Page 1

ERserver
iSeries
Networking
iSeries Communications Management
Page 2

Page 3

ER s e r v e r
iSeries
Networking
iSeries Communications Management
Page 4

© Copyright International Business Machines Corporation 1998, 2001. All rights reserved.
US Government Users Restricted Rights – Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP Schedule Contract
with IBM Corp.
Page 5

Contents
Part 1. Getting started with AS/400 communications ..............1
Chapter 1. Print this topic .............................3
Chapter 2. Configuring AS/400 for communications ...................5
Creating a network interface description ........................5
Creating a network server description .........................5
Creating a line description..............................5
Chapter 3. Optimizing communications performance ..................7
Improving wide area network performance ........................7
Adjusting WAN protocols for optimum AS/400 performance ................7
Adjusting the WAN line speed for optimum AS/400 performance...............7
WAN line speed considerations for IOPs .......................8
Improving local area network performance ........................9
Adjusting LANs for optimum communications performance .................9
Adjusting LAN lines for optimum communications performance ...............9
LAN line speed considerations for IOPs .......................10
Improving data path performance ..........................10
Considerations for subsystem configuration for error recovery performance ..........11
Communications performance considerations for interactive jobs ..............12
Communications performance considerations for batch jobs ................13
Mixing interactive and batch jobs on a WAN line ....................13
Performance considerations for AnyNet communications .................14
Subsystems .................................15
Chapter 4. Communications applications .......................17
User written APPC applications ...........................17
Distributed data management (DDM) .........................17
Application program interface (API) performance considerations ...............17
Performance considerations for intersystem communications function ............18
Performance considerations for Common Programming Interface Communications .......19
Chapter 5. Communicating with host systems .....................21
Matching AS/400 parameters for a host system .....................21
Matching AS/400 line description parameters for a host system ..............21
Matching AS/400 controller description parameters for a host system ............23
Matching AS/400 device description parameters for a host system .............24
Matching AS/400 mode and class-of-service description parameters for a host system ......25
Configuring dependent LU requester (DLUR) ......................31
Configuring the host controller description ......................31
Configuring the device descriptions .........................31
Chapter 6. Communicating with a remote AS/400 system ................33
Matching AS/400 line description parameters for a remote AS/400 system ...........33
Matching AS/400 controller description parameters for a remote AS/400 system .........35
Matching AS/400 device description parameters for a remote AS/400 system ..........36
Connecting one AS/400 to another AS/400 system ....................37
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers ..............41
Matching AS/400 parameters for 5494 controllers .....................41
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by token-ring ..............41
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by Ethernet ..............44
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 iii
Page 6

Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by frame relay .............46
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by SDLC ...............48
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by X.21 ................52
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by X.25 ................54
Matching AS/400 parameters for 3x74 controller .....................58
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 3174 controller ...................58
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 3274 controller ...................60
Matching AS/400 parameters for finance controllers ....................62
Matching AS/400 parameters for 470x finance controllers .................62
Matching AS/400 parameters for FBSS finance controllers ................64
Matching AS/400 parameters for retail controllers .....................67
Matching AS/400 parameters for 3651 retail controllers .................68
Matching AS/400 parameters for 3684 retail controllers .................70
Matching AS/400 parameters for 4680/4690 LINE parameter ...............72
Matching AS/400 parameters for 4680/4690 LINK parameter ...............73
Matching AS/400 parameters for 4684 retail controllers .................74
Chapter 8. Troubleshooting communications problems .................79
Displaying message queues to solve communication problems ................79
Displaying the Product Activity Log to solve communication problems .............80
Displaying the Print Error Log to solve communication problems ...............80
Job logs and communication problems .......................80
Solving communication problems using communications trace ................81
System service tools and communication problems ...................82
Trace Common Programming Interface (CPI) Communications (TRCCPIC) command ......82
Solving communication problems using the system problem log ...............83
Solving communication problems using status information .................84
Considerations for system tuning during error recovery...................84
Using error messages to aid in error recovery ......................84
Solving communication problems using reason codes ...................84
Chapter 9. Networking concepts ..........................87
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking ..........................87
Advanced program-to-program communications .....................88
Dependent LU requester support ...........................88
High-performance routing .............................89
HPR architecture option sets ...........................89
Internetwork packet exchange support .........................89
What is Systems Network Architecture.........................90
What is TCP/IP .................................90
Chapter 10. Common networking standards .....................91
Local area network standards ............................91
ATM on AS/400 ................................91
Distributed data interface network .........................91
Ethernet networks ...............................91
Token-ring networks ..............................92
Wireless network ...............................92
Wide area network standards ............................93
Asynchronous communications ..........................93
Binary synchronous communications ........................93
Frame relay networks ..............................93
Integrated services digital network .........................94
Synchronous data link control network ........................94
X.25 network .................................95
X.21 network .................................95
iv Version 5
Page 7

Part 1. Getting started with AS/400 communications
The AS/400 is an extremely versatile system for networking technologies, supporting a broad range of
communication protocols. Protocols that are supported include TCP/IP, APPC, APPN, HPR, Remote
workstation, asynchronous, and binary synchronous communications.
AS/400 communications configuration is done by either manually or automatically creating a set of
configuration objects that represent the local and remote systems that are to communicate. The types of
objects required for a communications configuration vary, depending on the type of communications being
configured.
Many factors can affect the performance of the AS/400 in a communications environment. To achieve the
best performance with your particular environment review the topics, Optimizing communications
performance, and Communications applications.
You can configure your AS/400 system to communicate with another AS/400 system, a non-AS/400
system, or a remote controller. For information on how to do this, see the following:
v Communicating with host systems
v Communicating with a remote AS/400 system
v Communicating with remote workstation controllers
Communication problems are inevitable and will probably be an issue as you manage your network. If you
suspect that you are having communication problems, review the topic Troubleshooting communication
problems.
Before beginning to work with AS/400 communications, you may want to review the topics, Chapter 9,
“Networking concepts” on page 87 and Chapter 10, “Common networking standards” on page 91. Here,
you can find information related to some of the technologies common to deploying modern networking
solutions in an AS/400 environment.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 1
Page 8

2 Version 5
Page 9

Chapter 1. Print this topic
To view or download the PDF version, select Getting started with AS/400 communications (about 721 KB
or 110 pages).
To save a PDF on your workstation for viewing or printing:
1. Open the PDF in your browser (click the link above).
2. In the menu of your browser, click File.
3. Click Save As...
4. Navigate to the directory in which you would like to save the PDF.
5. Click Save.
If you need Adobe Acrobat Reader to view or print these PDFs, you can download a copy from theAdobe
Web site (www.adobe.com/prodindex/acrobat/readstep.html).
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 3
Page 10

4 Version 5
Page 11
Chapter 2. Configuring AS/400 for communications
Follow these steps to configure your AS/400:
1. Depending on the type of hardware you have, you may need to refer to the following topics:
v Creating a network server description
v Creating a network interface description
2. You define lines by creating line descriptions. Depending on your hardware, the lines may be attached
to a network server, or a network interface.
Creating a network interface description
Network interface descriptions for asynchronous transfer mode (ATM), frame relay, and integrated services
digital network (ISDN) protocols describe the communications interface.
To create a network interface description, do the following:
1. Type one of these commands on any AS/400 command line for the type of network interface you are
creating and press F4:
v Create Network Interface (ATM) (CRTNWIATM)
v Create Network Interface (Frame Relay Network) (CRTNWIFR)
v Create Network Interface Description for ISDN (CRTNWIISDN)
2. Use the on-line help information to choose the correct parameter values.
3. Press Enter. The network interface description is created.
Creating a network server description
A network server description describes which Integrated PC Server the local area network (LAN) and the
application will be using.
To create a network server description, do the following:
1. Type the Create Network Server Description (CRTNWSD) command on any AS/400 command line and
press F4.
2. Use the on-line help information to choose the parameter settings.
3. Press Enter. The network server description is created.
Creating a line description
You create line descriptions to describe the physical line connection and the data link protocol to be used
between the AS/400 system and the network.
To create line descriptions, do the following:
1. Type one of these commands on any AS/400 command line to define the type of line you are creating
and press F4.
v Create Line Description (Ethernet) (CRTLINETH)
v Create Line Description (Distributed Data Interface (DDI)) (CRTLINDDI)
v Create Line Description (Frame Relay) (CRTLINFR)
v Create Line Description for (IDLC) (CRTLINIDLC)
v Create Line Description (Synchronous Data Link Control (SDLC)) (CRTLINSDLC)
v Create Line Description (Token-ring) (CRTLINTRN)
v Create Line Description (Wireless) (CRTLINWLS)
v Create Line Description (X.25) (CRTLINX25)
2. Use the online help information to choose the correct parameter values.
3. Press Enter. The line description is created.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 5
Page 12

6 Version 5
Page 13

Chapter 3. Optimizing communications performance
Many factors can affect the performance of AS/400 application programs. To achieve the best performance
with your particular communications environment, you may want to review these topics:
v Improving wide area network (WAN) performance.
v Improving local area network (LAN) performance.
v Improving data path performance.
Improving wide area network performance
To achieve better performance with your AS/400 when communicating in a wide area network (WAN), you
need to consider the following:
v “Adjusting WAN protocols for optimum AS/400 performance”
v “Adjusting the WAN line speed for optimum AS/400 performance”
v “WAN line speed considerations for IOPs” on page 8
Adjusting WAN protocols for optimum AS/400 performance
Wide area network (WAN) protocols affect the communications performance on AS/400. Let us use X.25
for our example. For each X.25 communications controller, the AS/400 has some processing limitation for
the line, the line speed, and the total number of virtual circuits that can be used. Performance degradation
can be reduced by observing these limitations.
To optimize AS/400 performance for wide area networks, perform these tasks:
v Reduce the total number of frames by using larger frames.
v To take advantage of these large frame sizes, change the MAXFRAME parameter on the line
description (LIND) to reflect the maximum value. For X.25, increase the DFTPKTSIZE and MAXFRAME
parameters to their maximum value.
v Configure a WAN line as full-duplex to provide you with a higher throughput for applications that can
take advantage of this mode. This can also provide higher throughput for multiple users.
v Increase frame relay to capacity.
The data rate for a given protocol may increase as frame size increases. Under these circumstances, the
central processing unit (CPU) and the input/output processor (IOP) do not do as much processing. Fewer
and larger frames also make more efficient use of the communications line (higher effective data rate)
because of fewer overhead bytes and line turn-arounds.
Frame relay has equivalent performance over RS449, X.21, and V.35 assuming equal line speeds and
conditions. Frame relay performance (CPU time) is similar to or slightly better than Synchronous Data Link
Control. For properly tuned large transfer applications, the CPU and IOP have no problem using the line
speed to capacity.
For information about configuring AS/400 communications, see the Communications Configuration
book.
Adjusting the WAN line speed for optimum AS/400 performance
In many cases, the communications line is the largest contributor to overall response time in the wide area
network (WAN). Therefore, you should closely plan and manage its performance. In general, having the
appropriate line speed is the key consideration for gaining the best performance.
To adjust the line speed for your wide area network, perform these tasks:
v Check the difference in performance between half-duplex utilization and full-duplex utilization on the line
description.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 7
Page 14

v For interactive environments, keep line use below 30% to maintain predictable and consistent response
times. Exceeding 50% line use usually slows down response time. The line use can be measured with
the AS/400 performance tools.
v For large transfer environments, or for environments in which only a small number of users are sharing
a line, increase line use to allow for acceptable response times.
v The CPU usage for fractional T1 support and other high-speed WAN connections is similar to any other
line that runs the same type of work. As the speed of a line increases from a traditional low speed to a
high-speed or full T1/E1/J1 speed, performance characteristics may change as follows:
– With interactive transactions, performance may be slightly faster.
– With a large transfer, performance may be significantly faster.
– With a single job, performance may be too serialized to use the entire bandwidth.
– With high throughput, performance is more sensitive to frame size.
– With high throughput, performance is more sensitive to application efficiency.
– With synchronous data link control (SDLC), the communications controller CPU usage increases
because of polling.
Additional considerations for adjusting the wide area network line speed are the following:
v A common misconception about the line speed of each attached communications line is that central
processing unit (CPU) resource is used in a uniform fashion. Exact statements cannot be made about
the number of lines that any given AS/400 model can support.
v Most communications applications use a lot of CPU resource (to process data, to support disk input and
output) and communications line resource (to send and receive data or display I/O). The amount of line
resource that is used is proportional to the total number of bytes that are sent or received on the line.
Some additional CPU resource is used to process the communications software to support the
individual sends (puts or writes) and receives (gets or reads). Communications input/output processor
resource is also used to support the line activity.
v When a single job is running disk operations or doing non-overlapped CPU processing, the
communications link is idle. If several sessions transfer concurrently, then the jobs are more interleaved
and make better use of the communications link.
v Polling is an important consideration for synchronous data link control (SDLC) environments. All SDLC
polling is handled by the communications controller and is governed by parameters in both the line and
controller descriptions.
v For information about AS/400 configuration, see the Communications Configuration
v For more information about performance tools, see the Performance Tools for AS/400 book.
book.
WAN line speed considerations for IOPs
When configuring a communications controller, you should consider both subsystem storage and
aggregate line speed. Subsystem storage is the amount of storage available on the communications
controller. Aggregate line speed is the sum of individual lines speeds that are attached to the
communications controller.
The following information can help you understand network line speed considerations for input/output
processors (IOPs).
v For interactive environments, you should not exceed 60% use on the communications IOP. Exceeding
this threshold in a large transfer environment or with a small number of concurrent users may still offer
acceptable performance. Use the AS/400 performance tools to get the utilization.
v You can attach multiple IOPs to an AS/400 system. The maximum number of IOPs that can be attached
is determined by the AS/400 model. It is important to distribute the work load across several IOPs if the
performance capabilities of a single IOP is exceeded.
v Even though an IOP can support certain configurations, a given AS/400 model may not have enough
system resource (for example, CPU processing capacity) to support the work load over the lines.
v The use of larger frames generally improves large transfer performance in terms of capacity for the
communications IOP and in terms of system response time. The amount of time that the IOP spends
8 Version 5
Page 15
processing a larger frame is only slightly more than the amount needed to process a smaller frame. If
you use larger frames to transfer a single system message or block of data, decreases the total number
of frames required to complete the transfer.
v The values for IOP use in synchronous data link control (SDLC) environments do not necessarily
increase consistently with the number of work stations or with the workload. An IOP can spend more
time polling when the application is not using the line. It is possible to see a relatively high IOP use at
low throughput levels.
v For information on AS/400 configuration, see the Communications Configuration
v For more information on performance tools, see the Performance Tools for AS/400
book.
book.
Improving local area network performance
To achieve better performance with your AS/400 when communicating in a local area network (LAN), you
need to consider the following.
v “Adjusting LANs for optimum communications performance”
v “Adjusting LAN lines for optimum communications performance”
v “LAN line speed considerations for IOPs” on page 10
Adjusting LANs for optimum communications performance
Local area networks (LAN) affect the communications performance on AS/400. Improvements to LAN
input/output (IOPs) in the areas of increased central processing unit (CPU) time, IOP capacity, and support
of IOP assist make them more efficient. This efficiency allows advanced program-to-program
communications (APPC) to send request units to the IOP, passing the processing cost of processing frame
to the IOP.
The following information can help you understand the protocol considerations for local area networks.
v A Data Link Control (DLC) can achieve a significantly higher data rate than other supported line types.
This is due to the desirable combination of having a high media speed along with large frame sizes.
v When several sessions use a line or LAN concurrently, the aggregate data rate may be higher than
when only one session is used.
v To achieve good performance in a multi-user interactive LAN environment, you should manage the
number of active users so that LAN media use does not exceed 50%. (A 25% utilization is
recommended for Ethernet environments because of media collisions that causes the program to loop).
Operating at higher utilization may decrease response time because of excess queueing time for the
line. In a large transfer environment in which a small number of users contend for the line, a higher line
use may still offer acceptable performance.
For more information about AS/400 configuration, see the Communications Configuration
book.
Adjusting LAN lines for optimum communications performance
Several parameters in the line description (LIND) and the controller description (CTLD) play an important
role in system performance that you can change.
The following information can help you to understand the line considerations for local area networks.
v MAXFRAME on the line description (LIND) and the controller description (CTLD): Maximizing the frame
size in a LAN environment supplies the best performance for large transfers. A large frame size does
not negatively affect performance for small transfers. Configure both the AS/400 system and the other
link station for large frames. Otherwise, of the two maximum frame size values, the smaller is used
when you transfer data. Bridges may also limit the maximum frame size. You should change the default
value from 1994 to a larger size.
v LANMAXOUT on the CTLD (for advanced program-to-program communications (APPC) environments):
This parameter governs how often the sending system waits for an acknowledgment. The LANACKFRQ
Chapter 3. Optimizing communications performance 9
Page 16
parameter value on one system should never have a greater value than the LANMAXOUT parameter
value on the other system. The parameter values of the sending system should match the values on the
receiving system.
v Setting appropriate values for the LANMAXOUT parameter along with the LAN acknowledgment
frequency (LANACKFRQ) parameter for both the sending stations and receiving stations is essential for
optimal performance. Other values may decrease throughput by 50% or even more if conditions trigger
time-outs.
v LANWDWSTP for advanced program-to-program communications (APPC) on the controller description
(CTLD): If there are network congestion or overruns to certain target system adapters, then increasing
the value from the default of *NONE to 2 or more may improve performance.
In general, setting the LANMAXOUT parameter value to *CALC or 2 offers the best performance for
interactive environments and adequate performance for larger transfer environments.
v For large transfer environments, changing the LANMAXOUT value may significantly increase
performance. As starting points, use the following guidelines:
– When you are communicating with a recent model personal computer, increase the LANMAXOUT
parameter, but keep the LANACKFRQ parameter set to *CALC. For older models of personal
computers, use *CALC for both values to limit buffer overruns.
– If LANACKFRQ and LANMAXOUT parameter values are changed without noticeable performance
improvements, change the values back to *CALC.
For more information on AS/400 communications, see the Communications Configuration
book.
LAN line speed considerations for IOPs
When configuring an AS/400 system with communications lines and local area networks (LANs), you
should not overload an input/output processor (IOP) to prevent possible system performance bottlenecks.
The following information can help you to understand the line speed considerations for IOPs.
v The integrated PC server performance is similar to the 2619 and the 2617 IOPs for host LAN functions.
For send and receive scenarios, performance is equivalent. For large transfers, the 6506 IOP is slightly
faster than the 2619 TRLAN IOP, but slightly slower than the 2617 Ethernet IOP. These differences are
not significant enough to choose one over the other.
v The 100 Mbps Ethernet support provides the best LAN performance. The IOP can be optimally
configured to have an aggregate transfer rate of 27 Mbps. Multiple concurrent large transfers may be
required to drive at that rate.
v When analyzing communications performance that includes the 2619 TRLAN IOP, you should be aware
that resources other than the IOP use can become the bottleneck.
v You should have the highest capacity IOP available for file serving. You should have the highest
capacity IOP available for environments that use many communications input and output operations for
each transaction. The highest capacity IOP also minimizes the overall response time.
See the following references for more detail:
v For more information about AS/400 communications, see the Communications Configuration book.
v For more information on IOP performance, see the Performance Tools for AS/400 book.
Improving data path performance
To assess the performance of your data path, you may want to review the following topics:
v Considerations for subsystem configuration for error recovery performance
v Communications performance considerations for interactive jobs
v Consider communications performance for batch jobs
10 Version 5
Page 17

v Mix interactive and batch jobs on a wide area network line
v Performance considerations for AnyNet communications
v Subsystems
Considerations for subsystem configuration for error recovery performance
Each piece of work that runs on the AS/400 system is called a job. Each job is a single, identifiable
sequence of processing actions that represents a single use of the system. The basic types of jobs
performed are interactive jobs, batch jobs, spooling jobs, autostart jobs, and prestart jobs.
Jobs that run in subsystems do all work that is performed on the AS/400. As the number of users on the
system increases, it becomes important for you to consider how the communications and interactive
subsystems should be configured.
The configuration of subsystems has little impact in normal data path operations. However, multiple
subsystems can provide multiple processes to do cleanup and recovery when error conditions occur. This
can result in improved performance.
As the number of users on the system increases, you must consider the importance of how subsystems
are configured:
v Consider limiting the number of devices that are serviced by a single subsystem. Between 200 and 300
devices for each subsystem are recommended. Use the following recommendations to divide these
users:
– The number of users in any given subsystem
– The connectivity used to access the system
– The type of work the users do
– The geographic location of the users
v Create additional communications and interactive subsystems to split the work into multiple subsystems.
v The work that is performed in the QCMN subsystem is for connecting and disconnecting from the
system. Error recovery considerations are important in the configuration of the communications
subsystem.
v To prevent a subsystem from ever allocating a device, ensure that there are no workstation or type
entries for the devices that you do what allocated by that subsystem.
v Only use the AT(*ENTER) option if you must allow jobs to transfer into that subsystem.
v For each subsystem you have defined, you need to identify which users will run in which subsystems.
Use the Add Work Station Entry (ADDWSE) command and the Remove Work Station Entry (RMVWSE)
command. You can set up work stations entries that identify which devices that subsystem should
allocate, as well as which devices a subsystem should not allocate.
Note: You can use the ADDWSE commands while the subsystem is active. However, subsystems do not
reallocate device locks dynamically. Eventually, it may be necessary to end and restart the
subsystems to have the device locks allocated to the desired subsystem.
To specify the devices a communications subsystem should allocate:
ADDCMNE SBSD(libname/sbsname) DEV(devname*) MODE(modename)
To specify the devices a communications subsystem should not allocate:
ADDCMNE SBSD(libname/sbsname) DEV(devname*) MODE(modename) MAXACT(0)
Note: Database and file servers run only in QSERVER. Do not attempt to allocate sessions running over
the QSERVER mode description. You can do this by adding the following communication entry to
your subsystem:
ADDCMNE (SBSD(libname/sbsname) DEV(devname*) MODE(QSERVER) MAXACT(0)
See the following example for a way of configuring your communications subsystem.
Chapter 3. Optimizing communications performance 11
Page 18

Example: Communications subsystem configuration
1. Create a duplicate of QCMN:
CRTDUPOBJ OBJ(QCMN) FROMLIB(QSYS) OBJTYPE(*SBSD) TOLIB(MYLIB) NEWOBJ(MYCMN)
2. Set up the communication entries:
ADDCMNE SBSD(MYLIB/MYCMN) DEV(PC*)
ADDCMNE SBSD(MYLIB/MYCMN) DEV(PC*) MODE(QSERVER) MAXACT(0)
ADDCMNE SBSD(QSYS/QCMN) DEV(PC*) MODE(QPCSUPP) MAXACT(0)
3. If desired, update your system startup program to start your new subsystems automatically.
Communications performance considerations for interactive jobs
An interactive job is one that uses a keyboard and character-type display. If a job needs the user to type
on the keyboard and display character results, that job is probably considered interactive. Interactive in this
sense means that the job and the user depend on each other to get the work done.
To optimize communications performance for interactive jobs, consider the following:
v Attach work stations through communications requires more CPU overhead than 5250 local
workstations.
v Use a twinaxial controller to provide better performance than an American National Standard Code for
Information Interchange (ASCII) controller.
v Keep the line utilization below 30 percent for best performance when interactive users are attached.
This will maintain predictable and consistent response times. Exceeding 50 to 60 percent line utilization
will usually cause unacceptable response times.
If your system has interactive users who are connected many different ways, you should consider
configuring your interactive subsystems to separate the users. Local workstation, remote workstations,
5250 display station pass-through, or Telnet are some examples of these types of connections that should
be separated. When you configure interactive subsystems, identify how you want the interactive users to
be separated and create the appropriate subsystem descriptions.
During error recovery, when many users risk losing their sessions at one time, an interactive subsystem
can be very busy performing device recovery. This device recovery can adversely affect the work of other
users in the subsystem who would otherwise be unaffected by the failure. Therefore, you may need to
change how the interactive subsystems are configured. However, multiple subsystems can provide multiple
processes to do cleanup and recovery when error conditions occur. This can result in improved
performance.
The example below shows how to configure an interactive subsystem to allocate devices that begin with
devname* and present a signon display on those display devices:
ADDWSE SBSD(libname/sbsname) WRKSTNDEV(devname*) AT(SIGNON)
Use the following example to configure an interactive subsystem so that the device name devname* is not
allocated and a signon display does not appear.
ADDWSE SBSD(libname/sbsname) WRKSTNDEV(devname*) AT(*ENTER)
Adding workstation entries with AT(*ENTER) allows you to use the Transfer Job (TFRJOB) function into
that subsystem. If the TFRJOB function is not required or necessary, there is no need to add the
workstation entries with AT(*ENTER).
To specify the devices an interactive subsystem should allocate when the subsystem is started:
ADDWSE SBSD(libname/sbsname) WRKSTN(devname*) AT(*SIGNON)
To specify the devices an interactive subsystem should not allocate when the subsystem is started:
ADDWSE SBSD(libname/sbsname) WRKSTN(devname*) AT(*ENTER)
v See the following example for a way of configuring your interactive subsystem.
12 Version 5
Page 19

Example: Interactive subsystem configuration
1. Create a subsystem description:
CRTSBSD SBSD(MYLIB/MYINTER) POOLS((1 *BASE) (2 *INTERACT))
2. Create a class
CRTCLS CLS(MYLIB/MYCLASS) RUNPTY(20)
3. add routing entries to your subsystem:
ADDRTGE SBSD(MYLIB/MYINTER) SEQNBR(10) CMPVAL(QCMDI) PGM(QSYS/QCMD) POOLID(2)
ADDRTGE SBSD(MYLIB/MYINTER) SEQNBR(9999) CMPVAL(*ANY) PGM(QSYS/QCMD) POOLID(2)
4. Create a job queue, and add the job queue entry to your new subsystem:
CRTJOBQ JOBQ(MYLIB/MYJOBQ)
ADDJOBQE SBSD(MYLIB/MYINTER) JOBQ(MYLIB/MYJOBQ) MAXACT(200)
5. Set up the workstation name entries. Remove all the *ALL workstation type entries first, and then add
the appropriate workstation name entries:
RMVWSE SBSD(QSYS/QINTER) WRKSTNTYPE(*ALL)
ADDWSE SBSD(QSYS/QINTER) WRKSTN(QPADEV*)
ADDWSE SBSD(MYLIB/MYINTER) WRKSTN(PC*)
6. If desired, update your system startup program to start your new subsystems automatically.
Communications performance considerations for batch jobs
Each piece of work run on the AS/400 system is called a job. Each job is a single, identifiable sequence of
processing actions that represents a single use of the system. The basic types of jobs that are performed
are interactive jobs, batch jobs, spooling jobs, autostart jobs, and prestart jobs.
Batch jobs are predefined groups of processing actions that are submitted to the system to be performed
with little or no interaction between the user and the system. Batch jobs can be tuned for optimized
performance.
To optimize batch jobs for communications, consider the following:
v Break the application into pieces and having multiple batch threads (jobs) operate concurrently.
v Reduce the number of open and close operations, input and output operations.
v If you have a considerable amount of main storage available, consider using the Set Object Access
(SETOBJACC) command. This command preloads the complete database file, database index, or
program into the assigned main storage pool if sufficient storage is available. The objective is to
improve performance by eliminating disk-read/write operations.
v Try to limit the number of communications input and output operations by doing fewer (and perhaps
larger) application sends and receives when communications lines are used.
v Block the data in the application. Try to place the application on the same system as the frequently
accessed data.
For more information about batch job performance, see the Communications Management
book.
Mixing interactive and batch jobs on a WAN line
When interactive users and large transfers are running on a communications line concurrently, you may
need to change configuration parameters. You should be able to configure AS/400 communications to work
with interactive and batch jobs.
To mix interactive and batch jobs on a wide area network (WAN) line, consider the following to keep
interactive performance acceptable:
v Use Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking (APPN) transmission priority to prioritize the interactive user’s
transfer over that of the large transfer. This is the preferred method to transfer batch and interactive
jobs.
Chapter 3. Optimizing communications performance 13
Page 20

v Change the request/response unit size to a lower value for the large transfer. This parameter setting
optimizes response time at the expense of large transfer performance.
v Reduce the pacing values for the large transfer to slow it down, which allows the interactive users more
windows for getting on the line.
Note: The overall central processing unit time increases for the large transfer.
For more information about AS/400 communications, see the Communications Configuration
book.
Performance considerations for AnyNet communications
AnyNet communications is a good performance factor for you to consider. It is more expensive to use than
any of the OS/400 protocols because you spend twice as much to run two protocols.
To optimize AnyNet performance, consider the following:
v For send and receive pairs, the most efficient use of an interface is with its own protocol stack. That is,
intersystem communications function (ICF) and common programming interface communications (CPI
Communications) perform the best with advanced program-to-program communications (APPC). There
is additional CPU time when the crossover between the protocols processes.
v Each communications interface performs differently depending on the scenario. ICF and CPI
Communications perform the best with APPC.
Note: An alternative to AnyNet communications is to have SNA and TCP/IP running parallel or over the
same lines in your network. Hence, performance implications can be surpassed by not using
AnyNet.
For more information about AnyNet/400 sockets, see the book Sockets Programming
Setting up the AnyNet environment
AnyNet/400 is an AnyNet family product. These products allow you to use application programs that are
written for a certain communications protocol but also run over non-native communications protocols
without changing (or even re-compiling) the application program. The choice of the destination address
controls whether the request is sent over the native protocols or through the AnyNet code and on to a
non-native protocol.
.
To configure Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) over advanced program-to-program
communications (APPC), you need to take two basic actions:
1. Identify the set of IP addresses to route over the SNA network.
2. Tell the system how to convert the IP address to the SNA format.
For more information about APPC Over TCP/IP Configuration, see the APPC Programming book.
For more information about IPX Support, see the Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX) Support.
For related information about AnyNet, see:
“AnyNet communications for the AS/400 system”
“Performance considerations for AnyNet communications”
AnyNet communications for the AS/400 system
AnyNet is an IBM implementation of the Multiprotocol Transport Networking (MPTN) architecture, such as
AnyNet/2 and AnyNet/Multiple Virtual Storage (MVS). AnyNet capability allows applications and associated
services that use application programming interfaces, such as sockets, intersystem communications
function (ICF), or CPI Communications, the flexibility to use alternative network protocols, such as
Systems Network Architecture (SNA) or TCP/IP. AnyNet is a family of products that allow applications that
14 Version 5
Page 21

are written for one type of network protocol to run over a different type of network protocol. For example,
without AnyNet, your choice of application program interface (API) dictates your choice of network
protocol, or your choice of network protocol dictates your choice of APIs.
AnyNet allows you to mix and match applications with network protocols. In fact, you can do this without
changing your application programs. Your destination address (such as a remote location) determines the
type of network protocol to use.
v AnyNet/400 Sockets
This support converts TCP/IP addresses to SNA addresses that are based on tables that are configured
by the network administrator. Programs supported include File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Simple Mail
Transfer Protocol (SMTP), Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), PING, and user-written
sockets programs.
– TCP/IP over SNA
– TCP/IP over IPX
v AnyNet/400 APPC (advanced program-to-program communications)
This support allows programs that are written to traditional APPC APIs (such as ICF,
CPI-Communications, and CICS/400) to be run over non-APPC networks. The application program uses
Location names to specify the source and destination address. A TCP/IP domain name server converts
these location names to IP addresses. Programs supported include distributed data management
(DDM), Distributed Relational Database Architecture (DRDA), SNA distribution services (SNADS),
display station pass-through, Client Access, user-written CPI-Communications programs, and
user-written ICF programs .
– APPC over TCP/IP
– APPC over IPX
For more information about using both AnyNet and nonAnyNet sockets, see the Sockets Programming
book.
Subsystems
A subsystem is a single, predefined operating environment through which the system coordinates work
flow and resource usage. OS/400 can contain several that are independent operating subsystems. The
run-time characteristics of a subsystem are defined in an object that is called a subsystem description.
IBM supplies several subsystem descriptions that can be used with or without modification:
QINTER
Used for interactive jobs
QBATCH
Used for batch jobs
QBASE
Used for both interactive and communications batch jobs
QCMN
Used for communications batch jobs
QSERVER
File server system
QSYSWRK
Used for general system work
QUSRWRK
This is the default subsystem used for TCP/IP Client Access Host Servers that used to run in
QSYSWRK.
A new subsystem can also be defined with the Create Subsystem Description (CRTSBSD) command.
Chapter 3. Optimizing communications performance 15
Page 22

For more information about creating subsystems, see the Work Management book.
16 Version 5
Page 23

Chapter 4. Communications applications
Communications applications that are used in an APPC (advanced program-to-program) environment are
also available to be used in an APPN and HPR environment; only the method by which data is transported
is changed. APPC delivers the data from applications higher in the SNA layers down to APPN for
transportation through the network. User-written APPC applications and distributed data management
(DDM) are fully supported in an APPN and HPR environment. The topic, Application programming
interface (API) performance considerations gives a more complete discussion of APPC applications.
When you encounter problems that indicate that the route to the remote location cannot be found, you can
attempt to make the connection again with the Start Pass-Through (STRPASTHR) command. See the
topic, Solving remote communication problems using STRPASTHR for more information.
For information on Connecting Windows 95/NT Clients to your AS/400, see Client Access.
User written APPC applications
APPN performs many functions in a communications environment. Therefore, it is important to consider
time-out parameters in APPC programs which use ICF. In particular, it may be important to increase the
WAITFILE parameter for these applications so that they do not time-out while waiting for APPN functions
to be performed.
APPN function is transparent to APPC programs using APPN take advantage of the following routing
functions:
v Non-adjacent nodes appear adjacent and so APPC programs may communicate directly to programs in
non-adjacent nodes (without any APPC programs on the intermediate nodes).
v Performance is improved for APPC programs with session endpoints that are not physically adjacent in
the network.
v APPC programs may communicate directly to programs in nodes in an adjacent APPN network through
network nodes.
Distributed data management (DDM)
DDM is a function of the operating system that allows an application program or user on one system to
use database files stored on remote systems. The systems must be connected by a communications
network, and the remote systems must also be using DDM.
DDM on the AS/400 allows application programs or users to:
v Access data files that reside on remote systems (target systems). The remote systems can also access
data files on the local AS/400 system.
v An application can add, change, and delete data records in a file that exist on a target system.
v Create, delete, or rename files on a remote system.
v Copy a file from one system to another.
When DDM is in use, neither the application program nor the program user needs to know if the file that is
needed exists locally or on a remote system. Remote and local file processing are essentially handled the
same way.
Application program interface (API) performance considerations
To achieve better performance with your AS/400, you need to consider the application programming
interface (API) available on the AS/400. To optimize APPC performance, consider the following:
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 17
Page 24

v Using larger sends for a given large transfer (record sizes) provides a higher application data rate and
decreases CPU time. With the larger record size, the CPU has less processing to do because there are
fewer application reads and writes to transfer the same amount of data.
v If a value of *CALC is selected for maximum Systems Network Architecture (SNA) request/response unit
(RU), the system selects an efficient size compatible with the frame size. The frame size is on the line
description that you choose. Changing the RU size to a value other than *CALC may negate the
performance feature.
v Compression with APPC should be used with caution and only for slower speed wide area network
(WAN) environments. Many suggest that compression should be used with speeds 19.2 kbps and
slower.
v If you are doing tasks that include repetitive, small puts; better performance is achieved if you use ICF
or CPI Communications.
See the following topics for a more complete discussion of APPC applications:
v Performance considerations for Intersystem Communications Function
v Performance considerations for Common Programming Interface communications
For information about AS/400 communications, see the Communications Configuration
For more information about CICS/400, see the CICS/400 Administration and Operations Guide
book.
.
Performance considerations for intersystem communications function
You can use intersystem communications function (ICF) to write application programs that you want to
communicate with advanced program-to-program communications (APPC). ICF also provides
program-to-device communications between the AS/400 system and hardware devices. You must
determine which system is to send data first before you write the program. ICF data management handles
the communication functions and the data for your program. In particular, ICF should be used to do tasks
that include repetitive, small inputs.
To optimize ICF performance, consider the following:
v Eliminate unused record formats.
v Use separate record formats instead of multipurpose record formats with option indicators.
v Code to use the same record format for repeated operations.
v Set the maximum program devices equal to 1.
v Use a nonshared file.
v Use a separate indicator area.
v The use of the ICF keywords force data and confirm should be minimized.
v Use the Request to Send keyword only when necessary.
v Use the Invite Only keyword when soliciting input from multiple devices, otherwise use the Read
keyword instead.
v If using the Invite keyword to solicit from multiple program devices, follow it with a Read-from-invited
operation, not a Read operation.
To create device descriptions to get your system set up for ICF, do the following:
1. Type the appropriate Create Device Description commands on the AS/400 command line and press
F4.
2. Use the online help information to choose the parameter values.
3. Press Enter. The device description is created.
For more information about ICF, see
v “Application program interface (API) performance considerations” on page 17
v ICF Programming
18 Version 5
Page 25

Performance considerations for Common Programming Interface Communications
You can use Common Programming Interface Communications (CPI Communications) to write application
programs that you want to communicate with advanced program-to-communications (APPC). The interface
makes use of the System Network Architecture (SNA) LU (logical unit) 6.2 architecture to do the following:
v Establish a conversation
v Send and receive data
v Exchange control information
v End a conversation
v Notify a partner program of errors.
Intersystem communications feature (ICF) and CPI Communications programs have similar performances
for small data transfers.
To optimize CPI Communications application programs, do the following:
v Minimize the use of flush and confirm.
v Receive a compile record and parse it in your buffer.
v Do not use multiple receive calls to receive a single record.
v Use Request-to-Send only when necessary.
To add or change communications entries to get the system set up for CPI Communications, do the
following:
1. Type appropriate command on the AS/400 command line and press F4.
v Add Communications Entry (ADDCMNE)
v Remove Communications Entry (RMVCMNE)
v Change Communications Entry (CHGCMNE)
2. Use the online help information to change, add, or remove parameter values.
3. Press Enter. The communications entries are added, changed or removed.
For more information about configuring CPI Communications, see:
v “Application program interface (API) performance considerations” on page 17
v CICS/400 Administration and Operations Guide
Chapter 4. Communications applications 19
Page 26

20 Version 5
Page 27

Chapter 5. Communicating with host systems
You can configure the AS/400 system to communicate with a host system by matching AS/400
parameters.
Another option for AS/400 users is Dependent LU Requester Support (DLUR). DLUR allows dependent
secondary logical units (LU 0, 1, 2, and 3) an entry point into the APPN network. DLUR support gives the
appearance of having an adjacent connection to VTAM, but allows traversing the APPN network through
intermediate nodes. To configure DLUR, see the page Configuring Dependent LU Requester (DLUR).
Matching AS/400 parameters for a host system
You can configure the AS/400 system to communicate with a host system. This configuration requires the
coordination of parameters and values. The list contains only those configuration prompts and parameters
that require coordination on both the AS/400 and the host system. In addition, some of the parameters that
are listed may not apply to your particular configuration.
For examples of connecting an AS/400 to a host system, see “Examples: Connecting AS/400 to a host
system” on page 26.
For information about configuring host systems, see the manuals VTAM Installation and Resource
Definition, SC23-0111, and Network Control Program Resource Definition Reference, SC30-3254.
v “Matching AS/400 line description parameters for a host system”
v “Matching AS/400 controller description parameters for a host system” on page 23
v “Matching AS/400 device description parameters for a host system” on page 24
v “Matching AS/400 mode and class-of-service description parameters for a host system” on page 25
v For more information on AS/400 parameters, see Communications Configuration
.
Matching AS/400 line description parameters for a host system
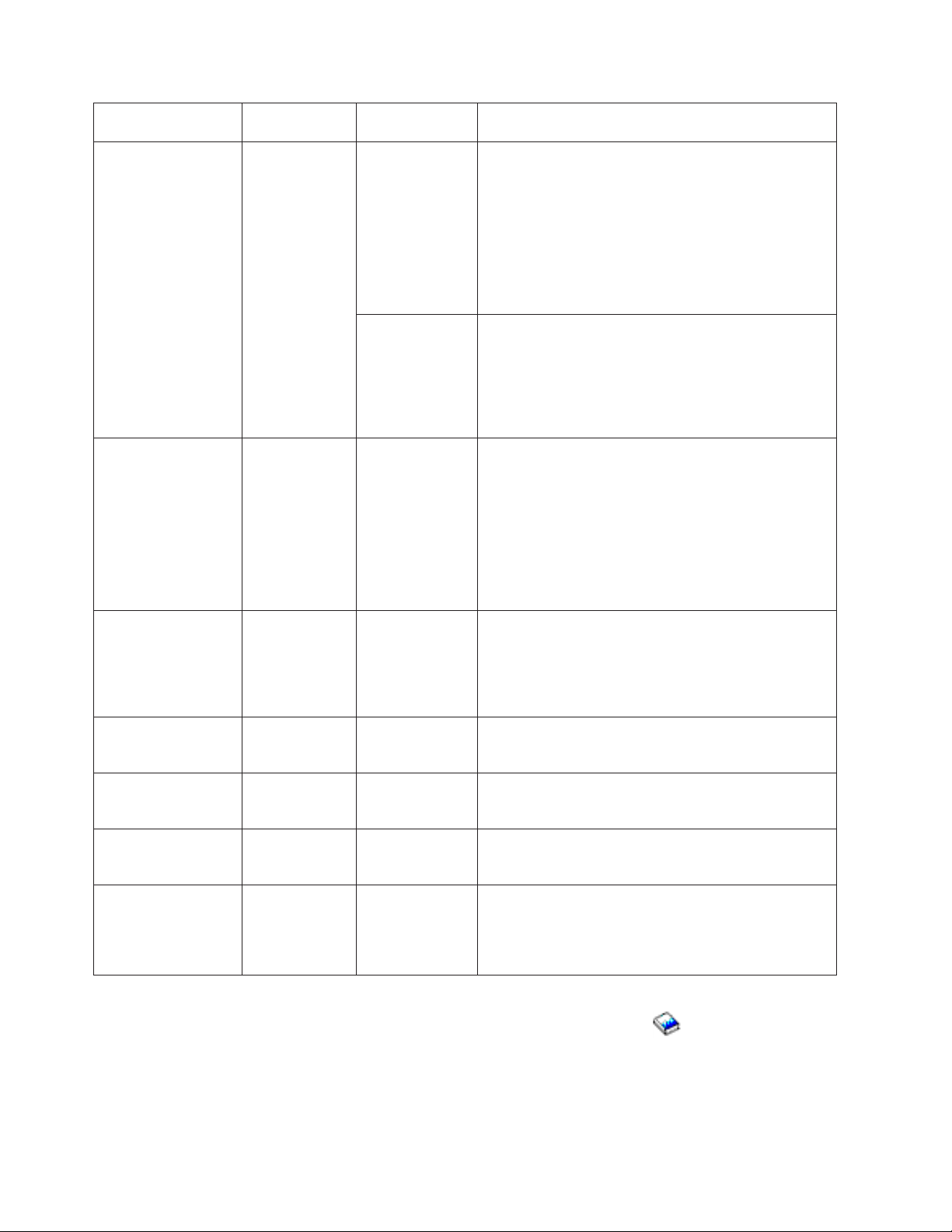
You must match host system communications configuration parameters with AS/400 values. A description
of these AS/400 values are in the following table. For information about configuring host systems, see the
manuals VTAM Installation and Resource Definition, SC23-0111, and Network Control Program Resource
Definition Reference, SC30-3254.
You can specify some host system parameters on multiple definition statements, such as the GROUP,
LINE, PU, and LU. The following table lists only the lowest level definition statement that is used by the
host system.
To configure an AS/400 to a host system:
v See “Examples: Connecting AS/400 to a host system” on page 26 for an example of connecting an
AS/400 to a host system.
v Use the following table for the line description parameter.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 21
Page 28
AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Local adapter address ADPTADR PATH DIALNO
Connection type CNN GROUP DIAL
Parameter
Host Definition
Statement Host Parameter
Host DIALNO parameter is a concatenation of:
SSAP/DSAP/remote-adapter-address.
AS/400 CRTLINTRN command ADPTADR value must
match the remote-adapter-address portion of the host
DIALNO parameter. The DSAP portion of the DIALNO
parameter must correspond to the SSAP value
specified on the AS/400 controller description.
PU MACADDR
For 9370/LAN only, the AS/400 line description
ADPTADR must match the host MACADDR parameter.
MACADDR can be coded as an 8- or 12-digit
hexadecimal number; the 8-digit variation assumes
4000 in the first four positions (4000xxxxxxxx).
If the AS/400 line description CNN parameter is
*SWTPP or *SHM, DIAL=YES must be specified for the
host system; if CNN is *MP or *NONSWTPP, DIAL=NO
must be specified.
If CNN(*MP) is specified, the SERVICE
macroinstruction must be used to specify the sequence
in which stations are served.
Exchange identifier EXCHID PU IDBLK, IDNUM
The AS/400 block number (digits 1-3 of the EXCHID) is
always 056. The remaining 5 digits (based on the
system serial number if *SYSGEN is used) are
specified in the IDNUM parameter.
Line speed LINESPEED LINE SPEED
Line speeds specified for each system must match.
Maximum frame size MAXFRAME PU MAXDATA
Values specified for each system must match.
NRZI data encoding NRZI LINE NRZI
Values specified for each system must match.
Station address STNADR PU ADDR
AS/400 system station address must be unique within
host PU definitions. (Ignored within 9370/LAN
environment.)
For more information on AS/400 parameters, see Communications Configuration .
For steps on how to create a line description, see “Creating a line description” on page 5.
22 Version 5
Page 29
Matching AS/400 controller description parameters for a host system
You must match host system communications configuration parameters with AS/400 values. A description
of the AS/400 values are in the following table. For information about configuring host systems, see the
manuals VTAM Installation and Resource Definition, SC23-0111, and Network Control Program Resource
Definition Reference, SC30-3254.
You can specify some host system parameters on multiple definition statements, such as the GROUP,
LINE, PU, and LU. The following table lists only the lowest level definition statement that is used by the
host system.
To configure an AS/400 to a host system:
v See “Examples: Connecting AS/400 to a host system” on page 26 for an example of connecting an
AS/400 to a host system.
v Use the following table for the controller description parameter.
AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Adjacent link station ADJLNKSTN PU name
LAN remote adapter
address
Destination service
access point
Parameter
ADPTADR LINE LOCADD
DSAP PORT SAPADDR
Host Definition
Statement Host Parameter
AS/400 adjacent link station name must match the
name assigned to the PU macro instruction in the host
system switched major node definition. This match is
required if AS/400 host controller description specifies
RMTCPNAME(*ANY), SWITCHED(*YES) or
SNBU(*YES), and LINKTYPE is *SDLC or *IDLC.
This parameter should be specified only if the host
system is running VTAM Version 4 Release 1 or later
and NCP Version 6 Release 2 or later.
Values specified for each system must match. If
LOCADD is specified, ECLTYPE=PHYSICAL must also
be specified on the GROUP definition statement.
PORT MACADDR
For 9370/LAN only, the AS/400 controller description
ADPTADR must match the host MACADDR parameter.
MACADDR can be coded as an 8- or 12-digit
hexadecimal number; the 8-digit variation assumes 4000
in the first four positions (4000xxxxxxxx).
For 9370/LAN only, the AS/400 controller description
DSAP must match the host SAPADDR parameter.
Local exchange
identifier
The SAPADDR parameter is a decimal value (4-252);
the AS/400 value is specified as a 2-digit hexadecimal
number.
LCLEXCHID PU IDBLK, IDNUM
For parallel connections only. Required if the AS/400
system specifies RMTCPNAME(*ANY),
SWITCHED(*YES), and LINKTYPE is *SDLC or *IDLC.
The LCLEXCHID specified must match the values
specified in the switched major node definition PU
macro instruction.
Chapter 5. Communicating with host systems 23
Page 30
AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Maximum frame size MAXFRAME GROUP MAXDATA
Remote control point
name
Remote network
identifier
Source service access
point
SSCP identifier SSCPID VTAMLST SSCPID
Parameter
RMTCPNAME VTAMLST SSCPNAME
RMTNETID VTAMLST NETID
SSAP PU SAPADDR
Host Definition
Statement Host Parameter
Values specified for each system must match.
Required only if APPN(*YES). AS/400 controller
description value must match SSCPNAME specified in
the Virtual Telecommunications Access Method (VTAM)
start options list (ATCSTRyy).
Required only if APPN(*YES). AS/400 controller
description value must match NETID specified in the
VTAM start options list (ATCSTRyy).
For 9370/LAN only, the AS/400 controller description
DSAP must match the host SAPADDR parameter.
The SAPADDR parameter is a decimal value (4-252);
the AS/400 value is specified as a 2-digit hexadecimal
number.
Required if APPN(*YES) or if RMTCPNAME is not
specified. AS/400 controller description value must
match SSCPID specified in the VTAM start options list
(ATCSTRyy).
The SSCPID parameter is a decimal value (0-65535);
the AS/400 value is specified as a 12-digit hexadecimal
number, of which the first 2 digits are 05.
Station address STNADR PU ADDR
AS/400 system station address must be unique within
host PU definitions. Controller description STNADR
must match the value specified in the line description.
For more information on AS/400 parameters, see Communications Configuration .
Matching AS/400 device description parameters for a host system
You must match host system communications configuration parameters with AS/400 values. A description
of the AS/400 values are in the following table. For information about configuring host systems, see the
manuals VTAM Installation and Resource Definition, SC23-0111, and Network Control Program Resource
Definition Reference, SC30-3254.
You can specify some host system parameters on multiple definition statements, such as the GROUP,
LINE, PU, and LU. The following table lists only the lowest level definition statement that is used by the
host system.
To configure an AS/400 to a host system:
v See “Examples: Connecting AS/400 to a host system” on page 26 for an example of connecting an
AS/400 to a host system.
24 Version 5
Page 31

v Use the following table for the device description parameter.
AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Local location name LCLLOCNAME DFHTCT NETNAME
Local location address LOCADR LU LOCADDR
Location password LOCPWD DFHTCT BINDPWD
Dependent location
name
Mode description
name
Remote location name RMTLOCNAME LU LOGAPPL
Parameter
DEPLOCNAME LU LU
MODE MODEENT LOGMODE
Host Definition
Statement Host Parameter
AS/400 LCLLOCNAME value must match CICS/VS
terminal control table NETNAME parameter and the
label used on the LU definition statement.
Values specified for each system must match.
The LOCADDR parameter is a decimal value (0-255);
the AS/400 value is specified as a 2-digit hexadecimal
number.
Values specified for each system must match.
This parameter is only used for DLUR support. This
value is optional. If specified, it must match LUNAME
received on ACTLUREQUEST.
AS/400 mode description name must be defined in the
host logon mode table using the LOGMODE parameter
on the MODEENT macro instruction. The mode name
must also be included in the CICS/VS terminal control
table (DFHTCT) MODENAM parameter.
Values specified for each system must match.
Remote network
identifier
RMTNETID BUILD NETID
Values specified for each system must match.
For more information on AS/400 parameters, see Communications Configuration.
Matching AS/400 mode and class-of-service description parameters for a host system
You must match host system communications configuration parameters with AS/400 values. A description
of the AS/400 values are in the following table. For information about configuring host systems, see the
manuals VTAM Installation and Resource Definition, SC23-0111, and Network Control Program Resource
Definition Reference, SC30-3254.
You can specify some host system parameters on multiple definition statements, such as the GROUP,
LINE, PU, and LU. The following table lists only the lowest level definition statement that is used by the
host system.
To configure an AS/400 to a host system:
v See “Examples: Connecting AS/400 to a host system” on page 26 for an example of connecting an
AS/400 to a host system.
v Use the following table for the mode and class-of-service description parameter.
Chapter 5. Communicating with host systems 25
Page 32

AS/400 Prompt
Mode description
name
Class-of-service
description name
AS/400
Parameter
MODD MODEENT LOGMODE
COSD MODEENT COS
Host Definition
Statement Host Parameter
AS/400 mode description name specified on the AS/400
CRTMODD command (MODD parameter) must be
defined in the host logon mode table using the
LOGMODE parameter on the MODEENT macro
instruction. The mode name must also be included in
the CICS/VS terminal control table (DFHTCT)
MODENAM parameter.
AS/400 class-of-service description name specified on
the AS/400 Create Class-of-Service Description
(CRTCOSD) command (COSD parameter) and
CRTMODD command (COS parameter) must be
defined in the host logon mode table using the COS
parameter on the MODEENT macro instruction. The
class-of-service description must also be defined in the
VTAM class-of-service table.
For more information on AS/400 parameters, see Communications Configuration .
Examples: Connecting AS/400 to a host system
Configuration parameters must be coordinated when you connect an AS/400 system to a host system.
Example 1: AS/400 to host system over a nonswitched SDLC line.
This diagram shows the AS/400 values that need to match the VTAM values when you use a nonswitched
SDLC line.
26 Version 5
Page 33

Example 2: AS/400 to host system over a token-ring line.
This diagram shows the AS/400 values that need to match the VTAM values when you use a token-ring
line.
Chapter 5. Communicating with host systems 27
Page 34

Example 3: AS/400 system for DLUR support with the host system.
28 Version 5
Page 35

This diagram shows the AS/400 values that need to match the VTAM values when you use AS/400 DLUR
and VTAM.
Example 4: AS/400 with APPN connection to VTAM
This diagram shows the AS/400 values that need to match the VTAM values when you connect with
APPN.
Chapter 5. Communicating with host systems 29
Page 36

30 Version 5
Page 37

Configuring dependent LU requester (DLUR)
Dependent LU Requester (DLUR) allows dependent secondary logical units (LU 0, 1, 2, and 3) an entry
point into the APPN network. DLUR support gives the appearance of having an adjacent connection to
VTAM, but allows traversing the APPN network through intermediate nodes.
Note: DLUR uses logmode CPSVRMGR. This is created internally as part of the APPN and DLUR
support. If CPSVRMGR exists as a user-defined logmode on any of the systems in your network, it
must be deleted. Use the Work with Mode Descriptions (WRKMODD) command and specify the
option to delete CPSVRMGR.
To configure the AS/400 system to communicate with DLUR, perform these steps:
1. Configure a host controller description
2. Configure device descriptions
3. Verify that an APPN connection into the network exists (host or APPC controller with *YES specified for
the APPN parameter).
Configuring the host controller description
Use the Create Controller Description (SNA Host) (CRTCTLHOST) command to create the controller
description. If you have already created a controller description for such functions as 3270 emulation or
NRF, you must change the link type to *DLUR. Follow these steps:
1. Retrieve the configuration description for the Dependent LU Requester (DLUR) controller description
using the Retrieve Configuration Source (RTVCFGSRC) command.
2. Edit the member to change the link type to *DLUR.
3. Convert the source to a CL program.
4. Create the CL program using the CRTCLPGM command.
5. Delete the configuration using the DLTCTLD command.
6. Call the CL program to create the new configuration.
An explanation of some of the fields on the Create Controller Description (SNA Host) (CRTCTLHOST)
screen are as follows:
Local exchange identifier
Matches the ID block and ID number parameters from the PU definition on VTAM.
Dependent PU name
Matches the name of the PU specified on the PU definition on VTAM.
Note: If the local exchange identifier and the dependent PU name are specified, both must match
the definitions on VTAM. If both parameter values do not match, the ACTPU will be
rejected.
If the *DIAL value is specified for the INLCNN parameter, the primary DLUS name
(PRIDLUS), and either the local exchange identifier (LCLEXCHID), or the dependent PU
name (DEPPUNAME) must be specified.
Control point name and network identifier for the primary DLUS name
Matches the SSCP name and NETID parameters on the VTAM startup options.
For the last step see, Configuring the device descriptions.
Configuring the device descriptions
Use the Create Device Description (CRTDEVDSP) command to create the device.
Dependent location name
Matches the LU name on the LU definition on VTAM.
Chapter 5. Communicating with host systems 31
Page 38

Note: This must match the VTAM LU name with the corresponding local location address
(LOCADDR) on VTAM.
For more information on DLUR see, Dependent LU Requester Support (DLUR).
32 Version 5
Page 39

Chapter 6. Communicating with a remote AS/400 system
Using advanced program-to-program communications (APPC), you can configure the AS/400 system to
communicate with another AS/400 system. This configuration requires the coordination of configuration
parameters and values. Only those configuration prompts and parameters that require coordination on
both the AS/400, and the remote AS/400 system are listed. In addition, some of the parameters that are
listed may not apply to your particular configuration. See the following topics for more information:
v “Matching AS/400 line description parameters for a remote AS/400 system”
v “Matching AS/400 controller description parameters for a remote AS/400 system” on page 35
v “Matching AS/400 device description parameters for a remote AS/400 system” on page 36
For an example of connecting one AS/400 to another AS/400 system, see “Connecting one AS/400 to
another AS/400 system” on page 37.
For more information on AS/400 parameters, see the Communications Configuration
book.
Matching AS/400 line description parameters for a remote AS/400 system
You must coordinate communications configuration parameters between local and remote AS/400 systems.
These parameters are described in the following table. This table shows those prompts and parameters
that must be coordinated when you specify line descriptions for the local and remote AS/400 systems.
To configure a local AS/400 to a remote AS/400:
v See “Connecting one AS/400 to another AS/400 system” on page 37 for an example of connecting one
AS/400 to another AS/400 system.
v Use the following table for the line descriptions.
AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Local adapter address ADPTADR ADPTADR Adapter address of the local system (specified on the
Insert network
address in packets
Data bits per
character
Parameter
ADRINSERT ADRINSERT If X.25 DCE support is specified (X25DCE(*YES) or
BITSCHAR BITSCHAR Values specified for each system must match.
Remote AS/400
Parameter Notes
line description) must be matched at the remote system
in the controller description ADPTADR parameter.
If the AS/400 system uses an Ethernet line through an
8209 LAN Bridge, see ″Appendix C: Local Area Network
Addressing Considerations″ in the Communications
Configurationbook.
X25DCE(*NEG)), ADRINSERT(*YES) should be
specified for both systems.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 33
Page 40

AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Connection initiation CNNINIT CNNINIT If X.25 DCE support is specified (X25DCE(*YES)) for
Duplex DUPLEX DUPLEX Depending on the type of communications used, the
Ethernet standard ETHSTD ETHSTD Values specified for each system must be coordinated.
Exchange identifier EXCHID EXCHID Remote AS/400 controller description EXCHID must
Logical channel
entries
Line speed LINESPEED LINESPEED For asynchronous lines, the line speeds specified for
Modulus MODULUS MODULUS If X.25 DCE support is specified (X25DCE(*YES) or
Parameter
LGLCHLE LGLCHLE If X.25 DCE support is specified (X25DCE(*YES) or
Remote AS/400
Parameter Notes
either system, CNNINIT(*LOCAL) should also be
specified on that system’s line description. The other
system (with X25DCE(*NO) specified) should specify
CNNINIT(*REMOTE) or CNNINIT(*WAIT).
For switched connections, both systems can also
specify X25DCE(*NEG) to negotiate the Distributed
Computing Environment (DCE) and data terminal
equipment (DTE) roles and CNNINIT(*CALLER) to allow
either system to initiate the connection by making the
call.
See the X25DCE parameter for additional
considerations.
values specified for the DUPLEX parameters may need
to be coordinated.
Both systems must specify the same standard (*ETHV2
or *IEEE8023) or at least one system must specify
*ALL.
match the local AS/400 line description EXCHID. The
first three digits of the exchange identifier, known as the
block number, is 056 for the AS/400 line. You can use
the Work with Line Descriptions (WRKLIND) command
to determine this value.
X25DCE(*NEG)), logical channel types and channel
numbers must be coordinated. See also the
considerations for the X25DCE parameter.
each system must match.
X25DCE(*NEG)), modulus values specified for each
system must match.
The values specified for this parameter should match for
all communications types.
Local network address NETADR CNNNBR For switched virtual circuits (SVCs), the NETADR
parameter on the local system line description must
match the CNNNBR parameter on the controller
description for the remote system.
NRZI data encoding NRZI NRZI Values specified for each system must match (*YES or
*NO).
Data link role ROLE ROLE The value specified for the local system line description
ROLE parameter should match the controller description
ROLE parameter specified at the remote system.
Number of stop bits STOPBITS STOPBITS Values specified for each system must match.
Switched connection
type
SWTCNN SWTCNN Values specified for each system must be compatible.
(*DIAL or *ANS must not be specified for both systems.)
34 Version 5
Page 41

AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
X.25 DCE support X25DCE X25DCE If X.25 DCE support is used (X25DCE(*YES)), only one
Parameter
Remote AS/400
Parameter Notes
of the AS/400 line descriptions should specify *YES.
The system specifying X25DCE(*YES) should also
specify CNNINIT(*LOCAL); the other AS/400 system
should specify X25DCE(*NO) and CNNINIT(*REMOTE)
or CNNINIT(*WAIT).
For switched connections, both systems can also
specify X25DCE(*NEG) to negotiate the DCE and DTE
roles, and CNNINIT(*CALLER) to allow either system to
initiate the connection by making the call.
For more information on AS/400 parameters, see the Communications Configuration
book.
For steps on how to create a line description, see “Creating a line description” on page 5.
Matching AS/400 controller description parameters for a remote AS/400 system
You must coordinate communications configuration parameters between local and remote AS/400 systems.
The parameters are described in the following table. This table shows those prompts and parameters that
must be coordinated when you specify controller descriptions for the local and remote AS/400 systems.
To configure a local AS/400 to a remote AS/400:
v See “Connecting one AS/400 to another AS/400 system” on page 37 for an example of connecting one
AS/400 to another AS/400 system.
v Use the following table for the controller descriptions.
AS/400 Prompt
local area network
(LAN) remote adapter
address
AS/400
Parameter
ADPTADR ADPTADR The adapter address specified on the local system
Remote AS/400
Parameter Notes
controller description must match the line description
ADPTADR parameter specified by the remote system.
If the AS/400 system uses an Ethernet line through an
8209 LAN Bridge, see ″Appendix C: Local Area Network
Addressing Considerations″ in the Communications
Configuration
Connection number CNNNBR NETADR For X.25 switched virtual circuits (SVCs), the CNNNBR
parameter on the local system controller description
must match the NETADR parameter on the line
description for the remote system.
Connection password CNNPWD CNNPWD For switched virtual circuits (SVCs), passwords
specified for each system must match.
Destination service
access point
DSAP SSAP DSAP specified for the local AS/400 system must match
the SSAP specified in the remote AS/400 controller
description.
Chapter 6. Communicating with a remote AS/400 system 35
book.
Page 42

AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Exchange identifier EXCHID EXCHID If used, the local AS/400 controller description EXCHID
Initial connection INLCNN INLCNN Values specified for each system must be coordinated;
Link protocol LINKPCL LINKPCL For X.25 connections, values specified for each system
Remote control point
name
Remote network
identifier
Data link role ROLE ROLE The value specified for the local AS/400 controller
X.25 reverse charging RVSCRG RVSCRG Values specified for each system must be coordinated.
Switched network
backup
Source service access
point
Station address STNADR STNADR Values specified for each system must match, unless
Note: For asynchronous controllers (CRTCTLASC command), if the remote system controller description specifies
RMTVFY(*YES), the local system controller description must specify a local identifier (LCLID parameter) and local
location name (LCLLOCNAME parameter). The remote system must also create a configuration list with the LCLID
and LCLLOCNAME values from the local system controller description.
Parameter
RMTCPNAME LCLCPNAME RMTCPNAME specified on the local AS/400 system
RMTNETID LCLNETID RMTNETID specified on the local AS/400 system
SNBU SNBU Values specified for each system must match.
SSAP DSAP SSAP specified for the local AS/400 system must match
Remote AS/400
Parameter Notes
must match the remote AS/400 line description
EXCHID. The first three digits of the exchange identifier,
known as the block number, is 056 for the AS/400 line.
You can use the WRKLIND command to determine this
value.
INLCNN(*ANS) must not be specified for both systems.
must match; both must be *QLLC or *ELLC.
controller description must match the local control point
name specified in the network attributes of the remote
AS/400 system.
controller description must match the local network ID
specified in the network attributes of the remote AS/400
system.
description ROLE parameter must match the remote
AS/400 line description ROLE value.
the DSAP specified in the remote AS/400 controller
description.
both controller descriptions specify ROLE(*NEG).
For more information on AS/400 parameters, see the Communications Configuration book.
Matching AS/400 device description parameters for a remote AS/400 system
You must coordinate communications configuration parameters between local and remote AS/400 systems.
The parameters are described in the following table. This table shows those prompts and parameters that
must be coordinated when you specify device descriptions for the local and remote AS/400 systems.
To configure a local AS/400 to a remote AS/400:
v See “Connecting one AS/400 to another AS/400 system” on page 37 for an example of connecting one
AS/400 to another AS/400 system.
v Use the following table for the device description.
36 Version 5
Page 43

AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Location Password LOCPWD LOCPWD This parameter must match on both the local and
Mode MODE MODE For systems not using APPN (APPN(*NO) specified for
Remote location name RMTLOCNAME LCLLOCNAME For systems not using APPN (APPN(*NO) specified for
Parameter
LCLLOCNAME RMTLOCNAME For systems not using APPN (APPN(*NO) specified for
Remote AS/400
Parameter Notes
the controller and device descriptions), this value must
match the value specified by the RMTLOCNAME
parameter on the remote system device description.
APPC device descriptions are automatically created as
needed by the AS/400 APPN support, when the
following is specified on the controller description:
v APPN(*YES)
v AUTOCRTDEV(*ALL)
remote APPC device.
Note: If you want a value other than *NONE for APPN
devices, this value must be configured on the
QAPPNRMT configuration list.
the controller and device descriptions), this value must
match the value specified by the MODE parameter on
the remote device description.
For systems using APPN (APPN(*YES) specified for the
controller and device descriptions), the specified mode
description must exist on the remote system. The mode
description name need not be specified in the remote
device description.
the controller and device descriptions), this value must
match the value specified by the LCLLOCNAME
parameter on the remote device description.
APPC device descriptions are automatically created as
needed by AS/400 APPN support if APPN(*YES) is
specified for the controller description.
RMTNETID LCLNETID RMTNETID specified on the local AS/400 system device
description must match the local network ID specified in
the network attributes of the remote AS/400 system.
Single session SNGSSN SNGSSN For Element 1 ( single-session device description), this
parameter must match on both the local and remote
APPC device.
Note: If you want a value other than *NO for APPN
devices, this value must be configured on the
QAPPNRMT configuration list.For Element 2 (number of
single-session conversations), this parameter does not
need to match the remote device.
For more information on AS/400 parameters, see the Communications Configuration book.
Connecting one AS/400 to another AS/400 system
Configuration parameters must be coordinated when you specify controller, device, and line descriptions
for the local and remote AS/400.
Example 1: AS/400 to AS/400 using X.25
Chapter 6. Communicating with a remote AS/400 system 37
Page 44

This example shows the matching parameters between an AS/400 connecting to another AS/400 that uses
X.25.
Example 2: AS/400 to AS/400 using SDLC
38 Version 5
Page 45

This example shows the matching parameters between an AS/400 connecting to another AS/400 that uses
SDLC.
Example 3: AS/400 to AS/400 using one-way automatic dialing
This example shows the matching parameters between an AS/400 connecting to another AS/400 that uses
one-way automatic-dial function.
Chapter 6. Communicating with a remote AS/400 system 39
Page 46

40 Version 5
Page 47

Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers
You can configure the AS/400 system to communicate with another AS/400 system, a non-AS/400 system,
or a remote controller. This configuration requires the coordination of configuration parameters and values.
To configure your AS/400 to communicate with remote workstation controllers, see the following:
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for 5494 controllers”
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for 3x74 controller” on page 58
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for finance controllers” on page 62
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for retail controllers” on page 67
Matching AS/400 parameters for 5494 controllers
You must coordinate the configuration parameters and values to configure the AS/400 system to
communicate with a 5494 controller. You can coordinate these values automatically or manually. Pick one
of the ways:
v To automatically connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller, you can use the automatic remote controller
(QAUTORMT) system value.
v To manually connect the AS/400 to a 5494, you can use the following examples and the tables.
The list contains only those configuration prompts and parameters that require coordination on both
AS/400 and the 5494 controller. In addition, some of the parameters that are listed may not apply to
your particular configuration.
–“Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by token-ring”
–“Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by Ethernet” on page 44
–“Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by frame relay” on page 46
–“Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by SDLC” on page 48
–“Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by X.21” on page 52
–“Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by X.25” on page 54
For more information about configuring the 5494, see these books:
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit Planning Guide, GA27-3936
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit User’s Guide, GA27-3852
v Remote Work Station Support
.
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by token-ring
You must coordinate communications configuration parameters between AS/400 and the 5494 controller
that is connected by token-ring. You can coordinate these values automatically or manually. Pick one of
these ways:
v To automatically connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller, you can use the automatic remote controller
(QAUTORMT) system value.
v To manually connect the AS/400 to a 5494:
– See “Example: Connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by token-ring” on page 43 for an
example of connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller by token-ring.
– Use the following table to configure the AS/400 to a 5494 controller that is connected by token-ring.
The following table gives a description of the parameters . The related fields and subfields from the
5494 configuration display, the AS/400 configuration value, and the matching 5494 value to enter are
shown.
For more information about configuring the 5494, see these books:
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit Planning Guide, GA27-3936,
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit User’s Guide, GA27-3852
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 41
Page 48

AS/400
Prompt AS/400 Parameter
Local
adapter
address
local area
network
(LAN)
remote
adapter
address
Destination
service
access
point
Local
location
name
Remote
control
point name
Remote
network
identifier
Remote
location
name
ADPTADR H1 5 - - Values specified in the AS/400
ADPTADR 15 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
(DSAP) F - - - Values specified for the AS/400
LCLLOCNAME H1 1 - - Values specified for the AS/400
RMTCPNAME 13 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
RMTNETID 11 3 - - Values specified for the AS/400
RMTLOCNAME 12 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
5494
AS/400
Value 5494 Value NotesField Subfield
line description (CRTLINTRN
command) and for the 5494
Remote Controller Unit must
match.
CRTCTLAPPC command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match.
CRTCTLAPPC command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match.
CRTCTLRWS command and for
the 5494 Remote Control Unit
must match. This will probably
match LCLLOCNAME in the
network attributes. This value
will probably match the
LCLLOCNAME in the network
attributes.
CRTCTLAPPC command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match.
CRTCTLAPPC and
CRTCTLRWS commands and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match. This will
probably match LCLNETID in
the network attributes and H1:2.
CRTCTLRWS command and for
the 5494 Remote Control Unit
must match.
42 Version 5
Page 49

AS/400
Prompt AS/400 Parameter
Link type LINKTYPE AA - *LAN 4 5494 configuration values must
5494
AS/400
Value 5494 Value NotesField Subfield
match the values specified for
the LINKTYPE parameter on the
CRTCTLAPPC command. For
advanced program-to-program
communications (APPC)
controllers that specify
LINKTYPE(*SDLC), the value
specified in the 5494
configuration must be
compatible with the physical
interface (INTERFACE
parameter) specified on the
CRTLINSDLC command.
Select 4 for the network
connections.
Example: Connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by token-ring
Configuration parameters must be coordinated when you connect an AS/400 system to a 5494 controller
that is connected by token-ring.
The following diagram shows the AS/400 parameters and 5494 parameters that need to match when you
use token-ring.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 43
Page 50

Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by Ethernet
You must coordinate communications configuration parameters between AS/400 and the 5494 controller
that is connected by Ethernet. A description of these parameters are in the following table. Then the
related fields and subfields from the 5494 configuration display, and the AS/400 configuration value and
the matching 5494 value entered in the display subfield. You can coordinate these values manually or
automatically. Pick one of these ways:
44 Version 5
Page 51

v To automatically connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller, you can use the automatic remote controller
(QAUTORMT) system value.
v To manually connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller:
– See “Example: Connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by Ethernet” for an example of
connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller by Ethernet.
– Use the following table to configure the AS/400 to a 5494 controller that is connected by Ethernet.
For more information about configuring the 5494, see these books:
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit Planning Guide, GA27-3936
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit User’s Guide, GA27-3852
AS/400
Prompt
Local
adapter
address
LAN remote
adapter
address
Local
location
name
Remote
control
point name
Remote
network
identifier
Remote
location
name
AS/400
Parameter
ADPTADR H1 5 - - Values specified in the AS/400 line
ADPTADR 15 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
LCLLOCNAME H1 1 - - Values specified for the AS/400
RMTCPNAME 13 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
RMTNETID 11 3 - - Values specified for the AS/400
RMTLOCNAME 12 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
5494
AS/400
Value 5494 Value NotesField Subfield
description (CRTLINTRN command)
and for the 5494 Remote Controller
Unit must match.
CRTCTLAPPC command and for
the 5494 Remote Control Unit must
match.
CRTCTLRWS command and for the
5494 Remote Control Unit must
match. This will probably match
LCLLOCNAME in the network
attributes. This value will probably
match the LCLLOCNAME in the
network attributes.
CRTCTLAPPC command and for
the 5494 Remote Control Unit must
match.
CRTCTLAPPC and CRTCTLRWS
commands and for the 5494
Remote Control Unit must match.
This will probably match LCLNETID
in the network attributes and H1:2.
CRTCTLRWS command and for the
5494 Remote Control Unit must
match.
Example: Connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by Ethernet
Configuration parameters must be coordinated when you connect an AS/400 system to a 5494 controller.
Example: AS/400 to 5494 controller that is connected by Ethernet
The following diagram shows the AS/400 parameters and 5494 parameters that need to match when you
use Ethernet.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 45
Page 52

Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by frame relay
You must coordinate the communications configuration parameters between AS/400 and the 5494
controller connected by frame relay. A description of the parameters are in the following table. Then,
related fields and subfields from the 5494 configuration display and the AS/400 configuration value and the
matching 5494 value. You can coordinate these values automatically or manually. Pick one of these ways:
v To automatically connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller, you can use the automatic remote controller
(QAUTORMT) system value.
v To manually configure the AS/400 to a 5494 controller:
– See “Example: Connecting an AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by frame relay” on page 47 for
an example of connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller by frame relay.
– Use the following table to configure the AS/400 to a 5494 that is connected by frame relay.
For more information about configuring the 5494, see these books:
46 Version 5
Page 53

v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit Planning Guide, GA27-3936
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit User’s Guide, GA27-3852
AS/400
Prompt AS/400 Parameter
Local
adapter
address
LAN
remote
adapter
address
Local
location
name
Link type LINKTYPE AA - *LAN 4 5494 configuration values must
ADPTADR H1 5 - - Values specified in the AS/400
ADPTADR 15 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
LCLLOCNAME H1 1 - - Values specified for the AS/400
5494
AS/400
Value 5494 Value NotesField Subfield
line description (CRTLINTRN
command) and for the 5494
Remote Controller Unit must
match.
CRTCTLAPPC command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match.
CRTCTLRWS command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match. This will
probably match LCLLOCNAME
in the network attributes. This
value will probably match the
LCLLOCNAME in the network
attributes.
match the values specified for
the LINKTYPE parameter on
the CRTCTLAPPC command.
For APPC controllers that
specify LINKTYPE(*SDLC), the
value specified in the 5494
configuration must be
compatible with the physical
interface (INTERFACE
parameter) specified on the
CRTLINSDLC command.
Select 4 for the network
connections.
Remote
control
point name
Remote
network
identifier
Remote
location
name
RMTCPNAME 13 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
CRTCTLAPPC command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match.
RMTNETID 11 3 - - Values specified for the AS/400
CRTCTLAPPC and
CRTCTLRWS commands and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match. This will
probably match LCLNETID in
the network attributes and
H1:2.
RMTLOCNAME 12 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
CRTCTLRWS command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match.
Example: Connecting an AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by frame relay
Configuration parameters must be coordinated when you connect an AS/400 system to a 5494 controller.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 47
Page 54

The following diagram shows the AS/400 parameters and 5494 parameters that need to match when you
use frame relay.
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by SDLC
You must coordinate communications configuration parameters between AS/400 and the 5494 controller
that is connected by SDLC. These parameters are described in the following table. Then the related fields
and subfields from the 5494 configuration display are listed next. These values are followed by the AS/400
configuration value and the matching 5494 value to be entered in the display subfield. You can coordinate
these values automatically or manually. Pick one of these ways:
v To automatically connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller, you can use the automatic remote controller
(QAUTORMT) system value.
v To manually connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller:
– See “Example: Connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by SDLC” on page 50 for an
example of connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller by SDLC
– Use the following table to configure the AS/400 connected by SDLC.
48 Version 5
Page 55

For more information about configuring the 5494, see these books:
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit Planning Guide, GA27-3936
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit User’s Guide, GA27-3852
AS/400
Prompt
Connection
type
Duplex Duplex 3 2 *HALF 0
NRZI data
encoding
Local
location
name
Link type LINKTYPE AA - *SDLC 0,2,3 5494 configuration values must
AS/400
Parameter
CNN 3 1 *NONSWTPP
NRZI 3 4 *YES 0
LCLLOCNAME H1 1 - - Values specified for the AS/400
5494
AS/400 Value 5494 Value NotesField Subfield
*MP
*SWTPP 1
3*MP 0
*NONSWTPP
*SWTPP
*FULL 1
*NO 1
0
1
CRTCTLRWS command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match. This will
probably match LCLLOCNAME
in the network attributes. This
value will probably match the
LCLLOCNAME in the network
attributes.
match the values specified for
the LINKTYPE parameter on
the CRTCTLAPPC command.
For APPC controllers that
specify LINKTYPE(*SDLC), the
value specified in the 5494
configuration must be
compatible with the physical
interface (INTERFACE
parameter) specified on the
CRTLINSDLC command.
Remote
control
point name
Remote
network
identifier
Select 0 for communications
using SDLC lines other than
X.21 connections.
RMTCPNAME 13 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
CRTCTLAPPC command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match.
RMTNETID 11 3 - - Values specified for the AS/400
CRTCTLAPPC and
CRTCTLRWS commands and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match. This will
probably match LCLNETID in
the network attributes and H1:2.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 49
Page 56

AS/400
Prompt
Remote
location
name
Station
address
AS/400
Parameter
RMTLOCNAME 12 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
STNADR 2 - - - Values specified in the AS/400
5494
AS/400 Value 5494 Value NotesField Subfield
CRTCTLRWS command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match.
controller description and for
the 5494 Remote Control Unit
must match. This value must
also be specified as the last 2
digits of the AS/400 EXCHID
parameter.
Example: Connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by SDLC
Configuration parameters must be coordinated when you connect an AS/400 system to a 5494 controller.
The following diagram shows the AS/400 parameters and 5494 parameters that need to match when you
use SDLC.
50 Version 5
Page 57

Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 51
Page 58

Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by X.21
You must coordinate communications configuration parameters between AS/400 and the 5494 remote
controller that is connected by X.21. These parameters are described in the following table. Then the
related fields and subfields from the 5494 configuration display are listed next. These values are followed
by the AS/400 configuration value and the matching 5494 value to be entered in the display subfield. You
can coordinate these values automatically or manually. Pick one of these ways:
v To automatically connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller, you can use the automatic remote controller
(QAUTORMT) system value.
v To manually connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller:
– See “Example: Connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by X.21” on page 53 for an
example of connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller by X.21.
– Use the following table to configure the AS/400 to a 5494 controller by X.21.
For more information about configuring the 5494, see these books:
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit Planning Guide, GA27-3936
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit User’s Guide, GA27-3852,
AS/400
Prompt
Connection
number
Local
location
name
Remote
control
point name
Remote
network
identifier
Remote
location
name
AS/400
Parameter
CNNNBR 15 - - -
LCLLOCNAME H1 1 - - Values specified for the AS/400
RMTCPNAME 13 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
RMTNETID 11 3 - - Values specified for the AS/400
RMTLOCNAME 12 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
5494
AS/400 Value 5494 Value NotesField Subfield
Values specified for the AS/400
CRTCTLAPPC command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match. If the AS/400
CRTCTLAPPC command
specifies CNNNBR(*DC), the
X.21 direct-call user facility
must be used to make the
connection.
CRTCTLRWS command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match. This will
probably match LCLLOCNAME
in the network attributes. This
value will probably match the
LCLLOCNAME in the network
attributes.
CRTCTLAPPC command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match.
CRTCTLAPPC and
CRTCTLRWS commands and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match. This will
probably match LCLNETID in
the network attributes and H1:2.
CRTCTLRWS command and
for the 5494 Remote Control
Unit must match.
52 Version 5
Page 59

AS/400
Prompt
Link type LINKTYPE AA - *X21 4 5494 configuration values must
Station
address
AS/400
Parameter
STNADR 2 - - - Values specified in the AS/400
5494
AS/400 Value 5494 Value NotesField Subfield
match the values specified for
the LINKTYPE parameter on
the CRTCTLAPPC command.
Select 2 for X.21 network
connections.
controller description and for
the 5494 Remote Control Unit
must match. This value must
also be specified as the last 2
digits of the AS/400 EXCHID
parameter.
Example: Connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by X.21
Configuration parameters must be coordinated when you connect an AS/400 system to a 5494 controller.
The following diagram shows the AS/400 parameters and 5494 parameters that need to match when you
use X.21.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 53
Page 60

Matching AS/400 parameters for a 5494 connected by X.25
You must coordinate communications configuration parameters between the AS/400 and the 5494
controller that is connected by X.25. These parameters are described in the following table. Then the
related fields and subfields from the 5494 configuration display are listed next. These values are followed
by the AS/400 configuration value and the matching 5494 value to be entered in the display subfield. You
can coordinate these values automatically or manually. Pick one of these ways:
v To automatically connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller, you can use the automatic remote controller
(QAUTORMT) system value.
v To manually connect the AS/400 to a 5494 controller:
– See “Example: Connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by X.25” on page 56 for an
example of connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller by X.25.
– Use the following table to connect an AS/400 to a 5494 controller that is connected by X.25.
For more information about configuring the 5494, see these books:
v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit Planning Guide, GA27-3936
54 Version 5
Page 61

v IBM 5494 Remote Control Unit User’s Guide, GA27-3852
AS/400
Prompt
Default
packet size
AS/400
Parameter
DFTPKTSIZE 5 1 64 0
5494
AS/400
Value 5494 Value NotesField Subfield
128 1
256 2
512 3
Local
location
name
LCLLOCNAME H1 1 - - Values specified for the AS/400
CRTCTLRWS command and for the
5494 Remote Control Unit must
match. This will probably match
LCLLOCNAME in the network
attributes. This value will probably
match the LCLLOCNAME in the
network attributes.
X.25 link
protocol
LINKPCL 6 2 *QLLC 01
*ELLC 10
Link type LINKTYPE AA - *X25 1 5494 configuration values must
match the values specified for the
LINKTYPE parameter on the
CRTCTLAPPC command. For
APPC controllers that specify
LINKTYPE(*SDLC), the value
specified in the 5494 configuration
must be compatible with the
physical interface (INTERFACE
parameter) specified on the
CRTLINSDLC command.
X.25
network
level
Remote
control
point name
Remote
network
identifier
Remote
location
name
Select 1 for communications using
X.25 lines.
NETLVL 6 5 1988 0 Used for X.25 communications only.
1984 1
1980 2
RMTCPNAME 13 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
CRTCTLAPPC command and for
the 5494 Remote Control Unit must
match.
RMTNETID 11 3 - - Values specified for the AS/400
CRTCTLAPPC and CRTCTLRWS
commands and for the 5494
Remote Control Unit must match.
This will probably match LCLNETID
in the network attributes and H1:2.
RMTLOCNAME 12 - - - Values specified for the AS/400
CRTCTLRWS command and for the
5494 Remote Control Unit must
match.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 55
Page 62

AS/400
Prompt
Station
address
AS/400
Parameter
STNADR 2 - - - Values specified in the AS/400
5494
AS/400
Value 5494 Value NotesField Subfield
controller description and for the
5494 Remote Control Unit must
match. This value must also be
specified as the last 2 digits of the
AS/400 EXCHID parameter.
Example: Connecting AS/400 to a 5494 controller connected by X.25
Configuration parameters must be coordinated when you connect an AS/400 system to a 5494 controller.
The following diagram shows the AS/400 parameters and 5494 parameters that need to match when you
use X.25.
56 Version 5
Page 63

Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 57
Page 64

Matching AS/400 parameters for 3x74 controller
You must match the AS/400 configuration parameters with some configuration questions and sequence
numbers when you configure the 3174 and 3274 controllers.
For an example of connecting an AS/400 to a 3174 retail controller, see “Example: Connecting an AS/400
to a 3174 control unit” on page 61.
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for a 3174 controller”
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for a 3274 controller” on page 60
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 3174 controller
You must match the AS/400 configuration parameters with the configuration questions and sequence
numbers to configure the 3174 controller. These parameters are described in the following table.
For more information about configuring the 3174 controllers, see these books:
v 3174 Subsystem Control Unit Customizing Guide
v 3174 Establishment Controller Supplemental Customer Information for Configuration Support C Release
4 Ethernet Attachment, GA27-3994 has information about Ethernet support.
To configure the AS/400 to a 3174 controller:
v See “Example: Connecting an AS/400 to a 3174 control unit” on page 61 for an example of connecting
an AS/400 to a 3174 retail controller.
v Use the following table to connect an AS/400 to a 3174 remote controller.
3174
AS/400
Prompt
LAN remote
adapter
address
1
AS/400
Parameter
ADPTADR 084, 106 Ethernet Address
Configuration
Questions Notes
If the AS/400 system uses an Ethernet line to connect to the
3174 controller, use table C-3 on page C-4 in ″Appendix C:
Local Area Network Addressing Considerations″ of the
Communications Configuration
value specified for question 084. Specify the converted
address for the ADPTADR parameter on the CRTCTLRWS
or CRTCTLAPPC command.
Token-Ring Network Address of the 3174
If the AS/400 system uses a Token-Ring network line to
connect to the 3174 controller, values specified for question
106 and for the ADPTADR parameter on the CRTCTLRWS
or CRTCTLAPPC command must match.
If the AS/400 system uses an Ethernet line through an 8209
LAN Bridge, see ″Appendix C: Local Area Network
Addressing Considerations″ in the Communications
Configuration book.
book to convert the
58 Version 5
Page 65

AS/400
Prompt
Local adapter
address
Connection
number
3174
AS/400
Parameter
Configuration
Questions Notes
ADPTADR 107 Token-Ring Network Address of the Gateway
If the AS/400 system uses a Token-Ring network line to
connect to the 3174 controller, values specified for question
107 and for the ADPTADR parameter on the CRTLINTRN
command must match.
If the AS/400 system uses an Ethernet line through an 8209
LAN Bridge, see ″Appendix C: Local Area Network
Addressing Considerations″ in the Communications
Configuration book, for information about specifying the
ADPTADR parameter on the CRTLINETH command.
CNNNBR 423 Host DTE Address (HNAD)
For X.25 lines, the numbers specified on the CRTLINX25
command and in question 423 must match.
368 X.21 Switched Short-Hold Mode Dial Number
For X.21 short-hold mode connections, the numbers
specified on the CRTCTLRWS command and in question
368 must match.
424 3174 DTE Address
For X.25 SVCs, the connection number specified on the
CRTCTLRWS command and in question 424 must match.
Destination
DSAP 940 Ring Address Assignment
service access
point
The value specified for the DSAP parameter on the
CRTCTLRWS command must match the SAP@ specified for
the 3174 on the Ring Address Assignment display. Used for
token-ring only.
Exchange
EXCHID 215 Physical Unit Identification
identifier
For switched connections, the 5-digit hexadecimal value
specified for question 215 must match the last 5 digits of the
exchange identifier specified on the CRTCTLRWS
command.
Link type LINKTYPE 101 Host Attachment (3174)
Values specified on the CRTCTLRWS command and for
question 101 must match as follows:
v LINKTYPE(*SDLC), 101 = 2
v LINKTYPE(*X25), 101 = 3
v LINKTYPE(*LAN), 101 = 7 (token ring)
v LINKTYPE(*LAN), 101=8(Ethernet)
Modem data
MODEMRATE 318 Full- or Half-Speed Transmission
rate select
The values specified for the MODEMRATE parameter on the
CRTLINSDLC and CRTLINX25 commands must match
question 318 as follows:
v If MODEMRATE(*FULL), 318 = 0
v If MODEMRATE(*HALF), 318 = 1
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 59
Page 66

3174
AS/400
Prompt
Local network
address
NRZI data
encoding
Source service
access point
Short-hold
mode
Station address STNADR 104 Control Unit Address
AS/400
Parameter
NETADR 423 Host DTE Address (HNAD)
NRZI 313 NRZ or NRZI Encoding
SSAP 940 Ring Address Assignment
SHM 367 X.21 Switched Short-Hold Mode
Configuration
Questions Notes
For X.25 SVCs, the network address specified on the
CRTLINX25 command and in question 423 must match.
For SDLC lines only, the values specified on the
CRTLINSDLC command and in question 313 must match as
follows:
v If NRZI(*NO), 313 = 0
v If NRZI(*YES), 313 = 1
The value specified for the SSAP parameter on the
CRTCTLRWS command must match the SAP@ associated
with the Ring@ (adapter address) of the AS/400 system on
the Ring Address Assignment display. Used for token-ring
only.
Values specified on the CRTCTLRWS command and in
question 367 match as follows:
v If SHM(*NO), 367 = 0
v If SHM(*YES), 367 = 2
Value specified for question 104 must match the STNADR
specified on the CRTCTLRWS command.
Switched
connection
Note: If you are using a 3174 Model 1L Gateway to connect an AS/400 system to a host system on a Token-Ring,
the value specified for item 900 (Token-Ring Network Address of the Gateway) must match the value specified for
the ADPTADR parameter on the CRTCTLHOST command.
SWITCHED 317 Telecommunication Facilities
Values specified on the CRTLINSDLC command and in
question 317 match as follows:
v If SWITCHED(*NO), 317 = 0
v If SWITCHED(*YES), 317 = 1
Matching AS/400 parameters for a 3274 controller
You match the AS/400 configuration parameters with the configuration questions and sequence numbers
to configure the 3274 controller. These parameters are described in the following table.
For more information about configuring the 3274 controller, see the 3274 Control Unit Planning, Setup, and
Customizing Guide.
To configure the AS/400 to a 3274 controller:
v See “Example: Connecting an AS/400 to a 3174 control unit” on page 61 for an example of connecting
an AS/400 to a 3174 retail controller.
v Use the following table to connect an AS/400 to a 3274 controller.
60 Version 5
Page 67

3274
AS/400
Prompt
Connection
number
Exchange
identifier
X.25 link
protocol
Link type LINKTYPE 331 BSC/SDLC/X.25 Protocol
Local network
address
Modem data
rate select
NRZI data
encoding
Short-hold
mode
Station address STNADR 302 Control Unit Address
AS/400
Parameter
CNNNBR 411 3274 DTE Address
EXCHID 215 Physical Unit Identification
LINKPCL 403 Logical Link Control
NETADR 410 Host DTE Address (HNAD)
MODEMRATE 318 Full- or Half-Speed Transmission
NRZI 313 NRZ or NRZI Encoding
SHM 362 X.21 Switched Options
Sequence
Number Notes
For X.25 SVCs, the connection number specified on the
CRTCTLRWS command and in sequence number 411 must
match.
For switched connections, the 5-digit hexadecimal value specified
for sequence number 215 must match the last 5 digits of the
exchange identifier specified on the CRTCTLRWS command.
For X.25 connections, values specified must match. Specify
LINKPCL(*QLLC) on the CRTCTLRWS command; specify 1
(QLLC) for sequence number 403.
Values specified on the CRTCTLRWS command and in
sequence number 331 must match as follows:
v If LINKTYPE(*SDLC), 331 = 1
v If LINKTYPE(*X25), 331 = 2
For X.25 SVCs, the network address specified on the
CRTLINX25 command and in sequence number 410 must match.
The values specified for the MODEMRATE parameter on the
CRTLINSDLC and CRTLINX25 commands must match sequence
number 318 as follows:
v If MODEMRATE(*FULL), 318 = 0
v If MODEMRATE(*HALF), 318 = 1
For SDLC lines only, the values specified must match as follows:
v If NRZI(*NO), 313 = 0
v If NRZI(*YES), 313 = 1
If SHM(*YES) is specified on the CRTCTLRWS command, digit 7
or 8 of question 362 must be set to 1. (For example, xxxxxx10
indicates that the DCE is supported for direct calls.)
Value specified for item 302 must match that specified on the
CRTCTLRWS command.
Example: Connecting an AS/400 to a 3174 control unit
Configuration parameters must be coordinated when you connect an AS/400 system to a 3174 controller.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 61
Page 68

The following diagram shows the AS/400 parameters and 3174 parameters that need to match when you
use token-ring.
Matching AS/400 parameters for finance controllers
You must coordinate several parameter values that are specified for the AS/400 system and in the
controller configuration for finance communications.
For an example of connecting an AS/400 to a 4701 finance controller, see “Example: Connecting AS/400
to a finance network” on page 67.
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for 470x finance controllers”
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for FBSS finance controllers” on page 64
Matching AS/400 parameters for 470x finance controllers
You must match the AS/400 configuration parameters with the configuration (CPGEN) for the 4701 and
4702 finance controllers. These parameters are described in the following table.
AS/400 prompts are listed in alphabetical order by parameter name; the AS/400 commands on which the
parameters are specified are included in the rightmost column of the table.
For more information about configuring the 4700 controllers, see Volume 6 of the 4700 Finance
Communication System Controller Programming Library, GC31-2068.
To configure the AS/400 to a 470x finance controller:
v See “Example: Connecting AS/400 to a finance network” on page 67 for an example of connecting an
AS/400 to a 4701 finance controller.
v Use the following table to connect an AS/400 to a 4701 finance controller.
62 Version 5
Page 69

AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Connection
Parameter 4700 Macro 4700 Parameter
CNN COMLINK ACB
type
For SDLC finance communications, if the line is switched
(CNN(*SWTPP) on the CRTLINSDLC command or
SWITCHED(*YES) on the CRTCTLFNC command), include the
SWM value on the ACB parameter (ACB = SWM).
Exchange
EXCHID X25CKT XID
identifier
The values specified for the 4700 and the AS/400 system must
match. The block number for the 4700 (first 3 digits of the
AS/400 EXCHID parameter) must be 057.
The 4700 parameter values are decimal numbers; the AS/400
values are hexadecimal.
X.25 link
LINKPCL X25CKT LLC
protocol
For X.25 finance communications, the LLC parameter must
specify QLLC for the type of logical link control.
LINKPCL(*QLLC) must also be specified on the AS/400
CRTCTLFNC command.
Link type LINKTYPE COMLINK TYPE
4700 TYPE parameter must match the LINKTYPE parameter
specified on the AS/400 CRTCTLFNC command.
v If LINKTYPE(*SDLC), specify TYPE = 4502.
v If LINKTYPE(*X25), specify TYPE = 1424.
Local location
LOCADR STATION ID
address
If the optional LUA parameter is not specified, the value
specified for the 4700 ID parameter must match the value
specified for the LOCADR parameter on the AS/400 create
device description command. If LUA is specified, the LUA
parameter value must match the LOCADR parameter.
The 4700 parameter values are decimal numbers; the AS/400
values are hexadecimal.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 63
Page 70

AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Maximum
frame size
NRZI data
encoding
Station address STNADR X25CKT CUA
Parameter 4700 Macro 4700 Parameter
MAXFRAME COMLINK CNL
Value specified for the 4700 CNL parameter must be
coordinated with the value specified for the AS/400 MAXFRAME
parameter on the CRTCTLFNC command. Because the
MAXFRAME parameter includes transmission and request
header lengths, MAXFRAME should be 9 bytes longer than the
4700 MWL parameter.
MWL
Value specified for the 4700 MWL parameter must be
coordinated with the value specified for the AS/400 MAXFRAME
parameter on the CRTCTLFNC command. Because the
MAXFRAME parameter includes transmission and request
header lengths, MAXFRAME should be 9 bytes longer than the
4700 MWL parameter.
If the AS/400 maximum length of request unit (MAXLENRU
parameter) specified for device descriptions attached to the 4700
controller is larger than the MAXFRAME parameter specified for
the controller description, the 4700 should also specify
OPTIONS=(SEGMENT).
NRZI COMLINK ACB
For SDLC finance communications, if the line does not use NRZI
data encoding (NRZI(*NO) on the CRTLINSDLC command),
include the DCE value on the ACB parameter (ACB = DCE).
The values specified for the AS/400 STNADR parameter on the
CRTCTLFNC command must match the physical address (CUA)
parameter specified for the 4700.
Matching AS/400 parameters for FBSS finance controllers
You must coordinate several parameter values that are specified for the AS/400 system and IBM Financial
Branch System Services (FBSS) finance controllers in the controller configuration. The following table
shows those AS/400 configuration parameters that must match values on the SDLC, Token-Ring, or
X.25DLC configuration displays for FBSS controllers.
AS/400 prompts are listed in alphabetical order by parameter name; the AS/400 commands on which the
parameters are specified are included in the rightmost column of the table.
For more information about configuring FBSS controllers, see the IBM Financial Branch System Services
Installation Planning and Administration Guide, SC19-5173.
For more information about configuring the 4700 controllers, see Volume 6 of the 4700 Finance
Communication System Controller Programming Library, GC31-2068.
To configure the AS/400 to a FBSS finance controller:
v See “Example: Connecting AS/400 to a finance network” on page 67 for an example of connecting an
AS/400 to a 4701 finance controller.
v Use the following table to connect an AS/400 to a 4701 finance controller.
64 Version 5
Page 71

FBSS
AS/400 Prompt
AS/400
Parameter
Configuration
Display FBSS Prompt
LAN adapter address ADPTADR Token Ring
Communications
PC address
If the AS/400 system uses a Token-Ring network line
to connect to the FBSS controller, values specified for
the FBSS and on the ADPTADR parameter on the
CRTLINTRN command must match.
If the AS/400 system uses an Ethernet line through
an 8209 LAN Bridge, see ″Appendix C: Local Area
Network Addressing Considerations″ in the
Connection type CNN SDLC
Communications
Destination service
access point
DSAP Token Ring
Communications
Duplex DUPLEX SDLC
Communications
Communications Configuration
book.
Host/37xx/4700 address
If the AS/400 system uses a Token-Ring network line
to connect to the FBSS controller, values specified for
the FBSS and on the ADPTADR parameter on the
CRTLINTRN command must match.
If the AS/400 system uses an Ethernet line through
an 8209 LAN Bridge, see ″Appendix C: Local Area
Network Addressing Considerations″ in the
Communications Configuration
book.
Switched line
Values specified for the FBSS and AS/400
configurations must match:
v If the FBSS response is Yes, CNN(*SWTPP) must
be specified for the CRTLINSDLC command and
SWITCHED(*YES) for the CRTCTLFNC command.
v If the FBSS response is No, CNN(*NONSWTPP) or
CNN(*MP) must be specified for the CRTLINSDLC
command and SWITCHED(*NO) for the
CRTCTLFNC command.
Service access point for PC
Values specified for the FBSS and for the DSAP
parameter on the CRTCTLFNC command must
match.
Line mode
Values specified for the FBSS and AS/400
configurations must match:
v If the FBSS response is Turn. required,
DUPLEX(*HALF) must be specified for the
CRTLINSDLC command.
v If the FBSS response is CRTS (Continuous request
to send), DUPLEX(*FULL) must be specified for
the CRTLINSDLC command.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 65
Page 72

FBSS
AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Exchange identifier EXCHID SDLC
Link type LINKTYPE Communication
Local location address LOCADR Session-Id and LU
Parameter
Configuration
Display FBSS Prompt
Communications
Servers
Assignments
Identification block and Identification number
The values specified for the FBSS controller must
match the value specified in the EXCHID parameter
of the CRTCTLFNC command. The EXCHID
parameter must be specified as: xxxyyyyy, where xxx
matches the FBSS Identification block and yyyyy
matches the FBSS Identification number.
Data Link Control
Values specified for the FBSS and AS/400
configurations must match:
v If the FBSS response is SDLC, LINKTYPE(*SDLC)
must be specified for the CRTCTLFNC command.
v If the FBSS response is TRDLC, LINKTYPE(*LAN)
must be specified for the CRTCTLFNC command.
v If the FBSS response is X25DLC, LINKTYPE(*X25)
must be specified for the CRTCTLFNC command.
Host Logical Unit Numbers
FBSS logical unit number must match the LOCADR
parameter value specified on the CRTDEVFNC
command.
The FBSS logical unit assignments are decimal
numbers; the AS/400 values must be hexadecimal.
LU Assignments
for Display
Emulators
LU Assignments
for 3287 Printer
Emulator
NRZI data encoding NRZI SDLC
Communications
Source service access
point
SSCP identifier SSCPID SSCP Names SSCP namexx
Station address STNADR SDLC
SSAP Token Ring
Communications
Communications
Host Logical Unit Numbers
FBSS logical unit number must match the LOCADR
parameter value specified on the CRTDEVDSP or
CRTDEVPRT command for 3270 devices attached to
the FBSS controller.
The FBSS logical unit assignments are decimal
numbers; the AS/400 values must be hexadecimal.
N.R.Z.I.
Values specified for the AS/400 CRTLINSDLC
command and the FBSS controller must match.
Service access point for Host/37xx/4700
Values specified for the FBSS and for the SSAP
parameter on the CRTCTLFNC command must
match.
If used, the value specified for the FBSS controller
must match the last 10 digits of the SSCPID
parameter on the CRTCTLFNC command.
Station address
Values specified for the AS/400 CRTCTLFNC
command and the FBSS controller must match.
66 Version 5
Page 73

Example: Connecting AS/400 to a finance network
Configuration parameters must be coordinated when you connect an AS/400 system to a 4701 finance
controller.
Finance communications use high-level language operations and communications functions that allow you
to communicate between an AS/400 system and finance controllers.
Matching AS/400 parameters for retail controllers
You must coordinate several AS/400 parameter values with retail controllers for retail communications.
These values are specified for the AS/400 system and in the controller configuration.
For an example on connecting an AS/400 to a 4690 retail controller, see “Examples: Connecting AS/400 to
a 4690 retail controller” on page 75.
To match parameters for VTAM definition statements, see the following.
v “Matching AS/400 controller description parameters for a host system” on page 23
v “Matching AS/400 device description parameters for a host system” on page 24
v “Matching AS/400 line description parameters for a host system” on page 21
For more information about configuring the 3651 controller, see the IBM Programmable Store System
Language and Host Services: Macro Reference, GC30-3076, book.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 67
Page 74

To configure an AS/400 to a retail controller, see the following.
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for 3651 retail controllers”
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for 3684 retail controllers” on page 70
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for 4680/4690 LINE parameter” on page 72
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for 4680/4690 LINK parameter” on page 73
v “Matching AS/400 parameters for 4684 retail controllers” on page 74
Matching AS/400 parameters for 3651 retail controllers
You must coordinate several parameter values for retail communications. These values are specified for
the AS/400 system and the 3651 retail controller. The following table lists those AS/400 parameters that
must match values for the 3651 retail controllers.
Before you match parameters for 3651 retail controllers, you need to match AS/400 controller, device, and
line descriptions parameters with the host system.
AS/400 parameters are listed in alphabetical order; the commands on which the parameters are specified
are included in the rightmost column of the table.
For more information about configuring the 3651 controller, see the IBM Programmable Store System
Language and Host Services: Macro Reference
To configure the AS/400 to a 3651 retail controller, use the following table.
AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Connection type CNN QFHOST SDLCLIN
Duplex DUPLEX QFHOST SDLCLIN
Exchange identifier EXCHID QFHOST SENDID
Modem data rate MODEMRATE QFHOST SDLCLIN
Parameter
3651 Definition
Statement 3651 Parameter
Value specified for the AS/400 CNN parameter on the
CRTLINSDLC command must match the values
specified for bits 2 and 3 of the 3651 SDLCLIN
parameter.
Value specified for the AS/400 DUPLEX parameter on
the CRTLINSDLC command must match the value
specified for bit 6 of the 3651 SDLCLIN parameter.
3651 SENDID parameter must match the last 5 digits of
the EXCHID parameter specified on the AS/400
CRTLINSDLC command. (This parameter is used only
for switched line communications.)
RECVID
3651 RECVID parameter must match the last 5 digits of
the EXCHID parameter specified on the AS/400
CRTCTLRTL command.
Value specified for the AS/400 MODEMRATE parameter
on the CRTLINSDLC command must match the value
specified for bit 5 of the 3651 SDLCLIN parameter.
NRZI data encoding NRZI QFHOST SDLCLIN
Value specified for the AS/400 NRZI parameter on the
CRTLINSDLC command must match the value specified
for bit 1 of the 3651 SDLCLIN parameter.
68 Version 5
Page 75

AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
SSCP identifier SSCPID QFHOST SSCPID
Station address STNADR QFHOST SDLCPOL
Switched connection SWITCHED QFHOST SDLCLIN
Note: For the AS/400 system, the 3651 QFHOST definition must specify DIRATT=NO.
The value specified for the AS/400 parameters on the CRTLINSDLC command must match the values specified on
the 3651 SDLCLIN parameter.
Parameter
3651 Definition
Statement 3651 Parameter
3651 SSCPID parameter must match the SSCPID
parameter specified on the AS/400 CRTCTLRTL
command.
3651 SDLCPOL parameter must match the STNADR
parameter specified on the AS/400 CRTCTLRTL
command.
Value specified for the AS/400 SWITCHED parameter
on the CRTCTLRTL command must match the values
specified for bits 2 and 3 of the 3651 SDLCLIN
parameter.
For information about the SDLCLIN parameter, see “Specifying the SDLCLIN parameter for 3651 retail
controllers”.
Specifying the SDLCLIN parameter for 3651 retail controllers
The following table describes how to coordinate values for parameters on the AS/400 CRTLINSDLC and
CRTCTLRTL commands with bits that are specified for the 3651 SDLCLIN parameter.
The SDLCLIN parameter is specified as a series of 8 bits, designated 0 through 7 (01234567). The default
value for the SDLCLIN parameter when used with an SDLC line is 01100001,orhex61.
The default value for each bit is underlined in the Bit Value column.
To configure the AS/400 to a 3651 controller, use the following table.
AS/400 Parameter
SDLCLIN Bit Bit Value
00
1 None
1 0 NRZI(*NO) Specify 1 if the data communications equipment
1
and Value Notes
None Data terminal ready. There is no equivalent
parameter for the AS/400 system. Specify 0 to
indicate that the data terminal ready (DTR) signal is
on when the controller is powered on, or 1 to
indicate that the DTR is off when the controller is
powered on.
This bit should be set to 1 only if the configuration
being defined includes IBM world trade data
communications equipment (DCE) in a switched
network.
NRZI(*YES)
(DCE) provides the clocking or if NRZI data
encoding is used.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 69
Page 76

AS/400 Parameter
SDLCLIN Bit Bit Value
2 and 3 00 SWITCHED(*YES)
01 Not valid
10
11 SWITCHED(*NO) and
40
1 None
50
1 MODEMRATE(*HALF)
60
1 DUPLEX(*FULL)
7 0 None Answer tone generation. There is no equivalent
1
and Value Notes
Bit 2: Specify 1 if using nonswitched
CNN(*SWTPP)
SWITCHED(*NO) and
CNN(*NONSWTPP)
CNN(*MP)
None (See Notes) Direct attachment. This bit must be set to 0 for
MODEMRATE(*FULL) Modem data rate.
DUPLEX(*HALF) Data carrier setting.
None
communications, or 0 if using switched
communications. If switched, the SENDID parameter
must also be specified.
Bit 3: Specify 1 if using a multipoint communications
protocol, or 0 if not. 01 is not a valid combination for
these bits.
communications with the AS/400 system. There is no
equivalent parameter for the AS/400 system.
parameter for the AS/400 system. Specify 0 to
indicate that the modem generates the answer tone,
or 1 to indicate that the controller generates the
answer tone.
For information about SDLC, see “Synchronous data link control network” on page 94.
Matching AS/400 parameters for 3684 retail controllers
You must coordinate parameters with the AS/400 system and the 3684 retail controller. The following table
lists those parameters.
AS/400 parameters are listed in alphabetical order; the commands on which the parameters are specified
are included in the rightmost column of the table.
To configure the AS/400 to a 3684 controller, use the following table.
3684
AS/400
Prompt
Connection
type
Duplex DUPLEX QFSFGLNK LINECON
AS/400
Parameter
CNN QFSFGLNK LINECON
Definition
Statement 3684 Parameter
Value specified for the AS/400 CNN parameter on the
CRTLINSDLC command must match the values specified for bits
2 and 3 of the 3684 LINECON parameter.
Value specified for the AS/400 DUPLEX parameter on the
CRTLINSDLC command must match the value specified for bit 6
of the 3684 LINECON parameter.
70 Version 5
Page 77

3684
AS/400
Prompt
Exchange
identifier
Modem data
rate
NRZI data
encoding
Switched
network backup
SSCP identifier SSCPID QVSFGLNK SSCPID
AS/400
Parameter
EXCHID QVSFGLNK SENDID
MODEMRATE QFSFGLNK LINECON
NRZI QFSFGLNK LINECON
SNBU QFSFGLNK LINECON
Definition
Statement 3684 Parameter
3684 SENDID parameter must match the last 5 digits of the
EXCHID parameter specified on the AS/400 CRTCTLRTL
command.
RECVID
3684 RECVID parameter must match the last 5 digits of the
EXCHID parameter specified on the AS/400 CRTLINSDLC
command. (This parameter is used only for switched line
communications.)
Value specified for the AS/400 MODEMRATE parameter on the
CRTLINSDLC command must match the value specified for bit 5
of the 3684 LINECON parameter.
Value specified for the AS/400 NRZI parameter on the
CRTLINSDLC command must match the value specified for bit 1
of the 3684 LINECON parameter.
Value specified for the AS/400 SNBU parameter on the
CRTLINSDLC command must match the value specified for bit 4
of the 3684 LINECON parameter.
3684 SSCPID parameter must match the SSCPID parameter
specified on the AS/400 CRTCTLRTL command.
Station address STNADR QVSFGLNK POLCHAR
3684 POLCHAR parameter must match the 2-digit hexadecimal
address specified for the STNADR parameter on the AS/400
CRTCTLRTL command. Allowed values are in the range 01
through FE.
Switched
connection
Note: For the AS/400 system, the 3684 QVSFGLNK, QVSFCOMM, and QVSFSESN definitions must each specify
DATALNK=SDLC.
Values specified for the AS/400 parameters on the CRTCTLRTL and CRTLINSDLC commands must match the
values specified on the 3684 LINECON parameter.
SWITCHED QFSFGLNK LINECON
Value specified for the AS/400 SWITCHED parameter on the
CRTCTLRTL command must match the values specified for bits
2 and 3 of the 3684 LINECON parameter.
Specifying the LINECON parameter for 3684 retail controllers
The following table describes how to coordinate values that are specified for parameters on the AS/400
CRTLINSDLC and CRTCTLRTL commands. You must coordinate the values with bits that are specified for
the 3684 LINECON parameter.
The LINECON parameter is specified as a series of 8 bits, designated 0 through 7 (01234567). The default
value for the LINECON parameter when used with an SDLC line is 01000001,orhex41.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 71
Page 78

The default value for each bit is underlined in the Bit Value column.
To configure the AS/400 to a 3684 retail controller, use the following table.
AS/400 Parameter and
LINECON Bit Bit Value
00
1 None
1 0 NRZI(*NO) Specifies NRZI data encoding with leading pads (1)or
1
2 and 3 00
01 Not valid
10 SWITCHED(*NO) and
11 SWITCHED(*NO) and
40
1 SNBU(*YES)
50
1 MODEMRATE(*HALF)
60
1 DUPLEX(*FULL)
7 0 None Answer tone generation. There is no equivalent
1
None Enabled at initial microprogram load (IML). There is no
NRZI(*YES)
SWITCHED (*YES) and
CNN(*SWTPP)
CNN(*NONSWTPP)
CNN(*MP)
SNBU(*NO) Switched network backup.
MODEMRATE(*FULL) Data rate select speed.
DUPLEX(*HALF) Data carrier setting.
None
Value Notes
equivalent parameter for the AS/400 system. Specify 0
to indicate that the controller is enabled at IML, or 1 to
indicate that the controller is not enabled at IML.
non-NRZI without leading pads (0).
Bit 2: Specify 1 is using nonswitched communications,
or 0 if using switched communications. If switched, the
SENDID parameter must also be specified.
Bit 3: Specify 1 if using a multipoint communications
protocol, or 0 if not. 01 is not a valid combination for
these bits.
parameter for the AS/400 system. Specify 0 to indicate
that the controller generates the answer tone, or 1 to
indicate that the answer tone is omitted.
Matching AS/400 parameters for 4680/4690 LINE parameter
You must coordinate parameters between the AS/400 and the 4680 or 4690 retail controller. The following
table lists those parameters. The 4680 controller requires configuration of the SDLC/SNA LINE parameter.
AS/400 parameters are listed in alphabetical order; the commands on which the parameters are specified
are included in the rightmost column of the table.
For more information about configuring the 4680, see the IBM 4680 Store System: Programming Guide.
To configure the AS/400 to a 4680/4690 controller:
v See “Examples: Connecting AS/400 to a 4690 retail controller” on page 75 for an example of an AS/400
connecting to a 4690 retail controller.
v Use the following table to connect an AS/400 to a 4690 retail controller.
72 Version 5
Page 79

AS/400 Prompt AS/400 Parameter 4680 Line Parameter
Connection type CNN 4680 CONNECTION TYPE parameter value must be coordinated with
the values specified for the AS/400 CNN and SWTCNN parameters on
the CRTLINSDLC command and with the SWITCHED and INLCNN
parameters on the CRTCTLRTL command.
v If CNN(*NONSWTPP) and SWITCHED(*NO) are specified for the
AS/400 system, specify CONNECTION TYPE=1forthe4680.
v If CNN(*MP) and SWITCHED(*NO) are specified for the AS/400
system, specify CONNECTION TYPE=2forthe4680.
v If CNN(*SWTPP), SWITCHED(*YES), INLCNN(*DIAL), and either
SWTCNN(*DIAL) or SWTCNN(*BOTH) are specified for the AS/400
system, specify CONNECTION TYPE=3forthe4680.
v If CNN(*SWTPP), SWITCHED(*YES), INLCNN(*DIAL), and either
SWTCNN(*DIAL) or SWTCNN(*BOTH) are specified for the AS/400
system, specify CONNECTION TYPE=4forthe4680. This
configuration allows the 4680 to manually answer calls from the
AS/400 system or to manually call the AS/400 system.
v If CNN(*SWTPP), SWITCHED(*YES), INLCNN(*ANS), and either
SWTCNN(*ANS) or SWTCNN(*BOTH) are specified for the AS/400
system, specify CONNECTION TYPE=4forthe4680. This
configuration requires the 4680 to manually call the AS/400 system.
Initial connection INLCNN See description for the CNN (Connection type) parameter.
Modem data rate
select
NRZI data encoding NRZI 4680 NRZI MODE parameter must match the NRZI parameter specified
Station address STNADR 4680 STATION ADDRESS parameter must match the STNADR
Switched
connection
Switched
connection
MODEMRATE 4680 DATA RATE parameter must match the MODEMRATE parameter
specified on the AS/400 CRTLINSDLC command.
on the AS/400 CRTLINSDLC command.
parameter specified on the AS/400 CRTCTLRTL command.
SWITCHED See description for the CNN (Connection type) parameter.
SWTCNN See description for the CNN (Connection type) parameter.
Matching AS/400 parameters for 4680/4690 LINK parameter
You must coordinate parameters between the AS/400 and the 4680 store controller. The following tables
lists the parameter values. The 4680 controller requires configuration of the SDLC/SNA LINK parameter.
AS/400 parameters are listed in alphabetical order; the commands on which the parameters are specified
are included in the rightmost column of the table.
For more information about configuring the 4680 controller, see the IBM 4680 Store System: Programming
Guide.
To configure the AS/400 to a 4680/4690 controller:
v See “Examples: Connecting AS/400 to a 4690 retail controller” on page 75 for an example of an AS/400
connecting to a 4690 retail controller.
v Use the following table to connect an AS/400 to a 4680/4690 retail controller.
AS/400 Prompt AS/400 Parameter 4680 Link Parameter
Exchange identifier EXCHID For switched lines only, the 4680 EXCHANGE ID parameter must match
the EXCHID parameter specified on the AS/400 CRTCTLRTL command.
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 73
Page 80

AS/400 Prompt AS/400 Parameter 4680 Link Parameter
Local location
address
SSCP identifier SSCPID 4680 SSCP ID parameter must match the SSCPID parameter specified on
LOCADR 4680 SESSION ADDRESS parameter must match the LOCADR
parameter specified on the AS/400 CRTDEVRTL command. Session
address 01 is reserved for host command processor sessions.
the AS/400 CRTCTLRTL command.
Matching AS/400 parameters for 4684 retail controllers
You must coordinate parameter values with the AS/400 and the 4684 retail controller when running IBM
Retail Industry Programming Support Services (RIPSS). The following table lists those parameters.
AS/400 parameters are listed in alphabetical order; the commands on which the parameters are specified
are included in the rightmost column of the table.
For more information about configuring for RIPSS on the 4684, see the IBM Retail Industry Programming
Support Services: Planning and Installation Guide, SC33-0650.
To configure the AS/400 to a 4684 controller:
v See “Examples: Connecting AS/400 to a 4690 retail controller” on page 75 for an example of an AS/400
connecting to a 4690 retail controller.
v Use the following table to connect to a 4690 retail controller.
AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
LAN remote
adapter address
Local adapter
address
Destination service
access point
Duplex DUPLEX SDLC Server Data 4-wire constant RTS?
Parameter
ADPTADR TRDLC Server Data Local node (Hex)
ADPTADR TRDLC Server Data Remote node (Hex)
DSAP TRDLC Server Data Local SAP (Hex)
RIPSS Configuration
Display RIPSS Prompt
For Token-Ring connections, the values specified
for the RIPSS configuration and for the AS/400
CRTCTLRTL command must match.
For Token-Ring connections, the values specified
for the RIPSS configuration and for the AS/400
CRTLINTRN command must match.
For Token-Ring connections, the values specified
for the RIPSS configuration and for the AS/400
CRTCTLRTL command must match.
For SDLC connections, the values specified for
RIPSS and AS/400 configurations must match:
v If the RIPSS response is N, DUPLEX(*HALF)
must be specified for the CRTLINSDLC
command.
v If the RIPSS response is Y, DUPLEX(YES) must
be specified for the CRTLINSDLC command.
74 Version 5
Page 81

AS/400
AS/400 Prompt
Exchange identifier EXCHID SDLC Server Data Block number (hex) and XID (hex)
Local location
address
NRZI data
encoding
SSCP identifier SSCPID HST Server Data SSCP Name
Parameter
LOCADR SNA Server Data,
NRZI SDLC Server Data Data coding/decoding
RIPSS Configuration
Display RIPSS Prompt
For SDLC connections, the values specified for the
RIPSS configuration must match the value
specified in the EXCHID parameter of the
CRTCTLRTL command. The EXCHID parameter
must be specified as: xxxyyyyy, where xxx
matches the RIPSS Block number and yyyyy
matches the RIPSS XID.
For switched connections, the block number must
be 005.
LOC Address (Dec)
Session Data
The values specified for the RIPSS configuration
must match the values specified on the LOCADR
parameter of the CRTDEVRTL command.
Note that the RIPSS LOC Address is a decimal
value; the AS/400 value is a 2-digit hexadecimal
number.
For SDLC connections, the values specified for the
AS/400 CRTLINSDLC command and the RIPSS
configuration must match:
v If the RIPSS response is NRZI, NRZI(*YES)
must be specified for the CRTLINSDLC
command.
v If the RIPSS response is NRZ, NRZI(*NO) must
be specified for the CRTLINSDLC command.
For SDLC connections, if used, the value specified
by the RIPSS configuration must match the last 10
digits of the SSCPID parameter specified on the
CRTCTLRTL command.
Station address STNADR SDLC Server Data Poll address (hex)
For SDLC connections, values specified for the
AS/400 CRTCTLRTL command and the RIPSS
configuration must match.
Examples: Connecting AS/400 to a 4690 retail controller
AS/400 retail communications provide the ability to attach retail controllers to the AS/400 system. Retail
communications manage data with the intersystem communications function (ICF) file. For communications
to begin between programs, the retail communications device must first be configured and varied on.
Example 1: AS/400 to 4690 LU0 connection over token-ring network
Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 75
Page 82

Example 2: AS/400 to 4690 PEER connection over token-ring network
76 Version 5
Page 83

Chapter 7. Communicating with remote workstation controllers 77
Page 84

78 Version 5
Page 85

Chapter 8. Troubleshooting communications problems
If you suspect you have a problem with communications connectivity, the AS/400 system provides a set of
tools to help you with problem analysis tasks. The list below contains some of the more common tools for
communications problem analysis.
You can do the following to identify communication problems:
v “Displaying message queues to solve communication problems”
v “Displaying the Product Activity Log to solve communication problems” on page 80
v “Displaying the Print Error Log to solve communication problems” on page 80
You can do the following to solve communication problems:
v “Solving communication problems using communications trace” on page 81
v “Solving communication problems using the system problem log” on page 83
v “Solving communication problems using status information” on page 84
v “Considerations for system tuning during error recovery” on page 84
v “Using error messages to aid in error recovery” on page 84
In addition, when a local system rejects an incoming program start request, a message is sent to the
system operator message queue. You can use reason codes to determine why the program start request
was rejected.
Displaying message queues to solve communication problems
Message queues receive some messages that are related to communications failures. The message lists
possible causes of the problem and additional information, depending on the problem, and the suggested
problem analysis tool.
To display message queues, follow these steps:
1. On the AS/400 command line, type DSPMSG MSGQ(XXXX), in which XXXX may be:
v The message queue identified by the QCFGMSGQ system value
– The default value is QSYSOPR
– Or, message queue if the system value has been changed
v For lines, controllers, and devices which support the MSGQ parameter, the message queue is
specified in the configuration object
v For display devices, the message queue that matches the device name
2. Press the Enter key.
3. In the Display Message display, read the messages pertaining to communications problems that are
displayed in the message queue. The object name in the message directs you to the communications
objects in error.
4. For messages in the queue with an * in the farthest left position, press F14 to perform additional tests.
This calls the Work with Problems tool.
For related information, see:
v Message queues
v “Solving communication problems using the system problem log” on page 83
v “Job logs and communication problems” on page 80
v “System service tools and communication problems” on page 82
v “Using error messages to aid in error recovery” on page 84
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 79
Page 86

Displaying the Product Activity Log to solve communication problems
The Print Error Log and the Product Activity Log provide you with important information for solving
communications problems.
To view the product activity log, do the following:
1. Display or print the product activity log using these steps:
v Type STRSST (Start System Service Tools) on any AS/400 command line, and press the Enter key.
v In the System Service Tools menu, select Option 1 to display or print the product activity log.
For more information about the Product Activity Log, see the Communications Management
For related information, see:
v History logs
v “System service tools and communication problems” on page 82
v “Using error messages to aid in error recovery” on page 84
book.
Displaying the Print Error Log to solve communication problems
The Print Error Log and the Product Activity Log provide you with important information for solving
communications problems.
To view the Print Error Log, do the following:
1. Type PRTERRLOG (Print Error Log) on any AS/400 command line. Press the Enter key.
The command places a formatted printer file of the machine error log in a spooled printer file that is
named QPCSMPRT or in a specified output file.
2. Find and read these error logs.
For more information about displaying the Print Error Log, see the Communications Management
book.
A variety of job logs may contain information that helps you determine the cause of a communications
problem. For a detailed description of these job logs, see: “Job logs and communication problems”
Job logs and communication problems
A variety of job logs may contain information that helps you determine the cause of a communications
problem. Many of these logs contain messages that can help you understand what the system has done
concerning your communications functions. The following are some of the most useful jobs to review when
you have a communications problem:
QSYSARB
System arbiter. This job log is for devices, and communications in general. It also contains
ONLINE at IPL messages.
QSYSCOMM1
Communications and input/output system job. This job log is for problem logging and for local area
network (LAN) manager messages. It also contains ONLINE at IPL messages for network servers
and their lines.
QCMNARB01 through QCMNARB99
Communications arbiter. These job logs contain information for communications startup,
take-down, and error recovery.
QLUS Logical unit services.
QLUR Logical unit (LU) 6.2 resynchronization job. This job log is for two-phase commit synchronization
processing.
80 Version 5
Page 87

QPASVRP
Target 5250 display station pass-through primary server job. This job log is for target pass-through
communications functions.
QPASVRS
Target 5250 display station pass-through secondary server job. These contain more detailed
messages for target pass-through communication functions
Subsystem jobs (QINTER and QCMN)
Interactive subsystem and communication subsystem. These job logs are for subsystem jobs.
For more information on pass-through primary jobs, see the Remote Work Station Support
book.
Solving communication problems using communications trace
Sometimes, program debugging tasks are easier if you can trace the data that is sent and received on the
communications line or within the network server. To run a communications trace, use the following
commands:
STRSST (Start Service Tools)
The STRSST command takes you to a menu of tools to obtain error log information and
communications trace information. For a detailed description of system service tools, see: “System
service tools and communication problems” on page 82
STRCMNTRC (Start Communications Trace)
The STRCMNTRC command starts a communications trace for the specified line, network interface
description, or network server description. The communications trace continues until one of the
following occurs:
v The system runs the End Communications Trace (ENDCMNTRC) command
v A physical line problem causes the trace to end
v The Communications Trace function of the STRSST command ends the trace
v The *STOPTRC parameter is specified, and the buffer becomes full
ENDCMNTRC (End Communications Trace)
The ENDCMNTRC command ends the trace currently running on the specified line, network interface
description, or network server description. The ENDCMNTRC command saves the communications
trace buffer and the associated System Licensed Internal Code (SLIC) data.
PRTCMNTRC (Print Communications Trace)
The PRTCMNTRC command writes the communications trace data for the specified line, network
interface description, or network server description to a spooled file or a database file. The system can
print trace data multiple times in either form, and parameters on the command allow for dividing and
formatting of the data.
DLTCMNTRC (Delete Communications Trace)
The DLTCMNTRC command deletes the communications trace buffer and associated SLIC data for
the specified line, network interface description, or network server description. The communications
trace can be deleted once the trace has ended.
CHKCMNTRC (Check Communications Trace)
The CHKCMNTRC command returns the communications trace status for a specific line, network
interface description, or network server description. The CHKCMNTRC command returns status for all
of the traces of a specific type that exist on the system. The system returns the status through a
message.
TRCCPIC (Trace Common Programming Interface (CPI) Communications)
You can start to trace Common Programming Interface (CPI) Communications either before running a
job or after a job is active to find out where the error might have occurred. The TRCCPIC command
captures information about CPI-Communications calls that is processed by your program.
For more information on how to access System Service Tools, see the Backup and Recovery
Chapter 8. Troubleshooting communications problems 81
book.
Page 88

System service tools and communication problems
You may sometimes need to obtain an error log printout or communications trace data that your IBM
service representative can review. For the line trace, someone familiar with the protocol used on the line
may need to review the files. You can use these additional functions through the system service tools,
using the Start System Services Tool (STRSST) command.
Because System Service Tool (SST) also provides other functions, only the correctly authorized user
profiles with CRTUSRPRF SPCAUT (*SERVICE) should use the STRSST command. The system-supplied
profiles QSECOFR and QSRV have this authority.
Use the communications trace function in the following situations:
v Message information or other problem analysis is not sufficient to identify a problem
v Communications support personnel suspects a protocol error
v To verify that the system sends and receives valid data
You can trace multiple lines from each workstation by using the communications trace option. The system
traces a maximum of two lines on the same communications controller subsystem at the same time. Only
one trace can exist for the same configuration object at the same time. The system supports all line
speeds and protocols.
For more information about these tests, contact your IBM service representative.
Trace Common Programming Interface (CPI) Communications (TRCCPIC) command
You can start to trace Common Programming Interface (CPI) Communications either before running a job
or after a job is active to find out where the error might have occurred. The TRCCPIC command captures
information about CPI-Communications calls that is processed by your program. The system collects trace
information in a current job, or in a job that is serviced by a Start Service Job (STRSRVJOB) command.
(For a CPI Communication program you could trace a job that is started as a result of a received program
start request.) You can issue the TRCCPIC command in one of the following ways:
v Using the System Menu
v Typing TRCCPIC *ON on a command line
v Adding the TRCCPIC command to a control language (CL) or a REstructured eXtended eXecutor
(REXX) program
v Typing TRCCPIC on the command line and pressing F4 (Prompt)
If you type TRCCPIC on the command line and press F4, an initial prompt is displayed for the Trace
Option Setting. If *ON is specified and you press enter, the Trace CPI Communications display appears.
This display enables you to set the following parameters:
Trace option setting
Specifies whether the collection of trace information is to be started, stopped, or ended.
*ON
Starts Trace CPI Communications. This is the default value for the command.
*OFF
Stops Trace CPI Communications. The current information is written to the spooled printer file or
to the database file, and the trace table. The trace information is then deleted.
*END
Ends Trace CPI Communications. The trace table and all trace information are destroyed.
Maximum storage to use
Specifies the maximum amount of storage to use for the trace information collected. The prompt
appears only if you have selected *ON for the Trace option setting prompt.
200 K
The number of bytes (1 K equals 1024 bytes) of storage. This is the default value.
82 Version 5
Page 89

1-16000 K
The valid range for the maximum number of bytes used for storing collected trace information.
Trace full
Specifies whether new trace records replace old trace records or whether the trace is stopped when
the maximum storage that you specified has been reached. This prompt appears only if you have
selected *ON for the Trace option setting prompt.
*WRAP
When the trace storage area is full, new trace information is written over the old trace information,
starting at the beginning of the storage area. This is the default value.
*STOPTRC
No new trace information is saved when the trace storage area is full. You must reissue the
TRCCPIC command, specifying (*OFF) for the SET parameter, to retrieve the output of the trace
information collected in the trace storage area.
User data length
Specifies the maximum length of user data to be saved for each trace record in the storage area. This
prompt affects only the tracing of user data on the Send_Data and Receive calls. This parameter does
not affect the tracing of log data on Set_Log_Data, Send_Error, or Deallocate calls. This prompt
appears only if you specified *ON on the Trace option setting prompt.
128
The number of bytes for the user data length. This is the default value.
0-4096
The valid range of bytes for the user data length.
Trace Common Programming Interface (CPI) Communications continues to collect trace records until you
stop the trace or until the trace storage area becomes full. The amount of trace storage depends on the
value that is specified on the Trace full prompt. If the trace storage area becomes full and the collection of
trace records stops, you must enter the TRCCPIC command again to create output. The output that is
created by the TRCCPIC command is directed either to the spooled printer file, QSYSPRT, or to a
database output file that you specify. If the output file that you specify already exists, it must have the
same attributes as the system-supplied file, QACM0TRC.
You can stop a trace procedure in one of the following ways:
v Using the System Menu
v Typing TRCCPIC *OFF on the command line
v Adding the TRCCPIC command to a CL or a REXX program
v Typing TRCCPIC on the command line and pressing F4 (Prompt)
Type TRCCPIC on the command line and press F4. Specify *OFF for the Trace option setting and you are
prompted for the OUTPUT parameter.
Solving communication problems using the system problem log
Error conditions that are communications-related can make entries in the system problem log. You can
access the log to see the lists of problems that are detected by the system or by the user.
To access the system problem log, type WRKPRB on any AS/400 command line, and press F4.
Tips: You can select a subset of the problems that are listed in the problem log by selecting the problem
status. A problem that is listed in the log has one of the following as a status:
v OPENED: The problem was identified; problem analysis has not been run.
v READY: The system has run problem analysis; the problem is ready to be prepared.
v PREPARED: The system added information that relates to the problem.
v SENT: The problem was sent to the service support location.
Chapter 8. Troubleshooting communications problems 83
Page 90

You can also sort the WRKPRB display by the date the problem was entered into the log.
Note: Use the WRKPRB command for the menu options, additional problem analysis, or documenting
problem records.
Solving communication problems using status information
You can often diagnose the communications problem by checking communications status. Status
information for network servers, network interfaces, lines, controllers, or devices may represent the
symptom of the problem.
To check and change the communication configuration on the system, do the following:
1. Type the Work with Configuration Status (WRKCFGSTS) command on any AS/400 command line.
2. Press F4. The Work with Configuration Status display appears.
3. Specify the configuration type for the CFGTYPE parameter.
4. Specify the configuration description for the CFGD parameter.
Note: You may subset this list produced by WRKCFGSTS based on the status of the objects using the
STATUS parameter. For example, if you want to see just the failed objects, specify
STATUS(*FAILED).
Considerations for system tuning during error recovery
The overall performance tuning that is done by the system can play a significant role during error recovery
scenarios. For example, you may need to change the machine pool if it is too small because it can cause
excessive error recovery times.
v Performance Adjustment – QPFRADJ
The automatic performance adjustment function of the system is set to 2 when the system is shipped.
The system can automatically adjust the performance of the system based on this value. Automatic
adjustment may be a desirable feature, particularly when unexpected loads hit the system. Automatic
adjustment can help the system perform better through these peak loads.
v Subsystem considerations
You should consider dividing communications users (whether they are remote workstation or APPC
communication users) into multiple subsystems. If communications fails, all users who are in a single
subsystem may be affected as a result of the communications recovery that is performed on their
systems. For more information, see:
–“Considerations for subsystem configuration for error recovery performance” on page 11
Using error messages to aid in error recovery
When problems occur in communications, there are many places you can look for error messages and
additional information to help resolve the problems. See the topics below for the most common places to
look for APPC error information.
v Messages queues, see “Displaying message queues to solve communication problems” on page 79
v Job logs, see “Job logs and communication problems” on page 80
v Other logs, see “Displaying the Product Activity Log to solve communication problems” on page 80 and
“Displaying the Print Error Log to solve communication problems” on page 80
v Start Service tools, see “System service tools and communication problems” on page 82
v Communications trace, see “Solving communication problems using communications trace” on page 81
Solving communication problems using reason codes
When the local system rejects an incoming program start request, a message is sent to the system
operator message queue. You can use the message information to determine why the program start
request was rejected.
84 Version 5
Page 91

Refer to Table 13 for an explanation on reason codes for failed program start requests.
Table 1. Reason Codes for Rejected Program Start Requests
Reason
Code Reason Description
401 Program start request received to a device that is not allocated to an active subsystem.
402 Requested device is currently being held by a Hold Communications Device (HLDCMNDEV) command.
403 User profile is not accessible.
404 Job description is not accessible.
405 Output queue is not accessible.
406 Maximum number of jobs defined by subsystem description are already active.
407 Maximum number of jobs defined by communications entry are already active.
408 Maximum number of jobs defined by routing entry are already active.
409 Library on library list is exclusively in use by another job.
410 Group profile cannot be accessed.
411 Insufficient storage in machine pool to start job.
412 System value not accessible.
413 QSERVER not started
501 Job description was not found.
502 Output queue was not found.
503 Class was not found.
504 Library on initial library list was not found.
505 Job description or job description library is damaged.
506 Library on library list is destroyed.
507 Duplicate libraries were found on library list.
508 Storage-pool defined size is zero.
602 Transaction program-name value is reserved but not supported.
604 Matching routing entry was not found.
605 Program was not found.
704 Password is not valid.
705 User is not authorized to device.
706 User is not authorized to subsystem description.
707 User is not authorized to job description.
708 User is not authorized to output queue.
709 User is not authorized to program.
710 User is not authorized to class.
711 User is not authorized to library on library list.
712 User is not authorized to group profile.
713 User ID is not valid.
714 Default user profile is not valid.
715 Neither password nor user ID was provided, and no default user profile was specified in the
communications entry.
718 No user ID.
722 A user ID was received but a password was not sent.
723 No password was associated with the user ID.
725 User ID does not follow naming convention.
726 User profile is disabled.
730 Password has expired.
801 Program initialization parameters are present but not allowed.
802 Program initialization parameter exceeds 2000 bytes.
803 Subsystem is ending.
804 Prestart job is inactive or is ending.
805 WAIT(NO) was specified on the prestart job entry and no prestart job was available.
806 The maximum number of prestart jobs that can be active on a prestart job entry was exceeded.
807 Prestart job ended when a program start request was being received.
Chapter 8. Troubleshooting communications problems 85
Page 92

Table 1. Reason Codes for Rejected Program Start Requests (continued)
Reason
Code Reason Description
901 Program initialization parameters are not valid.
902 Number of parameters for program not valid.
903 Program initialization parameters required but not present.
1001 System logic error. Function check or unexpected return code encountered.
1002 System logic error. Function check or unexpected return code encountered while receiving program
initialization parameters.
1501 Character in procedure name not valid.
1502 Procedure not found.
1503 System/36 environment library not found.
1504 Library QSSP not found.
1505 File QS36PRC not found in library QSSP.
1506 Procedure or library name is greater than 8 characters.
1507 Current library not found.
1508 Not authorized to current library.
1509 Not authorized to QS36PRC in current library.
1510 Not authorized to procedure in current library.
1511 Not authorized to System/36 environment library.
1512 Not authorized to file QS36PRC in System/36 environment library.
1513 Not authorized to procedure in System/36 environment library.
1514 Not authorized in library QSSP.
1515 Not authorized to file QS36PRC in QSSP.
1516 Not authorized to procedure in QS36PRC in QSSP.
1517 Unexpected return code from System/36 environment support.
1518 Problem phase program not found in QSSP.
1519 Not authorized to problem phase program in QSSP.
1520 Maximum number of target programs started (100 per System/36 environment).
2501 System logic error. Function check or unexpected return code encountered while processing a program
start request.
2502 Temporarily unable to allocate needed resources for a program start request.
2503 No subsystem accepting program start requests for this device.
86 Version 5
Page 93

Chapter 9. Networking concepts
If you would like more information on networking topics, review the following:
v Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking support
v Advanced Program-to-Program Communications
v Dependent LU Requester Support (DLUR)
v High-performance routing (HPR)
v Internet packet exchange support
v Systems Network Architecture
v TCP/IP
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking (APPN) is one type of data communications support that is provided
by the AS/400 system. This support routes data in a network between two or more advanced
program-to-program systems. The systems do not need to be directly connected in the same network or
adjacent networks.
The APPC/APPN support handles all of the SNA protocol requirements when your system is
communicating with a remote system that uses the LU session type 6.2 and node type 2.1 architectures.
The remote system can be any of the following systems:
v AS/400 system
v System/36
v System/38
v IBM personal computer
v Displaywriter
v Series/1
v 5520 Administrative System
v RISC System/600 (Reduced Instruction Set Computer)
v DPPX/370 (Distribute Processing Programming Executive
v One of the following host systems:
– System/370
– System/390
– 30XX processor
– 43XX processor
– 9370 system
– Another system that supports the appropriate level of architecture
The AS/400 APPN support is an enhancement to the SNA Node Type 2.1 architecture that supplies
networking functions. These enhancements are easy-to-use, are dynamic; and give control of the network
to the peer systems that make up the network. APPN provides you with the following advanced functions:
v Distributed directory services
v Dynamic route selection that is based on user-specified values
v Intermediate session routing
v Routing of data by using transmission priorities.
With the exception of intermediate session routing, HPR builds on and uses these APPN functions. For
more information on HPR, see high-performance routing.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 87
Page 94

Advanced program-to-program communications
Advanced program-to-program communications (APPC) is data communications support that allows
programs on an AS/400 system to communicate with programs on other systems having compatible
communications support, such as: System/38 and System/36. APPC on the AS/400 system provides an
application programming interface to the Systems Network Architecture (SNA) LU type 6.2 and node type
2.1 architectures that makes it possible to communicate with System/390.
The APPC support handles all of the SNA protocol requirements when your system is communicating with
a remote system that uses the LU type 6.2 and node type 2.1 architectures. You can connect your system
to any other system that supports the APPC program interface. APPC application programs can also
communicate over lines using the Internet Protocol (IP) of Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP).
The AS/400 APPC support handles the protocol needed for communicating between an application
program that runs on your AS/400 system, and an application that runs on a remote system. The protocol
consists of a set of verbs that are common to the local and remote systems in a network. However, the
way in which each system provides a program interface to the verbs may differ.
The AS/400 system provides the following program interfaces:
v The intersystem communications function (ICF) file interface. In ICF, the LU 6.2 verbs are carried out by
using data description specifications (DDS) keywords and system-supplied formats.
v The Common Programming Interface (CPI) Communications call interface. Using CPI Communication
calls carries the LU 6.2 verbs.
v The CICS file interface. In CICS/400 support, the LU 6.2 verbs are carried out by using EXEC CICS
commands.
v The sockets application program interface (API). For the sockets API, the LU 6.2 verbs are carried out
by using the socket functions.
The APPC support also handles networking functions, and allows peer systems in a network to start and
end sessions without a controlling host system.
The AS/400 Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking (APPN) support is an enhancement to the node type 2.1
architecture. APPN provides additional networking functions such as searching distributed directories,
dynamically selecting routes, routing of intermediate sessions, creating and starting remote locations, and
routing data by using transmission priorities.
Built upon APPN, high-performance routing (HPR) is an enhancemnet to APPN that enables improved
availability and persistence during network outages.
Dependent LU requester support
Dependent LU Requester Support (DLUR) allows dependent secondary logical units (LU 0, 1, 2, and 3) an
entry point into the APPN network. DLUR support gives the appearance of having an adjacent connection
to VTAM, but allows traversing the APPN network through intermediate nodes.
DLUR supports the following controllers, displays, and printers:
v Host devices, including 3270 emulation (*EML), remote job entry (*RJE), and program-to-program
communications (*PGM)
v SNA Passthrough upstream devices
v DHCF display devices
v NRF display and printer devices
v SNUF devices (DSNX)
The normal SSCP-PU and SSCP-LU flows for dependent LUs are encapsulated in a control point server
(CP-SVR) pipe. This pipe consists of two LU 6.2 sessions:
88 Version 5
Page 95

v Send
v Receive
At the primary end of the pipe is a Dependent LU Server (DLUS). At the secondary end of the pipe is a
Dependent LU Requester (DLUR). DLUS and DLUR support the activation and deactivation of dependent
physical units (PUs) and logical units (LUs) in the APPN network. The pipe consists of a pair of LU 6.2
conversations where two APPC applications (DLUR and DLUS) exchange dependent SNA SSCP flows.
The flows are encapsulated in a general data stream (GDS) variable and sent in LU 6.2 logical records.
The pair of conversations that are used to transmit encapsulated SNA is called the CP-SVR Pipe.
To configure DLUR, see the page Configuring Dependent LU Requester.
High-performance routing
High-Performance Routing (HPR) is the evolution of Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking (APPN). HPR
enhances APPN data routing performance and reliability, especially when using higher-speed lower-error
links.
To support high-speed communications facilities, certain changes to the APPN architecture are required.
These are necessary to allow switching in intermediate nodes to be done at a lower layer and to enable
faster switching than in base APPN support. HPR changes the existing APPN intermediate session routing
by using automatic network routing (ANR), which maximizes the storage and processing requirement in
intermediate nodes. Each outbound packet has a predetermined path through the network so that
intermediate routing nodes need not remember anything about HPR sessions that flow through them.
Intermediate routing nodes in HPR simply route data that is based on information that is contained within
the packet itself.
The HPR function can operate under a base architecture, or can operate under the base architecture plus
options. There are performance capabilities available under the Tower RTP option not available with the
base. The page, HPR architecture option sets can give you a more thorough explanation of what
architecture option is right for you.
HPR architecture option sets
HPR-base option: Its primary function is to provide automatic network routing (ANR). Products that only
use this function can participate as intermediate nodes in one or more rapid-transport protocol (RTP)
connections. This type of implementation cannot be an end point of an RTP connection.
An addition to the base option is HPR Link-Level Error Recovery. A system that supports high-speed links
does not always require link-level error recovery. It is optional because when link-level error recovery is
eliminated there can be faster communications when using high-quality data transmission.
RTP Tower Option: Implementations that support this option can act as an endpoint and are able to
transport logical unit (LU) to LU session traffic across HPR networks by using RTP connections. An RTP
connection can only be made between two systems that support RTP. That is, there can only be a mix of
systems in a given RTP connection’s path through the network (ones that only support the HPR base
option and ones that support the HPR tower option). However, there is the stipulation that at least the two
end points in the path support the HPR tower option. Otherwise, APPN is used.
Note: An implementation that has the RTP Tower Option also supports the base option. These systems
can run as intermediate systems in the path.
Internetwork packet exchange support
If your group or business has an established Novell LAN, you can connect AS/400 into your business
using the OS/400 Internetwork Packet Exchange (IPX).
Chapter 9. Networking concepts 89
Page 96

Internetwork Packet Exchange support is the AS/400 implementation of the NetWare communication
protocols. These protocols include IPX, Sequenced Packet Exchange (SPX), Router Information Protocol
(RIP), Service Advertising Protocol (SAP), and NetWare Link Service Protocol (NLSP). Other related
NetWare functions are also included. This set of communications protocols supports peer-to-peer
connectivity functions in both local area networks and wide area networks.
What is Systems Network Architecture
In IBM networks, Systems Network Architecture (SNA) is the layered logical structure, formats, protocols,
and operational sequences that are used for transmitting information units through networks. SNA also
controls the configuration and operation of networks.
APPC, APPN, and HPR are some examples of the protocols included within SNA. They can be used to
connect the AS/400 with other IBM systems, or non-IBM systems, to connect remote controllers, and to
maintain a high-level of security on your system.
What is TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is a set of network protocols that enables
computers to share resources and exchange information across a network. TCP/IP allows hosts to
communicate with each other regardless of the host or user’s physical location, the operating system, or
the network medium. TCP/IP operates in many different network environments, that include the Internet
and corporate Intranets.
For more information, see the topic TCP/IP configuration fastpath.
90 Version 5
Page 97

Chapter 10. Common networking standards
These topics introduce the types of common networking standards that are supported by the AS/400
system. See the following topics for more information:
v Local area network standards
v Wide area network standards
Local area network standards
A LAN (local area network) is a communications system that allows interconnection and the sharing of
resources between independent devices within a moderately sized geographic area. These topics
introduce the types of local area networks that are supported by the AS/400 system:
v Asynchronous transfer mode (ATM)
v DDI (distributed data interface) networks
v Ethernet
v Token-ring
v Wireless networks
ATM on AS/400
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) provides a very fast and flexible network protocol. When used with
LAN emulation, you can run token-ring and Ethernet on ATM to take advantage of ATM’s superior speed,
throughput, and flexibility.
ATM LAN emulation connects LAN clients at multi-megabit-per-second speeds over distances previously
possible only with a wide area network (WAN). LAN emulation makes client connections as they are
needed, without configuring the physical path between the end systems. Switching is the mechanism by
which the network completes connections from one device to another.
The AS/400 asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) network interface (NWI) describes everything that is
common across the ATM physical interface. Each AS/400 ATM input/output adapter (2809 or 2810) may
have one network interface attached. A single line description attaches to the NWI. The line description
can define either an Ethernet or token-ring local area network (LAN) emulation client by using switched
virtual circuit connections, permanent virtual circuit connections, or direct connections.
For more information on ATM, see the topic ATM on AS/400.
Distributed data interface network
FDDI is an optical fiber-based local area network (LAN) that uses the American National Standards
Institute (ANSI) 3T9.5 standard for a token-passing ring media access control (MAC) protocol. Stations,
concentrators, and bridges in a FDDI network are physically connected to one of the counter-rotating rings
or both of the counter-rotating rings. The rings operate at 100 Mbps.
FDDI networks allow devices to be attached to one or both of the rings. Usually only the primary ring in a
FDDI network is active. The secondary ring is used to maintain the network when a dual-access station or
a concentrator becomes inactive.
Ethernet networks
Ethernet is one type of local area network (LAN) topology that is supported by the Operating System/400
licensed program. OS/400 Ethernet provides support for the Digital Equipment Corporation, Intel
Corporation, and Xerox standard (Ethernet Version 2) and the IEEE 802.3 standard.
© Copyright IBM Corp. 1998, 2001 91
Page 98

Half-duplex Ethernet
Generally, multiple stations in an Ethernet network show a single data path. Therefore, only one
station may transmit data at a time. This is called half-duplex Ethernet. The station may transmit
only or receive only, but not both simultaneously.
Full-duplex Ethernet
Full-duplex Ethernet enables stations to simultaneously send and receive data on the network,
eliminating collisions. This is accomplished through the use of a full-duplex LAN switch. Ethernet
switching splits a large Ethernet into smaller segments. Full-duplex Ethernet requires the following:
v Twisted-pair cable transmission medium
v Ethernet network interface cards
v A full-duplex LAN switch
Full-duplex 10 Mbps ethernet has simultaneous 10 Mbps receiving and 10 Mbps sending paths.
Fast Ethernet
Fast Ethernet is a recently established standard (IEEE 802.3U) that increases Ethernet by
operating speeds from 10 Mbps to 100, half or full duplex. AS/400 Ethernet adapters support
100BASE-TX network devices that use category 5 shielded and unshielded twisted-pair (STP,
UTP) cable.
For more information, see Ethernet.
Token-ring networks
A token-ring network is one LAN topology that sends data in one direction throughout a specified number
of locations by using the token. The token is the symbol of authority for control of the transmission line.
This token allows any sending station in the network (ring) to send data when the token arrives at that
location.
Stations in a token-ring network are physically connected, usually in a star-wired ring topology, to a wiring
concentrator such as the IBM 8228 Multistation Access Unit. The concentrator serves as a logical ring
around which data is transmitted at 4 million or 100 million bits per second (Mbps). Each station is
connected to the concentrator typically by shielded twisted pair (STP) cabling.
Full-duplex token ring
In full-duplex token ring, which is also called DTR (dedicated token ring), switching hubs enable
stations to send and receive data on the network simultaneously. A token-ring switching hub
divides the network into smaller segments. When a station transmits its data packet, the token-ring
switch reads the packet’s destination address information and forwards the data directly to the
receiving station. The switch then establishes a dedicated connection between the two stations,
enabling data to be transmitted and received at the same time. In full-duplex token ring, the
token-passing protocol is suspended. The network in effect becomes a ’tokenless’ token ring.
Full-duplex token ring increases sending and receiving bandwidth for connected stations,
improving network performance.
For more information, see Token ring.
Wireless network
The more mobile your employees, the more you should consider a wireless network. The portable
transaction computers (PTCs) make it possible for direct connection between the office and offsite
locations.
The AS/400 wireless network is a LAN that uses a Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance
(CSMA/CA) protocol to provide media access to competing stations. AS/400 wireless communications use
spread-spectrum, direct sequence radio in the 2.4 gigahertz (GHz) band to provide connectivity between
92 Version 5
Page 99

the AS/400 wireless LAN adapter and remote stations. Remote stations can be PTCs that are running
5250 emulation or LAN-connected systems that are equipped with compatible wireless adapters. There are
other implementations of wireless LAN.
Wide area network standards
A wide area network (WAN) is a data communications network designed to serve an area of hundreds or
thousands of miles--for example, public and private packet-switching networks, and national telephone
networks.
These topics introduce the types of wide area networks that are supported by the AS/400 system:
v Asynchronous communications
v Binary synchronous communications
v Frame relay
v Integrated services digital network
v Synchronous data link control network
v X.25 network
v X.21 network
Asynchronous communications
OS/400 asynchronous communications support allows an AS/400 application program to exchange data
with a remote system or device using either an asynchronous (start-stop) or X.25 line. AS/400 application
programs can be written in ILE COBOL/400, ILE RPG/400, ILE C/400, or FORTRAN/400 languages.
Asynchronous communications support includes file transfer support (also used with other communications
types) and interactive terminal facility (ITF). Asynchronous communications support provides
program-to-program and program-to-device communications between systems that use asynchronous
(start-stop) or X.25 lines. For X.25 lines, it also supplies an integrated packet assembler/disassembler
(PAD) (1) that follows CCITT recommendations X.3, X.28, and X.29.
Asynchronous communications support allows you to send data to and receive data from a remote
program or device attached by either an asynchronous (start-stop) or an X.25 line. Your application
program must provide the data stream required by the remote device. Asynchronous communications
support packages your data stream in either a start-stop format or within X.25 data packets.
Binary synchronous communications
(BSC) is a data communications line protocol that uses a standard set of transmission control characters
and control character sequences to send binary-coded data over a communications line. Binary
synchronous communications equivalence link (BSCEL) support is the intersystem communications
function (ICF) support on the AS/400 system that provides binary synchronous communications with a
remote system or device. BSCEL also supplies online and batch communications between application
programs on different BSC systems. AS/400 application programs can be written in the Integrated
Language Environment (ILE) C/400*, ILE COBOL/400*, ILE FORTRAN/400*, or ILE RPG/400*
programming languages.
Frame relay networks
Frame relay is a protocol that defines how frames are routed through a fast-packet network based on the
address field in the frame. Frame relay takes advantage of the reliability of data communications networks
to minimize the error checking done by the network nodes. This provides a packet-switching protocol
similar to, but much faster than, X.25. The high speed that can be obtained through frame-relay networks
makes it well suited for wide area network (WAN) connectivity. Frame relay is commonly used to connect
two or more LAN bridges over large distances.
The AS/400 system supports these frame-relay network connections:
Chapter 10. Common networking standards 93
Page 100

v Frame relay direct network: Allows data that uses SNA, TCP/IP, or IPX communications over a
frame-relay network to move at speeds of up to 2.048 Mbps. This support allows a network of systems
to communicate using the frame-relay network as a backbone, without the need for multiple leased T1
lines.
v Bridged frame relay network: Allows AS/400 to communicate over a frame-relay network through a
remote bridge. The bridge is attached to a token-ring, Ethernet, or distributed data interface (DDI)
network. Bridged frame relay connections allow AS/400 to communicate with stations on the remote
local area network (LAN) as if they were attached locally to the LAN medium.
For more information, see Frame relay.
Integrated services digital network
You can connect your AS/400 to an Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) for faster, more accurate
data transmission. An ISDN is a public or private digital communications network that can support data,
fax, image, and otherservices over the same physical interface. Also, you can use other protocols on
ISDN, such as ISDN data link control (IDLC), PPP, fax, and X.25.
ISDN provides benefits that are not found in more conventional types of communications. These include
the following:
v High speed, low error rate communications
v Switched, high speed communications
v Switched, digital networking
v Advanced networking functions
v Integration of voice and data transmissions
v Integrated support of packet switching (X.31)
For more information on ISDN, see the topics ISDN on AS/400 and ISDN data link control network.
ISDN data link control network
You can use ISDN data link control (IDLC) to connect two systems to exchange information over an ISDN
B-channel.
IDLC complies with the data link control protocols that are defined in CCITT Recommendations Q.921 and
Q.922. IDLC defines a set of protocol rules and formats for use on D-channels and B-channels. On the
D-channel, IDLC provides a reliable link with the network equipment. On the B-channel, IDLC provides a
reliable link with another end user.
Similar to other data link protocols, IDLC has special considerations for operation:
v IDLC parameters used to establish the logical connection
v Delayed contact for permanent connection
v Frame size related to performance
v Disconnect parameters for a switched IDLC controller
Synchronous data link control network
SDLC has the following meanings:
v A form of communications line control that uses commands to control the transfer of data over a
communications line.
v A communications discipline that conforms to subsets of the Advanced Data Communication Control
Procedures (ADCCP) of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and high-level data link
control (HDLC). These standards are part of the International Organization of Standardization.
SDLC is used for transferring synchronous, code-transparent, serial-by-bit information over a
communications line. Transmission exchanges may be duplex or half-duplex over switched or nonswitched
lines. The configuration of the connection may be point-to-point, multipoint, or loop.
94 Version 5
 Loading...
Loading...