Page 1

7th Generation Intel® Processor
Family
Specification Update
Supporting 7th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Families
based on Y/U/H/S-Processor Line, Y/U With iHDCP2.2Processor Line and Intel® Pentium® Processors and Intel®
Celeron® Processor
February 2017
Revision 004
Document Number: 334663-004
Page 2

Revision History
You may not use or facilitate the use of this document in connection with any infringement or other legal analysis concerning Intel
products described herein. You agree to grant Intel a non-exclusive, royalty-free license to any patent claim thereafter drafted
which includes subject matter disclosed herein.
No license (express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise) to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document.
Intel technologies' features and benefits depend on system configuration and may require enabled hardware, software or service
activation. Learn more at Intel.com, or from the OEM or retailer.
No computer system can be absolutely secure. Intel does not assume any liability for lost or stolen data or systems or any
damages resulting from such losses.
The products described may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from
published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Intel disclaims all express and implied warranties, including without limitation, the implied warranties of merchantability, fitness
for a particular purpose, and non-infringement, as well as any warranty arising from course of performance, course of dealing, or
usage in trade.
Intel technologies' features and benefits depend on system configuration and may require enabled hardware, software or service
activation. Learn more at intel.com, or from the OEM or retailer.
All information provided here is subject to change without notice. Contact your Intel representative to obtain the latest Intel
product specifications and roadmaps.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document may be obtained by calling 1-800-5484725 or visit www.intel.com/design/literature.htm.
Intel, the Intel Core, Pentium, Celeron, and the Intel logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2017, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
2 Specification Update
Page 3

Revision History
Contents
Revision History .................................................................................................................. 4
Preface .............................................................................................................................. 5
Identification Information ..................................................................................................... 7
Summary Tables of Changes ............................................................................................... 15
Errata .............................................................................................................................. 23
Specification Changes ........................................................................................................ 48
Specification Clarifications ................................................................................................... 49
Documentation Changes ..................................................................................................... 50
Specification Update 3
Page 4
Revision History
Revision History
Revision Description Date
001 Initial release August 2016
• Errata
002
003
004
Added errata KBL068-078
Updated erratum KBL062
Fixed err a tum KBL063
• Added SKUs Y/U w/iHDCP2.2, S/H-Processor lines
• Added Table 2, S/H-Processor Lines Component Identification
• Identification Information
Added Table 4, Y-Processor Line With iHDCP2.2
Added Table 6, U-Processor Line With iHDCP2.2
Added Figure 3, S-Processor Line LGA Top-Side Markings
Added Table 7, S-Processor Line
Added Figure 4, H-Processor Line BGA Top-Side Markings
Added Table 8, H-Processor Line
• Errata
Updated Table 13, Errata Summary Table
Added errata KBL079-083
• Identification Information
Updated Table 4, Y-Processor Line With iHDCP2.2
• Errata
Updated Table 13, Errata Summary Table. Added J-1 stepping
Updated KBL080
Added errata KBL084-091
November 2016
January 2017
February 2017
§
4 Specification Update
Page 5

Preface
Preface
This document is an update to the specifications contained in the documents listed in
the following Affected Documents/Related Documents table. It is a compilation of
device and document errata and specification clarifications and changes, and is
intended for hardware system manufacturers and for software developers of
applications, operating system, and tools.
Information types defined in the Nomenclature section of this document are
consolidated into this update document and are no longer published in other
documents. This document may also contain information that has not been previously
published.
Affected Documents
7th Generation Intel® Processor Families for U/Y Platforms Datasheet,
Volume 1 of 2
7th Generation Intel® Processor Families for U/Y Platforms Datasheet,
Volume 2 of 2
Related Documents
AP-485, Intel® Processor Identification and the CPUID Instruction http://www.intel.com
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Dev eloper’s Manual,
Volume 1: Basic Architecture
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 2A: Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Dev eloper’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 2B: Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Dev eloper’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 3A: System Progra mming Guide
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Dev eloper’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 3B: System Programming Guide
®
64 and IA-32 Intel Architecture Optimization Reference Manual
Intel
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Dev eloper’s Manual
Documentation Changes
ACPI Specifications www.acpi.info
Document Title Document
Document Title Document
Number/Location
334661
334662
Number/Location
/design/processor/ap
plnots/241618.htm
http://www.intel.com
/products/processor/
manuals/index.htm
http://www.intel.com
/content/www/us/en/
processors/architectur
es-software-
developer-
manuals.html
Specification Update 5
Page 6

Nomenclature
Errata are design defects or errors. Errata may cause the processor’s behavior to
deviate from published specifications. Hardware and software designed to be used
with any given stepping must assume that all errata documented for that stepping are
present on all devices.
Specification Changes are modifications to the current published specifications.
These changes will be incorporated in the next release of the specifications.
Specification Clarifications describe a specification in greater detail or further
highlight a specification’s impact to a complex design situation. These clarifications will
be incorporated in the next release of the specifications.
Documentation Changes include typos, errors, or omissions from the current
published specifications. These changes will be incorporated in the next release of the
specifications.
Note: Errata remain in the specification update throughout the product’s lifecycle, or until a
particular stepping is no longer commercially available. Under these circumstances,
errata removed from the specification update are archived and available upon request.
Specification changes, specification clarifications, and documentation changes are
removed from the specification update when the appropriate changes are made to the
appropriate product specification or user documentation (datasheets, manuals, etc.).
Preface
§
6 Specification Update
Page 7

Identification Information
Identification Information
Component Identification via Programming Interface
The processor stepping can be identified by the following register contents:
Table 1. Y/U-Processor Lines Component Identification
Reserved Extended
31:28 27:20 19:16 15:14 13:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
0000000b 1000b 00b 0110b 1110b xxxxb
Family
Extended
Model
Reserved Processor
Table 2. S/H-Processor Lines Component Identification
Reserved Extended
31:28 27:20 19:16 15:14 13:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
0000000b 1001b 00b 0110b 1110b xxxxb
Family
Extended
Model
Reserved Processor
Notes:
1. The Extended Family, Bits [27:20] are used in conjunction with the Family
Code, specified in Bits[11:8], to indicate whether the processor belongs to the
Intel386™, Intel486™, Pentium®, Pentium 4, or Intel® Core™ processor
family.
2. The Extended Model, Bits [19:16] in conjunction with the Model Number,
specified in Bits [7:4], are used to identify the model of the processor within
the processor’s family.
3. The Family Code corresponds to Bits [11:8] of the EDX register after RESET,
Bits [11:8] of the EAX register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1
in the EAX register, and the generation field of the Device ID register
accessible through Boundary Scan.
4. The Model Number corresponds to Bits [7:4] of the EDX register after RESET,
Bits [7:4] of the EAX register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1
in the EAX register, and the model field of the Device ID register accessible
through Boundary Scan.
5. The Stepping ID in Bits [3:0] indicates the revision number of that model. See
Table 1 for the processor stepping ID number in the CPUID information.
6. Please refer to Kaby Lake Processor BIOS Writers Guide for additional
information. When EAX is initialized to a value of ‘1’, the CPUID instruction
returns the Extended Family, Extended Model, Processor Type, Family Code,
Model Number and Stepping ID value in the EAX register. Note that the EDX
processor signature value after reset is equivalent to the processor signature
output value in the EAX register.
Type
Type
Family
Code
Family
Code
Model
Number
Model
Number
Stepping
ID
Stepping
ID
Cache and TLB descriptor parameters are provided in the EAX, EBX, ECX and EDX registers after
the CPUID instruction is executed with a 2 in the EAX register.
Specification Update 7
Page 8

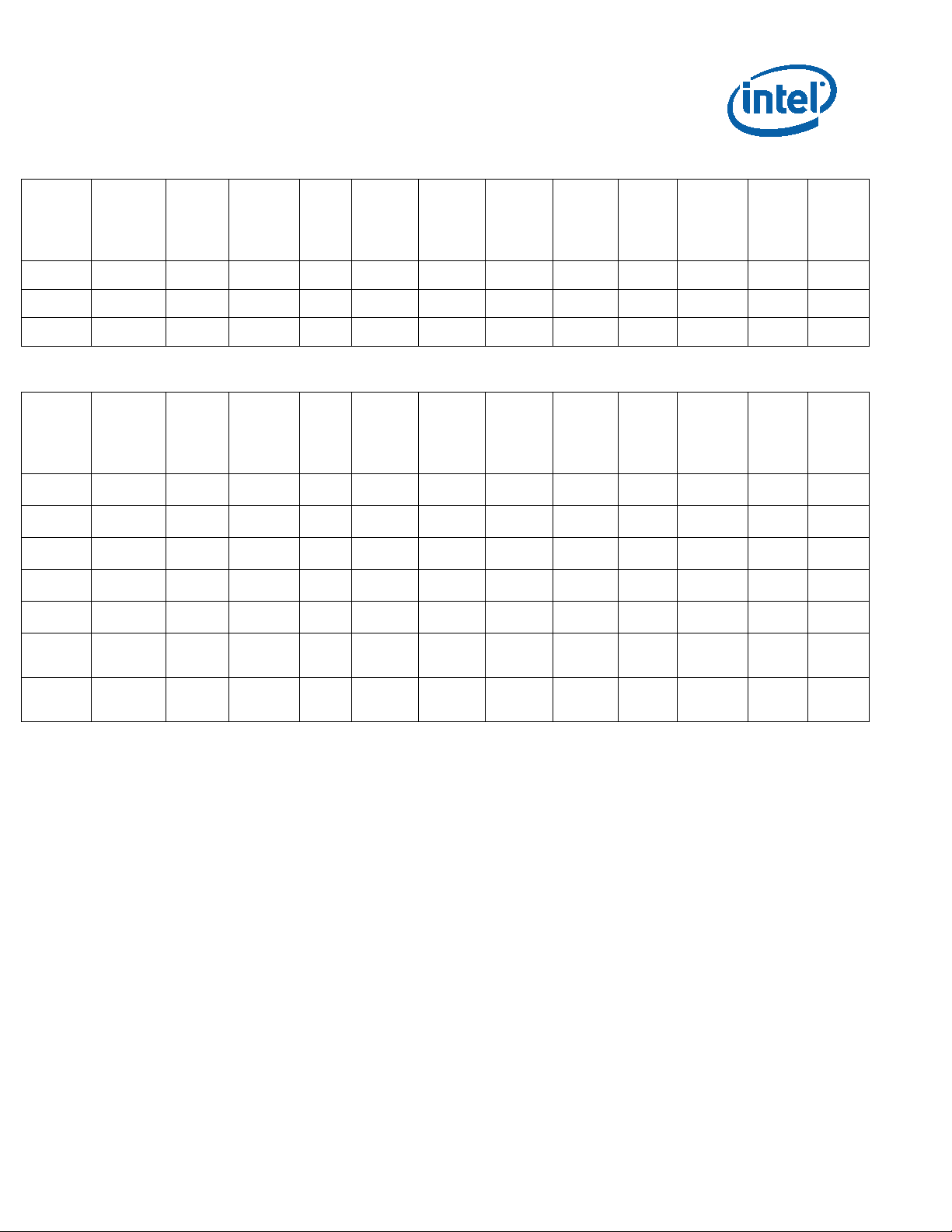
Component Marking Information
Figure 1. Y-Processor Line BGA Top-Side Markings
Identification Information
Pin Count: 1515 Package Size: 20 mm x 16.5 mm
Production (SSPEC):
GRP1LINE1: FPOxxxxxSSPEC
GRP2LINE1 (G2L1): Intel logo
GRP3LINE1 (G3L1): {eX}
8 Specification Update
Page 9
Identification Information
Table 3. Y -Processor Line
S-Spec #
Processor
Number
Step-
ping
Cache Size
Functional
Core
Processor
Graphics
Cores
Processor
Graphics
Freq.
Processor
Graphics
Maximum
Dynamic
Freq.
LPDDR3
Mem.
(MT/s)
Core
Freq.
Turbo 1
Core Freq.
Rate
Thermal
Design
Power
Slot /
Socket
Type
R2ZT I7-7Y75 H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 1.05 GHz 1866 1. 3 GHz 3.6 GHz 4.5 W BGA1515
R2ZX I5-7Y54 H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 0.95 GHz 1866 1.2 GHz 3.2 GHz 4.5 W BGA1515
R2ZY M3-7Y30 H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 0.9 GHz 1866 1 GHz 2.6 GHz 4.5 W BGA1515
Table 4. Y-Processor Line With iHDCP2.2
S-Spec #
Processor
Number
Step-
ping
Cache Size
Functional
Core
Processor
Graphics
Cores
Processor
Graphics
Freq.
Processor
Graphics
Maximum
Dynamic
Freq.
LPDDR3
Mem.
(MT/s)
Core
Freq.
Turbo 1
Core Freq.
Rate
Thermal
Design
Power
R33X I7-7Y75 H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 1.05 GHz 1866 1.3 GHz 3.6 GH z 4.5 W BGA1515
R33Y I5-7Y57 H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 0.95 GHz 1866 1.2 GHz 3.3 GHz 4.5 W BGA1515
R345 I5-7Y54 H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 0.95 GHz 1866 1.2 GHz 3.2 GHz 4.5 W BGA1515
R346 M3-7Y32 H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 0.9 GHz 1866 1.1 GHz 3 GHz 4.5 W BGA1515
R347 M3-7Y30 H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 0.9 GHz 1866 1 GHz 2.6 GHz 4.5 W BGA1515
Slot /
Socket
Type
R34B
R34E
Pentium
4410Y
Celeron
3965Y
H-0 2 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 0.85 GHz 1866 1.5 GHz 1.5 GHz 6 W BGA1515
H-0 2 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 0.85 GHz 1866 1.3 GHz 1.3 GHz 6 W BGA1515
Specification Update 9
Page 10
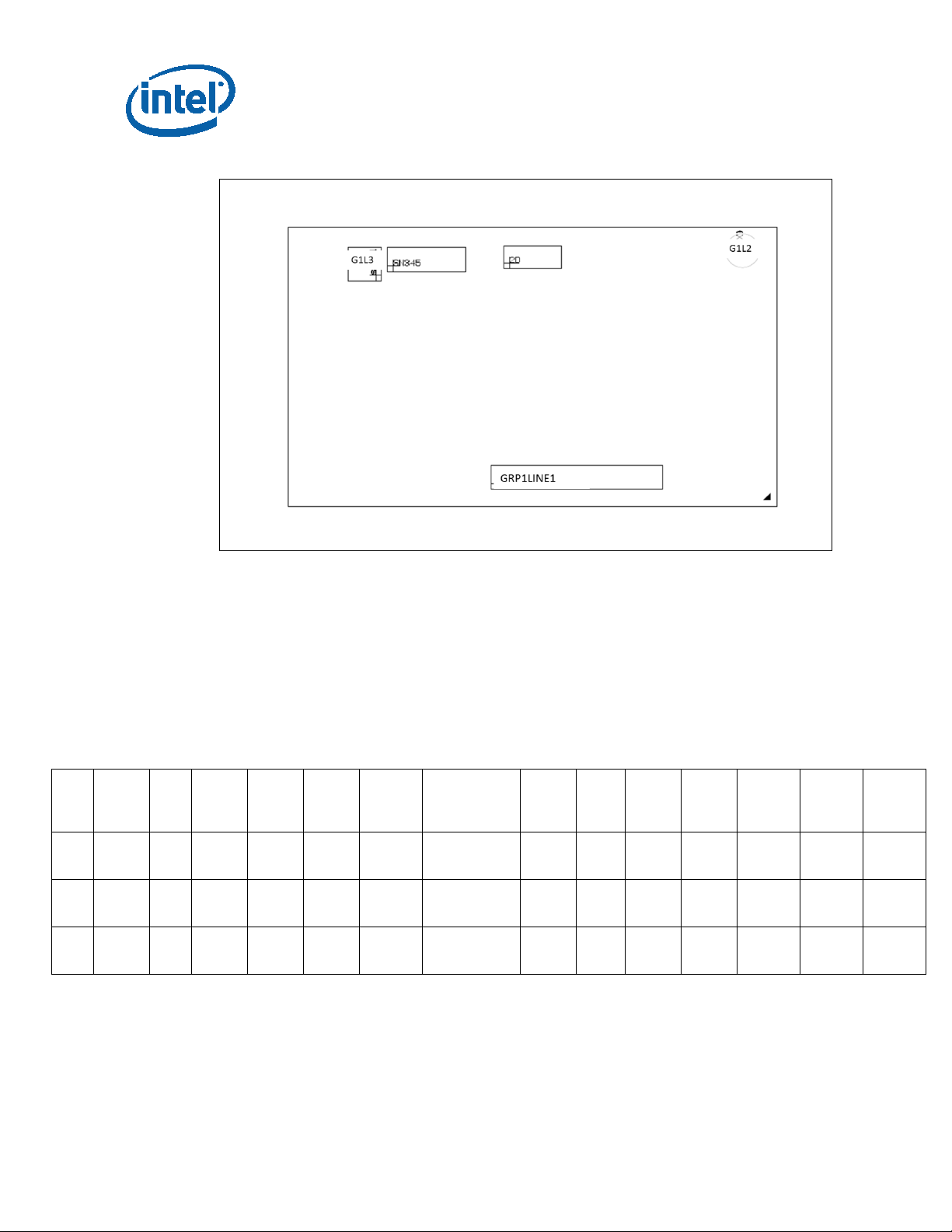
Figure 2. U-Processor Line BGA Top-Side Markings
Identification Information
S-Spec # Processor
Number
R2ZU I5-
R2ZV I7-
R2ZW I3-
7200U
7500U
7100U
Pin Count: 1356 Package Size: 42 mm x 24 mm
Production (SSPEC):
GRP1LINE1: FPOxxxxxSSPEC
GRP2LINE1 (G2L1): {eX}
GRP3LINE1 (G3L1): Intel logo
Table 5. U -Processor Line
Mem.
LPDDR3
Mem.
(MT/s)
Step-
Cache
ping
H-0 3 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 1 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.5 GHz 3.1 GHz 15 W BGA1356
H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 1.05 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.7 GHz 3.5 GHz 15 W BGA1356
H-0 3 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 1 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.4 GHz 2.4 GHz 15 W BGA1356
Size
Functional
Core
Processor
Graphics
Cores
Processor
Graphics
Freq.
Processor Graphics
Maximum Dynamic
Freq.
DDR3L
(MT/s)
DDR4
Mem.
(MT/s)
Core Freq. Turbo 1
Core Freq.
Rate
Thermal
Design
Power
Socket Type
Slot /
10 Specification Update
Page 11
Identification Information
Table 6. U-Processor Line With iHDCP2.2
S-Spec # Processor
Number
Step-
ping
Cache
Size
Functional
Core
Processor
Graphics
Cores
Processor
Graphics
Freq.
Processor Graphics
Maximum Dynamic
Freq.
DDR3L
Mem.
(MT/s)
LPDDR3
Mem.
(MT/s)
DDR4
Mem.
(MT/s)
Core Freq. Turbo 1
Core Freq.
Rate
Thermal
Design
Power
Slot /
Socket
Type
R33Z I7-7600U H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 1.15 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.8 GHz 3.9 GHz 15 W BGA1356
R340 I5-7300U H-0 3 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 1.1 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.6 GHz 3.5 GHz 15 W BGA1356
R341 I7-7500U H-0 4 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 1.05 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.7 GHz 3.5 GHz 15 W BGA1356
R342 I5-7200U H-0 3 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 1 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.5 GHz 3.1 GHz 15 W BGA1356
R343 I3-7100U H-0 3 MB 2 2 0.3 GHz 1 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.4 GHz 2.4 GHz 15 W BGA1356
Pentium
R348
R349
R34A
4415U
Celeron
3865U
Celeron
3965U
H-0 2 MB 2 1 0.3 GHz 0.95 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.3 GHz 2.3 GHz 15 W BGA1356
H-0 2 MB 2 1 0.3 GHz 0.9 GHz 1600 1866 2133 1.8 GHz 1.8 GHz 15 W BGA1356
H-0 2 MB 2 1 0.3 GHz 0.9 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.2 GHz 2.2 GHz 15 W BGA1356
R360 I5-7287U J-1 4 MB 2 3 0.3 GHz 1.1 GHz 1600 1866 2133 3.3 GHz 3.7 GHz 28 W BGA1356
R361 I3-7167U J-1 3 MB 2 3 0.3 GHz 1 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.8 GHz 2.8 GHz 28 W BGA1356
R362 I5-7267U J-1 4 MB 2 3 0.3 GHz 1.05 GHz 1600 1866 2133 3.1 GHz 3.5 GHz 28 W BGA1356
R363 I5-7260U J-1 4 MB 2 3 0.3 GHz 0.95 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.2 GHz 3.4 GHz 15 W BGA1356
R365 I5-7360U J-1 4 MB 2 3 0.3 GHz 1 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.3 GHz 3.6 GHz 15 W BGA1356
R366 I7-7560U J-1 4 MB 2 3 0.3 GHz 1.05 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.4 GHz 3.8 GHz 15 W BGA1356
R367 I7-7567U J-1 4 MB 2 3 0.3 GHz 1.15 GHz 1600 1866 2133 3.5 GHz 4 GHz 28 W BGA1356
R368 I7-7660U J-1 4 MB 2 3 0.3 GHz 1.1 GHz 1600 1866 2133 2.5 GHz 4 GHz 15 W BGA1356
Specification Update 11
Page 12
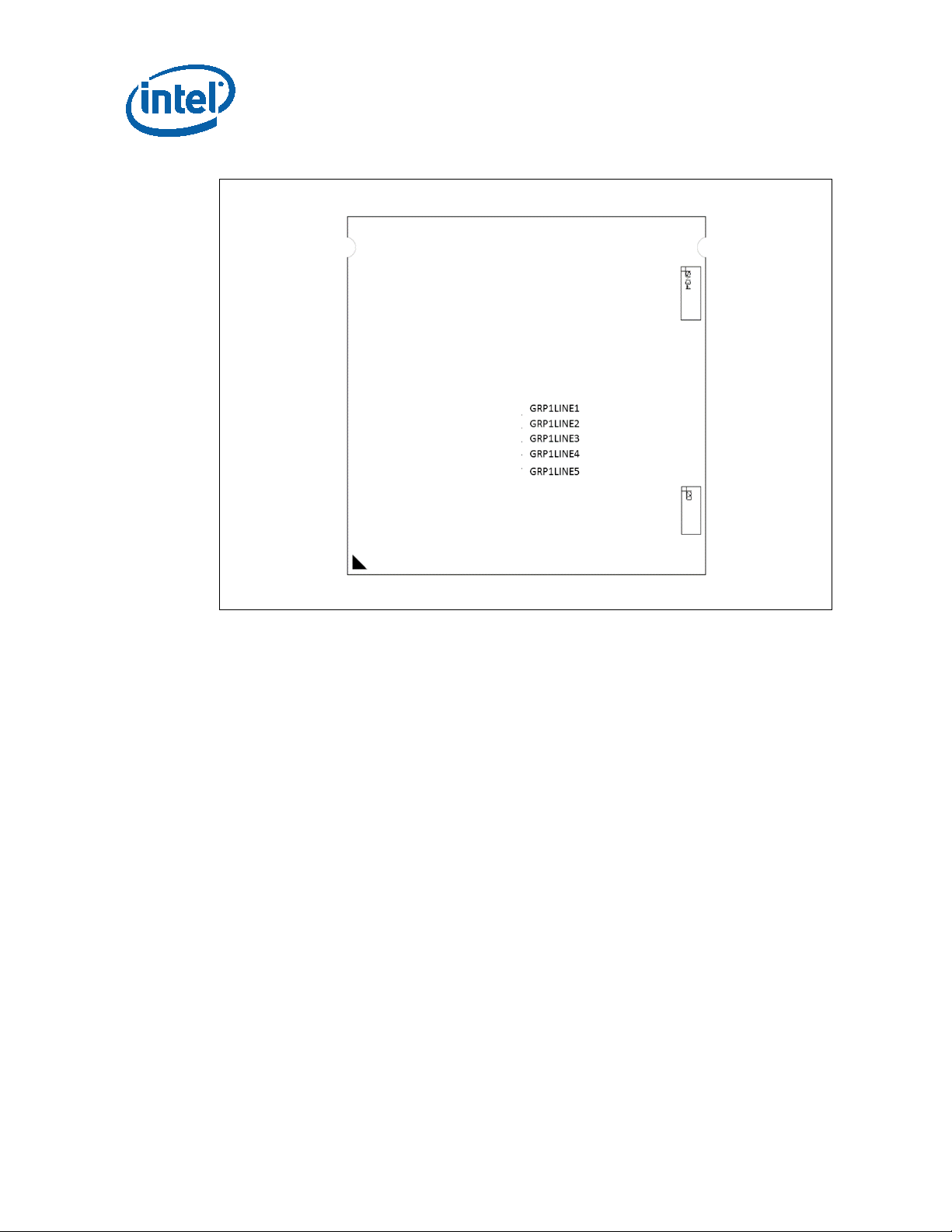
Figure 3. S-Processor Line LGA Top-Side Markings
Identification Information
Pin Count: 1151 Package Size: 37.5 mm x 37.5 mm
Production (SSPEC):
GRP1LINE1: Intel logo
GRP1LINE2: BRAND
GRP1LINE3: PROC#
GRP1LINE4: SSPEC SPEED
GRP1LINE5: {FPO} {eX}
12 Specification Update
Page 13
Identification Information
Table 7. S-Processor Line
S-Spec #
Processor
Number
Step-
ping
Cache Size
Functional
Core
Processor
Graphics
Cores
Processor
Graphics
Freq.
Processor
Graphics
Maximum
Dynamic
Freq.
DDR4
Mem.
(MT/s)
DDR3L
Mem.
(MT/s)
Core Freq.
Turbo 1
Core
Freq.
Rate
Thermal
Design
Power
Slot /
Socket
Type
R32V I5-7600K B-0 6 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.15 GHz 2400 1600 3.8 GHz 4.2 GHz 91 W LGA1151
R32W I5-7400 B-0 6 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1 GHz 2400 1600 3 GHz 3.5 GHz 65 W LGA1151
R332 I5-7400T B-0 6 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1 GHz 2400 1600 2.4 GHz 3 GHz 35 W LGA1151
R334 I5-7600 B-0 6 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.15 GHz 2400 1600 3.5 GHz 4.1 GHz 65 W LGA1151
R335 I5-7500 B-0 6 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.1 GHz 2400 1600 3.4 GHz 3.8 GHz 65 W LGA1151
R336 I5-7600T B-0 6 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.1 GHz 2400 1600 2.8 GHz 3.7 GHz 35 W LGA1151
R337 I5-7500T B-0 6 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.1 GHz 2400 1600 2.7 GHz 3.3 GHz 35 W LGA1151
R338 I7-7700 B-0 8 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.15 GHz 2400 1600 3.6 GHz 4.2 GHz 65 W LGA1151
R339 I7-7700T B-0 8 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.15 GHz 2400 1600 2.9 GHz 3.8 GHz 35 W LGA1151
R33A I7-7700K B-0 8 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.15 GHz 2400 1600 4.2 GHz 4.5 GHz 91 W LGA1151
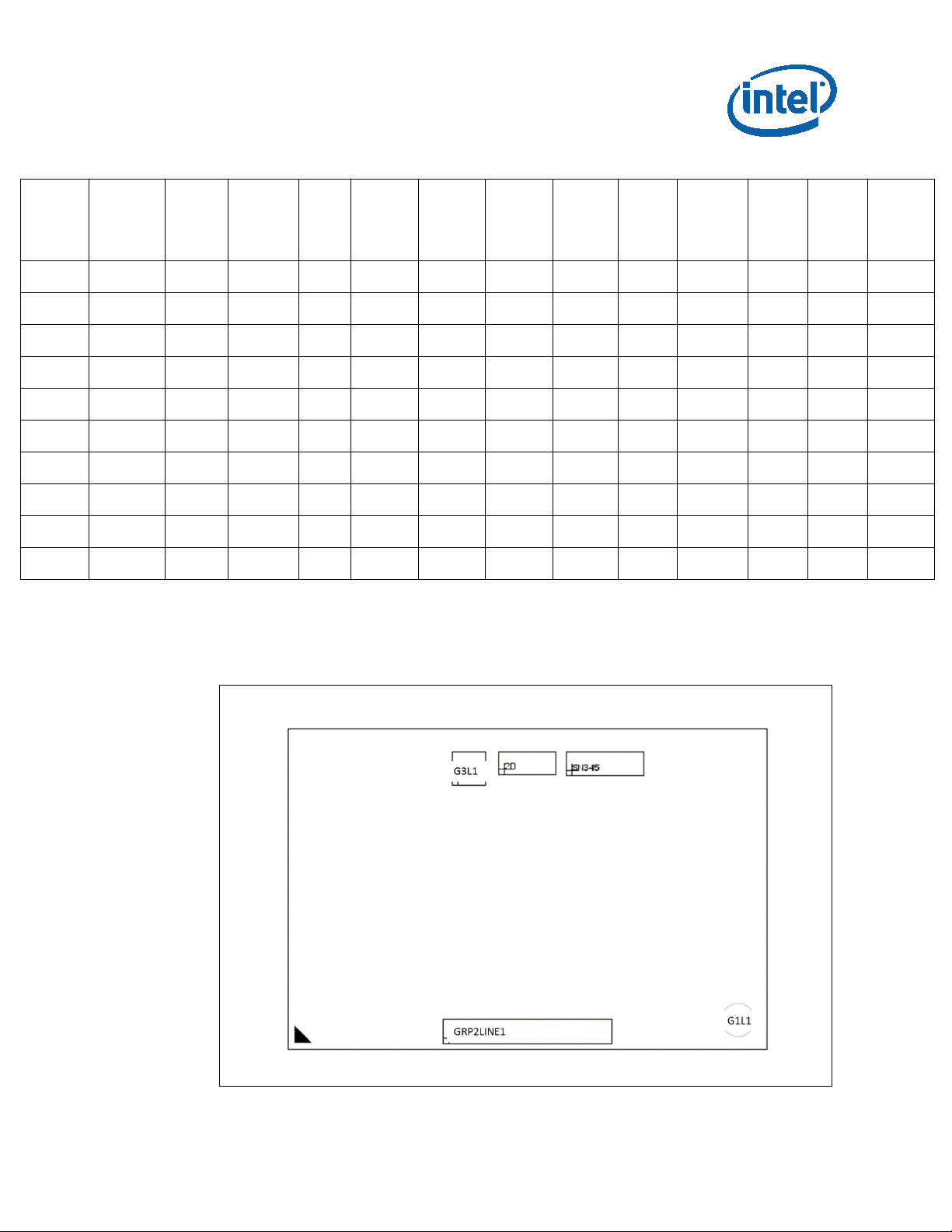
Figure 4. H-Processor Line BGA Top-Side Markings
Specification Update 13
Page 14

Pin Count: 1440 Package Size: 42 mm x 28 mm
Production (SSPEC):
GRP1LINE1 (G1L1): {eX}
GRP2LINE1: FPOxxxxxSSPEC
GRP3LINE1 (G3L1): Intel logo
Table 8. H-Processor Line
Identification Information
S-Spec #
Processor
Number
Step-
ping
Cache
Size
Func
tional
Core
Processor
Graphics
Cores
Processor
Graphics
Freq.
Processor
Graphics
Maximum
Dynamic
Freq.(GHz)
DDR4
Mem.
(MT/s)
LPDDR3
Mem.
(MT/s)
Core Freq.
Turbo 1
Core
Freq.
Rate
Thermal
Design
Power
Slot /
Socket
Type
R32H E3-1535MV6 B-0 8 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.1 GHz 2400 2133 3.1 GHz 4.2 GHz 45 W BGA1440
R32K E3-1505MV6 B-0 8 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.1 GHz 2400 2133 3 GHz 4 GHz 45 W BGA1440
R32L I7-7920HQ B-0 8 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.1 GHz 2400 2133 3.1 GHz 4.1 GHz 45 W BGA1440
R32N I7-7820HQ B-0 8 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.1 GHz 2400 2133 2.9 GHz 3.9 GHz 45 W BGA1440
R32P I7-7820HK B-0 8 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.1 GHz 2400 2133 2.9 GHz 3.9 GHz 45 W BGA1440
R32Q I7-7700HQ B-0 6 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1.1 GHz 2400 2133 2.8 GHz 3.8 GHz 45 W BGA1440
R32R I5-7440HQ B-0 6 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1 GHz 2400 2133 2.8 GHz 3.8 GHz 45 W BGA1440
R32S I5-7300HQ B-0 6 MB 4 2 0.35 GHz 1 GHz 2400 2133 2.5 GHz 3.5 GHz 45 W BGA1440
R32T I3-7100H B-0 3 MB 2 2 0.35 GHz 0.95 GHz 2400 2133 3 GHz 3 GHz 35 W BGA1440
§
14 Specification Update
Page 15

Summary Tables of Changes
Summary Tables of Changes
The following table indicates the Specification Changes, Errata, Specification
Clarifications or Documentation Changes, which apply to the listed processor stepping.
Intel intends to fix some of the errata in a future stepping of the component, and to
account for the other outstanding issues through documentation or Specification
Changes as noted. This table uses the following notations:
Codes Used in Summary Table
Stepping
X: Erratum, Specification Change or Clarification that applies
to this stepping.
(No mark) or (Blank Box): This erratum is fixed in listed stepping or specification
change does not apply to listed stepping.
Status
Doc: Document change or update that will be implemented.
Plan Fix: This erratum may be fixed in a future stepping of the
product.
Fixed: This erratum has been previously fixed.
No Fix: There are no plans to fix this erratum.
Specification Update 15
Page 16

Errata Summary Table
Table 13. Errata Summary Table
Processor Line / Stepping
Summary Tables of Changes
Erratum
ID
KBL-Y KBL-U KBL-H KBL-S
H-0 H-0
iHDCP2.2
H-0 H-0
iHDCP
2.2
J-1
(23e)
B-0 B-0
Status
KBL001 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL002 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL003 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL004 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL005 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL006 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL007 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL008 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL009 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL010 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL011 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL012 X X X X X X X No Fix
Title
Reported Memory Type May Not Be
Used to Access the VMCS and
Referenced Data Structures
Instruction Fetch May Cause Machine
Check if Page Size and Memory Type
Was Changed Without Invalidation
Execution of VAESIMC or
VAESKEYGENASSIST With An Illegal
Value for VEX.vvvv May Produce a
#NM Exception
The Corrected Error Count Overflow
Bit in IA32_ MC0_STATUS is Not
Updated When The UC Bit is Set
VM Exit May Set IA32_EFER.NXE
When IA32_MISC_ENABLE Bit 34 is
Set to 1
SMRAM State-Save Area Above the
4GB Boundary May Cause
Unpredictable System Behavior
x87 FPU Exception (#MF) May be
Signaled Earlier Than Expected
Incorrect FROM_IP Value For an RTM
Abort in BTM or BTS May be
Observed
DR6 Register May Contain an
Incorrect Value When a MOV to SS or
POP SS Instruction is Followed by an
XBEGIN Instruction
Opcode Bytes F3 0F BC May Execute
As TZCNT Even When TZCNT Not
Enumerated by CPUID
#GP on Segment Selector Descriptor
that Straddles Canonical Boundary
May Not Provide Correct Exception
Error Code
The SMSW Instruction May Execute
Within an Enclave
16 Specification Update
Page 17

Summary Tables of Changes
Processor Line / Stepping
Erratum
ID
KBL-Y KBL-U KBL-H KBL-S
H-0 H-0
iHDCP2.2
H-0 H-0
iHDCP
2.2
J-1
(23e)
B-0 B-0
Status
KBL013 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL014 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL015 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL016 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL017 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL018 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL019 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL020 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL021 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL022 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL023 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL024 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL025 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL026 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL027 X X X X X X X No Fix
Title
WRMSR to IA32_BIOS_UPDT_TRIG
Concurrent With an SMX
SENTER/SEXIT May Result in a
System Hang
Intel® PT TIP.PGD May Not Have
Target IP Payload
Operand-Size Override Prefix Causes
64-bit Operand Form of MOVBE
Instruction to Cause a #UD
Execution of FXSAVE or FXRSTOR
With the VEX Prefix May Produce a
#NM Exception
WRMSR May Not Clear The Sticky
Count Overflow Bit in The
IA32_MCi_STATUS MSRs’ Corrected
Error Count Field
PEBS Eventing IP Field May be
Incorrect After Not-Taken Branch
Debug Exceptions May Be Lost or
Misreported Following WRMSR to
IA32_BIOS_UPDT_TRIG
Complex Interactions With Internal
Graphics May Impact Processor
Responsiveness
Intel® Processor Trace PSB+ Packets
May Contain Unexpected Packets
Placing an Intel® PT ToPA in Non-WB
Memory or Writing It Within a
Transactional Region May Lead to
System Instability
VM Entry That Clears TraceEn May
Generate a FUP
Performance Monitor Event For
Outstanding Offcore Requests And
Snoop Requests May be Incorrect
ENCLU[EGETKEY] Ignores
KEYREQUEST.MISCMASK
POPCNT Instruction May Take Longer
to Execute Than Expected
ENCLU[EREPORT] May Cause a #GP
When TARGETINFO.MISCSELECT is
Non-Zero
Specification Update 17
Page 18

Processor Line / Stepping
Summary Tables of Changes
Erratum
ID
KBL-Y KBL-U KBL-H KBL-S
H-0 H-0
iHDCP2.2
H-0 H-0
iHDCP
2.2
J-1
(23e)
B-0 B-0
Status
KBL028 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL029 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL030 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL031 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL032 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL033 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL034 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL035 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL036 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL037 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL038 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL039 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL040 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL041 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL042 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL043 X X X X X X X No Fix
Title
A VMX Transition Attempting to Load
a Non-Existent MSR May Result in a
Shutdown
Transitions Out of 64-bit Mode May
Lead to an Incorrect FDP And FIP
Intel® PT FUP May be Dropped After
OVF
ENCLS[ECREATE] Causes #GP if
Enclave Base Address is Not
Canonical
Processor Graphics IOMMU Unit May
Report Spurious Faults
Processor DDR VREF Signals May
Briefly Exceed JEDEC Spec When
Entering S3 State
DR6.B0-B3 May Not Report All
Breakpoints Matched When a
MOV/POP SS is Followed by a Store
or an MMX Instruction
ENCLS[EINIT] Instruction May
Unexpectedly #GP
Intel® PT OVF Packet May be Lost if
Immediately Preceding a TraceStop
WRMSR to IA32_BIOS_UPDT_TRIG
May be Counted as Multiple
Instructions
Branch Instructions May Initialize
MPX Bound Registers Incorrectly
Writing a Non-Canonical Value to an
LBR MSR Does Not Signal a #GP
When Intel® PT is Enabled
Processor May Run Intel® AVX Code
Much Slower Than Expected
Intel® PT Buffer Overflow May Result
in Incorrect Packets
Last Level Cache Performance
Monitoring Events May Be Inaccurate
#GP Occurs Rather Than #DB on
Code Page Split Inside an Intel® SGX
Enclave
18 Specification Update
Page 19

Summary Tables of Changes
Processor Line / Stepping
Erratum
ID
KBL-Y KBL-U KBL-H KBL-S
H-0 H-0
iHDCP2.2
H-0 H-0
iHDCP
2.2
J-1
(23e)
B-0 B-0
Status
KBL044 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL045 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL046 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL047 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL048 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL049 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL050 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL051 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL052 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL053 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL054 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL055 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL056 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL057 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL058 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL059 X X X X X X X No Fix
Title
Execution of VAESENCLAST
Instruction May Produce a #NM
Exception Instead of a #UD
Exception
Intel® SGX Enclave Accesses to the
APIC-Access Page May Cause APICAccess VM Exits
CR3 Filtering Does Not Compar e Bits
[11:5] of CR3 and
IA32_RTIT_CR3_MATCH in PAE
Paging Mode
x87 FDP Value May be Saved
Incorrectly
PECI Frequency Limited to 1 MHz
Processor Graphics IOMMU Unit May
Not Mask DMA Remapping Faults
Intel® PT CYCThresh Value of 13 is
Not Supported
Enabling VMX-Preemption Timer
Blocks HDC Operation
Integrated Audio Codec May Not be
Detected
Display Flickering May be Observed
with Specific eDP Panels
Incorrect Branch Predicted Bit in
BTS/BTM Branch Records
MACHINE_CLEARS.MEMORY
ORDERING Performance Monitoring
Event May Undercount
Some Counters May Not Freeze On
Performance Monitoring Interrupts
Instructions And Branches Retired
Performance Monitoring Events May
Overcount
Some OFFCORE_RESPONSE
Performance Monitoring Events May
Overcount
#GP After RSM May Push Incorrect
RFLAGS Value When I n t el® PT is
Enabled
Specification Update 19
Page 20

Processor Line / Stepping
Summary Tables of Changes
Erratum
ID
KBL-Y KBL-U KBL-H KBL-S
H-0 H-0
iHDCP2.2
H-0 H-0
iHDCP
2.2
J-1
(23e)
B-0 B-0
Status
KBL060 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL061 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL0621 X X Fixed
KBL063 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL064 X X
KBL065 X X
No Fix
No Fix
KBL066 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL067 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL068 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL069 X X X X X X X No Fix
KBL070
KBL071
X X
X X
X X X X X No Fix
X X X X X No Fix
KBL072
X X
X X X X X No Fix
KBL073
X X X X X No Fix
X X X X X No Fix
KBL074
X X
X X
Title
Access to SGX EPC Page in BLOCKED
State is Not KBL062Reported as an
SGX-Induced Page Fault
MTF VM Exit on XBEGIN Instruction
May Save State Incorrectly
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology May
be Incorrectly Reported as Supported
on Intel® Core™ i3 U/H/S, Intel®
Mobile Pentium®, Intel® Mobile
Celeron®, Select Intel® Pentiu m®
and Intel® Celeron® Processors
Performance Monitoring Counters
May Undercount When Using CPL
Filtering
Executing a 256 Bit AVX Instruction
May Cause Unpredictable Behavior
System May Hang During Display
Power Cycles
Certain Non-Canonical
IA32_BNDCFGS Values Will Not
Cause VM-Entry Failures
PEBS EventingIP Field May Be
Incorrect Under Certain Conditions
HWP’s Guaranteed_Performance
Updated Only on Configurable TDP
Changes
RF May be Incorrectly Set in The
EFLAGS That is Saved on a Fault in
PEBS or BTS
Intel® PT ToPA PMI Does Not Freeze
Performance Monitoring Counters
HWP’s Maximum_Performance Value
is Reset to 0xFF
HWP’s Guaranteed_Performance and
Relevant Status/Interrupt May be
Updated More Than Once Per Second
Some Memory Performance
Monitoring Events May Produce
Incorrect Results When Filtering on
Either OS or USR Modes
HWP May Generate Thermal Interrupt
While Not Enabled
20 Specification Update
Page 21

Summary Tables of Changes
Processor Line / Stepping
Erratum
ID
KBL075
KBL076
KBL077
KBL078
KBL079
KBL080
KBL081
KBL082
KBL083
KBL084
KBL085
KBL086
KBL087
KBL088
KBL089
KBL090
KBL-Y KBL-U KBL-H KBL-S
H-0 H-0
iHDCP2.2
X X
X
X
X X
X X
X X
H-0 H-0
iHDCP
2.2
J-1
(23e)
B-0 B-0
X X X X X No Fix
X No Fix
X
X X X
X X No Fix
X X Fixed
X X No Fix
X X X X X No Fix
X X X X X No Fix
Status
No Fix
No Fix
X X No Fix
X X X X X X X No Fix
X No Fix
X X X X X No Fix
X X X X X X X No Fix
X X X X X X X No Fix
X X X X X X X No Fix
Title
Camera Device Does Not Issue an
MSI When INTx is Enabled
An x87 Store Instruction Which Pends
#PE May Lead to Unexpected
Behavior When EPT A/D is Enabled.
Use of VMASKMOV to Store When
Using EPT May Fail
PECI May Not be Functional After
Package C10 Resume
Attempts to Retrain a PCIe* Link May
be Ignored
PCIe* Expansion ROM Base Address
Register May be Incorrect
PCIe* Port Does Not Support DLL Link
Activity Reporting
BNDLDX And BNDSTX May Not Signal
#GP on Non-Canonical Bound
Directory Access
RING_PERF_LIMIT_REASONS May be
Incorrect
Processor May Exceed VCCCore
ICCMAX During Multi-core Turbo
Performance Monitoring Load Latency
Events May Be Inaccurate For Gather
Instructions
EDRAM Corrected Error Events May
Not be Properly Logged After a Warm
Reset
Unpredictable System Behavior May
Occur When System Agent Enhanced
Intel® Speedstep® is Enab led
Processor May Hang Under Complex
Scenarios
Some Bits in MSR_MISC_PWR_MGMT
May be Updated on Writing Illegal
Values to This MSR
Violations of Intel® Software Guard
Extensions (Intel® SGX) AccessControl Requirements Produce #GP
Instead of #PF
Specification Update 21
Page 22

Processor Line / Stepping
Summary Tables of Changes
Erratum
ID
KBL091
Notes:
1. Affects 7th Generation Intel® Core™ i3 U, Intel® Pentium®, Intel® Celeron® Processors.
2. Processor line and Stepping information:
– Y-Processor Line stepping H-0:
• Without iHDCP2.2 (Mobile)
• With iHDCP2.2 (Mobile)
– U-Processor Line stepping: H-0
• Without iHDCP2.2 (Mobile)
• With iHDCP2.2 (Mobile)
KBL-Y KBL-U KBL-H KBL-S
H-0 H-0
iHDCP2.2
H-0 H-0
iHDCP
2.2
J-1
(23e)
B-0 B-0
X X X X X X X No Fix
§
Status
Title
IA32_RTIT_CR3_MATCH MSR
Bits[11:5] Are Treated As Reserv ed
22 Specification Update
Page 23

Errata
Errata
KBL001
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
KBL002
Reported Memory Type May Not Be Used to Access the VMCS and
Referenced Data Structures
Bits 53:50 of the IA32_VMX_BASIC MSR report the memory type that the processor
uses to access the VMCS and data structures referenced by pointers in the VMCS.
Due to this erratum, a VMX access to the VMCS or referenced data struct ures will
instead use the memory typ e that the MTRRs (memory-type range registers) specify
for the physical address of the access.
Bits 53:50 of the IA32_VMX_BASIC MSR report that the WB (write-back) memory
type will be used but the processor may use a different memory type.
Software should ensure that the VMCS and referenced data struct ures are located at
physical addresses that are mapped to WB memory type by the MTRRs.
Instruction Fetch May Cause Machine Check if Page Size and Memory Type
Was Changed Without Invalidation
This erratum may cause a machine-check error
(IA32_MCi_STATUS.MCACOD=0150H) on the fetch of an instruction that crosses a 4KByte address boundary. It applies only if (1) the 4-KByte linear region on which the
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
instruction begins is originally translated using a 4-KByte page with the WB memory
type; (2) the paging structures are later modified so that linear regio n is translated
using a large page (2-MByte, 4-MByte, or 1-GByte) w ith the UC memory type; and
(3) the instruction fetch occurs after the paging-structure modif ic ation but before
software invalidates any TLB entries for the linear region.
Due to this erratum an unexpected machine check with error code 0150H may occur,
possibly resulting in a shutdown. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software.
Software should not write to a paging-structure entry in a way that would change, for
any linear address, both the page si ze and the memory type. It can instead use the
following algorithm: first clear the P flag in the relevant paging-structu re entry (e.g.,
PDE); then invalidate any transla tions for the affected linear add r esses; and then
modify the relevant paging-structure entry to set the P flag and establish the new
page size and memory type.
KBL003
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Execution of VAESIMC or VAESKEYGENASSIST With An Illegal Value for
VEX.vvvv May Produce a #NM Exception
The VAESIMC and VAESKEYGENASSIST instructions should produce a #UD (InvalidOpcode) exception if the value of the vvvv field in the VEX prefix is not 1111b. Due to
this erratum, if CR0.TS is “1”, the processor may instead produce a # NM (DeviceNot-Available) excep tion.
Due to this erratum, some undefined instruction encodings may produce a #NM
instead of a #UD exception.
Software should always set the vvvv field of the VEX prefix to 1111b for instances of
the VAESIMC and VAESKEYGENASSIST instructions.
Specification Update 23
Page 24

Errata
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
KBL004
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
The Corrected Error Count Overflow Bit in IA32_ MC0_STATUS is Not
Updated When The UC Bit is Set
After a UC (uncorrected) error is logged in the IA32_MC0_STATUS MSR (401H),
corrected errors will continue to b e counted in the lower 14 bits (bits 5 1:38) of the
Corrected Error Count. Due to this erratum, the sticky count overflow bit (bit 52) of
the Corrected Error Count will not get updated when the UC bit (bit 61) is set to 1.
The Corrected Error Count Overflow indication will be lost if the overflow occurs after
an uncorrectable error has been logged.
KBL005
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
VM Exit May Set IA32_EFER.NXE When IA32_MISC_ENABLE Bit 34 is Set to
1
When “XD Bit Disable” in the IA32_MISC_ENABLE MSR (1A0H) bit 34 is set to 1, it
should not be possible to enable t he “execute disable” feature by se tting
IA32_EFER.NXE. Due to th is erratum, a VM exit that occurs with the 1-setting of the
“load IA32_EFER” VM-exit control may set IA32_EFER.NXE even if
IA32_MISC_ENABLE bit 34 is set to 1. This erratum can occur only if
IA32_MISC_ENABLE bit 34 was set by guest software in VMX non-root operation.
Software in VMX root operation may execute with the “execute disable ” f eature
enabled despite the fact that the feature should be disabled by the
IA32_MISC_ENABLE MSR. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially
available software.
A virtual-machine monitor should not allow guest software to write to the
IA32_MISC_ENABLE MSR
KBL006
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
SMRAM State-Save Area Above the 4GB Boundary May Cause Unpredictable
System Behavior
If BIOS uses the RSM instruction to load the SMBASE register with a value that would
cause any part of the SMRAM state-save area to have an address above 4-GBytes,
subsequent transitions into and out of SMM (system-management mode) might save
and restore processor state from incorrect addresses.
This erratum may cause unpredictable system behavior. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available system.
Ensure that the SMRAM state-save area is loca ted entirely below the 4GB address
boundary.
24 Specification Update
Page 25

Errata
KBL007 x87 FPU Exception (#MF) May be Signaled Earlier Than Expected
x87 instructions that trigger #MF normally service interrupts before the #MF. Due to
this erratum, if an instruction that triggers #MF is executing when a n Enhanced Intel
Problem
Implication Software may observe #MF being signaled before pending interrupts ar e serviced.
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
SpeedStep® Technology transitions, an Intel® Turbo Boost Technology transitions,
or a Thermal Monitor events occurs, the #MF may be taken before pending interrupts
are serviced.
KBL008 Incorrect FROM_IP Value For an RTM Abort in BTM or BTS May be Observed
During RTM (Restricted Transactional Memory ) op er ation when branch tracing is
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
enabled using BTM (Branch Trace Message) or BTS (Branch Trace Store) , the
incorrect EIP value (From_IP pointer) may be observed for an RTM abort.
Due to this erratum, the From_IP pointer may be the same as that of the
immediately preceding taken branch.
KBL009
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
DR6 Register May Contain an Incorrect Value When a MOV to SS or POP SS
Instruction is Followed by an XBEGIN Instruction
If XBEGIN is executed immediately after an execution of MOV to SS or POP SS, a
transactional abort occurs and the logical processor restarts execution from the
fallback instruction address. If ex ecution of the instruction at that ad dress causes a
debug exception, bits [3:0] of the DR6 register may contain an incorrect value.
When the instruction at the fallba ck instruction address causes a debug exception,
DR6 may report a breakpoint that was not triggered by that instruction, or it may fail
to report a breakpoint that was triggered by the instruction.
Avoid following a MOV SS or POP SS instruction immediate ly with an XBEGIN
instruction.
KBL010
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Opcode Bytes F3 0F BC May Execute As TZCNT Even When TZCNT Not
Enumerated by CPUID
If CPUID.(EAX=07H, ECX=0):EBX.BMI1 (bit 3) is 1 then opcode bytes F3 0F BC
should be interpreted as TZCNT oth er wise they will be interpreted a s REP BSF. Due to
this erratum, opcode bytes F3 0F BC may execute as TZCNT even if
CPUID.(EAX=07H, ECX=0):EBX.BMI1 (bit 3) is 0 .
Software that expects REP prefix before a BSF instruction to be ignored may not
operate correctly since there are ca ses in which BSF and TZCNT differ with regard to
the flags that are set and how the destination operand is established.
Software should use the opcode bytes F3 0F BC only if CPUID.(EAX=07H,
ECX=0):EBX.BMI1 (bit 3) is 1 and only if the functionality of TZCNT (and not BSF) is
desired.
Specification Update 25
Page 26

Errata
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
KBL011
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
#GP on Segment Selector Descrip t or that Straddles Canonical Bound a ry May
Not Provide Correct Exception Error Code
During a #GP (General Protection E xception), the processor pushes an error code on
to the exception handler’s stack. If the segment selector descriptor s tr a ddles the
canonical boundary, the error code pushed onto the stack may be incorrect.
An incorrect error code may be pushed onto the stack. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
KBL012 The SMSW Instruction May Execute Within an Enclave
The SMSW instruction is illegal within an SGX (Software Guard Extensions) enclave,
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
and an attempt to execute it within an enclave should result in a #UD (invalid-opcode
exception). Due to this erratum, th e instruction executes normally within an enclave
and does not cause a #UD.
The SMSW instruction provides access to CR0 bits 15:0 and will provide that
information inside an enclave. These bits include N E, ET, TS, EM, MP and PE.
None identified. If SMSW execution inside an enclave is unacceptable, syste m
software should not enable SGX.
KBL013
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e Summary Table of Changes.
WRMSR to IA32_BIOS_UPDT_TRIG Concurrent With an SMX SENTER/SEXIT
May Result in a System Hang
Performing WRMSR to IA32_BIOS_UPDT_TRIG (MSR 79H) on a logical processor
while another logical processor is ex ecuting an SMX (Safer Mode Extensions)
SENTER/SEXIT operation (GETSEC[SENTER] or GETSEC[SEXIT] instruction) may
cause the processor to hang.
When this erratum occurs, the system will hang. Intel has not observ ed this erratum
with any commercial ly available system.
KBL014 Intel® PT TIP.PGD May Not Have Target IP Payload
When Intel PT (Intel Processor Trace) is enabled and a direct unconditional branch
Problem
Implication
Workaround
clears IA32_RTIT_STATUS.FilterEn (MSR 571H, bit 0), due to this erratum, the
resulting TIP.PGD (Target IP Packet, Packet Generation Disable) may not have an IP
payload with the target IP.
It may not be possible to tell which instruction in the flow caused the TIP.PGD using
only the information in trace packets when this erratum occurs.
The Intel PT trace decoder can compa re direct unconditional branc h tar gets in the
source with the FilterEn address range(s) to determine which branch cleared FilterEn.
26 Specification Update
Page 27

Errata
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
KBL015
Problem
Implication
Workaround Do not use a 66H instruction prefix with a 64-bit operand MOVBE instruction.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Operand-Size Override Prefix Causes 64-bit Oper a n d F orm of MOVBE
Instruction to Cause a #UD
Execution of a 64 bit operand MOVBE instruction with an operand-size override
instruction prefix (66H) may incorrectly cause an invalid-opcode exception (#UD).
A MOVBE instruction with both REX.W=1 and a 66H prefix will unexpectedly cause an
#UD (invalid-opcode excep tion). Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software.
KBL016
Problem
Implication
Workaround Software should not use FXSAVE or FXRSTOR with the VEX prefix.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Execution of FXSAVE or FXRSTOR With the VEX Prefix May Produce a #NM
Exception
Attempt to use FXSAVE or FXRSTOR with a VEX prefix should produce a #UD
(Invalid-Opcode) exception. If either the TS or EM flag bits in CR0 are set, a #NM
(device-not-available) exception will be raised instead of #UD exce ption.
Due to this erratum a #NM exception may be signaled instead of a #UD exception on
an FXSAVE or an FXRSTOR with a VEX prefix.
KBL017
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
WRMSR May Not Clear The Sticky Count Overflow Bit in The
IA32_MCi_STATUS MSRs’ Corrected Error Count Field
The sticky count overflow bit is the most significant bit (bit 52) of the Corrected Error
Count Field (bits[52:38]) in IA32_MCi_STATUS MSRs. Once set, the sticky count
overflow bit may not be cleared by a WRMSR instruction. When this occurs, that bit
can only be cleared by power-on reset.
Software that uses the Corrected Error Count field and expects to be able to clear the
sticky count overflow bit may misinterpret the number of corrected errors when the
sticky count overflow bit is set. This erratum does not affect threshold-based CMCI
(Corrected Machine Check Error Interrupt) signaling.
KBL018 PEBS Eventing IP Field May be Incorrect After Not-Taken Branch
When a PEBS (Precise-Event-Based-Sampling) record is logged immediately after a
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
not-taken conditional branch (Jcc instruction) , th e Ev enting IP field should contain
the address of the first byte of the Jcc instruction. Due to this erratum, it may instead
contain the address of the instruction preceding the Jcc instruct io n.
Performance monitoring software using PEBS may incorrectly attribute PEBS events
that occur on a Jcc to the preceding instruction.
Specification Update 27
Page 28

Errata
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
KBL019
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Debug Exceptions May Be Lost or Misreported Following WRMSR to
IA32_BIOS_UPDT_TRIG
If the WRMSR instruction writes to the IA32_BIOS_UPDT_TRIG MSR (79H)
immediately after an execution of MOV SS or POP SS that generated a debug
exception, the processor may fail to deliver the debug exception or, if it does, the
DR6 register contents may not correctly reflect the causes of the debug exception.
Debugging software may fail to operate properly if a debug exception is lost or does
not report complete information.
Software should avoid using WRMSR instruction immediately after executing MOV SS
or POP SS
KBL020
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, se e the Summary Table of Changes.
Complex Interactions With Internal Graphics May Impact Processor
Responsiveness
Under complex conditions associated with the use of internal graphics, the processor
may exceed the MAX_LAT CSR values (PCI configuration space, offset 03FH,
bits[7:0]).
When this erratum occurs, the processor responsiveness is affected . Intel has not
observed this erratum with any com mercially available software.
KBL021 Intel® Processor Trace PSB+ Packets May Contain Unexpected Packets
Some Intel Processor Trace packets should be issued only between TIP.PGE (Target
Problem
Implication Due to this erratum, FUP and MODE.Exe c may be generated unexpectedly.
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
IP Packet.Packet Generation Ena b le) and TIP.PGD (Target IP Packet.Packet
Generation Disable) packets. Due to this erratum, when a TIP.PGE packet is
generated it may be preceded by a PSB+ (Packet Stream Boundary) that incorrectly
includes FUP (Flow Update Packet) and MODE.Exec packets.
Decoders should ignore FUP and MODE.Exec packets tha t are not between TIP.PGE
and TIP.PGD packets.
KBL022
Problem
Implication Unusual treatment of the To P A may lead to system instabili ty .
Workaround
Placing an Intel® PT ToPA in Non-WB Memory or Writing It Within a
Transactional Region May Lead to System Instability
If an Intel PT (Intel® Processor Tra ce) T oPA (Table of Physical Addresses) is not
placed in WB (writeback) memory or is written by software executing within an
Intel® TSX (Intel® Transactional Synchroniz a tion Extension) transactional region,
the system may become unstable.
None identified. Intel PT ToPA should reside in WB me mory and should not be written
within a Transactional Region.
28 Specification Update
Page 29

Errata
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
KBL023 VM Entry That Clears TraceEn May Generate a FUP
If VM entry clears Intel® PT (In tel Processor Trace) IA32_RTI T _CTL.TraceEn (MSR
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
570H, bit 0) while PacketEn is 1 then a FUP (Flow Update Packet) will precede the
TIP.PGD (Target IP Packet, Packet Generation Disable). VM entry can clear TraceEn if
the VM-entry MSR-load area includes an entry for the IA32_RTIT_CTL MSR.
When this erratum occurs, an unexpected FUP may be generated that cre a tes the
appearance of an asynchronous event taking place immediately before or during the
VM entry.
The Intel PT trace decoder may opt to ignore any FUP whose IP matches that of a VM
entry instruction.
KBL024
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Performance Monitor Event For Out s t a n d ing Offcore Requests And Snoop
Requests May be Incorrect
The performance monitor event OFFCORE_REQUESTS _OUTSTANDING (Event 60H,
any Umask Value) should count the number of offcore outstanding transactions each
cycle. Due to this erratum, the counts ma y be higher or lower than expected.
The performance monitor event OFFCORE_REQUESTS_OUTSTANDING may reflect an
incorrect count.
KBL025 ENCLU[EGETKEY] Ignores KEYREQUEST.MISCMASK
The Intel® SGX (Software Guard Extensions) ENCLU[EGETKEY] instruction ignores
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
the MISCMASK field in KEYREQUEST structure when computing a provisioning key, a
provisioning seal key, or a seal key.
ENCLU[EGETKEY] will return the same key in response to two requests that differ
only in the value of KEYREQUEST.MISCMASK. Intel has not observed this erratum
with any commercially available software.
When executing the ENCLU[EGETKEY] instruction, software should ensure the bits set
in KEYREQUEST.MISCMASK are a subset of the bits set in the current SECS’s
MISCSELECT field.
KBL026 POPCNT Instruction May Take Longer to Execute Than Expected
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
POPCNT instruction execution with a 32 or 64 bit operand may be delayed until
previous non-dependent instructions have e xecuted.
Software using the POPCNT instruction may experience lower performance than
expected.
Specification Update 29
Page 30

KBL027
ENCLU[EREPORT] May Cause a #GP When TARGETINFO.MISCSELECT is NonZero
Errata
Problem
Implication This erratum may cause unexpected general-protection exceptions inside enclaves.
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
The Intel® SGX (Software Guard extensions) ENCLU[EREPORT] instruction may
cause a #GP (general protection fault) if any bit is set in TARGETINFO structure’s
MISCSELECT field.
When executing the ENCLU[EREPORT] instruction, software shou ld ensure the bits set
in TARGETINFO.MISCSELECT are a subset of the bits set in the current SECS’s
MISCSELECT field.
KBL028
Problem
Implication Due to this erratum, the hypervisor ma y experience an unexpected shu tdown.
Workaround Software should not configure VMX transitions to load non-existent MSRs.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
A VMX Transition Attempting to Load a Non-Existent MSR May Result in a
Shutdown
A VMX transition may result in a shutdown (without g enerating a machine-check
event) if a non-existent MSR is included in the associated MSR-load area. When such
a shutdown occurs, a machine check err or will be logged with
IA32_MCi_STATUS.MCACOD (bits [15:0]) of 406H, but the processor does not issue
the special shutdown cycle. A hard w are reset must be used to restart the processor.
KBL029 Transitions Out of 64-bit Mode May Lead to an Incorrect FDP And FIP
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
A transition from 64-bit mode to compatibility or legacy modes may result in cause a
subsequent x87 FPU state save to zeroing bits [63:3 2] of the FDP (x87 FPU Data
Pointer Offset) and the FIP (x87 FPU Instruction Pointer Offset).
Leaving 64-bit mode may result in incorrect FDP and FIP values when x8 7 FPU state
is saved.
None identified. 64-bit software should save x87 FPU sta te before leaving 64-bit
mode if it needs to access the FDP and/or FIP values.
KBL030 Intel® PT FUP May be Dropped After OVF
Problem
Implication When this erratum occurs, an unexpected packet sequence is generate d.
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Some Intel PT (Intel Processor Trace) OVF (Overflow) packets may not be followed by
a FUP (Flow Update Packet) or TIP.PGE (Target IP Packet, Packet Generation Enable).
When it encounters an OVF without a following FUP or TIP.P GE, the Intel PT trace
decoder should scan for the next TIP, TIP.PGE, or PSB+ to resume operation.
30 Specification Update
Page 31

Errata
KBL031 ENCLS[ECREATE] Causes #GP if Enclave Base Address is Not Canonical
The ENCLS[ECREATE] instruction uses an SECS (SGX enclave control structure)
referenced by the SRCPAGE pointer in the PAGEINFO structure, whi ch is referenced
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
by the RBX register. Due to this erratum, the instruction causes a #GP (generalprotection fault) if the S E CS attributes indicate th at the enclave should operate in 64bit mode and the enclave base linear address in the SECS is not canonical.
System software will incur a genera l-protection fault if it mistakenly programs the
SECS with a non-canonical address. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software.
System software should always specify a canonical address as the ba se address of
the 64-bit mode enclave.
KBL032 Processor Graphics IOMMU Unit May Report Spurious Faults
The IOMMU unit for Processor Graphics pre-fetches context (or extended-context)
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
entries to improve perfor mance. Due to the erratum, the IOMMU unit may repor t
spurious DMA remapping faults if prefetching encounters a contex t (or extendedcontext) entry which is not mark ed present.
Software may observe spurious DMA remapping faults when the present bit for the
context (or extended-context) en tr y corresponding to the Processor Graphics device
(Bus: 0; Device: 2; Function: 0) is cleared. These faults may be reported when the
Processor Graphics device is quiescent.
None identified. Instead of marking a context not present, software should mark the
context (or extended-context) en tr y present while using the page table to indicate all
the memory pages referenced by the context entry is not present.
KBL033
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Processor DDR VREF Signals May Bri efly Exceed JEDEC Spec When Ent erin g
S3 State
Voltage glitch of up to 200mV on the VREF signal lasting for about 1mS may be
observed when entering System S3 state. This violates the JEDEC DDR specifications.
Intel has not observed this erratum to impact the operation of any commercially
available system.
Specification Update 31
Page 32

Errata
KBL034
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
DR6.B0-B3 May Not Report All Breakpoints Matched When a MOV/POP SS is
Followed by a Store or an MMX Instruction
Normally, data breakpoints matches that occur on a MOV SS, r/m or POP SS will not
cause a debug exception immediately after MOV/POP SS but will be delayed until the
instruction boundary following the next instruction is reached. After the debug
exception occurs, DR6.B0-B3 bits will contain information about data breakpoints
matched during the MOV/POP SS as well as breakpoints detected by the following
instruction. Due to this erratum, DR6.B0-B3 bits may no t contain information about
data breakpoints matched during the MOV/POP SS when the following instruction is
either an MMX instruction that uses a memory addr essing mode with an index or a
store instruction.
When this erratum occurs, DR6 may not contain information about all breakpoints
matched. This erratum will not be observed under the recommended us age of the
MOV SS,r/m or POP SS instructions (i.e., following the m only with an instruction that
writes (E/R)SP).
KBL035 ENCLS[EINIT] Instruction May Unexpectedly #GP
When using Intel® SGX (Software Guard Extensio ns), the ENCLS[EINIT] instruction
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
will incorrectly cause a #GP (general protection fault) if the MISCSELECT field of the
SIGSTRUCT structure is not zero.
This erratum may cause an unexpected #GP, but only if software has set bits in the
MISCSELECT field in SIGSTRUCT structure that do not correspond to extended
features that can be written to the MISC region of the SSA (State Save Area). Intel
has not observed this erratum with any commercially available so ftw a r e.
When executing the ENCLS[EINIT] instruction, software should only set bits in the
MISCSELECT field in the SIGSTRUCT structure tha t ar e enumerated as 1 by
CPUID.(EAX=12H,ECX=0):EBX (the bit vect o r of extended features that can be
written to the MISC region of the SSA).
KBL036 Intel® PT OVF Packet May be Lost if Immediately Preceding a TraceStop
If an Intel PT (Intel® Processor Trace) internal buffer overflow occurs immediately
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
before software executes a taken branch or event that enters an Intel PT TraceStop
region, the OVF (Overflow) packet may be lost.
The trace decoder will not see the O V F p acket, nor any subsequent packets (e.g.,
TraceStop) that were lost due to overflow.
KBL037 WRMSR to IA32_BIOS_UPDT_TRIG May be Counted as Multiple Instructions
Problem
32 Specification Update
When software loads a microcode update by writing to MSR IA32_BIOS_UPDT_TRIG
(79H) on multiple logical processo rs in parallel, a logical processor may, due to this
erratum, count the WRMSR instru ction as multiple instruction-retired events.
Page 33

Errata
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Performance monitoring with the instruction-retired event may over count by up to
four extra events per instance of WRMSR which targets the IA32_BIOS_UPDT_TRIG
register.
KBL038 Branch Instructions May Initialize MPX Bound Registers Incorrectly
Depending on the current Intel® MPX (Memory Protection Extensions) configuratio n,
execution of certain branch instructions (near CALL, near RET, near JMP, and Jcc
instructions) without a BND prefix (F2H) initialize the MPX bound registers. Due to
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
this erratum, execution of such a branch instruction on a user-mode page may not
use the MPX configuration register appropriate to the current privilege level
(BNDCFGU for CPL 3 or BNDCFGS otherwise) for determining whether to initialize the
bound registers; it may thus initialize the bound registers when it should not, or fail
to initialize them wh en it should.
After a branch instruction on a user-mode page has executed, a #BR (bound-range)
exception may occur when it should not have or a #BR may not occur when one
should have.
If supervisor software is not expected to execute instructions on user-mode pages,
software can avoid this erratum by setting CR4.SMEP[bit 20] to enable supervisormode execution prevention (SMEP). If SMEP is not available or if supervisor software
is expected to execute instruction s on user-mode pages, no workaround is identified.
KBL039
Problem
Implication Due to this erratum, an expected #GP may not be signaled.
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Writing a Non-Canonical Value to an LBR MSR Does Not Signal a #GP When
Intel® PT is Enabled
If Intel PT (Intel Processor Trace) is enabled, WRMSR will not cause a generalprotection exception (#G P) on an attempt to write a non-canonical value to any of
the following MSRs:
• MSR_LASTBRANCH_{0 - 31}_FROM_IP (680H – 69FH)
• MSR_LASTBRANCH__{0 - 31}_TO_IP (6C0H – 6DFH)
• MSR_LASTBRANCH_FROM_IP (1DBH)
• MSR_LASTBRANCH_TO_IP (1DCH)
• MSR_LASTINT_FROM_IP (1DDH)
• MSR_LASTINT_TO_IP (1DEH)Instead the same behavior will occur as if a canonical
value had been written. Specifically, the WRMSR will be dropped and the MSR value
will not be changed.
KBL040 Processor May Run Intel® AVX Code Much Slower Than Expected
Problem After a C6 state exit, the execut io n r ate of AVX instructions may be reduced.
Implication Applications using AVX instructions may run slower than expected.
Specification Update 33
Page 34

Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
KBL041 Intel® PT Buffer Overflow May Result in Incorrect Packets
Errata
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Under complex micro-architectural conditions, an Intel PT (Processor Trace) OVF
(Overflow) packet may be issued after the first byte of a multi-byte CYC (Cycle
Count) packet, instead of any remaining bytes of the CYC.
When this erratum occurs, the splicing of the CYC and OVF packets may prevent the
Intel PT decoder from recognizing the overflow. The Intel PT decoder may then
encounter subsequent packets that are not consistent with expected behavior.
None Identified. The decoder may b e a b le to recognize that this erratum has
occurred when a two-byte CYC packet is followed by a single byte CYC, where the
latter 2 bytes are 0xf302, and where the CYC packets are followed by a FUP (Flow
Update Packet) and a PSB+ (Packet Stream Boundary+). It should then treat the
two CYC packets as indicating an overflow.
KBL042 Last Level Cache Performance Monitoring Events May be Inaccurate
The performance monitoring events LONGEST_LAT_CACHE.REFERENCE (Event 2EH;
Problem
Implication LONGEST_LAT_CACHE events may be incorrect.
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Umask 4FH) and LONGEST_LAT_CACHE.MISS (Event 2EH; Umask 41H) count
requests that reference or miss in the last level cache. However, due to this erratum,
the count may be incorrect.
None identified. Software may use the following OFFCORE_REQUESTS model-specific
sub events that provide related performance monitoring data:
DEMAND_DATA_RD, DEMAND_CODE_RD, DEMAND_RFO, ALL_DATA_RD,
L3_MISS_DEMAND_DATA_RD, ALL_REQUESTS.
KBL043
Problem
Implication Debugging software may not be invoked when an instruction breakpoint is detected.
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
#GP Occurs Rather Than #DB on Code Page Split Inside an Intel® SGX
Enclave
When executing within an Intel® SGX (Softwar e Guard Extensions) enclave, a #GP
(general-protection exception) may be delivered instead of a #DB (d eb ug exception)
when an instruction breakpoint is detected. This occurs when the instruction to be
executed spans two pages, the second o f which has an entry in the EPCM (enclave
page cache map) that is not valid.
Software should ensure that all pages containing enclave instructions have valid
EPCM entries.
34 Specification Update
Page 35

Errata
KBL044
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e id e nt ifi e d .
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Execution of VAESENCLAST Instruction May Produce a #NM Exception
Instead of a #UD Exception
Execution of VAESENCLAST with VEX.L= 1 should signal a #UD (Invalid Opcode)
exception, however, due to the erratum, a #NM (Device Not Available) exception
may be signaled.
As a result of this erratum, an operating system may restore AVX and other state
unnecessarily.
KBL045
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Intel® SGX Enclave Accesses to the APIC-Access Pa g e Ma y Ca u s e APICAccess VM Exits
In VMX non-root operation, Intel SGX (Software Guard Extensions) enclave accesses
to the APIC-access page may cause APIC-access VM exits instead o f page faults.
A VMM (virtual-machine monitor) may receive a VM exit due to an access that sho uld
have caused a page fault, which would be handled by the guest OS (operating
system).
A VMM avoids this erratum if it does not map any part of the EPC (Enclave Page
Cache) to the guest’s APIC-access address; an operating system a voids this erratum
if it does not attempt indirect enclave accesses to the APIC.
KBL046
CR3 Filtering Does Not Compare Bits [11:5] of CR3 and
IA32_RTIT_CR3_MATCH in PAE Paging Mode
In PAE paging mode, the CR3[11:5] are used to locate the page-directory-pointer
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e Su mmary Table of Changes.
table. Due to this erratum, those bits of CR3 are not compared to
IA32_RTIT_CR3_MATCH (MSR 572H) when IA32_RTIT_CTL.CR3Filter (MSR 570H, bit
7) is set.
If multiple page-directory-pointer tables are co-located within a 4KB region, CR3
filtering will not be able to distinguish between them so additional processes may be
traced.
KBL047 x87 FDP Value May be Saved Incorrectly
Execution of the FSAVE, FNSAVE, FSTENV, or FNSTENV instructions in real-address
Problem
Implication
Workaround
mode or virtual-8086 mode may save an incorrect value for the x87 FDP (FPU data
pointer). This erratum does not apply if the last non-control x87 instruction had an
unmasked exception.
Software operating in real-address mode or virtual-8086 mode that depends on the
FDP value for non-control x87 instructions without unmasked exceptions may not
operate properly.
None identified. Software should use the FDP value saved by the listed instructions
only when the most recent non-control x87 instruction incurred an unmasked
exception.
Specification Update 35
Page 36

Errata
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
KBL048 PECI Frequency Limited to 1 MHz
Problem
Implication Platforms attempting to run PECI above 1 MHz may not behave as expected.
Workaround None identified. Platforms should limit PECI operating frequency to 1 MHz.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
The PECI (Platform Environmental Control Interface) 3.1 specification’s operating
frequency range is 0.2 MHz to 2 MHz. Due to this erratu m, PECI may be unreliable
when operated above 1 MHz.
KBL049 Processor Graphics IOMMU Unit May Not Mask DMA Remapping Faults
Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O specification specifies setting the
FPD (Fault Processing Disable) field in the context (or extended-context) entry of
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
IOMMU to mask recording of qualified DMA remapping faults for DMA requests
processed through that context entry. Due to this erratum, the IOMMU unit for
Processor Graphics device may record DMA remapping faults from Processor Graphics
device (Bus: 0; Device: 2; Function: 0) even when the FPD field is s et to 1.
Software may continue to observe DMA remapping faults recorded in the IOMMU
Fault Recording Register even after setting the FPD field.
None identified. Software may mask the fault reporting event by setting the IM
(Interrupt Mask) field i n the IOMMU Fault Event Contr ol register (Offset 03 8H in
GFXVTBAR).
KBL050 Intel® PT CYCThresh Value of 13 is Not Supported
Intel PT (Intel® Processor Trace) CYC (Cycle Count) threshold is configured through
CYCThresh field in bits [22:19] of IA32_RTIT_CTL MSR (570H). A value of 13 is
Problem
Implication
Workaround None identified. Software should not use value of 13 for CYC threshold.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
advertised as supported by CPUID (leaf 14H, sub-lead 1H). Due to this erra tum, if
CYCThresh is set to 13 then the CYC threshold will be 0 cycles instead of 4096 (213-
1) cycles.
CYC packets may be issued in higher rate than expected if threshold value of 13 is
used.
KBL051 Enabling VMX-Preemp tion Timer Blocks HDC Operatio n
HDC (Hardware Duty Cycling) will not put the physical package into the forced idle
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
state while any logical processor is in VMX non-root operation and the “activate VMXpreemption timer” VM-execution control is 1.
HDC will not provide the desired power reduction when the VMX-preemption timer is
active in VMX non-root operation.
36 Specification Update
Page 37

Codec from losing power when LPSP mode is enabled.
Errata
KBL052 Integrated Audio Codec May Not be Detected
Integrated Audio Codec may lose power when LPSP (Low-Power Single Pipe) mode is
Problem
Implication
enabled for an eDP* (embedded DisplayPort) or DP/HDMI ports. Platforms with
Intel® SST (Intel® Smart S ound Technology) enab le d are not affected.
The Audio Bus driver may attempt to do enumeration of Codecs when eDP or
DP/HDMI port enters LPSP mode, due to this erratum, the Integrated A udio Codec
will not be detected and audio maybe be lost.
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Intel® Graphics Driver 15.40.11.4312 or later will prevent the Integrated Audio
KBL053 Display Flickering May be Observed with Specific eDP Panels
Problem
Implication Display flickering or display loss maybe observed.
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
The processor may incorrectly configure transmitter buffer characteristics if the
associated eDP panel requests VESA equalization preset 3, 5, 6, or 8.
Intel® Graphics Driver version 15.40.12.4326 or later contains a workaround for this
erratum.
KBL054 Incorrect Bra n ch Predicted Bit in BTS/BTM Branch Record s
BTS (Branch Trace Store) and BTM ( Branch Trace Message) send branch records to
the Debug Store management area and system bus respectively. The Br anch
Problem
Implication BTS and BTM cannot be used to determine the accuracy of branch prediction.
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Predicted bit (bit 4 of eighth byte in BTS/BTM records) should report whether the
most recent branch was predi cted correctly. Due to this erratum, the Branch
Predicted bit may be incorrect.
KBL055
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
MACHINE_CLEARS.MEMORY_ORDERING Performance Monitoring Event May
Undercount
The performance monitoring event MACHINE_C LE ARS.MEMORY_ORDERING (Event
C3H; Umask 02H) counts the number of machine clears caused b y memory ordering
conflicts. However due to this erratum, this event may undercount for
VGATHER*/VPGATHER* instructions of four or more elements.
MACHINE_CLEARS.MEMORY_ORDERING performance monitoring event may
undercount.
Specification Update 37
Page 38

KBL056 CTR_FRZ May Not Freeze Some Counters
IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_STATUS.CTR_FRZ (MS R 3 8EH, bit 59) is set when either (1)
IA32_DEBUGCTL.FREEZE_PERFMON_ON_P MI (MSR 1D9H, bit 12) is set and a PMI is
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
triggered, or (2) software sets bit 59 of IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_STATUS_SET (MSR
391H). When set, CTR_FRZ should stop all core performance monitoring counters
from counting. However, due to this erratum, IA 32_PMC4-7 (MSR C5-C8H) may not
stop counting. IA32_PMC4-7 are only available when a processor core is not shared
by two logical processors.
General performance monitoring counters 4-7 may not freeze when
IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_STATUS.CTR_FRZ is set.
KBL057
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Instructions And Branches Retired Performance Monitoring Ev ents May
Overcount
The performance monitoring events INST_RETIRED (Event C0H; any Umask value)
and BR_INST_RETIRED (Event C4H; any Umask value) count instructions retired and
branches retired, respectively. However, due to this erratum, these events may
overcount in certain conditions when:
- Executing VMASKMOV* instructions with at least one masked vector element
- Executing REP MOVS or REP STOS with Fast Strings enabled (IA32_MISC_ENABLES
MSR (1A0H), bit 0 set)
- An MPX #BR exception occurred on BNDLDX/BNDSTX instructions and the
BR_INST_RETIRED (Event C4H; Umask is 00H or 04H) is used.
INST_RETIRED and BR_INST_RETIRED performance monitoring events may
overcount.
Errata
KBL058 Some OFFCORE_RESPONSE Performance Monitoring Events May Overcount
The performance monitoring events OFFCORE_R ES PONSE (Events B7H and BBH)
should count off-core responses matching the request-response configuration
Problem
Implication Some OFFCORE_RESPONSE events may overcount.
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
specified in MSR_OFFCORE_RSP_0 and MSR_OFFCORE_RSP_1 (1A6H and 1A7H,
respectively) for core-originated requests. However, due to this erratum, DMND_RFO
(bit 1), DMND_IFETCH (bit 2) and OTHER (bit 15) req uest types may overcount.
None identified. Software may use the following model-specific events that provide
related performance monitoring data: OFFCORE_REQUESTS (all sub-events),
L2_TRANS.L2_WB and L2_RQSTS.PF_MISS.
38 Specification Update
Page 39

Errata
KBL059
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Instructions Fetch #GP After RS M Du ring Inter® PT May Push Incorrect
RFLAGS Value on Stack
If Intel PT (Processor T race) is enabled, a #GP (General Protection Fault) caused by
the instruction fetch immediately following execution of an RSM instruction may push
an incorrect value for RFLAGS onto the stack.
Software that relies on RFLAGS value pushed on the sta ck under the cond it ions
described may not work properly.
KBL060
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Access to SGX EPC Page in BLOCKED State is Not Reported as an SGXInduced Page Fault
If a page fault results from attempting to access a page in the SGX (Intel® Software
Guard Extensions) EPC (Enclave Page Cache) that is in the BLOCKED state, the
processor does not set bit 15 of the error code and thus fails to indicate that the page
fault was SGX-induced.
Due to this erratum, software may not recognize these page faults as being SGXinduced.
Before using the EBLOCK instruction to marking a page as BLOCKED, software should
use paging to mark the page not present.
KBL061 MTF VM Exit on XBEGIN Instruction May Save State Incorrectly
Execution of an XBEGIN instruction while the monitor trap flag VM-execution control
is 1 will be immediately followed by an MTF VM exit. If advanced debugging of RTM
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
transactional regions has been enabled, the VM exit will erroneous ly sa ve as
instruction pointer the address of the XBEGIN instruction instead of the fallback
instruction address specified by the XBEGIN instruction. In addition, it will
erroneously set bit 16 of the pending-debug-exceptions field in the VMCS indicating
that a debug exception or a breakpoint exception occurred.
Software using the monitor trap flag to debug or trace transactional regions may not
operate properly. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available
software.
KBL062
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology May be Incorrectly Reported as Supported
on Intel® Core™ i3 U/H/S, Select Intel® Mobile Pentium®, Intel® Mobile
Celeron®, Intel® Pentium® and Intel® Celeron® P rocessors
These processors may incorrectly report support for Intel® Turbo Boost Technology
via CPUID.06H.EAX bit 1.
The CPUID instruction may report Turbo Boost Technology as supported even though
the processor does not permit operation above the Base Frequency.
Specification Update 39
Page 40

KBL063 Performanc e Mon itoring Counters May Undercount When Using CPL Filtering
Performance Monitoring counters configured to count only OS or only USR events by
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
setting exactly one of bits 16 or 17 in IA32_PERFEVTSELx MSRs (186H-18DH) may
not count for a brief period during the transition to a new CPL.
A measurement of ring transitions (using the edge-detect bit 18 in
IA32_PERFEVTSELx) may undercount, such as CPL_CY C LES.RING0_TRANS (Event
5CH, Umask 01H). Additio n ally, the sum of an OS-only event and a USR-only event
may not exactly equal an event counting both OS and USR. Intel has not observed
any other software-visible impact
KBL064 Executing a 256 Bit AVX Instruction May Cause Unpredictab le Behavior
Errata
Problem
Implication When this erratum occurs, the system may behave unpredictably.
Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Under complex micro-architectural conditions, executing a 25 6 AVX bit instruction
may result in unpredictable system behavior.
KBL065 System May Hang During Display Power Cycles
Problem
Implication When this erratum occurs the system may hang.
Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
When the display is turned on after being shutoff to save power or when the display
is exiting PSR (Panel Self Refresh) mode, the system may hang.
KBL066
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Certain Non-Canonical IA32_BNDCFGS Values Will Not Cause VM-Entry
Failures
If the VM-entry controls Load IA32_BNDCFGS field (bit 16) is 1, VM-entry should fail
when the value of the guest IA32_BNDCFGS field in the VMCS is not canonical (that
is, when bits 63:47 are not identical). Due to this erratum, VM-entry does not fail if
bits 63:48 are identical but differ from bit 47. In this case, VM-entry loads the
IA32_BNDCFGS MSR with a value in which b its 63:48 are identic al to the value of bit
47 in the VMCS field.
If the value of the guest IA32_BNDCFGS field in the VMC S is not canonical, VM-entry
may load the IA32_BNDCFGS MSR with a value different from that of the VMCS field.
40 Specification Update
Page 41

Errata
KBL067 PEBS EventingIP Field May Be Incorrect Under Certain Conditions
The EventingIP field in the PEBS (Processor Event-Based Sampling) record reports
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
the address of the instruction that triggered the PEBS event. Under certa in complex
microarchitectural conditions, the EventingIP field may be incorrect.
When this erratum occurs, performance monitoring software may not attribute the
PEBS events to the correct instruction.
KBL068
Problem
Implication Software may read a stale value of the Guaranteed _Performance field.
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HWP’s Guaranteed_Performance Updated Only on Configurable TDP
Changes
According to HWP (Hardware P-states) specification, the Guaranteed_Performance
field (bits[15:8]) in the IA32_HWP_CAPABILITIES MSR (771H) should be updated as
a result of changes in the configuration of TDP, RAPL (Running Average Power Limit),
and other platform tuning options that may have dynamic effects on the actual
guaranteed performance support level. Due to this erratum, the processor will update
the Guaranteed_Performance field only as a result of configurable TDP dynamic
changes.
KBL069
Problem
Implication
Workaround Software should always prevent faults on PEBS or BTS.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
RF May be Incorrectly Set in The EFLAGS That is Saved on a Fault in PEBS or
BTS
After a fault due to a failed PEBS (Processor Event Based Sampling) or BTS (Branch
Trace Store) address translation, the RF (resume flag) may be incorrectly set in the
EFLAGS image that is saved .
When this erratum occurs, a code breakpoint on the instruction following the return
from handling the fault will not be detected. This er r a tum only happens when the
user does not prevent faults on PEBS or BTS.
KBL070 Intel® PT ToPA PMI Does Not Freeze Performance Monitoring Counters
Due to this erratum, if IA 32_DEBUGCTL.FREEZE_PERFMON_ON_PMI (MSR 1D9H, bit
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
12) is set to 1 when Intel PT (Processor T race) triggers a ToPA (Table of Phys ical
Addresses) PMI (PerfMon Interrupt), performance monitoring counters are not frozen
as expected.
Performance monitoring counters will continue to count for events that occur during
PMI handler execution.
PMI handler software can programmatically stop performance monitoring counters
upon entry.
Specification Update 41
Page 42

KBL071 HWP’s Maximum_Performance Value is Reset to 0xFF
According to HWP (Hardware P-states) specification, the reset value of the
Maximum_Performance field (bits [15:8]) in IA32_HWP_REQUEST MSR (774h) should
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified.
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
be set to the value of IA32_HWP_CAPABILITIE S MSR (771H) Highest_Performance
field (bits[7:0]) after reset. Due to this erratum, the reset value of
Maximum_Performance is always set to 0xFF.
Software may see an unexpected valu e in Maximum Performance field. Hardware
clipping will prevent invalid performance states.
KBL072
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
HWP’s Guaranteed_Performance and Relevant Status/Interrupt May be
Updated More Than Once Per Second
According to HWP (Hardware P-states) specification, the Guaranteed_Performance
field (bits[15:8]) in the IA32_HWP_CAPABILITIES MSR (771H) and the
Guaranteed_Performance_Change (bit 0) bit in IA32_HWP_STATUS MSR (777H)
should not be changed more than o n ce per second nor should the thermal interrupt
associated with the change to the se f ields be signaled more than once per second.
Due to this erratum, the processor may change these fields and genera te the
associated interrupt more than once per second
HWP interrupt rate due to Guaranteed_Performance field change ca n b e higher than
specified
Clearing the Guaranteed_Performanc e_ Cha ng e status b it no more than o nce per
second will ensure that interru p ts a re not generated at too fast a rate
Errata
KBL073
Problem
Some Memory Performance Monitoring Events May Produce Incorrect
Results When Filtering on Either OS or USR Modes
The memory at-retirement performance monitoring events (listed b elow) may
produce incorrect results when a p erformance counter is configured in OS-only or
USR-only modes (bits 17 or 16 in IA32_PERFEVTSELx MSR). Counters with both OS
and USR bits set are not affected by this erratum.
The list of affected memory at-retirement events is as follows:
MEM_INST_RETIRED.STLB_MISS_LOADS event D0H, umask 11H
MEM_INST_RETIRED.STLB_MISS_STO RES event D0H, umask 12H
MEM_INST_RETIRED.LOCK_LOADS event D0H , umask 21H
MEM_INST_RETIRED.SPLIT_LOADS event D 0H, umask 41H
MEM_INST_RETIRED.SPLIT_STORES event D0H , umask 42H
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L2_HIT event D1H, umask 02H
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L3_HIT event D1H, umask 04H
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L4_HIT event D1H, umask 80H
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L1_MISS event D1H, umask 08H
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L2_MISS event D1H, umask 10H
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L3_MISS event D1H, umask 20H
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.FB_HIT event D1H, umask 40H
42 Specification Update
Page 43

MEM_LOAD_L3_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_MISS e vent D2H, umask 01H
Errata
MEM_LOAD_L3_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_HIT event D2H, umask 02H
MEM_LOAD_L3_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_HITM event D2H, umask 04H
MEM_LOAD_L3_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_NONE event D2H, umask 08H
Implication
Workaround Non e identified
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
The listed performance monito ring events may produce incorrect results including
PEBS records generated at an incorrect point
KBL074 HWP May Generate Thermal Interrupt While Not Enabled
Due to this erratum, the conditions for HWP (Hardware P-states) to generate a
Problem
Implication
Workaround Software should configure HWP consistently on all logical processors of a core.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
thermal interrupt on a logical p r ocessor may generate thermal interrupts on both
logical processors of that core.
If two logical processors of a core have different configurations of HWP (e.g. only
enabled on one), an unexpected thermal interrupt may occur on one logical processor
due to the HWP settings of the other logical processor.
KBL075 Camera Device Does Not Issue an MSI When INTx is Enabled
When both MSI (Message Signaled Interrupts) and legacy INTx are enabled by the
Problem
Implication Due to this erratum, camera device i n terrupts can be lost leading to device failure.
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
camera device, INTx is asserted rather than issuing the MSI, in violation of the PCI
Local Bus Specification.
The camera device must disable legacy INTx by setting bit 10 of PCICMD (Bus 0;
Device 5; Function 0; Offset 04H) befo re MSI is enabled
KBL076
Problem
Implication
Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
An x87 Store Instruction Which Pends #PE May Lead to Unexpected
Behavior When EPT A/D is Enabled.
An x87 store instruction which causes a #PE (Precision Exception) to be pended and
updates an EPT (Extended Page Tables) A/D bit may lead to unexpected behavior.
The VMM may experience unexpected x87 fault or a machine check exception with
the value of 0x150 in IA32_MC0_STATUS.MCACOD (bits [15:0] in MSR 401H)
KBL077 Use of VMASKMOV to Store When Using EPT May Fail
Use of VMASKMOV instructions to store data that splits over two pages, when the
Problem
Specification Update 43
instruction resides on the first page may cause a hang if EPT (Extended Page Tables)
is in use, and the store to the second page requires setting the A/D bits in the EPT
entry.
Page 44

Implication Due to this erratum, the CPU may hang on the execu tion of VMASKMOV
Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
KBL078 PECI May Not be Functional After Package C10 Resume
Problem When resuming from Package C10, PECI may fail to function properly.
Implication When this erratum occurs, the PECI do es not respond to any command.
Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
KBL079 Attempts to Retrain a PCIe* Link May be Ignored
Errata
Problem
Implication The PCIe link may not behave as expected.
Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
A PCIe link should retrain when Retrain Link (bit 5) in the Link Control register (Bus
0; Device 1; Functions 0,1,2; Offset 0xB0) is set. Due to this erratum, if the link is in
the L1 state, it may ignore the retrain request
KBL080 PCIe* Expansion ROM Base Address Register May be Incorrect
After PCIe 8.0 GT/s Link Equalization on a root port (Bus 0; Device 1; Function 0, 1,
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
2) has completed, the Expansion ROM Base Address Register (Offset 3 8H) may be
incorrect.
Software that uses this BAR may behave unexpectedly. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercial ly available software.
KBL081 PCIe* Port Does Not Support DLL Link Activity Reporting
The PCIe Base specification requires DLL (Data Link Layer) Link Activity Reporting
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
when 8 GT/s link speed is supported. Due to this erratum, link activity reporting is
not supported
Due to this erratum, PCIe port does not support DLL Link Activity Reporting when 8
GT/s is supported.
44 Specification Update
Page 45

Errata
KBL082
Problem
Implication Intel has not observed this erratum with a ny commercially available software.
Workaround Software should use canonical addresses f or bound directory accesses.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
BNDLDX And BNDSTX May Not Signal #GP on Non-Canonical Bound Directory
Access
BNDLDX and BNDSTX instructions access the bound’s directory and table to load or
store bounds. These accesses shou ld signal #GP (general protection exception) when
the address is not canonical (i.e. bits 48 to 63 are not the sign extension of bit 47).
Due to this erratum, #GP may not be generated by the processor whe n a noncanonical address is used by BNDLDX or BNDSTX for their bound directory memory
access.
SKL0083 RING_PERF_LIMIT_REASONS May be Incorrect
Problem
Implication
Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
KBL084 Processor May Exceed VCCCore ICCMAX During Multi-core Turbo
Under certain conditions, RING_PERF_LIMIT_REASONS (MSR 6B1H) may incorrectly
assert the OTHER status bit (bit 8) as well as the OTHER log bit (bit 24).
When this erratum occurs, software using this register will incorrec tly report clipping
because of the OTHER reason.
Problem
Implication
Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Due to this erratum, the maximum ring frequency limit is incorrectly co n figured to be
100MHz higher than intended.
VCCCore ICCMAX may be temporarily exceeded when all the cores are executing at a
Turbo frequency.
KBL085
Problem
Implication
Workaround Non e identified
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Performance Monitoring Load Latency Events May Be Inaccurate For Gather
Instructions
The performance monitoring events MEM_TRANS_RETIRED.LOAD_LATENCY_* (E vent
CDH; UMask 01H; any latency) count load instructions whose latency exceed a
predefined threshold, where the lo a d s a re randomly selected using the load latency
facility (an extension of PEBS). However due to this erratum, these ev ents may count
incorrectly for VGATHER*/VPGATHER* instructions.
The Load Latency Performance Monitoring events may be Inaccurate for Gather
instructions.
Specification Update 45
Page 46

Errata
KBL086
Problem
Implication The EDRAM corrected error information may be lost when this erratum occurs.
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
EDRAM Corrected Error Events May Not be Properly Logged After a Warm
Reset
After a warm reset, an EDRAM corrected error may not be logged correctly until the
associated machine check register is initialized. This erratum ma y affect
IA32_MC8_STATUS or IA32_MC10_STATUS.
Data from the affected machine check registers should be read and the registers
initialized as soon as practical after a warm reset.
KBL087
Problem
Implication When this erratum occurs, the system may behave unpredictably.
Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Unpredictable System Behavior May Occur When System Agent Enhanced
Intel® Speedstep® is Enabled
Under complex system condition s, SA-GV (System Agent Enhanced Intel®
Speedstep®) may result in unpredi ctable system behavior.
KBL088 Processor May Hang Under Complex Scenarios
Problem
Implication This erratum may result in a processor hang.
Workaround It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Under a complex micro-architectural conditions, the processor may hang with an
internal timeout error (MCACOD 0400H) logged into IA32_MCi_STATUS.
KBL089
Problem
Implication
Workaround None identified. Software sh ould not attempt to write illegal values to this MSR.
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Some Bits in MSR_MISC_PWR_MGMT May be Updated on Writing Illegal
Values to This MSR
Attempts to write illegal values to MSR_MISC_PWR_MGMT (M SR 0x1AA) result in
#GP (General Protection Fault) and should not change the MSR value. Due to this
erratum, some bits in the MSR may be updated on writing an illegal value.
Certain fields may be updated with allowed values when writing illegal values to
MSR_MISC_PWR_MGMT. Such writes will always result in #GP as expected.
KBL090
Problem
46 Specification Update
Violations of Intel® Software Guar d Extensions (Intel® SGX) Access-Control
Requirements Produce #GP Inst ead of #PF
Intel® Software Guard Extensions (Intel® SGX) define new access-control
requirements on memory accesses. A violation of any of these requirements causes a
page fault (#PF) that sets bit 15 (SGX) in the page-fault error code. Due to this
erratum, these violations inst ea d ca use general-protection exceptions (#GP).
Page 47

Errata
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see th e S ummary Table of Changes.
Software resuming from system sleep states S3 or S4 and relying on receiving a page
fault from the above enclave access es may not operate properly.
Software can monitor #GP faults to detect that an enclav e ha s been destroyed and
needs to be rebuilt after resuming from S3 or S4
KBL091 IA32_RTIT_CR3_MATCH MSR Bits[11:5] Are Treated As Reserved
Due to this erratum, bits[11:5] in IA32_RTIT_CR3_MATCH (MSR 572H) are reserved;
Problem
Implication
Workaround
Status For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
an MSR write that attempts to set that field to a non-zero value will result in a #GP
fault.
The inability to write the identified bit field does not affect the functioning of Intel®
PT (Intel® Processor Trace) operation because, as described in erra tum SKL061, the
bit field that is the subject of this erratum is not used during Intel PT C R3 filtering.
Ensure that bits 11:5 of the value written to IA32_RTIT_CR3_MATCH are zero,
including cases where the selected page-directory-pointer-table base address has
non-zero bits in this range.
§
Specification Update 47
Page 48

Specification Changes
There are no Specification Changes in this Specification Update revision.
§
Specification Changes
48 Specification Update
Page 49

Specification Clarifications
Specification Clarifications
There are no specification clarifications in this Specification Update revision.
§
Specification Update 49
Page 50

Documentation Changes
There are no documentation changes in this Specification Update revision.
§
Documentation Changes
50 Specification Update
 Loading...
Loading...