Intel BX80646I54430, CM8064601465902, BX80646I54570, BX80646I54440, CM8064601466203 User Manual 3
...Page 1

Desktop 4th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family, Desktop Intel® Pentium® Processor Family, and Desktop Intel® Celeron® Processor Family
Specification Update
December 2013
Revision 007
Reference Number: 328899-007
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY
ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN
INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER AND INTEL DISCLAIMS
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES
RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
A “Mission Critical Application” is any application in which failure of the Intel Product could result, directly or indirectly, in personal injury or death.
SHOULD YOU PURCHASE OR USE INTEL'S PRODUCTS FOR ANY SUCH MISSION CRITICAL APPLICATION, YOU SHALL INDEMNIFY AND
HOLD INTEL AND ITS SUBSIDIARIES, SUBCONTRACTORS AND AFFILIATES, AND THE DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, AND EMPLOYEES OF
EACH, HARMLESS AGAINST ALL CLAIMS COSTS, DAMAGES, AND EXPENSES AND REASONABLE ATTORNEYS' FEES ARISING OUT OF,
DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY, ANY CLAIM OF PRODUCT LIABILITY, PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF SUCH
MISSION CRITICAL APPLICATION, WHETHER OR NOT INTEL OR ITS SUBCONTRACTOR WAS NEGLIGENT IN THE DESIGN,
MANUFACTURE, OR WARNING OF THE INTEL PRODUCT OR ANY OF ITS PARTS.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Designers must not rely on the absence or
characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined”. Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no
responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them. The information here is subject to change without
notice. Do not finalize a design with this information.
The products described in this document may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from
published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained by calling 1-800548-4725, or go to: http://www.intel.com/design/literature.htm.
Code names featured are used internally within Intel to identify products that are in development and not yet publicly announced for release.
Customers, licensees and other third parties are not authorized by Intel to use code names in advertising, promotion or marketing of any product or
services and any such use of Intel's internal code names is at the sole risk of the user.
®
Virtualization Technology requires a computer system with an enabled Intel® processor, BIOS, virtual machine monitor (VMM). Functionality,
Intel
performance or other benefits will vary depending on hardware and software configurations. Software applications may not be compatible with all
operating systems. Consult your PC manufacturer. For more information, visit: http://www.intel.com/go/virtualization.
®
Intel
Turbo Boost Technology requires a system with Intel® Turbo Boost Technology. Intel Turbo Boost Technology and Intel Turbo Boost Technology
2.0 are only available on select Intel
configuration. For more information, visit: http://www.intel.com/go/turbo.
®
Intel
Hyper-Threading Technology requires an Intel® HT Technology enabled system, check with your PC manufacturer. Performance will vary
depending on the specific hardware and software used. Not available on Intel
processors support HT Technology, visit http://www.intel.com/info/hyperthreading.
®
64 architecture requires a system with a 64-bit enabled processor, chipset, BIOS and software. Performance will vary depending on the specific
Intel
hardware and software you use. Consult your PC manufacturer for more information. For more information, visit: http://www.intel.com/info/em64t.
®
processors. Consult your PC manufacturer. Performance varies depending on hardware, software, and system
®
Core™ i5-750. For more information including details on which
Intel, Intel Core, Intel386, Intel486, Pentium, and the Intel logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2013, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
2 Specification Update
Page 3

Contents
Contents
Revision History............................................................................................................... 5
Preface ..............................................................................................................................6
Summary Tables of Changes.......................................................................................... 8
Identification Information ..............................................................................................14
Errata...............................................................................................................................17
Specification Changes...................................................................................................47
Specification Clarifications ...........................................................................................48
Documentation Changes ...............................................................................................49
§ §
Specification Update 3
Page 4

Contents
4 Specification Update
Page 5
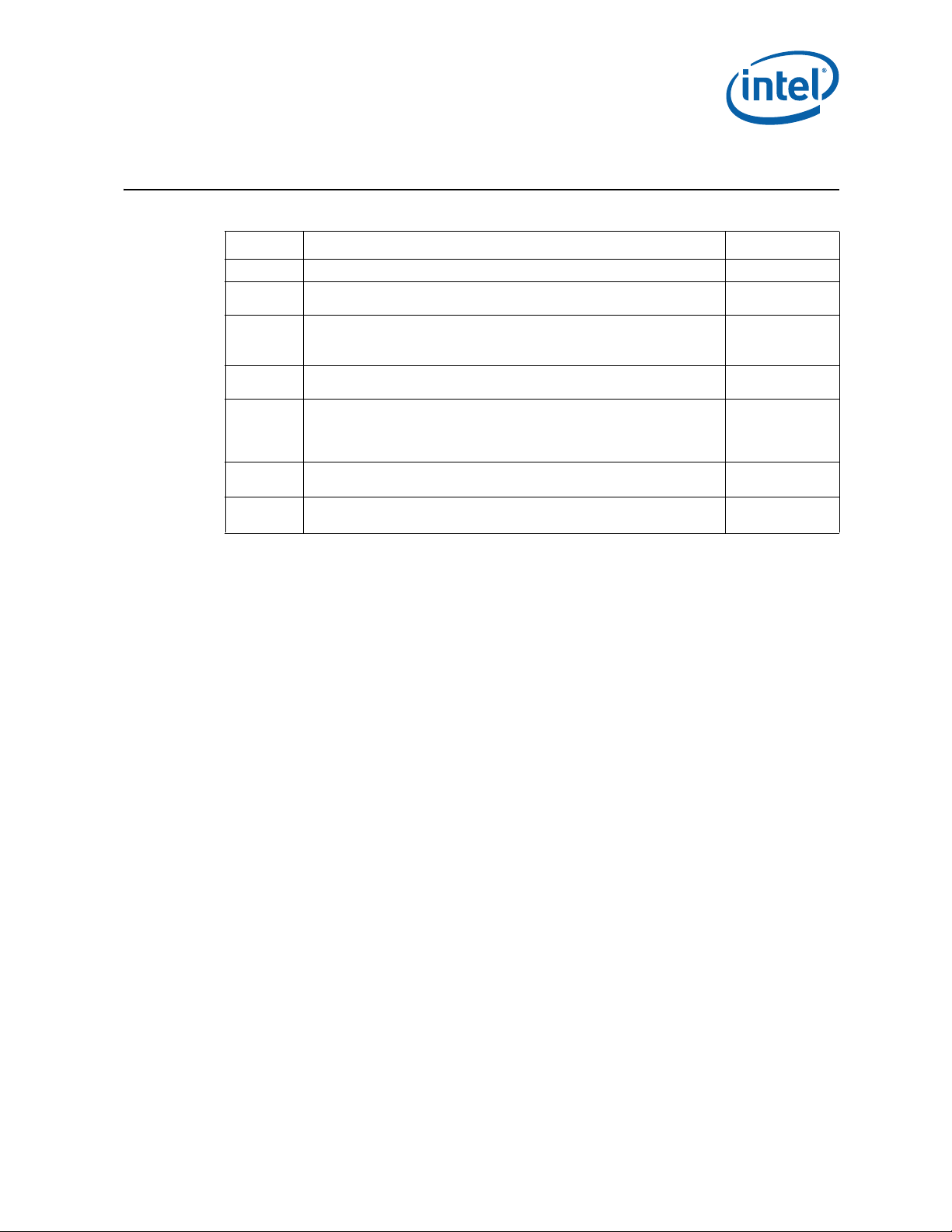
Revision History
Revision Description Date
001 • Initial Release. June 2013
002
003
004
005
006
007
• No Updates. Revision number added to Revision History to maintain
consistency with NDA Specification Update numbering.
•Errata
— Added HSD59-99
• Updated Identification Information
• No Updates. Revision number added to Revision History to maintain
consistency with NDA Specification Update numbering.
•Errata
— Moved previous HSD99 to HSD108
— Added HSD99-107 and HSD109-115
• Updated Identification Information
• Identification Information
— Updated Desktop Processor Identification table
•Errata
— Added HSD116-118
N/A
August 2013
N/A
November 2013
December 2013
December 2013
Specification Update 5
Page 6
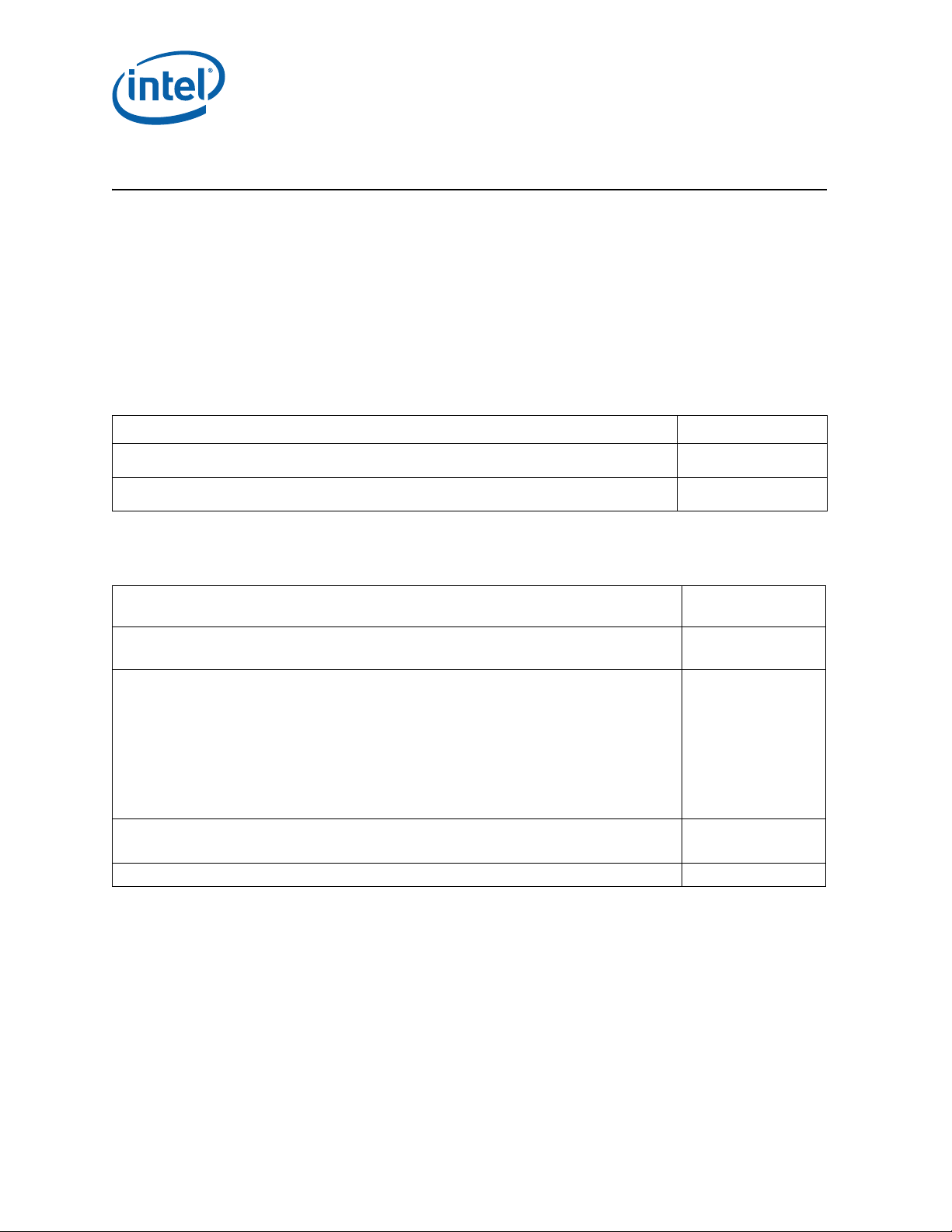
Preface
This document is an update to the specifications contained in the Affected Documents
table below. This document is a compilation of device and documentation errata,
specification clarifications and changes. It is intended for hardware system
manufacturers and software developers of applications, operating systems, or tools.
Information types defined in Nomenclature are consolidated into the specification
update and are no longer published in other documents.
This document may also contain information that was not previously published.
Affected Documents
Desktop 4th Generation Intel
and Desktop Intel
Desktop 4th Generation Intel
and Desktop Intel
®
Celeron® Processor Family Datasheet – Volume 1 of 2
®
Celeron® Processor Family Datasheet – Volume 2 of 2
Related Documents
®
Core™ Processor Family, Desktop Intel® Pentium® Processor Family,
®
Core™ Processor Family, Desktop Intel® Pentium® Processor Family,
Document Title Document Number
328897
328898
Document Title
AP-485, Intel
®
Intel
®
Intel
Reference Manual A-M
®
Intel
Reference Manual N-Z
®
Intel
Guide
®
Intel
Guide
®
Intel
®
Intel
®
Processor Identification and the CPUID Instruction
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1: Basic Architecture
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A: Instruction Set
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B: Instruction Set
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A: System Programming
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B: System Programming
64 and IA-32 Intel Architecture Optimization Reference Manual
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual Documentation Changes
Document Number/
Location
http://www.intel.com/
design/processor/
applnots/241618.htm
http://www.intel.com/
products/processor/
manuals/index.htm
http://www.intel.com/
design/processor/
specupdt/252046.htm
ACPI Specifications www.acpi.info
6 Specification Update
Page 7

Nomenclature
Errata are design defects or errors. These may cause the processor behavior to
deviate from published specifications. Hardware and software designed to be used with
any given stepping must assume that all errata documented for that stepping are
present on all devices.
S-Spec Number is a five-digit code used to identify products. Products are
differentiated by their unique characteristics such as, core speed, L2 cache size,
package type, etc. as described in the processor identification information table. Read
all notes associated with each S-Spec number.
Specification Changes are modifications to the current published specifications.
These changes will be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Specification Clarifications describe a specification in greater detail or further
highlight a specification’s impact to a complex design situation. These clarifications will
be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Documentation Changes include typos, errors, or omissions from the current
published specifications. These will be incorporated in any new release of the
specification.
Note: Errata remain in the specification update throughout the product’s lifecycle, or until a
particular stepping is no longer commercially available. Under these circumstances,
errata removed from the specification update are archived and available upon request.
Specification changes, specification clarifications and documentation changes are
removed from the specification update when the appropriate changes are made to the
appropriate product specification or user documentation (datasheets, manuals, and so
on).
Specification Update 7
Page 8

Summary Tables of Changes
The following tables indicate the errata, specification changes, specification
clarifications, or documentation changes which apply to the processor. Intel may fix
some of the errata in a future stepping of the component, and account for the other
outstanding issues through documentation or specification changes as noted. These
tables uses the following notations.
Codes Used in Summary Tables
Stepping
Page
Status
Row
X: Errata exists in the stepping indicated. Specification Change or
Clarification that applies to this stepping.
(No mark)
or (Blank box): This erratum is fixed in listed stepping or specification change
does not apply to listed stepping.
(Page): Page location of item in this document.
Doc: Document change or update will be implemented.
Plan Fix: This erratum may be fixed in a future stepping of the product.
Fixed: This erratum has been previously fixed.
No Fix: There are no plans to fix this erratum.
Change bar to left of a table row indicates this erratum is either new or modified from
the previous version of the document.
8 Specification Update
Page 9
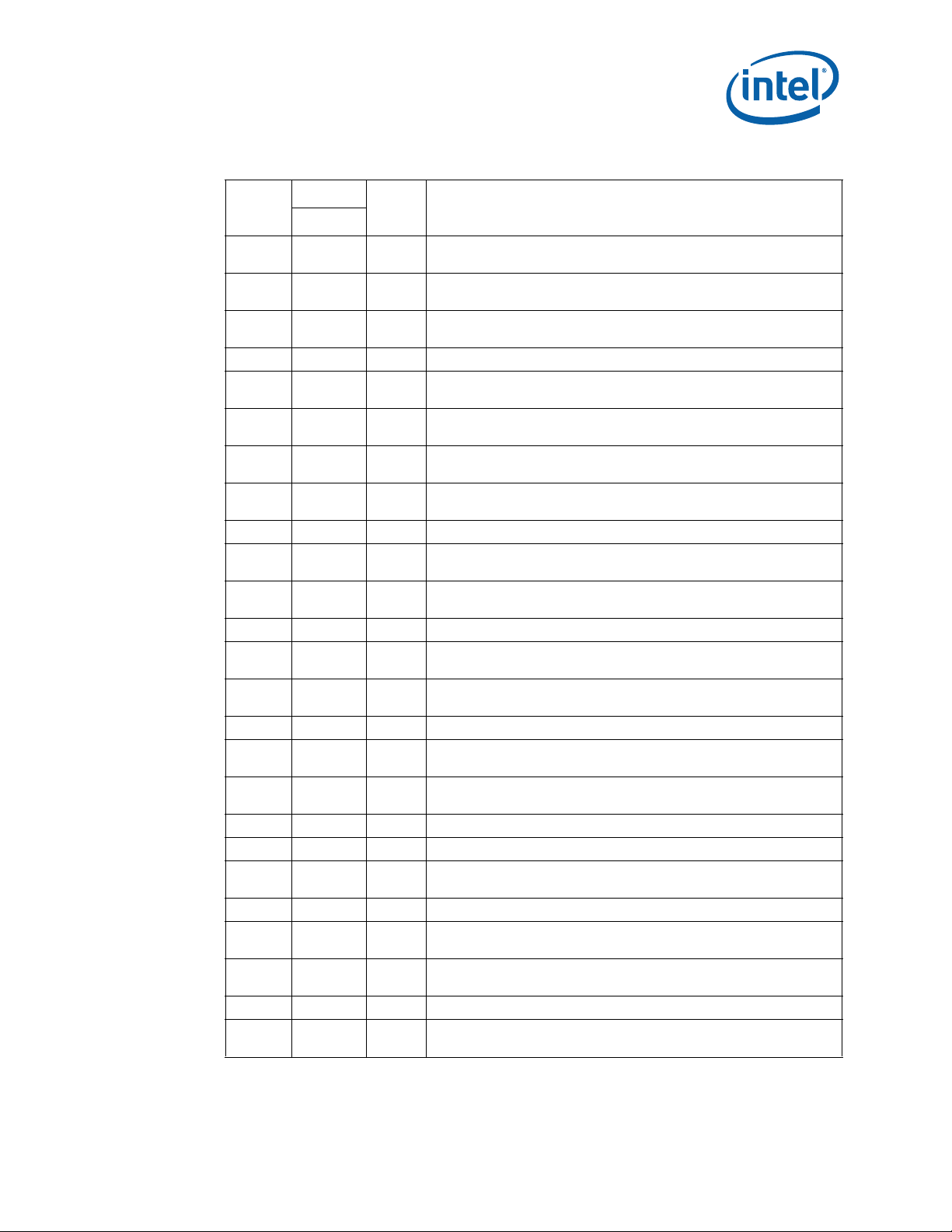
Errata (Sheet 1 of 5)
Number
HSD1
HSD2
HSD3
HSD4
HSD5
HSD6
HSD7
HSD8
HSD9
HSD10
HSD11
HSD12
HSD13
HSD14
HSD15
HSD16
HSD17
HSD18
HSD19
HSD20
HSD21
HSD22
HSD23
HSD24
HSD25
Steppings
C-0
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Status ERRATA
LBR, BTS, BTM May Report a Wrong Address when an Exception/
Interrupt Occurs in 64-bit Mode
EFLAGS Discrepancy on Page Faults and on EPT-Induced VM Exits after
a Translation Change
MCi_Status Overflow Bit May Be Incorrectly Set on a Single Instance of a
DTLB Error
XNo FixLER MSRs May Be Unreliable
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
MONITOR or CLFLUSH on the Local XAPIC's Address Space Results in
Hang
An Uncorrectable Error Logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS May also
Result in a System Hang
#GP on Segment Selector Descriptor that Straddles Canonical Boundary
May Not Provide Correct Exception Error Code
FREEZE_WHILE_SMM Does Not Prevent Event From Pending
PEBS During SMM
XNo FixAPIC Error “Received Illegal Vector” May be Lost
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Changing the Memory Type for an In-Use Page Translation May Lead to
Memory-Ordering Violations
Performance Monitor Precise Instruction Retired Event May Present
Wrong Indications
XNo FixCR0.CD Is Ignored in VMX Operation
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Instruction Fetch May Cause Machine Check if Page Size and Memory
Type Was Changed Without Invalidation
Execution of VAESIMC or VAESKEYGENASSIST With An Illegal Value
for VEX.vvvv May Produce a #NM Exception
XNo FixProcessor May Fail to Acknowledge a TLP Request
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Interrupt From Local APIC Timer May Not Be Detectable While Being
Delivered
PCIe* Root-port Initiated Compliance State Transmitter Equalization
Settings May be Incorrect
XNo FixPCIe* Controller May Incorrectly Log Errors on Transition to RxL0s
XNo FixUnused PCIe* Lanes May Report Correctable Errors
XNo Fix
Accessing Physical Memory Space 0-640K through the Graphics
Aperture May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior
XNo FixPCIe Root Port May Not Initiate Link Speed Change
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Pending x87 FPU Exceptions (#MF) May be Signaled Earlier Than
Expected
DR6.B0-B3 May Not Report All Breakpoints Matched When a MOV/POP
SS is Followed by a Store or an MMX Instruction
XNo FixVEX.L is Not Ignored with VCVT*2SI Instructions
XNo Fix
Certain Local Memory Read / Load Retired PerfMon Events May
Undercount
Specification Update 9
Page 10
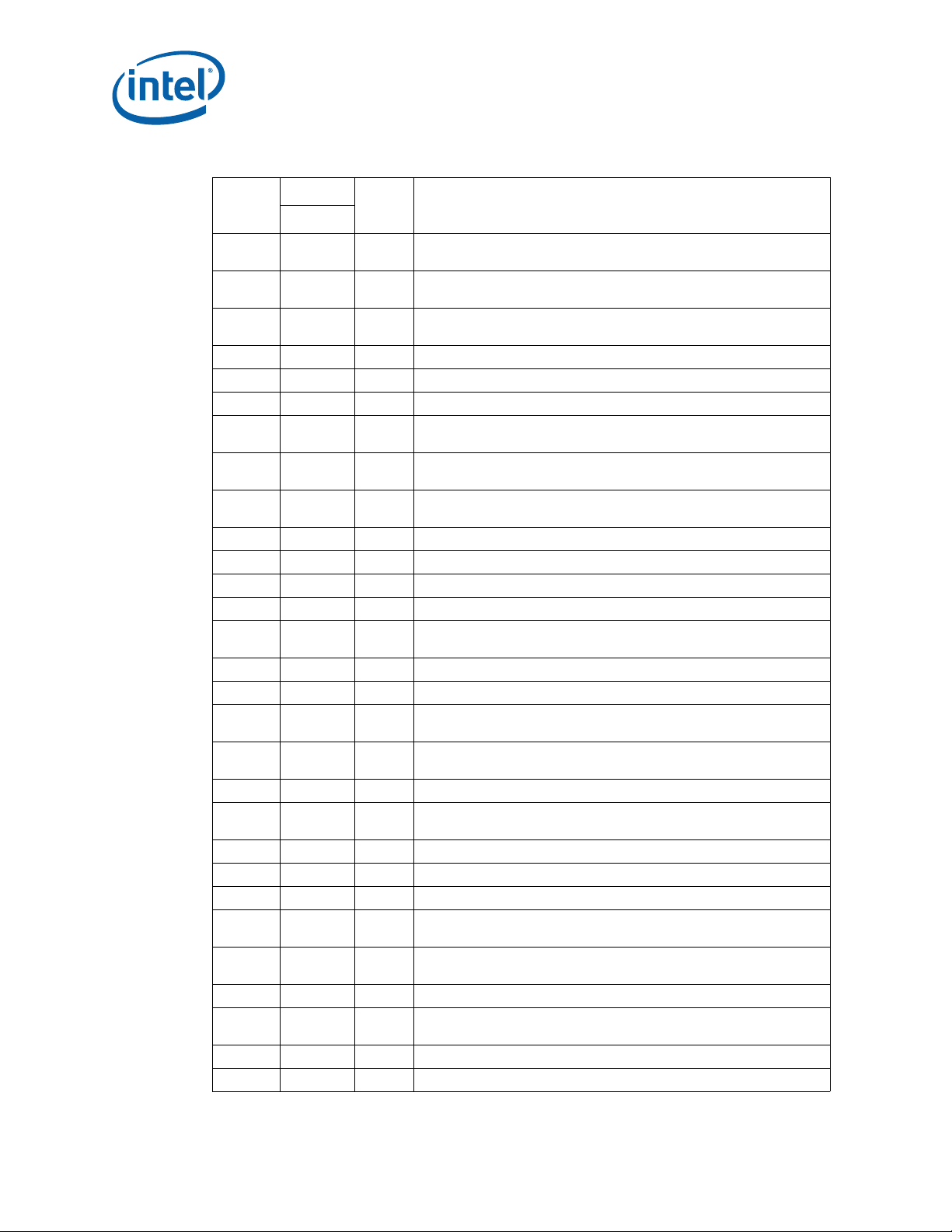
Errata (Sheet 2 of 5)
Number
HSD26
HSD27
HSD28
HSD29
HSD30
HSD31
HSD32
HSD33
HSD34
HSD35
HSD36
HSD37
HSD38
HSD39
HSD40
HSD41
HSD42
HSD43
HSD44
HSD45
HSD46
HSD47
HSD48
HSD49
HSD50
HSD51
HSD52
HSD53
HSD54
Steppings
C-0
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Status ERRATA
Specific Graphics Blitter Instructions May Result in Unpredictable
Graphics Controller Behavior
Processor May Enter Shutdown Unexpectedly on a Second
Uncorrectable Error
Modified Compliance Patterns for 2.5 GT/s and 5 GT/s Transfer Rates Do
Not Follow PCIe* Specification
XNo FixPerformance Monitor Counters May Produce Incorrect Results
XNo FixPerformance Monitor UOPS_EXECUTED Event May Undercount
XNo FixMSR_PERF_STATUS May Report an Incorrect Core Voltage
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
PCIe* Atomic Transactions From Two or More PCIe Controllers May
Cause Starvation
The Corrected Error Count Overflow Bit in IA32_ MC0_STATUS is Not
Updated After a UC Error is Logged
An AVX Gather Instruction That Causes an EPT Violation May Not
Update Previous Elements
XNo FixPLATFORM_POWER_LIMIT MSR Not Visible
XNo FixLPDDR Memory May Report Incorrect Temperature
XNo FixPCIe* Host Bridge DID May Be Incorrect
XNo FixTSC May be Incorrect After a Deep C-State Exit
XNo Fix
PCIe* Controller May Initiate Speed Change While in DL_Init State
Causing Certain PCIe Devices to Fail to Train
XNo FixSpurious VT-d Interrupts May Occur When the PFO Bit is Set
XNo FixN/A. Erratum has been removed.
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
AVX Gather Instruction That Causes a Fault or VM Exit May Incorrectly
Modify Its Destination Register
Inconsistent NaN Propagation May Occur When Executing (V)DPPS
Instruction
XNo FixDisplay May Flicker When Package C-States Are Enabled
XNo Fix
Certain Combinations of AVX Instructions May Cause Unpredictable
System Behavior
XNo FixProcessor May Incorrectly Estimate Peak Power Delivery Requirements
XNo FixIA32_PERF_CTL MSR is Incorrectly Reset
XNo FixProcessor May Hang During a Function Level Reset of the Display
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
AVX Gather Instruction That Should Result in #DF May Cause
Unexpected System Behavior
Throttling and Refresh Rate Maybe be Incorrect After Exiting Package CState
XNo FixProcessor May Livelock During On Demand Clock Modulation
XNo Fix
IA32_DEBUGCTL.FREEZE_PERFMON_ON_PMI is Incorrectly Cleared
by SMI
XNo FixThe From-IP for Branch Tracing May be Incorrect
XNo FixTM1 Throttling May Continue indefinitely
10 Specification Update
Page 11
Errata (Sheet 3 of 5)
Number
HSD55
HSD56
HSD57
HSD58
HSD59
HSD60
HSD61
HSD62
HSD63
HSD64
HSD65
HSD66
HSD67
HSD68
HSD69
HSD70
HSD71
HSD72
HSD73
HSD74
HSD75
HSD76
HSD77
HSD78
HSD79
HSD80
HSD81
Steppings
C-0
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Status ERRATA
Internal Parity Errors May Incorrectly Report Overflow in The
IA32_MCi_STATUS MSR
Performance Monitor Events OTHER_ASSISTS.AVX_TO_SSE And
OTHER_ASSISTS.SSE_TO_AVX May Over Count
XNo FixProcessor May Run at Incorrect P-State
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Performance Monitor Event DSB2MITE_SWITCHES.COUNT May Over
Count
Performance Monitor Register UNC_PERF_GLOBAL_STATUS Not
Restored on Package C7 Exit
Processor May Not Enter Package C6 or Deeper C-states When PCIe*
Links Are Disabled
Performance Monitor Event For Outstanding Offcore Requests And
Snoop Requests May Over Count
Some Performance Monitor Event Counts May be Inaccurate During SMT
Mode
XNo FixTimed MWAIT May Use Deadline of a Previous Execution
XNo FixThe Upper 32 Bits of CR3 May be Incorrectly Used With 32-Bit Paging
XNo Fix
Performance Monitor Events HLE_RETIRED.ABORTED_MISC4 And
RTM_RETIRED.ABORTED_MISC4 May Over Count
XNo FixA PCIe* LTR Update Message May Cause The Processor to Hang
XNo FixGETSEC Does Not Report Support For S-CRTM
XNo FixEPT Violations May Report Bits 11:0 of Guest Linear Address Incorrectly
XNo FixAPIC Timer Might Not Signal an Interrupt While in TSC-Deadline Mode
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM MSR (48AH) Does Not Properly Report The
Highest Index Value Used For VMCS Encoding
Incorrect FROM_IP Value For an RTM Abort in BTM or BTS May be
Observed
VT-d Hardware May Perform STRP And SIRTP Operations on a Package
C7 Exit
XNo FixGeneral-Purpose Performance Counters Can Unexpectedly Increment
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Performance Monitoring Events May Report Incorrect Number of Load
Hits or Misses to LLC
Performance Monitoring Event INSTR_RETIRED.ALL May Generate
Redundant PEBS Records For an Overflow
XNo FixLocked Load Performance Monitoring Events May Under Count
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Graphics Processor Ratio And C-State Transitions May Cause a System
Hang
Certain Performance Monitoring Events May Over Count Software
Demand Loads
Accessing Nonexistent Uncore Performance Monitoring MSRs May Not
Signal a #GP
XNo FixCall Stack Profiling May Produce Extra Call Records
XNo FixWarm Reset May Fail or Lead to Incorrect Power Regulation
Specification Update 11
Page 12
Errata (Sheet 4 of 5)
Number
HSD82
HSD83
HSD84
HSD85
HSD86
HSD87
HSD88
HSD89
HSD90
HSD91
HSD92
HSD93
HSD94
HSD95
HSD96
HSD97
HSD98
HSD99
HSD100
HSD101
HSD102
HSD103
HSD104
HSD105
HSD106
HSD107
HSD108
HSD109
Steppings
C-0
Status ERRATA
XNo FixPCIe* Host Bridge DID May Be Incorrect
XNo FixTransactional Abort May Produce an Incorrect Branch Record
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
SMRAM State-Save Area Above the 4GB Boundary May Cause
Unpredictable System Behavior
DMA Remapping Faults for the Graphics VT-d Unit May Not Properly
Report Type of Faulted Request
AVX Gather Instructions Page Faults May Report an Incorrect Faulting
Address
XNo FixIntel® TSX Instructions May Cause Unpredictable System behavior
XNo FixEvent Injection by VM Entry May Use an Incorrect B Flag for SS
XNo FixA Fault in SMM May Result in Unpredictable System Behavior
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Processor Frequency is Unexpectedly Limited Below Nominal P1 When
cTDP Down is Enabled
PMI May be Signaled More Than Once For Performance Monitor Counter
Overflow
Execution of FXSAVE or FXRSTOR With the VEX Prefix May Produce a
#NM Exception
RDRAND Execution in a Transactional Region May Cause a System
Hang
XNo FixUncore Clock Frequency Changes May Cause Audio/Video Glitches
XNo Fix
Processor May Experience a Spurious LLC-Related Machine Check
During Periods of High Activity
XNo FixThe Processor May Not Enter Package C7 When Using a PSR Display
XNo FixVideo/Audio Distortion May Occur
XNo FixSystem May Hang When Audio is Enabled During Package C3
XNo FixINVPCID May Not Cause #UD in VMX Non-Root Operation
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
XNo Fix
Non-Compliant PFAT Module Base Address May Cause Unpredictable
System Behavior
Incorrect LBR Source Address May be Reported For a Transactional
Abort
Address Translation Faults for Intel® VT-d May Not be Reported for
Display Engine Memory Accesses
L3 Cache Corrected Error Count May be Inaccurate After Package C7
Exit
XNo FixPCIe* Device’s SVID is Not Preserved Across The Package C7 C-State
XNo FixWarm Reset Does Not Stop GT Power Draw
XNo FixUnused PCIe* Lanes May Remain Powered After Package C7
XNo FixBMI1 And BMI2 Instruction Groups Are Not Available
XNo Fix
Virtual-APIC Page Accesses With 32-Bit PAE Paging May Cause a
System Crash
XNo FixProcessor Energy Policy Selection May Not Work as Expected
12 Specification Update
Page 13

Errata (Sheet 5 of 5)
Number
HSD110
HSD111
HSD112
HSD113
HSD114
HSD115
HSD116
HSD117
HSD118
Steppings
Status ERRATA
C-0
XNo Fix
XNo FixMSR_PP1_ENERGY_STATUS Reports Incorrect Energy Data
XNo Fix
XNo FixProcessor May Hang During Package C7 Exit
XNo FixIntel® TSX Instructions May Cause Unpredictable System behavior
XNo FixSpurious LLC Machine Check May Occur
XNo FixPage Fault May Report Incorrect Fault Information
XNo FixCATERR# Pin Assertion is Not Cleared on a Warm Reset
XNo Fix
Specification Changes
Number SPECIFICATION CHANGES
None for this revision of this specification update.
Specification Clarifications
A PEBS Record May Contain Processor State for an Unexpected
Instruction
x87 FPU DP May be Incorrect After Instructions That Save FP State to
Memory
Uncorrectable Machine Check Error During Core C6 Entry May Not be
Signaled
Number SPECIFICATION CLARIFICATIONS
None for this revision of this specification update.
Documentation Changes
Number DOCUMENTATION CHANGES
HSD1
”On-Demand Clock Modulation Feature Clarification”
Specification Update 13
Page 14
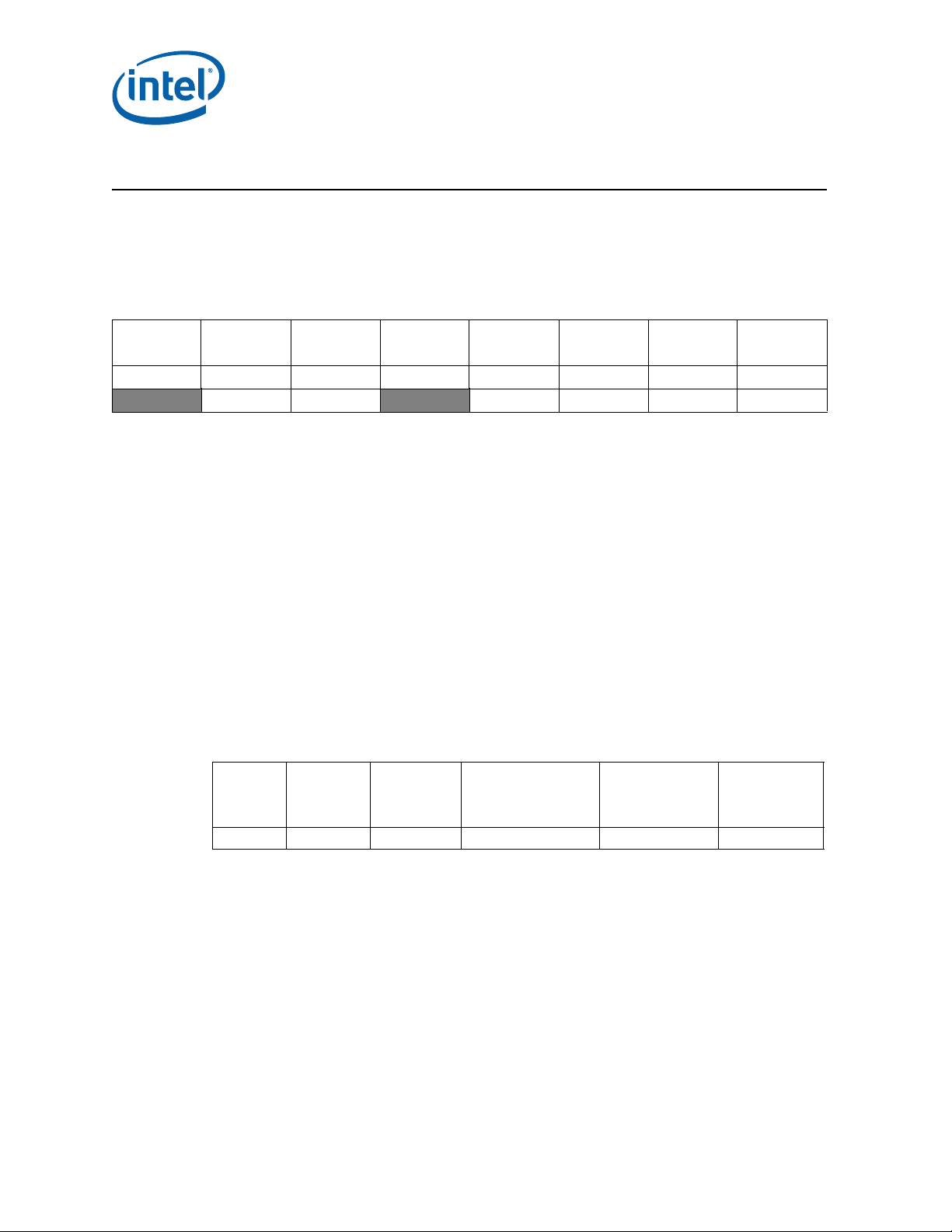
Identification Information
Component Identification using Programming Interface
The processor stepping can be identified by the following register contents.
Table 1. Desktop 4th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family Component
Identification
Reserved
Extended
Family
Extended
Model
Reserved
Processor
Type
Family
Code
Model
Number
Stepping
31:28 27:20 19:16 15:14 13:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
00000000b 0011b 00b 0110b 1100b xxxxb
Notes:
1. The Extended Family, Bits [27:20] are used in conjunction with the Family Code, specified in Bits[11:8], to
indicate whether the processor belongs to the Intel386™, Intel486™, Pentium
Core™ processor family.
2. The Extended Model, Bits [19:16] in conjunction with the Model Number, specified in Bits [7:4], are used to
identify the model of the processor within the processor’s family.
3. The Family Code corresponds to Bits [11:8] of the EDX register after RESET, Bits [11:8] of the EAX register
after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the generation field of the Device
ID register accessible through Boundary Scan.
4. The Model Number corresponds to Bits [7:4] of the EDX register after RESET, Bits [7:4] of the EAX register
after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the model field of the Device ID
register accessible through Boundary Scan.
5. The Stepping ID in Bits [3:0] indicates the revision number of that model. See the processor Identification
table for the processor stepping ID number in the CPUID information.
®
, Pentium 4, or Intel®
When EAX is initialized to a value of ‘1’, the CPUID instruction returns the Extended
Family, Extended Model, Processor Type, Family Code, Model Number and Stepping ID
value in the EAX register. Note that the EDX processor signature value after reset is
equivalent to the processor signature output value in the EAX register.
Cache and TLB descriptor parameters are provided in the EAX, EBX, ECX and EDX
registers after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 2 in the EAX register.
The processor can be identified by the following register contents.
ID
Host Device
Stepping Vendor ID
C-0 8086h 0C04h GT2 = 0416h 06h 06h
Notes:
1. The Vendor ID corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Vendor ID Register located at offset 00h–01h in the PCI
2. The Host Device ID corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Device ID Register located at Device 0 offset 02h–
3. The Processor Graphics Device ID (DID2) corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Device ID Register located at
4. The Revision Number corresponds to bits 7:0 of the Revision ID Re gister loc ated at offse t 08h in the PC I
14 Specification Update
function 0 configuration space.
03h in the PCI function 0 configuration space.
Device 2 offset 02h–03h in the PCI function 0 configuration space.
function 0 configuration space.
1
ID
2
Processor Graphics
Device ID
3
Revision ID
4
CRID
Page 15
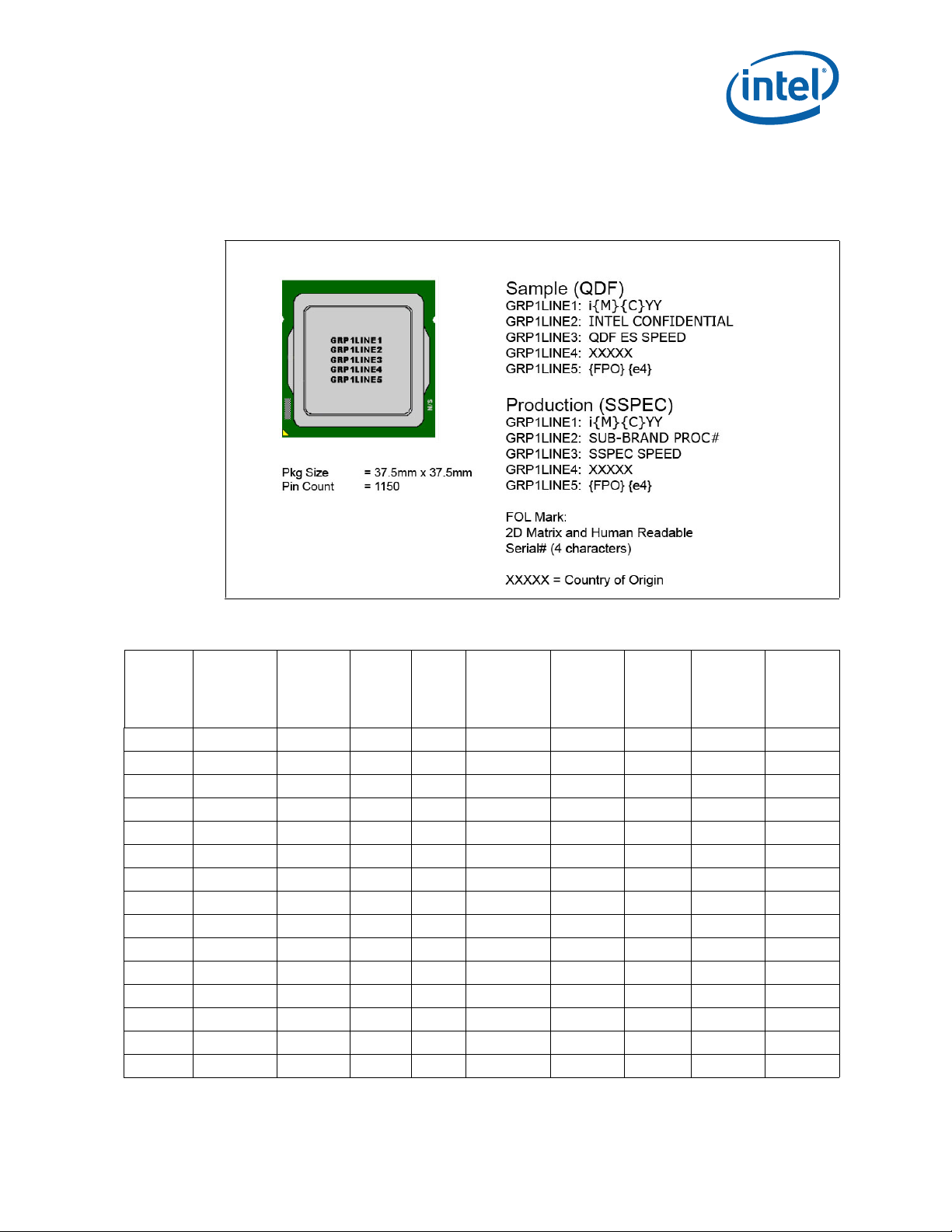
Component Marking Information
The processor stepping can be identified by the following component markings.
Figure 1. Desktop 4th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family Top-Side Markings
Table 2. Desktop Processor Identification (Sheet 1 of 2)
S-Spec
Number
SR147 I7-4770K C-0 8 4 2 3.9 1600 3.5 95
SR149 I7-4770 C-0 8 4 2 3.9 1600 3.4 95
SR14A I5-4670K C-0 6 4 2 3.8 1600 3.4 95
SR14D I5-4670 C-0 6 4 2 3.8 1600 3.4 95
SR14E I5-4570 C-0 6 4 2 3.6 1600 3.2 95
SR14F I5-4440 C-0 6 4 2 3.3 1600 3.1 95
SR14G I5-4430 C-0 6 4 2 3.2 1600 3 95
SR14H I7-4770S C-0 8 4 2 3.9 1600 3.1 65
SR14J I5-4570S C-0 6 4 2 3.6 1600 2.9 65
SR14K I5-4670S C-0 6 4 2 3.8 1600 3.1 65
SR14L I5-4440S C-0 6 4 2 3.3 1600 2.8 65
SR14M I5-4430S C-0 6 4 2 3.2 1600 2.7 65
SR14N I7-4770T C-0 8 4 2 3.7 1600 2.5 45
SR14P I5-4670T C-0 6 4 2 3.3 1600 2.3 45
SR14Q I7-4765T C-0 8 4 2 3 1600 2 35
Processor
Number
Stepping
Cache
Size
(MB)
Functional
Core
Integrated
Graphics
Cores
Max
Turbo
Freq.
Rate
(GHz)
Memory
(MHz)
Core
Freq.
(GHz)
Thermal
Design
Power
(W)
Specification Update 15
Page 16

Table 2. Desktop Processor Identification (Sheet 2 of 2)
Max
S-Spec
Number
SR18K I7-4770R C-0 6 4 3 3.9 1600 3.2 65
SR18M I5-4670R C-0 4 4 3 3.7 1600 3 65
SR18Q I5-4570R C-0 4 4 3 3.2 1600 2.7 65
SR1BW I7-4771 C-0 8 4 2 3.9 1600 3.5 95
SR1CA I5-4570T C-0 4 2 2 3.6 1600 2.9 35
SR1CE G3430 C-0 3 2 1 3.3 1600 3.3 65
SR1CG G3220 C-0 3 2 1 3 1333 3 65
SR1CL G3220T C-0 3 2 1 2.6 1333 2.6 35
SR1NB G3420 C-0 3 2 1 3.2 1333 3.2 65
SR1NK I3-4330T C-0 4 2 2 3 1600 3 35
SR1NL I3-4340 C-0 4 2 2 3.6 1600 3.6 65
SR1NM I3-4330 C-0 4 2 2 3.5 1600 3.5 65
SR1NN I3-4130T C-0 3 2 2 2.9 1600 2.9 35
SR1NP I3-4130 C-0 3 2 2 3.4 1600 3.4 65
SR1CN
SR1CP
SR1NC
Processor
Number
Celeron
G1820
Celeron
G1820T
Celeron
G1830
Stepping
C-0 2 2 1 2.7 1333 2.7 65
C-0 2 2 1 2.4 1333 2.4 35
C-0 2 2 1 2.8 1333 2.8 65
Cache
Size
(MB)
Functional
Core
Integrated
Graphics
Cores
Turbo
Freq.
Rate
(GHz)
Memory
(MHz)
Core
Freq.
(GHz)
Thermal
Design
Power
(W)
16 Specification Update
Page 17

Errata
HSD1. LBR, BTS, BTM May Report a Wrong Address when an Exception/
Interrupt Occurs in 64-bit Mode
Problem: An exception/interrupt event should be transparent to the LBR (Last Branch Record),
BTS (Branch Trace Store) and BTM (Branch Trace Message) mechanisms. However,
during a specific boundary condition where the exception/interrupt occurs right after
the execution of an instruction at the lower canonical boundary (0x00007FFFFFFFFFFF)
in 64-bit mode, the LBR return registers will save a wrong return address with bits 63
to 48 incorrectly sign extended to all 1’s. Subsequent BTS and BTM operations which
report the LBR will also be incorrect.
Implication: LBR, BTS and BTM may report incorrect information in the event of an exception/
interrupt.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD2. EFLAGS Discrepancy on Page Faults and on EPT-Induced VM Exits
after a Translation Change
Problem: This erratum is regarding the case where paging structures are modified to change a
linear address from writable to non-writable without software performing an
appropriate TLB invalidation. When a subsequent access to that address by a specific
instruction (ADD, AND, BTC, BTR, BTS, CMPXCHG, DEC, INC, NEG, NOT, OR, ROL/ROR,
SAL/SAR/SHL/SHR, SHLD, SHRD, SUB, XOR, and XADD) causes a page fault or an EPTinduced VM exit, the value saved for EFLAGS may incorrectly contain the arithmetic flag
values that the EFLAGS register would have held had the instruction completed without
fault or VM exit. For page faults, this can occur even if the fault causes a VM exit or if
its delivery causes a nested fault.
Implication: None identified. Although the EFLAGS value saved by an affected event (a page fault or
an EPT-induced VM exit) may contain incorrect arithmetic flag values, Intel has not
identified software that is affected by this erratum. This erratum will have no further
effects once the original instruction is restarted because the instruction will produce the
same results as if it had initially completed without fault or VM exit.
Workaround: If the handler of the affected events inspects the arithmetic portion of the saved
EFLAGS value, then system software should perform a synchronized paging structure
modification and TLB invalidation.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD3. MCi_Status Overflow Bit May Be Incorrectly Set on a Single Instance
of a DTLB Error
Problem: A single Data Translation Look Aside Buffer (DTLB) error can incorrectly set the
Overflow (bit [62]) in the MCi_Status register. A DTLB error is indicated by MCA error
code (bits [15:0]) appearing as binary value, 000x 0000 0001 0100, in the MCi_Status
register.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the Overflow bit in the MCi_Status register may not be an
accurate indication of multiple occurrences of DTLB errors. There is no other impact to
normal processor functionality.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 17
Page 18

HSD4. LER MSRs May Be Unreliable
Problem: Due to certain internal processor events, updates to the LER (Last Exception Record)
MSRs, MSR_LER_FROM_LIP (1DDH) and MSR_LER_TO_LIP (1DEH), may happen when
no update was expected.
Implication: The values of the LER MSRs may be unreliable.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD5. MONITOR or CLFLUSH on the Local XAPIC's Address Space Results in
Hang
Problem: If the target linear address range for a MONITOR or CLFLUSH is mapped to the local
xAPIC's address space, the processor will hang.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the processor will hang. The local xAPIC's address space
must be uncached. The MONITOR instruction only functions correctly if the specified
linear address range is of the type write-back. CLFLUSH flushes data from the cache.
Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: Do not execute MONITOR or CLFLUSH instructions on the local xAPIC address space.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD6. An Uncorrectable Error Logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS May also
Result in a System Hang
Problem: Uncorrectable errors logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS MSR (409H) may also result in a
system hang causing an Internal Timer Error (MCACOD = 0x0400h) to be logged in
another machine check bank (IA32_MCi_STATUS).
Implication: Uncorrectable errors logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS can further cause a system hang
and an Internal Timer Error to be logged.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD7. #GP on Segment Selector Descriptor that Straddles Canonical
Boundary May Not Provide Correct Exception Error Code
Problem: During a #GP (General Protection Exception), the processor pushes an error code on to
the exception handler’s stack. If the segment selector descriptor straddles the
canonical boundary, the error code pushed onto the stack may be incorrect.
Implication: An incorrect error code may be pushed onto the stack. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
18 Specification Update
Page 19

HSD8. FREEZE_WHILE_SMM Does Not Prevent Event From Pending
PEBS During SMM
Problem: In general, a PEBS record should be generated on the first count of the event after the
counter has overflowed. However, IA32_DEBUGCTL_MSR.FREEZE_WHILE_SMM
(MSR 1D9H, bit [14]) prevents performance counters from counting during SMM
(System Management Mode). Due to this erratum, if
1. A performance counter overflowed before an SMI
2. A PEBS record has not yet been generated because another count of the event has
not occurred
3. The monitored event occurs during SMM
then a PEBS record will be saved after the next RSM instruction.
When FREEZE_WHILE_SMM is set, a PEBS should not be generated until the event
occurs outside of SMM.
Implication: A PEBS record may be saved after an RSM instruction due to the associated
performance counter detecting the monitored event during SMM; even when
FREEZE_WHILE_SMM is set.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD9. APIC Error “Received Illegal Vector” May be Lost
Problem: APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) may not update the ESR (Error
Status Register) flag Received Illegal Vector bit [6] properly when an illegal vector
error is received on the same internal clock that the ESR is being written (as part of the
write-read ESR access flow). The corresponding error interrupt will also not be
generated for this case.
Implication: Due to this erratum, an incoming illegal vector error may not be logged into ESR
properly and may not generate an error interrupt.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD10. Changing the Memory Type for an In-Use Page Translation May Lead
to Memory-Ordering Violations
Problem: Under complex microarchitectural conditions, if software changes the memory type for
data being actively used and shared by multiple threads without the use of semaphores
or barriers, software may see load operations execute out of order.
Implication: Memory ordering may be violated. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software.
Workaround: Software should ensure pages are not being actively used before requesting their
memory type be changed.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 19
Page 20

HSD11. Performance Monitor Precise Instruction Retired Event May Present
Wrong Indications
Problem: When the PDIR (Precise Distribution for Instructions Retired) mechanism is activated
(INST_RETIRED.ALL (event C0H, umask value 00H) on Counter 1 programmed in PEBS
mode), the processor may return wrong PEBS/PMI interrupts and/or incorrect counter
values if the counter is reset with a SAV below 100 (Sample-After-Value is the counter
reset value software programs in MSR IA32_PMC1[47:0] in order to control interrupt
frequency).
Implication: Due to this erratum, when using low SAV values, the program may get incorrect PEBS
or PMI interrupts and/or an invalid counter state.
Workaround: The sampling driver should avoid using SAV<100.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD12. CR0.CD Is Ignored in VMX Operation
Problem: If CR0.CD=1, the MTRRs and PAT should be ignored and the UC memory type should
be used for all memory accesses. Due to this erratum, a logical processor in VMX
operation will operate as if CR0.CD=0 even if that bit is set to 1.
Implication: Algorithms that rely on cache disabling may not function properly in VMX operation.
Workaround: Algorithms that rely on cache disabling should not be executed in VMX root operation.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD13. Instruction Fetch May Cause Machine Check if Page Size and Memory
Type Was Changed Without Invalidation
Problem: This erratum may cause a machine-check error (IA32_MCi_STATUS.MCACOD=0150H)
on the fetch of an instruction that crosses a 4-KByte address boundary. It applies only
if (1) the 4-KByte linear region on which the instruction begins is originally translated
using a 4-KByte page with the WB memory type; (2) the paging structures are later
modified so that linear region is translated using a large page (2-MByte, 4-MByte, or 1GByte) with the UC memory type; and (3) the instruction fetch occurs after the pagingstructure modification but before software invalidates any TLB entries for the linear
region.
Implication: Due to this erratum an unexpected machine check with error code 0150H may occur,
possibly resulting in a shutdown. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software.
Workaround: Software should not write to a paging-structure entry in a way that would change, for
any linear address, both the page size and the memory type. It can instead use the
following algorithm: first clear the P flag in the relevant paging-structure entry (e.g.,
PDE); then invalidate any translations for the affected linear addresses; and then
modify the relevant paging-structure entry to set the P flag and establish the new page
size and memory type.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
20 Specification Update
Page 21

HSD14. Execution of VAESIMC or VAESKEYGENASSIST With An Illegal Value
for VEX.vvvv May Produce a #NM Exception
Problem: The VAESIMC and VAESKEYGENASSIST instructions should produce a #UD (Invalid-
Opcode) exception if the value of the vvvv field in the VEX prefix is not 1111b. Due to
this erratum, if CR0.TS is “1”, the processor may instead produce a #NM (Device-NotAvailable) exception.
Implication: Due to this erratum, some undefined instruction encodings may produce a #NM instead
of a #UD exception.
Workaround: Software should always set the vvvv field of the VEX prefix to 1111b for instances of
the VAESIMC and VAESKEYGENASSIST instructions.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD15. Processor May Fail to Acknowledge a TLP Request
Problem: When a PCIe root port’s receiver is in Receiver L0s power state and the port initiates a
Recovery event, it will issue Training Sets to the link partner. The link partner will
respond by initiating an L0s exit sequence. Prior to transmitting its own Training Sets,
the link partner may transmit a TLP (Transaction Layer Packet) request. Due to this
erratum, the root port may not acknowledge the TLP request.
Implication: After completing the Recovery event, the PCIe link partner will replay the TLP request.
The link partner may set a Correctable Error status bit, which has no functional effect.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD16. Interrupt From Local APIC Timer May Not Be Detectable While Being
Delivered
Problem: If the local-APIC timer’s CCR (current-count register) is 0, software should be able to
determine whether a previously generated timer interrupt is being delivered by first
reading the delivery-status bit in the LVT timer register and then reading the bit in the
IRR (interrupt-request register) corresponding to the vector in the LVT timer register. If
both values are read as 0, no timer interrupt should be in the process of being
delivered. Due to this erratum, a timer interrupt may be delivered even if the CCR is 0
and the LVT and IRR bits are read as 0. This can occur only if the DCR (Divide
Configuration Register) is greater than or equal to 4. The erratum does not occur if
software writes zero to the Initial Count Register before reading the LVT and IRR bits.
Implication: Software that relies on reads of the LVT and IRR bits to determine whether a timer
interrupt is being delivered may not operate properly.
Workaround: Software that uses the local-APIC timer must be prepared to handle the timer
interrupts, even those that would not be expected based on reading CCR and the LVT
and IRR bits; alternatively, software can avoid the problem by writing zero to the Initial
Count Register before reading the LVT and IRR bits.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 21
Page 22

HSD17. PCIe* Root-port Initiated Compliance State Transmitter Equalization
Settings May be Incorrect
Problem: If the processor is directed to enter PCIe Polling.Compliance at 5.0 GT/s or 8.0 GT/s
transfer rates, it should use the Link Control 2 Compliance Preset/De-emphasis field
(bits [15:12]) to determine the correct de-emphasis level. Due to this erratum, when
the processor is directed to enter Polling.Compliance from 2.5 GT/s transfer rate, it
retains 2.5 GT/s de-emphasis values.
Implication: The processor may operate in Polling.Compliance mode with an incorrect transmitter
de-emphasis level.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD18. PCIe* Controller May Incorrectly Log Errors on Transition to RxL0s
Problem: Due to this erratum, if a link partner transitions to RxL0s state within 20 ns of entering
L0 state, the PCIe controller may incorrectly log an error in “Correctable Error
Status.Receiver Error Status” field (Bus 0, Device 2, Function 0, 1, 2 and Device 6,
Function 0, offset 1D0H, bit 0).
Implication: Correctable receiver errors may be incorrectly logged. Intel has not observed any
functional impact due to this erratum with any commercially available add-in cards.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD19. Unused PCIe* Lanes May Report Correctable Errors
Problem: Due to this erratum, during PCIe* link down configuration, unused lanes may report a
Correctable Error Detected in Bus 0, Device 1, Function 0-2, and Device 6, Function 0,
Offset 158H, Bit 0.
Implication: Correctable Errors may be reported by a PCIe controller for unused lanes.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD20. Accessing Physical Memory Space 0-640K through the Graphics
Aperture May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior
Problem: The physical memory space 0-640K when accessed through the graphics aperture may
result in a failure for writes to complete or reads to return incorrect results.
Implication: A hang or functional failure may occur during graphics operation such as OGL or OCL
conformance tests, 2D/3D games and graphics intensive application.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
22 Specification Update
Page 23

HSD21. PCIe Root Port May Not Initiate Link Speed Change
Problem: The PCIe Base specification requires the upstream component to maintain the PCIe link at the
target link speed or the highest speed supported by both components on the link, whichever is
lower. PCIe root port will not initiate the link speed change without being triggered by the software
when the root port maximum link speed is configured to be 5.0 GT/s. System BIOS will trigger
the link speed change under normal boot scenarios. However, BIOS is not involved in
some scenarios such as link disable/re-enable or secondary bus reset and therefore the
speed change may not occur unless initiated by the downstream component. This
erratum does not affect the ability of the downstream component to initiate a link
speed change. All known 5.0Gb/s-capable PCIe downstream components have been
observed to initiate the link speed change without relying on the root port to do so.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the PCIe root port may not initiate a link speed change during
some hardware scenarios causing the PCIe link to operate at a lower than expected
speed. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available platform.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD22. Pending x87 FPU Exceptions (#MF) May be Signaled Earlier Than
Expected
Problem: x87 instructions that trigger #MF normally service interrupts before the #MF. Due to
this erratum, if an instruction that triggers #MF is executed while Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep
Thermal Monitor events occur, the pending #MF may be signaled before pending
interrupts are serviced.
Implication: Software may observe #MF being signaled before pending interrupts are serviced.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
®
Technology transitions, Intel® Turbo Boost Technology transitions, or
HSD23. DR6.B0-B3 May Not Report All Breakpoints Matched When a MOV/POP
SS is Followed by a Store or an MMX Instruction
Problem: Normally, data breakpoints matches that occur on a MOV SS, r/m or POP SS will not
cause a debug exception immediately after MOV/POP SS but will be delayed until the
instruction boundary following the next instruction is reached. After the debug
exception occurs, DR6.B0-B3 bits will contain information about data breakpoints
matched during the MOV/POP SS as well as breakpoints detected by the following
instruction. Due to this erratum, DR6.B0-B3 bits may not contain information about
data breakpoints matched during the MOV/POP SS when the following instruction is
either an MMX instruction that uses a memory addressing mode with an index or a
store instruction.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, DR6 may not contain information about all breakpoints
matched. This erratum will not be observed under the recommended usage of the MOV
SS,r/m or POP SS instructions (i.e., following them only with an instruction that writes
(E/R)SP).
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 23
Page 24

HSD24. VEX.L is Not Ignored with VCVT*2SI Instructions
Problem: The VEX.L bit should be ignored for the VCVTSS2SI, VCVTSD2SI, VCVTTSS2SI, and
VCVTTSD2SI instructions, however due to this erratum the VEX.L bit is not ignored and
will cause a #UD.
Implication: Unexpected #UDs will be seen when the VEX.L bit is set to 1 with VCVTSS2SI,
VCVTSD2SI, VCVTTSS2SI, and VCVTTSD2SI instructions.
Workaround: Software should ensure that the VEX.L bit is set to 0 for all scalar instructions.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD25. Certain Local Memory Read / Load Retired PerfMon Events May
Undercount
Problem: Due to this erratum, the Local Memory Read / Load Retired PerfMon events listed below
may undercount.
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L3_HIT
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L3_MISS
MEM_LOAD_L3_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_MISS
MEM_LOAD_L3_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_HIT
MEM_LOAD_L3_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_HITM
MEM_LOAD_L3_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_NONE
MEM_LOAD_L3_MISS_RETIRED.LOCAL_DRAM
MEM_LOAD_L4_RETIRED.LOCAL_HIT
MEM_TRANS_RETIRED.LOAD_LATENCY
Implication: The affected events may undercount, resulting in inaccurate memory profiles. Intel has
observed u
ndercounts as much as 40%.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD26. Specific Graphics Blitter Instructions May Result in Unpredictable
Graphics Controller Behavior
Problem: Specific source-copy blitter instructions in Intel® HD Graphics 4600 Processor may
result in unpredictable behavior when a blit source and destination overlap.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor may exhibit unpredictable graphics controller
behavior. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD27. Processor May Enter Shutdown Unexpectedly on a Second
Uncorrectable Error
Problem: If an IA32_MCi_STATUS MSR contains an uncorrectable error with MCACOD=0x406 and
a second uncorrectable error occurs after warm reset but before the first error is
cleared by zeroing the IA32_MCi_STATUS MSR, a shutdown will occur.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the processor will unexpectedly shut down instead of
executing the machine check handler.
Workaround: None identified. Software should clear IA32_MCi_STATUS MSRs as early as possible to
minimize the possibility of this erratum occurring.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
24 Specification Update
Page 25

HSD28. Modified Compliance Patterns for 2.5 GT/s and 5 GT/s Transfer Rates
Do Not Follow PCIe* Specification
Problem: The PCIe controller does not produce the PCIe specification defined sequence for the
Modified Compliance Pattern at 2.5 GT/s and 5 GT/s transfer rates. This erratum is not
seen at 8 GT/s transfer rates.
Implication: Normal PCIe operation is unaffected by this erratum.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD29. Performance Monitor Counters May Produce Incorrect Results
Problem: When operating with SMT enabled, a memory at-retirement performance monitoring
event (from the list below) may be dropped or may increment an enabled event on the
corresponding counter with the same number on the physical core’s other thread rather
than the thread experiencing the event. Processors with SMT disabled in BIOS are not
affected by this erratum.
The list of affected memory at-retirement events is as follows:
MEM_UOP_RETIRED.LOADS
MEM_UOP_RETIRED.STORES
MEM_UOP_RETIRED.LOCK
MEM_UOP_RETIRED.SPLIT
MEM_UOP_RETIRED.STLB_MISS
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.HIT_LFB
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.L1_HIT
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.L2_HIT
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.LLC_HIT
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_MISC_RETIRED.LLC_MISS
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_HIT
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_HITM
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_MISS
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_NONE
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.LLC_MISS
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_MISS_RETIRED.LOCAL_DRAM
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_MISS_RETIRED.REMOTE_DRAM
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.L2_MISS
Implication: Due to this erratum, certain performance monitoring event will produce unreliable
results during hyper-threaded operation.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD30. Performance Monitor UOPS_EXECUTED Event May Undercount
Problem: The performance monitor event UOPS_EXECUTED (Event B1H, any Unmask) should
count the number of UOPs executed each cycle. However due to this erratum, when
eight UOPs execute in one cycle, these UOPs will not be counted.
Implication: The performance monitor event UOPS_EXECUTED may reflect a count lower than the
actual number of events.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 25
Page 26

HSD31. MSR_PERF_STATUS May Report an Incorrect Core Voltage
Problem: The core operating voltage can be determined by dividing MSR_PERF_STATUS MSR
(198H) bits [47:32] by 2^13. However, due to this erratum, this calculation may report
half the actual core voltage.
Implication: The core operating voltage may be reported incorrectly.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD32. PCIe* Atomic Transactions From Two or More PCIe Controllers May
Cause Starvation
Problem: On a Processor PCIe controller configuration in which two or more controllers receive
concurrent atomic transactions, a PCIe controller may experience starvation which
eventually can lead to a completion timeout.
Implication: Atomic transactions from two or more PCIe controllers may lead to a completion
timeout. Atomic transactions from only one controller will not be affected by this
erratum. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available device.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD33. The Corrected Error Count Overflow Bit in IA32_ MC0_STATUS is Not
Updated After a UC Error is Logged
Problem: When a UC (uncorrected) error is logged in the IA32_MC0_STATUS MSR (401H),
corrected errors will continue to update the lower 14 bits (bits 51:38) of the Corrected
Error Count. Due to this erratum, the sticky count overflow bit (bit 52) of the Corrected
Error Count will not get updated after a UC error is logged.
Implication: The Corrected Error Count Overflow indication will be lost if the overflow occurs after an
uncorrectable error has been logged.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD34. An AVX Gather Instruction That Causes an EPT Violation May Not
Update Previous Elements
Problem: When execution of an AVX gather instruction causes an EPT (extended page table)
violation due to a specific element, all previous elements should be complete. Due to
this erratum, such an execution may fail to complete previous elements. In addition,
the instruction's mask operand is not updated. This erratum applies only if the EPT
violation occurs while updating an accessed or dirty flag in a paging-structure entry.
Instructions impacted by this erratum are: VGATHERDPS, VGATHERDPD, VGATHERQPS,
VGATHERQPD, VPGATHERDD, VPGATHERDQ, VPGATHERQD, and VPGATHERQQ.
Implication: This erratum may prevent a gather instruction from making forward progress.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
26 Specification Update
Page 27

HSD35. PLATFORM_POWER_LIMIT MSR Not Visible
Problem: The PLATFORM_POWER_LIMIT MSR (615H) is used to control the PL3 (power limit 3)
mechanism of the processor. Due to this erratum, this MSR is not visible to software.
Implication: Software is unable to read or write the PLATFORM_POWER_LIMIT MSR. If software
attempts to access this MSR, a general protection fault will occur.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD36. LPDDR Memory May Report Incorrect Temperature
Problem: When any of the four possible LPDDR ranks are not populated, the unpopulated ranks
will report a default temperature of 85C as a three bit value of 011b. If the system has
unpopulated ranks the temperature of memory will be reported as 85C
in PCU_CR_DDR_DIMM_HOTTEST_ABSOLUTE (MCHBAR Bus 0; Device 0; Function 0;
offset 58B8H) in bits [5:7], until any of the populated ranks report a higher
temperature than this.
Implication: When the memory temperature is less than or equal to 85C it may be reported as
85C. This erratum does not affect DDR3 and DDR3L memory types.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD37. PCIe* Host Bridge DID May Be Incorrect
Problem: The PCIe Host Bridge DID register (Bus 0; Device 0; Offset 2H) contents may be
incorrect after a Package C7 exit.
Implication: Software that depends on the Host Bridge DID value may not behave as expected after
a Package C7 exit.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD38. TSC May be Incorrect After a Deep C-State Exit
Problem: On exiting from Package C6 or deeper, the processor may incorrectly restore the TSC
(Time Stamp Counter).
Implication: Software using the TSC may produce incorrect result and/or may not behave as
expected.
Workaround: It is possible for BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD39. PCIe* Controller May Initiate Speed Change While in DL_Init State
Causing Certain PCIe Devices to Fail to Train
Problem: The PCIe controller supports hardware autonomous speed change capabilities. Due to
this erratum, the PCIe controller may initiate speed change while in the DL_Init state
which may prevent link training for certain PCIe devices.
Implication: Certain PCIe devices may fail to complete DL_Init causing the PCIe link to fail to train.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 27
Page 28

HSD40. Spurious VT-d Interrupts May Occur When the PFO Bit is Set
Problem: When the PFO (Primary Fault Overflow) field (bit [0] in the VT-d FSTS [Fault Status]
register) is set to 1, further faults should not generate an interrupt. Due to this
erratum, further interrupts may still occur.
Implication: Unexpected Invalidation Queue Error interrupts may occur. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: Software should be written to handle spurious VT-d fault interrupts.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD41. N/A. Erratum has been removed
HSD42. AVX Gather Instruction That Causes a Fault or VM Exit May Incorrectly
Modify Its Destination Register
Problem: An execution of a 128-bit AVX gather instruction zeroes the upper 128 bits of the
instruction's destination register unless access to the first unmasked element causes a
fault or VM exit. Due to this erratum, these bits may be cleared even when accessing
the first unmasked element causes a fault or VM exit. Instructions impacted by this
erratum are: VGATHERDPS, VGATHERDPD, VGATHERQPS, VGATHERQPD,
VPGATHERDD, VPGATHERDQ, VPGATHERQD, and VPGATHERQQ.
Implication: Software that depends on the destination register of a 128-bit AVX gather instruction to
remain unchanged after access of the first unmasked element results in fault or VM exit
may not behave as expected.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD43. Inconsistent NaN Propagation May Occur When Executing (V)DPPS
Instruction
Problem: Upon completion of the (V)DPPS instruction with multiple different NaN encodings in
the input elements, software may observe different NaN encodings in the destination
elements.
Implication: Inconsistent NaN encodings in the destination elements for the (V) DPPS instruction
may be observed.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
28 Specification Update
Page 29

HSD44. Display May Flicker When Package C-States Are Enabled
Problem: When package C-States are enabled, the display may not be refreshed at the correct
rate.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the user may observe flickering on the display.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD45. Certain Combinations of AVX Instructions May Cause Unpredictable
System Behavior
Problem: Execution of certain combinations of AVX instructions may lead to unpredictable system
behavior.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, unpredictable system behaviors, including system hang or
incorrect results can occur.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD46. Processor May Incorrectly Estimate Peak Power Delivery
Requirements
Problem: Under certain conditions, the processor may incorrectly calculate the frequency at
which the cores and graphics engine can operate while still meeting voltage regulator
and power supply peak power delivery capabilities. When this occurs, combined with
high power workloads, system shutdown may be observed.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, system shutdown may be observed under high power
workloads.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD47. IA32_PERF_CTL MSR is Incorrectly Reset
Problem: The IA32_PERF_CTL MSR (199H) is not initialized correctly after a processor reset.
Implication: If software reads the IA32_PERF_CTL MSR before writing it, software can observe an
incorrect reset value. Although incorrect values are reported to software, the correct
default values for this register are still used by the processor. No performance or power
impact occurs due to this erratum.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD48. Processor May Hang During a Function Level Reset of the Display
Problem: When package C-States are enabled, it is possible that the processor may hang when
software performs a Function Level Reset of the display via bit 1 of the Advanced
Features Control Register (Bus 0; Device 2; Function 0; Offset 0A8H).
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the processor may hang.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 29
Page 30

HSD49. AVX Gather Instruction That Should Result in #DF May Cause
Unexpected System Behavior
Problem: Due to this erratum, an execution of a 128-bit AVX gather instruction may fail to
generate a #DF (double fault) when expected. Instructions impacted by this erratum
are: VGATHERDPS, VGATHERDPD, VGATHERQPS, VGATHERQPD, VPGATHERDD,
VPGATHERDQ, VPGATHERQD, and VPGATHERQQ.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, an operation which should cause a #DF may result in
unexpected system behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD50. Throttling and Refresh Rate Maybe be Incorrect After Exiting Package
C-State
Problem: When the OLTM (Open Loop Thermal Management) feature is enabled, the DIMM
thermal status reported in DDR_THERM_PERDIMM_STATUS (MCHBAR Offset 588CH)
may be incorrect following an exit from Package C3 or deeper.
Implication: The incorrect DIMM thermal status may result in degraded performance from unneeded
memory throttling and excessive DIMM refresh rates.
Workaround: It is possible for BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD51. Processor May Livelock During On Demand Clock Modulation
Problem: The processor may livelock when (1) a processor thread has enabled on demand clock
modulation via bit 4 of the IA32_CLOCK_MODULATION MSR (19AH) and the clock
modulation duty cycle is set to 12.5% (02H in bits 3:0 of the same MSR), and (2) the
other processor thread does not have on demand clock modulation enabled and that
thread is executing a stream of instructions with the lock prefix that either split a
cacheline or access UC memory.
Implication: Program execution may stall on both threads of the core subject to this erratum.
Workaround: This erratum will not occur if clock modulation is enabled on all threads when using on
demand clock modulation or if the duty cycle programmed in the
IA32_CLOCK_MODULATION MSR is 18.75% or higher.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD52. IA32_DEBUGCTL.FREEZE_PERFMON_ON_PMI is Incorrectly Cleared by
SMI
Problem: FREEZE_PERFMON_ON_PMI (bit 12) in the IA32_DEBUGCTL MSR (1D9H) is
erroneously cleared during delivery of an SMI (system-management interrupt).
Implication: As a result of this erratum, the performance monitoring counters will continue to count
after a PMI occurs in SMM (system-management Mode).
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
30 Specification Update
Page 31

HSD53. The From-IP for Branch Tracing May be Incorrect
Problem: BTM (Branch Trace Message) and BTS (Branch Trace Store) report the “From-IP”
indicating the source address of the branch instruction. Due to this erratum, BTM and
BTS may repeat the “From-IP” value previously reported. The “To-IP” value is not
affected.
Implication: Using BTM or BTS reports to reconstruct program execution may be unreliable.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD54. TM1 Throttling May Continue indefinitely
Problem: TM1 (Thermal Monitor 1) throttling may continue when the processor’s temperature
decreases below the throttling point while the processor is in Package C3 or deeper.
Implication: The processor will continue thermal throttling but does not indicate it is hot.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD55. Internal Parity Errors May Incorrectly Report Overflow in The
IA32_MCi_STATUS MSR
Problem: Due to this erratum, uncorrectable internal parity error reports with an
IA32_MCi_STATUS.MCACOD (bits [15:0]) value of 0005H and an
IA32_MCi_STATUS.MSCOD (bits [31:16]) value of 0004H may incorrectly set the
IA32_MCi_STATUS.OVER flag (bit 62) indicating an overflow even when only a single
error has been observed.
Implication: IA32_MCi_STATUS.OVER may not accurately indicate multiple occurrences of
uncorrectable internal parity errors. There is no other impact to normal processor
functionality.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD56. Performance Monitor Events OTHER_ASSISTS.AVX_TO_SSE And
OTHER_ASSISTS.SSE_TO_AVX May Over Count
Problem: The Performance Monitor events OTHER_ASSISTS.AVX_TO_SSE (Event C1H; Umask
08H) and OTHER_ASSISTS.SSE_TO_AVX (Event C1H; Umask 10H) incorrectly
increment and over count when an HLE (Hardware Lock Elision) abort occurs.
Implication: The Performance Monitor Events OTHER_ASSISTS.AVX_TO_SSE And
OTHER_ASSISTS.SSE_TO_AVX may over count.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD57. Processor May Run at Incorrect P-State
Problem: The processor package may use stale software P-State (performance state) requests
when one or more logical processors are idle.
Implication: The processor package may run at a higher or lower than expected P-State. This issue
may persist as long as any logical processor is idle.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 31
Page 32

HSD58. Performance Monitor Event DSB2MITE_SWITCHES.COUNT May Over
Count
Problem: The Performance Monitor Event DSB2MITE_SWITCHES.COUNT (Event ABH; Umask
01H) should count the number of DSB (Decode Stream Buffer) to MITE (Macro
Instruction Translation Engine) switches. Due to this erratum, the
DSB2MITE_SWITCHES.COUNT event will count speculative switches and cause the
count to be higher than expected.
Implication: The Performance Monitor Event DSB2MITE_SWITCHES.COUNT may report count higher
than expected.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD59. Performance Monitor Register UNC_PERF_GLOBAL_STATUS Not
Restored on Package C7 Exit
Problem: MSR_UNC_PERF_GLOBAL_STATUS (392H) is a global status register which indicates
the overflow of uncore performance monitor counters. The content of this register is
lost in package C7 state.
Implication: If any uncore performance monitor counter has overflowed before entering the
package C7 state, the MSR_UNC_PERF_GLOBAL_STATUS register will no longer reflect
the overflow after exiting C7 state.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD60. Processor May Not Enter Package C6 or Deeper C-states When PCIe*
Links Are Disabled
Problem: If the PCIe links are disabled via Link Disable (Bus 0, Device 1, Functions [2:1], Offset
B0h, bit 4) and the PCIe controller is enabled (Bus 0, Device 0, Function 0, Offset 54h,
bits [2:1] = ’11), then the processor will be unable to enter Package C6 or deeper Cstates.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the process will not enter Package C6 or deeper C-states.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD61. Performance Monitor Event For Outstanding Offcore Requests And
Snoop Requests May Over Count
Problem: The performance monitor event OFFCORE_REQUESTS_OUTSTANDING (Event 60H, any
Umask Value) should count the number of offcore outstanding transactions each cycle.
Due to this erratum, the counts may be higher than actual number of events.
Implication: The performance monitor events OFFCORE_REQUESTS_OUTSTANDING may reflect
counts higher than the actual number of events.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
32 Specification Update
Page 33

HSD62. Some Performance Monitor Event Counts May be Inaccurate During
SMT Mode
Problem: The performance monitor event OFFCORE_REQUESTS_OUTSTANDING (Event 60H, any
Umask Value) should count the number of occurrences that loads or stores stay in the
super queue each cycle. The performance monitor event
CYCLE_ACTIVITY.CYCLES_L2_PENDING (Event A3H, Umask 01H) should count the
number of cycles that demand loads stay in the super queue. However, due to this
erratum, these events may count inaccurately during SMT mode.
Implication: The performance monitor events OFFCORE_REQUESTS_OUTSTANDING and
CYCLE_ACTIVITY.L2_ PENDING may be unreliable during SMT Mode.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD63. Timed MWAIT May Use Deadline of a Previous Execution
Problem: A timed MWAIT instruction specifies a TSC deadline for execution resumption. If a wake
event causes execution to resume before the deadline is reached, a subsequent timed
MWAIT instruction may incorrectly use the deadline of the previous timed MWAIT when
that previous deadline is earlier than the new one.
Implication: A timed MWAIT may end earlier than expected.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD64. The Upper 32 Bits of CR3 May be Incorrectly Used With 32-Bit Paging
Problem: When 32-bit paging is in use, the processor should use a page directory located at the
32-bit physical address specified in bits 31:12 of CR3; the upper 32 bits of CR3 should
be ignored. Due to this erratum, the processor will use a page directory located at the
64-bit physical address specified in bits 63:12 of CR3.
Implication: The processor may use an unexpected page directory or, if EPT (Extended Page Tables)
is in use, cause an unexpected EPT violation. This erratum applies only if software
enters 64-bit mode, loads CR3 with a 64-bit value, and then returns to 32-bit paging
without changing CR3. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially
available software.
Workaround: Software that has executed in 64-bit mode should reload CR3 with a 32-bit value
before returning to 32-bit paging.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD65. Performance Monitor Events HLE_RETIRED.ABORTED_MISC4 And
RTM_RETIRED.ABORTED_MISC4 May Over Count
Problem: The Performance Monitor Events HLE_RETIRED.ABORTED_MISC4 (Event C8H; Umask
40H) and RTM_RETIRED.ABORTED_MISC4 (Event C9H; Umask 40H) are defined to
count the number of transactional aborts due to incompatible memory types. Due to
this erratum, they may count additional unrelated transactional aborts.
Implication: The Performance Monitor Events HLE_RETIRED.ABORTED_MISC4 and
RTM_RETIRED.ABORTED_MISC4 counts may be greater than the number of aborts due
to incompatible memory types.
types are compatible.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
This can result in nonzero counts when all memory
Specification Update 33
Page 34

HSD66. A PCIe* LTR Update Message May Cause The Processor to Hang
Problem: If a PCIe device sends an LTR (Latency Tolerance Report) update message while the
processor is in a package C6 or deeper, the processor may hang.
Implication: Due to this Erratum the processor may hang if a PCIe LTR update message is received
while in a Package C6 or deeper.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD67. GETSEC Does Not Report Support For S-CRTM
Problem: Processors with Intel® Boot Guard Technology that has GETSEC[PARAMETERS] leaf 5
EAX bit 5 set indicates support for processor rooted S-CTRM (Static Core Root of Trust
for Measurement). Due to this erratum, that
rooted S-CRTM is supported.
Implication: Software may be unaware of support for processor rooted S-CTRM.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
bit will not be set even though processor
HSD68. EPT Violations May Report Bits 11:0 of Guest Linear Address
Incorrectly
Problem: If a memory access to a linear address requires the processor to update an accessed or
dirty flag in a paging-structure entry and if that update causes an EPT violation, the
processor should store the linear address into the “guest linear address” field in the
VMCS. Due to this erratum, the processor may store an incorrect value into bits 11:0 of
this field. (The processor correctly stores the guest-physical address of the pagingstructure entry into the “guest-physical address” field in the VMCS.)
Implication: Software may not be easily able to determine the page offset of the original memory
access that caused the EPT violation. Intel has not observed this erratum to impact the
operation of any commercially available software.
Workaround: Software requiring the page offset of the original memory access address can derive it
by simulating the effective address computation of the instruction that caused the EPT
violation.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD69. APIC Timer Might Not Signal an Interrupt While in TSC-Deadline Mode
Problem: If the APIC timer is in TSC-deadline mode and is armed when a timed MWAIT
instruction is executed, the timer expiration might not cause an interrupt.
Implication: Software depending on APIC timer TSC-deadline mode interrupts may not behave as
expected.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
34 Specification Update
Page 35

HSD70. IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM MSR (48AH) Does Not Properly Report The
Highest Index Value Used For VMCS Encoding
Problem: IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM MSR (48AH) bits 9:1 report the highest index value used for
any VMCS encoding. Due to this erratum, the value 21 is returned in bits 9:1 although
there is a VMCS field whose encoding uses the index value 23.
Implication: Software that uses the value reported in IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM[9:1] to read and
write all VMCS fields may omit one field.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD71. Incorrect FROM_IP Value For an RTM Abort in BTM or BTS May be
Observed
Problem: During RTM (Restricted Transactional Memory) operation when branch tracing is
enabled using BTM (Branch Trace Message) or BTS (Branch Trace Store), the incorrect
EIP value (From_IP pointer) may be observed for an RTM abort.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the From_IP pointer may be the same as that of the immediately
preceding taken branch.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD72. VT-d Hardware May Perform STRP And SIRTP Operations on a Package
C7 Exit
Problem: On a package C7 exit, VT-d hardware may spuriously perform SRTP (Set Root Table
Pointer) and SIRTP (Set Interrupt Remapping Table Pointer) operations. A package C7
exit can cause the value programmed by software in the RTA_REG (IRTA_REG) to be
visible to hardware before software executes a GCMD.SRTP command. This will result in
hardware using the new values for the DMA and interrupt translation page-walks,
possibly before they are intended to be used by software.
Implication: If software has updated the root table pointer but has not executed the SRTP command
then the root table pointer update will happen unexpectedly, causing the VMM to walk
incorrect or non-existent tables. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software.
Workaround: Privileged software should not execute a MWAIT (because it can trigger a package C7
entry/exit) between writing to RTA_REG (IRTA_REG) and GCMD_REG.SRTP
(GCMD_REG.SIRTP) registers.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD73. General-Purpose Performance Counters Can Unexpectedly Increment
Problem: A performance monitor event programmed in a general-purpose performance counter
should count the number of occurrences of the event selected in IA32_PERFEVTSEL{07} MSR (186H-18DH).
(Counter Mask) bits [31:24] value is used, due to this erratum, the event may over
count in the case that either of OS (Operating System mode, bit 17) or USR (User
mode, bit 16) is selected. Over counting will occur for the cycles spent in the nonmatching CPL.
Implication: General-purpose performance counters may reflect counts higher than the actual
number of events when the INV bit is set, CMASK is a non-zero value and either the OS
or USR bit is set.
Workaround: None identified.
If INV (invert, bit 23) is set to 1 and a non-zero CMASK
Specification Update 35
Page 36

Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD74. Performance Monitoring Events May Report Incorrect Number of Load
Hits or Misses to LLC
Problem: The following performance monitor events should count the numbers of loads hitting or
missing LLC. However due to this erratum, The L3_hit related events may over count
and the L3_miss related events may undercount.
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L3_HIT (Event D1H, Umask 40H)
MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L3_MISS (Event D1H, Umask 20H)
MEM_LOAD_L3_HIT_RETIRED. XSNP_NONE (Event D2H, Umask 08H)
MEM_LOAD_LLC_MISS_RETIRED. LOCAL_DRAM (Event D3H, Umask 01H)
Implication: The listed performance monitoring events may be inaccurate.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD75. Performance Monitoring Event INSTR_RETIRED.ALL May Generate
Redundant PEBS Records For an Overflow
Problem: Due to this erratum, the performance monitoring feature PDIR (Precise Distribution of
Instructions Retired) for INSTR_RETIRED.ALL (Event C0H; Umask 01H) will generate
redundant PEBS (Precise Event Based Sample) records for a counter overflow. This can
occur if the lower 6 bits of the performance monitoring counter are not initialized or
reset to 0, in the PEBS counter reset field of the DS Buffer Management Area.
Implication: The above event count will under count on locked loads hitting the L2 cache.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD76. Locked Load Performance Monitoring Events May Under Count
Problem: The performance monitoring events MEM_TRANS_RETIRED.LOAD_LATENCY (Event
CDH; Umask 01H), MEM_LOAD_RETIRED.L2_HIT (Event D1H; Umask 02H), and
MEM_UOPS_RETIRED.LOCKED (Event DOH; Umask 20H) should count the number of
locked loads. Due to this erratum, these events may under count for locked
transactions that hit the L2 cache.
Implication: The above event count will under count on locked loads hitting the L2 cache.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD77. Graphics Processor Ratio And C-State Transitions May Cause a System
Hang
Problem: If ratio or C-state changes involving the processor core and processor graphics occur at
the same time or while processor graphics are active, under certain internal conditions
the ratio change may not complete.
Implication: The system may hang during C-state or ratio changes.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
36 Specification Update
Page 37

HSD78. Certain Performance Monitoring Events May Over Count Software
Demand Loads
Problem: The following performance monitor events should count the number of software
demand loads. However due to this erratum, they may also include requests from the
Next Page Prefetcher and over count.
OFFCORE_REQUESTS_OUTSTANDING.DEMAND_DATA (Event 60H; Umask 01H)
OFFCORE_REQUESTS.DEMAND_DATA (Event B0H; Umask 01H)
CYCLE_ACTIVITY.L2_Pending (Event A3H; Umask 01H)
L2_HIT_MISS.LOAD (Event 24H; Umask 01H)
Implication: The listed performance monitoring events may reflect a count higher than the actual
number of events.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD79. Accessing Nonexistent Uncore Performance Monitoring MSRs May Not
Signal a #GP
Problem: An access to an uncore Performance Monitor MSR beyond the number reported in the
MSR_UNC_CBO_CONFIG MSR (396H) bits[3:0] should signal a #GP (generalprotection exception); due to this erratum, the processor may hang instead of signaling
#GP.
Implication: When software accesses nonexistent uncore performance monitoring MSRs, the logical
processor may hang instead of signaling a #GP.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD80. Call Stack Profiling May Produce Extra Call Records
Problem: The performance monitoring Call Stack Profiling function should not generate call
records for “zero length calls” (call instructions targeting the location following the
instruction). However, due to this erratum, the processor will produce call records for
zero length calls.
Implication: The performance monitoring LBR call stack MSRs are incorrect in the presence of “zero
length calls” because calls and returns do not match.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD81. Warm Reset May Fail or Lead to Incorrect Power Regulation
Problem: Due to this erratum, after a warm reset, the processor may fail to boot properly or may
cause power to be regulated to an incorrect level.
Implication: The processor may not be able to control the VR (Voltage Regulator) to advertised
specifications, leading to in a system hang, a machine check, or improper power
regulation.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 37
Page 38

HSD82. PCIe* Host Bridge DID May Be Incorrect
Problem: The PCIe Host Bridge DID register (Bus 0; Device 0; Function 0; Offset 2H) contents
may be incorrect.
Implication: Software that depends on the Host Bridge DID value may not behave as expected.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD83. Transactional Abort May Produce an Incorrect Branch Record
Problem: If an Intel® TSX transactional abort event occurs during a string instruction, the From-
IP in the LBR (Last Branch Record) is not correctly reported.
Implication: Due to this erratum, an incorrect From-IP on the LBR stack may be observed.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD84. SMRAM State-Save Area Above the 4GB Boundary May Cause
Unpredictable System Behavior
Problem: If BIOS uses the RSM instruction to load the SMBASE register with a value that would
cause any part of the SMRAM state-save area to have an address above 4-GBytes,
subsequent transitions into and out of SMM (system-management mode) might save
and restore processor state from incorrect addresses.
Implication: This erratum may cause unpredictable system behavior. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available system.
Workaround: Ensure that the SMRAM state-save area is located entirely below the 4GB address
boundary.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD85. DMA Remapping Faults for the Graphics VT-d Unit May Not Properly
Report Type of Faulted Request
Problem: When a fault occurs during DMA remapping of Graphics accesses at the Graphics VT-d
unit, the type of faulted request (read or write) should be reported in bit 126 of the
FRCD_REG register in the remapping hardware memory map register set. Due to this
erratum, the request type may not be reported correctly.
Implication: Software processing the DMA remapping faults may not be able to determine the type
of faulting graphics device DMA request.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD86. AVX Gather Instructions Page Faults May Report an Incorrect Faulting
Address
Problem: If software modifies a paging-structure entry to relax the access rights for a linear address
and does not perform a TLB invalidation, a subsequent execution of an AVX gather
instruction that accesses that address may generate a page fault that loads CR2 (which
should containing the faulting linear address) with an incorrect value.
Implication: Software handling an affected page fault may not operate correctly.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
38 Specification Update
Page 39

HSD87. Intel® TSX Instructions May Cause Unpredictable System behavior
Problem: Under certain system conditions, Intel TSX (Transactional Synchronization Extensions)
instructions may result in unpredictable system behavior.
Implication: Due to this erratum, use of Intel TSX may result in unpredictable behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD88. Event Injection by VM Entry May Use an Incorrect B Flag for SS
Problem: The stack accesses made by VM-entry event injection may use an incorrect value for
the B flag (default stack-pointer size and upper bound) for the stack segment (SS).
Implication: An affected stack access may use an incorrect address or an incorrect segment upper
bound. This may result in unpredictable system behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD89. A Fault in SMM May Result in Unpredictable System Behavior
Problem: The value of the SS register as well as the current privilege level (CPL) may be
incorrect following a fault in SMM (system-management mode). The erratum can occur
only if a fault occurs following an SMI (system-management interrupt) and before
software has loaded the SS register (e.g., with the MOV SS instruction).
Implication: This erratum may cause unpredictable system behavior. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD90. Processor Frequency is Unexpectedly Limited Below Nominal P1 When
cTDP Down is Enabled
Problem: When cTDP (Configurable Thermal Design Power) Down is enabled on a processor
branded as Core® i3 or Pentium®, the processor frequency will be limited to cTDP
Down P1 frequency (Max Non-Turbo Frequency) when it should be able to operate
between the cTDP Down frequency P1 and the nominal P1 frequency.
Implication: When cTDP is enabled, the processor cannot achieve expected frequencies.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD91. PMI May be Signaled More Than Once For Performance Monitor
Counter Overflow
Problem: Due to this erratum, PMI (Performance Monitoring Interrupt) may be repeatedly issued
until the counter overflow bit is cleared in the overflowing counter.
Implication: Multiple PMIs may be received when a performance monitor counter overflows.
Workaround: None identified. If the PMI is programmed to generate an NMI, software may delay the
EOI (end-of- Interrupt) register write for the interrupt until after the overflow
indications have been cleared.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 39
Page 40

HSD92. Execution of FXSAVE or FXRSTOR With the VEX Prefix May Produce a
#NM Exception
Problem: Attempt to use FXSAVE or FXRSTOR with a VEX prefix should produce a #UD (Invalid-
Opcode) exception. If either the TS or EM flag bits in CR0 are set, a #NM (device-notavailable) exception will be raised instead of #UD exception.
Implication: Due to this erratum a #NM exception may be signaled instead of a #UD exception on
an FXSAVE or an FXRSTOR with a VEX prefix.
Workaround: Software should not use FXSAVE or FXRSTOR with the VEX prefix.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD93. RDRAND Execution in a Transactional Region May Cause a System
Hang
Problem: Execution of the RDRAND (Random number generator) instruction inside an Intel® TSX
transactional region may cause the logical processor to hang.
Implication: A system hang may occur as a result of this erratum.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD94. Uncore Clock Frequency Changes May Cause Audio/Video Glitches
Problem: On some processors, the time required to change the uncore clock frequency may be
large enough to significantly lengthen the latency of I/O Requests to memory, possibly
resulting in audio or video glitches.
Implication: Audio/Video glitches may occur during uncore ratio changes.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD95. Processor May Experience a Spurious LLC-Related Machine Check
During Periods of High Activity
Problem: Due to certain internal conditions while running core and memory intensive operations,
some processors may incorrectly report an LLC (last level cache) related machine check
with a IA32_MCi_STATUS.MCACOD value of 110AH.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor may experience a machine check.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD96. The Processor May Not Enter Package C7 When Using a PSR Display
Problem: The processor datasheet specifies that entering package C7 requires enabling PSR
(Panel Self Refresh) for certain display resolutions, along with other conditions.
this erratum, the processor may not enter package C7 when connected to a PSRenabled display even if all of the required conditions are met.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor may not enter package C7.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Due to
40 Specification Update
Page 41

HSD97. Video/Audio Distortion May Occur
Problem: Due to this erratum, internal processor operations can occasionally delay the
completion of memory read requests enough to cause video or audio streaming
underrun.
Implication: Visible artifacts such as flickering on a video device or glitches on audio may occur.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD98. System May Hang When Audio is Enabled During Package C3
Problem: When audio is enabled while in package C3 state or deeper, audio memory traffic
continues to be generated. Due to this erratum, the processor logic required for
memory traffic may be powered down.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the processor logic required for audio memory traffic may
not be operational resulting in a system hang.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD99. INVPCID May Not Cause #UD in VMX Non-Root Operation
Problem: The INVPCID instruction should cause an invalid opcode exception (#UD) in VMX non-
root operation if either bit 31 of the primary processor-based VM-execution controls
(activate secondary controls) or bit 12 of the secondary processor-based VM-execution
controls (enable INVPCID) is 0.
cause #UD if “activate secondary controls” is 0 and “enable INVPCID” is 1.
Due to this erratum, the INVPCID instruction will not
Instead, the
instruction will either execute normally or cause a VM exit if the “INVLPG exiting” VMexecution control is 1.
Implication: The processor may cause a VM exit that software does not expect. Intel has not observed
this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD100. Non-Compliant PFAT Module Base Address May Cause Unpredictable
System Behavior
Problem: PFAT (Platform Firmware Armoring Technology) requires the PFAT module base address
be 256KB aligned and reside in the first 4GB of memory. If BIOS does not comply with
these requirements when setting up the PFAT module, the processor should GP# at
PFAT launch. Due to this erratum, a #GP fault may not be generated.
Implication: A PFAT module that does not follow the PFAT module base address requirements may
result in unpredictable system behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this issue.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 41
Page 42

HSD101. Incorrect LBR Source Address May be Reported For a Transactional
Abort
Problem: If the fetch of an instruction in a transactional region causes a fault, a transactional abort
occurs. If LBRs are enabled, the source address recorded for such a transactional abort
is the address of the instruction being fetched. If that instruction was itself the target of an
earlier branch instruction, this erratum may erroneously record the address of the branch
instruction as the source address for the transactional abort
Implication: Trace reconstruction software that uses LBR information may fail when this erratum
occurs
Workaround: None identified
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD102. Address Translation Faults for Intel® VT-d May Not be Reported for
Display Engine Memory Accesses
Problem: The Intel® VT-d (Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O) hardware unit
supporting the Processor Graphics device (Bus 0; Device 2; Function 0) may not report
address translation faults detected on Display Engine memory accesses when the
Context Cache is disabled or during time periods when Context Cache is being
invalidated.
Implication: Due to this erratum, Display Engine accesses that fault are correctly aborted but may
not be reported in the FSTS_REG fault reporting register (GFXVTDBAR offset 034H).
Workaround: None identified
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD103. L3 Cache Corrected Error Count May be Inaccurate After Package C7
Exit
Problem: The corrected error count for L3 cache errors reported in IA32_MCi_STATUS.Corrected
Error Count (bits [52:38]) with an MCACOD of 0001 0001 xxxx xxxx (x can be 0 or 1) may
be incorrectly restored to a smaller value during exit from Package C7.
Implication: The corrected error count for L3 cache errors in IA32_MCi_STATUS may be inaccurate
after Package C7 exit.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD104. PCIe* Device’s SVID is Not Preserved Across The Package C7 C-State
Problem: Bus 0, Device 7, Function 0’s SVID register (Subsystem Vendor Identification, Offset
2CH) is not preserved across package C7 C-State transitions.
Implication: This may cause the operating system to think the device has been replaced with a
different device.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
42 Specification Update
Page 43

HSD105. Warm Reset Does Not Stop GT Power Draw
Problem: Due to this erratum, if GT is enabled prior to a warm reset, it will remain powered after the
warm reset. The processor will make incorrect power management decisions because it
assumes the GT is not drawing power after a warm reset.
Implication: The processor may draw more current than expected from an external VR (Voltage
Regulator). The processor may also put the external VR into a low power state where it
will be unable to supply the sufficient power resulting in unpredictable system behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD106. Unused PCIe* Lanes May Remain Powered After Package C7
Problem: If a PCIe controller is enabled and either has unused lanes or no PCIe device is present,
the link and/or unused lanes should enter a low power state. Due to this erratum, after
exiting Package C7, the unused link and/or unused lanes may remain powered.
Implication: Power consumption may be greater than expected.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD107. BMI1 And BMI2 Instruction Groups Are Not Available
Problem: Feature flags BMI1 and BMI2 (CPUID leaf 7, sub-leaf 0, EBX bits 3 and 8) report these
two groups of bit manipulation instructions are not present for the Intel
®
Core™ i3-4330TE
but these instruction groups should be available. An attempt to execute any of these
instructions will generate a #UD fault.
Implication: Software attempting to use any of instructions in the BMI1 and BMI2 groups will result in a
#UD fault.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD108. Virtual-APIC Page Accesses With 32-Bit PAE Paging May Cause a
System Crash
Problem: If a logical processor has EPT (Extended Page Tables) enabled, is using 32-bit PAE paging, and
accesses the virtual-APIC page then a complex sequence of internal processor micro-architectural
events may cause an incorrect address translation or machine check on either logical processor.
Implication: This erratum may result in unexpected faults, an uncorrectable TLB error logged in
IA32_MCi_STATUS.MCACOD (bits [15:0]) with a value of 0000_0000_0001_xxxxb
(where x stands for 0 or 1), a guest or hypervisor crash, or other unpredictable system
behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Specification Update 43
Page 44

HSD109. Processor Energy Policy Selection May Not Work as Expected
Problem: When the IA32_ENERGY_PERF_BIAS MSR (1B0H) is set to a value of 4 or more, the
processor will try to increase the energy efficiency of Turbo mode. However, this
functionality is effectively disabled if the software requested P-state exceeds the
maximum P-state supported by the processer. This has the effect of decreasing the
energy efficiency of the processor while in Turbo mode.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, reduced battery life and reduced energy efficiency may
occur.
Workaround: BIOS should set the max ACPI _PST object to the max supported turbo ratio, ensuring
that the software P-state request does not exceed the maximum ratio supported by the
processor.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Note that this workaround will disable Core Ratio Overclocking.
HSD110. A PEBS Record May Contain Processor State for an Unexpected
Instruction
Problem: If a performance counter has overflowed and is configured for PEBS (precise event-
based sampling), the processor will arm the PEBS hardware within a bounded number
of cycles called the skid (see the discussion of skid and related topics in the Precise
Distribution of Instructions Retired section of the Intel
Software Developer Manual). Once the PEBS hardware is armed, the processor should
capture processor state in a PEBS record following the execution of the next instruction
that causes the counter to increment (a “triggering” instruction).
the capture of processor state may occur at an instruction after the first triggering
instruction following the skid but not beyond the second triggering instruction after the
skid.
Implication: A PEBS record may contain processor state (including instruction pointer) not
associated with the triggering instruction.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures
Due to this erratum,
HSD111. MSR_PP1_ENERGY_STATUS Reports Incorrect Energy Data
Problem: The MSR_PP1_ENERGY_STATUS MSR (641H) bits [31:0] reports incorrect energy data.
Implication: Due to this erratum, reported Intel Integrated Graphics domain energy consumption
may not be accurate.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD112. x87 FPU DP May be Incorrect After Instructions That Save FP State to
Memory
Problem: Under certain conditions, the value of the x87 FPU DP (Floating Point Unit Data Pointer)
saved by the FSAVE/FNSAVE, FSTENV/FNSTENV, FXSAVE, XSAVE, or XSAVEOPT
instructions may be incorrect.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the x87 FPU DP may be incorrect.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
44 Specification Update
Page 45

HSD113. Processor May Hang During Package C7 Exit
Problem: Under certain internal timing conditions, the processor might not properly exit package
C7 leading to a hang.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the package C7 state may not be reliable. Intel has not observed
this erratum with any commercially available system.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD114. Intel® TSX Instructions May Cause Unpredictable System behavior
Problem: Under a complex set of internal timing conditions and system events, software using
the Intel TSX (Transactional Synchronization Extensions) instructions may observe
unpredictable system behavior.
Implication: This erratum may result in unpredictable system behavior. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available system.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD115. Spurious LLC Machine Check May Occur
Problem: Under certain stressful conditions while running at ring ratios higher than 30, the
processor may experience a spurious LLC machine check as indicated by
IA32_MCi_STATUS.MCACOD (bits [15:0]) with value 000x 0001 0000 1010 (where x is
0 or 1).
Implication: When this erratum occurs, an uncorrectable LLC error will be logged and the system
may hang or restart.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD116. Page Fault May Report Incorrect Fault Information
Problem: Under the following conditions:
1. A read-modify-write instruction’s memory source/destination (e.g., ADD memory, reg)
crossing a cache line boundary.
2. That instruction executing without fault.
3. While the read-modify-write instruction is executing, one or more of the following page
table attributes associated with its memory operand are modified:
a. the D (dirty) flag was 0 when the instruction was initiated but was concurrently set to 1, and/
or
b. one of the relevant R/W flags was 0 when the instruction was initiated but was
concurrently set to 1, and/or
c. if the read-modify-write instruction executes at CPL = 3 and one of the relevant U/
S flags was 0 when the instruction was initiated but was concurrently set to 1.
4. A subsequent instruction executing within a narrow timing window that experiences a
page fault
5. There is no serializing instruction between the read-modify-write instruction and the
faulting instruction.
Specification Update 45
Page 46

The page fault (in #4) may report an incorrect error code and faulting linear address;
these would describe the read-modify-write instruction’s memory access instead of that
of the faulting instruction. (The address of the faulting instruction is reported correctly.)
Implication: The erratum makes it appear that the page fault resulted from an access that occurred
prior to the faulting instruction.
a page-fault handler may identify the page fault as transient (or spurious) and reexecute the faulting instruction (e.g., by executing IRET).
will not recur; the page fault on the later access will recur and will be reported
correctly. If the page-fault handler does not re-execute the faulting instruction, this
erratum may result in unpredictable system behavior.
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
Because the earlier access completed without faulting,
In such cases, the erratum
Intel has not observed this
HSD117. CATERR# Pin Assertion is Not Cleared on a Warm Reset
Problem: If the CATERR# pin is held asserted to indicate a fatal error, a subsequent warm reset
event will not cause the CATERR# pin to de-assert.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, platforms that monitor the CATERR# pin may be unable to
detect a fatal error after a warm reset or may incorrectly respond to a CATERR# pin
assertion although an error may not have occurred subsequent to the warm reset
event.
Workaround: The CATERR# pin can be de-asserted by a cold reset event.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
HSD118. Uncorrectable Machine Check Error During Core C6 Entry May Not be
Signaled
Problem: Machine Check exceptions occurring during core C6 entry may be ignored.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, incorrect state may be saved during core C6 entry and
subsequently restored during core C6 exit resulting in unpredictable system behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Table of Changes.
§ §
46 Specification Update
Page 47

Specification Changes
The Specification Changes listed in this section apply to the following documents:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1: Basic
Architecture
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A:
Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B:
Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A:
System Programming Guide
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B:
System Programming Guide
There are no new Specification Changes in this Specification Update revision.
§ §
Specification Update 47
Page 48

Specification Clarifications
The Specification Clarifications listed in this section may apply to the following
documents:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1: Basic
Architecture
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A:
Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B:
Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A:
System Programming Guide
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B:
System Programming Guide
There are no new Specification Changes in this Specification Update revision.
§ §
48 Specification Update
Page 49

Documentation Changes
The Documentation Changes listed in this section apply to the following documents:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1: Basic
Architecture
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A:
Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B:
Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A:
System Programming Guide
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B:
System Programming Guide
All Documentation Changes will be incorporated into a future version of the appropriate
Processor documentation.
Note: Documentation changes for Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture Software Developer's
Manual volumes 1, 2A, 2B, 3A, and 3B will be posted in a separate document, Intel
and IA-32 Architecture Software Developer's Manual Documentation Changes. Use the
following link to become familiar with this file: http://developer.intel.com/products/
processor/manuals/index.htm
There are no new Documentation Changes in this Specification Update revision.
HSD1. On-Demand Clock Modulation Feature Clarification
Software Controlled Clock Modulation section of the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures
Software Developer's Manual, Volume 3B: System Programming Guide will be modified
to differentiate On-demand clock modulation feature on different processors. The
clarification will state:
For Hyper-Threading Technology enabled processors, the IA32_CLOCK_MODULATION
register is duplicated for each logical processor. In order for the On-demand clock
modulation feature to work properly, the feature must be enabled on all the logical
processors within a physical processor. If the programmed duty cycle is not identical for
all the logical processors, the processor clock will modulate to the highest duty cycle
programmed for processors if the CPUID DisplayFamily_DisplayModel signatures is
listed in Table 14-2. For all other processors, if the programmed duty cycle is not
identical for all logical processors in the same core, the processor will modulate at the
lowest programmed duty cycle.
For multiple processor cores in a physical package, each core can modulate to a
programmed duty cycle independently.
For the P6 family processors, on-demand clock modulation was implemented through
the chipset, which controlled clock modulation through the processor’s STPCLK# pin.
®
64
Table 14-2. CPUID Signatures for Legacy Processors That Resolve to Higher
Performance Setting of Conflicting Duty Cycle Requests
Specification Update 49
Page 50

Display Family Display
Model
0F_xx 06_1C 06_1A 06_1E
06_1F 06_25 06_26 06_27
06_2C 06_2E 06_2F 06_35
06_36
Display Family Display
Model
§ §
Display Family Display
Model
Display Family Display
Model
50 Specification Update
 Loading...
Loading...