Page 1

Intel® NUC Products
NUC8i5INH / NUC8i7INH
Technical Product Specification
Regulatory Models: NUC8IN
June 2019
version 003
Page 2
The Intel NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH may contain design defects or errors known as errata that may cause the product to deviate from
Revision
Revision History
Date
001
First release of Intel NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH Technical Product
Specification
March 2019
002
First production release of the Intel NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH
Technical Product Specification
May 2019
003
Specification Clarification
June 2019
published specifications. Current characterized errata are documented in the Intel NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH Specification Update.
Revision History
Disclaimer
This product specification applies to only the standard Intel® NUC Boards, Kits and Mini PCs with BIOS
identifier INWHL357.0028.
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT.
EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO
LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR
USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED IN WRITING BY INTEL, THE INTEL PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED NOR INTENDED FOR
ANY APPLICATION IN WHICH THE FAILURE OF THE INTEL PRODUCT COULD CREATE A SITUATION WHERE PERSONAL
INJURY OR DEATH MAY OCCUR.
All Intel® NUC Boards are evaluated as Information Technology Equipment (I.T.E.) for use in personal computers (PC) for
installation in homes, offices, schools, computer rooms, and similar locations. The suitability of this product for other PC
or embedded non-PC applications or other environments, such as medical, industrial, alarm systems, test equipment, etc.
may not be supported without further evaluation by Intel.
Intel Corporation may have patents or pending patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property
rights that relate to the presented subject matter. The furnishing of documents and other materials and information does
not provide any license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any such patents, trademarks, copyrights, or
other intellectual property rights.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or
“undefined.” Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or
incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each
processor family, not across different processor families: Go to:
Learn About Intel® Processor Numbers
Intel NUC Boards and kits may contain design defects or errors known as errata, which may cause the product to deviate
from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications before placing your product
order.
Intel, Pentium and Celeron are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright 2019 Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
iii
Page 3
Intel NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH
Intel NUC Board
AA Revision
BIOS Revision
Notes
NUC8i5INB
K29935-300
INWHL357.0028 or newer
1, 2
NUC8i7iNB
K29936-402
INWHL357.0028 or newer
1, 2
Device
Stepping
S-Spec Number(s)
Intel Core i5-8265U
W0
SREJR
W0
SREJQ
V0
SRFFX
Intel Core i7-8565U
W0
SREJP
V0
SRFFW
Product Name
Intel® NUC Board
Differentiating Features
NUC8i5INHX
NUC8i5INB
8GB LPDDR3-2133 solder-down Memory with power
adapter
NUC8i5INHJA
HDD kit with power adapter, 16GB Intel® Optane™ Module,
1TB HDD, 8GB LPDDR3-2133 solder-down Memory,
Microsoft Windows 10 Home, “Intel® NUC 8 Home, a Mini
PC with Windows 10”
NUC8i5INHPA
SSD kit with power adapter, 256 M.2 SSD, 8GB LPDDR32133 solder-down Memory, Microsoft Windows 10 Home,
“Intel® NUC 8 Home, a Mini PC with Windows 10”
NUC8i5INHP
NUC8i5INB
SSD kit with power adapter, 256GB M.2 SSD, 8GB LPDDR32133 solder-down Memory
NUC8i7INHX
NUC8i7INB
8GB LPDDR3-2133 solder-down Memory with power
adapter
NUC8i7INHJA
HDD kit with power adapter, 16GB Intel® Optane™ Module,
1TB HDD, 8GB LPDDR3-2133 solder-down Memory,
Microsoft Windows 10 Home, “Intel® NUC 8 Home, a Mini
PC with Windows 10”
NUC8i7INHZ
HDD and SSD kit with power adapter, 1TB HDD and 256GB
M.2 SSD, 8GB LPDDR3-2133 solder-down Memory
Technical Product Specification
Note: For this Technical Products Specification, the use of
Intel NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH
Board Identification Information
Basic Intel® NUC Board Identification Information
Notes:
1 The AA number is found on a small label on the Front USB connectors.
2 Intel
3
®
Core™ i5-8265U/ i7-8565U processor are used on this AA revision consists of the following component:
Product Identification Information
Intel® NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH {x} † Identification Information
iv
Page 4
NUC8i7INHPA
SSD kit with power adapter, 256GB M.2 SSD, 8GB LPDDR32133 solder-down Memory, Microsoft Windows 10 Home,
“Intel® NUC 8 Home, a Mini PC with Windows 10”
NUC8i7INHP
SSD kit with power adapter, 256GB M.2 SSD, 8GB LPDDR32133 solder-down Memory
Specification Changes or Clarifications
Date
Type of Change
Description of Changes or Clarifications
The table below indicates the Specification Changes or Specification Clarifications that apply to
the Intel NUC Products NUC8i5INH / NUC8i7INH.
Specification Changes or Clarifications
Errata
Current characterized errata, if any, are documented in a separate Specification Update. See
http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/nuc/overview.html for the latest documentation.
v
Page 5
Intel NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH
Chapter
Description
1
A description of the hardware used in Intel NUC Product NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH
2
A map of the resources of the Intel NUC Board
3
The features supported by the BIOS Setup program
4
A description of the front panel blink codes and BIOS error messages
5
The features of the Intel NUC Kits and Mini PCs
Technical Product Specification
Preface
This Technical Product Specification (TPS) specifies the layout, components, connectors, power
and environmental requirements, and the BIOS for Intel® NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH
are with pre-installed Hard Drive Disk(HDD), Solid-state disk(SSD), Optane Memory, Soldereddown memory, and operating system.
Intended Audience
The TPS is intended to provide detailed technical information about Intel NUC Products
NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH and their components to the vendors, system integrators, and other
engineers and technicians who need this level of information. It is specifically not intended for
general audiences.
What This Document Contains
Typographical Conventions
This section contains information about the conventions used in this specification. Not all of
these symbols and abbreviations appear in all specifications of this type.
Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE
Notes call attention to important information.
CAUTION
Cautions are included to help you avoid damaging hardware or losing data.
vi
Page 6

Other Common Notation
#
Used after a signal name to identify an active-low signal (such as USBP0#)
bpp
Bits per pixel
GB
Gigabyte (1,073,741,824 bytes)
GBps
Gigabytes per second
Gbps
Gigabits per second
KB
Kilobyte (1024 bytes)
Kb
Kilobit (1024 bits)
kbps
1000 bits per second
MB
Megabyte (1,048,576 bytes)
MBps
Megabytes per second
Mb
Megabit (1,048,576 bits)
Mbps
Megabits per second
TDP
Thermal Design Power
xxh
An address or data value ending with a lowercase h indicates a hexadecimal value.
x.x V
Volts. Voltages are DC unless otherwise specified.
*
This symbol is used to indicate third-party brands and names that are the property of their respective
owners.
vii
Page 7

Page 8

Contents
Revision History .............................................................................................................. iii
Note: For this Technical Products Specification, the use of Intel NUC Products
NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH ........................................................................................................................... iv
Board Identification Information ..................................................................................................................... iv
Product Identification Information ................................................................................................................. iv
Errata ............................................................................................................................................................................ v
Preface .............................................................................................................................. vi
Intended Audience ................................................................................................................................................ vi
What This Document Contains ........................................................................................................................ vi
Typographical Conventions .............................................................................................................................. vi
Contents ........................................................................................................................... ix
1 Product Description ............................................................................................... 13
1.1 Overview ...................................................................................................................................................... 13
1.1.1 Feature Summary .................................................................................................................. 13
1.1.2 Board Layout (Top) ............................................................................................................... 15
1.1.3 Board Layout (Bottom) ........................................................................................................ 16
1.1.4 Block Diagram ......................................................................................................................... 18
1.2 Online Support .......................................................................................................................................... 19
1.3 Processor ..................................................................................................................................................... 19
1.4 Graphics Capabilities .............................................................................................................................. 20
1.4.1 AMD Radeon™ 540X Graphics .......................................................................................... 20
1.4.2 High Definition Multimedia Interface* (HDMI*) ......................................................... 20
1.4.3 Mini DisplayPort* (mDP*) .................................................................................................... 20
1.5 USB ................................................................................................................................................................. 22
1.6 SATA Interface ........................................................................................................................................... 22
1.6.1 AHCI Mode ................................................................................................................................ 22
1.7 Real-Time Clock Subsystem ................................................................................................................ 23
1.8 Audio Subsystem ..................................................................................................................................... 24
1.9 LAN Subsystem ......................................................................................................................................... 25
1.9.1 Intel® WGI219V Gigabit Ethernet Controller .............................................................. 25
1.9.2 LAN Subsystem Software ................................................................................................... 25
1.9.3 RJ-45 LAN Connector with Integrated LEDs .............................................................. 26
1.9.4 Wireless Network Module .................................................................................................. 26
1.10 Hardware Management Subsystem ................................................................................................. 27
1.10.1 Hardware Monitoring ........................................................................................................... 27
1.10.2 Fan Monitoring ........................................................................................................................ 27
1.10.3 Thermal Solution ................................................................................................................... 28
ix
Page 9

1.11 Power Management ................................................................................................................................ 29
1.11.1 ACPI ............................................................................................................................................. 29
1.11.2 Hardware Support ................................................................................................................. 31
1.11.3 HDMI Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) ................................................................ 33
1.12 Intel Platform Security Technologies .............................................................................................. 35
1.12.1 Intel® Virtualization Technology ...................................................................................... 35
1.12.2 Intel® Platform Trust Technology ................................................................................... 35
2 Technical Reference ............................................................................................... 37
2.1 Memory Resources .................................................................................................................................. 37
2.1.1 Addressable Memory ........................................................................................................... 37
2.2 Connectors and Headers....................................................................................................................... 37
2.2.1 Front Panel Connectors ...................................................................................................... 38
2.2.2 Back Panel Connectors ....................................................................................................... 38
2.2.3 Headers and Connectors (Top) ........................................................................................ 39
2.2.4 Connectors and Headers (Bottom) ................................................................................. 40
2.3 BIOS Security Jumper ............................................................................................................................ 44
2.4 Mechanical Considerations .................................................................................................................. 46
2.4.1 Form Factor .............................................................................................................................. 46
2.4.2 Weight ........................................................................................................................................ 47
2.5 Electrical Considerations ...................................................................................................................... 47
2.5.1 Power Supply Considerations .......................................................................................... 47
2.5.2 Fan Header Current Capability ......................................................................................... 47
2.6 Thermal Considerations ........................................................................................................................ 48
2.7 Reliability ..................................................................................................................................................... 51
2.8 Environmental ........................................................................................................................................... 51
3 Overview of BIOS Features ................................................................................... 53
3.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................................ 53
3.2 BIOS Flash Memory Organization ..................................................................................................... 53
3.3 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS) .............................................................................................. 53
3.4 Legacy USB Support ............................................................................................................................... 54
3.5 BIOS Updates ............................................................................................................................................. 54
3.5.1 Language Support ................................................................................................................. 55
3.6 BIOS Recovery ........................................................................................................................................... 55
3.7 Boot Options .............................................................................................................................................. 55
3.7.1 Network Boot........................................................................................................................... 55
3.7.2 Booting Without Attached Devices ................................................................................ 56
3.7.3 Changing the Default Boot Device During POST ...................................................... 56
3.7.4 Power Button Menu .............................................................................................................. 57
3.8 Hard Disk Drive Password Security Feature .................................................................................. 58
3.9 BIOS Security Features .......................................................................................................................... 58
4 Error Messages and Blink Codes ......................................................................... 60
4.1 Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes ................................................................................................ 60
x
Page 10

Contents
5 Intel NUC Kit Features ........................................................................................... 61
5.1 Chassis Front Panel Features .............................................................................................................. 61
5.2 Chassis Rear Panel Features ................................................................................................................ 62
Figures
Figure 1. Major Board Components (Top) ....................................................................................................... 15
Figure 2. Major Board Components (Bottom) ................................................................................................ 16
Figure 3. Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................................... 18
Figure 4. 4-Pin 3.5 mm (1/8 inch) Audio Jack Pin Out ............................................................................... 24
Figure 5. LAN Connector LED Locations........................................................................................................... 26
Figure 6. Thermal Solution and Fan Header ................................................................................................... 28
Figure 7. Location of the Standby Power LED ............................................................................................... 33
Figure 8. CEC Connector ......................................................................................................................................... 34
Figure 9. Front Panel Connectors, Controls and Indicators ..................................................................... 38
Figure 10. Back Panel Connectors ...................................................................................................................... 38
Figure 11. Headers and Connectors (Top) ....................................................................................................... 39
Figure 12. Connectors and Headers (Bottom) ............................................................................................... 40
Figure 13. Connection Diagram for Front Panel Header (2.0 mm Pitch) ...... Error! Bookmark not
defined.
Figure 14. Location of the CIR Sensor ............................................................................................................... 43
Figure 15. Location of the BIOS Security Jumper ........................................................................................ 44
Figure 16. Board Dimensions ................................................................................................................................ 46
Figure 17. Board Height Dimensions ................................................................................................................. 47
Figure 18. Localized High Temperature Zones ............................................................................................. 49
Figure 19. Intel® NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH Features – Front ....................................... 61
Figure 20. Intel® NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH Features – Rear ......................................... 62
Tables
Table 1. Feature Summary ..................................................................................................................................... 13
Table 2. Components Shown in Figure 1 ......................................................................................................... 15
Table 3. Components Shown in Figure 2 ......................................................................................................... 17
Table 4. LAN Connector LED States ................................................................................................................... 26
Table 5. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch ............................................................................................... 29
Table 6. Power States and Targeted System Power ................................................................................... 30
Table 7. Wake-up Devices and Events .............................................................................................................. 31
Table 8. HDMI 1 CEC expected behavior.......................................................................................................... 33
Table 9. Headers and Connectors Shown in Figure 11 .............................................................................. 39
Table 10. Connectors and Headers Shown in Figure 12 ........................................................................... 41
Table 11. SATA Power Header (0.5 mm Pitch) .............................................................................................. 41
Table 12. Single-Port Internal USB 2.0 Headers (1.25 mm Pitch) ......................................................... 42
Table 13. Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) Connector (1.25 mm Pitch) .................................... 42
Table 14. SDXC Card Reader Connector .......................................................................................................... 42
Table 15. BIOS Security Jumper Settings ........................................................................................................ 45
xi
Page 11

Table 16. Select Weights and ............................................................................................................................... 47
Table 17. Select Chassis Dimensions ................................................................................................................. 47
Table 18. Fan Header Current Capability ......................................................................................................... 47
Table 19. Thermal Considerations for Components ................................................................................... 50
Table 20. Tcontrol Values for Components ................................................................................................... 50
Table 21. Environmental Specifications ........................................................................................................... 51
Table 22. Acceptable Drives/Media Types for BIOS Recovery ............................................................... 55
Table 23. Boot Device Menu Options ................................................................................................................ 56
Table 24. Master Key and User Hard Drive Password Functions ........................................................... 58
Table 25. Supervisor and User Password Functions................................................................................... 59
Table 26. Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes ............................................................................................. 60
Table 27. Components Shown in Figure 19 ................................................................................................... 61
Table 28. Components Shown in Figure 20 ................................................................................................... 62
xii
Page 12
Board Form Factor
4.0 inches by 4.0 inches (101.60 millimeters by 101.60 millimeters)
Processor
Soldered-down 8th Generation Intel® Core™ i5 Quad-core Processors with 15W
TDP, 1.60 GHz
― TDP-up 25W
― 6 MB SmartCache, 3.60 GHz Max Turbo Frequency
― Integrated memory controller
― Integrated PCH
Soldered-down 8th Generation Intel® Core™ i7 Quad-core Processors with 15W
TDP, 1.80 GHz
― TDP-up 25W
― 8 MB SmartCache, 4.60 GHz Max Turbo Frequency
― Integrated memory controller
― Integrated PCH
Memory
Soldered-down LPDDR3 1866 MHz(4GB), LPDDR3 2133 MHz(8GB), Duel channel
Soldered-down 4 GB or 8 GB memory technology
Support for non-ECC memory
Support for 1.2 V low voltage JEDEC memory
Graphics
Discrete graphic support with AMD Radeon™ 540X:
― One full-sized High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) and one Mini
DisplayPort (mDP) interface of rear panel.
― HDMI™ 4K Support, DisplayPort 1.4 HDR
Audio
ADM Integrated HD-Audio Controller (Azalia) and Codec via the HDMI and mDP
interfaces supporting compressed 7.1digital audio
Realtek ALC256 HD Audio via a stereo microphone/headphone 3.5 mm jack on the
front panel and 3.5mm combination speaker
Expansion Capabilities
One M.2 connector supporting M.2 2280 (key type M) modules
Storage
One SATA 6.0 Gbps port (black)
― Supports one 2.5“ SSD or HDD up to 9.5mm
1TB Hard Drive Disk included.
One full-sized SDXC slot
BIOS
Intel
®
BIOS resident in the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Flash device
Support for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI), Plug and Play, and
System Management BIOS (SMBIOS)
1 Product Description
1.1 Overview
1.1.1 Feature Summary
Table 1 summarizes the major features of the product.
Table 1. Feature Summary
Continued
13
Page 13
Peripheral Interfaces
USB 3.1 gen2 ports:
― One USB TypeA and USB TypeC ports are implemented with external front
panel connectors.
― Two USB TypeA ports are implemented with external back panel connectors
(blue)
Consumer Infrared (CIR)
Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) header
Front panel header
USB 2.0 ports:
― Two ports via an internal common IO header
LAN Support
Gigabit (10/100/1000 Mbps) LAN subsystem using the Intel WGI219V Gigabit Ethernet
Controller
Hardware Monitor
Subsystem
Hardware monitoring subsystem, based on an ITE8991VG embedded controller,
including:
Voltage sense to detect out of range power supply voltages
Thermal sense to detect out of range thermal values
One processor fan header
Fan sense input used to monitor fan activity
Fan speed control
Wireless
Soldered down Intel® Wireless-AC 9560D2WG module
Intel wireless802.11ac R2, 2x2, Dual Band, Wi-Fi
Bluetooth® 5
Maximum Transfer speed up to 1.73Gbps
• Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF) 12x16 soldered-down package
Table 1. Feature Summary (continued)
14
Page 14
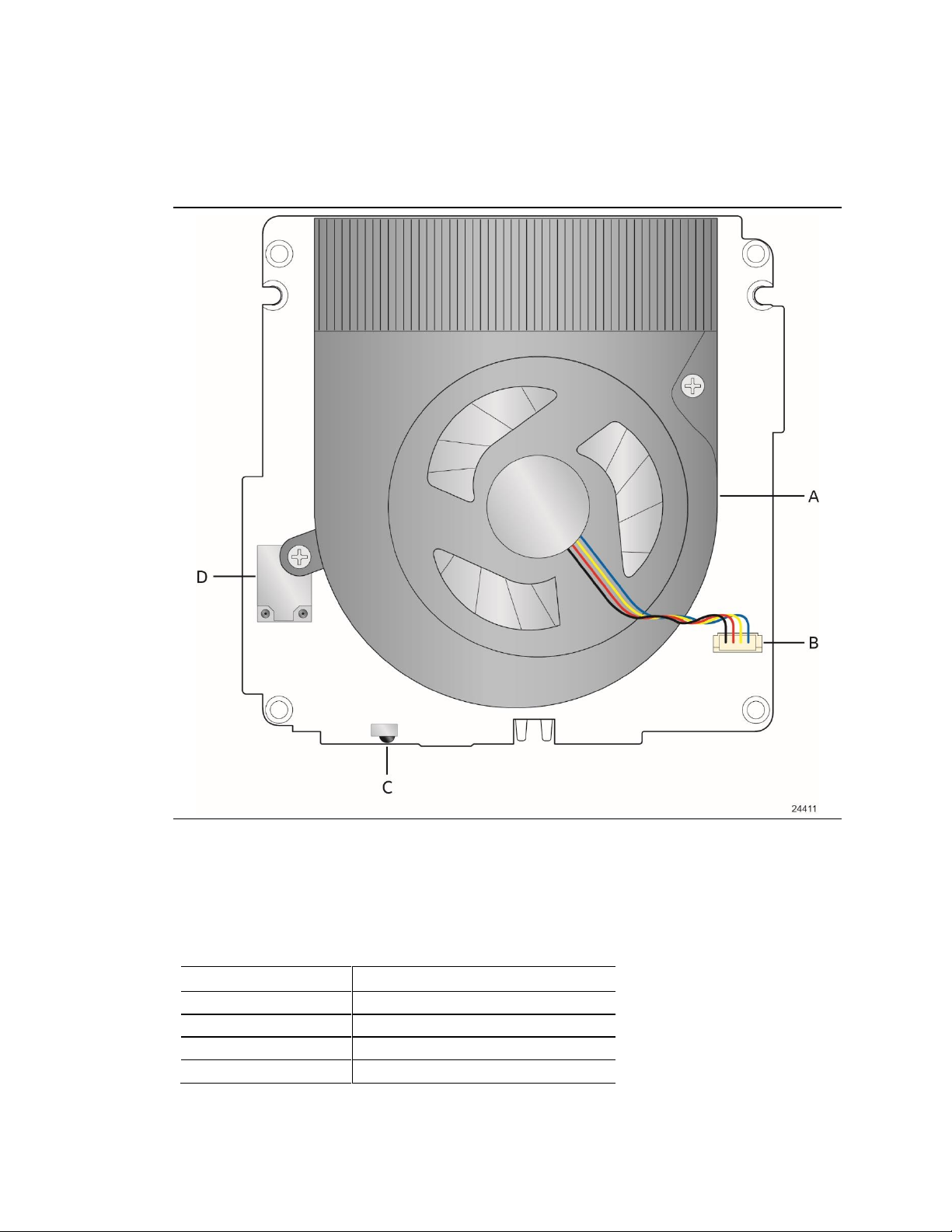
Product Description
Item from Figure 1
Description
A
Thermal solution
B
Processor fan header
C
Consumer Infrared (CIR) sensor
D
Wireless LAN module
1.1.2 Board Layout (Top)
Figure 1 shows the location of the major components on the top-side of Intel NUC Boards
NUC8INB
Figure 1. Major Board Components (Top)
.
Table 2 lists the components identified in Figure 1.
Table 2. Components Shown in Figure 1
15
Page 15
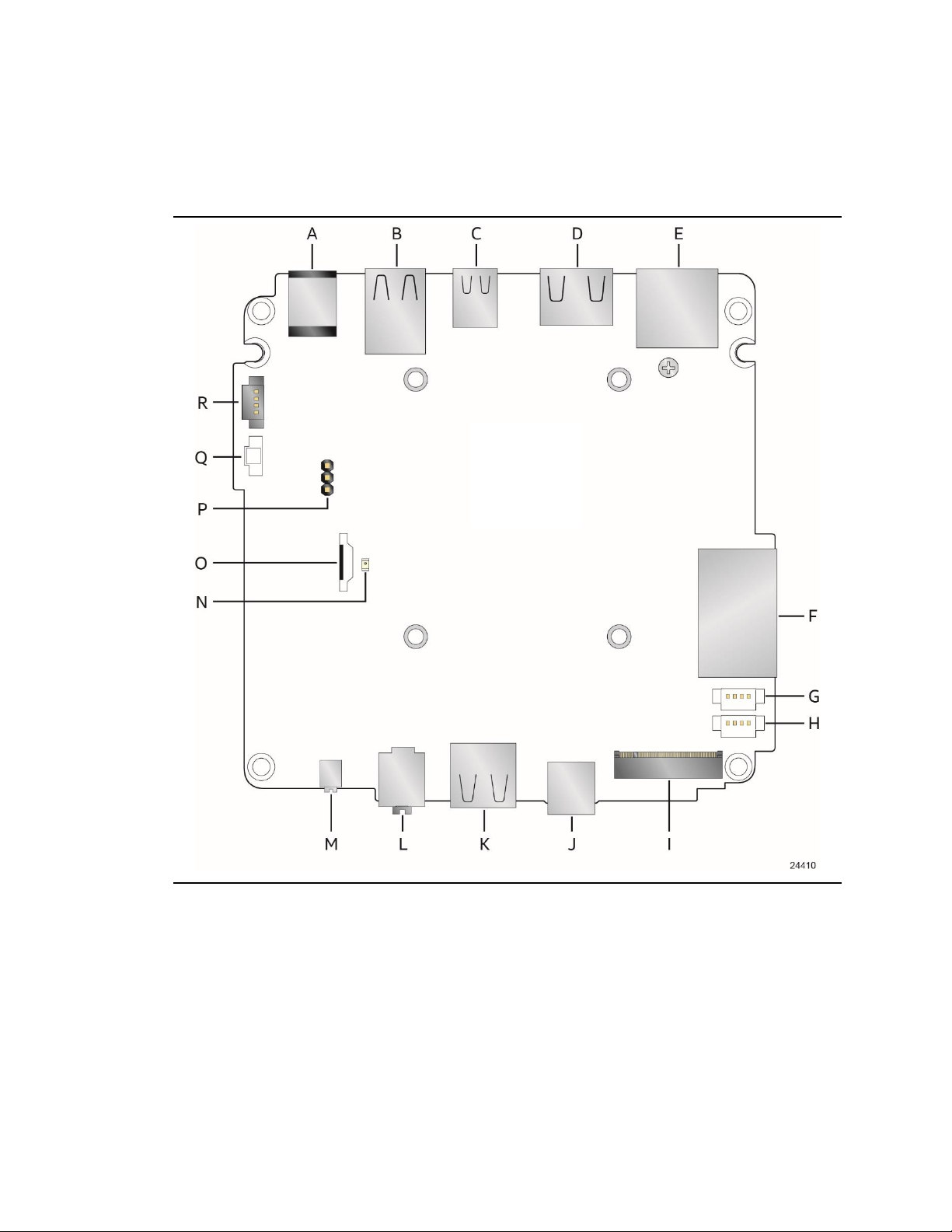
1.1.3 Board Layout (Bottom)
Figure 2 shows the location of the major components on the bottom-side of Intel NUC Mini PC
NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH.
16
Figure 2. Major Board Components (Bottom)
Page 16

Table 3. Components Shown in Figure 2
Item from
Figure 2
Description
A
19V DC input jack
B
Back panel USB 3.1 gen2 connectors
C
Mini Display Port
D
HDMI connector
E
LAN jack
F
SDXC card reader slot
G
Front panel single-port USB 2.0 connector (1.25 mm pitch)
H
Front panel single-port USB 2.0 connector (1.25 mm pitch)
I
M.2 connector
J
Front panel USB 3.1 gen2 connector
K
Front panel USB 3.1 gen2 connector
L
Front panel stereo speaker/headphone/microphone jack
M
Power button / power LED
N
+5 V Standby Power Indicator LED
O
SATA 6.0 Gb/s connector
P
BIOS security jumper
Q
Battery (lithium coin cell, CR2032, 3.0V)
R
Consumer Electronic Control (CEC) connector
Product Description
17
Page 17
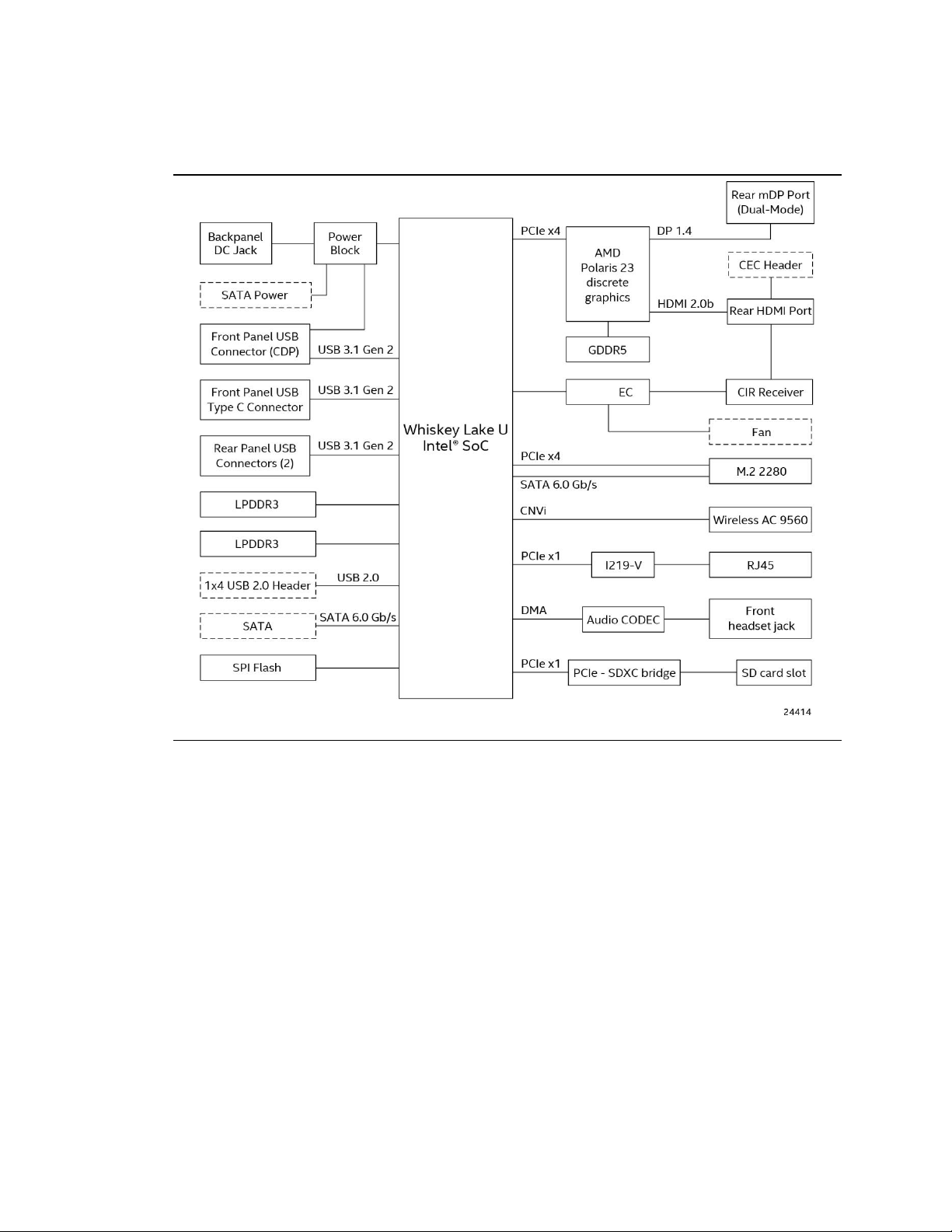
1.1.4 Block Diagram
Figure 3 is a block diagram of the major functional areas of the board.
Figure 3. Block Diagram
18
Page 18

Product Description
To find information about…
Visit this World Wide Web site:
Intel NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH
http://www.intel.com/NUC
NUC Board Support
http://www.intel.com/NUCSupport
Available configurations for Intel NUC Products
NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH
http://ark.intel.com
BIOS and driver updates
http://downloadcenter.intel.com
Integration information
http://www.intel.com/NUCSupport
1.2 Online Support
1.3 Processor
Intel NUC Mini PC NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH has a soldered-down System-on-a-Chip (SoC),
which consists of one of following:
Soldered-down 8th Generation Intel® Core™ i5 Quad-core Processors with 15W TDP, 1.60 GHz
TDP-up 25W
6 MB SmartCache, 3.60 GHz Max Turbo Frequency
Integrated memory controller
Integrated PCH
Soldered-down 8th Generation Intel® Core™ i7 Quad-core Processors with 15W TDP, 1.80 GHz
TDP-up 25W
8 MB SmartCache, 4.60 GHz Max Turbo Frequency
Integrated memory controller
Integrated memory
NOTE
The board has specific requirements for providing power to the processor. Refer to
Section 2.5.1 on page 47 for information on power supply requirements for the board.
19
Page 19

For information about
Refer to
HDMI technology
http://www.hdmi.org
1.4 Graphics Capabilities
The kit supports graphics computing through AMD Radeon™ 540X
1.4.1 AMD Radeon™ 540X Graphics
The AMD Radeon graphics controller features the following:
Supports HDR-10 video playback.
Multi View Coding (MVC) support for Blu-ray 3D content.
3D graphics hardware acceleration supporting DirectX 12, OpenCL* 2.0, OpenGL 4.5
Dedicated Unified Video Decoder hardware (UVD) for H.264, HEVC, VC-1, MPEG-4, MPEG-
2, and MVC decode
Non-HBR compressed audio pass-through up to 6.144 Mbps, support AC-3, MPEG1, MP3
(MPEG1 layer 3), MPEG2, AAC, DTS, ATRAC, Dolby Digital+, WMA Pro, and DTS-HD
HBR compressed audio pass-through up to 24.576 Mbps, support DTS-HD Master Audio
and Dolby True HD.
Supports content protection using High-Bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) 2.2
Support only GDDR5 DRAM.
Supports AMD FreeSync™ technology
1.4.2 High Definition Multimedia Interface* (HDMI*)
The HDMI ports are compliant with the HDMI 2.0b specification. The HDMI ports support
standard, enhanced, or high definition video, plus multi-channel digital audio on a single cable.
The maximum supported resolution is 4096 x 2160 @ 60 Hz, 36bpp.
1.4.2.1 Integrated Audio Provided by the HDMI Interfaces
The following audio technologies are supported by the HDMI 2.0b interfaces directly from
the SoC:
• AC3 - Dolby* Digital
• Dolby®-TrueHD Bitstream Capable
1.4.3 Mini DisplayPort* (mDP*)
DisplayPort is a digital communication interface that utilizes differential signaling to achieve a
high bandwidth bus interface designed to support connections between PCs and monitors,
projectors, and TV displays. DisplayPort is suitable for display connections between consumer
electronics devices such as high definition optical disc players, set top boxes, and TV displays.
The maximum supported resolution is 7680 x 4320 @ 30Hz, 24bpp. DisplayPort via mini
Display Port connector is compliant with the DisplayPort 1.4 specification.
20
DisplayPort output supports Multi-Stream Transport (MST) which allows for multiple
independent video streams (daisy-chain connection with multiple monitors) over a single
Page 20

Product Description
For information about
Refer to
DisplayPort technology
http://www.displayport.org
DisplayPort. This will require the use of displays that support DisplayPort 1.4 and allow for
this feature.
21
Page 21

For information about
Refer to
The location of the USB connectors on the back panel
Error! Reference source not
ound.
The location of the USB connector on the front panel
Figure 2
1.5 USB
The USB port arrangement is as follows:
USB 3.1 gen2 ports:
Two ports are implemented with external front panel connectors (one USB Type C and
one USB Type A with amber color charging capable)
Two ports are implemented with external back panel connectors (USB Type A with
blue color)
Maximum current is 900 mA for each blue port, 1.5 A for the amber charging port
USB 2.0 ports:
Two ports via two single-port internal 1x4 1.25 mm pitch headers (white)
Maximum current is 500 mA for each port of the white headers (1 A total)
All the USB ports are high-speed, full-speed, and low-speed capable.
NOTE
Computer systems that have an unshielded cable attached to a USB port may not meet FCC
Class B requirements, even if no device is attached to the cable. Use a shielded cable that
meets the requirements for full-speed devices.
1.6 SATA Interface
The SoC provides one SATA port with a theoretical maximum transfer rate of 6.0 Gb/s. A
point-to-point interface is used for host to device connections.
The underlying SATA functionality is transparent to the operating system. The SATA
controller can operate in both legacy and native modes. In legacy mode, standard IDE I/O and
IRQ resources are assigned (IRQ 14 and 15). In Native mode, standard PCI Conventional bus
resource steering is used. Native mode is the preferred mode for configurations using
Windows* operating systems.
1.6.1 AHCI Mode
The board supports AHCI storage mode.
NOTE
In order to use AHCI mode, AHCI must be enabled in the BIOS. Microsoft* Windows* 10 includes
the necessary AHCI drivers without the need to install separate AHCI drivers during the
operating system installation process. However, it is always good practice to update the AHCI
drivers to the latest available by Intel.
22
Page 22

Product Description
1.7 Real-Time Clock Subsystem
A coin-cell lithium battery (CR2032) powers the real-time clock and CMOS memory. When the
computer is not plugged into a wall socket, the battery has an estimated life of three years.
When the computer is plugged in, the standby current from the power supply extends the life
of the battery. The clock is accurate to 13 minutes/year at 25 ºC with 3.3 VSB applied via the
power supply 5 V STBY rail.
NOTE
If the battery and AC power fail, date and time values will be reset and the user will be notified
during the POST.
When the voltage drops below a certain level, the BIOS Setup program settings stored in
CMOS RAM (for example, the date and time) might not be accurate. Replace the battery with
an equivalent one. Figure 1 shows the location of the battery.
23
Page 23

Pin Number
Pin Name
Description
1
Tip
Left Audio Out
2
Ring
Right Audio Out
3
Ring
Common/Ground
4
Sleeve
Audio In
1.8 Audio Subsystem
The product supports Intel HD Audio via the Realtek ALC233 audio codec. The audio
subsystem supports the following features:
Analog line-out/Analog Headphone/Analog Microphone jack on the front panel
High Definition Audio via a stereo microphone/headphone/optical jack on the back panel
Support for 44.1 kHz/48 kHz/96 kHz sample rates on all analog outputs
Support for 44.1 kHz/48 kHz/96 kHz sample rates on all analog inputs
Back Panel Audio Jack Support (see Figure 4 for 3.5 mm audio jack pin out):
Speakers only
Headphones only
Microphone only
Combo Headphone/MicrophoneFront Panel Audio Jack Support (see Figure 4 for 3.5
mm audio jack pin out):
Speakers only
Headphones only
Microphone only
Combo Headphone/Microphone
Figure 4. 4-Pin 3.5 mm (1/8 inch) Audio Jack Pin Out
NOTE
The analog circuit of the back panel audio connector is designed to power headphones or
amplified speakers only. Poor audio quality occurs if passive (nonamplified) speakers are
connected to this output.
24
Page 24

1.9 LAN Subsystem
For information about
Refer to
LAN software and drivers
http://downloadcenter.intel.com
For information about
Refer to
Full LAN Hardware feature set
http://www.Intel.com/Networking
For information about
Refer to
Obtaining LAN software and drivers
http://downloadcenter.intel.com
The LAN subsystem consists of the following:
Intel® WGI219V Gigabit Ethernet Controller (10/100/1000 Mb/s)
RJ-45 LAN connector with integrated status LEDs
Intel® Wireless-AC 9560D2WG module
Additional features of the LAN subsystem include:
CSMA/CD protocol engine
Jumbo frame support 9K
LAN connect interface between the SoC and the LAN controller
Power management capabilities
ACPI technology support
LAN wake capabilities
LAN subsystem software
Product Description
1.9.1 Intel® WGI219V Gigabit Ethernet Controller
Intel® WGI219V Gigabit Ethernet Controller supports the following features:
10/100/1000 BASE-T IEEE 802.3 compliant
Energy Efficient Ethernet (EEE) IEEE802.3az support (Low Power Idle (LPI) mode)
Dual interconnect between the Integrated LAN Controller and the Physical Layer (PHY):
PCI Express-based interface for active state operation (S0) state
SMBUS for host and management traffic (Sx low power state)
Compliant to IEEE 802.3x flow control support
802.1p and 802.1q
TCP, IP, and UDP checksum offload (for IPv4 and IPv6)
Full device driver compatibility
1.9.2 LAN Subsystem Software
LAN software and drivers are available from Intel’s World Wide Web site.
25
Page 25

Item
Description
A
Link LED (Green)
B
Data Rate LED (Green/Yellow)
LED
LED Color
LED State
Condition
Link (A)
Green
Off
LAN link is not established.
On
LAN link is established.
Blinking
LAN activity is occurring.
Data Rate (B)
Green/Yellow
Off
10 Mb/s data rate is selected.
Green
100 Mb/s data rate is selected.
Yellow
1000 Mb/s data rate is selected.
For information about
Refer to
Obtaining WLAN software and drivers
http://downloadcenter.intel.com
Full Specifications
http://intel.com/wireless
1.9.3 RJ-45 LAN Connector with Integrated LEDs
Two LEDs are built into the RJ-45 LAN connector (shown in Figure 5).
Figure 5. LAN Connector LED Locations
Table 4 describes the LED states when the board is powered up and the LAN subsystem is
operating.
Table 4. LAN Connector LED States
1.9.4 Wireless Network Module
The Intel Wireless-AC 9560D2W module provides high performance low power wireless
connectivity with the following capabilities:
802.11ac R2, Dual Band, 2x2, Wi-Fi + Bluetooth 5.0
Supports 2.4 Ghz and 5 Ghz bands
Maximum transfer speed up to 1.73Gbps
Supports Intel® Smart Connect Technology
Supports Multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) technologies for wireless
communications
Soldered-down module
26
Page 26

Product Description
For information about
Refer to
Wired for Management (WfM) Specification
www.intel.com/design/archives/wfm/
1.10 Hardware Management Subsystem
The hardware management features enable the board to be compatible with the Wired for
Management (WfM) specification. The board has several hardware management features,
including thermal and voltage monitoring.
1.10.1 Hardware Monitoring
The hardware monitoring and fan control subsystem is based on an ITE IT8987VG embedded
controller, which supports the following:
Processor and system ambient temperature monitoring
Chassis fan speed monitoring
Voltage monitoring of DC Input Voltage, Memory Voltage Input, Processor Input Voltage,
GPU Core Voltage.
SMBus interface
1.10.2 Fan Monitoring
Fan monitoring can be implemented using third-party software.
27
Page 27

Item
Description
A
Thermal Solution
B
Processor fan header
1.10.3 Thermal Solution
Figure 6 shows the location of the thermal solution and processor fan header.
Figure 6. Thermal Solution and Fan Header
28
Page 28

Product Description
If the system is in this state…
…and the power switch is pressed for
…the system enters this state
Off
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
Less than four seconds
Power-on
(ACPI G0 – working state)
On
(ACPI G0 – working state)
Less than four seconds
Soft-off/Standby
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
Note
On
(ACPI G0 – working state)
More than six seconds
Fail safe power-off
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
Less than four seconds
Wake-up
(ACPI G0 – working state)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
More than six seconds
Power-off
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
1.11 Power Management
Power management is implemented at several levels, including:
Software support through Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
Hardware support:
Power Input
Instantly Available PC technology
LAN wake capabilities
Wake from USB
WAKE# signal wake-up support
Wake from S5
Wake from CIR
+5 V Standby Power Indicator LED
1.11.1 ACPI
ACPI gives the operating system direct control over the power management and Plug and Play
functions of a computer. The use of ACPI with this board requires an operating system that
provides full ACPI support. ACPI features include:
Plug and Play (including bus and device enumeration)
Power management control of individual devices, add-in boards (some add-in boards may
require an ACPI-aware driver), video displays, and disk drives
Methods for achieving less than 15-watt system operation in the power-on/standby
sleeping state
A Soft-off feature that enables the operating system to power-off the computer
Support for multiple wake-up events (see Table 7 on page Error! Bookmark not defined.)
Support for a front panel power and sleep mode switch
Table 5 lists the system states based on how long the power switch is pressed, depending on
how ACPI is configured with an ACPI-aware operating system.
Table 5. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch
Note: Depending on power management settings in the operating system.
29
Page 29

Global States
Sleeping States
Processor
States
Device States
Targeted System
Power
(Note 1)
G0 – working
state
S0 – working
C0 – working
D0 – working state.
Full power
G1 – sleeping
state
S3 – Suspend to RAM.
Context saved to
RAM.
No power
D3 – no power
except for wake-up
logic.
Power < 5 W
(Note 2)
G1 – sleeping
state
S4 – Suspend to disk.
Context saved to disk.
No power
D3 – no power
except for wake-up
logic.
Power < 5 W
(Note 2)
G2/S5
S5 – Soft off. Context
not saved. Cold boot
is required.
No power
D3 – no power
except for wake-up
logic.
Power < 5 W
(Note 2)
G3 – mechanical
off
AC power is
disconnected
from the
computer.
No power to the
system.
No power
D3 – no power for
wake-up logic,
except when
provided by battery
or external source.
No power to the
system. Service can be
performed safely.
1.11.1.1 System States and Power States
Under ACPI, the operating system directs all system and device power state transitions. The
operating system puts devices in and out of low-power states based on user preferences and
knowledge of how devices are being used by applications. Devices that are not being used can
be turned off. The operating system uses information from applications and user settings to
put the system as a whole into a low-power state.
Table 6 lists the power states supported by the board along with the associated system power
targets. See the ACPI specification for a complete description of the various system and power
states.
Table 6. Power States and Targeted System Power
Notes:
1. Total system power is dependent on the system configuration, including add-in boards and peripherals powered
by the system chassis’ power supply.
2. Dependent on the standby power consumption of wake-up devices used in the system.
30
Page 30

Product Description
Devices/events that wake up the
system…
…from this sleep state
Comments
Power switch
S3, S4, S5
RTC alarm
S3, S4, S5 1
Monitor to remain in sleep state
LAN
S3, S4, S5
1, 3, 4
“S5 WOL after G3” must be supported;
monitor to remain in sleep state
USB
S3, S4, S5
2, 3, 4
Wake S4, S5 controlled by BIOS option
PCIe via WAKE#
S3, S4, S5 1
Via WAKE; monitor to remain in sleep
state
Consumer IR
S3, S4, S5
2, 4
Bluetooth
N/A
Wake from Bluetooth is not supported
1.11.1.2 Wake-up Devices and Events
Table 7 lists the devices or specific events that can wake the computer from specific states.
Table 7. Wake-up Devices and Events
Notes:
1. Monitor will remain in “sleep” state from S3 only
2. S4 implies operating system support only
3. Will not wake from Deep S4/S5. USB S4/S5 Power is controlled by BIOS. USB S5 wake is controlled by BIOS. USB
S4 wake is controlled by OS driver, not just BIOS option.
4. Windows 10 Fast startup will block wake from LAN, USB, and CIR from S5
NOTE
The use of these wake-up events from an ACPI state requires an operating system that
provides full ACPI support. In addition, software, drivers, and peripherals must fully support
ACPI wake events.
1.11.2 Hardware Support
The board provides several power management hardware features, including:
Wake from Power Button signal
Instantly Available PC technology
LAN wake capabilities
Wake from USB
WAKE# signal wake-up support
Wake from S5
Wake from CIR
+5 V Standby Power Indicator LED
NOTE
The use of Wake from USB from an ACPI state requires an operating system that provides full
ACPI support.
31
Page 31

1.11.2.1 Power Input
When resuming from an AC power failure, the computer may return to the power state it was
in before power was interrupted (on or off). The computer’s response can be set using the Last
Power State feature in the BIOS Setup program’s Boot menu.
1.11.2.2 Instantly Available PC Technology
Instantly Available PC technology enables the board to enter the ACPI S3 (Suspend-to-RAM)
sleep-state. While in the S3 sleep-state, the computer will appear to be off (the power supply
is off, and the front panel LED is amber if dual colored, or off if single colored.) When signaled
by a wake-up device or event, the system quickly returns to its last known wake state. Table 7
lists the devices and events that can wake the computer from the S3 state.
The use of Instantly Available PC technology requires operating system support and drivers
for any installed PCI Express add-in card.
1.11.2.3 LAN Wake Capabilities
LAN wake capabilities enable remote wake-up of the computer through a network. The LAN
subsystem monitors network traffic at the Media Independent Interface. Upon detecting a
Magic Packet* frame, the LAN subsystem asserts a wake-up signal that powers up the
computer.
1.11.2.4 Wake from USB
USB bus activity wakes the computer from an ACPI S3, S4, and S5 states.
NOTE
Wake from USB requires the use of a USB peripheral that supports Wake from USB.
1.11.2.5 WAKE# Signal Wake-up Support
When the WAKE# signal on the PCI Express bus is asserted, the computer wakes from an ACPI
S3, S4, or S5 state.
1.11.2.6 Wake from S5
When the RTC Date and Time is set in the BIOS, the computer will automatically wake from an
ACPI S5 state.
1.11.2.7 Wake from Consumer IR
CIR activity wakes the computer from an ACPI S3, S4, or S5 state.
1.11.2.8 +5 V Standby Power Indicator LED
The standby power indicator LED shows that power is still present even when the computer
appears to be off. Figure 7 shows the location of the standby power LED.
32
Page 32

Product Description
Activity
Current Status
Action
Expected Behavior
PC
1,2
TV3
Wake On TV
Off
Off
TV on
PC on
Standby by TV
On
On
TV Standby
PC sleep or power off4
CAUTION
If AC power has been switched off and the standby power indicator is still lit, disconnect the
power cord before installing or removing any devices connected to the board. Failure to do so
could damage the board and any attached devices.
Figure 7. Location of the Standby Power LED
1.11.3 HDMI Consumer Electronics Control (CEC)
The board contains two mutually-exclusive methods for controlling HDMI CEC devices:
External CEC adaptor connected via CEC connector (see Figure 8; pinout in Table 13).
Onboard CEC control from the embedded controller via HDMI cable connected to HDMI 1
and BIOS setup. Expected behavior is provided in Table 8 below.
Table 8. HDMI 1 CEC expected behavior
33
Page 33

Auto Turn Off TV (S0 -> S5)
On
On
PC Shutdown
TV standby3
Auto Turn On TV (S5 -> S0)
Off
Off
PC On
TV on3
Auto Turn Off TV (S0 -> S3)
On
On
PC Sleep
TV standby3
Auto Turn On TV (S3 -> S0)
Off
Off
PC On
TV on3
Notes:
1. HDMI CEC Control enabled in BIOS Setup and in TV setup, if necessary. Please consult your TV’s documentation.
2. Fast Boot and Deep S4/S5 disabled in BIOS Setup.
3. Results seen with Panasonic LED TV VIERA TH-40A400W. Other TVs may have different results due to variable
implementations of CEC features.
4. PC power off behavior dependent upon power button setting in operating system.
5. If using external CEC adaptor, onboard CEC control must be disabled in BIOS Setup.
34
Figure 8. CEC Connector
Page 34

Product Description
For information about
Refer to
Intel Virtualization Technology
http://www.intel.com/technology/virtualization/technology.htm
For information about
Refer to
Intel Platform Trust Technology
http://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/public/us/en/documents
/white-papers/enterprise-security-platform-trust-technologywhite-paper.pdf
1.12 Intel Platform Security Technologies
Intel platform security technologies provides tools and resources to help the user protect their
information by creating a safer computing environment.
NOTE
Software with security capability is required to take advantage of Intel platform security
technologies.
1.12.1 Intel® Virtualization Technology
Intel Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) is a hardware-assisted technology that, when
combined with software-based virtualization solutions, provides maximum system utilization
by consolidating multiple environments into a single server or client.
NOTE
A processor with Intel VT does not guarantee that virtualization will work on your system. Intel
VT requires a computer system with a chipset, BIOS, enabling software and/or operating
system, device drivers, and applications designed for this feature.
1.12.2 Intel® Platform Trust Technology
Intel® Platform Trust Technology (Intel® PTT) Generation 3 is a platform functionality for
credential storage and key management. Intel® PTT supports Microsoft* BitLocker* Drive
Encryption for hard drive encryption and supports all Microsoft requirements for firmware
Trusted Platform Module (fTPM) 2.0.
NOTE
Support for fTPM version 2.0 requires a true UEFI-enabled operating system, such as Microsoft*
Windows* 10.
CAUTION
BIOS recovery using the BIOS security jumper clears Intel® Platform Trust Technology (Intel®
PTT) keys. These keys will not be restored after the BIOS recovery.
35
Page 35

Page 36

2 Technical Reference
2.1 Memory Resources
2.1.1 Addressable Memory
The board utilizes up to 8 GB of addressable system memory. Typically the address space that is
allocated for PCI Conventional bus add-in cards, PCI Express configuration space, BIOS (SPI Flash
device), and chipset overhead resides above the top of DRAM (total system memory). On a
system that has 8 GB of system memory installed, it is not possible to use all of the installed
memory due to system address space being allocated for other system critical functions. These
functions include the following:
BIOS/SPI Flash device (64 Mbit)
Local APIC (19 MB)
Direct Media Interface (40 MB)
PCI Express configuration space (256 MB)
SoC base address registers PCI Express ports (up to 256 MB)
Memory-mapped I/O (I/O fabric) that is dynamically allocated for PCI Express add-in cards
(256 MB)
The board provides the capability to reclaim the physical memory overlapped by the memory
mapped I/O logical address space. The board remaps physical memory from the top of usable
DRAM boundary to the 4 GB boundary to an equivalent sized logical address range located just
above the 4 GB boundary. All installed system memory can be used when there is no overlap of
system addresses.
2.2 Connectors and Headers
CAUTION
Only the following connectors and headers have overcurrent protection: back panel and front
panel USB.
The other internal connectors and headers are not overcurrent protected and should connect
only to devices inside the computer’s chassis, such as fans and internal peripherals. Do not use
these connectors or headers to power devices external to the computer’s chassis. A fault in the
load presented by the external devices could cause damage to the computer, the power cable,
and the external devices themselves.
Furthermore, improper connection of USB header single wire connectors may eventually
overload the overcurrent protection and cause damage to the board.
Front panel I/O connector
Back panel I/O connectors
37
Page 37

Item
Description
A
Power switch and LED
B
Front panel stereo microphone/headphone jack
C
USB 3.1 Gen2 charging-capable port (amber)
D
USB 3.1 Gen 2 USB Type C
E
CIR
F
Hard drive activity LED
Item
Description
A
RJ45 LAN connector
B
HDMI connector
C
Mini DP connector
D
USB 3.1 Gen2 ports
E
19V DC input jack
2.2.1 Front Panel Connectors
Figure 9 shows the location of the front panel connectors, controls and indicators for the board.
Figure 9. Front Panel Connectors, Controls and Indicators
2.2.2 Back Panel Connectors
Figure 10 shows the location of the back panel connectors for the board.
Figure 10. Back Panel Connectors
38
Page 38

2.2.3 Headers and Connectors (Top)
Item from Figure 11
Description
A
Processor fan header
Figure 11 shows the location of the headers and connectors on the top-side of the board.
Technical Reference
Figure 11. Headers and Connectors (Top)
Table 9 lists the headers and connectors identified in Figure 11.
Table 9. Headers and Connectors Shown in Figure 11
39
Page 39

2.2.4 Connectors and Headers (Bottom)
Figure 12 shows the locations of the connectors and headers on the bottom-side of the board.
40
Figure 12. Connectors and Headers (Bottom)
Page 40

Table 10 lists the connectors and headers identified in Figure 12.
Item from
Figure 12
Description
A
SDXC slot
B, C
Front panel single-port USB 2.0 header (USB1/USB2) (1.25 mm
pitch)
D
M.2 connector
E
SATA 6.0 Gb/s connector
F
BIOS security jumper (BIOS_SEC)
G
RTC Battery connector
H
Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) connector (1.25 mm pitch)
Pin
Signal Name
1, 2, 3, 4
5 V
5
Null
6, 7
3.3 V
8
Null
9, 10
GND
11
Rx Data(Positive)
12
Rx Data(Negative)
13
GND
14
Tx Data(Negative)
15
Tx Data(Positive)
16, 17, 18,
19, 20
GND
Table 10. Connectors and Headers Shown in Figure 12
Technical Reference
Signal Tables for the Connectors and Headers
Table 11. SATA Power Header (0.5 mm Pitch)
41
Page 41

Pin
Signal Name
1
GND
2
Data (positive)
3
Data (negative)
4
+5 V DC
Pin
Signal Name
1
+5VSB
2
Ground
3
CEC_PWR
4
HDMI_CEC
Pin
Signal Name
Descriptive Name
1
CD
Card Detection
2
DATA2
Serial Data 2
3
DATA3
Serial Data 3
4
CMD
Command
5
VSS1
Ground
6
VDD
Power (3.3 V)
7
CLK
Serial Clock
8
VSS2
Ground
9
DATA0
Serial Data 0
10
DATA1
Serial Data 1
11
WP
Write Protect
Table 12. Single-Port Internal USB 2.0 Headers (1.25 mm Pitch)
NOTE
Use only an internal USB connector that conforms to the USB 2.0 specification for high-speed
USB devices.
Table 13. Consumer Electronics Control (CEC) Connector (1.25 mm Pitch)
2.2.4.1 SDXC Card Reader
The board has a standard Secure Digital (SD) card reader that supports the Secure Digital
eXtended Capacity (SDXC) format, 3.01 specification.
Table 14. SDXC Card Reader Connector
42
NOTE
The SD card reader is not supported in Microsoft* Windows* 7
Page 42

Technical Reference
Item
Description
A
CIR Sensor
2.2.4.2 Power Supply Connector
The board has the following power supply connector:
External Power Supply – the board is powered through a 19 V DC connector on the back panel.
The back panel DC connector is compatible with a 5.5 mm/OD (outer diameter) and 2.5
mm/ID (inner diameter) plug, where the inner contact is 19 (±10%) V DC and the shell is GND.
The maximum current rating is 4.74 A.
2.2.4.2.1 Power Sensing Circuit
The board has a power sensing circuit that:
• Manages CPU power usage to maintain system power consumption below 90 W.
• Designed for use with 90 W AC-DC adapters.
2.2.4.3 Consumer Infrared (CIR) Sensor
The Consumer Infrared (CIR) sensor on the front panel provides features that are designed to
comply with Microsoft Consumer Infrared usage models.
The CIR feature is made up of the receiving sensor. The receiving sensor consists of a filtered
translated infrared input compliant with Microsoft CIR specifications.
Customers are required to provide their own media center compatible remote or smart phone
application for use with the Intel NUC. Figure 13 shows the location of the CIR sensor.
Figure 13. Location of the CIR Sensor
43
Page 43

2.3 BIOS Security Jumper
CAUTION
Do not move a jumper with the power on. Always turn off the power and unplug the power cord
from the computer before changing a jumper setting. Otherwise, the board could be damaged.
Figure 14 shows the location of the BIOS security jumper. The 3-pin jumper determines the BIOS
Security program’s mode. Table 15 describes the BIOS security jumper settings for the three
modes: normal, lockdown, and configuration.
44
Figure 14. Location of the BIOS Security Jumper
Page 44

Table 15. BIOS Security Jumper Settings
Function/Mode
Jumper Setting
Configuration
Normal
1-2
The BIOS uses current configuration information and passwords for
booting.
Lockdown
2-3
The BIOS uses current configuration information and passwords for
booting, except:
• All POST Hotkeys are suppressed (prompts are not displayed and keys
are not accepted. For example, F2 for Setup, F10 for the Boot Menu).
• Power Button Menu is not available (see Section 3.7.4 Power Button
Menu).
BIOS updates are not available except for automatic Recovery due to
flash corruption.
Configuration
None
BIOS Recovery Update process if a matching *.bio file is found. Recovery
Update can be cancelled by pressing the Esc key.
If the Recovery Update was cancelled or a matching *.bio file was not
found, a Config Menu will be displayed. The Config Menu consists of the
following (followed by the Power Button Menu selections):
[1] Suppress this menu until the BIOS Security Jumper is replaced.
[2] Clear BIOS User and Supervisor Passwords.
See Section 3.7.4 Power Button Menu.
Technical Reference
45
Page 45

2.4 Mechanical Considerations
2.4.1 Form Factor
The board is designed to fit into a custom chassis. Figure 15 illustrates the mechanical form
factor for the board. Dimensions are given in millimeters. The outer dimensions are
101.60 millimeters by 101.60 millimeters [4.0 inches by 4.0 inches].
46
Figure 15. Board Dimensions
Page 46

Technical Reference
Item
Weight (in kg)
Board with Thermal Solution
0.2
Mini PC (includes Board Assembly, memory,
and drive)
0.66
Item
Chassis Dimensions (WxDxH, in mm)
Tall Kit (includes chassis feet)
117 x 112 x 52
Fan Header
Maximum Available Current
Processor fan
.25 A
Figure 16 shows the height dimensions of the board.
Figure 16. Board Height Dimensions
2.4.2 Weight
Error! Reference source not found. lists select weights of boards and kits and Table 17 lists kit
dimensions.
Table 16. Select Weights and
Table 17. Select Chassis Dimensions
2.5 Electrical Considerations
2.5.1 Power Supply Considerations
System power requirements will depend on actual system configurations chosen by the
integrator, as well as end user expansion preferences. It is the system integrator’s responsibility
to ensure an appropriate power budget for the system configuration is properly assessed based
on the system-level components chosen.
2.5.2 Fan Header Current Capability
Table 18 lists the current capability of the fan header.
Table 18. Fan Header Current Capability
47
Page 47

2.6 Thermal Considerations
CAUTION
A chassis with a maximum internal ambient temperature of 55 oC at the processor fan inlet is
recommended. If the internal ambient temperature exceeds 55 oC, further thermal testing is
required to ensure components do not exceed their maximum case temperature.
CAUTION
Failure to ensure appropriate airflow may result in reduced performance of both the processor
and/or voltage regulator or, in some instances, damage to the board.
All responsibility for determining the adequacy of any thermal or system design remains solely
with the system integrator. Intel makes no warranties or representations that merely following the
instructions presented in this document will result in a system with adequate thermal
performance.
CAUTION
Ensure that the ambient temperature does not exceed the board’s maximum operating
temperature. Failure to do so could cause components to exceed their maximum case
temperature and malfunction. For information about the maximum operating temperature, see
the environmental specifications in Section 2.8.
CAUTION
Ensure that proper airflow is maintained in the processor voltage regulator circuit. Failure to do
so may result in shorter than expected product lifetime. Figure 17 shows the locations of the
localized high temperature zones. Figure 17 shows the locations of the localized high temperature
zones.
Figure 17 shows the locations of the localized high temperature zones.
48
Page 48

Figure 17. Localized High Temperature Zones
Item
Description
A
Thermal solution
B
Processor voltage regulator area
Technical Reference
49
Page 49

Component
Maximum Case Temperature
Processor
For processor case temperature, see processor datasheets and processor
specification updates
Component
Tcontrol
Processor
For processor case temperature, see processor datasheets and processor
specification updates
For information about
Refer to
Processor datasheets and specification updates
Section 1.2, page 19
Table 19 provides maximum case temperatures for the components that are sensitive to thermal
changes. The operating temperature, current load, or operating frequency could affect case
temperatures. Maximum case temperatures are important when considering proper airflow to
cool the board.
Table 19. Thermal Considerations for Components
To ensure functionality and reliability, the component is specified for proper operation when
Case Temperature is maintained at or below the maximum temperature listed in Table 20. This is
a requirement for sustained power dissipation equal to Thermal Design Power (TDP is specified
as the maximum sustainable power to be dissipated by the components). When the component is
dissipating less than TDP, the case temperature should be below the Maximum Case
Temperature. The surface temperature at the geometric center of the component corresponds to
Case Temperature.
It is important to note that the temperature measurement in the system BIOS is a value reported
by embedded thermal sensors in the components and does not directly correspond to the
Maximum Case Temperature. The upper operating limit when monitoring this thermal sensor is
Tcontrol.
Table 20. Tcontrol Values for Components
50
Page 50

Technical Reference
Parameter
Specification
Temperature
Non-Operating
-40 C to +60 C
Operating
0 C to +35 C
The operating temperature of the board may be determined by measuring the air
temperature from the junction of the heatsink fins and fan, next to the attachment
screw, in a closed chassis, while the system is in operation.
Shock
Unpackaged
50 g trapezoidal waveform
Velocity change of 170 inches/s²
Packaged
Free fall package drop machine set to the height determined by the weight of the
package.
Product Weight (pounds)
Free Fall (inches)
<20
36 21-40
30
41-80
24 81-100
18
Vibration
Unpackaged
5 Hz to 20 Hz: 0.01 g² Hz sloping up to 0.02 g² Hz
20 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.02 g² Hz (flat)
Packaged
5 Hz to 40 Hz: 0.015 g² Hz (flat)
40 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.015 g² Hz sloping down to 0.00015 g² Hz
2.7 Reliability
The Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) prediction is calculated using component and
subassembly random failure rates. The calculation is based on the Telcordia SR-332-2 Issue 2,
Method I, Case 3, 55⁰C ambient. The MTBF prediction is used to estimate repair rates and spare
parts requirements. The MTBF for the board is 61,444 hours.
2.8 Environmental
Table 21 lists the environmental specifications for the board.
Table 21. Environmental Specifications
Note: Before attempting to operate this board, the overall temperature of the board must be above the minimum
operating temperature specified. It is recommended that the board temperature be at least room temperature
before attempting to power on the board. The operating and non-operating environment must avoid condensing
humidity.
51
Page 51

Page 52

3 Overview of BIOS Features
3.1 Introduction
The board uses an Intel NUC BIOS that is stored in the Serial Peripheral Interface Flash Memory
(SPI Flash) and can be updated using a disk-based program. The SPI Flash contains the BIOS
Setup program, POST, the PCI auto-configuration utility, LAN EEPROM information, and Plug and
Play support. The initial production BIOSs are identified as INWHL357.
The BIOS Setup program can be used to view and change the BIOS settings for the computer. The
BIOS Setup program is accessed by pressing the <F2> key after the Power-On Self-Test (POST)
memory test begins and before the operating system boot begins.
NOTE
The config menu is displayed only when the board is in configuration mode. Section 2.3 on page
44 shows how to put the board in configuration mode (Jumper removed).
3.2 BIOS Flash Memory Organization
The Serial Peripheral Interface Flash Memory (SPI Flash) includes a 128 Mb (16384 KB) flash
memory device.
3.3 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS)
SMBIOS is a Desktop Management Interface (DMI) compliant method for managing computers in
a managed network.
The main component of SMBIOS is the Management Information Format (MIF) database, which
contains information about the computing system and its components. Using SMBIOS, a system
administrator can obtain the system types, capabilities, operational status, and installation dates
for system components. The MIF database defines the data and provides the method for
accessing this information. The BIOS enables applications such as third-party management
software to use SMBIOS. The BIOS stores and reports the following SMBIOS information:
BIOS data, such as the BIOS revision level
Fixed-system data, such as peripherals, serial numbers, and asset tags
Resource data, such as memory size, cache size, and processor speed
Dynamic data, such as event detection and error logging
Non-Plug and Play operating systems require an additional interface for obtaining the SMBIOS
information. The BIOS supports an SMBIOS table interface for such operating systems. Using
this support, an SMBIOS service-level application running on a non-Plug and Play operating
system can obtain the SMBIOS information. Additional board information can be found in the
BIOS under the Additional Information header under the Main BIOS page.
53
Page 53

3.4 Legacy USB Support
Legacy USB support enables USB devices to be used even when the operating system’s USB
drivers are not yet available. Legacy USB support is used to access the BIOS Setup program, and
to install an operating system that supports USB. However, this requires the addition of USB 3.1
drivers to the operating system image prior to beginning installation. By default, Legacy USB
support is set to Enabled.
Legacy USB support operates as follows:
1. When you apply power to the computer, legacy support is disabled.
2. POST begins.
3. Legacy USB support is enabled by the BIOS allowing you to use a USB keyboard to enter and
configure the BIOS Setup program.
4. POST completes.
5. The operating system loads. While the operating system is loading, USB keyboards and mice
are recognized and may be used to configure the operating system. (Keyboards and mice are
not recognized during this period if Legacy USB support was set to Disabled in the BIOS
Setup program.)
6. After the operating system loads the USB drivers, all legacy and non-legacy USB devices are
recognized by the operating system, and Legacy USB support from the BIOS is no longer
used. This requires the operating system to have USB 3.1 driver support in order to recognize
devices attached to any of the Intel NUC’s external USB ports.
To install an operating system that supports USB, verify that Legacy USB support in the BIOS
Setup program is set to Enabled and follow the operating system’s installation instructions.
3.5 BIOS Updates
The BIOS can be updated using either of the following utilities, which are available on the Intel
World Wide Web site:
Intel® Firmware Update Utility for Windows with a single .exe, which enables automated
updating while in the Windows environment. Using this utility, the BIOS can be updated from
a file on a hard disk, a USB drive (a flash drive or a USB hard drive), or from the file location on
the Web.
Intel® Firmware Update Utility, which support working on Windows, EFI shell and Linux
operating systems. Using this utility, the BIOS can be updated from a file on a hard disk, or a
USB drive (a flash drive or a USB hard drive).
Intel F7 switch during POST allows a user to select where the BIOS .CAP file is located and
perform the update from that location/device. Similar to performing a BIOS Recovery without
removing the BIOS configuration jumper.
All utilities verify that the updated BIOS matches the target system to prevent accidentally
installing an incompatible BIOS.
NOTE
Review the instructions distributed with the upgrade utility before attempting a BIOS update.
54
Page 54

Overview of BIOS Features
Media Type
(Note)
Can be used for BIOS recovery?
Hard disk drive (connected to SATA or USB)
Yes
USB flash drive
Yes
USB diskette drive (with a 1.4 MB diskette)
No (BIOS update file is bigger than 1.4 MB size limit)
For information about
Refer to
BIOS recovery
http://www.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb/CS-034524.htm
3.5.1 Language Support
The BIOS Setup program and help messages are supported in US English. Check the Intel web
site for support.
3.6 BIOS Recovery
It is unlikely that anything will interrupt a BIOS update; however, if an interruption occurs, the
BIOS could be damaged. Table 22 lists the drives and media types that can and cannot be used
for BIOS recovery. The BIOS recovery media does not need to be made bootable.
Table 22. Acceptable Drives/Media Types for BIOS Recovery
NOTE
Supported file systems for BIOS recovery:
NTFS (sparse, compressed, or encrypted files are not supported)
FAT32
FAT16
FAT12
3.7 Boot Options
In the BIOS Setup program, the user can choose to boot from a hard drive, optical drive,
removable drive, or the network. The default setting is for the optical drive to be the first boot
device, the hard drive second, removable drive third, and the network fourth.
NOTE
Optical drives are not supported by the onboard SATA connectors. Optical drives are supported
only via the USB interfaces.
3.7.1 Network Boot
The network can be selected as a boot device. This selection allows booting from the onboard
LAN or a network add-in card with a remote boot ROM installed.
55
Page 55

Boot Device Menu Function Keys
Description
<> or <>
Selects a default boot device
<Enter>
Exits the menu, and boots from the selected device
<Esc>
Exits the menu and boots according to the boot priority defined
through BIOS setup
Pressing the <F12> key during POST automatically forces booting from the LAN. To use this key
during POST.
3.7.2 Booting Without Attached Devices
For use in embedded applications, the BIOS has been designed so that after passing the POST,
the operating system loader is invoked even if the following devices are not present:
Video adapter
Keyboard
Mouse
3.7.3 Changing the Default Boot Device During POST
Pressing the <F10> key during POST causes a boot device menu to be displayed. This menu
displays the list of available boot devices. Table 23 lists the boot device menu options.
Table 23. Boot Device Menu Options
56
Page 56

Overview of BIOS Features
3.7.4 Power Button Menu
The Power Button Menu is accessible via the following sequence:
1. System is in S4/S5 (not G3)
2. User pushes the power button and holds it down
3. The power LED will change to its secondary color to signal the user to release the power
button (approximately 3 seconds) then stop. Release immediately.
4. User releases the power button before the 4-second shutdown override.
If this boot path is taken, the BIOS will use default settings of Performance settings, ignoring
settings in VPD where possible.
The BIOS will display the following prompt and wait for a keystroke:
[ESC] Normal Boot
[F2] BIOS Setup Menu
[F3] Disable Fast Boot
[F4] BIOS Recovery
[F7] Update BIOS
[F10] Enter Boot Menu
[F12] Network Boot
[F3] Disable Fast Boot is only displayed if at least one Fast Boot optimization is enabled.
If an unrecognized key is hit, then the BIOS will do nothing and wait for another keystroke. If one
of the listed hotkeys is hit, the BIOS will follow the indicated boot path. Password requirements
must still be honored.
If Disable Fast Boot is selected, the BIOS will disable all Fast Boot optimizations and reset the
system.
57
Page 57

Password Set
Password During Boot
Neither
None
Master only
None
User only
User
Master and User Set
User (Clear Master password in BIOS
setup will clear both Master and
User passwords)
3.8 Hard Disk Drive Password Security Feature
The Hard Disk Drive Password Security feature blocks read and write accesses to the hard disk
drive until the correct password is given. Hard Disk Drive Passwords are set in BIOS SETUP and
are prompted for during BIOS POST. For convenient support of S3 resume, the system BIOS will
automatically unlock drives on resume from S3. Valid length for passwords is 32 characters for
max. Valid characters for passwords are ASCII codes between 0x20 and 0x7E, which includes
numbers/English characters and special characters.
The User hard disk drive password, when installed, will be required upon each power-cycle until
the Master Key or User hard disk drive password is submitted.
The Master Key hard disk drive password, when installed, will not lock the drive. The Master Key
hard disk drive password exists as an unlock override in the event that the User hard disk drive
password is forgotten. Only the installation of the User hard disk drive password will cause a hard
disk to be locked upon a system power-cycle.
Table 24 shows the effects of setting the Hard Disk Drive Passwords.
Table 24. Master Key and User Hard Drive Password Functions
NOTE
The passwords are stored on the hard disk drive so if the drive is relocated to another computer
that does not support Hard Disk Drive Password Security feature, the drive will not be accessible.
Currently, there is no industry standard for implementing Hard Disk Drive Password Security on
AHCI or NVME drives. Hard drive encryption can still be implemented and does not require Hard
Disk Drive Password Security.
3.9 BIOS Security Features
The BIOS includes security features that restrict access to the BIOS Setup program and who can
boot the computer. A supervisor password and a user password can be set for the BIOS Setup
program and for booting the computer, with the following restrictions:
The supervisor password gives unrestricted access to view and change all the Setup options
in the BIOS Setup program. This is the supervisor mode.
The user password gives restricted access to view and change Setup options in the BIOS
Setup program. This is the user mode.
If only the supervisor password is set, pressing the <Enter> key at the password prompt of
the BIOS Setup program allows the user restricted access to Setup.
58
Page 58

Overview of BIOS Features
Password Set
Supervisor Mode
User Mode
Setup Options
Password to
Enter Setup
Password
During Boot
Neither
Can change all
options
(Note)
Can change all
options
(Note)
None
None
None
Supervisor only
Can change all
options
Can change a
limited number
of options
Supervisor Password
Supervisor
None
User only
N/A
Can change all
options
Enter Password
Clear User Password
User
User
Supervisor and
user set
Can change all
options
Can change a
limited number
of options
Supervisor Password
Enter Password
Supervisor or
user
Supervisor or
user
If both the supervisor and user passwords are set, users can enter either the supervisor
password or the user password to access Setup. Users have access to Setup respective to
which password is entered.
Setting the user password restricts who can boot the computer. The password prompt will be
displayed before the computer is booted. If only the supervisor password is set, the
computer boots without asking for a password. If both passwords are set, the user can enter
either password to boot the computer.
For enhanced security, use different passwords for the supervisor and user passwords.
Valid characters for passwords are ASCII codes between 0x20 and 0x7E, which includes
numbers/English characters and special characters. Valid length for passwords is 2 to 20
characters.
To clear a set password, enter a blank password after entering the existing password.
Table 25 shows the effects of setting the supervisor password and user password. This table is
for reference only and is not displayed on the screen.
Table 25. Supervisor and User Password Functions
Note: If no password is set, any user can change all Setup options.
59
Page 59

Type
Pattern
Note
BIOS update in progress
The BIOS will blink the front panel power LED during
flash update 0.5 sec On, then 1.5 sec Off. The pattern
repeats until the BIOS update is complete.
Memory error
On-off (1.0 second each) three times, then 2.5-second
pause (off), entire pattern repeats (blinks and pause)
until the system is powered off.
Thermal trip warning
Following the blink pattern: .25 seconds on, .25
seconds off, .25 seconds on, .25 seconds off in a total
of 16 blinks.
4 Error Messages and Blink Codes
4.1 Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes
Whenever a recoverable error occurs during POST, the BIOS causes the board’s front panel
power LED to blink an error message describing the problem (see Table 26).
Table 26. Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes
Note: Disabled per default BIOS setup option.
60
Page 60

Regulatory Compliance and Battery Disposal Information
Item from Figure 18
Description
Kensington* Anti-Theft Key Lock Hole
SD Card Reader
Power Switch and Power LED
Speaker/Headset Jack
USB 3.1 Gen2 Connectors
Consumer Infrared Sensor
5 Intel NUC Kit Features
5.1 Chassis Front Panel Features
Intel NUC Boards NUC8INB can be found integrated into Intel® NUC Mini PC
NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH. Figure 18 shows the location of the features located on or near the front
of the chassis.
Figure 18. Intel® NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH Features – Front
Table 27 lists the components identified in Figure 18.
Table 27. Components Shown in Figure 18
61
Page 61

Item from Figure 19
Description
19V DC Power Inlet
Cooling Vents
Speaker and Optical Audio Jack
High Definition Multimedia Interface Connectors
Ethernet Port
USB 3.1 Gen2 Connectors
Mini Display Port
5.2 Chassis Rear Panel Features
Figure 19 shows the location of the features located on the rear of the chassis.
Figure 19. Intel® NUC Products NUC8i5INH/NUC8i7INH Features – Rear
Table 28 lists the components identified in Figure 19.
Table 28. Components Shown in Figure 19
62
 Loading...
Loading...