Page 1

IP Media Server for Host Media
Processing
Demo Guide
July 2005
05-2389-003
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY
ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN
INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES
RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
This IP Media Server for Host Media Processing Demo Guide as well as the software described in it is furnished under license and may only be used
or copied in accordance with the terms of the license. The information in this manual is furnished for informational use only, is subject to change
without notice, and should not be construed as a commitment by Intel Corporation. Intel Corporation assumes no responsibility or liability for any
errors or inaccuracies that may appear in this document or any software that may be provided in association with this document.
Except as permitted by such license, no part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any
means without express written consent of Intel Corporation.
Copyright © 2003, Intel Corporation
BunnyPeople, Celeron, Chips, Dialogic, EtherExpress, ETOX, FlashFile, i386, i486, i960, iCOMP, InstantIP, Intel, Intel Centrino, Intel Centrino logo,
Intel logo, Intel386, Intel486, Intel740, IntelDX2, IntelDX4, IntelSX2, Intel Inside, Intel Inside logo, Intel NetBurst, Intel NetMerge, Intel NetStructure,
Intel SingleDriver, Intel SpeedStep, Intel StrataFlash, Intel Xeon, Intel XScale, IPLink, Itanium, MCS, MMX, MMX logo, Optimizer logo, OverDrive,
Paragon, PDCharm, Pentium, Pentium II Xeon, Pentium III Xeon, Perfor mance at Your Command, skoool, Sound Mark, The Computer Inside., The
Journey Inside, VTune, and Xircom are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other
countries.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Publication Date: July 2005
Document Number: 05-2389-003
Intel Converged Communications, Inc.
1515 Route 10
Parsippany, NJ 07054
For Technical Support, visit the Intel Telecom Support Resources website at:
http://developer.intel.com/design/telecom/support
For Products and Services Information, visit the Intel Telecom Products website at:
http://www.intel.com/design/network/products/telecom
For Sales Offices and other contact information, visit the Where to Buy Intel Telecom Products page at:
http://www.intel.com/buy/networking/telecom.htm
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide – July 2005
Page 3

Contents
Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
About This Publication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1 Demo Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2 System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.1 Hardware Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.2 Software Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3 Preparing to Run the Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.1 Editing Configuration Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.1.1 Configuration File Location . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.1.2 Editing the IPMediaServer.cfg Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.2 Compiling and Linking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
4 Running the Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.1 Starting the Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.2 Demo Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4.3 Using the Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.3.1 Keyboard Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.3.2 Using the Media Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.4 Stopping the Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5Demo Details. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.1 Files Used by the Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.1.1 Demo Source Code Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.1.2 PDL Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
5.2 Programming Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
5.2.1 Module Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
5.2.2 EventRouter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.2.3 Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
5.2.4 Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
5.3 Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5.4 Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5.5 Event Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
5.5.1 Event Mechanism . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
5.5.2 Handling Keyboard Input Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
5.5.3 Handling SRL Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
5.5.4 Handling Application Exit Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
5.5.5 TSUsrEvent Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
5.6 Typical Scenario . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide – July 2005 3
Page 4

Contents
Figures
1 Demo Voice Menu Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
2 IP Media Server Demo Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3 EventRouter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
4 IP Media Server Demo Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
5 System Initialization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
6 Typical Scenario: Call Offered . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
7 Typical Scenario: Play Prompts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
8 Typical Scenario: Fax Mailbox . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
9 Typical Scenario: Establish Fax Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
10 Typical Scenario: Fax Session Established . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
11 Typical Scenario: Fax Sent. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
12 Typical Scenario: Fax Session Closed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
13 Typical Scenario: Fax Complete. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
4 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide – July 2005
Page 5

Contents
Tables
1 Command Line Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2 Runtime Keyboard Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3 Files in IPMediaServer Folder Used by the IP Media Server Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4 Files in Modules Folder Used by the IP Media Server Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
5 PDL Files Used by the IP Media Server Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6 Application Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
7 IP Module Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
8 Voice Module Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
9 Fax Module Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide – July 2005 5
Page 6

Contents
6 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide – July 2005
Page 7
Revision History
This revision history summarizes the changes made in each published version of this document.
Document No. Publication Date Description of Revisions
05-2389-003 July 2005 Added updated Linux information.
05-2389-002 April 2005 Globally changed file paths to use installation directory environment variable, and to
reflect latest Windows directory hierarchy
Globally removed Linux-specific information and references to pre-1.3 HMP releases
Demo Description chapter : Added note about channel density and numbering
restrictions
Demo Voice Menu Flowchart figure : Multiple minor updates for clarity
05-2389-001 September 2004 Initial version under this title and part number as an HMP-specific document. Much of
the information contained in this document was previously published in the IP Media
Server (Global Call) Demo Guide for Windows Operating Systems, document
number 05-2065-001. The following changes were made in preparing this document:
Software Requirements section: Added HMP 1.2 Linux and HMP 1.1 Windows FP1
releases with description of differences
Configuration File Location section: Added location info for Linux
Editing the IPMediaServer.cfg Configuration File section: Updated descriptions of
QoS attributes to match IPML API Reference. Updated sample configuration file
listing.
Compiling and Linking section: Added compile info for Linux
Starting the Demo section : Added file location info for Linux
Using the Media Server section: Added CSP Barge-in to Main Menu listing.
Corrected description of CSP Prompt.
Demo Voice Menu Flowchart figure : Corrected description of CSP Prompt. Clarified
descriptions of fax prompts.
Demo Source Code Files section: Added Linux directory info. Added Linux makefiles
to file lists.
PDL Files section: Added file location info for Linux. Added Linux makefile to file list.
Application Classes table: Changed module order (now IP last) in description of init
method
Initialization section: Changed module initialization order (now IP last)
System Initialization figure: Changed module initialization order (now IP last)
Handling Application Exit Events section: Deleted Ctrl+C
TSUsrEvent Structure section: Updated field descriptions
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 7
Page 8

Revision History
8 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 9

About This Publication
This section describes the purpose of the guide, the intended audience, and provides references to
other documents that may be useful to the user.
• Purpose
• Intended Audience
• How to Use This Publication
• Related Information
Purpose
This guide provides information on the IP Media Server for HMP demo that is available with the
Intel NetStructure
its requirements, and provides details on how it works.
This guide specifically documents the IP Media Server for HMP demo as it is implemented and
supplied in the Host Media Processing Software 1.3 for Windows*, Host Media Processing
Software 1.5 for Linux* and later releases.
Note that the IP Media Server demo that is supplied with Intel
software has significantly different functionality than the Host Media Processing implementation,
and is therefore described in a separate Demo Guide document.
®
Host Media Processing Software product. The guide describes the demo, lists
®
Dialogic® System Release 6.x
Intended Audience
This guide is intended for application developers who will be developing a media server
application using the Global Call API. Developers should be familiar with the C++ programming
language and either the Windows or Linux programming environments.
This information is intended for:
• Distributors
• Toolkit Developers
• Independent Software Vendors (ISVs)
• Value Added Resellers (VARs)
• Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs)
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 9
Page 10

About This Publication
How to Use This Publication
Refer to this publication after you have installed the hardware and the system software.
This publication assumes that you are familiar with the Windows or Linux operating system and
the C++ programming language.
The information in this guide is organized as follows:
• Chapter 1, “Demo Description” introduces you to the demo and its features
• Chapter 2, “System Requirements” outlines the hardware and software required to run the
demo
• Chapter 3, “Preparing to Run the Demo” describes the preparations required before running
the demo
• Chapter 4, “Running the Demo” describes how to run the demo
• Chapter 5, “Demo Details” provides details on how the demo works
Related Information
See the following for more information:
• Intel NetStructure Host Media Processing Software Release Guide
• Global Call IP for Host Media Processing Technology Guide
• Global Call API Library Reference
• Voice API Programming Guide
• Voice API Library Reference
• Standard Runtime Library API Programming Guide
• Standard Runtime Library API Library Reference
• Fax Software Reference
• http://developer.intel.com/design/telecom/support/ (for technical support)
• http://www.intel.com/design/network/products/telecom (for product information)
10 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 11

1.Demo Description
This chapter describes the basic features of the IP Media Server for HMP demo.
The IP Media Server for HMP demo is an object-oriented host-based application that demonstrates
using the Global Call API to build an IP media server, providing voice and fax services via IP
technology. The demo source code can be used as sample code for those who want to begin
developing an application from a working application.
Note: The IP Media Server for HMP demo is limited to a maximum of four simultaneous channels.
Additionally, the channel numbers used must be below 120; the demo will fail to run if you attempt
to use a channel number higher than 120.
The IP Media Server for HMP demo supports the following features:
• Voice service
• Fax service
• CSP barge in
• Configuration file
• Command line options
Note: The IP Media Server for HMP demo does not function as a gateway. Therefore, it can only answer
calls from the IP network. Gateway functionality can be added by writing additional software code
within the IP module that will allow it to make outgoing calls to the IP network, and connecting a
gateway to interface with the PSTN.
1
The IP Media Server for HMPIP Media Server (Global Call) demo is a cross-OS demo, designed to
run under both the Windows and Linux environments. Most of the differences in the environments
are handled directly by the programming interface and are transparent to the user. Other
differences, due to inherent differences in the operating systems, are handled by the Platform
Dependency Library (PDL). For more information about the PDL refer to the source code in the
pdl_win or pdl_linux directories directory.
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 11
Page 12

Demo Description
12 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 13

2.System Requirements
This chapter discusses the system requirements for running the IP Media Server for HMP demo. It
contains the following topics:
• Hardware Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
• Software Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.1 Hardware Requirements
To run the IP Media Server for HMP demo, you need:
®
• Intel
• CD-ROM drive
• VGA display
• Pointing device (e.g., mouse)
• 100Base-T network interface card (NIC)
Pentium® III processor (minimum requirement). For detailed processor clock speed and
memory requirements, refer to the Release Guide (or Release Notes) for the HMP version you
are using.
Note: A 1000Base-T NIC will yield better performance.
2
Memory Requirements
For production purposes, a minimum of 512 MB of memory is required. For development and
demo purposes using a low-end configuration, 256 MB of memory may be sufficient.
IP Endpoints
The following H.323 IP devices were tested for interoperability with HMP:
• Microsoft* NetMeeting* (Version 3.0 or later)
• Polycom* SoundPoint* IP 500
• Intel NetStructure
• Intel Optimizers Internet Phone
The following SIP IP devices were tested for interoperability with HMP:
• Polycom SoundPoint IP 500
• Intel NetStructure PBX-IP Media Gateway
®
PBX-IP Media Gateway
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 13
Page 14

System Requirements
2.2 Software Requirements
To run the IP Media Server for HMP demo as documented in this guide, you need one of the
following software releases:
• Intel NetStructure Host Media Processing Software 1.3 for Windows (or later)
• Intel NetStructure Host Media Processing Software 1.5 for Linux (or later)
For operating system requirements, see the release documentation (Release Guide or Release
Notes) that accompanies your specific HMP release.
14 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 15

3.Preparing to Run the Demo
This chapter discusses the preparations necessary to run the IP Media Server for HMP demo. It
provides information about the following topics:
• Editing Configuration Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
• Compiling and Linking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.1 Editing Configuration Files
This section discusses how to configure the demo for your system. It contains the following topics:
• Configuration File Location
• Editing the IPMediaServer.cfg Configuration File
3.1.1 Configuration File Location
Before running the IP Media Server for HMP demo, modify the IPMediaServer.cfg file to reflect
your system environment. Use a text editor and open the file from the following location:
3
Windows
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\Demos\IPMediaServer\Release
Linux
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/demos/IPMediaServer/Release
3.1.2 Editing the IPMediaServer.cfg Configuration File
Below is an example of the IPMediaServer.cfg file. Update the following information:
ipProtocolName
The IP protocol for opening IP line devices. Possible vlues are:
• H323
• SIP
• both
DTMFmode
Specifies how DTMF tones are transmitted. Possible values are:
• OutofBand – usually used with low bandwith coders, such as GSM
Note: OutofBand is used for H.323 only.
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 15
Page 16

Preparing to Run the Demo
• InBand – usually used with G.711 coders
• RFC2833
Capability
Describes the transmit and receive coders. See the Global Call IP Technology Guide for
specific information about coder support. The parameters are as follows:
• TxType – the transmit voice coder
Note: By default, the fax demo is turned off. This feature may be enabled when tested with
T.38 capable IP endpoints. To do this, “uncomment” the line
in this section by removing the # from the start of the line, or add the line if not
present.
• TxFramesPerPkt – the number of frames per packet for the selected Tx coder
• TxVAD – specifies if VAD is active for the selected Tx coder
• RxType – the receive voice coder
• RxFramesPerPkt – the number of frames per packet for the selected Rx coder
Note: The G.711 coder defines frames per packet using the packet size in milliseconds, i.e.
10, 20, or 30 milliseconds. Refer to the Sample Configuration File, below, for the
correct syntax for all the parameters.
• RxVAD – specifies if VAD is active for the selected Rx coder
Quality of Service
The application can set threshold values to monitor the quality of service during calls. A fault
occurs when the result of a measurement of a QoS parameter crosses a predefined threshold. A
success occurs when the result of a measurement of a QoS parameter dis not cross a predefined
threshold. The QoS parameters are measured during time intervals, starting when a call is
established. The following parameters are supported:
• MediaAlarmLostPackets – monitors the number of lost IP packets during a call
• MediaAlarmJitter – monitors the jitter (as defined in RFC 1889) during IP transmission
TxType = t38UDPFax
QoS Attributes
The threshold for each QoS parameter is measured with the following six attributes:
• Threshold – defines when a QoS parameter is in a fault condition. A fault occurs when the
result of a measurement of a QoS parameter crossed the Threshold value.
• DebounceOn – the time during which faults are measured (in msec., must be multiple of
Interval)
• DebounceOff – the time during which successes are measured (in msec., must be multiple
of Interval)
• Interval – the amount of time between two QoS parameter measurements (in multiples of
100 msec)
• Percent_Fail – used to detect failure condition, together with DebounceOn (expressed as
a percentage of failures)
• Percent_Success – used to detect failure recovery, together with DebounceOff (expressed
as a percentage of successes)
The default values are as follows:
QoS Type Threshold DebounceOn DebounceOff Interval
Lost packets 20 10000 10000 1000 60 40
Jitter 60 20000 60000 5000 60 40
Percent_
Fail
Percent_
Success
16 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 17

Preparing to Run the Demo
Sample Configuration File
################################################################################################
# IP Protocol :
# The IP Protocol used for opening the IP Line devices, values: H323, SIP, both
#
# DTMFmode
# possible options:
# OutOfBand, inband, rfc2833
#
# Capability posiblities:
# g711Alaw
# g711Mulaw
# gsm
# gsmEFR
# g723_5_3k
# g723_6_3k
# g729a
# g729ab
# t38UDPFax
#
# Note: if you want to run the demo with coder g729 use:
# g729a for running with VAD disable
# and 729ab for running with VAD enable
#
# Caution:
# If capability is g711Alaw /Mulaw ==> FramesPerPkt = 10,20,30.
# G711 frame per packet defines the packet size in
# milliseconds
# If capability is g723_5_3k / 6_3k ==> FramesPerPkt = 1, 2, 3 .
# FrameSize isn't needed, default= 30ms.
# If capability is gsm ==> FramesPerPkt = 1, 2, 3 .
# FrameSize isn't needed, default= 20ms.
# If capability is gsmEFR ==> FramesPerPkt = 1, 2, 3 .
# FrameSize isn't needed, default= 20ms.
# If capability is g729a ==> FramesPerPkt = 3, 4 .
# FrameSize isn't needed, default= 10ms.
# VAD disable, the VAD parameter is ignored
# If capability is g729ab ==>FramesPerPkt = 3, 4 .
# FrameSize isn't needed, default= 10ms.
# VAD enable, the VAD parameter is ignored
#
################################################################################################
ipProtocolName = H323
DTMFmode = inBand
Channel = 1-120
{
Capability
{
# TxType = g711Alaw
# TxFramesPerPkt = 30
# TxVAD = 0
# RxType = g711Alaw
# RxFramesPerPkt = 30
# RxVAD = 0
TxType = g711Mulaw
TxFramesPerPkt = 20
TxVAD = 0
RxType = g711Mulaw
RxFramesPerPkt = 20
RxVAD = 0
# TxType = t38UDPFax
}
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 17
Page 18

Preparing to Run the Demo
MediaAlarmLostPackets
{
Threshold = 20 # Threshold value
DebounceOn = 10000 # Threshold debounce ON
DebounceOff = 10000 # Threshold debounce OFF
Interval = 1000 # Threshold Time Interval (ms)
PercentSuccess = 60 # Threshold Success Percent
PercentFail = 40 # Threshold Fail Percent
}
MediaAlarmJitter
{
Threshold = 60 # Threshold value
DebounceOn = 20000 # Threshold debounce ON
DebounceOff = 60000 # Threshold debounce OFF
Interval = 5000 # Threshold Time Interval (ms)
PercentSuccess = 60 # Threshold Success Percent
PercentFail = 40 # Threshold Fail Percent
}
# MediaAlarmResetAlarmState = 0
}
3.2 Compiling and Linking
Compile the IP Media Server demo project within one of the following environments:
Windows
To compile the IP Media Server demo on a Windows system, use Microsoft* Visual Studio* 6.0
with Service Pack 5.
Set IPMediaServer as the active project and build.
Linux
To compile the IP Media Server demo on a Linux system, use gcc version 3.2.3.
To compile the entire project, go to the directory
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/demos/IPMediaServer and issue the commands:
make clean
make
To compile an individual module, go to the specific module directory (for example,
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/demos/IPMediaServer/Modules/FaxModule for the fax module), and
issue the commands:
make clean
make
18 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 19

4.Running the Demo
This chapter discusses how to run the IP Media Server for HMP demo. It contains the following
topics:
• Starting the Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
• Demo Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
• Using the Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
• Stopping the Demo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
4.1 Starting the Demo
The demo executable file for the IP Media Server for HMP can be started as follows:
Windows
From a command prompt window, change to the directory:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\Demos\IPMediaServer\Release
4
Type
IPMediaServer to run the IP Media Server for HMP demo using the default settings.
Linux
Change to the directory:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/demos/IPMediaServer/Release
IPMediaServer to run the IP Media Server for HMP demo using the default settings.
Type
4.2 Demo Options
To specify certain options at run-time, launch the demo from a command line, using any of the
switches listed in Table 1.
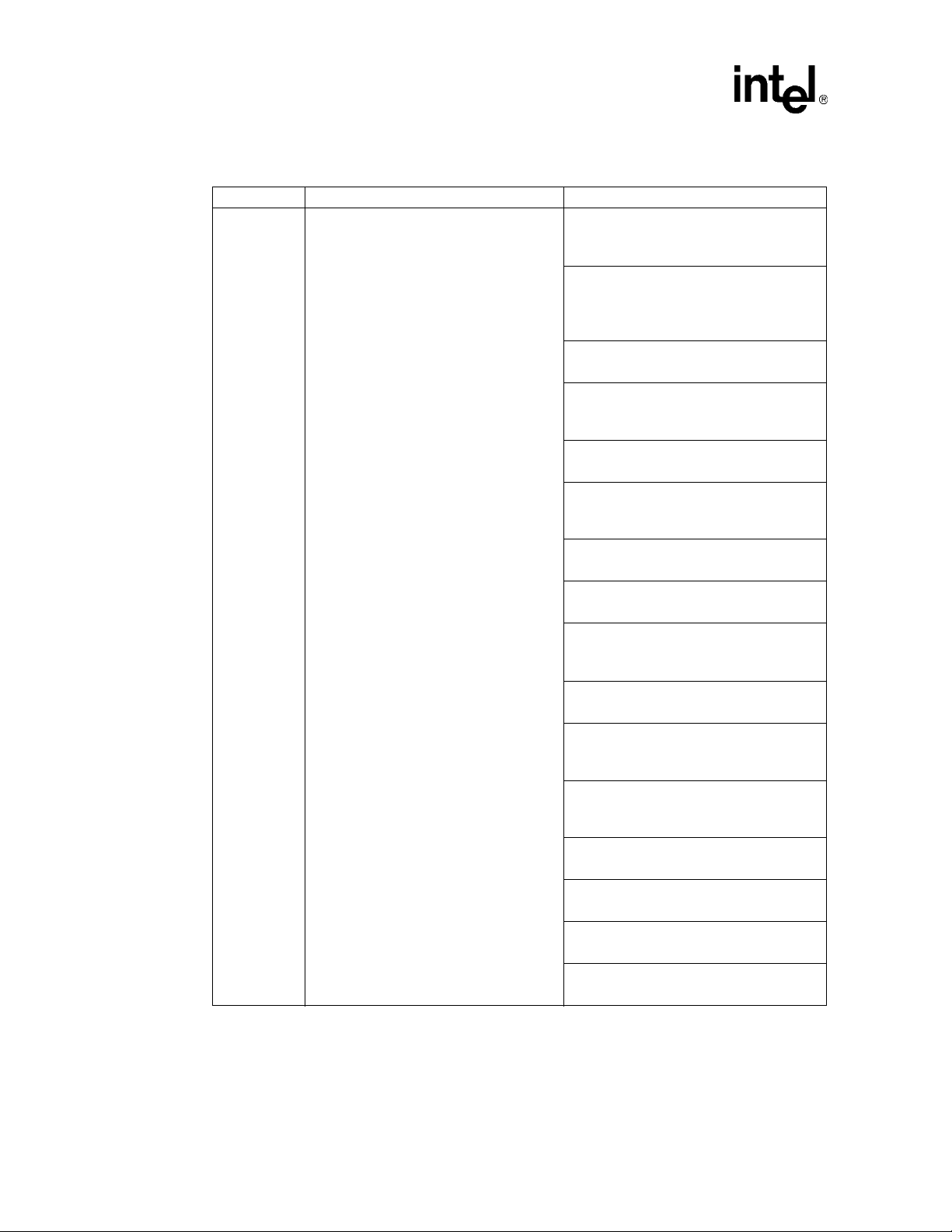
Table 1. Command Line Switches
Switch Action Default
-c<filename> Configuration file name -cIPMediaServer.cfg
-e<encoding type> Sets the encoding type:
-h or ? Prints the command syntax to the screen Off
•m – mu-law
•a – A-law
-em
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 19
Page 20

Running the Demo
Table 1. Command Line Switches (Continued)
-n<n> Sets the number of channels The lesser of Voice Devices
-q Activates Quality of Service Disabled
Example
The following example shows how to launch the demo from a command line with options:
IPMediaServer -n64 -cmyconfig.cfg -ea
This command launches the demo with 64 channels, using the myconfig.cfg configuration file and
A-law encoding.
4.3 Using the Demo
This section describes how to use the IP Media Server for HMP demo and contains the following
topics:
• Keyboard Commands
• Using the Media Server
or IP devices
4.3.1 Keyboard Commands
The demo always waits for input from the keyboard. While the demo is running, you may enter any
of the commands listed in Table 2.
Table 2. Runtime Keyboard Commands
Command Function
q or Q or Ctrl+c Terminates the application
4.3.2 Using the Media Server
The IP Media Server for HMP demo allows the caller to interact with a series of voice menus, using
the telephone keypad to enter an option. Basic operations include playing a pre-recorded message,
recording a new message, sending or receiving a fax, and barge-in for CSP. Each menu prompts the
caller to select an action by pushing a key. The call state within which the menu is called is
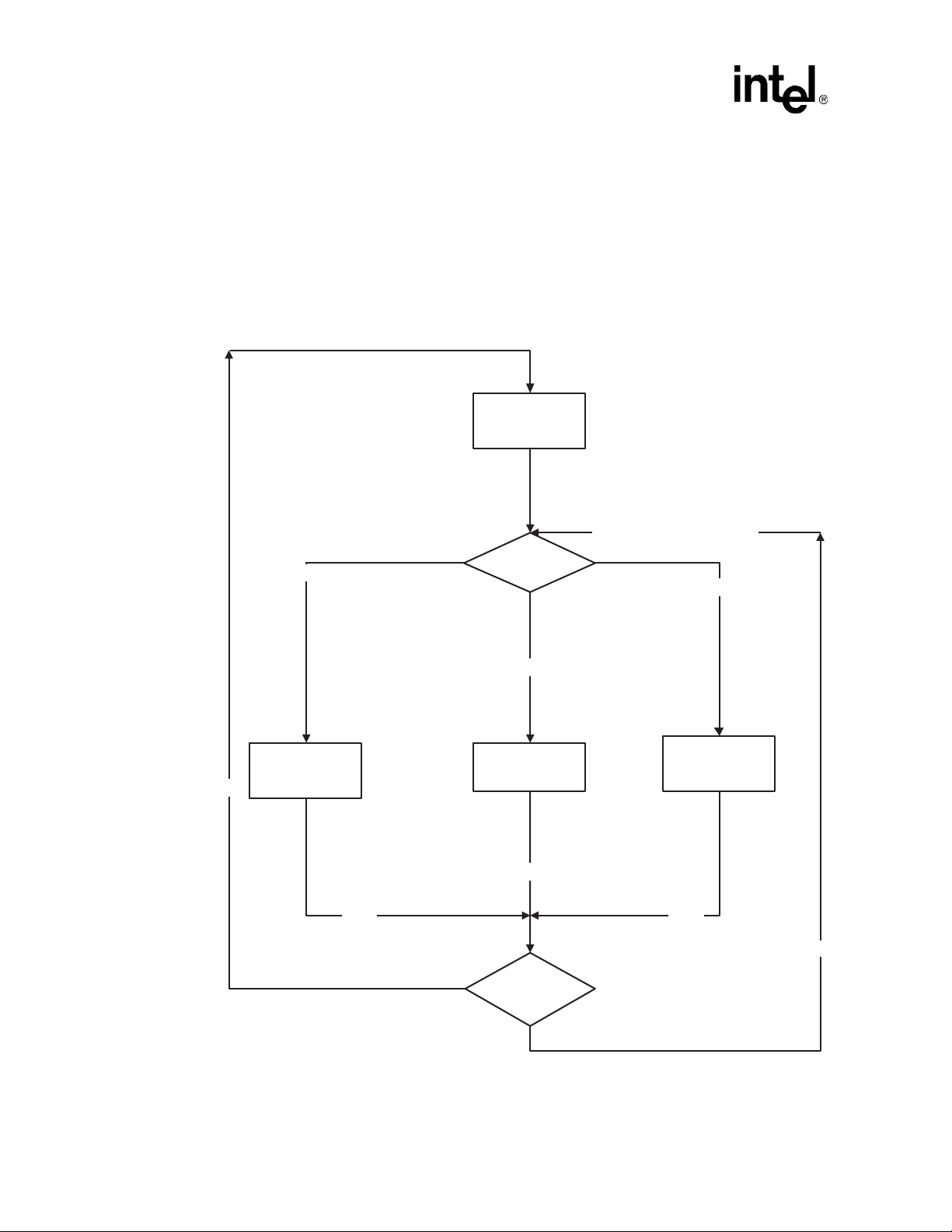
indicated by the square brackets. Figure 1 shows the voice prompt flow, grouping the prompts by
feature (voice, fax, CSP).
Note: By default, the fax demo is turned off. This feature may be enabled when tested with T.38 capable
IP endpoints. To do this, uncomment the line:
TxType = t38UDPFax
in the Capability section of the IPMediaServer.cfg file (or add the line if not present as a comment).
20 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 21

Main Menu [Main_Menu]
1 - Voice Mail
2 - Fax
3 - Conferencing (not supported in HMP 1.x)
4 - CSP Barge-in
* - Quit
Voice Mail Menu [Voicemail_Menu]
1 - Record Message
2 - Listen to message from a mailbox
* - Quit
Send Message Prompt [SendMsg_Menu]
Enter Mailbox Number - between 101 - 299
* - Quit
Start Record Prompt [Record_Menu]
Running the Demo
2 - Start Record
Press 2 at end of message to stop recording (at end, Stop Record Prompt is played)
* - Quit
Stop Record Prompt [StopRec_Menu]
2 - Discard Message and re-record message to same mailbox
3 - Confirm Message [Save_Confirm]
4 - Listen to Message (and replay Stop Record Prompt)
* - Quit without saving
Confirm Message Saved [StopRec_Menu]
1 - Record a message
2 - Listen to a message from a mailbox
* - Quit
Listen to Message Prompt [ListenMsg_Menu]
Enter Mailbox Number - between 101 - 299 (Recorded message is played)
* - Quit
Stop Listen Prompt [Listening]
2 - Discard message and quit
* - Save message and quit
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 21
Page 22

Running the Demo
Fax Menu [Fax_Menu]
1 - Send fax (to the IP Media Server demo)
2 - Receive fax (sent from the IP Media Server demo)
* - Quit
Send Fax Prompt [Send_Fax_Menu]
Dial fax number - between 101 - 299
* - Quit
Fax Sent Prompt [Fax_Sent_Menu]
Announces that fax was sent and repeats Fax Menu:
1 - Send fax
2 - Receive fax
* - Quit
Receive Fax Menu [Receive_Fax_Menu]
Dial fax number - between 101 - 299
* - Quit
Fax Received Prompt [Fax_Received_Menu]
Announces that fax was received and repeats Fax Menu:
1 - Send fax
2 - Receive fax
* - Quit
CSP Prompt [CSP_Menu]
Say something to barge in (new file will be created with barged-in message) or press any DTMF.
22 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 23

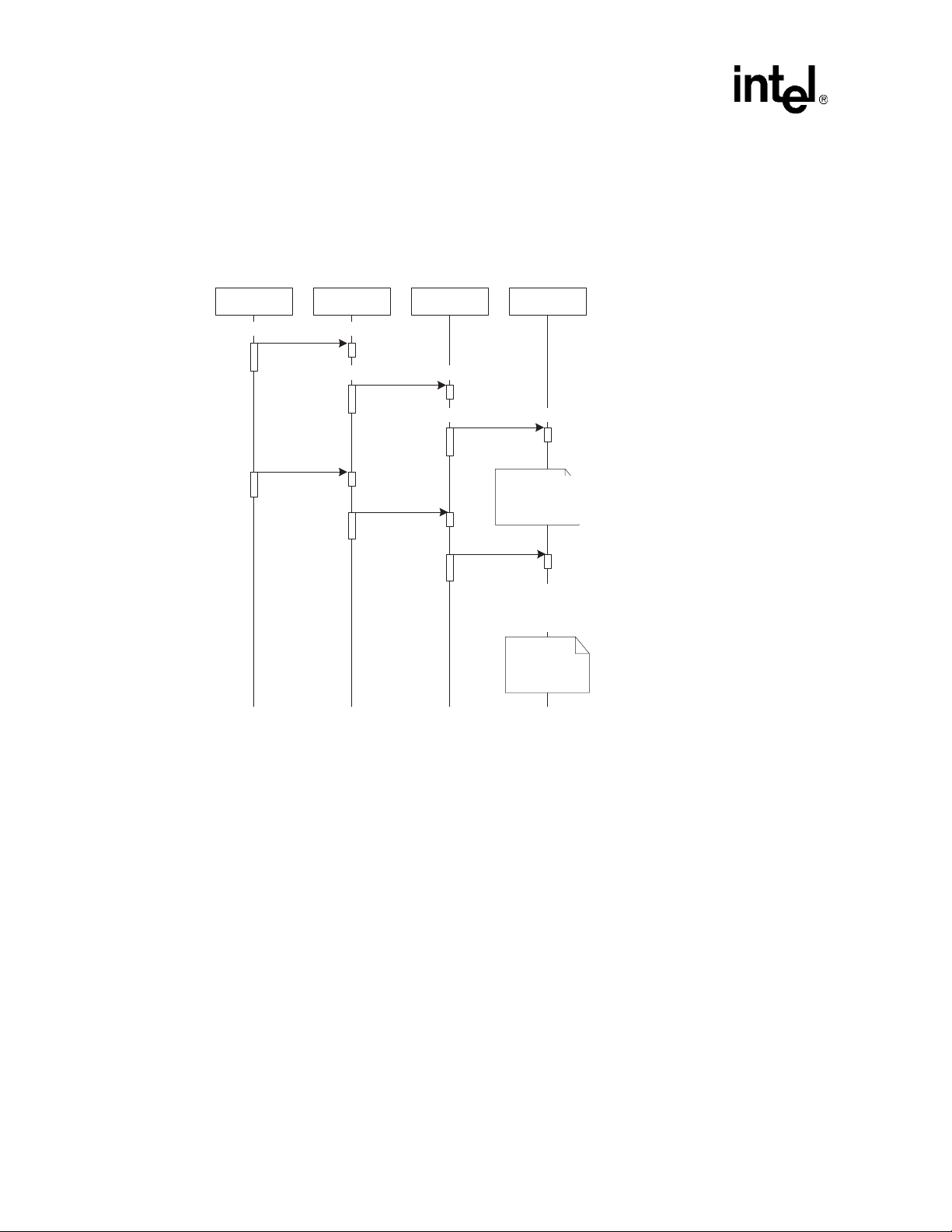
Figure 1. Demo Voice Menu Flowchart
4
Main Menu
Select one of the following:
1 - Voice Mail
2 - Fax
4 - CSP
* - Quit
Running the Demo
1
CSP Prompt
Say something to barge in
or press any DTMF
Fax Menu
1 - Send fax (to server)
2 - Receive fax (from server)
* - Quit
1
Send Fax Prompt
Dial server mailbox
number to store fax in
* - Quit
2
Receive Fax Prompt
Dial fax number that will
receive fax from server
* - Quit
2
Send Message Prompt
Enter Mailbox Number
* - Quit
Start Record Prompt
2 - Start/Stop Record
* - Quit
2
Voice Mail Prompt
1 - Record Message
2 - Listen to message
from a mailbox
* - Quit
1
2
2
Listen Message Prompt
Enter Mailbox Number
(Message is played)
* - Quit
Stop Listen Prompt
2 - Discard message
and quit
* - Save message and
quit
Fax Sent Prompt
Announces fax sent
Repeat Fax menu
Fax Received Prompt
Announces fax received
Repeat Fax menu
Confirm Message Saved
Prompt
Confirm message
Return to Voice Mail prompt
Stop Record Prompt
2 - Discard message and
re-record message to
same mailbox
3 - Confirm message
4 - Replay message
* - Quit
3
4
Replay Message
Replay Stop Record
Prompt
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 23
Page 24

Running the Demo
4.4 Stopping the Demo
The IP Media Server demo runs until it is terminated. Press “q” or “Q” to terminate the demo
application.
24 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 25

5.Demo Details
This chapter discusses the IP Media Server for HMP demo in more detail. It contains the following
topics:
• Files Used by the Demo. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
• Programming Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
• Threads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
• Initialization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
• Event Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
• Typical Scenario . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
5.1 Files Used by the Demo
This section lists the files used by the IP Media Server demo. It contains the following information
• Demo Source Code Files
• PDL Files
5
5.1.1 Demo Source Code Files
In Windows, the IP Media Server demo files listed in Table 3 are located within:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\Demos\IPMediaServer
In Linux, the IP Media Server demo files listed in Table 3 are located within:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/demos/IPMediaServer
Table 3. Files in IPMediaServer Folder Used by the IP Media Server Demo
Sub-Directory (if any) File Name Purpose
CConfig.cpp Implements the operations of the Configuration
class
CConfig.h Function prototype for config.cpp
CEventRouter.cpp Implements the operations of the EventRouter class
CEventRouter.h Function prototype for ceventrouter.cpp
IPMediaServer.dsp Visual C++ project file
IPMediaServer.dsw Visual C++ project workspace
main.cpp Contains the main function and the WaitForKey
main.h Function prototype for main.cpp
makefile Top-level make file (Linux only)
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 25
Page 26
Demo Details
Table 3. Files in IPMediaServer Folder Used by the IP Media Server Demo (Continued)
Sub-Directory (if any) File Name Purpose
Release 200.tif Sample fax file
Release unavConf.vox Voice file
Release cspPrompt.vox Voice file
Release errorInput.vox Voice file
Release faxMenu.vox Voice file
Release faxReceived.vox Voice file
Release faxSent.vox Voice file
Release IPMediaServer.cfg Demo configuration file
Release IPMediaServer.exe Demo executable
Release listenMenu.vox Voice file
Release mainMenu.vox Voice file
Release receivefaxMenu.vox Voice file
Release savecCnfirm.vox Voice file
Release sendfaxMenu.vox Voice file
Release sendMsg.vox Voice file
Release star tRec.vox Voice file
Release stopListen.vox Voice file
Release stopRec.vox Voice file
Release thankYou.vox Voice file
Release unavCsp.vox Voice file
Release unavFax.vox Voice file
Release unavMenu.vox Voice file
Release voicemailMenu.vox Voice file
In Windows, the IP Media Server demo files listed in Table 4 are located within:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\Demos\IPMediaServer\Modules
In Linux, the IP Media Server demo files listed in Table 4 are located within:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/demos/IPMediaServer/Modules
Table 4. Files in Modules Folder Used by the IP Media Server Demo
Sub-Directory File Name Purpose
common Defines.h Definitions and structures for the demo
common Interfaces.h Interfaces used in the demo
common Parameters.h Parameters used in the demo
common makefile Module make file (Linux only)
FaxModule CFaxDevice.cpp Implements the operations of the CFaxDevice class
26 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 27

Table 4. Files in Modules Folder Used by the IP Media Server Demo (Continued)
Sub-Directory File Name Purpose
FaxModule CFaxDevice.h Function prototype for cfaxdevice.cpp
FaxModule CFaxModule.cpp Implements the operations of the CFaxModule class
FaxModule CFaxModule.h Function prototype for cfaxmodule.cpp
FaxModule CFaxStateMachine.cpp Implements the operations of the
CFaxStateMachine class
FaxModule CFaxStateMachine.h Function prototype for cfaxstatemachine.cpp
FaxModule FaxModule.dsp Visual C++ project file
FaxModule makefile Module-level make file (Linux only)
FaxModule\Release or
FaxModule/Release
IPModule CIPDevice.cpp Implements the operations of the CIPDevice class
IPModule CIPDevice.h Function prototype for cipdevice.cpp
IPModule CIPMBoard.cpp Implements the operations of the CIPMBoard class
IPModule CIPMBoard.h Function prototype for cipmboard.cpp
IPModule CIPModule.cpp Implements the operations of the CIPModule class
IPModule CIPModule.h Function prototype for cipmodule.cpp
IPModule CIPStateMachine.cpp Implements the operations of the CIPStateMachine
IPModule CIPStateMachine.h Function prototype for cipstatemachine.cpp
IPModule CIPTBoard.cpp Implements the operations of the CIPTBoard class
IPModule CIPTBoard.h Function prototype for ciptboard.cpp
IPModule CMediaAlarms.cpp Implements the operations of the CMediaAlarms
IPModule CMediaAlarms.h Function prototype for cmediaalarms.cpp
IPModule IPModule.dsp Visual C++ project file
IPModule makefile Module-level make file (Linux only)
IPModule\Release or
IPModule/Release
VoiceModule CCSPDevice.cpp Implements the operations of the CCSPDevice class
VoiceModule CCSPDevice.h Function prototype for ccdspdevice.cpp
VoiceModule CMailBoxBtil.cpp Implements the operations of the CMailBoxUtil class
VoiceModule CMailBoxUtil.h Function prototype for cmailboxutil.cpp
VoiceModule CVoiceBoard.cpp Implements the operations of the voiceBoard class
VoiceModule CVoiceBoard.h Function prototype for cvoiceboard.cpp
VoiceModule CVoiceDevice.cpp Implements the operations of the CVoiceDevice
VoiceModule CVoiceDevice.h Function prototype for cvoicedevice.cpp
FaxModule.lib Compiled Fax Module library
class
class
IPModule.lib Compiled IP Module library
class
Demo Details
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 27
Page 28
Demo Details
Table 4. Files in Modules Folder Used by the IP Media Server Demo (Continued)
Sub-Directory File Name Purpose
VoiceModule CVoiceModule.cpp Implements the operations of the CVoiceModule
class
VoiceModule CVoiceModule.h Function prototype for cvoicemodule.cpp
VoiceModule CVoiceStateMachine.cpp Implements the operations of the
CVoiceStateMachine class
VoiceModule CVoiceStateMachine.h Function prototype for cvoicestatemachine.cpp
VoiceModule VoiceModule.dsp Visual C++ project file
VoiceModule makefile Module-level make file (Linux only)
VoiceModule\Release or
VoiceModule/Release
VoiceModule.lib Compiled Voice Module library
5.1.2 PDL Files
In Windows, the PDL files listed in Table 5 are located within the directory:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\Demos\Shared\pdl_win
In Linux, the PDL files listed in Table 5 are located within the directory:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/demos/Shared/pdl_Linux
Table 5. PDL Files Used by the IP Media Server Demo
Sub-Directory (if any) File Name Purpose
iptransport.cpp PDL IP transport functions
iptransport.h Function prototype for iptransport.cpp
pdl.c Platform dependency functions
pdl.h Function prototype for pdl.c
pdl.ver PDL version information
pdl_win.dsp PDL Visual C project file
pdl_win.dsw PDL Visual C project workspace
makefile PDL make file (Linux only)
release psl_win.lib Compiled PDL library
5.2 Programming Model
This section describes the IP Media Server for HMP demo architecture in the following topics:
• Module Structure
• EventRouter
• Interfaces
• Classes
28 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 29

5.2.1 Module Structure
The IP Media Server for HMP demo uses a modular architecture, in which each technology (IP,
voice, fax, CSP)) is wrapped inside a module so that a particular technology can be easily added or
removed.
The system contains three modules:
• IP module that serves as the front end to communicate with the IP network
• Voice module to provide voice service
• Fax module to provide fax service
The system also contains a software component, the EventRouter, to connect the modules. The
basic architecture of the system is illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2. IP Media Server Demo Architecture
Demo Details
Voice Module
Board Device
State Machine
IP Module
Board Device
State Machine
EventRouter
Fax Module
Board Device
State Machine
User
Module
Board Device
State Machine
Each module is composed of four elements:
• Board
• Device
• State Machine (call control)
• Wrapper
The Wrapper acts like a manager, receiving requests from the EventRouter and distributing the
request to the boards or devices. A device can have one or multiple state machines attached to it.
Each state machine represents one call.
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 29
Page 30
Demo Details
5.2.2 EventRouter
The EventRouter is responsible for communicating with the modules. It does the following:
• Maintains routing tables
• Retrieves event data from the SRL and routes it to a module for processing
• Forwards event process result to another module if so requested.
Figure 3. EventRouter
I P
Retrieve event
data from GC
library
Forward result to destination
For which
technology?
Fax
Ye s
IP Module
Voice
Voice Module
result
result result
result.destination
= NONE ?
Fax Module
No
30 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 31

5.2.3 Interfaces
The modular architecture implements a unified interface that allows replacement of modules by
including new header files and adjusting routing statements.
A module is treated by the EventRouter as a block box. It has three types of APIs:
Initialization
• Init( ) – for initializing a module
• GetNumOfDevices( ) – returns the number of devices available to the application
• GetDeviceHandle( ) – returns a device handle
• GetDeviceXmitSlot( ) – returns a device transmit timeslot
• SetDeviceReceiveSlot( ) – sets a device receive timeslot
Runtime
• ProcessEvent( ) – processes event data
Termination
• Exit( ) – exits a module
5.2.4 Classes
Demo Details
This section describes the classes contained in the demo and within each module. Each module
contains three classes: board, device, and state machine.
Table 6. Application Classes
Class Name Interface
CConfig
• Responsible for parsing configuration file and
populating configuration variables in the program.
ParseConfigFile( )
• Parses configuration file
ChannelNumber( )
• Gets the number of channels that are the
minimum of the number of voice lines and the
number of IP lines
IPParms( )
• Returns configured IP parameters
VoiceParms( )
• Returns configured voice parameters
FaxParms( )
• Returns configured fax parameters
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 31
Page 32

Demo Details
Table 6. Application Classes (Continued)
Class Name Interface
CEventRouter
Responsible for connecting all the modules. It does
the following:
• Maintains routing tables
• Retrieves event data from the SRL and routes
them to modules
• Gets event process results from the modules and
routes them to other modules if the destination is
not NONE
Table 7. IP Module Classes
Category Class Name Interface
Module CIPModule
• Interacts with CIPBoard and CIPDevice.
• Exports IP module functions to
CEventRouter.
Note: The public functions in this class can
be accessed by classes outside the
IP module.
Init( )
• Initializes the fax module, voice module, and IP
module
• Builds event routing tables
Exit( )
• Terminates the IP module, voice module, and fax
module
ProcessEvent( )
• Retrieves event data from Global Call and routes
them to a module for processing
• Routes processing result to other module(s) for
further processing.
Init( )
• Starts host based IP protocol
• Creates and initializes IPT (virtual) board
objects
• Creates and initializes IPM (media)
board objects
• Creates and initializes IP device objects
Exit( )
• Terminates and closes IPT boards
• Terminates and closes IPM boards
• Terminates and closes IP devices
ProcessEvent( )
• Receives event data from the event
router and distributes them, based on
handles, to IPT boards, IPM boards or IP
devices
GetNumOfDevices( )
• Returns number of IP devices engaging
in the communication
GetDeviceHandle( )
• Returns an IP device handle
GetDeviceXmitSlot( )
• Returns the transmit timeslot of an IP
device
SetDeviceReceiveSlot( )
• Sets the receiving timeslot of an IP
device
32 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 33

Table 7. IP Module Classes (Continued)
Category Class Name Interface
Board CIPTBoard
• Interacts with the Global Call library to
handle IP virtual boards
Note: The public function in this class
should only be accessed by classes
inside the IP module.
CIPMBoard
• Interacts with the Global Call library to
handle IP media boards
Note: The public functions in this class
should only be accessed by classes
inside the IP module.
Demo Details
Init( )
• Opens IPT (virtual) board and sets board
parameters
Exit( )
• Closes IPT (virtual) board
ProcessEvent( )
• Processes IPT (virtual) board events
GetNumOfDevicesOnBoard( )
• Returns the number of IPT devices
(signaling devices) on the board
Init( )
• Opens IP media boards
Exit( )
• Closes IP media boards
ProcessEvent( )
• Processes IP media board events
GetNumOfDevices( )
• Returns number of IPM devices on the
board
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 33
Page 34

Demo Details
Table 7. IP Module Classes (Continued)
Category Class Name Interface
Device CIPDevice
• Handles IP device operations, such as
making/dropping calls, sending H.323
messages, making timeslot connections,
etc.
• Holds CIPStateMachine (or call control)
Note: The public functions in this class
should only be accessed by classes
inside the IP module.
State
Machine
CIPStateMachine
• Handles IP events and maintains IP
state machine(s)
Note: The public functions in this class
should only be accessed by the
classes inside the IP module.
Init( )
• Opens an IP device. If successful,
creates an IP state machine. If QoS is
enabled, creates a media alarm object.
Exit( )
• Deletes IP state machine
• Deletes media alarm object
• Closes IP devices
ProcessEvent( )
• Processes IP device events
Connect( )
• Allows IP device to listen to its receiving
timeslot
Disconnect( )
• Allows IP device to unlisten to its
receiving timeslot
GetDeviceHandle( )
• Returns IP device handle
GetXmitSlot( )
• Returns IP device transmit timeslot
SetDeviceReceiveSlot( )
• Sets IP device receiving timeslot
SetFaxHandle( )
• Sets fax device handle associated with
the device
GetFaxHandle( )
• Returns fax device handle associated
with the device
Init( )
• Initializes the IP state machine
Exit( )
• Terminates the IP state machine
ProcessEvent( )
• Processes IP call events
34 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 35

Table 8. Voice Module Classes
Category Class Name Interface
Module CVoiceModule
• Interacts with CVoiceBoard and
CVoiceDevice.
• Exports Voice module functions to
CEventRouter.
Note: The public functions in this class can
be accessed by classes outside the
Voice module.
Board CVoiceBoard
• Interacts with the voice library to handle
voice boards
Note: The public function in this class
should only be accessed by classes
inside the Voice module.
Demo Details
Init( )
• Opens and initializes voice board objects
• Opens and initializes voice device objects
Exit( )
• Terminates and closes voice boards
• Terminates and closes voice devices
ProcessEvent( )
• Receives event data from the event router
and distributes them, based on
devicehandles, to voice boards or voice
devices for processing
Init( )
• Opens voice board
Exit( )
• Closes voice board
ProcessEvent( )
• Processes voice board events
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 35
Page 36
Demo Details
Table 8. Voice Module Classes (Continued)
Category Class Name Interface
Device CVoiceDevice
• Handles voice device operations, such
as playing, recording, tone detection,
and tone generation
• Holds CVoiceStateMachine
Note: The public functions in this class
should only be accessed by classes
inside the Voice module.
Init( )
• Opens the voice device. If successful,
creates voice state machine.
Exit( )
• Deletes the voice state machine from the
voice device
• Closes voice device
ProcessEvent( )
• Processes voice device events
Connect( )
• Allows IP device to listen to its receiving
timeslot
Play( )
• Plays a vox file
OnPlayComplete( )
• Replays a vox file when it has finished
playing
Record( )
• Records voice to a vox file
GetDigits( )
• Retrieves DTMF digits
GetDigitCount( )
• Returns the number of retrieved DTMF
digits
GetDigitString( )
• Returns retrieved DTMF string
Connect( )
• Allows the voice device to listen to its
receiving timeslot
Disconnect( )
• Allows voice device to unlisten to its
receiving timeslot
GetStoppedReason( )
• Tells why a played voice file stops
GetDeviceHandle( )
• Returns voice device handle
GetXmitSlot( )
• Returns voice device transmit timeslot
SetReceiveSlot( )
• Sets voice device receiving timeslot
36 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 37

Table 8. Voice Module Classes (Continued)
Category Class Name Interface
State
Machine
Misc CMailBoxUtil
CVoiceStateMachine
• Handles voice events and maintains
voice state machine(s)
Note: The public functions in this class
should only be accessed by the
classes inside the voice module.
• Provides utility function to manage
mailboxes
Note: The public functions in this class
should only be accessed by the
classes inside the voice module
Demo Details
Init( )
• Opens vox files
• Creates mailbox utility object that
manages mailboxes
Exit( )
• Closes vox files
• Deletes mailbox utility object that
manages mailboxes
ProcessEvent( )
• Processes voice events
InitMailBoxes( )
• Initializes mailboxes
CheckAndConvertDigits( )
• Checks if the extension number is in
allowed range. If it is, converts it into an
integer.
GetMailBox( )
• Checks if the mailbox is ready to be used.
If it is, gets the mailbox.
CreateMailBoxFileName( )
• Creates a filename for the mailbox
FreeMailBox( )
• Frees the mailbox for future use
Table 9. Fax Module Classes
Category Class Name Interface
Module CFaxModule
• Interacts with CFaxDevice.
• Exports Fax module functions to
CEventRouter.
Note: The public functions in this class can
be accessed by classes outside the
Fax module.
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 37
Init( )
• Creates fax device objects
Exit( )
• Deletes fax device objects
GetNumOfDevices( )
• Gets the number of fax resources
GetDeviceHandle( )
• Returns fax device handle
TSUserEventProcessEvent( )
• Processes fax events from the Global
Call library
ProcessEvent( )
• Processes the events from the other
modules
Page 38

Demo Details
Table 9. Fax Module Classes (Continued)
Category Class Name Interface
Board CFaxBoard
• Interacts with the fax library to handle fax
boards
• The public function in this class should
only be accessed by classes inside the
Fax module
Device CFaxDevice
• Handles fax device operations, such as
sending fax, receiving fax, etc.
• Holds CFaxStateMachine
Note: The public functions in this class
should only be accessed by classes
inside the Fax module.
Init( )
• Open fax board.
Exit( )
• Close fax board.
ProcessEvent( )
• Processes fax board events.
Init( )
• Opens the fax device. If successful,
creates fax state machine.
Exit( )
• Deletes the fax state machine from the
fax device
• Closes fax device
SetIott( )
• Sets up iott for the fax file
SetFaxState( )
• Sets initial fax state before fax
transmission
SendFax( )
• Starts to send a fax file
RecvFax( )
• Starts to receive a fax file
OpenFaxFile( )
• Gets fax file handle
CloseFaxFile( )
• Closes fax file handle
GetDeviceHandle( )
• Returns fax device handle
ToLower_String( )
• Converts a string from uppercase to
lowercase
SetFaxFileName( )
• Names the fax file to be sent or received
GetFaxFileName( )
• Returns the name of the fax file
SetNeighborHandle( )
• Sets IP device handle that is currently
connected with the fax device
GetNeighborHandle( )
• Gets IP device handle that is currently
connected with the fax device
GetFaxStateMachineObject( )
• Returns fax state machine object
38 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 39

Table 9. Fax Module Classes (Continued)
Category Class Name Interface
State Machine CFaxStateMachine
• Handles fax events and maintains fax
state machine
Note: The public functions in this class
should only be accessed by the
classes inside the fax module.
5.3 Threads
The IP Media Server for HMP demo operates with two threads, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4. IP Media Server Demo Threads
Demo Details
Init( )
• Initializes fax state machine
Exit( )
• Terminates fax state machine
ProcessEvent( )
• Processes fax events
Keyboard
Main Thread
The threads are created as follows:
1. The first (main) thread is created by the demo application to get the keyboard input.
2. The second thread is an SRL thread, created as a result of the demo application calling
PDLsr_enblhdlr( ). All Global Call events are received through the SRL.
5.4 Initialization
This section describes the IP Media Server for HMPdemo initialization as shown in Figure 5.
R4/GC
SRL
Sub-Thread
IP
A system is started in the following sequence:
1. The application creates CConfig( ) to parse the configuration file.
2. The application creates CEventRouter( ) to start the Event Router, which, in turn, starts the
Fax module, the Voice module, and the IP module. When a module is started, it initializes its
boards, devices and state machines.
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 39
Page 40

Demo Details
After all the modules are started, the EventRouter starts to build a static routing table that maps
voice devices to IP devices. It is important that each IP device has a dedicated voice resource, so
that when an IP channel is connected (an incoming call is answered) the user can get a voice
prompt immediately.
If the initialization should fails, the application shuts down. The shutdown sequence is the reverse
of the initialization sequence.
Figure 5. System Initialization
1. Parse .cfg file
Application Configuration
2. Start router
Event Router
3. Start Fax Module 4. Start Fax Board
Fax Module Fax Board
5. Start Fax Device
7. Start Voice Module 8. Start Voice Board
Voice Module Voice Board
9. Start VoiceDevice
11. Start IP Module 12. Start IP Board
IP Module IP Board
13. Start IP Device
Fax Device
6. Start Fax State Machine
Voice Device
10. Start Voice State
Fax State Machine
Machine
Voice State
Machine
IP Device
14. Start IP State Machine
IP State Machine
40 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 41

5.5 Event Handling
This section describes how the IP Media Server for HMP demo handles events. It contains the
following topics:
• Event Mechanism
• Handling Keyboard Input Events
• Handling SRL Events
• Handling Application Exit Events
• TSUsrEvent Structure
5.5.1 Event Mechanism
The IP Media Server demo uses the SRL mechanism to retrieve events. When an event occurs, SRL
calls event handlers automatically. All events are received by the SRL and then passed to the
CallbackHdlr( ) function for handling.
In the initialization phase of the demo, the main( ) function sets up the call-back handler, by calling
PDLsr_enbhdlr( ).
Demo Details
5.5.2 Handling Keyboard Input Events
There is an endless loop {while(0)} in the main( ) function in the Main.cpp file. In that loop, the
application waits forever for a keyboard event by calling the waitForKey( ) function. The event
must be handled immediately and event-specific information should be retrieved before the next
call to waitForKey( ).
5.5.3 Handling SRL Events
When the R4/Global Call event is received, the application performs the following:
1. Get METAEVENT by calling gc_GetMetaEvent( ).
2. Get channel ID through device handle to channel mapping.
3. Get device type through device handle to type mapping.
4. Route meta event to the module specified by device type.
5.5.4 Handling Application Exit Events
Normal application exit events, such as pressing either q or Q, don’t enter the SRL. The main( )
function calls PDLSetApplicationExitPath( ) before initialization. In Linux, this function sets the
signals (SIGINT, SIGTERM, SIGABRT) for making the appropriate exit from the application. In
Windows, this function enables the detection of CTRL_CLOSE_EVENT (closing the window).
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 41
Page 42

Demo Details
5.5.5 TSUsrEvent Structure
The TSUsrEvent structure is used by the demo modules to return event processing results to the
event router.
The TSUserEvt structure is defined as follows:
typedef struct
{
int event;
TDeviceType destination;
int lineDevice;
long xmitSlot;
long neighborDevice;
char dialString[MAX_STRING_LENGTH]}
TSUserEvent;
The fields of the TSUserEvt structure are described as follows:
event
the name of a user-defined event, such as USR_CONNECTED, USR_SENDFAX, etc.
destination
the name of the module that this event is destined for. Possible vavues are IP, VOICE, FAX, or
NONE.
lineDevice
the device handle in this module. It will be later used by the Event Router as an index to find its
counterpart in the destination module.
xmitSlot
an integer that normally indicates a time slot number
neighborDevice
the neighbor device handle
dialString
a char string that is normally filled with a DTMF dialing string
5.6 Typical Scenario
This section describes a typical scenario for sending a fax, which involves all the IP Media Server
demo modules.
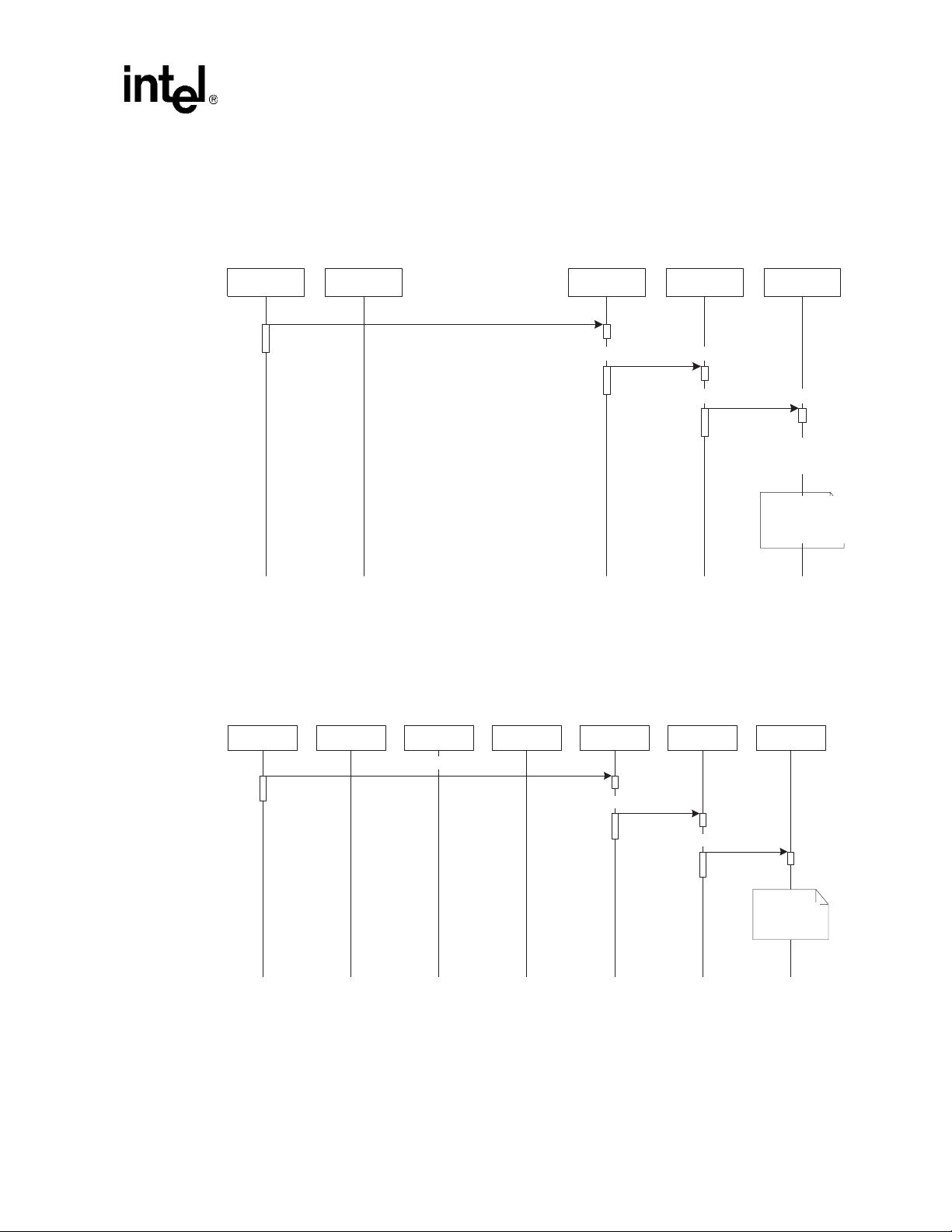
Call Offered
When an incoming call is received by the server, the IP module answers the call until the call is
connected.
42 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 43

Figure 6. Typical Scenario: Call Offered
Demo Details
CEventRouter CIPModule CIPDevice
GCEV_OFFERED
GCEV_OFFERED
GCEV_EXTENSIONCMPLT
GCEV_EXTENSIONCMPLT
GCEV_EXTENSIONCMPLT
GCEV_CONNECTED
GCEV_CONNECTED
GCEV_CONNECTED
GCEV_OFFERED
call
gc_extension( )
to get call related
information
gc_AnswerCall( )
Call
voice device
CIPState
Machine
Call
gc_listen( )
listen to
CVoiceModule
to
Format TSUserEvent
to request voice
module to play
prompt
source=IP
destination=VOICE
event=
USR_CONNECTED
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 43
Page 44

Demo Details
Play Prompts
After the call is connected, the Voice module is notified to play prompts and accept DTMF.
Figure 7. Typical Scenario: Play Prompts
CEventRouter CIPModule CIPDevice
USR_CONNECTED
TDX_PLAY (finish playing main menu)
TDX_GETDIG (press "2" to play fax menu)
TDX_GETDIG (press "1" to play send fax menu)
CIPState
Machine
CVoiceModule
USR_CONNECTED
TDX_GETDIG "2"
TDX_GETDIG "1"
TDX_PLAY
CVoiceDevice
USR_CONNECTED
TDX_GETDIG "2"
TDX_GETDIG "1"
1. Call
to listen to IP
device
2. Call
play Main_Menu
TDX_PLAY
CVoiceState
Machine
dx_listen( )
dx_play( )
Call
dx_getdig( )
detect digits
Call
dx_play( )
play Fax_Menu
to
to
to
TDX_GETDIG (press "101" to select fax box number)
Call
dx_play( )
to
TDX_GETDIG "101"
TDX_GETDIG "101"
play
Send_Fax_Menu
Format TSUserEvent to
request fax module to
send fax to faxbox 101
source=IP
destination=FAX
event=
USR_SENDFAX
dialString="101"
44 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 45

Fax Mailbox
The user selects to send a fax to mailbox “101”. The Fax module is requested to send a fax.
Figure 8. Typical Scenario: Fax Mailbox
Demo Details
CEventRouter CIPModule CFaxModule
USR_SENDFAX "101"
...
USR_SENDFAX
CFaxDevice
"101"
Find an available
fax device and put it
into busy Q
Format TSUserEvent
to request IP module
to get ready to send
fax
source=FAX
destination=IP
event=
USR_ESTABLISH
FAXSESSIONREQ
CFaxState
Machine
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 45
Page 46
Demo Details
Establish Fax Session
The Fax module requests the front end to get ready to send a fax. If the front end is IP, it should first
move from an RTP port to a UDP port in order to send a fax.
Figure 9. Typical Scenario: Establish Fax Session
CEventRouter CIPModule CIPDevice
USR_ESTABLISHFAXSESSIONREQ
USR_ESTABLISHFAXSESSIONREQ
USR_ESTABLISHFAXSESSIONREQ
GCEV_EXTENSION
GCEV_EXTENSION
CIPState
Machine
1. Call
gc_setConfigData( )
2. Call
gc_unlisten ( )
3. Call
gc_setUserInfo( )
4. Call
gc_extension( )
GCEV_EXTENSION
Format TSUserEvent to
reply to fax module that
T.38 session is
established
source=IP
destination=FAX
event=
USR_ESTABLISHF
AXSESSIONCONF
to set to manual (fax) mode.
to disconnect from voice
to set T.38 info.
to start T.38 session
46 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 47

Fax Session Established
The Fax module gets a reply from the front end that the fax session has been established.
Figure 10. Typical Scenario: Fax Session Established
Demo Details
CEventRouter CIPModule CFaxModule CFaxDevice
USR_ESTABLISHFAXSESSIONCONF
TFX_FAXSEND
...
USR_ESTABLISHFAXSESSIONCONF
Call
TFX_FAXSEND
Format TSUserEvent
to request IP module
to close fax session
source=FAX
destination=IP
event=
USR_CLOSEFAX
SESSIONREQ
CFaxState
Machine
fx_sndfax( )
send fax
Close fax file
to
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 47
Page 48

Demo Details
Fax Sent
The fax is sent. The front end is requested to close the fax session.
Figure 11. Typical Scenario: Fax Sent
CEventRouter CIPModule CIPDevice
USR_CLOSEFAXSESSIONREQ
USR_CLOSEFAXSESSIONREQ
USR_CLOSEFAXSESSIONREQ
GCEV_EXTENSION
GCEV_EXTENSION
GCEV_EXTENSION
CIPState
Machine
1. Call
gc_stop( )
2. Call
3. Call
Format TSUserEvent to
reply to fax module that
T.38 session is closed
source=IP
destination=FAX
event=
USR_CLOSEFAX
SESSIONCONF
to stop T.38 session
gc_extension ( )
gc_listen( )
listen to voice prompts
to start audio session
48 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 49
Fax Session Closed
The Fax module gets a reply from the front end that the fax session has been closed.
Figure 12. Typical Scenario: Fax Session Closed
Demo Details
CEventRouter CIPModule CFaxModule CFaxDevice
USR_CLOSEFAXSESSIONCONF
Fax Complete
The Voice module gets a reply from the Fax module that a fax has been sent.
Figure 13. Typical Scenario: Fax Complete
...
USR_CLOSEFAXSESSIONCONF
USR_CLOSEFAXSESSIONCONF
CFaxState
Machine
Format TSUserEvent
to notify voice
module fax is sent
source=FAX
destination=VOICE
event=
USR_FAXSENT
CEventRouter CIPModule CIPDevice
USR_FAXCOMPLETE
CIPState
Machine
CVoiceModule CVoiceDevice
USR_FAXCOMPLETE
USR_FAXCOMPLETE
CVoiceState
Machine
Call
dx_play( )
play fax menu
to
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 49
Page 50

Demo Details
50 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 51

Glossary
Codec: see COder/DECoder
COder/DECoder: A circuit used to convert analog voice data to digital and digital voice data to analog audio.
Computer Telephony (CT): Adding computer intelligence to the making, receiving, and managing of
telephone calls.
DTMF: Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency
Dual-Tone Multi-Frequency: A way of signaling consisting of a push-button or touch-tone dial that sends out a
sound consisting of two discrete tones that are picked up and interpreted by telephone switches (either PBXs or
central offices).
Emitting Gateway: called by a G3FE. It initiates IFT service for the calling G3FE and connects to a Receiving
Gateway.
E1: The 2.048 Mbps digital carrier system common in Europe.
FCD file: An ASCII file that lists any non-default parameter settings that are necessary to configure a DM3
hardware/firmware product for a particular feature set. The downloader utility reads this file, and for each
parameter listed generates and sends the DM3 message necessary to set that parameter value.
Frame: A set of SCbus/CT Bus timeslots which are grouped together for synchronization purposes. The period of
a frame is fixed (at 125 µsec) so that the number of time slots per frame depends on the SCbus/CT Bus data rate.
G3FE: Group 3 Fax Equipment. A traditional fax machine with analog PSTN interface.
Gatekeeper: An H.323 entity on the Internet that provides address translation and control access to the network
for H.323 Terminals and Gateways. The Gatekeeper may also provide other services to the H.323 terminals and
Gateways, such as bandwidth management and locating Gateways.
Gateway: A device that converts data into the IP protocol. It often refers to a voice-to-IP device that converts an
analog voice stream, or a digitized version of the voice, into IP packets.
H.323: A set of International Telecommunication Union (ITU) standards that define a framework for the
transmission of real-time voice communications through Internet protocol (IP)-based packet-switched networks.
The H.323 standards define a gateway and a gatekeeper for customers who need their existing IP networks to
support voice communications.
IAF: Internet Aware Fax. The combination of a G3FE and a T.38 gateway.
IFP: Internet Facsimile Protocol
IFT: Internet Facsimile Transfer
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 51
Page 52

International Telecommunications Union (ITU): An organization established by the United Nations to set
telecommunications standards, allocate frequencies to various uses, and hold trade shows every four years.
Internet: An inter-network of networks interconnected by bridges or routers. LANs described in H.323 may be
considered part of such inter-networks.
Internet Protocol (IP): The network layer protocol of the transmission control protocol/Internet protocol
(TCP/IP) suite. Defined in STD 5, Request for Comments (RFC) 791. It is a connectionless, best-effort packet
switching protocol.
Internet Service Provider (ISP): A vendor who provides direct access to the Internet.
Internet Telephony: The transmission of voice over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Also called Voice over IP
(VoIP), IP telephony enables users to make telephone calls over the Internet, intranets, or private Local Area
Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) that use the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP).
ITU: See International Telecommunications Union.
Jitter: The deviation of a transmission signal in time or phase. It can introduce errors and loss of synchronization
in high-speed synchronous communications.
NIC (Network Interface Card): Adapter card inserted into computer that contains necessary software and
electronics to enable a station to communicate over network.
PCD file: An ASCII text file that contains product or platform configuration description information that is used
by the DM3 downloader utility program. Each of these files identifies the hardware configuration and firmware
modules that make up a specific hardware/firmware product. Each type of DM3-based product used in a system
requires a product-specific PCD file.
PSTN: see Public Switched Telephone Network
Public Switched Telephone Network: The telecommunications network commonly accessed by standard
telephones, key systems, Private Branch Exchange (PBX) trunks and data equipment.
Reliable Channel: A transport connection used for reliable transmission of an information stream from its
source to one or more destinations.
Reliable Transmission: Transmission of messages from a sender to a receiver using connection-mode data
transmission. The transmission service guarantees sequenced, error-free, flow-controlled transmission of messages
to the receiver for the duration of the transport connection.
RTCP: Real Time Control Protocol
RTP: Real Time Protocol
SIP: Session Initiation Protocol: an Internet standard specified by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in
RFC 3261. SIP is used to initiate, manage, and terminate interactive sessions between one or more users on the
Internet.
52 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 53

T1: A digital transmission link with a capacity of 1.544 Mbps used in North America. Typically channeled into 24
digital subscriber level zeros (DS0s), each capable of carrying a single voice conversation or data stream. T1 uses
two pairs of twisted pair wires.
TCP: see Transmission Control Protocol
Terminal: An H.323 Terminal is an endpoint on the local area network which provides for real-time, two-way
communications with another H.323 terminal, Gateway, or Multipoint Control Unit. This communication consists
of control, indications, audio, moving color video pictures, and/or data between the two terminals. A terminal may
provide speech only, speech and data, speech and video, or speech, data, and video.
Transmission Control Protocol: The TCP/IP standard transport level protocol that provides the reliable, full
duplex, stream service on which many application protocols depend. TCP allows a process on one machine to send
a stream of data to a process on another. It is connection-oriented in the sense that before transmitting data,
participants must establish a connection.
UDP: see User Datagram Protocol
UDPTL: Facsimile UDP Transport Layer protocol
User Datagram Protocol: The TCP/IP standard protocol that allows an application program on one machine to
send a datagram to an application program on another machine. Conceptually, the important difference between
UDP datagrams and IP datagrams is that UDP includes a protocol port number, allowing the sender to distinguish
among multiple destinations on the remote machine.
VAD: Voice Activity Detection
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 53
Page 54

54 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
Page 55

Index
A
application classes 31
application exit events 41
C
CallbackHdlr( ) 41
CConfig( ) 39
CEventRouter( ) 39
ChannelNumber( ) 31
CheckAndConvertDigits( ) 37
classes 31
application classes 31
Fax module classes 37
IP module classes 32
CloseFaxFile( ) 38
command-line switches 19
commands, keyboard 20
compiling and linking 18
configuration files, editing 15
Connect( ) 34
CreateMailBoxFileName( ) 37
, 36
FreeMailBox( ) 37
G
gc_GetMetaEvent( ) 41
GetDeviceXmitSlot( ) 31
GetDigitCount( ) 36
GetDigits( ) 36
GetDigitString( ) 36
GetFaxFileName( ) 38
GetFaxHandle( ) 34
GetFaxStateMachineObject( ) 38
GetMailBox( ) 37
GetNeighborHandle( ) 38
GetNumOfDevices( ) 31
GetNumOfDevicesOnBoard( ) 33
GetStoppedReason( ) 36
GetXmitSlot( ) 34
, 32
, 32, 33, 37
, 36
H
hardware requirements 13
D
Disconnect( ) 34, 36
E
editing configuration files 15
event handling 41
application exit events 41
keyboard input events 41
SRL events 41
TSUsrEvent structure 42
event mechanism 41
EventRouter 30
Exit( ) 31
I
Init( ) 31
initialization 39
InitMailBoxes( ) 37
interfaces 31
IP module classes 32
ipmediaserver.cfg configuration file 15
IPParms( ) 31
K
keyboard commands 20
keyboard input events, handling 41
L
F
Fax module classes 37
FaxParms( ) 31
files, used by demo 25
IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005 55
linking 18
Page 56

M
main( ) 41
module structure 29
O
OnPlayComplete( ) 36
OpenFaxFile( ) 38
P
ParseConfigFile( ) 31
PDL files 28
PDLSetApplicationExitPath( ) 41
PDLsr_enbhdlr( ) 41
PDLsr_enblhdlr( ) 39
Play( ) 36
ProcessEvent( ) 31
programming model 28
R
Record( ) 36
RecvFax( ) 38
requirements
hardware 13
software 13
runtime commands, keyboard 20
source code files 25
SRL events, handling 41
starting the demo 19
stopping the demo 24
switches, command line 19
system initialization 40
system requirements 13
T
threads 39
ToLower_String( ) 38
TSUserEventProcessEvent( ) 37
TSUsrEvent structure 42
U
using the media server 20
V
voice menu flowchart 23
Voice Module classes 35
VoiceParms( ) 31
W
waitForKey( ) 41
S
scenarios 42
call offered 43
establish fax session 46
fax complete 49
fax mailbox 45
fax sent 48
fax session closed 49
fax session established 47
play prompts 44
SendFax( ) 38
SetDeviceReceiveSlot( ) 31
SetFaxFileName( ) 38
SetFaxHandle( ) 34
SetFaxState( ) 38
SetIott( ) 38
SetNeighborHandle( ) 38
SetReceiveSlot( ) 36
software requirements 13
56 IP Media Server for HMP Demo Guide — July 2005
, 32, 34
 Loading...
Loading...