ADE-6050
Intel Core Duo/Solo
945GM Mini ITX Board
User’s Manual
Rev. 1.0
2007/1/8
P/N: 600C002605010

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
Copyright
All rights reserved. The information contained in this guide has been validated and
reviewed for accuracy. No patent liability is assumed with respect to the use of the
information contained herein. While every precaution has been taken in the preparation of
this guide, the Manufacturer assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions.
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in
any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise,
without the prior written permission of Manufacturer.
Trademark
Intel®, Pentium® and Celeron® are registered trademarks of Intel® Corporation.
Microsoft® and Windows® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All products and company names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective holders.
These specifications are subject to change without notice.
Technical Support
We hope you to get the maximum performance from your products and be willing to help if
running into technical difficulties. For the most frequently asked questions, it’s easily found
answers from the product documentation and usually a lot more detailed, so please take
reference to this manual first. If the answer still can not be found, gather all the information
or questions apply ing to the problem, and with the product on hand, contact your distributor,
sales representative, or customer service center for technical support. Most problems
reported are minor and able to be easily solved over the phone. In addition, free technical
support is available and always ready to give advices on application requirements or
specific information on the installation and operation of any of our products.
Please have the following information ready before you call:
1. Product name and serial number
2. Description of your peripheral attachments
3. Description of your software (operating system, version, application software, etc.)
4. A complete description of the problem
5. The exact wording of any error messages
2 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
How to Use This Manual
This manual is written for the system integrator, PC technician and knowledgeable PC end
user. It describes how to configure your system board to meet various operating
requirements. The user’s manual is divided into four chapters, with each chapter
addressing a basic concept and operation of the server board.
Chapter 1: Introduction - presents what you have inside the box and gives you an
overview of the product specifications and basic system architecture for the system board.
Chapter 2: Hardware Configuration Setting - shows the definitions and locations of
Jumpers and Connectors so that you can easily configure your system.
Chapter 3: System Installation - describes how to properly mount the CPU and main
memory for a safe installation. It will also introduce and show you the driver installation
procedure for the Graphics Controller and Ethernet Controller.
Chapter 4: BIOS Setup Information - specifies the meaning of each setup parameter, how
to get advanced BIOS performance.
3 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
Table of Content
1. Introduction..........................................................................................................................8
1.1 Description.......................................................................................................................8
1.2 Packing Check List.........................................................................................................9
1.3 Specifications................................................................................................................10
1.4 System Architecture.....................................................................................................12
1.5 Dimensions.....................................................................................................................13
2. Hardware Configuration Setting.............................................................................15
2.1 Board Layout..................................................................................................................16
2.2 Jumpers & Connectors...............................................................................................17
2.3 Jumpers- Setting & Connectors description.........................................................18
2.3.1 LCD power setting select: JP1..............................................................................18
2.3.2 Clear CMOS setting select: JP2...........................................................................18
2.3.3 Auto power on select: JP3.....................................................................................18
2.3.4 BIOS write protection setting: JP4........................................................................18
2.3.5 Audio connector: CN1 ............................................................................................18
2.3.6 COM2/1 RS232 connectors: CN2 ........................................................................18
2.3.7 PS/2 mouse & keyboard connectors: CN3 .........................................................18
2.3.8 VGA / DVI Connector: CN4 ...................................................................................18
2.3.9 LAN 1 + USB 0/1 & LAN 2 + USB 2/3 Connectors: CN6 & CN5.....................19
2.3.10 Internal USB 4/5 & 6/7 Connectors: CN12 & CN11...........................................19
2.3.11 External K/B & M/S Connector: CN7 ...................................................................19
2.3.12 CD-In Connector: CN8 ...........................................................................................19
2.3.13 Line out Connector: CN9 .......................................................................................20
2.3.14 LVDS Connector: CN10.........................................................................................20
2.3.15 System Fan Connector: CN14..............................................................................20
2.3.16 CPU Fan Connector: CN15...................................................................................20
2.3.17 ATX power Connector: CN16................................................................................20
2.3.18 COM3 / COM4 Connectors: CN18/CN19............................................................20
2.3.19 8-bit Digital I/O Connector: CN20.........................................................................21
2.3.20 Front Panel Connector: CN21...............................................................................21
2.3.21 Primary IDE Connector: IDE1...............................................................................21
2.3.22 Serial ATA Connectors: SATA1, SATA2...............................................................21
4 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
3. System Installation.........................................................................................................23
3.1 Socket 478 Processors ................................................................................................23
3.1.1 Installing CPU..........................................................................................................23
3.2 Installing Cooling Fan..................................................................................................23
3.3 Main Memory..................................................................................................................24
3.4 Installations....................................................................................................................24
4. BIOS Setup ..........................................................................................................................26
4.1 Entering Setup...............................................................................................................26
4.2 Main Menu.......................................................................................................................26
4.2.1 Standard CMOS Features .....................................................................................27
4.2.2 Advanced BIOS Features......................................................................................28
4.2.3 Advanced Chipset Features..................................................................................33
4.2.4 Integrated Peripheral..............................................................................................36
4.2.5 Power Management Setup....................................................................................41
4.2.6 PnP/PCI/PCI-E Configurations .............................................................................44
4.2.7 PC Health Status.....................................................................................................45
4.2.8 Load Fail -Safe Default............................................................................................46
4.2.9 Load Optimized Defaults........................................................................................46
4.2.10 Supervisor/User Password Setting ......................................................................47
4.2.11 Exit Selecting ...........................................................................................................48
5 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
6 / 48
ADE-6050 User’s Manual
CHAPTER 1
7 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
1. Introduction
1.1 Description
The ADE-6050 all-in-one Mini-ITX is designed to fit a high performance IntelR CoreTM Duo
based processor and compatible for high -end computer system applications with PCI bus
architecture to meet today’s demanding pace and keep complete compatibility with
hardware and software designed. The onboard devices support one PCI Express x1 and
one PCI slot, integrated graphics, and onboard dual Marvell Gigabit Ethernet controllers.
It’s beneficial to build up a high performance and high data availability system for VARs, or
system integrators.
The ADE-6050 supports IntelR CoreTM Duo socket M processors built IntelR 945GM and
ICH7M chipset integrated GMA 950 graphics with DVMT 3.0 display memory up to 224 MB
for dual display function by VGA/LVDS, VGA/DVI, and DVI/LVDS. The board supports two
SODIMMs up to 2 GB with dual channel DDR2 533/667, enhanced onboard one PCI-IDE
interface supporting one drive up to PIO mode 4 timing and Ultra ATA 33/66/100
synchronous mode feature, one CF socket interface, and two SATAII high -speed data
transferring at up to 3 GB/s, integrated RealtekR ALC655 AC97 codec. The onboard Super
I/O chipsets support four serial ports: two RS-232 serial port interfaces and two RS-232 pin
headers, Hardware Monitor function, eight Hi-speed USB 2.0 ports offering up to 40X
greater bandwidth over USB 1.1, and two 6-pin Mini-DIN connectors for PS/2 mouse and
keyboard. Besides, high precision Real Time Clock built to support Y2K for accurate
scheduling and storing configuration information, one 20-pin standard connector designed
to support ATX power function, and a feature of CPU overheat protection will provide user
more security and stability.
Target for key embedded applications such as Point of Sales (POS), automated KIOSKs,
medical instruments, advanced automation for buildings and homes, and gaming machines.
All of these features make ADE-6050 excellent in all-in-one applications.
8 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
1.2 Packing Check List
The ADE-6050 package includes the following basic items accompany with this manual.
Ø One Mini ITX ADE-6050 SBC
Ø One Installation Guide for ADE-6050
Ø One 40-pin IDE cable
Ø One Serial ATA cable
Ø One USB cable
Ø One Serial port for RS232 cable
Ø One I/O Shield cover
Ø One Supporting CD Driver contains internal VGA display driver, Ethernet network
controller driver and on board devices drivers
If any of these items is damaged or missed, please contact your vendor and save all
packing materials for future replacement and maintenance.
9 / 48
ADE-6050 User’s Manual
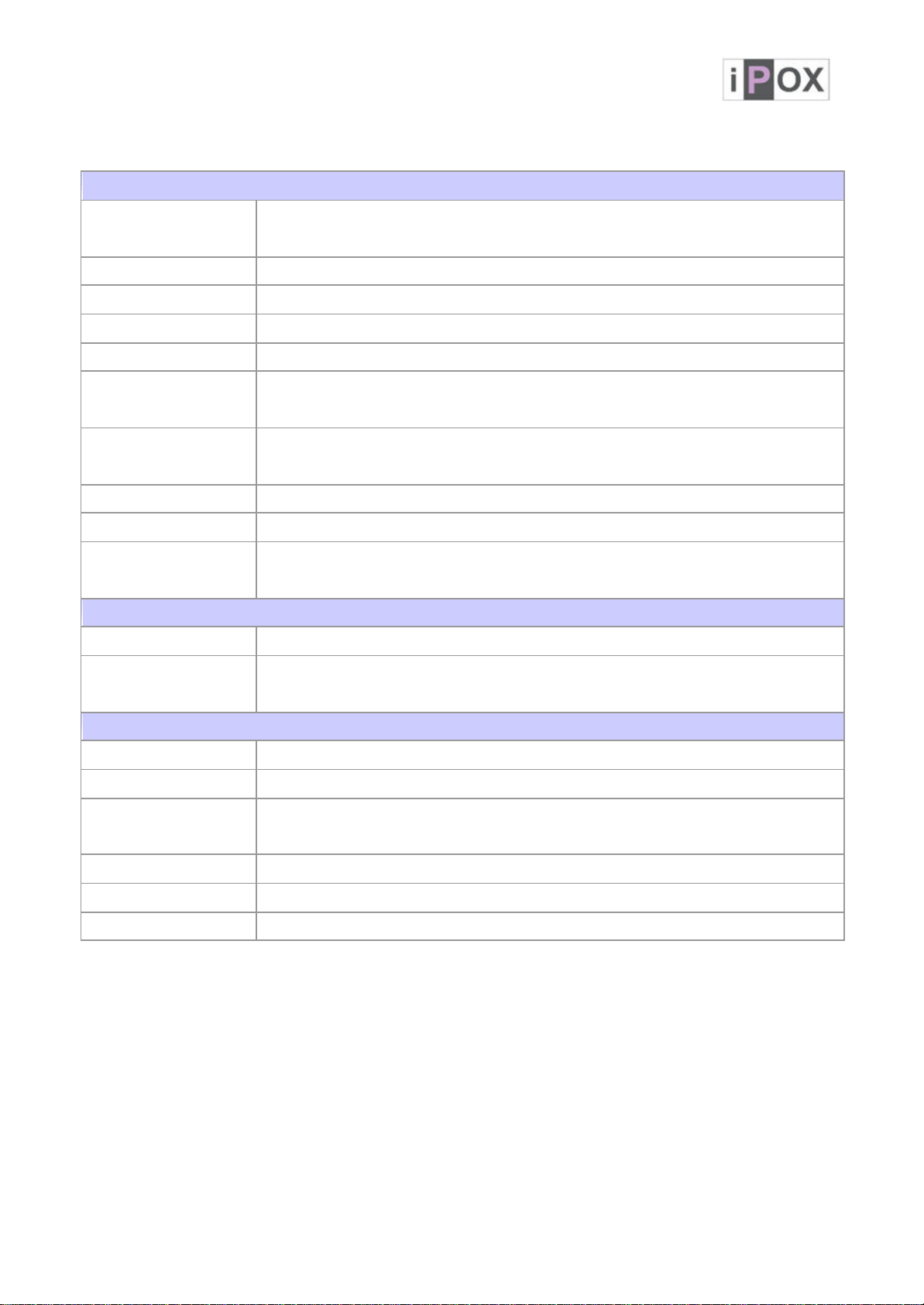
1.3 Specifications
System
CPU
Intel® Core™ Duo / Solo and Celeron® M processor (Yonah Core)
Intel® Core™ 2 Duo Mobile processor on Napa refresh (Merom/Socket M)
FSB FSB 533/667 MHz
BIOS Award BIOS with 4 Mb Flash ROM
System Chipset Intel® 945GM + ICH7M
I/O Chip ITE® IT8712F
2 x 200-pin SODIMM sockets support dual-channel DDR2 533/667
System Memory
SDRAM up to 2GB
1 x Ultra DMA33 supports two IDE devices by 40-Pin IDE connector,
Storage
2 x Serial ATA connectors high-speed data transfer at up to 300 MB/s
SSD 1 x CompactFlash™ Type I/II Socket
Watchdog Timer Reset: 1 sec.~255 min. and 1 sec. or 1 min./step
Monitoring system temperature, voltage, and cooling fan status.
H/W Status Monitor
Auto throttling control when CPU overheats.
MIO
Internal I/O 2 x RS-232, 4 x USB 2.0, 1 x IrDA, 1 x external KB/MS
Rear I/O
1 x KB/MS, 1 X VGA, 1 x DVI, 2 x RS-232, 2 x LAN, 4 x USB,
1 x Audio Jack
Display
Chipset Intel® 945GM + ICH7M
Display Memory Intel® DVMT 3.0 supports u p to 224 MB video memory
Analog Display : up to 2048 x 1536 @ 75MHz video memory(QXGA)
Digital LVDS : up to 2048 x 1536 (QXGA)
VGA/LCD Interface DSUB-15 & DVI connectors
LVDS Dual Channel (2 x 18-bit) LVDS
DVI Chrontel® CH7307 DVI transmitter
10 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
Audio
AC97 Codec Realtek® ALC655 5.1CH 3D audio codec
Audio Interface Line in, Line out, Mic in by jack, CD-in by pin header
Ethernet
Chipset Dual Marvell® 88E8053 PCI -E Gigabit Ethernet controllers
Ethernet Interface IEEE 802.3 10/100/1000 BASE-TX
Mechanical & Environmental
Power Requirement +3.3V@0.32A, +5V@2.67A, +12V@2.13A. 5VSB@0.02A
Power Type 20-pin ATX power connector
Operating Temperature 0~60°C (32~140°F)
Operating Humidity 0%~90% relative humidity, non-condensing
Size (L x W) 6.69" x 6.69" (170 mm x 170 mm)
Weight 0.94lbs (430g)
11 / 48
ADE-6050 User’s Manual
CK-410M
DDR2SODIMM
533/667 X2
Keyboard
533/667 MHz FSB
Super I/O
COM 3 / 4
Marvell 88E8053x2
10/100/1000 Base-TX
PCI-E BUS
PCISLOT
DigitalIO
PCIEby1SLOT
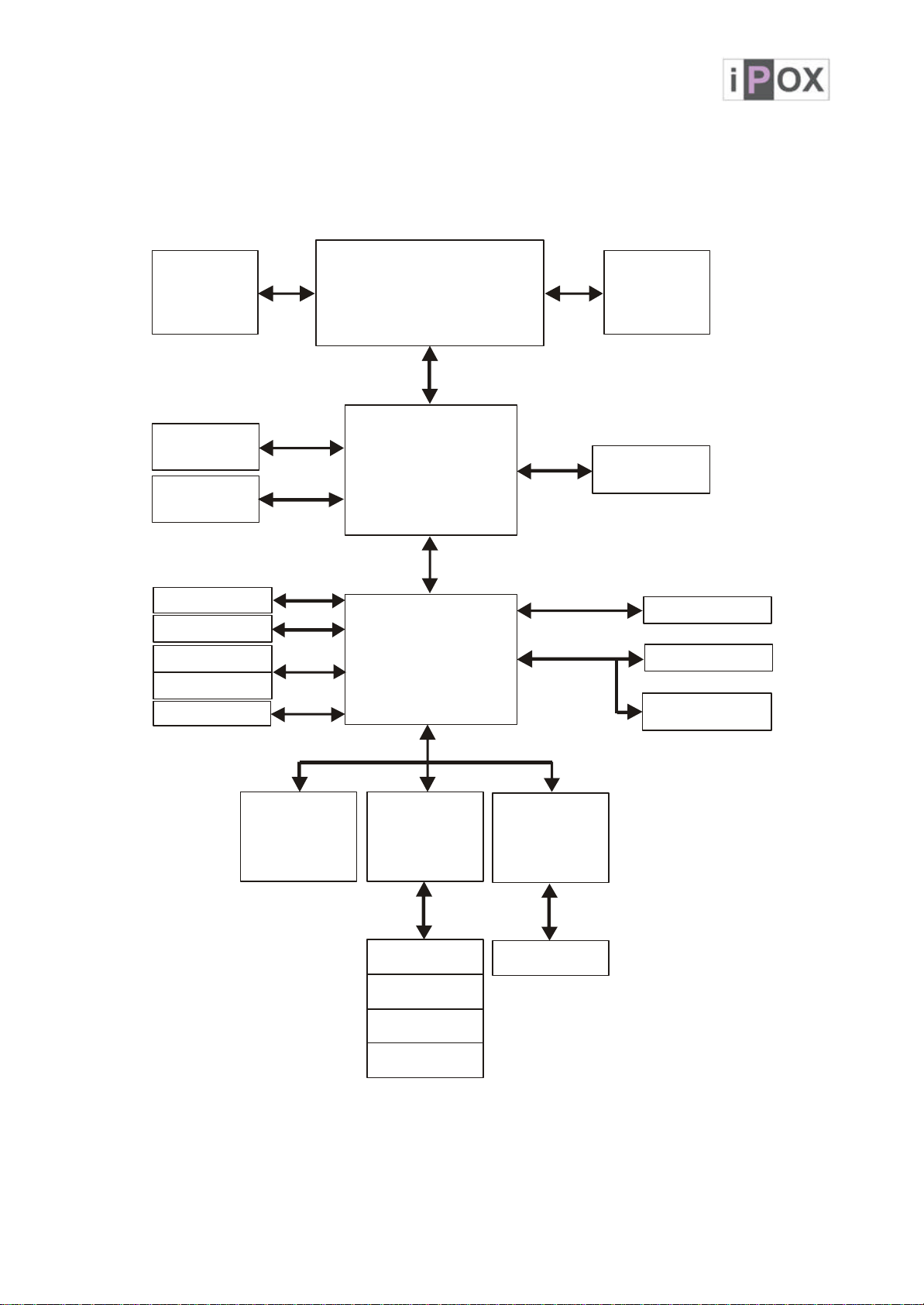
1.4 System Architecture
All of details operating relations are shown in ADE-6050 system block diagram.
Micro FCPGA
IMVP6
CRT & LCD
DVI
for Intel CoreDuoSolo
LVDS
&
VGA
GMCH (945GM)
/
Processor
1466 FCBGA
-
IDE Primary
SATAPort12
/
USB Port 1/2/3/4
USB Port 5/6/7/8
AC97 Audio Codec
ATA100
SATAII
USB2.0
FWH
ICH7M
652 mBGA
Super I/O
IT8712F
Mouse
DMIBus
PCI BUS
IT8712F
-
COM 1 / 2
/
12 / 48
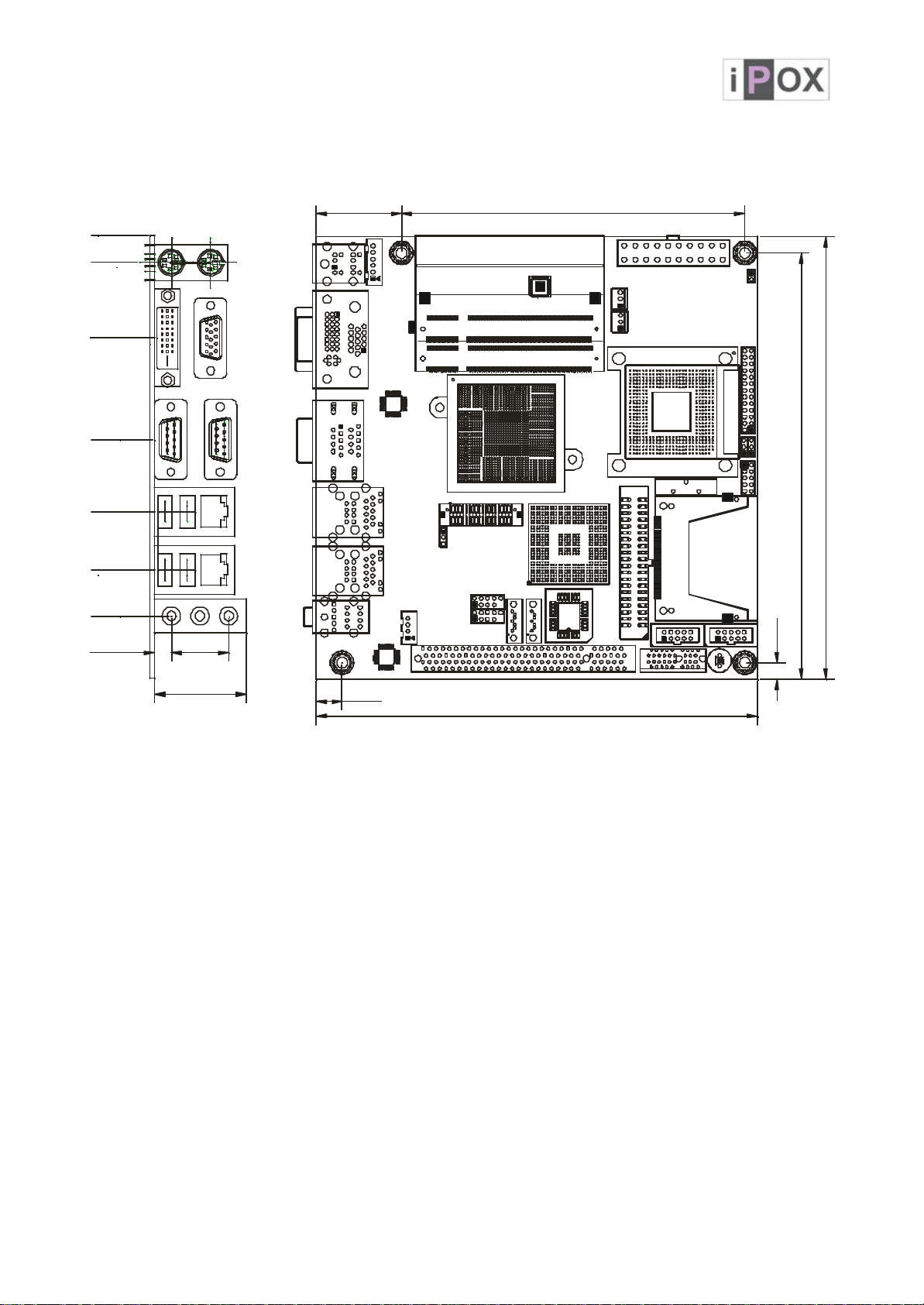
ADE-6050 User’s Manual
33.0
10.2
132.1
6.2163.7170
170
1.5 Dimensions
0
10.51
39.5
78.51
G G
106.17
128.61
146.35
6.5 22.0
35.5
Unit: mm
13 / 48
ADE-6050 User’s Manual
CHAPTER 2
14 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
2. Hardware Configuration Setting
This chapter gives the definitions and shows the positions of jumpers, headers and
connectors. All of the configuration jumpers on the board are in the proper position. The
default settings shipped from factory are marked with an asterisk («).
In general, jumpers on the board are used to select options for certain features. Some of
the jumpers are designed to be user-configurable, allowing for system enhancement. The
others are for testing purpose only and should not be altered. To select any option, cover
the jumper cap over (SHORT) or remove (NC) it from the jumper pins according to the
following instructions. Here, NC stands for “Not Connect”.
15 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
CN12
CN11
EXT. KB/MS
PCI1PCIEX
1
CN14
CN15
CN16
2.1 Board Layout
95P08
AUDIO
CN1
CN8
CDIN
-
LINEOUT
LINEOUT
USB67
LAN2USB23
CN9
USB45
/
SATA2
SATA1
/
/
CN10
LVDS-CONN
LAN1USB01
/
CN6CN5
JP1
CN2
COM1
COM2
DVI
KB/MS
CN3
CRT
CN4
CN7
DIMM2
DIMM1
COM4
CN19
IDE1
CN18
COM3
CF
CN20
JP2
JP4
CN21
ATXPOWER
JP3
16 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
2.2 Jumpers & Connectors
JUMPERS FUNCTION REMARK
JP1
JP2
JP3
JP4
LVDS power select 1 x 3 header
Clear CMOS select 1 x 3 header
Auto power on select 1 x 2 header
BIOS write protection select 1 x 3 header
CONNECTORS FUNCTION REMARK
CN1
CN2
CN3
CN4
CN5
CN6
CN7
CN8
CN9
CN10
Audio connector
COM1/2 RS232 serial port connectors
PS/2 mouse & keyboard connectors
D-sub 15-pin VGA & DVI 24-pin connectors
USB 2, 3 & LAN 2 connectors
USB 0, 1 & LAN 1 connectors
External keyboard & mouse connector 1 x 6 wafer
CD-In connector 1 x 4 header
Line out connector 1 x 4 wafer
LVDS connector HIROSE
CN11
CN12
CN14
CN15
CN16
CN18
CN19
CN20
CN21
IDE1
SATA1, SATA2
CFII
DIMM1/2
PCI
PCIEX1
Internal USB connector 6 & 7 2 x 5 header
Internal USB connector 4 & 5 2 x 5 header
System fan connector 1 x 3 wafer
CPU fan connector 1 x 3 wafer
ATX power connector 2 x 10 connector
COM3 RS-232 serial port pin-header 2 x 5 header
COM4 RS-232 serial port pin-header 2 x 5 header
8-bit Digital I/O pin-header 2 x 5 header
Front panel connector 2 x 13 header
Primary IDE connector 2 x 20 header
Serial ATA1/2 connectors
Type II CompactFlash™ connector
200-pin DDR2 SODIMM socket s
PCI slot
PCI-E by 1 slot
17 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
DCD
6 DSR
2 RXD
7 RTS
3 TXD
8 CTS
4 DTR
9 RI
5 Ground
2.3 Jumpers- Setting & Connectors description
2.3.1 LCD power setting select: JP1 2.3.2 Clear CMOS setting select: JP2
PIN No. Description
1-2 3.3V«
2-3 5V
PIN No. Description
1-2 Normal operation «
2-3 Clear CMOS
2.3.3 Auto power on select: JP3 2.3.4 BIOS write protection setting: JP4
PIN No. Description
1-2 Auto power on
Open Disabled«
PIN No. Description
1-2 Write-protection (Default) «
2-3 Disable
2.3.5 Audio connector: CN1 2.3.6 COM2/1 RS232 connectors: CN2
PIN No. Description
Blue Line-in
Green Speaker out
Pink MIC-in
PIN No.
1
Description PIN No. Description
2.3.7 PS/2 mouse & keyboard connectors: CN3
PS/2 Mouse
PIN No. Description
1 Mouse data
2 NC
3 Ground
4 +5V
5 Mouse clock
6 NC
2.3.8 VGA / DVI Connector: CN4
VGA
PIN No. Description
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Red Signal
Green Signal
Blue Signal
NC
Ground 13 HSYNC
Ground 14 VSYNC
Ground 15 DCC_CLK
Ground
PIN No. Description
9
10
11
12
+5V
Ground
NC
DCC_DATA
18 / 48
PS/2 Keyboard
PIN No. Description
1 Keyboard data
2 NC
3 Ground
4 +5V
5 Keyboard clock
6 NC
PIN No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Description PIN No. Description
TDC2#
TDC2
GND
NC
NC
SC_DDC
SD_DDC
NC
TDC1#
TDC1
GND
NC
DVI
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
NC
DVI_5V
GND
DVI_DET
TDC0#
TDC0
GND
NC
NC
GND
TLC
TLC#

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
2.3.9 LAN 1 + USB 0/1 & LAN 2 + USB 2/3 Connectors: CN6 & CN5
LAN 1/2
PIN No.
1 MDI0+ 5 MDI2+
2 MDI0- 6 MDI23 MDI1+ 7 MDI3+
4 MDI1- 8 MDI3-
Description PIN No. Description
PIN No.
1 +5 V (fused) 5 +5 V (fused)
2 USBP0-/2- 6 USBP1-/33 USBP0+/2+ 7 USBP1+/3+
4 Ground 8 Ground
Description PIN No. Description
USB 0/1/2/3
2.3.10 Internal USB 4/5 & 6/7 Connectors: CN12 & CN11
Description PIN No. PIN No. Description
VCC 1 2 VCC
USBP4-/6- 3 4 USBP5-/7-
USBP4+/6+
Ground 7 8 Ground
NC 9 10 NC
5 6 USBP5+/7+
Note :
1) If you are using a USB 2.0 device with Windows
2000/XP, you will need to install the USB 2.0 driver
from the Microsoft® website. If you are using Service
pack 1 (or later) for Windows® XP, and using Service
pack4 (or later) for Windows® 2000, you will not have
to install the driver.
2.3.11 External K/B & M/S Connector: CN7 2.3.12 CD-In Connector: CN8
PIN No. Description
1 MS Clock
2 MS Data
3 KB Clock
4 KB Data
5 Ground
6 VCC
PIN No. Description
1 CD-L
2 CD-Ground
3 CD-Ground
4 CD-R
19 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
Signal
Type
Description
DCD
1 2
DSR
RXD
3 4
RTS TXD 5 6 CTS DTR 7 8 RI Ground
9 10 VCC
2.3.13 Line out Connector: CN9 2.3.14 LVDS Connector: CN10
PIN No. Description
1 LOUT_L
2 Ground
3 Ground
4 LOUT_R
Description
NC 2 1 NC
Ground 4 3 Ground
LVDS_YAM1 6 5 LVDS_YAM0
LVDS_YAP1 8 7 LVDS_YAP0
Ground 10 9 Ground
LVDS_CLKAM
LVDS_CLKAP
Ground 16 15 Ground
LVDS_YBM0 18 17 NC0
LVDS_YBP0 20 19 NC
Ground 22 21 Ground
LVDS_YBM2 24 23 LVDS_YBM1
LVDS_YBP2 26 25 LVDS_YBP1
Ground 28 27 Ground
NC 30 29 LVDS_CLKBM
NC 32 31 LVDS_CLKBP
+12V 34 33 NC
+12V 36 35 NC
VCC_LCD 38 37 NC
VCC_LCD 40 39 LCD_BKL
PIN
12 11 LVDS_YAM2
14 13 LVDS_YAP2
PIN
Description
LDDC_CLKL I/O EDID support for flat panel display
LDDC_DATAL I/O EDID support for flat panel display
2.3.15 System Fan Connector: CN14 2.3.16 CPU Fan Connector: CN15
PIN No. Description
1 Ground
2 +12V
3 Fan Speed Control
PIN No. Description
1 Ground
2 +12V
3 Fan Speed Control
2.3.17 ATX power Connector: CN16 2.3.18 COM3 / COM4 Connectors: CN18/CN19
PIN No.
1 +3.3V 11
2 +3.3V 12
3 Ground 13
4 +5V 14
5 Ground 15
6 +5V 16
7 Ground 17
8 NC 18
9 5VSB 19
10 +12V 20
Description PIN No. Description
+3.3V
-12V
Ground
PS-ON
Ground
Ground
Ground
-5V
+5V
+5V
Description
PIN
PIN
Description
20 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
2.3.19 8-bit Digital I/O Connector: CN20 2.3.20 Front Panel Connector: CN21
Description
EXT_VDD 1 2 I1
O1 3 4 I2
O2 5 6 I3
O3 7 8 I4
O4 9 10 EXT_VSS
PIN
No.
PIN
No.
Description
Description
IRDA RESET
+5V 1 2 RESET+
NC 3 4 RESET-
IRRX 5 SPEAKER
Ground 7 8 SPEAKER
IRTX 9 10 BUZZ
HDD LED 12 Ground
HDLED+ 13 14 +5V
HDLED- 15 PW_ LED
TB LED 18 PWLED+
NC 17 20 NC
Ground 19 22 PWLED-
PW_ON KB_LOCK
PWRBT+ 23 24 KBLOCK
PWRBT- 25 26 Ground
PIN
No.
PIN
No.
Description
2.3.21 Primary IDE Connector: IDE1 2.3.22 Serial ATA Connectors: SATA1, SATA2
Description
Reset IDE 1 2 Ground
Host Data 7 3 4 Host Data 8
Host Data 6 5 6 Host Data 9
Host Data 5 7 8 Host Data 10
Host Data 4 9 10 Host Data 11
Host Data 3 11 12 Host Data 12
Host Data 2 13 14 Host Data 13
Host Data 1 15 16 Host Data 14
Host Data 0 17 18 Host Data 15
Ground 19 20 ---
DRQ 0 21 22 Ground
Host IOW 23 24 Ground
Host IOR 25 26 Ground
IOCHRDY 27 28 Ground
DACK 0 29 30 Ground
IRQ 14 31 32 NC
Address 1 33 34 Ground
Address 0 35 36 Address 2
Chip Select 0 37 38 Chip Select 1
Activity 39 40 Ground
PIN
No.
PIN
No.
Description
PIN No. Description
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
These SATA connectors support Serial ATA II. Each SATA
connector can only support one serial ATA device.
Note: With most storage devices, there is a power cable
that you need attach to a power source (power
supply).
Ground
SATA_TX+
SATA_TX -
Ground
SATA_RX-
SATA_RX+
Ground
21 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
CHAPTER 3
22 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
3. System Installation
This chapter provides you with instructions on how to setup your system. The additional
information shows you how to install CPU / FAN and memory.
3.1 Socket 478 Processors
3.1.1 Installing CPU
w Check and confirm that you are going to install correctly CPU type and pin numbers.
w Take the screwdriver and releasing screw-nut of the socket 478.
w Rotate mark of screw -nut to face the “OPEN”.
w Align the pins of the CPU against the pinholes of the socket 478. Be sure to pay
attention to the orientation of the CPU.
OPEN
Screw Nut
CLOSED
w Push down the CPU into the socket 478.
w Rotate mark of screw -nut to face the “CLOSED”.
Note: Do not force the CPU into the socket. It may bend the pins and damage the
CPU.
3.2 Installing Cooling Fan
Warning: For a safety landing, avoid leaving prongs on hard surface.
Instructions:Smear thermal grease on the top of the CPU. Lower the CPU fan onto
the CPU/CPU socket and secure it using the attachments or screws
provided on the fan. Finally, attach the fan power cable to the CPUFAN
adapter and be careful not to place the cable on the CPU cooling fan.
23 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
3.3 Main Memory
The figures display the notch marks and what they should look like on your SO-DIMM
memory module.
SO-DIMM ha s 200-pins and two notches, that will match with the onboard SO-DIMM socket.
Memory modules are installed by placing the chip firmly into the socket at a parallel angle
and pressing straight down until it fits tightly into the SO-DIMM socket.
SO-DIMM Memory and 200-pins Socket
Memory Installation
NOTE: For maintaining system stability, do not change any of memory parameters in BIOS
setup to upgrade your system performance without acquiring technical information.
3.4 Installations
To install the board into standard chassis or proprietary environment, you need to perform
the following steps:
1. Check all jumpers setting on proper position
2. Install and configure CPU and memory module on right position
3. Place the board into the dedicated position in your system
4. Attach cables to existing peripheral devices and secure it
24 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
CHAPTER 4
25 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4. BIOS Setup
4.1 Entering Setup
PHOENIX-AWARD™ has a built-in setup program that allows users to modify the basic
system configuration. This information is stored in CMOS RAM whose power is supplied by
a battery so that it can retain the setup information even when the power is turned off. Press
the key “Delete” when you Power on or Reboot the computer system. (i.e. After the logo
appears at the center of the screen, please press Delete to enter the BIOS setup program).
In the BIOS, make sure that everything is working fine before you try to optimize it for
maximum performance.
It is possible for the CMOS battery to fail, this will cause data loss in the CMOS only. If this
does happen you will need to reconfigure your BIOS settings.
4.2 Main Menu
When you enter the PHOENIX-AWARD™ CMOS Setup Utility, the Main will appear on the
screen. The Main allows you to select several configuration options. Use the left/right arrow
keys to highlight a particular configuration screen from the top menu bar or use the down
arrow key to access and configure the information below.
26 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.1 Standard CMOS Features
4.2.1.1 Date (mm/date/year):
Set the system date. Note that the ‘Day’ automatically changes when you set the date.
4.2.1.2 Time (hh/mm/ss):
Set the system time.
4.2.1.3 IDE Channel 0 / 1 Master:
Press <Enter> to enter the sub menu of detailed options.
4.2.1.4 IDE Channel 0 / 1 Slave:
Press <Enter> to enter the sub menu of detailed options.
4.2.1.5 SATA Channel 1 / 2:
Press <Enter> to enter the sub menu of detailed options.
4.2.1.6 Video:
It allows you to select the type of displaying standard you are using.
The Choice: EGA/VGA/CGA 40/CGA 80/MONO.
27 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.1.7 Halt On:
Select the situation in which you want the BIOS to stop the POST process and notify you.
The Choice: All Errors/No Errors/All, but Keyboard/All, but Diskette/
All, but Disk/Key .
4.2.1.8 Base Memory:
Displays the amount of conventional memory detected during boot up.
4.2.1.9 Extended Memory:
Displays the amount of extended memory detected during boot up.
4.2.1.10 Total Memory:
Displays the total memory available in the system.
4.2.2 Advanced BIOS Features
28 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.2.1 CPU Feature
4.2.2.1.1 Delay Prior to Thermal :
Select this item allows the delay prior to thermal time.
The Choice: Auto, 4, 8, 16, 32Min.
4.2.2.1.2 Execute Disable Bit:
Select when disable, forces the XD feature flag to always return 0.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.2.2 Virus Warning:
Allow you to choose the VIRUS Warning feature for IDE Hard Disk boot sector protection.
If this function is enabled and someone attempts to write data into this area, BIOS will show
a warning message on screen and alarm beep.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.2.3 Hyper-Threading Technology :
When you install a CPU featuring Hyper-Threading Technology, this item will allow you to
enable or disable the Hyper-Threading technology.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
29 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.2.4 Quick Power On Self Test
This category speeds up Power On Self Test (POST) after you power up the computer. If
it is set to Enable, BIOS will shorten or skip some check items during POST.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.2.5 Boot Up NumLock Status
Select power on state for NumLock.
The choice: On, Off.
4.2.2.6 Gate A20 Option
Select if chipset or keyboard controller should control GateA20.
The choice: Normal, Fast.
4.2.2.7 Typematic Rate Setting
Keystrokes repeat at a rate determined by the keyboard controller. When enabled, the
typematic rate and typematic delay can be selected.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.2.8 Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)
Sets the number of times a second to repeat a keystroke when you hold the key down.
The choice: 6, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 24 and 30.
4.2.2.9 Typematic Del ay (Msec)
Sets the delay time after the key is held down before it begins to repeat the keystroke.
The choice: 250, 500, 750 and 1000.
4.2.2.10 Security Option
Select whether the password is required every time the system boots or only when you
enter setup.
The choice: System, Setup.
4.2.2.11 APIC Mode
This item allows you to enable or disable APIC Mode.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.2.12 MPS Version Control For OS
Select the operating system that is Multi-Processors Version Control for OS.
The choice: 1.4, 1.1.
30 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.2.13 OS Select For DRAM > 64MB
Select the operating system that is running with greater than 64MB of RAM on the system.
The choice: Non-OS2, OS2.
4.2.2.14 Cache Setup
4.2.2.14.1 CPU L1& L2 Cache
These two categories speed up memory access. However, it depends on CPU/chipset
design.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.2.14.2 CPU L3 Cache
The option enables Level 3 cache memory. However, it depends on CPU/chipset design.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
31 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.2.15 Boot Seq & Floppy Setup
4.2.2.15.1 Hard Disk Boot Priority
Press Enter and It shows Bootable add-in Card.
4.2.2.15.2 First/Second/Third Boot Device
The BIOS attempts to load the operating system from the devices in the sequence selected
in these items.
The choice: Floppy, LS/ZIP, HDD, SCSI, CDROM, LAN and Disabled.
4.2.2.15.3 Boot Other Device
When enabled, the system searches all other possible locations for an operating system if it
fails to find one in the devices specified under the first, second, and third boot devices.
The Choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.2.15.4 Onboard LAN Boot ROM
Select “Enabled” if your system has a LAN device installed on the system board and you
wish to use it.
The Choice: Enabled, Disabled.
32 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.3 Advanced Chipset Features
4.2.3.1 DRAM Timing Selectable
Select the operating system that is selecting DRAM timing, so select SPD for setting
SDRAM timing by SPD.
The Choice: Manual, By SPD.
4.2.3.2 CAS Latency Time
When synchronous DRAM is installed, the number of clock cycles of CAS latency depends
on the DRAM timing.
4.2.3.3 DRAM RAS# to CAS# Delay
The system board designer should set the values in this field, depending on the DRAM
installed. Do not change the values in this field unless you change specifications of the
installed DRAM or the installed CPU. This field is locked when “DRAM Timing Selectable” is
set to “By SPD” and is automatically determined by the system.
The choice: Auto, 5, 4, 3, 2.
33 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.3.4 DRAM RAS# Precharge
If an insufficient number of cycles are allowed for the RAS to accumulate its charge before
DRAM refresh, the refresh may be incomplete and the DRAM may fail to retain data. Fast
gives faster performance; and Slow gives more stable performance. This field applies
only when synchronous DRAM is installed in the system.
4.2.3.5 Precharge Delay (tRAS)
Select the operating system that is active to precharge delay.
4.2.3.6 System Memory Frequency
You can use this item to select operating frequency for the main system memory.
4.2.3.7 SLP_S4# Assertion Width
The item allows you to select the assertion width of SLP_S4#
The choice: 4 to 5 Sec, 3 to 4 Sec, 2 to 3 Sec, 1 to 2 Sec.
4.2.3.8 System BIOS Cacheable
Selecting “Enabled” allows caching of the system BIOS ROM at F0000h -FFFFFh, resulting
in better system performance. However, if any program writes to this memory area, a
system error may result.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.3.9 Video BIOS Cacheable
Select “Enabled” allows caching of the video BIOS, resulting in better system performance.
However, if any program writes to this memory area, a system error may result.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
34 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.3.10 PCI Express Root Port Function
4.2.3.10.1 PCI Express x1 Slot
This item allows you to active PCI Express.
The choice: Auto, Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.3.10.2 PCI-E Compliancy Mode
This item allows you to choose PCI-E Compliancy Mode.
The choice: v1.0a, v1.0.
4.2.3.11 PEG/Onchip VGA Control
This item allows you to control the PEG or on -chip VGA.
The choice: Onchip VGA, PEG Port, Auto.
4.2.3.12 On-Chip Frame Buffer Size
Select this item allows you to control the on-chip frame buffer size.
4.2.3.13 DVMT Mode
This item allows you to select the DVMT mode.
The choice: FIXED, DVMT, BOTH.
35 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.3.14 DVMT/FIXED Memory Size
This item allows you to select the DVMT or FIXED memory size.
4.2.3.15 Boot Display
This item allows you to select the boot display device.
4.2.3.16 Panel Scaling
This item allows you to enable or disable the Scaling function.
The choice: AUTO, ON, OFF.
4.2.3.17 Panel Number
This item allows you to select the panel resolution that will be displayed depending on the
LCD panel (LFP).
4.2.4 Integrated Peripheral
36 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.4.1 Onchip IDE Device
4.2.4.2.1. IDE HDD Block Mode
Block mode is also called block transfer, multiple commands, or multiple sector read/write.
If your IDE hard drive supports block mode (most new drives do), select Enabled for
automatic detection of the optimal number of block read/writes per sector the drive can
support.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.4.2.2. IDE DMA Transfer Access
This item could allows you to enabled/disabled the IDE UDMA transfer function and only
use PIO mode.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.4.2.3. On-Chip Primary/Secondary PCI IDE
The integrated peripheral controller contains an IDE interface with support for two IDE
channels. Select “Enabled” to activate each channel separately.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
37 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.4.2.4. IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave PIO
The four IDE PIO (Programmed Input/Output) fields let you set a PIO mode (0-4) for each
of the four IDE devices that the onboard IDE interface supports. Modes 0 through 4
provide successively increased performance. In Auto mode, the system automatically
determines the best mode for each device.
The choice: Auto, Mode 0, Mode 1, Mode 2, Mode 3 and Mode 4.
4.2.4.2.5. IDE Primary/Secondary Master/Slave UDMA
Ultra DMA/33 implementation is possible only if your IDE hard drive supports it and the
operating environment includes a DMA driver (Windows 95 OSR2 or a third-party IDE bus
master driver). If your hard drive and your system software both support Ultra DMA/33,
select “Auto” to enable BIOS support.
The choice: Auto, Disabled.
4.2.4.2.6. On-Chip Serial ATA
There are five Serial ATA fields let you set the Serial ATA.
The choice: Disabled---Disabled SATA Controller.
Auto---Auto arrange by BIOS.
SATA Only ---SATA is operating in legacy mode.
Combined Mode---PATA and SATA are combined. Max. of 2 IDE drives in
each channel.
Enhanced Mode---Enable both SATA and PATA. Max. of
4 IDE drives are supported.
4.2.4.2.7. SATA Ports Speed Settings
This item allows you set the SATA Ports Speed.
The choice: Disabled, Force GEN I, Force GEN II.
4.2.4.2.8. PATA IDE Mode
This function allows t o select PATA IDE mode.
38 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.4.2 Onboard Device
4.2.4.2.1. Onboard Giga Lan 2
Select “Enabled” if your system has a LAN device installed on the system board and you
wish to use it.
The choice: Auto, Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.4.2.2. USB Controller
Select “Enabled” if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller and you
have USB peripherals.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.4.2.3. USB 2.0 Controller
Select “Enabled” if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus 2.0 (USB 2.0) controller
and you have USB peripherals.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.4.2.4. USB Keyboard Support
Select “Enabled” if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller and you
have a USB keyboard.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
39 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.4.2.5. USB Mouse Support
Select “Enabled” if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus (USB) controller and you
have a USB mouse.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.4.2.6. Azalia/AC97 Audio Select
This item allows you to select the chipset family to support AC97 Audio
The choice: Auto, Azalia, AC97 Audio only, All disabled.
4.2.4.3 Super IO Device
4.2.4.2.1. Onboard Serial Port 1/2
Select an address and corresponding interrupt for the first and second serial ports.
The choice: 3F8/IRQ4, 2E8/IRQ3, 3E8/IRQ4, 2F8/IRQ3, Disabled and Auto.
4.2.4.2.2. UART Mode Select
This item allows you to determine which Infra Red (IR) function of onboard I/O chip.
The Choice: Normal, IrDA and ASKIR
40 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.4.2.3. UR2 Duplex Mode
Select the value required by the IR device connected to the IR port. Full-duplex mode
permits simultaneous two-direction transmission. Half-duplex mode permits transmission in
one direction only at a time.
The choice: Half, Full.
4.2.4.2.4. PWRON After PWR-Fail
This item allows you to select if you want to power on the system after power failure.
The choice: Off, On and Former-Sts.
4.2.5 Power Management Setup
4.2.5.1 ACPI Function
This function enables PCs to implement Power Management functions through Operating
System and also provides the opportunity to integrated the interface for controlling power
management and Plug-n-Play features on system devices.
4.2.5.2 ACPI Suspend Type
When ACPI function is Enabled, ACPI Suspend Type will be supported S1. In S1 the
computer consumes less power because HDDs and some other devices are powered off,
but CPU is still running and it requires its fan to rotate.
41 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.5.3 Power Management
This category allows you to select the type (or degree) of power saving and is directly
related to the following modes:
1. HDD Power Down , 2. Doze Mode, 3. Suspend Mode
Min. Power Saving:
Minimum power management. Doze Mode = 1 hr. Standby Mode = 1 hr., Suspend
Mode = 1 hr., and HDD Power Down = 15 min.
Max. Power Saving:
Maximum power management -- ONLY AVAILABLE FOR SL CPU’s. Doze Mode =
1 min., Standby Mode = 1 min., Suspend Mode = 1 min., and HDD Power Down = 1
min.
User Defined:
Allow you to set each mode individually. When not disabled, each of the ranges is
from 1 min. to 1 hr. except for HDD Power Down, which ranges from 1 min. to 15 min.
and disable.
4.2.5.4 Video Off Method
This determines the manner in which the monitor is blanked.
V/H SYNC+Blank:
This selection will cause the system to turn off the vertical and horizontal
synchronization ports and write blanks to the video buffer.
Blank Screen:
This option only writes blanks to the video buffer.
DPMS:
Initial display power management signaling.
4.2.5.5 Video Off In Suspend
This item allows you to on/off Method function.
The choice: Yes, No.
4.2.5.6 Suspend Type
Select the Suspend Type.
The choice: PwrOn Suspend, Stop Grant.
4.2.5.7 Suspend Mode
When “Enabled” and after the set time of system inactivity. All devices except the CPU will
be shut off.
The choice: Disabled, 1, 2, 4, 8, 12, 20, 30, 40 Min and 1Hour.
42 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.5.8 HDD Power Down
When “Enabled” and after the set time of system inactivity, the hard disk drive will be
powered down while all other devices remain active.
The choice: Disabled, 1~15Min.
4.2.5.9 Sort-Off by PWR-BTTN
Pressing the power button for more than 4 seconds forces the system to enter the Soft-Off
state when the system has “hung.
The choice: Delay 4 Sec, Instant-Off.
4.2.5.10 Wake-Up by PCI Card
An input signal from PME on the PCI card awakens the system from a soft off state.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.5.11 Power On by Ring
An input signal on the serial Ring Indicator (RI) line (in other words, an incoming call on the
modem) awakens the system from a soft off state.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.5.12 Resume by Alarm
When “Enabled”, your can set the date and time at which the RTC (real-time clock) alarm
awakens the system from Suspend mode.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.5.13 Primary/Secondary IDE 0/1
This function is for setting IDE 0/1 on primary/secondary mode.
4.2.5.14 FDD,COM,LPT Port
System can be awaked by Floppy Drive, COM or LPT port.
4.2.5.15 PCI PIRQ[A-D]#
This function will cause the system waking up completely from the power management
mode.
43 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.6 PnP/PCI/PCI-E Configurations
4.2.6.1 Init Display First
This item allows you to decide to active whether PCI Slot or on-chip VGA first.
4.2.6.2 Reset Configuration Data
Normally, you leave this field Disabled. Select “Enabled” to reset Extended System
Configuration Data (ESCD) when you exit Setup if you have installed a new add-on and the
system reconfiguration has caused such a serious conflict that the operating system cannot
boot.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.6.3 Resources Cont rolled By
The Award Plug and Play BIOS has the capacity to automatically configure all of the boot
and Plug and Play compatible devices. However, this capability means absolutely nothing
unless you are using a Plug and Play operating system such as Windows®95. If you set
this field to “Manual” choose specific resources by going into each of the sub menu that
follows this field.
The choice: Auto (ESCD), Manual.
44 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.6.3.1 IRQ Resources
When resources are controlled manually, assign each system interrupt a type, depending
on the type of device using the DMA channel.
4.2.6.4 PCI/VGA Palette Snoop
This function determines if the graphics card should allow VGA palette snooping by a fixed
function display card. It is only useful if a fixed-function display card using that requi res a
VGA-compatible graphics card to be present . Otherwise, leave the setting as default
Disabled.
The choice: Enabled, Disabled.
4.2.6.5 Maximum Payload Size
Set maximum TLP playload size for the PCI Express devices. The unit is byte.
The choice: 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048, 4096.
4.2.7 PC Health Status
4.2.7.1 VDIMM
The voltage level of the DRAM.
45 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.7.2 Vcore
The voltage level of CPU (Vcore).
4.2.7.3 +3.3V/+5V/+12V/-12V/5Vsb
Show you the voltage of +3.3V/+5V/+12V/-12V.
4.2.7.4 Voltage Battery
Show you the voltage level of the battery.
4.2.7.5 System/CPU Temperature
Show you the current system/CPU temperature.
4.2.7.6 System/CPU FAN Speed
Show you the current System/CPU FAN operating speed.
4.2.8 Load Fail-Safe Default
When you press <Enter> on this item you get a confirmation dialog box with a
message similar to:
Load Fail-Safe Defaults (Y/N)? N
Pressing ‘Y’ loads the BIOS default values for the most stable, minimal-performance
system operations.
4.2.9 Load Optimized Defaults
When you press <Enter> on this item you get a confirmation dialog box with a
message similar to:
Load Optimized Defaults (Y/N)? N
Pressing ‘Y’ loads the default values that are factory settings for optimal performance
system operations.
46 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.10 Supervisor/User Password Setting
You can set either supervisor or user password, or both of then. The differences
between are:
Set Supervisor Password: can enter and change the options of the setup menus.
Set User Password: just can only enter but do not have the right to change the options of
the setup menus. When you select this function, the following message will appear at the
center of the screen to assist you in creating a password.
ENTER PASSWORD:
Type the password, up to eight characters in length, and press <Enter>. The
password typed now will clear any previously entered password from CMOS memory. You
will be asked to confirm the password. Type the password again and press <Enter>. You
may also press <Esc> to abort the selection and not enter a password.
To disable a password, just press <Enter> when you are prompted to enter the
password. A message will confirm the password will be disabled. Once the password is
disabled, the system will boot and you can enter Setup freely.
PASSWORD DISABLED.
When a password has been enabled, you will be prompted to enter it every time you try
to enter Setup. This prevents an unauthorized person from changing any part of your
system configuration.
Additionally, when a password is enabled, you can also require the BIOS to request a
password every time your system is rebooted. This would prevent unauthorized use of
your computer.
You determine when the password is required within the BIOS Features Setup Menu and its
Security option (see Chapter 4). If the Security option is set to “System”, the password will
be required both at boot and at entry to Setup. If set to “Setup”, prompting only occurs
when trying to enter Setup.
47 / 48

ADE-6050 User’s Manual
4.2.11 Exit Selecting
Save & Exit Setup
Pressing <Enter> on this item asks for confirmation:
Save to CMOS and EXIT (Y/N)? Y
Pressing “Y” stores the selections made in the menus in CMOS – a special section of
memory that stays on after you turn your system off. The next time you boot your
computer, the BIOS configures your system according to the Setup selections stored in
CMOS. After saving the values the system is restarted again.
Exit Without Saving
Pressing <Enter> on this item asks for confirmation:
Quit without saving (Y/N)? Y
This allows you to exit Setup without storing in CMOS any change. The previous
selections remain in effect. This exits the Setup utility and restarts your computer.
48 / 48
 Loading...
Loading...