Page 1

SERVICE
MANUAL
UHF TRANSCEIVER
iF510
iF520
Page 2

VERSION
Europe
General
U.S.A.
SYMBOL
EUR
GEN
USA
INTRODUCTION
This service manual describes the latest service information
for the IC-F510 and IC-F520 VHF TRANSCEIVERS at the
time of publication.
DANGER
NEVER connect the transceiver to an AC outlet or to a DC
power supply that uses more than 16 V. This will ruin the
transceiver.
DO NOT expose the transceiver to rain, snow or any liquids.
DO NOT reverse the polarities of the power supply when
connecting the transceiver.
DO NOT apply an RF signal of more than 20 dBm (100 mW)
to the antenna connector. This could damage the transceiver’s front end.
ORDERING PARTS
Be sure to include the following four points when ordering
replacement parts:
1. 10-digit order numbers
2. Component part number and name
3. Equipment model name and unit name
4. Quantity required
<SAMPLE ORDER>
1110003490 S.IC TA31136FN IC-F510 MAIN UNIT 5 pieces
8810009990 Screw PH BT M3
×8 ZK IC-F520 Bottom cover 10 pieces
Addresses are provided on the inside back cover for your
convenience.
REPAIR NOTES
1. Make sure a problem is internal before disassembling the
transceiver.
2. DO NOT open the transceiver until the transceiver is
disconnected from its power source.
3. DO NOT force any of the variable components. Turn
them slowly and smoothly.
4. DO NOT short any circuits or electronic parts. An insulated tuning tool MUST be used for all adjustments.
5. DO NOT keep power ON for a long time when the transceiver is defective.
6.
DO NOT transmit power into a signal generator or a
sweep generator.
7.
ALWAYS connect a 40 dB to 50 dB attenuator between
the transceiver and a deviation meter or spectrum analyzer when using such test equipment.
8.
READ the instructions of test equipment thoroughly
before connecting equipment to the transceiver.
MODEL
IC-F510
IC-F520
To upgrade quality, any electrical or mechanical parts and
internal circuits are subject to change without notice or
obligation.
Page 3
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEW
SECTION 3 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4 - 1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 1
4 - 2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 2
4 - 3 PLL CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 3
4 - 4 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 4
4 - 5 PORT ALLOCATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 - 4
SECTION 5 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
5 - 1 PREPARATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 - 1
5 - 2 PLL ADJUSTMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 - 3
5 - 3 SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 - 4
SECTION 6 PARTS LIST
SECTION 7 MECHANICAL PARTS
SECTION 8 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
SECTION 9 BOARD LAYOUTS
9 - 1 FRONT UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 1
9 - 2 MAIN UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9 - 3
SECTION 10 BLOCK DIAGRAM
SECTION 11 VOLTAGE DIAGRAMS
11 - 1 FRONT UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 - 1
11 - 2 MAIN UNIT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11 - 2
EXPLICIT DEFINITIONS
136 – 174 MHz
FREQUENCY COVERAGE
12.5 kHz / 25.0 kHz
15.0 kHz / 30.0 kHz
12.5 kHz / 20.0 kHz
Narrow/Wide-type
Narrow/Middle-type
CHANNEL SPACING
Page 4
1 - 1
All stated specifications are subject to change without notice or obligation.
SECTION 1 SPECIFICATIONS
Measurement method
Frequency coverage
Type of emission
Number of conventional channels
Power supply voltage (negative ground)
Current drain (approx.)
Frequency error
Usable temperature range
Dimensions (proj. not included)
Weight
RF output power
Modulation system
Maximum permissible deviation
Spurious emissions
Adjacent channel power
Audio frequency response
Audio hormonic distortion
FM hum and noise (typical)
(without CCICT filter)
Residual modulation (typical)
(with CCICT filter)
Limitting charact of modulator
Microphone connector
Receive system
Intermediate frequencies
Sensitivity (typical)
Squelch sencitivity (at threshold) (typical)
Adjcent channel selectivity (typical)
Spurious response
Intermoduration (typical)
Hum and noise
(without CCITT filter)
(typical)
(with CCITT filter)
Audio output power
External SP connector
USA/GEN EUR
RECEIVER TRANSMITTER GENERAL
EIA-152-C/204D or TIA-603 ETS 300 086
136.000–174.000 MHz
N/W (15 kHz; Narrow/30 kHz; Wide): 8K50F3E/16K0F3E [USA],
N/W (12.5 kHz; Narrow/25 kHz; Wide): 8K50F3E/16K0F3E [EUR/GEN],
N/M (12.5 kHz; Narrow/20 kHz; Middle): 8K50F3E/14K0F3E [EUR]
Max. 256 ch (16 channels
× 16 banks)
13.6 V DC nominal 13.2 V DC nominal
TX at 25 W 7.0 A
Rx max. audio 1200 mA
stand-by 300 mA
5.0 ppm ±1.5 kHz
–30˚C to +60˚C (–22˚F to +140˚F) –25˚C to +55˚C (–13˚F to +131˚F)
140(W)
× 40(H) × 170(D) mm; 5
1
⁄2(W) × 19⁄16(H) × 611⁄16(D) inch
1.2 kg; 2 lb 10 oz
25 W / 10 W / 2.5 W (High/Low2/Low1)
Variable reactance frequency modulation
±2.5 kHz [Narrow], ±4.0 kHz [Middle], ±5.0 kHz [Wide]
70 dBc typical 0.25 µW ≤ 1GHz, 1.0 µW > 1 GHz
60 dB [Narrow], 70 dB [Middle/Wide]
+2 dB to –5 dB of 6 dB/octarve
range from 300 Hz to 2550 Hz [Narrow]/3000 Hz [Middle/Wide]
3% typical at 1 kHz, 40% deviation
40 dB [Narrow], 46 dB [Wide] ——
——
50 dB [Narrow], 53 dB [Middle],
55 dB [Wide]
70–100% of max. deviation
8-pin modular (600 Ω)
Double-conversion superheterodyne system
1st: 46.35 MHz, 2nd: 450 kHz
0.25 µV at 12 dB SINAD –4 dBµV (emf) at 20 dB SINAD
0.25 µV –4 dBµV (emf)
65 dB [Narrow], 75 dB [Middle/Wide]
75 dB
74 dB 67 dB
40 dB [Narrow], 45 dB [Wide] ——
——
50 dB [Narrow], 53 dB [Middle], 55 dB [Wide]
4 W typical at 10% distortion with a 4 Ω load
2-conductor 3.5 (d) mm (
1
⁄8")/4 Ω
Page 5
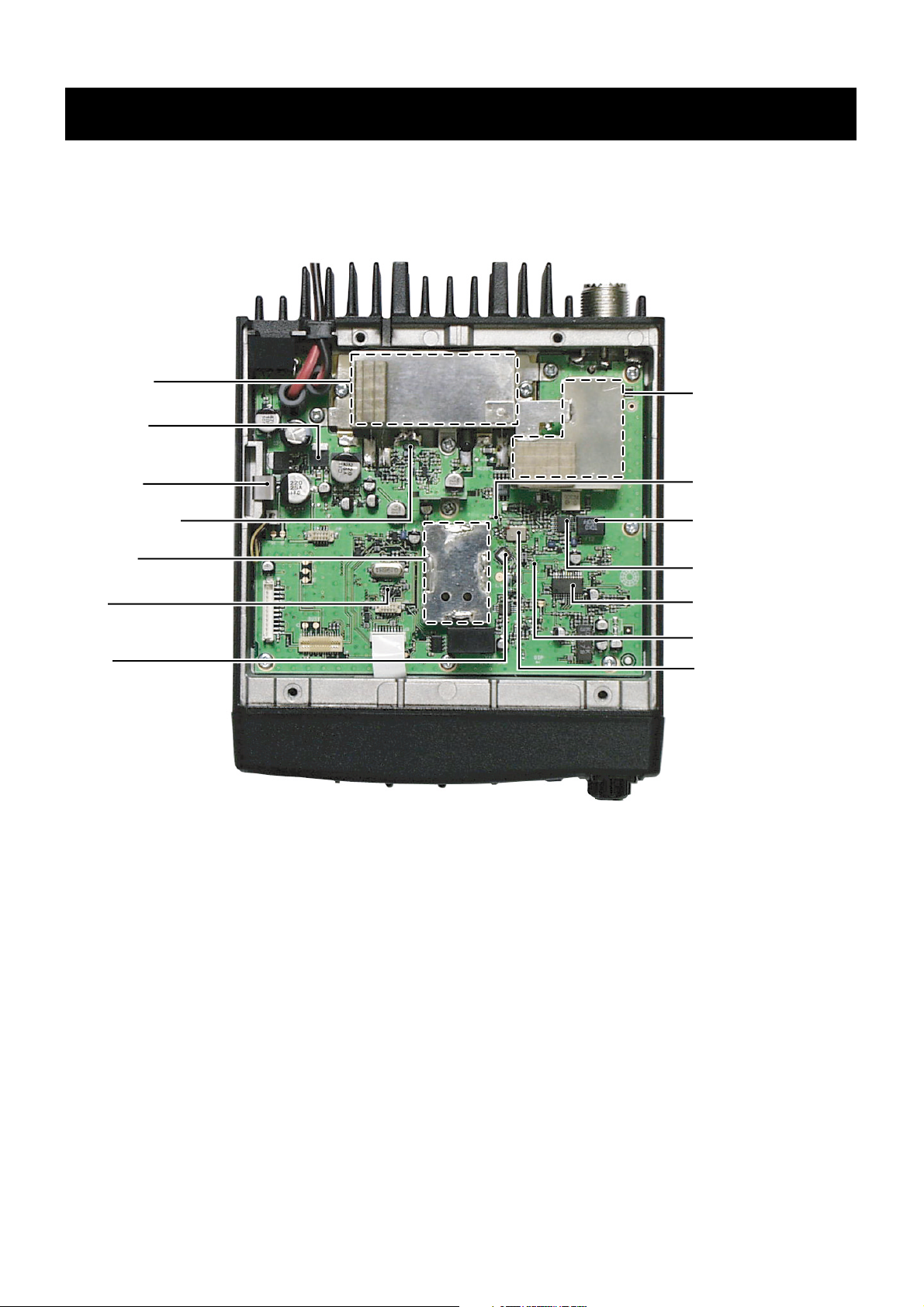
SECTION 2 INSIDE VIEW
2 - 1
Power module
(IC3: RA30H1317)
8V regurator
(IC9: TA7808F)
AF amplifier
(IC8: LA4425A)
CPU 5V regurator*
(IC10: AN78L05M)
VCO circuit
CPU*
(IC20: HD64F2268TF)
Antenna switch/
Low-pass filter circuits
1st mixer*
(Q3: 3SK272)
2nd IF filter
(FI2: ALFYM450F=K [N/W]
CFWM450G [N/M])
FM IF IC
(IC1: TA31136FN)
D/A converter
(IC6: M62364FP)
Referance crystal osillator
(X2: CR-664A 15.3 MHz)
PLL IC
(IC4: TB31256FL)
*Located under side of the point.
1st IF filter
FI1: FL-335
Page 6
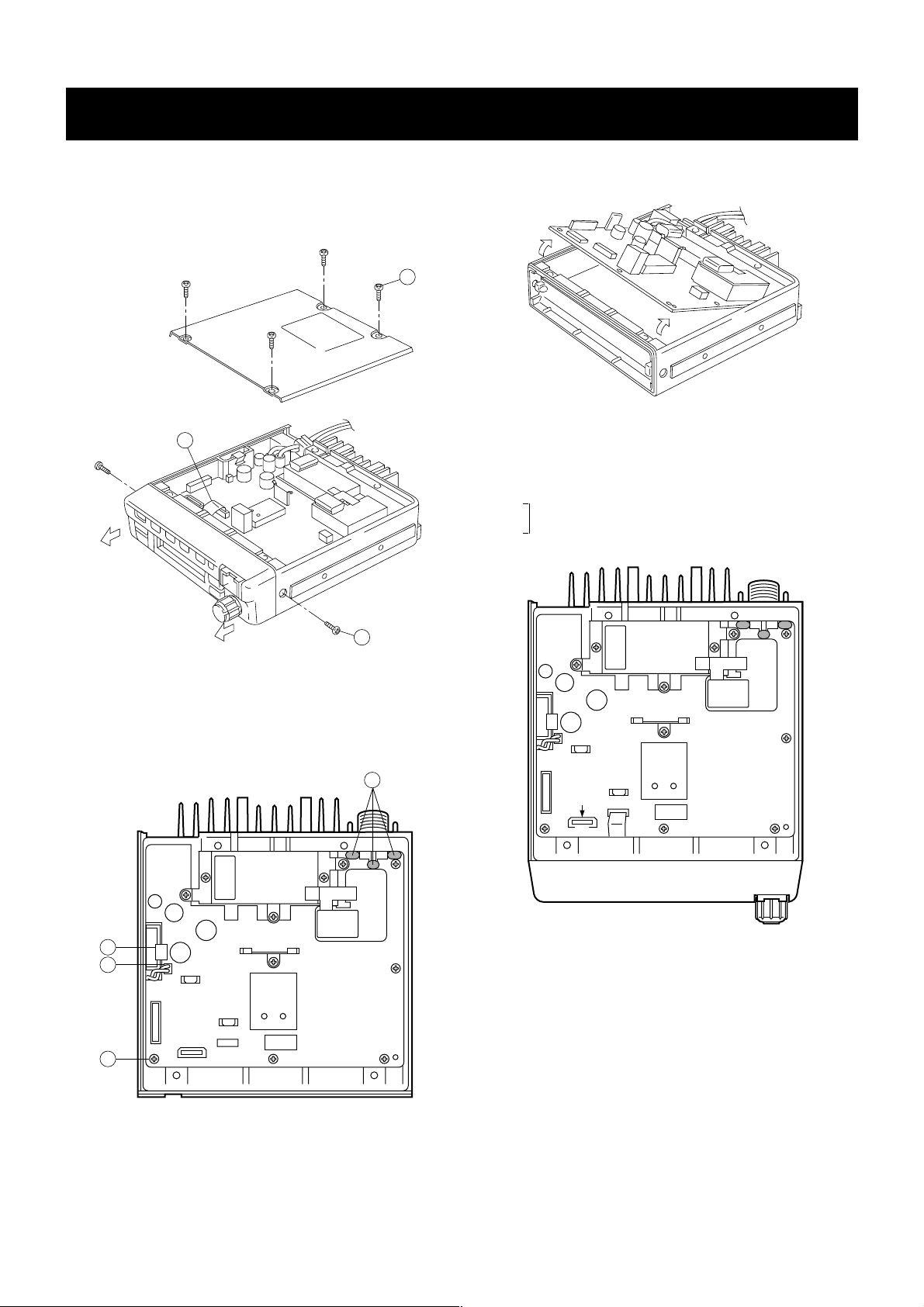
SECTION 3 DISASSEMBLY INSTRUCTIONS
3 - 1
• Opening case
➀ Unscrew 4 screws A, and remove the bottom cover.
➁ Disconnect the flat cable B from J2.
➂ Unscrew 2 screws c, and remove the front unit.
A
B
C
J2
➃ Unsolder 3 points D from the antenna connector.
➄ Remove the clip E.
➅ Disconnect the cable F from J5.
➆ Unscrew 11 screws G.
G
F
E
J5
D
➇ Lift up the front portion of the main unit and remove it.
• Instllation location
UT-105 SmarTrank2 Logic Board
UT-108 DTMF decoder unit
UT-109
Voice scrambler unit
UT-110
UT-111 Trunking unit
UT-105
UT-108
UT-109
UT-110
UT-111
J1
Page 7
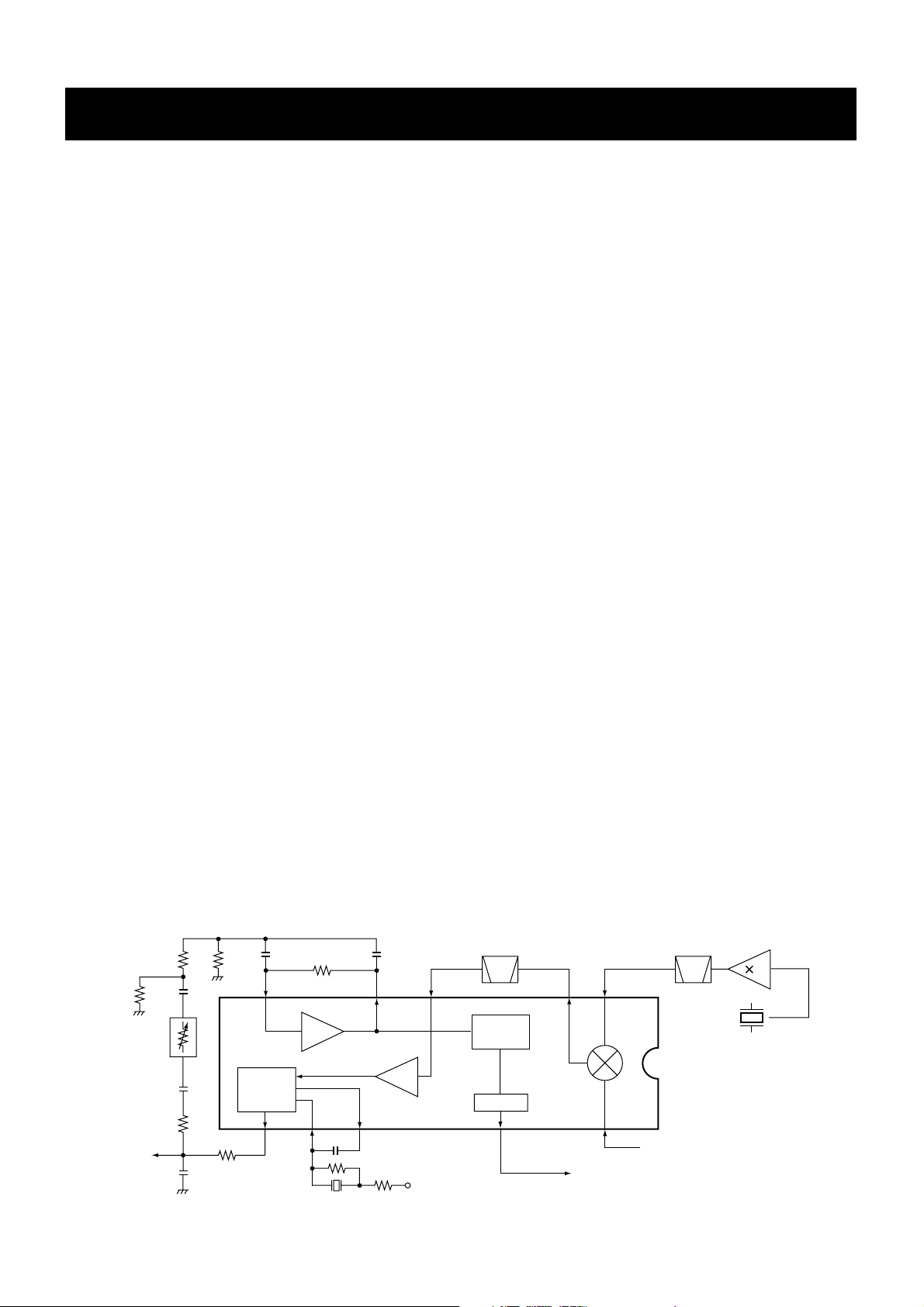
SECTION 4 CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
4 - 1
4-1 RECEIVER CIRCUITS
4-1-1 ANTENNA SWITCHING CIRCUIT (MAIN unit)
The antenna switching circuit functions as a low-pass filter
while receiving and as resonator circuit while transmitting.
The circuit does not allow transmit signals to enter receiver
circuits.
Received signals enter the antenna connector and pass
through the low-pass filter (L1–L3, C1, C2, C6–8). The fil-
tered signals are then applied to the RF circuit passed
through the λ⁄4 type antenna switching circuit (D5, D6, L6).
4-1-2 RF CIRCUIT (MAIN unit)
The RF circuit amplifies signals within the range of frequency coverage and filters out-of-band signals.
The signals from the antenna switching circuit pass through
the two-stage tunable bandpass filters (D8, D4). The filtered
signals are amplified at the RF amplifier (Q2) and then enter
other two-stage bandpass filters (D9, D10) to suppress
unwanted signals. The filtered signals are applied to the 1st
mixer circuit (Q3).
The tunable bandpass filters (D4, D8–D10) employ varactor
diodes to tune the center frequency of the RF passband for
wide bandwidth receiving and good image response rejection. These diodes are controlled by the CPU (IC20) via the
D/A converter (IC7).
The gate control circuit reduces RF amplifier gain and attenuates RF signal to keep the audio output at a constant level.
The receiver gain is determined by the voltage on the “RSSI”
line from the FM IF IC (IC1, pin 12). The gate control circuit
supplies control voltage to the RF amplifier (Q2) and sets
the receiver gain.
When receiving strong signals, the “RSSI” voltage increases
and the gate control voltage decreases. As the gate control
voltage is used for the bias voltage of the RF amplifier (Q2),
then the RF amplifier gain is decreased.
4-1-3 1ST MIXER AND 1ST IF CIRCUITS
(MAIN unit)
The 1st mixer circuit converts the received signals to a fixed
frequency of the 1st IF signal with the PLL output frequency.
By changing the PLL frequency, only the desired frequency
will pass through a MCF (Monolithic Crystal Filter; FI1) at the
next stage of the 1st mixer.
The RF signals from the bandpass filter are applied to the
1st mixer circuit (Q3). The applied signals are mixed with the
1st LO signal coming from the RX VCO circuit (Q13) to produce a 46.35 MHz 1st IF signal. The 1st IF signal passes
through a MCF (Monolithic Crystal Filter; FI1) to suppress
out-of-band signals. The filtered signal is amplified at the 1st
IF amplifier (Q4) and applied to the 2nd IF circuit.
4-1-4 2ND IF AND DEMODULATOR CIRCUITS
(MAIN unit)
The 2nd mixer circuit converts the 1st IF signal to a 2nd IF
signal. A double-conversion superheterodyne system
improves the image rejection ratio and obtains stable receiver gain.
The 1st IF signal from the 1st IF amplifier (Q4) is applied to
the 2nd mixer section of the FM IF IC (IC1, pin 16) and is
then mixed with the 2nd LO signal for conversion to a 450
kHz 2nd IF signal.
IC1 contains the 2nd mixer, limiter amplifier, quadrature
detector, active filter and noise amplifier circuits, etc. A
tripled frequency from the PLL reference oscillator is used
for the 2nd LO signal (45.9 MHz).
The 2nd IF signal from the 2nd mixer (IC1, pin 3) passes
through a ceramic filter (FI2) to remove unwanted heterodyned frequencies. It is then amplified at the limiter amplifier section (IC1, pin 5) and applied to the quadrature detector section (IC1, pins 10, 11 and X1) to demodulate the 2nd
IF signal into AF signals.
The AF signals are output from pin 9 (IC1) and are then
applied to the AF amplifier circuit.
• 2nd IF and demodulator circuits
FI2
2nd IF filter
450 kHz
Noise
detector
Q34
Limiter
amp.
FM
detector
Active
filter
AF signals
5V
X1 Discriminator
IC6
RSSI
Mixer
X2
15.3 MHz
45.9 MHz
1st IF from the IF amplifier (Q4)
NOIS signal to the CPU (IC20)
8
24
23
7
5
BPF
32
3
161311109
IC1
TA31136FN
Page 8

4 - 2
4-1-5 AF AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (MAIN unit)
The AF amplifier circuit amplifies the demodulated AF signals to drive a speaker.
The AF signals from the FM IF IC (IC1, pin 9) are amplified
at the AF amplifier section of the compander IC (IC14, pins
5, 4) and are then applied to the high-pass filter circuit
(IC21b).
The high-pass filter characteristics are controlled by the
FSW signal from the LCD driver IC (FRONT unit; IC1, pin 6).
When FSW signal is high, the cut-off frequency is shifted
higher to remove CTCSS or DTCS signals.
The filtered AF signals from the high-pass filter (IC21b,
pin 7) are applied to the de-emphasis section of compander
IC (IC14, pin 3) with frequency characteristics of –6
dB/octave, and are then passed through the low-pass filter,
high-pass filter, expander sections of compander IC (IC14).
The output signal from IC14 (pin 38) is applied to the electronic volume controller (IC6, pin 1).
The output AF signals from the electronic volume controller
(IC6, pin 2) are applied to the AF power amplifier (IC8) to
drive the speaker.
4-1-6 RECEIVER MUTE CIRCUITS (MAIN unit)
• NOISE SQUELCH
The noise squelch circuit cuts out AF signals when no RF
signals are received. By detecting noise components in the
AF signals, the squelch circuit switches the AF mute switch.
Some noise components in the AF signals from the FM IF IC
(IC1, pin 9) are passed through the level controller (IC6, pins
24, 23). The level controlled signals are applied to the active
filter section in the FM IF IC (IC1, pin 8). Noise components
about 10 kHz are amplified and output from pin 7.
The filtered signals are converted into the pulse-type signals
at the noise detector section and output from pin 13 (NOIS).
The NOIS signal from the FM IF IC is applied to the CPU
(IC20, pin 37). The CPU then analyzes the noise condition
and controls the AF mute signal via “AFON” line (IC20, pin
18) to the AF regulator (Q39, Q40, D31).
• CTCSS AND DTCS
The tone squelch circuit detects AF signals and opens the
squelch only when receiving a signal containing a matching
subaudible tone (CTCSS or DTCS). When tone squelch is in
use, and a signal with a mismatched or no subaudible tone
is received, the tone squelch circuit mutes the AF signals
even when noise squelch is open.
A portion of the AF signals from the FM IF IC (IC1, pin 9)
passes through the low-pass filter (IC5) to remove AF
(voice) signals and is applied to the CTCSS or DTCS
decoder inside the CPU (IC20, pin 46) via the “CDEC” line
to control the AF mute switch.
4-2 TRANSMITTER CIRCUIT
4-2-1 MICROPHONE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT
(MAIN unit)
The microphone amplifier circuit amplifies audio signals
within +6 dB/octave pre-emphasis characteristics from the
microphone to a level needed for the modulation circuit.
The AF signals (MIC) from the FRONT unit via J2 (pin 1) are
passed through the level controller (IC6, pins 9, 10) to the
microphone amplifier circuit.
The AF signals from the level controller (IC6) are applied to
the microphone amplifier section of compander IC (IC14, pin
12). The amplified signals are passed through the compres-
sor, low-pass filter and high-pass filter sections of IC14.
The filtered AF signals are amplified at the buffer amplifier
(Q21) and pre-emphasized with +6dB/octave at the preemphasis circuit (R122, C187), and are then applied to the
IDC amplifier section of IC14 (pin 8).
The amplified AF signals are passed through the limitter
amplifier, low-pass filter and smoothing filter sections of
IC14 after being passed through the AF mute switch inside
of IC14.
The output signals from pin 6 are passed through the analog switch (IC15), splatter filter (IC21d) and applied to the
level controller (IC6, pins 21, 22). The deviation level controlled signals are then applied to modulation circuit as the
“MOD” signal.
The narrow/wide switch (Q22) is connected to the input of
the splatter filter (IC21d) and switched by the “NWC” signal
coming from the CPU (IC20, pin 19). When “NWC” is at a
high level, the narrow/wide switch (Q22) shifts the filter cutoff frequency for narrow deviation selection.
4-2-2 MODULATION CIRCUIT
The modulation circuit modulates the VCO oscillating signal
(RF signal) using the microphone audio signals.
The AF signals from the level controller (IC6, pin 22) change
the reactance of varactor diode (D18) to modulate the oscillated signal at the TX VCO circuit (Q14, D17, D53–D55).
The modulated VCO signal is amplified at the buffer amplifiers (Q11, Q10) and is then applied to the drive amplifier circuit via the T/R switch (D14).
The CTCSS/DTCS signals from the CPU (IC20, pins 89–91)
are passed through the low-pass filter (Q37), level controller
(IC6, pins 12, 11) and mixer (IC21a), and are then applied to
the VCO circuit via the splatter filter (IC21d).
4-2-3 DRIVE AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (MAIN unit)
The drive amplifier circuit amplifies the VCO oscillating signal to the level needed at the power amplifier.
The RF signal from the buffer amplifier (Q10) passes
through the T/R switch (D14) and is amplified at the YGR
(Q9) and pre-drive (Q8) amplifiers. The amplified signal is
applied to the power amplifier circuit.
Page 9
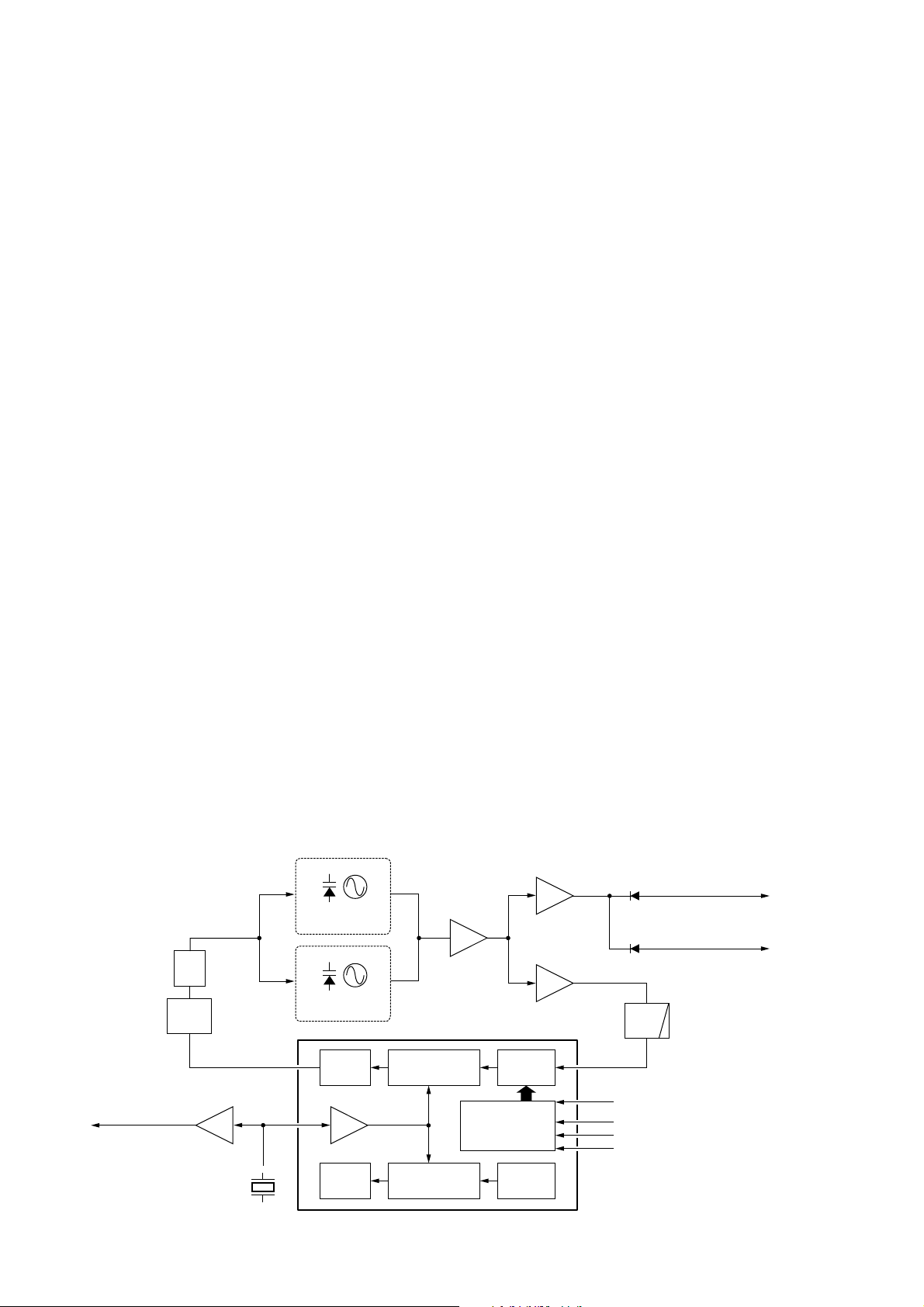
4 - 3
4-2-4 POWER AMPLIFIER CIRCUIT (MAIN unit)
The power amplifier circuit amplifies the driver signal to an
output power level.
The RF signal from the pre-drive amplifier (Q8) is applied to
the power module (IC3) to obtain 25 W of RF power.
The amplified signal is passed through the antenna switching circuit (D2), low-pass filter and APC detector, and is then
applied to the antenna connector.
Control voltage for the power amplifier (IC3, pin 3) comes
from the APC amplifier (IC2) to stabilize the output power.
The transmit mute switch (D32) controls the APC amplifier
when transmit mute is necessary.
4-2-5 APC CIRCUIT (MAIN unit)
The APC circuit protects the power amplifier from a mismatched output load and stabilizes the output power.
The APC detector circuit detects forward signals and reflection signals at D11 and D1 respectively. The combined voltage is at minimum level when the antenna impedance is
matched at 50 Ω, and is increased when it is mismatched.
The detected voltage is applied to the APC amplifier (IC2,
pin 3), and the power setting “T4” signal from the D/A converter (IC7, pin 4), controlled by the CPU (IC20), is applied
to the other input for reference. When antenna impedance is
mismatched, the detected voltage exceeds the power setting voltage. Then the output voltage of the APC amplifier
(IC2, pin 4) controls the input current of the power module
(IC3) to reduce the output power.
4-3 PLL CIRCUITS
4-3-1 PLL CIRCUIT
A PLL circuit provides stable oscillation of the transmit frequency and receive 1st LO frequency. The PLL output compares the phase of the divided VCO frequency to the reference frequency. The PLL output frequency is controlled by
the divided ratio (N-data) of a programable divider.
The PLL circuit contains the TX/RX VCO circuit (Q14, Q13).
The oscillated signal is amplified at the buffer amplifiers
(Q11, Q12) and then applied to the PLL IC (IC4, pin 17) via
the low-pass filter (L32, C298, C299, C509).
The PLL IC contains a prescaler, programable counter, programable divider and phase detector, etc. The entered signal is divided at the prescaler and programable counter section by the N-data ratio from the CPU. The reference signal
is generated at the reference oscillator (X2) and is also
applied to the PLL IC. The PLL IC detects the out-of-step
phase using the reference frequency, and outputs it from
pin 13. The output signal is passed thorough the charge
pump (Q50, Q51, Q54, Q55) and active loop filter (Q52,
Q53), and is then applied to the VCO circuit as the lock voltage.
If the oscillated signal drifts, its phase changes from that of
the reference frequency, causing a lock voltage change to
compensate for the drift in the oscillated frequency.
4-3-2 VCO CIRCUIT
The VCO circuit contains a separate RX VCO (Q13, D16,
D50–D52) and TX VCO (Q14, D17, D18, D53–D55). The
oscillated signal is amplified at the buffer amplifiers (Q11,
Q10) and is then applied to the T/R switch circuit (D14,
D15). Then the receive 1st LO (Rx) signal is applied to the
1st mixer (Q3) and the transmit (Tx) signal to the YGR
amplifier circuit (Q9).
A portion of the signal from the buffer amplifier (Q11) is fed
back to the PLL IC (IC4, pin 5) via the buffer amplifier (Q12)
and low-pass filter (L32, C298, C299, C509) as the comparison signal.
• PLL circuit
Controller
×3
16/17
Phase
detector
Loop
filter
Charge
pump
LPF
PLL2
32/33
Phase
detector
PLL1
X2
15.3 MHz
45.9 MHz signal
to the FM IF IC
10
Q13, D16,
D50–D52
RX VCO
TX VCO
Buffer
Buffer
Buffer
Q10
Q12
Q11
Q34
20
21
22
SCK
19
FSW2
IC4 (PLL IC)
SO
PLST
to transmitter circuit
to 1st mixer circuit
D15
D14
13
17
Q14, D17, D18,
D53–D55
Page 10
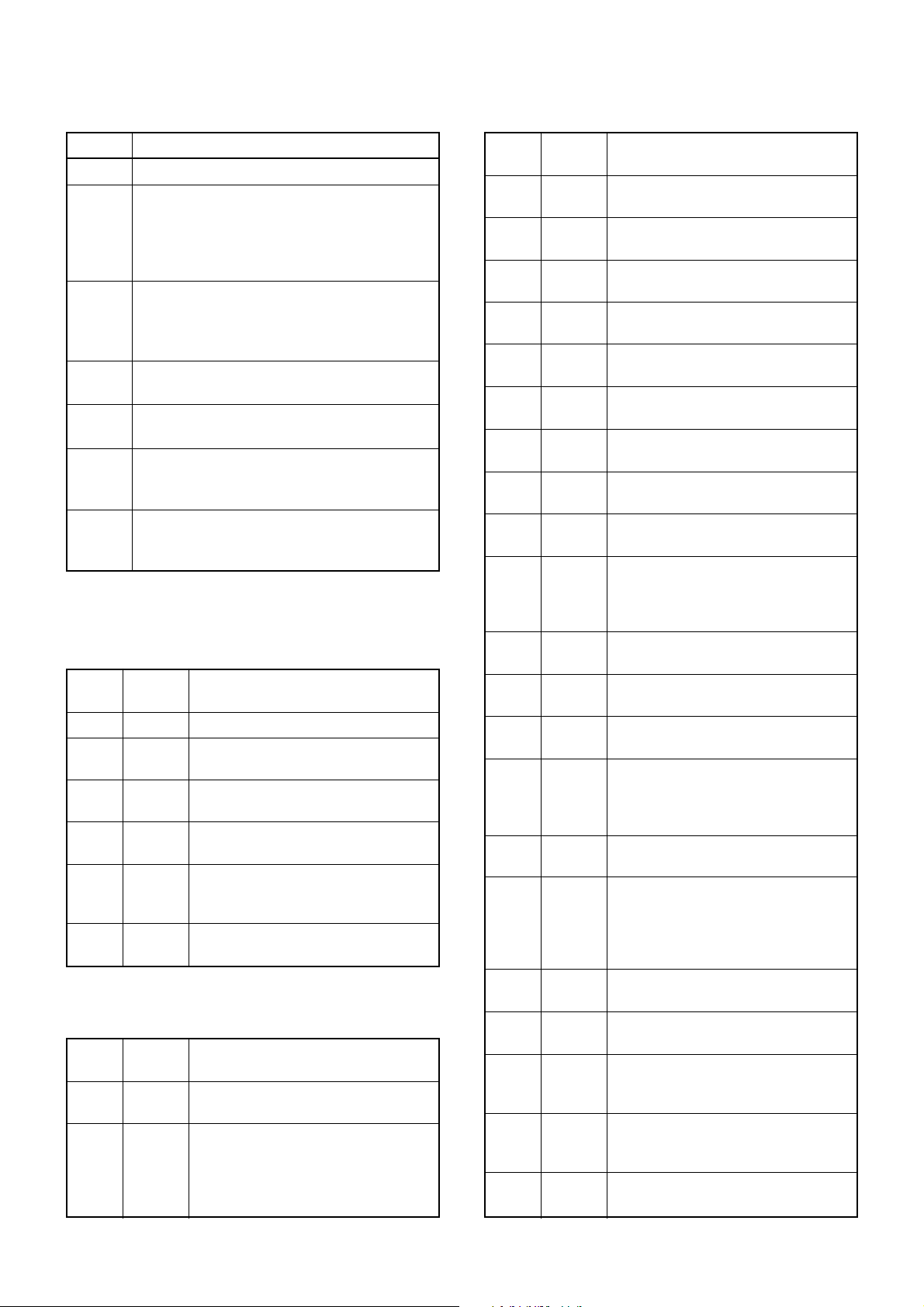
4-4 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUITS
4-4-1 VOLTAGE LINES (MAIN unit)
4-5 PORT ALLOCATIONS
4-5-1 OUTPUT EXPANDER (FRONT unit; IC1)
4-5-2 OUTPUT EXPANDER (MAIN unit; IC7)
4-5-3 CPU (MAIN unit; IC20)
Description
The voltage from a DC power supply.
The same voltage as the HV line which is controlled by the power switching circuit (Q23, Q24).
When the [POWER] switch is pushed, the CPU
outputs the “PWON” control signal to the power
switching circuit to turn the circuit ON.
Common 5 V for the CPU converted from the HV
line by the CPU5V regulator circuit (IC10). The
circuit outputs the voltage regardless of the
power ON/OFF condition.
Common 8 V converted from the VCC line by the
8V regulator circuit (IC9).
Common 5 V converted from the VCC line by the
5V regulator circuit (Q27, Q28).
Receive 8 V controlled by the R8 regulator circuit
(Q26, Q30, D24) using the “TXC” signal from the
CPU (IC20, pin 16).
Transmit 8 V controlled by the T8 regulator circuit
(Q25, Q29, D23) using the “TMUT” signal from
the CPU (IC20, pin 17).
Line
HV
VCC
CPU5V
8V
5V
R8V
T8V
I/O port for data signals from/to the D/A
converter (IC7).
Outputs strobe signals for the level
controller (or D/A converter) (IC6).
Output ports for LCD control signals to
the LCD driver (FRONT unit; IC1)
Outputs clock signal for the LCD driver
(FRONT unit; IC1)
Outputs data signals for the LCD driver
(FRONT unit; IC1)
Outputs strobe signals for the PLL IC
(IC4).
Outputs control signal for the PLL IC
(IC4).
Outputs R8 regulator circuit (Q26, Q30,
D24) control signal.
Outputs T8 regulator circuit (Q25, Q29,
D23) control signal.
Outputs control signal for the AF mute
circuit (Q39, Q40, D31).
High : While AF amplifier (IC8) is acti-
vated.
Outputs IF bandwidth control signal.
High : While IF bandwidth is narrow.
Input port for the data signals from the
DTMF decoder (IC19).
Outputs clock signal to the DTMF
decoder (IC19).
Outputs data signals to the PLL IC
(IC4), level controller (or D/A converter)
(IC6), compander IC (IC14) and optional board (connect to J1).
Input port for the clock signal from the
optional board via J1.
Outputs clock signal to the PLL IC
(IC4), level controller (or D/A converter)
(IC6), D/A converter (IC7), compander
IC (IC14) and optional board (connect
to J1).
Outputs chip select signal for the
optional board via J1.
Input ports for the key matrix.
Input port for the PTT switch from the
optional board via J1.
Low : External PTT switch is ON.
Input port for the microphone hanger
detection signal.
Low : Microphone on hook
Outputs BUSY detection signal for the
optional board via J1.
1
2
8,
9
10
11
13
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26–28
29
30
31
DSDA
DAST
LINH,
LCS
LCK
LSO
PLST
FSW2
TXC
TMUT
AFON
NWC
DDSD
DDAC
SO
SI
SCK
CCS
KR2–
KR0
PTTO
HANG
BUSY
Pin Port
Description
number name
4 - 4
Output tunable band pass filter control
signals.
Output port for
tunable band pass filter control signal
while receiving.
output power control signal while
transmitting.
1–34T1–T3
T4
Pin Port
Description
number name
Output ports for key matrix.
Outputs LCD backlight control signal.
Low : While LCD backlight is dim.
Outputs LCD backlight control signal.
Low : While LCD backlight is OFF.
Outputs high-pass filter’s characteris-
tics select signal.
Outputs external device control signal.
High :
When matched 2/5-tone signals
are received.
Output ports for LCD control signal.
1–3
4
5
6
7
12–55
KS0–KS2
DIM1
DIM2
FSW
HORN
SEG1–SEG40,
COM1–COM4
Pin Port
Description
number name
Page 11
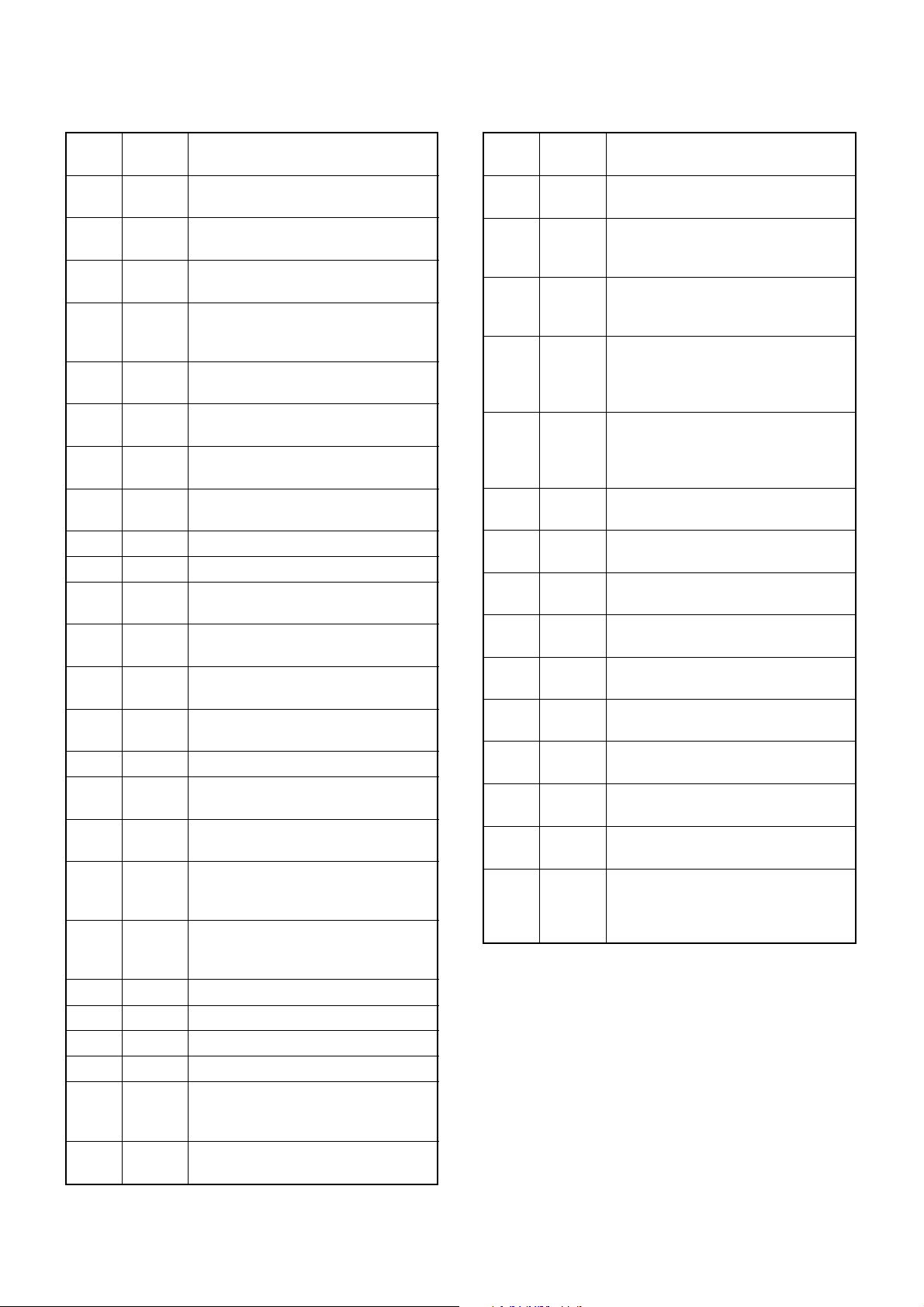
4 - 5
CPU (IC20)—continued CPU (IC20)—continued
Input port for AF mute signal from the
optional board via J1.
Input port for MIC mute signal from the
optional board via J1.
I/O ports for the optional board control
signals.
NOIS signal input port from the FM IF
IC (MAIN unit; IC1) for noise squelch
operation.
Input for the POWER switch.
Low : While POWER switch pushed.
Input port for DTMF detection signal
from the DTMF decoder (IC19).
Remote power control signal input port
from the external connector (J6).
Outputs control signal for the power
switching circuit (Q24, Q23) via D28.
Outputs single tone signal.
Outputs beep audio signals.
Single tone signal input port for decoding.
CTCSS/DTCS signals input port for
decoding.
Input port for the PLL unlock signal
from the PLL IC (IC4).
Input port for the overvoltage detection
from the connected power supply.
Input port for the PLL lock voltage.
Input port for receiving signal strength
level detection.
Input port for the transceiver’s internal
temperature.
Input port for the AF volume control
(FRONT unit; R12).
High : [VOL] is maximum clockwise.
Input port for the PTT switch from the
external connector (J6).
Low : External PTT switch is ON.
Input port for the reset signal.
Output port for the cloning signal.
Input port for the cloning signal.
Outputs CPU clock shift signal.
Outputs cut-off frequency control signal
to the low-pass filter (IC5) for
CTCSS/DTCS switching.
Input port for the connected modem
unit via external connector (J9).
32
33
34–36
37
38
39
40
41
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
55
59
68
69
70
71
74
RMUT
MMUT
OPT1–
OPT3
NOIS
POSW
DDST
IGSW
PWON
SENC
BEEP
SDEC
CDEC
ULCK
BATV
LVIN
RSSI
TEMP
AFVI
EPTT
RES
CLO
CLI
CSFT
DUSE
XCTS
Pin Port
Description
number name
Output port for the connected modem
unit via external connector (J9).
Input port for serial data signals from
the connected MAP27 unit via external
connector (J9).
Outputs serial data signals for the connected MAP27 unit via external connector (J9).
Output serial data signals (data format
is in accordance with NMEA0183) for
the connected unit via external connector (J8).
Input port for serial data signals (data
format is in accordance with
NMEA0183) from the connected unit
via external connector (J8).
Input port for interruption signal from
the optional board via J1
Input port for the LCD backlight control
signal from the external connector (J6).
Output ports for the CTCSS/ DTCS signals.
Outputs reset signal for the compander
IC (IC14).
Output control signals for the compander IC (IC14).
Outputs strobe signals to the compander IC (IC14).
Outputs control signal for the MSK
PM/FM switching circuit (IC15).
I/O port for the data signals from the
EEPROM (IC23).
Outputs clock signal for the EEPROM
(IC23).
Outputs MIC audio select signal for the
analog switch (IC25).
Low :
While
“Public-address” function
is ON.
75
76
77
79
80
81
88
89–91
92
94,
95
96
97
98
99
100
XRTS
XTXD
XRXD
NTXD
NRXD
CIRQ
DIM
CENC2–
CENC0
AFCL
AMSK,
ADIN
APST
PMFM
ESDA
ESCL
PA
Pin Port
Description
number name
Page 12

5-1 PREPARATION
When you adjust the contents on pages 5-5 and 5-6, SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENT, the optional CS-F500 ADJ ADJUST-
MENT SOFTWARE (Rev. 1.0 or later), *OPC-1122 JIG CABLE
(modified OPC-1122 CLONING CABLE; see illustration below)
are required.
■ SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS
• IBM PC compatible computer with an RS -232C serial port
(38400 bps or faster).
• Microsoft Windows 95/98 or Windows ME
• Intel Pentium 100 MHz processor or faster
• At least 16 MB RAM and 10 MB of hard disk space
• 640×480 pixel display (800×600 pixel display recommend-
ed)
■ ADJUSTMENT SOFTWARE INSTALLATION
q Boot up Windows.
- Quit all applications when Windows is running.
w Insert the ‘CS-F500’ into the appropriate CD-ROMdrive.
e Select ‘Run’ from the [Start] menu.
r Type the setup program name using the full path name,
then push [Enter] key.
(ex. D:\CSF500ADJ\disk1\Setup.exe)
t Follow the prompts.
y Program group ‘CS-F500 ADJ’ appears in the ‘Programs’
folder of the [Start] menu.
■ STARTING SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENT
q Connect IC-F510 or F520 and PC with *OPC-1122 JIG
CABLE
.
w Turn the transceiver power ON.
e Boot up Windows, and click the program group ‘CS-F500
ADJ’ in the ‘Programs’ folder of the [Start] menu, then
CS-F500 ADJ’s window appears.
r Click ‘Connect’ on the CS-F500’s window, then appears
IC-F510 or F520’s up-to-date condition.
t Set or modify adjustment data as desired.
5 - 1
SECTION 5 ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
+
Audio generator
300 Hz to 3 kHz
AC
millivoltmeter
MICE
MIC
PTT
PTT switch
PTTE
Add a jumper wire here
• *OPC-1122 (JIG CABLE)
Electrolytic
capacitor
47 µF
OPC-1122
(Cloning cable)
IBM is a registered trademark of International Bussiness
Machines Corporation in the U.S.A. and other countries.
Microsoft and Windows are registered trademarks of
Microsoft Corporation in the U.S.A. and other countries.
Screen shots produced with permission from Microsoft
Corporation. All other products or brands are registered
trademarks or trademarks of their respective holders.
Page 13

■ REQUIRED TEST EQUIPMENT
EQUIPMENT
DC power supply
RF power meter
(terminated type)
Frequency counter
FM deviation meter
DC voltmeter
GRADE AND RANGE
Output voltage : 13.2 (13.6) V DC
Current capacity : 15 A or more
Measuring range : 1–50 W
Frequency range : 100–300 MHz
Impedance : 50 Ω
SWR : Less than 1.2 : 1
Frequency range : 0.1–300 MHz
Frequency accuracy : ±1 ppm or better
Sensitivity : 100 mV or better
Frequency range : DC–300 MHz
Measuring range : 0 to ±10 kHz
Input impedance : 50 kΩ/V DC or better
EQUIPMENT
Audio generator
Standard signal
generator (SSG)
Oscilloscope
AC millivoltmeter
External speaker
Attenuator
GRADE AND RANGE
Frequency range : 300–3000 Hz
Measuring range : 1–500 mV
Frequency range : 0.1–300 MHz
Output level : 0.1 µV–32 mV
(–127 to –17 dBm)
Frequency range : DC–20 MHz
Measuring range : 0.01–20 V
Measuring range : 10 mV–10 V
Input impedance : 4 Ω
Capacity : 5 W or more
Power attenuation : 40 or 50 dB
Capacity : 50 W or more
5 - 2
FM deviation meter
(DC measurable)
Attenuator
40 dB or 50 dB
to the MIC
connector
to the antenna connector
to DC cable
to an RS-232C port
DB9 female plug
Personal
computer
Standard signal generator
–17 to –125 dBm
(32 mV to 0.13 µV)
CAUTION:
DO NOT transmit while
SSG is connected to
the antenna connector.
RF power meter
50 Ω / 1–50 W
DC power supply
13.2 (13.6) V /15 A
Frequency
counter
RS-232C cable
(straight)
*OPC-1122
(JIG CABLE)
AC millivoltmeter
Audio generator
• Connections
Page 14

5 - 3
CS-F500 ADJ Rev.1.0
File
COM 1: OPEN
Option
Connect
Reload (F5) Disp para
[A / D]
VIN : 156 : 9Ch : 12.24 V
TEMPS : 187 : BBh : 30.81 'C
LVIN : 57 : 32h : 0.98 V
SD : 36 : 24h : 0.71 V
Power (Hi) : 181 [ # # # # # # # # # # # # # # – – – – – – ]
Power (L2) : 120 [ # # # # # # # # # – – – – – – – – – – – ]
Power (L1) : 69 [ # # # # # – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – ]
Ballance : 54 [ # # # # – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – ]
MOD W : 157 [ # # # # # # # # # # # # – – – – – – – – ]
MOD N : 83 [ # # # # # # # – – – – – – – – – – – – – ]
CTCS/DTCS : 67 [ # # # # # – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – ]
SQL : 0 [ – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – – ]
BPF ALL : [Enter] to sweep
BPF T1 : 0 [ # # # # # # # # # – – – – – – – – – – – ] [Enter] to sweep
BPF T2 : 0 [ # # # # # # # # # – – – – – – – – – – – ] [Enter] to sweep
BPF T3 : 0 [ # # # # # # # # # – – – – – – – – – – – ] [Enter] to sweep
BPF T4 : 0 [ # # # # # # # # # – – – – – – – – – – – ] [Enter] to sweep
TXF : [Enter] to start
S-METER : [Enter] to start
[D / A]
BPF T1 : 50 : 32h : 0.98 V
BPF T2 : 50 : 32h : 0.98 V
BPF T3 : 50 : 32h : 0.98 V
T4/POW : 50 : 32h : 0.98 V
REF : 45 : 2Dh : 0.88 V
MOD BAL : 54 : 36h : 21.18 %
Dev : 157 : 9Dh : 3.08 V
CTCSS : 66 : 42h : 1.29 V
SQL Lev : 0 : 00h : 0.00 %
CH No. : 01 RX Freq = 136.050, TX Freq = <– RF Power: High Mode: Wide
: Transceiver's connection state
: Reload adjustment data
: Receive sensitivity measurement
: Connected DC voltage
: PLL lock voltage
: Operating channel select
: RF output power
: Modulation balance
NOTE:
• Screen display exampe
1
5
4
6
10
11
12
15
9
14
16
1
2
3
4
5
6
9
10
7
8
11
12
13
: FM deviation
: CTCSS/DTCS deviation
: Squelch level
: Receive sensitivity (automatically)
: Receive sensitivity (manually)
: Reference frequency
: S-meter
: Adjustment items
14
15
16
The above values for settings are example only.
Each transceiver has its own specific values for each setting.
3
2
8
7
13
Page 15

5 - 4
LV
PLL lock voltage
check point
C134
PLL lock voltage
adjustment for TX
C133
PLL lock voltage
adjustment for RX
DC power supply
13.2 (13.6) V / 15 A
5-2 PLL ADJUSTMENT
PLL LOCK
VOLTAGE
1
2
3
4
• Operating freq. : 136.000 MHz
• Receiving
• Output power : Low1
• Transmitting
• Operating freq. : 174.000 MHz
• Receiving
• Output power : Low1
• Transmitting
MAIN Connect a digital multi-
meter or an oscilloscope to the check
point, “LV”.
1.4 V
1.0 V
3.5–4.5 V
3.0–4.0 V
MAIN C133
C134
Verify
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITIONS
UNIT LOCATION
VALUE
UNIT ADJUST
MEASUREMENT ADJUSTMENT
Page 16

5 - 5
5-3 SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENT
Select an operation using [↑] / [↓] keys, then set specified value using [←] / [→] keys on the connected computer keyboard.
1
1
2
3
1
1
2
• Operating freq. : 174.000 MHz
• Output power : Low1
• Connect the RF power meter or 50 Ω
dummy load to the antenna connector.
• Transmitting
• Operating freq. : 155.000 MHz
• Output power : High
• Transmitting
• Output power : Low2
• Transmitting
• Output power : Low1
• Transmitting
• Operating freq. : 155.000 MHz
• Output power : Low1
• Push [P0] key while transmitting
• Operating freq. : 155.000 MHz
• Output power : Low1
• IF bandwidth : Wide
• Connect an audio generator to the [MIC]
jack through the JIG cable and set as:
1.0 kHz/40 mVrms
• Set an FM deviation meter as:
HPF : OFF
LPF : 20 kHz
De-emphasis: OFF
Detector : (P–P)/2
• Transmitting
• IF bandwidth : Narrow
• Transmitting
• Operating freq. : 155.000 MHz
• Output power : Low1
• IF bandwidth : Wide
• CTCSS : 88.5 Hz
• DTCS code : 007
• Set the FM deviation meter as:
HPF : OFF
LPF : 20 kHz
De-emphasis: OFF
Detector : (P–P)/2
• No audio applied to the [MIC] connector.
• Transmitting
REFERENCE
FREQUENCY
[TXF]
OUTPUT
POWER
[Power (Hi)]
[Power (L2)]
[Power (L1)]
MODULATION
BALLANCE
[Ballance]
FM
DEVIATION
[MOD W]
[MOD N]
CTCSS/DTCS
DEVIATON
[CTCS/DTCS]
Rear
panel
Rear
panel
Rear
panel
Rear
panel
Rear
panel
Loosely couple a frequnecy
counter to the antenna connector.
Connect an RF power meter to
the antenna connector.
Connect an FM deviation meter
with an oscilloscope to the
antenna connector through an
attenuator.
Connect an FM deviation meter
to the antenna connector
through the attenuator.
Connect an FM deviation meter
to the antenna connector
through the attenuator.
1740.0000 MHz
25.0 W
10.0 W
2.5 W
±4.1 kHz [N/W]
±3.3 kHz [N/M]
±2.1 kHz
0.7 kHz
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITION
MEASUREMENT
VALUE
UNIT LOCATION
Set to square wave
form
Page 17

*The output level of the standard signal generator (SSG) is indicated as the SSG’s open circuit.
5 - 6
SOFTWARE ADJUSTMENT – continued
Select an operation using [↑] / [↓] keys, then set specified value using [←] / [→] keys on the connected computer keyboard.
Minimum distortion
level
Push [ENTER] key
on the connected
computer keyboard
to set “S3 level”.
Push [ENTER] key
on the connected
computer keyboard
to set “S1 level”.
Set “SQL level” to
close squelch.
Then set “SQL level”
at the point where
the audio signals
just appears.
1
1
2
1
• Operating freq. : 136.000 MHz
• IF bandwidth : Wide
• Connect a standard signal generator to
the antenna connector and set as:
Frequency : 136.000 MHz
Level : 10 µV* (–87 dBm)
Modulation : 1 kHz
Deviation : ±3.5 kHz
• Receiving
• Operating freq. : 136.000 MHz
• IF bandwidth : Wide
• Connect an SSG to the antenna con-
nector and set as:
Frequency : 136.000 MHz
Level : 14 µV* (–84 dBm)
Modulation : 1 kHz
Deviation : ±3.5 kHz
• Receiving
• Set an SSG as :
Level : 0.45 µV* (–114 dBm)
Modulation : 1 kHz
Deviation : ±3.5 kHz
• Receiving
• Operating freq. : 155.000 MHz
• IF bandwidth : Narrow
• Connect an SSG to the antenna con-
nector and set as:
Frequency : 155.000 MHz
Level : 0.2 µV* (–121 dBm)
Modulation : 1 kHz
Deviation : ±1.75 kHz
• Receiving
RX
SENSITIVITY
[BPF T1] –
[BPF T4]
S-METER
[S-METER]
SQUELCH
LEVEL
[SQL]
MAIN
Rear
panel
Connect a SINAD meter with a
4 Ω load to the external [SP]
jack.
Connect a SINAD meter with a
4 Ω load to the external [SP]
jack.
ADJUSTMENT ADJUSTMENT CONDITION
MEASUREMENT
VALUE
UNIT LOCATION
CONVENIENT:
The BPF T1–BPF T4 can be adjusted automatically.
q-1: Set the cursol to “BPF ALL” on the adjustment program and then push [ENTER] key.
q-2: The connected PC tunes BPF T1–BPF T4 to peak levels.
or
w-1: Set the cursol to one of BPF T1, T2, T3, or T4 as desired.
w-2: Push [ENTER] key to start tuning.
w-3: Repeat w-1 and w-2 to perform additional BPF tuning.
Page 18

[FRONT UNIT][FRONT UNIT]
IC1 1130010800 S.IC LC75824W
IC2 1130008560 S.IC TC75S51F (TE85L)
Q1 1590000720 S.TRANSISTOR DTA144EUA T106
Q2 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q3 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q4 1590000720 S.TRANSISTOR DTA144EUA T106
D1 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D2 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D3 1790001670 S.DIODE RB706F-40T106
D4 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D5 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D6 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
L1 6200003960 S.COIL MLF1608A 1R0K-T
R1 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R2 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R3 7030003390 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 391 V (390 Ω)
R4 7030003390 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 391 V (390 Ω)
R5 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R6 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R7 7030000330 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 390 Ω (391)
R8 7410000950 S.ARRAY EXB-V8V 102JV
R9 7410000770 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 102JV (1 kΩ)
R10 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R11 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R12 7210003020 VARIABLE EVU-F2KFK1 B14 (10KB)
R13 7030003730 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 274 V (270 kΩ)
R14 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R16 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R17 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R18 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R19 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R20 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R21 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R22 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R23 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R24 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R25 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
C1 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C2 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C3 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C4 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C5 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C6 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C7 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C8 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C9 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C10 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C11 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C12 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C13 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C14 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C15 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C16 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C17 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C18 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C19 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C20 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C21 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C22 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C23 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C24 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C25 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C26 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C27 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C28 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C29 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C30 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
S.=Surface mount
C31 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C32 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C33 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C34 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C35 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C37 4550000550 S.TANTALUM TESVA 1V 224M1-8L
C39 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C40 4550005980 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA 1A 475M-8L
C41 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
J1 6450002210 CONNECTOR 3017-8821
J2 6510023090 S.CONNECTOR 20FLT-SM1-TB
DS1 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS2 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS3 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS4 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS5 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS6 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS7 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS8 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS9 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS10 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS11 5040002310 S.LED SML-311YTT86
DS12 5030002230 LCD L1-0483TAT
W1 8900010950 CABLE OPC-1126 (P=0.5 N=20 L=90)
EP1 0910054932 PCB B 5809B
EP2 8930057820 LCD CONTACT SRCN-2526-SP-N-W
IC1 1110003490 S.IC TA31136FN (D, EL)
IC2 1130008560 S.IC TC75S51F (TE85L)
IC3 1150002040 IC RA30H1317M-01
IC4 1130010860 S.IC TB31256FL (EB)
IC5 1110005330 S.IC NJM12904V-TE1
IC6 1190001350 S.IC M62364FP 600D
IC7 1190001340 S.IC M62334FP 600C
IC8 1110003090 IC LA4425A
IC9 1180001250 S.IC TA7808F (TE16L)
IC10 1180000970 S.IC AN78L05M-(E1)
IC11 1130008560 S.IC TC75S51F (TE85L)
IC14 1130009330 S.IC TC35453F (BR, DRY)
IC15 1130006220 S.IC TC4W53FU (TE12L)
IC18 1110002750 S.IC TA75S01F (TE85R)
IC19 1130009700 S.IC LC73872M-TRM
IC20 1140010190 S.IC HD64F2268TF (EMPTY)
IC21 1110005340 S.IC NJM12902V-TE1
IC22 1130004200 S.IC TC4S66F (TE85R)
IC23 1140009240 S.IC HN58X24128FPI
IC24 1130009110 S.IC S-80942ANMP-DD6-T2
IC25 1130004200 S.IC TC4S66F (TE85R)
IC26 1180001150 S.IC S-81230SG-QB-T1
Q1 1560000840 S.FET 2SK1829 (TE85R)
Q2 1580000730 S.FET 3SK293 (TE85L)
Q3 1580000660 S.FET 3SK272-(TX)
Q4 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R)
Q5 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q6 1590000720 S.TRANSISTOR DTA144EUA T106
Q8 1530002620 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC3585-T1B R44
Q9 1530003310 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC5107-O (TE85R)
Q10 1530003310 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC5107-O (TE85R)
Q11 1530003310 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC5107-O (TE85R)
6 - 1
SECTION 6 PARTS LIST
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
[MAIN UNIT]
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 19

S.=Surface mount
[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
Q12 1530003310 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC5107-O (TE85R)
Q13 1530002920 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4226-T1 R25
Q14 1530002920 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4226-T1 R25
Q15 1590001400 S.TRANSISTOR XP1214 (TX)
Q16 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q17 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q18 1560000540 S.FET 2SK880-Y (TE85R)
Q19 1530002600 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4215-O (TE85R)
Q20 1530003090 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4213-B (TE85R)
Q21 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q22 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q23 1550000020 S.FET 2SJ377 (TE16R)
Q24 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q25 1540000550 S.TRANSISTOR 2SD1664 T100Q
Q26 1540000550 S.TRANSISTOR 2SD1664 T100Q
Q27 1520000460 S.TRANSISTOR 2SB1132 T100 R
Q28 1590001190 S.TRANSISTOR XP6501-(TX) .AB
Q29 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q30 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q31 1590001450 S.FET 2SJ144-GR (TE85R)
Q32 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q33 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q34 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q35 1590001400 S.TRANSISTOR XP1214 (TX)
Q36 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q37 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q38 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q39 1590000990 S.TRANSISTOR DTC363EK T146
Q40 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q41 1590000720 S.TRANSISTOR DTA144EUA T106
Q42 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q43 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q44 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q48 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q49 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q50 1530002060 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4081 T106 R
Q51 1510000510 S.TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A T106R
Q52 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q53 1530002850 S.TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-BL (TE85R)
Q54 1590003090 S.TRANSISTOR XP2401-(TX)
Q55 1590003100 S.TRANSISTOR XP2501-(TX)
Q56 1590000430 S.TRANSISTOR DTC144EUA T106
Q57 1590001050 S.TRANSISTOR DTC114TUA T106
D1 1790001210 S.DIODE 1SS375-TL
D2 1750000510 S.DIODE UM9401F
D4 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D5 1750000760 S.DIODE MA4PH224
D6 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D7 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX)
D8 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D9 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D10 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D11 1790001210 S.DIODE 1SS375-TL
D14 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D15 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D16 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D17 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D18 1720000400 S.VARICAP 1SV245 (TPH3)
D19 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D20 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D21 1750000830 S.VARICAP HVC362TRF
D22 1790000700 DIODE DSA3A1
D23 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL
D24 1750000370 S.DIODE DA221 TL
D25 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D26 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D27 1790000620 S.DIODE MA77 (TX)
D28 1160000070 S.DIODE DAN202K T146
D31 1160000070 S.DIODE DAN202K T146
D32 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX)
D34 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D35 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D50 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D51 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D52 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D53 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D54 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D55 1750000710 S.VARICAP HVC350BTRF
D56 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D58 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX)
D59 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX)
D60 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX)
D61 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX)
D63 1160000070 S.DIODE DAN202K T146
D65 1160000070 S.DIODE DAN202K T146
D67 1160000070 S.DIODE DAN202K T146
D68 1750000150 S.DIODE DA204K T146
D69 1790001240 S.DIODE MA2S728-(TX)
D70 1790001250 S.DIODE MA2S111-(TX)
D71 1750000520 S.DIODE DAN222TL
D72 1750000350 S.VARICAP 1SV252 (TE85L)
FI1 2030000150 S.MONOLITH FL-335 (46.350 MHz)
FI2 2020001840 CERAMIC ALFYM450F=K [N/W]
2020001410 CERAMIC CFWLB450KGFA-B0 [N/M]
FI3 2040001440 S.LC NFE31PT152Z1E9L
FI4 2040001440 S.LC NFE31PT152Z1E9L
X1 6070000190
S.DISCRIMINATOR
CDBCB450KCAY24-R0
X2 6050011070 S.XTAL CR-664A (15.300 MHz)
X3 6050009910 S.XTAL CR-563 (3.579545 MHz)
X4 6050009520 S.XTAL CR-520 (19.6608 MHz+)
L1 6110001670 COIL LA-253
L2 6110001600 COIL LA-243
L3 6110001670 COIL LA-253
L4 6200008150 S.COIL 0.35-1.6-7TL 44N
L5 6170000230 COIL LW-25
L6 6200008150 S.COIL 0.35-1.6-7TL 44N
L7 6200008260 S.COIL 0.30-1.7-8TL 60N
L8 6200007750 S.COIL LQW2BHN56NJ01L
L9 6200004660 S.COIL MLF1608A 1R8K-T
L11 6200008090 S.COIL LQW2BHN68NJ01L
L12 6200009180 S.COIL ELJRE R10J-F3
L13 6200003330 S.COIL NL 322522T-1R0J-3
L16 6110001670 COIL LA-253
L18 6200005740 S.COIL ELJRE 47NG-F
L19 6200009570 S.COIL ELJRE R12G-F3
L20 6200009530 S.COIL ELJRE R15G-F3
L21 6200009530 S.COIL ELJRE R15G-F3
L23 6200002000 S.COIL NL 252018T-3R3J
L24 6200002000 S.COIL NL 252018T-3R3J
L25 6200009460 S.COIL 0.25-1.9-7TL 67N
L26 6200009460 S.COIL 0.25-1.9-7TL 67N
L27 6200002610 S.COIL NL 252018T-R47J
L28 6200002610 S.COIL NL 252018T-R47J
L29 6200004660 S.COIL MLF1608A 1R8K-T
L31 6200007750 S.COIL LQW2BHN56NJ01L
L32 6200005720 S.COIL ELJRE 33NG-F
L33 6200002850 S.COIL NL 252018T-R82J
L35 6200002840 S.COIL NL 252018T-R22J
L36 6200002860 S.COIL NL 252018T-4R7J
L37 6200003960 S.COIL MLF1608A 1R0K-T
L50 6200008150 S.COIL 0.35-1.6-7TL 44N
L51 6200009460 S.COIL 0.25-1.9-7TL 67N
L52 6200006670 S.COIL ELJRE 68NG-F
L53 6200004660 S.COIL MLF1608A 1R8K-T
L54 6200007750 S.COIL LQW2BHN56NJ01L
L55 6200006980 S.COIL ELJRE R10G-F
R1 7030000620 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 100 kΩ
R2 7030000220 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 47 Ω (470)
R3 7030000220 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 47 Ω (470)
R4 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R5 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R6 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R7 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R8 7030001170 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 220 Ω (221)
R9 7030001170 S.RESISTOR MCR50JZHJ 220 Ω (221)
R10 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R11 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R12 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R13 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R14 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R15 7030003750 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 394 V (390 kΩ)
R16 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R18 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R19 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R20 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R21 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
6 - 2
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 20

S.=Surface mount
[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
R22 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R23 7030003700 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 154 V (150 kΩ)
R24 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R25 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R26 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R27 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R28 7030003210 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 120 V (12 Ω)
R29 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R30 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R31 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R32 7030004050 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 1R0 V (1 Ω)
R33 7030003340 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 151 V (150 Ω)
R34 7030003690 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ)
R35 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R36 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R37 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R38 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R39 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R40 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R41 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R42 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R43 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R44 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R45 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R46 7030003410 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 561 V (560 Ω)
R47 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R50 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R52 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R53 7030004050 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 1R0 V (1 Ω)
R54 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R55 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R56 7030003700 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 154 V (150 kΩ)
R57 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R58 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R59 7030003690 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ)
R61 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R63 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
R65 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R66 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R67 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R68 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R69 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R70 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R71 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R73 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R74 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R75 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R76 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R77 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R78 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R79 7030003470 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 182 V (1.8 kΩ)
R80 7030003410 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 561 V (560 Ω) [N/W]
7030003430 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 821 V (820 Ω) [N/M]
R83 7030003470 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 182 V (1.8 kΩ)
R84 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R85 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R86 7030003690 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ)
R89 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R90 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R91 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
R92 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R93 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R94 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R95 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R96 7030003380 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 331 V (330 Ω)
R97 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R98 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R100 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R101 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R102 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R103 7030003470 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 182 V (1.8 kΩ)
R104 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
R105 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R106 7030003670 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 823 V (82 kΩ)
R107 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R108 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R109 7410000800 S.ARRAY EXB-V8V 103JV (10 kΩ)
R110 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R111 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R112 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R113 7030003750 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 394 V (390 kΩ)
R115 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
R116 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R117 7030003530 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ)
R118 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
R119 7030003710 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 184 V (180 kΩ)
R120 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R121 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R122 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R123 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R124 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
R125 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R126 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R127 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R128 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R129 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R130 7030003610 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ)
R131 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
R132 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R133 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R134 7030003700 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 154 V (150 kΩ)
R135 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R136 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R137 7410000770 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 102JV (1 kΩ)
R138 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R139 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R140 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R141 7410000750 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ)
R142 7410000750 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ)
R143 7410000750 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ)
R144 7410000750 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ)
R145 7410000750 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ)
R146 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R147 7410000750 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ)
R148 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R149 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R151 7410000750 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ)
R152 7410000750 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ)
R153 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R154 7410000750 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ)
R155 7410000750 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 104JV (100 kΩ)
R156 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R157 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R158 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R159 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R173 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R174 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R175 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R176 7030003740 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 334 V (330 kΩ)
R177 7030003740 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 334 V (330 kΩ)
R178 7030003740 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 334 V (330 kΩ)
R179 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
R180 7030003530 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 562 V (5.6 kΩ)
R181 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
R182 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
R185 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
R186 7030003630 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 393 V (39 kΩ)
R187 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R188 7030003590 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 183 V (18 kΩ)
R189 7030003610 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ)
R190 7030004040 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω)
R191 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R192 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R193 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R194 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R195 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R196 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R197 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R198 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R199 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R200 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R201 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R202 7030000460 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 4.7 kΩ
R203 7030000460 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 4.7 kΩ
R204 7030000460 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 4.7 kΩ
R205 7030000460 S.RESISTOR MCR10EZHJ 4.7 kΩ
R206 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R207 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R208 7030004040 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 4R7 V (4.7 Ω)
R209 7510001280 S.THERMISTOR NTCCM20124AG473J-T
R210 7030005871 S.RESISTOR ERA3YKD 104V
R215 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R216 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
R217 7030003610 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ)
R218 7030003610 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ)
R219 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
6 - 3
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 21

S.=Surface mount
[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
R220 7030003620 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 333 V (33 kΩ)
R221 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R222 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R223 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R224 7030003280 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 470 V (47 Ω)
R225 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R226 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R227 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R228 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R229 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R230 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R231 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R232 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R233 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R234 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ)
R235 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R236 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
R237 7030003780 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 684 V (680 kΩ)
R238 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R239 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R240 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R241 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R242 7030003630 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 393 V (39 kΩ)
R243 7030003670 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 823 V (82 kΩ)
R244 7030003750 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 394 V (390 kΩ)
R245 7030003710 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 184 V (180 kΩ)
R246 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R247 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R248 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R249 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R250 7030003690 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 124 V (120 kΩ)
R251 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
R252 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R253 7030003590 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 183 V (18 kΩ)
R254 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R255 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R256 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R257 7030003760 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 474 V (470 kΩ)
R258 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R259 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R260 7030003740 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 334 V (330 kΩ)
R261 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R262 7030003590 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 183 V (18 kΩ)
R263 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R264 7030003490 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 272 V (2.7 kΩ)
R265 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R266 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R267 7030003600 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 223 V (22 kΩ)
R268 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R269 7030003710 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 184 V (180 kΩ)
R270 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R271 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R272 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R273 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R274 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R275 7030003610 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 273 V (27 kΩ)
R276 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
R277 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
R278 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
R280 7030003200 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 100 V (10 Ω)
R281 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R282 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R284 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R285 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R286 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R287 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R288 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R289 7030004050 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 1R0 V (1 Ω)
R290 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R291 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R292 7030003720 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 224 V (220 kΩ)
R293 7410000950 S.ARRAY EXB-V8V 102JV
R294 7410000950 S.ARRAY EXB-V8V 102JV
R295 7410000950 S.ARRAY EXB-V8V 102JV
R296 7410000770 S.ARRAY EXB-V4V 102JV (1 kΩ)
R297 7030005651 S.RESISTOR ERA3YKD 304V
R298 7030005871 S.RESISTOR ERA3YKD 104V
R299 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R302 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R303 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R304 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R305 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R306 7030003320 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 101 V (100 Ω)
R307 7030003650 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 563 V (56 kΩ)
R308 7030003800 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 105 V (1 MΩ)
R312 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R316 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R317 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R318 7030003570 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 123 V (12 kΩ)
R319 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R320 7030003500 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 332 V (3.3 kΩ)
R322 7030004050 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 1R0 V (1 Ω)
R323 7030004050 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 1R0 V (1 Ω)
R324 7030003660 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 683 V (68 kΩ)
R500 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
R501 7030003290 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 560 V (56 Ω)
R502 7030003340 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 151 V (150 Ω)
R503 7030003510 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 392 V (3.9 kΩ)
R504 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R507 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R508 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R509 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R510 7030003550 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 822 V (8.2 kΩ)
R511 7030003400 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 471 V (470 Ω)
R512 7030003540 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 682 V (6.8 kΩ)
R513 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
R515 7030003370 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 271 V (270 Ω)
R516 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R517 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R518 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R519 7030003640 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 473 V (47 kΩ)
R520 7510001230 S.THERMISTOR NTCCM1608 4BH 222KC
R521 7030003450 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 122 V (1.2 kΩ)
R522 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R523 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R524 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R525 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
R526 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R527 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R528 7030003290 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 560 V (56 Ω)
R529 7030003580 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 153 V (15 kΩ)
R530 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R534 7030003680 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 104 V (100 kΩ)
R535 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R536 7030003520 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 472 V (4.7 kΩ)
R537 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R538 7030003560 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 103 V (10 kΩ)
R539 7030003460 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 152 V (1.5 kΩ)
R540 7030003480 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 222 V (2.2 kΩ)
R541 7030003420 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 681 V (680 Ω)
R542 7030003440 S.RESISTOR ERJ3GEYJ 102 V (1 kΩ)
C1 4030011120 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H100JV01L
C2 4030011120 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H100JV01L
C3 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C4 4030008560 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 300J-T
C5 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C6 4030011210 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H330JV01L
C7 4030011510 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H560JV01L
C8 4030011210 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H330JV01L
C9 4030011170 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H180JV01L
C10 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C11 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C12 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C13 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C14 4030017200 S.CERAMIC GRM31BR32J102KY01L
C15 4030011190 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H270JV01L
C17 4030007030 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 150J-T
C18 4030011770 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 060B-T
C19 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C20 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C21 4030009500 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 0R5B-T
C22 4030009540 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 1R5B-T
C23 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C24 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C25 4030011770 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 060B-T
C26 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C27 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C28 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C29 4030009920 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 050B-T
C30 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C32 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C33 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C34 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C35 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
6 - 4
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 22

S.=Surface mount
[MAIN UNIT][MAIN UNIT]
C37 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C38 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C39 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C40 4030009540 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 1R5B-T
C41 4030009350 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 3R5B-T
C42 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C43 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C44 4030009520 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 020B-T
C45 4030007170 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 221J-T
C46 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C47 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C48 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C49 4030006990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 080D-T
C50 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C51 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C52 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T
C53 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C54 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C55 4030006990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 080D-T
C56 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C58 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C59 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C60 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C61 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C62 4030007120 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 820J-T
C63 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C64 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C65 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C66 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C67 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C69 4030011330 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 391J-T
C70 4030011330 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 391J-T
C71 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C72 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C74 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C75 4550006050 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA 0J 106M8L
C76 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C77 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C78 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C79 4030011810 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 224K-T
C80 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C81 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C82 4030011270 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H200JV01L
C83 4030011270 S.CERAMIC GRM31M2C2H200JV01L
C84 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C85 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C86 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C87 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C88 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C89 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T
C90 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T
C91 4510005750
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA220SP
C92 4030006990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 080D-T
C93 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C94 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C95 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C96 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C97 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C98 4030007030 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 150J-T
C99 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C100 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T
C101 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C102 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C103 4030006990 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 080D-T
C104 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C105 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C106 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C107 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C108 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C109 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C110 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C111 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C113 4030009500 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 0R5B-T
C114 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T
C115 4030007070 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 330J-T
C116 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C117 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C118 4030009560 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H R75B-T
C119 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C120 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C121 4030007070 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 330J-T
C122 4030007070 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 330J-T
C123 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C124 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C126 4030007110 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 680J-T
C127 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T
C128 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T
C129 4030009510 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 010B-T
C130 4030009980 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 152K-T
C132 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C133 4610001970 S.TRIMMER TZC3P200A110R00
C134 4610001970 S.TRIMMER TZC3P200A110R00
C139 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C140 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C141 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C142 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C143 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C145 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C146 4550000530 S.TANTALUM TESVA 1V 104M1-8L
C147 4550006150 S.TANTALUM ECST1CY105R
C148 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C151 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C152 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C153 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C154 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C155 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C156 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C157 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C158 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C159 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C160 4030007000 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 090D-T
C161 4030007130 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 101J-T
C162 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C163 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C164 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C165 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C166 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C167 4030008890 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 273K-T
C168 4030008910 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 393K-T
C169 4030008910 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 393K-T
C170 4030008900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 333K-T
C171 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C173 4510004650
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA4R7SR
C174 4510005950
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HA0R1SR
C176 4510004650
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA4R7SR
C177 4030007030 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 150J-T
C178 4030007040 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 180J-T
C179 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C180 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C181 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C182 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C183 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C184 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C185 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C186 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T
C187 4030006870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 222K-T
C188 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C189 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C190 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C191 4030008910 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 393K-T
C192 4030006880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 472K-T
C193 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C194 4030007140 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 121J-T
C195 4510005950
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HA0R1SR
C196 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C199 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C200 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C201 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C202 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C203 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C204 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C205 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C206 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C207 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C209 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C214 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C215 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C217 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C219 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C220 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C224 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C227 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C228 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C229 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C231 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C235 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
6 - 5
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
Page 23

S.=Surface mount
[MAIN UNIT]
[MAIN UNIT]
C236 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C237 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C238 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C239 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C240 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 223K-T
C241 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C242 4030010020 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 122K-T
C243 4030011280 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 271J-T
C244 4030007100 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 560J-T
C246 4030010760 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 331J-T
C247 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C248 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C249 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C250 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C251 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C252 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C253 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C254 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C255 4510005290
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA221P
C256 4510006260
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1AA471UP
C257 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C258 4510004510 ELECTROLYTIC 25 MV 470 HC
C259 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C260 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C261 4030004760 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1H 104Z-T
C262 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C263 4030004760 S.CERAMIC C2012 JF 1H 104Z-T
C264 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C265 4510005290
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA221P
C266 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C268 4550006700 S.TANTALUM ECST1AY106R
C269 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C270 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C271 4510005860
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1HA2R2SR
C272 4510004650
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA4R7SR
C273 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C274 4510004650
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA4R7SR
C278 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C279 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C280 4510004650
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA4R7SR
C281 4030011340 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 471J-T
C282 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C283 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C284 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C286 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C287 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C288 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C289 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C290 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C291 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C292 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C293 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C294 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C295 4510004630
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1CA100SR
C296 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C297 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C298 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T
C299 4030007020 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 120J-T
C301 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C302 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C303 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C304 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C305 4030007100 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 560J-T
C306 4030009910 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 040B-T
C307 4030006980 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 070D-T
C308 4030009530 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 030B-T
C309 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C310 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C311 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C313 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C314 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C315 4030008880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 223K-T
C316 4030009490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 821K-T
C317 4030009490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 821K-T
C318 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C319 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C320 4030008910 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 393K-T
C321 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C322 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C323 4030009880 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 682K-T
C324 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C325 4030008900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 333K-T
C327 4510004650
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA4R7SR
C328 4030017490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 105K-T
C329 4030008870 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 183K-T
C330 4030007110 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 680J-T
C331 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C332 4030017490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 105K-T
C333 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C334 4030009630 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 822K-T
C335 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C336 4030009490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 821K-T
C337 4030017480 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 474K-T
C338 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C339 4030007070 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 330J-T
C340 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C341 4030006980 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 070D-T
C342 4030007050 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 220J-T
C343 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C344 4030008890 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 273K-T
C345 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C348 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C349 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C350 4030017490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 105K-T
C351 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C352 4510005430
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV0JA220SR
C353 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C354 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C358 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C359 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C360 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C361 4030010020 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 122K-T
C362 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C363 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C365 4550006170 S.TANTALUM ECST1AY225R
C371 4030006900 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 103K-T
C377 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C378 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C379 4030017490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 105K-T
C380 4510005750
S.ELECTROLYTIC
ECEV1EA220SP
C381 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C382 4030008920 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 473K-T
C384 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C385 4030009910 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 040B-T
C386 4030017480 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 474K-T
C500 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C501 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C502 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C503 4030007090 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 470J-T
C504 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C509 4030007010 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 100D-T
C510 4030011770 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 060B-T
C511 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C512 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C513 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C514 4030011600 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1E 104K-T
C515 4550006150 S.TANTALUM ECST1CY105R
C516 4550006700 S.TANTALUM ECST1AY106R
C518 4030006860 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1H 102K-T
C519 4030017490 S.CERAMIC C1608 JB 1A 105K-T
C520 4030009530 S.CERAMIC C1608 CH 1H 030B-T
C522 4550006480 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA 1C 475M-8L
C523 4550006480 S.TANTALUM TEMSVA 1C 475M-8L
C524 4550006410 S.TANTALUM ECST1VY334R
C525 4550006700 S.TANTALUM ECST1AY106R
J1 6510018430 S.CONNECTOR AXN330C038P
J2 6510023090 S.CONNECTOR 20FLT-SM1-TB
J4 6450000140 CONNECTOR HSJ0807-01-010
J5 6510007080 CONNECTOR PI28A-02M
J6 6510019250 S.CONNECTOR B11B-ZR-SM3-TF
J8 6510021300 S.CONNECTOR 52365-1091
J9 6510021300 S.CONNECTOR 52365-1091
W1 7120000470 JUMPER ERDS2T0
W2 8900004540 CABLE OPC-453
W3 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W4 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
W5 7030003860 S.JUMPER ERJ3GE JPW V
EP1 6910013370 S.BEAD BLM18BB221SN1D
EP2 0910055012 PCB B 5818B
EP3 6910011560 BEAD HF70BB4.5X5X1.6
EP4 6910010280 BEAD HF70BB9.5X10.4X4.9
EP5 6910010280 BEAD HF70BB9.5X10.4X4.9
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
REF ORDER
DESCRIPTION
NO. NO.
6 - 6
Page 24

J4 6450000140 Connector HSJ0807-01-010 1
W2 8900004540 Cable OPC-453 1
MP1 8930045070 2055 M-plate 1
MP2 8510009980 1705 VCO case 1
MP3 8510010080 1705 VCO cover 1
MP4 8510011460 2055 filter case 1
MP5 8510011610 2055 filter cover (A) 1
MP6 8930057900 2526 module holder assembly 1
MP7 8930057730 Shield sponge (J) 1
MP8 8930045390 Sponge (FL) 1
MP12 8930056510 2055 shield plate 1
MP13 8510005070 599 sheild plate 1
MP14 8930057830 Shield sponge (L) 1
MP15 8930046150 Rubber sheet (AK)-1 1
SECTION 7 MECHANICAL PARTS
7 - 1
[CHASSIS PARTS]
J1 6510004880 Connector MR-DS-E 01 1
SP1 2510001030 Speaker VS-57-0837A 1
WS1 8600036900 Cable FX2526 P01CH 1
MP1 8010018880 2526 chassis 1
MP2 8010018902 2055 cover (A)-2 1
MP3 8210018571 2526 front panel-1 1
MP4 8930057090 2526 front key 1
MP5 8610011180 Knob N292 1
MP7 8930044761 2055 SP net-1 1
MP8 8930044100 2055 SP plate 1
MP9 8930027480 1126 TR-A clip 1
MP11 8810008660 Screw PH BT M3 × 8 NI-ZU 15
MP12 8810008760 Screw PH BT M2 × 8 NI-ZU 4
MP13 8810009990 Screw PH BT M3 × 8 ZK 6
MP14 8930057890 Non-woven sheet (CF) 1
MP15 8930057940 Shield sponge (N) 2
[UNPACKING]
F1 5210000120 Fuse FGB 15A 2
MC1
Optional product
Microphone HM-100N 1
W1
Optional product
Cable OPC-345 1
W2
Optional product
Cable OPC-049 1
MP1 8010016380 1542 mobil bracket (B) 1
MP3 8820000530 Flange volt M4 × 8 NI 4
MP4 8810000470 Screw PH M5 × 12 (+–) 4
MP5 8810005840 Screw PH A M5 × 20 4
MP6 8850000150 Flat washer M5 NI BS 4
MP7 8850000390 Springe washer M5 4
MP8 8830000120 Nut M5 4
MP9 6910004210 731 mic hanger set 1
MP10 8310053310 Label 1705 LCD seal (D) 1
[FRONT UNIT]
R12 7210003020 Variable resistor EVU-F2KFK1 1
J1 6450002210 Connector 3017-8821 1
DS12 5030002230 LCD L1-0483TAT 1
W1 8900010950 Cable OPC-1126 1
EP2 8930057820 LCD contact SRCN-2526-SP-N-W 1
MP1 8210018630 2526 reflector 1
MP2 8930057150 2526 LCD holder 1
MP3 8930057140 2526 earth plate 2
MP4 8930057650 2526 LCD filter 1
[MAIN UNIT]
Screw abbreviations BT: Self-tapping PH: Pan head
ZK: Black BS: Brass
NI: Nickel NI-ZU: Nickel-Zinc
MC1
MP1
MP9
W2
W1
MP3
MP4
MP5
MP6 MP7 MP8 F1
IC
O
M
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
ORDER
NO.
REF.
NO.
DESCRIPTION QTY.
Page 25

7 - 2
MP3 (C)
MP5 (C)
MP4 (C)
MP2 (F)
DS12 (F)
EP2 (F)
MP1 (F)
MP3 (F)
MP4 (F)
FRONT UNIT
W1 (F)
J1 (F)
MP12 (C)
MP1 (C)
MP13 (C)
MP11 (C)
MP5 (M)
MP2 (M)
MP3 (M)
MP11 (C)
MP6 (M)
MP13 (C)
MP9 (C)
MP8 (M)
W2 (M)
J4 (M)
MP15 (M)
MP1 (M)
MAIN UNIT
MP4 (M)
MP13 (M)
MP11 (C)
J1 (C)
MP7 (C)
SP1 (C)
MP8 (C)
MP11 (C)
Unit abbreviations (F): FRONT UNIT
(M): MAIN UNIT
(C): CHASSIS PARTS
MP2 (C)
WS1 (C)
MP14 (C)
R12 (F)
MP12 (M)
MP7 (M)
MP15 (C)
MP14 (M)
Page 26

8 - 1
SECTION 8 SEMI-CONDUCTOR INFORMATION
• TRANSSISTORS AND FET’S • DIODES
E1
B1
B2
C1
C2
2SA1576A T106 R 2SB1132 T100 R 2SC3585 T1B R44 2SC4081 T106 R 2SC4116 BL
2SC4213 B 2SC4215 O 2SC4226 T1 R25 2SC5107 O
2SD1664 T100Q
2SJ144 GR 2SJ377 2SK880 Y 2SK1829
3SK272
3SK293 DTA144EUA T106 DTC114TUA T106 DTC144EUA T106
DTC363 EK
XP1214 XP2401 XP2501 XP6501 AB
(Symbol: FR) (Symbol: BAR) (Symbol: R44) (Symbol: BR) (Symbol: LL)
(Symbol: AB) (Symbol: QO) (Symbol: R25) (Symbol: MFO)
(Symbol: DAQ)
(Symbol: VG) (Symbol: 4L) (Symbol: XY) (Symbol: K1)
(Symbol: K)
(Symbol: UF) (Symbol: 16) (Symbol: 04) (Symbol: 26)
(Symbol: H27)
(Symbol: 9H) (Symbol: 7R) (Symbol: 5W) (Symbol: 5N)
1SS375-TL 1SV245 1SV252 DA204 K T146 DA221 TL
DAN202 K T146 DAN222TL HVC350B HVC362
MA2S111
MA2S728 MA4PH224 MA77 RB706F-40 T106
UM9401F
(Symbol: FH) (Symbol: T3) (Symbol: BE) (Symbol: K) (Symbol: K)
(Symbol: N) (Symbol: N) (Symbol: B0) (Symbol: V2)
(Symbol: A)
(Symbol: B) (Symbol: Red dot) (Symbol: 4B) (Symbol: 3J)
B
C
E
B
E
G
S
B
E
C
D
G
D
S
C
E
G1
B
C
B
C
E
S
G
D
S
G2
D
B
C
E
B
C
E
S
G
D
B
C
E
B
E
B
E
G
S
B
E
C
C
D
C
G1
G2
B
E
B
E
B
C
E
C
A1
C
A2
S
AC
D
C
AC
A1
C
A2
red dot
AC
AC
A
C
AC
AC
Black line
AC
E1
B
E2
C1
C2
E1
B
E2
C1
C2
E1
E2
B2
C1
B1
C2
Page 27

SECTION 9 BOARD LAYOUTS
9-1 FRONT UNIT
• TOP VIEW
9 - 1
8V
28
to
Microphone
17
J1
AFO
MICE
GND
CLO
PTT
MIC
CLI
Page 28

1
to MAIN unit J2
19
220
J2
GND
PWR
LINH
LCS
LCK
LSO
AFVI
CLI
GND
MIC
8V
5V
KR0
KR1
KR2
FSW
HORN
CLO
PTT
AFO
1
16
48
33
32 17
49 64
9 - 2
• BOTTOM VIEW (FRONT UNIT)
Page 29

1
4
8
5
1
4
8
5
112
24 13
1
6
7
12
13
18
19
24
1
8
16
9
14
85
19
to FRONT
unit J2
1
20
2
J2
GND
PWR
LINH
LCS
LCK
LSO
AFVI
CLI
GND
MIC
8V
5V
KR0
KR1
KR2
FSW
HORN
CLO
PTT
AFO
GND
30 16
115
J1
5V
VCC
MMUT
AFON
BEPO
RMUT
DET
DISC
REM
CCS
CIRQ
SO
SI
SCK
PTTI
PTTO
MCOT
MCIN
AUX
BUSY
MDWN
SIG
OPT1
OPT2
OPT3
GND
OPV3
OPV2
OPV1
to Optional unit
PTT11
to Optional
cable OPC-617
1
J6
GND
IN
GND
DISC
GND
AFO
GND
HORN
DIM
VCC
PGO2
91
10 2
J8
PGI3
PGI1
NRXD
8V
GND
PGO1
PGI2
IGSW
NTXD
10 2
91
J9
VCC
MD1
XCTS
XRXD
5V
GND
GND
RES
XRTS
XTXD
SP-2
1
to speaker
J5
SP+
ANT
J1
W1
GND
to DC cable
HV
9-2 MAIN UNIT
• TOP VIEW
9 - 3
Page 30

1
4
8
1
7
14
8
5
12
11 1
1
7
14
8
23 33
22
44
34
1
25
26
50
51
75
76
100
9 - 4
• BOTTOM VIEW (MAIN UNIT)
Page 31

SECTION 10 BLOCK DIAGRAM
CONTROL LINE
RX LINE
TX LINE
COMMON LINE
Explanatory notes
DIMDIM
HORNOHORN
DISC DET
PTT
IN
ACC
EPTT
SW
LINE
MOD
VCC
PWR
SW
POWER
HV
19.66 MHz
HN58X24128FPI
CR
-
520
X4
MA77
D27
EEPROM
SW
IC23
FRONT UNIT
AF VR
PWR
DN*2
UP
*
2
P0
-
P4
AFVI
POSW
ESDA
ESCL
KR0
-
KR2
KEY MATRIX
OPC-453
W2
IC24
S-80942ANMP-DD6
CSFT
RES
RESET
SHIFT
DTC144EU
Q24
2SJ377
Q23
CPU5
AN78L05M
IC10
Q38
REM
DTC144EU
CENC2
TENC
DUSE
SW
FIL
IC9 TA7808F
Q29 DTC144EU
8V
T8V
R8V
TXC
TMUT
+8
REG
Q25 2SD1664
Q26 2SD1664
REG
T8
REG
R8
E
D
F
2SJ144
Q31
SIG
SIGOUT
J6
PROG
IO
MD1
RES
XRTS
XCTS
IGSW
PGO1, 2
PGI1
-
3
XRXD
XTXD
USB
232C
MAP27
FLAH
J9
NRXD
J8
NTXD
GPS
DTC144EU
Q42
DTC144EU
Q46, Q47
Q44, Q45
SIGOUT
AFONO
REM
BEPO
MCOT
MCIN
PTTO
PTTI
SCK
BUSY
OPV3 (AFCL)
OPV2 (AMSK)
OPV1 (APST)
J1
OPT3
OPT2
OPT1
CCS
MMUT
RMUT
SO
SI
CIRQ
UNIT
OPTION
AFCL
ARDT
ARTM
SO
APST
ADIN
ATRD
SO
SCK
DAST
SCK
AMSK
Q30 DTC144EU
5V
DDSO
DDAC
DDST
DEC
LPF
LPF
+5
REG
DTMF
2SC4116
(J1)
3.58 MHz
CR-563
IC14
X3
TC35453F
Q28 XP6501
Q27 2SB1132
MCINCOMPANDER
REG
+5
TONE
SENC
Q37
2SC4116
Q36
(J1)
MCOT
2SC4116
CENC1
CENC0
IC20
HD64F2268TF
DSDA
SCK
CPU
LINH, LCS, LCK, LSO
FSW
HORN
LC75824W
COM1-4
SEG1
-
40
KS0-KS2
IC1
LCD DRIVER
Q2, Q3 DTC144EU
DIM2
DIM1
8V
DS7
-
DS11
DS1-DS6
8V
Q1, Q4 DTA144EU
SML
-
311YT
SML
-
311YT
SW
LED
AFO
MIC
MIC JACK
PTT
J1
CLO CLI
C
PTTO (J1)
PTTI (J1)
DS12
LCD
MICI
D35 MA2S111
NJM12902V
IC21
D31 DAN202K
M62334FP
IC7
TONE
CTCS
SIG
TC4W53FU
IC15
PM/FM
AMP
D/A
A
DER
EXPAN
Q21
DEMOD
MSK
HPF
AMP
AMP
LPF
AMP
LPF
MOD
MSK
NJM12902V
CTCS
MICO
IC6
IC21
HPF
AMP LPF
HPF
AMP
LPF
HPF
BUFF
LIMIT
AMP
BPF
M62364FP
SSOR
COMPRE
D/A
REF
DUSE
TENC
MICI
B
DISC
BAL
MOD
TC4S66F
IC22
XP1214
Q35
SW
FIL
CDEC
NJM12904V
IC5
NJM12902V
IC21
SDEC
SW
FIL
RATION
RESTO
-
450 kHz
NOIS
CDBC450CX24
X1
Q6 DTA144EU
Q5 2SC4116
NWC
SW
W/N
DET
ALFYM450F=K [N/W]
CFWM450G [N/M]
FI2
RSSI
SQIN
SQL AMP
DETECTOR
2SC4213
Q20
FSW
SW
FIL
TONE
BEEPO
BEEP
NJM12902V
IC21
W/N
DTC144EU
Q22
MIXER
SW
NWC
T4
M62364FP
IC6
Q40 DTC144EU
Q39 DTC363EK
TA75S01F
IC18
AFONO
AFON
Q2
3SK293
T2T3
HG
LA4425A
IC8
T1
J4
SP
-
SP+
INT SP
MA2S728
D32
TMUT
SW
MUTE
DET
PWR
D8 HVC350B
TC75S51F
IC2
T4
D4 HVC350B
Q1
2SK1829
RSSI
D10 HVC350B D9 HVC350B
RX LO
182.35
-
220.35 MHz
46.35 MHz
Q3
3SK272
Q12
Q4
FL
-
335
FI1
2SC4215
2SC4226
Q14
2SC5107
PUMP
CHARGE
FILTER
LOOP
1SV245
HVC350B
D17, D53
-
D55
D18
IC1
TA31136FN (D)
TX VCO
MOD
LPF
AMP
BUFF
BUFF BUFF
ATT
BPF
BPF
D/A
AMP
BPF
PWR
AMP
BPF
AF
MUTE
AF
AMP
TX/RX
SW
YGR
AMP
PRE
DRIVE
LPF
GATE
CTRL
RF
AMP
ATT
LPF
LPF
LPF
ANT
SW
APC
AMP
XTAL
BPF
CERAMIC
BPF
IF AMP
SECOND MIXER
FSW2
DET
LPF
LPF
REF
AMP
x3
UNLK
SCK
SO
PLST
Q34
2SC4116
45.9 MHz
15.3 MHz
FRACTIONAL N
MOD
BPF
TC75S51F
IC11
BAL
TB31256FL Q55 XP2501
Q54 XP2401
Q51 2SA1576
Q50 2SC4081
CR-664A
X2 IC4
PLL
IC
LVIN
Q53 2SC4116
Q52 2SC4116
ACTIVE
HVC350B
D16, D50
-
D52
8V2SK880
Q18
2SC4116
Q17
RIPPLE
FIL
BUFF
RX VCO
TXC
Q11
Q16
Q10
2SC4226
Q13
XP1214Q15
DTC144EU
2SC5107 2SC5107
SW
VCO
D14, D15
MA77 2SC5107
Q9
2SC3585
MAIN UNIT
1SV252
D72
RA30H1317
IC3Q8
1SS375
D2 UM9401F
D6 MA77
D5 MA4PH224
D1, D11
136-174 MHz
10 - 1
Page 32

SECTION 11 VOLTAGE DIAGRAMS
5V
8V
5V
5V
GND
to MAIN
unit J2
AFO
HORN
FSW
MIC
CLI
GNDPTT
CLO
AFVI
LSO
LCK
LCS
LINH
KR2
KR1
KR0
PWR5V
8V
8V
AFVI
CLI (HANG)
CLO
GND
MIC
MICE
PTT
AFO
CLI
8V
COM4
COM3
COM2
COM1
SEG40
SEG39
SEG38
SEG37
SEG36
SEG35
SEG34
SEG33
SEG32
SEG31
SEG30
SEG29
SEG28
SEG27
SEG26
SEG25
SEG24
SEG23
SEG22
SEG21
SEG20
SEG19
SEG18
SEG17
SEG16
SEG15
SEG14
SEG13
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG1
COM1
SEG3
SEG2
COM2
COM3
COM4
KS2
KS1
KR2
5V
MIC
PTT
PWR
8V
CLI
CLO
MIC
PWR
AFVI
HORN
FSW
COM4
COM3
COM2
COM1
SEG40
SEG39
SEG38
SEG37
SEG36
SEG35
SEG34
SEG33
SEG32
SEG31
SEG30
SEG29
SEG28
SEG27
SEG26
SEG25
SEG24
SEG23
SEG22
SEG21
SEG20
SEG19
SEG18
SEG17
SEG16
SEG15
SEG14
SEG13
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
COM1
HORN
FSW
KS0
AFO
COM4
COM3
COM2
DIM2
CLI
CLO
AFO
LINH
LCS
LCK
LSO
AFVI
KR0
KR1
KR2
PTT
KS1
LCS
LCK
LSO
LINH
COM4
COM3
COM2
COM1
SEG40
SEG39
SEG38
KS0
KS2
DIM1
DIM2
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
SEG16
SEG17
SEG18
SEG19
SEG20
SEG21
SEG34
SEG33
SEG32
SEG31
SEG30
SEG29
SEG28
SEG27
SEG26
SEG25
SEG24
SEG23
SEG22
SEG35
SEG36
SEG37
KR1
KR0
DIM1
D5
D6
MA2S111
MA2S111
MA2S111
D4
0.22
C37
47k
R25
5
4
3
2
1
IC2
TC75S51F
2.2k
R24
10k
R23
10k
R22
1M
R21
4.7k
R20
4.7
C39
0.001
C41
0.01
C40
R8
1k
10k
R19
10k
R18
10k
R17
R12
EVU
-
F2KFK1B14
1k
R9
1k
R16
C2-C17, C35 47p
48
COM4
47
COM3
46
COM2
45
COM1
44
SEG40
43
SEG39
42
SEG38
41
SEG37
40
SEG36
39
SEG35
38
SEG34
37
SEG33
36
SEG32
35
SEG31
34
SEG30
33
SEG29
32
SEG28
31
SEG27
30
SEG26
29
SEG25
28
SEG24
27
SEG23
26
SEG22
25
SEG21
24
SEG20
23
SEG19
22
SEG18
21
SEG17
20
SEG16
19
SEG15
18
SEG14
17
SEG13
16
SEG12
15
SEG11
14
SEG10
13
SEG9
12
SEG8
11
SEG7
10
SEG69SEG5
8
SEG4
7
SEG3
6
SEG2
5
SEG1
4
COM1
3
COM2
2
COM3
1
COM4
DS12
FRONT UNIT
L1-0483TAT
100k
R14
RB706F-40
D1
100k
R11
100k
R10
DTA144EU
Q4
SML-311YT
DS11
DS1
-
DS11
DTC144EU
Q3
DTC144EU
Q2
J2
100p
C33
270k
R13
DI64CL63CE62INH61OSC60VSS59VDD2
58
VDD1
57
VDD56COM4
55
COM3
54
COM2
53
COM1
52
S5151S5050S49
49
S48
48
S47
47
S46
46
S45
45
S44
44
S43
43
S42
42
S41
41
S40
40
S39
39
S38
38
S37
37
S36
36
S35
35
S34
34
S33
33
S3232S3131S3030S2929S2828S2727S2626S2525S2424S2323S2222S2121S2020S1919S1818S17
17
S16
16
S15
15
S14
14
S13
13
P12/S12
12
P11/S11
11
P10/S10
10
P9/S9
9
P8/S8
8
P7/S7
7
P6/S6
6
P5/S5
5
P4/S4
4
P3/S3
3
P2/S2
2
P1/S1
1
IC1
LC75824W
0.1
C32
0.1
C31
0.1
C30
S4
^
47p
C29
47p
C28
47p
C27
47p
C26
47p
C25
47p
C24
47p
C34
S10
P4
S9
P3
S8
P2
S6
P1
S5
P0
S7
V
S3
V
S2
^
S1
PWR
DTA144EU
Q1
390
R7
1k
R6
4.7k
R5
390
R4
390
R3
DS10
DS9
DS8
DS7
DS6
DS5
DS4
DS3
DS2
DS1
RB706F-40
D3
RB706F-40
D2
47pC23
47pC22
47pC21
47pC20
0.001C19
47p
C18
1µ
L1
1kR2
1kR1
J1
to
mic
jack
47p
C1
C17
C16
C15
C14
C13
C12
C11
C10
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
C8
C9
C35
TX: 5.0V
RX: 0V
2.2V
ON: 7.6V
DIM: 6.1V
OFF: 0V
11 - 1
11-1 FRONT UNIT
Page 33

MAIN
UNIT
(2)
J1
to
MIC
JACK
J2
GND
PWR
LINH
LCS
LCK
LSO
AFVI
CLI
GND
MIC
8V
5V
KR0
KR1
KR2
FSW
HORN
CLO
PTT
AFO
8V
CL0
AFO
PTT
FRONT UNIT
J2
J1
PTTI
PTTO
MCOT
MCIN
AUX
BUSY
MDWN
SIG
OPT1
OPT2
OPT3
GND
OPV3
OPV2
OPV1
GND
5V
VCC
MMUT
AFON
BEPO
RMUT
DET
DISC
REM
CCS
CIRQ
SO
SI
SCK
to
Optional
unit
BUS LINE1
R138 47k
R139 47k
R140 47k
8V
5V
R178 330k
R516 100k
R177 330k
R176 330k
R175 1M
R174 1M
R173 1M
R141
100k
R142
100k
C237 47p
CP4
APST
SI
AMSK
SO
AFCL
CCS
OPT3
OPT2
DISC
OPT1
DET
SIGOUT
RMUT
BEPO
BUSY
AFONO
FSW2
SCK
SO
PLST
UNLK
5V
MMUT
MCIN
MCOT
PTTO
AFO
MIC
PTT
GND
CLO
CLI
HORN
AFVI
FSW
LSO
KR2
LCK
KR1
LCS
KR0
LINH
5V
PWR
8V
GND
BUS LINE2
R296
1k
R295
1k
10k
R109
R293
1k
R294
1k
C207
0.1
R316
100k
CP10
MICI
AFO
R284
1k
R144
100k
C219 47p
C228 47p
C227 47p
C220 47p
C217 47p
C229 47p
C199 47p
C231 47p
C224 47p
C206 47p
C353 47p
C204 47p
C235 47p
C354 47p
C214 47p
C209 47p
R145
100k
POSW
LINH
LCS
LSCK
KR0
KR1
KR2
FSW
LSO
AFVI
CLI
HANG
HORNO
CLO
135
2
4
R108
4.7
C523
56k
BAL
R306
100
C363
0.1
R534
D70
100k
MA2S111
C162
0.01
IC11
TC75S51F
IC26
S-81230SG
IC4
TB31256FL
R308
1M
C163
10
REF
R107
47k
D21
HVC362
C161
100p
C160
9p
X2
CR-664A
R106
82k
R110
47
Q19
2SC4215
Q50
2SC4081
Q51
2SA1576
Q55
XP2501
Q54
XP2401
Q52
Q53
2SC4116
2SC4116
R105
47k
D20
MA2S111
C157
100p
C158
100p
R104
R322
1
2.2k
R530
R527
1.5k
R526
1.2k
R209
NTCCM20124AG473JCT
C203
0.1
R210
100k
TEMP
C156
47p
C159
0.1
LVIN
R101
1k
C143
0.001
Q18
2SK880
R100
1k
R524
R96
330
321
123
4
5
5
4
6.8k
C141
0.001
CP1
R91
33k
C132
0.001
R89
R92 100k
10k
R95
11
C147 C515
22k
R97
1kR507
6.8k
C146
0.1
10
C516
56k
R536
4.7k
4.7
R307
C522
FSW2
CLK
DATA
STB
LD
FSW1
VCC-PLL2
FIN2
GND
NC
SW2
CP2
VCC-PLL1
FIN1
GNDNCSW1
CP1
BS2
19
1817161514
13
12345
6
20
21
22
23
24
12
11
10
9
8
7
VCC-XIN
TCXO
GND
GND
BS1
R535
4.7k
R519
47k
C358
47p
R90
100k
MOD
R291
100k
R504
100k
C350
1
R292
8V
5V
VCC
220k
C145
47p
8V
5V
D19
MA2S111
C148
10
R98
2.2k
Q17
2SC4116
R93
10
R94
10
L27
1.8µ
L29
0.47
µ
C510
D51
D52
D16
D50
C123
100p
C121
33p
C122
33p
W3
R84
22p 67n
C124 L25
C127
270p
67n
44n
L26
L50
C128
12p
D54
D55
HVC350B
HVC350B
HVC350B
HVC350B
HVC350B
HVC350B
HVC350B
HVC350B
D53
D18
1SV245
D17
67n
L51
3.9k
R83
1.8k
Q13
2SC4226
L24
3.3
µ
C119
0.01
C120
470p
C139
0.1
EP1
L28
0.47
µ
C126
68p
C114
18p
C129
1p
C115
33p
W4
R85
3.9k
R79
1.8k
L23
3.3
µ
C117
470p
C116
0.001
R78
1k
R80
560 [N/W]
820 [N/M]
C299
12p
C298
C509
10p
12p
L32 33n
Q15
XP1214
5
4
1
2
3
C118
0.75p
C113
0.5p
R77
10k
Q16
DTC144EU
C111
47p
C110
470p
R76
47
56 0.001
C104
0.001
R74
L52
68n
10k
Q11
2SC5107
R73
100
R525
1k
R102R521R522R523
4.7k1.2k4.7k4.7k
R520
NTCCM16084BH
L55
0.1µ
Q12
2SC5107
R75
10k
C105
0.001
C103
8p
C102
10p
R71
470
C301
0.001
R234
8.2k
Q10
2SC5107
R70
100
L21
0.15µ
C109
0.001
C100
18p
D14
MA77
C108
0.01
R68
1k
R67
10k
C98
15p
R66
3.9k
C99
0.001
Q9
2SC5107
R65
100
C107
0.001
L20
0.15µ
C101
0.001
C93
22p
C96
0.001
C97
47p
L19
0.12µ
R61
100
Q8
2SC3538
C106
47p
C92
8p
R500
6p
1.2k
20p
C133
20pC134
C90
12p
C89
12p
L18
D72
1SV252
DA204K
D68
D11
D1
1SS375
1SS375
DAN222
D71
47n
IN
VCC1
VCC2
OUT
65
432
1
IC3
RA30H1317
0.33
C524
2.2
C365
C87
0.001
C86
L37
1µ
47p
C83
20p
C84
47p
C85
0.001
C91
22
L16
LA-253
C82
20p
FI4
NFM60R20T152
FI3
NFM60R20T152
R9
220R8220
L5
LW-25
C12
470p
C13
47p
D2
UM9401F
L4
44n
C15
27p
T8V
R69
4.7k
R503 3.9k
D15
MA77
R50
10k
R235
1k
C303
0.001
C302
10p
R8V
ANT
C304
10p
Q34
2SC4116
R237
680k
L35
0.22µ
R236
1.2k
C309
0.01
C305
56p
C306
4p
C307
7p
L33
0.82µ
R63
12k
R501
680
C95
0.001
C94
47p
0.001
R541
C88
C501
56
0.001
R502
C502
150
0.001
R509
R508
6.8k
C511
470
0.001
1.2k
R513
R512
6.8k
C513
0.001
R511
R510
C512
470
8.2k
0.001
TXC
T8V
T8V
R8V5VANT
HV
R8V
5V
R8V
T8V
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
89
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
OSCIN
OSCOUT
MIXOUT
VCC
IFIN
DEC
FILOUT
FILIN
MIXIN
GND
N-REC
N
-
DET
RSSI
IFOUT
QUAD
AFOUT
IC1
TA31136FN
1
2
3
4
5
GND
3V
VIN
VOUT
NC
NC
R44
56k
C70
390p
C71
0.1
C69
390p
C371
0.01
R515
270
R45
15k
R46
560
R47
3.3k
OI
FI2
ALFYM450F=K [N/W]
CFWM450G [N/M]
C308
3p
5V
R39
47
C67
0.001
C75
10
SQIN
R38
100k
NOIS
R36
3.9k
X1
CDBC450CX24
C61
100p
C62
82p
C348
0.001
C65
0.001
RSSI
C64
470p
C66
0.001
Q5
2SC4116
R41
47k
R42
47k
C72
0.1
Q6
DTA144EU
C9
18pC833pC756p
C6
33p
C14
0.001
L3
LA-253L2LA-243
C5
470p
C4
30pR347
C3
470p
C2
10p
C1
10p
L1
LA-253
R1
10k
1.5kR537
2.2k
1.5k
10
R538
R540
R539
C525
100k
R7
270
R4
270
R35
1k
R8V
T8V
R8V
SQIN
R290
470
C60
0.001
R34
120k
C58
0.001
R33
150
Q4
2SC4215
FI1
FL-335
C56
22p
R32
1
C51
0.001
L13
1µ
C52
12p
R31
100
R30
1k
R29
470
C50
0.001
C48
47p
C54
0.001
8p
C55
C53
0.01
Q3
3SK272
R25
47k
C45
220p
D10
HVC350B
C44
2p
L11
68n
R23
150k
R24
10k
C47
0.001
C46
0.001
12
R28
C49
8p
L12
0.1µ
470
470
R27
R26
C38
0.001
R289
1
C37
0.001
R20
100L91.8µ
T4
C39
0.001
D9
HVC350B
R21
220k
C42
0.001
R22
10k
C43
0.001
T3
Q2
3SK293
C32
0.001
C520
L54
3p
56n
C503
47p
R16
270
R15
390k
L8
56n
C35
0.001
R19
100k
R18
22k
R208
4.7
C59
0.1
C34
0.001
R10
4.7k
Q1
2SK1829
C30
22p
C29
5p
C28
0.001
R14
10k
C27
0.001
R13
100k
D4
HVC350B
C26
0.001
T2
RSSI
R206
470k
R207
10k
D25
MA2S111
C22
1.5p
L7
60n
C21
0.5p
C23
0.001
R12
10k
C24
0.001
R11
100k
D8
HVC350B
C20
0.001T1L31
56n
C18
6p
D6
D7 MA2S728
MA77
D5
MA4PH224
C17 15p
C19
0.001
L6
44n
C81
0.001
R58
100
C77
0.001
0.001
0.001
0.001
C11
C500
C10
100 100
R6 R5
R53
1
C76
0.01
4
2
3
1
5
R56
150k
C79
0.22
D32
MA2S728
C379
1
IC2
TC75S51F
Q57
DTC114TU
R59
120k
C80
0.1
R52
15k
D56
MA2S111
T4
R57
10k
15k
R529
C78
0.001
R54
10k
C33
47p
TMUT
R55
4.7k
C313
47p
1
C519
R2
FWD
REV
47
R43
470
REM
DET
NWC
NWC
VCC
VCC
C236 47p
C152
R323
1
C153
C154
C151
47p
47p
47p
47p
0.047
47p
C382
C155
C247 0.001
C239 0.001
C238 0.001
C215 47p
J9
J8
XTXD
XRXD
XRTS
XCTS
RES
MD1
R155
100k
NTXD
NRXD
R151
100k
R152
100k
Q44
DTC144EU
IGSW
D63
DAN202K
PGI1
D67
DAN202K
PGI2
R153
100k
PGI3
R158 10k
R157 10k
PGO1
PGO2
SCK
CIRQ
D34
MA2S111
C142
D69
MA2S728
D61
D60
D59
D58
MA2S728
MA2S728
MA2S728
MA2S728
0.001
C74
0.1
C41
3.5p
C40
1.5p 4p
C385
EP3
R86
120k
MICE
MIC
GND
CLI
MAIN UNIT (1)
C205 47p
R143
100k
R154
100k
Q42
DTC144EU
D65
DAN202K
C314
0.01
C381 0.1
C130
4.7k
0.0015
C514
0.1
C140 0.1
1.8k
R528 C518
R103
C297
22p
Q14
2SC4226
R40
1.5k
C63
0.001
R37
3.3k
C25
6p
C380
22
0.8Vp-p
(15.3MHz)
5.0V
7.0V
TX:4.3V
RX:0V
TX:4.3V
RX:0V
TX:0V
RX:5.0V
800mVrms
6.9V
LOCK:5.0V
UNLOCK:0V
6.6V
7.4V
TX:1.2V
RX:1.2V
6.5V
TX:0V
RX:2.9V
TX:2.9V
RX:0V
TX:2.2V
RX:3.1V
TX:0V
RX:3.3V
TX:6.5V
RX:0V
TX:6.4V
RX:0V
3.0V
WIDE:0V
NAR:5.0V
4.9V
4.9V
1.0V
TX:0V
RX:5.4V
TX:3.3V
RX:1.9V
TX:0V
RX:7.7V
TX:0V
RX:1.2V
Lo Level:1
-
6dBm
MEASUREMENT CONDITIONS
VOLTMETER
Amplitude(Oscilloscope):100MHz
Frequency:155MHz
Transmission:25W
TX:0V
RX:7.9V
TX:0V
RX:4.6V
TX:0V
RX:7.9V
TX:0V
RX:6.3V
TX:3.7V
RX:0V
TX:3.6V
RX:0V
TX:0V
RX:5.0V
TX:3.3V
RX:0V
11 - 2
11-2 MAIN UNIT
Page 34

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
7677787980818283848586878889909192939495969798
99
100
MAIN
UNIT
(1)
IC20
HD64F2268TF
PM6/SEG31
PM5/SEG30
PM4/SEG29
PM3/SEG28
PM2/SEG27
PM1/SEG26
PM0/SEG25
PL7/SEG24
PL6/SEG23
PL5/SEG22
PL4/SEG21
CVCC
PL3/SEG20
PL2/SEG19
PL1/SEG18
PL0/SEG17
PK7/SEG16
PK6/SEG15
PK5/SEG14
PK4/SEG13
PK3/SEG12
PK2/SEG11
PK1/SEG10
PK0/SEG9
VSS
PJ7/WKP7/SEG8
PJ6/WKP6/SEG7
PJ5/WKP5/SEG6
PJ4/WKP4/SEG5
PJ3/WKP3/SEG4
PJ2/WKP2/SEG3
PJ1/WKP1/SEG2
PJ0/WKP0/SEG1
P10/TIOCA0
P11/TIOCB0
P12/TIOCC0/TCLKA
P13/TIOCD0/TCLKB
P14/TIOCA1/IRQ0
P15/TIOCB1/TCLKC
P16/TIOCA2/IRQ1
P17/TIOCB2/TCLKD
AVSS
P97/AN9/DA1
P96/AN8/DA0
P47/AN7
P46/AN6
P45/AN5
P44/AN4
P43/AN3
P42/AN2
P41/AN1
P40/AN0
VREF
AVCC
PH7/TONED/TMCI4
MD1
OSC2
OSC1
RES
NMI
STBY
VCC
XTAL
VSS
EXTAL
FWE
MD2
P77/TXD2
P76/RXD2
P75/TMO3/SCK2
P74/TMO2
P73/TMO1
P72/TMO0
P71/TMRI23/TMCI23
P70/TMRI01/TMCI01
P30/TXD0
P31/RXD0
P32/SCK0/SDA1/IRQ4
P33/TXD1/SCL1
P34/RXD1/SDA0
P35/SCK1/SCL0/IRQ5
PF3/ADTRG/IRQ3
C2C1V3V2V1
PH3/COM4
PH2/COM3
PH1/COM2
PH0/COM1
PN7/SEG40
PN6/SEG39
PN5/SEG38
PN4/SEG37
PN3/SEG36
PN2/SEG35
PN1/SEG34
PN0/SEG33
PM7/SEG32
BUS LINE1
8V
5V
BUS LINE2
T8V
R8V
ANT
1234567891011
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2324252627282930313233
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
RXFO
RXGS
RXIN
MSKGS
MSKIN
TXOUT
IDCGS
IOCIN
TXFO
AGND
CST
MICIN
MICGS
CALO
ALCO
CMPIN
CCHG
CMPO
TXFI
VDDA
VDDD
STB
DIN
DCK
REGS1
REGS2
XOUT
XIN
MSKE
TRD
RTM
RDT
FCLR
VSSD
VSSA
MSKST
PWROP
PWRON
PWRGS
PWRIN
EXPO
ECHG
EXPGS
EXPIN
IC14
TC35453F
DET
DISC
CP2
R111
22k
C164
0.001
C165
0.001
C166
0.001
R113
390k
R285
4.7k
SDEC
R241
100k
R320
3.3k
R319
47k
R242
39k
C316
820p
R243
82k
C317
820p
R245
180k
C318
0.1
+
9
10
8
IC21c
NJM12902V
R244
390k
R246
1.5k
C319
0.047
R233
100k
R120
100k
Q20
2SC4213
R118
68k
R119
180k
R115
12k
C167
0.027
C168
0.039
C169
0.039
R116
1.5k
+
-
5
6
7
IC21b
NJM12902V
R117
5.6k
C170
0.033
C171
0.0047
MCOT
MCIN
CP3
C187
0.0022
C186
0.0022
C188
0.1
R122
10k
Q21
2SC4116
R121
10k
C185
0.1
R123
4.7k
R125
22k
R124
33k
C189 0.1
C176
4.7
R230 10k
R129 470k
C190
47p
R130 27k R131 68k
C180 0.1
C174 0.1
C181 0.1
R127
22k
C361
0.0012
R126
22k
APST
5V
X3
CR-563
C177
15p
C178
18p
ADIN
SCK
ADIN
AMSK
ATRDSOAFCL
R137
1k
ARTM
ARDT
C193 0.1
R136 1k
C195 0.1
C194
120p
R135
100k
R134
150k
R133
220k
C192
0.0047
C191
0.039
R132
47k
C196
0.01
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
VCC
WP
SCL
SDA
A0
A1
A2
VSS
IC23
HN58X24128FPI
ESDA
ESCL
R282
100k
R281 10k
C343
0.1
1
2
3
4
5
6
78
9
10
11
12
13
14
IC19
LC73872M
INPUT
NC
PD
OSCO
OSCI
NC
VSS
LOADB
SD
ACK
STD
EST
NC
VDD
MICI
FSW
C311
0.1
C182
0.1
DDAC
R238
100k
R221
100k
DDST
DDSD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12 13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
VIN1
VOUT1
VOUT2
VIN2
VDD
LD
CLK
DI
VIN3
VOUT3
VOUT4
VIN4 VIN5
VOUT5
VOUT6
VIN6
DO
VDAREF
RESET
GND
VIN7
VOUT7
VOUT8
VIN8
IC6
M62364FP
R216 33k
W5
R215 3.9k
BEPO
R218
27k
C360
0.1
BEEP
DAST
C183
0.047
SCK
SO
MICI
R146
100k
CTCS
TENC
C284
0.01
R220
33k
C283
0.001
R231
1k
DET
SQIN
MOD
REF
5
4
1
2
3
CDNCOUT
VDD
VSS
C344
0.027
IC24
S-80942ANMP-DD6
TEMP
AFVI
EPTT
RES
CLO
CLI
CSFT
DUSE
XCTS
XRTS
5V
R288
10k
MD1
R299
100k
PWR
PWON
D28
DAN202K
BAL
1
5
3
2
IC25
TC4S66F
4
Q49
DTC144EU
Q56
DTC144EU
R317
100k
C377
0.1
R324
68k
C384
0.1
Q41
DTA144EU
PA
R280
10
X4
CR-520
C3417pC342
22p
R277
12k
100k
R517
C339
33p
R278
12k
D27
MA77
C340
0.01
1
2
3
45
6
7
8
AO1
AO2
AO3
AO4 GND
SDA
SCL
VCC
IC7
M62334FP
VAG
R302
10k
R222
470
C286
0.1
T1
T2
T3
T4
R276
12k
DET
R247
22k
C320
0.039
R248
22k
C323
0.0068
C322
0.01
R249
R518 1k
22k
+
-
5
6
IC5
NJM12904V
7
C321 0.1
R252
220k
C327
4.7
C325
0.033
C324
0.1
R253
18k
R254
47k
R255
47k
+
3
2
1
IC5
NJM12904V
IC22
TC4S66F
2
4
3
1
5
V+
GND
8
4
C349
0.1
CDEC
R258
470
VAG
SQIN
Q35
XP1214
1
2
3
5
4
R251
68k
DUSE
5V
SENC
C328
1
R259
56k
R261
22k
R263
220k
R260
330k
C329
0.018
R262
18k
C330
68p
C331
0.01
Q36
2SC4116
R264
2.7k
R219
22k
C333
0.001
C332
1
TONE
REM
CENC2
CENC1
CENC0
R267 22k
R268 56k
R269 180k
R286 1k
R312
3.9k
R266
3.9k
R270
47k
C334
0.0082
R271
47k
IC5
NJM12904V
R256 100k
SCK
DSDA
R272
47k
C336
820p
R274
47k
Q37
2SC4116
R273
4.7k
TENC
R275
27k
C337
0.47
Q38
DTC144EU
XTXD
XRXD
ATRD
NTXD
NRXD
CIRQ
ARTM
DIM
R303
100k
CENC2
CENC1
CENC0
AFCL
ARDT
AMSK
ADIN
APST
PMFM
ESDA
ESCL
PA
R149
100k
RSSI
LVIN
BATV
UNLK
CDEC
SDEC
BEEP
SENC
PWON
IGSW
DDST
POSW
NOIS
OPT3
OPT2
OPT1
MMUT
RMUT
BUSY
HANG
PTTO
KR0
KR1
KR2
C345 0.1
DSDA
DAST
PGO2
PGO1
PGI3
PGI2
PGI1
LINH
LCS
LCK
LSO
PLST
TXC
TMUT
NWC
DDSD
DDAC
SO
SI
SCK
R542 1k
CCS
5678
4321
PMFM
R180
5.6k
C240
0.022
C241
0.001
R179
33k
IC15
TC4W53FU
+
-
14
12
13
IC21d
NJM12902V
NWC
C244
56p
C243
270p
Q22
DTC144EU
R182
68k
C242
0.0012
R181
68k
R185
33k
C246
330p
R186
39k
R189
27k
R187
56k
TONE
CTCS
-
+
2
3
1
IC21a
NJM12902V
C296
0.1
C504
0.001
R190
4.7
VAG
C362 0.1 R304 56k
5V
C378 0.1 R318 12k
C200 0.1
C201 0.1
C202 0.1
R147
100k
1
3
5
2
4
R193
100k
C249
470p
R191
220k
R192 220k
VCC
CPU5V
R8VR8V
T8V5V8V
VCC
CPU5V5V8V
C250 0.1
C359
0.1
C351
0.047
R196
22k
R1951kC251
0.1
C386
0.47
D35
MA2S111
R194
2.2k
AFON
SIG
AFONO
CPU5V
AFON
D31
DAN202K
C253
0.1
VCC
IC18
TA75S01F
4
3
5
2
1
C255
220
R198
10k
C256
470
R199
10k
C254 0.001
J4
R188
18k
CP9CP8
C252
0.1
R197
10k
J5
C257 47p
D23
DA221
C269
0.001
Q25
2SD1664
R203
4.7k
R202
4.7k
C272
4.7
Q29
DTC144EU
TMUT
D24
DA221
C270
0.001
Q26
2SD1664
C271
2.2
TXC
R204
4.7k
R205
4.7k
Q30
DTC144EU
654
123
Q27
2SB1132
Q28
XP6501
R156
4.7k
R239 100k
R305 100k
C273
5V
VCC
0.001
C274
4.7
C26610C262
0.1
OI
G
IC9
TA7808F
C261
0.1
C265
220
R200
10k
R201
470
Q23
2SJ377
HV HV
HV
VCC
8V
5V
C260 47p
C259 0.001
C258 470
D22 DSA3A1
EP4
EP5
W2
C26810C264
0.1
G
OI
IC10
AN78L05M
C263
0.1
R298
100k
R297
300k
J6
C293 0.001
VCC
DIM
HORN
GND
AFO
GND
DISC
GND
IN
GND
PTT
C292 47p
C290 0.001
C291 0.001
C294 0.001
Q48
DTC144EU
PA
Q33
DTC144EU
DIM
Q32
DTC144EU
HORNO
DET
DET
VCC VCC
CPU5V
EPTT
R228
100k
Q31
2SJ144
R227
1M
C295
10
C287
0.001
CP5
MOD
CP6
CP7
SIG
SIGOUT
D26
MA2S111
R229
1M
R226
100k
P1
+
-
CHASSIS
SP1
AFO
Q24
DTC144EU
PWR
CPU5
L36
4.7µ
C352
22
GND
V+
4
11
C248
0.001
IC21
NJM12902V
8V
5V
T8V
R8V
ANT
VCC
8V
5V
T8V
R8V
ANT ANT
ANT
VCC
VCC
8V
5V
T8V
R8V
VCC
CPU5
R112
10k
R128
47k
C184
0.1
LINH
5V
Q43
DTC144EU
C173
4.7
C179
470p
C279
0.1
R217
27k
C278 0.1
R250
120k
R265
47k
C338
0.01
Q40
DTC144EU
Q39
DTC363EK
IC8
LA4425A
R224 47
C289 0.1
R225 10k C288 0.1
R223 1k
MAIN UNIT (2)
R240
100k
C315
0.022
VAG
C310
0.1
C282
0.1
C280
4.7
C281
470p
R257
470k
C335
0.047
R148
100k
FSW2
CHASSIS
J1
W1
R159
10k
R287
10k
to
OPC-617
L53
1.8µ
5V
5V
5V
2.5V
2.5V
4.3Vp-p
(3.579MHz)
16mVrmS
1.7Vp-p
(2/5 TONE)
TX:0.5V
RX:1.1V
2.5Vp-P
(19.66MHz)
1.8V
0.6Vp-p
(CTCSS)
4.9V
5.0V
(AFON)
1.3V
TX:8.0V
RX:0V
TX:0V
RX:8.0V
5.0V
8.0V
13.1V
5.0V
4.5V
MEASUREMENT CONDITIONS
VOLTMETER
Amplitude(Oscilloscope):100MHz
Frequency:155MHz
Transmission:25W
11 - 3
Page 35

Communication Equipment
Himmelgeister Str. 100, D-40225 Düsseldorf, Germany
Phone : 0211 346047 Fax : 0211 333639
URL : http://www.icomeurope.com
Unit 9, Sea St., Herne Bay, Kent, CT6 8LD, U.K.
Phone : 01227 741741 Fax : 01227 741742
URL : http://www.icomuk.co.uk
Zac de la Plaine, Rue Brindejonc des Moulinais
BP 5804, 31505 Toulouse Cedex, France
Phone : 561 36 03 03 Fax : 561 36 03 00
URL : http://www.icom-france.com
Crta. de Gracia a Manresa Km. 14,750
08190 Sant Cugat del Valles Barcelona, SPAIN
Phone : (93) 590 26 70 Fax : (93) 589 04 46
URL : http://www.icomspain.com
<
Corporate Headquarters
>
2380 116th Avenue N.E., Bellevue, WA 98004, U.S.A.
Phone : (425) 454-8155 Fax : (425) 454-1509
URL : http://www.icomamerica.com
<
Customer Service
>
Phone : (425) 454-7619
Glenwood Centre #150-6165
Highway 17 Delta, B.C., V4K 5B8, Canada
Phone : (604) 952-4266 Fax : (604) 952-0090
URL : http://www.icomcanada.com
A.B.N. 88 006 092 575
290-294 Albert Street, Brunswick, Victoria, 3056, Australia
Phone : 03 9387 0666 Fax : 03 9387 0022
URL : http://www.icom.net.au
146A Harris Road, East Tamaki,
Auckland, New Zealand
Phone : 09 274 4062 Fax : 09 274 4708
URL : http://www.icom.co.nz
6F No. 68, Sec. 1 Cheng-Teh Road, Taipei, Taiwan, R.O.C.
Phone : (02) 2559 1899 Fax : (02) 2559 1874
1-1-32, Kamiminami, Hirano-ku, Osaka 547-0003, Japan
Phone : 06 6793 5302
Fax : 06 6793 0013
URL : http://www.icom.co.jp/world/index.html
Icom America Inc.
Icom (Europe) GmbH
Asia Icom Inc.
Icom Spain S.L
Icom (UK) Ltd.
Icom France S.a
1305, Wanshang Plaza, Shijingshan Road, Beijing China
Phone : (010) 6866 6337 Fax : (010) 6866 3553
Beijing Icom Ltd.
Icom Canada
Icom (Australia) Pty. Ltd.
Icom New Zealand
Page 36

1-1-32, Kamiminami, Hirano-ku, Osaka 547-0003, Japan
S-13817HZ-C1V
C 2002 Icom Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...