Page 1
SBC-658
Half Size Intel FC-370 Pentium III
CPU Card with LCD, Ethernet &
SSD
Page 2

Copyright Notice
This document is copyrighted, 2000. All rights are reserved. The
original manufacturer reserves the right to make improvements to
the products described in this manual at any time without notice.
No part of this manual may be reproduced, copied, translated, or
transmitted in any form or by any means without the prior written
permission of the original manufacturer. Information provided in
this manual is intended to be accurate and reliable. However, the
original manufacturer assumes no responsibility for its use, nor for
any infringements upon the rights of third parties which may result
from its use.
Acknowledgements
AMD is a trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
AMI is a trademark of American Megatrends, Inc.
A ward is a trademark of A ward Software International, Inc.
IBM, PC/A T , PS/2, and VGA are trademarks of International
Business Machines Corporation.
Intel and Pentium II are trademarks of Intel Corporation.
Microsoft Windows® is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corp.
SMC is a trademark of Standard Microsystems Corporation.
RTL is a trademark of Realtek Semi-Conductor Co., Ltd.
C&T is a trademark of Chips and T echnologies, Inc.
UMC is a trademark of United Microelectronics Corporation.
ITE is a trademark of Integrated T echnology Express, Inc.
SiS is a trademark of Silicon Integrated Systems Corp.
VIA is a trademark of VIA T echnology, Inc.
All other product names or trademarks are properties of their
respective owners.
Part No. 2047658011 SBC-658 3rd. Edition
Printed in Taiwan Dec., 2001
Page 3

A Message to the Customer
AAEON Customer Services
Each and every AAEON product is built to the most exacting
specifications to ensure reliable performance in the harsh and
demanding conditions typical of industrial environments. Whether
your new AAEON equipment is destined for the laboratory or the
factory floor, you can be assured that your product will provide the
reliability and ease of operation for which the name AAEON has
come to be known.
Y our satisfaction is our primary concern. Here is a guide to
AAEON's customer services. To ensure you get the full benefit of
our services, please follow the instructions below carefully.
Technical Support
W e want you to get the maximum performance from your products.
So if you run into technical difficulties, we are here to help. For the
most frequently asked questions, you can easily find answers in
your product documentation. These answers are normally a lot
more detailed than the ones we can give over the phone.
So please consult this manual first. If you still cannot find the
answer, gather all the information or questions that apply to your
problem, and with the product close at hand, call your dealer. Our
dealers are well trained and ready to give you the support you need
to get the most from your AAEON products. In fact, most problems
reported are minor and are able to be easily solved over the phone.
In addition, free technical support is available from AAEON
engineers every business day. We are always ready to give advice
on application requirements or specific information on the installation and operation of any of our products.
Page 4

Product Warranty
AAEON warrants to you, the original purchaser, that each of its
products will be free from defects in materials and workmanship for
two years from the date of shipment.
This warranty does not apply to any products which have been
repaired or altered by persons other than repair personnel authorized by AAEON, or which have been subject to misuse, abuse,
accident or improper installation. AAEON assumes no liability
under the terms of this warranty as a consequence of such events.
Because of AAEON's high quality-control standards and rigorous
testing, most of our customers never need to use our repair service.
If an AAEON product is defective, it will be repaired or replaced at
no charge during the warranty period. For out-of-warranty repairs,
you will be billed according to the cost of replacement materials,
service time, and freight. Please consult your dealer for more
details.
If you think you have a defective product, follow these steps:
1 . Collect all the information about the problem encountered. (For
example, CPU type and speed, AAEON products used, other
hardware and software used, etc.) Note anything abnormal and
list any on-screen messages you get when the problem occurs.
2 . Call your dealer and describe the problem. Please have your
manual, product, and any helpful information readily available.
3. If your product is diagnosed as defective, obtain an RMA
(return material authorization) number from your dealer. This
allows us to process your return more quickly .
4 . Carefully pack the defective product, a fully-completed Repair
and Replacement Order Card and a photocopy proof of purchase date (such as your sales receipt) in a shippable container.
A product returned without proof of the purchase date is not
eligible for warranty service.
5. Write the RMA number visibly on the outside of the package
and ship it prepaid to your dealer.
Page 5

Packing list
Before you begin installing your card, please make sure that the
following materials have been shipped:
• 1 SBC-658 All-in-One Single Board Computer Card
• 1 Quick Installation Guide
• 1 Support CD contains the followings:
-- User's Manual (this manual in PDF file)
-- Ethernet drivers and utilities
-- VGA drivers and utilities
• 1 hard disk drive (IDE) interface cable (44-pin, pitch 2.0mm)
• 1 floppy disk drive interface cable (34-pin, pitch 2.0mm)
• 1 6-pin mini-DIN dual outlet adapter for keyboard and PS/2
mouse
• 1 parallel port (26-25-pin, pitch 2.0mm) and serial port (10-9 pin,
pitch 2.0mm) adapter kit.
• 1 bag of screws and miscellaneous parts
If any of these items are missing or damaged, contact your distributor or sales representative immediately.
Page 6

Notice
Dear Customer,
Thank you for purchasing the SBC-658 board. This user's
manual is designed to help you to get the most out of the SBC-658,
please read it thoroughly before you install and use the board. The
product that you have purchased comes with an two-year limited
warranty , but AAEON will not be responsible for misuse of the
product. Therefore, we strongly urge you to first read the manual
before using the product.
To receive the lastest version of the user manual, please visit our
Web site at:
http://www.aaeon.com
Page 7

Contents
Chapter 1: General Information............................ 1
Introduction ........................................................................... 2
Features.................................................................................. 3
Specifications ......................................................................... 4
Board layout........................................................................... 7
Board dimensions ................................................................. 8
Chapter 2: Installation .............................................. 9
Jumpers and connectors .................................................... 10
Locating jumpers ................................................................ 1 2
Locating connectors ........................................................... 13
Setting jumpers ................................................................... 1 4
CPU installing and upgrading............................................ 1 5
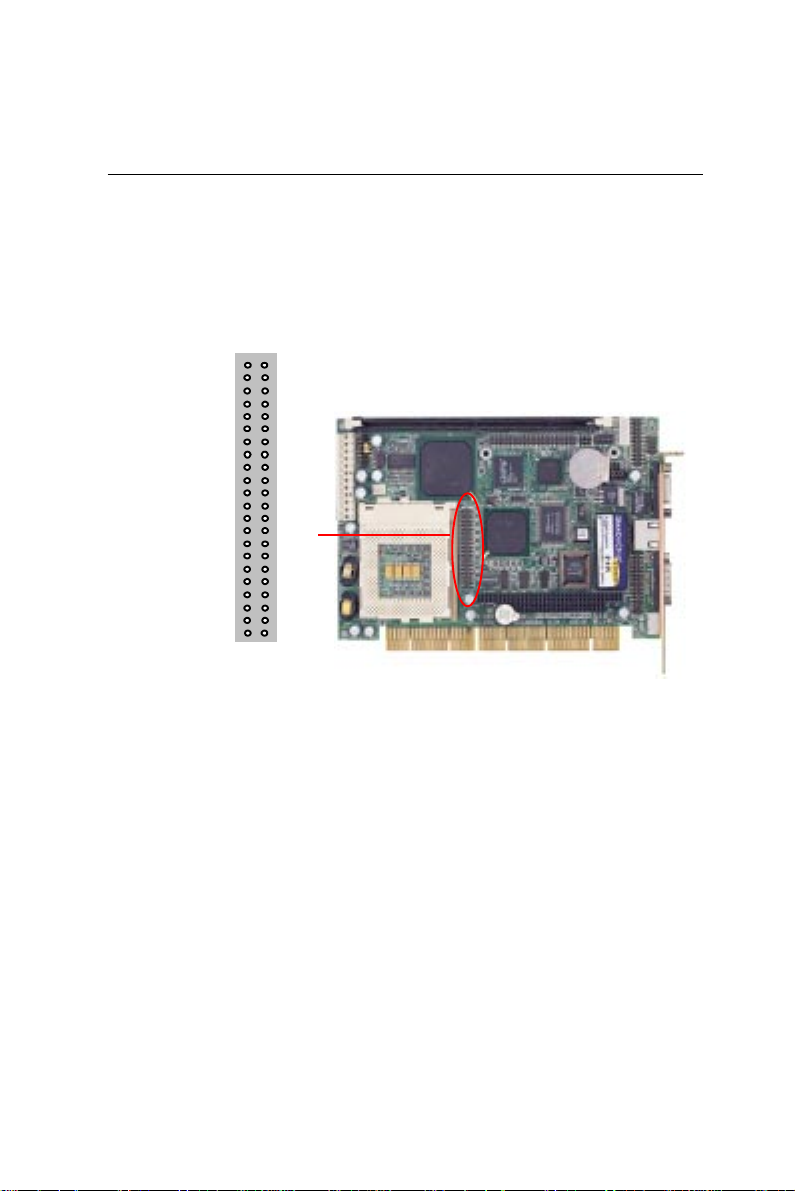
Installing DRAM (DIMMs) .............................................. 17
System Memory ......................................................................17
Supplementary information about DIMM ...............................17
Memory Installation Procedures .............................................17
DOC address & CPU frequency ratio select SW1 (S1 ~
S6) .......................................................................................... 18
Doc address select .................................................................. 18
LCD clock signal & driving voltage select (J1) ............ 1 9
COM2 RS-232/422/485 select (J2, J3) ........................... 20
Clear CMOS (J4) ................................................................ 2 1
Power connectors P8 & P9 (PWR1) ................................ 2 2
USB connector (CN1) .........................................................23
Display connectors (CN8, CN2) ....................................... 2 4
VGA display connector (CN8) ...............................................2 5
LCD display connector (CN2) ................................................26
Keyboard and PS/2 mouse connector (CN3, CN5) ........ 2 7
Parallel port connector (CN4) ........................................... 2 9
Parallel port IRQ .....................................................................30
Page 8

Parallel port connector table (CN4) ........................................30
Serial ports (CN11, CN5) ................................................... 3 1
IrDA connector (CN6, Pin 1~5) ........................................ 3 2
Reset switch (CN6, Pin 6,7) .............................................. 3 3
External / internal speaker (CN6, Pin 8~11) .................. 3 4
Hard drive LED (CN6, Pin 13, 14) ................................... 3 5
CPU fan power connector (CN7) ...................................... 3 6
100Base-Tx Ethernet connector (CN9) .......................... 37
IDE hard drive connector (CN10) .................................... 3 8
IDE hard drive connector (CN10) ..........................................39
Floppy drive connector (CN12) ........................................ 4 0
Connecting the floppy drive.....................................................41
Floppy drive connector (CN12)...............................................4 2
DiskOnChip socket (U10) ................................................. 43
DiskOnChip (DOC) 2000 Installation ............................. 4 4
Chapter 3: Award BIOS Setup................................4 5
Starting setup ....................................................................... 4 6
Setup keys ............................................................................ 47
Getting help ......................................................................... 4 8
In case of problem...................................................................48
Main setup menu ................................................................ 4 9
Standard CMOS setup ....................................................... 5 1
BIOS features setup ........................................................... 57
CHIPSET features setup ................................................... 60
Power management setup .................................................. 6 0
PNP/PCI congfiguration setup .......................................... 6 9
Load BIOS defaults/Load setup defaults ........................ 7 1
Integrated peripherals setup .............................................72
Supervisor/User password setting ................................... 75
IDE HDD auto detection ................................................... 7 7
Save & exit setup ................................................................78
Page 9

Chapter 4: Flat Panel/CRT controller Display
Drivers and Utilities...........................7 9
Software drives .................................................................... 8 0
Hardware configuration ..........................................................80
Necessary prerequisites .......................................................... 81
Before you begin .....................................................................81
Windows 95 .......................................................................... 8 2
Driver installation ....................................................................82
Windows 3.51 ....................................................................... 9 0
Driver installation ....................................................................90
Windows NT 4.0 .................................................................. 9 1
Driver installation ....................................................................91
Chapter 5: Ethernet Software configuration....
....................................................................9 3
Ethernet software configuration ........................................ 94
Appendix A: Programming the Watchdog
Timer ..................................................... 9 5
Programming the watchdog timer .................................... 9 6
W atchdog timer .......................................................................96
Configuration register ..............................................................99
Appendix B: Installing PC/104 Modules........................104
Installing PC/104 modules ...............................................105
Page 10

1
CHAPTER
General
Information
This chapter gives background information on the mainboard.
Sections include:
• Board specifications
• Layout and dimensions
Chapter 1 General Information 1
Page 11

Introduction
The SBC-658 is an all-in-one Celeron/Pentium III FC-chip processor
based single board computer (SBC) with a PCI Flat Panel controller,
a PCI 100Base-T Ethernet interface. When using an Intel Pentium
III processors, the SBC-658 achieves outstanding performance that
surpasses any other SBC in its class. In addition, the onboard SSD
interface supports M-Systems DiskOnChip 2000 series, memory
capacity up to 288 MB.
Onboard features include two serial ports (one RS-232, one RS-232/
422/485), one multi-mode parallel (ECP/EPP/SPP) port, Pin header
for two USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports, a floppy drive controller,
and a keyboard/PS/2 mouse interface. The built-in high speed PCI
IDE controller supports Ultra DMA/33 mode. Up to two IDE
devices can be connected, including large hard disks, CD-ROM
drives, and tape backup drives, etc.
The SBC-658 also features power management to minimize power
consumption. It complies with the ACPI standard and supports
three types of power saving features: Doze mode, Standby mode,
and Suspend mode. In addition, the board's watchdog timer can
automatically reset the system or generate an interrupt in case the
system stops due to a program bug or EMI.
Highly integrated SBC
The SBC-658 is a highly integrated SBC that combines, video, and
network functions on a single computer board. It provides up to
1024 x 768 resolution @ 64K colors with on-chip 2MB SDRAM
display memory. Major onboard devices adopt PCI technology to
achieve outstanding computing performance making the SBC-658
one of the world's best and most powerful all-in-one Single Board
Computer.
2 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 12

Features
• Supports Intel Celeron /Pentium III FC-370
• Supports DiskOnChip (SSD) up to 288MB
• C&T 69000 LCD controller supports 36-bit TFT Panels
• 10/100Base-T Fast Ethernet
• Supports H/W status monitoring
Chapter 1 General Information 3
Page 13

Specifications
Standard SBC functions
• CPU: FC-370 Pentium III (Coppermine), Celeron, and compatible CPUs
(With system bus frequencies of 66/100MHz)
• Bus interface: PISA bus
• CPU socket: 370 pins Socket
• BIOS: A ward 256KB Flash BIOS
• Chipset: Intel 440BX
• I/O chipset: Winbond W83977TF with fully 16-bit I/O decoded
• Memory : Onboard one 168 pins DIMM socket supports up to
256Mbytes SDRAM
• Enhanced IDE: Supports two IDE devices. Supports Ultra DMA/
33 mode with data transfer rate 33MB/Sec.
• FDD interface: Supports two floppy disk drives, 5.25" (360KB and
1.2MB) and/or 3.5" (720KB, 1.44MB, and 2.88MB)
• Parallel port: One bi-directional parallel port. Supports SPP , ECP, and
EPP modes
• Serial port: One RS-232 and one RS-232/422/485 serial port. Ports can be
configured as COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4, or disabled individually .
16C550 serial UAR T s.
• IR interface: Supports one IrDA Tx/Rx header
• KB/Mouse connector : 6-pin mini-DIN connector supports PC/A T
keyboard and PS/2 mouse. Additional 5 pins header supports PC/AT
keyboard for IPC applications
• USB connectors: 5 x 2 header onboard supports dual USB ports
• Battery: Lithium battery for data retention
• Watchdog timer: Can generate a system reset, IRQ15, or NMI. Software
selectable time-out interval (32 sec. ~ 254 min., 1 min./step)
4 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 14

• DMA: 7 DMA channels (8237 equivalent)
• Interrupt: 15 interrupt levels (8259 equivalent)
• Power management: I/O peripheral devices support power saving and
doze/stanby/suspend modes. APM 1.2 ocmpliant
• H/W status monitoring: Winbond W83781D H/W status monitoring IC
supports power supply voltages, and temperatures monitoring
Flat Panel/CRT Interface
• Chipset: C&T 69000
• Display memory: 2MB SDRAM built in chip
• Display type: Supports non-interlaced CRT and LCD (TFT , DSTN, and
Mono) displays. Can display both CRT and Flat Panel simultaneously
• Resolution: Up to 1024x768@64K colors
Ethernet Interface
• Chipset: Intel 82559ER 10/100Base-T Fast Ethernet controller
• Ethernet interface : Onboard 10/100Base-Tx RJ-45 connector
SSD Interface
• One 32 pins DIP socket supports M-Systems DiskOnChip 2000 series up
to 288MB
Chapter 1 General Information 5
Page 15

Mechanical and environmental
• Power supply voltage: +5V (4.75V to 5.25V),
+12V (11.4V to 12.6V)
• Power requirement: +5V @ 4.1A(Celeron 300MHz)
• Operating temperature: 32 to 140o F (0 to 60o C)
• Board size: 7.3"(L) x 4.8"(W) (185mm x 122mm)
• Weight: 0.5lb. (0.3 Kg)
6 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 16
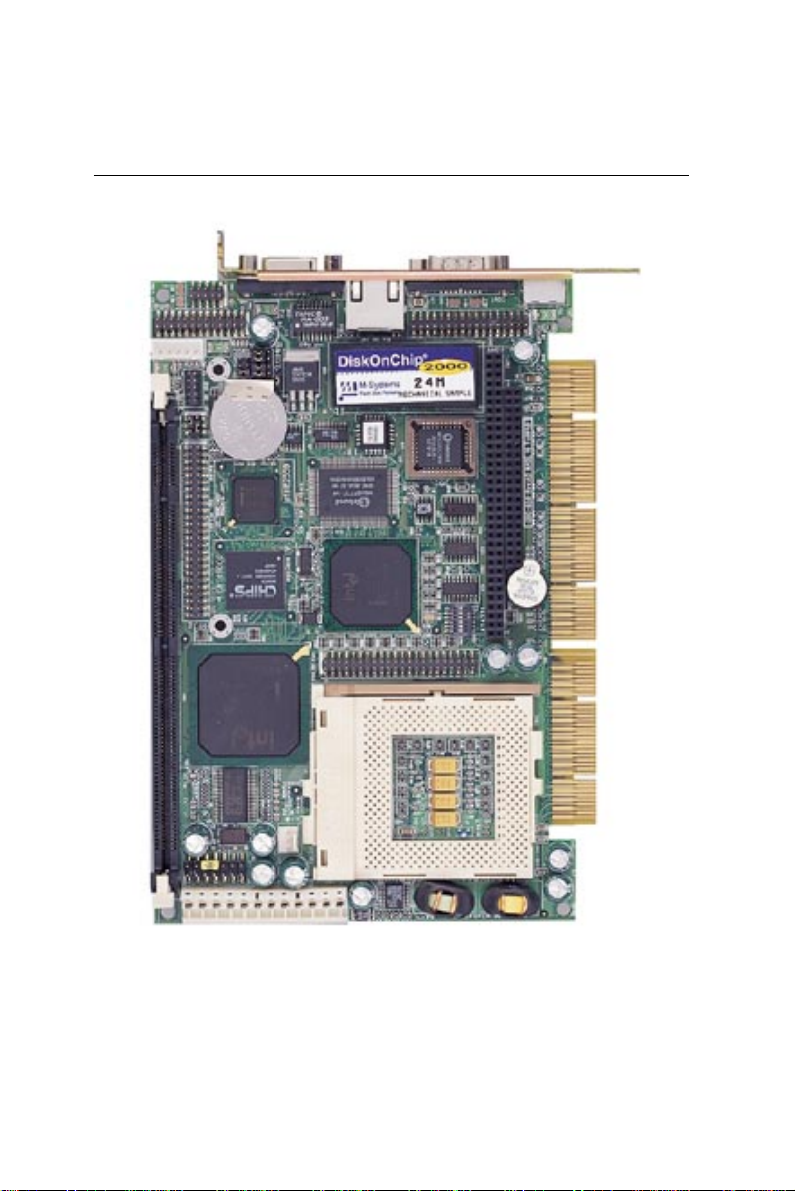
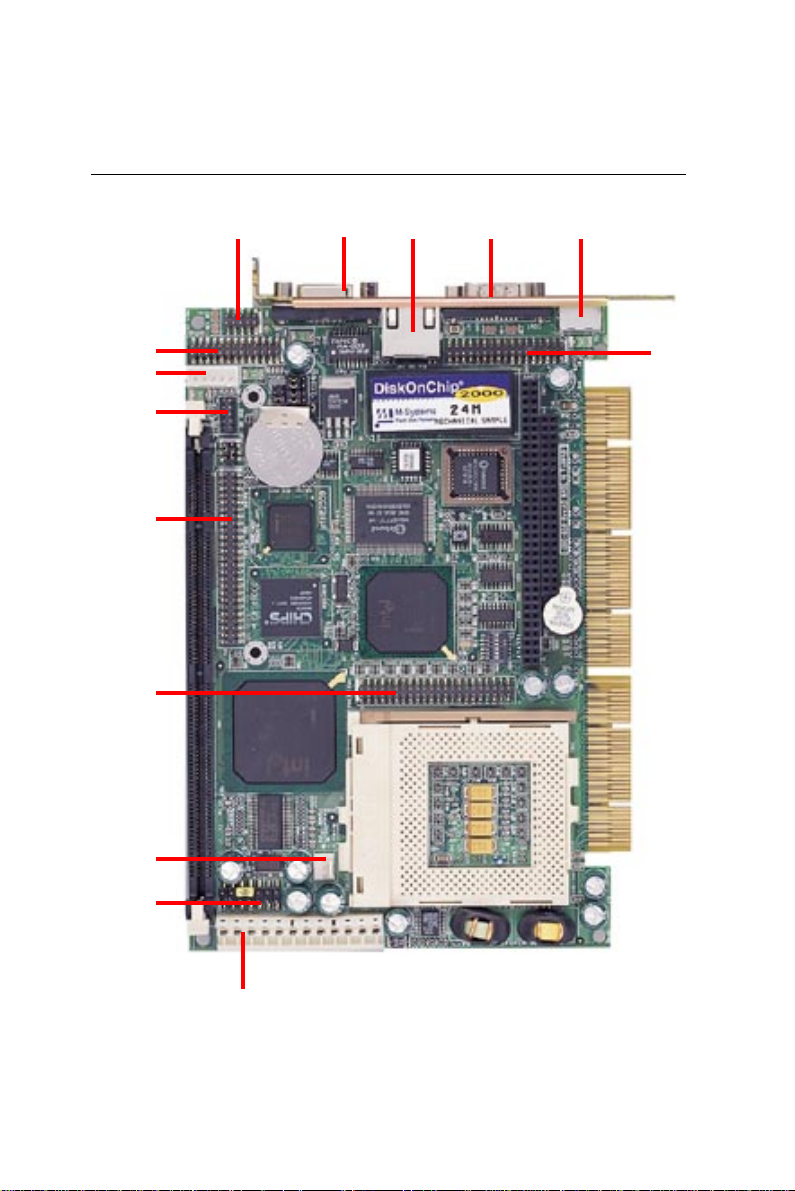
Board layout
Chapter 1 General Information 7
Page 17
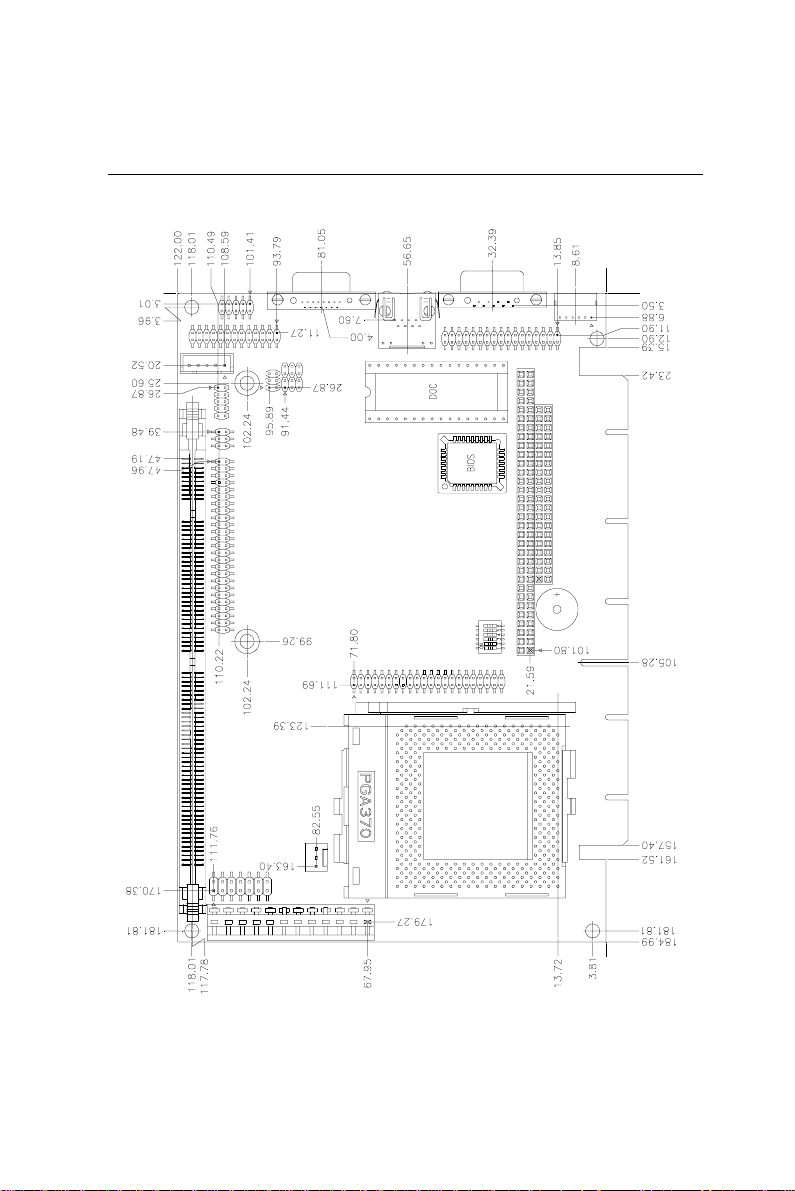
Board dimensions
0.00
0.000.00
0.00
8 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 18

2
CHAPTER
Installation
This chapter describes how to set up the
main board hardware, including instructions on setting jumpers and connecting
peripherals, switches, and indicators. Be
sure to read all the safety precautions
before you begin the installation procedure.
Chapter 2 Installation 9
Page 19

Jumpers and connectors
Connectors on the board link it to external devices such as hard
disk drives, a keyboard, or floppy drives. In addition, the board
has a number of jumpers that allow you to configure your system
to suit your application.
The following tables list the function of each of the board's
jumpers and connectors.
Jumpers
Label Function
SW1 (S5, S6) DOC address select
J1 LCD clock signal & driving voltage select
J2 COM2 RS-232/422/485 select
J3 COM2 RS-232/422/485 select
J4 Clear CMOS Connectors
10 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 20

Label Function
CN 1 USB connector
CN 2 LCD display connector
CN 3 Internal keyboard connector
CN 4 Parallel port connector
CN 5 COM2 RS-232/422/485 serial port
connector
CN6 (Pin 1~5) IrDA connector
CN6 (Pin 6, 7) Reset switch
CN6 (Pin 8~11) External speaker
CN6 (Pin 13, 14) IDE drive LED
CN 7 CPU fan power connector
CN 8 VGA display connector
CN 9 100Base-Tx Ethernet connector
CN10 IDE hard drive connector
CN11 COM1 RS-232 serial port connector
CN12 Floppy drive connector
CN15 Keyboard and PS/2 mouse connector
PWR1 Power connector
Chapter 2 Installation 11
Page 21
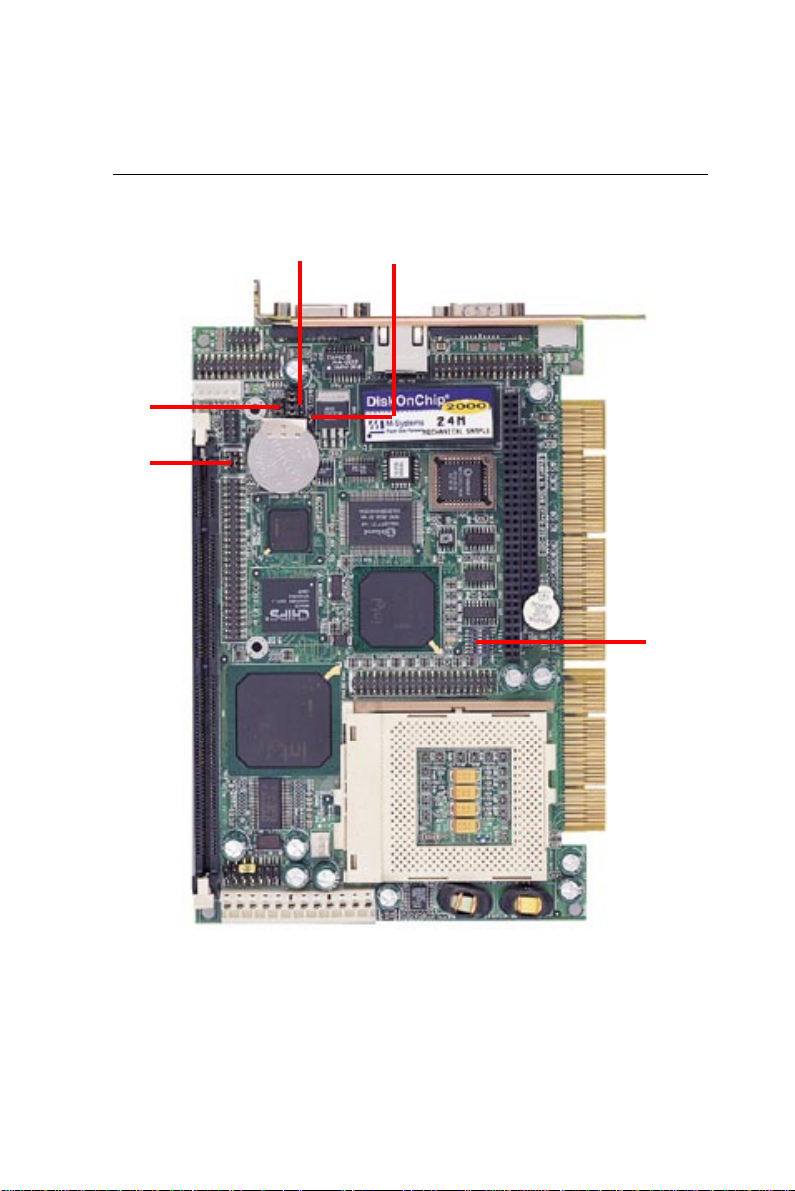
Locating jumpers
J2
J1
J4J3
SW1
12 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 22
Locating connectors
CN4
CN3
CN1
CN2
CN10
CN5
CN8
CN9
CN11
CN15
CN12
CN7
CN6
PWR1
Chapter 2 Installation 13
Page 23
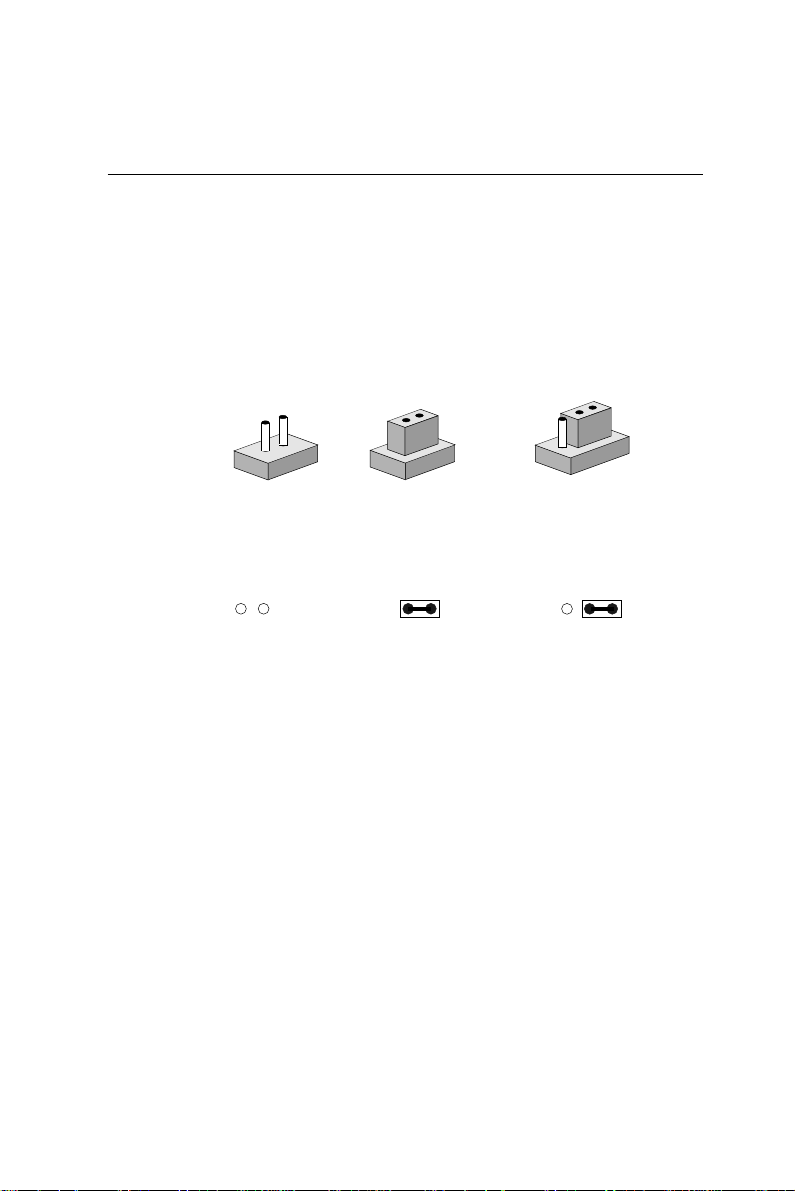
Setting jumpers
You can configure your card to match the needs of your application
by setting jumpers. A jumper is the simplest kind of electric switch.
It consists of two metal pins and a small metal clip (often protected
by a plastic cover) that slides over the pins to connect them. To
“close” a jumper you connect the pins with the clip. T o “open” a
jumper you remove the clip. Sometimes a jumper will have three
pins, labeled 1, 2, and 3. In this case you would connect either pins
1 and 2 or 2 and 3.
1
Open Closed Closed 2-3
The jumper settings are schematically depicted in this manual as
follows:
1 2 3
Open Closed Closed 2-3
A pair of needle-nose pliers may be helpful when working with
jumpers.
3
2
If you have any doubts about the best hardware configuration for
your application, contact your local distributor or sales representative before you make any changes.
14 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 24

CPU installing and upgrading
Y ou can upgrade to a more powerful Celeron CPU at any time.
Simply remove the old CPU, install the new one, and set the
jumpers for the new CPU speed.
Warning! Always disconnect the power cord from your
chassis when you are working on it. Do not
make connections while the power is on as
sensitive electronic components can be damaged by the sudden rush of power. Only experienced electronics personnel should open the
system chassis.
Caution! Always ground yourself to remove any static
charge before touching the system board.
Modern electronic devices are very sensitive to
static electric charges. Use a grounding wrist
strap at all times. Place all electronic components
on a static-dissipative surface or in a staticshielded bag when they are not in the chassis.
Install a CPU in the FC-370 socket
SBC-658 Series provides a Flip-Chip (FC) socket for easy CPU
installation.
1 . Make sure the FC-370 socket lever is in the upright position. To
raise the lever, pull it out to the side a little and raise it as far as
it will go.
2 . Place the CPU in the empty socket. Follow the instructions that
came wth the CPU. If you have no instructions, do the following: Carefully align the CPU so it is parallel to the socket and
the notch on the corner of the CPU corresponds with the notch
on the inside of the socket. Gently slide the CPU in. It should
insert easily. If it doesn't, pull the lever up a little more.
Chapter 2 Installation 15
Page 25

3 . Press the lever down. The plate will slide forward. Y ou will feel
some resistance as the pressure starts to secure the CPU in the
socket. This normal and won't damage the CPU.
When the CPU is installed, the lever should snap into place at the
side of the socket.
Note: T o remove a CPU, pull the lever out to the side a
little and raise it as far as it will go. Lift out the
CPU chip.
When you install a new CPU, be sure to adjust the board settings,
such as CPU type and CPU clock. Improper settings may damage
the CPU.
16 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 26
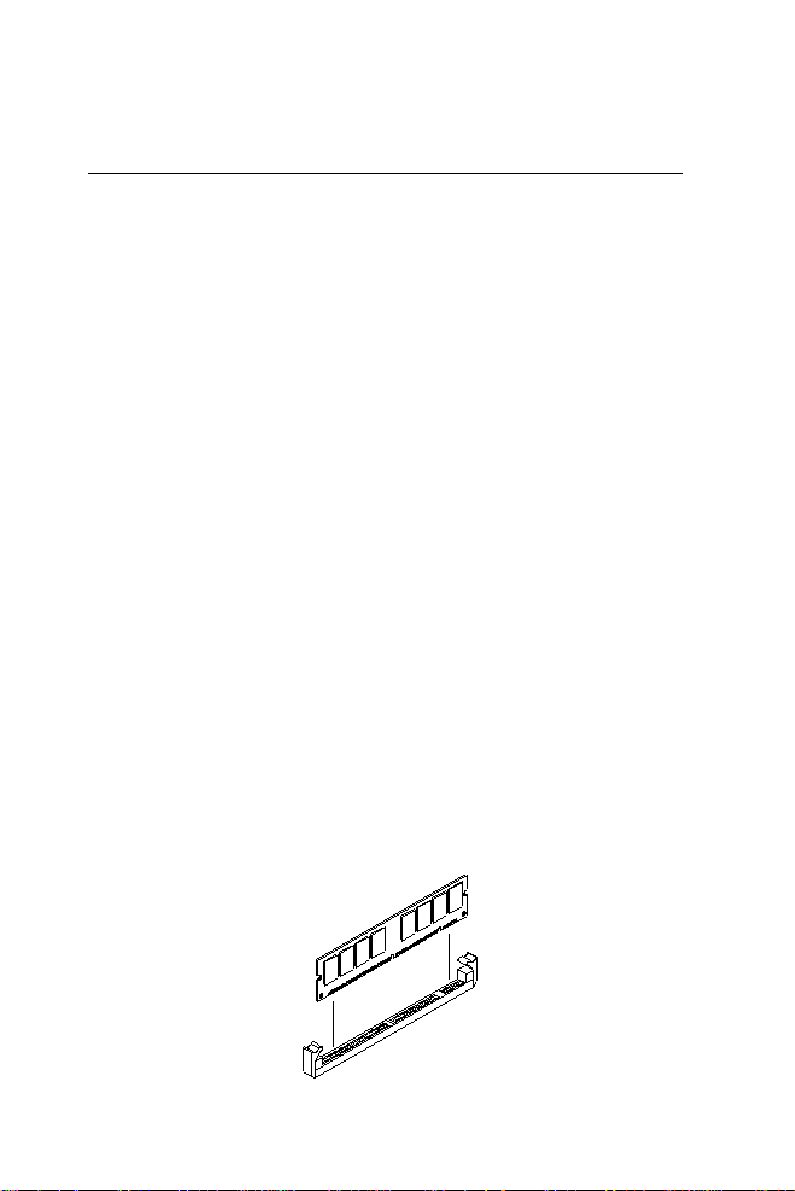
Installing SDRAM (DIMMs)
System Memory
The upper edge of the SBC-658 contains one sockets for 168 pins
dual inline memory module (DIMM). The socket uses 3.3 V
unbuffered synchronous (SDRAM). DIMM is available in capacities of 16, 32, 64, 128, or 256 MB. The socket can be filled in the
DIMM of any size, giving your SBC-658 single board computer
between 16 and 256 MB of memory.
Supplementary information about DIMM
The SBC-658 can only accept PC-100 SDRAM DIMM Module.
Single-sided modules are typically 16 or 128 MB; double-sided
modules are usually 32 or 256 MB.
Memory Installation Procedures
T o install DIMM, first make sure the two handles of the DIMM
socket are in the "open" position. i.e. The handles remain outward.
Slowly slide the DIMM module along the plastic guides on both
ends of the socket. Then press the DIMM module right down into
the socket, until you hear a click. This is when the two handles
have automatically locked the memory module into the correct
position of the DIMM socket. (See Figure below) T o take away the
memory module, just push both handles outward, and the memory
module will be ejected by the mechanism in the socket.
Chapter 2 Installation 17
Page 27

DOC address select SW1 (S5 ~ S6)
The DiskOnChip 2000 occupies a 8KB window in the upper memory
address range of D400 to DC00. You should ensure this does not
conflict with any other device's memory address. SW1 (S5, S6)
controls the momory address of the Flash disk.
SW1 DOC Address ( On : 0 Off : 1 )
DOC Address S5 S6
D400 1 1
D800 1 0
DC00 0 1
Disable 0 0
Note:
These addresses might conflict with the ROM BIOS of
other peripheral boards. Please select the appropriate
memory address to avoid memory conflicts
CPU frequency ratio select
With commercially produce Intel CPU, frequency ratios are prelocked. Which means that it comes with automatic settings and
end users are ready to operate without worry.
.
18 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 28
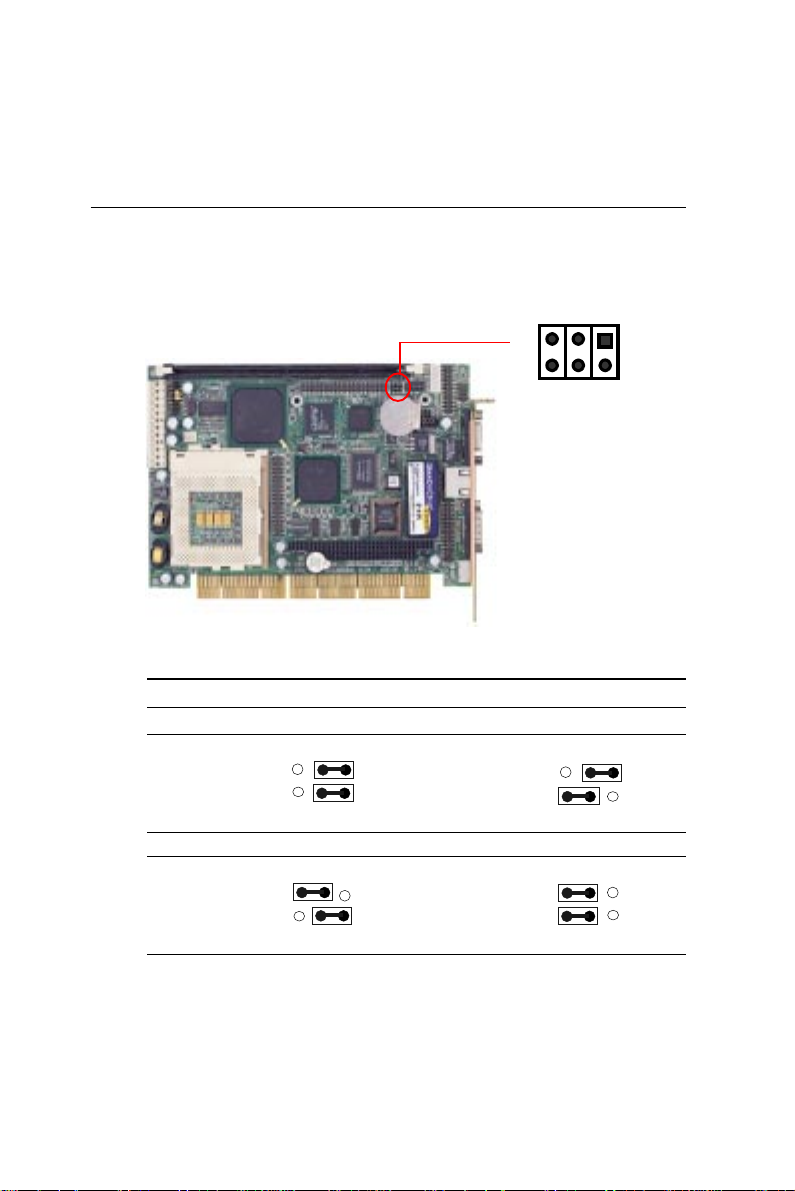
LCD clock signal & driving voltage
select (J1)
Y ou can select the LCD connector CN2 driving voltage & control
signal by setting J1. The configurations are as follows:
5 3 1
6 4 2
LCD clock signal & driving voltage select (J1)
ASHF CLK / +5V ASHFCLK / +3.3V
J1
5 3 1
5 3 1
*default
6 4 2
SHFCLK / +5V SHFCLK / +3.3V *
5 3 1
6 4 2
Chapter 2 Installation 19
6 4 2
5 3 1
6 4 2
Page 29
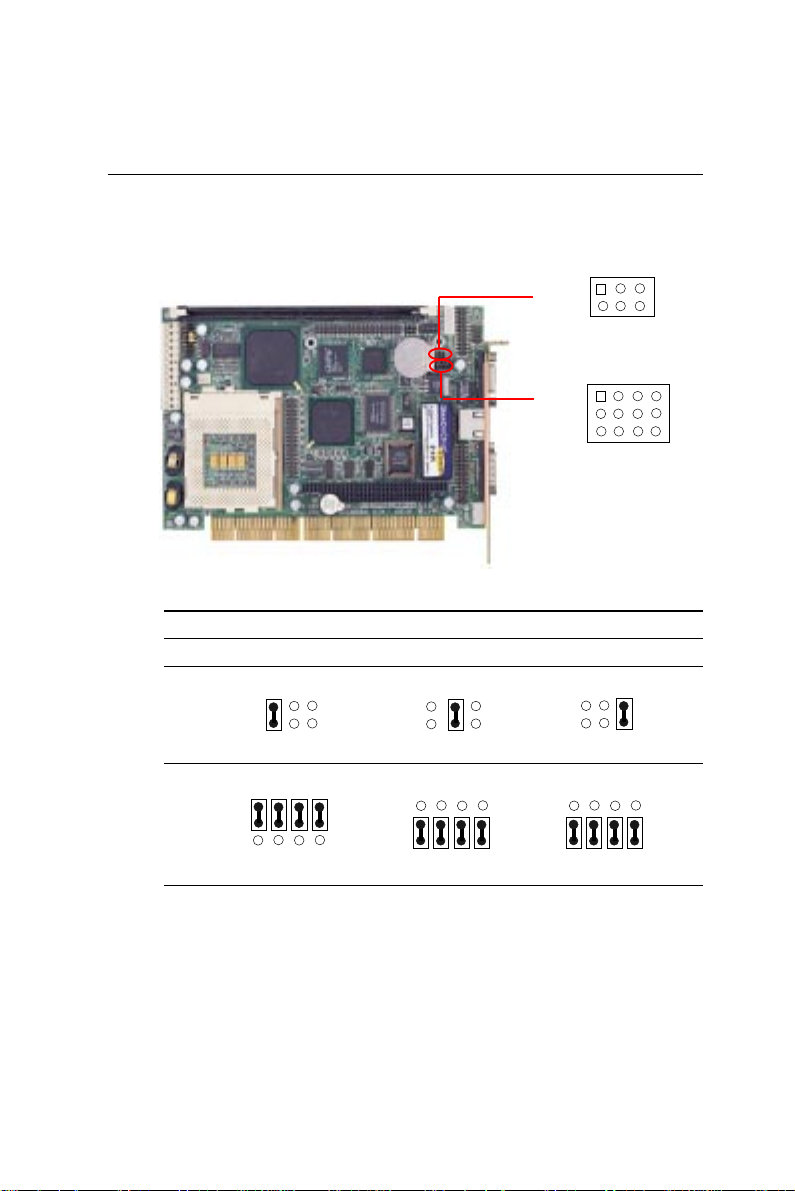
COM2 RS-232/422/485 select (J2, J3)
The SBC-658 COM2 serial port can be selected as RS-232, RS-422,
or RS-485 by setting J2 & J3.
1 3 5
J2
2 4 6
1 4 7 10
J3
3 6 9 12
COM2 Select (J2, J3)
RS-232* RS-422 RS-485
J2
1 3 5
1 3 5
1 3 5
2 4 6
1 4 7 10
J3
3 6 9 12
*default
20 SBC-658 User Manual
2 4 6
1 4 7 10
3 6 9 12
2 4 6
1 4 7 10
3 6 9 12
Page 30
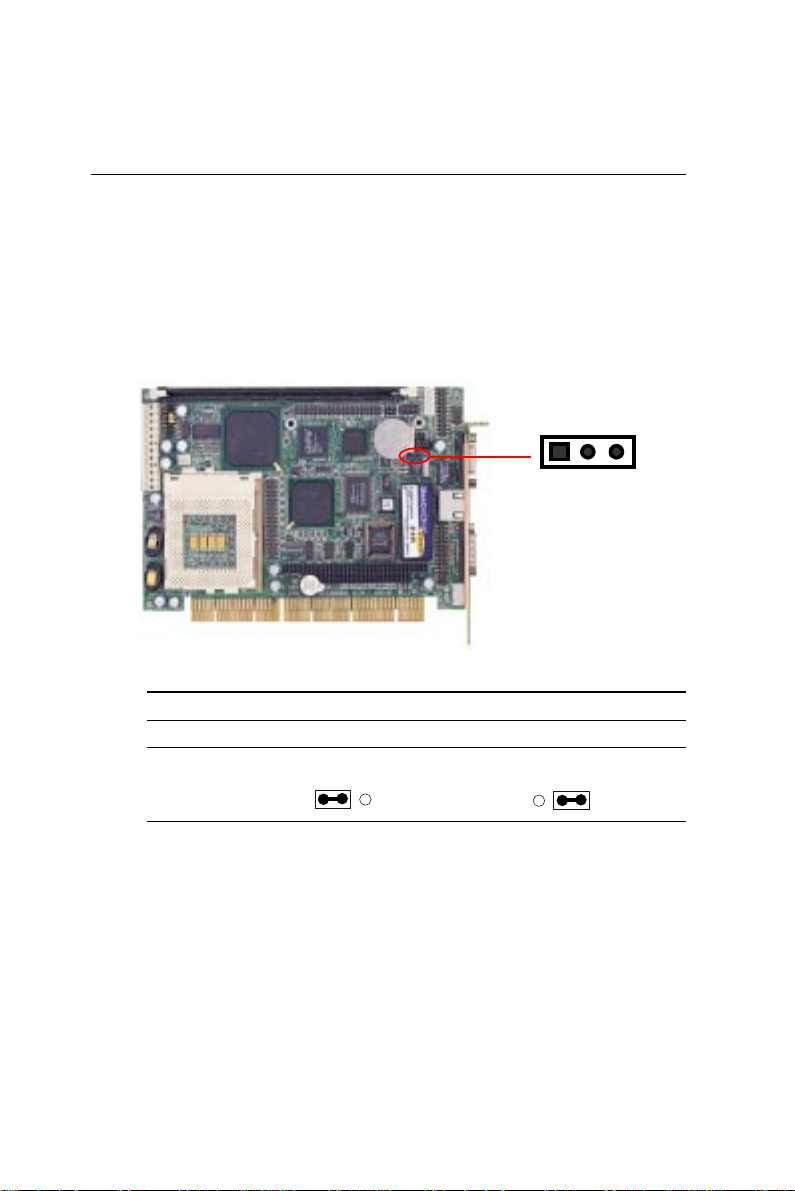
Clear CMOS (J4)
Y ou can connect an external jumper cap or switch to clear CMOS.
Clear CMOS procedure:
1. Disconnect all power source.
2. Move J4 from 1-2 to 2-3 for few seconds.
3. Move J4 back to 1-2.
Clear CMOS (J4)
Protect* Clear CMOS
1 2 3
J4
*default
1 2 3
1 2 3
Chapter 2 Installation 21
Page 31

Power connectors P8 & P9 (PWR1)
In single board computer (non-passive backplane) application. You
will need to connect the power directly to the SBC-658 board using
PWR1. This connector is fully compatible with the standard PC AT
power supply connector, P8 & P9. See the following table for its pin
assignments:
1
2
3
P9 from standard
4
AT power supply
5
6
1
2
3
P8 from standard
4
AT power supply
5
6
Power connector pin assignments (PWR1)
Pin (P8) Signal Pin (P9) Signal
1 GND 1 +5V
2 GND 2 +5V
3 -12V 3 +5V
4 +12V 4 -5V
5 +5V 5 GND
6 NC 6 GND
Power connector pin assignments (PWR1)
Pin (P8) Color Pin (P9) Color
1 Black 1 Red
2 Black 2 Red
3 Blue 3 Red
4 Yellow 4 White
5 Red 5 Black
6 Orange 6 Black
22 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 32

USB connector (CN1)
The SBC-658 provides two USB (Universal Serial Bus) interfaces,
which give complete plug and play, hot attach/detach for up to 127
external devices. The USB interfaces comply with USB specification Rev. 1.0, and can be disabled in the system BIOS setup.
9 7 5 3 1
10 8 6 4 2
USB connector (CN1)
Pin Function Pin Function
1 Vcc 2 GN D
3 USBDO- 4 GND
5 USBDO+ 6 USBD1+
7 GND 8 USBD19 GND 10 Vcc
Chapter 2 Installation 23
Page 33

Display connectors (CN8, CN2)
The SBC-658's PCI SVGA interface can drive conventional CRT
displays and is capable of driving a wide range of flat panel
displays, including electroluminescent (EL), gas plasma, passive
LCD, and active LCD displays. The board has two connectors to
support these displays, one for standard CRT VGA monitors and
one for flat panel displays.
CN2
49
50
1
2
CN8
24 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 34

VGA display connector (CN8)
VGA display connector (CN8)
Pin Signal
1 Red video
2 Green video
3 Blue video
4 Not used
5 GND
6 Red return (GND)
7 Green return (GND)
8 Blue return (GND)
9 Vcc
10 Sync return (GND)
11 NC
12 DDCDAT
13 Horizontal sync
14 Vertical sync
15 DDC CLK
Chapter 2 Installation 25
Page 35

LCD display connector (CN2)
CN2 is a 50-pin, dual-in-line header used for flat panel displays.
When the SBC-658's power is applied, the control signal is low until
just after the relevant flat panel signals are present.
Configuration of the VGA interface is done completely via the
software utility. You do not have to set any jumpers.
LCD display connector (CN2)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 +12 V
DC
3 GND 4 GND
5 LCD Vcc 6 LCD Vcc
7 ENAVEE 8 GND
9P0 10 P1
11 P2 12 P3
13 P4 14 P5
15 P6 16 P7
17 P8 18 P9
19 P10 20 P11
21 P12 22 P13
23 P14 24 P15
25 P16 26 P17
27 P18 28 P19
29 P20 30 P21
31 P22 32 P23
33 P24 34 P25
35 SHF CLK 36 FLM (V SYS)
37 M 38 LP (H SYS)
39 GND 40 ENABKL
41 P26 42 P27
43 P28 44 P29
45 P30 46 P31
47 P32 48 P33
49 P34 50 P35
2 +12 V
DC
26 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 36

Keyboard and PS/2 mouse connector
(CN3, CN15)
The SBC-658 provides a keyboard connector which supports both
a keyboard and a PS/2 style mouse. In most cases, especially in
embedded applications, a keyboard is not used. The standard PC/
A T BIOS will report an error or fail during power-on-self-test
(POST) after a reset if the keyboard is not present. The mainboard BIOS Advanced setup menu allows you to select "Present"
or "Absent" under the "System Keyboard" section. This allows
no-keyboard operation in embedded system applications without
the system halting under POST (power-on-self-test).
5
4
CN3
3
2
1
CN15
6
4
2
Chapter 2 Installation 27
5
3
1
Page 37

Keyboard and PS/2 mouse connector (CN15) (Mini-DIN 6 pins)
Pin Signal
1 KB DAT A
2 MS DAT A
3 GND
4 Vcc
5 KB CLOCK
6 MS CLOCK
Internal keyboard connector (CN3)
Pin Signal
1 KB_CLOCK
2 KB_DAT A
3NC
4 GND
5 Vcc
28 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 38

Parallel port connector (CN4)
Normally, the parallel port is used to connect the board to a
printer. The SBC-658 includes an onboard parallel port, accessed
through CN4, a 26-pin flat-cable connector. You need an adapter
cable if you use a traditional DB-25 connector. The cable has a 26pin connector on one end and a DB-25 connector on the other.
2526
2
1
Chapter 2 Installation 29
Page 39

Parallel port IRQ
The SBC-658 supports one parallel port. The port is designated as
LPT1 and can be disabled or changed to LPT2 or LPT3 in the
system BIOS setup.
Parallel port connector table (CN4)
Parallel port connector (CN4)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 STROBE 2 AUTOFD
3 DO 4 ERR
5 D1 6 INIT
7 D2 8 SLCTINI
9 D3 10 GND
11 D4 12 GND
13 D5 14 GND
15 D6 16 GND
17 D7 18 GND
19 ACK 20 GND
21 BUST 22 GND
23 PE 24 GND
25 SLCT 26 NC
30 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 40

Serial ports (CN11, CN5)
The SBC-658 offers two serial ports, one RS-232 (CN11) and one
RS-232/422/485 (CN5). These ports allow you to connect them to
serial devices (mouse, printers, etc.).
CN5
(COM2)
10
9
2
1
51
9
6
CN11
(COM1)
COM2 RS-232/422/485 serial ports (CN5)
COM2 RS-232/422/485 serial port (CN5)
PIN SIGNAL PIN SIGNAL
COM2 1 DCDB 6 DSRB
(422TXD-/485DATA-)
2 RXDB 7 RTSB
(422RXD+)
3 TXDB 8 CTSB
(422TXD+/485DATA+)
4 DTRB 9 RIB
(422RXD-)
5 GND 10 N.C.
Chapter 2 Installation 31
Page 41
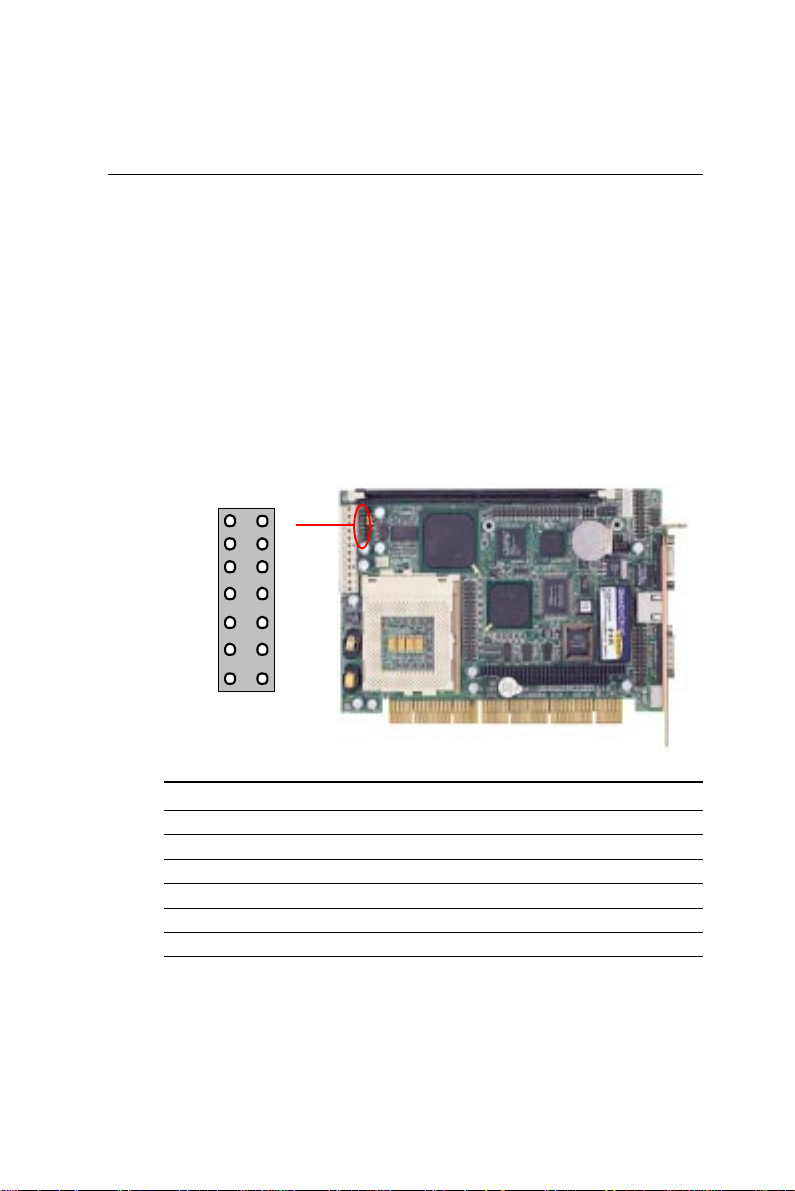
IrDA connector (CN6, Pin 1~5)
The IrDA connector (CN6, Pin 1~5) can be configured to support
wireless infrared module, with this module and application software
such as laplink or Win95 Direct Cable connection, user can transfer
files to or from laptops, notebooks, PDA and printers. This
connector supports HPSIR (115.2Kbps, 2 meters), ASK-IR
(56Kbps).
Install infrared module onto IrDA connector and enable infrared
function from BIOS setup. Make sure to have correct orientation
when you plug onto IrDA connector CN6 (Pin 1~5).
CN6
1
2
3
4
5
IrDA connector (CN6, Pin1~5)
Pin Signal
1 Vcc
2NC
3 IrRx
4 GND
5 IrTx
32 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 42

Reset switch (CN6, Pin6, 7)
You can connect an external switch to easily reset your computer.
This switch restarts your computer as if you had turned off the
power, then turned it back on.
CN6
6
7
Reset switch (CN6, Pin6, 7)
Pin Function
6 RST-IN
7 GND
Chapter 2 Installation 33
Page 43
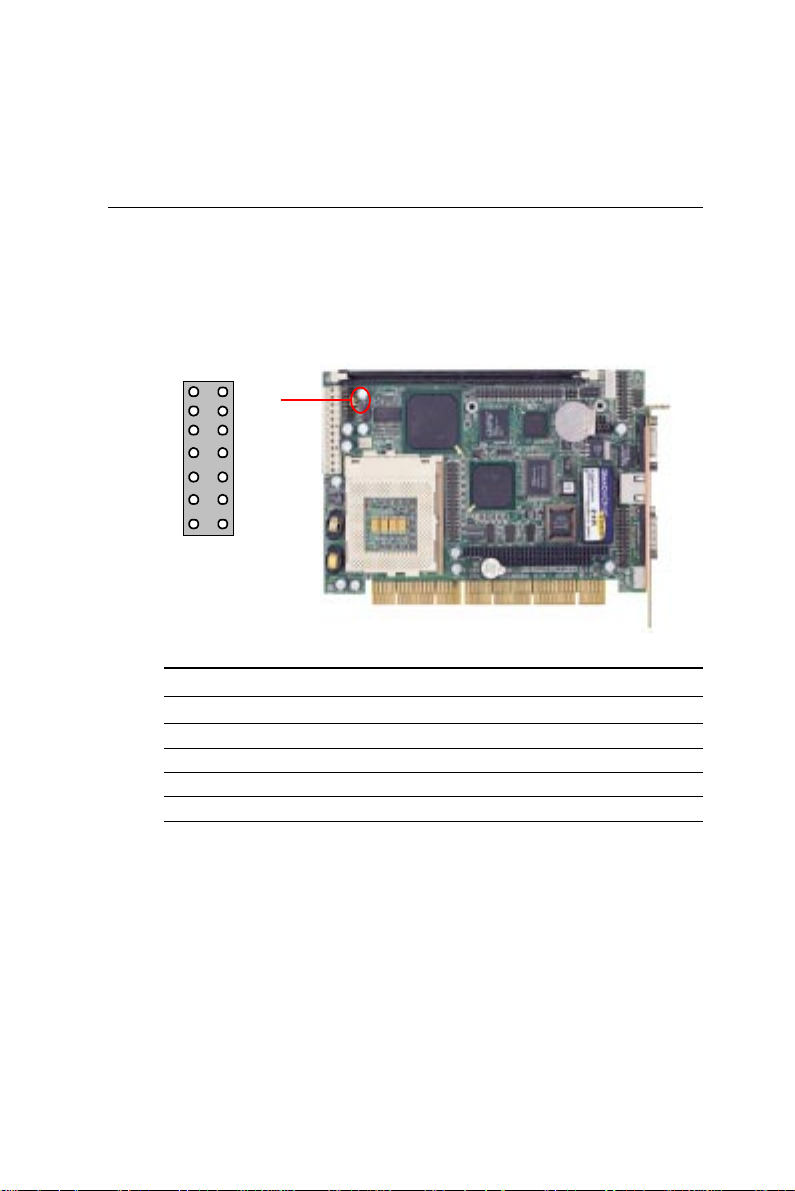
External/internal speaker (CN6, Pin
8~11)
The CPU card has its own buzzer. You can also connect to the
external speaker on your computer chassis. Pin assignments for
CN6 (Pin8~11)are shown below:
CN6
8
9
10
11
6
7
External speaker (CN6, Pin 8~11)
Pin Function
8 Vcc (For external speaker use)
9NC
10 BZ_IN*
11 BUZZ*
* default
For external speaker connection :
Remove the default jumper cap from the pin 10~11away .
(+) : Please connect to pin 8
(-) : Please connect to pin 11
34 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 44

Hard drive LED (CN6, Pin 13, 14)
Y ou can connect an LED to indicate when an IDE device is in use.
The pin assignments for this connector are as follows:
CN6
13
14
Hard drive LED (CN6, Pin 13, 14)
Pin Function
13 HD-LED+
14 HD-LED-
Chapter 2 Installation 35
Page 45

CPU fan power connector (CN7)
The SBC-658 onboard offer +12V power for the CPU cooling fan.
Plug in the fan cable onto the 3 pins fan power connector onboard.
The fan connector is marked CN7.
1 2 3
CPU fan power connector (CN7)
Pin Signal
1 GND
2 +12V
3 Fan speed sense
36 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 46

100Base-T Ethernet connector (CN9)
This 100Base-T Ethernet connector CN9 is a standard RJ-45
connector.
The onboard Intel 82559ER fast Ethernet controller supports
10Mb/s and 100 Mb/s N-way auto-negotiation operation.
CN9
Chapter 2 Installation 37
Page 47
IDE hard drive connector (CN10)
You can attach up to two Enhanced Integrated Device Electronics
hard disk drives to the SBC-658's CN10. The SBC-658's IDE
controller uses a PCI local bus interface. This advanced interface
supports faster data transfer and allows the IDE hard drive to
exceed 528 MB.
12
43
44
CN10
38 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 48

IDE hard drive connector (CN10)
IDE hard drive connector (CN10)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 IDE RESET 2 GN D
3DATA 7 4 DATA 8
5DATA 6 6 DATA 9
7DATA 5 8 DATA 10
9 DA T A 4 10 DA T A 1 1
11 DA T A 3 12 DA T A 12
13 DA T A 2 14 DA T A 13
15 DA T A 1 16 DA T A 14
17 DA T A 0 18 DA T A 15
19 SIGNAL GND 20 NC
21 NC 22 GND
23 IO WRITE 24 GND
25 IO READ 26 GND
27 IO CHANNEL READY 28 ALE
29 NC 30 GND
31 IRQ14 32 IOCS16
33 ADDR 1 34 NC
35 ADDR 0 36 ADDR 2
37 HARD DISK SELECT 0 38 HARD DISK SELECT 1
39 IDE ACTIVE 40 MGND
41 VCC 42 MVCC
43 GND 44 NC
Chapter 2 Installation 39
Page 49

Floppy drive connector (CN12)
You can attach up to two floppy drives to the mainboard controller. You can use any combination of 5¼" (360 KB and 1.2 MB)
and/or 3½" (720 KB, 1.44 MB, and 2.88 MB) drives.
A 34-pin daisy-chain drive connector cable is required for a dualdrive system. On one end of the cable is a 34-pin flat-cable
connector. On the other end are two sets of floppy disk drive
connectors. Each set consists of a 34-pin flat-cable connector
(usually used for 3½" drives) and a printed-circuit board connector (usually used for 5¼" drives).
Wire number 1 on the cable is normally red or blue, and the other
wires are usually gray.
3334
40 SBC-658 User Manual
2
CN12
1
Page 50

Connecting the floppy drive
1 . Plug the 34-pin flat-cable connector into CN12. Make sure that
the red or blue wire corresponds to pin 1 on the connector.
2. Attach the appropriate connector on the other end of the cable
to the floppy drive(s). You can use only one connector in the
set. The set on the end (after the twist in the cable) connects to
the A: drive. The set in the middle connects to the B: drive.
3 . If you are connecting a 5¼" floppy drive, line up the slot in the
printed circuit board with the blocked-off part of the cable
connector.
If you are connecting a 3½" floppy drive, you may have trouble
determining which pin is pin number 1. Look for a number
printed on the circuit board indicating pin number 1. Also,
the connector on the floppy drive connector may have a slot.
When the slot is up, pin number 1 should be on the right.
Check the documentation that came with the drive for more
information.
If you desire, connect the B: drive to the connectors in the
middle of the cable as described above.
Chapter 2 Installation 41
Page 51

Floppy drive connector (CN12)
Floppy drive connector (CN12)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 GND 2 DENSITY SELECT 0
3 GND 4 N C
5 N C 6 DENSITY SELECT 1
7 GND 8 INDEX
9 GN D 10 MOTOR 0
11 GND 12 DRIVE SELECT 1
13 GND 14 DRIVE SELECT 2
15 GND 16 MOTOR 1
17 GND 18 DIRECTION
19 GND 20 STEP
21 GND 22 WRITE DA T A
23 GND 24 WRITE GA TE
25 GND 26 TRACK 0
27 GND 28 WRITE PROTECT
29 GND 30 READ DATA
31 GND 32 HEAD DELECT
33 GND 34 DISK CHANGE
42 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 52

DiskOnChip socket (U10)
The DiskOnChip 2000 family of products provides a single chip
solid-state flash disk in a standard 32 pins DIP package. The
DiskOnChip 2000 is a solid-state disk with no moving parts,
resulting in a significant reduction in power consumption and an
increase in reliability . The DiskOnChip is a small plug and play
Flash disk. It is easy to use. And it saves integration overhead.
The DiskOnChip 2000 family of products is available in capacities
ranging from 4MB up to 288MB, unformatted. In order to manage
the disk, the DiskOnChip 2000 includes the TrueFFS, M-Systems
Flash File System proprietary software. The DiskOnChip 2000
package is pin-to-pin compatible with a standard 32-pin EPROM
device.
pin
Name
A0-A12 Address bus 4-12, 23,25-27 Inputs
A13-A16 Address bus 2,3,28,29 Inputs 1
D0-D7 Data bus 13-15,17-21 I/O
CE/ C hip Enable 22 Input
OE /
OE/ Output Enable 24 Input
WE/ Write En able 31 Input
NC Not connected 1.30 2
VCC Power 32
GND Ground 16
Description PinNumber Direction Note
Note 1: Pins A13 through A16 are not used
by the MD2200. They are kept for socket
backward compatibility with ED 1100
(DiskOnChip 1000)
Note 2: Pins 1 and 30 are not used by
MD2200
Chapter 2 Installation 43
Page 53

DiskOnChip (DOC) 2000 Installation
When the DOC is installed correctly, a DOC will work like an HDD
or an FDD. T o install the DOC on the SBC-658, follow the instructions below:
1 . Plug the DOC into the socket. Make sure pin 1 of the DOC is
aligned with pin 1 of the socket.
2. Push the DOC into the socket until it is firmly seated in the
socket.
Caution: the DOC may be permanently damage if it is installed
incorrectly .
3. Set the jumper for the memory address of the DOC.
Note:
The memory shadow function sometimes will create conflicts with
the memory window. You should disable the memory shadow from
the BIOS SETUP if the DOC cannot be accessed.
Configure DOC as a boot device
To configure a DOC as a boot drive, you should copy the operating
system files onto the DOC. The following procedure is an example
of the initialization process.
1 . Install a DOC into your system.
2. Insert a bootable floppy disk in drive A: and boot the system.
3 . At the DOS prompt, type SYS C: to transfer the DOS system
files to the DOC (assuming the DiskOnChip is installed as drive
C:). Reboot the system.
4 . Go to the BIOS Setup Utility by hitting the <DEL> key. Set the
type of Primary Master or C: Drive as Not Installed.
5 . Remove the floppy disk from the drive A: and leave the BIOS
Setup Utility. The system should boot from the DOC.
44 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 54

3
CHAPTER
Award BIOS Setup
This chapter describes how to configure
the BIOS for the system.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 45
Page 55

Starting setup
The A ward BIOS is immediately activated when you first turn on
the computer. The BIOS reads system configuration information in
CMOS RAM and begins the process of checking out the system
and configuring it through the power-on self test (POST).
When these preliminaries are finished, the BIOS seeks an operating
system on one of the data storage devices (hard drive, floppy
drive, etc.). The BIOS launches the operating system and hands
control of system operations to it.
During POST , you can start the Setup program in one of two ways:
1.By pressing Del immediately after switching the system on, or
2.By pressing Del or pressing Ctrl-Alt-Esc when the following
message appears briefly at the bottom of the screen during POST:
TO ENTER SETUP BEFORE BOOT PRESS DEL KEY
If the message disappears before you respond and you still wish to
enter Setup, restart the system to try again by turning it OFF then
ON or pressing the RESET button on the system case. You may
also restart by simultaneously pressing Ctr-Alt-Del. If you do not
press the keys at the correct time and the system does not boot, an
error message appears and you are again asked to
PRESS F1 TO CONTINUE, DEL TO ENTER SETUP
46 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 56

Setup keys
These keys helps you navigate in Setup:
Up arrow Move to previous item
Down arrow Move to next item
Left arrow Move to the item in the left hand
Right arrow Move to the item in the right hand
Es c Main Menu: Quit and not save changes into
CMOS RAM
Other pages: Exit current page and return to
Main Menu
PgDn/+ Increase the numeric value or make
changes
PgDn/- Decrease the numeric value or make
changes
F1 General help, only for Status Page Setup
Menu and Option Page Setup Menu
F2 Change color from total 16 colors. F2 to
select color forward, Shift-F2 to select color
backward
F3 Calendar, only for Status Page Setup Menu
F4 Reserved
F5 Restore the previous CMOS value from
CMOS, only for Option Page Setup Menu
F6 Load the default CMOS RAM value from
BIOS default table, only for Option Page
Setup Menu
F7 Load the default
F8 Reserved
F9 Reserved
F10 Save all the CMOS changes, only for Main
Menu
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 47
Page 57

Getting help
Press F1 to pop up a small help window that describes the appropriate keys to use and the possible selections for the highlighted
item. T o exit the Help Window press Esc or the F1 key again.
In Case of Problems
If, after making and saving system changes with Setup, you
discover that your computer no longer is able to boot, the Award-
BIOS supports an override to the CMOS settings that resets your
system to its default configuration.
You can invoke this override by immediately pressing Insert; when
you restart your computer. You can restart by either using the ON/
OFF switch, the RESET button or by pressing Ctrl-Alt-Delete.
The best advice is to alter only settings that you thoroughly
understand. In particular, do not change settings in the Chipset
screen without a good reason. The Chipset defaults have been
carefully chosen by A ward Software or your system manufacturer
for the best performance and reliability . Even a seemingly small
change to the Chipset setup may causing the system to become
unstable.
48 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 58

Main setup Menu
Standard CMOS Options in the original PC AT-compatible
BIOS.
BIOS Features Award Software enhanced BIOS options.
Chipset Features Options specific to your system chipset.
Power Advanced Power Management (APM)
Management options.
PnP/PCI Plug and Play standard and PCI Local Bus
Configuration configuration options.
Integrated I/O subsystems that depend on the inte-
Peripherals grated peripherals controller in your
system.
Supervisor/User Change, set, or disable a password. In
Password Setting BIOS versions that allow separate user and
supervisor passwords, only the supervisor
password permits access to Setup. The
user password generally allows only
power-on access.
IDE HDD Auto Automatically detect and configure IDE hard
Detection disk parameters.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 49
Page 59

Load BIOS BIOS defaults are factory settings for the
Defaults most stable, minimal-performance system
operations.
Load Setup Setup defaults are factory settings for
Defaults optimal-performance system operations.
Save & Exit Save settings in nonvolatile CMOS
Setup RAM and exit Setup.
Exit Without Abandon all changes and exit Setup.
Save
50 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 60

Standard CMOS setup
When you choose the ST ANDARD CMOS SETUP option from the
INITIAL SETUP SCREEN menu, the screen below is displayed.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 51
Page 61

This standard setup menu allows users to configure system
components such as the date, time, hard disk drive, floppy drive,
display, and memory. Online help for each field can be accessed by
pressing F1.
Date and Time Configuration
The BIOS determines the day of the week from the other date
information. This field is for information only .
Press the left or right arrow key to move to the desired field (date,
month, year). Press the PgUp/- or PgDn/+ key to increment the
setting, or type the desired value into the field.
The time format is based on the 24-hour military-time clock. For
example, 1 p.m. is 13:00:00. Press the left or right arrow key to move
to the desired field. Press the PgUp/- or PgDn/+ key to increment
the setting, or type the desired value into the field.
HARD DISKS
The BIOS supports up to two IDE drives. This section does not
show information about other IDE devices, such as a CD-ROM
drive, or about other hard drive types, such as SCSI drives.
NOTE: W e r ecommend that you select type AUT O for all drives.
The BIOS can automatically detect the specifications and optimal
operating mode of almost all IDE hard drives. When you select
type AUTO for a hard drive, the BIOS detects its specifications
during POST , every time the system boots.
If you do not want to select drive type AUTO, other methods of
52 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 62

selecting the drive type are available:
1.Match the specifications of your installed IDE hard drive(s) with
the preprogrammed values for drive types 1 through 45.
2.Select USER and enter values into each drive parameter field.
3.Use the IDE HDD AUTO DECTECTION function in Setup.
Here is a brief explanation of drive specifications:
•T ype: The BIOS contains a table of pre-defined drive types. Each
defined drive type has a specified number of cylinders,
number of heads, write precompensation factor, landing
zone, and number of sectors. Drives whose specifications
do not accommodate any pre-defined type are classified as
type USER.
•Size: Disk drive capacity (approximate). Note that this size is
usually slightly greater than the size of a formatted disk
given by a disk-checking program.
• Cyls: Number of cylinders
• Head: Number of heads
• Precomp: Write precompensation cylinder
• Landz: Landing zone
• Sector: Number of sectors
• Mode: Auto, Normal, large, or LBA
- Auto: The BIOS automatically determines the optimal mode.
- Normal: Maximum number of cylinders, heads, and sectors
supported are 1024, 16, and 63.
- Large: For drives that do not support LBA and have more than
1024 cylinders.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 53
Page 63

- LBA (Logical Block Addressing): During drive accesses, the
IDE controller transforms the data address described by
sector, head, and cylinder number into a physical block
address, significantly improving data transfer rates. For
drives with greater than 1024 cylinders.
Drive A
Drive B
Select the correct specifications for the diskette drive(s) installed in
the computer.
None No diskette drive installed
360K, 5.25 in 5-1/4 inch PC-type standard drive; 360
kilobyte capacity
1.2M, 5.25 in 5-1/4 inch AT-type high-density drive; 1.2
megabyte capacity
720K, 3.5 in 3-1/2 inch double-sided drive; 720 kilobyte
capacity
1.44M, 3.5 in 3-1/2 inch double-sided drive; 1.44 mega
byte capacity
2.88M, 3.5 in 3-1/2 inch double-sided drive; 2.88 mega
byte capacity
LCD & CRT
This field may appear as an alternative to The Video field. select
your video display device:
LC D Liquid crystal display
CRT Auxiliary monitor
Both Display on both devices
Pannel:
This selection item allow user to select LCD BIOS to match the LCD
types.
54 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 64

Halt On
During the power-on-self-test (POST), the computer stops if the
BIOS detects a hardware error. You can tell the BIOS to ignore
certain errors during POST and continue the boot-up process.
These are the selections:
• No errors: POST does not stop for any errors.
• All errorsIf: the BIOS detects any non-fatal error, POST stops
and prompts you to take corrective action.
• All, But Keyboard: POST does not stop for a keyboard error, but
stops for all other errors.All, But DiskettePOST does not stop for
diskette drive errors, but stops for all other errors.
• All, But Disk/Key: POST does not stop for a keyboard or disk
error, but stops for all other errors.
Memory
You cannot change any values in the Memory fields; they are only
for your information. The fields show the total installed random
access memory (RAM) and amounts allocated to base memory,
extended memory , and other (high) memory . RAM is counted in
kilobytes (KB: approximately one thousand bytes) and megabytes
(MB: approximately one million bytes).
RAM is the computer's working memory, where the computer
stores programs and data currently being used, so they are
accessible to the CPU. Modern personal computers may contain up
to 64 MB, 128 MB, or more.
•Base Memory
Typically 640 KB. Also called conventional memory . The DOS
operating system and conventional applications use this area.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 55
Page 65

•Extended Memory
Above the 1-MB boundary. Early IBM personal computers could
not use memory above 1 MB, but current PCs and their software
can use extended memory.
•Other Memory
Between 640 KB and 1 MB; often called High memory. DOS may
load terminate-and-stay-resident (TSR) programs, such as device
drivers, in this area, to free as much conventional memory as
possible for applications. Lines in your CONFIG.SYS file that start
with LOADHIGH load programs into high memory.
56 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 66

BIOS features setup
By choosing the BIOS FEA TURES SETUP option from the INITIAL
SETUP SCREEN menu, the screen below is displayed.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 57
Page 67

The displayed configuration is based on the manufacturer's SETUP
DEF AUL TS settings.
Virus Warning
When enabled, you receive a warning message if a program
(specifically , a virus) attempts to write to the boot sector or the
partition table of the hard disk drive. You should then run an antivirus program. Keep in mind that this feature protects only the boot
sector, not the entire hard drive.
NOTE: Many disk diagnostic programs that access the boot
sector table can trigger the virus warning message. If you plan to
run such a program, we recommend that you first disable the virus
warning.
CPU Internal Cache/External Cache
Cache memory is additional memory that is much faster than
conventional DRAM (system memory). CPUs from 486-type on up
contain internal cache memory , and most, but not all, modern PCs
have additional (external) cache memory. When the CPU requests
data, the system transfers the requested data from the main DRAM
into cache memory , for even faster access by the CPU.
The External Cache field may not appear if your system does not
have external cache memory .
CPU L2 Cache ECC Checking
When you select Enabled, memory checking is enable when the
external cache contains ECC SRAMs.
Quick Power On Self Test
Select Enabled to reduce the amount of time required to run the
power-on-self-test (POST). A quick POST skips certain steps. W e
recommend that you normally disable quick POST . Better to find a
problem during POST than lose data during your work.
58 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 68

Shadow
Software that resides in a read-only memory (ROM) chip on a
device is called firmware. The A wardBIOS permits shadowing of
firmware such as the system BIOS, video BIOS, and similar operating instructions that come with some expansion peripherals, such
as, for example, a SCSI adaptor.
Shadowing copies firmware from ROM into system RAM, where
the CPU can read it through the 16-bit or 32-bit DRAM bus.
Firmware not shadowed must be read by the system through the 8bit X-bus. Shadowing improves the performance of the system
BIOS and similar ROM firmware for expansion peripherals, but it
also reduces the amount of high memory (640 KB to 1 MB) available for loading device drivers, etc.
Enable shadowing into each section of memory separately. Many
system designers hardwire shadowing of the system BIOS and
eliminate a System BIOS Shadow option.
Video BIOS shadows into memory area C8000-DFFFF . The remaining areas shown on the BIOS Features Setup screen may be
occupied by other expansion card firmware. If an expansion
peripheral in your system contains ROM-based firmware, you need
to know the address range the ROM occupies to shadow it into the
correct area of RAM.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 59
Page 69

CHIPSET features setup
By choosing the CHIPSET FEA TURES SETUP option from the
INITIAL SETUP SCREEN menu, the screen below is displayed.
60 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 70

The displayed configuration is based on the manufacturer's SETUP
DEF AUL TS settings.
This section allows you to configure the system based on the
specific features of the installed chipset. This chipset manages bus
speeds and access to system memory resources, such as SDRAM.
It also coordinates communications between the conventional ISA
bus and the PCI bus. It must be stated that these items should
never need to be altered. The default settings have been chosen
because they provide the best operating conditions for your
system. The only time you might consider making any changes
would be if you discovered that data was being lost while using
your system.
Because of the complexity and technical nature of some of the
options, not all of the options are described here.
SDRAM RAS-to-CAS Delay
This field lets you control the number of DCLKs between a Row
Activate command and a read or write command.
SDRAM RAS Precharge Time
The precharge time is the number of cycles it takes for the RAS to
accumulate its charge before DRAM refresh. If insufficient time is
allowed, refresh may be incomplete and the DRAM may fail to
retain data. This field applies only if synchronous DRAM is
installed in the system.
SDRAM CAS Latency Time
When synchronous DRAM is installed, you can control the
number of CLKs between when the SDRAMs sample a read
command and when the contoller samples read data from the
SDRAMs. Do not reset this field from the default value specified
by the system designer.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 61
Page 71

SDRAM Precharge Control
When Enabled, all CPU cycles to SDRAM result in an All Banks
Precharge Command on the SDRAM interface.
DRAM Data Integrity Mode
Select Non-ECC or ECC (error-correcting code), according to the
type of installed DRAM.
System BIOS Cacheable
Selecting Enabled allows caching of the system BIOS ROM at
F0000h-FFFFFh, resulting in better system performance. However,
if any program writes to this memory area, a system error may
result.
Video BIOS Cacheable
Selecting Enabled allows caching of the video BIOS ROM at
C0000h to C7FFFh, resulting in better video performance. However,
if any program writes to this memory area, a system error may
result.
Video RAM Cacheable
Selecting Enabled allows caching of the video memory (RAM) at
A0000h to AFFFFh, resulting in better video performance. However, if any program writes to this memory area, a memory access error
may result.
8/16 Bit I/O Recovery Time
The I/O recovery mechanism adds bus clock cycles between PCIoriginated I/O cycles to the ISA bus. This delay takes place
because the PCI bus is so much faster than the ISA bus.
These two fields let you add recovery time (in bus clock cycles) for
16-bit and 8-bit I/O.
62 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 72

Memory Hole at 15M-16M
Y ou can reserve this area of system memory for ISA adapter ROM.
When this area is reserved, it cannot be cached. The user information of peripherals that need to use this area of system memory
usually discusses their memory requirements.
Passive Release
When Enabled, CPU to PCI bus accesses are allowed during
passive release. Otherwise, the arbiter only accepts another PCI
master access to local DRAM.
Delayed Transaction
The chipset has an embedded 32-bit posted write buffer to support
delay transactions cycles. Select Enabled to support compliance
with PCI specification version 2.1.
Auto Detect DIMM/PCI Clk
When the Auto Detect DIMM/PCI clk enable, the Utility will
automatically detect the DIMM/PCI clock in your system.
Spread Spectrum
When the system clock generator pulses, the extreme values of the
pulse generate excess EMI. Enabling pulse spectrum spread
modulation changes the extreme values from spikes to flat curves,
thus reducing EMI. This benefit may in some cases be outweighed
by problems with timing-critical devices, such as a clock-sensitive
SCSI device
IN0-IN6(V)
These fields display the current voltage of up to seven voltage
input lines, if your computer contains a monitoring system.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 63
Page 73

Power management setup
By choosing the POWER MANAGEMENT option from the
INITIAL SETUP SCREEN menu, the screen below is displayed.
64 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 74

The displayed configuration is based on the manufacturer's SETUP
DEF AUL TS settings.
Power Management
This option allows you to select the type (or degree) of power
saving for Doze, Standby, and Suspend modes.
This table describes each power management mode:
Max Saving Maximum power savings. Only Available for
SL CPUs. Inactivity period is 1 minute in
each mode.
User Define Set each mode individually. Select time-out
periods in the section for each mode,
below.
Min Saving Minimum power savings. Inactivity period is
1 hour in each mode (except the hard
drive).
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 65
Page 75

PM Control by APM
If Advanced Power Management (APM) is installed on your
system, selecting Yes gives better power savings.
Video Off Method
Determines the manner in which the monitor is blanked.
V/H SYNC+Blank System turns off vertical and horizontal
synchronization ports and writes blanks to
the video buffer.
DPMS Support Select this option if your monitor supports
the Display Power Management Signaling
(DPMS) standard of the Video Electronics
Standards Association (VESA). Use the
software supplied for your video subsystem
to select video power management values.
Blank Screen System only writes blanks to the video
buffer.
Video Off After
As the system moves from lesser to greater power-saving modes,
select the mode in which you want the monitor to blank.
MODEM Use IRQ
Name the interrupt request (IRQ) line assigned to the modem (if
any) on your system. Activity of the selected IRQ always awakens
the system.
Doze Mode
After the selected period of system inactivity, the CPU clock
throttles to a small percentage of its duty cycle between 10
percent and 25 percent for most chipsets. All other devices still
operate at full speed.
66 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 76

Standby Mode
After the selected period of system inactivity, the CPU clock stops,
the hard drive enters an idle state, and the L2 cache enters a powersave mode. All other devices still operate at full speed.
Suspend Mode
After the selected period of system inactivity, the chipset enters a
hardware suspend mode, stopping the CPU clock and possibly
causing other system devices to enter power management modes.
HDD Power Down
After the selected period of drive inactivity , any system IDE
devices compatible with the ATA-2 specification or later power
manage themselves, putting themselves into an idle state after the
specified timeout and then waking themselves up when accessed.
Throttle Duty Cycle
When the system enters Doze mode, the CPU clock runs only part
of the time. Y ou may select the percent of time that the clock runs.
VGA Active Monitor
When Enabled, any video activity restarts the global timer for
Standby mode.
IRQ8 Break [Event From] Suspend
Y ou can select Enabled or Disabled for monitoring of IRQ8 (the
Real Time Clock) so it does not awaken the system from Suspend
mode.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 67
Page 77

Reload Global Timer Events
When Enabled, an event occurring on each device listed below
restarts the global timer for Standby mode.
IRQ3-7, 9-15, NMI
Primary IDE 0
Primary IDE 1
Floppy Disk
Serial Port
Parallel Port
68 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 78

PNP/PCI configuration setup
By choosing the PNP/PCI CONFIGURA TION SETUP option from
the initial SETUP SCREEN menu, the screen below is displayed.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 69
Page 79

The displayed configuration is based on the manufacturer's SETUP
DEF AUL TS settings.
NOTE: This chapter describes all fields offered by Award Software
in this screen. Your system board designer may omit or modify
some fields.
PNP OS Installed
Select Yes if the system operating environment is Plug-and-Play
aware (e.g., Windows 95).
Resources Controlled By
The Plug and Play A wardBIOS can automatically configure all the
boot and Plug and Play-compatible devices. If you select Auto, all
the interrupt request (IRQ) and DMA assignment fields disappear,
as the BIOS automatically assigns them.
Reset Configuration Data
Normally, you leave this field Disabled. Select Enabled to reset
Extended System Configuration Data (ESCD) when you exit Setup if
you have installed a new add-on and the system reconfiguration
has caused such a serious conflict that the operating system
cannot boot.
Assign IRQ for VGA
If you are not using your system's VGA controller, select Disabled
to free the IRQ resource.
Assign IRQ for USB
Select Enabled if your system has a USB controller and you have
one or more USB devices connected. If you are not using your
system’s USB controller , select Disabled to free the IRQ resource.
70 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 80

Load BIOS defaults/Load setup
defaults
LOAD BIOS DEF AUL TS loads the default system values directly
from ROM. The BIOS DEF AUL TS provides the most stable
settings, though they do not provide optimal performance. LOAD
SETUP DEF AUL TS, on the other hand, provides for maximum
system performance. If the stored record created by the setup
utility becomes corrupted (and therefore unusable), BIOS defaults
will load automatically when you turn the system on.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 71
Page 81

Integrated peripherals setup
By choosing the INTEGRA TD PERIPHERALS option from the
initial SETUP SCREEN menu, the screen below is displayed.
72 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 82

The displayed configuration is based on the manufacturer's SETUP
DEF AULSTS settings.
IDE HDD Block Mode
Select Enabled only if your hard drives support block mode.
IDE Primary Master/Slave UDMA
UDMA (Ultra DMA) is a DMA data transfer protocol that utilizes
ATA commands and the ATA bus to allow DMA commands to
transfer data at a maximum burst rate of 33 MB/s. When you select
Auto in the four IDE UDMA fields (for each of up to four IDE
devices that the internal PCI IDE interface supports), the system
automatically determines the optimal data transfer rate for each IDE
device.
On-Chip PCI IDE Primary
The system chipset contains a PCI IDE interface with support for
two IDE channels. Select Enabled to activate the primary and/or
secondary IDE interface. Select Disabled to deactivate this interface, if you install a primary and/or secondary add-in IDE interface.
USB Keyboard Support
Select Enabled if your system contains a Universal Serial Bus
(USB) controller and you have a USB keyboard.
Onboard FDC Controller
Select Enabled if your system has a floppy disk controller (FDC)
installed on the system board and you wish to use it. If you install
an add-in FDC or the system has no floppy drive, select Disabled in
this field.
Onboard Serial Ports (1, 2)
Select a logical COM port address for the first and second serial
ports.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 73
Page 83

RxD, TxD Active
Consult your IR peripheral documentation to select the correct
setting of the TxD and RxD signals.
ECP Mode Use DMA
Select a DMA channel for the port.
EPP Mode select
Select EPP port type 1.7 or 1.9.
74 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 84

Supervisor/User password setting
Y ou can set either SUPER VISOR or USER P ASSWORD, or both of
them. The difference between the two is that the supervisor
password allows unrestricted access to enter and change the
options of the setup menus, while the user password only allows
entry to the program, but not modify options.
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 75
Page 85

When you select this function, a message appears at the center of
the screen:
ENTER PASSWORD:
Type the password, up to eight characters, and press Enter. Typing
a password clears any previously entered password from CMOS
memory.
Now the message changes:
CONFIRM PASSWORD:
Again, type the password and press Enter.
To abort the process at any time, press Esc.
In the Security Option item in the BIOS Features Setup screen,
select System or Setup:
System Enter a password each time the system boots and when
ever you enter Setup.
Setup Enter a password when ever you enter Setup.
NOTE: To clear the password, simply press Enter when asked to
enter a password. Then the password function is disabled.
76 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 86

IDE HDD auto detection
The IDE HDD AUTO DETECTION utility can automatically detect
the IDE hard disk installed in your system. You can use it to selfdetect and/or correct the hard disk type configuration. You need to
repeat the setup for each of the IDE combinations:
Chapter 3 Award BIOS Setup 77
Page 87

Save & exit setup
If you select this option and press <ENTER>, the values entered in
the setup utility will be recorded in the chipset's CMOS memory .
The microprocessor will check this every time you turn your
system on and compare this to what it finds as it checks the
system. This record is required for the system to operate.
78 SBC-658 User Manual
Page 88

4
CHAPTER
Flat Panel/CRT
Controller Display
Drivers and Utilities
This chapter provides information about:
• Driver types and installation
Chapter 4 Driver Installation
79
Page 89

Software drivers
This chapter describes the operation and installation of the display
drivers supplied on the Supporting CD-ROM that are shipped with
your product.
The onboard VGA adapter is based on the CHIPS VGA Flat Panel/CRT
controller and is fully IBM VGA compatible. This controller offers a
large set of extended functions and higher resolutions. If you intend to
use your VGA adapter in standard VGA modes only, you do not need
to install any of these drivers. Since your VGA adapter is fully compatible, it does not require any special drivers to operate in standard
modes.
The purpose of the enclosed software drivers is to take advantage of
the extended features of the CHIPS VGA Flat Panel/CR T controller.
Hardware configuration
Some of the high-resolution drivers provided in this package will work
only in certain system configurations. If a driver does not display
correctly , try the following:
1 . Change the display controller to CR T-only mode, rather than flat
panel or simultaneous display mode. Some high-resolution drivers
will display correctly only in CRT mode.
2. If a high-resolution mode is not supported on your system, try
using a lower-resolution mode. For example, 1024 x 768 mode will
not work on some systems, but 800 x 600 mode is supported on
most.
80
SBC-658 User Manual
Page 90

Necessary prerequisites
The instructions in this manual assume that you understand elementary concepts of MS-DOS and the IBM Personal Computer. Before you
attempt to install any driver or utility, you should:
• Know how to copy files from a CD-ROM to a directory on the hard
disk
• Understand the MS-DOS directory structure
If you are uncertain about any of these concepts, please refer to the
DOS or OS/2 user reference guides for more information before you
proceed with the installation.
Before you begin
Make sure you know the version of the application for which you are
installing drivers. The Supporting CD-ROM contain drivers for several
versions of certain applications. For your driver to operate properly ,
you must install the driver for your version of the application program.
Chapter 4 Driver Installation
81
Page 91

Windows® 95
These drivers are designed to work with Microsoft Windows. You
just install these drivers through the Windows operating system.
Driver installation
1 . Install Windows 95 as you normally would for a VGA display.
Click the Start button, go to Settings and click on Control
Panel. Choose the Display icon and double click on the icon. In
the Display Properties window , show as figure 1:
82
SBC-658 User Manual
figure 1
Page 92

Click the setting buttom, then click the Advanced Properties icon
into the Advanced Display properties windows, show as figure2:
figure 2
Chapter 4 Driver Installation
83
Page 93

click on Change Display T ype. In the Change Display Type
window, click on the Change button under Adapter Type into the
select Device window show as figure(3):This will bring up the
Select Device window.
figure 3
84
SBC-658 User Manual
Page 94

2 . Place the Supporting CD-ROM in your CD-ROM drive.
figure 4
Chapter 4 Driver Installation
85
Page 95

The name of the Chips And T echn "69000 PCI " driver will appear
highlighted in the Models list boxfhow as figure. Click OK to start
the driver installation show as figure 6:
figure 6
86
SBC-658 User Manual
Page 96

3. Once the installation is complete, the Advanced display Properties
window will reappear. Show as figure (7):
figure 7
Chapter 4 Driver Installation
87
Page 97

Click on close to close the window . Then the Display Properties
window will reappear. Show as figure (8):
figure 8
88
SBC-658 User Manual
Page 98

Click on Apply. Restart the system for the new settings to take
effect, show as figure (9):
figure 9
Chapter 4 Driver Installation
89
Page 99

Windows® NT 3.51
These drivers are designed to work with Microsoft Windows.
Driver installation
1. Install Windows NT 3.51 as you normally would for a VGA
display. Click the Star buttom, go to Settings and click on Control
Panel icon. Then choose the Display and double click on the icon.
In the Display Properties window , click the Setting buttom, then
click the Display T ype buttom into the Display T ype windows, then
click on Change buttom from the Adapter T ype icon. And click on
Have Disk buttom in the change display window .
2. Place the Supporting CD-ROM into your CD-ROM drive.
and type:
cd-rom: \CD ROM\model name\drive\vga drive\
win98 nt\windows.nt\nt35\Oemsetup.inf
"cd-rom:": the drive letter of your CD-ROM drive
"model name": the model number of your product
Select the adapter "Chips and T ech 69000PCI" and click OK.
Click on Install to install the selected driver. Once the installation is
complete, shut down and restart the system.
90
SBC-658 User Manual
Page 100

Windows® NT 4.0
Driver installation
1. Install Windows NT 4.0 as you normally would for a VGA
display. Click the Star buttom, go to Settings and click on Control
Panel icon. Then choose the Display and double click on the icon.
In the Display Properties window , click the Setting buttom, then
click the Display T ype buttom into the Display T ype windows, then
click on Change buttom from the Adapter T ype icon. And click on
Have Disk buttom in the change display window .
2. Place the Supporting CD-ROM into your CD-ROM dirve. In the
Select Device window, click on Have Disk, select "Browse" and
find the NT 4.0 driver from:
cd-rom : \CD ROM\model name\dirver\vga driver\
win98 nt\windows.nt\nt40\Oemsetup.inf
"cd-rom:": the drive letter of your CD-ROM drive
"model name": the model number of your product
and then click OK. The name of the Chips and T echnologies, Inc.
Video Controller driver will appear highlighted in the Modules list
box. Select Chips and Tech. 69000 and Click OK . Click OK to start
the driver installation.
3. Once the installation is complete, the Change Display Type window
will reappear. Click on close to close the window. Then the
Display Properties window will reappear. Click on Apply. Restart
the system for the new settings to take effect.
Chapter 4 Driver Installation
91
 Loading...
Loading...