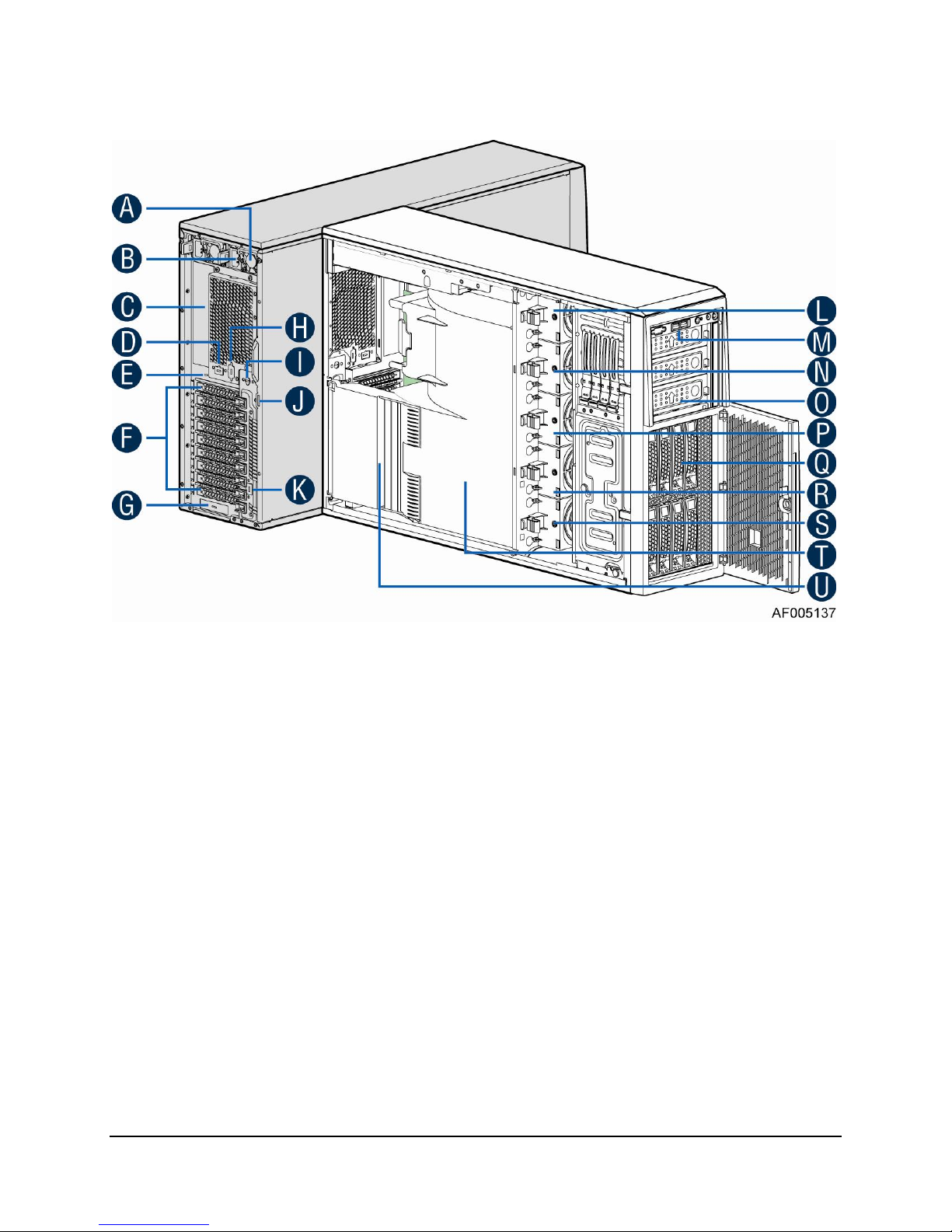
1.1.7 Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHKC View
A. 1600W CRPS Power supply
B. AC Input Power connecotor
C. I/O ports
D. Serial port knockout
E. A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
F. PCI Add-in card slot covers
G. IO module slot cover
H. Alternate knockout
I. Opening for SPDIF cable
J. Padlock loop
K. RMM4 knockout
L. Hot swap system fan 5
M. Front panel
N. Hot swap system fan 4
O. 5.25'' peripheral bays
P. Hot swap system fan 3
Q. One 8x3.5'' Hot-swap HDD Cage
R. Hot swap system fan 2
S. Hot swap system fan 1
T. Air duck
U. PCI card retainer
Figure 7. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Server System P4308IP4LHKC
12 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 25
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
13
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
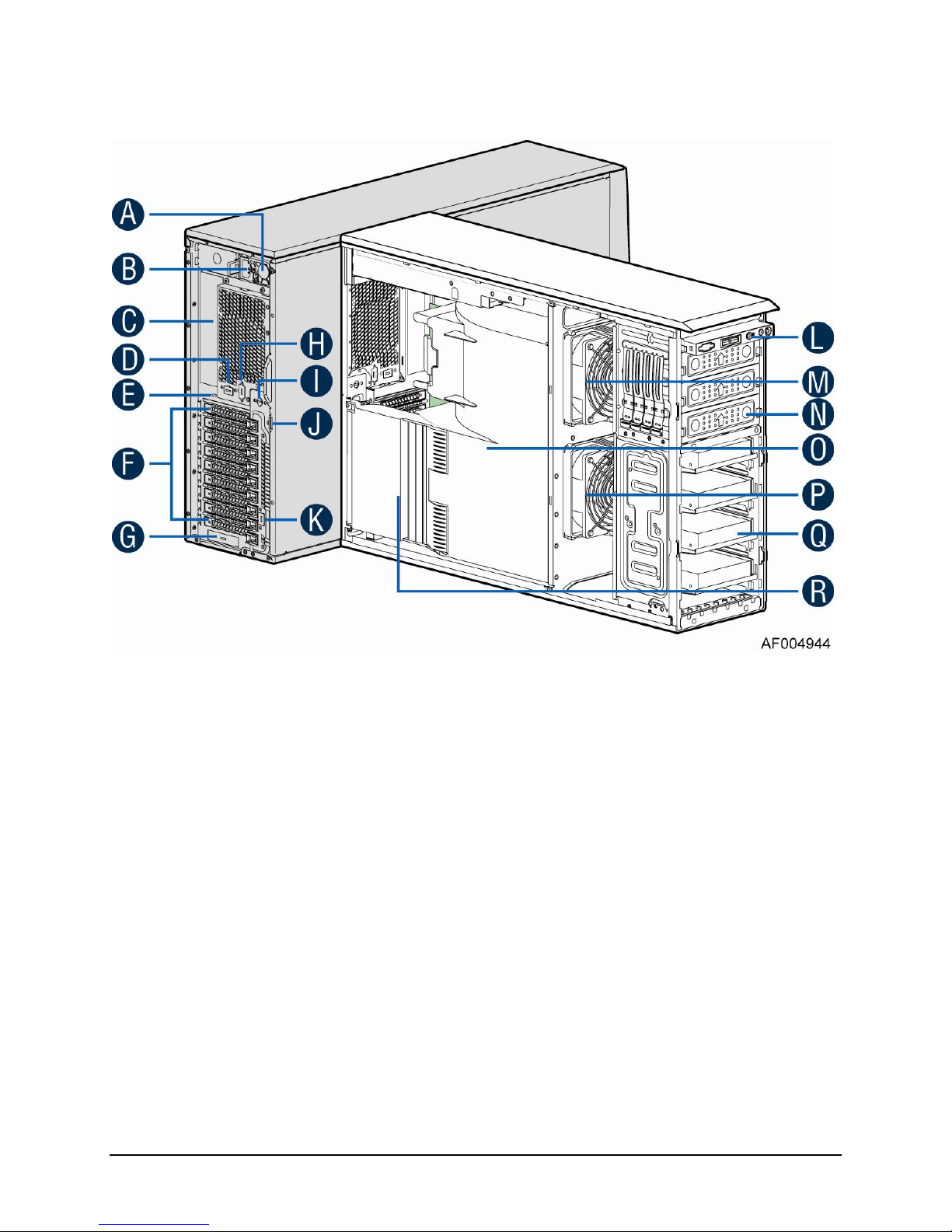
1.1.8 Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFGN View
A. 750W CRPS Power supply
B. AC Input Power connecotor
C. I/O ports
D. Serial port knockout
E. A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
F. PCI Add-in card slot covers
G. IO module slot cover
H. Alternate knockout
I. Opening for SPDIF cable
J. Padlock loop
K. RMM4 knockout
L. Front panel
M. CPU zone system fan(fan 2)
N. 5.25'' peripheral bays
O. Air duck
P. PCI zone system fan(fan 1)
Q. Fixed Hard driver carrier tray
R. PCI card retainer
Figure 8. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFGN
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 26
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
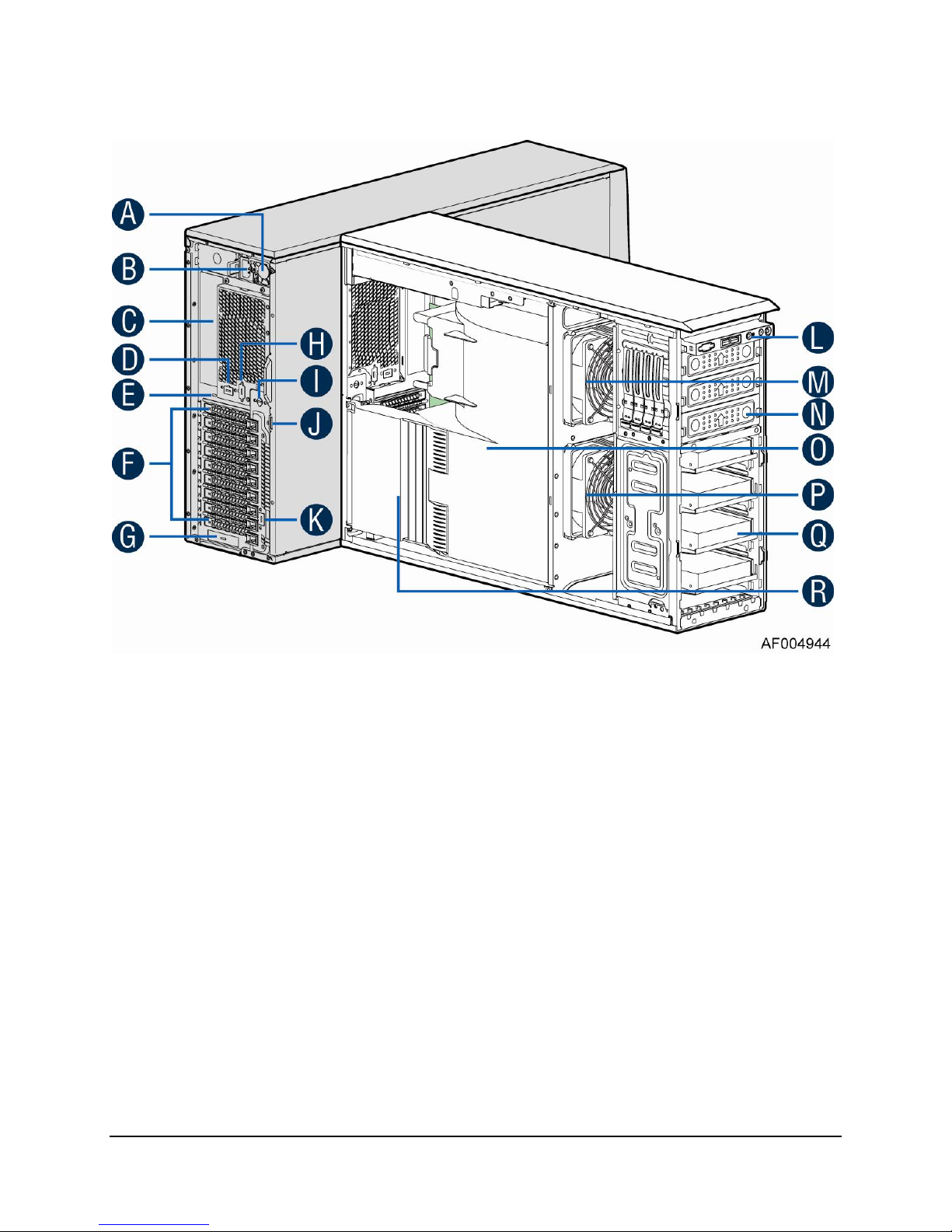
1.1.9 Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFJN(L) View
A. 1200W CRPS Power supply
B. AC Input Power connecotor
C. I/O ports
D. Serial port knockout
E. A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
F. PCI Add-in card slot covers
G. IO module slot cover
H. Alternate knockout
I. Opening for SPDIF cable
J. Padlock loop
K. RMM4 knockout
L. Front panel
M. CPU zone system fan(fan 2)
N. 5.25'' peripheral bays
O. Air duck
P. PCI zone system fan(fan 1)
Q. Fixed Hard driver carrier tray
R. PCI card retainer
Figure 9. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFJN
14 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 27
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
15
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
1.1.10 Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFKN View
A. 1600W CRPS Power supply
B. AC Input Power connecotor
C. I/O ports
D. Serial port knockout
E. A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
F. PCI Add-in card slot covers
G. IO module slot cover
H. Alternate knockout
I. Opening for SPDIF cable
J. Padlock loop
K. RMM4 knockout
L. Front panel
M. CPU zone system fan(fan 2)
N. 5.25'' peripheral bays
O. Air duck
P. PCI zone system fan(fan 1)
Q. Fixed Hard driver carrier tray
R. PCI card retainer
Figure 10. Internal Chassis View of Intel® Workstation System P4304CR2LFKN
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 28
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
1.2 Chassis dimensions
Length:
656 mm (without bezel)
698.3 mm (with bezel)
Height:
438 mm
Width:
173 mm
1.3 Front control panel feature Overview
This Front Control Panel conforms to SSI specification with one exception that up to 4 LAN
act/link LEDs are supported. The common front panel can support either the standard SSI 2x12
cable interconnect (2 LAN ports) or an Intel customized 2x15 cable interconnect (4 LAN ports).
The Front Control Panel has the following features:
Power button with integrated power LED (green)
System ID with integrated ID LED (blue)
System Status LED (green/amber)
System Reset button
HDD activity LED
4 NIC activity/link LEDs
NMI button
Two USB ports
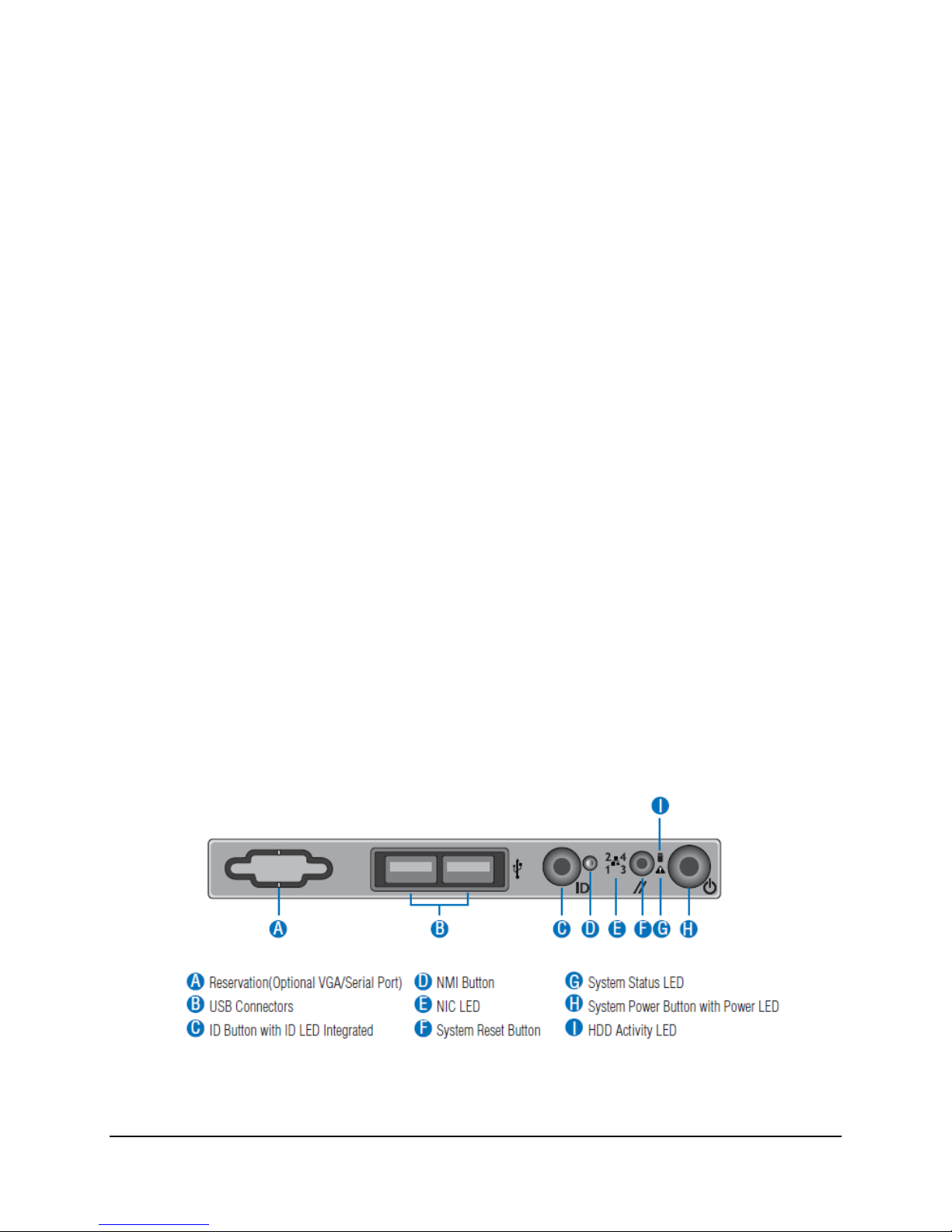
1.3.1 Front Control Panel LED/Button Functionality
The following figure shows the layout of Front Control Panel:
Figure 11. Front Control Panel LED/Button Arragement
16 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 29
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
17
State
Power
Mode
LED
Description
Power-off
Non-ACPI
Off
System power is off, and the BIOS has not initialized the chipset.
Power-on
Non-ACPI
On
System power is on
S5
ACPI
Off
Mechanical is off, and the operating system has not saved any context
to the hard disk.
S4
ACPI
Off
Mechanical is off. The operating system has saved context to the hard
disk.
S3-S1
ACPI
Slow blink1
DC power is still on. The operating system has saved context and
gone into a level of low-power state.
S0
ACPI
Steady on
System and the operating system are up and running.
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
ID Button with integrated ID LED – Toggles the integrated ID LED and the Blue server board
ID LED on and off. The ID LED is used to identify the system for maintenance when installed in
a rack of similar server systems. The ID LED can also be toggled on and off remotely using the
IPMI “Chassis Identify” command which will cause the LED to blink for 15 seconds.
NMI Button – When the NMI button is pressed, it puts the server in a halt state and issues a
non-maskable interrupt (NMI). This can be useful when performing diagnostics for a given issue
where a memory download is necessary to help determine the cause of the problem. To
prevent an inadvertent system halt, the actual NMI button is located behind the Front Control
Panel faceplate where it is only accessible with the use of a small tipped tool like a pin or paper
clip.
Network Activity LEDs (NIC LED) – The Front Control Panel includes an activity LED indicator
for each on-board Network Interface Controller (NIC). When a network link is detected, the LED
will turn on solid. The LED will blink once network activity occurs at a rate that is consistent with
the amount of network activity that is occurring.
System Reset Button – When pressed, this button will reboot and re-initialize the system.
System Status LED – The System Status LED is a bi-color (Green/Amber) indicator that
shows the current health of the server system. The system provides two locations for this
feature; one is located on the Front Control Panel, the other is located on the back edge of the
server board, viewable from the back of the system. Both LEDs are tied together and will show
the same state. The System Status LED states are driven by the on-board platform
management sub-system.
System Power Button with power LED – Toggles the system power on and off. This button
also functions as a sleep button if enabled by an ACPI compliant operating system. Pressing
this button will send a signal to the iBMC, which will either power on or power off the system.
The integrated LED is a single color (Green) and is capable of supporting different indicator
states as defined in the following table.
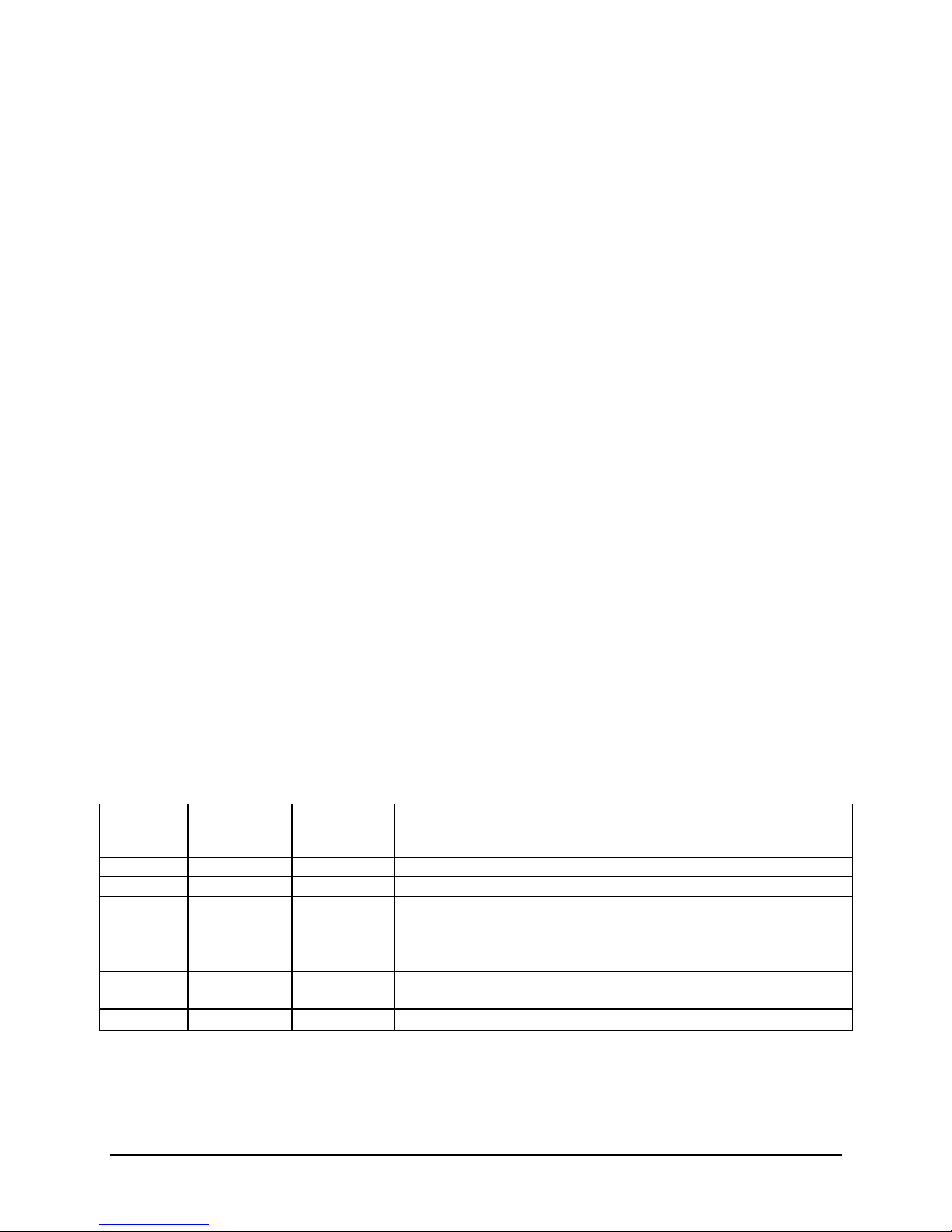
Table 4. Power/Sleep LED Functional States
HDD Activity LED - The drive activity LED on the front panel indicates drive activity from the
on-board hard disk controllers. The server board also provides a header giving access to this
LED for add-in controllers.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 30
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
LED
Color
Condition
What It Means
Power/Sleep
Green
On
Power on or S0 sleep.
Green
Blink
S1 sleep or S3 standby only for workstation baseboards.
Off
Off (also sleep S4/S5 modes).
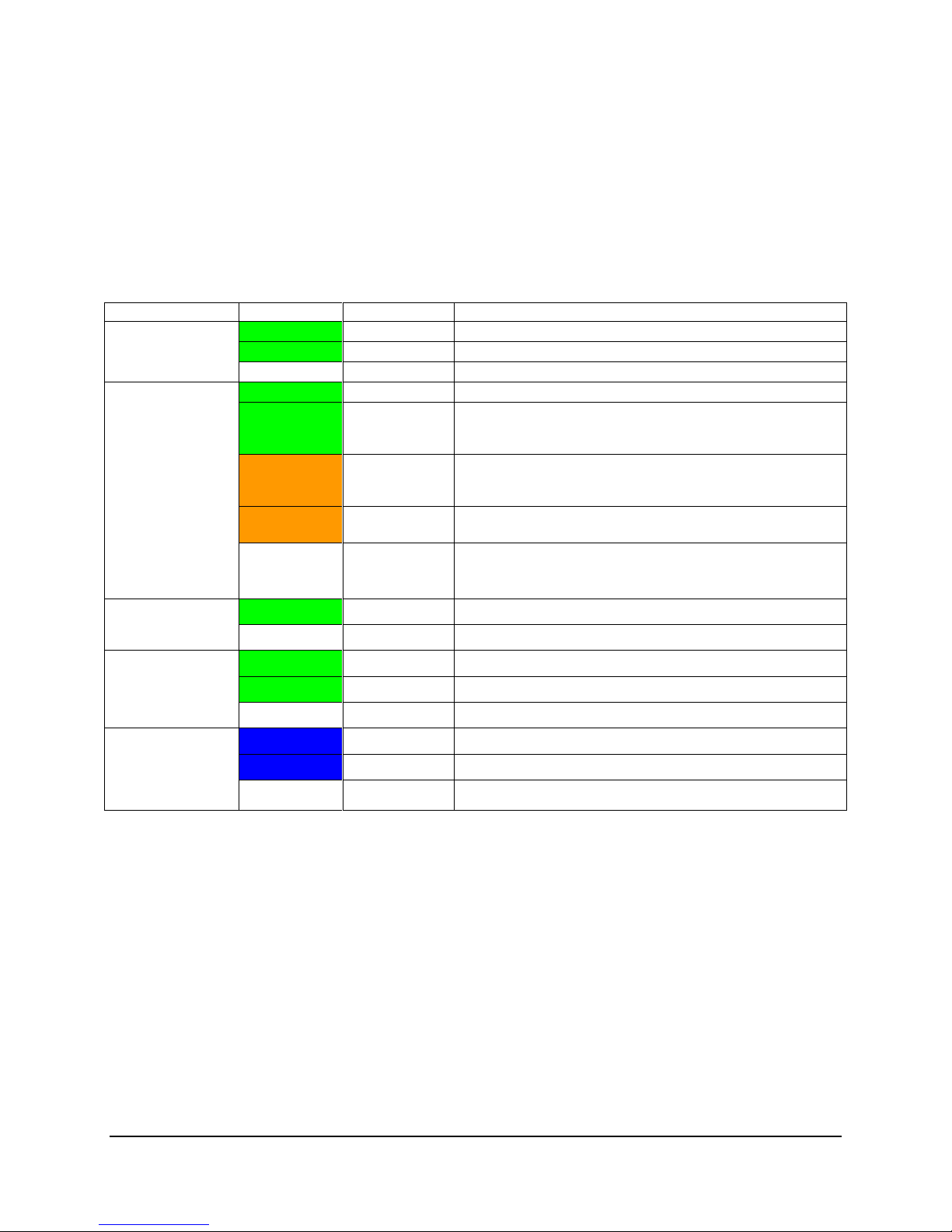
Status
Green
On
System ready/No alarm.
Green
Blink
System ready, but degraded: redundancy lost such as PS
or fan failure; non-critical temp/voltage threshold; battery
failure; or predictive PS failure.
Amber
On
Critical alarm: Voltage, thermal, or power fault; CPU
missing; insufficient power unit redundancy resource offset
asserted.
Amber
Blink
Non-Critical failure: Critical temp/voltage threshold; VDR hot
asserted; min number fans not present or failed.
Off
AC power off: System unplugged.
AC power on: System powered off and in standby, no prior
degraded/non-critical/critical state.
Global HDD Activity
Green
Blink
HDD access.
Off
No access and no fault.
LAN 1-4 Activity/Link
Green
On
LAN link
Green
Blink
LAN access.
Off
Idle.
Chassis Identification
Blue
On
Front panel chassis ID button pressed.
Blue
Blink
Unit selected for identification by software.
Off
No identification.
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
USB Ports – In addition, the front panel provides two USB ports. The USB ports are cabled to
the 2x5 connector on the server board.
1.3.2 Front Control Panel LED Status
The following table provides a description of each LED status.
Table 5. Front Control Panel LED Status
18 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 31

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
19
A
CRPS Power supply
G
IO module slot cover
B
AC Input Power connecotor
H
Alternate RMM4 knockout
C
I/O ports
I
Opening for SPDIF cable
D
Serial port knockout
J
Padlock loop
E
A Kensington cable lock mounting hole
K
RMM4 knockout
F
PCI Add-in card slot covers
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
1.4 Back panel feature Overveiw
Figure 12. Back panel feature
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 32

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
1.5 Hot swap Hard Drivers and front panel options
Figure 13. Hot-Swap Hard Disk Drive Cage
1.6 Chassis Security
A variety of chassis security options are provided at the system level:
A removable padlock loop at the rear of the system access cover can be used to prevent
access to the microprocessors, memory, and add-in cards. A variety of lock sizes can be
accommodated by the 0.270-inch diameter loop.
A Kensington* cable lock mounting hole is provided on the rear chassis I/O panel.
A chassis intrusion switch is provided, allowing server management software to detect
unauthorized access to the system side cover.
In hot-swap hard drives configuration, a door lock is provided on the front bezel assembly
with the door to prevent access to the hot-swap hard drives and the interior of the chassis.
Note: See the technical product specificationappropriate to the server board and System
Service Guide for a description of BIOS and management security features for each specific
supported platform. Technical product specifications can be found at
http://www.intel.com/support.
20 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 33

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
21
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
1.7 Front Bezel Features
There are two type of front bezel assembly.
1. Front bezel assembly for fixed hard drives configuration on Intel
®
Workstation System
P4000CR.
Figure 14. Front Closed Chassis View for Fixed Hard Drives Configuration
2. Front bezel assembly with the door for hot-swap hard drives configuration on Intel
System P4000IP.
®
Server
Figure 15. Front Closed Chassis View for Hot-swap Hard Drives Configuration
Both two pedestal front bezel are constructed of molded plastic and attaches to the front of the
chassis with three clips on the right side and two snaps on the left. The snaps at the left attach
behind the access cover, thereby preventing accidental removal of the bezel. The bezel can
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
A. Security Lock
Page 34

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System Overview
only be removed by first removing the server access cover. This provides additional security to
the hard drive and peripheral bay area.
For the front bezel assembly for fixed hard drives configuration, removing the bezel, there is an
EMI shield covering the fixed hard drives bay area.
For the front bezel assembly for hot-swap hard drives configuration, the bezel includes a keylocking door that covers the drive cage area and allows access to hot swap drives when a hot
swap drive cage is installed.
The peripheral bays are covered with plastic snap-in cosmetic pieces that must be removed to
add peripherals to the system. Front panel buttons and lights are located above the
peripheral bays.
22 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 35

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
23
Pin
Name
Pin
Name
A1
GND
B1
GND
A2
GND
B2
GND
A3
GND
B3
GND
A4
GND
B4
GND
A5
GND
B5
GND
73.5
mm
FCI 2x25 card
edge connector
10035388-102
A25
A1
B25
B1
3mm
Retention Latch
Airflow direction
185mm
40mm fan
8.5mm
39mm
11mm
2. System Power Sub-system
2.1 750-W Power Supply
This specification defines a 750W redundant power supply that supports server systems. This
power supply has 2 outputs; 12V and 12V standby. The AC input is auto ranging and power
factor corrected.
2.1.1 Mechanical Overview
The physical size of the power supply enclosure is 39/40mm x 73.5mm x 185mm. The power
supply contains a single 40mm fan. The power supply has a card edge output that interfaces
with a 2x25 card edge connector in the system. The AC plugs directly into the external face of
the power supply. Refer to the following Figure 16. All dimensions are nominal.
Figure 16. 750-W Power Supply Outline Drawing
2.1.1.1 DC Output Connector
The power supply uses a card edge output connection for power and signal that is compatible
with a 2x25 Power Card Edge connector (equivalent to 2x25 pin configuration of the FCI power
card connector 10035388-102LF).
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Table 6. DC Output Connector
Page 36

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Pin
Name
Pin
Name
A6
GND
B6
GND
A7
GND
B7
GND
A8
GND
B8
GND
A9
GND
B9
GND
A10
+12V
B10
+12V
A11
+12V
B11
+12V
A12
+12V
B12
+12V
A13
+12V
B13
+12V
A14
+12V
B14
+12V
A15
+12V
B15
+12V
A16
+12V
B16
+12V
A17
+12V
B17
+12V
A18
+12V
B18
+12V
A19
PMBus SDA
B19
A0 (SMBus address)
A20
PMBus SCL
B20
A1 (SMBus address)
A21
PSON
B21
12V stby
A22
SMBAlert#
B22
Cold Redundancy Bus
A23
Return Sense
B23
12V load share bus
A24
+12V remote Sense
B24
No Connect
A25
PWOK
B25
Compatibility Check pin
Min λd Wavelength
Nominal λd Wavelength
Max λd Wavelength
Units
Green
562
565
568
nm
Amber
607
610
613
nm
2.1.1.2 Handle Retention
The power supply has a handle to assist extraction. The module is able to be inserted and
extracted without the assistance of tools. The power supply has a latch which retains the power
supply into the system and prevents the power supply from being inserted or extracted from the
system when the AC power cord is pulled into the power supply.
The handle protects the operator from any burn hazard.
2.1.1.3 LED Marking and Identification
The power supply uses a bi-color LED: Amber and Green. Below are table showing the LED
states for each power supply operating state and the LED‟s wavelength characteristics. Refer to
the Intel LED Wavelength and Intensity specification for more details.
Table 7. LED Characteristics
24 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Table 8. Power Supply LED Functionality
Page 37

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
25
Power Supply Condition
LED State
Output ON and OK
GREEN
No AC power to all power supplies
OFF
AC present/Only 12VSB on (PS off) or PS in Cold redundant state
1Hz Blink GREEN
AC cord unplugged or AC power lost; with a second power supply in parallel still with AC
input power.
AMBER
Power supply warning events where the power supply continues to operate; high temp,
high power, high current, slow fan.
1Hz Blink Amber
Power supply critical event causing a shutdown; failure, OCP, OVP, Fan Fail
AMBER
Power supply FW updating
2Hz Blink GREEN
Item
Description
Min
Max
Units
T
op_sc_red
Operating temperature range; spreadcore redundant
( 60% load, 3000m, spreadcore system flow impedance2 )
0
60
C
T
op_sc_nr
Operating temperature range; spreadcore non-redundant
(100% load, 3000m, spreadcore system flow impedance2 )
0
50
C
T
op_rackped_
900
Operating temperature range; rack/pedestal 900m
( 100% load, 900m, rack/pedestal system flow impedance2 )
0
45
C
T
op_rackped_
3000
Operating temperature range; rack/pedestal 3000m
( 100% load, 3000m, rack/pedestal system flow impedance2 )
0
40
C
Texit
Maximum exit air temperature
68
C
T
non-op
Non-operating temperature range.
-40
70
C
Altitude
Maximum operating altitude 3
3050
m
2.1.1.4 Temperature Requirements
The power supply operates within all specified limits over the Top temperature range. All airflow
passes through the power supply and not over the exterior surfaces of the power supply.
Table 9. Environmental Requirements
Notes:
1. Under normal conditions, the exit air temperature shall be less than 65C. 68C is provided for absolute
worst case conditions and is expected only to exist when the inlet ambient reaches 60C.
2. T
op_rackped_900
condition only requires max altitude of 900m.
The power supply meets UL enclosure requirements for temperature rise limits. All sides of the
power supply with exception to the air exhaust side are classified as “Handle, knobs, grips, etc.
held for short periods of time only”.
2.1.2 AC Input Requirements
2.1.2.1 Power Factor
The power supply meets the power factor requirements stated in the Energy Star® Program
Requirements for Computer Servers. These requirements are stated below.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 38

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Output power
10% load
20% load
50% load
100% load
Power factor
> 0.65
> 0.80
> 0.90
> 0.95
PARAMETER
MIN
RATED
V
MAX
Start up VAC
Power Off VAC
Voltage (110)
90 V
rms
100-127 V
rms
140 V
rms
85VAC +/4VAC
74VAC +/5VAC
Voltage (220)
180 V
rms
200-240 V
rms
264 V
rms
Frequency
47 Hz
50/60
63 Hz
Loading
Holdup time
70%
12msec
Table 10. Power Factor Requirements for Computer Servers
Tested at 230Vac, 50Hz and 60Hz and 115VAC, 60Hz
Tested according to Generalized Internal Power Supply Efficiency Testing Protocol, Rev 6.4.3.
This is posted at http://efficientpowersupplies.epri.com/methods.asp.
2.1.2.2 AC Inlet Connector
The AC input connector is an IEC 320 C-14 power inlet. This inlet is rated for 10A/250VAC.
2.1.2.3 AC Input Voltage Specification
The power supply operates within all specified limits over the following input voltage range.
Harmonic distortion of up to 10% of the rated line voltage does not cause the power supply to
go out of specified limits. Application of an input voltage below 85VAC does not cause damage
to the power supply, including a blown fuse.
Table 11. AC Input Voltage Range
Notes:
1. Maximum input current at low input voltage range shall be measured at 90VAC, at max load.
2. Maximum input current at high input voltage range shall be measured at 180VAC, at max load.
3. This requirement is not to be used for determining agency input current markings.
2.1.2.4 AC Line Dropout/Holdup
An AC line dropout is defined to be when the AC input drops to 0VAC at any phase of the AC
line for any length of time. During an AC dropout the power supply meets dynamic voltage
regulation requirements. An AC line dropout of any duration does not cause tripping of control
signals or protection circuits. If the AC dropout lasts longer than the holdup time the power
supply recovers and meets all turn on requirements. The power supply meets the AC dropout
requirement over rated AC voltages and frequencies. A dropout of the AC line for any duration
does not cause damage to the power supply.
Table 12. AC Line Holdup Time
26 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 39

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
27
AC Line Sag (10sec interval between each sagging)
Duration
Sag
Operating AC Voltage
Line Frequency
Performance Criteria
0 to 1/2 AC
cycle
95%
Nominal AC Voltage ranges
50/60Hz
No loss of function or performance
> 1 AC cycle
>30%
Nominal AC Voltage ranges
50/60Hz
Loss of function acceptable, self
recoverable
AC Line Surge
Duration
Surge
Operating AC Voltage
Line Frequency
Performance Criteria
Continuous
10%
Nominal AC Voltages
50/60Hz
No loss of function or performance
0 to ½ AC
cycle
30%
Mid-point of nominal AC
Voltages
50/60Hz
No loss of function or performance
2.1.2.5 AC Line 12VSBHoldup
The 12VSB output voltage stays in regulation under its full load (static or dynamic) during an
AC dropout of 70ms min (=12VSB holdup time) whether the power supply is in ON or OFF
state (PSON asserted or de-asserted).
2.1.2.6 AC Line Fuse
The power supply has one line fused in the single line fuse on the line (Hot) wire of the AC
input. The line fusing is acceptable for all safety agency requirements. The input is a slow blow
type. AC inrush current does not cause the AC line fuse to blow under any conditions. All
protection circuits in the power supply does not cause the AC fuse to blow unless a component
in the power supply has failed. This includes DC output load short conditions.
2.1.2.7 AC Line Transient Specification
AC line transient conditions are defined as “sag” and “surge” conditions. “Sag” conditions are
also commonly referred to as “brownout”, these conditions is defined as the AC line voltage
dropping below nominal voltage conditions. “Surge” is defined to refer to conditions when the
AC line voltage rises above nominal voltage.
The power supply meets the requirements under the following AC line sag and surge conditions.
Table 13. AC Line Sag Transient Performance
Table 14. AC Line Surge Transient Performance
2.1.2.8 Power Recovery
The power supply shall recover automatically after an AC power failure. AC power failure is
defined to be any loss of AC power that exceeds the dropout criteria.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 40

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Loading
100% of maximum
50% of maximum
20% of maximum
10% of maximum
Minimum Efficiency
91%
94%
90%
82%
Parameter
Min
Max.
Peak 2, 3
Unit
12V main
0.0
62.0
70.0
A
12Vstby 1
0.0
2.1
2.4
A
2.1.3 Efficiency
The following table provides the required minimum efficiency level at various loading conditions.
These are provided at three different load levels; 100%, 50%, 20%, and 10%. Output shall be
load according to the proportional loading method defined by 80 Plus in Generalized Internal
Power Supply Efficiency Testing Protocol, Rev. 6.4.3. This is posted at
http://efficientpowersupplies.epri.com/methods.asp.
Table 15. Silver Efficiency Requirement
The power supply passes with enough margins to make sure in production all power supplies meet these
efficiency requirements.
2.1.4 DC Output Specification
2.1.4.1 Output Power/Currents
The following table defines the minimum power and current ratings. The power supply meets
both static and dynamic voltage regulation requirements for all conditions.
Table 16. Minimum Load Ratings
Notes:
1. 12Vstby must provide 4.0A with two power supplies in parallel. The Fan may work when stby
current >1.5A
2. Length of time peak power can be supported is based on thermal sensor and assertion of the
SMBAlert# signal. Minimum peak power duration shall be 20 seconds without asserting the SMBAlert#
signal at maximum operating temperature.
2.1.4.2 Pmax Power support
The PSU should support 3msec peak power duration at a 50msec period; 5.7% duty cycle,
Step loading from 730W to 1050W, Average power = 750W. Full AC input range; 100127VAC/200-240VAC
2.1.4.3 Standby Output
The 12VSB output is present when an AC input greater than the power supply turn on voltage is
applied.
2.1.4.4 Voltage Regulation
The power supply output voltages stay within the following voltage limits when operating at
steady state and dynamic loading conditions. These limits include the peak-peak ripple/noise.
These shall be measured at the output connectors.
28 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 41

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
29
Parameter
Tolerance
Min
Nom
Max
Units
+12V
- 5%/+5%
+11.40
+12.00
+12.60
V
rms
+12V stby
- 5%/+5%
+11.40
+12.00
+12.60
V
rms
Output
Step Load Size
(See note 2)
Load Slew Rate
Test capacitive Load
+12VSB
1.0A
0.25 A/sec
20 F
+12V
60% of max load
0.25 A/sec
2000 F
Output
Min
Max
Units
+12VSB
20
3100
F
+12V
500
25000
F
Table 17. Voltage Regulation Limits
2.1.4.5 Dynamic Loading
The output voltages remains within limits specified for the step loading and capacitive loading
specified in the table below. The load transient repetition rate is tested between 50Hz and 5kHz
at duty cycles ranging from 10%-90%. The load transient repetition rate is only a test
specification. The step load may occur anywhere within the MIN load to the MAX
load conditions.
Table 18. Transient Load Requirements
Note:
For dynamic condition +12V min loading is 1A.
2.1.4.6 Capacitive Loading
The power supply is stable and meets all requirements with the following capacitive loading
ranges.
Table 19. Capacitive Loading Conditions
2.1.4.7 Grounding
The output ground of the pins of the power supply provides the output power return path. The
output connector ground pins are connected to the safety ground (power supply enclosure).
This grounding is well designed to ensure passing the max allowed Common Mode Noise levels.
The power supply is provided with a reliable protective earth ground. All secondary circuits is
connected to protective earth ground. Resistance of the ground returns to chassis does not
exceed 1.0 m. This path may be used to carry DC current.
2.1.4.8 Residual Voltage Immunity in Standby mode
The power supply is immune to any residual voltage placed on its outputs (Typically a leakage
voltage through the system from standby output) up to 500mV. There is neither additional heat
generated, nor stressing of any internal components with this voltage applied to any individual
or all outputs simultaneously. It also does not trip the protection circuits during turn on.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 42

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
+12V main
+12VSB
120mVp-p
120mVp-p
The residual voltage at the power supply outputs for no load condition does not exceed 100mV
when AC voltage is applied and the PSON# signal is de-asserted.
2.1.4.9 Common Mode Noise
The Common Mode noise on any output does not exceed 350mV pk-pk over the frequency
band of 10Hz to 20MHz. The measurement is made across a 100Ω resistor between each of
DC outputs, including ground at the DC power connector and chassis ground (power
subsystem enclosure). The test set-up shall use a FET probe such as Tektronix model P6046
or equivalent.
2.1.4.10 Hot Swap Requirements
Hot swapping a power supply is the process of inserting and extracting a power supply from an
operating power system. During this process the output voltages remains within the limits with
the capacitive load specified. The hot swap test is conducted when the system is operating
under static, dynamic, and zero loading conditions. The power supply uses a latching
mechanism to prevent insertion and extraction of the power supply when the AC power cord is
inserted into the power supply.
2.1.4.11 Forced Load Sharing
The +12V output will have active load sharing. The output will share within 10% at full load. The
failure of a power supply does not affect the load sharing or output voltages of the other
supplies still operating. The supplies are able to load share in parallel and operate in a hotswap/redundant 1+1 configurations. The 12VSB output is not required to actively share current
between power supplies (passive sharing). The 12VSB output of the power supplies are
connected together in the system so that a failure or hot swap of a redundant power supply
does not cause these outputs to go out of regulation in the system.
2.1.4.12 Ripple/Noise
The maximum allowed ripple/noise output of the power supply is defined in below Table. 41.
This is measured over a bandwidth of 10Hz to 20MHz at the power supply output connectors. A
10F tantalum capacitor in parallel with a 0.1F ceramic capacitor is placed at the point of
measurement.
Table 20. Ripples and Noise
The test set-up shall be as shown below:
30 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 43

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
31
AC HOT
POWER SUPPLY
AC NEUTRAL
V
OUT
RETURN
V
AC GROUND
LOAD
SCOPE
LOAD MUST BE
ISOLATED FROM
THE GROUND OF
THE POWER
SUPPLY
10uF
.1uF
GENERAL NOTES:
1. LOAD THE OUTPUT WITH ITS MINIMUM
LOAD CURRENT.
2. CONNECT THE PROBES AS SHOWN.
3. REPEAT THE MEASUREMENTS WITH THE
MAXIMUM LOAD ON THE OUTPUT.
SCOPE NOTE:
USE A TEKTRONIX 7834 OSCILLOSCOPE WITH 7A13 AND
DIFFERENTIAL PROBE P6055 OR EQUIVALENT.
Item
Description
Min
Max
Units
T
vout_rise
Output voltage rise time
5.0 *
70 *
ms
T
sb_on_delay
Delay from AC being applied to 12VSBbeing
within regulation.
1500
ms
T
ac_on_delay
Delay from AC being applied to all output
voltages being within regulation.
3000
ms
T
vout_holdup
Time 12Vl output voltage stay within regulation
after loss of AC.
13 ms
T
pwok_holdup
Delay from loss of AC to de-assertion of PWOK
12 ms
T
pson_on_delay
Delay from PSON# active to output voltages
within regulation limits.
5
400
ms
T
pson_pwok
Delay from PSON# deactivate to PWOK being
de-asserted.
5 ms
T
pwok_on
Delay from output voltages within regulation limits
to PWOK asserted at turn on.
100
500
ms
T
pwok_off
Delay from PWOK de-asserted to output voltages
dropping out of regulation limits.
1 ms
T
pwok_low
Duration of PWOK being in the de-asserted state
during an off/on cycle using AC or the PSON
100 ms
Figure 17. Differential Noise test setup
Note: When performing this test, the probe clips and capacitors should be located close to
the load.
2.1.4.13 Timing Requirements
These are the timing requirements for the power supply operation. The output voltages must
rise from 10% to within regulation limits (T
) within 5 to 70ms. For 12VSB, it is allowed to
vout_rise
rise from 1.0 to 25ms. All outputs must rise monotonically. Table below shows the timing
requirements for the power supply being turned on and off by the AC input, with PSON held low
and the PSON signal, with the AC input applied.
Table 21. Timing Requirements
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 44

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Item
Description
Min
Max
Units
signal.
T
sb_vout
Delay from 12VSBbeing in regulation to O/Ps
being in regulation at AC turn on.
50
1000
ms
T
12VSB_holdup
Time the 12VSBoutput voltage stays within
regulation after loss of AC.
70 ms
AC Input
Vout PWOK
12Vsb
PSON
T
sb_on_delay
T
AC_on_delay
T
pwok_on
T
vout_holdup
T
pwok_holdup
T
pson_on_delay
T
sb_on_delay
T
pwok_on
T
pwok_off
T
pwok_off
T
pson_pwok
T
pwok_low
T
sb_vout
AC turn on/off cycle
PSON turn on/off cycle
T
5Vsb_holdup
* The 12VSBoutput voltage rise time shall be from 1.0ms to 25ms.
Figure 18. Turn On/Off Timing (Power Supply Signals)
2.1.5 Protection Circuits
Protection circuits inside the power supply causes only the power supply‟s main outputs to
shutdown. If the power supply latches off due to a protection circuit tripping, an AC cycle OFF
for 15sec and a PSON# cycle HIGH for 1sec is able to reset the power supply.
2.1.5.1 Current Limit (OCP)
The power supply has current limit to prevent the outputs from exceeding the values shown in
table below. If the current limits are exceeded the power supply shuts down and latches off. The
latch will be cleared by toggling the PSON# signal or by an AC power interruption. The power
supply does not be damaged from repeated power cycling in this condition. 12VSB will be autorecovered after removing OCP limit.
32 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 45

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
33
Output VOLTAGE
Input voltage range
Over Current Limits
+12V
90 – 264VAC
72A min; 78A max
12VSB
90 – 264VAC
2.5A min; 3.5A max
Output voltage
Min (v)
Max (v)
+12V
13.0
14.5
+12VSB
13.0
14.5
Signal Type
Accepts an open collector/drain input from the system. Pull-up to VSB
located in power supply.
PSON# = Low
ON
PSON# = High or Open
OFF
MIN
MAX
Table 22. Over Current Protection
2.1.5.2 Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
The power supply over voltage protection is locally sensed. The power supply shuts down and
latches off after an over voltage condition occurs. This latch is cleared by toggling the PSON#
signal or by an AC power interruption. The values are measured at the output of the power
supply‟s connectors. The voltage does not exceed the maximum levels when measured at the
power connectors of the power supply connector during any single point of fail. The voltage
doesn‟t trip any lower than the minimum levels when measured at the power connector.
12VSBwill be auto-recovered after removing OVP limit.
Table 23. Over Voltage Protection (OVP) Limits for 750W PSU
2.1.5.3 Over Temperature Protection (OTP)
The power supply will be protected against over temperature conditions caused by loss of fan
cooling or excessive ambient temperature. In an OTP condition the PSU will shut down. When
the power supply temperature drops to within specified limits, the power supply shall restore
power automatically, while the 12VSB remains always on. The OTP circuit must have built in
margin such that the power supply will not oscillate on and off due to temperature recovering
condition. The OTP trip level shall have a minimum of 4C of ambient temperature margin.
2.1.6 Control and Indicator Functions
The following sections define the input and output signals from the power supply. Signals that
can be defined as low true use the following convention: Signal# = low true.
2.1.6.1 PSON# Input Signal
The PSON# signal is required to remotely turn on/off the power supply. PSON# is an active low
signal that turns on the +12V power rail. When this signal is not pulled low by the system, or left
open, the outputs (except the +12VSB) turn off. This signal is pulled to a standby voltage by a
pull-up resistor internal to the power supply.
Table 24. PSON# Signal Characteristic
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 46

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Signal Type
Accepts an open collector/drain input from the system. Pull-up to VSB
located in power supply.
Logic level low (power supply ON)
0V
1.0V
Logic level high (power supply OFF)
2.0V
3.46V
Source current, Vpson = low
4mA
Power up delay: T
pson_on_delay
5msec
400msec
PWOK delay: T
pson_pwok
50msec
Signal Type
Open collector/drain output from power supply. Pull-up to VSB located
in the power supply.
PWOK = High
Power OK
PWOK = Low
Power Not OK
MIN
MAX
Logic level low voltage, Isink=400uA
0V
0.4V
Logic level high voltage, Isource=200A
2.4V
3.46V
Sink current, PWOK = low
400uA
Source current, PWOK = high
2mA
PWOK delay: T
pwok_on
100ms
1000ms
1.0 V PS is
enabled
2.0 V PS is
disabled
1.0V
2.0V
Enabled
Disabled
0.3V ≤ Hysterisis ≤ 1.0V
In 1.0-2.0V input voltages range is required
3.46V
0V
Figure 19. PSON# Required Signal Characteristic
2.1.6.2 PWOK (Power OK) Output Signal
PWOK is a power OK signal and will be pulled HIGH by the power supply to indicate that all the
outputs are within the regulation limits of the power supply. When any output voltage falls below
regulation limits or when AC power has been removed for a time sufficiently long so that power
supply operation is no longer guaranteed, PWOK will be de-asserted to a LOW state. See
Table 46 for a representation of the timing characteristics of PWOK. The start of the PWOK
delay time shall inhibited as long as any power supply output is in current limit.
Table 25. PWOK Signal Characteristics
34 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 47

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
35
Signal Type
Open collector/drain output from power supply. Pull-up to VSB located
in the power supply.
PWOK rise and fall time
100sec
Power down delay: T
pwok_off
1ms
200msec
Signal Type (Active Low)
Open collector/drain output from power supply. Pull-up to
VSB located in system.
Alert# = High
OK
Alert# = Low
Power Alert to system
MIN
MAX
Logic level low voltage, Isink=4 mA
0 V
0.4 V
Logic level high voltage, Isink=50 A
3.46 V
Sink current, Alert# = low
4 mA
Sink current, Alert# = high
50 A
Alert# rise and fall time
100 s
A recommended implementation of the Power Ok circuits is shown below.
Note: The Power Ok circuits should be compatible with 5V pull up resistor (>10k) and 3.3V pull
up resistor (>6.8k).
2.1.6.3 SMBAlert# Signal
This signal indicates that the power supply is experiencing a problem that the user should
investigate. This shall be asserted due to Critical events or Warning events. The signal shall
activate in the case of critical component temperature reached a warning threshold (see sec.
4.10), general failure, over-current, over-voltage, under-voltage, failed fan. This signal may also
indicate the power supply is reaching its end of life or is operating in an environment exceeding
the specified limits.
This signal is to be asserted in parallel with LED turning solid Amber or blink Amber.
Table 26. SMBAlert# Signal Characteristics
2.1.7 Thermal CLST
The power supply shall assert the SMBAlert signal when a temperature sensor crosses a
warning threshold. Refer to the Intel® Common Hardware and Firmware Requirements for
CRPS Power Supplier for detailed requirements.
2.1.8 Power Supply Diagnostic “Black Box”
The power supply saves the latest PMBus data and other pertinent data into nonvolatile
memory when a critical event shuts down the power supply. This data is accessible by the
SMBus interface with an external source providing power to the 12Vstby output.
Refer to the Intel® Common Hardware and Firmware Requirements for CRPS Power Supplier
for detailed requirements.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 48

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
73.5mm
A1
3mm
Retention Latch
Airflow
direction
Airflow direction
8.5mm
11mm
FCI 2x25 card
edge connector
10035388-106
40x56mm fan
A25
B25
B1
265mm
39mm
2.1.9 Firmware Uploader
The power supply has the capability to update its firmware from the PMBus interface while it is
in standby mode. This FW can be updated when in the system and in standby mode and
outside the system with power applied to the 12Vstby pins.
Refer to the Intel® Common Hardware and Firmware Requirements for CRPS Power Supplier
for detailed requirements.
2.2 1200-W Power Supply
This specification defines a 1200W redundant power supply that supports server systems. The
parameters of this power supply are defined in this specification. This specification defines a
power supply with 2 outputs; 12V and 12V standby. The AC input shall be auto ranging and
power factor corrected.
2.2.1 Mechanical Overview
The physical size of the power supply enclosure is 39/40mm x 73.5mm x 265mm. The power
supply contains a single 40mm fan. The power supply has a card edge output that interfaces
with a 2x25 card edge connector in the system. The AC plugs directly into the external face of
the power supply. Refer to the following figure. All dimensions are nominal.
2.2.1.1 DC Output Connector
The power supply shall use a card edge output connection for power and signal that is
compatible with a 2x25 Power Card Edge connector (equivalent to 2x25 pin configuration of the
FCI power card connector 10035388-102LF).
36 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Figure 20. Power Supply Outline Drawing
Page 49

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
37
Pin
Name
Pin
Name
A1
GND
B1
GND
A2
GND
B2
GND
A3
GND
B3
GND
A4
GND
B4
GND
A5
GND
B5
GND
A6
GND
B6
GND
A7
GND
B7
GND
A8
GND
B8
GND
A9
GND
B9
GND
A10
+12V
B10
+12V
A11
+12V
B11
+12V
A12
+12V
B12
+12V
A13
+12V
B13
+12V
A14
+12V
B14
+12V
A15
+12V
B15
+12V
A16
+12V
B16
+12V
A17
+12V
B17
+12V
A18
+12V
B18
+12V
A19
PMBus SDA
B19
A0 (SMBus address)
A20
PMBus SCL
B20
A1 (SMBus address)
A21
PSON
B21
12V stby
A22
SMBAlert#
B22
Cold Redundancy Bus
A23
Return Sense
B23
12V load share bus
A24
+12V remote Sense
B24
No Connect
A25
PWOK
B25
Compatibility Check pin*
Table 27. DC Output Connector
Note: Refer the specifications mentioned in the Intel® Common Hardware and Firmware Requirements for CRPS
Power Supplier.
2.2.1.2 Handle Retention
The power supply shall have a handle to assist extraction. The module shall be able to be
inserted and extracted without the assistance of tools. The power supply shall have a latch
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 50

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Min λd Wavelength
Nominal λd Wavelength
Max λd Wavelength
Units
Green
562
565
568
nm
Amber
607
610
613
nm
Power Supply Condition
LED State
Output ON and OK
GREEN
No AC power to all power supplies
OFF
AC present/Only 12VSB on (PS off) or PS in Cold redundant state
1Hz Blink GREEN
AC cord unplugged or AC power lost; with a second power supply in parallel still with
AC input power.
AMBER
Power supply warning events where the power supply continues to operate; high
temp, high power, high current, slow fan.
1Hz Blink Amber
Power supply critical event causing a shutdown; failure, OCP, OVP, Fan Fail
AMBER
Power supply FW updating
2Hz Blink GREEN
Item
Description
MIN
MAX
UNITS
T
op_rackped_
900
Operating temperature range; rack/pedestal 900m
( 100% load, 900m, rack/pedestal system flow impedance )
0
50
C
which retains the power supply into the system and prevents the power supply from being
inserted or extracted from the system when the AC power cord is pulled into the power supply.
The handle shall protect the operator from any burn hazard through the use of the Intel
Corporation Industrial designed plastic handle or equivalent Intel approved material.
2.2.1.3 LED Marking and Identification
The power supply shall use a bi-color LED; Amber and Green. Below are table showing the
LED states for each power supply operating state and the LED‟s wavelength characteristics.
Refer to the Intel® LED Wavelength and Intensity Specification for more details.
Table 28. LED Characteristics
Table 29. LED Status
2.2.1.4 Temperature Requirements
The power supply shall operate within all specified limits over the Top temperature range. All
airflow shall pass through the power supply and not over the exterior surfaces of the power
supply.
Table 30. Environmental Requirements
38 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 51

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
39
Item
Description
MIN
MAX
UNITS
T
op_rackped_
3000
Operating temperature range; rack/pedestal 3000m
( 100% load, 3000m, rack/pedestal system flow impedance )
0
45
C
Texit
Maximum exit air temperature
681
C
T
non-op
Non-operating temperature range.
-40
70
C
Altitude
Maximum operating altitude 3
3050
m
Output power
10% load
20% load
50% load
100% load
Power factor
> 0.80
> 0.90
> 0.90
> 0.95
Parameter
MIN
Rated
VMAX
Startup VAC
Power Off VAC
Notes:
1. Under normal conditions, the exit air temperature shall be less than 65C. 68C is provided for absolute worst
case conditions and is expected only to exist when the inlet ambient reaches 60C.
2. T
op_rackped_900
condition only requires max altitude of 900m.
The power supply must meet UL enclosure requirements for temperature rise limits. All sides of
the power supply with exception to the air exhaust side must be classified as “Handle, knobs,
grips, and so on, held for short periods of time only”.
2.2.2 AC Input Requirements
2.2.2.1 Power Factor
The power supply must meet the power factor requirements stated in the Energy Star® Program
Requirements for Computer Servers. These requirements are stated below:
Tested at 230Vac, 50Hz and 60Hz and 115VAC, 60Hz.
Tested according to Generalized Internal Power Supply Efficiency Testing Protocol, Rev 6.4.3.
This is posted at http://efficientpowersupplies.epri.com/methods.asp.
2.2.2.2 AC Inlet Connector
The AC input connector shall be an IEC 320 C-14 power inlet. This inlet is rated for
10A/250VAC.
2.2.2.3 AC Input Voltage Specification
The power supply must operate within all specified limits over the following input voltage range.
Harmonic distortion of up to 10% of the rated line voltage must not cause the power supply to
go out of specified limits. Application of an input voltage below 85VAC shall not cause damage
to the power supply, including a blown fuse.
Table 31. AC Input Voltage Range
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 52
Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Voltage (110)
90 V
rms
100-127 V
rms
140 V
rms
85VAC +/4VAC
74VAC +/5VAC
Voltage (220)
180 V
rms
200-240 V
rms
264 V
rms
Frequency
47 Hz
50/60
63 Hz
Loading
Holdup time
70%
10.6msec
Notes:
1. Maximum input current at low input voltage range shall be measured at 90VAC, at max load.
2. Maximum input current at high input voltage range shall be measured at 180VAC, at max load.
3. This requirement is not to be used for determining agency input current markings.
2.2.2.4 AC Line Dropout/Holdup
An AC line dropout is defined to be when the AC input drops to 0VAC at any phase of the AC
line for any length of time. During an AC dropout the power supply must meet dynamic voltage
regulation requirements. An AC line dropout of any duration shall not cause tripping of control
signals or protection circuits. If the AC dropout lasts longer than the holdup time the power
supply should recover and meet all turn on requirements. The power supply shall meet the AC
dropout requirement over rated AC voltages and frequencies. A dropout of the AC line for any
duration shall not cause damage to the power supply.
2.2.2.5 AC Line 12VSBHoldup
The 12VSB output voltage should stay in regulation under its full load (static or dynamic) during
an AC dropout of 70ms min (=12VSB holdup time) whether the power supply is in ON or OFF
state (PSON asserted or de-asserted).
2.2.2.6 AC Line Fuse
The power supply shall have one line fused in the single line fuse on the line (Hot) wire of the
AC input. The line fusing shall be acceptable for all safety agency requirements. The input fuse
shall be a slow blow type. AC inrush current shall not cause the AC line fuse to blow under any
conditions. All protection circuits in the power supply shall not cause the AC fuse to blow unless
a component in the power supply has failed. This includes DC output load short conditions.
2.2.2.7 AC Line Transient Specification
AC line transient conditions shall be defined as “sag” and “surge” conditions. “Sag” conditions
are also commonly referred to as “brownout”, these conditions will be defined as the AC line
voltage dropping below nominal voltage conditions. “Surge” will be defined to refer to conditions
when the AC line voltage rises above nominal voltage.
The power supply shall meet the requirements under the following AC line sag and surge
conditions.
40 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 53

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
41
AC Line Sag (10sec interval between each sagging)
Duration
Sag
Operating AC Voltage
Line Frequency
Performance Criteria
0 to 1/2 AC
cycle
95%
Nominal AC Voltage ranges
50/60Hz
No loss of function or performance.
> 1 AC cycle
>30% Nominal AC Voltage ranges
50/60Hz
Loss of function acceptable, selfrecoverable.
AC Line Surge
Duration
Surge
Operating AC Voltage
Line Frequency
Performance Criteria
Continuous
10%
Nominal AC Voltages
50/60Hz
No loss of function or performance
0 to ½ AC
cycle
30%
Mid-point of nominal AC
Voltages
50/60Hz
No loss of function or performance.
Loading
100% of maximum
50% of maximum
20% of maximum
10% of maximum
Minimum Efficiency
91%
94%
90%
82%
Table 32. AC Line Sag Transient Performance
Table 33. AC Line Surge Transient Performance
2.2.2.8 Power Recovery
The power supply shall recover automatically after an AC power failure. AC power failure is
defined to be any loss of AC power that exceeds the dropout criteria.
2.2.3 Efficiency
The following table provides the required minimum efficiency level at various loading conditions.
These are provided at three different load levels; 100%, 50%, 20%, and 10%. Output shall be
load according to the proportional loading method defined by 80 Plus in Generalized Internal
Power Supply Efficiency Testing Protocol, Rev 6.4.3. This is posted at
http://efficientpowersupplies.epri.com/methods.asp
Table 34. Platinum Efficiency Requirement
The power supply must pass with enough margins to make sure in production all power
supplies meet these efficiency requirements.
2.2.4 DC Output Specification
2.2.4.1 Output Power/Currents
The following table defines the minimum power and current ratings. The power supply must
meet both static and dynamic voltage regulation requirements for all conditions.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 54

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Parameter
Min
Max.
Peak 2, 3
Unit
12V main (200240VAC)
0.0
100
133
A
12V main (100127VAC)
0.0
83
110
A
12Vstby 1
0.0 3 3.5
A
Parameter
Tolerance
MIN
NOM
MAX
UNITS
+12V
- 5%/+5%
+11.40
+12.00
+12.60
V
rms
+12V stby
- 5%/+5%
+11.40
+12.00
+12.60
V
rms
Table 35. Minimum Load Ratings
Notes:
1. 12Vstby must provide 6A with two power supplies in parallel. The power supply fan is allowed to run in
standby mode for loads > 1.5A.
2. Length of time peak power can be supported is based on thermal sensor and assertion of the SMBAlert#
signal.
2.2.4.2 Pmax Power support
The PSU should support 3msec peak power duration at a 50msec period; 5.7% duty cycle,
Step loading from 1140W to 2200W, Average power = 1200W. High line only: 200-240VAC
2.2.4.3 Standby Output
The 12VSB output shall be present when an AC input greater than the power supply turn on
voltage is applied.
2.2.4.4 Voltage Regulation
The power supply output voltages must stay within the following voltage limits when operating
at steady state and dynamic loading conditions. These limits include the peak-peak ripple/noise.
These shall be measured at the output connectors.
Table 36. Voltage Regulation Limits
2.2.4.5 Dynamic Loading
The output voltages shall remain within limits specified for the step loading and capacitive
loading specified in the table below. The load transient repetition rate shall be tested between
50Hz and 5kHz at duty cycles ranging from 10%-90%. The load transient repetition rate is only
a test specification. The step load may occur anywhere within the MIN load to the MAX load
conditions.
42 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 55

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
43
Output
Step Load Size (See note)
Load Slew Rate
Test capacitive Load
+12VSB
1.0A
0.25 A/sec
20 F
+12V
60% of max load
0.25 A/sec
2000 F
Output
MIN
MAX
Units
+12VSB
20
3100
F
+12V
500
25000
F
Table 37. Transient Load Requirements
Note: For dynamic condition +12V min loading is 1A.
2.2.4.6 Capacitive Loading
The power supply shall be stable and meet all requirements with the following capacitive
loading ranges.
Table 38.Capacitive Loading Conditions
2.2.4.7 Grounding
The output ground of the pins of the power supply provides the output power return path. The
output connector ground pins shall be connected to the safety ground (power supply enclosure).
This grounding should be well designed to ensure passing the max allowed Common Mode
Noise levels.
2.2.4.8 Residual Voltage Immunity in Standby mode
The power supply should be immune to any residual voltage placed on its outputs (Typically a
leakage voltage through the system from standby output) up to 500mV. There shall be no
additional heat generated, nor stressing of any internal components with this voltage applied to
any individual or all outputs simultaneously. It also should not trip the protection circuits during
turn on.
The residual voltage at the power supply outputs for no load condition shall not exceed 100mV
when AC voltage is applied and the PSON# signal is de-asserted.
2.2.4.9 Common Mode Noise
The Common Mode noise on any output shall not exceed 350mV pk-pk over the frequency
band of 10Hz to 20MHz.
1. The measurement shall be made across a 100Ω resistor between each of DC outputs,
including ground at the DC power connector and chassis ground (power subsystem
enclosure).
2. The test set-up shall use a FET probe such as Tektronix model P6046 or equivalent.
2.2.4.10 Hot Swap Requirements
Hot swapping a power supply is the process of inserting and extracting a power supply from an
operating power system. During this process the output voltages shall remain within the limits
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 56

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
+12V main
+12VSB
120mVp-p
120mVp-p
AC HOT
POWER SUPPLY
AC NEUTRAL
V
OUT
RETURN
V
AC GROUND
LOAD
SCOPE
LOAD MUST BE
ISOLATED FROM
THE GROUND OF
THE POWER
SUPPLY
10uF
.1uF
GENERAL NOTES:
1. LOAD THE OUTPUT WITH ITS MINIMUM
LOAD CURRENT.
2. CONNECT THE PROBES AS SHOWN.
3. REPEAT THE MEASUREMENTS WITH THE
MAXIMUM LOAD ON THE OUTPUT.
SCOPE NOTE:
USE A TEKTRONIX 7834 OSCILLOSCOPE WITH 7A13 AND
DIFFERENTIAL PROBE P6055 OR EQUIVALENT.
with the capacitive load specified. The hot swap test must be conducted when the system is
operating under static, dynamic, and zero loading conditions. The power supply shall use a
latching mechanism to prevent insertion and extraction of the power supply when the AC power
cord is inserted into the power supply.
2.2.4.11 Forced Load Sharing
The +12V output will have active load sharing. The output will share within 10% at full load. The
failure of a power supply should not affect the load sharing or output voltages of the other
supplies still operating. The supplies must be able to load share in parallel and operate in a hotswap/redundant 1+1 configurations. The 12VSBoutput is not required to actively share current
between power supplies (passive sharing). The 12VSBoutput of the power supplies are
connected together in the system so that a failure or hot swap of a redundant power supply
does not cause these outputs to go out of regulation in the system.
2.2.4.12 Ripple/Noise
The maximum allowed ripple/noise output of the power supply is defined in the table below.
This is measured over a bandwidth of 10Hz to 20MHz at the power supply output connectors. A
10F tantalum capacitor in parallel with a 0.1F ceramic capacitor is placed at the point of
measurement.
Table 39. Ripples and Noise
The test set-up shall be as shown below:
Figure 21. Differential Noise test setup
Note: When performing this test, the probe clips and capacitors should be located close to the load.
44 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 57

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
45
Item
Description
MIN
MAX
UNITS
T
vout_rise
Output voltage rise time
5.0 *
70 *
ms
Tsb_on_delay
Delay from AC being applied to 12VSBbeing within
regulation.
1500
ms
T ac_on_delay
Delay from AC being applied to all output voltages being
within regulation.
3000
ms
Tvout_holdup
Time 12Vl output voltage stay within regulation after loss of
AC.
13 ms
Tpwok_holdup
Delay from loss of AC to de-assertion of PWOK
10.6
ms
Tpson_on_del
ay
Delay from PSON# active to output voltages within regulation
limits.
5
400
ms
T pson_pwok
Delay from PSON# deactivate to PWOK being de-asserted.
5 ms
Tpwok_on
Delay from output voltages within regulation limits to PWOK
asserted at turn on.
100
500
ms
T pwok_off
Delay from PWOK de-asserted to output voltages dropping
out of regulation limits.
1 ms
Tpwok_low
Duration of PWOK being in the de-asserted state during an
off/on cycle using AC or the PSON signal.
100
ms
Tsb_vout
Delay from 12VSBbeing in regulation to O/Ps being in
regulation at AC turn on.
50
1000
ms
T12VSB_holdu
p
Time the 12VSBoutput voltage stays within regulation after
loss of AC.
70 ms
2.2.4.13 Timing Requirements
These are the timing requirements for the power supply operation. The output voltages must
rise from 10% to within regulation limits (T
) within 5 to 70ms. For 12VSB, it is allowed to
vout_rise
rise from 1.0 to 25ms. All outputs must rise monotonically. Table below shows the timing
requirements for the power supply being turned on and off by the AC input, with PSON held low
and the PSON signal, with the AC input applied.
Table 40. Timing Requirements
* The 12VSBoutput voltage rise time shall be from 1.0ms to 25ms
2.2.5 Protection Circuits
Protection circuits inside the power supply shall cause only the power supply‟s main outputs to
shut down. If the power supply latches off due to a protection circuit tripping, an AC cycle OFF
for 15sec and a PSON# cycle HIGH for 1sec shall be able to reset the power supply.
2.2.5.1 Current Limit (OCP)
The power supply shall have current limit to prevent the outputs from exceeding the values
shown in table below. If the current limits are exceeded the power supply shall shutdown and
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 58

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Output Voltage
Input voltage range
Over Current Limits
+12V
90 – 264VAC
140A min; 170A max
12VSB
90 – 264VAC
2.5A min; 3A max
Output Voltage
MIN (V)
MAX (V)
+12V
13.3
14.5
+12VSB
13.3
14.5
latch off. The latch will be cleared by toggling the PSON# signal or by an AC power interruption.
The power supply shall not be damaged from repeated power cycling in this condition. 12VSB
will be auto-recovered after removing OCP limit.
Table 41. Over Current Protection
2.2.5.2 Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
The power supply over voltage protection shall be locally sensed. The power supply shall
shutdown and latch off after an over voltage condition occurs. This latch shall be cleared by
toggling the PSON# signal or by an AC power interruption. The values are measured at the
output of the power supply‟s connectors. The voltage shall never exceed the maximum levels
when measured at the power connectors of the power supply connector during any single point
of fail. The voltage shall never trip any lower than the minimum levels when measured at the
power connector. 12VSBwill be auto-recovered after removing OVP limit.
Table 42. Over Voltage Protection (OVP) Limits for 1200W PSU
2.2.5.3 Over Temperature Protection (OTP)
The power supply will be protected against over temperature conditions caused by loss of fan
cooling or excessive ambient temperature. In an OTP condition the PSU will shut down. When
the power supply temperature drops to within specified limits, the power supply shall restore
power automatically, while the 12VSB remains always on. The OTP circuit must have built in
margin such that the power supply will not oscillate on and off due to temperature recovering
condition. The OTP trip level shall have a minimum of 4C of ambient temperature margin.
2.2.6 Control and Indicator Functions
The following sections define the input and output signals from the power supply.
Signals that can be defined as low true use the following convention: Signal# = low true
2.2.6.1 PSON# Input Signal
The PSON# signal is required to remotely turn on/off the power supply. PSON# is an active low
signal that turns on the +12V power rail. When this signal is not pulled low by the system, or left
open, the outputs (except the +12VSB) turn off. This signal is pulled to a standby voltage by a
pull-up resistor internal to the power supply.
Table 43. PSON# Signal Characteristic
46 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 59
System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
47
Signal Type
Accepts an open collector/drain input from the system. Pull-up to VSB
located in power supply.
PSON# = Low
ON
PSON# = High or Open
OFF
MIN
MAX
Logic level low (power supply ON)
0V
1.0V
Logic level high (power supply OFF)
2.0V
3.46V
Source current, Vpson = low
4mA
Power up delay: T
pson_on_delay
5msec
400msec
PWOK delay: T pson_pwok
50msec
Signal Type
1.0 V PS
is enabled
2.0 V PS
is disabled
1.0V
2.0V
Enabled
Disabled
0.3V ≤ Hysteresis ≤ 1.0V
In 1.0-2.0V input voltages range is required
3.46V
0V
Figure 22. PSON# Required Signal Characteristic
2.2.6.2 PWOK (Power OK) Output Signal
PWOK is a power OK signal and will be pulled HIGH by the power supply to indicate that all the
outputs are within the regulation limits of the power supply. When any output voltage falls below
regulation limits or when AC power has been removed for a time sufficiently long so that power
supply operation is no longer guaranteed, PWOK will be de-asserted to a LOW state. See the
table below for a representation of the timing characteristics of PWOK. The start of the PWOK
delay time shall inhibited as long as any power supply output is in current limit.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Table 44. PWOK Signal Characteristics
Page 60

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
PWOK = High
Power OK
PWOK = Low
Power Not OK
MIN
MAX
Logic level low voltage, Isink=400uA
0V
0.4V
Logic level high voltage, Isource=200A
2.4V
3.46V
Sink current, PWOK = low
400uA
Source current, PWOK = high
2mA
PWOK delay: T
pwok_on
100ms
1000ms
PWOK rise and fall time
100sec
Power down delay: T
pwok_off
1ms
200msec
Q2
2N4401
PWOK out
PWOK in
Q1
2N4401
12V
3.3VSB
R2
20
R4
820
R3
10k
R1
10k
Figure 23. PWOK Circuit Requirement
2.2.6.3 SMBAlert# Signal
This signal indicates that the power supply is experiencing a problem that the user should
investigate. This shall be asserted due to Critical events or Warning events. The signal shall
activate in the case of critical component temperature reached a warning threshold (see sec.
4.10), general failure, over-current, over-voltage, under-voltage, failed fan. This signal may also
indicate the power supply is reaching its end of life or is operating in an environment exceeding
the specified limits.
This signal is to be asserted in parallel with LED turning solid Amber or blink Amber.
48 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Table 45. SMBAlert# Signal Characteristics
Page 61

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
49
Signal Type (Active Low)
Open collector/drain output from power supply. Pull-up to
VSB located in system.
Alert# = High
OK
Alert# = Low
Power Alert to system
MIN
MAX
Logic level low voltage, Isink=4 mA
0 V
0.4 V
Logic level high voltage, Isink=50 A
3.46 V
Sink current, Alert# = low
4 mA
Sink current, Alert# = high
50 A
Alert# rise and fall time
100 s
2.2.7 Thermal CLST
The power supply shall assert the SMBAlert signal when a temperature sensor crosses a
warning threshold. Refer to the Intel® Common Hardware and Firmware Requirements for
CRPS Power Supplier for detailed requirements.
2.2.8 Power Supply Diagnostic “Black Box”
The power supply shall save the latest PMBus data and other pertinent data into nonvolatile
memory when a critical event shuts down the power supply. This data shall be accessible from
the SMBus interface with an external source providing power to the 12Vstby output.
Refer to Intel® Common Hardware and Firmware Requirements for CRPS Power Supplier for
detailed requirements.
2.2.9 Firmware Update
The power supply shall have the capability to update its firmware from the PMBus interface
while it is in standby mode. This FW can be updated when in the system and in standby mode
and outside the system with power applied to the 12Vstby pins.
Refer to the Intel® Common Hardware and Firmware Requirements for CRPS Power Supplier
for detailed requirements.
2.3 1600-W Power Supply
This specification defines a 1600W redundant power supply that supports server systems. The
parameters of this power supply are defined in this specification. This specification defines a
power supply with 2 outputs; 12V and 12V standby. The AC input shall be auto ranging and
power factor corrected.
2.3.1 Mechanical Overview
The physical size of the power supply enclosure is 39/40mm x 73.5mm x 265mm. The power
supply contains a single 40mm fan. The power supply has a card edge output that interfaces
with a 2x25 card edge connector in the system. The AC plugs directly into the external face of
the power supply. All dimensions are nominal.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 62

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Pin
Name
Pin
Name
A1
GND
B1
GND
A2
GND
B2
GND
A3
GND
B3
GND
A4
GND
B4
GND
A5
GND
B5
GND
A6
GND
B6
GND
A7
GND
B7
GND
A8
GND
B8
GND
A9
GND
B9
GND
A10
+12V
B10
+12V
A11
+12V
B11
+12V
A12
+12V
B12
+12V
A13
+12V
B13
+12V
73.5m
m
A1
Retention Latch
Airflow direction
FCI 2x25 card
edge connector
10035388-106
8.5mm
40x56mm fan
265mm
39mm
A25
B25
B1
Figure 24. Power Supply Outline Drawing
2.3.1.1 DC Output Connector
The power supply shall use a card edge output connection for power and signal that is
compatible with a 2x25 Power Card Edge connector (equivalent to 2x25 pin configuration of the
FCI power card connector 10035388-102LF).
Table 46. DC Output Connector
50 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 63

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
51
Pin
Name
Pin
Name
A14
+12V
B14
+12V
A15
+12V
B15
+12V
A16
+12V
B16
+12V
A17
+12V
B17
+12V
A18
+12V
B18
+12V
A19
PMBus SDA 1
B19
A0 (SMBus address) 1
A20
PMBus SCL 1
B20
A1 (SMBus address) 1
A21
PSON
B21
12V stby
A22
SMBAlert#
B22
Cold Redundancy Bus 1
A23
Return Sense
B23
12V load share bus
A24
+12V remote Sense
B24
No Connect
A25
PWOK
B25
Compatibility Bus 1
Min λd Wavelength
Nominal λd Wavelength
Max λd Wavelength
Units
Green
562
565
568
nm
Amber
607
610
613
nm
Power Supply Condition
LED State
Note1: Refer to the CRPS Common Requirements specification.
2.3.1.2 Handle Retention
The power supply shall have a handle to assist extraction. The module shall be able to be
inserted and extracted without the assistance of tools. The power supply shall have a latch
which retains the power supply into the system and prevents the power supply from being
inserted or extracted from the system when the AC power cord is pulled into the power supply.
The handle shall protect the operator from any burn hazard through the use of the Intel
Corporation Industrial designed plastic handle or equivalent Intel approved material.
2.3.1.3 LED Marking and Identification
The power supply shall use a bi-color LED; Amber and Green. The following tables show the
LED states for each power supply operating state and the LED‟s wavelength characteristics.
Refer to the Intel® LED Wavelength and Intensity Specification for more details.
Table 47. LED Characteristics
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Table 48. LED Indicator States
Page 64

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Power Supply Condition
LED State
Output ON and OK
Solid GREEN
No AC power to all power supplies
OFF
AC present/Only 12VSB on (PS off) or PS in Cold redundant state
1Hz Blink GREEN
AC cord unplugged; with a second power supply in parallel still with AC input
power.
Solid AMBER
Power supply warning events where the power supply continues to operate;
high temp, high power, high current, slow fan.
1Hz Blink AMBER
Power supply critical event causing a shutdown; failure, OCP, OVP, Fan Fail
Solid AMBER
Power supply in FW upload mode
2Hz Blink GREEN
ITEM
DESCRIPTION
MIN
MAX
UNITS
Top
Operating temperature range; 900m
0
55
C
T
exit
Maximum exit air temperature
681
C
T
non-op
Non-operating temperature range.
-40
70
C
Altitude
Maximum operating altitude 3
3000
m
Output power
10% load
20% load
50% load
100% load
Power factor
> 0.80
> 0.90
> 0.90
> 0.95
2.3.1.4 Thermal Requirements
The power supply shall operate within all specified limits over the Top temperature range. All
airflow shall pass through the power supply and not over the exterior surfaces of the power
supply.
Table 49 Environmental Requirements
The power supply must meet UL enclosure requirements for temperature rise limits. All sides of
the power supply with exception to the air exhaust side must be classified as “Handle, knobs,
grips, etc. held for short periods of time only”.
2.3.2 AC Input Requirements
2.3.2.1 Power Factor
The power supply must meet the power factor requirements stated in the Energy Star® Program
Requirements for Computer Servers. These requirements are stated below.
Table 50 Environmental Requirements
Tested at 230Vac, 50Hz and 60Hz and 115VAC, 60Hz
Tested according to Generalized Internal Power Supply Efficiency Testing Protocol, Rev 6.4.3.
This is posted at http://efficientpowersupplies.epri.com/methods.asp.
52 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 65

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
53
PARAMETER
MIN
RATED
VMAX
Start up VAC
Power Off VAC
Voltage (110)
90 V
rms
100-127 V
rms
140 V
rms
85VAC +/4VAC
75VAC +/5VAC
Voltage (220)
180 V
rms
200-240 V
rms
264 V
rms
Frequency
47 Hz
50/60
63 Hz
Loading
Holdup time
75%
10msec
2.3.2.2 AC Inlet Connector
The AC input connector shall be an IEC 320 C-14 power inlet. This inlet is rated for
10A/250VAC.
2.3.2.3 AC Input Voltage Specification
The power supply must operate within all specified limits over the following input voltage range.
Harmonic distortion of up to 10% of the rated line voltage must not cause the power supply to
go out of specified limits. Application of an input voltage below 85VAC shall not cause damage
to the power supply, including a blown fuse.
Table 51 AC Input Voltage Range
Notes:
1. Maximum input current at low input voltage range shall be measured at 90VAC, at max load.
2. Maximum input current at high input voltage range shall be measured at 180VAC, at max load.
3. This requirement is not to be used for determining agency input current markings.
2.3.2.4 AC Line Dropout/Holdup
An AC line dropout is defined to be when the AC input drops to 0VAC at any phase of the AC
line for any length of time. During an AC dropout the power supply must meet dynamic voltage
regulation requirements. An AC line dropout of any duration shall not cause tripping of control
signals or protection circuits. If the AC dropout lasts longer than the hold up time the power
supply should recover and meet all turn on requirements. The power supply shall meet the AC
dropout requirement over rated AC voltages and frequencies. A dropout of the AC line for any
duration shall not cause damage to the power supply.
Table 52. AC Line Holdup Time
2.3.2.5 AC Line 12VSBHoldup
The 12VSB output voltage should stay in regulation under its full load (static or dynamic) during
an AC dropout of 70ms min (=12VSB holdup time) whether the power supply is in ON or OFF
state (PSON asserted or de-asserted).
2.3.2.6 AC Line Fuse
The power supply shall have one line fused in the single line fuse on the line (Hot) wire of the
AC input. The line fusing shall be acceptable for all safety agency requirements. The input fuse
shall be a slow blow type. AC inrush current shall not cause the AC line fuse to blow under any
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 66

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
AC Line Sag (10sec interval between each sagging)
Duration
Sag
Operating AC Voltage
Line Frequency
Performance Criteria
0 to 1/2 AC
cycle
95%
Nominal AC Voltage ranges
50/60Hz
No loss of function or performance
> 1 AC cycle
>30% Nominal AC Voltage ranges
50/60Hz
Loss of function acceptable, self
recoverable
AC Line Surge
Duration
Surge
Operating AC Voltage
Line Frequency
Performance Criteria
Continuous
10%
Nominal AC Voltages
50/60Hz
No loss of function or performance
0 to ½ AC
cycle
30%
Mid-point of nominal AC
Voltages
50/60Hz
No loss of function or performance
Loading
100% of maximum
50% of maximum
20% of maximum
10% of maximum
Minimum Efficiency
91%
94%
90%
82%
conditions. All protection circuits in the power supply shall not cause the AC fuse to blow unless
a component in the power supply has failed. This includes DC output load short conditions.
2.3.2.7 AC Line Transient Specification
AC line transient conditions shall be defined as “sag” and “surge” conditions. “Sag” conditions
are also commonly referred to as “brownout”, these conditions will be defined as the AC line
voltage dropping below nominal voltage conditions. “Surge” will be defined to refer to conditions
when the AC line voltage rises above nominal voltage. The power supply shall meet the
requirements under the following AC line sag and surge conditions.
Table 53 AC Line Sag Transient Performance
Table 54 AC Line Surge Transient Performance
2.3.2.8 Power Recovery
The power supply shall recover automatically after an AC power failure. AC power failure is
defined to be any loss of AC power that exceeds the dropout criteria.
2.3.3 Efficiency
The following table provides the required minimum efficiency level at various loading conditions.
These are provided at three different load levels; 100%, 50%, 20%, and 10%. Output shall be
load according to the proportional loading method defined by 80 Plus in Generalized Internal
Power Supply Efficiency Testing Protocol, Rev. 6.4.3. This is posted at:
http://efficientpowersupplies.epri.com/methods.asp.
Table 55 Platinum Efficiency Requirement
The power supply must pass with enough margin to make sure in production all power supplies
meet these efficiency requirements.
54 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 67

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
55
Parameter
Min
Max.
Peak 2, 3
Unit
12V main (200-240VAC)
0.0
133
175 A 12V main (100-127VAC)
0.0
83
110
A
12Vstby 1
0.0
3.5
4.0
A
PARAMETER
TOLERANCE
MIN
NOM
MAX
UNITS
+12V
- 5%/+5%
+11.40
+12.00
+12.60
V
rms
+12V stby
- 5%/+5%
+11.40
+12.00
+12.60
V
rms
Output
Step Load Size
Load Slew Rate
Test capacitive Load
2.3.4 DC Output Specification
2.3.4.1 Output Power/Currents
The following tables define the minimum power and current ratings. The power supply must
meet both static and dynamic voltage regulation requirements for all conditions.
Table 56 Minimum Load Ratings
Notes:
1. 12Vstby must be able to provide 4.0A peak load with single power supply.The power supply fan is allowed
to run in standby mode for loads > 1.5A.
2. Peak combined power for all outputs shall not exceed 2100W.
3. Length of time peak power can be supported is based on thermal sensor and assertion of the SMBAlert#
signal. Minimum peak power duration shall be 20 seconds without asserting the SMBAlert# signal.
2.3.4.2 Standby Output
The 12VSB output shall be present when an AC input greater than the power supply turn on
voltage is applied.
2.3.4.3 Voltage Regulation
The power supply output voltages must stay within the following voltage limits when operating
at steady state and dynamic loading conditions. These limits include the peak-peak ripple/noise.
These shall be measured at the output connectors.
Table 57 Voltage Regulation Limits
2.3.4.4 Dynamic Loading
The output voltages shall remain within limits specified for the step loading and capacitive
loading specified in the table below. The load transient repetition rate shall be tested between
50Hz and 5kHz at duty cycles ranging from 10%-90%. The load transient repetition rate is only
a test specification. The step load may occur anywhere within the MIN load to the MAX load
conditions.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Table 58. Transient Load Requirements
Page 68

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
(See note 2)
+12VSB
1.0A
0.25 A/sec
20 F
+12V
60% of max load
0.25 A/sec
2000 F
Output
MIN
MAX
Units
+12VSB
20
3100
F
+12V
500
25000
F
Note: For dynamic condition +12V min loading is 1A.
2.3.4.5 Capacitive Loading
The power supply shall be stable and meet all requirements with the following capacitive
loading ranges.
Table 59. Capacitive Loading Conditions
2.3.4.6 Grounding
The output ground of the pins of the power supply provides the output power return path. The
output connector ground pins shall be connected to the safety ground (power supply enclosure).
This grounding should be well designed to ensure passing the max allowed Common Mode
Noise levels.
The power supply shall be provided with a reliable protective earth ground. All secondary
circuits shall be connected to protective earth ground. Resistance of the ground returns to
chassis shall not exceed 1.0 m. This path may be used to carry DC current.
2.3.4.7 Residual Voltage Immunity in Standby mode
The power supply should be immune to any residual voltage placed on its outputs (Typically a
leakage voltage through the system from standby output) up to 500mV. There shall be no
additional heat generated, nor stressing of any internal components with this voltage applied to
any individual or all outputs simultaneously. It also should not trip the protection circuits during
turn on.
The residual voltage at the power supply outputs for no load condition shall not exceed 100mV
when AC voltage is applied and the PSON# signal is de-asserted.
2.3.4.8 Common Mode Noise
The Common Mode noise on any output shall not exceed 350mV pk-pk over the frequency
band of 10Hz to 20MHz.
1. The measurement shall be made across a 100Ω resistor between each of DC outputs,
including ground at the DC power connector and chassis ground (power subsystem
enclosure).
2. The test set-up shall use a FET probe such as Tektronix model P6046 or equivalent.
2.3.4.9 Hot Swap Requirements
Hot swapping a power supply is the process of inserting and extracting a power supply from an
operating power system. During this process the output voltages shall remain within the limits
with the capacitive load specified. The hot swap test must be conducted when the system is
operating under static, dynamic, and zero loading conditions. The power supply shall use a
56 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 69

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
57
+12V main
+12VSB
120mVp-p
120mVp-p
AC HOT
POWER SUPPLY
AC NEUTRAL
V
OUT
RETURN
V
AC GROUND
LOAD
SCOPE
LOAD MUST BE
ISOLATED FROM
THE GROUND OF
THE POWER
SUPPLY
10uF
.1uF
GENERAL NOTES:
1. LOAD THE OUTPUT WITH ITS MINIMUM
LOAD CURRENT.
2. CONNECT THE PROBES AS SHOWN.
3. REPEAT THE MEASUREMENTS WITH THE
MAXIMUM LOAD ON THE OUTPUT.
SCOPE NOTE:
USE A TEKTRONIX 7834 OSCILLOSCOPE WITH 7A13 AND
DIFFERENTIAL PROBE P6055 OR EQUIVALENT.
latching mechanism to prevent insertion and extraction of the power supply when the AC power
cord is inserted into the power supply.
2.3.4.10 Forced Load Sharing
The +12V output will have active load sharing. The output will share within 10% at full load. The
failure of a power supply should not affect the load sharing or output voltages of the other
supplies still operating. The supplies must be able to load share in parallel and operate in a hotswap/redundant 1+1 configurations. The 12VSB output is not required to actively share current
between power supplies (passive sharing). The 12VSB output of the power supplies are
connected together in the system so that a failure or hot swap of a redundant power supply
does not cause these outputs to go out of regulation in the system.
2.3.4.11 Ripple/Noise
The maximum allowed ripple/noise output of the power supply is defined in Table below. This is
measured over a bandwidth of 10Hz to 20MHz at the power supply output connectors. A 10F
tantalum capacitor in parallel with a 0.1F ceramic capacitor is placed at the point of
measurement.
Table 60. Ripples and Noise
The test set-up shall be as shown below.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Figure 25 Differential Noise test setup
Page 70

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Item
Description
MIN
MAX
UNITS
T
vout_rise
Output voltage rise time
5.0 *
70 *
ms
Tsb_on_delay
Delay from AC being applied to 12VSBbeing
within regulation.
1500
ms
T
ac_on_delay
Delay from AC being applied to all output voltages
being within regulation.
3000
ms
Tvout_holdup
Time 12V output voltage stay within regulation
after loss of AC.
11 ms
Tpwok_holdup
Delay from loss of AC to de-assertion of PWOK
10 ms
Tpson_on_del
ay
Delay from PSON# active to output voltages within
regulation limits.
5
400
ms
T pson_pwok
Delay from PSON# deactivate to PWOK being deasserted.
5 ms
Tpwok_on
Delay from output voltages within regulation limits
to PWOK asserted at turn on.
100
500
ms
T pwok_off
Delay from PWOK de-asserted to output voltages
dropping out of regulation limits.
1 ms
Tpwok_low
Duration of PWOK being in the de-asserted state
during an off/on cycle using AC or the PSON
signal.
100 ms
Tsb_vout
Delay from 12VSBbeing in regulation to O/Ps
being in regulation at AC turn on.
50
1000
ms
T12VSB_hold
up
Time the 12VSBoutput voltage stays within
regulation after loss of AC.
70 ms
Note: When performing this test, the probe clips and capacitors should be located close to the
load.
2.3.4.12 Timing Requirements
These are the timing requirements for the power supply operation. The output voltages must
rise from 10% to within regulation limits (T
) within 5 to 70ms. For 12VSB, it is allowed to
vout_rise
rise from 1.0 to 25ms. All outputs must rise monotonically. Table below shows the timing
requirements for the power supply being turned on and off by the AC input, with PSON held low
and the PSON signal, with the AC input applied.
Table 61. Timing Requirements
* The 12VSB output voltage rise time shall be from 1.0ms to 25ms.
58 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 71

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
59
Output VOLTAGE
Input voltage range
OVER CURRENT LIMITs
+12V
90 – 264VAC
180A min; 200A max
12VSB
90 – 264VAC
4A min; 5A max
AC Input
Vout PWOK
12Vsb
PSON
T
sb_on_delay
T
AC_on_delay
T
pwok_on
T
vout_holdup
T
pwok_holdup
T
pson_on_delay
T
sb_on_delay
T
pwok_on
T
pwok_off
T
pwok_off
T
pson_pwok
T
pwok_low
T
sb_vout
AC turn on/off cycle
PSON turn on/off cycle
T
5Vsb_holdup
Figure 26 Turn On/Off Timing (Power Supply Signals)
2.3.5 Protection Circuits
Protection circuits inside the power supply shall cause only the power supply‟s main outputs to
shutdown. If the power supply latches off due to a protection circuit tripping, an AC cycle OFF
for 15sec and a PSON# cycle HIGH for 1sec shall be able to reset the power supply.
2.3.5.1 Current Limit (OCP)
The power supply shall have current limit to prevent the outputs from exceeding the values
shown in table below. If the current limits are exceeded the power supply shall shutdown and
latch off. The latch will be cleared by toggling the PSON# signal or by an AC power interruption.
The power supply shall not be damaged from repeated power cycling in this condition. 12VSB
will be auto-recovered after removing OCP limit.
Table 62 Over Current Protection
2.3.5.2 Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
The power supply over voltage protection shall be locally sensed. The power supply shall
shutdown and latch off after an over voltage condition occurs. This latch shall be cleared by
toggling the PSON# signal or by an AC power interruption. The values are measured at the
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 72

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Output Voltage
MIN (V)
MAX (V)
+12V
13.3
14.5
+12VSB
13.3
14.5
Signal Type
Accepts an open collector/drain input from the system. Pull-up to VSB
located in power supply.
PSON# = Low
ON
PSON# = High or Open
OFF
MIN
MAX
Logic level low (power supply ON)
0V
1.0V
Logic level high (power supply OFF)
2.0V
5.25V
Source current, Vpson = low
4mA
Power up delay: T
pson_on_delay
5msec
400msec
PWOK delay: T
pson_pwok
50msec
output of the power supply‟s connectors. The voltage shall never exceed the maximum levels
when measured at the power connectors of the power supply connector during any single point
of fail. The voltage shall never trip any lower than the minimum levels when measured at the
power connector. 12VSB will be auto-recovered after removing OVP limit.
Table 63. Over Voltage Protection (OVP) Limits for 1600W PSU
2.3.5.3 Over Temperature Protection (OTP)
The power supply will be protected against over temperature conditions caused by loss of fan
cooling or excessive ambient temperature. In an OTP condition the PSU will shutdown. When
the power supply temperature drops to within specified limits, the power supply shall restore
power automatically, while the 12VSB remains always on. The OTP circuit must have built in
margin such that the power supply will not oscillate on and off due to temperature recovering
condition. The OTP trip level shall have a minimum of 4C of ambient temperature margin.
2.3.6 Control and Indicator Functions
The following sections define the input and output signals from the power supply.
Signals that can be defined as low true use the following convention: Signal# = low true
2.3.6.1 PSON# Input Signal
The PSON# signal is required to remotely turn on/off the power supply. PSON# is an active low
signal that turns on the +12V power rail. When this signal is not pulled low by the system, or left
open, the outputs (except the +12VSB) turn off. This signal is pulled to a standby voltage by a
pull-up resistor internal to the power supply.
Table 64 PSON# Signal Characteristic
60 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 73

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
61
Signal Type
PWOK = High
Power OK
PWOK = Low
Power Not OK
MIN
MAX
Logic level low voltage, Isink=400uA
0V
0.4V
Logic level high voltage, Isource=200A
2.4V
3.46V
Sink current, PWOK = low
400uA
Source current, PWOK = high
2mA
PWOK delay: T
pwok_on
100ms
1000ms
PWOK rise and fall time
100sec
Power down delay: T
pwok_off
1ms
200msec
1.0 V PS
is enabled
2.0 V PS
is disabled
1.0V
2.0V
Enabled
Disabled
0.3V ≤ Hysterisis ≤ 1.0V
In 1.0-2.0V input voltages range is required
3.46V
0V
Figure 27. PSON# Required Signal Characteristic
2.3.6.2 PWOK (Power OK) Output Signal
PWOK is a power OK signal and will be pulled HIGH by the power supply to indicate that all the
outputs are within the regulation limits of the power supply. When any output voltage falls below
regulation limits or when AC power has been removed for a time sufficiently long so that power
supply operation is no longer guaranteed, PWOK will be de-asserted to a LOW state. See the
following table for a representation of the timing characteristics of PWOK. The start of the
PWOK delay time shall inhibited as long as any power supply output is in current limit.
Table 65 PWOK Signal Characteristics
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 74

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Q2
2N4401
PWOK out
PWOK in
Q1
2N4401
12V
3.3VSB
R2
20
R4
820
R3
10k
R1
10k
Signal Type (Active Low)
Open collector/drain output from power supply. Pull-up to
VSB located in system.
Alert# = High
OK
Alert# = Low
Power Alert to system
MIN
MAX
Logic level low voltage, Isink=4 mA
0 V
0.4 V
Logic level high voltage, Isink=50 A
3.46 V
Sink current, Alert# = low
4 mA
Sink current, Alert# = high
50 A
Alert# rise and fall time
100 s
Figure 28. PWOK Circuit Requirement
2.3.6.3 SMBAlert# Signal
This signal indicates that the power supply is experiencing a problem that the user should
investigate. This shall be asserted due to Critical events or Warning events. The signal shall
activate in the case of critical component temperature reaching a warning threshold, general
failure, over-current, over-voltage, under-voltage, failed fan. This signal may also indicate the
power supply is reaching its end of life or is operating in an environment exceeding the
specified limits.
This signal is to be asserted in parallel with LED turning solid Amber or blink Amber.
Table 66 SMBAlert# Signal Characteristics
2.3.7 Thermal CLST
The power supply shall assert the SMBAlert signal when a temperature sensor crosses a
warning threshold.
Refer to the CRPS Common Requirements Specification for detailed requirements.
2.3.8 Power Supply Diagnostic “Black Box”
The power supply shall save the latest PMBus data and other pertinent data into nonvolatile
memory when a critical event shuts down the power supply. This data shall be accessible from
the SMBus interface with an external source providing power to the 12Vstby output.
Refer to the CRPS Common Requirements Specification for detailed requirements.
62 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 75

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
63
2.3.9 Firmware Update
The power supply shall have the capability to update its firmware from the PMBus interface
while it is in standby mode. This FW can be updated when in the system and in standby mode
and outside the system with power applied to the 12Vstby pins.
Refer to the CRPS Common Requirements Specification for detailed requirements.
2.4 Higer Current Power Common Redundant Power
Distribution Board (PDB)
The Power Distribution Board (PDB) for Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation
System P4000CR supports the Common Redundant power supply in a 1+1 redundant
configuration. The PDB is designed to plug directly to the output connector of the PS and it
contains 3 DC/DC power converters to produce other required voltages: +3.3VDC, +5VDC and
5V standby along with additional over current protection circuit for the 12V rails.
This power distribution board is intended to be used in the Intel® Server System P4000IP and
Intel® Workstation System P4000CR with various common redundant power supplies; 750W,
1200W, 1600W.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 76

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
2.4.1 Mechanical Overview
64 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Figure 29. Outline Drawing
Page 77

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
65
Item
Description
Min
Max
Units
Top
Operating temperature range.
0
50
C
T
non-op
Non-operating temperature range.
-40
70
C
Airflow direction
Rear power supply
Front power supply
PDB
2.4.1.1 Airflow Requirements
The power distribution board shall get enough airflow for cooling DC/DC converters from the
fans located in the Power Supply modules. Below is a basic drawing showing airflow direction.
The amount of cooling airflow that will be available to the DC/DC converters is to be no less
than 1.2M/s.
Figure 30. Airflow Diagram
2.4.1.2 DC/DC converter cooling
The dc/dc converters on the power distribution board are in series airflow path with the power
supplies.
2.4.1.3 Temperature Requirements
The PDB operates within all specified limits over the Top temperature range. Some amount of
airflow shall pass over the PDB.
Table 67. Thermal Requirements
2.4.1.4 Efficiency
Each DC/DC converter shall have a minimum efficiency of 85% at 50% ~ 100% loads and over
+12V line voltage range and over temperature and humidity range.
2.4.2 DC Output Specification
2.4.2.1 Input Connector (power distribution mating connector)
The power distribution provides two power pins, a card edge output connection for power and
signal that is compatible with a 2x25 Power Card Edge connector (equivalent to 2x25 pin
configuration of the FCI power card connector 10035388-102LF). The FCI power card edge
connector is a new version of the PCE from FCI used to raise the card edge by 0.031'' to allow
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 78

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Pin
Name
Pin
Name
A1
GND
B1
GND
A2
GND
B2
GND
A3
GND
B3
GND
A4
GND
B4
GND
A5
GND
B5
GND
A6
GND
B6
GND
A7
GND
B7
GND
A8
GND
B8
GND
A9
GND
B9
GND
A10
+12V
B10
+12V
A11
+12V
B11
+12V
A12
+12V
B12
+12V
A13
+12V
B13
+12V
A14
+12V
B14
+12V
A15
+12V
B15
+12V
A16
+12V
B16
+12V
A17
+12V
B17
+12V
A18
+12V
B18
+12V
A19
PMBus SDA
B19
A0 (SMBus address)
A20
PMBus SCL
B20
A1 (SMBus address)
A21
PSON
B21
12V stby
A22
SMBAlert#
B22
Cold Redundancy Bus
A23
Return Sense
B23
12V load share
A24
+12V remote Sense
B24
No Connect
A25
PWOK
B25
Compatibility Pin
*
From
Length, mm
To connector
#
No of pins
Description
Power Supply cover exit hole
470
P1
24
Baseboard Power Connector
for future 0.093'' PCBs in the system. The card edge connector has no keying features; the
keying method is accomplished by the system sheet metal.
Table 68. Input Connector and Pin Assignment Diagrams
Note: *The compatibility Pin is used for soft compatibility check. The two compatibility pins are connected directly.
2.4.2.2 Output Wire Harness
The power distribution board has a wire harness output with the following connectors.
Listed or recognized component appliance wiring material (AVLV2), CN, rated min 85C shall
be used for all output wiring.
66 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Table 69. PDB Cable Length
Page 79

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
67
From
Length, mm
To connector
#
No of pins
Description
Power Supply cover exit hole
320
P2 8 Processor 0 connector
Power Supply cover exit hole
450
P3 8 Processor 1 connector
Power Supply cover exit hole
800
P4 5 Power FRU/PMBus connector
Power Supply cover exit hole
350
P5
5
SATA peripheral power connector for 5.25''
Extension from P5
100
P6
5
SATA peripheral power connector for 5.25''
Extension from P6
100
P7
4
Peripheral Power Connector for 5.25''/HSBP
Power
Power Supply cover exit hole
400
P8 4 1x4 legacy HSBP Power Connector
Extension from P8
75
P9 4 1x4 legacy HSBP Power Connector
Power supply cover exit hole
500
P10
4
1x4 legacy HSBP Power/Fixed HDD adaptor
Connection
Extension from P10
75
P11
4
1x4 legacy HSBP Power/Fixed HDD adaptor
Connection
PCI power connector
800
P12 4 2x2 Legacy PCI Power Connector
Connector only (no cable)
na
P13
4
GFX card aux connectors
Connector only (no cable)
na
P14
4
Connector only (no cable)
na
P15
4
Connector only (no cable)
na
P16
4
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
1
+3.3VDC
Orange
13
+3.3VDC
Orange
3.3V RS
Orange (24AWG)
2 +3.3VDC
Orange
14
-12VDC
Blue
3
COM
Black
15
COM
Black
4
+5VDC
Red
16
PSON#
Green (24AWG)
5
COM
Black
17
COM
Black
6
+5VDC
Red
18
COM
Black
7
COM
Black
19
COM
Black
2.4.2.2.1 Baseboard power connector (P1)
Connector housing: 24-Pin Molex* Mini-Fit Jr. 39-01-2245 or equivalent
Contact: Molex* Mini-Fit, HCS Plus, Female, Crimp 44476 or equivalent
Table 70. P1 Baseboard Power Connector
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 80

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
8
PWR OK
Gray (24AWG)
20
Reserved
N.C.
9
5 VSB
Purple
21
+5VDC
Red
10
+12V1
Yellow
22
+5VDC
Red
11
+12V1
Yellow
23
+5VDC
Red
12
+3.3VDC
Orange
24
COM
Black
Pin
Signal
18 AWG color
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
1
COM
Black
5*
+12V1
Yellow
2
COM
Black
6
+12V1
Yellow
3
COM
Black
7
+12V1
Yellow
4
COM
Black
8
+12V1
Yellow
Pin
Signal
18 AWG color
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
1
COM
Black
5
+12V1
Yellow
2
COM
Black
6
+12V1
Yellow
3
COM
Black
7
+12V1
Yellow
4
COM
Black
8
+12V1
Yellow
Pin
Signal
24 AWG Color
1
I2C Clock
White
2
I2C Data
Yellow
3
SMBAlert#
Red
4
COM
Black
5
3.3RS
Orange
2.4.2.2.2 Processor#0 Power Connector (P2)
Connector housing: 8-Pin Molex* 39-01-2080 or equivalent
Contact: Molex* Mini-Fit, HCS Plus, Female, Crimp 44476 or equivalent
Table 71. P0 Processor Power Connector
2.4.2.2.3 Processor#1 Power Connector (P3)
Connector housing: 8-Pin Molex* 39-01-2080 or equivalent
Contact: Molex* Mini-Fit, HCS Plus, Female, Crimp 44476 or equivalent
Table 72. P1 Processor Power Connector
2.4.2.2.4 Power Signal Connector (P4)
Connector housing: 5-pin Molex* 50-57-9405 or equivalent
Contacts: Molex* 16-02-0087 or equivalent
Table 73. Power Signal Connector
68 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 81

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
69
Pin
Signal
18 AWG color
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
1
COM
Black
5
+12V1
Yellow
2
COM
Black
6
+12V1
Yellow
Pin
Signal
18 AWG color
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
1
COM
Black
5
+12V2
Green
2
COM
Black
6
+12V2
Green
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
1
+12V4
White
2
COM
Black
3
COM
Black
4
+5 VDC
Red
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
1
+12V3
Brown
2
COM
Black
3
COM
Black
4
+5 VDC
Red
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
1
+3.3VDC
Orange
2
COM
Black
3
+5VDC
Red
2.4.2.2.5 2x2 12V connector (P12-P16)
Connector header: Foxconn p/n HM3502E-P1 or equivalent
Table 74. P12 12V connectors
Table 75. P13 - P16 12V connectors
2.4.2.2.6 Legacy 1x4 Peripheral Power Connectors (P7, P8, P9, P10, P11)
Connector housing: Molex* 0015-24-4048 or equivalent;
Contact: Molex* 0002-08-1201 or equivalent
Table 76. P8, P9, P10, P11 Legacy Peripheral Power Connectors
Table 77. P7Legacy Peripheral Power Connectors
2.4.2.2.7 SATA 1x5 Peripheral Power Connectors (P5, P6)
Connector housing: Molex* 0675-82-0000 or equivalent;
Contact: Molex* 0675-81-0000 or equivalent
Table 78. SATA Peripheral Power Connectors
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 82

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Pin
Signal
18 AWG Color
4
COM
Black
5
+12V3
Yellow
Converter
+ sense location
- sense location
Power supply main 12V
On PDB
On PDB
12V/3.3V
P20 (1x5 signal connector)
P20 (1x5 signal connector)
12V/5V
On PDB
On PDB
12V/-12V
none
none
12Vstby/5Vstby
none
none
Characteristic
Requirement
+3.3V remote sense input
impedance
200 (measure from +3.3V on P1 2x12 connector to +3.3V sense
on P20 1x5 signal connector)
+3.3V remote sense drop
200mV (remote sense must be able to regulate out 200mV drop
on the +3.3V and return path; from the 2x12 connector to the
remote sense points)
Max remote sense current draw
< 5mA
2.4.2.3 Grounding
The ground of the pins of the PDB output connectors provides the power return path. The
output connector ground pins is connected to safety ground (PDB enclosure). This grounding is
well designed to ensure passing the max allowed Common Mode Noise levels.
2.4.2.4 Remote Sense
Below is listed the remote sense requirements and connection points for all the converters on
the PDB and the main 12V output of the power supply.
Table 79. Remote Sense Connection Points
Table 80. Remote Sense Requirements
70 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 83

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
71
P2
P3
P12
P1
P8
P9
P10
P11
P5,6,7
P13
P14
P15
P16
P17
P18
P19
P20
2x4
2x4
2x2
2x12
1x4
1x4
1x4
1x4
(2)
1x5,
1x4
GPU1
GPU2
GPU3
GPU4
OCP
CPU1 Memo
ry1
CPU2
Memo
ry2
PCIe
Fans
Misc
HDD and peripherals
2x3
2x4
2x3
2x4
2x3
2x4
2x3
2x4
Total
Curr
ent
Min
Nom
inal
Max
12V1
17.8
A
10.5 A
17.8 A
10.5 A
21.7
A
10.0
A
3.0
A 91 A
91
95.5
100
12V2
6.3 A 12.5
A
6.3 A 12.5
A
6.3 A 12.5
A
6.3 A 12.5
A
76 A
76
88
100
12V3
18.0 A
18 A
18
19
20
12V4
18.0A
18A
18
19
20
2.4.2.5 12V Rail Distribution
The below table shows the configuration of the 12V rails and what connectors and components
in the system they are powering.
Table 81. 12V Rail Distribution
Note:
P12 is reserved for board that needs 4 x GPU cards powered. P1 is the main 12V power for PCIe slot; but
additional 12V power can be connected to P2 and/or P3. The motherboard MUST NOT short any of the 12V
rails or connectors together.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 84

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
P8
P9
P10
P11
P5
P6
P7 1x4
1x4
1x4
1x4
1x5
1x5
1x4 18
3 x 2.5'' 8xHDD
BP
HDD1
8 x 2.5
na
HDD2
8 x 2.5
na
na
na
HDD3
8 x 2.5
2 x 3.5'' 4xHDD
BP
HDD1
4x3.5
HDD1
4x3.5
peripheral bay
1 x 3.5'' 8xHDD
BP
HDD1
8x3.5
na
na
peripheral bay
8 x 3.5'' fixed
SATA
2xfixed
2xfixed
2xfixed
2xfixed
peripheral bay
8 x 3.5'' fixed
SAS
2xfixed
2xfixed
2xfixed
2xfixed
peripheral bay
+12VDC Input DC/DC
Converters
+3.3V Converter
+5V Converter
-12V Converter
MAX Load
25A
15A
0.5A
MIN Static/Dynamic Load
0A
0A
0A
Max Output Power
3.3V x25A =82.5W
5V x15A =75W
12V x0.5A =6W
12V stby/5V stby
DC/DC Converters
MAX Load
8A
MIN Static/Dynamic Load
0.1
Max Output Power
5V x8A =40W
2.4.2.6 Hard Drive 12V rail configuration options
The below table shows the hard drive configuration options using the defined power connectors.
In some cases additional converter or „Y‟ cables are needed.
Table 82. Hard Drive 12V rail configuration options
2.4.2.7 DC/DC Converters Loading
The following table defines power and current ratings of three DC/DC converters located on the
PDB, each powered from +12V rail. The 3 converters meet both static and dynamic voltage
regulation requirements for the minimum and maximum loading conditions.
Table 83. DC/DC Converters Load Ratings
2.4.2.8 5VSB Loading
There is also one DC/DC converter that converts the 12V standby into 5V standby.
Table 84. 5VSB Loading
72 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 85

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
73
Converter output
Tolerance
Min
Nom
Max
Units
+ 3.3VDC
-4%/+5%
+3.20
+3.30
+3.46
VDC
+ 5VDC
-4%/+5%
+4.80
+5.00
+5.25
VDC
5Vstby
-4%/+5%
+4.80
+5.00
+5.25
VDC
Output
Max Step Load Size
Max Load Slew Rate
Test capacitive Load
+ 3.3VDC
5A
0.25 A/s
250 F
+ 5VDC
5A
0.25 A/s
400 F
+5Vsb
0.5A
0.25A/s
20 F
Converter output
Min
Max
Units
+3.3VDC
250
6800
F
+5VDC
400
4700
F
5Vstby
20
350
F
2.4.2.9 DC/DC Converters Voltage Regulation
The DC/DC converters‟ output voltages stay within the following voltage limits when operating
at steady state and dynamic loading conditions. These limits include the peak-peak ripple/noise
specified in Table 95. The 3.3V and 5V outputs are measured at the remote sense point, all
other voltages measured at the output harness connectors.
Table 85. Voltage Regulation Limits
2.4.2.10 DC/DC Converters Dynamic Loading
The output voltages remains within limits specified in table above for the step loading and
capacitive loading specified in Table 93 below. The load transient repetition rate is only a test
specification. The step load may occur anywhere within the MIN load to the MAX load shown
in Tables 93 and 94.
Table 86. Transient Load Requirements
2.4.2.11 DC/DC Converter Capacitive Loading
The DC/DC converters is stable and meet all requirements with the following capacitive loading
ranges.Minimum capacitive loading applies to static load only.
Table 87. Capacitive Loading Conditions
2.4.2.12 DC/DC Converters Closed Loop stability
Each DC/DC converter is unconditionally stable under all line/load/transient load conditions
including capacitive load ranges specified in Section 2.4.2.11. A minimum of: 45 degrees
phase margin and -10dB-gain margin is required. The PDB provides proof of the unit‟s
closed-loop stability with local sensing through the submission of Bode plots. Closed-loop
stability must be ensured at the maximum and minimum loads as applicable.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 86

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
+3.3V
+5V
-12V
+5VSB
50mVp-p
50mVp-p
120mVp-p
50mVp-p
AC HOT
POWER SUPPLY
AC NEUTRAL
V
OUT
RETURN
V
AC GROUND
LOAD
SCOPE
LOAD MUST BE
ISOLATED FROM
THE GROUND OF
THE POWER
SUPPLY
10uF
.1uF
GENERAL NOTES:
1. LOAD THE OUTPUT WITH ITS MINIMUM
LOAD CURRENT.
2. CONNECT THE PROBES AS SHOWN.
3. REPEAT THE MEASUREMENTS WITH THE
MAXIMUM LOAD ON THE OUTPUT.
SCOPE NOTE:
USE A TEKTRONIX 7834 OSCILLOSCOPE WITH 7A13 AND
DIFFERENTIAL PROBE P6055 OR EQUIVALENT.
2.4.2.13 Common Mode Noise
The Common Mode noise on any output does not exceed 350mV pk-pk over the frequency
band of 10Hz to 20MHz.
The measurement shall be made across a 100Ω resistor between each of DC outputs,
including ground, at the DC power connector and chassis ground (power subsystem
enclosure).
The test set-up shall use a FET probe such as Tektronix model P6046 or equivalent.
2.4.2.14 Ripple/Noise
The maximum allowed ripple/noise output of each DC/DC Converter is defined in below Table
95. This is measured over a bandwidth of 0Hz to 20MHz at the PDB output connectors. A 10F
tantalum capacitor in parallel with a 0.1F ceramic capacitor are placed at the point of
measurement.
Table 88. Ripple and Noise
The test set-up shall be as shown below.
Note:
When performing this test, the probe clips and capacitors should be located close to the load.
Figure 31. Differential Noise test setup
2.4.2.15 Timing Requirements
Below are timing requirements for the power on/off of the PDB DC/DC converters. The +3.3V,
+5V and +12V output voltages should start to rise approximately at the same time. All outputs
must rise monotonically.
74 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Table 89. Output Voltage Timing
Page 87

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
75
Description
Min
Max
Units
Output voltage rise time for each main output; 3.3V, 5V, -12V and
5Vstby.
1.0
20
msec
The main DC/DC converters (3.3V, 5V, -12V) shall be in regulation
limits within this time after the 12V input has reached 11.4V.
20
msec
The main DC/DC converters (3.3V, 5V, -12V) must drop below
regulation limits within this time after the 12V input has dropped
below 11.4V.
20
msec
The 5Vstby converter shall be in regulation limits within this time
after the 12Vstby has reach 11.4V.
20
msec
The 5Vstby converter must power off within this time after the
12Vstby input has dropped below 11.4V.
100
msec
2.4.2.16 Residual Voltage Immunity in Standby Mode
Each DC/DC converter is immune to any residual voltage placed on its respective output
(typically a leakage voltage through the system from standby output) up to 500mV. This
residual voltage does not have any adverse effect on each DC/DC converter, such as: no
additional power dissipation or over-stressing/over-heating any internal components or
adversely affecting the turn-on performance (no protection circuits tripping during turn on).
While in Stand-by mode, at no load condition, the residual voltage on each DC/DC converter
output does not exceed 100mV.
2.4.3 Protection Circuits
The PDB shall shut down all the DC/DC converters on the PDB and the power supply (from
PSON) if there is a fault condition on the PDB (OVP or OCP). If the PDB DC/DC converter
latches off due to a protection circuit tripping, an AC cycle OFF for 15sec min or a PSON# cycle
HIGH for 1sec shall be able to reset the power supply and the PDB.
2.4.3.1 Over-Current Protection (OCP)/240VA Protection
Each DC/DC converter output on PDB has individual OCP protection circuits. The PS+PDB
combo shall shutdown and latch off after an over current condition occurs. This latch shall be
cleared by toggling the PSON# signal or by an AC power interruption. The values are measured
at the PDB harness connectors. The DC/DC converters shall not be damaged from repeated
power cycling in this condition. Also, the +12V output from the power supply is divided on the
PDB into 3 channels and +12V3 is limited to 240VA of power. There are current sensors and
limit circuits to shut down the entire PS+PDB combo if the limit is exceeded. The limits are listed
in below table. -12V and 5VSB is protected under over current or shorted conditions so that no
damage can occur to the power supply. Auto-recovery feature is a requirement on 5VSB rail.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 88

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS System Power Sub-system
Output Voltage
Min OCP Trip Limits
Max OCP Trip Limits
Usage
+3.3V
27A
Meet 240VA
PCIe, Misc
+5V
27A
PCIe, HDD, Misc
+12V1
91A
100A
CPU and memory
+12V2
76A
100A
GPU cards
+12V3
18A
20A
HDD and peripherals
+12V4
18A
20A
HDD and peripherals
Output voltage
OVP min (v)
OVP max (v)
+3.3V
3.9
4.8
+5V
5.7
6.5
+5VSB
5.7
6.5
Motherboard pull-up voltage
MIN resistance value (ohms)
5V
10K
3.3V
6.8K
Table 90. PDB Over Current Protection Limits/240VA Protection
2.4.3.2 Over Voltage Protection (OVP)
Each DC/DC converter output on PDB have individual OVP protection circuits built in and it
shall be locally sensed. The PS+PDB combo shall shutdown and latch off after an over voltage
condition occurs. This latch shall be cleared by toggling the PSON# signal or by an AC power
interruption. Table 135 contains the over voltage limits. The values are measured at the PDB
harness connectors. The voltage shall never exceed the maximum levels when measured at the
power pins of the output harness connector during any single point of fail. The voltage shall
never trip any lower than the minimum levels when measured at the power pins of the PDB
connector.
Table 91. Over Voltage Protection (OVP) Limits
2.4.4 PWOK (Power OK) Signal
The PDB connects the PWOK signals from the power supply modules and the DC/DC
converters to a common PWOK signal. This common PWOK signal connects to the PWOK pin
on P1. The DC/DC convert PWOK signals have open collector outputs.
2.4.4.1 System PWOK requirements
The system will connect the PWOK signal to 3.3V or 5V from a pull-up resistor. The maximum
sink current of the power supplies are 0.5mA. The minimum resistance of the pull-up resistor is
stated below depending upon the motherboard‟s pull-up voltage. Refer to the CRPS power
supply specification for signal details.
Table 92. System PWOK Requirements
2.4.5 PSON Signal
The PDB connects the power supplies PSON signals together and connect them to the PSON
signal on P1.
Refer to the CRPS power supply specification for signal details.
76 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 89

System Power Sub-system Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
77
Power Supply Position 1
Power Supply Position 2
PDB addressing Address0/Address1
0/0
0/1
Power supply PMBus device address
B0h
B2h
2.4.6 PMBus
The PDB has no components on it to support PMBus. It only needs to connect the power
supply PMBus signals (clock, data, SMBAlert#) and pass them to the 1x5 signal connector.
2.4.6.1 Addressing
The PDB address the power supply as follows on the PDB.
0 = open, 1 = grounded
Table 93. PDB addressing
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 90

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS Thermal Management
3. Thermal Management
The Intel® Server System P4000IP is designed to operate at external ambient temperatures of
between 10ºC- 35ºC. Working with integrated platform management, several features within the
system are designed to move air in a front to back direction, through the system and over
critical components in order to prevent them from overheating and allow the system to operate
with best performance.
3.1 Thermal Operation and Configuration Requirements
To keep the system operating within supported maximum thermal limits, the system must meet
the following operating and configuration guidelines:
Ambient in-let temperature cannot exceed 35º C and should not remain at this maximum
level for long periods of time. Doing so may affect long term reliability of the system.
All hard drive bays must be populated. Hard drive carriers either can be populated with a
hard drive or supplied drive blank.
The air duct must be installed at all times.
In single power supply configurations, the second power supply bay must have the
supplied filler blank installed at all times.
The system top-cover must be installed at all times.
CPU2 Memory Socket Dummy Dimm must be installed.
3.2 Thermal Management Overview
In order to maintain the necessary airflow within the system, all of the previously listed
components and top cover need to be properly installed. For best system performance, the
external ambient temperature must remain below 35ºC and all system fans should be
operational.
In the event that system thermals should continue to increase with the system fans operating at
their maximum speed, platform management may begin to throttle performance of either the
memory subsystem or the processors or both, in order to keep components from overheating
and keep the system operational. Throttling of these sub-systems will continue until system
thermals are reduced.
Should system thermals increase to a point beyond the maximum thermal limit as preprogrammed in platform management for this system, the system will shut down, the System
Status LED will change to a solid Amber state, and the event will be logged to the system event
log.
3.3 System Fan Configuration
Two cooling solutions are used in the Intel
solution consists of two 120 x 38mm fixed fans to provide sufficient system cooling. The second
redundant solution is designed for maximum up time by providing five 80 x 38 mm replaceable hotswap fans. The fans can maintain proper system cooling, even with a single failed fan.
®
Server Chassis P4000L series. The base non-redundant
78 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 91

Thermal Management Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
79
Corresponding air ducts are needed in both configurations for supported boards.
3.3.1 Non-Redundant Cooling Solution
Non-Redundant cooling solution is used in the Intel® Workstation System P4000CR.
Two 120 x 38 mm fans provide cooling for the processors, memory, hard drives and add-in cards.
The two fans draw air through the rear of each hard drive bay to provide drive, processors, and
memory cooling. All system fans provide a signal for RPM detection the server board can make
available for server management functions.
In addition, the power supply fan provides cooling for the power supply.
Figure 32. Fixed Fans in Intel® Workstation System P4000CR
3.3.2 Redundant Cooling Solution
Redundant cooling solution is used in the Intel
Five hot-swap 80x38mm fans provide cooling for the processors, hard drives, and add-in cards.
When any single fan fails, the remaining fans increase in speed and maintain cooling until the
failed unit is replaced. All system fans provide a signal for RPM detection that the server board
can make available for server management functions.
In addition, the power supply fan provides cooling for the power supply.
®
Server System P4000IP.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 92

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS Thermal Management
Figure 33. Hot-swap Fans in Intel® Server System P4000IP
3.4 Fan Control
The fans provided in the Intel® Server Chassis P4000M Family contains a tachometer signal
that can be monitored by the server management subsystem of the Intel® Server Boards for
RPM (Revolutions per Minute) detection.
The server board monitors several temperature sensors and adjusts the PWM (Pulse Width
Modulated) signal to drive the fan at the appropriate speed.
The front panel of the chassis has a digital temperature sensor connected to the server board
through the front panel‟s bus. The server board firmware adjusts the fan speed based on the
front panel intake temperature and processor temperatures.
Refer to the baseboard documentation for additional details on how fan control is
implementation.
3.5 Fan Header Connector Descriptions
All system fan headers support pulse width modulated (PWM) fans for cooling the processors in the
chassis. PWM fans have an improved RPM range (20% to 100% rated fan speed) when compared
to voltage controlled fans.
Fixed chassis fans are a 4-wire/4-pin style designed to plug into 4-pin or 6-pin SSI Fan headers.
When plugged into a 6-pin header, only the first four signals are used (Pwr, Gnd, Tach,PWM).
Hot-swap chassis fans are a 6-wire/6-pin style designed to plug into 6-pin headers. The extra
signals provide for fan redundancy and failure indications (Pwr, Gnd, Tach, PWM, Presence, and
Failure).
80 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 93

Storage and Peripheral Drive Bays Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
81
4. Storage and Peripheral Drive Bays
The Intel® Server System P4000IP and the Intel® Workstation System P4000CR product family
has support for many storage device options, including:
Hot Swap 2.5'' Hard Disk Drives
Hot Swap 3.5'' Hard Disk Drives
SAS Expender Option
SATA Optical Drive
eUSB Solid State Device (eUSB SSD)
Support for different storage and peripheral device options will vary depending on the system
SKU. This section will provide an overview of each available option.
4.1 2.5‟„ Hard Disk Drive Support
The Intel® Server System P4000IP support 8x2.5'' drive configuration. The drive bay can
support either SATA or SAS hard disk drives. Mixing of drive types within the hard drive bay is
not supported. Hard disk drive type is dependent on the type of host bus controller used, SATA
only or SAS. Each 2.5'' hard disk drive is mounted to a drive tray, allowing for hot swap
extraction and insertion. Drive trays have a latching mechanism that is used to extract and
insert drives from the chassis, and lock the tray in place.
Light pipes integrated into the drive tray assembly direct light emitted from Amber drive status
and Green activity LEDs located next to each drive connector on the backplane, to the drive
tray faceplate, making them visible from the front of the system.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Figure 34. 2.5'' Hard Disk Drive Cage
Page 94

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS Storage and Peripheral Drive Bays
Amber
Off
No access and no fault
Solid On
Hard Drive Fault has occurred
Blink
RAID rebuild in progress (1 Hz), Identify (2 Hz)
Green
Condition
Drive Type
Behavior
Power on with no drive activity
SAS
LED stays on
SATA
LED stays off
Power on with drive activity
SAS
LED blinks off when processing a command
SATA
LED blinks on when processing a command
Power on and drive spun down
SAS
LED stays off
SATA
LED stays off
Power on and drive spinning up
SAS
LED blinks
SATA
LED stays off
Amber Status LED
Green Activity LED
Figure 35. 2.5'' Hard Disk Drive Support - LED Status
Table 94. 2.5'' Hard Disk Drive Status LED States
Table 95. 2.5'' Hard Disk Drive Activity LED States
4.1.1 2.5'' Drive Hot-Swap Backplane Overview
Depending on the number of hard disk drives supported by a given system SKU, a system can
be configured with 1, 2, or 3 eight drive backplanes. Each backplane is attached to the back of
the drive bay assembly. On the front side of each backplane are mounted eight hard disk drive
interface connectors (A), each providing both power and I/O signals to attached hard disk
drives.
82 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Figure 36. 2.5'' Backplane, Front Side
Page 95

Storage and Peripheral Drive Bays Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
83
Label
Description
A
4-port Mini-SAS cable connectors
B
SMBus-Out cable connector for multi-backplane support
C
Power connector
D
SMBus-In cable connector – From Server board or other
backplane
There are several connectors on the backside of each backplane. The following illustration
identifies each of them:
Figure 37. 2.5'' Backplane, Back Side
A – Multi-port Mini-SAS Cable Connectors – The backplane includes two multi-port mini-SAS
cable connectors, each providing I/O signals for four SAS/SATA hard drives on the backplane.
Cables can be routed from matching connectors on the server board, add-in SAS/SATA RAID
cards, or optionally installed SAS expander cards.
B and D – SMBus Cable Connectors – The backplane includes two 1x5 cable connectors used
as a management interface between the server board and the installed backplanes. In systems
configured with multiple backplanes, a short jumper cable is attached between backplanes, with
connector B used on the first board and connector D used on the second board, extending the
SMBus to each installed backplane.
C – Power Harness Connector – The backplane includes a 2x2 connector supplying power to
the backplane. Power is routed to each installed backplane by a multi-connector power cable
harness from the server board.
4.1.2 Cypress* CY8C22545 Enclosure Management Controller
The backplanes support enclosure management using a Cypress* CY8C22545 Programmable
System-on-Chip (PSoC*) device. The CY8C22545 drives the hard drive activity/fault LED, hard
drive present signal, and controls hard drive power-up during system power-on.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 96

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS Storage and Peripheral Drive Bays
Amber
Off
No access and no fault
Solid
On
Hard Drive Fault has occurred
Blink
RAID rebuild in progress (1 Hz), Identify (2
Hz)
Amber Status LED
Green Activity LED
4.2 3.5'' Hard Disk Drive Support
The Intel® Server System P4308CP4MHEN and P4308CP4MHGC support 8x3.5'' drive
configuration. The drive bay can support either SATA or SAS hard disk drives. Mixing of drive
types within the hard drive bay is not supported. Hard disk drive type is dependent on the type
of host bus controller used, SATA only or SAS. Each 3.5'' hard disk drive is mounted to a drive
tray, allowing for hot swap extraction and insertion. Drive trays have a latching mechanism that
is used to extract and insert drives from the chassis, and lock the tray in place.
Figure 38. 3.5'' Hard Disk Drive Cage
Light pipes integrated into the drive tray assembly direct light emitted from Amber drive status
and Green activity LEDs located next to each drive connector on the backplane, to the drive
tray faceplate, making them visible from the front of the system.
Figure 39. 3.5'' Hard Disk Drive Support - LED Status
Table 96. 3.5'' Hard Disk Drive Status LED States
84 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 97

Storage and Peripheral Drive Bays Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
85
Green
Condition
Drive Type
Behavior
Power on with no drive activity
SAS
LED stays on
SATA
LED stays off
Power on with drive activity
SAS
LED blinks off when processing a
command
SATA
LED blinks on when processing a
command
Power on and drive spun down
SAS
LED stays off
SATA
LED stays off
Power on and drive spinning
up
SAS
LED blinks
SATA
LED stays off
Table 97. 3.5'' Hard Disk Drive Activity LED States
4.2.1 3.5'' Drive Hot-Swap Backplane Overview
The backplane mount to the back of the drive bay assembly. On the front side the back plane
are mounted eight hard disk drive interface connectors (A), each providing both power and I/O
signals to the attached hard disk drives.
On the backside of each backplane are several connectors. The following illustration identifies
each.
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Figure 40. 3.5'' Backplane, Front Side
Page 98

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS Storage and Peripheral Drive Bays
Label
Description
A
Reserved
B
Power connector
C
4-port mini-SAS connectors
D
SMBus connector
E
Drive connector interface
Figure 41. 2.5'' Backplane, Back Side
A – Reserved
B – Power Harness Connector - The backplane includes a 2x2 connector supplying power to
the backplane. Power is routed to the backplane by a power cable harness from the server
board
C – 4-port Mini-SAS Connectors – The backplane includes two or three multi-port mini-SAS
cable connectors, each providing I/O signals for four SAS/SATA hard drives on the backplane.
Cables can be routed from matching connectors on the server board, add-in SAS/SATA RAID
cards, or optionally installed SAS expander cards. Each mini-SAS connector will include a silkscreen identifying which drives the connector supports; Drives 0-3 and Drives 4-7.
D – SMBus Cable Connectors – The backplane includes a 1x5 cable connector used as a
management interface to the server board.
86 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
Page 99

Storage and Peripheral Drive Bays Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS
87
4.2.2 Cypress* CY8C22545 Enclosure Management Controller
The backplanes support enclosure management using a Cypress* CY8C22545 Programmable
System-on-Chip (PSoC*) device. The CY8C22545 drives the hard drive activity/fault LED, hard
drive present signal, and controls hard drive power-up during system power-on.
4.3 SAS Expander Card Option
The 24-port SAS expander card and 36-port expander card is an optional accessory that can
support up to 16 Hard drivers and 24 Hard drivers 2.5'' hard disk drives. The expander card can
be mounted directly behind the drive bay assembly as shown in the following illustration.
Figure 42. Internal SAS Expander Installation
The following diagrams are used to help identify the mini-SAS connectors found on the SAS
expander cards. Care should be taken when connecting connectors from the SAS expander to
the connectors on the backplane because each connector is pre-programmed at the factory to
provide specific drive identification mapping. Improper connections may provide undesirable
drive mappings.
Figure 43. Internal 24-Port SAS Expander Card
Revision 1.0 Intel order number G38159-001
Page 100

Intel® Server System P4000IP and Intel® Workstation System P4000CR Family TPS Storage and Peripheral Drive Bays
Figure 44. 24-Port Expander SAS Connector/Drive Identification Block Diagram
0
1
2
5
4
3
16-19
E
20-23
F
24-port SAS
Expander
0-3
A
4-7
B
8-11
C
12-15
D
7
0
1
2
8
6
5
4
3
0-3
A
4-7
B
8-11
C
12-15
D
16-19
E
20-23
F
36-port SAS
Expander
24-27
G
32-35
I
28-31
H
Figure 46. 36-Port Expander SAS Connector/Drive Identification Block Diagram
Figure 45. Internal 36-Port SAS Expander Card
88 Intel order number G38159-001 Revision 1.0
 Loading...
Loading...