Page 1

Mobile 3rd Generation Intel® Core™ Processor Family
Specification Update
September 2013
Revision 015
Reference Number: 326770
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY
ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PRO PERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN
INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHAT SOEVER AND INTEL DISCLAIMS
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES
RELATING T O FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
A “Mission Critical Application” is any application in which failure of the Intel Product could result, directly or indirectly, in personal injury or death.
SHOULD YOU PURCHASE OR USE INTEL'S PRODUCTS FOR ANY SUCH MISSION CRITICAL APPLICATION, YOU SHALL INDEMNIFY AND
HOLD INTEL AND ITS SUBSIDIARIES, SUBCONTRACTORS AND AFFILIATES, AND THE DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, AND EMPLOYEES OF
EACH, HARMLESS AGAINST ALL CLAIMS COSTS, DAMAGES, AND EXPENSES AND REASONABLE ATTORNEYS' FEES ARISING OUT OF,
DIRECTLY OR INDIRECTLY, ANY CLAIM OF PRODUCT LIABILITY, PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF SUCH
MISSION CRITICAL APPLICATION, WHETHER OR NOT INTEL OR ITS SUBCONTRACTOR WAS NEGLIGENT IN THE DESIGN,
MANUFACTURE, OR WARNING OF THE INTEL PRODUCT OR ANY OF ITS PARTS.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Designers must not rely on the absence or
characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined”. Int el reserves these for future definition and shall have no
responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibili ties arising from future changes to them. The information here is subject to change without
notice. Do not finalize a design with this information.
The products described in this document may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from
published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained by calling 1-800-
548-4725, or go to: http://www.intel.com/design/literature.htm.
®
Virtualization Technology requires a computer system with an enabled Intel® processor, BIOS, virtual machine monitor (VMM). Functionality,
Intel
performance or other benefits will vary depending on hardware and software configurations. Software applications may not be compatible with all
operating systems. Consult your PC manufacturer. For more information, visit: http://www.intel.com/go/virtualization.
®
Intel
Turbo Boost Technology requires a system with Intel® Turbo Boost Technology. Intel Turbo Boost Technology and Intel Turbo Boost Technology
2.0 are only available on select Intel
®
processors. Consult your PC manufacturer. Performance varies depending on hardware, software, and syst em
configuration. For more information, visit: http://www.intel.com/go/turbo.
®
Intel
Hyper-Threading Technology requires an Intel® HT T echnology enabled system, check with your PC manufacturer. Performance will vary
depending on the specific hardware and software used. Not available on Intel
processors support HT Technology, visit http://www.intel.com/info/hyperthreading.
®
Intel
64 architecture requires a system with a 64-bit enab led processor, chipset, BIOS and so f tware. Per formance wil l vary depending on the specific
®
Core™ i5-750. For more information including details on which
hardware and software you use. Consult your PC manufacturer for more information. For more information, visit: http://www.intel.com/info/em64t.
Intel, Intel Core, Pentium, and the Intel logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2012-2013, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
2 Specification Update
Page 3

Contents
Contents
Revision History...............................................................................................................5
Preface ..............................................................................................................................6
Summary Tables of Changes..........................................................................................8
Identification Information..............................................................................................14
Errata...............................................................................................................................21
Specification Changes...................................................................................................53
Specification Clarifications...........................................................................................54
Documentation Changes...............................................................................................55
§ §
Specification Update 3
Page 4

Contents
4 Specification Update
Page 5
Revision History
Revision Description Date
001 • Initial Release. April 2012
002
003
004 • Added Errata BU86-BU90 June 2012
005
006 • Added Errata BU91-BU94 November 2012
007 • Added Errata BU95-BU98 December 2012
008 • Documentation Change January 2013
009 • Added Errata BU99, BU100 March 2013
010 • Added Errata BU101 April 2013
011 • Added Errata BU102, BU103, BU104 May 2013
012
013 • Added Erratum BU109 July 2013
014 • Added Errata BU110, BU111 August 2013
015 • Added Errata BU112 September 2013
• Added Errata BU69–BU85
• Updated Processor Identification Table
• Added L-1 stepping to Component Identification using Programming
• Added L-1 stepping to errata summary table
• Updated Processor Identification Table
®
• Added Mobile 3rd Generation Intel
processors
• Added Errata BU105, BU106, BU107, BU108
• Made changes to Erratum BU101
Core™ i7-3940XM, i7-3840QM, i7-3740QM
May 2012
June 2012
October 2012
June 2013
Specification Update 5
Page 6
Preface
This document is an update to the specifications contained in the Affected Documents
table below. This document is a compilation of device and documentation errata,
specification clarifications and changes. It is intended for hardware system
manufacturers and software developers of applications, operating systems, or tools.
Information types defined in Nomenclature are consolidated into the specification
update and are no longer published in other documents.
This document may also contain information that was not previously published.
Affected Documents
Mobile 3rd Generation Intel
Mobile 3rd Generation Intel
Related Documents
Document Title Document Number
®
Core™ Processor Family Datasheet, Volume 1 326768-004
®
Core™ Processor Family Datasheet, Volume 2 326769-002
Document Title
AP-485, Intel® Processor Identification and the CPUID Instruction http://www.intel.com/
®
Intel
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Volume 1: Basic Architecture
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 2A: Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 2B: Instruction Se t Reference Manual N-Z
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 3A: System Programming Guide
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 3B: System Programming Guide
®
64 and IA-32 Intel Architecture Optimization Reference
Intel
Manual
®
Intel
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual
Documentation Changes
ACPI Specifications www.acpi.info
Document Number/
Location
design/processor/
applnots/241618.htm
http://www.intel.com/
products/processor/
manuals/index.htm
http://www.intel.com/
design/processor/
specupdt/252046.htm
6 Specification Update
Page 7

Nomenclature
Errata are design defects or errors. These may cause the processor behavior to
deviate from published specifications. Hardware and software designed to be used with
any given stepping must assume that all errata documented for that stepping are
present on all devices.
S-Spec Number is a five-digit code used to identify products. Products are
differentiated by their unique characteristics such as, core speed, L2 cache size,
package type, etc. as described in the processor identification information table. Read
all notes associated with each S-Spec number.
Specification Changes are modifications to the current published specifications.
These changes will be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Specification Clarifications describe a specification in greater detail or further
highlight a specification’s impact to a complex design situation. These clarifications will
be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Documentation Changes include typos, errors, or omissions from the current
published specifications. These will be incorporated in any new release of the
specification.
Note: Errata remain in the specification update throughout the product’s lifecycle, or until a
particular stepping is no longer commercially available. Under these circumstances,
errata removed from the specification update are archived and available upon request.
Specification changes, specification clarifications and documentation changes are
removed from the specification update when the appropriate changes are made to the
appropriate product specification or user documentation (datasheets, manuals, and so
on).
Specification Update 7
Page 8
Summary Tables of Changes
The following tables indicate the errata, specification changes, specification
clarifications, or documentation changes which apply to the processor. Intel may fix
some of the errata in a future stepping of the component, and account for the other
outstanding issues through documentation or specification changes as noted. These
tables uses the following notations:
Codes Used in Summary Tables
Stepping
X: Errata exists in the stepping indicated. Specification Change or
(No mark)
or (Blank box): This erratum is fixed in listed stepping or specification change
Page
(Page): Page location of item in this document.
Status
Doc: Document change or update will be implemented.
Plan Fix: This erratum may be fixed in a future stepping of the product.
Fixed: This erratum has been previously fixed.
No Fix: There are no plans to fix this erratum.
Row
Change bar to left of a table row indicates this erratum is either new or modified from
the previous version of the document.
Errata (Sheet 1 of 5)
Number
BU1
BU2
BU3
BU4
BU5
BU6
Steppings
Status ERRATA
E-1 L-1
XXNo FixThe Processor May Report a #TS Instead of a #GP Fault
XXNo Fix
XXNo FixIO_SMI Indication in SMRAM State Save Area May be Set Incorrectly
XXNo FixPerformance Monitor SSE Retired Instructions May Return Incorrect Values
XXNo FixIRET under Certain Conditions May Cause an Unexpected Alignment Check Exception
XXNo Fix
Clarification that applies to this stepping.
does not apply to listed stepping.
REP MOVS/STOS Executing with Fast Strings Enabled and Crossing Page Boundaries
with Inconsistent Memory Types may use an Incorrect Data Size or Lead to MemoryOrdering Violations.
Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX May Not Count Some
Transitions
8 Specification Update
Page 9
Errata (Sheet 2 of 5)
Number
BU7
BU8
BU9
BU10
BU11
BU12
BU13
BU14
BU15
BU16
BU17
BU18
BU19
BU20
BU21
BU22
BU23
BU24
BU25
BU26
BU27
BU28
BU29
BU30
BU31
BU32
BU33
Steppings
E-1 L-1
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Status ERRATA
General Protection Fault (#GP) for Instructions Greater than 15 Bytes May be
Preempted
LBR, BTS, BTM May Report a Wrong Address when an Exception/Interrupt Occurs in
64-bit Mode
Incorrect Address Computed For Last Byte of FXSAVE/FXRST OR or XSAVE/XRSTOR
Image Leads to Partial Memory Update
XXNo FixValues for LBR/BTS/BTM Will be Incorrect after an Exit from SMM
XXNo Fix
EFLAGS Discrepancy on Page Faults and on EPT-Induced VM Exits after a T ranslation
Change
XXNo FixB0-B3 Bits in DR6 For Non-Enabled Breakpoints May be Incorrectly Set
XXNo FixMCi_Status Overflow Bit May Be Incorrectly Set on a Single Instance of a DTLB Error
XXNo FixDebug Exception Flags DR6.B0-B3 Flags May be Incorrect for Disabled Breakpoints
XXNo FixLER MSRs May Be Unreliable
XXNo FixStorage of PEBS Record Delayed Following Execution of MOV SS or STI
XXNo FixPEBS Record not Updated when in Probe Mode
XXNo FixMONITOR or CLFLUSH on the Local XAPIC's Address Space Results in Hang
XXNo FixFaulting MMX Instruction May Incorrectly Update x87 FPU Tag Word
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
An Uncorrectable Error Logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS May also Result in a
System Hang
#GP on Segment Selector Descriptor that Straddles Canonical Boundary May Not
Provide Correct Exception Error Code
DR6.B0-B3 May Not Report All Breakpoints Matched When a MOV/POP SS is
Followed by a Store or an MMX Instruction
XXNo FixAPIC Error “Received Illegal Vector” May be Lost
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Changing the Memory Type for an In-Use Page Translation May Lead to Memory-
Ordering Violations
Reported Memory Type May Not Be Used to Access the VMCS and Referenced Data
Structures
LBR, BTM or BTS Records May have Incorrect Branch From Information After an EIST/
T-state/S-state/C1E Transition or Adaptive Thermal Throttling
Fault Not Reported When Setting Reserved Bits of Intel® VT-d Queued Invalidation
Descriptors
FP Data Operand Pointer May Be Incorrectly Calculated After an FP Access Which
Wraps a 4-Gbyte Boundary in Code That Uses 32-Bit Address Size in 64-bit Mode
VMREAD/VMWRITE Instruction May Not Fail When Accessing an Unsupported Field in
VMCS
XXNo FixSpurious Interrupts May be Generated From the Intel® VT-d Remap Engine
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Malformed PCIe Transactions May be Treated as Unsupported Requests Instead of as
Critical Errors
Reception of Certain Malformed Transactions May Cause PCIe Port to Hang Rather
Than Reporting an Error
XXNo FixClock Modulation Duty Cycle Cannot be Programmed to 6.25%
Specification Update 9
Page 10
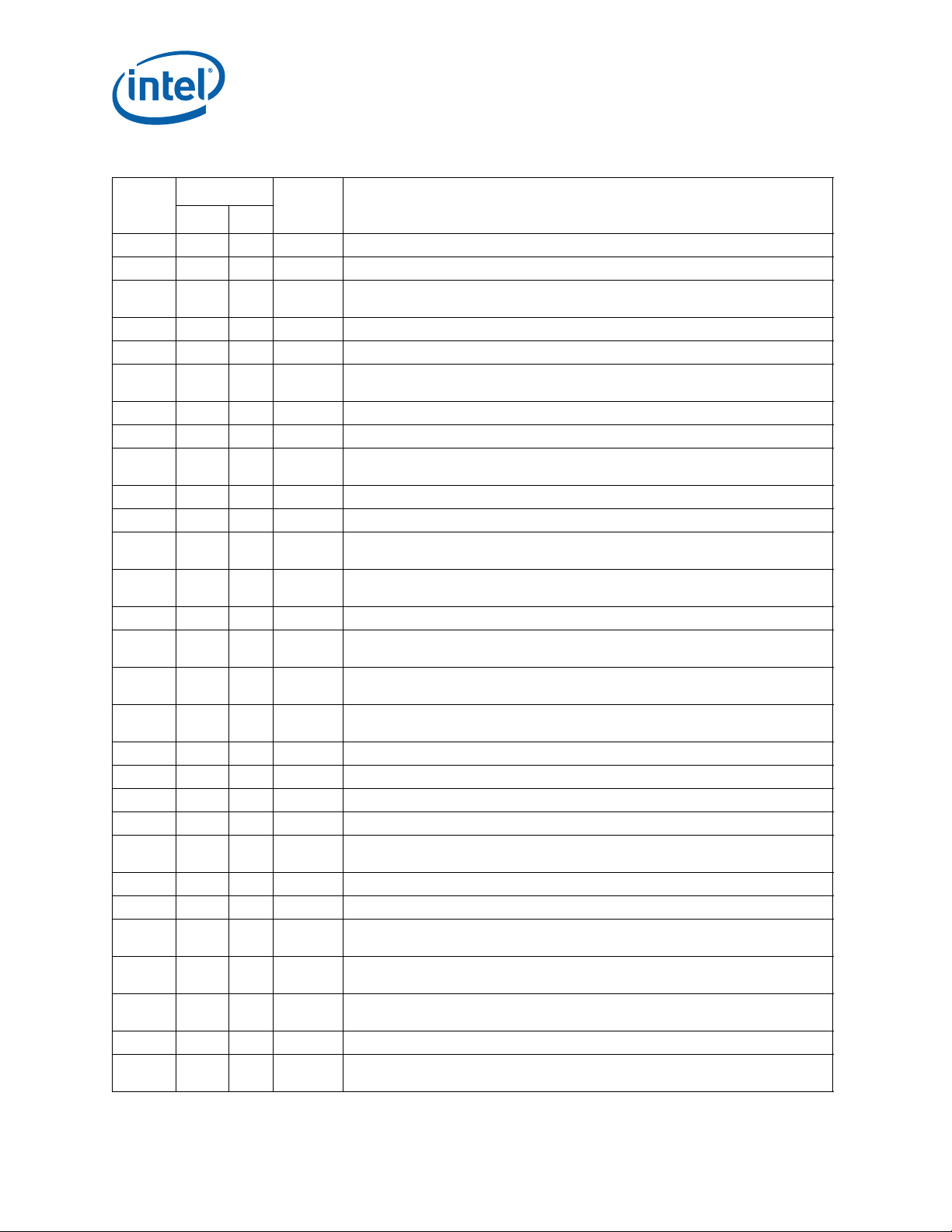
Errata (Sheet 3 of 5)
Number
BU34
BU35
BU36
BU37
BU38
BU39
BU40
BU41
BU42
BU43
BU44
BU45
BU46
BU47
BU48
BU49
BU50
BU51
BU52
BU53
BU54
BU55
BU56
BU57
BU58
BU59
BU60
BU61
BU62
Steppings
E-1 L-1
Status ERRATA
XXNo FixProcessor May Fail to Acknowledge a TLP Request
XXNo FixAn Unexpected PMI May Occur After Writing a Large Value to IA32_FIXED_CTR2
XXNo Fix
A Write to the IA32_FIXED_CTR1 MSR May Result in Incorrect Value in Certain
Conditions
XXNo FixPCIe* LTR Incorrectly Reported as Being Supported
XXNo FixPerfMon Overflow Status Can Not be Cleared After Certain Conditions Have Occurred
XXNo Fix
#GP May be Signaled When Invalid VEX Prefix Precedes Conditional Branch
Instructions
XXNo FixInterrupt From Local APIC Timer May Not Be Detectable While Being Delivered
XXNo FixPCI Express* Differential Peak-Peak Tx Voltage Swing May Violate the Specification
XXNo Fix
PCMPESTRI, PCMPESTRM, VPCMPESTRI and VPCMPESTRM Always Operate with
32-bit Length Registers
XXNo FixMultiple Performance Monitor Interrupts are Possible on Overflow of Fixed Counter 0
XXNo FixIA32_FEATURE_CONTROL MSR May be Uninitialized on a Cold Reset
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
DR6.B0-B3 May Not Report All Breakpoints Matched When a MOV/POP SS is
Followed by a REP MOVSB or STOSB
Setting Hardware Autonomous Speed Disable Configuration Bit Will Block Initial Speed
Upgrade
XXNo FixLTR Message is Not Treated as an Unsupported Request
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
64-bit REP MOVSB/STOSB May Clear The Upper 32-bits of RCX, RDI And RSI Before
Any Data is Transferred
An Interrupt Recognized Prior to First Iteration of REP MOVSB/STOSB May Result
EFLAGS.RF Being Incorrectly Set
Accessing Physical Memory Space 0-640K through the Graphics Aperture May Cause
Unpredictable System Behavior
XXNo FixPEBS May Unexpectedly Signal a PMI After The PEBS Buffer is Full
XXNo FixInstructions Retired Event May Over Count Execution of IRET Instructions
XXNo FixPCIe* Link May Unexpectedly Exit Loopback State
XXNo FixThe RDRAND Instruction Will Not Execute as Expected
XXNo Fix
A PCIe* Device That Initially Transmits Minimal Posted Data Credits May Cause a
System Hang
XXNo FixPCI Express* Gen3 Receiver Return Loss May Exceed Specifications
XXNo FixDirect Access Via VT-d to The Processor Graphics Device May Lead to a System Hang
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
An Event May Intervene Before a System Management Interrupt That Results from IN
or INS
PCIe* May Associate Lanes That Are Not Part of Initial Link Training to L0 During
Upconfiguration
The Processor May Not Comply With PCIe* Equalization Preset Reflection
Requirements for 8 GT/s Mode of Operation
XXNo FixProcessor May Issue PCIe* EIEOS at Incorrect Rate
XXNo Fix
Reduced Swing Output Mode Needs Zero De-emphasis to be Supported in PCIe* 5GT/
s Speed
10 Specification Update
Page 11
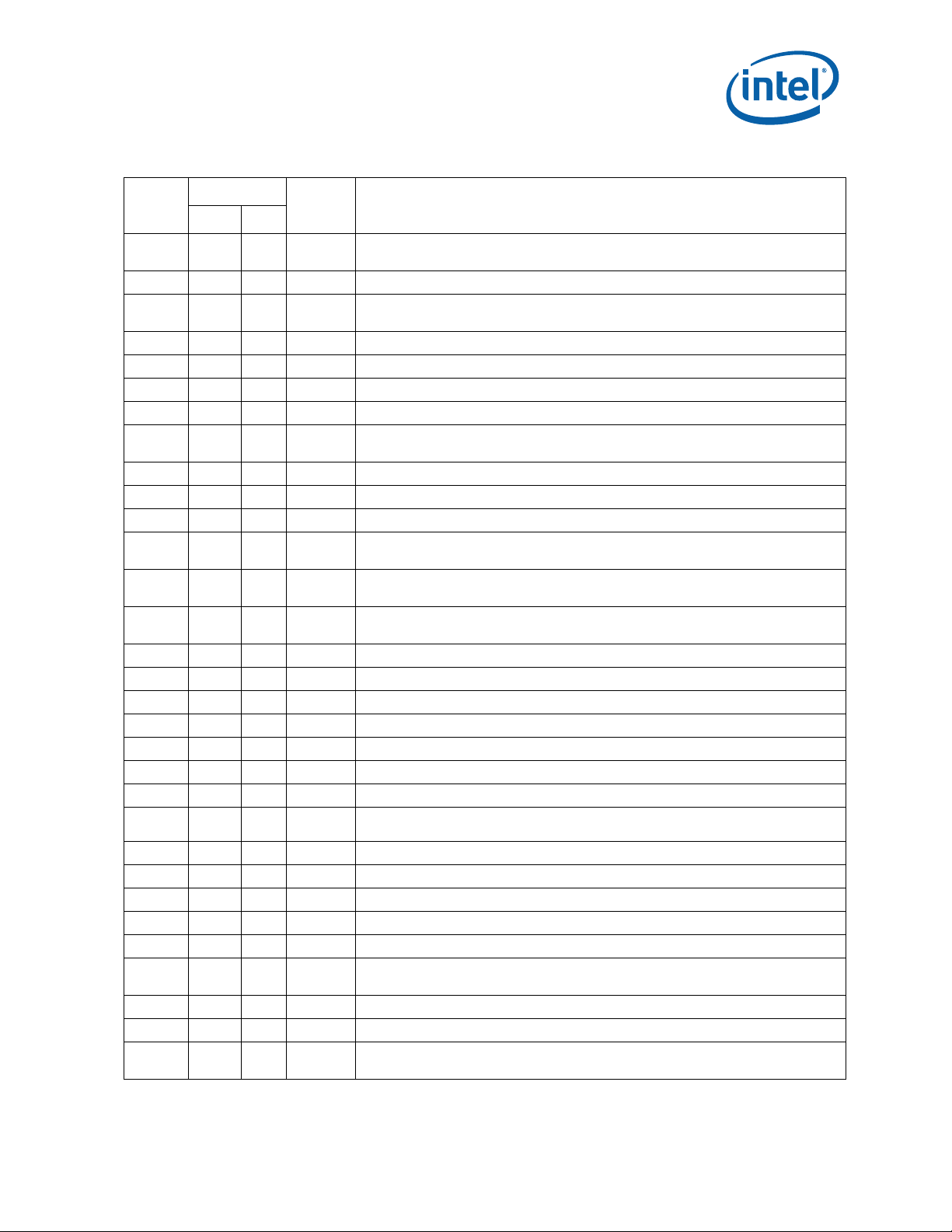
Errata (Sheet 4 of 5)
Number
BU63
BU64
BU65
BU66
BU67
BU68
BU69
BU70
BU71
BU72
BU73
BU74
BU75
BU76
BU77
BU78
BU79
BU80 X X No Fix
BU81 X X No Fix
BU82 X X No Fix
BU83 X X No Fix
BU84 X X No Fix
Steppings
E-1 L-1
XXNo Fix
Status ERRATA
PCIe* Root-port Initiated Compliance State Transmitter Equalization Settings May be
Incorrect
XXNo FixPCIe* Controller May Incorrectly Log Errors on Transition to RxL0s
XXNo Fix
Reception of Certain Malformed Transactions May Cause PCIe* Port to Hang Rather
Than Reporting an Error
XXNo FixPCIe* Link Width May Degrade After a Warm Reset
XXNo FixMSR_PKG_Cx_RESIDENCY MSRs May Not be Accurate
XXNo FixExecution of Package C7 May Result in a Hang
XXNo FixPCIe* Link May Not Enter Loopback.Active When Directed
XXNo Fix
Execution of VAESIMC or VAESKEYGENASSIST With An Illegal Value for VEX.vvvv
May Produce a #NM Exception
XXNo FixUnexpected #UD on VZEROALL/VZEROUPPER
XXNo FixPCIe* Root Port May Not Initiate Link Speed Change
XXNo FixSuccessive Fixed Counter Overflows May be Discarded
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Execution of FXSAVE or FXRSTOR With the VEX Prefix May Produce a #NM
Exception
VM Exits Due to “NMI-Window Exiting” May Not Occur Following a VM Entry to the
Shutdown State
Execution of INVVPID Outside 64-Bit Mode Cannot Invalidate Translations For 64-Bit
Linear Addresses
XXNo FixPCIe* Controller May Not Properly Indicate Link Electrical Idle Condition
XXNo FixPCIe* Controller May Not Enter Loopback
XXNo FixLink Margin Characterization May Hang Link
Unused PCIe* Lanes May Report Correctable Errors
RDMSR of IA32_PERFEVTSEL{4-7} May Return Erroneous Information
PCIe* Link May Fail Link Width Upconfiguration
Graphics L3 Cache Parity Errors May Not be Detected
A PCIe* Link That is in Link Disable State May Prevent DDR I/O Buffers From Entering
a Power Gated State
BU85 X X No Fix Graphics L3 Cache Redundancy May Not Behave as Expected
BU86 X X No Fix REP MOVSB May Incorrectly Update ECX, ESI, and EDI
BU87 X X No Fix Performance-Counter Overflow Indication May Cause Undesired Behavior
BU88 X X No Fix RDMSR of IA32_PERFEVTSEL4-7 May Return an Incorrect Result
BU89 X XX No Fix VEX.L is Not Ignored with VCVT*2SI Instructions
BU90 X X No Fix
Intel® Turbo Boost Technology May be Incorrectly Reported as Supported on Intel®
Core™ i3-3217U
BU91 X X No Fix Concurrently Changing the Memory Type and Page Size May Lead to a System Hang
BU92 X X No Fix MCI_ADDR May be Incorrect For Cache Parity Errors
BU93 X X No Fix
During Package Power States Repeated PCIe* and/or DMI L1 T ransitions May Cause a
System Hang
Specification Update 11
Page 12
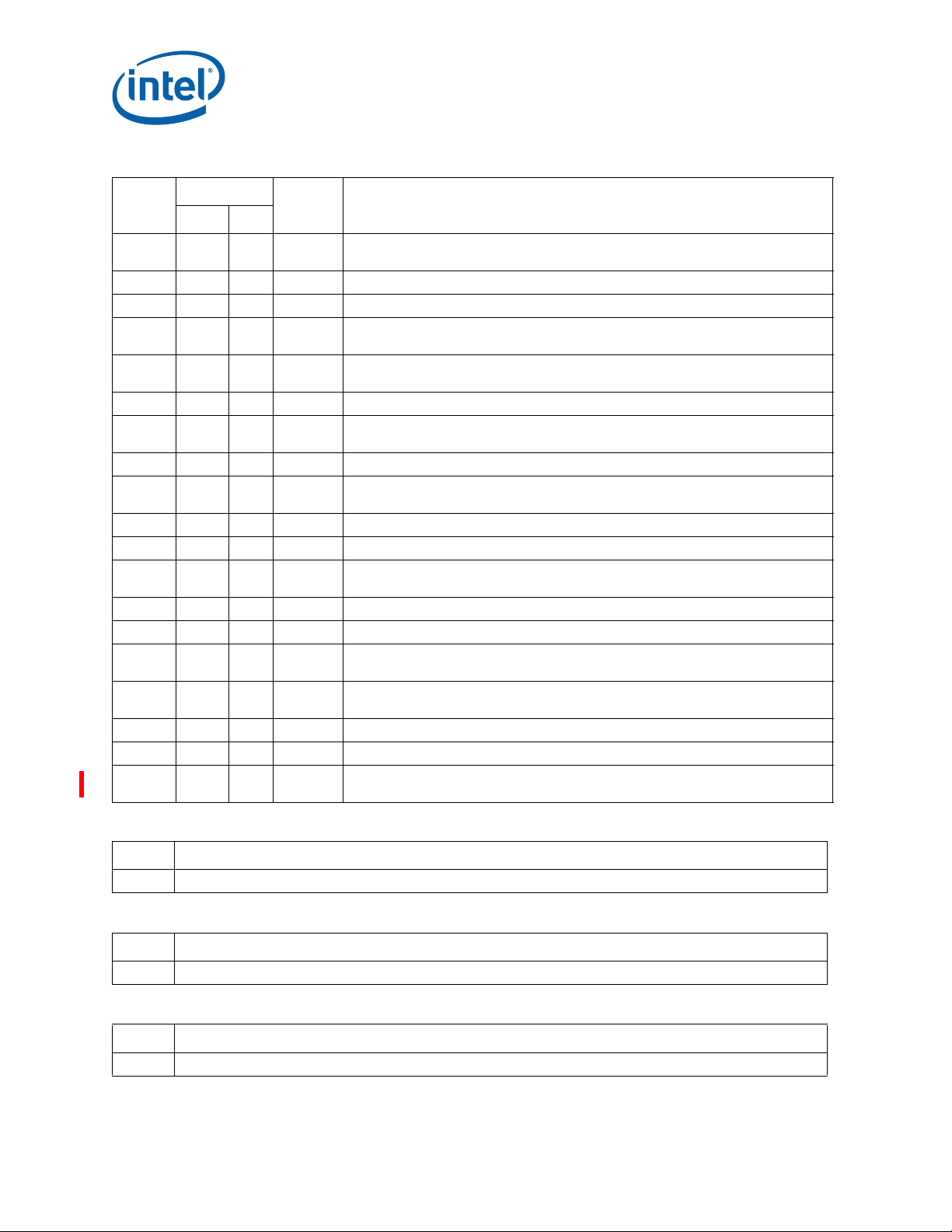
Errata (Sheet 5 of 5)
Number
BU94 X X No Fix
BU95 X X No Fix The Processor May Not Properly Execute Code Modified Using A Floating-Point Store
BU96 X X No Fix Execution of GETSEC[SEXIT] May Cause a Debug Exception to be Lost
BU97 X X No Fix
BU98 X X No Fix
BU99 X X No Fix IA32_MC5_CTL2 is Not Cleared by a Warm Reset
BU100 X X No Fix
BU101 X X No Fix Performance Monitor Counters May Produce Incorrect Results
BU102 X X No Fix
BU103 X X No Fix Spurious VT-d Interrupts May Occur When the PFO Bit is Set
BU104 X X No Fix Processor May Livelock During On Demand Clock Modulation
BU105 X X No Fix
BU106 X X No Fix The Upper 32 Bits of CR3 May be Incorrectly Used With 32-Bit Paging
BU107 X X No Fix EPT Violations May Report Bits 11:0 of Guest Linear Address Incorr ectly
BU108 X X No Fix
BU109 X X No Fix
BU110 X X No Fix Intel® Trusted Execution Technology ACM Authentication Failure
BU111 X X No Fix Virtual-APIC Page Accesses With 32-Bit PAE Paging May Cause a System Crash
BU112 X X No Fix
Steppings
Status ERRATA
E-1 L-1
Instruction Fetches Page-Table Walks May be Made Speculatively to Uncacheable
Memory
VM Exits Due to GETSEC May Save an Incorrect Value for “Blocking by STI” in the
Context of Probe-Mode Redirection
Specific Graphics Blitter Instructions May Result in Unpredictable Graphics Controller
Behavior
CPUID Instruction May Not Report the Processor Number in the Brand String for Intel®
Core™ i3-3227U and i5-3337U Processors.
The Corrected Error Count Overflow Bit in IA32_ MC0_STA TUS is Not Updated After a
UC Error is Logged
IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM MSR (48AH) Does Not Properly Report The Highest Index
Value Used For VMCS Encoding
IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM MSR (48AH) Does Not Properly Report The Highest Index
Value Used For VMCS Encoding
DMA Remapping Faults for the Graphics VT-d Unit May Not Properly Report Type of
Faulted Request
Address Translation Faults for Intel® VT-d May Not be Reported for Display Engine
Memory Accesses
Specification Changes
Number SPECIFICATION CHANGES
None for this revision of this specification update.
Specification Clarifications
Number SPECIFICATION CLARIFICATIO NS
None for this revision of this specification update.
Documentation Changes
Number DOCUMENTATION CHANGES
BU1
12 Specification Update
On-Demand Clock Modulation Feature Clarification
Page 13

§ §
Specification Update 13
Page 14
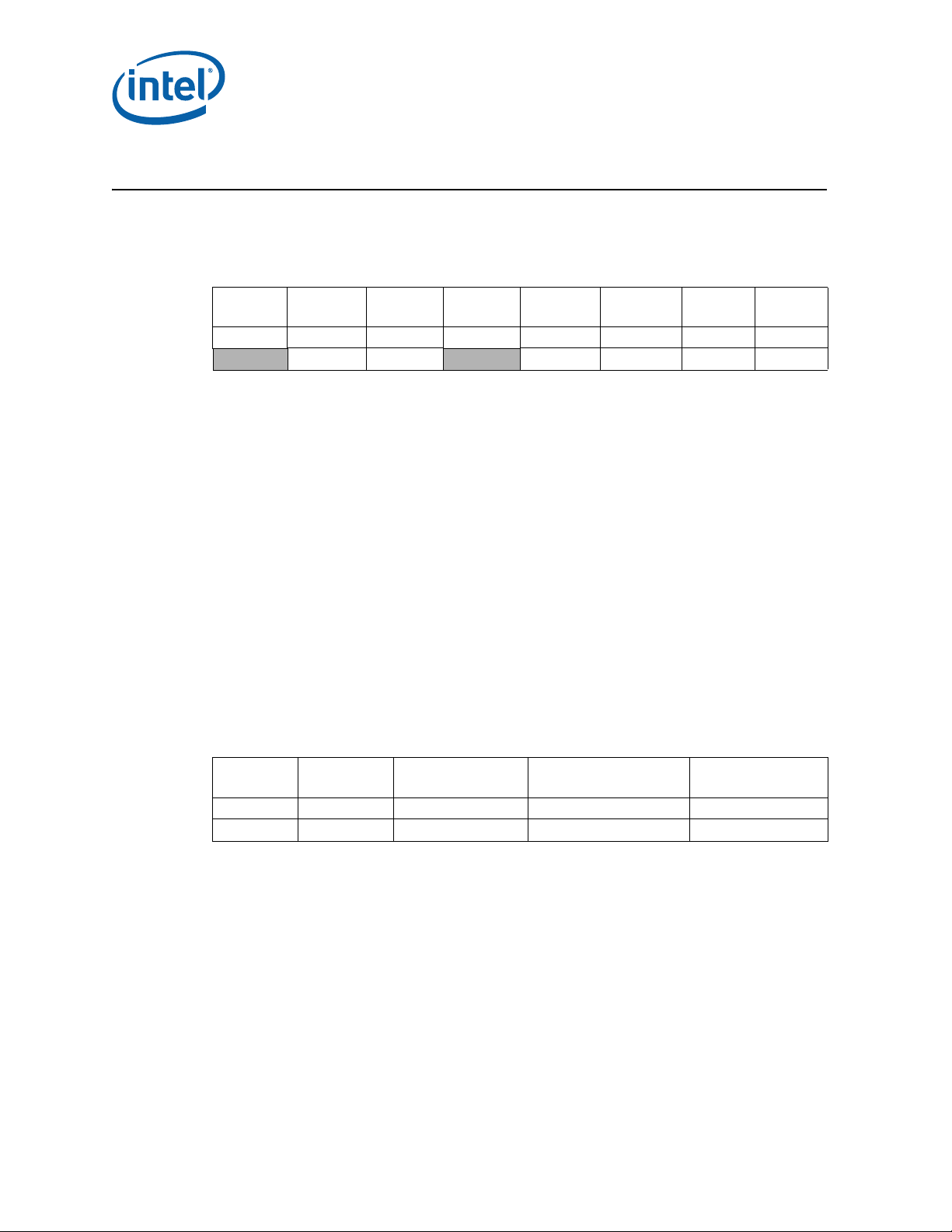
Identification Information
Component Identification using Programming Interface
The processor stepping can be identified by the following register contents:
1
Extended
2
Model
Reserved
Reserved
31:28 27:20 19:16 15:14 13:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
Notes:
1. The Extended F amily , bits [27:20] are used in con junction with the F amily Code, specif ied in bits [11:8],
2. The Extended Model, bits [19:16] in conjunction with the Model Number, specified in bits [7:4], are
3. The Processor Type, specified in bits [13:12] indicates whether the processor is an original OEM
4. The Family Code corresponds to bits [11:8] of the EDX register after RESET, bits [11:8] of the EAX
5. The Model Number corresponds to bits [7:4] of the EDX register after RESET, bits [7:4] of the EAX
6. The Stepping ID in bits [3:0] indicates the revision number of that model. See Table 1 for the processor
Extended
Family
00000000b 0011b 00b 0110 1010b xxxxb
to indicate whether the processor belongs to the Intel386, Intel486, Pentium, Pentium Pro, Pentium 4,
®
or Intel
used to identify the model of the processor within the processor’s family.
processor, an OverDrive processor, or a dual processor (capable of being used in a dual processor
system).
register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the generation field of
the Device ID register accessible through Boundary Scan.
register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the model field of the
Device ID register accessible through Boundary Scan.
stepping ID number in the CPUID information.
Core™ processor family.
Processor
3
Type
Family
Code
4
Model
Number
5
Stepping
6
ID
When EAX is initialized to a value of ‘1’, the CPUID instruction returns the Extended
Family, Extended Model, Processor Type, Family C ode, Mode l Number and Step ping ID
value in the EAX register. Note that the EDX processor signature value after reset is
equivalent to the processor signature output value in the EAX register.
Cache and TLB descriptor parameters are provided in the EAX, EBX, ECX and EDX
registers after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 2 in the EAX register.
The processor can be identified by the following register contents:
Stepping Vendor ID
E-1 8086h 0154h 0166h 09h
L-1 8086h 0154h 0166h 09h
Notes:
1. The Vendor ID corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Vendor ID Register located at offset 00h–01h in the PCI
2. The Host Device ID corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Device ID Register located at Device 0 offset 02h–
3. The Processor Graphics Device ID (DID2) corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Device ID Register located at
4. The Revision Number corre sponds to bits 7:0 of the Re vision ID Register located at offset 08h in the PCI
14 Specification Update
function 0 configuration space.
03h in the PCI function 0 configuration space.
Device 2 offset 02h–03h in the PCI function 0 configuration space.
function 0 configuration space.
1
Host Device ID
2
Processor Graphics
Device ID
3
Revision ID
4
Page 15
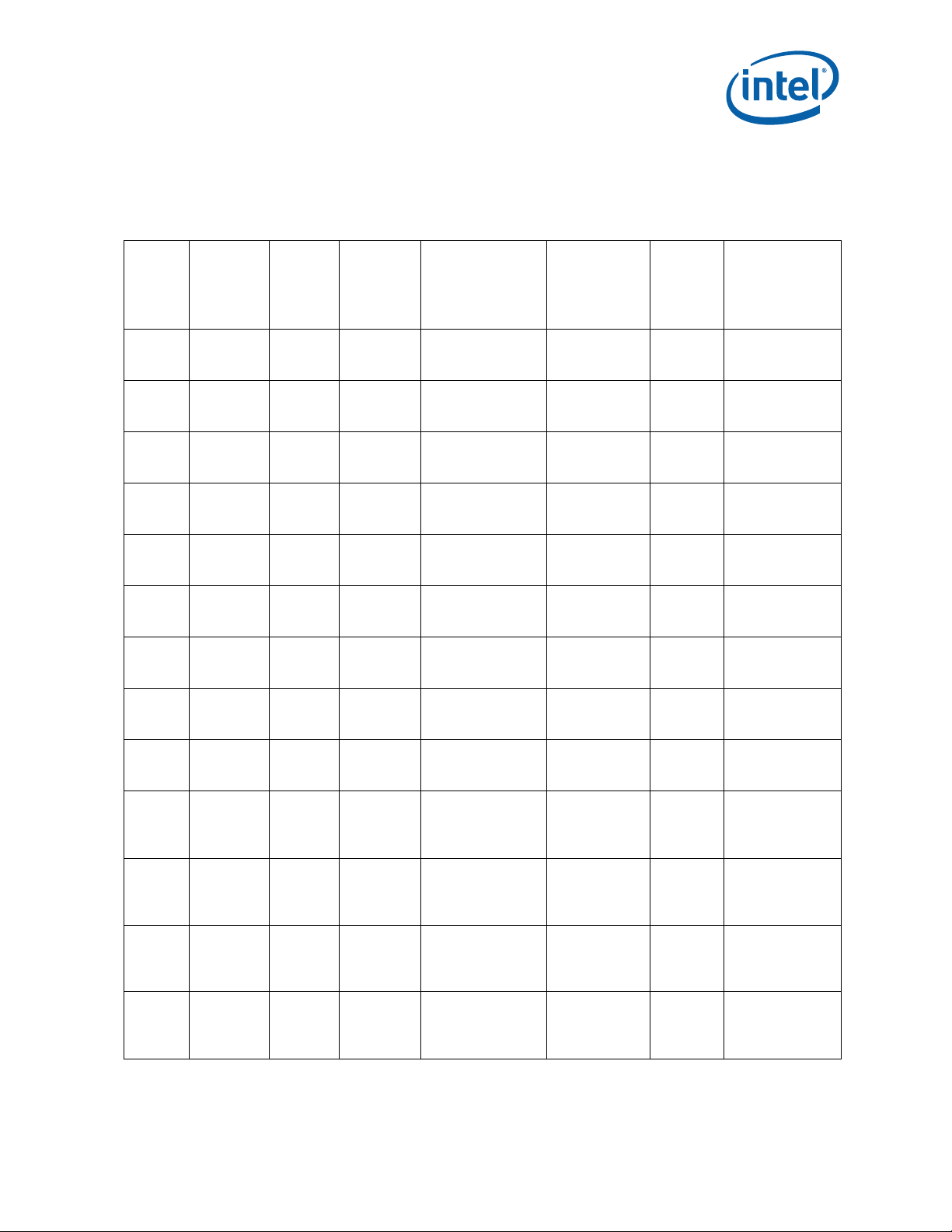
Component Marking Information
The processor stepping can be identified by the following component markings.
Table 1. Processor Identification (Sheet 1 of 6)
Core Frequency
Number
SR0T2 i7-3920XM E-1 000306A9h 2.9 / 1600 / 650
SR0MJ i7-3820QM E-1 000306A9h 2.7 / 1600 / 650
SR0MK i7-3820QM E-1 000306A9h 2.7 / 1600 / 650
SR0ML i7-3720QM E-1 000306A9h 2.6 / 1600 / 650
SR0MM i7-3720QM E-1 000306A9h 2.6 / 1600 / 650
SR0MN i7-3610QM E-1 000306A9h 2.3 / 1600 / 650
SR0MP i7-3615QM E-1 000306A9h 2.3 / 1600 / 650
SR0MQ i7-3612QM E-1 000306A9h 2.1 / 1600 / 650
SR0MR i7-3612QM E-1 000306A9h 2.1 / 1600 / 650
SR0MT i7-3520M L-1 000306A9h 2.9 / 1600 / 650
SR0MU i7-3520 M L-1 000306A9h 2.9 / 1600 / 650
SR0MV i5-3360M L-1 000306A9h 2.8 / 1600 / 650
SR0MW i5-3360M L-1 000306A9h 2.8 / 1600 / 650
Processor
Number
Stepping
Processor
Signature
(GHz) /
DDR3 (MHz) /
Processor
Graphics
Frequency
®
Max Intel
Turbo Boost
Technology
2.0 Frequency
(GHz)
3/4 core: 3.6
2 core: 3.7
1 core: 3.8
3/4 core: 3.5
2 core: 3.6
1 core: 3.7
3/4 core: 3.5
2 core: 3.6
1 core: 3.7
3/4 core: 3.4
2 core: 3.5
1 core: 3.6
3/4 core: 3.4
2 core: 3.5
1 core: 3.6
3/4 core: 3.1
2 core: 3.2
1 core: 3.3
3/4 core: 3.1
2 core: 3.2
1 core: 3.3
3/4 core: 2.8
2 core: 3
1 core: 3.1
3/4 core: 2.8
2 core: 3
1 core: 3.1
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 3.4
1 core: 3.6
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 3.4
1 core: 3.6
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 3.3
1 core: 3.5
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 3.3
1 core: 3.5
1
Shared
L3 Cache
Size (MB)
8 2,3,4,5,6
8 2,3,4,5,6
8 2,3,4,5,6
6 2,3,4,5,6
6 2,3,4,5,6
6 2,4,6
6 2,4,5,6
6 2,4,6
6 2,4,5,6
4 2,3,4,5,6
4 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,3,4,5,6
Notes
Specification Update 15
Page 16
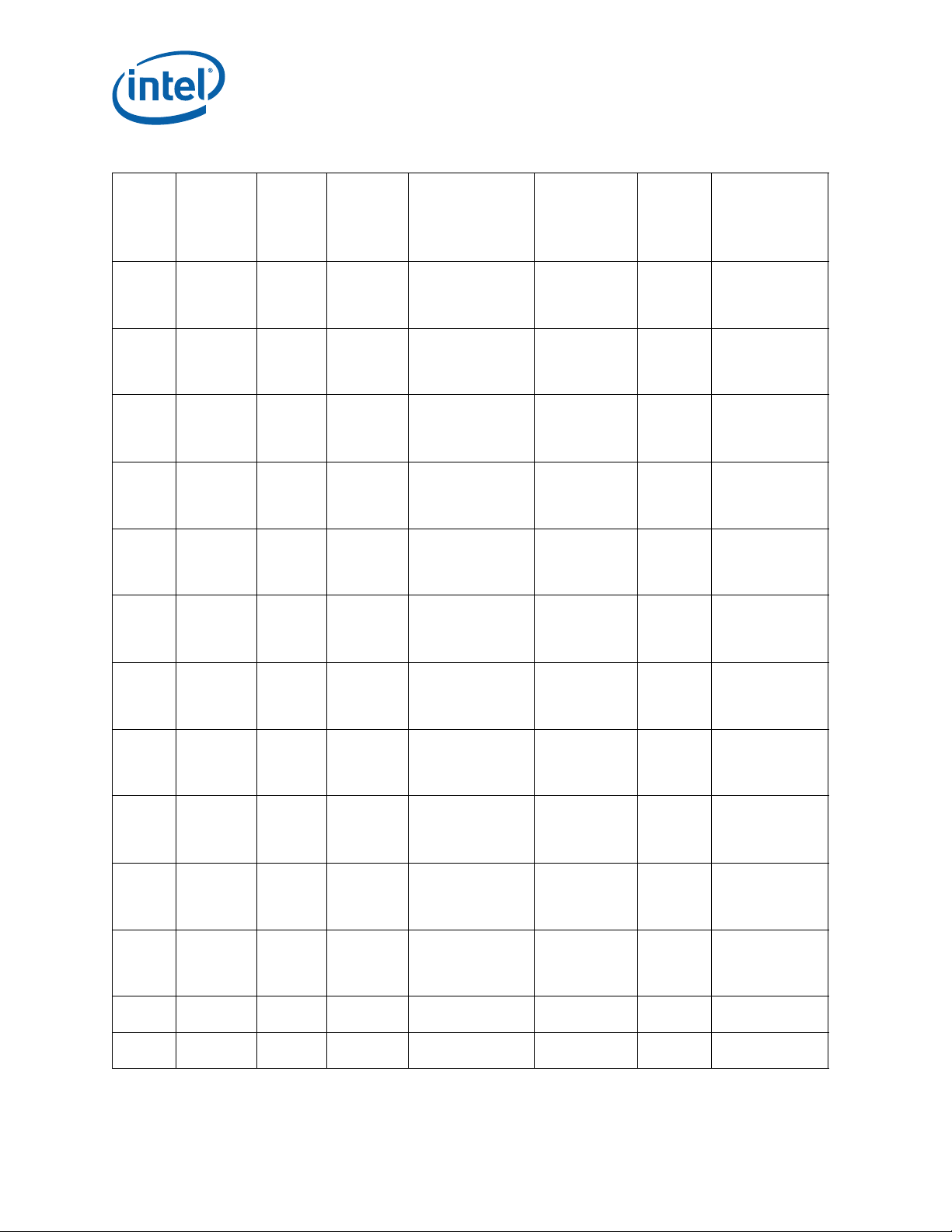
Table 1. Processor Identification (Sheet 2 of 6)
Core Frequency
(GHz) /
DDR3 (MHz) /
Processor
Graphics
Frequency
Number
Processor
Number
Stepping
Processor
Signature
SR0MX i5-3320M L-1 000306A9h 2.6 / 1600 / 650
SR0MY i5-3320M L-1 000306A9h 2.6 / 1600 / 650
SR0MZ i5-3210M L-1 000306A9h 2.5 / 1600 / 650
SR0N0 i5-3210M L-1 000306A9h 2.5 / 1600 / 650
SR0N1 i3-3110M L-1 000306A9h 2.4 / 1600 / 650
SR0N2 i3-3110M L-1 000306A9h 2.4 / 1600 / 650
SR0N5 i7-3667U L-1 000306A9h 2 / 1600 / 350
SR0N6 i7-3517U L-1 000306A9h 1.9 / 1600 / 350
SR0N7 i5-3427U L-1 000306A9h 1.8 / 1600 / 350
SR0N8 i5-3317U L-1 000306A9h 1.7 / 1600 / 350
SR0N9 i3-3217U L-1 000306A9h 1.8 / 1600 / 350
SR0X6 i7-3540M L-1 000306A9h 3.0 / 1600 / 1300
SR0X8 i7-3540M L-1 000306A9h 3.0 / 1600 / 1300
(GHz)
®
1
Max Intel
Turbo Boost
Technology
2.0 Frequency
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 3.1
1 core: 3.3
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 3.1
1 core: 3.3
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 2.9
1 core: 3.1
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 2.9
1 core: 3.1
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 0
1 core: 2.4
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 0
1 core: 2.4
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 3
1 core: 3.2
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 2.8
1 core: 3
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 2.6
1 core: 2.8
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 2.4
1 core: 2.6
4 core: 0
3 core: 0
2 core: 0
1 core: 0
2 core: 3.5
1 core: 3.7
2 core: 3.5
1 core: 3.7
Shared
L3 Cache
Notes
Size (MB)
3 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,3,4,5,6
32,4,6
3 2,4,5,6
32,4
32,4
4 2,3,4,5,6
4 2,4,5,6
3 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,4,5,6
32,4
4 2,3,4,5,6
4 2,3,4,5,6
16 Specification Update
Page 17
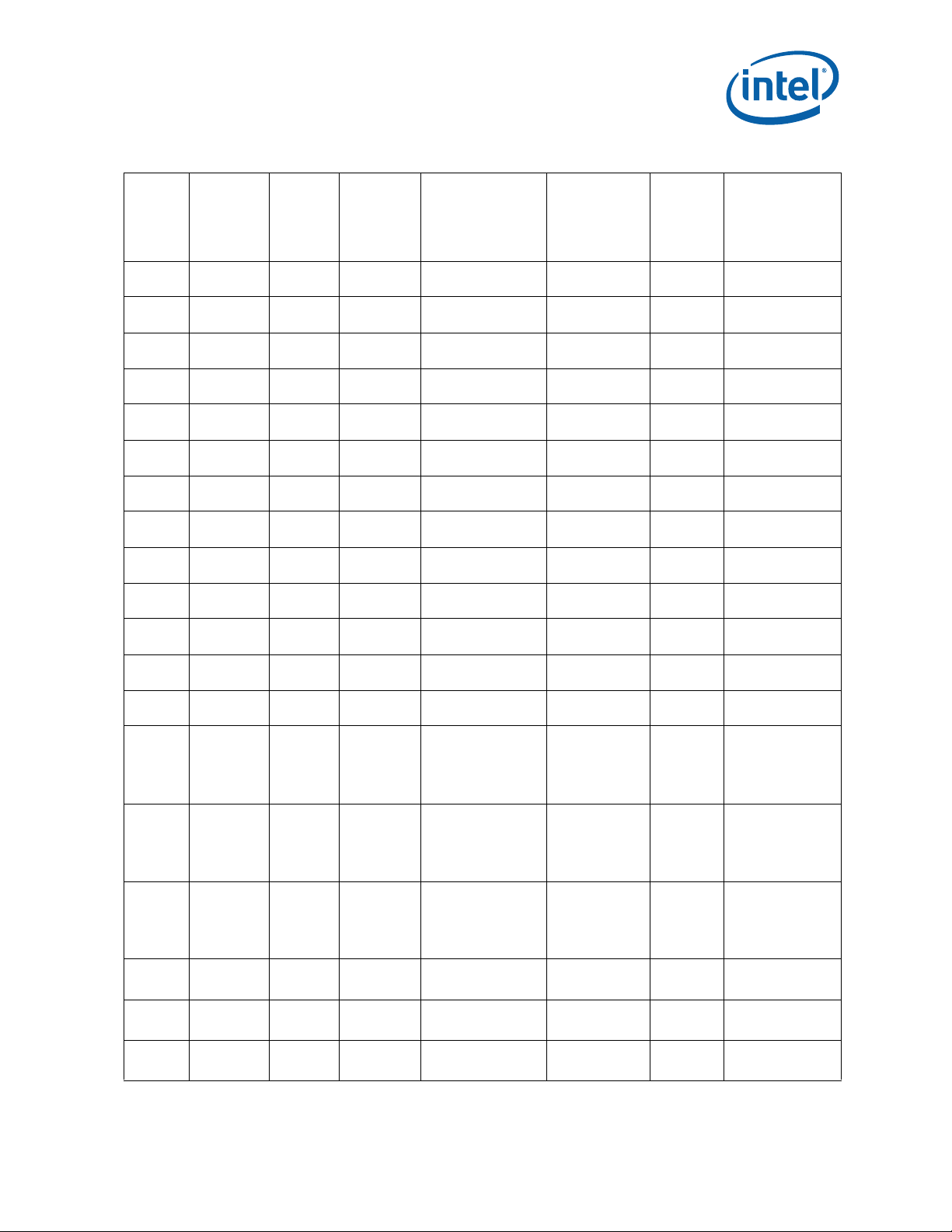
Table 1. Processor Identification (Sheet 3 of 6)
Core Frequency
Number
SR0X7 i5-3380 M L-1 000306A9h 2.9 /1600 /650
SR0X9 i5-3380 M L-1 000306A9h 2.9 /1600 /650
SR0XA i5-3340M L-1 000306A9h 2.7 / 1600 /650
SR0XB i5-3340M L-1 000306A9h 2.7 / 1600 /650
SR0WY i5-3230M L-1 000306A9h 2.6 / 1600 / 650
SR0WX i5-3230M L-1 000306A9h 2.6 / 1600 / 650
SR0XD i3-3130M L-1 000306A9h 2.6 / 1600 / 650
SR0XC i3-3130M L-1 000306A9h 2.6 / 1600 / 650
SR0XH i7-3687U L-1 000306A9h 2.1 /1600 /350
SR0XG i7-3537U L-1 000306A9h 2 / 1600/ 350
SR0XE i5-3437U L-1 000306A9h 1.9 / 1600 / 350
SR0XL i5-3337U L-1 000306A9h 1.8 / 1600 / 350
SR0XF i3-3227U L-1 000306A9h 1.9 / 1600 / 350
Processor
Number
Stepping
Processor
Signature
SR0US i7-3940XM E-1 000306A9h 3.0 / 1200 / 650
SR0UT i7-3840QM E-1 000306A9h 2.8 / 1200 / 650
SR0UV i7-3740QM E-1 000306A9h 2.7 / 1200 / 650
SR12R i7-3689Y L-1 000306A9h 1.5 /1600/ 350
SR0ZP i7-3689Y L-1 000306A9h 1.5 /1600/ 350
SR12Q i5-3439Y L-1 000306A9h 1.5 /1600/ 350
(GHz) /
DDR3 (MHz) /
Processor
Graphics
Frequency
®
Max Intel
Turbo Boost
Technology
2.0 Frequency
(GHz)
2 core: 3.4
1 core: 3.6
2 core: 3.4
1 core: 3.6
2 core: 3.2
1 core: 3.4
2 core: 3.2
1 core: 3.4
2 core: 3.0
1 core: 3.2
2 core: 3.0
1 core: 3.2
2 core:
1 core: 2.6
2 core:
1 core: 2.6
2 core: 3.1
1 core: 3.3
2 core: 2.9
1 core: 3.1
2 core: 2.7
1 core: 2.9
2 core: 2.5
1 core: 2.7
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.9
1
4 core: 3.7
3 core: 3.8
2 core: 3.9
1 core: 3.9
4 core: 3.6
3 core: 3.7
2 core: 3.8
1 core: 3.8
4 core: 3.5
3 core: 3.6
2 core: 3.7
1 core: 3.7
2 core: N/A
1 core: 2.6
2 core: N/A
1 core: 2.6
2 core: N/A
1 core: 2.3
Shared
L3 Cache
Size (MB)
3 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,4,5,6
3 2,4,5,6
32,4
32,4
4 2,3,4,5,6
4 2,4,5,6
3 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,4,5,6
3 2,4,7
Notes
8 1,2,3,4,5,6
8 1,2,3,4,5,6
6 1,2,3,4,5,6
4 2,3,4,5,6
4 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,3,4,5,6
Specification Update 17
Page 18

Table 1. Processor Identification (Sheet 4 of 6)
Core Frequency
(GHz) /
DDR3 (MHz) /
Processor
Graphics
Frequency
Number
Processor
Number
Stepping
Processor
Signature
SR0ZN i5-3439Y L-1 000306A9h 1.5 /1600/ 350
SR12S i5-3339Y L-1 000306A9h 1.5 /1600/ 350
SR0ZQ i5-3339Y L-1 000306A9h 1.5 /1600/ 350
SR12P i3-3229Y L-1 000306A9h 1.4 /1600/ 350
SR0ZM i3-3229Y L-1 000306A9h 1.4 /1600/ 350
SR12M 2129Y P-0 000306A9h 1.1 / 1600/ 350
SR13W 1019Y P-0 000306A9h 1.1 / 1600/ 350
SR0ZZ 2030M P-0 000306A9h 2.5/ 1600/ 650
SR0VN 2020M P-0 000306A9h 2.4/ 1600/ 650
SR0ZY 1020M E-1 000306A9h 2.1/ 1600/ 650
SR103 1005M P-0 000306A9h 1.9/ 1600/ 650
SR102 1000M P-0 000306A9h 1.8/ 1600/ 650
SR105 2127U P-0 000306A9h 1.9/ 1600/ 350
SR0VQ 2117U P-0 000306A9h 1.8/ 1600/ 350
SR108 1037U P-0 000306A9h 1.8/ 1600/ 350
SR109 1007U P-0 000306A9h 1.5/ 1600/ 350
SR10A 1017U P-0 000306A9h 1.6/ 1600/ 350
SR0NP i7-3610QE E-1 00306A9h 2.3 / 1600/ 650
SR0NC i7-3615QE E-1 00306A9h 2.3 / 1600/ 650
(GHz)
®
1
Max Intel
Turbo Boost
Technology
2.0 Frequency
2 core: N/A
1 core: 2.3
2 core: N/A
1 core: 2.2
2 core: N/A
1 core: 2.2
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.4
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.4
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.1
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.1
2 core: N/A
1 core: 2.5
2 core: N/A
1 core: 2.4
2 core: N/A
1 core: 2.1
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.9
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.8
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.9
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.8
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.8
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.5
2 core: N/A
1 core: 1.6
3/4 Core: 3.1
2 Core: 3.2
1 Core: 3.3
3/4 Core: 3.1
2 Core: 3.2
1 Core: 3.3
Shared
L3 Cache
Size (MB)
Notes
3 2,3,4,5,6
3 2,4,5,6
3 2,4,5,6
32,4
32,4
24
24
24
24
24
24
24
24
24
24
24
24
6 2,3,4,5,6,8
6 2,3,4,5,6,8
18 Specification Update
Page 19

Table 1. Processor Identification (Sheet 5 of 6)
Core Frequency
(GHz) /
DDR3 (MHz) /
Processor
Graphics
Frequency
Number
Processor
Number
Stepping
Processor
Signature
SR0ND i7-3612QE E-1 00306A9h 2.3 / 1600/ 650
SR0T5 i7-3555LE L-1 00306A9h 2.5 / 1600/ 550
SR0T6 i7-3517UE L-1 00306A9h 1.7 / 1600/ 350
SR0QJ i5-3610ME L-1 00306A9h 2.7 / 1600/ 650
SR0QK i5-3610ME L-1 00306A9h 2.7 / 1600/ 650
SR0WL i3-3210ME L-1 00306A9h 2.4 / 1600/ 650
SR0WM i3-3120ME L-1 00306A9h 2.4 / 1600/ 650
SR0WN i3-3217UE L-1 00306A9h 1.6 / 1600/ 350
SR10E 1047UE P-0 00306A9h 1.4 / 1600/ 350
SR10D 1020E P-0 00306A9h 2.2 / 1600/ 650
®
Max Intel
Turbo Boost
Technology
2.0 Frequency
(GHz)
1
3/4 Core: 2.8
2 Core: 3.0
1 Core: 3.1
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 3.0
1 Core: 3.2
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 2.6
1 Core: 2.8
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 3.2
1 Core: 3.3
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 3.2
1 Core: 3.3
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 0
1 Core: 0
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 0
1 Core: 0
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 0
1 Core: 0
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 0
1 Core: 0
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 0
1 Core: 0
Shared
L3 Cache
Size (MB)
Notes
6 2,3,4,5,6,8
4 2,3,4,5,6,8
4 2,3,4,5,6,8
3 2,3,4,5,6,8
3 2,3,4,5,6,8
3 2,4,8
3 2,4,8
3 2,4,8
24,8
24,8
Specification Update 19
Page 20

Table 1. Processor Identification (Sheet 6 of 6)
Core Frequency
(GHz) /
DDR3 (MHz) /
Processor
Graphics
Frequency
Number
Processor
Number
Stepping
Processor
Signature
SR0VR 1020E P-0 00306A9h 2.2 / 1600/ 650
SR10F 927UE P-0 00306A9h 1.5 / 1600/ 350
(GHz)
®
1
Max Intel
Turbo Boost
Technology
2.0 Frequency
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 0
1 Core: 0
4 Core: 0
3 Core: 0
2 Core: 0
1 Core: 0
Shared
L3 Cache
Size (MB)
Notes
24,8
14,8
Notes:
1. This column indicates maximum Intel
2. Intel
3. Intel
4. Intel
5. Intel
6. Intel
cores active respectively.
®
Hyper-Threading Technology enabled.
®
Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT) enabled.
®
Virtualization Technology for IA-32, Intel® 64 and Intel® Architecture (Intel® VT-x) enabled.
®
Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d) enabled.
®
AES-NI enabled.
®
Turbo Boost Technology 2.0 frequency (GHz) for 4,3, 2 or 1
20 Specification Update
Page 21

Errata
BU1. The Processor May Report a #TS Instead of a #GP Fault
Problem: A jump to a busy TSS (Task-State Segment) may cause a #TS (invalid TSS exception)
instead of a #GP fault (general protection exception).
Implication: Operation systems that access a busy TSS may get invalid TSS fault instead of a #GP
fault. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU2. REP MOVS/STOS Executing with Fast Strings Enabled and Crossing
Page Boundaries with Inconsistent Memory Types may use an
Incorrect Data Size or Lead to Memory-Ordering Violations.
Problem: Under certain conditions as described in the Software Developers Manual section “Out-
of-Order Stores For String Operations in Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6 Family
Processors” the processor performs REP MOVS or REP STOS as fast strings. Due to this
erratum fast string REP MOVS/REP STOS instructions that cross page boundaries from
WB/WC memory types to UC/WP/WT memory types, may start using an incorrect data
size or may observe memory ordering violations.
Implication: Upon crossing the page boundary the following may occur, dependent on the new page
memory type:
• UC the data size of each write will now always be 8 bytes, as opposed to the
original data size.
• WP the data size of each write will now always be 8 bytes, as opposed to the
original data size and there may be a memory ordering violation.
• WT there may be a memory ordering violation.
Workaround: Software should avoid crossing page boundaries from WB or WC memory type to UC,
WP or WT memory type within a single REP MOVS or REP STOS instruction that will
execute with fast strings enabled.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU3. IO_SMI Indication in SMRAM State Save Area May be Set Incorrectly
Problem: The IO_SMI bit in SMRAM’s location 7F A4H is set to “1” by the CPU to indicate a System
Management Interrupt (SMI) occurred as the result of executing an instruction that
reads from an I/O port. Due to this erratum, the IO_SMI bit may be incorrectly set by:
• A non-I/O instruction
• SMI is pending while a lower priority event interrupts
•A REP I/O read
• A I/O read that redirects to MWAIT
Implication: SMM handlers may get false IO_SMI indication.
Workaround: The SMM handler has to evaluate the saved context to determine if the SMI was
triggered by an instruction that read from an I/O port. The SMM handler must not
restart an I/O instruction if the platform has not been configured to generate a
synchronous SMI for the recorded I/O port address.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 21
Page 22

BU4. Performance Monitor SSE Retired Instructions May Return Incorrect
Values
Problem: Performance Monitoring counter SIMD_INST_RETIRED (Event: C7H) is used to track
retired SSE instructions. Due to this erratum, the processor may also count other types
of instructions resulting in higher than expected values.
Implication: Performance Monitoring counter SIMD_INST_RETIRED may report count higher than
expected.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU5. IRET under Certain Conditions May Cause an Unexpected Alignment
Check Exception
Problem: In IA-32e mode, it is possible to get an Alignment Check Exception (#AC) on the IRET
instruction even though alignment checks were disabled at the start of the IRET. This
can only occur if the IRET instruction is returning from CPL3 code to CPL3 code. IRETs
from CPL0/1/2 are not affected. This erratum can occur if the EFLAGS value on the
stack has the AC flag set, and the interrupt handler's stack is misaligned. In IA-32e
mode, RSP is aligned to a 16-byte boundary before pushing the stack frame.
Implication: In IA-32e mode, under the conditions given above, an IRET can get a #AC even if
alignment checks are disabled at the start of the IRET. This erratum can only be
observed with a software generated stack frame.
Workaround: Software should not generate misaligned stack frames for use with IRET.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU6. Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX May Not
Count Some Transitions
Problem: Performance Monitor Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX (Event CCH, Umask 01H) counts
transitions from x87 Floating Point (FP) to MMX™ instructions. Due to this erratum, if
only a small number of MMX instructions (including EMMS) are executed immediately
after the last FP instruction, a FP to MMX transition may not be counted.
Implication: The count value for Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX may be
lower than expected. The degree of undercounting is dependent on the occurrences of
teption). Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU7. General Protection Fault (#GP) for Instructions Greater than 15 Bytes
May be Preempted
Problem: When the processor encounters an instruction that is greater than 15 bytes in length, a
#GP is signaled when the instruction is decoded. Under some circumstances, the #GP
fault may be preempted by another lower priority fault (e.g. Page Fault (#PF)).
However, if the preempting lower priority faults are resolved by the operating system
and the instruction retried, a #GP fault will occur.
Implication: Software may observe a lower-priority fault occurring before or in lieu of a #GP fault.
Instructions of greater than 15 bytes in length can only occur if redundant prefixes are
placed before the instruction.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
22 Specification Update
Page 23

BU8. LBR, BTS, BTM May Report a Wrong Address when an Exception/
Interrupt Occurs in 64-bit Mode
Problem: An exception/interrupt event should be transparent to the LBR (Last Branch Record),
BTS (Branch Trace Store) and BTM (Branch Trace Message) mechanisms. However,
during a specific boundary condition where the exception/interrupt occurs right after
the execution of an instruction at the lower canonical boundary (0x00007FFFFFFFFFFF)
in 64-bit mode, the LBR return registers will save a wrong return address with bits 63
to 48 incorrectly sign extended to all 1’s. Subsequent BTS and BTM operations which
report the LBR will also be incorrect.
Implication: LBR, BTS and BTM may report incorrect information in the event of an exception/
interrupt.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU9. Incorrect Address Computed For Last Byte of FXSAVE/FXRSTOR or
XSAVE/XRSTOR Image Leads to Partial Memory Update
Problem: A partial memory state save of the FXSAVE or XSAVE image or a partial memory state
restore of the FXRSTOR or XRSTOR image may occur if a memory address exceeds the
64KB limit while the processor is operating in 16-bit mode or if a memory address
exceeds the 4GB limit while the processor is operating in 32-bit mode.
Implication: FXSAVE/FXRSTOR or XSAVE/XRSTOR will incur a #GP fault due to the memory limit
violation as expected but the memory state may be only partially saved or restored.
Workaround: Software should avoid memory accesses that wrap around the respective 16-bit and
32-bit mode memory limits.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU10. Values for LBR/BTS/BTM Will be Incorrect after an Exit from SMM
Problem: After a return from SMM (System Management Mode), the CPU will incorrectly update
the LBR (Last Branch Record) and the BTS (Branch Trace Store), hence rendering their
data invalid. The corresponding data if sent out as a B TM on the system bus will also be
incorrect. Note: This issue would only occur when one of the 3 above mentioned debug
support facilities are used.
Implication: The value of the LBR, BTS, and BTM immediately after an RSM operation should not be
used.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 23
Page 24

BU11. EFLAGS Discrepancy on Page Faults and on EPT-Induced VM Exits
after a Translation Change
Problem: This erratum is regarding the case where paging structures are modified to change a
linear address from writable to non-writable without software performing an
appropriate TLB invalidation. When a subsequent access to that address by a specific
instruction (ADD, AND, BTC, BTR, BTS, CMPXCHG, DEC, INC, NEG, NOT, OR, ROL/ROR,
SAL/SAR/SHL/SHR, SHLD, SHRD, SUB, XOR, and XADD) causes a page fault or an EPTinduced VM exit, the value saved for EFLAGS may incorrectly contain the arithmetic flag
values that the EFLAGS register would have held had the instruction completed without
fault or VM exit. For page faults, this can occur even if the fault causes a VM exit or if
its delivery causes a nested fault.
Implication: None identified. Although the EFLAGS value saved by an affected event (a page fault or
an EPT-induced VM exit) may contain incorrect arithmetic flag values, Intel has not
identified software that is affected by this erratum. This erratum will have no further
effects once the original instruction is restarted because the instruction will produce the
same results as if it had initially completed without fault or VM exit.
Workaround: If the handler of the affected events inspects the arithmetic portion of the saved
EFLAGS value, then system software should perform a synchronized paging structure
modification and TLB invalidation.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU12. B0-B3 Bits in DR6 For Non-Enabled Breakpoints May be Incorrectly Set
Problem: Some of the B0-B3 bits (breakpoint conditions detect flags, bits [3:0]) in DR6 may be
incorrectly set for non-enabled breakpoints when the following sequence happens:
1. MOV or POP instruction to SS (Stack Segment) selector;
2. Next instruction is FP (Floating Point) that gets FP assist
3. Another instruction after the FP instruction completes successfully
4. A breakpoint occurs due to either a data breakpoint on the preceding instruction or
a code breakpoint on the next instruction.
Due to this erratum a non-enabled breakpoint triggered on step 1 or step 2 may be
reported in B0-B3 after the breakpoint occurs in step 4.
Implication: Due to this erratum, B0-B3 bits in DR6 may be incorrectly set for non-enabled
breakpoints.
Workaround: Software should not execute a floating point instruction directly after a MOV SS or POP
SS instruction.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
24 Specification Update
Page 25

BU13. MCi_Status Overflow Bit May Be Incorrectly Set on a Single Instance
of a DTLB Error
Problem: A single Data Translation Look Aside Buffer (DTLB) error can incorrectly set the
Overflow (bit [62]) in the MCi_Status register. A DTLB error is indicated by MCA error
code (bits [15:0]) appearing as binary value, 000x 0000 0001 0100, in the MCi_Status
register.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the Overflow bit in the MCi_Status register may not be an accur ate
indication of multiple occurrences of DTLB errors. There is no other impact to normal
processor functionality.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU14. Debug Exception Flags DR6.B0-B3 Flags May be Incorrect for Disabled
Breakpoints
Problem: When a debug exception is signaled on a load that crosses cache lines with data
forwarded from a store and whose corresponding breakpoint enable flags are disabled
(DR7.G0-G3 and DR7.L0-L3), the DR6.B0-B3 flags may be incorrect.
Implication: The debug exception DR6.B0-B3 flags may be incorrect for the load if the
corresponding breakpoint enable flag in DR7 is disabled.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU15. LER MSRs May Be Unreliable
Problem: Due to certain internal processor events, updates to the LER (Last Exception Record)
MSRs, MSR_LER_FROM_LIP (1DDH) and MSR_LER_TO_LIP (1DEH), may happen when
no update was expected.
Implication: The values of the LER MSRs may be unreliable.
Workaround: None Identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU16. Storage of PEBS Record Delayed Following Execution of MOV SS or STI
Problem: When a performance monitoring counter is configured for PEBS (Precise Event Based
Sampling), overflow of the counter results in storage of a PEBS record in the PEBS
buffer. The information in the PEBS record represents the state of the next instruction
to be executed following the counter overflow. Due to this erratum, if the counter
overflow occurs after executio n of eithe r MOV SS or STI, storage of the PEBS record is
delayed by one instruction.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, software may observe storage of the PEBS record being
delayed by one instruction following execution of MOV SS or STI. The state information
in the PEBS record will also reflect the one instruction delay.
Workaround: None identified.
Specification Update 25
Page 26

BU17. PEBS Record not Updated when in Probe Mode
Problem: When a performance monitoring counter is configured for PEBS (Precise Event Based
Sampling), overflows of the counter can result in storage of a PEBS record in the PEBS
buffer. Due to this erratum, if the overflow occurs during probe mode, it may be
ignored and a new PEBS record may not be added to the PEBS buffer.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the PEBS buffer may not be updated by overflows that occur
during probe mode.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU18. MONITOR or CLFLUSH on the Local XAPIC's Address Space Results in
Hang
Problem: If the target linear address range for a MONITOR or CLFLUSH is mapped to the local
xAPIC's address space, the processor will hang.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the processor will hang. The local xAPIC's address space
must be uncached. The MONITOR instruction only functions correctly if the specified
linear address range is of the type write-back. CLFLUSH flushes data from the cache.
Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: Do not execute MONITOR or CLFLUSH instructions on the local xAPIC address space.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU19. Faulting MMX Instruction May Incorrectly Update x87 FPU Tag Word
Problem: Under a specific set of conditions, MMX stores (MOVD, MOVQ, MOVNTQ, MASKMOVQ)
which cause memory access faults (#GP, #SS, #PF, or #AC), may incorrectly update
the x87 FPU tag word register.
This erratum will occur when the following additional conditions are also met.
• The MMX store instruction must be the first MMX instruction to operate on x87 FPU
state (i.e. the x87 FP tag word is not already set to 0x0000).
• For MOVD, MOVQ, MOVNTQ stores, the instruction must use an addressing mode
that uses an index register (this condition does not apply to MASKMOVQ).
Implication: If the erratum conditions are met, the x87 FPU tag word register may be incorrectly set
to a 0x0000 value when it should not have been modified.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU20. An Uncorrectable Error Logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS May also
Result in a System Hang
Problem: Uncorrectable errors logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STA TUS MSR (409H) may also result in a
system hang causing an Internal Timer Error (MCACOD = 0x0400h) to be logged in
another machine check bank (IA32_MCi_STATUS).
Implication: Uncorrectable errors logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STA TUS can further cause a system hang
and an Internal Timer Error to be logged.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
26 Specification Update
Page 27

BU21. #GP on Segment Selector Descriptor that Straddles Canonical
Boundary May Not Provide Correct Exception Error Code
Problem: During a #GP (General Protection Exception), the processor pushes an error code on to
the exception handler’s stack. If the segment selector descriptor straddles the
canonical boundary, the error code pushed onto the stack may be incorrect.
Implication: An incorrect error code may be pushed onto the stack. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU22. DR6.B0-B3 May Not Report All Breakpoints Matched When a MOV/POP
SS is Followed by a Store or an MMX Instruction
Problem: Normally, data breakpoints matches that occur on a MOV SS, r/m or POP SS will not
cause a debug exception immediately after MOV/POP SS but will be delayed until the
instruction boundary following the next instruction is reached. After the debug
exception occurs, DR6.B0-B3 bits will contain information about data breakpoints
matched during the MOV/POP SS as well as breakpoints detected by the following
instruction. Due to this erratum, DR6.B0-B3 bits may not contain information about
data breakpoints matched during the MOV/POP SS when the following instruction is
either an MMX instruction that uses a memory addressing mode with an index or a
store instruction.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, DR6 may not contain information about all breakpoints
matched. This erratum will not be observed under the recommended usage of the MOV
SS,r/m or POP SS instructions (i.e., following them only with an instruction that writes
(E/R)SP).
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU23. APIC Error “Received Illegal Vector” May be Lost
Problem: APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) may not update the ESR (Error
Status Register) flag Received Illegal V ector bit [6] properly when an illegal vector error
is received on the same internal clock that the ESR is being written (as part of the
write-read ESR access flow). The corresponding error interrupt will also not be
generated for this case.
Implication: Due to this erratum, an incoming illegal vector error may not be logged into ESR
properly and may not generate an error interrupt.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 27
Page 28

BU24. Changing the Mem ory Type for an In-Use Page Translation May Lead
to Memory-Ordering Violations
Problem: Under complex microarchitectural conditions, if software changes the memory type for
data being actively used and shared by multiple threads without the use of semaphores
or barriers, software may see load operations execute out of order.
Implication: Memory ordering may be violated. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software.
Workaround: Software should ensure pages are not being actively used before requesting their
memory type be changed.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU25. Reported Memory Type May Not Be Used to Access the VMCS and
Referenced Data Structures
Problem: Bits 53:50 of the IA32_VMX_BASIC MSR report the memory type that the processor
uses to access the VMCS and data structures referenced by pointers in the VMCS. Due
to this erratum, a VMX access to the VMCS or referenced data structures will instead
use the memory type that the MTRRs (memory-type range registers) specify for the
physical address of the access.
Implication: Bits 53:50 of the IA32_VMX_BASIC MSR report that the WB (write-back) memory type
will be used but the processor may use a different memory type.
Workaround: Software should ensure that the VMCS and referenced data structures are located at
physical addresses that are mapped to WB memory type by the MTRRs.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU26. LBR, BTM or BTS Records May have Incorrect Branch From
Information After an EIST/T-state/S-state/C1E Transition or Adaptive
Thermal Throttling
Problem: The “From” address associated with the LBR (Last Branch Record), BTM (Branch Trace
Message) or BTS (Branch Trace Store) may be incorrect for the first branch after a
transition of:
• EIST (Enhanced Intel® SpeedStep Technology)
• T-state (Thermal Monitor states)
• S1-state (ACPI package sleep state)
• C1E (Enhanced C1 Low Power state)
• Adaptive Thermal Throttling
Implication: When the LBRs, BTM or BTS are enabled, some records may have incorrect branch
“From” addresses for the first branch after a transition of EIST, T-states, S-states, C1E,
or Adaptive Thermal Throttling.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
28 Specification Update
Page 29

BU27. Fault Not Reported When Setting Reserved Bits of Intel® VT-d Queued
Invalidation Descriptors
Problem: Reserved bits in the Queued Invalidation descriptors of Intel VT-d (Virtualization
Technology for Directed I/O) are expected to be zero, meaning that software must
program them as zero while the processor checks if they are not zero. Upon detection
of a non-zero bit in a reserved field an Intel VT-d fault should be recorded. Due to this
erratum the processor does not check reserved bit values for Queued Invalidation
descriptors.
Implication: Due to this erratum, faults will not be reported when writing to reserved bits of Intel
VT-d Queued Invalidation Descriptors.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU28. FP Data Operand Pointer May Be Incorrectly Calculated After an FP
Access Which Wraps a 4-Gbyte Boundary in Code That Uses 32-Bit
Address Size in 64-bit Mode
Problem: The FP (Floating Point) Data Operand Pointer is the effective address of the operand
associated with the last non-control FP instruction executed by the processor. If an 80bit FP access (load or store) uses a 32-bit address size in 64-bit mode and the memory
access wraps a 4-Gbyte boundary and the FP environment is subsequently saved, the
value contained in the FP Data Operand Pointer may be incorrect.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the FP Data Operand Pointer may be incorrect. W rapping an 80-bit
FP load around a 4-Gbyte boundary in this way is not a normal programming practice.
Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: If the FP Data Operand Pointer is used in a 64-bit operating system which may run code
accessing 32-bit addresses, care must be taken to ensure that no 80-bit FP accesses
are wrapped around a 4-Gbyte boundary.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU29. VMREAD/VMWRITE Instruction May Not Fail When Accessing an
Unsupported Field in VMCS
Problem: The Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B states
that execution of VMREAD or VMWRITE should fail if the value of the instruction’s
register source operand corresponds to an unsupported field in the VMCS (Virtual
Machine Control Structure). The correct operation is that the logical processor will set
the ZF (Zero Flag), write 0CH into the VM-instruction error field and for VMREAD leave
the instruction’s destination operand unmodified. Due to this erratum, the instruction
may instead clear the ZF, leave the VM-instruction error field unmodified and for
VMREAD modify the contents of its destination operand.
Implication: Accessing an unsupported field in VMCS will fail to properly report an error . In addition,
VMREAD from an unsupported VMCS field may unexpectedly change its destination
operand. Intel has not observed this err atum with an y commercially available software.
Workaround: Software should avoid accessing unsupported fields in a VMCS.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 29
Page 30

BU30. Spurious Interrupts May be Generated From the Intel® VT-d Remap
Engine
Problem: If software clears the F (Fault) bit 127 of the Fault Recording Register (FRCD_REG at
offset 0x208 in Remap Engine BAR) by writing 1b through RW1C command (Read Write
1 to Clear) when the F bit is already clear then a spurious interrupt from Intel VT-d
(Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O) Remap Engine may be observed.
Implication: Due to this erratum, spurious interrupts will occur from the Intel VT-d Remap Engine
following RW1C clearing F bit.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU31. Malformed PCIe Transactions May be Treated as Unsupported
Requests Instead of as Critical Errors
Problem: PCIe MSG/MSG_D TLPs (T ransaction Layer P ackets) with incorrect R outing Code as well
as the deprecated TCfgRD and TCfgWr types should be treated as malformed
transactions leading to a critical error. Due to this erratum, the integrated PCIe
controller's root ports may treat such messages as UR (Unsupported Requests).
Implication: Legacy malformed PCIe transactions may be treated as UR instead of as critical errors.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU32. Reception of Certain Malformed Transactions May Cause PCIe Port to
Hang Rather Than Reporting an Error
Problem: If the processor receives an upstream malformed non posted packet for which the type
field is IO, Configuration or the deprecated TCfgRd and the format is 4 DW header, then
due to this erratum the integrated PCIe controller may hang instead of reporting the
malformed packet error or issuing an unsupported request completion transaction.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor may hang without reporting errors when receiving a
malformed PCIe transaction. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially
available device.
Workaround: None identified. Upstream transaction initiators should avoid issuing unsupported
requests with 4 DW header formats.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU33. Clock Modulation Duty Cycle Cannot be Programmed to 6.25%
Problem: When programming field T_STA TE_REQ of the IA32_CLOCK_MODULA TION MSR (19AH)
bits [3:0] to '0001, the actual clock modulation duty cycle will be 12.5% instead of the
expected 6.25% ratio.
Implication: Due to this erratum, it is not possible to program the clock modulation to a 6.25% duty
cycle.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
30 Specification Update
Page 31

BU34. Processor May Fail to Acknowledge a TLP Request
Problem: When a PCIe root port’s receiver is in Receiver L0s power state and the port initiates a
Recovery event, it will issue Training Sets to the link partner. The link partner will
respond by initiating an L0s exit sequence. Prior to transmitting its own Training Sets,
the link partner may transmit a TLP (Transaction Layer Packet) request. Due to this
erratum, the root port may not acknowledge the TLP request.
Implication: After completing the Recovery event, the PCIe link partner will replay the TLP request.
The link partner may set a Correctable Error status bit, which has no functional effect.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU35. An Unexpected PMI May Occur After Writing a Large Value to
IA32_FIXED_CTR2
Problem: If the fixed-function performance counter IA32_FIXED_CTR2 MSR (30BH) is configured
to generate a performance-monitor interrupt (PMI) on overflow and the counter’ s value
is greater than FFFFFFFFFFC0H, then this erratum may incorrectly cause a PMI if
software performs a write to this counter.
Implication: A PMI may be generated unexpectedly when programming IA32_FIXED_CTR2. Other
than the PMI, the counter programming is not affected by this erratum as the
attempted write operation does succeed.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU36. A Write to the IA32_FIXED_CTR1 MSR May Result in Incorrect Value in
Certain Conditions
Problem: Under specific internal conditions, if software tries to write the IA32_FIXED_CTR1 MSR
(30AH) a value that has all bits [31:1] set while the counter was just about to overflow
when the write is attempted (i.e. its value was 0xFFFF FFFF FFFF), then due to this
erratum the new value in the MSR may be corrupted.
Implication: Due to this erratum, IA32_FIXED_CTR1 MSR may be written with a corrupted value.
Workaround: Software may avoid this erratum by writing zeros to the IA32_FIXED_CTR1 MSR,
before the desired write operation.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU37. PCIe* LTR Incorrectly Reported as Being Supported
Problem: LTR (Latency Tolerance Reporting) is a new optional feature specified in PCIe rev. 2.1.
The processor reports L TR as supported in LTRS bit in DCAP2 register (bus 0; Device 1;
Function 0; offset 0xc4), but this feature is not supported.
Implication: Due to this erratum, LTR is always reported as supported by the LTRS bit in the DCAP2
register.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 31
Page 32

BU38. PerfMon Overflow Status Can Not be Cleared After Certain Conditions
Have Occurred
Problem: Under very specific timing conditions, if software tries to disable a PerfMon counter
through MSR IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL (0x38F) or through the per-counter eventselect (e.g. MSR 0x186) and the counter reached its overflow state very close to that
time, then due to this erratum the overflow status indication in MSR
IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_STAT (0x38E) may be left set with no way for software to clear it.
Implication: Due to this erratum, software may be unable to clear the PerfMon counter overflow
status indication.
Workaround: Software may avoid this erratum by clearing the PerfMon counter value prior to
disabling it and then clearing the overflow status indication bit.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU39. #GP May be Signaled When Invalid VEX Prefix Precedes Conditional
Branch Instructions
Problem: When a 2-byte opcode of a conditional branch (opcodes 0F8xH, for any value of x)
instruction resides in 16-bit code-segment and is associated with invalid VEX prefix, it
may sometimes signal a #GP fault (illegal instruction length > 15-bytes) instead of a
#UD (illegal opcode) fault.
Implication: Due to this erratum, #GP fault instead of a #UD may be signaled on an illegal
instruction.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU40. Interrupt From Local APIC Timer May Not Be Detectable While Being
Delivered
Problem: If the local-APIC timer’s CCR (current-count register) is 0, software should be able to
determine whether a previously generated timer interrupt is being delivered by first
reading the delivery-status bit in the LV T timer register and then reading the bit in the
IRR (interrupt-request register) corresponding to the vector in the L VT timer register. If
both values are read as 0, no timer interrupt should be in the process of being
delivered. Due to this erratum, a timer interrupt may be delivered even if the CCR is 0
and the LVT and IRR bits are read as 0. This can occur only if the DCR (Divide
Configuration Register) is greater than or equal to 4. The erratum does not occur if
software writes zero to the Initial Count Register before reading the LVT and IRR bits.
Implication: Software that relies on reads of the LVT and IRR bits to determine whether a timer
interrupt is being delivered may not operate properly.
Workaround: Software that uses the local-APIC timer must be prepared to handle the timer
interrupts, even those that would not be expected based on reading CCR and the LVT
and IRR bits; alternatively, software can avoid the problem by writing zero to the Initial
Count Register before reading the LVT and IRR bits.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
32 Specification Update
Page 33

BU41. PCI Express* Differential Peak-Peak Tx Voltage Swing May Violate the
Specification
Problem: Under certain conditions, including extreme voltage and temperature, the peak-peak
voltage may be higher than the specification.
Implication: Violation of PCI Express® Base Specification of the VTX--DIFF-PP voltage. No failures
have been observed due to this erratum.
Workaround: None identified.
BU42. PCMPESTRI, PCMPESTRM, VPCMPESTRI and VPCMPESTRM Always
Operate with 32-bit Length Registers
Problem: In 64-bit mode, using REX.W=1 with PCMPESTRI and PCMPESTRM or VEX.W=1 with
VPCMPESTRI and VPCMPESTRM should support a 64-bit length operation with RAX/
RDX. Due to this erratum, the length registers are incorrectly interpreted as 32-bit
values.
Implication: Due to this erratum, using REX.W=1 with PCMPESTRI and PCMPESTRM as well as
VEX.W=1 with VPCMPESTRI and VPCMPESTRM do not result in promotion to 64-bit
length registers.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU43. Multiple Performance Monitor Interrupts are Possible on Overflow of
Fixed Counter 0
Problem: The processor can be configured to issue a PMI (performance monitor interrupt) upon
overflow of the IA32_FIXED_CTR0 MSR (309H). A single PMI should be observed on
overflow of IA32_FIXED_CTR0, however multiple PMIs are observed when this erratum
occurs.
This erratum only occurs when IA32_FIXED_CTR0 overflows and the processor and
counter are configured as follows:
•Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology is enabled
• IA32_FIXED_CTR0 local and global controls are enabled
• IA32_FIXED_CTR0 is set to count events only on its own thread
(IA32_FIXED_CTR_CTRL MSR (38DH) bit [2] = ‘0).
• PMIs are enabled on IA32_FIXED_CTR0 (IA32_FIXED_CTR_CTRL MSR bit [3] = ‘1)
• Freeze_on_PMI feature is enabled (IA32_DEBUGCTL MSR (1D9H) bit [12] = ‘1)
Implication: When this erratum occurs there may be multiple PMIs observed when
IA32_FIXED_CTR0 overflows.
Workaround: Disable the FREEZE_PERFMON_ON_PMI feature in IA32_DEBUGCTL MSR (1D9H)
bit [12].
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 33
Page 34

BU44. IA32_FEATURE_CONTROL MSR May be Uninitialized on a Cold Reset
Problem: IA32_FEATURE_CONTROL MSR (3Ah) may have random values after RESET (including
the reserved and Lock bits), and the read-modify-write of the rese rved bits and/or the
Lock bit being incorrectly set may cause an unexpected GP fault.
Implication: Due to this erratum, an unexpected GP fault may occur and BIOS may not complete
initialization.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU45. DR6.B0-B3 May Not Report All Breakpoints Matched When a MOV/POP
SS is Followed by a REP MOVSB or STOSB
Problem: Normally, data breakpoints matches that occur on a MOV SS, r/m or POP SS will not
cause a debug exception immediately after MOV/POP SS but will be delayed until the
instruction boundary following the next instruction is reached. After the debug
exception occurs, DR6.B0-B3 bits will contain information about data breakpoints
matched during the MOV/POP SS as well as breakpoints detected by the following
instruction. Due to this erratum, DR6.B0-B3 bits may not contain information about
data breakpoints matched during the MOV/POP SS when the following instruction is
either an REP MOVSB or REP STOSB.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, DR6 may not contain information about all breakpoints
matched. This erratum will not be observed under the recommended usage of the MOV
SS,r/m or POP SS instructions (i.e., following them only with an instruction that writes
(E/R)SP).
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU46. Setting Hardware Autonomous Speed Disable Configuration Bit Will
Block Initial Speed Upgrade
Problem: The PCI Express* Base Specification Revision 3.0 states that the Hardware
Autonomous Speed Disable bit (Link Control Register 2, bit 5) does not block the initial
transition to the highest supported common link speed. Setting this bit will block all
autonomous speed changes.
Implication: Due to this erratum, if the Hardware Autonomous Speed Disable bit is set, a given PCIe
link may remain at 2.5 GT/s transfer rate. This erratum has not been observed with any
commercially available add-in cards.
Workaround: It is possible for software to initiate a directed speed change.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU47. LTR Message is Not Treated as an Unsupported Request
Problem: The PCIe* root port does not support LTR (Latency Tolerance Reporting) capability.
However, a received LTR message is not treated as a UR (Unsupported Request).
Implication: Due to this erratum, an LTR message does not generate a UR error.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
34 Specification Update
Page 35

BU48. 64-bit REP MOVSB/STOSB May Clear The Upper 32-bits of RCX, RDI
And RSI Before Any Data is Transferred
Problem: If a REP MOVSB/STOSB is executed in 64-bit mode with an address size of 32 bits, and
if an interrupt is being recognized at the start of the instruction operation, the upper
32-bits of RCX, RDI and RSI may be cleared, even though no data has yet been copied
or written.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the upper 32-bits of RCX, RDI and RSI may be prematurely
cleared.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU49. An Interrupt Recognized Prior to First Iteration of REP MOVSB/STOSB
May Result EFLAGS.RF Being Incorrectly Set
Problem: If a REP MOVSB/STOSB is executed and an interrupt is recognized prior to completion
of the first iteration of the string operation, EFLAGS may be saved with RF=1 even
though no data has been copied or stored. The Software Developer’s Manual states that
RF will be set to 1 for such interrupt conditions only after the first iteration is complete.
Implication: Software may not operate correctly if it relies on the value saved for EFLAGS.RF when
an interrupt is recognized prior to the first iteration of a string instruction. Debug
exceptions due to instruction breakpoints are delivered correctly despite this erratum;
this is because the erratum occurs only after the processor has evaluated instructionbreakpoint conditions.
Workaround: Software whose correctness depends on value saved for EFLAGS.RF by delivery of the
affected interrupts can disable fast-string operation by clearing F ast- String Enable in bit
0 in the IA32_MISC_ENABLE MSR (1A0H).
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU50. Accessing Physical Memory Space 0-640K through the Graphics
Aperture May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior
Problem: The physical memory space 0-640K when accessed through the graphics aperture may
result in a failure for writes to complete or reads to return incorrect results.
Implication: A hang or functional failure may occur during graphics operation such as OGL or OCL
conformance tests, 2D/3D games and graphics intensive application.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU51. PEBS May Unexpectedly Signal a PMI After The PEBS Buffer is Full
Problem: The Software Developer’s Manual states that no PMI should be generated when PEBS
index reaches PEBS Absolute Maximum. Due to this erratum, a PMI may be generated
even though the PEBS buffer is full.
Implication: PEBS may trigger a PMI even though the PEBS index has reached the PEBS Absolute
Maximum.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 35
Page 36

BU52. Instructions Retired Event May Over Count Execution of IRET
Instructions
Problem: Under certain conditions, the performance monitoring event Instructions Retired (Event
C0H, Unmask 00H) may over count the execution of IRET instruction.
Implication: Due to this erratum, performance monitoring event Instructions Retired may over
count.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU53. PCIe* Link May Unexpectedly Exit Loopback State
Problem: The PCIe Port is capable of functioning as 3 independent PCIe controllers. Due to this
erratum, if more than one of the controllers is in Loopback.Active state and configured
as a loopback slave and if any one of these controllers transition to Loopback.Exit, all
controllers in Loopback.Active will transition to Loopback.Exit.
Implication: Loopback.Active state on a given Link may unexpectedly exit. Software should avoid
configuring more than one of the PCIe Controllers as Loopback slave concurrently.
Workaround: PCIe endpoints should avoid configuring more than one of PCIe Controllers as Loopback
slave.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU54. The RDRAND Instruction Will Not Execute as Expected
Problem: On processors that support the RDRAND instruction, that capability should be reported
via the setting of CPUID.01H:ECX.RDRAND[bit 30]. Due to this erratum, that bit will
not be set, and the execution of the RDRAND instruction will result in a #UD exception.
Implication: Software will not be able to utilize the RDRAND instruction
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum to report RDRAND
as present via CPUID and allow proper execution of RDRAND.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU55. A PCIe* Device That Initially Transmits Minimal Posted Data Credits
May Cause a System Hang
Problem: Under certain conditions, if a PCIe device that initially transmits posted data credits
less than Max_Payload_Size/16 + 4 (16B/4DW is unit of data flow control) and is the
target of a Peer-to-Peer write of Max_Payload_Size, the system may hang due to
Posted Data credit starvation.
Implication: Under certain conditions, the processor may encounter a Posted Data credit starvation
scenario and hang.
Workaround: A BIOS code change has been identified and may be implemented as a workaround for
this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
36 Specification Update
Page 37

BU56. PCI Express* Gen3 Receiver Return Loss May Exceed Specifications
Problem: The PCIe Base Specification includes a graph that sets requirements for maximum
receiver return loss versus frequency. Due to this erratum, the receiver return loss for
common mode and differential mode may exceed those requirements at certain
frequencies. Under laboratory conditions, Intel has observed violations of as much as
dB.
1
Implication: The PCI Express Gen3 Base Specification for receiver return loss may be exceeded. No
functional failures have been observed due to this erratum.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU57. Direct Access Via VT-d to The Processor Graphics Device May Lead to a
System Hang
Problem: Under a complex set of conditions, while using VT-d (Virtualization Technology for
Directed I/O) with the processor graphics device, direct access to the virtualized
processor graphics device can lead to a system hang or restart.
Implication: Systems providing direct access to processor graphics device via VT-d may hang or
restart. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available system.
Workaround: VMM’s should ensure that all processor graphics device interactions conform to
guidance published in the Intel® Open Source HD Graphics Programmer's Reference
Manual and driver writers guide.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU58. An Event May Intervene Before a System Management Interrupt That
Results from IN or INS
Problem: If an I/O instruction (IN, INS, OUT, or OUTS) results in an SMI (system-management
interrupt), the processor will set the IO_SMI bit at offset 7FA4H in SMRAM. This
interrupt should be delivered immediately after execution of the I/O instruction so that
the software handling the SMI can cause the I/O instruction to be re-executed. Due to
this erratum, it is possible for another event (e.g., a nonmaskable interrupt) to be
delivered before the SMI that follows the execution of an IN or INS instruction.
Implication: If software handling an affected SMI uses I/O instruction restart, the handler for the
intervening event will not be executed.
Workaround: The SMM handler has to evaluate the saved context to determine if the SMI was
triggered by an instruction that read from an I/O port. The SMM handler must not
restart an I/O instruction if the platform has not been configured to generate a
synchronous SMI for the recorded I/O port address.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 37
Page 38

BU59. PCIe* May Associate Lanes That Are Not Part of Initial Link Training to
L0 During Upconfiguration
Problem: The processor should not associate any lanes that were not part of the initial link
training in subsequent upconfiguration requests from an endpoint. Due to this erratum,
the processor may associate any Lane that has exited Electrical Idle, even if it is
beyond the width of the initial Link training.
Implication: Upconfiguration requests may result in a Link wider than the initially-traine d Link.
Workaround: Endpoints must ensure that upconfiguration requests do not request a Link width wider
than that negotiated during initial Link training.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU60. The Processor May Not Comply With PCIe* Equalization Preset
Reflection Requirements for 8 GT/s Mode of Operation
Problem: In endpoint-initiated transitions to Polling.Compliance at the 8 GT/s transfer rate, the
processor must reflect, in its ordered sets, the Transmitter Preset requested by the
endpoint regardless of preset legality . Due to this erratum, the processor will reflect the
Transmitter Preset in use after an endpoint requests a reserved Transmitter Preset
rather than the requested preset.
Implication: Endpoints requiring reserved Transmitter Presets to be reflected may be adversely
affected. Intel has not observed failures due to this erratum with any commercially
available devices.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU61. Processor May Issue PCIe* EIEOS at Incorrect Rate
Problem: When initiating a Secondary Bus Reset or Link Disable procedure while a PCIe Link is in
Recovery state, the processor should send an EIEOS (Electrical Idle Exit Ordered Set)
after every 32 TS (Training Set) Ordered Sets. Due to this erratum, the processor may
send an EIEOS after every 33 TS Ordered Sets.
Implication: The processor may send an incorrect number of TS Ordered Sets between two EIEOS
Ordered Sets when it initiates Secondary Bus Reset or Link Disable. Intel has not
observed any failures with commercially available devices due to this erratum.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU62. Reduced Swing Output Mode Needs Zero De-emphasis to be
Supported in PCIe* 5GT/s Speed
Problem: It may not be possible to support the PCIe Transmitter Preset 1 and/or Transmitter
Preset 0 equalization requests in Phase 0 or Phase 2 of Recovery.Equalization LTSSM
states when operating in 8GT/s in reduced or half swing mode, if 0dB transmitter de-
emphasis needs to be supported when operating at 5GT/s.
Implication: This erratum does not affect normal full swing mode of operation. Endpoints requiring
0dB support in half-swing mode should avoid requesting Transmitter Preset 1 and/or
Transmitter Preset 0 as preset requests in Phase 0 or Phase 2 of Recovery.Equalization
when operating in 8GT/s.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
38 Specification Update
Page 39

BU63. PCIe* Root-port Initiated Compliance State Transmitter Equalization
Settings May be Incorrect
Problem: If the processor is directed to enter PCIe Polling.Compliance at 5.0 GT/s or 8.0 GT/s
transfer rates, it should use the Link Control 2 Compliance Preset/De-emphasis field
(bits [15:12]) to determine the correct de-emphasis level. Due to this erratum, when
the processor is directed to enter Polling.Compliance from 2.5 GT/s transfer rate, it
retains 2.5 GT/s de-emphasis values.
Implication: The processor may operate in Polling.Compliance mode with an incorrect transmitter
de-emphasis level.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU64. PCIe* Controller May Incorrectly Log Errors on Transition to RxL0s
Problem: Due to this erratum, if a link partner transitions to RxL0s state within 20 ns of entering
L0 state, the PCIe controller may incorrectly log an error in ?Correctable Error
Status.Receiver Error Status? field (Bus 0, Device 2, Function 0, 1, 2 and Device 6,
Function 0, offset 1D0H, bit 0).
Implication: Correctable receiver errors may be incorrectly logged. Intel has not observed any
functional impact due to this erratum with any commercially available add-in cards.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU65. Reception of Certain Malformed Transactions May Cause PCIe* Port to
Hang Rather Than Reporting an Error
Problem: If the processor receives an upstream malformed non posted packet for which the type
field is IO, Configuration or the deprecated TCfgRd and the format is 4 DW header, then
due to this erratum the integrated PCIe controller may hang instead of reporting the
malformed packet error or issuing an unsupported request completion transaction.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor may hang without reporting errors when receiving a
malformed PCIe transaction. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially
available device.
Workaround: None identified. Upstream transaction initiators should avoid issuing unsupported
requests with 4 DW header formats.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU66. PCIe* Link Width May Degrade After a Warm Reset
Problem: PCIe link width may degrade after a warm reset if the Link is operating at 8.0 GT/s or
5.0 GT/s transfer speeds prior to the reset.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the PCIe link may retain to a narrower width, e.g. from x16 to x4.
Workaround: A BIOS code change has been identified and may be implemented as a workaround for
this erratum. .
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 39
Page 40

BU67. MSR_PKG_Cx_RESIDENCY MSRs May Not be Accurate
Problem: If the processor is in a package C-state for an extended period of time (greater
than 40 seconds) with no wake events, the value in the
MSR_PKG_C{2,3,6,7}_RESIDENCY MSRs (60DH and 3F8H–3FAH) will not be accurate.
Implication: Utilities that report C-state residency times will report incorrect data in cases of long
duration package C-states.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU68. Execution of Package C7 May Result in a Hang
Problem: Under certain conditions, execution of Package C7 may result in a system hang on a
subsequent C7 exit.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor package may not exit Package C7, resulting in a
system hang.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU69. PCIe* Link May Not Enter Loopback.Active When Directed
Problem: When an endpoint directs the processor to enter loopback slave mode at 8 GT/s via TS1
ordered sets with both the Loopback and Compliance Receive bits set, the PCIe link
should directly enter Loopback.Active state. Due to this erratum, the processor must
achieve block alignment on all looped back lanes prior to entering Loopback.Active.
Implication: The processor will not enter Loopback.Active state as a loopback slave if any lane in a
link cannot achieve block alignment.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU70. Execution of VAESIMC or VAESKEYGENASSIST With An Illegal Value
for VEX.vvvv May Produce a #NM Exception
Problem: The VAESIMC and VAESKEYGENASSIST instructions should produce a #UD (Invalid-
Opcode) exception if the value of the vvvv field in the VEX prefix is not 1111b. Due to
this erratum, if CR0.TS is “1”, the processor may instead produce a #NM (Device-Not-
Available) exception.
Implication: Due to this erratum, some undefined instruction encodings may produce a #NM instead
of a #UD exception.
Workaround: Software should always set the vvvv field of the VEX prefix to 1111b for instances of
the VAESIMC and VAESKEYGENASSIST instructions.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU71. Unexpected #UD on VZEROALL/VZEROUPPER
Problem: Execution of the VZEROALL or VZEROUPPER instructions in 64-bit mode with VEX.W set
to 1 may erroneously cause a #UD (invalid-opcode exception).
Implication: The affected instructions may produce unexpected invalid-opcode exceptions in 64-bit
mode.
Workaround: Compilers should encode VEX.W = 0 for the VZEROALL and VZEROUPPER instructions.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
40 Specification Update
Page 41

BU72. PCIe* Root Port May Not Initiate Link Speed Change
Problem: The PCIe Base specification requires the upstream component to maintain the PCIe link
at the target link speed or the highest speed supported by both components on the
link, whichever is lower. PCIe root port will not initiate the link speed change without
being triggered by the software when the root port maximum link speed is configured
to be 5.0 GT/s. System BIOS will trigger the link speed change under normal boot
scenarios. However, BIOS is not involved in some scenarios such as link disable/reenable or secondary bus reset and therefore the speed change may not occur unless
initiated by the downstream component. This erratum does not affect the ability of the
downstream component to initiate a link speed change. All known 5.0Gb/s-capable
PCIe downstream components have been observed to initiate the link speed change
without relying on the root port to do so.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the PCIe root port may not initiate a link speed change during
some hardware scenarios causing the PCIe link to operate at a lower than expected
speed. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available platform.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU73. Successive Fixed Counter Overflows May be Discarded
Problem: Under specific internal conditions, when using Freeze PerfMon on PMI feature (bit 12 in
IA32_DEBUGCTL.Freeze_PerfMon_on_PMI, MSR 1D9H), if two or more PerfMon Fixed
Counters overflow very closely to each other, the overflow may be mishandled for some
of them. This means that the counter’s overflow status bit (in
MSR_PERF_GLOBAL_STATUS, MSR 38EH) may not be updated properly; additionally,
PMI interrupt may be missed if software programs a counter in Sampling-Mode (PMI bit
is set on counter configuration).
Implication: Successive Fixed Counter overflows may be discarded when Freeze PerfMon on PMI is
used.
Workaround: Software can avoid this by:
1. Avoid using Freeze PerfMon on PMI bit
2. Enable only one fixed counter at a time when using Freeze PerfMon on PMI
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU74. Execution of FXSAVE or FXRSTOR With the VEX Prefix May Produce a
#NM Exception
Problem: Attempt to use FXSAVE or FXRSTOR with a VEX prefix should produce a #UD (Invalid-
Opcode) exception. If either the TS or EM flag bits in CR0 are set, a #NM (device-not-
available) exception will be raised instead of #UD exception.
Implication: Due to this erratum a #NM exception may be signaled instead of a #UD exception on
an FXSAVE or an FXRSTOR with a VEX prefix.
Workaround: Software should not use FXSAVE or FXRSTOR with the VEX prefix.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 41
Page 42

BU75. VM Exits Due to “NMI-Window Exiting” May Not Occur Following a VM
Entry to the Shutdown State
Problem: If VM entry is made with the “virtual NMIs” and “NMI-window exiting”, VM-execution
controls set to 1, and if there is no virtual-NMI blocking after VM entry, a VM exit with
exit reason “NMI window” should occur immediately after VM entry unless the VM entry
put the logical processor in the wait-for SIPI state. Due to this erratum, such VM exits
do not occur if the VM entry put the processor in the shutdown state.
Implication: A VMM may fail to deliver a virtual NMI to a virtual machine in the shutdown state.
Workaround: Before performing a VM entry to the shutdown state, software should check whether
the “virtual NMIs” and “NMI-window exiting” VM-execution controls are both 1. If they
are, software should clear “NMI-window exiting” and inject an NMI as part of VM entry.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU76. Execution of INVVPID Outside 64-Bit Mode Cannot Invalidate
Translations For 64-Bit Linear Addresses
Problem: Executions of the INVVPID instruction outside 64-bit mode with the INVVPID type
“individual-address invalidation” ignore bits 63:32 of the linear addres s in the INVV PID
descriptor and invalidate translations for bits 31:0 of the linear address.
Implication: The INVVPID instruction may fail to invalidate translations for linear addresses that set
bits in the range 63:32. Because this erratum applies only to executions outside 64-bit
mode, it applies only to attempts by a 32-bit virtual-machine monitor (VMM) to
invalidate translations for a 64-bit guest. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU77. PCIe* Controller May Not Properly Indicate Link Electrical Idle
Condition
Problem: The processor supports a x16 PCIe* port, which can be bifurcated into three
independent links, enumerated as Bus 0, Device 1, Function 0-2. Due to this erratum, if
the port is bifurcated and Function 1 or 2 is disabled, the PCIe controller may not
properly indicate Link electrical idle condition to the Power Control Unit.
Implication: An incorrect Link electrical idle indication may prevent the processor from entering the
lowest power mode, which may cause higher power consumption on VccIO and VccSA.
Intel has not observed any functional failure or performance impact due to this
erratum.
Workaround: If Bus 0, Device 1, Function 1 or 2 is disabled, do not configure the x16 port to allo cate
lanes to those functions.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
42 Specification Update
Page 43

BU78. PCIe* Controller May Not Enter Loopback
Problem: The PCIe controller is expected to enter loopback if any lane in the link receives two
consecutive TS1 ordered sets with the Loopback bit set. Due to this erratum, if two
consecutive TS1 ordered sets are received only on certain lanes, the controller may not
enter loopback.
Implication: Intel has not observed any functional issue with any commercially available PCIe
devices.
Workaround: None Identified
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU79. Link Margin Characterization May Hang Link
Problem: The processor supports tools and mechanisms to characterize and measure margins for
the PCIe interface. Due to this erratum, when performing link margin-to-failure
characterization, it is possible that a high bit error rate may cause the link to hang.
Implication: Under extreme conditions, poor link quality during link characterization may result in
processor hang. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available
platforms under normal operating conditions.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU80. Unused PCIe* Lanes May Report Correctable Errors
Problem: Due to this erratum, during PCIe* link down configuration, unused lanes may report a
Correctable Error Detected in Bus 0, Device 1, Function 0-2, and Device 6, Function 0,
Offset 158H, Bit 0.
Implication: Correctable Errors may be reported by a PCIe controller for unused lanes.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU81. RDMSR of IA32_PERFEVTSEL{4-7} May Return Erroneous Information
Problem: When CPUID.0AH:EAX[15:8] reports 8 general-purpose performance monitoring
counters per logical processor, RDMSR of IA32_PERFEVTSEL{4-7} (MSR 18AH-18DH)
may not return the same value previously written by software.
Implication: Software should not rely on values read from these MSRs.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 43
Page 44

BU82. PCIe* Link May Fail Link Width Upconfiguration
Problem: The processor supports PCIe Hardware Autonomous Width management, in which a
PCIe link can autonomously vary its width. Due to this erratum, a link that performs a
speed change while in a reduced width may no longer be able to return to a wider link
width.
Implication: PCIe links that perform speed changes while at a reduced link width may be limited to
the link width in effect at the time of the speed change. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available devices or platforms.
Workaround: A BIOS code change has been identified and may be implemented as a workaround for
this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU83. Graphics L3 Cache Parity Errors May Not be Detected
Problem: The graphics engine should detect parity errors within the Graphics L3 cache. However,
due to this erratum, graphics L3 cache parity errors may not be detected.
Implication: There may be undetected parity errors from workloads submitted to the execution units
of the graphics engine leading to unpredictable graphics system behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the graphics driver to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU84. A PCIe* Link That is in Link Disable State May Prevent DDR I/O
Buffers From Entering a Power Gated State
Problem: When entering Link Disable L TSSM state, the PCIe controller may not properly indicate
the Link electrical idle condition.
Implication: An incorrect Link electrical idle indication may prevent the DDR I/O buffers from
entering a power gated state, which may cause higher power consumption on VccIO
and VccSA. Intel has not observed any functional failure or performance impact due to
this erratum.
Workaround: A BIOS code change has been identified and may be implemented as a workaround for
this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU85. Graphics L3 Cache Redundancy May Not Behave as Expected
Problem: The processor graphics L3 cache is designed to have redundancy to improve resilience
to cache related errors. Due to this erratum, that redundancy may not function as
expected, resulting in a potential increase in L3 cache related errors.
Implication: Under certain conditions, the lack of redundancy may lead to unpredictable graphics
system behavior when processor graphics L3 cache is utilized.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
44 Specification Update
Page 45

BU86. REP MOVSB May Incorrectly Update ECX, ESI, and EDI
Problem: Under certain conditions, if the execution of a REP MOVSB instruction is interrupted,
the values of ECX, ESI and EDI may contain values that represent a later point in the
execution of the instruction than the actual interruption point.
Implication: Due to this erratum ECX, ESI, and EDI may be incorrectly advanced, resulting in
unpredictable system behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
BU87. Performance-Counter Ov erflow Indication May Cause Undesired
Behavior
Problem: Under certain conditions (listed below) when a performance counter overflows, its
overflow indication may remain set indefinitely. This erratum affects the general-
purpose performance counters IA32_PMC{0-7} and the fixed-function performance
counters IA32_FIXED_CTR{0-2}. The erratum may occur if any of the following
conditions are applied concurrent to when an actual counter overflow condition is
reached:
1. Software disables the counter either globally through the IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL
MSR (38FH), or locally through the IA32_PERFEVTSEL{0-7} MSRs (186H-18DH), or the
IA32_FIXED_CTR_CTRL MSR (38DH).
2. Software sets the IA32_DEBUGCTL MSR (1D9H) FREEZE_PERFMON_ON_PMI bit
[12].
3. The processor attempts to disable the counters by updating the state of the
IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL MSR (38FH) as part of transitions such as VM exit, VM entry ,
SMI, RSM, or processor C-state.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the corresponding overflow status bit in
IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_STATUS MSR (38DH) for an affected counter may not get cleared
when expected. If a corresponding counter is configured to issue a PMI (performance
monitor interrupt), multiple PMIs may be signaled from the same overflow condition.
Likewise, if a corresponding counter is configured in PEBS mode (applies to only the
general purpose counters), multiple PEBS events may be signaled.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
BU88. RDMSR of IA32_PERFEVTSEL4-7 May Return an Incorrect Result
Problem: When CPUID.A.EAX[15:8] reports 8 general-purpose performance monitoring counters
per logical processor, RDMSR of IA32_PERFEVTSEL4-7 (MSR 18AH:18DH) may not
return the same value as previously written.
Implication: Software should not rely on the value read from these MSRs. Writing these MSRs
functions as expected.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
Specification Update 45
Page 46

BU89. VEX.L is Not Ignored with VCVT*2SI Instructions
Problem: The VEX.L bit should be ignored for the VCVTSS2SI, VCVTSD2SI, VCVTTSS2SI, and
VCVTTSD2SI instructions, however du e to this err atum the VEX.L bit is not ignored and
will cause a #UD.
Implication: Unexpected #UDs will be seen when the VEX.L bit is set to 1 with VCVTSS2SI,
VCVTSD2SI, VCVTT SS2SI, and VCVTTSD2S I instructions .
Workaround: Software should ensure that the VEX.L bit is set to 0 for all scalar instructions.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
BU90. Intel® Turbo Boost Technology May be Incorrectly Reported as
Supported on Intel
Problem: The Intel® Core™ i3-3217U processor may incorrectly report support for Intel® Turbo
Boost Technology via CPUID.06H.EAX bit 1.
Implication: The CPUID instruction may report Turbo Boost Technology as supported even though
the processor does not permit operation above the Maximum Non-Turbo Frequency.
Workaround: None identified
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes
®
Core™ i3-3217U
BU91. Concurrently Changing the Memory Type and Page Size May Lead to a
System Hang
Problem: Under a complex set of microarchitectural conditions, the system may hang if software
changes the memory type and page size used to translate a linear address while a TLB
(Translation Lookaside Buffer) holds a valid translation for that linear address.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the system may hang. Intel has not observed this erratum with
any commercially available
Workaround: None identified. Please refer to Software Developer’s Manual, volume 3, section
“Recommended Invalidation” for the proper procedure for concurrently changing page
attributes and page size.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
software.
BU92. MCI_ADDR May be Incorrect Fo r Cache Parity Errors
Problem: In cases when a WBINVD instruction evicts a line containing an address or data parity
error (MCACOD of 0x124, and MSCOD of 0x10), the address of this error should be
logged in the MCi_ADDR register.
incorrect, even though MCi_Status.ADDRV (bit 63) is set.
Implication: The address reported in MCi_ADDR may not be correct for cases of a parity error found
during WBINVD execution.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Due to this erratum, the logged address may be
46 Specification Update
Page 47

BU93. During Package Power States Repeated PCIe* and/or DMI L1
Transitions May Cause a System Hang
Problem: Under a complex set of internal conditions and operating temperature, when the
processor is in a deep power state (package C3, C6 or C7) and the PCIe and/or DMI
links are toggling in and out of L1 state, the system may hang.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the system may hang.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU94. Instruction Fetches Page-Table Walks May be Made Speculatively to
Uncacheable Memory
Problem: Page-table walks on behalf of instruction fetches may be made speculatively to
uncacheable (UC) memory.
Implication: If any paging structures are located at addresses in uncacheable memory that are used
for memory-mapped I/O, such I/O operations may be invoked as a result of speculative
execution that would never actually occur in the executed code path. Intel has not
observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: Software should avoid locating paging structures at addresses in uncacheable memory
that are used for memory-mapped I/O.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU95. The Processor May Not Properly Execute Code Modified Using A Floating-Point
Store
Problem: Under complex internal conditions, a floating-point store used to modify the next
sequential instruction may result in the old instruction being executed instead of the
new instruction.
Implication: Self- or cross-modifying code may not execute as expected. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified. Do not use floating-point stores to modify code.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU96. Execution of GETSEC[SEXIT] May Cause a Debug Exception to be Lost
Problem: A debug exception occurring at the same time that GETSEC[SEXIT] is executed or when
an SEXIT doorbell event is serviced may be lost.
Implication: Due to this erratum, there may be a loss of a debug exception when it happens
concurrently with the execution of GETSEC[SEXIT]. Intel has not observed this erratu m
with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 47
Page 48

BU97. VM Exits Due to GETSEC May Save an Incorrect Value for “Blocking by STI” in the
Context of Probe-Mode Redirection
Problem: The GETSEC instruction causes a VM exit when executed in VMX non-root
operation. Such a VM exit should set bit 0 in the Interruptability-state field in the
virtual-machine control structure (VMCS) if the STI instruction was blocking interrupts
at the time GETSEC commenced execution.
VMX non-root operation may erroneously clear bit 0 if redirection to probe mode occurs
on the GETSEC instruction.
Implication: After returning from probe mode, a virtual interrupt may be incorrectly delivered prior
to GETSEC instruction. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially
software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Due to this erratum, a VM exit executed in
BU98. Specific Graphics Blitter Instructions May Result in Unpredictable Graphics
Controller Behavior
Problem: Specific source-copy blitter instructions in Intel® HD Graphics 2500 and 4000 Processor
may result in unpredictable behavior when a blit source and destination overlap.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor may exhibit unpredictable graphics controller
behavior. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU99. IA32_MC5_CTL2 is Not Clea red by a Warm Reset
Problem: IA32_MC5_CTL2 MSR (285H) is documented to be cleared on any reset. Due to this
erratum this MSR is only cleared upon a cold reset.
Implication: The algorithm documented in Software Developer's Manual, Volume 3, section titled
"CMCI Initialization” or any other algorithm that counts the IA32_MC5_CTL2 MSR being
cleared on reset will not function as expected after a warm reset.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU100. CPUID Instruction May Not Report the Processor Number in the Brand
String for Intel
Problem: When the CPUID instruction is executed with EAX = 80000002H, 80000003H, and
80000004H, the returned brand string may be incomplete; it may be missing the
processor number.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the processor may be missing the processor number in the
brand string. In addition, if the affected processors are paired with the Intel
Chipset BD82UM77 chipset, the BIOS may incorrectly report this combination as
unsupported.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum, except if paired
with the Intel 7 Series Chipset BD82UM77 chipset.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Core™ i3-3227U and i5-3337U Processors.
®
7 Series
BU101. Performance Monitor Counters May Produce Incorrect Results
Problem: When operating with SMT enabled, a memory at-retirement performance monitoring
event (from the list below) may be dropped or may increment an enabled event on the
48 Specification Update
Page 49

corresponding counter with the same number on the physical core’s other thread rather
than the thread experiencing the event. Processors with SMT disabled in BIOS are not
affected by this erratum.
The list of affected memory at-retirement events is as follows:
MEM_UOP_RETIRED.LOADS
MEM_UOP_RETIRED.STORES
MEM_UOP_RETIRED.LOCK
MEM_UOP_RETIRED.SPLIT
MEM_UOP_RETIRED.STLB_MISS
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.HIT_LFB
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.L1_HIT
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.L2_HIT
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.LLC_HIT
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_MISC_RETIRED.LLC_MISS
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_HIT
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_HITM
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_MISS
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_HIT_RETIRED.XSNP_NONE
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.LLC_MISS
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_MISS_RETIRED.LOCAL_DRAM
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_LLC_MISS_RETIRED.REMOTE_DRAM
MEM_LOAD_UOPS_RETIRED.L2_MISS
Implication: Due to this erratum, certain performance monitoring event may produce unreliable
results when SMT is enabled.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU102. The Corrected Error Count Overflow Bit in IA32_ MC0_STATUS is Not
Updated After a UC Error is Logged
Problem: When a UC (uncorrected) error is logged in the IA32_MC0_STATUS MSR (401H),
corrected errors will continue to update the lower 14 bits (bits 51:38) of the Corrected
Error Count. Due to this erratum, the sticky count ov erflow bit (bit 52) of the Corrected
Error Count will not get updated after a UC error is logged.
Implication: The Corrected Error Count Overflow indication will be lost if the overflow occurs after an
uncorrectable error has been logged.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU103. Spurious VT-d Interrupts May Occur When the PFO Bit is Set
Problem: When the PFO (Primary Fault Overflow) field (bit [0] in the VT-d FSTS [Fault Status]
register) is set to 1, further faults should not generate an interrupt. Due to this
erratum, further interrupts may still occur.
Implication: Unexpected Invalidation Queue Error interrupts may occur. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: Software should be written to handle spurious VT-d fault interrupts.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update 49
Page 50

BU104. Processor May Livelock During On Demand Clock Modulation
Problem: The processor may livelock when (1) a processor thread has enabled on demand clock
modulation via bit 4 of the IA32_CLOCK_MODULATION MSR (19AH) and the clock
modulation duty cycle is set to 12.5% (02H in bits 3:0 of the same MSR), and (2) the
other processor thread does not have on demand clock modulation enabled and that
thread is executing a stream of instructions with the lock prefix that either split a
cacheline or access UC memory.
Implication: Program execution may stall on both threads of the core subject to this erratum.
Workaround: This erratum will not occur if clock modulation is enabled on all threads when using on
demand clock modulation or if the duty cycle programmed in the
IA32_CLOCK_MODULATION MSR is 18.75% or higher.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU105. IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM MSR (48AH) Does Not Properly Report The Highest Index
Value Used For VMCS Encoding
Problem: IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM MSR (48AH) bits 9:1 report the highest index value used for
any VMCS encoding.
Due to this erratum, the value 21 is returned in bits 9:1 although
there is a VMCS field whose encoding uses the index value 23.
Implication: Software that uses the value reported in IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM[9:1] to r ead and write
all VMCS fields may omit one field.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU106. The Upper 32 Bits of CR3 May be Incorrectly Used With 32-Bit Paging
Problem: When 32-bit paging is in use, the processor should use a p age dir ectory located at the 32-
bit physical address specified in bits 31:12 of CR3; the upper 32 bi ts of CR3 should be
ignored.
Due to this erratum, the processor will use a page directory located at the 64-bit
physical address specified in bits 63:12 of CR3.
Implication: The processor may use an unexpected page directory or, if EPT (Extended Page Tables)
is in use, cause an unexpected EPT violati on. This erra tum applies only if software enters
64-bit mode, loads CR3 with a 64-bit value, and then returns to 32-bit paging without
changing CR3. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available
software.
Workaround: Software that has exec uted in 64-bit mode should reload CR 3 with a 32-bit value before
returning to 32-bit paging.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU107. EPT Violations May Report Bits 11:0 of Guest Linear Address
Incorrectly
Problem: If a memory access to a linear address requires the processor to update an accessed or
dirty flag in a paging-structure entry and if that update causes an EPT violation, the
processor should store the linear address into the “guest linear address” field in the
VMCS. Due to this erratum, the processor may store an incorrect value into bits 11:0 of
50 Specification Update
Page 51

this field. (The processor correctly stores the guest-physical address of the pagingstructure entry into the “guest-physical address” field in the VMCS.)
Implication: Software may not be easily able to determine the page offset of the original memory
access that caused the EPT violation. Intel has not observed this erratum to impact the
operation of any commercially available software.
Workaround: Software requiring the page offset of the original memory access address can derive it by
simulating the effective address computation of
the instruction that caused the EPT
violation.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU108. IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM MSR (48AH) Does Not Properly Report The
Highest Index Value Used For VMCS Encoding
Problem: IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM MSR (48AH) bits 9:1 report the highest index value used for
any VMCS encoding.
Due to this erratum, the value 21 is returned in bits 9:1 although
there is a VMCS field whose encoding uses the index value 23.
Implication: Software that uses the value reported in IA32_VMX_VMCS_ENUM[9:1] to read and
write all VMCS fields may omit one field.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU109. DMA Remapping Faults for the Graphics VT-d Unit May Not Properly
Report Type of Faulted Request
Problem: When a fault occurs during DMA remapping of Graphics accesses at the Graphics VT-d
unit, the type of faulted request (read or write) should be reported in bit 126 of the
FRCD_REG register in the remapping hardware memory map register set.
Due to this
erratum, the request type may not be reported correctly.
Implication: Software processing the DMA remapping faults may not be able to determine the type
of faulting graphics device DMA request.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU110. Intel® Trusted Execution Technology ACM Authentication Failure
Problem: SINIT ACM 3rd_gen_i5_i7-SINIT_51.BIN or earlier are revoked and will not launch with
new processor configuration information.
Implication: Due to this erratum, SINIT ACM 3rd_gen_i5_i7-SINIT_51.BIN or earlier will fail to run.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum. All Intel® TXT enabled
software must use SINIT ACM 3rd_gen_i5_i7-SINIT_67.BIN or later.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU111. Virtual-APIC Page Accesses With 32-Bit PAE Paging May Cause a
System Crash
Problem: If a logical processor has EPT (Extended Page Tables) enabled, is using 32-bit PAE
paging, and accesses the virtual-APIC page then a complex sequence of internal
Specification Update 51
Page 52

processor micro-architectural events may cause an incorrect address translation or
machine check on either logical processor.
Implication: This erratum may result in unexpected faults, an uncorrectable TLB error logged in
IA32_MCi_STATUS.MCACOD (bits [15:0]) with a value of 0000_0000_0001_xxxxb
(where x stands for 0 or 1), a guest or hyper visor crash, or other unpredictable system
behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
BU112. Address Translation Faults for Intel® VT-d May Not be Reported for
Display Engine Memory Accesses
Problem: The Intel® VT-d (Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O) hardware unit
supporting the Processor Graphics device (Bus 0; Device 2; Function 0) may no t report
address translation faults detected on Display Engine memory accesses when the
Context Cache is disabled or during time periods when Context Cache is being
invalidated.
Implication: Due to this erratum, Display Engine accesses that fault are correctly aborted but may not
be reported in the FSTS_REG fault reporting register (GFXVTDBAR offset 034H).
Workaround: None identified
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
§ §
52 Specification Update
Page 53

Specification Changes
The Specification Changes listed in this section apply to the following documents:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1: Basic
Architecture
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A:
Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B:
Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A:
System Programming Guide
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B:
System Programming Guide
There are no new Specification Changes in this Specification Update revision.
§ §
Specification Update 53
Page 54

Specification Clarifications
The Specification Clarifications listed in this section may apply to the following
documents:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1: Basic
Architecture
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A:
Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B:
Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A:
System Programming Guide
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B:
System Programming Guide
There are no new Specification Changes in this Specification Update revision.
§ §
54 Specification Update
Page 55

Documentation Changes
The Documentation Changes listed in this section apply to the following documents:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1: Basic
Architecture
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A:
Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B:
Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A:
System Programming Guide
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B:
System Programming Guide
All Documentation Changes will be incorporated into a future version of the appropriate
Processor documentation.
Note: Documentation changes for Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture Software Developer's
Manual volumes 1, 2A, 2B, 3A, and 3B will be posted in a separate document, Intel
and IA-32 Architecture Software Developer's Manual Documentation Changes. Follow
the link below to become familiar with this file.
http://developer.intel.com/products/processor/manuals/index.htm
There are no new Documentation Changes in this Specification Update revision.
BU1. On-Demand Clock Modulation Feature Clarification
Software Controlled Clock Modulation section of the Intel
Software Developer's Manual, Volume 3B: S ystem Progr amming Guide will be modified
to differentiate On-demand clock modulation feature on different processors. The
clarification will state:
For Hyper-Threading Technology enabled processors, the IA32_CLOCK_MODULATION
register is duplicated for each logical processor. In order for the On-demand clock
modulation feature to work properly, the feature must be enabled on all the logical
processors within a physical processor. If the programmed duty cycle is not identical for
all the logical processors, the processor clock will modulate to the highest duty cycle
programmed for processors if the CPUID DisplayFamily_DisplayModel signatures is
listed in Table 14-2. For all other processors, if the programmed duty cycle is not
identical for all logical processors in the same core, the processor will modulate at the
lowest programmed duty cycle.
For multiple processor cores in a physical package, each core can modulate to a
programmed duty cycle independently.
For the P6 family processors, on-demand clock modulation was implemented through
the chipset, which controlled clock modulation through the processor’s STPCLK# pin.
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures
®
64
Table 14-2. CPUID Signatures for Legacy Processors That Resolve to Higher
Performance Setting of Conflicting Duty Cycle Requests
Specification Update 55
Page 56

DisplayFamily_Displa
yModel
0F_xx 06_1C 06_1A 06_1E
06_1F 06_25 06_26 06_27
06_2C 06_2E 06_2F 06_35
06_36
DisplayFamily_Display
Model
§ §
DisplayFamily_Displa
yModel
DisplayFamily_Display
Model
56 Specification Update
 Loading...
Loading...