ICST MK1422STR, MK1422S Datasheet
MK1422
OPL3/4+Codec Portable Clock Source
Description
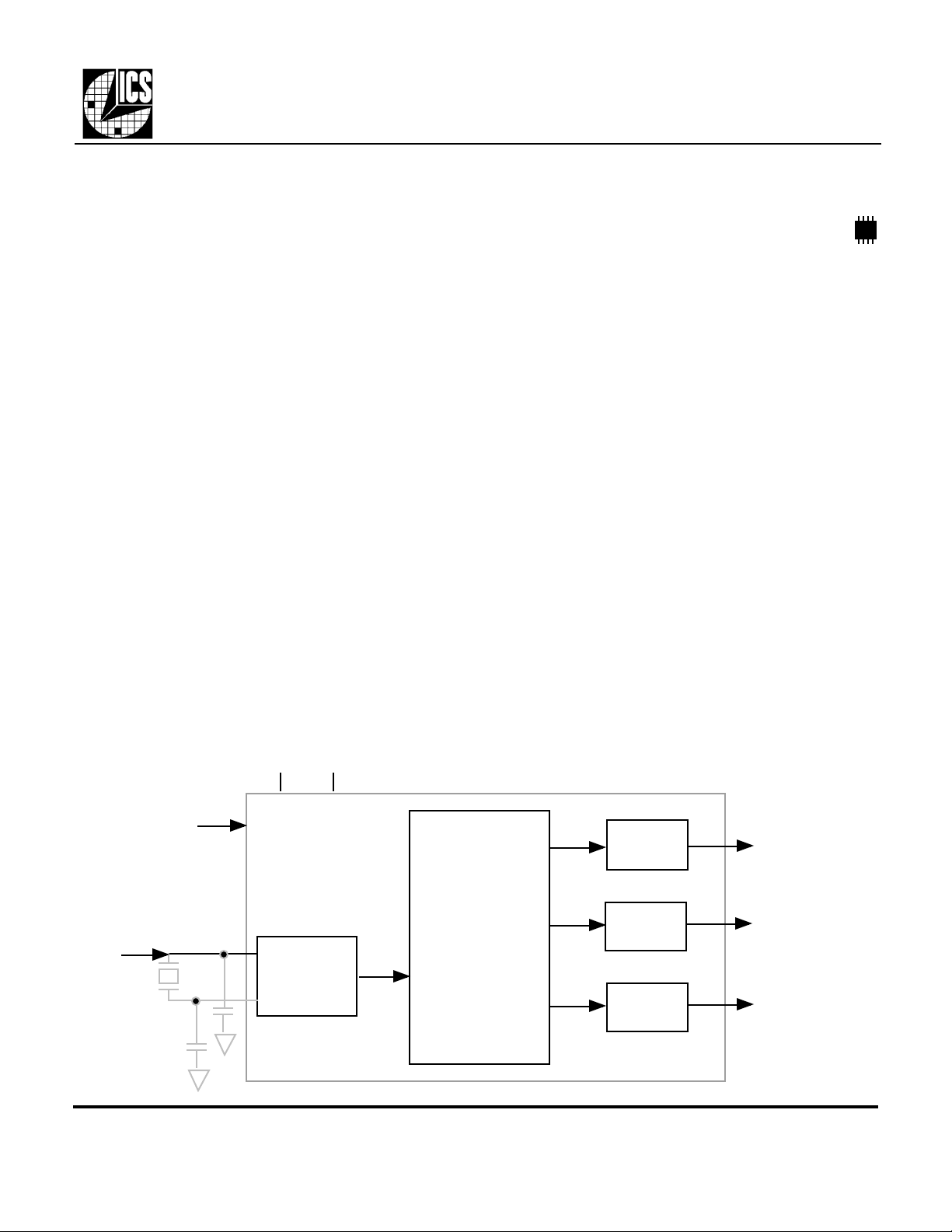
The MK1422 is the ideal way to generate clocks
for sound in portable computers. It provides clocks
for Analog Devices’ or Crystal Semiconductor’s
stereo codecs, and Yamaha’s OPL3L, OPL3LS,
and OPL4. The MK1422 uses either a
14.318 MHz crystal, or a 14.318 MHz bus clock
input to synthesize the clocks required to drive the
codec, and the 33.868 MHz required for the FM
or wavetable music synthesizer. It includes a power
down pin to save power without using a FET. In an
8 pin SOIC, the MK1422 can save component
count, board space, and cost over surface mount
crystals, and increase reliability by eliminating
three mechanical devices from the board.
MicroClock offers many other parts with stereo
codec support. MicroClock invented sound clocks,
and has the widest product offering and greatest
production experience on these devices. The
MK1422 is pin compatible with MicroClock’s
popular MK1420 when the 14.318MHz clock
output is not used. See the MK14223 for 3.3V.
Block Diagram
VDD GND
Features
• Packaged in 8 pin SOIC
• Input crystal or clock frequency of 14.318 MHz
• Output clock frequencies of 16.934 MHz,
24.576 MHz, and 33.868 MHz
• 25mA drive capability at TTL levels
• Advanced, low power CMOS process
• Low jitter ensures full 16 bit S/N ratio
• Insensitive to input clock duty cycle
• Power down for portable computers
AC Coupling/Portable Applications
For applications in portable computers, see the
MK14223, which is specified to operate at 3.3V. It
is possible to drive the MK1422 with a 3.3V,
14.318MHz clock by a.c. coupling using a 0.01µF
capacitor connected in series to the X1 pin. But the
operating VDD on pin 2 must be 5V±10%. This
technique is also effective if the input clock doesn’t
meet the VIH and VIL specifications on page 3.
Additional Clocks or Features
If more than these three output clocks or features
such as output enable are needed, MicroClock can
provide a quick turn modification for your custom
requirements.
All Chip
Power Down
14.318 MHz
crystal or clock
X1/ICLK
Crystal
Oscillator
X2
MDS 1422 B 1 Revision 080698 Printed 11/15/00
Integrated Circuit Systems•525 Race Street•San Jose•CA•95126•(408)295-9800tel•www.icst.com
Clock Synthesis
Circuitry
Output
Buffer
Output
Buffer
Output
Buffer
16.934 MHz
24.576 MHz
33.868 MHz
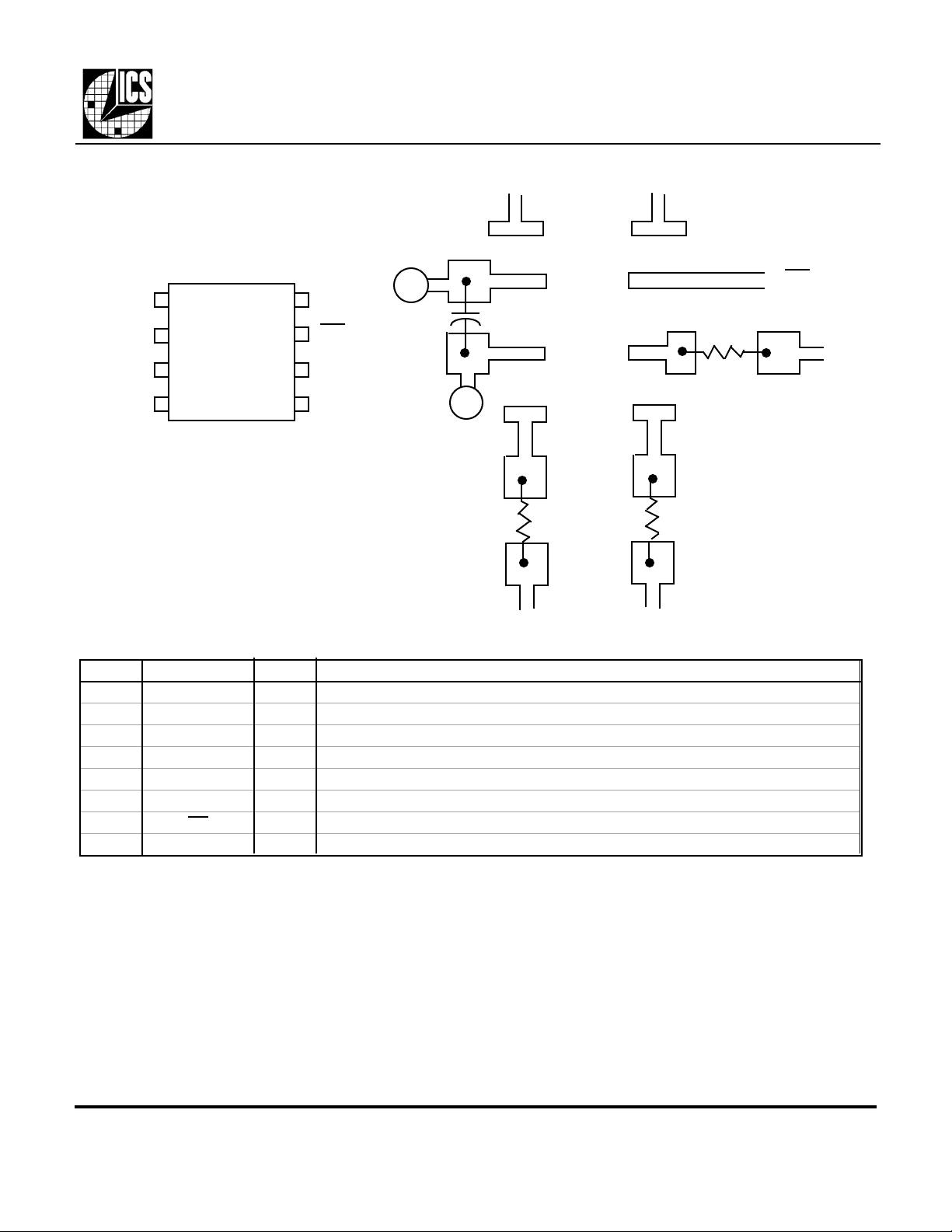
Pin Assignment
MK1422
OPL3/4+Codec Portable Clock Source
Suggested Layout
14.318 MHz in
X1/ICLK
1 8
X2
V
Pin 1
2
8
7
0.1µF
VDD
GND
2
3
7
PD
3
6
33.9M
6
33Ω (optional)
16.9M
4
5
24.6M
33Ω (optional)
G
16.9MHz out
4
5
33Ω (optional)
24.6MHz out
Pin Descriptions
Number Name Type Description
1 X1/ICLK I Crystal Connection. Connect to a 14.318 MHz crystal or clock.
2 VDD P Connect to +5V.
3 GND P Connect to ground.
4 16.9M O 16.9344 MHz clock output for stereo codec.
5 24.6M O 24.576 MHz clock output for stereo codec.
6 33.9M O 33.868 MHz clock output for OPL4.
7 PD I Power Down. Shuts off entire chip when low. All clock outputs stop low.
8 X2 O Crystal Connection to a 14.318 MHz crystal, or leave unconnected for clock input.
PD
33.9MHz
out
Key: I = Input, O = output, P = power supply connection
External Components/Crystal Selection
A minimum number of external components are required for proper oscillation. For a crystal input, one
22pF load capacitor should be connected to each of the X1 and X2 pins and ground, and a parallel
resonant 14.318 MHz, 16pF load, crystal is recommended. Load capacitor values near these are acceptable,
as is a series resonant crystal, but either will result in frequencies which are further off of the target
frequency. For a clock input, connect to X1 and leave X2 unconnected. A decoupling capacitor of 0.1µF
should be connected between VDD and GND, and 33Ω terminating resistors may be used on the clock
outputs.
MDS 1422 B 2 Revision 080698 Printed 11/15/00
Integrated Circuit Systems•525 Race Street•San Jose•CA•95126•(408)295-9800tel•www.icst.com
 Loading...
Loading...