Page 1
X-SEL Controller P/Q/R/S
Vision System I/F Function
Instruction Manual Sixth Edition
Page 2

Page 3

Please Read Before Use
Thank you for purchasing our product.
This Instruction Manual describes all necessary information to operate this product safely such as
the operation procedure, structure and maintenance procedure.
Before operation, read this manual carefully and fully understand it to operate this product safely.
The enclosed CD or DVD in this product package includes the Instruction Manual for this product.
For the operation of this product, print out the necessary sections in the Instruction Manual or
display them using the personal computer.
After reading through this manual, keep this Instruction Manual at hand so that the operator of this
product can read it whenever necessary.
[Important]
x This Instruction Manual is original.
x The product cannot be operated in any way unless expressly specified in this Instruction
Manual.
IAI shall assume no responsibility for the outcome of any operation not specified herein.
x Information contained in this Instruction Manual is subject to change without notice for
the purpose of product improvement.
x If you have any question or comment regarding the content of this manual, please
contact the IAI sales office near you.
x Using or copying all or part of this Instruction Manual without permission is prohibited.
x The company names, names of products and trademarks of each company shown in the
sentences are registered trademarks.
x CV-2000, CV-3000, CV-5000 and XG-7000 are the registered trademarks of Keyence
Corporation.
x F210-CIO, FZ3 are the registered trademarks of OMRON Corporation.
x In-Sight 5000 Series and In-Sight Explorer are the registered trademarks of Cognex
Corporation.
Page 4

Page 5

Table of Contents
Safety Guide ·····················································································································1
Precautions in Handling···································································································· 8
1. Overview ·······················································································································9
2. Work Flow before Operation Start···············································································10
2.1 Starting Procedures ····································································································10
2.2 Items to Prepare Beforehand······················································································ 11
3. Coordinates·················································································································13
3.1 Coordinate Axes for Orthogonal Robot······································································· 13
4. Installation ··················································································································· 14
4.1 Wiring·························································································································· 14
4.1.1 Example of wiring layout when connecting Cognex camera ·······························14
4.1.2 Example of wiring layout when connecting Keyence camera······························ 15
4.1.3 Example of wiring layout when connecting OMRON camera······························ 16
4.2 Installing XSEL Controller PC Software······································································ 17
4.3 Installing the Camera·································································································· 18
4.3.1. Cognex Camera··································································································· 18
4.3.2 Keyence Camera ·································································································19
4.3.3 OMRON Camera·································································································· 20
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting ············································································· 21
5.1 Setting Procedure ······································································································· 21
5.2 About Parameter Change ···························································································23
5.2.1 Regarding to Value Setting ··················································································23
5.2.1.1 Binary Number ····························································································· 23
5.2.1.2 Hexadecimal Number ·················································································· 23
5.3 Communication Channel Setting ················································································24
5.3.1 When Ethernet TCP/IP Message Communication is Used··································24
5.3.2 When Standard SIO (RS232C) Channel Communication is Used ······················ 26
5.4 Communication Format Setting ·················································································· 27
5.5 Unit Conversion (pixel mm) ···················································································· 29
5.6 Coordinate Setting ······································································································ 29
5.7 Detailed Function Settings·························································································· 30
Page 6

5.8 Vision System I/F adjustment ·····················································································32
5.8.1 Initial Settings for Simple Calibration
(When EZ-110XL camera is used) ·······································································33
5.8.2 When Camera Not Mounted on Robot
(When EZ-110XL is used) ····················································································37
5.8.3 When Camera Mounted on Robot
(When EZ-110XL is used) ····················································································57
5.8.4 When Camera Not Mounted on Robot
(When camera other than EZ-110XL is used)······················································77
5.8.5 When Camera Mounted on Robot
(When camera other than EZ-110XL is used)······················································85
5.9 Variance Adjustment ··································································································· 92
6. Program Construction for Operation ··········································································· 94
6.1 SEL Command············································································································94
6.1.1 SLVS (Select Vision System I/F) Command ························································94
6.1.2 GTVD (Vision System I/F Image-Capture Data Acquirement) Command ··········· 96
6.2 Outline for SEL Program Construction (Basic Frame)················································98
7. Error Treatment········································································································· 100
7.1 Common Errors for All Vision Systems ·····································································100
7.2 Simple Calibration Execution Error for EZ-110XL·····················································105
7.3 Return Code List in READ Command (SEL Language) Execution ··························109
8. Appendix··················································································································· 110
8.1 Communication Format Setting Values····································································· 110
8.2 General-purpose RS232C Port················································································· 117
8.3 Operation of High Speed Cartesian Robot (CT4) ····················································· 118
9. Change History ········································································································· 119
Page 7
1
Safety Guide
“Safety Guide” has been written to use the machine safely and so prevent personal injury or
property damage beforehand. Make sure to read it before the operation of this product.
Safety Precautions for Our Products
The common safety precautions for the use of any of our robots in each operation.
No.
Operation
Description
Description
1 Model
Selection
Ɣ This product has not been planned and designed for the application
where high level of safety is required, so the guarantee of the protection
of human life is impossible. Accordingly, do not use it in any of the
following applications.
1) Medical equipment used to maintain, control or otherwise affect
human life or physical health.
2) Mechanisms and machinery designed for the purpose of moving or
transporting people (For vehicle, railway facility or air navigation
facility)
3) Important safety parts of machinery (Safety device, etc.)
Ɣ Do not use the product outside the specifications. Failure to do so may
considerably shorten the life of the product.
Ɣ Do not use it in any of the following environments.
1) Location where there is any inflammable gas, inflammable object or
explosive
2) Place with potential exposure to radiation
3) Location with the ambient temperature or relative humidity exceeding
the specification range
4) Location where radiant heat is added from direct sunlight or other
large heat source
5) Location where condensation occurs due to abrupt temperature
changes
6) Location where there is any corrosive gas (sulfuric acid or
hydrochloric acid)
7) Location exposed to significant amount of dust, salt or iron powder
8) Location subject to direct vibration or impact
Ɣ For an actuator used in vertical orientation, select a model which is
equipped with a brake. If selecting a model with no brake, the moving
part may drop when the power is turned OFF and may cause an
accident such as an injury or damage on the work piece.
Page 8
2
No.
Operation
Description
Description
2 Transportation Ɣ When carrying a heavy object, do the work with two or more persons or
utilize equipment such as crane.
Ɣ When the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who
is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well
with each other to ensure the safety of the workers.
Ɣ When in transportation, consider well about the positions to hold,
weight and weight balance and pay special attention to the carried
object so it would not get hit or dropped.
Ɣ Transport it using an appropriate transportation measure.
The actuators available for transportation with a crane have eyebolts
attached or there are tapped holes to attach bolts. Follow the
instructions in the instruction manual for each model.
Ɣ Do not step or sit on the package.
Ɣ Do not put any heavy thing that can deform the package, on it.
Ɣ When using a crane capable of 1t or more of weight, have an operator
who has qualifications for crane operation and sling work.
Ɣ When using a crane or equivalent equipments, make sure not to hang a
load that weighs more than the equipment’s capability limit.
Ɣ Use a hook that is suitable for the load. Consider the safety factor of the
hook in such factors as shear strength.
Ɣ Do not get on the load that is hung on a crane.
Ɣ Do not leave a load hung up with a crane.
Ɣ Do not stand under the load that is hung up with a crane.
3 Storage and
Preservation
Ɣ The storage and preservation environment conforms to the installation
environment. However, especially give consideration to the prevention
of condensation.
Ɣ Store the products with a consideration not to fall them over or drop due
to an act of God such as earthquake.
4 Installation
and Start
(1) Installation of Robot Main Body and Controller, etc.
Ɣ Make sure to securely hold and fix the product (including the work part).
A fall, drop or abnormal motion of the product may cause a damage or
injury.
Also, be equipped for a fall-over or drop due to an act of God such as
earthquake.
Ɣ Do not get on or put anything on the product. Failure to do so may
cause an accidental fall, injury or damage to the product due to a drop
of anything, malfunction of the product, performance degradation, or
shortening of its life.
Ɣ When using the product in any of the places specified below, provide a
sufficient shield.
1) Location where electric noise is generated
2) Location where high electrical or magnetic field is present
3) Location with the mains or power lines passing nearby
4) Location where the product may come in contact with water, oil or
chemical droplets
Page 9
3
No.
Operation
Description
Description
(2) Cable Wiring
Ɣ Use our company’s genuine cables for connecting between the actuator
and controller, and for the teaching tool.
Ɣ Do not scratch on the cable. Do not bend it forcibly. Do not pull it. Do
not coil it around. Do not insert it. Do not put any heavy thing on it.
Failure to do so may cause a fire, electric shock or malfunction due to
leakage or continuity error.
Ɣ Perform the wiring for the product, after turning OFF the power to the
unit, so that there is no wiring error.
Ɣ When the direct current power (+24V) is connected, take the great care
of the directions of positive and negative poles. If the connection
direction is not correct, it might cause a fire, product breakdown or
malfunction.
Ɣ Connect the cable connector securely so that there is no disconnection
or looseness. Failure to do so may cause a fire, electric shock or
malfunction of the product.
Ɣ Never cut and/or reconnect the cables supplied with the product for the
purpose of extending or shortening the cable length. Failure to do so
may cause the product to malfunction or cause fire.
4 Installation
and Start
(3) Grounding
Ɣ The grounding operation should be performed to prevent an electric
shock or electrostatic charge, enhance the noise-resistance ability and
control the unnecessary electromagnetic radiation.
Ɣ For the ground terminal on the AC power cable of the controller and the
grounding plate in the control panel, make sure to use a twisted pair
cable with wire thickness 0.5mm
2
(AWG20 or equivalent) or more for
grounding work. For security grounding, it is necessary to select an
appropriate wire thickness suitable for the load. Perform wiring that
satisfies the specifications (electrical equipment technical standards).
Ɣ Perform Class D Grounding (former Class 3 Grounding with ground
resistance 100: or below).
Page 10
4
No.
Operation
Description
Description
4 Installation
and Start
(4) Safety Measures
Ɣ When the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who
is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well
with each other to ensure the safety of the workers.
Ɣ When the product is under operation or in the ready mode, take the
safety measures (such as the installation of safety and protection
fence) so that nobody can enter the area within the robot’s movable
range. When the robot under operation is touched, it may result in
death or serious injury.
Ɣ Make sure to install the emergency stop circuit so that the unit can be
stopped immediately in an emergency during the unit operation.
Ɣ Take the safety measure not to start up the unit only with the power
turning ON. Failure to do so may start up the machine suddenly and
cause an injury or damage to the product.
Ɣ Take the safety measure not to start up the machine only with the
emergency stop cancellation or recovery after the power failure. Failure
to do so may result in an electric shock or injury due to unexpected
power input.
Ɣ When the installation or adjustment operation is to be performed, give
clear warnings such as “Under Operation; Do not turn ON the power!”
etc. Sudden power input may cause an electric shock or injury.
Ɣ Take the measure so that the work part is not dropped in power failure
or emergency stop.
Ɣ Wear protection gloves, goggle or safety shoes, as necessary, to
secure safety.
Ɣ Do not insert a finger or object in the openings in the product. Failure to
do so may cause an injury, electric shock, damage to the product or
fire.
Ɣ When releasing the brake on a vertically oriented actuator, exercise
precaution not to pinch your hand or damage the work parts with the
actuator dropped by gravity.
5 Teaching Ɣ When the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who
is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well
with each other to ensure the safety of the workers.
Ɣ Perform the teaching operation from outside the safety protection
fence, if possible. In the case that the operation is to be performed
unavoidably inside the safety protection fence, prepare the “Stipulations
for the Operation” and make sure that all the workers acknowledge and
understand them well.
Ɣ When the operation is to be performed inside the safety protection
fence, the worker should have an emergency stop switch at hand with
him so that the unit can be stopped any time in an emergency.
Ɣ When the operation is to be performed inside the safety protection
fence, in addition to the workers, arrange a watchman so that the
machine can be stopped any time in an emergency. Also, keep watch
on the operation so that any third person can not operate the switches
carelessly.
Ɣ Place a sign “Under Operation” at the position easy to see.
Ɣ When releasing the brake on a vertically oriented actuator, exercise
precaution not to pinch your hand or damage the work parts with the
actuator dropped by gravity.
* Safety protection Fence : In the case that there is no safety protection
fence, the movable range should be indicated.
Page 11
5
No.
Operation
Description
Description
6 Trial
Operation
Ɣ When the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who
is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well
with each other to ensure the safety of the workers.
Ɣ After the teaching or programming operation, perform the check
operation one step by one step and then shift to the automatic
operation.
Ɣ When the check operation is to be performed inside the safety
protection fence, perform the check operation using the previously
specified work procedure like the teaching operation.
Ɣ Make sure to perform the programmed operation check at the safety
speed. Failure to do so may result in an accident due to unexpected
motion caused by a program error, etc.
Ɣ Do not touch the terminal block or any of the various setting switches in
the power ON mode. Failure to do so may result in an electric shock or
malfunction.
7 Automatic
Operation
Ɣ Check before starting the automatic operation or rebooting after
operation stop that there is nobody in the safety protection fence.
Ɣ Before starting automatic operation, make sure that all peripheral
equipment is in an automatic-operation-ready state and there is no
alarm indication.
Ɣ Make sure to operate automatic operation start from outside of the
safety protection fence.
Ɣ In the case that there is any abnormal heating, smoke, offensive smell,
or abnormal noise in the product, immediately stop the machine and
turn OFF the power switch. Failure to do so may result in a fire or
damage to the product.
Ɣ When a power failure occurs, turn OFF the power switch. Failure to do
so may cause an injury or damage to the product, due to a sudden
motion of the product in the recovery operation from the power failure.
Page 12
6
No.
Operation
Description
Description
8 Maintenance
and
Inspection
Ɣ When the work is carried out with 2 or more persons, make it clear who
is to be the leader and who to be the follower(s) and communicate well
with each other to ensure the safety of the workers.
Ɣ Perform the work out of the safety protection fence, if possible. In the
case that the operation is to be performed unavoidably inside the safety
protection fence, prepare the “Stipulations for the Operation” and make
sure that all the workers acknowledge and understand them well.
Ɣ When the work is to be performed inside the safety protection fence,
basically turn OFF the power switch.
Ɣ When the operation is to be performed inside the safety protection
fence, the worker should have an emergency stop switch at hand with
him so that the unit can be stopped any time in an emergency.
Ɣ When the operation is to be performed inside the safety protection
fence, in addition to the workers, arrange a watchman so that the
machine can be stopped any time in an emergency. Also, keep watch
on the operation so that any third person can not operate the switches
carelessly.
Ɣ Place a sign “Under Operation” at the position easy to see.
Ɣ For the grease for the guide or ball screw, use appropriate grease
according to the Instruction Manual for each model.
Ɣ Do not perform the dielectric strength test. Failure to do so may result in
a damage to the product.
Ɣ When releasing the brake on a vertically oriented actuator, exercise
precaution not to pinch your hand or damage the work parts with the
actuator dropped by gravity.
Ɣ The slider or rod may get misaligned OFF the stop position if the servo
is turned OFF. Be careful not to get injured or damaged due to an
unnecessary operation.
Ɣ Pay attention not to lose the cover or untightened screws, and make
sure to put the product back to the original condition after maintenance
and inspection works.
Use in incomplete condition may cause damage to the product or an
injury.
* Safety protection Fence : In the case that there is no safety protection
fence, the movable range should be indicated.
9 Modification
and Dismantle
Ɣ Do not modify, disassemble, assemble or use of maintenance parts not
specified based at your own discretion.
10 Disposal Ɣ When the product becomes no longer usable or necessary, dispose of it
properly as an industrial waste.
Ɣ When removing the actuator for disposal, pay attention to drop of
components when detaching screws.
Ɣ Do not put the product in a fire when disposing of it.
The product may burst or generate toxic gases.
11 Other Ɣ Do not come close to the product or the harnesses if you are a person
who requires a support of medical devices such as a pacemaker. Doing
so may affect the performance of your medical device.
Ɣ See Overseas Specifications Compliance Manual to check whether
complies if necessary.
Ɣ For the handling of actuators and controllers, follow the dedicated
instruction manual of each unit to ensure the safety.
Page 13
7
Alert Indication
The safety precautions are divided into “Danger”, “Warning”, “Caution” and “Notice” according to
the warning level, as follows, and described in the Instruction Manual for each model.
Level Degree of Danger and Damage Symbol
Danger
This indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if the
product is not handled correctly, will result in death or serious
injury.
Danger
Warning
This indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if the
product is not handled correctly, could result in death or serious
injury.
Warning
Caution
This indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if the
product is not handled correctly, may result in minor injury or
property damage.
Caution
Notice
This indicates lower possibility for the injury, but should be kept to
use this product properly.
Notice
Page 14

8
Precautions in Handling
x The number of work pieces that the camera can detect in 1 shot of image capturing is as
described below:
Cognex In-Sight EZ110 8 pieces at max.
Cognex In-Sight 5000 12 pieces at max.
Keyence CV-2000 7 pieces at max.
Vision systems of Keyence other than CV-2000 and I/F applicable vision systems 12 pieces at max.
OMRON vision systems 12 pieces at max.
x Build the system with care so that the work after being captured would not get moved off the
position by an external force (vibration, air blow, crash of another work, etc.).
x If the image-capturing conditions, such as the light (diffusers), focus, diaphragm, shutter speed,
etc., are inefficient, such problems like the work not being detected or inaccurate position
detection may occur. (Please refer to the Instruction Manual for Vision System to have the
appropriate adjustments.)
x Please ask each vision system supplier for the adjustment of Vision System (detection settings,
format settings indicated for our products [refer to Section 8.1], etc.).
When using Cognex In-Sight EZ110, the sample job data is available to download from the
enclosed CD or IAI homepage. (* Please ask the distributor to have the detection settings done
for you so it suits to the work that you will use.)
x Regarding Operation of High Speed Cartesian Robot CT4
Refer to 8.3 Operation of High Speed Cartesian Robot (CT4) for the details.
Page 15

9
1. Overview
Vision System I/F Function is a function to store the coordinate data
(Note 1) (Note 2)
sent from the work
directly to the position data.
When using the vision system, the specialized window in the PC software always backups the
adjustment (calibration) of coordinates of the necessary camera and robot
(Note 3)
.
(Note 1) In the existing systems, the data from Vision System needs to be treated as characters
and the user needs to convert the values to store the position data. In Vision System I/F
Function, the user does not need to convert the values, and the coordinates are directly
stored to the position data.
(Note 2) It is necessary to send the data in the format indicated by our products.
(Note 3) If conducting the dedicated calibration with EZ-110XL, the procedure of manual
alignment of the work to the robot which is necessary for the existing models will be
dramatically reduced.
This manual explains how to set up the system to utilize Vision System I/F Function.
1. Overview
Page 16

2. Work Flow before Operation Start
10
2. Work Flow before Operation Start
Note
Make sure to have the settings of the vision system such as the work detection setting and
communication setting done before having the vision system I/F function settings.
2.1 Starting Procedures
No
No
No
Yes
Check of Packed Items
Are there all the delivered items?
Do you have all the equipment listed in Section 2.2 that needs to be
prepared beforehand?
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Installation and Wiring
Have the actuator and encoder installed and connected following the instructions in XSEL Controller Instruction
Manual, Actuator Instruction Manual and this manual (see Section 4).
Are the frame grounding (FG) and protection earthing (PE) conducted?
Has the noise countermeasure been taken?
Power Supply and Alarm Check
Connect the PC, put AUTO/MANU switch to “MANU” side and
turn the power on.
Is the status display showing “rdy” ?
Check of Safety Circuit
Actuator Setting
Check that the emergency stop circuit (or motor drive power cutoff
circuit) operates normally to turn off the servo.
Vision System I/F Function Setting (Refer to Section 5)
The setting details differ depending if the camera is mounted to the robot or not.
Creating Program (Refer to Section 6)
Create a program based on SEL program construction capacity.
Power-up and Operation Check
Have the program run to check the sensor input, axis data from the camera and tracking position.
Have an appropriate treatment following
the content of the status display.
[Refer to the trouble shootings in Instruction Manuals for XSEL Controller and PC
Software.]
No
Is the motor cable connected?
No
Contact the sales shop.
Connect the motor cable.
Check the emergency stop circuit.
Check the alarm content on the PC to
have an appropriate treatment if an
alarm is generated.
Write the target position to the position table.
Press the SV button in the button display for each axis in the PC
software to turn the servo on.
After the servo is on, press the HM button in the button display for
each axis to conduct a home-return operation.
Did the servo turn on and home without error?
Now, the operation adjustment is complete.
Conduct an adjustment by the system.
Page 17
11
2.2 Items to Prepare Beforehand
The Vision System explained in this manual is in regard to the equipment’s operation and its
program. The equipment and components that construct the system need to be prepared
separately.
1) Vision System
Corresponding Product
(Note) Please ask each vision system supplier to have the settings on Vision System such as the work
detection setting and the output communication format indicated by our products [refer to Section
8.1].
x PIO Cable
(There are some cases that the dedicated accessary is required. Please refer to the
Instruction Manual for each Vision System.
e.g. FZ-VP, Parallel I/O cable dedicated for OMRON FZ3)
x For Ethernet Connection
LAN cable (Category 5 or higher)
Hub
x For RS232C Connection
Apply a cable that has a connector suitable for the camera controller on one end and D-sub
9-pin connector (female) on the other end (XSEL end).
[Refer to the Instruction Manual for each Vision System for the wiring on the camera controller
side.]
[Refer to the Appendix at the end for the wiring on XSEL side.]
x If Using Work Detection Sensor
Photoelectric sensor
Examples of Vision System Models
Supplier Model Interface
Cognex
In-Sight EZ-110 (EZ-110XL)
In-Sight 5000 Series
Ethernet
OMRON F210-C10 FZ3 RS232C
Keyence CV2000 CV3000 CV5000 XG-7000
Ethernet
RS232C
2. Work Flow before Operation Start
Page 18
12
2) Other Requirement of IAI Products
x XSEL Controller
(Main application Version XSEL-P/Q : V1.05 or later
XSEL-R/S : V1.04 or later)
x Ethernet Board
(Option … If Ethernet is used for communication between the vision system and XSEL)
x XSEL controller PC software
(If the vision system is In-Sight EZ110 (EZ-110XL);
• XSEL-P/Q : Version V7.07.08.00 or later
• XSEL-R/S : Version V9.0.0.0 or later
(If the vision system is not In-Sight EZ110 (EZ-110XL);
• XSEL-P/Q : Version V7.06.08.00 or later
• XSEL-R/S : Version V9.0.0.0 or later
Note
When using the conveyor tracking function and the vision system I/F function at the same time, it
is not possible to have Ethernet to both of the functions as the communication interface. Connect
one of them with RS232C.
Available interface combination when using vision system
Conveyer Tracking Vision System I/F
Interface
Ethernet
Standard SIO
(RS232C)
Ethernet
Standard SIO
(RS232C)
Ethernet × ż
Conveyer
Tracking
Standard SIO
(RS232C)
ż ż
Ethernet
× ż
Vision System
I/F
Standard SIO
(RS232C)
ż ż
If the vision system is EZ-110XL and the dedicated software is used, the simple adjustment function
that enables to reduce the procedure of manual alignment in the matching process of the robot and
the vision system coordinates can be used.
When using the simple adjustment function, the work to be used in the adjustment process and a
tool to hold the work (chuck, grip, etc.) are necessary for the settings.
2. Work Flow before Operation Start
Page 19
13
3. Coordinates
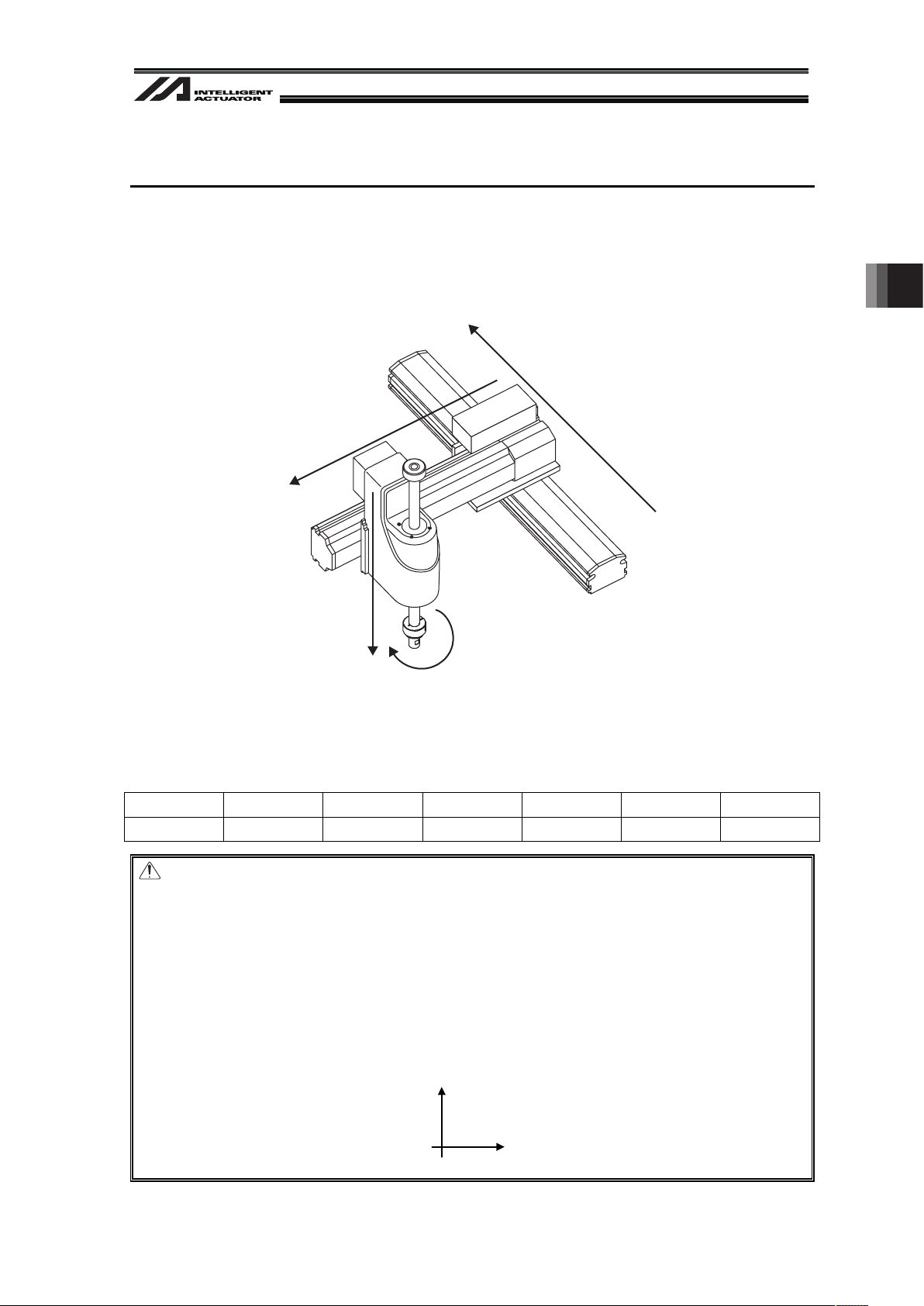
3.1 Coordinate Axes for Orthogonal Robot
The coordinate axes are fixed. (Refer to table below.)
Y-axis (2-axis)
X-axis (1-axis)
Rotary Axis (4-axis)
Z-axis (3-axis)
+
+
+
+
The work coordinates data received from the vision system (position information) is saved to the
position data as shown below.
No. (Name)
Axis1 (1-axis) Axis2 (2-axis) Axis3 (3-axis) Axis4 (4-axis)
Axis5 Axis6
1 ( ) 10.000 0.000 45.000
Note
x The position data of the axes that are not indicated as the valid axis pattern (All-Axes Parameter
No.1) (invalid axes) do not get updated.
x If there is an axis that is not to be used in Axis1, Axis2 and Axis4, declare the axis that uses the
position data in GRP Command.
x Ensure the applied actuators lie across each other in the right angle. Failure to do so may
disable to obtain accurate work coordinate data.
x The positive directions are premised as shown below for the robot X and Y axes coordinates.
㪯
㪰
Work X
Coordinate
ω
Work Y
Coordinate
ω
Work
T
Coordinate
ω
3. Coordinates
Page 20
4. Installation
14
4. Installation
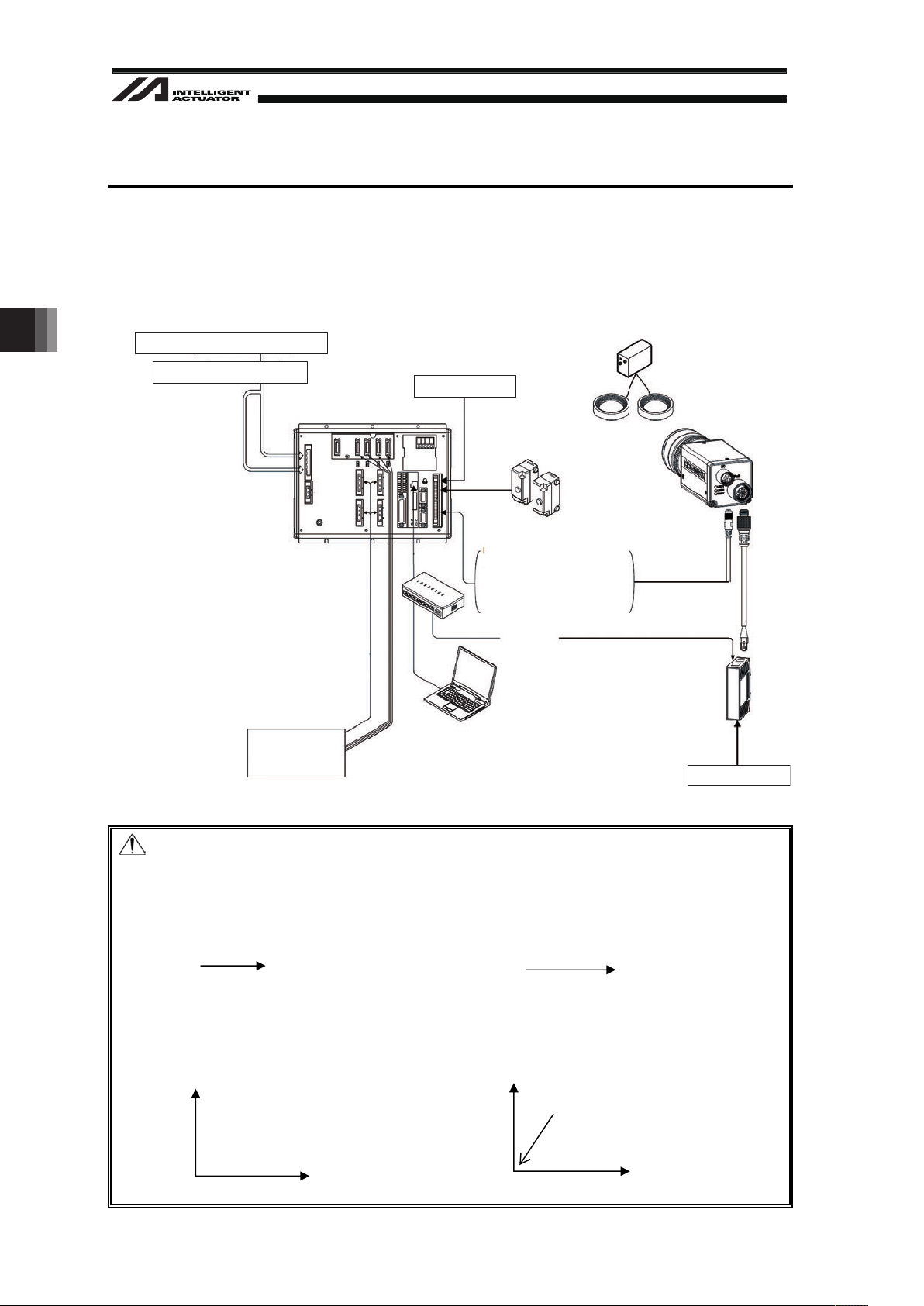
4.1 Wiring
Shown below is an example of the vision system wiring layout when each camera controller is
connected.
4.1.1 Example of wiring layout when connecting Cognex camera
Example for Vision System Wiring (Cognex)
Note:
• 24V I/O signal (PIO) is used for the capture command to the camera. Use the dedicated I/O
cable for the vision systems if it is equipped with a dedicated cable.
• For EZ-110XL
Set the robot axes and the vision system X-axes so they are orienting the same directions.
Robot Axes Vision System Axes
• For those other than In-Sight EZ110
Set the robot axes and the vision system axes so they are orienting the same directions.
Also, allocate the vision system origin to the bottom left of the screen.
Robot Axes Vision System Axes
Y
X
Allocate the origin to
bottom left of screen
(Utilize the spread sheet)
X
Y
X
X
Power Supply Supprtive Circuit
3-phase 200V AC to 230V power supply
+24V Power Supply
Brake and
Power Supply for I/O
Camera
Work Detection Sensor
(when applied as the
image-capture trigger)
Light
PIO Signals (2 signals)
• Camera start-up signal
(Camera → XSEL)
(Note)
• Image Capturing Command
(XSEL → Camera)
PoE Injector
Robot
+24V Power Supply
Ethernet
M Cable
PC
Hub
Power Supply Unit for
Light Equipment
(Note) The setting not to use the camera startup signal is
also available. (It is described later.)
Page 21
15
4.1.2 Example of wiring layout when connecting Keyence camera
Example for Vision System Wiring (Keyence)
Note:
• 24V I/O signal (PIO) is used for the capture command to the camera. Use the dedicated I/O
cable for the vision systems if it is equipped with a dedicated cable.
• Set the robot axis and the vision system axes directions so the X-axes are orienting the same
direction and Y-axes the opposite. Also, allocate the vision system origin to the top left of the
screen.
Robot Axes Vision System Axes
Y
X
Y
X
Allocate the origin to top
left of screen
Power Supply Supprtive Circuit
PIO Signals (2 signals)
• Camera Controller
Startup Complete Signal
(Camera Controller→XSEL)
(Note 1)
• Image Capturing Command
(XSEL→Camera Controller)
Ethernet or RS232C
(Note 2)
M Cable
Robot
Monitor
Camera
PC
Hub
+
24V
3-phase 200V AC to 230V power supply
Brake and
Power Supply for I/O
Power Supply
Work Detection Sensor
(when applied as the image-capture trigger)
Light
Console
Camera Controller
Main Body
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
The setting not to use the camera controller startup signal is
also available. (It is described later.)
There is no need for a hub for RS232C connection.
Refer to the Appendix at the end for wiring on XSEL side.
Refer to the Instruction Manual for each Vision System for
wiring on camera controller side.
4. Installation
Page 22
4. Installation
16
4.1.3 Example of wiring layout when connecting OMRON camera
Example for Vision System Wiring (OMRON)
Note:
• 24V I/O signal (PIO) is used for the capture command to the camera. Use the dedicated I/O
cable for the vision systems if it is equipped with a dedicated cable.
• Set the robot axes and the vision system axes so they are orienting the same directions. Also,
allocate the vision system origin to the bottom left of the screen.
Robot Axes Vision System Axes
Y
X
Y
X
Allocate the origin to
bottom left of screen
RS232C
(Note 3)
Power Supply Supprtive Circuit
M Cable
Robot
Monitor
Camera
PC
24V
+
3-phase 200V AC to 230V power supply
Power Supply
Light
Console
Camera Controller
Main Body
Work Detection Sensor
(when applied as the image-capture trigger)
Power Supply Unit for Light Equipment
(Pin Input)
PIO Signals (2 signals)
(Note1)
• Camera Controller
Startup Complete Signal
(Camera Controller→XSEL)
(Note 2)
• Image Capturing Command
(XSEL→Camera Controller)
Brake and
Power Supply for I/O
(Note 1)
(Note 2)
(Note 3)
There are some cases that the dedicated parallel I/O
cable is required.
[Refer to the Instruction Manual for Vision System]
The setting not to use the camera controller startup signal is
also available. (It is described later.)
Refer to the Appendix at the end for wiring on XSEL side.
Refer to the Instruction Manual for each Vision System for
wiring on camera controller side.
Page 23
17
4.2 Installing XSEL Controller PC Software
Refer to the Instruction Manual for XSEL Controller PC Software for how to install XSEL Controller
PC Software and how to implement the initial settings.
4. Installation
Page 24
4. Installation
18
4.3 Installing the Camera
4.3.1 Cognex Camera
The camera products of Cognex Corporation applicable to the vision system are limited only to
“In-Sight EZ110 (EZ110-XL)” and “In-Sight 5000 Series”.
The way to install the camera can be selected from mounting on the robot and fixing on the
equipment.
Install the camera considering how to use it.
Lighting equipment is separately required when capturing an image with the camera.
It is possible to identify the following numbers of work pieces in 1 shot of image capturing.
• In-Sight EZ110 (EZ110-XL) : 8 pieces at max.
• In-Sight 5000 Series : 12 pieces at max.
Refer to the following Cognex instruction manuals for the details of how to connect the devices.
• In-Sight EZ110 (EZ110-XL) : “In-Sight EZ Series Vision System Installation Guide”
• In-Sight 5000 Series : “In-Sight 5000 Series Vision System Installation Guide”
“CIO-1400C I/O Expansion Module Instruction Manual”
Shown below is an example of the basic construction of Vision System with one unit of camera
connected.
XSEL P/Q Controller Main Unit
Hub
100V AC Power Supply
PoE Injector
Camera
Camera
Cable
Example for Cognex Camera Controller Basic Construction
Page 25
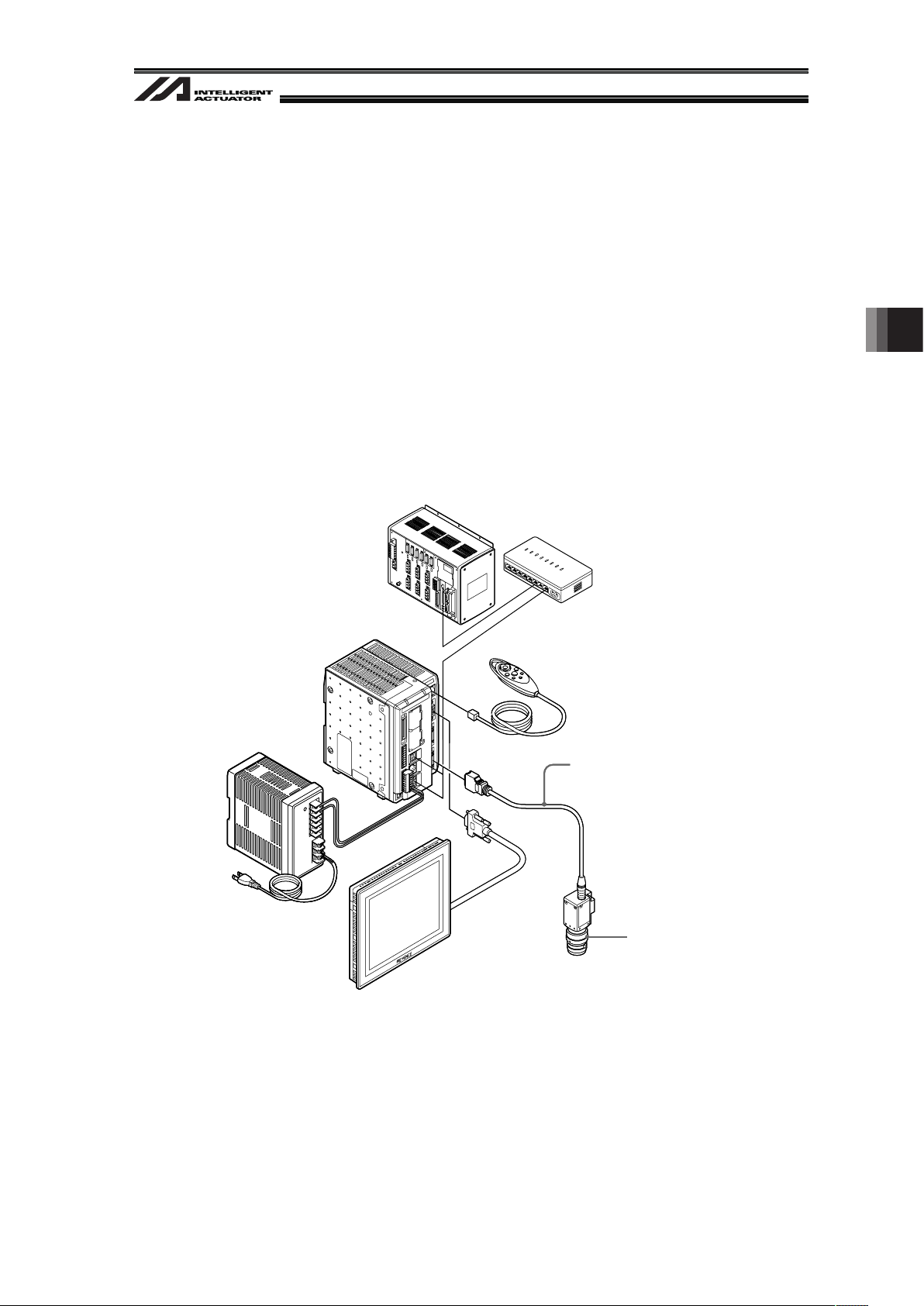
19
4.3.2 Keyence Camera
The camera manufactured by Keyence Corporation that is applicable for Vision System is
“In-CV-2000/CV-3000/CV-5000/XG-7000” only.
The way to install the camera can be selected from mounting on the robot and fixing on the
equipment.
Install the camera considering how to use it.
Lighting equipment is separately required when capturing an image with the camera.
12 pieces (0 to 7 pieces for CV-2000) of works can be identified at maximum in 1 shot.
Shown below is an example of the basic construction of Vision System with one unit of camera
connected.
XSEL P/Q Controller Main Unit or Hub, etc.
Camera Cable
Camera Controller Monitor
24V DC Power Supply
SD Card
(Inserted to SD1 Slot
on the main unit of controller)
Lens
Camera
Camera Controller
Main Body
Console
Example for Keyence Camera Controller Basic Construction
4. Installation
Page 26
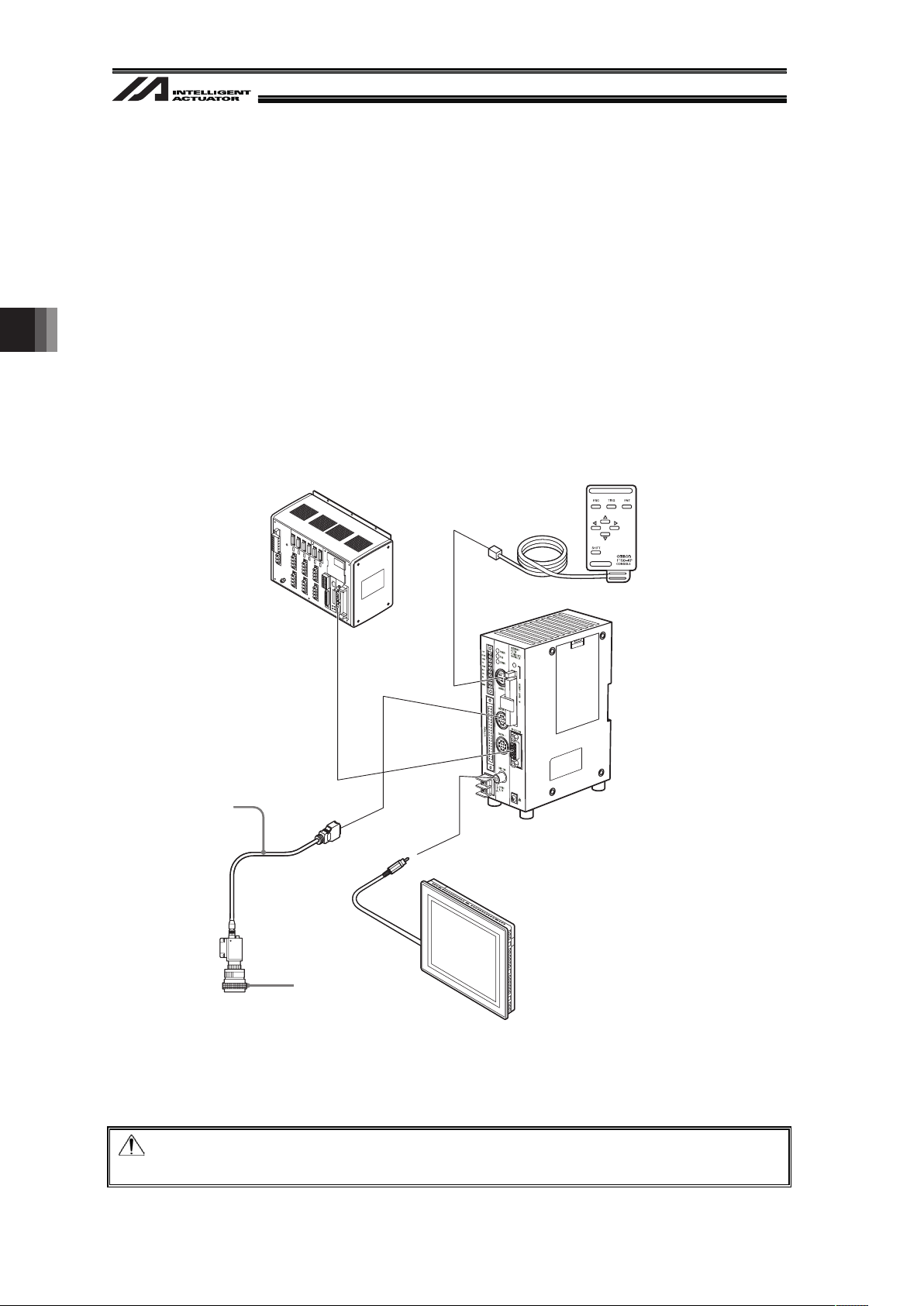
4. Installation
20
4.3.3 OMRON Camera
The camera manufactured by OMRON Corporation that is applicable for Vision System is OMRON
Camera Controller “F210-C10 or FZ3” only.
The way to install the camera can be selected from mounting on the robot and fixing on the
equipment.
Install the camera considering how to use it.
Lighting equipment is separately required when capturing an image with the camera.
12 pieces of works can be identified at maximum in 1 shot.
Shown below is an example of the basic construction of Vision System with one unit of camera
connected.
Example for OMRON Camera Controller Construction(for F210-C10)
Note:
USB and Ethernet are not supported for the camera connection.
XSEL P/Q
Controller Main Body
SD Card
(Inserted to SD1 Slot
on the main unit of controller)
Monitor
Camera
Camera Cable
Console
Camera Controller
Main Body
Lens
(Pin Input)
Page 27

21
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Refer to the materials such as the Instruction Manual for the connected camera controller for the
details of how to set up on the camera controller side.
This manual explains how to set up the system to utilize the vision system I/F function.
The setting is to be conducted using XSEL Controller, PC software and the setting tool of each
vision system.
5.1 Setting Procedure
Continues to the next page
RS232C Channel Setting (setting on XSEL)
Follow Section 5.3.2.
Which of the following is used for the communication between the vision system (camera)
and XSEL Controller?
1) Ethernet 2) RS232C
(Cognex or Keyence) (OMRON or Keyence)
Start up the PC software and connect with XSEL Controller.
Start up the vision system setting tool and connect with the vision system.
Supplier Setting of Connected Camera (setting on XSEL)
Set the supplier name of the connected camera following Section 5.4.
Vision System Check and Communication Setting (setting on vision system)
Perform the necessary settings such as image setting, tool setting, inspection, input,
output and communication with using the vision system setting tool.
Set the unit of the output of the coordinate data from the vision system to mm except for
when using the dedicated calibration with EZ-110XL. (Refer to Section 5.5)
Coordinate Setting (setting on vision system)
Set the coordinate origin of the vision system following Section 5.6.
This setting is not necessary when using the dedicated calibration with EZ-110XL.
Detailed Function Settings (setting on XSEL)
Set the image-capture command input port number and other necessary numbers
following Section 5.7.
Ethernet Channel Setting (setting on XSEL)
Follow Section 5.3.1.
Setting Start
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 28
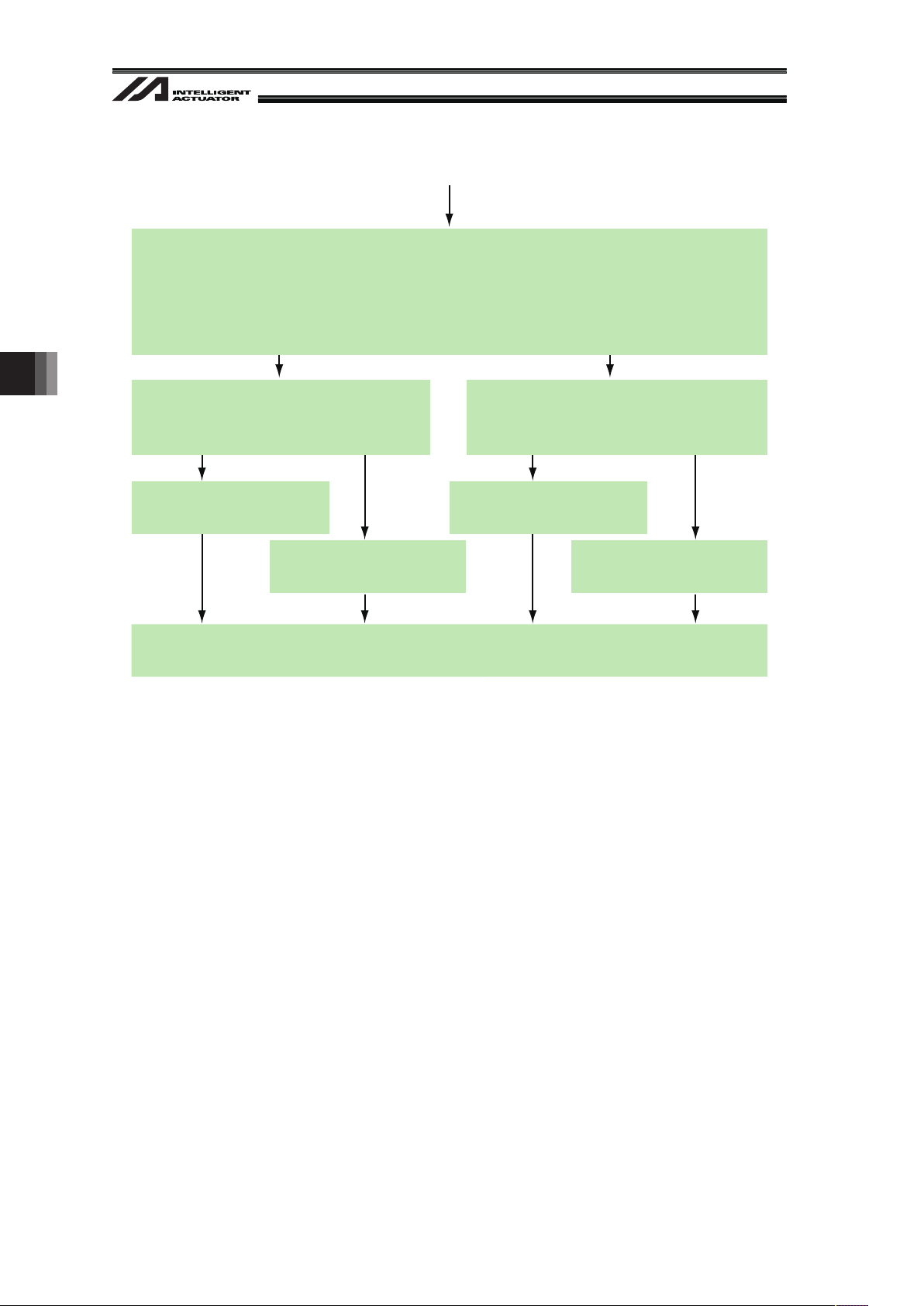
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
22
Continued from the previous page
Perform the adjustment
following Section 5.8.3.
Perform the adjustment
following Section 5.8.2.
Adjustment of Vision System Coordinates and Robot Coordinates
(setting on XSEL and Vision System)
Which vision system of the following is to be used?
1) Cognex 2) Other (except for 1))
EZ-110XL
In which way the camera is installed?
1) On the robot 2) Not on the robot
(Fix on equipment)
In which way the camera is installed?
1) On the robot 2) Not on the robot
(Fix on equipment)
Perform the adjustment
following Section 5.8.1.
Perform the adjustment
following Section 5.8.4.
Program Edit (setting on XSEL)
Create the program by following the SEL Program construction guideline.
Page 29
23
5.2 About Parameter Change
5.2.1 Regarding to Value Setting
If the last digit of the set value is H, set with hexadecimal number.
Refer to the following.
Input the value of hexadecimal number transformed from the binary number.
5.2.1.1 Binary Number
Binary number expresses a numeral figure with using 2 numbers, 0 and 1.
The number increases in the order of 0, 1, and then the number of digit increases, and goes 10, 11
…
Decimal Number 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Binary Number 0 1 10 11 100 101 110 111 1000 1001 1010
5.2.1.2 Hexadecimal Number
Hexadecimal number expresses a numeral figure with using numbers from 0 to 9 and alphabets
from A to F. The number increases in the order of 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B,C, D, E, F, and then
the number of digit increases, and goes 10, 11, …
Decimal Number 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
Hexadecimal
Number
0 to 9
(Same for decimal and
hexadecimal numbers)
A B C D E F 10
Example 1 : 001340
H
Bit
20-23
0000
Bit
16-19
0000
Bit
12-15
0001
Bit
8-11
0011
Bit
4-7
0100
Bit
0-3
0000
0 0 1 3 4 0
H
Example 2 : 123456
H
Bit
20-23
0001
Bit
16-19
0010
Bit
12-15
0011
Bit
8-11
0100
Bit
4-7
0101
Bit
0-3
0110
1 2 3 4 5 6
H
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 30
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
24
5.3 Communication Channel Setting
Either RS232C (standard for XSEL), Ethernet Communication Board
(*1)
(option for XSEL-P/Q type)
or EtherNet/IP Communication Board (option for XSEL-R/S type) is used for the vision system I/F
function.
*1 Not applicable for XSEL-R/S
If using Ethernet, follow the instructions in Section 5.3.1 to perform the settings.
If using RS232C, follow the instructions in Section 5.3.2 to perform the settings.
5.3.1 When Ethernet TCP/IP Message Communication is Used
When using the Ethernet TCP/IP message communication (Cognex or Keyence), set the XSEL
parameters in the right order.
[Setting 1] Ethernet TCP/IP Message Communication Attribute [compulsory] (I/O Parameter
No.124)
Set the Ethernet TCP/IP message communication attribute in I/O Parameter No.124.
Select one channel from channels 31 to 34 and set it as the client (setting value = 1).
(Note) When using Cognex In-Sight EZ110 (EZ-110XL), set the parameter to;
I/O Parameter No.124 = 003100
H
I/O Parameters No.124
Bit 20-23 Bit 16-19 Bit 12-15 Bit 8-11 Bit 4-7 Bit 0-3
Free-for-User
Channel 34
Set Value=1
Free-for-User
Channel 33
Set Value=1
Free-for-User
Channel 32
Set Value=1
Free-for-User
Channel 31
Set Value=1
Set Value=0 Set Value=0
Set Value = 0 : Channel not in use
Set Value = 1 : Set X-SEL as the client
Set Value = 3 : Set X-SEL as the server
(Example 1) When using the channel 31 for Vision System I/F
I/O Parameter No.124 = 000100
H
(Example 2) When using the channel 32 for Vision System I/F and 31 for another program
(server) (and not using 33 and 34)
I/O Parameter No.124 = 001300
H
Page 31

25
[Setting 2] Ethernet Operation Prescription [compulsory] (I/O Parameters No.129)
Set the Ethernet operation prescription in I/O Parameters No.129.
Set the bits 4-7 to “1”.
I/O Parameter No.129 = 10
H
I/O Parameters No.129
Bit 4-7 Bit 0-3
TCP/IP Message Communication is Used
Set Value=1
Set Value 0
[Setting 3] Controller Network Address Setting [compulsory]
(I/O Parameters No.132 to 143,146)
Set the I/O Parameters No.132 to 143 and 145 to 148 following the network
environment.
I/O Parameters No.132 to 135 Self IP Address (IP address of X-SEL)
I/O Parameters No.136 to 139 Subnet Mask
I/O Parameters No.140 to 143 Default Gateway
I/O Parameters No.146
Free-for-User Channel 32 (TCP/IP)
Self-Port Number
(Note)
Set it in
accordance with
the network
environment to
be used
(Note) Do not change I/O Parameter No.146 from “64513” (initial setting value) when using
EZ-110XL.
[Setting 4] Vision System Network Address Setting [compulsory] (I/O Parameters No.160 to 164)
Set the parameters such as the network address of the vision system to be connected in
I/O Parameters No.160 to 164.
Refer to the IP address settings on the controller side (I/O Parameters No.132 to 134) for
the IP address to set it to have the controller and the vision system exist on the same
network.
(Note) When setting the IP addresses, be sure not to duplicate the entire address.
(Example) IP address of Vision System 192.168. 0. 11 (I/O Parameter No.160 to 163)
IP address of X-SEL 192.168. 0. 12 (I/O Parameter No.132 to 135)
I/O Parameters
No.160 to 163
Vision System I/F connected IP address
Input Vision System IP
address setting value
I/O Parameters
No.164
Vision System I/F Connected Port Number
(Example)
Cognex
:3000
H
Keyence :8500
H
Continue to Section 5.4 to complete the setting procedures.
A
void duplication
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 32

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
26
5.3.2 When Standard SIO (RS232C) Channel Communication is Used
When using the standard SIO (RS232C) channel communication (OMRON or Keyence), set the
XSEL parameters in the right order.
[Setting 1] Free-for-User SIO Channel Attribute 1 [compulsory] (I/O Parameters No.201 and 213)
Set the parameters in accordance with the application environment.
Note :
x Do not fail to have the same communication setting as that on the camera controller
side.
x Set I/O Parameter No.201 if Channel 1 is used, and No.213 if Channel 2 is used.
I/O Parameter No.201 (when Standard SIO Channel 1 is used)
I/O Parameter No.213 (when Standard SIO Channel 2 is used)
Bit 28-31 Bit 24-27 Bit 20-23 Bit 16-19 Bit 4-15 Bit 0-3
Baud Rate Type
[kbps]
Set Value=2
(Default)
*Set Value
Set Value=0 (9.6)
Set Value=1 (19.2)
Set Value=2 (38.4)
Set Value=3 (57.6)
Set Value=4 (76.8)
Set Value=5 (115.2)
Data Length
(7 to 8)
Set Value=8
(Default)
Stop Bit Length
(1 to 2)
Set Value=1
(Default)
Parity Type
Set Value=0
(Default)
*Set Value
Set Value=0 (None)
Set Value
=
1
(Odd Number)
Set Value
=
2
(Even Number)
For future
extension
Set Value=000
(Default)
Standard SIO
Usage Selection
Set Value=1
*Set Value
Set Value=0
(Not used)
Set Value=1
(Used)
(Example) Example of using the standard SIO channel 1 and establishing the
communication with the following conditions:
<Conditions>
Communication Speed : 115.2kbps (Set Value 5)
Data Length : 8 (Set Value 8)
Stop Bit Length : 1 (Set Value 1)
Parity Type : None (Set Value 0)
<Set Value>
I/O Parameter No.201 = 58100001
H
Page 33

27
5.4 Communication Format Setting
There are fixed formats for the communication format and can be set by I/O Parameters.
[Setting 1] Vision System I/F Function Selection 2 [compulsory] (I/O Parameters No.352)
Select the communication format to receive from the vision system on I/O Parameter
No.352, Bits 0 to 7. The setting values differ depending on the vision system supplier.
I/O Parameters No.352
Bit 0-7
Communication Format Select
Set Value=0
: Vision System of Cognex (including EZ-110XL)
Set Value=1
: Vision System of OMROM
Set Value=2
: Vision System of Keyence
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 34

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
28
[Setting 2] Vision System I/F Function Selection 3 [compulsory] (I/O Parameters No.353)
Set the header and delimiter for the communication format to receive from the vision
system.
The setting values differ depending on the vision system supplier.
I/O Parameters No.353
Bit 16-31 Bit 8-15 Bit 0-7
Vision System I/F
Communication Header 2
(Effective when Keyence is
selected in Setting 1)
Set Value=5431 (Default)
Setting change is not
necessary.
Vision System I/F
Communication Header 1
(Effective when Cognex or
OMRON is selected in Setting 1)
Set Value=3C (Default)
Cognex : 3C
OMRON : 39
Vision System I/F
Communication Delimiter
Set Value=0D (Default)
Setting change is not
necessary.
[Setting 3] Vision System Settings [compulsory]
Perform the settings on the vision system so the specified communication format can be
output.
(1) When using EZ-110XL and simple (dedicated) calibration (refer to Section 5.8)
Refer to [Setting 1] in 8.1 Appendix
(2) When using the vision system of Cognex or OMRON
Refer to [Setting 2] in 8.1 Appendix
(3) When using the Keyence vision system
Refer to [Setting 3] in 8.1 Appendix
(Note) Move to Section 5.7 if using Cognex In-Sight EZ110.
Page 35

29
5.5 Unit Conversion (pixel mm)
This manual is provided on the premise that the unit of the coordinate data that is received in Vision
System I/F Function is [mm]. Provide a setting on the camera controller side to have the unit of the
output coordinate data in [mm]. [Refer to the Instruction Manual for the Vision System to be
connected for the details.]
(Note) The setting is not necessary when using the simple (dedicated) calibration with EZ-110XL
since the setting is conducted in Section 5.8.
5.6 Coordinate Setting
Set the coordinate axes of the vision system.
Refer to the following to set the coordinates on the camera controller side in accordance with the
parameter settings in Vision System I/F Function. [Refer to the Instruction Manual for the Vision
System to be connected for the details.]
(Note) The setting is not necessary when using the simple (dedicated) calibration with EZ-110XL
since the setting is conducted in Section 5.8.
[For Cognex (except for EZ-110XL) or OMRON : I/O Parameter No.352=0 or 1]
Conduct the setting to place the origin on the bottom left of the captured data.
㪯
㪰
[For Keyence : I/O Parameter No.352=2]
Conduct the setting to place the origin on the upper left of the captured data.
㪯
㪰
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 36

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
30
5.7 Detailed Function Settings
To operate Vision System I/F Function properly, set the following parameters.
Note :
Do not fail to set the following parameters.
x Vision System I/F Function Selection 1(I/O Parameters No.351)
x Setting of Vision System I/F Image-Capture Command Physical Output Number (I/O
Parameters No.357)
[Setting 1] Vision System I/F Function Selection 1 [compulsory] (I/O Parameters No.351)
Set I/O Parameter No.351.
(Note) Set the Bit 4-7 to “2” when using EZ-110XL and simple (dedicated) calibration
(refer to Section 5.8).
I/O Parameters No.351
Bit 24-31 Bit 20-23 Bit 12-19 Bit 8-11 Bit 4-7 Bit 0-3
Number of tries
for Image-Capture
Command
[times]
Image-Capture
Delay Estimation
Timer Value
[msec]
Image-Capture
Command Cutoff
Extension Timer
Value
[msec]
Response timeout
value
[sec]
Communication
Device Selection
(Note1)
Function Usage
Selection
No need to
change
Set Value=3
(Default)
No need to
change
Set Value=1
(Default)
No need to
change
Set Value=05
(Default)
No need to
change
Set Value=5
(Default)
Set Value=0
(Channel 1)
Set Value=1
(Channel 2)
Set Value=2
(Channel 31)
Set Value=3
(Channel 32)
Set Value=4
(Channel 33)
Set Value=5
(Channel 34)
Set Value=1
(to use Vision
System I/F)
Set Value=0
(not to use Vision
System I/F)
Note 1 : Match the setting to the channels that are set to Usage Selection (either one in Channels 31 to 34)
in Parameter No.124 if the communication with Vision System is performed with Ethernet.
Set the channel (channel 1 or 2) to the selected one when the communication is established with
the standard SIO (RS232C). (I/O Parameters No.201 = Channel 1, No.213 = Channel 2)
[Refer to Section 5.3]
Page 37

31
[Setting 2] Setting of Vision System I/F Image-Capture Command Physical Output Number
[compulsory] (I/O Parameters No.357)
Set the Output port number to be used as the image-capture trigger to the vision system.
I/O Parameters No.357
Set Value=Output Port No.
[Setting 3] Setting of Vision System I/F Initializing Complete Status Physical Input Port Number
[Option] (I/O Parameters No.356)
By having I/O Parameter No.356 set, the operation complete judgment of the vision
system becomes enabled.
Note :
If this parameter is used and the vision system is not switched on when SLVS command is
executed, Return Code 23 (Vision System Initializing Incomplete Error) will be issued.
I/O Parameters No.356
Set Value=Input Port No.
* Set the value to 0 when not to be used.
[Setting 4] Vision System I/F Control 1 [Option] (All-Axes Parameter No.129)
Set if the signal of rotary axis is to be reversed or not.
All-Axes Parameters No.129
Bit 20-23 Bit 12-19 Bit 4-11 Bit 0-3
Rotary Axis Correction
Direction Reverse
(0
= no signal reverse
1
= signal to be reversed)
Set Value
=0
(Default)
System
Reservation
No need to
change
Set Value
=00
(Default)
System
Reservation
No need to
change
Set Value
=00
(Default)
System
Reservation
No need to
change
Set Value
=0
(Default)
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 38

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
32
5.8 Vision System I/F adjustment
To make the relation to the robot coordinates and the vision system coordinates, adjustment
(calibration) of the vision system I/F is required.
The method of Vision system I/F adjustment differs depending on the vision system model and the
location of the camera installation.
If using EZ-110XL, “Simple Calibration” is available which enables you to reduce the steps of
manual adjustment of positions of the robot tool tip and the work. [Refer to Section 5.8.1 to 5.8.3]
In the case of using a vision system other than those mentioned above, refer to Section 5.8.4 or
Section 5.8.5.
Precautions
1) Vision system IF adjustment puts a relation of the robot X, Y and T coordinates to the vision
system coordinates. It is not applied when the center of the rotation and that of the tool to
retain the work are offset.
2) Camera cannot be mounted on the robot rotation axis.
3) Make sure to execute the vision system I/F adjustment after parameter settings are
completed.
4) For absolute type actuator, execute it after the absolute reset is completed.
5) Applicable PC software is required for the vision system I/F adjustment.
6) The vision system I/F adjustment includes steps to capture images of the work piece with the
vision system. Register the work piece to the vision system in advance so it can be detected.
Also, when using a vision system other than EZ-110XL, unit conversion (from pixel to mm) is
to be conducted on the camera controller side.
7) The following parameters are updated automatically by executing the vision system I/F
adjustment. It is no need to change them manually.
All-Axes Parameters Description
No.122
Vision System I/F 1 Coordinate Datum Point
Offset X
No.123
Vision System I/F 1 Coordinate Datum Point
Offset Y
No.124
Vision System I/F 1 Coordinate Datum Point
Offset Angle
No.125
Vision System I/F 1 Robot Vision Mounted
Z-axis Direction Vision Position Judgment
Datum
No.130
Vision System I/F 1 Control 2
Bits 8 to 11 Vision Installation Type
( 0 (Camera being installed on a position other
than on the robot))
( 1 (Camera being installed on the robot))
Updated
automatically by
execution of “Vision
System I/F
adjustment”
Page 39

33
5.8.1 Initial Settings for Simple Calibration
(When EZ-110XL camera is used)
Conduct the initial settings following the steps below with using the Cognex Setup software (In-Sight
Explorer) or PC software for XSEL.
(Note) It is necessary to redo the initial settings (1) to (3) if the version of In-Sight Explorer is
updated.
ڏ Please contact us for the files necessary for the initial settings.
[Initial Setting 1]
Copy the file “IAIClassLibrary.dll” stored in the PC software installation CD and put it into the folder
stated below:
¥Program Files¥Cognex¥In-Sight¥In-Sight Explorer *.*.*
(*.*.* indicates the software version: applied in 4.4.1 and later)
[Initial Setting 2]
Copy the file “IAICalib_EN.cxd” stored in the PC software installation CD and put it into the folder
stated below:
¥Program Files¥Cognex¥In-Sight¥In-Sight Explorer *.*.*¥Snippets¥EasyBuilder
(*.*.* indicates the software version: applied in 4.4.1 and later)
[Initial Setting 3]
Start up In-Sight Explorer.
Select Options in In-Sight Explorer System Menu and tick on “Use English Symbolic Tags for
EasyBuilder” in the User Interface items.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 40

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
34
[Initial Setting 4]
In this calibration, the adjustment is conducted by actually moving the work using the robot within
the image capturing range of the camera.
Therefore, it is necessary to create a program considering the method of retaining the work (gripping,
chucking, etc.). Please contact IAI for a program file you need.
Make sure to write the program for “Hold” and “Release” to the specified points.
(Note 1) The program can be edited even if the controller is not connected to the PC software
(offline).
(Note 2) Make sure to conduct the relative interlock of Hold and Release in the SEL program that
you edit.
Write the program for “Hold” here
(Z-axis is lowered enough to hold the work.)
If a sensor to judge the success/fail of the hold is to be added, add;
• a command to jump to TAG 52 after success (Write GOTO 52), and
• a command to jump to TAG 53 if fail (Write GOTO 53)
(Rise of Z-axis is conducted automatically later on.)
Page 41

35
Example 1 : When holding with grip
(grip when I/O Port 314 is ON and release when 315 is ON)
BTOF (315) ĸI/O Port No. (315) turns OFF
TIMW (0.1) ĸKeep time for electromagnetic valve to turn OFF
BTON (314) ĸI/O Port No. (314) turns ON (grip)
TIMW (0.3) ĸRetain the gripping time
GOTO 52 ĸTo the process for work hold success
Example 2 : When holding with an electrical gripper connectable to XSEL (connected to the
4th axis)
GRP (1000) ĸCommand to make only gripper available for operation
PAPR (10) (20) ĸPressing (10) : approach distance
(20) : approach speed
PUSH (30) (900) ĸ (30) : Position number of the pressing position
(900) : Turns ON when pressing succeeded
Turns OFF when failed
GRP (111) ĸCommand to make all the operations available except for gripper
(900) GOTO 52 ĸTo the process for work hold success
N (900) GOTO 53 ĸTo the process of work hold fail
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 42

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
36
Example 1 : When holding with grip
(grip when I/O Port 314 is ON and release when 315 is ON)
BTOF (314) ĸI/O Port No. (314) turns OFF
TIMW (0.1) ĸKeep time for electromagnetic valve to turn OFF
BTON (315) ĸI/O Port No. (315) turns ON (release)
TIMW (0.03) ĸRetain the release time
BTOF (315) ĸI/O Port No. (315) turns OFF
GOTO 57 ĸTo the process of work release success
Example 2 : When holding with an electrical gripper connectable to XSEL (connected to the
4th axis)
GRP (1000) ĸCommand to make only gripper available for operation
MOVP (30) ĸPosition number when the gripper is open
GRP (111) ĸCommand to make all the operations available except for gripper
GOTO 57 ĸTo the process of work release success
Write the program for “Release” here
(Z-axis is lowered enough to hold the work.)
If a sensor to judge the success/fail of the release is to be added, add;
• a command to jump to TAG 57 after success (Write GOTO 57), and
• a command to jump to TAG 58 if fail (Write GOTO 58)
(Rise of Z-axis is conducted automatically later on.)
Page 43

37
5.8.2 When Camera Not Mounted on Robot
(When EZ-110XL is used)
This section explains how to setup when the camera is installed as shown in the picture below.
Conduct the home return of the incremental type robot in advance.
If the camera is to be mounted on the robot, refer to “5.8.3 When Camera Mounted on Robot”.
When Camera Not Mounted on Robot
[Procedure 1] Select Vision System I/F easy adjustment from the PC software.
A warning dialog box opens.
Note :
In the case “Vision System I/F easy adjustment” is not displayed in the main menu,
check the version of the PC software and the settings of related I/O parameters.
I/O Parameter
No.351 Bit 0-3=1
PC software version for
Vision System I/F Adjustment
XSEL-P/Q: V7.07.08.00 or later
XSEL-R/S: V9.0.0.0 or later
Camera being
mounted on a place
such as the frame
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 44

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
38
[Procedure 2] Finish all operations and click “OK” button.
Vision System I/F easy adjustment window opens.
[Procedure 3] Click “OK” button.
Vision System I/F easy adjustment opens. [See the next page]
Note :
If no vision system I/F number is displayed, check the parameter settings [5.7
Parameter Settings] on the controller.
Activate this one.
Set this to “1”
Page 45

39
Vision System I/F easy adjustment Window
ڏ For those items pointed with a red arrow, confirm the contents or acquire the necessary values
and click the button on the right to proceed to the next one.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 46

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
40
[Procedure 4] Start up the Cognex Setup Software (In-Sight Explorer).
After it is confirmed the software is open, click “OK” button.
[Procedure 5] Connect the camera and conduct the settings following the instructions (1) to (3)
indicated below.
Click “OK” button.
(1) In Application Step in In-Sight Explorer, select “Start” ĺ “Get Connected”.
(2) In “Select an In-Sight Sensor or Emulator”, select “ez110” and then select “Connect”.
(3) Select “New Job…” from “File” in the menu bar or “Open Job…” if there is an existing job.
Page 47

41
[Procedure 6] Conduct the settings following the instructions (1) to (3) indicated below.
Click “OK” button.
(1) Confirm “Online” shown at the bottom of the camera image display screen of In-Sight Explorer
and then select “Sensor” ĺ “Online” from the menu bar.
A message box asking “Are you sure you want to go Offline?”. Click “Yes” button.
(2) Select “Start” ĺ “Set Up Image” in Application Steps.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 48

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
42
(3) In “Acquire/Load Image”, click “Trigger” to capture the image.
Page 49

43
[Procedure 7] Select the necessary tools
(Note)
from the positioning or inspection of the tool setting.
(At this stage, do not select the IAI Robot Tool in the inspection.)
Click “OK” button.
(Note) In this manual, explains with an example of when using PatMax pattern from
the positioning tool. For other tools, refer to the instruction manual selected
from Windows start menu ĺ Program ĺ Cognex ĺ In-Sight ĺ In-Sight
Explorer*.*.* ĺ “Document”.
(1) Select “Set Up Tools” ĺ “Locate Part” in Application Steps of In-Sight Explorer.
(2) In “Add Tool”, select “PatMax® Pattern” ĺ “Add”.
(3) Surround the area of the work that you wish to detect with the model area. Also, set the search
area to the desired range. Click “OK” in Usage Method.
Search area
Model area
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 50

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
44
[Procedure 8] Now perform the settings for Inspection Tool. Follow the following instructions.
After all the settings are complete, click “OK” button.
(1) In Application Steps in In-Sight Explorer, select “Set Up Tools” ĺ “Inspect Part”.
(2) From IAI Robot Tool in Tool Setting Inspection, select IAI N-Point Calibration and click “Add”.
Page 51

45
(3) Select the detection point set by either the positioning or the inspection tool and click “OK” in
Usage.
(Example) When the detection point is set at the center of the work with using the positioning
pattern tool PatMax, click on the cross cursor on the screen (the cursor color
changes) and click “OK”.
(4) In Calibration General window, confirm that Tool Enabled is On.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 52

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
46
(5) Set the IP address and Port Number of XSEL in the Calibration Setting Window.
Input the value set in I/O Parameters No.132 to 135 for the IP address.
Input the value set in I/O Parameter No.146 for the Port Number.
(Note) The set value is displayed at the item that is currently set (it is displayed with an arrow
ψ) in the Vision System I/F Simple Adjustment Window in the PC software.
(6) Set the number of points. It should basically be 4 points, however, in the case an improvement
in the accuracy is required the number of point can be increased to 16 at the maximum.
(Allocate the points evenly as much as possible in the range that the work can be detected and
that for image capturing.)
Input the value set in I/O Parameters No.132 to
135 in XSEL
Input the value set in I/O Parameter No.146 in
XSEL
Input a number from 4 to 16
Page 53

47
(7) Set the amount of robot movement
(Note 1 and 2)
considering the set points are in the image
capturing range.
(Note 1) The movement is relative movement.
(Note 2) In the case the camera is mounted on the robot and the case not, the movement
directions may be opposite in up/down, right/left directions.
Example1 : Number of Calibration Points = 4 points (When Camera Not Mounted on Robot)
In this example, select the Move tag and set the values as shown below for Move1.X to
Move3.Y in the right order.
indicates the image capturing range
(60 u 60mm)
X
Coordinates of
Vision System
Y
Ԙ
ԙԚ
Moves 50mm in X direction
60mm
60mm
Moves -40mm in Y direction
Moves -50mm in X direction
0
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 54

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
48
Example 2 : Number of Calibration Points = 16 points (When Camera Not Mounted on Robot)
In this example, select the Move tag and set the values as shown below for Move1.X to
Move15.Y in the right order.
Click here and the
boxes for Move 8-15
will appear.
X
Coordinates of
Vision System
Y
60mm
60mm
Ԙ ԙ Ԛ
ԛ
Ԣ
ԣ
ԜԝԞ
ԟ
Ԡ
ԡ
Ԥԥ
Ԧ
15mm 15mm 15mm
15mm
15mm
15mm
indicates the image capturing range
(60 u 60mm)
0
Page 55

49
(8) Confirm that “Default” is shown in the file name on the top of the export window.
If a different name or nothing is shown, type it manually.
(9) Confirm a tick mark in the check box.
If not, put a tick mark in it.
(10) Select “File” ĺ “Save Job” or “Save Job As…” from the menu bar.
Store the created job file to the camera and PC (for backup).
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 56

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
50
[Procedure 9] Set the vision system to the continuous capturing mode.
Select “Live Video” in Acquire/Load Image in In-Sight Explorer.
Click “OK” button.
(1) Toggle button
to online/offline
ψ Set it to offline.
(2)
(3)
Page 57

51
[Procedure 10] Click “OK” button.
[Procedure 11] Click “OK” button if the IP addresses of the vision system are correct.
If incorrect, set the right IP addresses to XSEL I/O Parameters No.160 to 163.
[Procedure 12] Input the program number that is not used in XSEL to the forwarding program
number.
After inputting, click “OK” button.
The programs not in use can be found with the method stated below.
From the menu of XSEL PC software, select “Program” ĺ “Edit”.
Program Number Select Window opens. In the list, the numbers with 0 in Step
Number column are not in use. If all the lines are occupied, make a backup to the
PC temporarily to ensure an empty program field.
Not in use
No.2
No.9
No.10
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 58

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
52
[Procedure 13] Input the position number not in use. (Select a position number that 10 positions in
a row can be ensured.)
After inputting, click “OK” button.
If all the lines are occupied, make a backup to the PC temporarily to ensure an
empty program field.
[Procedure 14] (1) Please contact IAI for a program file you need.
(2) Select the file (X-SEL-P/Q: cognex_worksub.x2pg2, X-SEL-R/S:
cognex_worksub.x4pg) as the work hold/release sub-routine for the calibration
(please prepare separately) from the data downloaded in (1) in Procedure 14.
(It is necessary to create a program which suits to the work in advance. Refer to
Section 5.8.1.)
After selecting the file, click “OK” button.
[Procedure 15] Move the robot to the position where it can hold (grip) the work.
Press the “Work Holding” button in the jog movement screen shown below to hold
the work.
(Note) Watch for the interference to the peripheral equipment.
Perform the moving operation with the jog buttons at the bottom of the calibration
window.
Servo ON Button
Jog operation buttons for 1st axis
Jog operation buttons for 2nd axis
Jog operation buttons for 3rd axis
Jog Speed
(in common with Calibration Speed)
Jog/inch switching
(Inching operation if input except 0)
Work Hold (Grip)
Work Release (Release)
A
cceleration Setting
Deceleration Setting
(1)
(2)
Page 59

53
[Procedure 16] Move the robot to a position out of image capturing range of the camera and click
“OK” button.
(Note) Watch for the interference to the peripheral equipment. [Refer to Procedure
15 for how to operate.]
[Procedure 17] Click the “Acquire” button to read the current robot coordinates information.
Confirm that the current coordinates are shown as the position out of image
capturing range coordinates and click “OK” button.
[Procedure 18] With the work held on the robot, transport it to a position near the calibration start
point (point above the position 0 set in Procedure 8 (5)). Do not move the robot from
where it released the work.
Click “OK” button.
Perform the moving operation with the jog buttons at the bottom of the calibration
window. [Refer to Procedure 15]
[Procedure 19] Click the “Acquire” button to read the current robot coordinates information.
Confirm that the coordinates where released is displayed as the coordinates for the
calibration start point.
When fine-tuning is required for the height of Z-axis for holding or that of Z-axis for
releasing, input values directly to the Z-axis boxes.
Click “OK” button.
Put values directly when a fine-tuning is
required for the Z-axis height.
(Note) Do not click the “Acquire” button if
putting the values directly.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 60

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
54
[Procedure 20] Perform the following settings to make the camera condition to wait for calibration
execution.
(1) Click on Live Video at “Import/Load Image” in Application Step to release the
Live Video condition.
(2) Make the camera online.
(3) Select “Finish” ĺ “Run Job” in Application Steps.
Click “OK” button.
[Procedure 21] Click “Execute” button. The calibration starts.
Warning : The calibration work includes the robot operation. Make sure to be away
from the robot operation range before executing the work.
(1) Toggle button
to online/offline
ψ Set it to offline.
(2)
Page 61

55
[Procedure 22] The calibration is complete in normal condition after the adjustment of specified
point number is conducted.
Click “OK” to close the information window.
[Procedure 23] If desired to finish the calibration, click the “Finish” button.
If an error occurred, refer to Section 7.2 to solve the problem and retry the
calibration.
[Procedure 24] Click the “Update” button.
[Procedure 25] After closing this window (Vision System Settings), write to the flash ROM and
reboot the system, confirm that the contents in the program numbers and the
position numbers selected in [Procedure 12] and [Procedure 13] are all cleared up.
If the data was stored in the PC temporarily, put them back to where they originally
were.
[Procedure 26] Close the window by clicking the “×” button on the top right corner of the window.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 62

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
56
[Procedure 27] The window shown below will appear. Click the “Yes” button.
Confirmation window for the controller reboot appears next. Click the “Yes” button
to reboot the controller.
[Procedure 28] After setting the camera to offline, select the settings of In-Sight Explorer images
and set Calibration Type to Import. Select “DefaultCalib.cxd”
(Note)
from the
selectable file names.
Select “File” ĺ “Save Job” or “Save Job As…” from the menu bar.
(Note) Select the file name that includes “Calib.cxd” in it that was set in [Procedure
8] (6).
Note :
The job file created here is for the calibration use only. It is necessary to create another
job file for the ordinary operation, or otherwise ask the distributor to create one for you.
(1) Select Set Up Image
(2) Select Import
(3) Select the file name + Calib.cxd
registered in calibration setting window
(4) Select Millimeters
Page 63

57
5.8.3 When Camera Mounted on Robot
(When EZ-110XL is used)
This section explains how to setup when the camera is installed on the camera as shown in the
picture below.
Conduct the home return of the incremental type robot in advance.
When Camera Mounted on Robot
[Procedure 1] Select Vision System I/F easy adjustment from the PC software.
A warning dialog box opens.
Note :
In the case “Vision System I/F easy adjustment” is not displayed in the main menu,
check the version of the PC software and the settings of related I/O parameters.
I/O Parameter
No.351 Bit 0-3=1
PC software version for
Vision System I/F Adjustment
XSEL-P/Q: V7.07.08.00 or later
XSEL-R/S: V9.0.0.0 or later
Camera
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 64

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
58
[Procedure 2] Finish all operations and click “OK” button.
Vision System I/F easy adjustment window opens.
[Procedure 3] Click “OK” button.
Vision System I/F easy adjustment window appears. [See the next page]
Note :
If no vision system I/F number is displayed, check the parameter settings [5.7
Parameter Settings] on the controller.
Activate this one.
Set this to “1”
Page 65

59
Vision System I/F easy adjustment Window
ڏ For those items pointed with a red arrow, confirm the contents or acquire the necessary values
and click the button on the right to proceed to the next one.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 66

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
60
[Procedure 4] Start up the Cognex Setup Software (In-Sight Explorer).
After it is confirmed the software is open, click “OK” button.
[Procedure 5] Connect the camera and conduct the settings following the instructions (1) to (3)
indicated below.
Click “OK” button.
(1) In Application Step in In-Sight Explorer, select “Start” ĺ “Get Connected”.
(2) In “Select In-Sight Sensor or Emulator”, select “ez110” and then select “Connect”.
(3) Select “New Job…” from “File” in the menu bar or “Open Job…” if there is an existing job.
Page 67

61
[Procedure 6] Conduct the settings following the instructions (1) to (3) indicated below.
Click “OK” button.
(1) Confirm “Online” shown at the bottom of the camera image display screen of In-Sight Explorer
and then select “Sensor” ĺ “Online” from the menu bar.
A message box asking “Are you sure you want to go Offline?”. Click “Yes” button.
(2) Select “Start” ĺ “Set Up Image” in Application Steps.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 68

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
62
(3) In “Acquire/Load Image”, click “Trigger” to capture the image.
Page 69

63
[Procedure 7] Select the necessary tools
(Note)
from the positioning or inspection of the tool setting.
(At this stage, do not select the IAI Robot Tool in the inspection.)
Click “OK” button.
(Note) In this manual, explains with an example of when using PatMax pattern from
the positioning tool. For other tools, refer to the instruction manual selected
from Windows start menu ĺ Program ĺ Cognex ĺ In-Sight ĺ In-Sight
Explorer*.*.* ĺ “Document”.
(1) Select “Set Up Tools” ĺ “Locate Part” in Application Steps of In-Sight Explorer.
(2) In “Add Tool”, select “PatMax® Pattern” ĺ “Add”.
(3) Surround the area of the work that you wish to detect with the model area. Also, set the search
area to the desired range. Click “OK” in Usage Method.
Search area
Model area
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 70

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
64
[Procedure 8] Now perform the settings for Inspection Tool. Follow the following instructions.
After all the settings are complete, click “OK” button.
(1) In Application Steps in In-Sight Explorer, select “Set Up Tools” ĺ “Inspect Part”.
(2) From IAI Robot Tool in Tool Setting Inspection, select IAI N-Point Calibration and click “Add”.
Page 71

65
(3) Select the detection point set by either the positioning or the inspection tool and click “OK” in
Usage.
(Example) When the detection point is set at the center of the work with using the positioning
pattern tool PatMax, click on the cross cursor on the screen (the cursor color
changes) and click “OK”.
(4) In Calibration General window, confirm that Tool Enabled is On.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 72

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
66
(5) Set the IP address and Port Number of XSEL in the Calibration Setting Window.
Input the value set in I/O Parameters No.132 to 135 for the IP address.
Input the value set in I/O Parameter No.146 for the Port Number.
(Note) The set value is displayed at the item that is currently set (it is displayed with an arrow
ψ) in the Vision System I/F Simple Adjustment Window in the PC software.
(6) Set the number of points. It should basically be 4 points, however, in the case an improvement
in the accuracy is required the number of point can be increased to 16 at the maximum.
(Allocate the points evenly as much as possible in the range that the work can be detected and
that for image capturing.)
Input the value set in I/O Parameters No.132 to
135 in XSEL
Input the value set in I/O Parameter No.146 in
XSEL
Input a number from 4 to 16
Page 73

67
(7) Set the amount of robot movement
(Note 1 and 2)
considering the set points are in the image
capturing range.
(Note 1) The movement is relative movement.
(Note 2) In the case the camera is mounted on the robot and the case not, the movement
directions may be opposite in up/down, right/left directions.
Example1 : Number of Calibration Points = 4 points (When Camera Not Mounted on Robot)
In this example, select the Move tag and set the values as shown below for Move1.X to
Move3.Y in the right order.
indicates the image capturing range
(60 u 60mm)
X
Coordinates of
Vision System
Y
Ԙ
ԙԚ
Moves 50mm in X direction
60mm
60mm
Moves -40mm in Y direction
Moves -50mm in X direction
0
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 74

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
68
Example 2 : Number of Calibration Points = 16 points (When Camera Not Mounted on Robot)
In this example, select the Move tag and set the values as shown below for Move1.X to
Move15.Y in the right order.
Click here and the
boxes for Move 8-15
will appear.
X
Coordinates of
Vision System
Y
60mm
60mm
Ԙ ԙ Ԛ
ԛ
Ԣ
ԣ
ԜԝԞ
ԟ
Ԡ
ԡ
Ԥԥ
Ԧ
15mm 15mm 15mm
15mm
15mm
15mm
indicates the image capturing range
(60 u 60mm)
0
Page 75

69
(8) Confirm that “Default” is shown in the file name on the top of the export window.
If a different name or nothing is shown, type it manually.
(9) Confirm a tick mark in the check box.
If not, put a tick mark in it.
(10) Select “File” ĺ “Save Job” or “Save Job As…” from the menu bar.
Store the created job file to the camera and PC (for backup).
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 76

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
70
[Procedure 9] Set the vision system to the continuous capturing mode.
Select “Live Video” in Acquire/Load Image in In-Sight Explorer.
Click “OK” button.
(1) Toggle button
to online/offline
ψ Set it to offline.
(2)
(3)
Page 77

71
[Procedure 10] Click “OK” button.
[Procedure 11] Click the “OK” button if the IP addresses of the vision system are correct.
If incorrect, set the right IP addresses to XSEL I/O Parameters No.160 to 163.
[Procedure 12] Input the program number that is not used in XSEL to the forwarding program
number.
After inputting, click “OK” button.
The programs not in use can be found with the method stated below.
From the menu of XSEL PC software, select “Program” ĺ “Edit”.
Program Number Select Window opens. In the list, the numbers with 0 in Step
Number column are not in use. If all the lines are occupied, make a backup to the
PC temporarily to ensure an empty program field.
Not in use
No.2
No.9
No.10
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 78

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
72
[Procedure 13] Input the position number not in use. (Select a position number that 10 positions in
a row can be ensured.)
After inputting, click “OK” button.
If all the lines are occupied, make a backup to the PC temporarily to ensure an
empty program field.
[Procedure 14] (1) Please contact IAI for a program file you need.
(2) Select the file (X-SEL-P/Q: cognex_worksub.x2pg2, X-SEL-R/S:
cognex_worksub.x4pg) as the work hold/release sub-routine for the calibration
(please prepare separately) from the data downloaded in (1) in Procedure 14.
(It is necessary to create a program which suits to the work in advance. Refer to
Section 5.8.1.)
After selecting the file, click “OK” button.
[Procedure 15] Move the robot to the position where it can hold (grip) the work.
Press the “Work Holding” button in the jog movement screen shown below to hold
the work.
(Note) Watch for the interference to the peripheral equipment.
Perform the moving operation with the jog buttons at the bottom of the calibration
window.
Servo ON Button
Jog operation buttons for 1st axis
Jog operation buttons for 2nd axis
Jog operation buttons for 3rd axis
Jog Speed
(in common with Calibration Speed)
Jog/inch switching
(Inching operation if input except 0)
Work Hold (Grip)
Work Release (Release)
A
cceleration Setting
Deceleration Setting
(1)
(2)
Page 79

73
[Procedure 16] With the work held on the robot, transport it to a position near the calibration start
point (point above the position 0 set in Procedure 8 (5)).
Keep the work at the height of Z-axis where it is to be released. (Keep the work with
being held.)
Click “OK” button.
Perform the moving operation with the jog buttons at the bottom of the calibration
window. [Refer to Procedure 15]
(Note) Watch for the interference to the peripheral equipment.
[Procedure 17] Click the “Acquire” button to read the current robot coordinates.
Confirm that the current coordinates are displayed as the work placing position
coordinates and click the “OK” button.
[Procedure 18] Click the “Work Release” button to release the work.
Click “OK” button.
[Procedure 19] Move the robot to a point near the calibration start point set in Procedure 8 (5)
where the work can be captured.
Click “OK” button.
[Procedure 20] Click the “Acquire” button to read the current robot coordinates.
Confirm the current coordinates are displayed at the image capturing start point
coordinates and click the “OK” button.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 80

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
74
[Procedure 21] Perform the following settings to make the camera condition to wait for calibration
execution.
(1) Click on Live Video at “Import/Load Image” in Application Step to release the
Live Video condition.
(2) Make the camera online.
(3) Select “Finish” ĺ “Run Job” in Application Steps.
Click “OK” button.
[Procedure 22] Click “Execute” button. The calibration starts.
Warning : The calibration work includes the robot operation. Make sure to be away
from the robot operation range before executing the work.
(1) Toggle button
to online/offline
ψ Set it to offline.
(2)
Page 81

75
[Procedure 23] The calibration is complete in normal condition after the adjustment of specified
point number is conducted.
Click “OK” to close the information window.
[Procedure 24] If desired to finish the calibration, click the “Finish” button.
If an error occurred, refer to Section 7.2 to solve the problem and retry the
calibration.
[Procedure 25] Click the “Update” button.
[Procedure 26] After closing this window (Vision System Settings), write to the flash ROM and
reboot the system, confirm that the contents in the program numbers and the
position numbers selected in [Procedure 12] and [Procedure 13] are all cleared up.
If the data was stored in the PC temporarily, put them back to where they originally
were.
[Procedure 27] Close the window by clicking the “×” button on the top right corner of the window.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 82

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
76
[Procedure 28] The window shown below will appear. Click the “Yes” button.
Confirmation window for the controller reboot appears next. Click the “Yes” button
to reboot the controller.
[Procedure 29] After setting the camera to offline, select the settings of In-Sight Explorer images
and set Calibration Type to Import. Select “DefaultCalib.cxd”
(Note)
from the
selectable file names.
Select “File” ĺ “Save Job” or “Save Job As…” from the menu bar.
(Note) Select the file name that includes “Calib.cxd” in it that was set in
[Procedure 8] (6).
Note :
The job file created here is for the calibration use only. It is necessary to create another
job file for the ordinary operation, or otherwise ask the distributor to create one for you.
(1) Select Set Up Image
(2) Select Import
(3) Select the file name + Calib.cxd
registered in calibration setting window
(4) Select Millimeters
Page 83

77
5.8.4 When Camera Not Mounted on Robot
(When camera other than EZ-110XL is used)
This section explains how to setup when the camera is installed as shown in the picture below.
If the camera is to be mounted on the robot, refer to “5.8.5 When Camera Mounted on Robot”.
When Camera Not Mounted on Robot
[Procedure 1] Select Vision System I/F adjustment from the PC software.
A warning dialog box opens.
Note :
If “Vision System I/F adjustment” is not shown in the main menu, check the version of
PC software or the related I/O parameter settings.
PC Software Version Capable for Vision
System I/F adjustment
XSEL-P/Q: V7.06.08.00 or later
XSEL-R/S: V9.0.0.0 or later
I/O Parameter
No.351 Bit 0-3=1
Camera being
mounted on a place
such as the frame
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 84

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
78
[Procedure 2] Finish all operations and click “OK” button.
Adjustment vision system I/F selection window appears.
[Procedure 3] Click “OK” button.
Vision System I/F adjustment window opens. [See the next page]
Note :
If no vision system I/F number is displayed, check the parameter settings [5.7
Parameter Settings] on the controller.
Do not check
in this box
Set this to “1”
Page 85

79
[Procedure 4] Confirm that the vision system is installed within the range of the robot operation
and click “OK” button.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 86

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
80
[Procedure 5] Click “OK” button.
[Procedure 6] Set a work piece in the range of robot operation and also the bottom left (refer to the
diagram below) of the image capture range.
After the setting is complete, click “OK” button.
There will be 2 times that the image capturing is required in the vision system I/F adjustment
procedure. Set the work piece within the image capture range considering it is placed as far
as possible from the camera as shown in the following diagram.
X-axis
Y-axis
Camera
Work
Camera View Range
Work piece location
for the first shot
Actuator
Actuator
Page 87

81
[Procedure 7] Capture an image of the work piece and input the vision system coordinates (X
coordinate and Y coordinate) detected on the vision system side. After inputting,
click “OK” button.
[Procedure 8] Match a tool head to the detection reference point.
Click “OK” button.
[Reference]
It will be able to make the variance small if putting up a needle on the detection reference
point on the work piece and have a sharp tip on the tool.
Tool Tip
Needle
䊪䊷䉪
Detection reference point is a point (position)
that is output as the work coordinates values
when the work piece is detected on the vision
system side.
Tool Tip
Work
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 88

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
82
[Procedure 9] Click “Acquire” button.
The current robot coordinates (X coordinate and Y coordinate) are acquired.
[Procedure 10] Set a work piece in the range of robot operation and also the top right (refer to the
diagram below) of the image capture range, and then click “OK” button.
X-axis
Y-axis
Camera
Work
Work
Camera View Range
Work piece position
of 1st shot image (before moved)
Actuator
Actuator
Move the work piece
Work piece position
of 2nd shot image (after moved)
Page 89

83
[Procedure 11] Capture an image of the work piece and input the vision system coordinates (X
coordinate and Y coordinate) detected on the vision system side. After inputting,
click “Acquire” button.
[Procedure 12] Match a tool head to the detection reference point.
Click “OK” button.
[Procedure 13] Click “Acquire” button.
The current robot coordinates (X coordinate and Y coordinate) are acquired.
[Procedure 14] Click “Calc.” button.
The result of the vision system offset value calculation is displayed.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 90

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
84
[Procedure 15] Click “Update” button.
Parameters related to the vision system I/F to be adjusted will be updated.
[Procedure 16] Close the window by clicking the “×” button on the top right corner of the window.
[Procedure 17] If the vision system adjustment is implemented, the following dialog box appears
after Vision System I/F adjustment window is closed. Click “Yes” button.
[Procedure 18] A confirmation dialog box appears after the flash ROM writing is complete. Click
“Yes” button.
Page 91

85
5.8.5 When Camera Mounted on Robot
(When camera other than EZ-110XL is used)
This section explains how to setup when the camera is installed on the camera as shown in the
picture below.
When Camera Mounted on Robot
[Procedure 1] Open the Vision System I/F adjustment window from the PC software.
A warning dialog box opens.
Note :
If “Vision System I/F adjustment” is not shown in the main menu, check the version of
PC software or the related I/O parameter settings.
I/O Parameter
No.351 Bit 0-3=1
PC Software Version Capable for Vision
System I/F adjustment
XSEL-P/Q: V7.06.08.00 or later
XSEL-R/S: V9.0.0.0 or later
Camera
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 92

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
86
[Procedure 2] Finish all operations and click “OK” button.
Adjustment vision system I/F selection window appears.
[Procedure 3] Place a tick mark on the check box beside “Robot fixation” and click “OK” button.
Vision System I/F adjustment window opens.
Note :
If no vision system I/F number is displayed, check the parameter settings [5.7
Parameter Settings] on the controller.
Set this to “1”
Page 93

87
[Procedure 4] Confirm the vision system is installed on the camera and click “OK” button.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 94

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
88
[Procedure 5] Click “OK” button.
[Procedure 6] Move the robot to a position closest to the origin within the operation range. Set the
work piece on the top left corner of the image capture range. Click “OK” button after
the setting is complete.
X-axis
Y-axis
Camera
Work
Actuator
Actuator
Camera View Range
for 1st Shot Image
[Procedure 7] Click “Acquire” button.
The current robot coordinates (X, Y and Z coordinates) are acquired.
Page 95

89
[Procedure 8] Capture an image of the work piece and input the vision system coordinates (X
coordinate and Y coordinate) detected on the vision system side. After inputting,
click “OK” button.
[Procedure 9] Move the robot so the work piece is placed on the bottom right corner of the image
capture range.
Click “OK” button after it is moved.
Actuator
Camera
X-axis
Y-axis
Camera
Work
Actuator
Camera View Range
for 1st Shot Image
Camera View Range
for 2nd Shot Image
Move
the
Robot
Work Position in
Camera View Range
for 1st Shot
Work Position in
Camera View Range
for 2nd Shot
Work piece is not to be
physically moved.
Work
Work
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 96

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
90
[Procedure 10] Click “Acquire” button.
The current robot coordinates (X coordinate and Y coordinate) are acquired.
[Procedure 11] Capture an image of the work piece and input the vision system coordinates (X
coordinate and Y coordinate) detected on the vision system side. After inputting,
click “OK” button.
[Procedure 12] Match a tool head to the detection reference point. [Refer to [Procedure 8] in
Section 5.8.4] Click “OK” button.
[Procedure 13] Click “Acquire” button.
The current robot coordinates (X coordinate and Y coordinate) are acquired.
[Procedure 14] Click “Calc.” button.
The result of the vision system offset value calculation is displayed.
Page 97

91
[Procedure 15] Click “Update” button.
Parameters related to the vision system I/F to be adjusted will be updated.
[Procedure 16] Close the window by clicking the “×” button on the top right corner of the window.
[Procedure 17] If the vision system adjustment is implemented, the following dialog box appears
after Vision System I/F adjustment window is closed. Click “Yes” button.
[Procedure 18] A confirmation dialog box appears after the flash ROM writing is complete. Click
“Yes” button.
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 98

5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
92
5.9 Variance Adjustment
Perform the following procedure if the robot is OFF the position in large amount after the movement
to the point above the work piece, and then reboot the system.
1) Set the work piece and perform an operation.
2) Stop the operation once the robot reaches the point above the work piece (Input ABPG
Command after the command to move above the work piece to stop the program), and
measure the distance variance in X-axis and Y-axis directions from the datum point on the work
piece to the robot (and write the values down).
3) Rotate the work piece in 90
q from the posture in Step 1) and execute an operation.
4) Stop the operation once the robot reaches the point above the work piece and measure the
distance variance in X-axis and Y-axis directions from the datum point on the work piece to the
robot (and write the values down).
Distance variance
in Y-axis
Distance variance
in X-axis
Distance variance
in Y-axis
Distance variance
in X-axis
Page 99

93
5) Rotate the work piece in 180
q from the posture in Step 1) and execute an operation.
6) Stop the operation once the robot reaches the point above the work piece and measure the
distance variance in X-axis and Y-axis directions from the datum point on the work piece to the
robot (and write the values down).
7) Draw a circle that goes through the points of the values noted in Steps 1) to 6) an find the
center of the circle.
It will be very easy if using CAD.
8) Figure out the difference [mm] from the origin to the center of the circle in X-axis direction and
Y-axis direction of the robot coordinates.
9) Put the value figured in Step 8) multiplied by 1000 in the parameter.
X-axes : All-Axes Parameters No.126
Y-axes : All-Axes Parameters No.127
10) Rotation axis adjustment is to be conducted by putting values to the following parameters.
Rotation axis : All-Axes Parameters No.128
Distance variance
in Y-axis
Distance variance
in X-axis
X
Y
, and are the points of variance
obtained in Steps 1) to 3).
5. Vision System I/F Function Setting
Page 100

6. Program Construction for Operation
94
6. Program Construction for Operation
6.1 SEL Command
Vision System I/F Function supports 2 types of the dedicated SEL commands listed below.
SEL Command Description
SLVS Selects Vision System I/F to be used
GTVD
Acquires the captured image data (Stores the work data to the
variables and positions)
* [XSEL-P/Q]
Applicable PC soft version: V7.06.08.00 or later (Except for Cognex In-Sight EZ110)
Applicable PC soft version: V7.07.08.00 or later (For EZ-110XL)
[XSEL-R/S]
Applicable PC soft version: V9.0.0.0 or later (Except for Cognex In-Sight EZ110)
Applicable PC soft version: V9.0.0.0 or later (For EZ-110XL)
6.1.1 SLVS (Select Vision System I/F) Command
zSLVS (Select Vision System)
Command and Declaration
Expansion
Condition
(LD,A,O,AB,OB)
Input Condition
(I/O • Flag)
Command and
Declaration
Operation 1 Operation 2
Output section
(Output • Flag)
Free Free SLVS
Select Vision
System I/F
(Timeout time) CC
[Function] Select whether using Vision System I/F in this command (GTVD Command).
Operation 1 : Select Vision System I/F
0 : To use Vision System I/F
1 : Not to use Vision System I/F
Operation 2 : Operation 1=Invalid when set to “0”.······· Prohibited
Operation 1=Except for “0”·······Timeout time (sec) when GTVD Command is
executed
The setting range for the timeout time is from
0.01 to 99.00 sec.
When no indication (Operation 2 = blank) is
defined, the timeout setting is not established
and is set to no limitation.
 Loading...
Loading...