Page 1
Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
1
Product Guide
September 2008
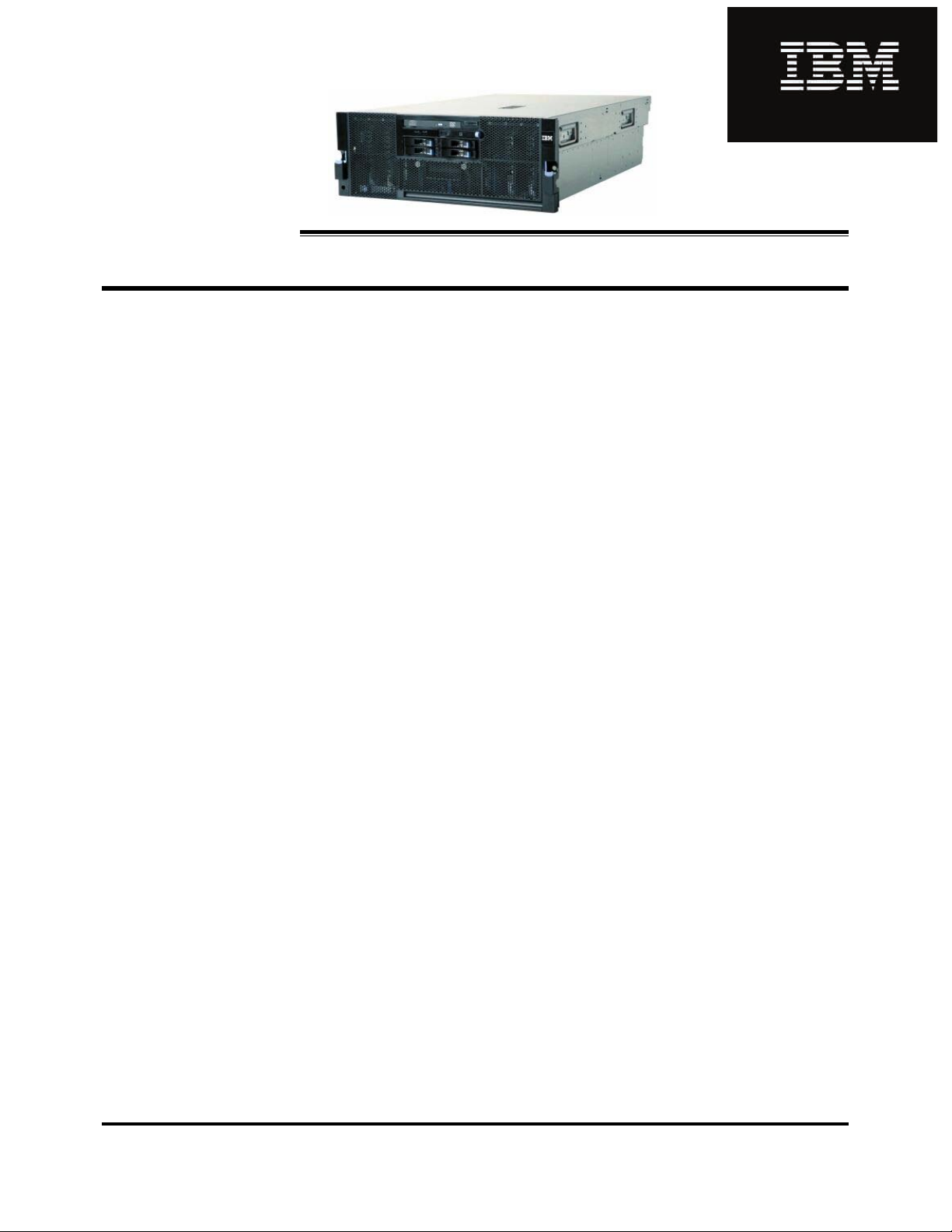
IBM System x3850 M2 / x3950 M2
Architecture
Overview
CONTENTS
Architecture Overview
1
Key Highlights
2
Key Features
3
Key Options
11
x3850/x3950 M2 Images
12
x3850/x3950 M2 Specs
14
The Bottom Line
16
For More Information
19
Legal Information
19
Outstanding performance, superior mainframe-like
reliability, and fault-tolerant memory characteristics
IBM® has been designing and implementing chipsets under the X-Architecture™ name since
2001. eX4 technology represents the fourth generation of products based on the same design
principle IBM began with in 1997: to offer systems that are expandable, offer “big iron” reliability,
availability, and serviceability (RAS) features, with extremely competitive price/performance on
an Intel® Xeon® processor-based system.
The eX4 technology is primarily designed around three major workloads. These workloads are
database servers, server consolidation using virtualization services, and Enterprise Resource
Planning (application and database) servers.
If you are adopting industry-standard Xeon EM64T servers for running business critical
applications, the systems that run these applications need the type of technology designed into
IBM’s eX4 technology systems. The eX4 chipset represents a $100M+ investment in designing
a flagship offering that can harness the power of 4-socket-and-up 64-bit x86 (x64) Xeon
processors. The eX4 design includes two 4U 4-socket rack-optimized chassis (x3850 M2 and
x3950 M2) with the ability to scale up to 16 sockets and up to 96 cores. In fact, you can start
with a single-node x3850 M2 chassis, and by adding a ScaleXpander Option Kit, you can turn
it into an x3950 M2, ready to expand into a multi-node configuration providing more flexibility in
deploying your scalable solution than ever before.
The x3850 M2 now offers selected models integrated with VMware ESXi 3.5 preloaded on an
IBM 4GB USB 2.0 Flash Key. It operates in a diskless configuration, offers a smaller memory
footprint, extremely high performance, and stronger security, making getting a system up and
running in a virtualized environment faster and easier than ever before.
IBM X-Architecture pioneered XpandOnDemand™ (“pay as you grow”) scalability, which allows
chassis to be simply cabled together to form larger scale-up systems. This unique capability
allows IBM to sell a large SMP (symmetric multiprocessing) system at entry price points. Other
Intel OEMs can’t match this capability. If they offer a 16-socket product at all, they require you to
start out with a 16-socket chassis, whether you’ll ever grow into it or not. With
XpandOnDemand, you can start small, with a 4- or 8-socket configuration, and later expand as
your needs change, without requiring you to buy more than you need up-front or throw away
parts later as you expand.
IBM’s eX4 technology-based systems are the ideal solution for scale-up database-serving
applications on Microsoft® Windows® with Microsoft SQL Server® or IBM DB2®, as well as Linux®
with Oracle 9i RAC and 10g, or IBM DB2. Database hosting demands ultimate server reliability
features, and once installed, they grow and grow. The eX4 design offers two strong selling
arguments against the competition: lower initial purchase price, and potentially much lower longterm TCO.
Another strong application area for the eX4-based systems is enterprise server consolidation
activities. Larger servers have more processor, memory and I/O resources, which make
maximum use of any applicable virtual machine software licensing fees and deliver superior
system utilization levels. The name of the game in consolidation activities is to deploy the fewest
new servers possible and help IT staff manage more images with the same or fewer overall
people.
One of the fastest growing application areas for eX4-based systems is ERP workloads, including
SAP and Oracle. eX4-based systems can offer considerable savings over UNIX deployments,
using our certified solution stacks on either Windows or Linux.
The 4-socket eX4 servers are designed to protect your data with high performance, high
reliability, and high availability. They support the latest six-, quad- and dual-core Intel® Xeon™
processors, designed with high-performance quad 1066MHz front-side buses (FSB), 64-bit
extensions (EM64T), and either 8MB (dual-core); 4MB, 6MB, or 8MB (quad-core); or 9MB of
L2 cache; 8MB, 12MB or 16MB (six-core) of L3 cache, and up to 256MB of L4 cache per
chassis (all models), to help provide you with the computing power you need to match your
Page 2
Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
2
business needs and growth. In addition, the x3850 M2 and x3950 M2 use industry-standard
DDR II memory with Chipkill™ ECC (Error Checking and Correcting) protection—for high
performance and reliability and lower energy consumption than fully buffered memory. For even
higher levels of availability, the eX4 servers also offer Memory ProteXion™, memory
scrubbing, and selectable memory mirroring. A dual-port integrated high-speed Gigabit
Ethernet controller with TOE (TCP Offload Engine) is standard, as are seven high-performance
PCIe x8 adapter slots (two of them hot-plug).
The x3850 M2 and x3950 M2 offer industry-leading scalability, including quad-processor
support (upgradeable to 16 processors/96 cores), up to 256GB of memory per chassis
(upgradeable to 1TB overall), 256MB of L4 cache per chassis (upgradeable to 1GB), and up to
four 2.5-inch internal high-performance Serial-Attach SCSI (SAS) hot-swap hard disk drives
with an internal storage capacity of 587.2GB per chassis (up to 16 drives and 2.3TB overall).
Hardware-based RAID-0/1 support is standard. An optional IBM ServeRAID-MR10k SAS RAID
controller adds 256MB of battery-backed cache to the onboard controller to provide five
additional RAID levels, including RAID-10/5/50/6/60. The 4U size of the chassis helps you
maximize your rack investments. Up to 10 of these chassis can be installed in a single 42U rack,
for a total of up to 40 processors, 70 PCIe slots (20 of them hot-plug), and 40 HDDs, offering an
ideal balance of performance, storage and I/O slots per rack. Optional Advanced Connectivity
Technology (ACT) interconnect cabling helps reduce cable clutter and cost and minimizes
installation time when interconnecting many rack-mounted servers.
Standard in both the x3850 M2 and the x3950 M2 is the Remote Supervisor Adapter II that
communicates with the Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) to enable the user to
manage and control the server easily—both locally and remotely. This high level of
manageability is designed to help keep management costs down and the system up. The dropdown light path diagnostics panel enables quick servicing of the system if a problem develops.
These advanced features help maximize network availability by increasing uptime, as do hot-
swap/redundant HDDs, power and fans; Active Memory™; temperature-controlled fans with
Calibrated Vectored Cooling™; IPMI 2.0 support, including highly secure remote power
control and Serial over LAN; as well as text- and graphics-console redirect over LAN.
With the inclusion of unique IBM service and support features such as IBM Systems Director,
IBM Systems Director Active Energy Manager™ for x86 (formerly known as
PowerExecutive), and IBM ServerGuide™, the x3850/x950 M2 is designed for maximum
uptime.
If you need a balance of high-performance four-socket processing, scalability beyond eight
sockets, and large I/O capacity in a rack-dense environment, these are the ideal systems.
Key Highlights
eX4 Design Features
eX4 design offers numerous features per chassis to boost performance and reduce product and
operating costs:
• Support for up to four Intel Xeon processors with four 1066MHz front side buses and 4MBto-16MB of integrated Level 2 cache (model dependant), 8MB, 12MB, or 16MB of external
L3 cache (model dependant), Intel VT technology, and Intel EM64T technology
• Supports Xeon six-core, quad-core or dual-core processors (scalable to 16 processors
and 32-to-96 cores, using the ScaleXpander Option Kit)
• A built-in ‘snoop’ filter to lower the amount of inter-processor communication needed in an
SMP system
• Fast PC2-5300 DDR II ECC memory with Chipkill error correction, Memory ProteXion™
(redundant bit steering), memory scrubbing, selectable memory mirroring, and hot-
add/hot-swap memory protection provides speed and high availability
• Seven 64-bit high-speed (4Gbps) PCIe x8 adapter slots offer investment protection by
supporting high-performance adapters, such as 10Gb Ethernet, Fibre Channel and
InfiniBand cards; the two Active™ PCIe hot-plug slots help increase system availability
• Up to 587.2GB of internal SAS storage using four 2.5-inch HDDs per chassis (scalable to
2.3TB using the ScaleXpander Option Kit)
• Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) and Remote Supervisor Adapter II standard
• Support for an optional ServeRAID-MR10k RAID controller that supports RAID-
0/1/10/5/50/6, and 60
IBM System x3850 M2-specific
• A 4U rack-optimized model (expandable to 16U using a ScaleXpander Option Kit and
three additional chassis)
• Installing the ScaleXpander Option Kit turns the x3850 M2 into an x3950 M2 (including a
new bezel, cable management arm, and scalability “key”)
• 4GB USB 2.0 Flash Key with VMware ESXi preinstalled (in selected models)
Page 3

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
3
IBM System x3950 M2-specific
• ScaleXpander Option Kit standard
• Offers physical partitioning at four-socket granularity allowing you to run multiple
operating systems on the same integrated hardware
• Support for up to two ServeRAID-MR10k options if a multi-chassis configuration is used
Key Features
High-Performance Xeon Processors
The x3850 M2 and x3950 M2 ship with two high-performance Intel Xeon processors, and
support up to four, allowing you to upgrade as business needs require. The eX4 servers also go
a step further by allowing you to add additional nodes (chassis) to increase the number of
sockets from 4 to as many as 16 (using four total chassis). (The ScaleXpander Option Kit
converts a 4-socket x3850 M2 into an ultra-expandable x3950 M2.) With multiple chassis, you
can use physical partitioning to segment the one physical server into multiple logical servers for
virtualization.
Processors can be added or replaced through the top cover of the system. The system offers a
choice of processor clock rates, FSB speeds and power draw:
• 130W six-core Xeon processor model X7460 at 2.67GHz, with 64-bit extensions, low power
draw per core (21.67W), quad 1066MHz FSBs, 9MB of L2 processor cache (3 x 3MB; 1.5MB
per core), and 16MB of shared L3 cache
• 130W quad-core Xeon processor model X7350 at 2.93GHz, with 64-bit extensions, 32.5W
per core of power draw, quad 1066MHz FSBs, and 8MB of L2 cache (2 x 4MB; 2MB per
core)
• 90W six-core Xeon processor model E7450 at 2.4GHz, with 64-bit extensions, extremely low
power draw per core (15W), quad 1066MHz FSBs, 9MB of L2 processor cache (3 x 3MB;
1.5MB per core), and 12MB of shared L3 cache
• 90W quad-core Xeon processor model E7420 at 2.13GHz, with 64-bit extensions, low power
draw per core (22.5W), quad 1066MHz FSBs, 9MB of L2 processor cache (3 x 3MB; 1.5MB
per core), and 8MB of shared L3 cache
• 80W quad-core Xeon processor model E7330 at 2.4GHz, with 64-bit extensions, low power
draw per core (20W), quad 1066MHz FSBs, and 6MB of L2 cache (2 x 3MB; 1.5MB per core)
• 80W quad-core Xeon processor models E7320 at 2.13GHz, with 64-bit extensions, low
power draw per core (20W), quad 1066MHz FSBs, and 4MB of L2 cache (2 x 2MB; 1MB per
core)
• 80W dual-core Xeon processor model E7210 at 2.4GHz, with 64-bit extensions, 40W per
core of power draw, quad 1066MHz FSBs, and 8MB of L2 cache (2 x 4MB; 4MB per core)
• 50W quad-core Xeon processor model L7445 at 2.13GHz, with 64-bit extensions, extremely
low power draw per core (12.5W), quad 1066MHz FSBs, 9MB of L2 processor cache (3 x
3MB; 1.5MB per core), and 12MB of L3 cache
Also available via special bid/configure-to-order:
• 90W quad-core Xeon processor model E7440 at 2.4GHz, with 64-bit extensions, extremely
low power
draw per core (15W), quad 1066MHz FSBs, 9MB of L2 processor cache (3 x
3MB; 1.5MB per core), and 16MB of shared L3 cache
• 90W quad-core Xeon processor model E7430 at 2.13GHz, with 64-bit extensions, extremely
low power draw per core (12.5W), quad 1066MHz FSBs, 9MB of L2 processor cache (3 x
3MB; 1.5MB per core), and 12MB of shared L3 cache
• 65W six-core Xeon processor model L7455 at 2.13GHz, with 64-bit extensions, extremely
low power draw per core (10.83W), quad 1066MHz FSBs, 9MB of L2 processor cache (3 x
3MB; 1.5MB per core), and 12MB of shared L3 cache
The dual-core Xeon processors contain two complete processor cores. Each processor
contains two 4MB L2 caches, 4MB per core (8MB total per processor). The two cores appear
to software as separate physical processors. The dual-core processors can offer more than
double the performance of a same-speed single-core Xeon processor (depending on workload).
Similarly, quad-core Xeon processors contain four processor cores. The cores share dual
2MB, 3MB, or 4MB L2 caches (4MB, 6MB, or 8MB total per processor). That is, two cores per
L2 cache. They can offer more than double the performance of dual-core Xeon processors
(again, depending on workload). The six-core processors contain six processor cores. The
cores share dual 4MB, 6MB, or 8MB L2 caches (8MB, 12MB, or 16MB total per processor).
The servers provide four separate 1066MHz FSBs (front-side buses), one per processor. Each
of the four FSBs (which connect memory and I/O to the processor) boasts a peak rate of
8.53GBps (34.1GBps aggregate).This contrasts to the two 667MHz FSBs (with up to two
Page 4
Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
4
twice as many FSBs as before and each is 60% faster than before.
Intel Extended Memory 64 Technology (EM64T) 64-bit extensions allow the Xeon processor
to use large memory addressing when running with a 64-bit operating system. This in turn lets
individual software processes directly access more than 4GB of RAM, which was the limit of 32bit addressing. This can result in much higher performance for certain kinds of programs, such
as database management and CAD. Additional registers and instructions (SSE3) can further
boost performance for applications written to use them. Customers should contact their software
provider to determine their software support for EM64T.
Intel’s Virtualization Technology (VT) integrates hardware-level virtualization hooks that allow
operating system vendors to better utilize the hardware for virtualization workloads, a key
workload for the eX4 platform.
eX4 Chipset ‘Snoop’ Filtering
One of the core features of the eX4 chipset that gives the platform a performance advantage is
the snoop filter. The Xeon Coherency Protocol or “snoop” is an operation that occurs whenever
a processor in an SMP system needs to update a memory address during normal operation.
The snoop occurs when the processor getting ready to operate on a piece of data asks the other
processors in the SMP complex to verify they have not modified the same piece of data without
writing back from their cache. This operation increases traffic on the front side bus.
The eX4 chipset contains 324MB of EDRAM within the Northbridge chip. This copies all data as
it is written to the processor cache, allowing the chipset to respond directly to the snoop
requests. This reduces the overall traffic across the FSB and helps to improve system
performance over other architectures. (Intel now offers a first-generation snoop filter in their
7300 chipset; however it contains only 64MB of RAM which is 80% smaller than the eX4 fourth-
generation solution.)
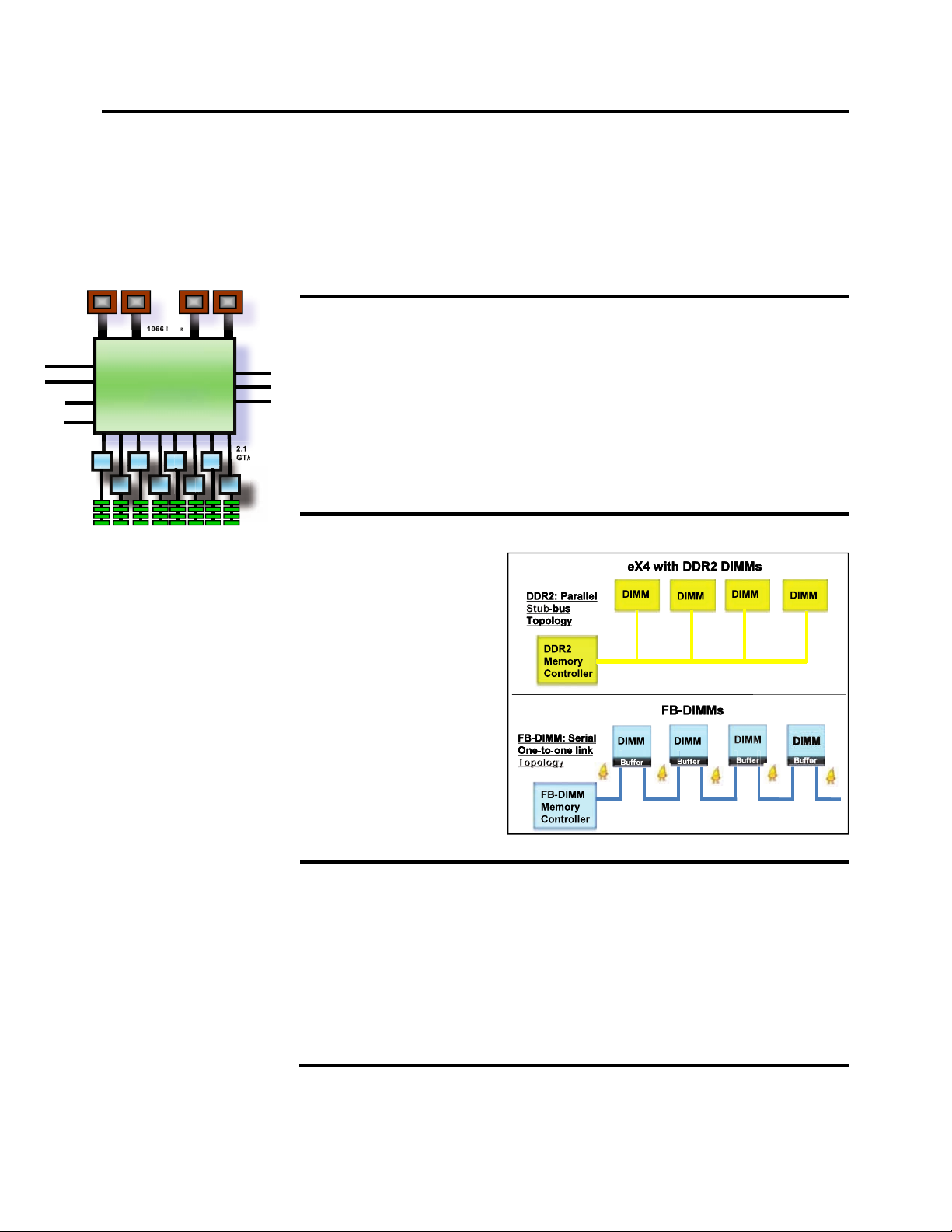
Advanced Buffer eXecution
The IBM Advanced Buffer
eXecution (ABX) chips (2 per
chassis) provide the x3850 M2 /
3950 M2’s DDR2 memory with
up to 60% more bandwidth than
other vendors can manage using
more expensive (and more
energy-hungry) Fully Buffered
DIMMs (FB-DIMMs). The ABX
chip uses two buffers per
memory card to re-drive the
signals from the eX4 memory
controller to the DIMMs,
bypassing the latency-adding
buffers used on each FB-DIMM.
The use of ABX reduces
latency by 20% vs. FB-DIMMs.
This feature is a unique IBM
enhancement, not offered by
other x86 server architectures
(using either Intel or AMD processors).
XceL4v Dynamic Server Cache
Another performance feature of the eX4 chipset is the XceL4v L4 cache. When using a single
node (chassis), the cache works with the snoop filter to help reduce FSB traffic. When more
than one node is used, 256MB of virtual cache per node (taken from main memory) is used for
interprocessor communications between chassis, to keep data in synch. In a 4chassis
configuration, this amounts to as much as 1GB of L4 cache. This not only compensates for any
performance hit that might otherwise result from sending data across the distances between
processors in multiple chassis, it actually results in a performance improvement versus a single
chassis. (IBM X3 and eX4 servers have achieved well over 100 #1 results on industry-standard
benchmarks, such as TPC-C, TPC-E, TPC-H, SAP SD, vConsolidate, Vmark, and more.)
This feature is a unique IBM enhancement, not offered by other x86 server architectures (using
either Intel or AMD processors).
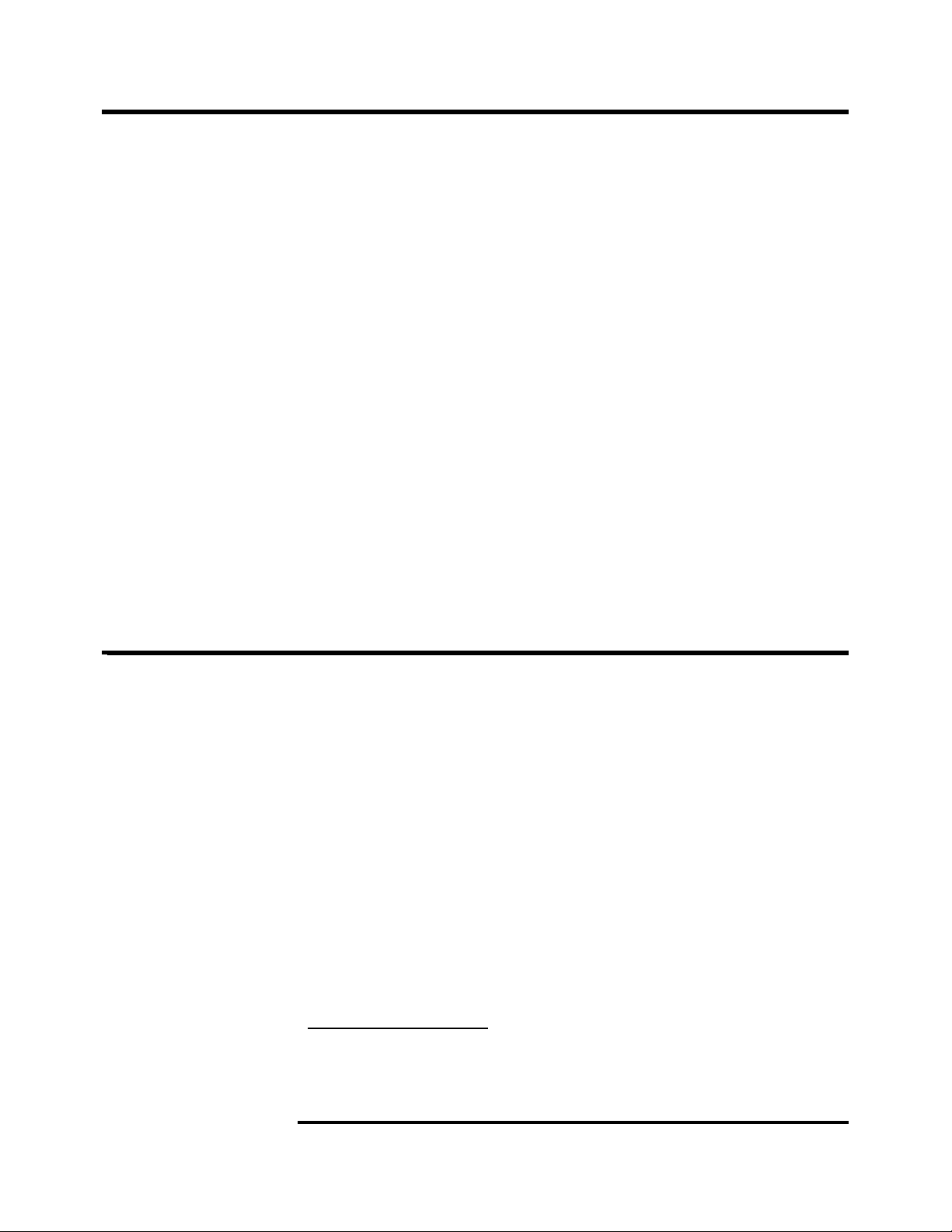
Scalable Virtual L 4
cache
IB: 2 x12
533
MT/s
1066 MT/s
2.5 GT/s
SP: 3 x8
2.1
GT/s
2.1
GT/s
LP
ES
South
Bridge
I/F
Memory
DIMMS
Flash
I/F
eX4 chipset
NNNNNNN
N
Page 5
Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
5
High-Speed Scalability Ports
When more than one chassis is used, they are simply cabled together via one or more
scalability cables. Up to three cables connected to low-latency, 10.24Gbps full-duplex ports
(5.12Gbps in each direction), supported by up to 1GB of L4 cache, provide exceptional
interchassis throughput (30.72Gbps aggregate). Because of this design, an x3950 M2 server
has the incredible flexibility of starting out as a 4-socket server with up to 256GB of memory,
256MB of L4 cache, seven PCIe adapter slots, and four HDD bays, and then doubling, tripling,
or even quadrupling those numbers while maintaining first-in-class performance.
This feature is another unique IBM enhancement, not offered by other x86 server architectures.
DDR II ECC Memory with Active Memory Protection
The eX4 servers support up to 256GB of memory per node (chassis) in 32 DIMM sockets (up to
1TB for a 4-node/16-processor configuration). It uses PC5300 double data rate II (DDR II)
memory (operating at 533MHz) for faster access, and provides IBM Active Memory features,
including advanced IBM Chipkill memory protection, for up to 16X better error correction than
standard ECC memory, IBM Memory ProteXion, hot-add/hot-swap memory support, and
optional memory mirroring. (Notes: Hot-add capability requires operating system support. Hotadd memory and mirroring are mutually exclusive. Conversely, hot-swap requires mirroring.)
The standard configuration includes two memory cards, which support up to eight DIMMs
apiece. The system is upgradeable to four memory cards with eight DIMMs each. With
configurations of 8-to-16 DIMMs, using two memory cards saves cost, but using four cards
increases performance. (With more than 16 DIMMs, four memory cards are required.)
The memory architecture of the eX4 chipset provides up to 60% more aggregate memory
bandwidth (up to 34.1GBps when using four memory cards vs. a maximum of 21.3GBps
bandwidth in the previous generation), for exceptional memory performance, and quadruple the
system memory capacity of the predecessor x3850 server. By performing reads and writes
simultaneously, it eliminates the previous memory read-to-write blocking latency. In addition, it
also offers innovative data reliability and security features to help improve data integrity,
including enhanced CRC protection, data retry on error detect and buffer registers for improved
fault isolation. Even running at 533Mhz, with twice the number of channels and twice the DIMM
capacity supported, the x3850 M2 and x3950 M2 deliver a memory subsystem with greater
throughput than the competition. In addition, the DDR2 DIMMs use up to 37% less energy than
the competition’s FB-DIMMs.
Memory scrubbing is an automatic daily test of all system memory. It detects and reports
memory errors that might be developing before they cause a server outage. Memory scrubbing
and Memory ProteXion work together. When a bit error is detected, memory scrubbing
determines whether the error is recoverable. If the error is recoverable Memory ProteXion
technology will write the data to new location; if it is not recoverable, scrubbing sends an alert to
light path diagnostics, which then notifies IBM Systems Director.
Memory ProteXion technology (also called redundant bit steering) provides multichip error
protection and works in conjunction with Chipkill technology—which provides multibit protection
per chip—and standard ECC protection, to provide three-level memory correction. For increased
availability, the eX4 design offers an additional level of Active Memory protection: memory
mirroring.
Memory mirroring works much like disk mirroring. The total memory is divided into two
channels. Data is written concurrently to both channels. If a DIMM fails in one of the DIMMs in
the primary channel, it is instantly disabled and the mirrored (backup) memory in the other
channel becomes active (primary) until the failing DIMM is replaced. Note: Mirroring requires
DIMMs to be installed in multiples of four (one pair per memory channel).
A secondary benefit of memory mirroring is that the failed DIMM and its memory card can be
hot-swapped out to replace the failed DIMM. This is a hardware feature that is operating system
independent.
DIMMs must be installed in matching pairs. Memory is available in kits consisting of two 1GB,
2GB, 4GB or 8GB DIMMs.
Flexible Internal Storage Capacity
The eX4 servers offer a choice of internal storage, supporting up to four (2.5-inch) hot-swap
high-performance Serial-Attach SCSI (SAS) drives per chassis. In addition, selected models of
the x3850 M2 include an integrated 4GB USB 2.0 Flash Key with VMware preloaded as an
embedded virtualization hypervisor.
Page 6

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
6
2.5-inch SAS
• 10,000 RPMs — 73.4 or 146.8GB (587.2GB maximum per chassis; 2.349TB in a 4-chassis
configuration)
• 15,000 RPMs — 73.4GB (293.6GB per chassis; 1.174TB per 4 chassis)
2-5-inch drives not only require less space than 3.5-inch drives, they weigh less, consume half
the power, produce less noise, seek faster, and offer increased reliability.
The hot-swap SAS drives use the Converged Tray for interchangeability with other IBM System
x™ systems. If you need more storage space, terabyte capacities are possible with external
direct-attach NAS and SAN solutions.
Integrated Virtualization
Selected models of the x3850 M2 ship with an IBM 4GB USB 2.0 Flash Key installed preloaded
with VMware ESXi 3.5. This is an embedded version of VMware ESX 3.5, fully contained on the
flash drive and requiring no disk space—not an “ESX Lite.” Rather than management through a
Service Console based on a Linux operating system, ESXi 3.5 relies on aggregate management
tools, including VirtualCenter, the Remote Command Line interface and the introduction of CIM
for standards-based and agentless hardware monitoring.
VMware ESXi 3.5 includes all the performance, scalability and compatibility features of ESX 3.5,
including full VMFS support across FC SAN, iSCSI SAN, and NAS, and 4-way VSMP. Because
it runs from flash memory, it’s extremely fast and ideal for diskless configurations. It also offers
enhanced security, because it runs without an operating system-based console and is
updated/patched much like firmware. Licensing works the same as for “standard” ESX 3.5.
If you prefer Microsoft Hyper-V™ to VMware, the intent is for the x3850 M2 and x3950 M2 to
fully support Microsoft’s hypervisor software installed on the system HDD at a future date.
Disk/Tape Controllers
All models include an integrated eight-port LSI 1078 Serial-Attach SCSI (SAS) controller. This
controller supports up to four internal SAS LVD (low-voltage differential) drives.
The integrated SAS controller offers hardware RAID-0/1 support for those SAS drives. The
ServeRAID-MR10k option adds additional RAID levels, including RAID-10, 5, 50, 6 and 60,
along with 256MB of battery-backed cache memory for higher performance and data integrity,
without consuming a valuable PCIe adapter slot.
The SAS controller provides data transfer speeds of up to 300MB per second1 in each direction
(full-duplex) across the SAS bus, for an aggregate speed of 600MBps, nearly double that of
Ultra320 SCSI’s 320MBps (half-duplex) bandwidth. The serial design of the SAS bus allows
maximum performance to be maintained as additional drives are added.
Additional external SAS/SATA disk storage, as well as tape backup, is available using the
external SAS port on the system unit, or via one of several supported iSCSI or FC SAN
controllers.
Drive Bays
The eX4 servers contain five drive bays (per chassis) in all—including four 2.5-inch HDD bays
that support hot-swap SAS drives totaling up to 587.6GB.
A 24X/10X/24X/8X2 speed (ultraslim, 0.5”) CD-RW/DVD-ROM combo drive with an IDE
interface ships standard in all x3850 M2 and x3950 M2 servers. No floppy drive is supplied with
any model; an external USB floppy drive may be used, if needed.
For still more storage, a direct-attach, iSCSI, or FC SAN external expansion option can be
added, using an optional controller.
High-Performance Adapter Slots
There are seven physical x8 (“by 8”) PCIe (PCI Express) adapter slots standard (per chassis).
Each is capable of supporting x4 or x8 adapters. All slots are half-length/full-height.
Electrically they are x8 slots as well (meaning that they operate at full x8 4GBps speeds). Slots
6 and 7 are Active PCIe hot-add/hot-swap slots, offering the capability to add or replace
adapters without having to shut down the system.
PCI Express is a high-performance, low-latency, next-generation serial I/O bus that is rapidly
replacing the older parallel PCI and PCI-X buses. A x8 PCIe adapter offers approximately four
1
Data transfer rates depend on many factors and are often less than the maximum possible.
Page 7

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
7
times the maximum throughput of a 133MHz PCI-X adapter3. (A x1 adapter offers throughput
similar to a 66MHz PCI-X slot.)
Because the SAS, ServeRAID-MR10k, dual Gigabit Ethernet, and systems management
controllers are integrated onto the system board, the seven adapter slots are all available, which
offers you a wide degree of latitude in expansion options.
(Even though the HP DL580G5 has eleven total slots, they offer lower throughput, providing no
more aggregate bandwidth than the seven slots of the eX4 servers.)
Dual Gigabit Ethernet Controller
The eX4 systems include one integrated dual-port Broadcom 5709C Gigabit Ethernet
controller, with TOE (TCP Offload Engine) acceleration support (available 1Q/08), as well as
load-balancing and failover capabilities between the two ports.
TOE support helps improve overall system performance by offloading TCP/IP protocol
processing from the system microprocessor to the onboard Ethernet TOE processor. iSCSI
support works similarly for iSCSI workloads.
The controller also supports highly secure remote power management using IPMI 2.0, plus
Wake on LAN® and PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) flash interface. Optional PCI
adapters offering failover and load balancing between adapters are available for added
throughput and increased system availability.
Ultra-Efficient Cooling
Six strategically located hot-swap/redundant fans, combined with efficient airflow paths,
provide highly effective system cooling for the eX4 systems, known as Calibrated Vectored
Cooling. The fans are arranged to cool three separate zones, left, center, and right, with one
pair of redundant fans per zone.
The fans automatically adjust speeds in response to changing thermal requirements, depending
on the zone, redundancy, and internal temperatures. When the temperature inside the server
increases, the fans speed up to maintain the proper ambient temperature. When the
temperature returns to a normal operating level, the fans return to their default speed. Why not
simply run the fans at 100% capacity all the time? For several good reasons: to reduce the
ambient noise, reduce the wear-and-tear on the fans and reduce the server power draw. The
reduction in ambient noise and power draw may be relatively minor for a single server, but if you
have a larger number of systems the aggregate savings in power and noise pressure can be
significant.
In addition, the server uses hexagonal ventilation holes in the chassis. Hexagonal holes can
be grouped more densely than round holes, providing greater airflow through the system cover.
This cooling scheme is important because newer, more powerful processors generate a
significant amount of heat, and heat must be controlled for the system to function properly.
Hot-Swap/Redundant Components
System availability is maximized through the extensive use of hot-swap and redundant
components, including:
• Hot-add/hot-swap redundant memory protection (with Chipkill, Memory ProteXion,
and selectable memory mirroring capabilities)
• Hot-swap redundant hard disk drives (with standard LSI 1078 controller and optional
ServeRAID-MR10k providing multiple levels of RAID support)
• Hot-swap PCIe adapter slots (with optional failover support)
• Hot-swap redundant cooling fans (three redundant pairs)
• Hot-swap redundant power supplies4
Light Path Diagnostics
Light path diagnostics enables a technician to quickly identify and locate a failed or failing
system component, such as a specific memory DIMM. (Monitored components include
processors, memory, power supplies, fans, HDDs, adapters, and voltage regulator modules
(VRMs), plus system temperature.) This enables quick replacement of the component, which
helps increase server uptime and lower operating costs.
The front of the server has an LED indicator light to show possible component failures. If the
2
Variable read rate. Actual playback speed varies and is often less than the maximum possible.
3
Actual throughput will depend on the adapter vendor’s implementation.
4
At 220V both power supplies are redundant; at 110V only the first power supply is redundant.
Page 8

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
8
front LED indicates an error condition, by pressing a button on the front of the server an LED
panel will pop out and drop down for easy viewing without the need to open the server cover or
remove the server from the rack. The light path diagnostics panel tells the servicer which
component requires attention. In addition, many components have their own identifying LEDs.
For example, each of the memory modules has an LED next to the socket, as do all processors,
all adapter slots, all fans, all power supplies, all voltage regulator modules and the service
processor, allowing the servicer to easily identify exactly which component needs servicing. By
following the “light path,” the component can be replaced quickly, and without guesswork. (Note:
In the event of a failed DIMM, the system will restart and mark the DIMM as bad while offline,
thus allowing the system to continue running, with reduced memory capacity, until serviced.)
In addition to the outstanding diagnostic detection, there is a new feature with a digital readout
that indicates at what stage of the boot process your system may have experienced trouble.
This can reduce the troubleshooting time and help get your system up and running quickly and
efficiently.
Other Features
• Trusted Platform Module standard — This module provides a highly secure start-up
process from power-on through hand-off to the operating system boot loader. ACPI support is
provided to allow ACPI-enabled operating systems to access the security features of this
module. (TCG V1.2-compliant.)
• Six USB 2.0 ports — Provides flexibility to add high-speed external devices. The USB 2.0
specification supports up to 480Mbps transfer rates. (Note: Not all USB 2.0 devices are
capable of achieving this rate.) Two ports are provided on the front of the server, three are
on the back, and one is internal to support the embedded 4GB USB 2.0 Flash Memory Key
in selected models.
• Remote Supervisor Adapter II standard — This full-function systems management adapter
provides local and remote management functions in a dedicated PCI-X slot, without
consuming one of the seven PCIe adapter slots.
• Video — An ATI Radeon ES1000 SVGA video controller on the Remote Supervisor Adapter
II provides up to 1024x768 resolution, with a color depth of 32 bits at 85Hz refresh rate, with
16MB of video memory.
• Toolless slides — Allows quick rack installation and quicker upgrade and servicing of the
server.
• Toolless chassis — The cover can be opened without tools, and many components can be
removed and replaced without tools, including the CD-RW/DVD combo drive, hot-add/hotswap memory, hot-swap HDDs, adapters, and the integrated optional ServeRAID-MR10k
and Remote Supervisor Adapter II. This can save a servicer significant time.
Rack Cable Management and KVM Console Switching
IBM Advanced Cabling Technology (ACT) is an optional feature that offers many advantages
over standard KVM cabling across the entire System x and xSeries product line. So now you
can interconnect all of your servers with one smart cabling architecture. ACT cabling eliminates
the need for one-to-one direct connections between each server and a KVM switch by using a
daisy-chain approach.
The snarl of cabling behind most racks is at best inconvenient to work around and at worst an
expensive logistical nightmare, requiring the rewiring of servers, PDUs, KVM switches, and
other equipment whenever a rack server is added or removed. Even worse, the veil of cables
blocks rack airflow and can actually contribute to equipment failure due to overheating. ACT
cabling is the solution for reducing behind-the-rack cabling by as much as 87%.
Conventional cabling has bulky KVM cables exiting each server, which then connect to a KVM
switch. The cables exiting a series of KVM switches must then be aggregated via additional
KVM switches and PDUs, which only increases the number—and cost—of cables, KVM
switches and PDUs. Instead, the daisy-chain approach of ACT cabling uses readily available,
inexpensive CAT5 and 6 cabling to considerably reduce the number of cables, KVM switches,
and PDUs needed, rather than increasing them. If a server is removed or added, no complicated
rewiring is needed. One cable connects the first server in the rack to the next, and so on. Up to
16 servers form a chain; up to 8 chains can connect to one Local Console Manager (LCM); 16
LCMs can connect to one Global Console Manager (GCM). In this manner, up to 2,048 servers
can be centrally managed. Equally importantly, with ACT—unlike some other offerings—
everything is done externally via cabling; no special adapters are required.
The illustration below shows a sample ACT configuration:
Page 9

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
9
Advanced Systems Management Capabilities
The x3850 M2 and x3950 M2 have a high level of systems management capabilities that are
well-suited to remote locations as well as to stand-alone environments. Features include the
Baseboard Management Controller (BMC), IBM Systems Director Active Energy Manager for
x86 (formerly known as PowerExecutive), Automatic Server Restart, Wake on LAN® support,
PXE support, text console redirect, Predictive Failure Analysis, IBM Systems Director, IBM
Systems Director Active Energy Manager for x86, and the Remote Supervisor Adapter II.
The BMC provides industry-standard Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) 2.0compliant systems management. It provides a number of important system functions, including:
• Monitoring of system and battery voltage, system temperature, fans, power supplies,
processor and DIMM status
• Fan speed control
• Product ID and Family ID detection
• Highly secure remote power on/off
• System reset control
• NMI/SMI detection and generation
• System diagnostic LED control (power, HDD, activity, alerts, heartbeat)
• IPMI over LAN
• Serial Over LAN
• Proxy server support
• LAN messaging and alerting
• Text console redirection over LAN
• VLAN support
• Enhanced authentication and encryption algorithms (RMCP+, SHA-1, AES)
• Local update of BMC firmware
• Firmware firewall
• Support for IPMI v2.0 compliant management software (e.g., xCAT)
• Other mandatory and optional IPMI BMC functions
The BMC alerts IBM Systems Director to anomalous environmental factors, such as voltage and
thermal conditions—even if the server has failed.
The IBM Remote Supervisor Adapter II provides additional systems management capabilities,
including:
• Graphical console redirection over LAN
• Web-based out-of-band control
• Windows “blue screen” capture
• Remote virtual floppy and CD-ROM
• High-speed remote redirection of PCI video, keyboard and mouse
Directly
Via Secondary
Switch
Via Daisy-Chain
• Max.16 servers per port
All CAT5, 5e, 6
cabling
Page 10

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
10
• SSL (Secure Socket Layer) and LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) support
Automatic Server Restart (ASR) helps reduce downtime by restarting the server automatically
in the event of a system lockup. ASR technology is a combination of hardware circuitry tied into
the server’s system reset function and a device driver. As long as the server continues running,
the ASR watchdog timer will keep being reset, but if the operating system crashes or the
hardware freezes somehow the ASR software will be unable to reset the hardware timer. If the
timer is not reset within five minutes, it automatically triggers the ASR hardware, which
immediately restarts the server (and logs an ASR event with IBM Systems Director). These
features are designed so that no more than five minutes can pass before the server is restarted.
Wake on LAN permits the server to be remotely powered on if it has been shut off. Once
powered up, the server can be controlled across the network, using the Preboot Execution
Environment (PXE).
Like Wake on LAN, PXE is system firmware. It enables software such as the optional IBM
Remote Deployment Manager to take control of a system before the BIOS, operating system
or applications are loaded (using Wake on LAN/PXE) and lets an administrator perform many
low-level tasks remotely that would otherwise require a visit to each system. These tasks may
include such things as formatting a hard disk drive, updating system firmware, or deploying a
Windows or Linux operating system.
Text and Graphical Console Redirection support allows the administrator to remotely view
system text messages and graphics over serial or LAN.
Predictive Failure Analysis (PFA) is designed to allow the x3850 M2/x3950 M2 to detect
impending failure of supported components (processors, memory, PCIe slots, VRMs, power
supplies, fans, and hard disk drives) before actual failure, and alert the administrator through
IBM Systems Director. This gives you the ability to replace the failing component before it fails,
resulting in increased uptime.
IBM Systems Director software for advanced workgroup management is included with the eX4
servers. IBM Systems Director comes with a portfolio of tools, including Management Processor
Assistant, Rack Manager, RAID Manager, Update Assistant and Software Distribution. IBM
Systems Director Active Energy Manager for x86, System Availability (a no-charge download)
and Capacity Manager (sold separately) are available as add-ons for additional server
management and increased availability. IBM Systems Director provides a single uniform
graphical interface for all of these systems management functions.
IBM Systems Director enables you to customize thresholds and monitor system components
(for things like temperature, voltage regulation, etc.) to help maximize uptime.
IBM developed IBM Systems Director Active Energy Manager for x86 to put control of
system power-saving features at the fingertips of administrators. Active Energy Manager is a
combination of hardware and software designed to take advantage of new features, such as
monitoring power usage and balancing the performance of the system according to available
power input. It provides the ability to plan and predict power consumption based on your
hardware configuration. It also helps enable you to reduce the infrastructure required for
redundancy, by using fewer servers on smaller power feeds and potentially lowering your overall
data center support costs. It does this by inventorying all components, then adding up the total
power draw and tracking the usage.
Extensive System Support Features
The IBM services and technical support portfolio provides world-class, consistent, high-quality
service and support. The eX4 servers offers a number of tools and services designed to make
ownership a positive experience. From the start, IBM programs make it easier for you to plan
for, configure and purchase System x or xSeries servers, get them running and keep them
running long-term. These features include IBM Express Portfolio, IBM ServerProven
®
, the IBM
Standalone Solutions Configuration Tool, IBM System x and BladeCenter Power Configurator,
IBM ServerGuide, IBM Electronic Service Agent
™
, Product Customization Services and
extensive technical support offerings.
The IBM ServerProven program provides the confidence that specific options and operating
systems have been tested on the server and are officially supported to work together. It is
updated frequently to ensure that the latest compatibility information is always at your fingertips.
The IBM Standalone Solutions Configuration Tool (SSCT) is a downloadable tool that
simplifies the often complex chore of configuring a full rack of servers (including blade servers)
and confirming that you have all the cables, power distribution units, KVM (keyboard, video and
mouse) switch boxes and other components you need, as well as the proper airflow clearances,
electrical circuits and other environmental conditions.
IBM System x and BladeCenter Power Configurator helps IT managers plan for data center
power needs, by providing the following information for specific configurations of System x and
Page 11

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
11
BladeCenter systems: power input (watts), PDU sizing (amps), heat output (BTUs), airflow
requirements through chassis (CFM), VA rating, leakage current (mA), and peak inrush current
(amps).
IBM ServerGuide (installed from CD) simplifies the process of installing and configuring System
x and xSeries servers. ServerGuide goes beyond mere hardware configuration by assisting with
the automated installation of the Microsoft® Windows® Server 2000 and 2003 operating
systems, device drivers and other system components, with minimal user intervention. (Drivers
are also included for support of Novell NetWare, Red Hat Linux and SUSE LINUX.) This focus
on deployment helps you reduce both your total cost of ownership and the complexity that
administrators and technical personnel face.
IBM Electronic Service Agent™ is an innovative “call home” feature that allows System x and
BladeCenter servers to automatically report hardware problems to IBM support, which can even
dispatch onsite service5 if necessary to those customers entitled to onsite support under the
terms of their warranty or an IBM Maintenance Agreement. Electronic Service Agent resides on
a server and provides electronic support and problem management capabilities through a highly
secure electronic dialogue between your systems and IBM. It monitors networked servers for
hardware errors and it can perform hardware and software inventories and report inventory
changes to IBM. All information sent to IBM is stored in a highly secure database and used for
improved problem determination.
Additional services include hardware warranty upgrades and factory-installed Product
Customization Services (PCS), such as asset tagging, hardware integration, software imaging
and operating systems personalization.
IBM offers extensive technical support by phone and via the Web. Support options include
links to forums/newsgroups, problem submission, online shopping support, service offerings,
device drivers for all IBM product lines, software downloads and even upcoming technical
seminar worldwide schedules and registration. Also available are remote installation,
configuration and usage support for System x and xSeries hardware and software, as well as
onsite custom services to provide the level of expertise you require.
Key Options
IBM options for System x servers help you take your servers to a
higher level
You can rely on System x options to supply a complete solution for your business needs.
Options help you create an optimized server system to meet your data protection, storage and
availability needs. Every IBM option is designed and tested for peak performance and flexibility,
helping to maximize your return on investment. The combination of System x servers and
options lets you keep your fingers on the pulse of your e-business.
Processors — The Intel Xeon processor provides high clock rates, a choice of dual-, quad-, or
six cores, 64-bit extensions, a large cache and advanced features for availability and
manageability. Large cache size, combined with a fast 1066MHz front-side bus, reduces
memory latency and facilitates the movement of data through the processor and I/O devices.
(Note: System performance depends not only on the number of processors in the server but
also on the power and functionality of each processor.) Adding a second, third, or fourth
processor may be a cost-effective way to achieve significant performance improvements.
Memory — Memory is a significant factor in systems application performance. Adding more
memory to a System x server is one of the most effective ways to increase application
performance. For best performance in a server with dual-core processors, there should be twice
as much memory available as for a server using single-core processors. A server with six-core
processors should have three times as much memory as a server using dual-core processors.
The eX4 servers take memory upgrades in pairs and provide two-way interleaving.
Hard Disk Drives — IBM hard disk drives help you improve the transaction and cost
performance of your System x servers. The choice of hard disk drives can be a critical aspect of
maximizing the I/O throughput of the system. 2.5-inch SAS hard disk drives are available for the
eX4 servers with capacities up to 146.8GB apiece at 10,000 RPMs, or up to 73.4GB apiece at
15,000 RPM.
Remote Supervisor Adapter II — The x3850 M2 and x3950 M2 include a plethora of systems
management features built-in. The Remote Supervisor Adapter II not only offers powerful new
features, it does so without taking up a valuable PCIe adapter slot, instead using a dedicated
PCI-X slot on the motherboard.
ServeRAID Controllers — System x servers using ServeRAID technology allow companies to
build a reliable foundation for business-critical computing. IBM ServeRAID technology allows an
array consisting of multiple physical hard disk drives to be treated as one logical drive.
5
For onsite labor, IBM will attempt to diagnose and resolve the problem remotely before sending a technician.
Page 12

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
12
ServeRAID technology also allows data to be stored redundantly, across multiple hard disk
drives— enhancing both the integrity and the availability of the data. SAS and SATA ServeRAID
controllers offer enhanced performance due to onboard processors and cache. Because IBM
ServeRAID controllers can help significantly improve data transfer rates, this technology is
extremely effective when implementing demanding, transaction-oriented applications. By
employing the advanced fault tolerance of IBM ServeRAID technology, companies can
effectively implement networked business systems that require large amounts of storage space
for data and applications that must be available for their businesses to continue operating.
The optional integrated ServeRAID-MR10k SAS/SATA controller offers enhanced performance
over the integrated LSI 1078 SAS controller, 256MB of battery-backed cache memory, and
supports seven RAID levels: 0 (striping), 1 (mirroring), 10 (mirroring and striping), 5 (striping
with parity), and 6 (striping with double parity), 50 (striping with parity across multiple arrays)
and 60 (striping with double parity across multiple arrays). Note: RAID-50 and -60 require
external storage, due to the minimum requirement of six or eight drives, respectively.
External SAN, NAS and direct-attach storage is available using one of several IBM System
Storage™ and TotalStorage™ host bus adapters.
The IBM TotalStorage DS4000, DS6000, and DS8000 series, as well as the System Storage
DS4000, N3000, N5000, and N7000 series, comprise a powerful and broad shared storage
family with integrated management software designed to meet midrange and enterprise needs.
x3850 M2 / x3950 M2 Images
Front View
Hexagonal
Ventilation Holes
USB Ports
Hot-Swap
SAS Drives
Pop-Out Light
Path Diagnostics
Panel
Optical Drive
Carrying handles
Power Button
Page 13

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
13
Rear View
Interior View
Redundant
H/S Power
Supply Bays
PCIe
Slots
Video
Port
Scalability
Ports
Hot-swap
PCIe slots
USB
Ports
Serial
Port
Remote
Supervisor
Adapter II
Gb Ethernet
Ports
Hexagonal
Ventilation Holes
SAS
Port
Remote Supervisor
Adapter II
7 Adapter
Slots
ServeRAID
Adapter
Slot
2 Memory
Cards
6 Hot-Swap
Fans
4 HDD Bays /
2 Processors
2 Processors
2 Hot-Swap
Power
Supply
Bays
2 Memory
Cards
Page 14

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
14
x3850 M2 / x3950 M2 Specifications
Machine type
x3850 M2
7141-1RX/1RY, 2RX/2RY, 3HX/3HY,
3RX/3RY, 4RX/4RY—3 yr. warranty;
7233-2RX/2RY, 5RX/5RY, 6RX/6RY,
7RX/7RY—3 yr. warranty;
7234-6RX/6RY—4 yr. warranty
x3950 M2
7144-1SX/1SY, 3SX/3SY, 4SX/4SY—3
yr. warranty;
7233-2SX/2SY, 5SX/5xSY, 6SX/6SY,
7SX/7SY—3 yr. warranty;
7234-6SX/6SY—4 yr. warranty
Form factor (standard/maximum)
4U / 16U
Processor type
Six-core Xeon
(E74xx/L74xx/X74xx)
2.13GHz E7420
(2xX/2xY), 2.13GHz
L7445 (7xX/7xY), 2.4GHz
E7450 (5xX/5xY),
2.66GHz X7460 (6xX/6xY)
Quad-core Xeon
(E73xx/X73xx)
1.6GHz E7310 (1SX/1SY),
2.13GHz E7320
(2xX/2xY), 2.4GHz E7330
(3xX/3xY), 2.93GHz
X7350 (4xX/4xY)
Dual-core Xeon
(72xx)
2.4GHz E7210 (1RX/1RY)
Maximum processor power draw
130W (7141/7144-
4xX/4xY; 7233-
6xX/6xY)
90W (7233-
2xX/2xY, 5xX/5xY)
80W (7141/7144-
1xX/1xY, 2xX/2xY,
3xX/3xY)
50W (7xX/7xY)
Front-side bus (FSB) speed
1066MHz x 4 FSBs
# of independent front-side buses
4
# of processors standard / maximum
2 / 4 (per chassis)
Internal L2 cache
9MB (3 x 3MB)—
7233/7234 (all)
8MB (2 x 4MB)—
7141/7144-
1xX/1xY, 4xX/4xY
6MB (2 x 3MB)—
7141/7144-
3xX/3xY
4MB (2 x 2MB)—
7141/7144-
2xX/2xY
External L3 cache
16MB shared cache—
7233-6xX/6xY
12MB shared cache—
7233-5xX/5xY, 7xX/7xY
8MB shared cache—
7233-2xX/2xY
XceL4v Dynamic Server (L4) cache
Up to 256MB per chassis (1TB max.)
Chipset
IBM eX4
ScaleXpander Option Kit
Standard (7144-1SX/1SY, 3SX/3SY,
4SX/4SY)
Optional (7141-1RX/1RY, 2RX/2RY,
3HX/3HY, 3RX/3RY, 4RX/4RY; 7233-
2RX/2RY, 5RX/5RY, 6RX/6RY,
7RX/7RY)
Scalability ports
3 (per chassis)
# of interconnected nodes (chassis)
maximum
4
Standard / maximum memory6 (per
chassis)
8GB (4 x 2GB on 2
memory cards) / 256GB
(3HX/3HY)
8GB (8 x 1GB on 4
memory cards) / 256GB
(3RX/3RY, 3SX/3SY,
4xX/4xY, 5RX/5RY,
5SX/5SY, 6xX/6xY)
4GB (4 x 1GB on 2
memory cards) / 256GB
(1xX/1xY, 2xX/2xY,
7xX/7xY)
Standard memory type
Registered PC2-5300 (533MHz) DDR II ECC with Chipkill protection
Memory interleaving
Yes (two-way using pairs of DIMMs)
DIMM capacities supported
1GB, 2GB, 4GB, 8GB
# of DIMM sockets total / available
32 / 24 (3RX/3RY, 3SX/3SY, 4xX/4xY,
5RX/5RY, 5SX/5SY, 6xX/6xY)
32 / 28 (3HX/3HY, 4xX/4xY, 7xX/7xY)
Memory mirroring supported
Yes
6
Maximum memory and disk capacity may require the replacement of standard components with the largest supported component
available.
Page 15

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
15
x3850 M2 / x3950 M2 Specifications
# of drive bays total / available
5 / 4
# of HDD drive bays total / available
4 / 4 2.5-inch
# of 5.25" bays total / available
1 / 0 (CD-RW/DVD installed)
Maximum HDD capacity
2.5-inch SAS
587.2B (4 x 146.8GB) hot-swap SAS
Internal HDD capacities supported
2.5-inch SAS
73.4, 146.8GB — 10K RPMs;
73.4GB — 15K RPMs
# of HDDs standard
None
# of optical drives standard
1 CD-RW/DVD Combo (24X/10X/24X/8X, in dedicated 5.25" UltraBay)
# of diskette drives standard
None (USB-attached)
Embedded USB Flash Key standard
4GB (preloaded with VMware ESXi 3.5 (3HX/3HY)
Disk drive technology
Hot-swap SAS
Integrated disk controller
Eight-port LSI 1078 SAS
# of disk drives supported per port
1
External disk drives supported
standard
Yes, via external 4-port SAS connector
External disk storage devices
supported
System Storage DS4100, DS4200, DS4300, DS4400, DS4500, DS4700, DS4800,
DS6800, DS8100, DS8300, N3700, N5200, N5300, N5500, N5600, N7600, and N7800
storage subsystems
Integrated RAID controller / cache
LSI 1078 (no cache) standard—internal SAS
Optional RAID controllers supported
ServeRAID-MR10k (256MB)—internal/external SAS
# of adapter slots total / available
7 / 7
# of PCIe physical x8/electrical x8
slots (4GBps)
7 full-height/half-length (including 2 Active PCIe hot-plug slots)
# of PCI-X slots
None
# of legacy PCI slots
None
# of video ports
1
Video controller
ATI Radeon ES1000
Video memory
16MB SDRAM
Maximum video resolution at 32-bit
color
1024 x 758 x 32-bit color at 85Hz
Gigabit Ethernet controller
Dual-port Broadcom BCM5709C
TOE acceleration
Yes
Failover / load-balancing-capable
Yes / Yes
# of Gigabit Ethernet ports
2 (rear)
# of RS485 ports
None
# of serial ports
1 (rear)
# of parallel ports
None (USB-attached)
# of mouse ports
None (USB-attached)
Page 16

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
16
x3850 M2 / x3950 M2 Specifications
# of keyboard ports
None (USB-attached)
# of SAS ports
1 (rear)
# of USB 2.0 ports
5 external (2 front, 2 rear) ports, plus 1 internal USB connector for flash drive
Integrated systems management
controller
Remote Supervisor Adapter II
Light path diagnostics support
Processors, memory, power supplies, fans, HDDs, adapters, voltage regulator
modules (VRMs), and system temperature, with external pop-out/drop-down panel
Predictive Failure Analysis support
Processors, memory, PCIe slots, VRMs, power supplies, fans, and hard disk drives
Power supply size
1440W universal, autoswitching, hot-swap (rear access)
# of power supplies standard /
maximum
2 / 2
Hot-swap/redundant power supported
Yes
# of fans/blowers standard / maximum
6 / 6
Hot-swap/redundant fans supported
Yes
Heat emitted: typical / maximum
2,730 / 5,527 BTUs;
800 / 1,620 Watts
Rack mount method
Slides and Cable Management Arm (provided standard)
Maximum altitude
7,000 ft;
2,133 m
Operating temperature range
50–95º F; 10–35º C (up to 3,000 ft /
914.4 m)
50–90º F; 10–32º C (3,000 ft to 7,000 ft /
914.4m to 2,133m)
Dimensions (HWD) / weight
6.8” (172.8mm) H
17.5” (444mm) W
28.35” (720.2mm) D
70-95 lb (maximum)
31.75-43.2 kg
Operating systems supported
7141/7144
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 R2
(Standard/Web/Enterprise Editions)
32/64-bit, RHEL 4 AS/ES 32/64-bit,
RHEL 5 Server 32/64-bit, SLES 9/10
32/64-bit, VMware ESX Server 3.0.2+
7233/7244
Microsoft Windows Server 2008
(Standard/Web/Enterprise/Datacenter
Editions) 64-bit, Microsoft Windows
Server 2003 R2 (Standard/Web/
Enterprise/Datacenter Editions) 32/64-bit,
RHEL 4 AS/ES 64-bit, RHEL 5 Server
32/64-bit (with and without Xen), SLES 9
64-bit , SLES 10 32/64-bit (with and
without Xen), VMware ESX 3.5/ESXi 3.5
Length of limited warranty
3 years (parts and labor)7
(7141/7144/7233)
4 years (parts and labor) (7234)
The Bottom Line
The eX4 servers are extremely powerful systems, incorporating leading-edge industry-standard
features and adding IBM-unique innovations:
Price/Performance
• High-throughput processors — 2.13 to 2.66GHz six-core, 2.13 to 2.93GHz quad-core or
2.4GHz dual-core Xeon processors; up to 24 (six-core), 16 (quad-core) or 8 (dual-core)
processor cores per chassis
7
For terms and conditions or copies of the IBM Statement of Limited Warranty, call 800-772-2227 in the U.S. In Canada call 800-
426-2255. IBM makes no representation or warranty regarding third-party products or services including those designated as
ServerProven or ClusterProven. Telephone support may be subject to additional charges. For warranties including onsite labor, a
technician is sent after IBM attempts to resolve the problem remotely. International warranty service is available in any country in
which this product is sold.
Page 17

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
17
• Large L2 cache — 9MB, 8MB, 6MB or 4MB of internal processor cache (model-specific)
• Large L3 cache — 16MB, 12MB, or 8MB of external processor cache (model-specific)
• Huge L4 cache — 256GB per chassis (up to 1GB in a 4-chassis configuration) of IBM-unique
XceL4v Dynamic Server cache
• 64-bit extensions (EM64T)
• Fast front-side buses — 4 x 1066MHz (one per processor)
• Fast memory — PC2-5300 DDR II ECC memory standard with two-way interleaving and a
low-latency memory controller
• Embedded virtualization (in selected models)
• Fast disk technology — Integrated Serial-Attach SCSI (SAS) controller and slotless
hardware-based RAID-0 data striping
• Fast communications — Integrated dual-port Gigabit Ethernet controller, supporting loadbalancing and failover, as well as TOE, RDMA, and iSCSI
• Fast I/O — PCIe x8 (4Gbps) adapter slots
Flexibility
• Scale up or scale out — 1 to 4 chassis, with 2 to 16 processors and 4 to 96 processor
cores, scalable on demand (using the ScaleXpander Option Kit and four chassis)
• Large memory capacity — 256GB of DDR2 memory, with 32 DIMM slots per chassis
(expandable to 1TB of RAM, using the ScaleXpander Option Kit and four chassis)
• Integrated 4GB flash drive, preloaded with VMware ESXi 3.5 (selected models) for “instant”
virtualization
• A choice of four 2.5-inch hot-swap SAS drives internally and one external SAS port for
optional external storage (per chassis); up to 16 drives in a 4-chassis configuration)
• High-performance external I/O expansion — Six 480Mbps USB 2.0 ports (two front, three
rear, one internal); one external SAS port
• Hardware-based RAID-0/1 support standard; optional slotless RAID support for RAID-
10/5/50/6/60 (up to two ServeRAID-MR10k controllers in a multi-chassis configuration)
• Seven available x8 PCIe slots (4Gbps) per chassis, including 2 Active PCI (hot-plug) slots
per chassis (28 total slots, including 8 Active PCIe slots, in a 4-chassis configuration)
• Integrated DVD/CD-RW combo drive
Manageability, Serviceability and Availability
• IBM Systems Director systems management software, including:
IBM Systems Director Active Energy Manager for x86
IBM Management Processor Assistant
IBM Rack Manager
IBM RAID Manager
IBM Update Assistant
IBM Software Distribution
IBM System Availability
• Integrated Baseboard Management Controller (BMC):
IPMI 2.0 compliance, including highly secure remote power control
Text console redirection systems management standard
• Remote Supervisor Adapter II daughter card standard (uses dedicated slot)
Supports LDAP and SSL industry standards
• Active Memory protection:
Advanced Chipkill ECC memory correction
Memory ProteXion
Memory mirroring
Memory scrubbing
• Slotless hardware-based RAID-1 disk mirroring standard; optional slotless RAID-10/5/50/6/60
highly available arrays
• Ultra-efficient cooling incorporating Calibrated Vectored Cooling features
• Hot-swap hard disk drives
• Hot-add/hot-swap memory
• Hot-swap/redundant power supplies and cooling
Page 18

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
18
• Hot-swap/redundant cooling
• Light path diagnostics (front LED panel, drop-down light path panel)
• Toolless chassis and toolless slide design; integrated Cable Management Arm simplify
installation and removal of the server from the rack
Page 19

Combining high-performance architecture with high-performance Xeon processors
Please see the Legal Information section for important notices and information.
19
For More Information
IBM System x Servers http://www.ibm.com/systems/x
Electronic Service Agent http://www.ibm.com/support/electronic
IBM System x and BladeCenter Power Configurator http://www.ibm.com/systems/bladecenter/powerconfig
Standalone Solutions Configuration Tool http://www.ibm.com/servers/eserver/xseries/library/configtools.html
Configuration and Options Guide http://www.ibm.com/servers/eserver/xseries/cog
ServerProven Program http://www.ibm.com/servers/eserver/serverproven/compat/us
Technical Support http://www.ibm.com/server/support
Other Technical Support Resources http://www.ibm.com/servers/eserver/techsupport.html
Legal Information
© IBM Corporation 2008
IBM Systems and Technology Group
Dept. U2SA
3039 Cornwallis Road
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709
Produced in the USA
September 2008
All rights reserved
Visit http://ibm.com/pc/safecomputing periodically for the
latest information on safe and effective computing. Warranty
Information: For a copy of applicable product warranties, write
to: Warranty Information, P.O. Box 12195, RTP, NC 27709,
Attn: Dept. JDJA/B203. IBM makes no representation or
warranty regarding third-party products or services including
those designated as ServerProven or ClusterProven.
Telephone support may be subject to additional charges. For
onsite labor, IBM will attempt to diagnose and resolve the
problem remotely before sending a technician.
IBM, the IBM logo, the e-business logo, Active Memory,
Chipkill, DB2, Memory ProteXion, Predictive Failure Analysis,
ServeRAID, System Storage, Systems Director Active Energy
Manager, System x, TotalStorage, xSeries, and
XpandOnDemand are trademarks of IBM Corporation in the
United States, other countries, or both. If these and other IBM
trademarked terms are marked on their first occurrence in this
information with a trademark symbol (® or ™), these symbols
indicate U.S. registered or common law trademarks owned by
IBM at the time this information was published. Such
trademarks may also be registered or common law
trademarks in other countries. A current list of IBM trademarks
is available on the Web at
http://ibm.com/legal/copytrade.shtml.
Intel and Intel Xeon are trademarks or registered trademarks
of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and
other countries.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Microsoft, Hyper-V, SQL Server, Windows and the Windows
logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation.
Other company, product and service names may be
trademarks or service marks of others.
WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS
OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
IBM reserves the right to change specifications or other
product information without notice. References in this
publication to IBM products or services do not imply that IBM
intends to make them available in all countries in which IBM
operates. IBM PROVIDES THIS PUBLICATION “AS IS”
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. Some jurisdictions do not allow disclaimer of
express or implied warranties in certain transactions;
therefore, this statement may not apply to you.
This publication may contain links to third party sites that are
not under the control of or maintained by IBM. Access to any
such third party site is at the user's own risk and IBM is not
responsible for the accuracy or reliability of any information,
data, opinions, advice or statements made on these sites. IBM
provides these links merely as a convenience and the
inclusion of such links does not imply an endorsement.
Information in this presentation concerning non-IBM products
was obtained from the suppliers of these products, published
announcement material or other publicly available sources.
IBM has not tested these products and cannot confirm the
accuracy of performance, compatibility or any other claims
related to non-IBM products. Questions on the capabilities of
non-IBM products should be addressed to the suppliers of
those products.
MB, GB and TB = 1,000,000, 1,000,000,000 and
1,000,000,000,000 bytes, respectively, when referring to
storage capacity. Accessible capacity is less; up to 3GB is
used in service partition. Actual storage capacity will vary
based upon many factors and may be less than stated.
Performance is in Internal Throughput Rate (ITR) ratio based
on measurements and projections using standard IBM
benchmarks in a controlled environment. The actual
throughput that any user will experience will depend on
considerations such as the amount of multiprogramming in the
user’s job stream, the I/O configuration, the storage
configuration and the workload processed. Therefore, no
assurance can be given that an individual user will achieve
throughput improvements equivalent to the performance ratios
stated here.
Maximum internal hard disk and memory capacities may
require the replacement of any standard hard drives and/or
memory and the population of all hard disk bays and memory
slots with the largest currently supported drives available.
When referring to variable speed CD-ROMs, CD-Rs, CD-RWs
and DVDs, actual playback speed will vary and is often less
than the maximum possible.
XSO03033-USEN-01
 Loading...
Loading...