
Data Sheet, V0.2, Feb. 2006
TC1165/TC1166
32-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller
TriCore
TM
Microcontrollers

Edition 2006-02
Published by Infineon Technologies AG,
81726 München, Germany
© Infineon Technologies AG 2006.
All Rights Reserved.
Attention please!
The information herein is given to describe certain components and shall not be considered as a guarantee of
characteristics.
Terms of delivery and rights to technical change reserved.
We hereby disclaim any and all warranties, including but not limited to warranties of non-infringement, regarding
circuits, descriptions and charts stated herein.
Information
For further information on technology, delivery terms and conditions and prices please contact your nearest
Infineon Technologies Office (www.infineon.com).
Warnings
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous substances. For information on the types in
question please contact your nearest Infineon Technologies Office.
Infineon Technologies Components may only be used in life-support devices or systems with the express written
approval of Infineon Technologies, if a failure of such components can reasonably be expected to cause the failure
of that life-support device or system, or to affect the safety or effectiveness of that device or system. Life support
devices or systems are intended to be implanted in the human body, or to support and/or maintain and sustain
and/or protect human life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of the user or other persons may
be endangered.

Data Sheet, V0.2, Feb. 2006
TC1165/TC1166
32-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller
TriCore
TM
Microcontrollers

TC1165/TC1166
Revision History: 2006-02 V0.2
Previous Version: V0.1, December 2005
Page Subjects (major changes since last revision)
3-82 The reset value for RTID is corrected.
4-95 A new footnote is added to V
AREF
.
4-100 The footnote on FADC callibration interval is updated.
4-105 Max. values for power supply current section is defined.
4-116 A new section is added for JTAG signals timing based on 40 MHz JTAG
clock.
We Listen to Your Comments
Any information within this document that you feel is wrong, unclear or missing at all?
Your feedback will help us to continuously improve the quality of this document.
Please send your proposal (including a reference to this document) to:
mcdocu.comments@infineon.com
Template: mc_a5_um_tmplt.fm / 5 / 2005-10-01

TC1165/TC1166
Table of ContentsAdvance Information
Table of Contents
1 Summary of Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 General Device Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.1 Block Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.2 Logic Symbol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.3 Pin Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.4 Pad Driver and Input Classes Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.5 Pin Definitions and Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.1 System Architecture and On-Chip Bus Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
3.2 On-Chip Memories . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
3.3 Memory Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3.3.1 Architectural Address Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3.3.2 How to Read the Address Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
3.3.3 Contents of the Segments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
3.3.4 Address Map of the FPI Bus System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
3.3.4.1 Segments 0 to 14 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
3.3.4.2 Segment 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3.3.5 Address Map of the Local Memory Bus (LMB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
3.4 Memory Protection System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3.5 Peripheral Control Processor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
3.6 DMA Controller and Memory Checker . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
3.7 Interrupt System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
3.8 Asynchronous/Synchronous Serial Interfaces (ASC0, ASC1) . . . . . . . . . . 51
3.9 High-Speed Synchronous Serial Interfaces (SSC0 and SSC1) . . . . . . . . . 53
3.10 Micro Second Bus Interface (MSC0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
3.11 MultiCAN Controller (CAN) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
3.12 Micro Link Serial Bus Interface (MLI0, MLI1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
3.13 General Purpose Timer Array . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
3.13.1 Functionality of GPTA0 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
3.14 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
3.15 Fast Analog-to-Digital Converter Unit (FADC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
3.16 System Timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
3.17 Watchdog Timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
3.18 System Control Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
3.19 Boot Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
3.20 Power Management System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
3.21 On-Chip Debug Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
3.22 Clock Generation and PLL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
3.23 Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
3.24 Identification Register Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Data Sheet 1 V0.2, 2006-02

TC1165/TC1166
Table of ContentsAdvance Information
4 Electrical Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
4.1 General Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
4.1.1 Parameter Interpretation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
4.1.2 Pad Driver and Pad Classes Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
4.1.3 Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
4.1.4 Operating Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
4.2 DC Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
4.2.1 Input/Output Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
4.2.2 Analog to Digital Converter (ADC0) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
4.2.3 Fast Analog to Digital Converter (FADC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
4.2.4 Oscillator Pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
4.2.5 Temperature Sensor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
4.2.6 Power Supply Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
4.3 AC Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
4.3.1 Testing Waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
4.3.2 Output Rise/Fall Times . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
4.3.3 Power Sequencing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
4.3.4 Power, Pad and Reset Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
4.3.5 Phase Locked Loop (PLL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
4.3.6 Debug Trace Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
4.3.7 Timing for JTAG Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
4.3.8 Peripheral Timings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
4.3.8.1 Micro Link Interface (MLI) Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
4.3.8.2 Micro Second Channel (MSC) Interface Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
4.3.8.3 Synchronous Serial Channel (SSC) Master Mode Timing . . . . . . . . 122
5 Package and Reliability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
5.1 Package Parameters (PG-LQFP-176-2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
5.2 Package Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
5.3 Flash Memory Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
5.4 Quality Declaration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Data Sheet 2 V0.2, 2006-02

Advance Information
TC1165/TC116632-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller
TriCore
TM
1 Summary of Features
The TC1165/TC1166 has the following features:
• High-performance 32-bit super-scaler TriCore v1.3 CPU with 4-stage pipeline
– Superior real-time performance
– Strong bit handling
– Fully integrated DSP capabilities
– Single precision Floating Point Unit (FPU)
– 80 MHz operation at full temperature range
• Peripheral Control Processor with single cycle instruction (PCP2)
– 8 Kbyte Parameter Memory (PRAM)
– 12 Kbyte Code Memory (CMEM)
• Multiple on-chip memories
– 56 Kbyte Local Data Memory (SRAM)
– 8 Kbyte Overlay Memory
– 16 Kbyte Scratch-Pad RAM (SPRAM)
– 8 Kbyte Instruction Cache (ICACHE)
– 1504 Kbyte Program Flash (for instruction code and constant data)
– 32 Kbyte Data Flash (e.g. 4 Kbyte EEPROM emulation)
– 16 Kbyte Boot ROM
• 8-channel DMA Controller
• Fast-response interrupt system with 2 x 255 hardware priority arbitration levels
serviced by CPU or PCP2
• High-performance on-chip bus structure
– 64-bit Local Memory Bus (LMB) to Flash memory
– System Peripheral Bus (SPB) for interconnections of functional units
• Versatile on-chip Peripheral Units
– Two Asynchronous/Synchronous Serial Channels (ASCs) with baudrate
generator, parity, framing and overrun error detection
– Two High Speed Synchronous Serial Channels (SSCs) with programmable data
length and shift direction
– One Micro Second Bus (MSC) interface for serial port expansion to external power
devices
– Two high-speed Micro Link Interfaces (MLIs) for serial inter-processor
communication
– One MultiCAN Module with two CAN nodes and 64 free assignable message
objects for high efficiency data handling via FIFO buffering and gateway data
transfer
1)
Data Sheet 3 V0.2, 2006-02

TC1165/TC1166
Summary of FeaturesAdvance Information
– One General Purpose Timer Array Module (GPTA) with a powerful set of digital
signal filtering and timer functionality to realize autonomous and complex
Input/Output management
– One 16-channel Analog-to-Digital Converter unit (ADC) with selectable 8-bit, 10-
bit, or 12-bit, supporting 32 input channels
– One 2-channel Fast Analog-to-Digital Converter unit (FADC) with concatenated
comb filters for hardware data reduction: supporting 10-bit resolution, with
minimum conversion time of 262.5ns
• 32 analog input lines for ADC and FADC
• 81 digital general purpose I/O lines
• Digital I/O ports with 3.3 V capability
• On-chip debug support for OCDS Level 1 and 2 (CPU, PCP, DMA)
• Power Management System
• Clock Generation Unit with PLL
• Core supply voltage of 1.5 V
• I/O voltage of 3.3 V
• Full Industrial and Multi-Market temperature range: -40° to +85°C
• PG-LQFP-176-2 package
1) Not applicable to TC1165
Data Sheet 4 V0.2, 2005-12
TC1165/TC1166
Summary of FeaturesAdvance Information
Ordering Information
The ordering code for Infineon microcontrollers provides an exact reference to the
required product. This ordering code identifies:
• The derivative itself, i.e. its function set, the temperature range, and the supply
voltage
• The package and the type of delivery
For the available ordering codes for the TC1165/TC1166, please refer to the “Product
Catalog Microcontrollers” that summarizes all available microcontroller variants.
This document describes the derivatives of the device.The Table 1-1 enumerates these
derivatives and summarizes the differences.
Table 1-1 TC1165/TC1166 Derivative Synopsis
Derivative Ambient Temperature Range
SAF-TC1165-192F80HL T
SAF-TC1166-192F80HL T
= -40oC to +85oC
A
= -40oC to +85oC
A
Data Sheet 5 V0.2, 2005-12
General Device InformationAdvance Information
m
2 General Device Information
Chapter 2 provides the general information for the TC1165/TC1166.
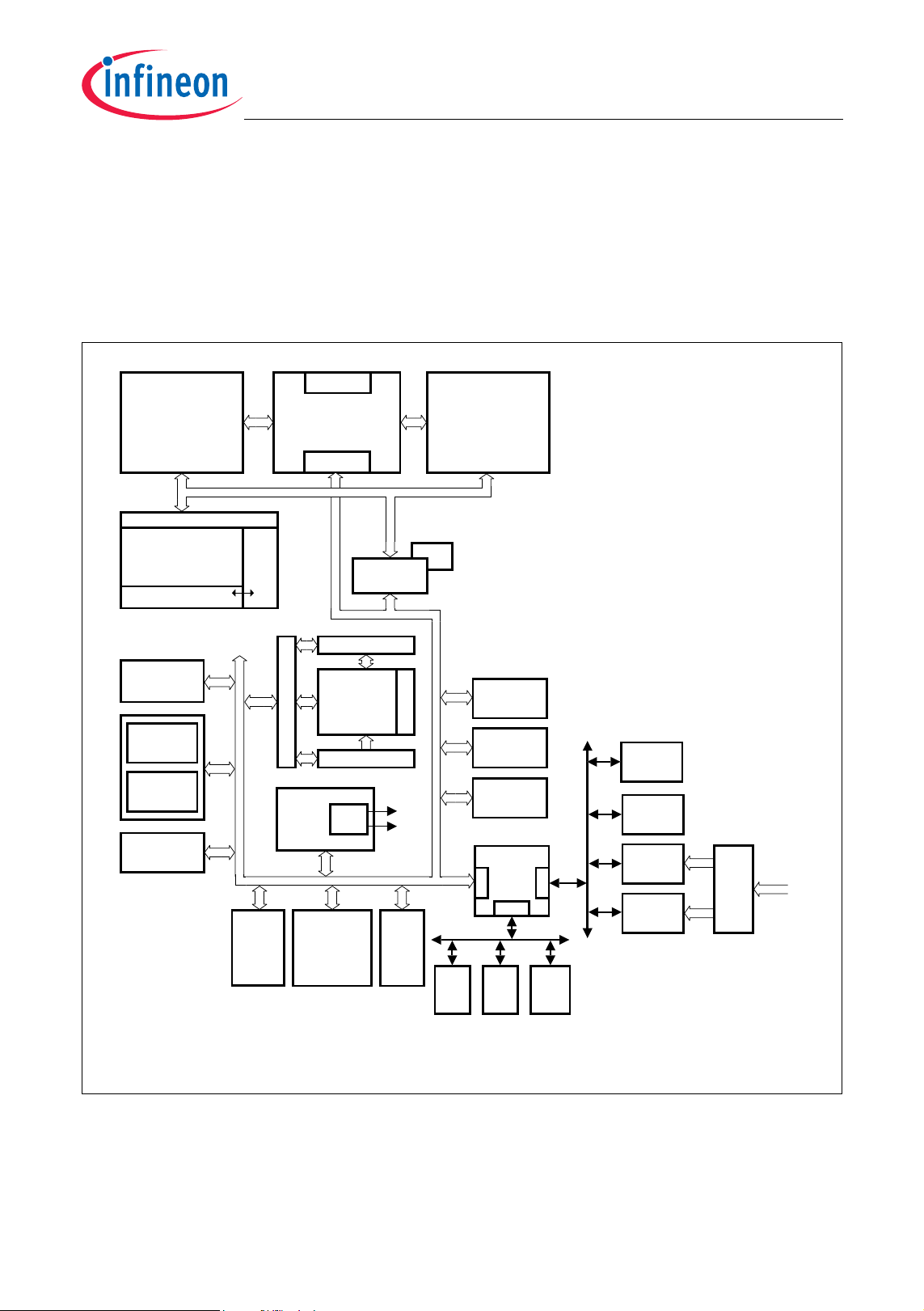
2.1 Block Diagram
Figure 2-1 shows the TC1165/TC1166 block diagram.
TC1165/TC1166
PMI
16 KB SPRAM
8 KB ICACHE
PMU
16 KB BROM
1504 KB Pf las h
32 KB DFlash
8 KB O VRAM
OCDS Debug
Interface/JTAG
ASC0
ASC1
GPTA
Overlay
System Peripheral Bus (SPB)
Ext.
Request
Unit
Me chan ism
(TC1.3M)
FPI-Bus Interface
Mult i CAN
(2 Nodes ,
64 Buffer)
FPU
TriCore
CPS
LF I Bridge
8 KB PRAM
PCP2
Core
12 KB CMEM
PLL SCU PLL
1)
DMI
56 KB LDRAM
Local M emor y B us ( LMB )
LBCU
Interrupts
f
FP I
f
CPU
BI0
MSC0
MLI1
STM
SBCU
Ports
DMA
8 ch.
SMIF
MLI0
Abbr eviat ions:
ICACHE : Inst ruct ion Cac he
SP RAM : Sc ratc h-Pad RAM
LDRAM : Local Dat a RA M
O VRA M: O verlay RAM
BROM: Boot ROM
PF lash: P rogr am F las h
DFlash: Dat a F lash
PRA M: Par amet er Mem ory in PCP
CMEM: Code Memory in PCP
SSC0
DMA Bus
BI1
Mem
Check
SSC1
ADC0
32 ch.
FADC
2 ch.
Assi gnme nt
Analog Input
1) Not appl icabl e to TC1165
TC1165/TC1166 Block Diagra
Figure 2-1 TC1165/TC1166 Block Diagram
Data Sheet 6 V0.2, 2006-02
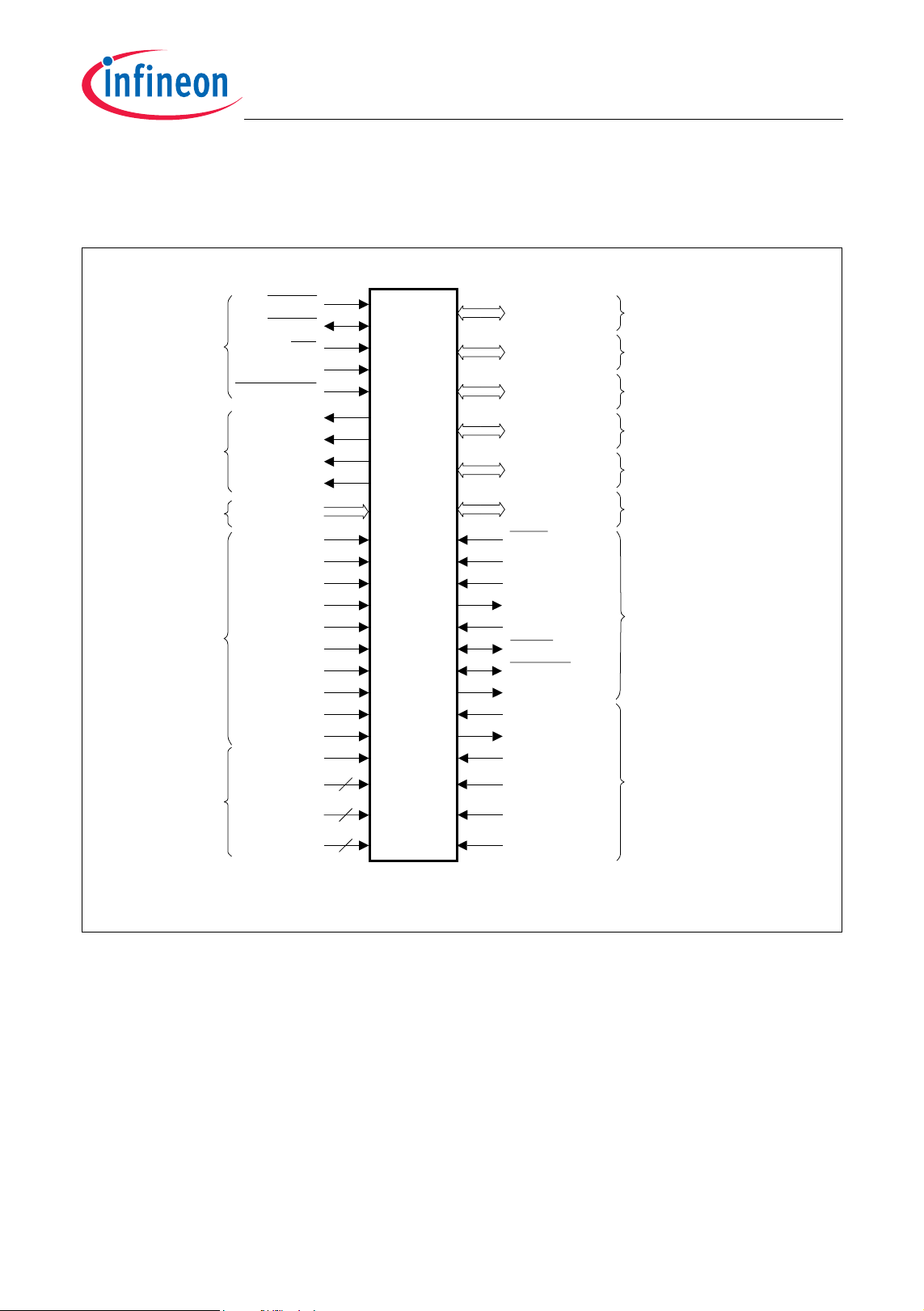
2.2 Logic Symbol
Figure 2-2 shows the TC1165/TC1166 logic symbol.
General Control
PORST
HDRST
NMI
BYPASS
TEST MODE
Port 0 16-bit
Port 1 15-bit
Port 2 14-bit
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Alter nate Functions
GPTA, SCU
GPTA, SSC1, ADC
SSC0/1, MLI0, GPTA, MSC0
MSC0 Contr ol
ADC/ F ADC Anal og
Power Supply
Di gi tal Cir c ui tr y
Power Supply
FCLP0A
FCLN0
SOP0A
SON0
AN[35:0]ADC Analog Inputs
V
DDM
V
SSM
V
DDMF
V
SSMF
V
DDAF
V
SSAF
V
AR EF0
V
AGN D 0
V
FAREF
V
FAGND
V
DDFL3
V
V
DDP
V
DD
SS
Port 3 16-bit
Por t 4 4- bit
Port 5 16-bit
ASC0/1, SSC0/1, SCU, CAN
GPTA, SCU
GPTA, OCDS L2, MLI0/1
1)
TRST
TC1165/
TC1166
TCK
TDI
TDO
TMS
OCDS / J T AG Contr ol
BRKIN
BRKOUT
TRCLK
XTAL1
XTAL2
V
7
8
9
DDOSC3
V
SSOSC 3
V
DDOSC
V
SSOSC
Osci l l ator
TC1165/TC1166 Logic S ym bol
1) A lternat e f unct ions f or CAN m odule is not applic able f or T C1165.
Figure 2-2 TC1165/TC1166 Logic Symbol
Data Sheet 7 V0.2, 2006-02
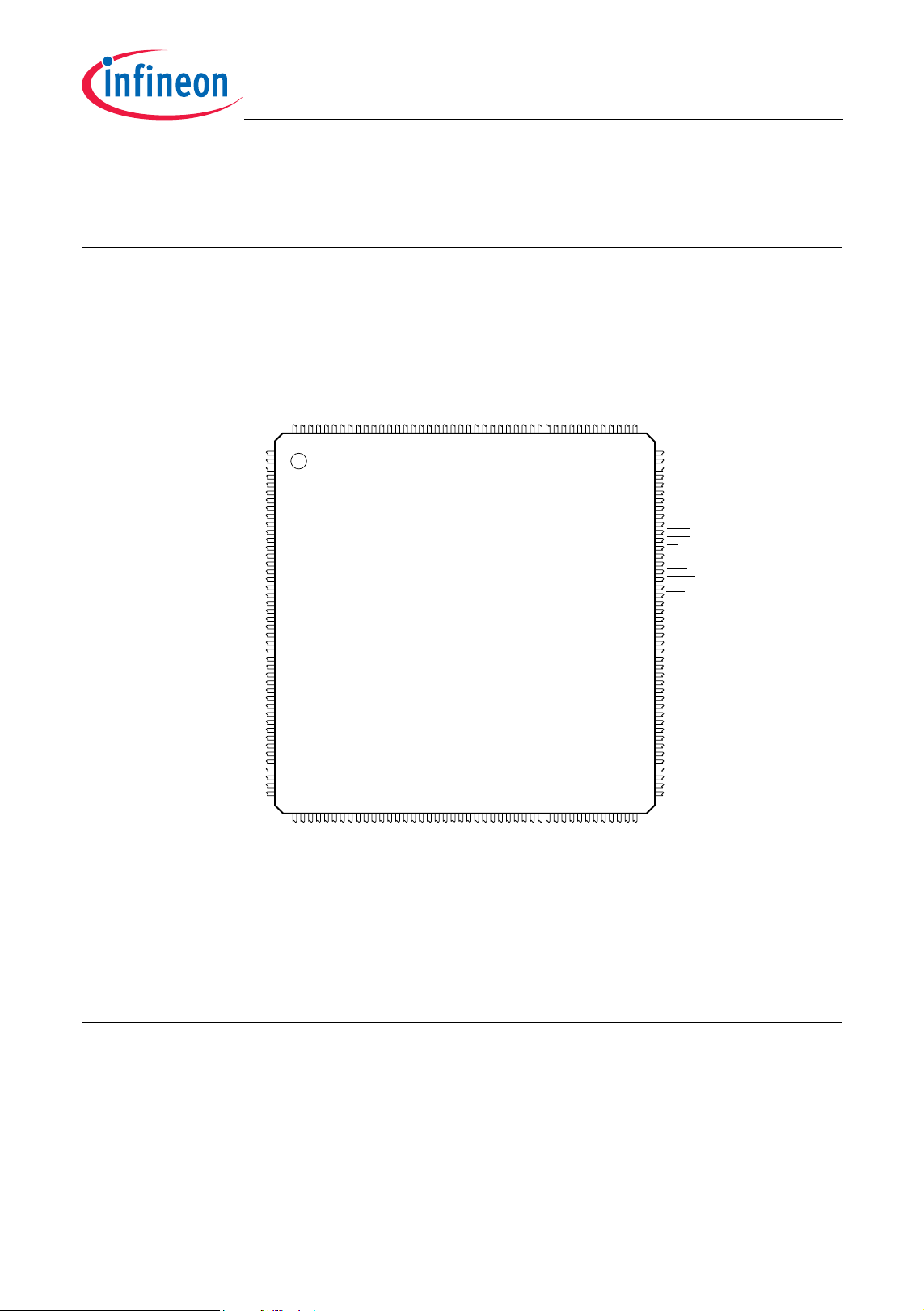
2.3 Pin Configuration
Figure 2-3 shows the TC1165/TC1166 pin configuration.
/RXD0B
1)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
/TXD0B
1)
/RXD1B
/TXD1B
1)
1)
OCDSDBG0/OUT40/IN40/P5.0
OCDSDBG1/OUT41/IN41/P5.1
OCDSDBG2/OUT42/IN42/P5.2
OCDSDBG3/OUT43/IN43/P5.3
OCDSDBG4/OUT44/IN44/P5.4
OCDSDBG5/OUT45/IN45/P5.5
OCDSDBG6/OUT46/IN46/P5.6
OCDSDBG7/OUT47/IN47/P5.7
OCDSDBG8/TDATA1/RDATA0B/P5.8
OCDSDBG9/TVALID 1/RVALID0B/P5.9
OC D SD BG 1 0 / R R EAD Y0 B/ T R EAD Y1 / P5 . 1 0
OCD SDBG11/TC LK1/R CLK0B/P5.11
OC D SD BG 1 2 / T D ATA0 B/ R D ATA1 / P5 . 1 2
OCDSDBG13/TVALID0B/RVALID1/P5.13
OCDSDBG14/RREADY1/TREADY0B/P5.14
OCD SDBG15/TC LK0B/RC LK1/P5.15
TR CL K
V
V
V
V
V
FA R E F
V
FA G N D
AN 3 5
AN 3 4
AN 3 3
AN 3 2
AN 3 1
AN 3 0
AN 2 9
AN 2 8
AN 2 7
AN 2 6
AN 2 5
AN 2 4
AN 2 3
AN 2 2
AN 2 1
AN 2 0
1) Not applic able t o T C1165
V
V
N.C.
SSAF
DDAF
DDMF
SSMF
AN 7
DD
DDP
V
SS
P0.6/IN6/S WC FG6/RE Q2/OU T6/OUT62
P0.7/IN7/S WC FG7/RE Q3/OU T7/OUT63
P0.14/I N14/S WCFG14/RE Q4/ OUT14/OUT70
P0.15/I N15/S WCFG15/RE Q5/ OUT15/OUT71
173
174
175
176
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
454647484950515253
AN16
AN17
AN18
AN19
DDPVSS
VDDV
170
171
172
P2.8/SLSO04/S LSO14/EN00
P2.9/SLSO05/S LSO15/EN01
P2.10/M RS T1A
P2.11/SC LK1A/F CLP 0B
P2.12/M TSR1A/S OP0B
P2.13/SLSI1/S DI0
P0.4/IN4/S WC FG4/OUT4/OUT60
P0.5/IN5/S WC FG5/OUT5/OUT61
P0.12/I N12/S WCFG12/OU T12/OUT68
P0.13/I N13/S WCFG13/OU T13/OUT69
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
168
169
167
DDPVSS
P0.10/I N10/S WCFG10/OU T10/OUT66
P0.11/I N11/S WCFG11/OU T11/OUT67
FCLP0A
FCL N0
SOP 0 A
SON 0
VDDV
151
152
153
154
155
156
158
159
157
P0.0/IN0/S WC FG0/OUT0/OUT56
P0.1/IN1/S WC FG1/OUT1/OUT57
P0.2/IN2/S WC FG2/OUT2/OUT58
P0.3/IN3/S WC FG3/OUT3/OUT59
P0.8/IN8/S WC FG8/OUT8/OUT64
P0.9/IN9/S WC FG9/OUT9/OUT65
150
P3.11/RE Q1
144
145
146
147
148
149
TC1165/TC1166
5455565758596061626364656667686970717273747576777879808182838485868788
DD
DD MVSSM
AN9
V
AREF0VAGND0
AN12
AN13
AN14
AN15
V
AN4
AN5
AN6
AN8
AN10
AN11
SS
V
DDP
V
V
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
AD0EMUX0/P1.12
AD0EMUX1/P1.13
AD0EMUX2/P1.14
TCLK0A/OUT32/IN32/P2.0
TDAT A0A /OUT35/IN 54/P2.3
T VALID0A /OU T34/IN34/P2.2
SLSO13/SLSO03/OUT33/TREADY0A/IN33/ P2.1
DDFL3VDDPVSS
P3.0/RX D0A
P3.1/T XD0A
P3.9/RX D1A
P3.10/RE Q0
P3. 1 2 / R X DC AN 0
V
P3.13/T XDCAN0
141
142
143
OUT36/R CLK 0A/IN 36/P2.4
OUT 38/RVALID0A/IN38/ P2.6
RRE ADY0A/OU T37/IN37/P2.5
P3. 1 4 / R X DC AN 1
P3.15/T XDCAN1
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
132
P3.4/MTSR 0
131
P3.7/SLSI0/SLSO02/SLSO12
130
P3.3/MRST0
129
P3.2/SCLK0
128
P3.8/SLSO06/TXD1A
127
P3.6/SLSO01/SLSO11/SLSO01&SLSO11
126
P3.5/SLSO00/SLSO10/SLSO00&SLSO10
V
125
SS
V
124
DDP
V
123
DD
122
HDRST
121
POR ST
120
NMI
BYPASS
119
TESTM O D E
118
117
BR KI N
116
BR KO U T
TCK
115
TRST
114
TDO
113
TMS
112
TDI
111
P1.7/IN23/OU T23/OUT79
110
P1.6/IN22/OU T22/OUT78
109
P1.5/IN21/OU T21/OUT77
108
P1.4/IN20/EMG_IN/OU T20/OUT76
107
V
106
DDOSC3
V
105
DDOSC
V
104
SSOSC
XTAL 2
103
XTAL 1
102
V
SS
101
V
DDP
100
V
DD
99
P1.3/IN19/OU T19/OUT75
98
P1.11/IN27/IN51/SCLK1B/OUT27/OUT51
97
P1.10/IN26/IN 50/OU T26/OUT50/SLSO17
96
P1.9/IN25/IN49/MRST1B/OUT25/OUT49
95
P1.8/IN24/IN48/MTSR1B/OUT24/OUT48
94
P1.2/IN18/OU T18/OUT74
93
P1.1/IN17/OU T17/OUT73
92
P1.0/IN16/OU T16/OUT72
91
P4. 3 / I N 3 1 / I N 5 5 / O U T3 1 / O U T 5 5 / SYSC LK
90
N.C.
89
DD
SS
V
DDP
VSSV
V
OUT39/R DATA 0A/IN39/P2.7
OU T52/OUT28/HWCF G0/IN52/IN28/P4.0
OU T53/OUT29/HWCF G1/IN53/IN29/P4.1
OU T54/OUT30/HWCF G2/IN54/IN30/P4.2
TC1165/TC1166 Pinning
Figure 2-3 TC1165/TC1166 Pinning for PG-LQFP-176-2 Package
Data Sheet 8 V0.2, 2006-02

TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
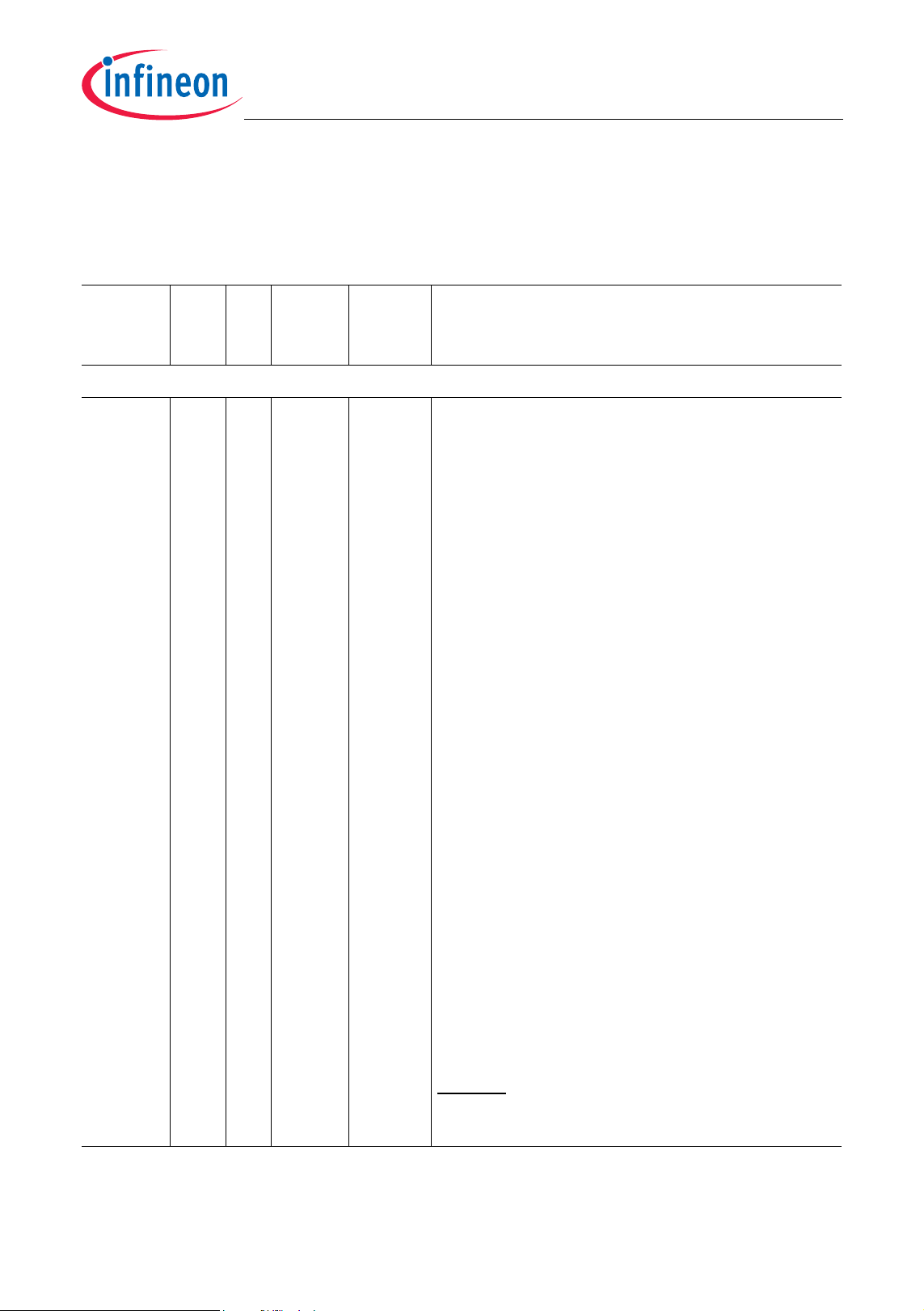
2.4 Pad Driver and Input Classes Overview
The TC1165/TC1166 provides different types and classes of input and output lines. For
understanding of the abbreviations in
gives an overview on the pad type and class types.
Table 2-1 starting at the next page, Table 4-1
Data Sheet 9 V0.2, 2006-02
General Device InformationAdvance Information
2.5 Pin Definitions and Functions
Table 2-1 shows the TC1165/TC1166 pin definitions and functions.
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions
TC1165/TC1166
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Class
Parallel Ports
P0
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2
P0.3
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6
P0.7
P0.8
P0.9
P0.10
P0.11
P0.12
P0.13
P0.14
P0.15
145
146
147
148
166
167
173
174
149
150
151
152
168
169
175
176
I/O A1 V
Power
Supply
DDP
Functions
Port 0
Port 0 is a 16-bit bi-directional generalpurpose I/O port which can be alternatively
used for GPTA I/O lines or external trigger
inputs.
IN0 / OUT0 /
IN1 / OUT1 /
IN2 / OUT2 /
IN3 / OUT3 /
IN4 / OUT4 /
IN5 / OUT5 /
IN6 / OUT6 /
REQ2
IN7 / OUT7 /
REQ3
IN8 / OUT8 /
IN9 / OUT9 /
IN10 / OUT10 /
IN11 / OUT11 /
IN12 / OUT12 /
IN13 / OUT13 /
IN14 / OUT14 /
REQ4
IN15 / OUT15 /
REQ5
OUT56 line of GPTA
OUT57 line of GPTA
OUT58 line of GPTA
OUT59 line of GPTA
OUT60 line of GPTA
OUT61 line of GPTA
OUT62 line of GPTA
External trigger input 2
OUT63 line of GPTA
External trigger input 3
OUT64 line of GPTA
OUT65 line of GPTA
OUT66 line of GPTA
OUT67 line of GPTA
OUT68 line of GPTA
OUT69 line of GPTA
OUT70 line of GPTA
External trigger input 4
OUT71 line of GPTA
External trigger input 5
In addition, the state of the port pins are
latched into the software configuration input
register SCU_SCLIR at the rising edge of
HDRST. Therefore, Port 0 pins can be used
for operating mode selections by software.
Data Sheet 10 V0.2, 2006-02
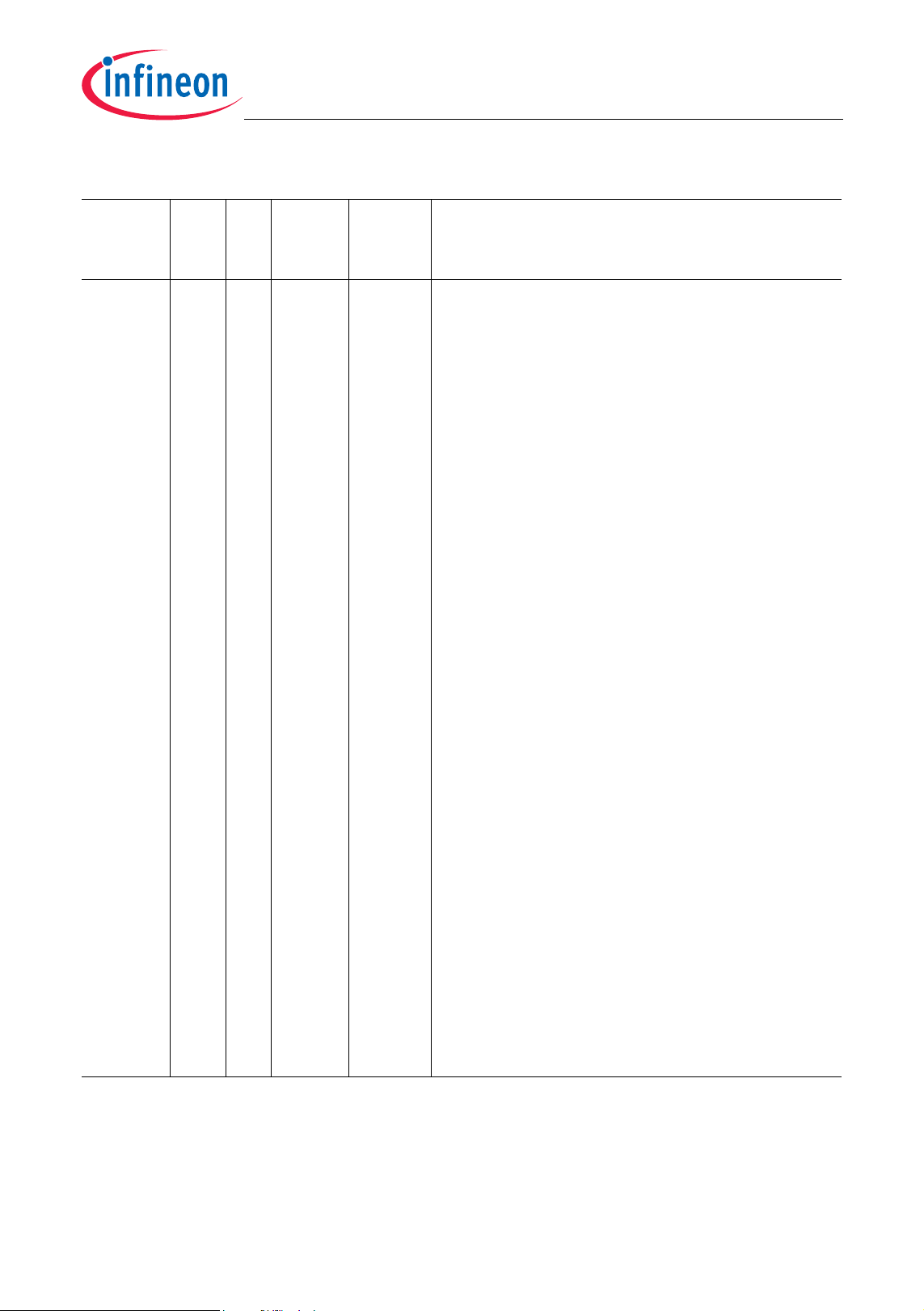
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Power
Supply
Class
P1 I/O V
P1.0
P1.1
P1.2
P1.3
P1.4
P1.5
P1.6
P1.7
P1.8
P1.9
P1.10
P1.11
P1.12
P1.13
P1.14
91
92
93
98
107
108
109
110
94
95
96
97
73
72
71
A1
A1
A1
A1
A1
A1
A1
A1
A2
A2
A2
A2
A1
A1
A1
DDP
Functions
Port 1
Port 1 is a 15-bit bi-directional general
purpose I/O port which can be alternatively
used for GPTA I/O lines, SSC1 and ADC0
interface.
IN16 / OUT16 /
IN17 / OUT17 /
IN18 / OUT18 /
IN19 / OUT19 /
IN20 / OUT20 /
IN21 / OUT21 /
IN22 / OUT22 /
IN23 / OUT23 /
IN24 / OUT24 /
MTSR1B
OUT72 line of GPTA
OUT73 line of GPTA
OUT74 line of GPTA
OUT75 line of GPTA
OUT76 line of GPTA
OUT77 line of GPTA
OUT78 line of GPTA
OUT79 line of GPTA
IN48 / OUT48 line of GPTA
SSC1 master transmit
output / slave rec. input B
IN25 / OUT25 /
MRST1B
IN49 / OUT49 line of GPTA
SSC1 master receive input /
slave transmit output B
IN26 / OUT26 /
SLSO17
IN27 / OUT27 /
SCLK1B
AD0EMUX0
IN50 / OUT50 line of GPTA
SSC1 slave select output 7
IN51 / OUT51 line of GPTA
SSC1 clock input / output B
ADC0 external multiplexer
control output 0
AD0EMUX1
ADC0 external multiplexer
control output 1
AD0EMUX2
ADC0 external multiplexer
control output 2
In addition, P1.4 also serves as emergency
shut-off input for certain I/O lines (e.g. GPTA
related outputs).
Data Sheet 11 V0.2, 2006-02
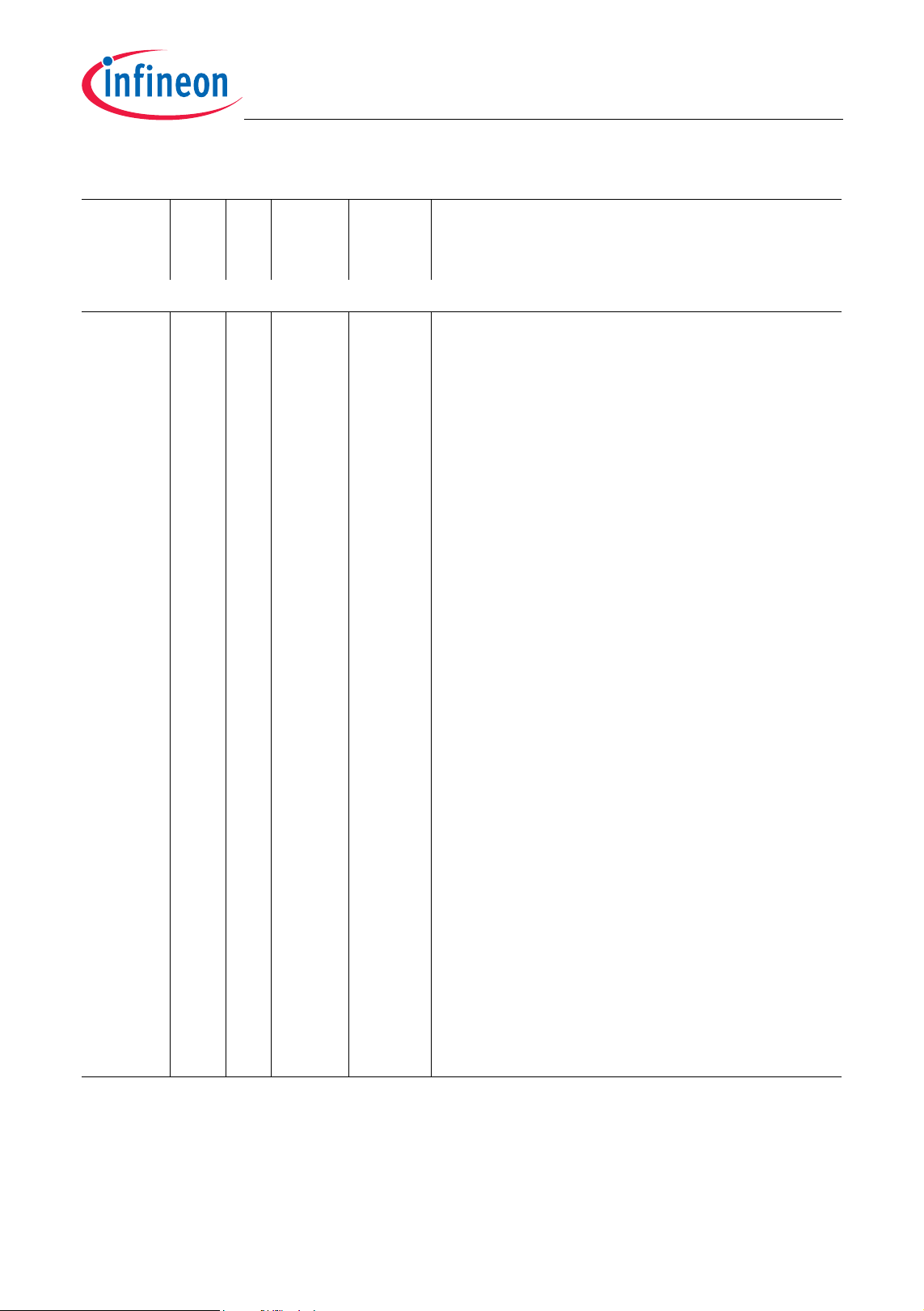
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Power
Supply
Class
P2 I/O V
P2.0
P2.1
P2.2
P2.3
P2.4
P2.5
P2.6
P2.7
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
A2
A2
A2
A2
A1
A2
A1
A1
DDP
Functions
Port 2
Port 2 is a 14-bit bi-directional generalpurpose I/O port which can be alternatively
used for GPTA I/O, and interface for MLI0,
MSC0 or SSC0/1.
TCLK0A
MLI0 transmit channel clock
output A
IN32 / OUT32
TREADY0A
line of GPTA
MLI0 transmit channel ready
input A
IN33 / OUT33
SLSO03
SLSO13
TVALID0A
line of GPTA
SSC0 slave select output 3
SSC1 slave select output 3
MLI0 transmit channel valid
output A
IN34 / OUT34
TDATA0A
line of GPTA
MLI0 transmit channel data
output A
IN35 / OUT35
RCLK0A
IN36 / OUT36
RREADY0A
line of GPTA
MLI0 receive channel clock
A
input
line of GPTA
MLI0 receive channel ready
output A
IN37 / OUT37
RVALID0A
line of GPTA
MLI0 receive channel valid
input A
IN38 / OUT38
RDATA0A
IN39 / OUT39
line of GPTA
MLI0 receive channel data
A
input
line of GPTA
Data Sheet 12 V0.2, 2006-02
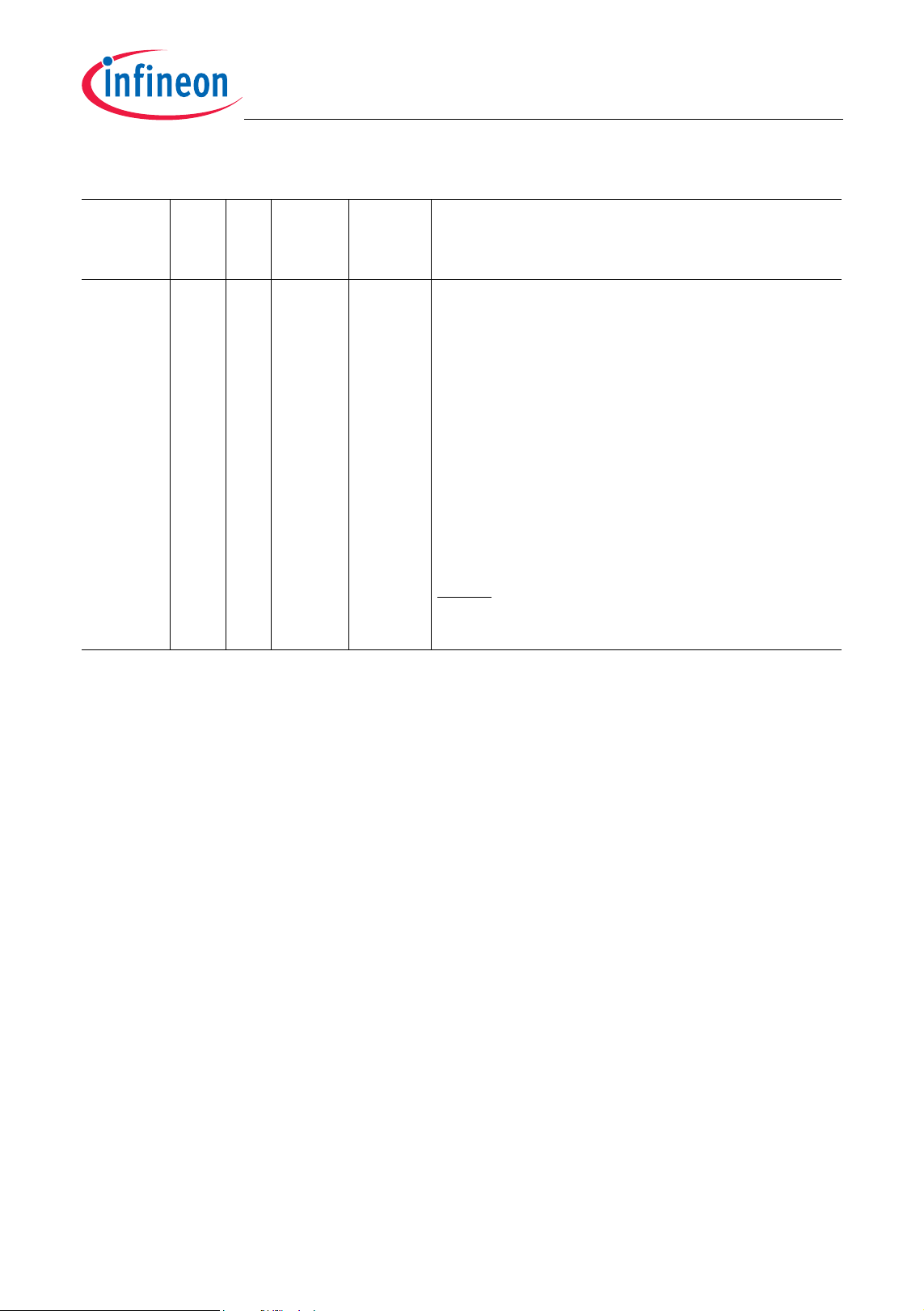
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Class
P2.8
P2.9
P2.10
P2.11
P2.12
P2.13
164
160
161
162
163
165
A2
A2
A2
A2
A2
A1
Power
Supply
Functions
SLSO04
SLSO14
EN00
SLSO05
SLSO15
EN01
MRST1A
SCLK1A
FCLP0B
MTSR1A
SOP0B
SLSI1
SDI0
SSC0 Slave Select output 4
SSC1 Slave Select output 4
MSC0 enable output 0
SSC0 Slave Select output 5
SSC1 Slave Select output 5
MSC0 enable output 1
SSC1 master receive input /
slave transmit output A
SSC1 clock input/output A
MSC0 clock output B
SSC1 master transmit out /
slave receive input A
MSC0 serial data output B
SSC1 slave select input
MSC0 serial data input
Data Sheet 13 V0.2, 2006-02
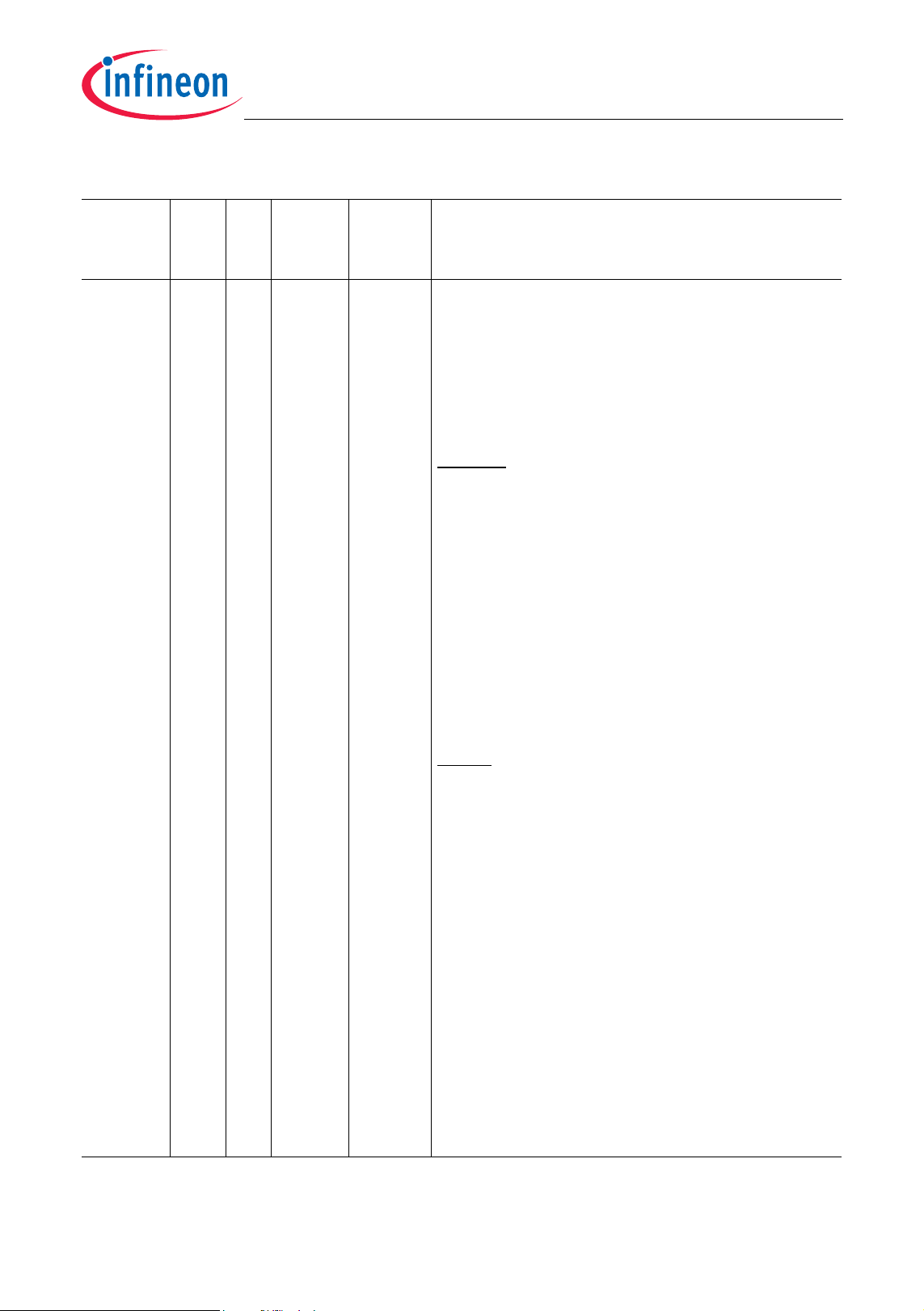
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Power
Supply
Class
P3 I/O V
P3.0
P3.1
P3.2
P3.3
P3.4
P3.5
P3.6
P3.7
P3.8
P3.9
P3.10
P3.11
P3.12
P3.13
P3.14
P3.15
136
135
129
130
132
126
127
131
128
138
137
144
143
142
134
133
A2
A2
A2
A2
A2
A2
A2
A2
A2
A2
A1
A1
A2
A2
A2
A2
DDP
Functions
Port 3
Port 3 is a 16-bit bi-directional generalpurpose I/O port which can be alternatively
used for ASC0/1, SSC0/1 and CAN lines.
RXD0A
TXD0A
ASC0 receiver inp./outp. A
ASC0 transmitter output A
This pin is sampled at the rising edge of
PORST. If this pin and the BYPASS input pin
are both active, then oscillator bypass mode is
entered.
SCLK0
MRST0
SSC0 clock input/output
SSC0 master receive input/
slave transmit output
MTSR0
SSC0 master transmit
output/slave receive input
SLSO00
SLSO10
SLSO01
SLSO11
SLSI0
SLSO02
SLSO12
SLSO06
TXD1A
RXD1A
REQ0
REQ1
RXDCAN0
RXD0B
TXDCAN0
TXD0B
RXDCAN1
RXD1B
TXDCAN1
TXD1B
1)
1)
1)
1)
SSC0 slave select output 0
SSC1 slave select output 0
SSC0 slave select output 1
SSC1 slave select output 1
SSC0 slave select input
SSC0 slave select output 2
SSC1 slave select output 2
SSC0 slave select output 6
ASC1 transmitter output A
ASC1 receiver inp./outp. A
External trigger input 0
External trigger input 1
CAN node 0 receiver input
ASC0 receiver inp./outp. B
CAN node 0 transm. output
ASC0 transmitter output B
CAN node 1 receiver input
ASC1 receiver inp./outp. B
CAN node 1 transm. output
ASC1 transmitter output B
2)
2)
Data Sheet 14 V0.2, 2006-02
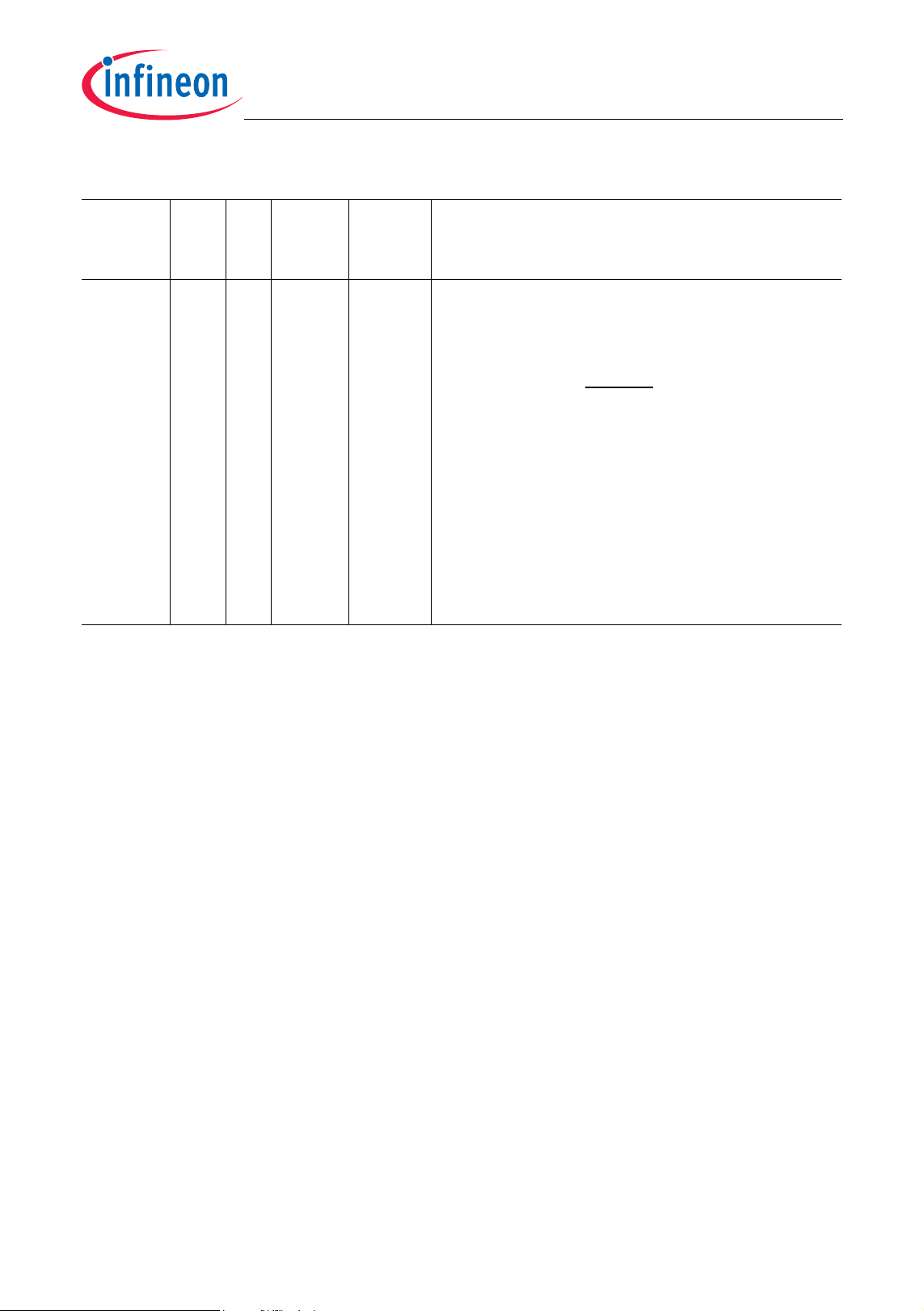
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Power
Supply
Functions
Class
P4 I/O V
DDP
Port 4 / Hardware Configuration Inputs
P4.[3:0] HWCFG[3:0] Boot mode and boot location
inputs; inputs are latched
with the rising edge of
HDRST.
During normal operation, Port 4 pins may be
used as alternate functions for GPTA or
system clock output.
P4.0
P4.1
P4.2
P4.3
86
87
88
90
A1
A1
A2
A2
IN28 / OUT28 /
IN29 / OUT29 /
IN30 / OUT30 /
IN31 / OUT31 /
SYSCLK
IN52 / OUT52 line of GPTA
IN53 / OUT53 line of GPTA
IN54 / OUT54 line of GPTA
IN55 / OUT55 line of GPTA
System Clock Output
Data Sheet 15 V0.2, 2006-02
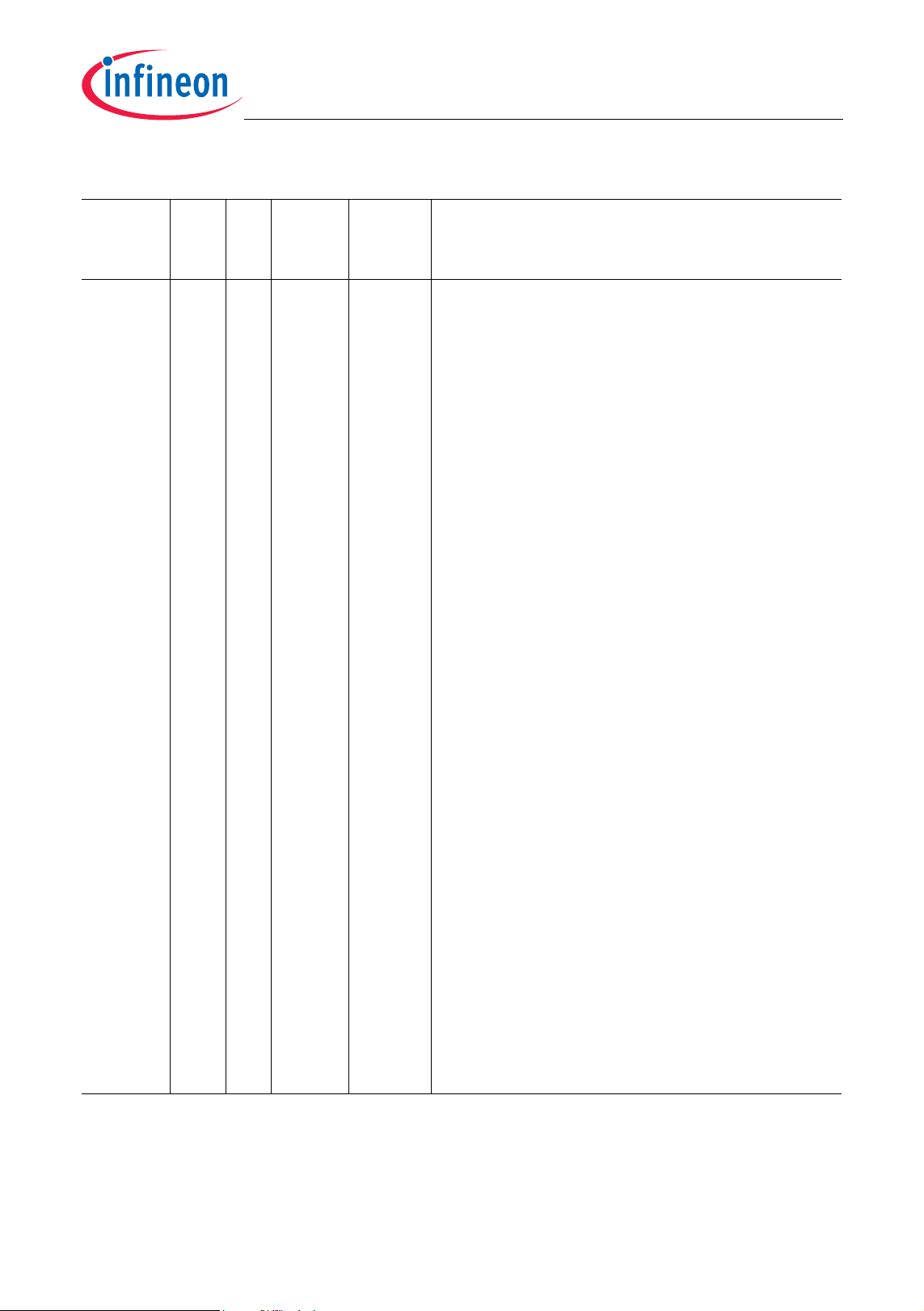
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Power
Supply
Class
P5 I/O A2 V
P5.0
P5.1
P5.2
P5.3
P5.4
P5.5
P5.6
P5.7
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
DDP
Functions
Port 5
Port 5 is a 16-bit bi-directional generalpurpose I/O port. In emulation, it is used as a
trace port for OCDS Level 2 debug lines. In
normal operation, it is used for GPTA I/O or
the MLI0/1 interface.
OCDSDBG0
OCDS L2 Debug Line 0
(Pipeline Status Sig. PS0)
IN40 / OUT40
OCDSDBG1
line of GPTA
OCDS L2 Debug Line 1
(Pipeline Status Sig. PS1)
IN41 / OUT41
OCDSDBG2
line of GPTA
OCDS L2 Debug Line 2
(Pipeline Status Sig. PS2)
IN42 / OUT42
OCDSDBG3
line of GPTA
OCDS L2 Debug Line 3
(Pipeline Status Sig. PS3)
IN43 / OUT43
OCDSDBG4
line of GPTA
OCDS L2 Debug Line 4
(Pipeline Status Sig. PS4)
IN44 / OUT44
OCDSDBG5
line of GPTA
OCDS L2 Debug Line 5
(Break Qualification Line
BRK0)
IN45 / OUT45
OCDSDBG6
line of GPTA
OCDS L2 Debug Line 6
(Break Qualification Line
BRK1)
IN46 / OUT46
OCDSDBG7
line of GPTA
OCDS L2 Debug Line 7
(Break Qualification Line
BRK2)
IN47 / OUT47
line of GPTA
Data Sheet 16 V0.2, 2006-02
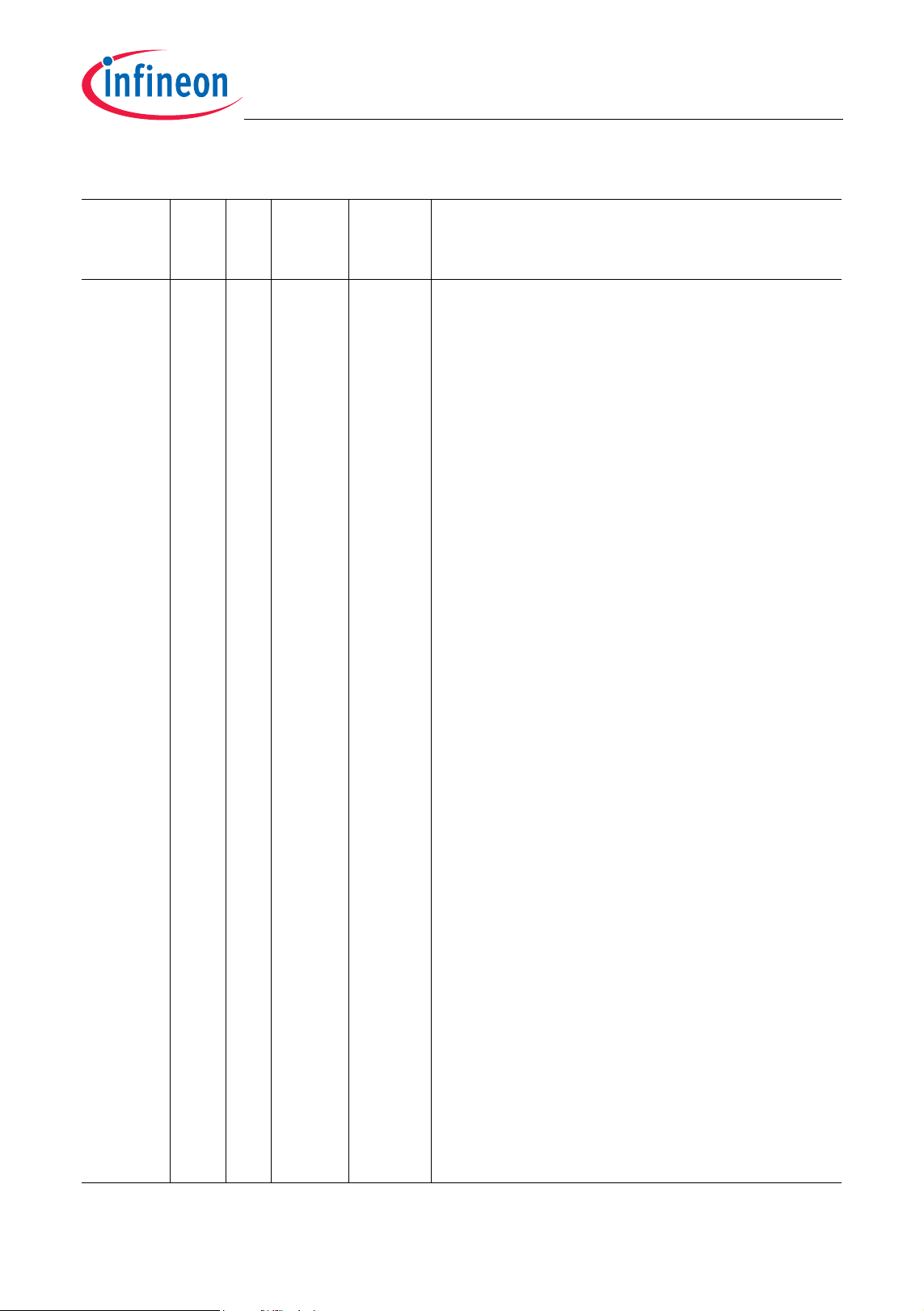
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Class
P5.8
P5.9
P5.10
P5.11
P5.12
P5.13
13
14
15
16
17
18
Power
Supply
Functions
OCDSDBG8
TDATA1
RDATA0B
OCDSDBG9
TVALID1
RVALID0B
OCDSDBG10
TREADY1
RREADY0B
OCDSDBG11
TCLK1
RCLK0B
OCDSDBG12
RDATA1
TDATA0B
OCDSDBG13
RVALID1
TVALID0B
OCDS L2 Debug Line 8
(Indirect PC Addr. PC0)
MLI1 transmit channel data
output
MLI0 receive channel data
B
input
OCDS L2 Debug Line 9
(Indirect PC Addr. PC1)
MLI1 transmit channel valid
output
MLI0 receive channel valid
input B
OCDS L2 Debug Line 10
(Indirect PC Addr. PC2)
MLI1 transmit channel ready
input
MLI0 receive channel ready
output B
OCDS L2 Debug Line 11
(Indirect PC Addr. PC3)
MLI1 transmit channel clock
output
MLI0 receive channel clock
B
input
OCDS L2 Debug Line 12
(Indirect PC Addr. PC04)
MLI1 receive channel data
input
MLI0 transmit channel data
output B
OCDS L2 Debug Line 13
(Indirect PC Addr. PC05)
MLI1 receive channel valid
input
MLI0 transmit channel valid
output B
Data Sheet 17 V0.2, 2006-02
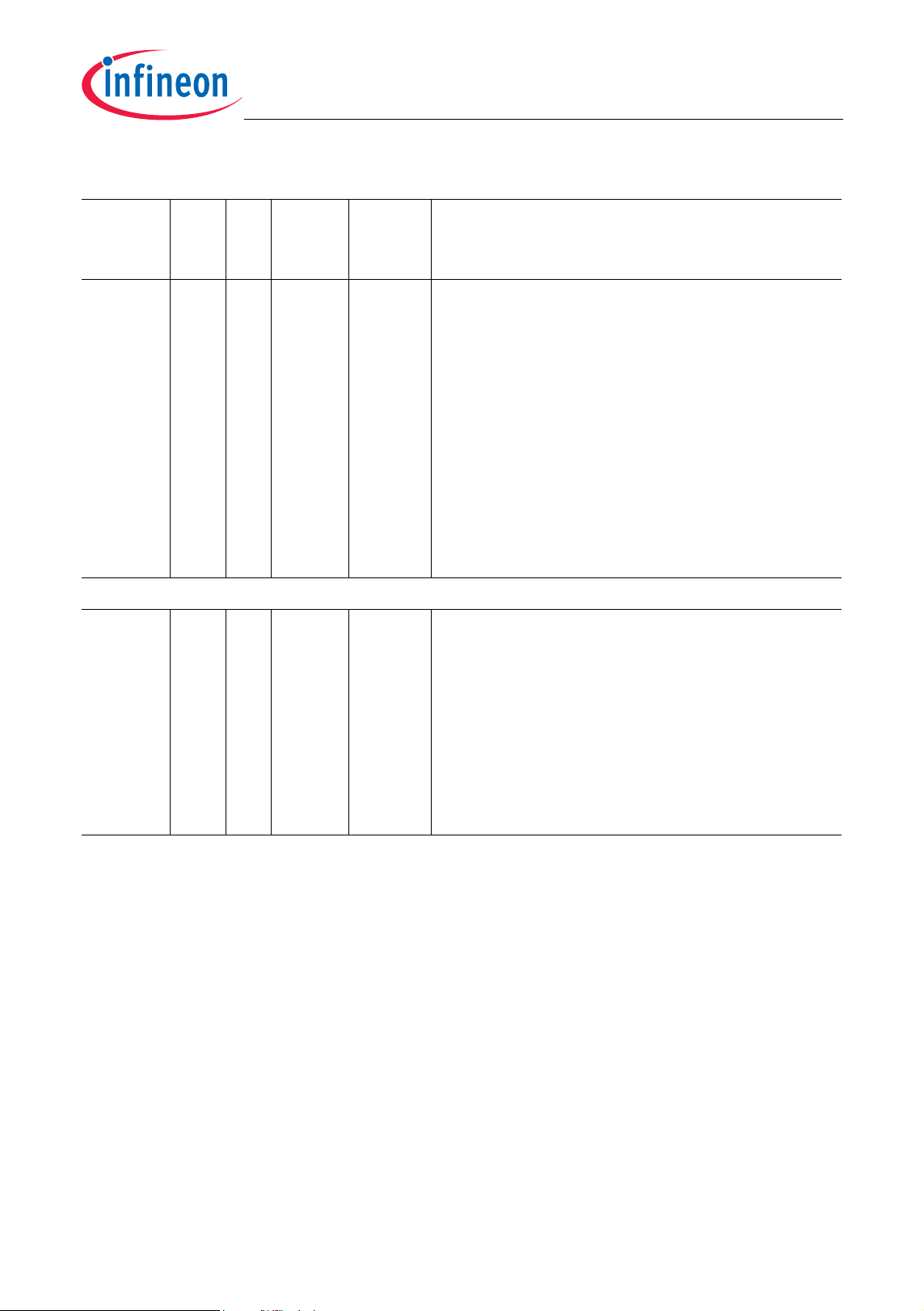
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Class
P5.14
P5.15
19
20
MSC0 Outputs
C V
FCLP0A
FCLN0
SOP0A
SON0
157
156
159
158
O
O
O
O
Power
Supply
DDP
Functions
OCDSDBG14
OCDS L2 Debug Line 14
(Indirect PC Address PC6)
RREADY1
MLI1 receive channel ready
output
TREADY0B
MLI0 transmit channel ready
input B
OCDSDBG15
OCDS L2 Debug Line 15
(Indirect PC Address PC7)
RCLK1
MLI1 receive channel clock
input
TCLK0B
MLI0 transmit channel clock
output B
LVDS MSC Clock and Data Outputs
4)
MSC0 Differential Driver Clock Output
Positive A
MSC0 Differential Driver Clock Output
Negative
MSC0 Differential Driver Serial Data Output
Positive A
MSC0 Differential Driver Serial Data Output
Negative
Data Sheet 18 V0.2, 2006-02
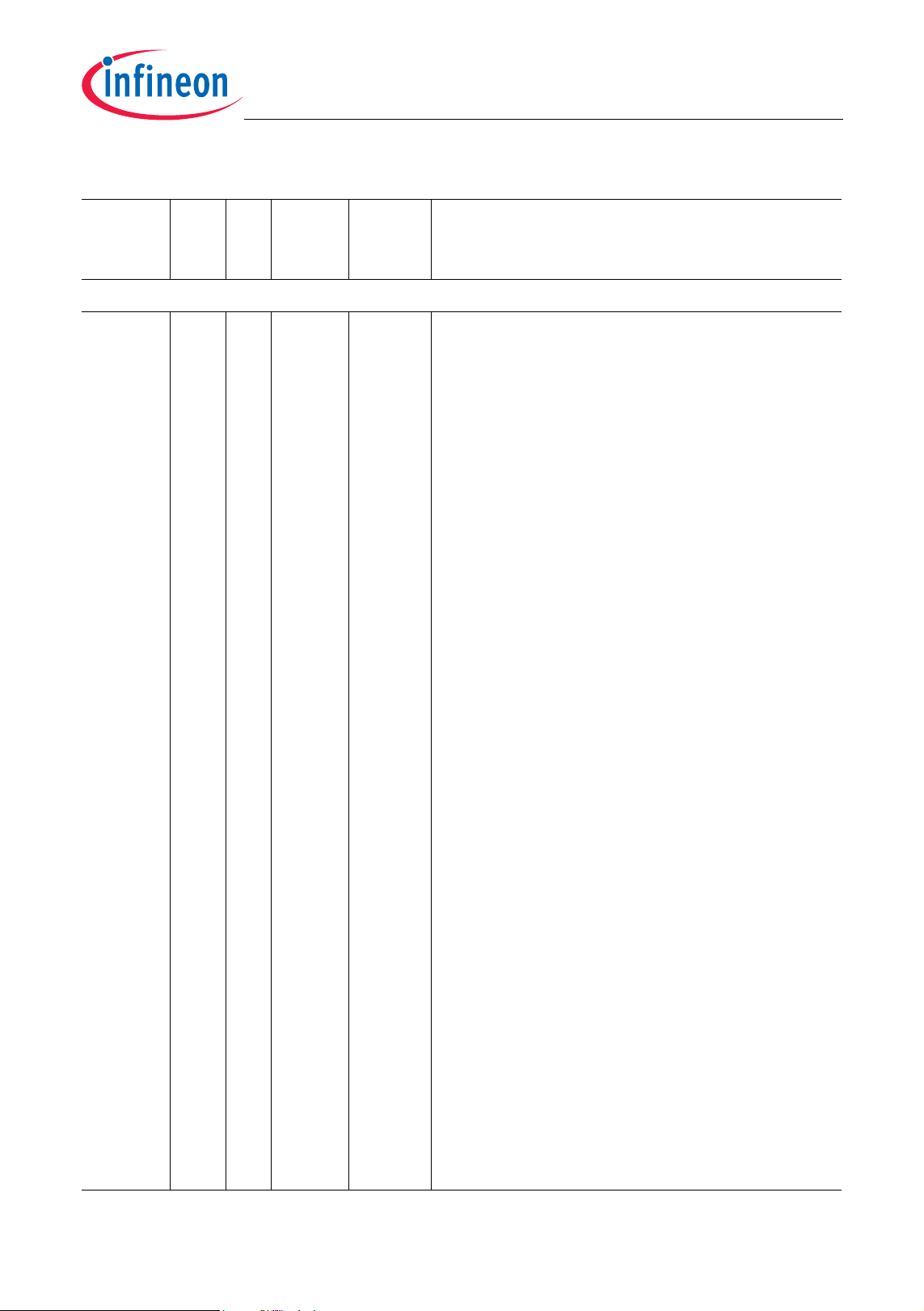
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Class
Analog Inputs
AN[35:0]
AN0
AN1
AN2
AN3
AN4
AN5
AN6
AN7
AN8
AN9
AN10
AN11
AN12
AN13
AN14
AN15
AN16
AN17
AN18
AN19
AN20
AN21
AN22
AN23
AN24
AN25
AN26
AN27
AN28
AN29
AN30
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
36
60
59
58
57
56
55
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
35
34
33
I D – Analog Input Port
Power
Supply
Functions
The Analog Input Port provides altogether 36
analog input lines to ADC0 and FADC.
AN[31:0]: ADC0 analog inputs [31:0]
AN[35:32]: FADC analog differential inputs
Analog input 0
Analog input 1
Analog input 2
Analog input 3
Analog input 4
Analog input 5
Analog input 6
Analog input 7
Analog input 8
Analog input 9
Analog input 10
Analog input 11
Analog input 12
Analog input 13
Analog input 14
Analog input 15
Analog input 16
Analog input 17
Analog input 18
Analog input 19
Analog input 20
Analog input 21
Analog input 22
Analog input 23
Analog input 24
Analog input 25
Analog input 26
Analog input 27
Analog input 28
Analog input 29
Analog input 30
Data Sheet 19 V0.2, 2006-02
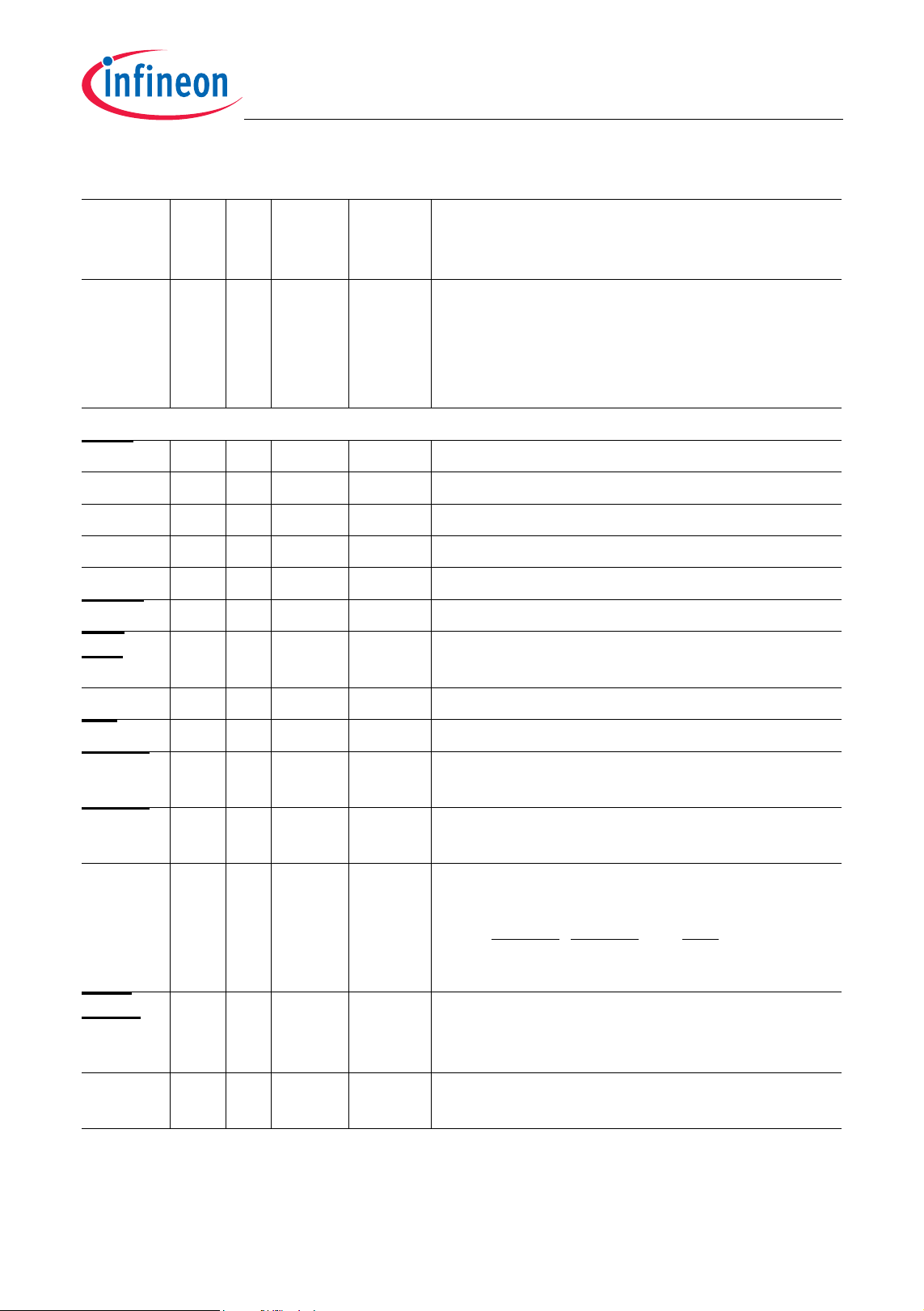
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Power
Supply
Class
AN31
AN32
AN33
AN34
AN35
32
31
30
29
28
I D – Analog input 31
System I/O
TRST
114 I A2
TCK 115 I A2
TDI 111 I A1
3)
3)
3)
V
V
V
TDO 113 O A2 V
TMS 112 I A2
3)
V
BRKIN 117 I/O A3 V
BRK
116 I/O A3 V
OUT
TRCLK 9 O A4 V
NMI 120 I A2
HDRST 122 I/O A2
PORST 9)121 I A2
6)7)
8)
6)7)
V
V
V
DDP
DDP
DDP
DDP
DDP
DDP
DDP
DDP
DDP
DDP
DDP
Functions
Analog input 32
Analog input 33
Analog input 34
Analog input 35
JTAG Module Reset/Enable Input
JTAG Module Clock Input
JTAG Module Serial Data Input
JTAG Module Serial Data Output
JTAG Module State Machine Control Input
OCDS Break Input (Alternate Output)
OCDS Break Output (Alternate Input)
Trace Clock for OCDS_L2 Lines
4)5)
4)5)
4)
Non-Maskable Interrupt Input
Hardware Reset Input /
Reset Indication Output
Power-on Reset Input
BYPASS 119 I A1
3)
V
DDP
PLL Clock Bypass Select Input
This input has to be held stable during poweron resets. With BYPASS = 1, the spike filters
in the
HDRST, PORST and NMI inputs are
switched off.
TEST
MODE
118 I A2
6)10)
V
DDP
Test Mode Select Input
For normal operation of the TC1165/TC1166,
this pin should be connected to high level.
XTAL1
XTAL2
Data Sheet 20 V0.2, 2006-02
102
103I O
n.a. V
DDOSC
Oscillator/PLL/Clock Generator
Input/Output Pins
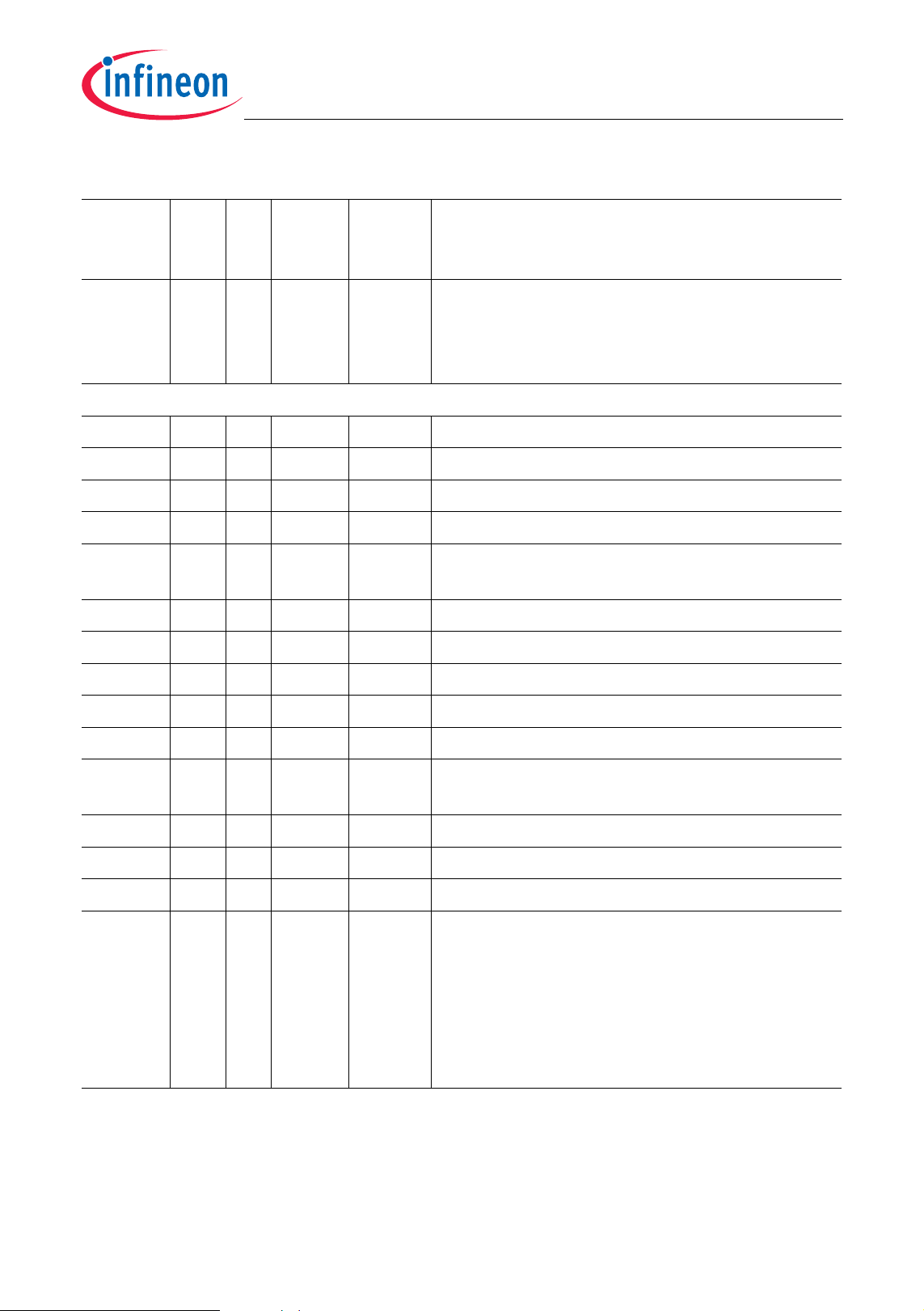
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Power
Supply
Functions
Class
N.C. 21, 89– – – Not Connected
These pins are reserved for future extension
and must not be connected externally.
Power Supplies
V
V
V
V
V
DDM
SSM
DDMF
SSMF
DDAF
54 – – – ADC Analog Part Power Supply (3.3 V)
53 – – – ADC Analog Part Ground for V
24 – – – FADC Analog Part Power Supply (3.3 V)
25 – – – FADC Analog Part Ground for V
23 – – – FADC Analog Part Logic Power Supply
(1.5 V)
V
SSAF
V
AREF0
V
AGND0
V
FAREF
V
FAGND
V
DDOSC
22 – – – FADC Analog Part Logic Ground for V
52 – – – ADC Reference Voltage
51 – – – ADC Reference Ground
26 – – – FADC Reference Voltage
27 – – – FADC Reference Ground
105 – – – Main Oscillator and PLL Power Supply
(1.5 V)
DDM
DDMF
DDAF
V
DDOSC3
V
SSOSC
V
DDFL3
V
DD
106 – – – Main Oscillator Power Supply (3.3 V)
104 – – – Main Oscillator and PLL Ground
141 – – – Power Supply for Flash (3.3 V)
10,
– – – Core Power Supply (1.5 V)
68,
84,
99,
123,
153,
170
Data Sheet 21 V0.2, 2006-02
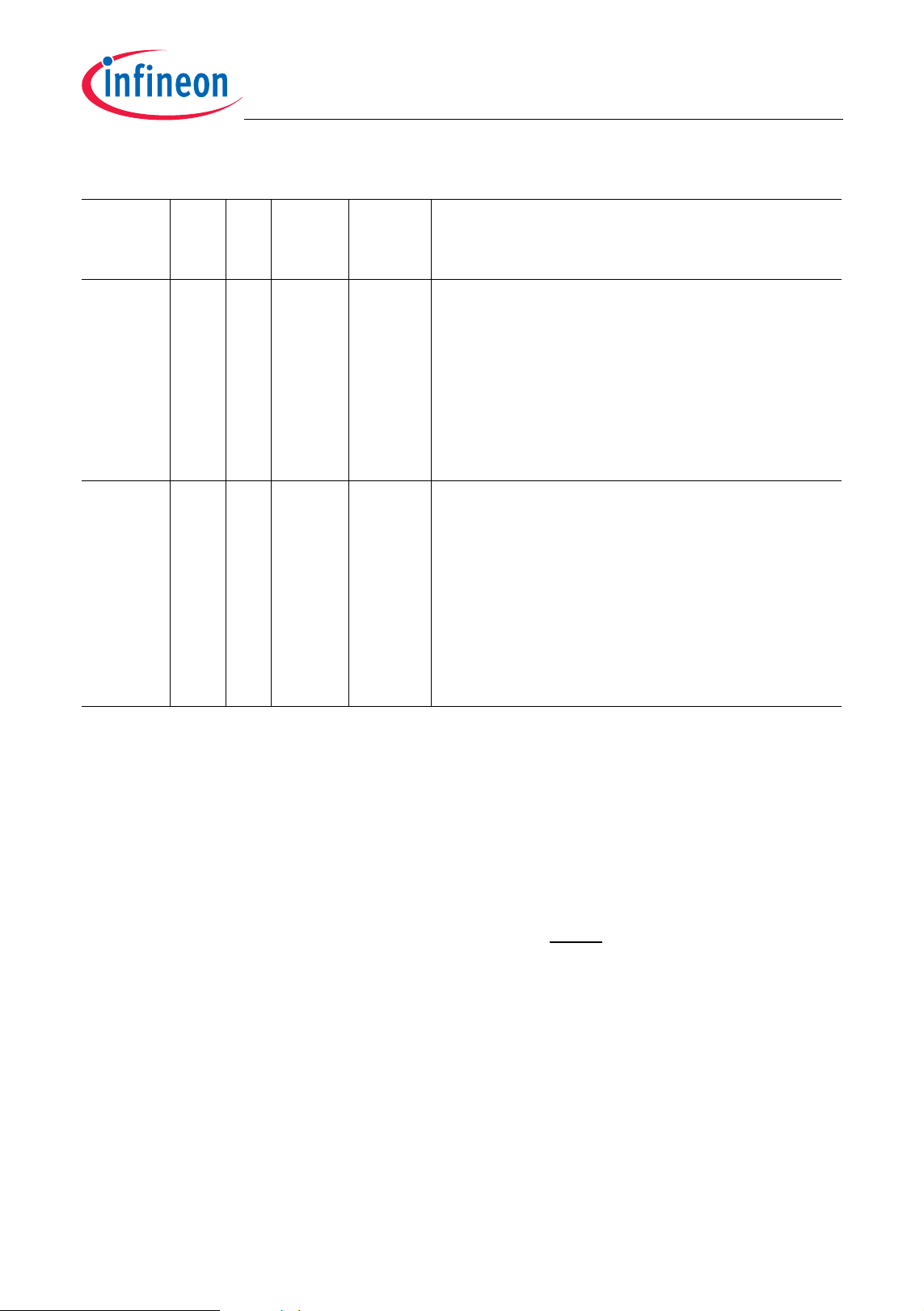
Table 2-1 Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Symbol Pins I/O Pad
Driver
Power
Supply
Functions
Class
V
DDP
11,
– – – Port Power Supply (3.3 V)
69,
83,
100,
124,
154,
171,
139
V
SS
12,
– – – Ground
70,
85,
101,
125,
155,
172,
140,
82
1) Not applicable to TC1165
2) The logical AND function of the two slave select outputs is available as a third alternate output function.
3) These pads are I/O pads with input only function. Its input characteristics are identical with the input
characteristics as defined for class A pads.
4) In case of a power-fail condition (one or more power supply voltages drop below the specified voltage range),
an undefined output driving level may occur at these pins.
5) Programmed by software as either break input or break output.
6) These pads are input only pads with input characteristics.
7) Input only pads with input spike filter.
8) Open drain pad with input spike filter.
9) The dual input reset system of TC1165/TC1166 assumes that the PORST reset pin is used for power on reset
only.
10) Input only pads without input spike filter.
Data Sheet 22 V0.2, 2006-02

TC1165/TC1166
General Device InformationAdvance Information
Table 2-2 List of Pull-up/Pull-down Reset Behavior of the Pins
Pins PORST = 0 PORST = 1
All GPIOs, TDI, TMS, TDO Pull-up
HDRST Drive-low Pull-up
BYPASS Pull-up High-impedance
TRST, TCK High-impedance Pull-down
TRCLK High-impedance
BRKIN, BRKOUT, TESTMODE Pull-up
NMI, PORST Pull-down
Data Sheet 23 V0.2, 2006-02

TC1165/TC1166
Functional DescriptionAdvance Information
3 Functional Description
Chapter 3 provides an overview of the TC1165/TC1166 functional description.
3.1 System Architecture and On-Chip Bus Systems
The TC1165/TC1166 has two independent on-chip buses (see also TC1165/TC1166
block diagram on Page 2-6):
• Local Memory Bus (LMB)
• System Peripheral Bus (SPB)
The LMB Bus connects the CPU local resources for data and instruction fetch. The Local
Memory Bus interconnects the memory units and functional units, such as CPU and
PMU. The main target of the LMB bus is to support devices with fast response times,
optimized for speed. This allows the DMI and PMI fast access to local memory and
reduces load on the FPI bus. The Tricore system itself is located on LMB bus.
The Local Memory Bus is a synchronous, pipelined, split bus with variable block size
transfer support. It supports 8-, 16-, 32- and 64-bit single transactions and variable
length 64-bit block transfers.
The SPB Bus is mainly governed by the PCP and is accessible to the CPU via the LMB
Bus bridge. The System Peripheral Bus (SPB Bus) in TC1165/TC1166 is an on-chip FPI
Bus. The FPI Bus interconnects the functional units of the TC1165/TC1166, such as the
DMA and on-chip peripheral components. The FPI Bus is designed to be quick to be
acquired by on-chip functional units, and quick to transfer data. The low setup overhead
of the FPI Bus access protocol guarantees fast FPI Bus acquisition, which is required for
time-critical applications.The FPI Bus is designed to sustain high transfer rates. For
example, a peak transfer rate of up to 320 Mbyte/s can be achieved with a 80 MHz bus
clock and 32-bit data bus. Multiple data transfers per bus arbitration cycle allow the FPI
Bus to operate at close to its peak bandwidth.
Both the LMB Bus and the SPB Bus runs at full CPU speed. The maximum CPU speed
is 80 MHz.
Additionally, two simplified bus interfaces are connected to and controlled by the DMA
Controller:
•DMA Bus
• SMIF Interface
Data Sheet 24 V0.2, 2006-02

TC1165/TC1166
Functional DescriptionAdvance Information
3.2 On-Chip Memories
As shown in the TC1165/TC1166 block diagram on Page 2-6, some of the
TC1165/TC1166 units provide on-chip memories that are used as program or data
memory.
• Program memory in PMU
– 16 Kbyte Boot ROM (BROM)
– 1504 Kbyte Program Flash (PFlash)
• Program memory in PMI
– 16 Kbyte Scratch-Pad RAM (SPRAM)
– 8 Kbyte Instruction Cache (ICACHE)
• Data memory in PMU
– 32 Kbyte Data Flash (DFlash)
– 8 Kbyte Overlay RAM (OVRAM)
• Data memory in DMI
– 56 Kbyte Local Data RAM (LDRAM)
• Memory of PCP2
– 12 Kbyte Code Memory (CMEM) with parity error protection
– 8 Kbyte Parameter RAM (PRAM) with parity error protection
• On-chip SRAM with parity error protection
Features of Program Flash
• 1504 Kbyte on-chip program Flash memory
• Usable for instruction code or constant data storage
• 256-byte program interface
– 256 bytes are programmed into PFLASH page in one step/command
• 256-bit read interface
– Transfer from PFLASH to CPU/PMI by four 64-bit single cycle burst transfers
• Dynamic correction of single-bit errors during read access
• Detection of double-bit errors
• Fixed sector architecture
– Eight 16 Kbyte, one 128 Kbyte, one 256 Kbyte, one 512 Kbyte and one 480 Kbyte
sectors
– Each sector separately erasable
– Each sector separately write-protectable
• Configurable read protection for complete PFLASH with sophisticated read access
supervision, combined with write protection for complete PFLASH (protection against
“Trojan horse” software)
• Configurable write protection for each sector
– Each sector separately write-protectable
– With capability to be re-programmed
– With capability to be locked forever (OTP)
• Password mechanism for temporary disabling of write and read protection
Data Sheet 25 V0.2, 2006-02

TC1165/TC1166
Functional DescriptionAdvance Information
• On-chip generation of programming voltage
• JEDEC-standard based command sequences for PFLASH control
– Write state machine controls programming and erase operations
– Status and error reporting by status flags and interrupt
• Margin check for detection of problematic PFLASH bits
Features of Data Flash
• 32 Kbyte on-chip data Flash memory, organized in two 16 Kbyte banks
• Usable for data storage with EEPROM functionality
• 128 Byte of program interface
– 128 bytes are programmed into one DFLASH page by one step/command
• 64-bit read interface (no burst transfers)
• Dynamic correction of single-bit errors during read access
• Detection of double-bit errors
• Fixed sector architecture
– Two 16 Kbyte banks/sectors
– Each sector separately erasable
• Configurable read protection (combined with write protection) for complete DFLASH
together with PFLASH read protection
• Password mechanism for temporary disabling of write and read protection
• Erasing/programming of one bank possible while reading data from the other bank
• Programming of one bank while erasing the other bank possible
• On-chip generation of programming voltage
• JEDEC-standard based command sequences for DFLASH control
– Write state machine controls programming and erase operations
– Status and error reporting by status flags and interrupt
• Margin check for detection of problematic DFLASH bits
Data Sheet 26 V0.2, 2006-02
 Loading...
Loading...