Page 1

i
IBM SPSS Modeler 15 User’s Guide
Page 2

Note: Before using this information and the product it supports, read the general information
under Notices on p. 249.
This edition applies to IBM SPSS Modeler 15 and to all subsequent releases and modifications
until otherwise indicated in new editions.
Adobe product screenshot(s) reprinted with permission from Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Microsoft product screenshot(s) reprinted with permission from Microsoft Corporation.
Licensed Mate
© Copyright IBM Corporation 1994, 2012.
rials - Property of IBM
U.S. Government Users Restricted Rights - Use, duplication or disclosure restricted by GSA ADP
Schedule Contract with IBM Corp .
Page 3

Preface
IBM® SPSS® Modeler is the IBM Co r p. enterprise-strength data mining workbench. SPSS
Modeler helps organizations to improve customer and citizen relat ionships th r ough an in-depth
understandi
profitable customers, identify cross-selling opportunities, attract new customers, detect f raud,
reduce risk, and improve government service delivery.
SPSS Modeler
leads to more powerful predictive models and shortens time-to-solution . SPSS Modeler offers
many modeling techniques, such as prediction, c lassification, segmentation, and association
detection a
enables t heir deliver y enterprise-wide to decision makers or to a database.
ng of data. Organizations use the insight gained from SPSS M odeler to retain
’s visual interface invites users to apply t heir specific business expertise, which
lgorithms. Once models are created, IBM® SPSS® Modeler Solution Publisher
About IBM Bu
IBM Business Analytics software delivers complete, consistent and accurate information that
decision-makers trust to improve business performance. A comprehensive portfolio of business
intelligence, predictive analytics, financial performance and strategy m anagement, and analytic
applications provides clear, immediate and actionable in sights into current performance and the
ability to predict future outcomes. Combined with rich industry solution s, proven practices and
professional services, organizations of every size can drive the highest productivity, confidently
automate decisions and deliver better results.
As part of
future events and proactively act upon that insight to drive bet ter business outcomes. Commercial,
government and academic customers worldwide rely on IBM SPSS technology as a competitive
advantag
risk. By incorporating IBM SPSS software into their daily operations, organizations become
predictive enterprises – able to direct and automate decisions to meet busin ess goals and achieve
measura
http://www.ibm.com/spss.
Techni
cal support
Technical support is available to maintenance custome r s. Customers may contact Technical
Support for assistance in using IBM Corp. products or for installation help for one of the
supported hardware environments. To reach Technical Support, see the IBM Corp. web site
at http://www.ibm.com/support. Be prepared to identify yourself, your organization, and your
support agreement when requesting assistance.
siness Analytics
this portfolio, IBM SPSS Predictive Analytics software helps organizations predict
e in attracting, retaining and growing customers, while reducing fraud and mitigating
ble competitive advantage. For further information or to reach a representative visit
© Copyright IBM Corporation 1994, 2012.
iii
Page 4

Contents
1 About IBM SPSS Modeler 1
IBM SPSS Modeler Products . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
IBM SPSS Modeler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
IBM SPSS Modeler Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
IBM SPSS Modeler Administration Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
IBM SPSS Modeler Batch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
IBM SPSS Modeler Solution Publisher. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
IBM SPSS Modeler Server Adapters for IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment Services . 2
IBM SPSS Modeler Editions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
IBM SPSS Modeler Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
SPSS Modeler Professional Documentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
SPSS Modeler Premium Documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Application Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Demos Folder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 New Features 7
New and Changed Features in IBM SPSS Modeler 15 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
New features in IBM SPSS Modeler Professional . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
New features in IBM SPSS Modeler Premium . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
New Nodes in This Release . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3 IBM SPSS Modeler Overview 12
Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Starting IBM SPSS Modeler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Launching from the Command Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Connecting to IBM SPSS Modeler Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Changing the Temp Directory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Starting Multiple IBM SPSS Modeler Sessions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
IBM SPSS Modeler Interface at a Glance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
IBM SPSS Modeler Stream Canvas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Nodes Palette . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
IBM SPSS Modeler Managers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
IBM SPSS Modeler Projects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
IBM SPSS Modeler Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Customizing the Toolbar. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Customizing the IBM SPSS Modeler Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
© Copyright IBM Corporation 1994, 2012.
iv
Page 5

Changing the icon size for a stream . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Using the Mous
Using Shortcut Keys . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Printing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Automating IB
e in IBM SPSS Modeler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
M SPSS Modeler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
4 Understandin
Data Mining Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Assessing the Data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
A Strategy for Data Mining . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
The CRISP-DM Process Model . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Types of Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Data Mining Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
g Data Mining 29
5 Building Streams 41
Stream-Building Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Building Data Streams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Working with Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Working with Streams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Stream Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Running Streams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Working with Models. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Adding Comments and Annotations to Nodes and Streams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Saving Data Streams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Loading Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Mapping Data Streams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Tips and Shortcuts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
6 Handling Missing Values 99
Overview of Missing Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Handling Missing Values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Handling Records with Missing Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Handling Fields with Missing Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Imputing or Filling Missing Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
CLEM Functions for Missing Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
v
Page 6

7 Building CLEM Expressions 105
About CLEM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
CLEM Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Values and Data Types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Expressions and Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Stream, Session, and SuperNode Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Working with Strings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Handling Blanks and Missing Values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Working with Numbers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Working with Times and Dates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Summarizing Multiple Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Working with Multiple-Response Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
The Expression Builder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Accessing the Expression Builder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Creating Expressions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Selecting Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Selecting Fields, Parameters, and Global Variables . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Viewing or Selecting Values. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Checking CLEM Expressions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Find and Replace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
8 CLEM Language Reference 127
CLEM Reference Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
CLEM Datatypes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Integers. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Reals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Characters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Strings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Lists. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Fields. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Dates. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
CLEM Operators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Functions Reference. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Conventions in Function Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Information Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Conversion Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Comparison Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
vi
Page 7

Logical Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Numeric Funct
Trigonometric Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Probability Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Bitwise Integ
Random Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
String Functions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
SoundEx Functi
Date and Time Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Sequence Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Global Functio
Functions Handling Blanks and Null Values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Special Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
ions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
er Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
ons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
ns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
9 Using IBM SPSS Modeler with a Repository 158
About the IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment Services Repository . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
Storing and Deploying Repository Objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Connecting to the Repository . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Entering Credentials for the Repository . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Browsing the Repository Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Storing Objects in the Repository . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Setting Object Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Storing Streams. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Storing Projects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Storing Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Storing Output Objects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Storing Models and Model Palettes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Retrieving Objects from the Repository . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Choosing an Object to Retrieve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Selecting an Object Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Searching for Objects in the Repository . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Modifying Repository Objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Creating, Renaming, and Deleting Folders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Locking and Unlocking Repository Objects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Deleting Repository Objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Managing Properties of Repository Objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Viewing Folder Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Viewing and Editing Object Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Managing Object Version Labels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
vii
Page 8

Deploying Streams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Stream Deployment Options. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
The Scoring Br
anch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
10 Exporting to E
About Exporting to External Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Opening a Stream in IBM SPSS Modeler Advantage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Importing and Exporting Models as PMML . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196
Model Types Supporting PMML . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 198
xternal Applications 195
11 Projects and Reports 200
Introduction to Projects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 200
CRISP-DM View. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
Classes View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Building a Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Creating a New Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 202
Adding to a Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Transferring Projects to the IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment Services Repository . 204
Setting Project Properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Annotating a Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Object Properties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Closing a Project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Generating a Report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Saving and Exporting Generated Reports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 212
12 Customizing IBM SPSS Modeler 215
Customizing IBM SPSS Modeler Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
Setting IBM SPSS Modeler Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
System Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 215
Setting Default Directories. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 216
Setting User Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 217
Setting User Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 222
viii
Page 9

Customizing the Nodes Palette . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Customizing the Palette Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 223
Changing a Pal
CEMI Node Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 229
ette Tab View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 228
13 Performance Considerations for Streams and Nodes 230
Order of Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 230
Node Caches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 231
Performance: Process Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 233
Performance: Modeling Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
Performance: CLEM Expressions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 234
Appendices
A Accessibility in IBM SPSS Modeler 236
Overview of Accessibility in IBM SPSS Modeler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
Types of Accessibility Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
Accessibility for the Visually Impaired . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 236
Accessibility for Blind Users . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 237
Keyboard Accessibility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 238
Using a Screen Reader . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 245
Tips for Use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 246
Interference with Other Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
JAWS and Java. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
Using Graphs in IBM SPSS Modeler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 247
B Unicode Support 248
Unicode Support in IBM SPSS Modeler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 248
ix
Page 10

C Notices 249
Index 252
x
Page 11

About IBM SPSS Modeler
IBM® SPSS® Modeler is a set of data mining tools that enable you to quickly deve lop predictive
models using business expertise and deploy them into business o pe r ations to improve decision
making. Desi
entire data mining process, from data to better business results.
SPSS Modeler offers a va r iety of modeling methods taken from machine learning, art ificial
intelligence, and statistics. The methods available on the Modeling palette allow you to derive
new information from your data and to develop predictive models. Each method has certain
strengths and is best suited for particular types of problems.
SPSS Modeler can be purchased as a standalone p r oduct, or used as a client in
combination with SPSS Modeler Server. A number of additional options are also
available, as summarized in the following sections. For more information, see
http://www.ibm.com/software/analytics/spss/products/modeler/.
gned aroun d the industry-standard CRISP-DM model, SPSS Modeler supports t he
Chapter
1
1
11
IBM SPSS Modeler Products
The IBM® SPSS® Modeler family of products and associated software comprises the following.
IBM SPSS Modeler
IBM SPSS Modeler Server
IBM SPSS Modeler Administration Console
IBM SPSS Modeler Batch
IBM SPSS Modeler Solution Publisher
IBM SPSS Modeler Server adapters for I BM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment Services
IBM SPSS Modeler
SPSS Modeler is a functionally complete version of the produc t that you install and run on your
personal computer. You can run SPSS Modeler in local mode as a standalone product, or use it
in distributed mode along with IBM® SPSS® Modeler Server for im proved performance on
large data sets.
With SPSS Modeler, you can build a ccurate p r edictive models quickly and intuitively, withou t
programming. Using the un ique visual interface, you can easily visualize the data mining process.
With the support of the advanced analytics embedded in the product, you can discover previously
hidden patterns and trends in your data. You can mode l outcomes and understand the factors that
influence them, enabling you to take advantage of business opportunities and mitigate risks.
SPSS Modeler is available in two editions: SPSS Modeler Professional and SPSS Modeler
Premium. For more information, see the topic IBM SPSS Modeler Editions on p. 3.
© Copyright IBM Corporation 1994, 2012.
1
Page 12

2
Chapter 1
IBM SPSS Modeler Server
SPSS Modeler uses a client/server architecture to distribute requests for resource-intensive
operations to powerful server software, resulting in faster performance on larger data sets.
SPSS Modeler Server is a separately-licensed product that runs continually in distributed analysis
mode on a server host in conjunction with one or more IBM® SPSS® Modeler installations.
In this way, SPSS Modeler Server provides superior performance on large data sets because
memory-intensive operations can be done on the server without downloading data to the client
computer. IBM® SPSS® Modeler S erver also provides support for SQL optimization and
in-database modeling capabilities, delivering further benefits in performance and automation.
IBM SPSS Modeler Administration Console
The Modeler Administration Console is a graphical application for managing many of the SPSS
Modeler Server configuration options, which are also configurable by means of an options file.
The appl ication provides a console user interface to monitor and configure your SPSS Modeler
Server installations, and is available free-of-charge to current SPSS Modeler Server customers.
The applicatio n can be installed only o n Windows computers; however, it can administer a server
installed on any supported platform.
IBM SPSS Modeler Batch
While data mining is usually an interactive process, it is also possible to run SPSS Modeler
from a command line, with out the need for the graphical user interf ace. For example, you might
have long-running or repetitive tasks that you want to perform with no user intervention. SPSS
Modeler Batch is a special ver sion of the product that provides support f or the complete analytical
capabilities of SPSS Modeler without access to t he regular user interface. An SPSS Modeler
Server license is required to use SPSS Modeler Batch.
IBM SPSS Modeler Solution Publisher
SPSS Modeler Solution Pub lisher is a tool that enables you to create a packaged version of an
SPSS Modeler stream that can be run by an external runtime engine or embedded in an external
application. In this way, you can publish and deploy complete SPSS Modeler streams for use in
environments that do not have SPSS Modeler installed. SPSS Modeler Solution Publisher is
distributed as part of the IBM SPSS Collaborat ion and Deployment Services - Scoring service,
for which a separate license is required. With this lice nse, you receive SPSS Modeler Solution
Publisher Runtime, which enables you to execute the published streams.
IBM SPSS Modeler Server Adapters for IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment Services
A number of adapters for IBM® SPSS® Collaboration and Deployment Services are available that
enable SPSS Modeler and SPSS Modeler Server to interact with an IBM SPSS Collaboration and
Deployment Services repo sitory. In this way, an SPSS Modeler stream deployed to the repository
Page 13

can be shared by multiple users, or accessed from the thin-cl ient application IBM SPSS Modeler
Advantage. Yo
u install the adapter on the system that hosts the repository.
IBM SPSS Modeler Editions
SPSS Modeler is available in the following editions.
SPSS Modeler Professional
SPSS Modeler Professional provides all the tools you need to work with most types of structured
data, such as behaviors and interactions tracked in C RM systems, demographics, purchasing
behavior and sales data.
SPSS Modeler Premium
3
About IBM SPSS Modeler
SPSS Modeler Premium is a separately-licensed product that extends SPSS Modeler Pro f essional
to work with specialized data such as that us ed for entity analytics or social networkin g, and with
unstructured text data. SPSS Modeler Premium comprises the following components.
IBM® SPSS® Modeler Entity Analytics adds a completely new dimension to IBM® SPSS®
Modeler predictive analytics. Whereas predictive analytics attempts to predict future behavior
from pas t data, entity analytics focuses on improving the cohere nce and consistency of current
data by resolving identity conflicts within the records themselves. An identity can be that of an
individual, an organization, an object, or any other entity for whic h ambiguity might exist. Identity
resolution can be vital in a number of fields, including customer relationship management, fraud
detection, anti-money laundering, and national and international security.
IBM SPSS Modeler Social Network Analysis transforms information about relationships into
fields that characterize the social behavior of individuals and groups. Using data describing
the relati onships underlying social networ ks, IBM® SPSS® Modeler Social Network Analysis
identifies social leaders who influence the behavior of others in the network. In addition, you can
determine which people are most affected by other network participants. By combining these
results with othe r measure s, you can create comprehensive profiles of individuals on which to
base your predictive models. Models that include this social information will perform better than
models that do not.
IBM® SPSS® Modeler Text Analytics uses advanced ling uistic technologies and Natural
Language Processing (NLP) to rapidly process a large variety of unstructured text data, extract
and organize the key concepts, and group th
categories can be combined with existing structured da ta, such as demographics, and applied to
modeling using the full suite of SPSS Modeler data mining tools to yield better and more focu sed
decisions.
ese concepts into categories. Extracted concepts and
Page 14

4
Chapter 1
IBM SPSS Modeler Documentation
Documentation in online help form at is available from the Help menu of SPSS Modeler. This
includes documentation for S PSS Modeler, SPSS Modeler Server, and SPSS Modeler Solution
Publisher, as well as the Applications Guide and other supporting materials.
Complete do cumentation for each product (including installation instructions) is available in PDF
format under the \Documentation folder on each product DVD. Installation documents can also be
downloaded from the web at http://www-01.ibm.com/support/docview.wss?uid=swg27023172.
Documentation in both formats is also available from the SPSS Modeler Information Center at
http://publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/spssmodl/v15r0m0/.
SPSS Modeler Professional Documentation
The SPSS Modeler Professional documentation suite (excluding installation instruc tions) is
as follows.
IBM SPSS Modeler User’s Guide.
to build data streams, handle missing values, build CLEM expressions, work w ith projects and
reports, and package streams for deployment to IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment
Services, Predictive Applications, or IBM SPSS Modeler Advantage.
IBM SPSS Modeler Source, Process, and Output Nodes.
read, process, and o utput data in different formats. Effective ly this means all nodes other
than modeling nodes.
IBM SPSS Modeler Modeling Nodes.
models. IBM® SPSS® Modeler offers a v ariety of modeling methods taken from machine
learning, artificial intelligence, and sta tistics.
IBM SPSS Modeler Algorithms Guide.
modeling methods used in SPSS Modeler. This guide is available in P DF format only.
IBM SPSS Modeler Applications Guide.
introductions to specific modeling methods and techniques. An on line version of this guide
is also available from the Help menu. For more information, see the topic Application
Examples on p. 5.
IBM SPSS Modeler Scripting and Automation.
scripting, including the properties that can be used to manipulate nodes and streams.
IBM SPSS Modeler Deployment Guide.
scenarios as steps in processing jobs under IBM® SPSS® Collaboration and Deployment
Services Deployment Manager.
IBM SPSS Modeler CLEF Developer’s Guide.
programs such as data processing routines or modeling algorithms as nodes in SPSS M odeler.
IBM SPSS Modeler In-Database Mining Guide.
database to improve performance and extend the range of analytical capabilities through
third-party algorithms.
IBM SPSS Modeler Server Administration and Performance Guide.
configure and administer IBM® SPSS® Modeler Server.
General introduction to using SPSS Modeler, including how
Descriptions of all the nodes used to create data mining
Descriptions of a ll the nodes used to
Descriptions of the mathematical foundations of the
The examples in this guide provide brief, targeted
Information on automating th e system through
Information on running SPSS Modeler streams and
CLEF provides the ability to integrate third-party
Information on how to use the power of your
Information on how to
Page 15

IBM SPSS Modeler Administration Console User Guide.
console user interface for monitoring and configuring SPSS Modeler Server. The console is
implemented a
IBM SPSS Modeler Solution Publisher Guide.
s a plug-in to the Deployment Manager application.
component that enables organizations to publish streams for use outside of the standard
SPSS Modeler environment.
IBM SPSS Modeler CRISP-DM Guide.
for data mining with SPSS Modeler.
IBM SPSS Mod
eler Batch User’s Guide.
mode, including de tails of batch mode execution and command-line arguments. This guide
is available in PDF format only.
SPSS Modeler Premium Documentation
The SPSS Modeler Premium documentation suite (excluding installation instr uctions) is as
follows.
IBM SPSS Modeler Ent
SPSS Modeler, covering repos itory insta llation and co nfiguration, entity analytics nodes,
and administrative tasks.
IBM SPSS Modeler Social Network Analysis User Guide.
analysis with SPSS Mo
SPSS Modeler Text Analytics User’s Guide.
Modeler, covering the text mining nodes, interactive workbench, templates, and other
resources.
IBM SPSS Modeler Text Analytics Administration Console User Guide.
and using the console us er interface for monitoring and configuring IBM® SPSS® Modeler
Server for use with SPSS Modeler Text Analytics . The cons ole is implemented as a plug-in
to the Deployment Manager application.
ity Analytics User Guide.
deler, including group an alysis and diffusion analysis.
5
About IBM SPSS Modeler
Information on installing and using the
SPSS Modeler Solution Publis her is an add-on
Step-by-step guide to using the CRISP-DM methodology
Complete guide to using IBM SPSS Modeler in batch
Information on using entity analytics with
A guide to perform ing social network
Information on using text analytics with SPSS
Information on installing
Application Examples
While the d ata mining tools in SPS S Modeler can help solve a wide variety of business and
organizational pro blems, t
modeling methods and techniques. The data sets used here are much smaller than the enormous
data stores managed by some data miners, but the concepts and methods involved should be
scalable to real-world app
You can access the examples by clicking
Modeler. The data files and sam ple streams are installed in the Demos folder under the product
installation directory.
Database modeling examples.
Guide.
Scripting examples.
See the examples in the IBM SPSS Modeler Scripting and Automation Guide.
he application examples provide brief, targeted introductions to specific
lications.
Application Examples
on the Help menu in SPSS
For more information, see the topic Demos Folder on p. 6.
See the examples in the IBM SPSS Modeler In-Database Mining
Page 16
6
Chapter 1
Demos Folder
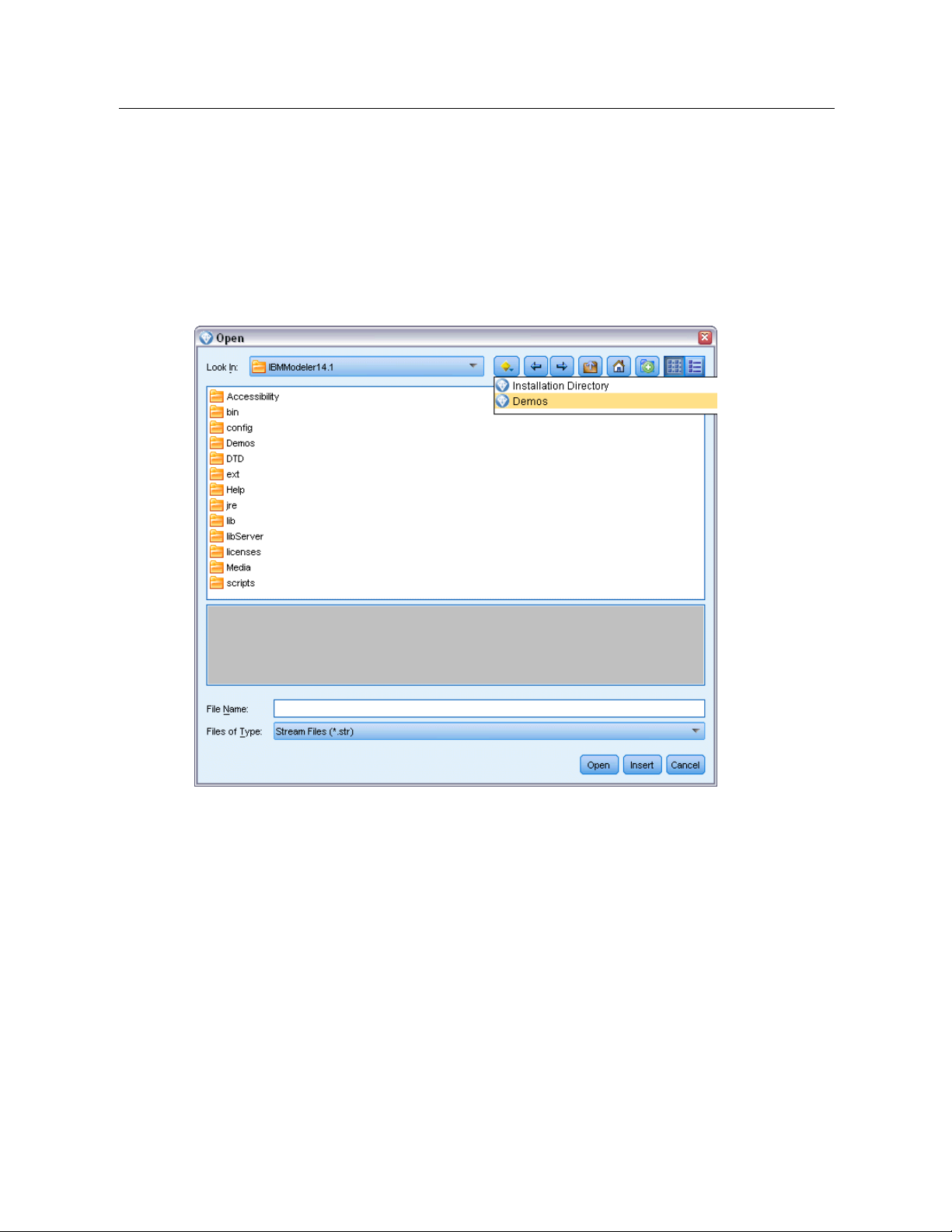
The data files and sample streams used with the application examples are installed in the Demos
folder under the product installation directory. This folder can also be accessed from the
SPSS Modeler 15
recent directories in the File Open dialog box.
Figure 1-1
Selecting the Demos folder from the list of recently-used directories
IBM
program gr oup on the Windows Start menu, or by clicking Demos on the list of
Page 17

New Features
New and Changed Features in IBM SPSS Modeler 15
From this release onwards, IBM® SPSS® Modeler has the following editions.
IBM® SPSS® Modeler Professional
IBM® SPSS® Modeler Premium
features to those supplied by SPSS Modeler Professional.
The new features for these edit ions are described in the following sections.
New features in IBM SPSS Modeler Professional
The IBM® SPSS® Modeler Professional edition adds the following features in this release.
is the new name for the existing SPSS Modeler product.
is a sepa r ately-licensed product that provides additio nal
Chapter
2
2
22
GLMM modeling node.
that: the target is linearly related to the factors and covariates via a specified link function; the
target can have a non-normal d is tribution; and the observations can be correlated. Generalized
linear mixed models cover a wide variety of models, from simple linear regression to co mplex
multilevel models for non-normal longitudinal data. For more information, see the topic New
Nodes in This Release on p. 10.
Support for maps in the Graphboard node.
number of map types. These include choropleths (wher e regions can be given different colors
or patterns to indicate different values) and point overlay maps (where geospatial points are
overlaid on the map).
IBM® SPSS® Modeler ships with several map file s, but you can use the Map Conversion Utility
to convert your existing map shapefiles for use with the Graphboard Template Chooser.
Netezza Time Series and Generalized Linear nodes.
Netezza® Analytics in - database mining: Time Series and Generalized Linear. For more
information, see the topic New Nodes in This Release on p. 10.
Netezza nodes enabled through Helper Applications.
nodes are now enabled in the same way as the other database modeling nodes.
Generalized linear mixed models (GLMMs) extend the linear model so
The Graphboard node now includes support for a large
Two new nodes are available for IBM®
The Netezza Analytics database modeling
Zooming in and out on the stream view.
from the standard size. This feature is particularly useful for gaining an overall view of a complex
stream, or for minimizing the number of pages needed to pri nt a stream. For more information,
see the topic Changing the icon size for a stream in Chapter 3 on p. 24.
© Copyright IBM Corporation 1994, 2012.
It is now possible to scale the entire stream view up or down
7
Page 18

8
Chapter 2
Default settings for database connections.
and Ora cle dat
abase connections, as we ll as those already supported for IBM DB2 InfoSphere
You can now specify default settings for SQL Server
Warehouse.
Stream properties and optimization redesign.
The Options tab on the Stream Properties dialog box
has been redesigned to group the options into categories. The Optimizatio n options have also
moved from User Options to Stream Properties. For more information, see the topic Setting
Options for Streams in Chapter 5 on p. 54.
Node execution timing.
You can now set an option to display individ ual execution times for
the nodes in a stream. For more information, see the topic Viewing Node Execution Times in
Chapter 5 on p. 67.
You can also set an option (time_ecode_execution_log) in the server configuration file to record
these execution times in the message log.
Stream parameters in SQL queries from Database source node.
You can now include SPSS Modeler
stream parameters in SQL queries that you enter in the Database source node.
Expression Builder supports in-database functions.
If a stream connects to a database through a
Database source node and you use the Expression Builder with a downstream node, you can
include in-database functions from the connected database directly in the expression you are
building. For more in f ormation, see the t opic Selecting Functions in Cha pter 7 on p. 120.
IBM Cognos BI node enhancements.
The Cognos BI source node now supports importing C ognos
list reports as we ll as data, and additionally supports the use of parameters and filters.
For the Cognos BI source a nd export nodes, SPSS Modeler now automatically detects the version
of IBM Cognos BI in use.
Enhancements to Aggregate node.
The Aggregate node n ow supports several new aggregation
modes for aggregate fields: median, count, variance, and first and third quartiles.
Merge node supports conditional merge.
You can now perform input record merges that depend on
satisfying a condition. You can specify the condition directly in the n ode, or build the conditio n
using the Expression Builder.
Enhancements to in-database mining nodes for IBM DB2 InfoSphere Warehouse.
For in-database
mining with IBM DB2 InfoSphere Warehouse, the ISW Clustering node now supports the
Enhanced BIRCH algorithm in addition to demographic and Koho nen clustering. In addition, the
ISW Associ ation node provides a choice of layout for non-transactional (tabular) data.
Table compression for database export.
When exporting to a database, you can now specify table
compression options for SQL Server and Oracle database connections, as well as those already
supported for IBM DB2 InfoSphere Warehouse.
Bulk loading for database export.
Additional help information is available for database bulk loading
using an external loader program.
Page 19

New Features
9
SQL generation enhancements.
timestamp, an
d string data types, in additi on to integer and real. With IBM Netezza databases, the
The Aggregate node now supports SQL generation for date, time,
Sample node supports SQL generation for simple and complex sampling, and the Binn ing node
supports SQL generation for all binning methods except Tiles.
In-database model scoring.
For I B M DB2 for z/OS, IBM Netezza and Teradata da tabases, it is
possible to enable SQL pushback of many of the model nuggets to carry out model scoring (as
opposed to in-database mining) within the database. To do this, you can install a scoring adapter
into the database. When you publish a model for the scoring adapter, the model is enabled to use
the user-defined function (UDF) capabilities of the database to perform the scoring.
A new configuration option, db_udf_enabled in options.cfg, causes the SQL generation option
to generate UDF SQL by default.
New format for database connection in batch mode.
The format for specifying a database connection
in batch mode has changed to a single argument, to be consistent with the way it is specified in
scripting.
Enhancements to SPSS Statistics integration.
are available on the Syntax tab th r ough the
On the Statistics Output node, additional procedures
Select a dialog
button. The Regres sion submenu
now supports Partial Least Squares regression, and there is a new Forecasting submenu with the
following op tions: Spectral Analysis, Sequence Charts, Autocorrelations, and Cross-correlations.
For mor e information, see the SPSS Statistics documentation.
The Syntax tab of the Statistics Output node also has a new option to generate a Statistics File
source node for importing the data that results fr om running a stream containing the node. This is
useful where a procedure writes fields such as scores to the active datas et in addition to displaying
output, as these fields would otherwise not be visible.
Non-root user on UNIX servers.
If you have SPS S Modeler Server installed on a UNIX server, you
can now install, configure, and start and stop SPSS Modeler Server as a non-root user without the
need for a pr ivate password database.
Deployed streams can now access IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment Services model
management features.
When a stream is deployed to IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment
Services as a str eam, it can now use the same model management features as it could if deployed
as a scenario. These features include evaluation, refresh, score, and champion/challenger.
Improved method of changing ODBC connection for SPSS Modeler stream and scenario job steps.
For
stream and scenario job steps in IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment Services, changes to
an ODBC connection and related logon credentials apply to all rela ted job steps. This means that
you no longer have to change the job steps one by one.
Choice of execution branch in deployed streams.
For stream job steps in IBM SPSS Collaboration
and Deployment Services, if the stream contains branches you can now choose one or more
stream branches to execute.
Page 20

10
Chapter 2
New features in IBM SPSS Modeler Premium
IBM® SPSS® Modeler Premium is a separately-licensed product that provides additional features
to those supplied by IBM® SPSS® Modeler Professional. Previously, SPSS Mode ler Premi um
included only IBM® SPSS® Modeler Text Analytics . The full set of SPS S Modeler Premium
features is now as follows.
SPSS Modeler Text Analytics
IBM® SPSS® Modeler Entity Analytics
IBM® SPSS® Modeler Social Network Analysis
SPSS Modeler Text Analytics uses advanc ed linguistic technologies and Natural Language
Processing (NLP) to rapidly process a large variety of unstructured text data, extract and organize
the key concepts, and group these concepts into categories. Extracted concepts and categories
can be combined with existing structured data, such as demographics, and applied to modeling
using the full suite of IBM® SPSS® Modeler data mining tools to yield better and more focused
decisions.
IBM SPSS Modeler Entity Analytics adds a complet ely ne w dimension to SPSS Modeler
predictive analytics. Whereas predictive analytics attempts to predict future behavior from past
data, entity analytics focuses on improving the coherence and consistency of current data by
resolving identity conflicts within the records themselves. An identity can be that of an individual,
an organization, an object, or any other entity for which ambiguity might exist. Identity resolution
can be vital in a number of fields, including customer relationship management, fraud detection,
anti-money laundering, and national and international security.
IBM SPSS Modeler Social Network Analysis transforms information about relationships into
fields that characterize the social behavior of individuals and groups. Using data describing the
relationships underlying social networks, IBM SPSS Modeler Social Network Analysis identifies
social leaders who influence the behavior of others in the network. In addition, you can determine
which people are most affected by other network participants. By combining these results with
other measures, you can create comprehensive profiles of individuals on which to base your
predictive models. Models that inclu de this social information will perform better than models
that do not.
Note: SPSS Modeler Professional must be installed before installing any of the SPSS Modeler
Premium features.
New Nodes in This Release
IBM SPSS Modeler Professional
A generalized linear mixed model (GLMM) extends th e linear model so that the target
can have a non-normal distribution, is linearly related to the factors and covariates via
a specified link function, and so that the observations can be correlated. Generalized
linear mixed models cover a wide variety of models, from simple linear regression to
complex multilevel models for non-normal longitudinal data.
Page 21

The Netezza Time Series node analyzes time series data and can predict future
behavior from past events.
The Netezza Generalized Linear model expands the linear regression model so that
the dependent variable is related to the predictor vari ables by means of a specified
link function. Moreover, the model all ows for the dependent variable to have a
non-normal distribution.
IBM SPSS Modeler Premium
The EA Export node is a terminal node that reads entity data from a data source and
exports the data to a repository for the purpose of entity resolution.
11
New Features
The Entity Analytics(EA) source node reads the resolved entities from th e repository
and passes th
is data to the stream for further processing, such as formatting into
a report.
The Streaming EA node compares new cases against the entity data in the repository.
The SNA Group Analysis node builds a model of a social net w ork based on input
data about the social groupings within the network. This technique identifies links
between the group members, and analyzes the interactions within the groups to
produce key performance indicators (KPIs). The KPIs can be used for purposes such
as churn prediction, anomaly detection, or group leader identification.
The SNA Diffusion Analysis node models the flow of information from a group
member to t heir social environment. A group member is assigned an initial weighting,
which is propagated across the network as a gradually reducing figure. This process
continues until each member of the network has been assigned a weighting relative to
the original group member, according to the amount of information that has reached
them. The individual member scores are then derived directly from these weightings.
In this way, for examp l e, a service provider could identify customers that are at a
higher risk of churn according to their relationship with a recent churner.
Page 22
IBM SPSS Modeler Overview
Getting Started
As a data mining application, IBM® SPSS® Modeler offers a strategic approa ch to finding useful
relationships in large data sets. I n contrast to more traditional statistical methods, you do not
necessarily need to know what you are looking for when you start. You can explore y our data,
fitting different models and investigating different relationships, until you find useful information.
Starting IBM SPSS Modeler
To start the application, cli ck:
Start > [All] Programs > IBM SPSS Modeler15 > IBM SPSS Modeler15
Chapter
3
3
33
The main window is displayed after a few seconds.
Figure 3-1
IBM SPSS Modeler main application window
© Copyright IBM Corporation 1994, 2012.
12
Page 23
Launching from the Command Line
You can use the command li ne of your operating system to launch IBM® SPSS® Modeler
as follows:
E
On a computer where IBM® SPSS® Modeler is installed, open a DOS, or command-prompt,
window.
E
To launch the SPSS Modeler interface in interactive mode, type the modelerclient command
followed by the re quired arguments; for example:
modelerclient -stream report.str -execute
The ava ilable arguments (flags) allow you to connect to a se r ver, load streams, run scripts, or
specify other parameters as needed.
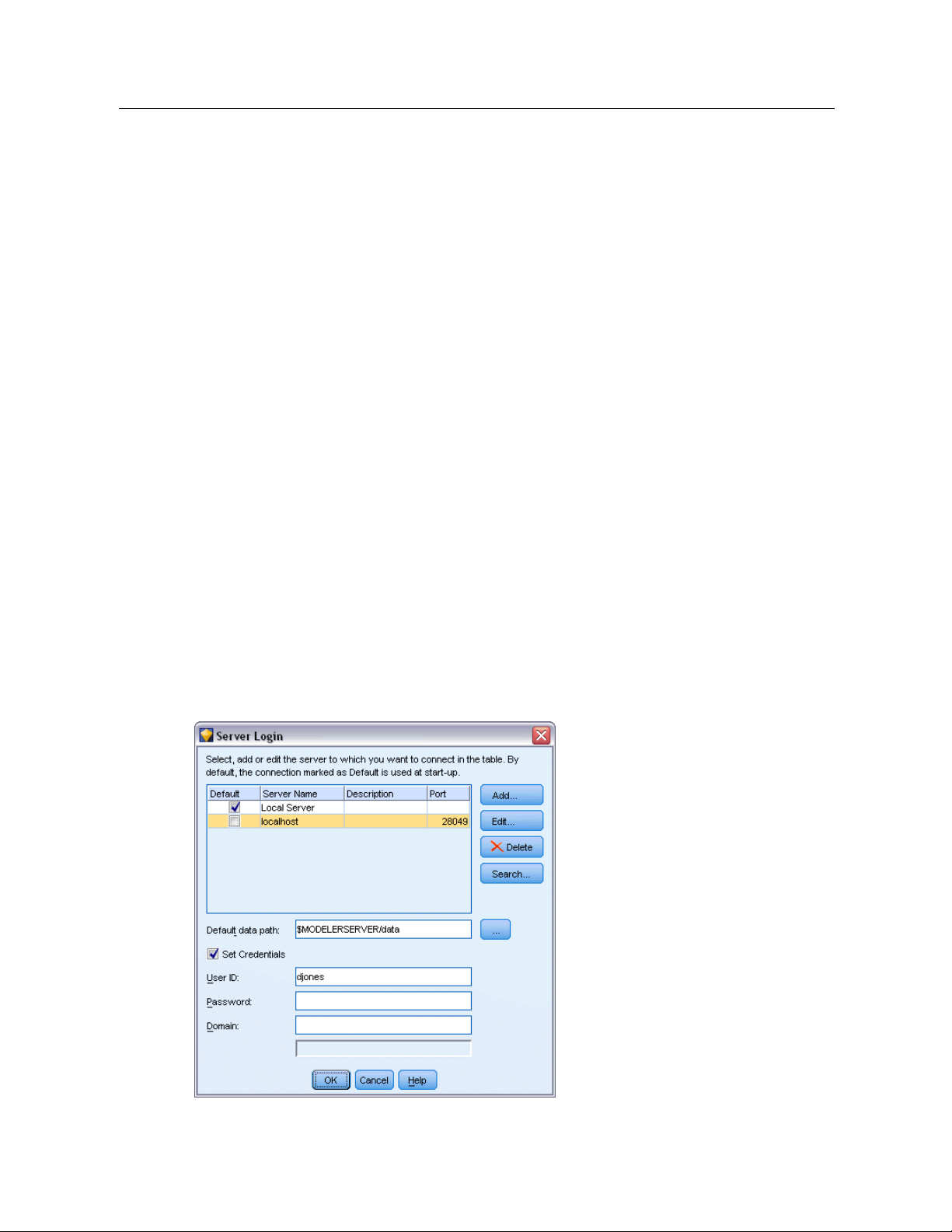
Connecting to IBM SPSS Modeler Server
IBM® SPSS® Modeler can be run as a standalone application, or as a client connected to IBM®
SPSS® Modeler Server directly or to an SPSS Modeler Server or server cluster through the
Coordinator of Processes plug- in from IBM® SPSS® Collaboration and Deployment Services.
The current connection status is displayed at the bottom left of the SPSS Modeler window.
Whenever you want to connect to a server, you can ma nually enter the server name to which
you want to connect or select a name that you have previously defined. How ever, if you have I B M
SPSS Collaboration an d Deployme nt Services, you can search through a list of servers or server
clusters fro m the Server Login dialog box . The ability to browse through the Statistics services
running o n a network is made available through the Coordinator of Processes.
13
IBM SPSS Modeler Overview
Figure 3-2
Server Login dialog box
Page 24

14
Chapter 3
To Connect to a Server
E
On the Tools menu, click
Server Login
. The Server Login dialog box opens. Alternatively,
double-click the connection status area of the SPSS Modeler window.
E
Using the dialog box, specify options to connect to the local server computer or select a connection
from the table.
Click
AddorEdit
to add or edit a connection . For mor e information, see the topic Adding and
Editing the IBM SPSS Modeler Server Connection on p. 14.
Click
Search
to acces s a server or server cluster in the Coordinator of Processes. For more
information, s ee the topic Searching for Servers in IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment
Services on p. 16.
Server table.
This table c ontains the set of defined server connections. The table displays the
default connection, server name, description, and port number. You can manually add a new
connection, as well as select or search for an existing connection. To set a particular server as the
default conne ction, select the check box in the Default column in the table for the connection.
Default data path.
Specify a path used for data on the server com puter. C lick the ellipsis button
to browse to the required location.
Set Credentials.
Leave this box unchecked to enable the single sign-on feature, which attempts
to log you in to the server using your local computer username and password details. If single
sign-on is not possible, or if you check this box to disable single sign-on (for example, to log in to
an administrator account), the following fields are enabled for you to enter your credentials.
User ID.
Password.
Domain.
Enter the user name with which to log on to the server.
Enter the passwo r d associa ted with the specified user name.
Specify the domain used to log on to the server. A domain name is required only when
the server computer is in a different Windows domain th an the client computer.
E
ClickOKto complete the connection.
To Disconnect from a Server
E
On the Tools menu, click
double-click the con
Server Login
. The Server Login dialog box opens. Alternatively,
nection status area of the SPSS Modeler window.
(...)
E
In the dialog box, select the Local Server and clickOK.
Adding and Editing the IBM SPSS Modeler Server Connection
You can manually edit or add a server connection in the Server Login dialog box. By clicking
Add, you can access an empty Add/Edit Server dialog box in which you can enter server
connection details. By selecting an existing connection and clicking Edit in the Server Login
dialog box, the Add/Edit Server dialog box opens with the details for that connection so that
you can make any changes.
Page 25
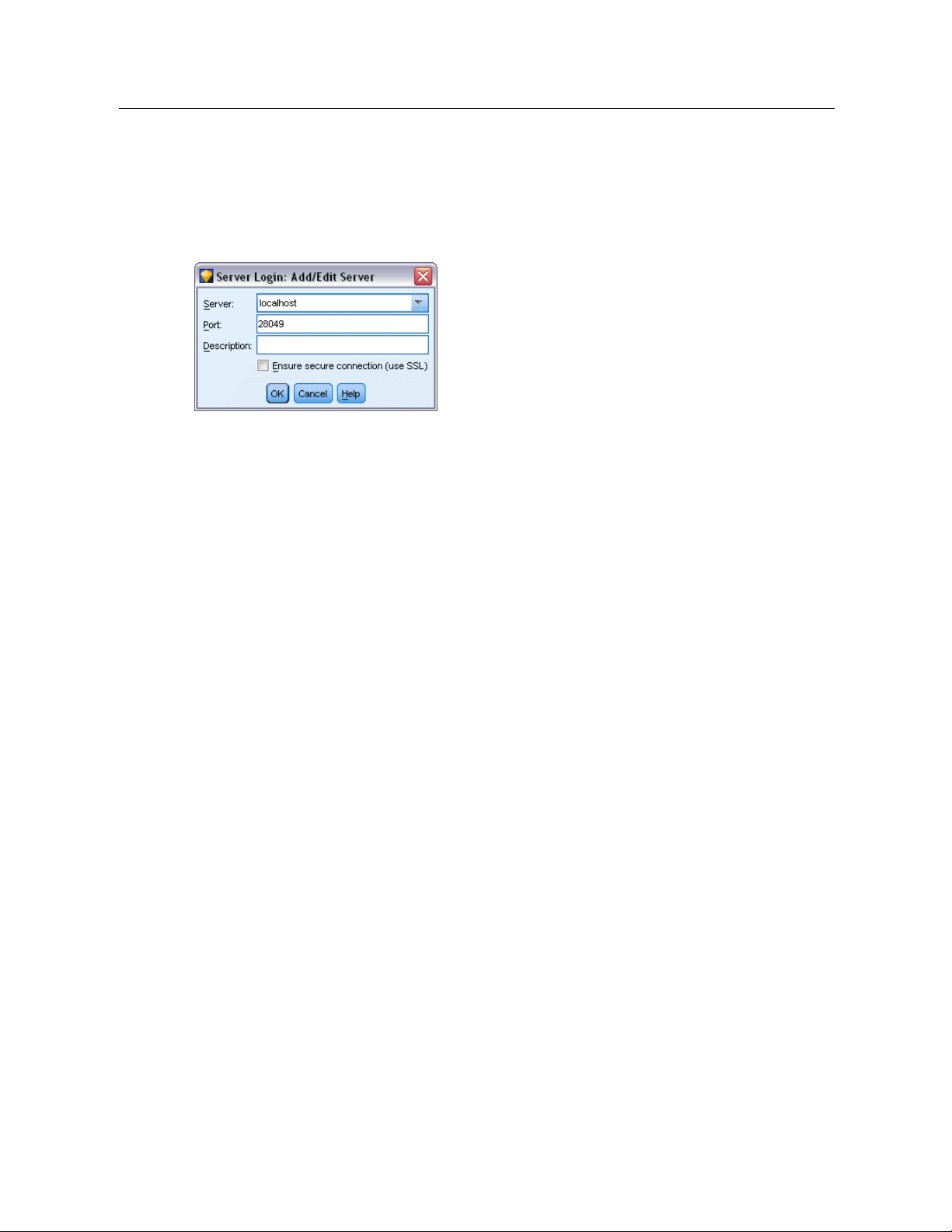
IBM SPSS Modeler Overview
Note: You cannot edit a server connection that was added f r om IBM® SPSS® Collaboration
and Deploymen
t Services, since the name, port, and other deta ils are defined in IBM SPSS
Collaboration and Deployment Services.
15
Figure 3-3
Server Login
Add/Edit Server dialog box
To Add Server Connections
E
On the Tools menu, click
E
In this dialog box, click
E
Enter the server connection details and clickOKto save the connection and retu r n to the Server
Server Login
Add
. The Server Login Add/Ed it Server dialog box opens .
. The Server Login dialog box opens.
Login dialog box.
Server.
Specify an ava ilable server or select one from the list. The server computer can be
identified by an alphanumeric name (for example, myserver) or an IP address assigned to the
server computer (for example, 202.123.456.78).
Port.
Give the port number on which the server is listening. If the d efault does not work, ask
your system administrator for the corre ct port number.
Description.
Ensure secure connection (use SSL).
Enter an optional description for this server con ne ction.
Specifies whether an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer)
connection should be used. SSL is a commonly used protocol for securing data sent over a
network. To use this feature, SSL must be enabled on the server hosting IBM® SPSS®
Modeler Server. If necessary, contact your local administrator for details.
To Edit Server Connections
E
On the Tools menu, click
E
In this dialog box, select the connec tion you want to ed it and then click
Server Login
. The Server Login dialog box opens.
Edit
. The Server Login
Add/Edit Server dialog box opens.
E
Change the server connection details and clickOKto save the changes and return to the Server
Login dialog box.
Page 26
16
Chapter 3
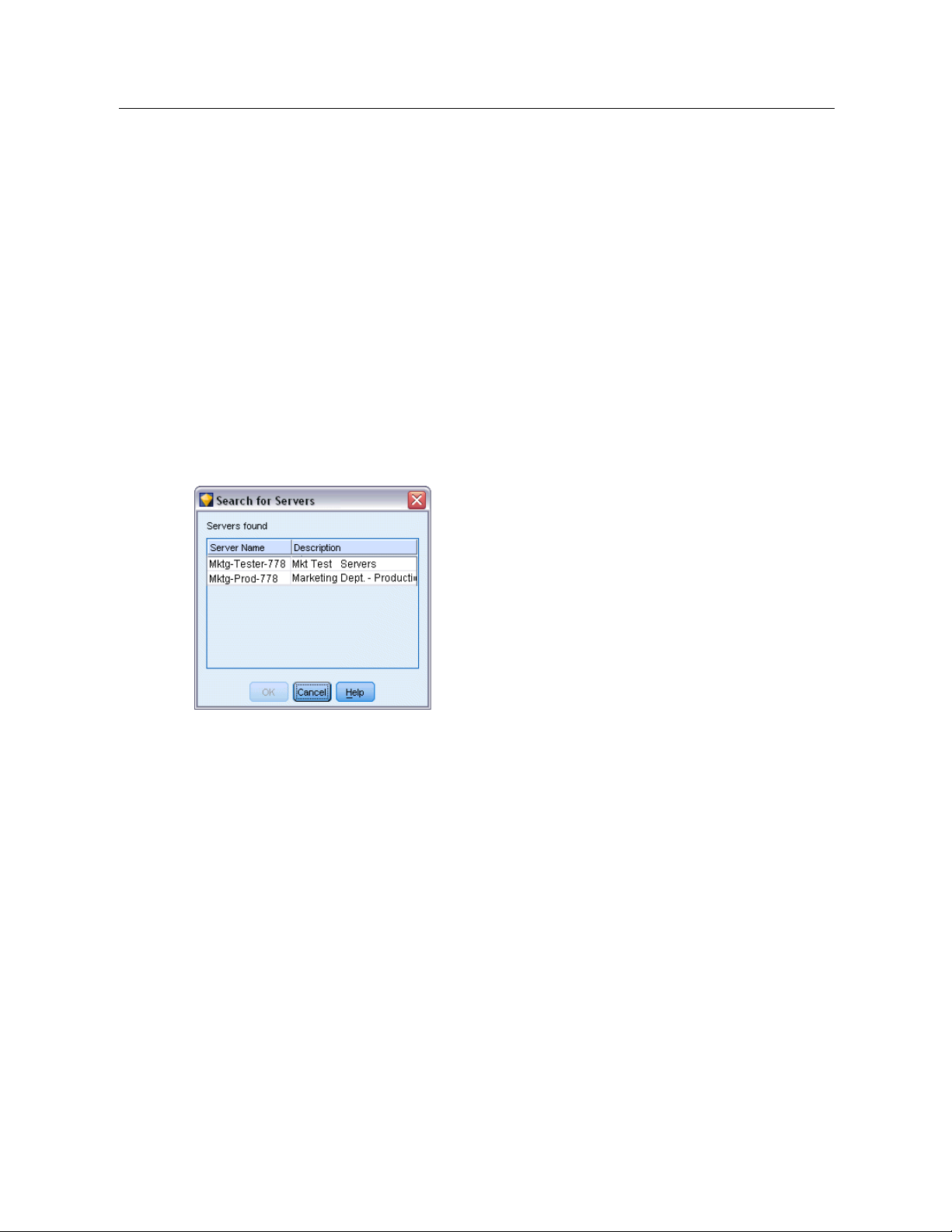
Searching for Servers in IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment Services
Instead of entering a server connection manually, you can select a server or server cluster available
on the network through the Coor dinator of Processes, available in IBM® SP SS® Collab oration
and Deployment Services. A server cluster is a group of servers from which the Coordinator of
Processes determines the server best suited to respond to a processing request.
Although you can ma nually add servers in the Ser ver Login dialog box, searching for available
servers lets you connect to servers without requiring that you know the correct server name and
port number. This information is autom atically provided. However, you still need the correct
logon information, such as username, domain, and pass word.
Note: If you do not have access to the Coordinator of Proc esses capability, you can still manually
enter the server name to which you want to connect or select a name that you have previously
defined. For more information, see the topic Adding and Editing the IBM SPSS Modeler Server
Connection on p. 14.
Figure 3-4
Search for Servers dialog box
To search for servers and clusters
E
On the Tools menu, click
E
In this dialog box, click
logged on to IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deployment Services when you attempt to browse
the Coordinator of Processes, you will be prompted to do so. For more information, see th e
topic Connecting to the Repository in Chapter 9 on p. 161.
E
Select the server or server cluster from th e list.
E
ClickOKto close the dialog box and add this connection to the table in the Server Login dialog box.
Changing the Temp Directory
Some operations perfor med by IBM® SPSS® Modeler Server may require temporary files to be
created. By default, IBM® SPSS® Modeler uses the system temporary directory to create temp
files. You can alter the location of the temporary directory using the following steps.
E
Create a new directory called spss and subdirectory called servertemp.
Server Login
Search
to open the Search for Ser ve r s dialog box. If you are not
. The Server Login dialog box opens.
Page 27

E
Edit options.cfg, located in the /config directory of y our SPSS Modeler ins tallation directory. Edit
the temp_dire
E
After doing this, you must restart the SPSS Modeler Server service. You can do this by clicking
the
Services
ctory parameter in this file to read:
tab on your Windows Control Panel. Just stop the service and then start it to activate
the changes you made. Restarting the m achine will also restart the service.
All temp files will now be written to this new directory.
Note: The most common error when you are attempting to do this is to use the wrong type of
slashes. Because of SPSS Modeler’s UNIX history, forward slashes are used.
Starting Multiple IBM SPSS Modeler Sessions
If you need to launch more than one IBM® SPSS® Modeler s ession at a time, you must make
some changes to your IBM® SPSS® Modeler and Windows settings. For example, you may
need to do th is if you have two separate se r ver license s and want to run two streams against two
different servers from the same client machine.
To enable multiple SPSS Modeler sessions:
IBM SPSS Modeler Overview
temp_directory, "C:/spss/servertemp"
17
.
E
Click:
Start > [All] Programs > IBM SPSS Modeler15
E
On the IBM SPSS Modeler15 shortcut (the one with the icon), right-click and select
E
In the
Target
text box , add
E
In Windows Explorer, select:
Tools > Folder Options...
E
On the File Types tab, select the SPSS Modeler Stream option and click
E
In the Edit File Type dialog box, select
E
In the
Application used to perform action
-noshare
to the end of the string.
Open with SPSS Modeler
text box, add
IBM SPSS Modeler Interface at a Glance
At each point in the data mining proce ss, IBM® SPSS® Modeler’s easy-to-use interface invites
your specific business e xpertise. Modeling algorithms, such as prediction, classification,
segmentation, and association detection, ensure powerful and accurate models. Model results
can easily be deployed a nd read into databases, IBM® SPSS® Statistics, and a wide variety
of other applications.
-noshare
and click
before the
Advanced
Edit
.
-stream
Properties
.
argument.
.
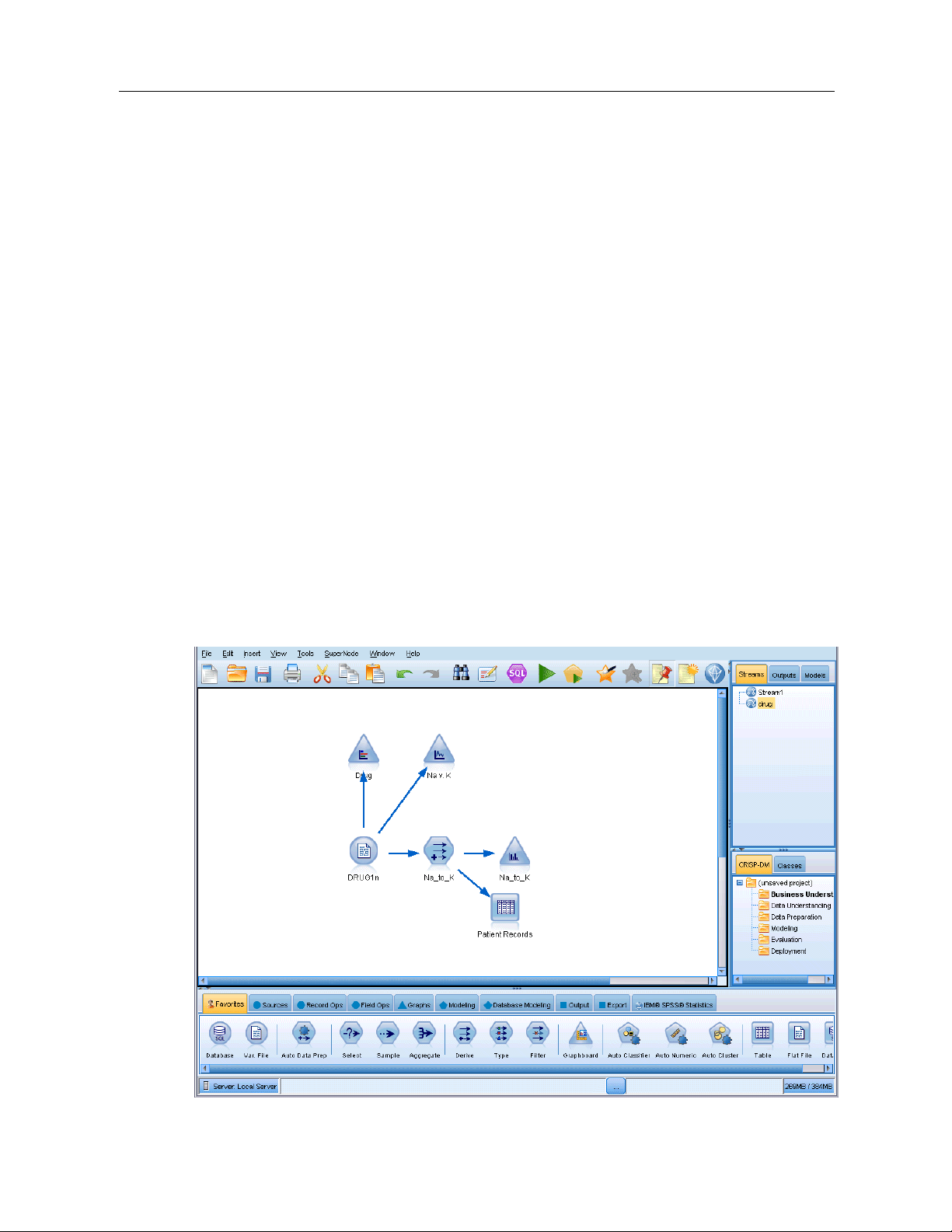
Working with SPSS Modeler is a three-step process of working with data.
First, you read data into SPSS Modeler.
Next, you run the data through a series of manipulations.
Finally, you send the data to a destination.
Page 28

18
Chapter 3
This sequ ence of operations is known as a data stream because the data flows record by record
from the sourc
e through each manipulation and, finally, to the destination—either a model or
type of data output.
Figure 3-5
A simple stream
IBM SPSS Modeler Stream Canvas
The stream canvas is the largest area of the IBM® SPSS® Modeler window and is where you will
build and manipulate data streams.
Streams are created by drawing diagrams of data operations relevant t
main canvas in the interface. Each operation is represented by an icon or node, and the nodes are
linked together in a stream representing the flow of data through each operation.
You can work with multiple streams at one time in SPSS Modeler, either i
canvas or by opening a new stream canvas. During a sessi on, streams are stored in the Streams
manager, at the upper right of the SPSS Modeler window.
o your business on the
n the same stream
Nodes Palette
Most of the data and modeling tools in IBM® SPSS® Modeler reside in the Nodes Palette, acr oss
the b ottom o f the window below the stream canvas.
For example, the Record Ops palette tab contains nodes that you can use to perform operations
on the data records, such as selecting, merging, and appending.
To add nodes to the canvas, double-click icons from the Nodes Palette or drag and drop them
onto the canvas. You then connect them to create a stream, representing the flow of data.
Figure 3-6
Record Ops tab on the nodes palette
Each palette tab contains a collection of related nodes used for different p hases of stream
operations, such as :
Sources.
Record Ops.
appending.
Nodes bring data into SPSS Modeler.
Nodes perform operations on data records, such as selecting, merging, an d
Page 29
IBM SPSS Modeler Overview
Field Ops.
Nodes perform operations on data fields, such as filtering, deriving new fields, and
determining the measurement level for given fields.
Graphs.
Nodes graphically display data before and after modeling. Graphs include plots,
histograms, web nodes, and evaluation charts.
Modeling.
des use the modeling algorithms available in SPSS Modeler, such as neural nets ,
No
decision trees, clustering algorithms, and data sequencing.
Database Modeling.
Nodes use the modeling algorithms available in Microsoft SQL Server,
IBM DB2, and Oracle database s.
Output.
Nodes produce a variety of output for d ata, charts, and model results that can be
viewed in SPSS Modeler.
Export.
es prod uce a variety of output that can be viewed in external applications, such
Nod
as IBM® S PSS® Data Collection or Excel.
SPSS Statistics.
Nodes import data from, or export data to, IBM® SPSS® Stat is tics, as well as
running SPSS Statistics procedures.
As you become more familiar with SPSS Modeler, you can customize the palette contents for
your own use. For more information, see the topic Customizing the Nodes Palette in Chapter 12
on p. 223.
Located below the Nodes Palette, a report pane provides feedback on the progress of various
operations, such as when data is being read into t he data stream. Also located below the Nodes
Palette, a status pane provides info r mation on what the application is currently doing, as well as
indications of when user feedback is required.
19
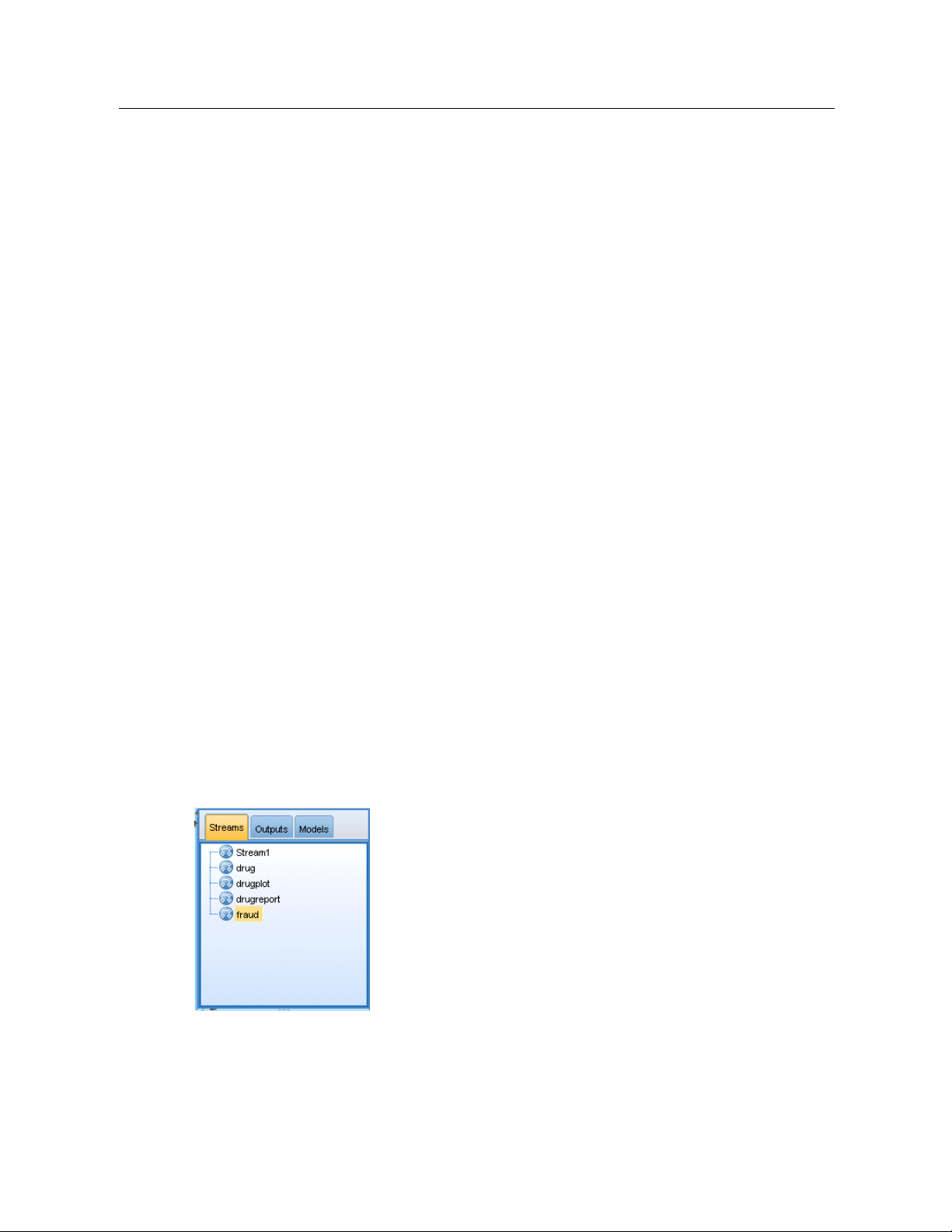
IBM SPSS Modeler Managers
At the top right of the window is the managers pane . This has three tabs, which are used to
manage streams, output and models.
You can use the Streams tab to open, rename, save, and dele te the streams created in a session.
Figure 3-7
Streams tab
The Outputs tab contains a variety of files , such as graphs and tables, produced by stream
operations in IBM® SPSS® Modeler. You can display, save, rename, and close the tables, graphs,
and reports listed on this tab.
Page 30
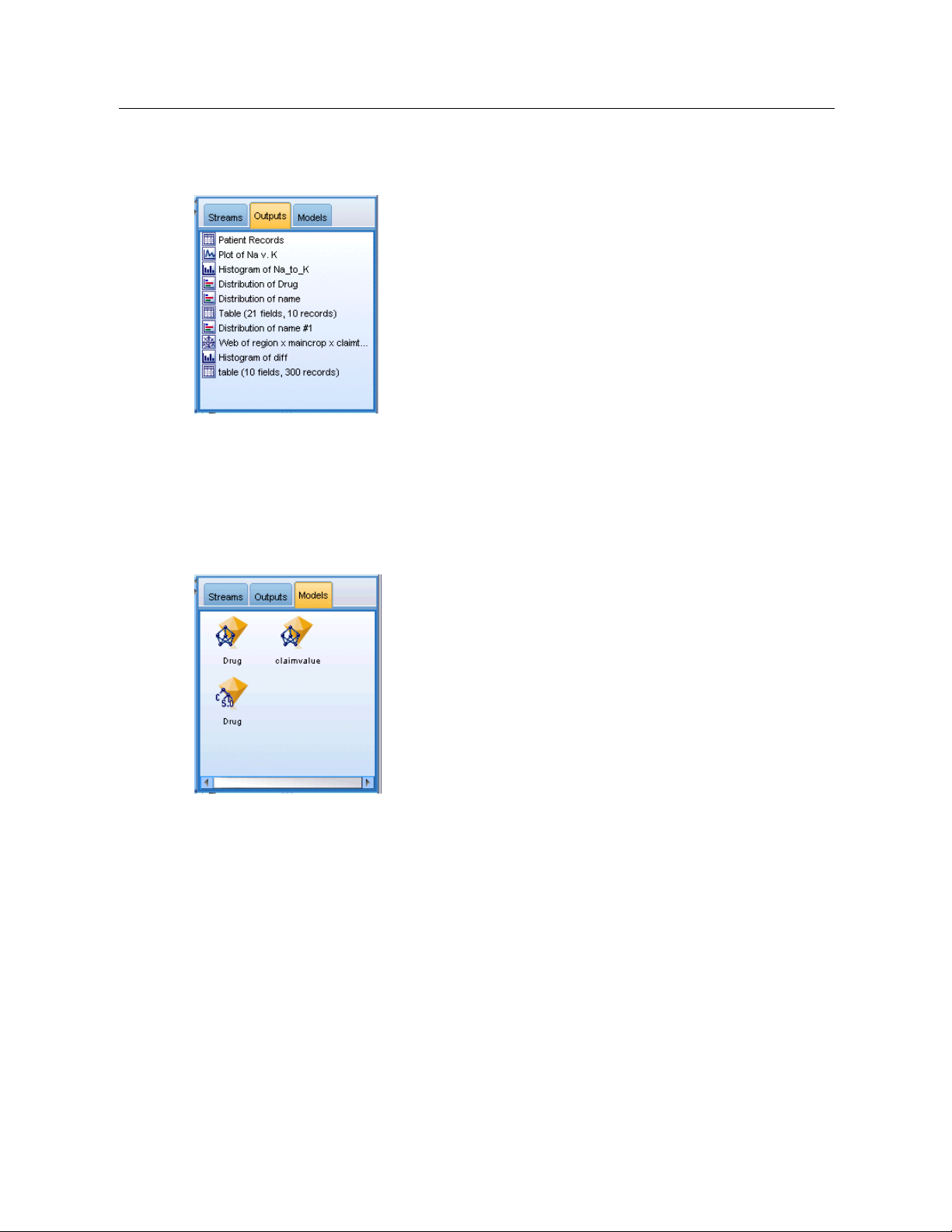
20
Chapter 3
Figure 3-8
Outputs tab
The Models tab is the most powerful of the manager tabs. This tab contains all model nuggets,
which contain the models generated in SPSS Modeler, for the current session. These models can
be browsed directly from the Models tab or added to the stream in the c anvas.
Figure 3-9
Models tab containing model nuggets
IBM SPSS Modeler Projects
On the lower right side of the window is the project pane, used to create and manage data mining
projects (groups of files related to a data mining task). There are two ways to view projects you
in IBM® SPSS® Modeler—in the Classes view and the CRISP-DM view.
create
The CRISP-DM tab provides a way to organize projects according to the Cross-Industry
Standard Process for Data Mining, an industry-proven, nonproprietary methodology. For both
enced and first-time data miners, using the CRISP-DM tool will help you to better o rganize
experi
and communicate your efforts.
Page 31

IBM SPSS Modeler Overview
Figure 3-10
CRISP-DM view
The Classes tab provides a way to organize your work in SPSS Modeler categorically—by the
types of objects you create. This view is useful when taking inventory of data, streams, and
models.
Figure 3-11
Classes view
21
IBM SPSS Modeler Toolbar
At the top of the IBM® SPSS® Modeler window, you will find a toolbar of icons that provides a
number of useful functions. Following a r e the toolbar buttons and their functions.
Create new stream Open stream
Save stream
Print current stream
Page 32

22
Chapter 3
Cut & move to clipboard Copy to clipboard
Paste selection Undo last action
Redo Search for nodes
Edit stream properties Preview SQL generation
Run current stream
Stop stream (Active only while
stream is running)
Zoom in (SuperNodes only) Zoom out (SuperNodes only)
No markup in stream
Hide stream markup (if any) Show hidden stream markup
Open stream in IBM® SPSS®
Modeler Advantage
Run stream selection
Add SuperNode
Insert comment
Stream markup consists of stream comments, model links, and scoring branch indications.
For mor e information on stream comments , see Adding Comments and Annotations to Nodes
and Streams on p. 78.
For more i
nformation on scoring branch indications, see The Scoring Branch on p. 188.
Model links are described in the IBM SPSS Modeling Nodes guide.
Page 33

Customizing the Toolbar
You can change various aspects of the toolbar, such as:
Whether it is displayed
Whether the icons have tooltips available
Whether it uses large or small icons
To turn the toolbar display on and off:
E
On the main menu, click:
View > Toolbar > Display
To change the tooltip or icon size settings:
E
On the main menu, click:
View > Toolbar > Customize
23
IBM SPSS Modeler Overview
Click
Show Too
lTipsorLarge Buttons
as required.
Customizing the IBM SPSS Modeler Window
Using the dividers between vario us portions of the IBM® SPSS® Modeler interface, you can
resize or close tools to meet your preferen ces. For example, if you are working with a large
stream, you can use the small arrows located on each divider to close the nodes palette, managers
pane, and project pane. This maximizes the stream canvas, providing enough work space for
large or multiple streams.
Alternativ
ely, on the View menu, click
these items on or off.
Nodes Palette,Managers
, or
Project
to turn the dis play of
Page 34

24
Chapter 3
Figure 3-12
Maximized stream canvas
As an alternative to closing the nodes palette, and the managers and project panes, you can use the
stream canvas as a scrollable page by moving vertically and horizontally with the scrollbars a t the
side and b ottom of the SPSS Mode ler window.
You can also co ntrol the display of screen markup, which consists of stream comments, model
and scoring branch indications. To turn this display on or off, click:
links,
View > Stream Markup
Changing the icon size for a stream
You can
You can
standard icon size.
change the size of the s tream icons in the following ways.
Through a stream property settin g
gh a p op-up menu in the stream
Throu
Using the keyboard
scale the entire stream view to one of a nu mber of sizes between 8% and 200% of the
Page 35

Figure 3-13
Changing the icon size
25
IBM SPSS Modeler Overview
To scale the entire stream (stream properties method)
E
From the main menu, choose
Tools > Stream Properties > Options > Layout.
E
Choose the size y ou want from the Icon Size menu.
E
Click
Apply
to see the result.
E
ClickOKto save the change.
To scale the entire stream (menu method)
E
Right-click the stream background on the canvas.
E
Choose
Icon Size
and select th e size you want .
To scale the entire stream (keyboard method)
E
Press Ctrl + [-] on the main keyboard to zoom out to the next smaller size.
E
Press Ctrl + Shift + [+] on the main key board to zoom in to the next larger size.
This feature is particularly useful for gaining an overall view of a complex stream. You can also
use it to minimize the number of pages needed to print a stream.
Page 36

26
Chapter 3
Using the Mouse in IBM SPSS Modeler
The most common uses of the mouse in IBM® SPSS® Modeler include the follow ing:
Single-click.
pop-up m enus,
Use either the right or left mouse button to select options from m enus, open
and ac cess vario us other standard controls and options. Click and hold the
button to move and drag nodes.
Double-click.
Double-click using the left mouse button to place nodes on the stream canvas
and edit existing nodes.
Middle-click.
Click the middle mouse bu tton an d drag the cursor to connect nodes on the
stream canvas. Double-click the middle mouse button to disconnect a node. If you do not
have a three-button mouse, you can simulate this feature by pressing the Alt key while
clicking and dragging the mouse.
Using Shortcut Keys
Many visual progra mming operations in IBM® SPSS® Modeler have s hortcut keys associated
with them. For example, you can delete a node by clicking the node and pressing the Delete key
on your keyboard. Likewise, you can quickly save a stream by pr essing the S ke y while holding
down th e Ctrl key. Control commands like this one are indicated by a combination of Ctrl and
another key—for example, Ctrl+S.
There are a number of shortcut keys used in standard Windows operations, such as Ctrl+X to
cut. These shortcuts are supported in SPSS Modeler along with the following application-specific
shortcuts.
Note: In some cases, old shortcut keys us ed in SPSS Modeler conflict with standard Windows
shortcut keys. These old shortcuts are supported with the addition of the Alt key. For example,
Ctrl+Alt+C can be used to toggle the cache on and off.
Table 3-1
Supported shortcut keys
Shortcut
Key
Ctrl+A Select all
Ctrl+X Cut
Ctrl+N
Ctrl+O
Ctrl+P Print
Ctrl+C
Ctrl+V
Ctrl+Z Undo
Ctrl+Q Select all nodes down stream of the selected node
Ctrl+W Deselect all downstream nodes (toggles with Ctrl+Q)
Ctrl+E Run from selected node
Ctrl+S
Alt+Arrow
keys
Shift+F10 Open the pop-up menu for the selected node
Function
New stream
Open stream
Copy
Paste
Save current stream
Move selected nodes on the stream canvas in the direction
of the arrow used
Page 37

Printing
IBM SPSS Modeler Overview
Table 3-2
Supported shortcuts for old hot keys
Shortcut
Key
Ctrl+Alt+D Duplicate node
Ctrl+Alt+L Load node
Ctrl+Alt+R Rename node
Ctrl+Alt+U Create User Input node
Ctrl+Alt+C Toggle cache on/off
Ctrl+Alt+F Flush cache
Ctrl+Alt+X Expand SuperNode
Ctrl+Alt+Z Zoom in/zoom out
Delete Delete node or connection
Function
The fol lowing ob jects can be printed in IBM® SPSS® Modeler:
Stream diagrams
Graphs
Tables
Reports (from the Report node and Project Reports)
Scripts (from the stream propertie s, Standalone Script, or SuperNode script dialog boxes)
Models (Model browsers, dialog box tabs with current focus, tree viewers)
Annotations (using the Annotations tab for output)
27
To print an object:
To print without previewing, click the Print button on the toolbar.
To set up the page before printing, select
To preview before printing, select
To view the standard print dialog box w ith options for selecting printers, and specifying
appearance options, select
Print
Automating IBM SPSS Modeler
Since a dvanced data mining can be a co mplex and sometimes lengthy process, IBM® SPSS®
Modeler includes several ty pes of coding and automation support.
Control Language for Expression Manipulation (CLEM) is a language for an alyzing
and manipulating the data that flows along SPSS Modeler streams. Data miners use CLEM
extensively in stream operations to perform tasks as simple as deriving profit from cost and
Page Setup
Print Preview
from the File menu.
from the File menu.
from the File menu.
Page 38

28
Chapter 3
revenue data or as complex as tran sforming web log data into a set of fields and records with
usable information. For more in f ormation, see the topic About CLEM in Chapter 7 on p. 105.
Scripting is a powerful tool for automating pro cesses in the user interface. Scripts can
perform the same kinds of actions that users perform with a mouse or a keyboard. You can
set options for n odes and perform derivations using a subset of CLEM. You can also spec ify
output and manipulate generated models.
Page 39

Understanding Data Mining
Data Mining Overview
Through a variety of techniques, data mining identifies nuggets of information in bodies of data.
Data m ining extracts information in such a way that it can be used in areas such as decision
support, pred iction, forecasts, and estimation. Data is often vol
little direct usefulness in its raw form. It is the hidden information in the data that has value.
In data mining, success comes from combining your (or your expert’s) knowledge of the
data with advanced, active analysis techniques in which the com pu
relationships and features in the data. The process of data mining generates models from historical
data that are later used for predictions, pattern detection, and more. The technique for building
these models is called machine learning or modeling.
Modeling Techniques
Chapter
4
4
44
uminous but of low value and with
ter identifies the underlying
IBM® SPSS® Modeler includes a number of machine-learning and modeling technologies, which
can be roughly grouped according to the types of problems the y are intended to solve.
Predictive modeling method s include decision trees, neural networks, and statistical models.
Clustering models focus on identifying groups of similar records and labeling the records
according to the group to which they belong. Clustering methods include Kohonen, k-means,
and TwoStep.
Association rules associate a particular conclusion (such as the purchase of a particular
product) with a set of conditions (the purchase of several other products).
Screening models can be used to screen d ata to locate fields and records that are most likely to
be of interest in modeling and identify outliers that may not fit known patterns. Available
methods include feature selection and anomaly detection.
Data Manipulation and Discovery
SPSS Modeler also includes many facilities that le t you apply your expertise to the data:
Data manipulation.
data into meaningful subsets. Data from a variety of sources can be merged and filtered.
Browsing and visualization.
an initia l audit including graphs and statistics. Advanced visualization includes interactive
graphics, which can be exported for inclusion in project reports.
Statistics.
IBM® SPSS® Statistics can also be used within SPSS Modeler.
Hypothesis testing.
Confirms suspected relationships between variables in the data. Statistic s from
Constructs new data items derived from existing ones and breaks down the
Displays aspects of the data using the Data Audit node to perform
Constructs models of how the data behaves and verifies these models.
© Copyright IBM Corporation 1994, 2012.
29
Page 40

30
Chapter 4
Typically, you will use these faci lities to identify a promising set of attributes in the data. These
attributes ca
n then be fed to the modeling techniques, which will attempt to identify underlying
rules and relationships .
Typical Applications
Typical applications of data mining techniques include the following:
Direct mail.
Determine which demograp hic groups have the highest response rate. Use this
information to maximize the response to fu ture mailings.
Credit scoring.
Human resources.
Use an individual’s credit history to make credit decisions.
Understand past hiring practices and create decision rules to streamline the
hiring process.
Medical research.
Create decision rules tha t suggest appropriate procedures based on medical
evidence.
Market analysis.
Determine which variables, such as geography, price, and customer
characteristics, are associated with sales.
Quality control.
Analyze data from product manufacturing and identify variables determining
product defects.
Policy studies.
Use surv ey data to for mulate polic y by applying decision rules to select the most
important variables.
Health care.
User surveys and clinical data can be combined to discover variables that contribute
to health.
Terminology
The terms attribute, field, and variable refer to a single data item common to all cases under
consideration. A collection of attribute values that refers to a specific case is called a record, an
example, or a case.
Assessing the Data
Data mining is not likely to be fruitful unless the data you want to use meets certain criteria. The
following sections present some of the asp ects of the data and its application that you should
consider.
Ensure that the data is available
This ma y seem obvious, but be aware that although data might be available, it may not be in a
form that can be used easily. IBM® SPSS® Modeler can import data from databa ses (through
ODBC) o r from files. The data, however, might be held in some other form on a machine tha t
cannot be directly accessed. It will need to be downloaded or du mped in a suitable form bef ore it
can be used. It might be scattered among different databases a nd sources and need to be pulled
Page 41

Understanding Data Mining
together. It may not even be online. If it exists only on paper, data entry will be required before
you can begin d
Check whether the data covers the relevant attributes
ata mining.
The object of data mining is to identify relevant attributes, so including this check may seem odd
at first. It is very useful, however, to look at what data is available and to try to identify the likely
relevant factors that are no t recorded. In trying to predict ice cream sales, for example, you may
have a lot of information about retail outlets or sales history, but you may not have weather
and t emperature information, which is likely to play a significant role. Missing attributes do
not necessarily mean that data mining will not produce useful results, but they can limit the
accuracy of resulting predictions.
A qu ick way of assessing the situation is to perform a comprehensive audit of your data.
Before moving on, consider attaching a Data Audit node to your data source and running it to
generate a full report.
Beware of noisy data
31
Data often contains errors or may contain subjective, and therefore variable, judgments. These
phenomena are collectively referred to as noise. Sometimes noise in data is normal. There may
well be underlying rules, but they may not hold for 100% of the cases.
Typically, the more noise there is in data, the more difficult it is to get accurate results.
However, SPSS Modeler’s machine-learning methods are able to handle noisy data and have been
used successfully on data sets containing almost 50% noise.
Ensure that there is sufficient data
In data mining, it is not necessarily the size of a data set that is important. The representativeness
of the data set is far more significant, together with its coverage of possible outcomes and
combinations of variable s.
Typically, the more attributes that are considered, the more records that will be needed to
give representative covera ge.
If the data is representative and there are general underlying rules, it may well be that a data
sample of a few thousand (or even a f ew hundred) records will give equally good results as a
million—and you will get the results more quickly.
Seek out the experts on the data
In many cases, you will be working on your own data and will therefore be highly familiar with
its content and meaning. However, if you a r e worki ng on data for another department of your
organization o r for a client, it is highly desirable th at you have access to experts who know the
data. They can guide you in the identification of relevant attributes and can help to interpret the
results of data mining, distinguishing the true nuggets of information from “fool’s gold,” or
artifacts caused by anomalies in the data sets.
Page 42

32
Chapter 4
A Strategy for Data Mining
As with most business endeavors, data mining is much more effective if done in a planned,
systematic way. Even with cutting-edge data mining tools, such as IBM® SPSS® Modeler, the
majority of the work in data mining requires a knowledge ab le business analyst to keep the pr ocess
on track. To guide your planning, answer the following questions:
What substantive problem do you want to solve?
What data sources a r e available, and what parts of the data are relevant to the current problem?
What kind of prep rocessing and data cleaning do yo u need to do before you start mining
the data?
What data mining technique(s) will you use?
How w ill you evaluate the results of the data mining analysis?
How will you get the most out of the information you obtained from data mining?
The typical data mining process can become com plicated very quickly. There is a lot to k eep track
of—complex business pr oblems, multiple data sources, varying data quality across data sources,
an array of data mining techniques, different ways of measuring data mining success, and so on.
To stay on track, it helps to have an explicitly defined proces s model for data mining. The
process model helps you answer the questions listed earlier in this section, and makes sure the
important po ints are addressed. It serves as a data mining road map so that you will not lose your
way as you dig into the complexities of your data.
The data mining process suggested for use with SPSS Modeler is the Cross-Industry Standard
Process for Data Mining (CRISP-DM). As you can tell from t he name, this model is designed as a
general mode l that can be applied to a wide variety of industries and business problems.
The CRISP-DM Process Model
The genera
mining. The six phases fit together in a cyclical process d esigned to incorporate data mining
into your larger business practices.
l CRISP-DM process model includes six phases that addres s the main issues in data
Page 43

Understanding Data Mining
Figure 4-1
CRISP-DM process model
The six phases include:
Business understanding.
This is perhaps the most important phase of data mining. Business
understanding includes d etermining business objectives, assessing the situation, determining
data mining goals, and producing a project plan.
Data understanding.
Data provides the “raw materials” of data mining. This phase addresses
the need to understand what yo ur data resources are and the characteristics of those resources.
It includes collecting initial data, describing data, exploring data, and verifying data quality.
The Data Audit node available from the Output nodes palette is an indispensable tool for
data understanding.
Data preparation.
After cataloging your data res ources, you will need to prepare your data for
mining. Preparations include selecting, cleaning, constructing, integrating, and formatting
data.
Modeling.
This is, of course, the flashy part of data mining, where sophisticated analysis
methods are used to extract information from the data. This phase involves selecting modeling
techniques, generating test designs, and building and assessing models.
Evaluation.
Once you have chosen your models, you are ready to evaluate how the data min ing
results can h elp you to achieve your busine ss obje ctives. Elements of this phase include
evaluating results, reviewing the data mining process, and determining the next steps.
Deployment.
Now that you have invested all of this effort, it is time to reap the benefits. This
phase focuses on integrating your new knowledge into your everyday business processes to
solve your original business problem. This phase includes plan deployment, monitoring and
maintenance, producing a final report, and reviewing the project.
33
There are some key points in this process model. First, while there is a general tendency for the
process to flow th r ough the steps in the order outlined in the previous paragraphs, there are also a
number of places where the phases influence each other in a nonlinear way. For example, data
preparation usually precedes modeling. However, decisions made and information gathered
during the modeling phase can often lead you to rethink parts of the data prepa r ation phase, which
can then present new modelin g issues. The two phases feed back on each other until bo th phases
Page 44

34
Chapter 4
have been resolved adequately. Similarly, the evaluation phase can lead y ou to reevaluate your
original busi
ness understanding, and you may decide that you have been trying to answer the
wrong question. At this point, you can revise your business understanding and proceed through
the rest of the process again with a better target in mind.
The second ke
y point is the iterative nature of data mining. You will rarely, if ever, simply
plan a data mining project, complete it, and then pack up your data and go home. Data mining to
address your customers’ demands is an ongoing endeavor. The knowledge gained from one cycle
of data minin
g will almost invariably lead to new questions, new issues, and new opportunities
to identify and meet you r customer s’ needs. Those new questions, issues, and opportunities can
usually be addressed by mining your data once again. This process of mining and identifyin g new
opportunit
ies shou ld become part of the way you think about you r business and a cornerstone of
your overall business strategy.
This introduction provides only a brief overview of the CRISP-DM process model. For
complete de
The CRISP-DM Guide, which can be accessed along with o ther documentation from the
tails on the model, consult the following resources:
\Documentation folder on the installation disk.
The CRISP-DM Help system, available from the Start menu or by clicking
CRISP-DM Help
on
the Help menu in IBM® SPSS® Modeler.
Types of Models
IBM® SPSS® Modeler offers a variety of modeling methods taken from machine learning,
artificial intelligence, and statistics. The methods available on the Modeling palette allow you
to derive new information from your data and to develop predictive models. Each method has
certain strengths and is best suited for parti cular types of problems.
The SPSS Modeler Applications Guide provides examples for many of these methods, along
with a general introduction to the modeling process. This guide is available as an online tutorial,
and also in PDF format. For more information, see the topic Application Examples in Chapter 1
on p. 5.
Modeling methods are divided into three categories:
Classification
Association
Segmentation
Classification Models
Classification models use the values of one or more input fields to predict the value of one or
more output, or target, fields. Some examples of these techniques are: decision trees (C&R Tree,
QUEST, CHAID and C5.0 algorithms), regression (linear, logistic, generalized linear, and Cox
regression algorithms), neural networks, support vector machines, and Bayesian networks.
Classification models helps organization s to predict a known result, such as whether a customer
will buy or leave or whether a transaction fits a known pattern of fraud. Modeling techniqu es
include machine learning, rule induction, subgroup identification, statistical m ethods, and multiple
model generation.
Page 45

Classification nodes
35
Understanding Data Mining
The Auto Classifier node creates and compares a number of different models for
binary outcomes (yes or no, churn or do not churn, and so on), allowing you to
choose the best approach for a given analysis. A number of modeling algorithms are
supported, making it possible to select the methods you want to use, the specific
options for each, and the criteria for comparing the results. The node generates a set
of models based on the specified options and ranks the best candidat es according to
the criteria you specify.
The Auto Numeric node estimates and compares models for continuous numeric
range outcomes using a number of d i fferent methods. The node works in the same
manner as the Auto Classifier node, allowing you to choose the algorithms to use
and to experiment wit h multiple combinations of options in a single modeling pass.
Supported algorithms include neural networks, C&R Tree, CHAID, linear regression,
generalized linear reg res sion, and support vector machines (SVM). Models can be
compared based on correlation, relative error, or number of variables used.
The Classification and Regression (C&R) Tree node generates a decision tree that
allows you to predict or classify future observations. The method uses recursive
partitioning to split the training r ecords into segments by minimizing the impurity
at each step, where a node in the tree is considered “pure” if 100% of cases in t he
node fall into a specific category of the target field. Target and input fields can
be numeric ranges or categorical (nominal, ordinal, or flags); all splits are binary
(only two subgroups).
The QUEST node provides a binary classification method for building decision trees,
designed to reduce t he processing time required for large C&R Tree analyses while
also reducing the tendency found in classification tree methods to favor inputs that
allow more splits. Input fields can be numeric ranges (continuous), but the target field
must be categorical. All splits are binary.
The CHAID node generates decision tre es using chi-square statistics to identify
optimal splits. Unlike the C&R Tree and QUEST nodes, CHAID can g enerate
nonbinary trees, meaning that some splits have more than two branches. Target and
input fields can be numeric range (continuous) or categorical. Exhaustive CHAID is
a modification of CHAID that doe s a more thorough job of examining all possible
splits but takes longer to compute.
The C5.0 node builds either a decision tree or a rule set. The model works by splitting
the sample based on the field that provides the maximum information gain at each
level. The target field must be categorical. Multiple splits into more than two
subgroups are allowed.
The Decision List node identifies subgroups, or segments, that show a higher or lower
likelihood of a given binary outcome relative to the overall population. For example,
you might look for customers who are unlikely to churn or are most likely to respon d
favorably to a campaign. You can incorporate your business knowledge into the
model by adding your own custom segments and previewing alternative models side
by side to compare the results. Decision List models consist of a list of rules in which
each rule has a condition and an outcome. Rules are applied in order, and the first rule
that matches determines the outcome.
Linear regression models predict a continuous target based on linear relationships
between the target and one or more predictors .
Page 46

36
Chapter 4
The PCA/Factor node provides powerful data-reduction techniques to reduce
the complexity of your data. Principal components analysis (PCA) finds linear
combinations of the inp ut fields that do the best job of capturing the variance in the
entire set of fields, where the components are orthogona l (perpendicular) to each
other. Fact or analysis attempts to identify underlying factors that expla i n the pattern
of correlations within a set of observed fields. For both approaches, the goal is to
find a small number o f derived fields that effectively summarizes the information in
the original set of fields.
The Feature Selection node screens input fields for removal based on a set of criteria
(such as the percentage of missin g values); it then ranks the importance of remaining
inputs relative to a specified target. For example, given a data set with hundreds of
potential inputs, which are most likely to be useful in modeling patient outcomes?
Discriminant analysis makes more stringent assumptions than logis t i c regression but
can be a valuable alternative or supplement to a logistic regression analysis when
those assumptions are met.
Logistic regression is a statistical technique for classifying records based on values
of input fields. It is analogous to linear regression but takes a categorical target field
instead of a numeric range.
The Ge neralized Linear model expands the general linear model so that the
dependent variable is linearly related to the factors and covariates through a specified
link function. Moreover, the model all ows for the dependent variable to have a
non-normal distribution. It covers the functionality of a wide number of statistical
models, including lin ear regression, logisti c regression, loglinear models for count
data, and interval-censored survival models.
A generalized linear mixed model (GLMM) extends th e linear model so that the target
can have a non-normal distribution, is linearly related to the factors and covariates via
a specified link function, and so that the observations can be correlated. Generalized
linear mixed models cover a wide variety of models, from simple linear regression to
complex multilevel models for non-normal longitudinal data.
The Cox regression node enables you to build a survival model for time-to-event data
in the presence of censored records. The model produces a survival function that
predicts the probability that the event of interest has occurred at a gi ven time (t)
for given values of the input variables.
The Support Vector Machine (SVM) node enables you to classify data into one of
two groups without ov erfitt i ng. SVM w orks well with wide data sets, such as th ose
with a v ery large number of input fields.
The Bayesian Network node enables you to build a probability model by combining
observed and recorded evidence with real -world knowledge to establish the likelihood
of occurrences. The node focuses on Tree Augmented Naïve Bayes (TAN) and
Markov Blanket networks that are primarily used for classification.
Page 47

37
Understanding Data Mining
The Self-Learning Response Model (SLRM) node enables you to build a model in
which a single new case, or small number of new cases, can be used to reestimate the
model without having to retrain the model using all data.
The Time Series node estimates exponential smoothing, univariate Autoregressive
Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA), an d multivariate ARIMA (or transfer function)
models for time series data and produces forecasts of future performance. A Time
Series node must always be preceded by a Time Intervals node.
The k-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) node associates a new case with the category or value
of the k objects nearest to it in the predictor space, where k is an integer. Similar cases
are near each other and dissimilar cases are distant from each other.
Association Models
Association models find patterns in your data where on e or more entities (such as events ,
purchases, o r attributes) are asso ciated with one or more other entities. The models construct rule
sets that define the se relationships. Here the fields within the data can act as both inputs and
targets. You could find these associations manually, but association rule algorithms do so much
more quickly, and can explore more complex patterns. Apriori and Carma models are examples of
the use of such algorithms. One other type of asso ciation model is a sequence detection model,
which finds sequential patterns in time-structured data.
Association models are most useful when predicting multiple outcomes—for example, customers
who bought product X also bought Y and Z. Association models associate a particular conclusion
(such as the decision to buy something) with a set of conditions. The advantage of association rule
algorithms over the more standard decision tree algorithms (C5.0 and C&RT) is that associations
can ex is t between any of the attributes. A decision tree algorithm will build rules with only a
single concl usion, whereas association algorithms attempt to find many rules, each of which may
have a different conclusion.
Association nodes
The Apriori node extracts a set of rules from the data, pulling out the rules with
the highest information content. Apriori offers five different methods of s elect i ng
rules and uses a soph i sticated indexing scheme to process large data sets efficiently.
For large problems, Apriori is generally faster to train; it has no arbitrary limit on
the number of rules that can be retained, and it can h andle rules with up to 32
Page 48

38
Chapter 4
preconditions. Apriori requires that input and output fields all be categorical but
delivers better performance because it is optimized for this type of data.
The CARMA model extracts a set of rules from the data without requiring you to
specify input or target fields. In contrast to Apriori the CARMA node offers build
settings for rule support (support for both antecedent and consequent) rather than just
antecedent support. This means that the rules generated can be used for a wider variety
of applications—for example, to find a list of products or services (ante cedents)
whose consequent is the item that you want to promote this holiday season.
The Sequence node discovers associatio n rules in sequential or time-oriented d at a. A
sequence is a list of item sets that tends to occur in a predictable order. For example, a
customer who purchases a razor and aftershave lotion may purchase shaving cream
the next time he shops. The Sequence node is based on the CARMA association rules
algorithm, which uses an efficient two-pass method for finding sequences.
Segmentation Models
Segmentation models divide the data into segments, or clusters, of records that have similar
patterns of input fields. As they are only interested in the input fields, segmentation models have
no concept of output or target fields. Examples o f segmentation models are Kohonen networks,
K-Means clustering, two-step clustering and anomaly detection.
Segmentation models (als o known as “clustering m odels”) are useful in cases where the spec ific
result is unknown (for example, when i de ntifying new patterns of fraud, or when identifying
groups of interest in y our customer base). Clustering models focus on identifying groups of
similar records and labeling the records according to the group to which they belong. This is
done w ithout the benefit of prior knowledge about the groups and their characteristics, and it
distinguishes clustering models from the ot her modeling techniques in that there is no predefined
output or target field for the model to predict. There are no right or wrong answers for these
models. Their value is determined by their ability to capture interesting groupings in the data and
provide useful descriptions of those groupings. Clustering models are often used to create clusters
or segments t hat are then used as inputs in subsequent analyses (for example, by segmenting
potential customers into homogeneous subgroups).
Page 49

Segmentation nodes
39
Understanding Data Mining
The Auto Cluster node estimates and compares clustering models, which identify
groups of records that have similar characteristics. The node works in the sam e
manner as other automated modeling n odes, allowing you to experiment with multiple
combinations of options in a single modeling pass. Models can be compared using
basic measures with which to attempt to fil t er and rank the usefulness of the cluster
models, and provide a measure based on the importance of particular fields.
The K-Means node clusters the data set into distinct groups (or clusters). The method
defines a fixed number of clusters, iteratively assigns records to clusters, and adjusts
the cluster centers until further refinement can no longer impro ve the model. Instead
of trying to predict an outcome, k-means uses a process known as unsupervised
learning to uncover patterns in the set of input fields.
The Kohonen node generates a type of neural network that can be used to cluster the
data set into distinct groups. When the network is fully trained, records that are
similar should be close together on the output map, whi l e records that are different
will be far apart. You can look at the number of observations captured by each unit
in the model nugget to identify the strong units. This may give you a sense of the
appropriate number of clusters.
The TwoStep node uses a two-step clustering method. The first step makes a single
pass through the data to compress the raw input data into a manageable set of
subclusters. The second step uses a hierarchical clustering method to progressively
merge the subclusters into larger and larger clusters. TwoStep has the advantage of
automatically estimating the optimal number of clusters for the training data. It can
handle mixed field types and large data sets efficiently.
The Anomaly Detection node identifies unusual cases, or outliers, that do not conform
to patterns of “normal” data. With this n ode, it is possible to identify outliers even if
they do not fit any previously known patterns and even if you are not exactly sure
what you are looking for.
In-Database Mining Models
SPSS Modeler suppor ts integration with data mining and modeling tools that are available from
database vendors, including Oracle Data Mi ner, IBM DB2 InfoSphere Warehouse, and Microsoft
Analysis Services. You can build, score, and store models inside the database—all fr om within the
SPSS Modeler app lication. For full details, see the SPSS Modeler In-Database Mining Guide,
available on the product DVD.
IBM SPSS Statistics Models
If you have a copy of IBM® SPSS® Statistics installed and licensed on your c omputer, you can
access and run certain SPSS Statistics routines from within SPSS Modeler to build and score
models.
Further Information
Detailed documentation on the modeling algorithms is also available. For more information, see
the SPSS Modeler Algorithms Guide, available on the product DVD.
Page 50

40
Chapter 4
Data Mining Examples
The best way to learn about data mining in practice is to start with an example. A number of
application examples are available in the IBM® SPSS® Modeler Applications Guide, which
provides brief, targeted int r oductions to specific mode ling methods and techniq ues. For more
information, see t he topic Application Examples in Chapter 1 on p. 5.
Page 51

Building Streams
Stream-Building Overview
Data mining using IBM® SPSS® Modeler focuses on the process of running data through a series
of nodes, referred to as a stream. This series of nodes represents operations to be performed on
the data, while links between the node s indicate the direction of data flow. Typically, you use a
data str eam to read data into SPSS Modeler, run it throu gh a series of manipulations, and then
send it to a destination, such as a table or a view er.
For example, suppose that you want to open a data source, add a new field, select records
based on values in the new field, and then display the results in a table. In this case, your data
stream would consist of four nodes:
A Variable File node, which you set up to read the data from the data source.
Chapter
5
5
55
A Derive node, which you use to add the new, calculated field to the data set.
A Select node, which you use to set up selection criteria to exclude records from the
data stream.
A Table node, which you use to display the results of your manipulations on screen.
Building Data Streams
IBM® SPSS® Modeler’s unique interface lets you mine your data visually by working with
diagram
steps:
s of data streams. At the most basic level, you can build a data stream us ing the following
Add nodes to the stream canvas.
Connect the nodes to form a stream.
Specify any node or stream options.
Run the stream.
© Copyright IBM Corporation 1994, 2012.
41
Page 52

42
Chapter 5
Figure 5-1
Completed stream on the stream canvas
This secti on contains more detailed information on working with nodes to creat e more complex
data streams. It also discusses options and settings for nodes and streams. For step-by-step
examples of stream building using the data shipped with SPSS Modeler (in the Demos folder of
your pr ogram installation), see Application Examples on p. 5.
Working with Nodes
Nodes are used in IBM® SPSS ® M odeler to help you explore data. Various nodes in the
workspace represent different objects a nd actions. The palette at the bottom of the SPSS Modeler
window contains all of the possible nodes used in stream building.
There are several types of nodes. Source nodes bring data into the stream, and are located on
the Sources tab of the nodes palette. Process nodes perform operations on individual data records
and fields, and can be found in the Record Ops and Field Ops tabs of the palette. Output nodes
produce a variety of output for data, charts and model results, and are included on the Graphs,
Output and Export tabs of the nodes palette. Modeling nodes use statistical algorithms to create
model nuggets, and are located on the Mo deling tab, and (if activated) the Database Modeling tab,
of the nodes palette. For more information, see the topic Nodes Palette in Chap ter 3 on p. 18.
You connect the nodes to form streams which, when run, let you visualize relationships and
draw co nclusions. Streams are like scripts—you can save them and reuse them with different
data files.
Page 53

A runnable node that processes s tream data is known as a terminal node. A modeling or
output node is
a terminal node i f it is located at the end of a stream or stream branch. You cannot
connect further nodes to a terminal node.
Note: You can customize the Nodes palette. For more information, see the topic Customiz ing
the Nodes Palette in Chapter 12 on p. 223.
Adding Nodes to a Stream
There are several ways to ad d nodes to a stream from the nodes pale tte:
Double-click a node on the palette. Note: Double-clicking a node automatically connects it
to the current stream . For more information, see the topic Connecting Nodes in a Stre am
on p. 43.
Drag and drop a node from the palette to the stream canvas.
Click a node on the palette, and then click the stream canvas.
Select an appropriate option from the Insert menu of IBM® SPSS® Modeler.
43
Building Streams
Once you have added a node to the stream canvas, double-click the node to display its dialog box.
The ava ilable options depend on the type of node that you are adding. For information about
specific controls within the dialog box, click its
Removing Nodes
Help
button.
To remove a node from the data stream, click it and either press the Delete key, or right-click and
select
Delete
from the menu.
Connecting Nodes in a Stream
Nodes added to the stream canvas do not form a data stream un til they have been connected .
Connections between the nodes indicate the direction of the data as it flows from one operation
to the next. There are a number of ways to connect nodes to form a stream: double-clicking,
using the middle mouse button, or manually.
To Add and Connect Nodes by Double-Clicking
The simplest way to form a stream is to do uble-click nodes on the palette. This method
automatically connects the new node to the selected node on the stream canvas. For example, if
the canvas contains a Database node, you can sele ct this node and then double-cl ick the next node
from the palette, such as a Derive node. This action automatically connects the Derive node to
the existing Database node. You can repeat this process until you have reached a terminal node,
such as a Histogram or Table node , at which point any new nodes will be connected to the last
non-terminal node upstream.
Page 54

44
Chapter 5
Figure 5-2
Stream created by double-clicking nodes from the palettes
To Connect Nodes Using the Middle Mouse Button
On the stream canvas, you can click and drag from one node to another using the middle mouse
button. (If your mouse does not have a middle button, you can simulate this by pressing the Alt
key wh ile dragging with the mouse from one node to another.)
Figure 5-3
Using the middle mouse button to connect nodes
To Manually Connect Nodes
If you do not have a middle mouse button and prefer to manually connect nodes, you can use the
pop-up m enu for a nod e to connect it to another node already on the canvas.
E
Right-click the node from which you want to start the connection. Doing so opens the node menu.
E
On the menu, click
E
A conn ection icon is display ed both on the start node and th e curs or. Click a second node on
Connect
.
the canvas to connect the two nodes.
Figure 5-4
Connecting nodes using the Connect option from the pop-up menu
Page 55

Building Streams
Figure 5-5
Connected nodes
When connecting nodes, there are several guidelines to follow. You will receive an error message
if you attempt to make any of the following types of connections:
A connection leading to a source node
A connection leading from a terminal node
A node having more than its maximum number of input connections
Connecting two nodes that are already connected
Circularity (data returns to a node fr om which it has alr eady flowed)
Bypassing Nodes in a Stream
45
When you bypass a node in the data stream, all of its input and output connections are replaced by
connections that lead directly from its input nodes to its output nodes. If the n ode does not have
both input and output connections, then all of its connections are deleted rather than rerouted.
For example, you might have a stream that derives a new field, filters fields, and then explores
the results in a histogram and table. If you want to also view the same graph and table for data
before fields are filtered, you can add either new Histogram and Table nodes to the stream, or you
can bypass the Filter node. When you bypass the Filter node, the connections to the graph and
table pass directly from the Derive node. The Filter node is disconnected from the stream.
Figure 5-6
Bypassing a previously connected Filter node
To Bypass a Node
E
On the stream canvas, use the middle mouse button to double-click the node that you want to
bypass. Alternatively, you c an use Alt+do uble-click.
Note: You can undo this action clicking
Undo
on the Edit menu or by pressing Ctrl+Z.
Page 56

46
Chapter 5
Disabling Nodes in a Stream
Process nod es with a single input within s treams can be disabled, with the result that the node is
ignored during running of the stream. This saves you from having to remove or bypass the node
and means you can leave it connected to the remaining nodes. You can still open and edit the node
settings; however, any changes will not take effect until you enable the node again.
For example, you might have a stream that filters s everal fields, and then builds models with
the reduce d data set. If you want to also build the same models without fields being filtered, to
see if they improve the model results, you can disable the Filter node. When you disable the
Filter node, the connections to the modeling nodes pass directly through from the Derive node to
the Type node.
Figure 5-7
Disabled Filter node in a stream
To Disable a Node
E
On the s
E
Click
Alterna
node back in the stream, click
Note: You can undo this action clicking
You can u
tream canvas, right-click the node that you want to disable.
Disable Node
tively, you can click
ndo this action clicking
on the pop-up menu.
Node>Disable Node
Enable Node
Undo
on the Edit menu. When you want to inc lude the
in the same way.
Undo
on the Edit menu or by pressing Ctrl+Z.
on the Edit menu or by pressing Ctrl+Z.
Adding Nodes in Existing Connections
You can add a new node between two connected nodes by dragging the arrow that connects
the two nodes.
Page 57

Building Streams
Figure 5-8
Connecting a new node between two connected nodes
E
With the middle mouse button, click and drag the connection arrow into which you want to insert
the node. Alternatively, you can hold down the Alt key while clicking and dragging to simulate a
middle mouse button.
Figure 5-9
New stream
47
E
Drag the connection to the node that you want to include and release the mouse button.
Note: You can remove new connections from the node and restore the original by bypassing
the node.
Deleting Connections between Nodes
To delete the connection between two nodes:
E
Right-click the connection arr ow.
E
On the m enu, click
Delete Connection
.
Page 58

48
Chapter 5
Figure 5-10
Deleting the connection between nodes in a stream
To delete all connections to and from a node, do one of the fo llowing:
Select the node and press F3.
Select the node, and on the m ain menu click:
Edit > Node > Disconnect
Setting Options for Nodes
Once you have created and connected nodes, there are several options for customizing nodes.
Right-click a node and select one of the menu options.
Page 59

Figure 5-11
Pop-up menu options for nodes
49
Building Streams
Click
Edit
to open the dialog box for the s elected node.
Click
Connect
Click
Disconnect
Click
Rename and Annotate
Click
New Comment
to manually connect one node to another.
to delete all links to and from the node.
to open the Annotations tab of the editing dialog box.
to ad d a comment related to the node. For more information, see the
topic Adding Comments and Annotations to Nodes and Streams on p . 78.
Click
isable Node
D
for proc essing, click
to “hide” the node during processing. To make the node visible again
Enable Node
. For more information, see the topic Disabling Nodes in
a Stream on p. 46.
Click
allows
Click
CutorDelete
you to pa ste nodes , while
Copy Node
to remove the selected node(s) from the stream canvas. Note: Clicking
Delete
does not.
to make a copy of the node with no connections. This can be added to
a new or existing stream.
Click
Load Node
to open a previously saved node and load its options into the currently
selected node. Note: The nodes must be of identical types.
Click
Retrieve Node
Deploy
ment Services Repository.
to retrieve a node from a connected IBM® SPSS® Collaboration and
Cut
Page 60

50
Chapter 5
Click
another node of the same type.
Click
Deployment Services Repository.
Click
Click
specifying mandatory fie lds.
Click
current stream.
Click
will h ave th e
Click
Caching Options for Nodes
To optimize stream running, you can set up a cache on any nonterminal node. When you set up a
cache on a no
run the data stream. From then on, the data is read from the cache (which is stored on disk in a
temporary directory) rather than from the data so urce.
Caching is m
aggregation. For example, suppose that you have a source node set to read sales data from a
database and an Aggregate node that summarizes sales by location. You can set up a cache on the
Aggregate n
data rather than the entire data set.
Save Node
Store Node
Cache
Data Mapping
Create SuperNode
Generate User Input Node
to save the node’s details in a file. You can load node de tails only into
to st ore the selected node in a connected IBM SPSS Collaboration and
o expand the m enu, wit h options for caching the selected node.
t
to expa nd the menu, with options for mapping data to a new source or
to expa nd the menu, with options for cr eating a SuperNode in the
to replace the selec ted node. Examples generated by this node
same fields as the current node.
Run From Here
to run all terminal nodes downstream from the selected node.
de, the cache is filled with the d ata that passes through the node the next time you
ost useful following a time-con suming operation such as a sort, merge, or
ode rather than on the source node because you want the cache to store the aggregated
Note: Caching at source nodes, wh ich simply stores a copy of the or iginal data as it is read into
IBM® SPSS®
Modeler, will not improve performance in most circumstances.
Nodes w ith caching enabled are displayed with a small document icon at the top right corner.
When t he data is cached at the node, the document icon is green.
Page 61

Figure 5-12
Caching at the Type node to store newly derived fields
51
Building Streams
To Enable a Cache
E
On the stream canvas, right-click the node and click
E
On the c aching submenu, click
E
You can turn the cache off by right-clicking the node and cli cking
Caching Nodes in a Database
Enable
.
Cache
on the menu.
Disable
on the caching submenu.
For streams run in a database, da ta can be cached midstream to a temporary table in the database
rather than the file system. When combined with SQL optimization, this may result in significant
gains in performance. For example, the output from a stream that merges multiple tables to create
a data mining view may be cached and reused as needed. By automatically generating SQL for
all downstream n odes, performance can b e further improved.
When using database caching with strings longer than 255 characters, either ensure that there
is a Type node upstream from the caching node and that the field values are read, or set the
string length by means of the default_sql_string_length parameter in the options.cfg file. Doing
so ensures that the corresponding column in the temporary table is set to the correct width to
accommodate the strings .
To take advantage of database caching , both SQL optimization and database caching must
be enabled. Note that Server optimization settings override those on the Client. For more
information, see the topic Setting optimization options for streams on p. 60.
With database caching enabled, s imply right-click any nonterminal node to cache data at
that point, and the cache will be created automatically directly in the database the next time the
stream is run. If database caching or SQL optimization is not enabled, the cache will be written
to the file system instead.
Page 62

52
Chapter 5
Note: The following databases support temporary tables for the purpose of caching: DB2,
Netezza, Orac
le, SQL Server, and Teradata. Other databases will use a norma l table for database
caching. The SQL code can be customized for s pe cific databases - contact Support for assistance.
To Flush a Cache
A white document icon on a node indicates that its cache is empty. When the cache is full, the
document icon becomes solid green. If you want to replace the contents of the cache, you must
first flush the cache and then re-run the data stream to refill it.
E
On the stream canvas, right-click the node and click
E
On the c aching submenu, click
To Save a Cache
Flush
.
Cache
on the menu.
You can save the contents of a cache as an IBM® SPSS® Statistics data file (*.sav). You can then
either reload the file as a cache, or you can set up a node that uses the c ache file as its data source.
You can also load a cache that you saved from another project.
E
On the stream canvas, right-click the node and click
Cache
on the menu.
E
On the caching submenu, click
E
In the Save Cache dialog box, browse to the location where yo u want to save the cache file.
E
Enter a name in the File Na me text box.
E
Be sure that
To Load a Cache
*.sav
is selec ted in the Files of Type list, and click
Save Cache
.
Save
.
If you have saved a cache file before removing it from the node, you can reload it.
E
On the stream canvas, right-click the node and click
E
On the caching submenu, click
E
In the Load Cache dialog box, browse to the location of the cache file, select it, and click
Load Cache
.
Cache
on the menu.
Previewing Data in Nodes
To ensure that data is being changed in the way you expect as you build a stream, you could run
your data through a Table node at each significant step. To save you from having
to do this you
can generate a preview from each node that displays a sample of the data that will be created,
thereby reducing the time it takes to build each node.
For nodes upstream of a model nugget, the preview shows the input fields; for
a model
nugget or nodes downstream of the nugget (except terminal nodes), the preview shows input
and generated fields.
The default number of rows displayed is 10; however, you can change this in
the stream
properties. For more information, see the to pic Setting general options for streams on p. 55.
Load
.
Page 63

Figure 5-13
Data Preview from a model nugget
From the Generate menu, you can create several types of nodes.
53
Building Streams
Locking Nodes
To prevent other users from amending the settings of one or more nodes in a stream, you can
encapsulate the node or nodes in a special type of node called a SuperNode, and then lock the
SuperNode by applying password protect ion.
Working with Streams
Once you have connected source, process, and terminal nodes on the stream can vas, you have
created a stream. As a collection of n odes, streams can be saved, annotated, and added to projects.
You can also set numerous options for streams, such as optimization, date and time settings,
parameters, and scripts. These properties are d is cussed in the topics that follow.
In IBM® SPSS® Modeler, you c an use and modify more than one data stream in the same
SPSS Modeler se ssion. The right side of the main window contains the managers pane, which
helps you to navigate the streams, outputs and models that are currently open. If you cannot see
the managers pane, click
Managers
on the View menu, then click the
Streams
tab.
Page 64

54
Chapter 5
Figure 5-14
Streams tab in the managers pane with pop-up menu options
From this tab, you can:
Access streams.
Save streams.
Save streams to the current project.
Close streams.
Open new streams.
Store and retrieve streams from an IBM SPSS Collaboration and Deploymen t Services
repository (if a vailable at your site). For more information, see the topic Abou t the IBM SPSS
Collaboration and Deployment Services Repository in Chapter 9 on p. 158.
Right-click a stream on the Streams tab to access these options.
Setting Options for Streams
You can specify a number of options to apply to the current stream. You can also save these
options as defaults to apply to all your streams. The options are as follows.
General.
Miscellaneous options such as symbols and text encoding to use in the stream. For
more information, see the topic Setting general options for streams on p. 55.
Date/Time.
Options relating to the format of date and tim e expressions. For more information,
see the topic Setting date and time options for streams on p. 57.
Number formats.
Options controlling th e format of numeric expressions. For more information,
see the topic Setting number format options for streams on p. 59.
Optimization.
Options for optimizing stream performance. For more information, see the
topic Se tting op timization options for streams on p. 60.
Page 65

Logging and status.
see the topic Setting SQL logging and record status options for streams on p. 63 .
Layout.
Options relating to the lay out of the stream on the canvas. For more information, see
the topic Setting layou t options for streams on p. 64.
To Set Stream Options
E
On the File menu, click
managers pan
E
Click the
e, right-click and then click
Options
Building Streams
Options controlling SQL logging and record status. For more information,
Stream Properties
(or select the stream from the Streams tab in the
Stream Properties
on the pop-up menu).
tab.
55
Alternative
Stream Properties > Options
ly, on the Tools menu, click:
Setting general options for streams
The general o
ptions are a set of misce llaneous options that apply to various as pects of the current
stream.
Page 66

56
Chapter 5
Figure 5-15
Setting general options for a stream
Decimal symbol.
Grouping symbol.
Select either a comma (,) or a period (.) as a decimal separator.
For number display formats, select the symbol used to group values (for example,
the comma in 3,000.00). Options include none, period, comma, space, and locale-defined (in
which case t he default for the current locale is used).
Encoding.
Specify the stream default method for text encoding . (Note: Applies to Var. File
source node and Flat File export node only. No other nodes use this setting; most data files have
embedded encoding information.) You can c hoose either the system default or UTF-8. The
system default is specified in the Windows Control Panel or, if running in distributed mode, on the
server computer. For more information, see the t opic Unicode Supp ort in IBM SPSS Modeler
in Appendix B on p. 248.
Ruleset Evaluation.
Determines how rule set models are evaluated. By default, rule sets use
Voting
to combine predictions from individual rules and determine the fina l prediction. To ensure that
rule set s use the first hit rule by default, select
First Hit
. Note that this option does not apply to
Decision List models, which always use the first hit as defined by the algorithm.
Page 67

57
Building Streams
Maximum number of rows to show in Data Preview.
a previe w of th
e data is requested for a node. For more info r mation, see th e topic Previewing
Specify the number of rows to be shown when
Data in Nodes on p. 52.
Maximum members for nominal fields.
Select to specify a maximum number of members for
nominal (set) fields after which the data type of the field becomes Typeless. Th is option is useful
when working with large nominal fields. Note: When the measurement level of a field is set to
Typeless, its role is automatically set to None. This means that the fields are not available for
modeling.
Limit set size for Kohonen, and K-Means modeling.
Select to specify a maximum number of members
for nominal fields used in Kohonen nets and K-Mean s modeling. The default set size is 20, after
which the field is ignored and a warning is raised, providing information on the field in question.
Note that, f or compatibility, this option also applies to the old Neural Network node that was
replaced in version 14 of IBM® SPSS® Modeler; some legacy streams may still contain this node.
Refresh source nodes on execution.
the current stream. This action is analogous to clicking the
Select to automatically refresh all source nodes when running
Refresh
button on a source node,
except that this option automatically refreshes all source nodes (excep t User Input nodes) for the
current stream.
Note: Selecting this option flushes the caches of downstream nodes even if the data has not
changed. Flushing occurs only once per running of the stream, though, which means that you can
still use downstream caches as temporary storage f or a single running. For example, say that you
have set a cache midstream after a complex derive operation and that you have several gra phs
and reports attached downstream of this Derive node. When running the stream, the cache at the
Derive node will be flushed and refilled but only for the first g r aph or re port. Subsequent terminal
nodes will read data from the Derive node cache.
Display field and value labels in output.
Displays field and value labels in tables, charts, and other
output. If labels do not exist, the field names and data values will be displayed instead. Labels are
turned off by default; however, you can toggle labels on an individual basis elsewher e in SPSS
Modeler. You can also choose to display labels on the output window using a toggle button
available on the toolbar.
Figure 5-16
Toolbar icon used to toggle field and value labels
Display execution times.
Displays individual e xecution times for stream nodes on the Execution
Times tab after the stream is run. For more information, see the topic Viewing Node Execution
Times on p. 67.
Save As Default.
The optio ns specified app
ly only to the c urrent stream. Click this button to set
these options as the default for all streams.
Setting date and time options for streams
These options specify the format to use for various date and time expressions in the current stream.
Page 68

58
Chapter 5
Figure 5-17
Setting date and time options for a stream
Import date/time as.
Select whether to use date/time storage for date/time fields or whether
to import them as string variables.
Date format.
Select a date format to be used for date storage fields or when strings are interprete d
as dates by CLEM date functions.
Time format.
Select a time format to be used for time storage fields or when strings are interpreted
as times by CLEM time functions.
Rollover days/mins.
For time formats, select whether negative time differences should be
interpreted as referring to the previous day or hour.
Date baseline (1st Jan).
Select the baseline years (always 1 January) to be used by CLEM date
functions that work with a single date.
Page 69

59
Building Streams
2-digit dates start from.
two digits. Fo
r example, specifying 193 0 as the cutoff year will assume that 05/11/02 is in the
Specify the cutoff year to add century digits for years denoted with only
year 2002. The same setting will use the 20th century for dates after 30; thus 05/11/73 is assumed
to be in 1973.
lt.
Save As Defau
The optio ns specified apply only to the current stream. Click this b utton to set
these options as the default for all streams.
Setting numb
er format options for streams
These options specify the format to use for various numeric expressions in the current stream.
Figure 5-18
Setting number format options for a stream
Number display format.
You can choose from standard (
currency display formats (
$###.##
####.###
), scientific (
#.###E+##
), or
).
Page 70

60
Chapter 5
Decimal places (standard, scientific, currency).
of decim al pla
ces to be used when displaying or printing real numbers. This option is specified
For number display formats, specifies the numb er
separately for each display format.
Calculations in.
Select
RadiansorDegrees
as the unit of measurement to be used in trigonometric
CLEM expressions. For more infor mation, see the topic Trigonometric Functions in Chapter 8
on p. 139.
Save As Default.
The optio ns specified apply only to the current stream. Click this b utton to set
these options as the default for all streams.
Setting optimization options for streams
You can use the Optimization settings to optimize stream performance. Note that the performance
and optimization settings on IBM® SPSS® Modeler Ser ver (if used) override any equivalent
settings in
the client.
Note: Database modeling and SQL optimization require that SPSS Modeler Server con ne ctivity
be enabled on the IBM® SPSS® Modeler computer. With this setting enabled, you can access
database al
gorithms, push back SQL directly from SPSS Modeler, and access SPSS Modeler
Server. To verify the current license status, choose the following from the SPSS Modeler menu.
Help > About > Additional Details
If connectivity is enabled, you see the option
Server Enablement
in the License Status tab.
For mor e information, see the topic Connecting to IBM SPSS Modeler Server in Chapter 3 on
p. 13.
Page 71

Figure 5-19
Setting stream optimization options
61
Building Streams
Note: W
hether SQL pushback and optimization are supported depends on the type of database in
use. For the latest information on which databases and ODBC drivers are supported and tested for
use with IBM® SPSS® Modeler 15, see the corporate Support si te at http://www.ibm.com/support.
Enable stream rewriting.
Select this option to enable stream rewriting in SPSS Modeler. Two types
of rewriting are available, and you can select one or both. Stream rewriting r eo r ders the nodes in a
stream behind the s cenes for more efficient operation, without altering stream semantics.
Optimize SQL generation.
This opti on enables nodes to be reordered within the stream so that
more operations can be pushed back using SQL generation for execution in the database.
When it find s a node that cannot be rendered into SQL, the optimizer will look ahead to
see if there are any dow nstream nodes that can be rendered into SQL and safely moved in
t of the problem node without affecting the stream semantics. Not only can the database
fron
perform operations more efficiently than SPSS Modeler, but such pushbacks act to reduce
the size of the data set that is returned to SPSS Modeler for processing. This, in turn, can
Page 72

62
Chapter 5
reduce network traffic and speed stream operations. Note that the
Generate SQL
check box
must be selected for SQL optimization to have any effect.
Optimize syntax execution.
This method of stream rewriting increases the efficiency of
operations that incorporate more than one node containing IBM® SPSS® Statistics syntax.
Optimization is achieved by com bining the syntax commands in to a single operation, instead
of running each as a separate operation.
Optimize other execution.
This method of stream rewriting increases the efficiency of
operations that cannot be delegated to the database. Optimization is achieved by reducin g the
amount of data in the stream as early as possible. While maintaining data integrity, t he stream
is rewritten to push operations c loser to the data source, thus reducing data downstream for
costly oper
Enable parallel processing.
ations, such as joins.
When running on a computer with multiple processors, this option
allows the system to balance the load across those processors, which may result in faster
performanc
e. Use of multiple nodes or use of the following individual n odes may benefit from
parallel processing: C5.0, Merge (by key), Sort, Bin (rank and tile methods), and Aggregate
(using one or more key fields).
QL.
Generate S
Select this option to enable SQL generation, allowing stream opera tions to be pushed
back to the database by using SQL code to generate execution processes, whic h may improve
performance. To further improve performance,
maximize t
he number o f operations pus hed back to the database. When operations for a node have
Optimize SQL generation
can also be selected to
been pushed back to the database, the node will be highlighted in purple when the stream is run.
Database caching.
cached mi
dstream to a temporary table in the database rather than to the file system. When
For streams that generate SQ L to be executed in the database, data can be
combined with SQ L optimization, this may result in significant gains in per f ormance. For
example, the output from a stream that merges multiple tables to create a data mining view
may be cached and reused as nee ded. With database caching enabled, simply righ t-click any
nonterminal no de to cac he data a t that po int, and the cache is automatically created directly in
the database the next time the stream is run. This allows SQL to be generated for downstream
nodes, f
urther improving performance. Alternatively, this option can be disabled if needed,
such as when policies or permissions preclude data being written to the database. If database
caching or SQL optimization is not enabled, the cache will be written to the file system
instead. For more information, see the topic Caching Options for Nodes on p. 50.
laxed conversion.
Use re
This option enables the conversion of data from either strings to
numbers, or numbers to strings, if stored in a suitable format. For example, if the data is
kept in the database as a string, but a ctually contains a meaningful number, the data can be
converted for use when the pushback occurs.
Note: Due to minor differences in SQL implementation, streams run in a database may return
slightly different results from those returned when run in SPSS Modeler. For similar reasons, the se
differences may also vary depending on the database vendor.
Save As Default.
The optio ns specified apply only to the current stream. Click this b utton to set
these options as the default for all streams.
Page 73

Building Streams
Setting SQL logging and record status options for streams
These settings include various options controlling the display of SQL statements generated by the
stream, and the display of the number of records processed by the stream.
Figure 5-20
Setting SQL logging and record status options for a stream
63
Display SQL in the messages log during stream execution.
Specifies whether SQL generated while
running the stream is passed to the message log .
Display SQL generation details in the messages log during stream preparation.
During stream
preview, specifies whether a preview of the SQL that would be generated is passed to the
messages log.
Display SQL.
Specifies whether a ny SQL that is displayed in the log should contain native SQL
functions or standard ODBC functions of the form {fn FUNC(…)}, as generated by IBM® SPSS®
Modeler. The former relies on ODBC driver functionality that may not be implemented. For
example, this control w ould have no effect for SQL Server.
Page 74

64
Chapter 5
Reformat SQL for improved readability.
formatted for
Show status for records.
readability.
Specifies when records should be reported as they ar rive at terminal
Specifies whether SQL displayed in the log should be
nodes. Specify a number that is used for updating the status every N records.
Save As Default.
The optio ns specified apply only to the current stream. Click this b utton to set
these options as the default for all streams.
Setting layout options for streams
These settings provide a number of options relating to the display and use of the stream canvas.
Figure 5-21
Setting display layout options for a stream
Minimum stream canvas width.
Minimum stream canvas height.
Specify the minimum width of the stream canvas in pixels.
Specify the minimum height of the stream canvas in pixels.
Page 75

65
Building Streams
Stream scroll rate.
stream canvas
Specify the scrolling rate for the stream canvas to control how quickly the
pane scrolls when a node is being dragged from one place to another on the canvas.
Higher numbers specify a faster scroll rate.
Icon name maximum.
Icon size.
ect an option to scale the entire stream view to one of a number of sizes between 8%
Sel
Specify a limit in characters for the names of nodes on the strea m canvas.
and 200% of the standard icon size.
Grid cell size.
stream canva
Snap to Grid.
Generated icon placement.
model nugget
Save As Default.
Select a grid cell size from the list. This number is used for aligning nodes on the
s using an invisible grid. The def au lt grid cell size is 0.25.
Select to align icons to an invisible g r id pattern (selected by default).
Choose where on the canvas to place icons for nodes generated from
s. Defau lt is top left.
The optio ns specified apply only to the current stream. Click this b utton to set
these options as the default for all streams.
Viewing Stream Operation Messages
Messages reg arding stream operations, such as running, optimization, and time elapsed for model
building and evaluation, can easily be viewed using the Messages tab in the stream properties
dialog b ox. Error messages are also reported in this table.
To View Stream Messages
E
On the File menu, click
managers pa
E
Click the
Alternati
Stream Properties > Messages
ne, right-click and then click
Messages
tab.
vely, on the Tools menu, click:
Stream Properties
(or select the stream from the Streams tab in the
Stream Properties
on the pop-up menu).
Page 76

66
Chapter 5
Figure 5-22
Messages tab in stream properties dialog box
In addition to messages regarding stream opera tions, er r or messages are reported here. When
stream running is terminated because of an erro r, this dialog box will open to the Messages tab
with t he error message visible. Additionally, the node with errors is highlighted in red on the
stream canvas.
Page 77

Figure 5-23
Stream running with error reported
67
Building Streams
If SQL optimization and logging options are e nabled in the User Options dialog box, then
information on generated SQL is also displayed. For more information, see the topic Setting
optimization options for streams on p. 60.
You can save messages reported here for a stream by clicking
Save Messages
on the Save
button drop-down list (on t he left, just below the Messages tab). You can also clear all messages
for a given stream by clicking
Clear All Messages
on the Save button list.
Viewing Node Execution Times
On the Messages tab you can also choose to display Execution Times, where you can see the
individual execution times for all the nodes in the stream.
Note: For this featu r e to work, the
General
setting of the
Options
Display execution times
tab.
check box must b e selected on the
Page 78

68
Chapter 5
Figure 5-24
Viewing execution times for nodes in the stream
In the table of node execution times, the columns are as follows. Click a column heading to sort
the entries into ascending or descending order (for example, to see which nodes have the longest
execution times).
Terminal Node.
The identifier of the branch to w hich the node belongs. The identifier is the name
of the terminal node a t the end of the branch.
Node Label.
Node Id.
The nam e of the node to which the execution time refers.
The unique identifier of the node to which the execution time refers. This identifier is
generated by the system when th e node is created.
Execution Time(s).
The time in seconds taken to execute this node.
Setting Stream and Session Parameters
Parameters can be defined for use in CLEM expressions and in scripting. They are, in effect,
user-defined variables that are saved and persisted with the current stream, session, or SuperNode
and can be accessed from the user interface as well as through scripting. If you save a stream, for
example, any parameters set for that stream are also saved. (This distinguishes them from local
script varia bles, which can be used only in the script in which they are declared.) Parameters are
often used in scripting as part of a CLEM expression in which the parameter value is specified in
the script.
The scope of a parameter depends on where it is set:
Stream parameters can be set in a stream script or in the stream properties dialog box, and
they are availab
le to all nodes in the stream. They are displayed on the Parameters list in the
Expression Builder.
Session parameters can be set in a s tand-alone script or in the session parameters dialog
box. They are available to all streams used in the current session (all streams listed on the
Streams tab in th
e managers pane).
Page 79

Parameters can also be set for SuperNodes, in which case they are visible only to nodes
encapsulated
To Set Stream and Session Parameters through the User Interface
E
To set stream parameters, on the main menu, click:
Tools > Stream Properties > Parameters
E
To set session parameters, click
Figure 5-25
Setting parameters for the session
within that SuperNode.
Set Session Parameters
on the Tools menu.
69
Building Streams
Prompt?.
Check this box if you want the user to be prompted at runtime to enter a value for
this parameter.
Name.
Parameter nam es are listed here. You can create a new parameter by entering a n ame in this
field. For example, to cre ate a p arameter for the minimum tempera ture, you could type
Do not include the
$P-
prefix that denotes a parameter in CLEM expressions. This name is also
minvalue
used for display in the CLEM Expression Builder.
Long name.
Storage.
Lists the descriptive name for each parameter created.
Select a storage type from th e list. Storage indicates how the data values are stored in
the para meter. For example, when working with values containing leading zeros that you want
to preserve (such as 008), you should select
String
as the storage type. Otherwise, the zeros
will be stripped from the value. Avai lable storag e types are string, integer, real, time, date, and
timestamp. For date param eters, note that values must be specified using ISO standard notation as
shown in the next paragraph.
Value.
Lists the current value for each parameter. Adjust the parameter as required. Note that for
date parameters, values must be specified in ISO standard notation (that is, YYYY-MM-DD). Dates
specified in other formats are not accepted.
Type (optional).
If you plan to deploy the s tream to an exte
rnal appl ication, select a measurement
level from the list. Otherwise, it is advisable to leave the Type column as is. If you want to
specify value constraints for the parameter, such as upper and lower bounds for a numeric range,
select
Specify
from the list.
.
Page 80

70
Chapter 5
Note that long name, storage, and type options can be set for parameters through the user
interface onl
y. These options cannot be set using scripts.
Click the ar r ows at the right to move the selected parameter further up or down the list of
available parameters. U se the delete button (marked with an X) to remove the selected paramet er.
Specifying Runtime Prompts for Parameter Values
If you have streams where you might need to enter different values for the same parameter on
different occasions, you can specify runtime prompts for one or more stream or sess ion parameter
values.
Figure 5-26
Runtime prompting for parameter values
Parameters.
Turn off these prompts.
run the stream. You can cause them to be redisplayed by sele cting the
(Optional) Enter a v alue for the parameter, or leave the default value if there is one.
Select this box if you do not want these prompts to be displayed when you
Prompt?
check box on the
stream properties or session properties dialog box where the parameters w ere defined. For more
information, see the topic Setting Stream and Session Parameters on p. 68.
Specifying Value Constraints for a Parameter Type
You can make value constraints for a parameter av ailable during stream deployment to an external
application that reads data modeling streams. This dialog box allows you to specify the values
available to an external user running the stream. Depending on the data type, value constraints
vary dynamically in the dialog box. The options shown here are identical to the options available
for values from the Type node.
Page 81

Building Streams
Figure 5-27
Specifying available values for a parameter
Type.
Displays the currently selected measurement level. You can change this value to reflect the
way that you intend to use the parameter in IBM® SPSS® Modeler.
71
Storage.
Displays the storage type if known. Storage types are unaffected by the measurement
level (continuous, nominal or flag) that you choose for work in SPSS Modeler. You can alter
the storage type on the main Parameters tab.
The bottom half of the dialog box dynamically changes depending on the measurement level
selected in the
Continuous Measurement Levels
Lower.
Upper.
Labels.
Specify a lower limit for the parameter values.
Specify an upper limit for the parameter values.
You can specify labels for any value of a range field. Click the
Type
field.
Labels
button to open a
separate dialog box for specifying value labels.
Nominal Measurement Levels
Values.
This option allows you to specify values for a parameter that will be used as a nominal
field. Values will not be coerced in the SPSS Modeler stream but will be used in a drop-down
list for external deploym en t applications. Using the arrow and delete buttons, you can modify
existing values as well as reorder or delete values.
Flag Measurement Levels
True.
Specify a flag value for the parameter when the condition is met.
False.
Specify a flag value for the parameter when the condition is not met.
Labels.
You can specify labels for the values of a flag field.
Stream Deployment Options
The Deployment tab of the stream properties dialo g bo x enables you to specify options for
deploying the stream as a scenario within IBM® SPSS® Collaboration and Deployment
Services for the purposes of model refresh, a utomated job scheduling, or further use by IBM®
Page 82

72
Chapter 5
Analytical Dec ision Management or Predictive Applications 5.x. All streams require a designated
scoring bra nc
h before they can be deployed; additional requirements and options depend on the
deployment type. For more information, see the topic Storing and Deploying Repository Objects
in Chapter 9 on p. 160.
Viewing Global Values for Streams
Using the Globals tab in the stream properties dialog box, you can view the global values set for
the current stream. Global values are created using a Set Globals node to determine statistics such
as mean, sum, or standard dev iation for selecte d fields.
Once the Set Globals node is run, these values are then available for a variety of uses in stream
operations. For more information, see the topic Glob al Functions in Chapter 8 on p. 155.
To View Global Values for a Stream
E
On the File menu, click
managers pane, right-click and then click
Stream Properties
(or select the stream from the Streams tab in the
Stream Properties
on the pop-up menu).
E
Click the
Globals
tab.
Alternatively, on the Tools menu, click:
Stream Properties > Globals
Figure 5-28
Viewing global values available for the stream
Globals available.
Av ailable globals are listed in this table. You cannot edit global values here,
but you can clear al l global values for a stream using the Clear All Values button to the right of
the table.
Page 83

Building Streams
Searching for Nodes in a Stream
You can search for nodes in a stream by specifying a number of search criteria, such as node name,
category a nd identifier. This feature can be especially us eful for complex streams containing a
large number of nodes.
To Search for Nodes in a Stream
E
On the File menu, click
managers pane, right-click and then click
E
Click the
Search
Stream Properties
tab.
(or select the stream from the Streams tab in the
Stream Properties
on the pop-up menu).
Alternatively, on the Tools menu, click:
Stream Properties > Search
Figure 5-29
Searching for nodes in a stream
73
You can specify more th an one option to limit the search, e xcept that searching by node ID (using
the
ID equals
Node label contains.
field) excludes the other options.
Check thi s box and enter all or part of a node label to search for a par ticular
node. Searches are not case-sensitive, and mu ltiple words are treated as a single piece of text.
Page 84

74
Chapter 5
Node category.
node.
Process
Apply Model Node
Keywords include.
Check this box and click a category on the list to search for a particula r type of
Node
means a node from the Record Ops or Fiel d Ops tab of the nod es palette;
refers to a model n ugget.
Check thi s box and enter one or more complete keywords to search for nodes
having that text in the Keywor ds field on the Annotations tab of the node dialog box. Keyword
text that you enter must be an exact match. Separate multiple keywords with semicolons to search
for alternatives (for example, entering proton;neutron will find all nodes with either of these
keywords. For more information, see the topic Annotations on p. 86.
Annotation contains.
Check this box and enter one or more words to search for nodes that contain
this text in the main text area on the Annotations tab of the node dialog box. Searches are not
case-sensitive, and multiple words are treated as a single piece of te xt. For more information,
see the topic Annotations on p. 86.
Generates field called.
Check this box and enter the name of a generated field (for example,
$C-Drug). You can use this option to search for modeling nodes that generate a particular field.
Enter o nly one field name, which must be an exact ma tch.
ID equals.
Check thi s box and enter a node ID to search for a particular node with that identifier
(selecting this option disables all the preceding options). Node IDs ar e assigne d by the system
when the node is created, and can be use d to reference the no de for the purposes of scripting or
automation. Enter only one node ID, which must be an exact match. For more information,
see the topic Annotations on p. 86.
Search in SuperNodes.
nodes both inside and outside SuperNode s. Clear the box if you want to perform the search only
on nodes outside SuperNodes, at the top level of the stream.
Find.
When you have specified all the options you want, click this button to start the search.
Nodes that match the specified options are listed in the lo wer part of the dialog box. Select a node
in the list to highlight it on the stream canvas.
Renaming Streams
Using the Annotations tab in the stream properties dialog box, you can add descriptive annotations
for a stream and create a custom name for the stream. These options are useful especially
when g enerating reports for streams ad de d to the project pane. For more information, see the
topic Annotations on p. 86.
Stream Descriptions
For each stream that you crea te, IBM® SPSS® Modeler produces a stream description containing
information on the contents of the stream. This can be useful if you are trying to see what a stream
does but you do not have SPSS Modeler installed, for exa mple when accessing a stream through
IBM® SPSS® Collaboration and Deployment Services.
This box is checked by default, meaning that the search is performed on
Page 85

Figure 5-30
Opening section of stream description
75
Building Streams
The stream description is displayed in the form of an HTML document consisting of a number
of sections.
General Stream Information
This section contains the stream name, together with details of when the stream was created
and last saved.
Description and Comments
This section includes any:
Stream annotations (see Annotations on p. 86)
Comments not connected to specific nodes
Comments connected to nodes in both the modeling and scoring branc hes of the stream
Scoring Information
This section contains information under various headings rel ating to the scoring branch of the
stream.
Comments.
Includes comments linked only to nodes in the scoring bra nch.
Page 86

76
Chapter 5
Inputs.
Lists the input fields together with their storage types (for example, string, integer,
real and so on).
Outputs.
Lists the output fields, including the additional fields generated by the modeling node,
together with their storage types.
Parameters.
Lists any parameters relating to the scoring branch of the stream and which can be
viewed or edited each time the model is scored. These parameters are identified when you
click the
Model Node.
on). This is t
Scoring Parameters
button on the
Deployment
tab of t he stream properties dialog box.
Shows the mode l name and type (for example, Neural Net, C&R Tree and so
he m odel nugget selected for the
Model node
field on th e
Deployment
the stream properties dialog box.
Model Details.
Shows details of the model n ugget identified under the previous heading.
Where possible, predictor importance and evalu ation charts for the model are included.
Modeling Information
Contains information relating to the modeling branch of the stream.
Comments.
Lists any comments or annotations that are connected to nodes in the modeling
branch.
Inputs.
Lists the input fields together with their role in the modeling branch (in the form of the
field role value, for example, Input, Target, Split and so on).
Parameters.
Lists any parameters r
elating to the modeling branch of the stream and which can
be viewed or edited each time the model is updated. These parameters are identified when
you click the
Model Build Parameters
button on the
Deployment
tab of the stream properties
dialog box.
Modeling node.
Shows the name and ty
pe of the modeling node used to generate or update
the model.
tab of
Previewing Stream Descriptions
You can view the contents of a stream description in a web browser by clicking an option on the
stream properties dialog box. The con tents of the description depend on the options you specify
on the D eployment tab of the dialog box. For more information, see the topic Stream D eployment
Options in Chapter 9 on p. 185.
To view a stream description:
E
On the main IBM® SPSS® Modeler menu, click:
Tools > Stream Properties > Deployment
E
Set the deployment type, the designated scoring node and any scoring parameters.
E
If the deployment type is Model Refresh, you can optionally select a:
Modeling node and any model build parameters
Model nugget on the sc oring branch of the stream
E
Click the
Preview Stream Description
button.
Page 87

Exporting Stream Descriptions
77
Building Streams
You can export the conten
To export a stream description:
E
On the main menu, click:
File > Export Stream Description
E
Enter a name for the HTML file and click
Running Streams
Once you have specified the required options for streams and connected the required nodes, you
can run the stream by running the data through nodes in the stre am. There are several ways to run
a strea m w ithin IBM® SPSS® Modeler. You can:
Click
Click one of the
stream or simply the selected terminal node. For more information, see the topic IBM SPSS
Modeler Toolbar in Chapter 3 on p. 21.
Run a single data stream by right-clicking a terminal node and clicking
menu.
Run part of a data stream by right-clicking any non-terminal node and clicking
Here
be performed.
ts of the stream description to an HTML file.
Save
.
Run
on the Tools menu.
Run...
buttons on the toolbar. These butto ns allow you to run the entire
Run
on the pop-up
Run From
on the pop-up menu. Doing so causes only those operations after the selected node to
To halt the running of a stream in progress, y ou can click the red Stop button on the toolbar, or
click
Stop Execution
on the Tools menu.
If any stream takes longer than three seconds to run, the Execution Feedback dialog box is
displayed to indicate the progress.
Figure 5-31
Execution Feedback dialog box
Page 88

78
Chapter 5
Some nodes have further displays giving additional information about stream execution. These
are displayed
by selecting the corresponding row in the dialog box. The first row is selected
automatically.
Working with Models
If a stream includes a modeling node (that is, one from the Modeling or Database Modeling tab
of the nodes palette), a model nugget is created when the stream is run. A model nugget is a
container for a model, that is, the set of rules, formulas or equa tions that enables you to generate
predictions against your source data, and which lies at the heart of predictive analytics.
Figure 5-32
Model nugget
When you su ccessfully run a modeling node, a corresponding model nugget is placed on the
stream canvas, where it is re pre sented by a gold diamond-shaped icon (hence the name “nugget”).
You can open the nugget and browse its contents to view details about the model. To view the
predictions, you attach and run one or more terminal nodes, the output from which presents
the predictions in a readable form.
Figure 5-33
Modeling and scoring branches in a stream
A typical modeling stream consists of two branches. The modeling branch contains the modeling
node, together with the source and processing nodes that precede it. The scoring branch is
created when you r un the modeling node, and contains the model nugget and the terminal node or
nodes that you use t o view the predictions.
For more information, see the IBM® SPSS® Modeler Modeling Nodes guide.
Adding Comments and Annotations to Nodes and Streams
You may need to describe a stream to others in your organization . To help you do this, you can
attach explanatory comments to streams, nodes and model nuggets.
Page 89

Figure 5-34
Stream with comments added
79
Building Streams
Others can then view these comments on-screen, or you can print out an image of the stream
that includes the comments.
You can list all the comments for a stream or SuperNode, change the order of comments in the
list, edit the comment text, and change the foreground or background color of a comment. For
more information, see the topic Listing Stream Comments on p. 84.
You can also add notes in the form of text annotations to streams, nodes and nuggets by
means of the Annotations tab of a stream properties dialog box, a node dialog box, or a model
nugget window. These notes are visible only when the Annotations tab is open, except that
stream annotations can also be show n as on-screen comments. For m ore information, see the
topic Annotations on p. 86.
Comments
Comments take the form of text box es in which you can enter any amount of text, and you can
add as many comments a s you like. A comment can be freestan ding (not attached to any stream
objects), or it can be conne cted to one or more nodes or model nuggets in the stream. Freestanding
comments a r e typically used to describe the overall purpose of the stream; connected comments
describe the node or nugget to which they a r e attached. Nodes and nuggets can have more than
one comment attached, and the stream can have any number of freestanding comments.
Note: You can also show stream annotations as on-screen comments, though these cannot be
attached to nodes or nuggets. For more information, see the topic Converting Annotations to
Comments on p. 85.
Page 90

80
Chapter 5
The appearance of the text box c hanges to indicate the current mode of the comment (or annotation
shown as a comm
Table 5-1
Comment and an
Comment text box Annotation text
ent), as the follow ing t able shows.
notation text box modes
Mode
box
Edit Comment is open for
Last
selected
View Ed i t i ng is complete. Clicking on another node,
Indicates Obtained by...
editing.
Comment can be moved,
resized or deleted.
Creating a new comment
or annotation, or
double-clicking an
existing one.
Clicking the stream
background after editing,
or single-clicking an
existing comment or
annotation.
comment or annotation
after editing.
When you create a new freestanding comment, it is initially displayed in the top left corner
of the stream canvas.
Figure 5-35
New freestanding comment
If you are attaching a comment to a node or nugget, the comment is initially displayed above the
stream object to which it is attached.
Figure 5-36
New comment attached to node
The text box is colored white to show that text can be entered. When you have entered the text,
you click outside the text box. The comment background changes to yell ow to show that text entry
is complete. The comment remains selected, allowing you to move, resize, or delete it.
Page 91

Building Streams
Figure 5-37
Comment in edit mode
When you click again, the border changes to solid lines to show that editing is complete.
Figure 5-38
Completed comment
81
Double-clicking a comment changes the text box to edit mode—the background changes
to white and the comm ent text can be edited.
You can also attach comments to SuperNodes.
Operations Involving Comments
You can perform a number of operations on comments. You can:
Add a freestanding comment
Attach a comment to a node or nugget
Edit a comment
Resize a comment
Move a comment
Disconnect a comment
Delete a comment
Show or hide all comments for a stream
To add a freestanding comment
E
Ensure that nothing is selected on the stream.
E
Do one of the following:
On the main menu, click:
Insert > New Comment
Page 92

82
Chapter 5
Right-click the stream background and click
Click the
E
Enter the comme nt text (or paste in text from the clipboard).
E
Click a node in the stream to save the comment.
New Comment
button in the toolbar.
New Comment
To attach a comment to a node or nugget
E
Select one or more nodes or nuggets on the stream canvas.
E
Do one of the following:
On the main menu, click:
Insert > New Comment
Right-click the stream background and click
Click the
E
Enter the comment text.
E
Click another node in the stream to save the comment.
New Comment
button in the toolbar.
New Comment
on the pop-up menu.
on the pop-up menu.
Alternatively, you can:
E
Insert a freestanding comment (see previous section).
E
Do one of the following:
Select the comment, pres s F2, then select the node or nugget.
Select the node or nugget, press F2, then se lect the comment.
(Three-button mice only) Move the mouse pointer over the comment, hold down the middle
button, drag the mouse pointer over the node or nugget, and release the mouse button.
To attach a comment to an additional node or nugget
If a comment is already attached to a node or nugget, or if it is currently at stream level, and you
want to attach it to an additional node o r nugget, do one of the following:
Select the comment, pres s F2, then select the node or nugget.
Select the node or nugget, press F2, then se lect the comment.
(Three-button mice only) Move the mouse pointer over the comment, hold
down th e middle
button, drag the mouse pointer over the node or nugget, and release the mouse button.
To edit an existing comment
E
Do one of the following:
Double-click the comment text box.
Select the text box and press Enter.
Right-click the text bo x to display its menu, and click Edit .
Page 93

Building Streams
E
Edit the comment text. You can us e standard Windows shortcut keys when editing, for example
Ctrl+C to copy
E
Click outside the text box once to display the resizing controls, then again to complete th e
text. Other options during edit ing are listed in the pop-up menu for the comment.
comment.
To resize a comment text box
E
Select the comment to display the resizing controls.
E
Click and drag a control to resize the box.
E
Click outside the text box to save th e change.
To move an existing comment
If you want to move a comment but not its attached objects ( if any), do one of the following:
Move the mouse pointer over the comment, hold down the left mouse button, and drag the
comment to the new position.
Select the comment, hold down the Al t key, and move the comment using the arrow keys.
83
If you want to move a comment together with any nodes or nuggets to which
attached:
E
Select all the objects you want to move.
E
Do one of the following:
Move the mouse pointer over one of the o bjects, hold down the left mouse button, and drag
the objects to the new position.
Select one of the objects, hold down the Alt key, and move the objects using the arrow keys.
To disconnect a comment from a node or nugget
E
Select one or more comments to be disconnected.
E
Do one of the following:
Press F3.
Right-click a sel ected comment and click Disconnect on its menu.
To delete a comment
E
Select one or more comments to be deleted.
E
Do one of the following:
Press the Delete key.
Right-click a selected co mment and click Delete on its menu.
the comment is
If the comment was attached to a node o r nugget, the connection line is deleted as well.
Page 94

84
Chapter 5
If the comment was originally a stream or SuperNode annotation that had been converted to a
freestanding
comment, the comment is deleted from the canvas but its text is retained on the
Annotations tab for the stream or SuperNode.
To show or hid
E
Do one of the following:
On the main m
View > Comments
Click the
e comments for a stream
enu, click:
w/hide comments
Sho
button in the toolbar.
Listing Stream Comments
You can view a list of all the comments that have been made for a particular stream or SuperNode.
On this list, you can
Change the order of comments
Edit the comment text
Change the foreground or background color of a comment
Listing Comments
To list the comments made for a stream, do one of th e following:
On the main menu, click:
Tools > Stream Properties > Comments
Right-click a stream in the managers pane and click
Right-click a stream background o n the canvas and click
Stream Properties
Stream Properties
, then
Comments
, then
Comments
.
.
Page 95

Figure 5-39
Listing comments for a stream
85
Building Streams
Text.
The text of the comment. Double-click the text to change the field to an ed itable text box.
Links.
The name of the node to which the comment is attached. If this field is empty, the comment
applies to the stream.
Positioning buttons.
Comment Colors.
select the
Custom colors
both). Click
These move a selected comment up or down in the list.
To change the foreg r ound or background color of a comment, select the comment,
check box, then select a color from the
Apply
, then click the stream background, to see the effect of the change. Click
BackgroundorForeground
to save the change.
Converting Annotations to Comments
Annotations made to streams or Su perNodes can be converted into comm ents.
In the case of streams, the annotation is converted to a freestanding comment (that is, it is not
attached to any nodes) on the stream canvas.
When a SuperNode annotation is conve r ted to a comment, the comment is not attached to the
SuperNode on the stream canvas, but is visible when you zoom in to the SuperNode.
To convert a stream annotation to a comment
E
Click
Stream Properties
managers pane and click
on the Tools menu. (Alternatively, you can right-click a stream in the
Stream Properties
.)
list (or
OK
Page 96

86
Chapter 5
Annotations
E
Click the
E
Select the
E
ClickOK.
Annotations
Show annotation as comment
tab.
check box.
To convert a SuperNode annotation to a comment
E
Double-click the SuperNode icon on the canvas.
E
Click the
E
Select the
E
ClickOK.
Annotations
Show annotation as comment
tab.
check box.
Nodes, streams, and models can be annotated in a number of ways. You can add descriptive
annotations and specify a custom nam e. These options are u seful especially when generating
reports for streams added to the project pane. For nodes and model nuggets, you can also add
ToolTip text to help distinguish between similar nodes on the stream canvas.
Adding Annotations
Editing a node or model nugget opens a tabbed dialog box containing an Annotations tab used to
set a variet
E
To annotate a node or nugget, right-click the node or nugget on the stream canvas and click
Rename and Annotate
E
To annotate a stream, click
a stream in the managers pane and click
y of annotation options. You can also open the Annotations tab directly.
. The editing dialog box opens with the Annotations tab visible.
Stream Properties
on the Tools menu. (A lternatively, you can right-click
Stream Properties
.) Click the Annotations tab.
Page 97

Figure 5-40
Annotations tab options
87
Building Streams
Name.
Select
Custom
to adjust the autogenerated name or to create a unique name for the node
as displayed on the stream canvas.
Tooltip text.
(For nodes and mod el nuggets only) Enter text used as a tooltip on the stream canvas.
This is particularly useful when working with a la rge number of similar nodes.
Keywords.
Specify keywords to be used in project reports and when searching for nodes in a
stream, or tracking objects stored in the repository (see About the IBM SPSS Collaboration
and Deployment Services Repository on p. 158). Multiple keywords can be s eparated by
semicolons—for example,
of each keyword are trimmed—for example,
income;crop type
type
with one space and
. (White spaces within keywo r ds are not trimmed, however. For example,
income; crop type; claim value
income ; crop type
crop type
with two spaces are not the same.)
. White spaces at the beginning and end
will produce the same resul ts as
crop
The main text area can be used to enter lengthy annotations regarding the operations of the
node or decisions m ade in the node. For example, when you are sharing and reusing streams, it is
helpful to take notes on decisions such as discarding a field with numerous blanks using a Filter
node. Annotating the node stores this information with the node. You can also choose to includ e
these annotations in a project report created from the project pane. For more information, see the
topic Introduction to Projects in Ch ap ter 11 on p. 200.
Page 98

88
Chapter 5
Show annotation as comment.
to convert the
For mor e information, see the topic Adding Comments and Annotations to Nodes and Streams
on p. 78.
ID.
Displays a unique ID that can be used to reference the node for the purpos e of scripting or
automation. This value is automatically generated when the node is created and will not change.
Also note that to avoid confusion with the letter “O”, zeros are not used in node IDs. Use the copy
button at the right to copy and paste the ID into scripts or elsewhere as needed.
Saving Data Streams
After you have created a stream, you can save it for future reuse.
To Save a Stream
E
On the File menu, click
E
In the Save dialo g box, browse to the folder in which you want to save the stream file.
E
Enter a name for the stream in the File Name text box.
E
Select
Add to project
(For stream and SuperNode annotations only) Check this box
annotation to a freestanding comment that will be visible on the stream canvas.
Save StreamorSave Stream As
.
if you would like to add the saved stream to the current projec t.
Clicking
Automatic backup files.
Save
stores the stream with th e extension *.str in the specified directory.
Each time a stream i s saved, t he previously saved version of the file
is automatically preserved as a backup, with a hyphen appended to the filename (for example
mystream.str-). To restore the backed-up version, simply delete the hyphen and reopen the file.
Saving States
In addition to streams, you can save states, wh ich include the currently displayed stream diagram
and any model nuggets that you have created (listed on the Models tab in the managers pane).
To Save a State
E
On the File menu, click:
State > Save State or Save State As
E
In the Save dialog box, browse to the folder in which you want to save the state file.
Clicking
Save
stores the state with the extension *.cst in the specified d irectory.
Saving Nodes
You can also save an individual node by right-clicking the node on the stream canvas and clicking
Save Node
on the pop-up menu. Use the file extension *.nod.
Page 99

Building Streams
Saving Multiple Stream Objects
When you exit IBM® SPSS® Modeler with multiple unsaved objects, such as streams, projects,
or model nuggets, you will be prompted to save before completely closing the software. If you
choose to save items, a dialog box wil l open with options for saving each object.
Figure 5-41
Saving multiple objects
89
E
Simply select the check boxes for the objects that you want to save.
E
ClickOKto save each object in the required location.
You will then be prompted with a standard Save dialog box for each object. After you have
finished saving, the application will close as origina
lly instructed.
Saving Output
Tables, grap hs,
and reports generated from IBM® SP SS® Modeler output nodes can be saved in
output object (*.cou) format.
E
When viewing the output you want to s ave, on the output window menus click:
File > Save
E
Specify a name and location for the output file.
E
Optionally, select
Add file to project
in the Save dialog box to include th e file in the current project.
For more information, see the topic Introduction to Projects in Chapter 11 on p. 200.
Alternatively, you can right-click any output object listed in the managers pane and select
from the pop-up menu.
Save
Page 100

90
Chapter 5
Encrypting and Decrypting Information
When you save a stream, node, project, output file, or model nugget, you can encrypt it to prevent
its unauthorized use. To do this, you select an extra option when saving, and add a password to the
item bei ng saved. This encryption can be set for any of the i tems that you save and adds extra
security to them; it is not the same as the SSL encryption used if you are passing files between
IBM® SPSS® Modeler and IBM® SPSS® Modeler Server.
When you try to open an encrypted item, you are prompted to enter the password. After you
enter the correct password, the item is de crypted automatically and opens as usual.
To Encrypt an Item
E
In the Sav e dialog box, for the item to be encrypted, click
dialog box opens.
Figure 5-42
Encryption options when saving a file
Options
. The Encryption Options
E
Select
E
Optionally, for further security, select
series of dots.
E
Enter the password. Warning: If you forget the pa ssword, the file or model c an not be opened.
E
If you selected
E
ClickOKto return to the Save dialog box.
Note: If you s ave a copy of any encryption-protected item, the new item is automatic ally saved in
an encrypted format using the original password unless you change the settings in the Encryption
Options dialog box.
Loading Files
You can reload a number of saved objects in IBM® SPSS® Modeler:
Encrypt this file
Mask password
Streams (.str)
States (.cst)
Models (.gm)
.
Mask password
. This displays anything you enter as a
, re-enter the password to confirm that you entered it correctly.
 Loading...
Loading...