Page 1

ProfiBus
Gateway Unit
RCM-GW-PR
Operation Manual, Second Edition
Page 2

CAUTION
Note on Connecting a PC or Teaching Pendant to the Gateway
Unit Grounded via the Positive Terminal of Its 24-V Power Supply
If the positive terminal of the gateway unit’s 24-V power supply is grounded, use a SIO converter as
shown below to connect a teaching pendant or PC to the gateway unit. In this case, do not connect the FG
of the SIO converter.
Teaching pendant
Do not
connect
the FG.
24-V power
supply
PC, etc.
PC software
RS232 connection type
<Model number: RCM-101-MW>
USB connection type
<Model number: RCM-101-USB>
* The cables are supplied with the
PC software.
Controller link cable
Model number: CB-RCB-CTL002
SIO converter (optional)
(with built-in terminal resistor)
Model number: RCB-TU-SIO-A (B)
* One e-CON connector, one junction
and one terminal resistor are supplied
with each controller link cable.
Gateway unit
e-CON connector (3-1473562-4 by AMP)
Junction (5-1473574-4 by AMP)
Terminal resistor
R = 220Ω
Page 3

If the positive terminal of the gateway unit’s 24-V power supply is grounded, the gateway unit cannot be
connected directly to a teaching pendant or PC.
If a teaching pendant or PC is connected directly to the gateway unit grounded in this cond ition, the
power-supply circuit may be shorted and the PC/teaching pendant may be damaged.
This teaching
pendant cannot be
used this way.
Cannot be connected directly.
CAUTION
Gateway unit
24-V power
supply
Page 4

PfofiBus Gateway
Table of Contents
1. Overview ................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 ProfiBus Gateway Unit ................................................................................................................ 1
1.2 What Is ProfiBus? .................................................................................................................. ...... 2
1.3 Application Example of Gateway Unit ................................................................. ........................ 3
1.4 Features and Key Functions ....................... ................... ................... .................. ....................... .. 4
1.4.1 Features ............................................ ............... ............... ................... ............... .......... ... 4
1.4.2 Key Functions ......................................... ... .... .... .... .... ....... .... .... .... ... .... ........ ... .... .... .... ... ...... 4
1.5 Description of Model Name ......................................................................................................... 7
1.6 Accessories ..................................... ..................................... .................................. ................... .. 7
2. Specifications and Name of Each Part ...................................................................... 8
2.1 General Specifications ................. ................... ................... ...................... ................... ................. 8
2.2 External Dimensions .................................................................................................................... 9
2.3 Name and Function of Each Part ....... .... .... .... .... ... ........ .... ... .... .... .... ....... .... .... ... .... .... .... ....... .... 10
3. Installation and Noise Elimination Measures ........................................................... 16
3.1 Installation Environment. ........................................................................................................... 16
3.2 Supply Voltage ............................................... .... ... .... .... .... ... ........ .... ... .... .... .... ....... .... .... ........... 16
3.3 Noise Elimination Measures and Grounding ............................................................................. 16
3.4 Installation.................................................................................................................................. 18
4. Wiring ...................................................................................................................... 19
4.1 Overall Configuration .......................................... ................................................................... .... 19
4.2 I/O Signals of Gateway Unit ...................................................................................................... 22
4.3 Design of SIO Communication Network (SIO Communication) ................................................ 25
4.3.1 Wiring ........................................ ........ ....... ........ ....... ............ ....... ........ ....... ........ ........... 25
4.3.2 Axis Number Setting ............................. ........................................................................ 33
4.4 How to Connect the Teaching Tool When the Positive Terminal of the 24-V Power Supply Is
Grounded ................................................................................................................................... 34
5. Address Configuration of Gateway Unit ................................. .. ... .. .. .. .. .................... 35
5.1 Position Number Specification Mode ................................... ..................................................... 35
5.1.1 Overall address configuration ........................... ...................... ................... ................... 36
5.1.2 Gateway Control/Status Si gnals ............................................. ................... ................... 37
5.1.3 Assignment for Each Axis ............................................................................................ 40
5.2 Direct Numerical Specification Mode ........................................................................................ 43
5.2.1 Overall Address Configuration .......... .... ... .... .... .... ... .... .... .... ... .... .... .... .... ... .... .... .... ... .... 44
5.2.2 Gateway Control/Status Si gnals ............................................. ................... ................... 46
5.2.3 Assignment for each axis ............................................................................................. 49
5.3 Command Specification Mode...................................................... .... ... .... .... .... .... ....... .... .... .... ... 53
5.3.1 Overall Address Configuration .......... .... ... .... .... .... ... .... .... .... ... .... .... .... .... ... .... .... .... ... .... 55
5.3.2 Gateway Control/Status Si gnals ............................................. ................... ................... 57
5.3.3 Assignment for Each Axis ............................................................................................ 60
5.3.4 Command Area ............................................................................................................ 65
6 Communication Signal Details ................................................................................ 75
6.1 Overview of Communication Signal Timings ............................................................................. 75
6.2 Communication Signals and Operation Timings ....................................................................... 77
6.3 Basic Operation Timings ................. ....... .... .... ... .... .... .... ....... .... .... .... ... .... ........ ... .... .... .... .... ....... 85
Page 5

6.4 Command Transmission .................................................................................. ................... ....... 95
PfofiBus Gateway
7. Building Your Network System ................................................................................ 96
7.1 Procedure ........................................ ................................................................... ....................... 96
7.2 Setting the Controller .......................................... ....... .... .... ... .... .... .... ....... .... .... .... ... .... ............... 97
7.3 Setting the Gateway Unit and PLC Master ..................................................................... ........... 99
7.4 PLC Address Assignment ................................................................. ...................... ................. 100
8. Supported S7 Function Blocks/Functions........................... .. .. .. ... .. .. .. .. .. ... .. .. .. .. .. ... 106
8.1 GW_CTL_11 ............................................................................................................................ 107
8.2 RC_NVC_11 ..................................................................................................................... ....... 108
8.3 RC_ESYNC_00 ................................... ........................................................................... ......... 109
8.4 RC_BCMOVP_00 .................................................................................................................... 110
8.5 RC_READ_00 ........................................ ........ ........... ........ ....... ........ ....... ............ ....... ............. 111
8.6 RC_WRITE_00 ................................................................................................................... ..... 112
8.7 RC_PROM_00 ......................................................................................................................... 113
8.8 RC_PMSL_00 .......................................................................................................................... 113
Appendix 1. Sample Programs for S7-300 .............................................. ... .. .. .. .. .. ... 114
Appendix 2. Supply Format and Use Procedure of FB/FCt ..................................... 117
Page 6

Page 7

PfofiBus Gateway
1. Overview
1.1 ProfiBus Gateway Unit
The ProfiBus Gateway Unit (hereinafter referred to as “ProfiBus Gateway” or “Gateway Unit”) is used to
connect a ProfiBus communication protocol network on which a host programmable controller (hereinafter
“PLC”) operates, to a SIO communication sub-network (Modbus communication protocol) linking ROBO
Cylinder controllers.
The physical standard to which the SI O com mu nic ation network conforms is RS -48 5, an d the s lav e
addresses on this network are 1 through 16.
All data exchanged between the ProfiBus communication network and the Modbus SIO communication
network are tentatively saved in the internal memory of the Gateway Unit, and then transferred cyclically.
The PLC recognizes the G ateway Unit as a remote I/O device.
The Gateway Unit supports PCON-C/CG/SE, ACON-C/CG/SE, SCON-C and ERC2-NP/PN/SE
controllers.
* “Gateway” is a term used in communication networks, referring to a device that converts data to/from
different media and protocols to enable communication be tween networks.
* ProfiBus protocols include ProfiBus-DP for factory automation (FA) and ProfiBus-PA for process
automation (PA). Of these two protoco ls, this ma nua l covers ProfiBus-DP. Accordingly, “Pro fiB us ”
refers to ProfiBus-DP throughout this manual.
Caution
This manual only describes the controls feasible using the Gateway Unit. In the event of any conflict
between this manual and the operation manual for the controller, the content of this manual will
prevail. Refer to the operation manual for each controller for any function, parameter setting, alarm
detail or any other information not described in this manual.
1
Page 8

PfofiBus Gateway
1.2 What Is ProfiBus?
(1) FA communication system
In FA communication, each communication specification varies depending on the communicating
equipment, type of information, and purp os e of c omm unication, among others. In general, however,
the FA communication system is divided into the information level, controller level and field level, as
shown below.
level
Information
FA computer
Controller level Field level
Device level
Robot
Remote
I/O
Motor
driver
Installed
instrument
Solenoid
valve
Sensor level
Limit
switch
(2) Information level
Also called “PLC upper network.” The main purpose of this network level is to transmit production
information, etc., to information terminals. Ethernet is the most commonly used communication
method for the information level.
(3) Controller level
Also called “Inter-PLC network.” This network level often handles real-time information of production lines.
(4) Field level
Also called “PLC lower network.” This network level is mainly used to save wirings for systems
controlled by a single controller. In this sense, this network is regarded as a means for “wire-saving
communication.” The field level is largely divided into the device level and the sensor level.
Key open network
2
Page 9

PfofiBus Gateway
(5) ProfiBus
ProfiBus is an open field network most commonly used in the world today. It was first established
under DIN 19245 (German standard) in Germany in 1989, and standardized under EN 50170
(European standard) in July 1996. In January 2000, ProfiBus became an international standard under
IEC 61158. There are two ProfiBus protocols designed for different purposes: ProfiBus-DP for factory
automation (FA), and ProfiBus-PA for process automation.
This manual covers ProfiBus-DP.
The key features of ProfiBus-DP are as follows:
[1] A field network realizing complete multi-vendor connectivity
[2] Able to send large amounts of data at high speed.
• Up to 244 bytes of data per device
• Maximum baud rate of 12 Mbps
[3] Up to 125 nodes can be connected.
* For details on ProfiBus, refer to the operation manuals for your master unit and PLC.
Along with this manual, also read the operation manual for each controller connected.
This ProfiBus Gateway cannot be used in any way not described as feasible in this manual.
To prevent malfunction, the customer is also advised not to use settings, wirings and other uses other
than those described as feasible in this manual.
1.3 Application Example of Gateway Unit
The network illustrated below gives an application example of the Gateway Unit.
Remote I/O
station
CPU
unit
ProfiBus Gateway
(Remote I/O station)
ProfiBus
unit
(master
station)
Remote I/O
station
SIO communication network (Modbus)
Remote I/O
station
3
Page 10

PfofiBus Gateway
1.4 Features and Key Functions
1.4.1 Features
The ProfiBus gateway unit lets you select a desired operation mode from three modes including the
position number specification mode, direct numerical specification mode and command specification
mode.
(1) Position number specification mode
In this mode, a desired position number is specified to operate the actuator. Up to 16 axes can be
connected. The position data, speed, acceleration/deceleration, etc., must be input to the position
table beforehand.
Although the input/output of various status signals and completed position number can be read, the
current position cannot be monitored in this mode.
(2) Direct numerical specification mode
In the direct numerical specification mode, the position data, speed, acceleration/deceleration,
positioning band and push-current limiting value are specified directly as numeric al values to operate
the actuator.
Various status signals can be input/output and current position data can be read.
There are five patterns in the numerical specification mode, each accommodating a different number
of connected axes.
[1] Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 4 axes can be connected
[2] Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 6 axes can be connected
[3] Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 8 axes can be connected
[4] Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 10 axes can be connected
[5] Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 16 axes can be connected
(3) Command specification mode
In this mode, the actuator can be operated in one of two operation patterns: “positioner operation” in
which a desired position number is specified to operate the actuator, and “simple direct operation”
where only the position data is specified directly as a numerical value and all other items such as the
speed, acceleration/deceleration, positioning band and push-current limiting value are specified via a
position number. As for the axis configurations, these two operation patterns can be used separately
or in combination. If the two patterns are combined, the axis numbers must be assigned sequentially
from the axes used in positioner operation, followed by the axes used in simple direct operation. You
can select the Large mode (160 input bytes, 160 output bytes), Middle mode (128 input bytes, 128
output bytes) or Small mode (64 input bytes, 64 output bytes) depending on the size of the assigned
areas, and up to 16 axes can be connected.
1.4.2 Key Functions
A comparison table of key functions provided by the gateway unit in the respective modes is given on the
following page.
Use this table as a reference in conjunction with the explanation of each operation mode in Chapter 5.
4
Page 11

Key function
Operation by position data specification X (P table specification)
Direct specification of speed and
acceleration/deceleration
Direct specification of positioning band X (P table specification)
Push-motion operation { (P table specification)
Operation by position number specification
Position table enabling
Maximum number of storable position
numbers
Reading of completed position number
Selection of controller PIO pattern X X { *2 X
Zone (parameter) { (2) X { *3 X
Position zone (P table) X X { *4 X
Reading of various status signals
Speed change during movement
Operation at different acceleration and
deceleration
Monitoring of current position *5 X
Sending/receiving of
commands/responses
Reading/writing of P table data X X
Reading of current position *6 X X
Reading of alarm code X X
Command
Broadcasting X X
Number of connectable axes 16 4 6 8 10 16 16 16
Maximum specifiable value of position data P table specification 9999.99 mm 9999.99 mm 9999.99 mm
Mode setting SW1 2 0 4 8 13 12 1 5 9
Gateway I/O bytes
Input 48 28 40 52 64 100 160 128 64
Output 48 52 76 100 124 196 160 128 64
Position number
specification mode
X (P table specification)
{
{
64 - 512 512
{
{ { { {
{ { { {
{ { {
X X
Direct numerical specification
mode
{
{
{
{
X
X
X
{
Positioner operation Simple direct operation
{ (P table rewriting)
{ (P table rewriting) X (P table specification)
{ (P table rewriting) X (P table specification)
{ (P table specification) { (P table specification)
Large mode Middle mode Small mode
Command specification mode
{
{
{ {
{
{ (P table specification)
X
{ {
{
{ {
{ {
{
X
X
{
X
X
*1 P table: Position table
*2 PIO patterns 0 to 4 can be selected.
*3 PIO patterns 1 to 3 are not supported.
*4 PIO pattern 3 is not supported.
*5 In the current position monitoring function, the current position data is assigned to a gateway output signal.
Accordingly, the current position can be read directly from the PLC.
*6 Reading the current position means reading the current position data indirectly with the PLC issuing a read command to the gateway.
PROFIBUS Gateway
Page 12

Command
ifi ti
PfofiBus Gateway
Next, the relationship of the number of positions supported by each controller under each PIO pattern, and
the maximum number of positions that can be stored in the gateway unit, is explained. Take note that the
number of positions may become subject to restrictions.
PIO pattern (Parameter No. 25)
0 1 2 3 4
ERC2
PCON
ACON
SCON
Operation type
Number of positioning
points
Home return signal
Zone signal
Standard
8 3 16 16 - 64
{
{
Solenoid
type
X X X X
P zone signal X X X
Position number
specification mode
Positioner
operation
Simple direct
Command
specification
Gateway control
operation
Operation type
Number of positioning
points
Home return signal
Zone signal
P zone signal
Position number
specification mode
Positioner
operation
Gateway control
Simple direct
Command
specification
operation
8
*1
*1 *3
8 (0)
X
X
- X - - - - 512
Positioning
mode
Teaching
mode
64 64 256 512 7 64
{ { { { { {
{
X X X
{ { {
64 64
*3
64 (0)
*3
64 (1)
- - - - - - 512
Zone
signal
type
{
16
*1
*1 *3
16 (2)
256-point
mode
256
↓
64 *2
*3
256 (2)
Position
zone type
-
X -
{
16
*1
*1 *3
16 (3)
512-point
mode
-
- 64 64
-
Solenoid
mode 1
{ {
X
{ {
512
↓
7 64 64
64 *2
*3
512 (3)
*3
7 (4)
SE
Dedicated
SIO
operation
*3
64 (0)
Dedicated
SIO
operation
*3
64 (0)
{
{
{
Maximum
number of
gateway
positions
512
Maximum
number of
gateway
positions
512
*1 In the operation mode based on position number specification, the number of positions is limited
according to the selected PIO pattern (parameter No. 25). (The gateway can handle more positions.)
*2 Since the gateway can handle 64 positions, the number of controller positions is limited.
*3 In the case of a positioner operation axes operating in the command specification mode, the PIO
pattern selection parameter of the controller must correspond to the I/O pattern set by gateway
control signals PPS0 to PPS2. The numbers of positions shown in parentheses ( ) indicate values set
by PPS0 to PPS2.
6
Page 13

1.5 Description of Model Name
Base model ProfiBus specification
Gateway Unit
1.6 Accessories
[1] Power-supply input connector plug 1 pc
MC1•5/4-ST-3•5 (Phoenix Contact)
[2] SIO communication connector plug 1 pc
MC1•5/6-ST-3•81 (Phoenix Contact)
PfofiBus Gateway
7
Page 14

PfofiBus Gateway
2. Specifications and Name of Each Part
2.1 General Specifications
Item Specification
Power supply
Current consumption 300 mA max.
Communication standard Group 2 only server
Communication specification Master-slave connection Bit strobe
Baud rate 9.6 kbps to 12 Mbps (Set automatically)
Communication cable length (*1) 9.6 kbps 1500 m
ProfiBus specifications
Transmission path configuration IAI’s original multi-drop differential communication
Communication method Half-duplex
Synchronization method Asynchronous
Transmission path type EIA RS485, 2-wire type
Baud rate 230.4 kbps
Error control method No parity bit, CRC (*2)
Communication cable length Total cable length: 100 m max.
specifications
Communication cable Double shielded twisted-pair cable
SIO communication
Connected units 16 axes max.
Ambient operating temperature
Ambient operating humidity 85% RH or below (non-condensing)
Operating ambience Free from corrosive or flammable gases, oil mist or pow der dust
Storage temperature
Storage humidity 90% RH or below (non-condensing)
Environment
Vibration durability 4.9 m/s2 (0.5 G)
Protection class IP20
Weight 480 g or below
*1 Refer to the operation manuals for your master unit and PLC in the case of T-branch communication.
*2 CRC: Cyclic Redundancy Check
A data error detection method commonly used in synchronous transmission.
24 VDC ± 10%
Insulated node of network powered operation type
Polling
Cyclic
500 kbps 400 m
1.5 Mbps 200 m
3 Mbps 200 m
12 Mbps 100 m
(Recommended cable:
HK-SB/20276 X L, 2P X AWG22 by Taiyo E lectric Wire & Ca ble)
0 to 40°C
-10 to 65° C
8
Page 15

2.2 External Dimensions
(Installed dimension)
PfofiBus Gateway
9
Page 16

2.3 Name and Function of Each Part
[1] Gateway Status LEDs
RUN: Normal
G.ER: Error
C.ER: ProfiBus controller error
T.ER: SIO link error
[2] SIO communication status
LEDs
TxD: Sending data
RxD: Receiving data
[3] Mode setting switch
[4] Port switching input
PORT IN: Port switching input
PORT N: N
[5] Controller communication lines
SDA: Communication line
SDB: Communication line
GND: Ground
FG: Frame ground
[10] Port switch
ON: Port ON
OFF: Port OFF
PfofiBus Gateway
[6] ProfiBus communication connector
[7] Termination switch
[8] Address setting switches
X10 and X1 (decimal, 2 digits)
[9] ProfiBus communication Status LEDs
ON: Online
OFF: Offline
ERR: Error
[11] Teaching pendant/PC connector
[12] Power-supply input connector
10
Page 17

PfofiBus Gateway
[1] Gateway stat us LEDs
Indicated status Description
RUN Steady green The Gateway CPU is operating.
Unlit CPU operation is stopped. If this LED does not come on after turning on
the power, the Gateway is experiencing a CPU error.
G.ER Steady red The Gateway is experiencing a CPU error or major shutdown failure.
Unlit Normal state.
C.ER Steady red The ProfiBus module is experiencing an error or the Gateway CPU
cannot recognize the ProfiBus connection. (Check the ProfiBus
communication stat us in [9].)
Even if this LED is lit, the teaching pendant or PC software can still be
connected as long as the RUN LED is lit.
Blinking red While the port is ON, this LED blinks at 1-second intervals.
Unlit Normal state.
T.ER Steady red All axes generated a communication error based on SIO communication
between the ProfiBus gateway and controller.
Blinking red At least one axis generated a communication error based on SIO
communication between the ProfiBus gateway and controller. (No
response, overrun, flaming error or CR C
(*)
error)
Unlit Normal state.
* CRC: Cyclic Redundancy Check
A data error detection method commonly used in synchronous transmission.
[2] SIO communication status LEDs
These LEDs are used to check the communication status between the ProfiBus Gateway and the
controller.
Each LED blinks when the host PLC and controller are not communicating via the ProfiBus Gateway,
or when the controller is communicating with the teaching pendant or PC software connected via the
ProfiBus Gateway.
Indicated status Description
TxD Blinking green
Unlit
RxD Blinking green
Unlit
Sending data (ProfiBus Gateway → Controller)
Not sending data (ProfiBus Gateway → Controller)
Receiving data (Controller → ProfiBus Gateway)
Not receiving data (Controller → ProfiBus Gateway)
11
Page 18

PfofiBus Gateway
[3] Mode setting switch
This switch is used to set the operation mode of the ProfiBus gateway.
Before operating this switch, turn off the ProfiBus gateway power.
If any position between No. 1 and No. 5 is selected, the position table settings of the controller will
become invalid.
SW1 turns ON when tilted
to the right.
{: ON X: OFF
No.
4 3 2 1 Description Output Input
1 X X X X
2 X
{
3
{ {
4
{ {
5
6 X X
7 X X X
8 X
{
9
SW1 I/O bytes
{
X X
X X X
{
X
X X
{
X
{
{
X X
X
{
{
Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 4
axes can be connected
Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 6
axes can be connected
Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 8
axes can be connected
Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 10
axes can be connected
Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 16
axes can be connected
Position-number specification mode,
maximum 16 axes
Command specification mode Large 160 160
Command specification mode Middle 128 128
Command specification mode Small 64 64
52 28
76 40
100 52
124 64
196 100
48 48
[4] External port switching input
The ON/OFF status of the teaching pendant/PC connector port can be switched using external
signals (no-voltage cont act type).
The connector port is enabled when the port switch [10] on the ProfiBus Gateway is OFF. When the
input signal is ON, the port is also ON. (Refer to [10], “Port switch.”)
PORT IN: Port control input
PORT N: Port control input, N side
Use an input current of 7 mA and external si gnals of no-voltage contact type
[5] Controller communication lines
This terminal is used to connect the communication lines to the SIO communication connector.
12
Page 19

PfofiBus Gateway
[6] ProfiBus communication connector
This connector is used to connect the ProfiBus communication lines.
D-sub, 9-pin connector (female)
ProfiBus communication c onnector
Pin No. Signal name Description
1 NC Not connected
2 NC Not connected
3 B-Line Communication line B (RS485)
4 RTS Request to send
5 GND Signal ground (insulated)
6 +5V +5-V output (insulated)
7 NC Not connected
8 A-Line Communication line A (RS485)
9 NC Not connected
Housing Shield
Cable shield
Connected to the frame.
The mating connector (cable end) is not supplied.
[7] Termination switch
A terminal resistor must be provided at the end of the ProfiBus trunk line to prevent bus reflection.
Set the termination switch to the ON position when the ProfiBus Gateway is the terminal module.
However, the switch should be set to the OFF position if an external termination connector is used.
Set the switch to the OFF position if the Gateway is not the terminal module.
[8] Address setting switches
The two rotary switches are used to set a decimal node address in a range of 1 to 99.
X10: Set the 10’s digit of the two-digit decimal address.
X1: Set the 1’s digit of the two-digit decimal address.
This switch is normally set to 2 for the master unit, and 3 or greater for the slave.
13
Page 20

PfofiBus Gateway
[9] ProfiBus status LEDs
The three LEDs of (LINE-) ON, LINE-OFF and ERR on the front face of the board indicate the node
status and network st atu s. (Th e re ma i ning LED is not used.)
These LEDs illuminate in one of two colors (red or green), and each LED indicates a different
monitored status, as shown in the table below.
LED name Color Indicated status Description (meaning of indication)
(LINE-) ON
LINE-OFF
ERR
Green
Red
Red
Lit Online
Unlit Not online
Lit Offline
Unlit Not offline
Blinking at 1-Hz
frequency
Configuration error
Example: The I/O size determined by
Blinking at 4-Hz
frequency
Communication ASIC initialization error
Unlit No error
the mode setting switch [3]
does not match the I/O size
set by the configuration tool.
14
Page 21

PfofiBus Gateway
[10] Port switch
This switch is used to enable the teaching pendant/PC connector (TP) (PORT ON = Start
communication).
Set this switch to the OFF position when connecting/removing the communication cable connector for
teaching pendant or PC software. To use the teaching pendant or PC software, plug in the connector
first, and then set the switch to the OFF position.
(Also check the signal status of the port switching input [4].)
Port switch ON: Power (24 VDC) is supplied to the teaching pendant. The emergency stop circuit
of the teaching pendant is enabled.
Port switch OFF: Power (24 VDC) to the teaching pendant is cut off. The emergency stop circuit of
the teaching pendant is disabled.
The baud rate between the teaching pendant or PC software and ProfiBus gateway can be set to a
maximum of 115.2 kbps. For your information, the baud rate between the ProfiBus gateway and
controller is fixed to 230.4 kbps.
When the port switch is turned ON, no ProfiBus communication error will generate, but the data
exchange via SIO communication will stop. Accordingly, the PLC’s output signals (data) will no longer
be output to the controller and the input signals (data) from the controller will remain as the values
that were effective immediately before the port switch was turned ON.
A PORT ON status signal (TPC) is output from the ProfiBus gateway to the PLC, so provide an
interlock or other process as necessary.
[11] Teaching pendant/PC connector
This connector is used to connect the communication cable connector for teaching pendant or PC
software.
[12] Power-supply input connector
This connector is used to connect the ProfiBus Gateway power (24 VDC).
15
Page 22

PfofiBus Gateway
3. Installation and Noise Elimination Measures
Exercise due caution regarding the installation environment.
3.1 Installation Environment.
a. The Gateway Unit is not dustproof or waterproof (oilproof). Accordingly, avoid using the Gateway
Unit in a dusty place or place where the unit may come in contact with oil mist or splashed
cutting fluid.
b. Prevent the Gateway Unit from receiving direct sunlight or irradiated heat from large heat
sources such as heat treatment ovens.
c. Use the Gateway Unit in an enviro nment of 0 to 40°C in ambient temperature and 85% or below
in humidity (non-condensing) and free from corrosive or flammable gases.
d. Use the Gateway Unit in an environment where the unit will not receive external vibration or
shock.
e. Prevent electrical noise from entering the Gateway Unit or its cables.
3.2 Supply Voltage
24 VDC ± 10% / Current consumption: 300 mA max.
3.3 Noise Elimination Measures and Grounding
a. Installing the Gateway Unit
Connect the Gateway Unit by directly securing it onto a metal enclosure using screws.
* Provide class D (3) grounding for the enclosure.
Use as thick a cable as
possible and connect it
over the shortest possible
distance.
Metal
enclosure
16
Page 23

b. Notes on wiring method
Separate the communication lines of the Gateway Unit and ProfiBus module from lines carrying
large current such as power circuits. (Do not bundle them together or place them in the same
cable duct.)
c. Noise sources and elimination of noise
There are many noise sources, but the ones you should pay most attention to when building
your system are solenoid valves, magnet switches and relays. Noise from these sources can be
eliminated using the following measures.
[1] AC solenoid valves, magnet switches, relays
Measure --- Install a surge killer in parallel with the coil.
[2] DC solenoid valves, magnet switches, relays
Measure --- Install a diode in parallel with the coil. Determine an appropriate diode capacity
in accordance with the load capacity.
In a DC system, connecting the diode in reverse polarities may
damage the diode, internal controller parts, and DC power supply.
Exercise due caution.
+24 V
0 V
PfofiBus Gateway
← Point
Install the surge killer in a location as close as
possible to each coil.
If the surge killer is installed on a terminal block
or away from the coil, its noise elimination
effect will decrease.
17
Page 24

PfofiBus Gateway
3.4 Installation
Examine appropriate settings for the control box size, installation position of the Gateway Unit and cooling
method of the control box, so that the temperature around the Gateway Unit will remain at or below 40°C.
Install the Gateway Unit vertically on a wall, as shown below, and provide a minimum clearance of 50 mm
above and below the unit, with a minimum clearance of 100 mm provided on all sides for wiring access.
If multiple Gateway Units are installed side by side, provide a sufficient space between the adjacent units
so that any unit can be installed and removed easily.
If heat or noise is of concern, also provide appropriate measures.
18
Page 25

4. Wiring
4.1 Overall Configuration
The following is an example of ProfiBus system configuration using the Gateway Unit.
Host system (PLC master)
Gateway
Unit
SIO communication network
Terminal resistor
cable
Controller link
4-way junction
Teaching pendant
PfofiBus Gateway
24-V
power
supply
19
Page 26

PfofiBus Gateway
The ProfiBus network is wired as shown below.
For details on ProfiBus-DP, check the operation manual for the master (PLC) or website of the
Japanese PROFIBUS Organization.
Master
(Node address 2)
Terminal
resistor
Terminal
resistor
Slave
Slave Slave Slave
(Node address 3) (Node address 4) (Node address 5) (Node address 6)
[1] A device connected to a network and assigned an address is called a “node.” A node may be a
master or slave. Up to 32 nodes can be connected to one segment.
[2] It is recommended that the master be connected to one end of the network. Normally the master has
node address 2, while each slave has node address 3 to 32.
Node address 0 is reserved for a monitoring or diagnostic device, while node address 1 is reserved
for a monitoring device.
[3] One segment of the network must have a terminal resistor connected to both ends.
[4] For each ProfiBus cable, use the ProfiBus-DP type A cable specified by the EN 50170 standard. This
cable is a 2-core twisted pair cable with shield.
Cable
Red: Line B (positive side)
Green: Line A (negative side)
Shield
[5] All network connectors should be the D-sub, 9-pin connector specified by the EN 50170 standard.
The network bus connector can be of the screw type shown below or the quick connection type
where the wires are inserted into provided holes.
If the connector has a terminal resistor, turn the
terminal resistor switch ON only for the terminal slave,
and turn the switch OFF for all other slaves.
20
Page 27

PfofiBus Gateway
[6] The ProfiBus gateway connector should be the D-sub, 9-pin (female) connector recommended by the
ProfiBus DP Standard under EN 50170, as shown below.
The network connectors are not supplied.
Pin No. Signal name Description
1 NC Not connected
2 NC Not connected
3 B-Line Communication line B (Positive side)
4 NC Not connected
5 GND Signal ground
6 +5V +5-V output
7 NC Not connected
8 A-Line Communication line A (Negative side)
9 NC Not connected
Housing Shield Cable shield
Caution
The ProfiBus gateway has a built-in terminal resistor setting switch. If the ProfiBus gateway becomes
a terminal module on the network, turn this terminal resistor setting switch ON. If the ProfiBus gateway
is not a terminal module or an external terminal connector is used, turn the switch OFF.
21
Page 28

4.2 I/O Signals of Gateway Unit
(1) Connection diagram
ProfiBus communication
Emergency stop signal output for
teaching pendant
Allowable load voltage: 30 VDC
Allowable load current: 1 A
cable
Teaching pendant
Emergency stop
Gateway power supply
24 VDC ±10%,
300 mA max.
External port switching input
(provided by the customer)
(Load: 24 VDC, 7 mA)
SIO communication
cable
PfofiBus Gateway
Gateway Unit
Teaching pendant/
PC connector
Port switch
22
Page 29

PfofiBus Gateway
(2) Port control and emergency stop signal output
The teaching pendant/PC connector port can be operated by external signals, other than by ON/OFF
switching of the port switch on the Gateway Unit.
While the port is ON, the Gateway Unit outputs contact signals of the emergency stop pushbutton
switch on the teaching pendant. Therefore, you can design an emergency stop circuit or other
protective circuit for the entire system by incorporating these signals.
External port
switching input
Port switch
OFF OFF Disabled (S1 and S2 shorted) Disabled
ON OFF
ON ON
An example of the emergency stop circuit is shown below.
Emergency
stop reset
Emergency stop
button switches
Teaching-pendant emergency stop
signal output
S1, S2 =
Enabled
Teaching pendant
Emergency stop
Gateway power
supply
(24 VDC ± 10%,
300 mA max.)
External port switching input
(provided by the customer)
SIO
communication
cable
Teaching-pendant
emergency stop contacts
ProfiBus
cable
(Load 24 VDC, 7 mA)
Teaching pendant/PC
connector port
Enabled OFF ON
Gateway unit
Teaching pendant/PC
connector
Port switch
23
Page 30

2
24
(3) I/O signal specifications and wires
Symbol Description Specification Connector and applicable wire
Power-supply
SIO communication
ProfiBus
communication
Positive side of the 24-VDC
Gateway power supply
Negative side of the 24-VDC
Gateway power supply
Teaching-pendant
emergency stop signal output
External port switching input
24 VDC ±10%
Power consumption: 300 mA
max.
Allowable load voltage: 30 VDC 0.08 to 1.5 mm2
No-voltage (dry) contact input
Load: 24 VDC, 7 mA
input connector
24 V
N
S1
S2 Allowable load current: 1 A AWG 28 to 16
PORT IN
PORT N
SDA SIO communication line A Align the potential level of the
SDB SIO communication line B
GND Ground
connector
FG Frame ground
B-Line
Communication line B
(RS485)
connected controller or ERC
actuator with the potential level
of the GND (ground).
Internally connected to the
frame.
RTS Request to send
GND Signal ground (insulated)
+5V +5-V output (insulated)
connector
A-Line
Communication line A
(RS485)
0.8 to 1.3 mm
AWG 18 to 16
0.08 to 1.5 mm
AWG 28 to 16
Double shielded twistedpair cable (AWG22)
Recommended cable:
HK-SB/20276 X L
2P X AWG22 by Taiyo
Electric Wire & Cable
ProfiBus-DP type A cable
(2-core twisted pair cable
with shield)
2
The connection plug is a
standard accessory.
MC1.5/4-ST-3 y 5 (Phoenix
Contact)
The connection plug is a
standard accessory.
MC1.5/6-ST-3 y 81 (Phoenix
Contact)
The Gateway Unit has a
built-in terminal resistor, so
connect the terminal resistor
at the end of the SIO
communication line.
The connection plug should
be a D-sub, 9-pin connector,
but this plug is not supplied.
With ProfiBus, a terminal
resistor*1 must be
connected to both ends of
the trunk line. For details,
check the operation manual
for the master (PLC).
*1 The gateway unit has a built-in terminal resistor. Set the terminal switch ON/OFF to enable/disable this built-in terminal resistor.
PROFIBUS Gateway
Page 31

PfofiBus Gateway
4.3 Design of SIO Communication Network (SIO Communication)
4.3.1 Wiring
(1) Basics
Item Description
Number of connected units
Communication cable length Total cable length: 100 m max.
Communication cable
Terminal resistor
16 axes max. (The specific number varies depending on the operation
mode. Refer to 1.4, “Features of Gateway Unit.”)
Double shielded twisted-pair cable (AWG22)
Recommended cable: HK-SB/20276 X L 2P X AWG22
by Taiyo Electric Wire & Cable
220 Ω 1/4 W
Caution
1. Connect the communication path to a bus and always connect a terminal resistor at the end. A
terminal resistor is not needed on the Gateway Unit end, as the unit has a built-in terminal resistor.
2. The customer must provide the communication cable. If the recommended cable is not used, make
sure the size of the cable to be used is AWG22.
(2) Communication connection for PCON, ACON and SCON
SIO communication
trunk line (provided
by the customer)
Gateway Unit
(Built-in terminal resistor)
Axis 1 Axis 2 Axis n
*1 A terminal resistor (220 Ω, 1/4 W) is supplied with the controller link cable.
e-CON connector (4-1473562-4 by AMP, green)
e-CON connector (3-1473562-4 by AMP, orange)
Junction (5-1473574-4 by AMP)
Recommended cable: SB/20276 X L 2P X AWG22
Controller link cable
Terminal resistor *1
25
Page 32
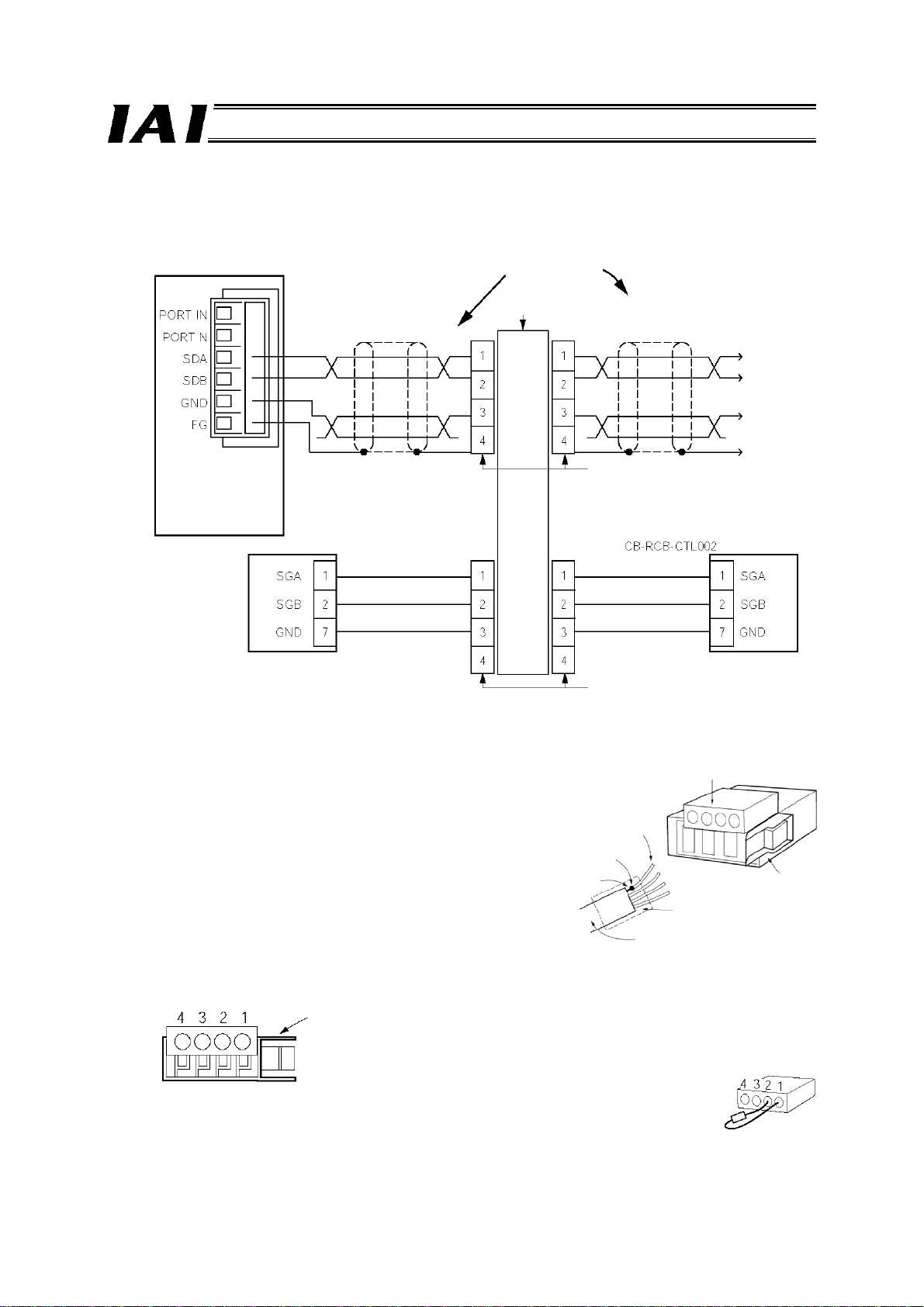
PfofiBus Gateway
a. Detail connection diagram
Details of SIO link connection are illustrated below. Controller link cables are available as options, but
the customer must provide the communication trunk.
Gateway Unit
Double shielded
twisted-pair cable
Recommended cable:
HK-SB/20276 X L
2P X AWG22 by Taiyo
Electric Wire & Cable
Yellow
Orange
Blue
Unit 1 Unit 2
b. Producing a communication trunk
[1] Strip the sheath of a double shielded twisted-pair cable by
approx. 15 to 20 mm.
[2] Twist the shield wires and solder them onto the vinyl
wires of AWG22 or equiv alent.
[3] Place a cable protection tube over the cable.
[4] Insert the core wires, without stripping them, into the
cable insertion holes in the connector (SDA, SDB,
GND, FG).
[5] With the cable inserted in the press-fit cable housing, apply
pressure from above to pressure-weld the core wires.
[6] Heat-treat the cable protection tube.
e-CON connect or pin numbers
Always insert a terminal resistor (220 Ω, 1/4 W) at the end of the communication trunk
(between pins 1 and 2 of the e-CON connector).
Locking tab
SIO communication trunk
4-way junction (5-1473574-4 by AMP)
e-CON connector (4-1473562-4 by AMP)
Housing color: Green
Controller link cable
Yellow
Orange
Blue
e-CON connector (3-1473562-4 by AMP)
Housing color: Orange
e-CON connector
Apply pressure.
Vinyl wire
(AWG22)
Solder
Shield
wire
Cable tube
Double shielded twisted-pair shielded
Locking tab
26
Page 33

c. Controller link cable (CB-RCB-CTL002)
This is an optional cable for the controller. You must purchase this cable separately.
The following parts are supplied with the controller link cable.
[1] 4-way junction Model: 5-1473574-4 by AMP x 1 unit
[2] e-CON connector 4-1473562-4 by AMP x 1 unit
Outer diameter of applicable wire 1.35 to 1.6 mm
[3] Terminal resistor 220 Ω 1/4 W With e-CON connector x 1 unit
Controller end
Mini DIN connector
Signal
Yellow
Orange
Blue
e-CON connector
3-1473562-4
(Housing color: Orange)
Signal
PfofiBus Gateway
27
Page 34

PfofiBus Gateway
(3) SIO communication connection for ERC2-SE
For details, refer to the ERC2-SE operation manual.
Use 4-way junctions to connect the cables as shown below.
The power-supply & I/O cable and network connection cable (including the 4-way junction and eCON connector) are standard accessories of the ERC2-SE.
Gateway unit
Fabricated by
the customer
4-way junction
e-CON connector
Terminal resistor
Network connection cable (CB-ERC2-CTL001)
Power-supply & I/O cable (CB-ERC2-PWBIO)
JST JST
PIO & 24-VDC control power, motor
power, brake signal, ground, shield
Axis 1
Axis 2
Axis 3
Axis 16
Caution
(1) When the total communication cable length is 10 m or longer, communication may not be
established properly and a communication error may occur. In this case, connect a terminal
resistor to the last axis.
(2) If the actuators have different power supplies, use a common line for 0 [V].
(3) Use a common line for 0 [V] for the power supply of the gateway unit and control power supply of
the ERC2.
(4) Connect the shield wire to the FG for each axis.
(5) If the total link cable length exceeds 30 m, use wires with a size of 22AWG or larger.
28
Page 35

(4) SIO communication connection for ERC2-NP/PN
Use relay terminal blocks to connect the cables as shown below.
Gateway unit
Pair shield cable
(fabricated by the
customer)
Terminal resistor
Relay terminal
block
PIO & 24-VDC control power, motor
power, brake signal, ground, shield
Orange
(black 1)
Orange
(red 1)
PfofiBus Gateway
PIO type power-supply & I/O cable
Axis 1
Axis 2
Axis 16
Caution
(1) When the total communication cable length is 10 m or longer, communication may not be
established properly and a communication error may occur. In this case, connect a terminal
resistor to the last axis.
(2) If the actuators have different power supplies, use a common line for 0 [V].
(3) Use a common line for 0 [V] for the power supply of the gateway unit and control power supply of
the ERC2.
(4) Connect the shield wire to the FG for each axis.
(5) If the total link cable length exceeds 30 m, use wires with a size of 22AWG or larger.
29
Page 36

PfofiBus Gateway
(5) Wiring the emergency stop (EMG) circuit
When designing an emerg ency stop circuit that incorporates the emergency stop switch on the teaching
pendant connected to the Gateway Unit, emergency stop signals output from the “S1” and “S2” terminals
of the Gateway Unit can be used.
This way, all connected ROBO Cylinder controllers can be stopped instantly in case of emergency by
operating the emergency stop switch on the teaching pendant connected to the Gateway Unit.
Caution
1. For details on the emergency stop processing of ROBO Cylinders, refer to the operation manual for
your PCON, ACON, SCON or ERC-2 controller.
30
Page 37

y
y
[1] Example of cutting off drive signals
Emergency stop
reset switch
Teaching
pendant
Emergency
stop button
Emergency
stop button
Gatewa
power suppl
Gateway Unit
TP connector
Port
switch
24-VDC input
power supply
(2 A max. per unit)
SIO
communication
SIO connector
Power-supply
terminal block
Power-supply terminal block (unit 2)
Power-supply terminal block (unit 3)
PCON, ACON controller
Motor drive
power
Control
power
PfofiBus Gateway
Connection
detection
signal (H)
EMG signal
detection (H)
Drive stop
signal (L)
Time
cons-
tant
SIO
connector
connection
detection
circuit
Motor
drive
circuit
Caution
The input current specification for the EMG terminal is 5 mA. When connecting the EMG relay CR
contacts to the EMG terminals of multiple controllers, check the current capacity of the relay contacts.
31
Page 38

y
y
[2] Example of cutting off motor drive power
Emergency stop
reset switch
Teaching
pendant
Emergency
stop button
Emergency
stop button
Gatewa
power suppl
Gateway Unit
TP connector
Port
switch
24-VDC input
power supply
(2 A max. per unit)
SIO connector
SIO
communication
PCON, ACON controller
Power-supply
terminal block
Motor drive
power
Control
power
Power-supply terminal block (unit 2)
Power-supply terminal block (unit 3)
Connection
detection
signal (H)
EMG signal
detection (H)
Time
cons-
tant
PfofiBus Gateway
SIO
connector
connection
detection
circuit
Drive stop
signal (L)
Motor
drive
circuit
32
Page 39

PfofiBus Gateway
4.3.2 Axis Number Setting
The following explanation applies to PCON, ACON and ERC2 controllers.
Set an axis number as a SIO-linked slave station number.
The axis number of axis 1 is “0,” while that of axis 16 is “F.” Set an appropriate axis number using a
hexadecimal value between 0 and F.
Axis numbers can be set on the teaching pendant or in the PC software.
~ Operation in the PC software
[1] Open the main window → [2] Click Settings (S) → [3] Bring the cursor to Controller
Settings (C) → [4] Click Assign Axis Number (N) → [5] Enter a number in the axis
number table.
~ Operation on the teaching pendant RCM-T
[1] Open the User Adjustment window → [2] Bring the cursor to Assigned No. using the T key
→ [3] Enter an axis number, and press Enter → [4] Enter “2” under Adjustment No., and
press Enter.
~ Operation on the simple teaching pendant RCM-E
[1] Open the User Adjustment window Æ [2] Press Enter to open the Assigned No. window →
[3] Enter an axis number, and press Enter → [4] Enter “2” under Adjustment No., and press
Enter.
For details on each setting method, refer to the operation manual for your teaching pendant or PC
software.
Caution
1. Each axis number must be unique.
2. Before setting an axis number for a given axis, disconnect the link cable of the applicable axis.
3. Connect a terminal resistor between SGA and SGB on the terminal module.
33
Page 40

PfofiBus Gateway
4.4 How to Connect the Teaching Tool When the Positive Terminal of the
24-V Power Supply Is Grounded
If the positive terminal of the 24-V power supply is grounded (= +24 V is grounded), use a SIO converter
as shown below to connect a teaching pendant or PC to the gateway unit. In this case, do not connect the
FG of the SIO converter.
Teaching pendant
Do not
connect
the FG.
24-V power
supply
With the gateway unit system, the negative terminal of the 24-V power supply should be grounded (= 0 V
should be grounded), as a rule. Since most teaching pendants and PCs have their communication ground
line and FG (frame ground) shorted internally, grounding the positive terminal of the 24-V power supply (=
grounding +24 V) will cause shorting of the 24-V power-supply circuit when a teaching pendant or PC is
connected to the gateway unit, thereby damaging the teaching pendant or PC.
PC, etc.
PC software
RS232 connection type
<Model number: RCM-101-MW>
USB connection type
<Model number: RCM-101-USB>
* The cables are supplied with the
PC software.
Controller link cable
Model number: CB-RCB-CTL002
SIO converter (optional)
(with built-in terminal resistor)
Model number: RCB-TU-SIO-A (B)
* One e-CON c onnector, one junction
and one terminal resistor are supplied
with each controller link cable.
Do not allow the FG of the PC to be connected to
ground. If the FG may be connected to ground via
other COM port, disconnect the communication
cable from the applicable COM port.
Gateway unit
e-CON connector (3-1473562-4 by AMP)
Junction (5-1473574-4 by AMP)
Terminal resistor
Caution
Do not connect the FG of the SIO converter.
34
Page 41

∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
PfofiBus Gateway
5. Address Configuration of Gateway Unit
All data exchanged between the master station and the controller are tentatively stored in the internal
memory of the Gateway Unit, and then transmitted cyclically. Accordingly, the PLC program recognizes
these data as remote ProfiBus I/Os.
Up to 16 ROBO Cylinder controllers can be connected to the Gateway Unit, with the connected controllers
assigned an axis number of 0 to 15, respectively. The Gateway Unit simultaneously sends and receives
data to/from the master station for all ROBO Cylinder controllers connected via SIO link.
As explained in the features of the Gateway unit in section 1.4, controllers can be operated in there major
modes.
In each mode, an address configuration varies as the slave.
5.1 Position Number Specification Mode
In this operation mode, a desired position number in the position table is specified to operate the actuator,
and up to 16 axes can be controlled. The position table must be set for each axis using the PC software or
teaching pendant.
A desired position number is written in the PLC to operate the actuator.
Up to 64 positions from Nos. 0 to 63 can be specified, but the number of positions may be limited
depending on the PIO pattern (PIO pattern selection parameter) specified for each axis.
(Refer to the table in 1.4.2.)
The key functions that can be controlled in this mode are summarized in the table below.
{: Direct control
Key function
Home return operation
Positioning operation
Speed and
acceleration/deceleration setting
Pitch (incremental) feed
Push-motion operation
Speed change during movement
Operation with acceleration and
deceleration set differently
Pause
Zone signal output
PIO pattern selection X *1
*1 Since the number of position is limited according to the PIO pattern selection (parameter No. 25)
specified for each connected controller, specify the position numbers in a manner avoiding
inconsistency. For your information, up to 64 positions can be specified.
∆: Indirect control
X: Disabled
{
∆
{
{
This operation is performed by
specifying a number in the
position table.
Set in the position table.
Set in the position table.
Set in the position table.
This operation is performed by
combining two or more position
numbers. (Refer to the operation
manual for the controller.)
Set in the position table.
Each zone is set by parameters.
Remarks
35
Page 42

PfofiBus Gateway
5.1.1 Overall address configuration
In the position number specification mode, four bytes are used by the gateway control signals, and
also by the status signals, to be input/output. For each axis, each control signal occupies two bytes in
the PLC I/O area, and a total of 48 bytes are occupied by signal inputs, and also by signal outputs,
for the entire gateway unit. The values in parentheses ( ) indicate axis numbers.
Output from PLC ⇒ Gateway Unit ⇒ Input to each axis Output from each axis ⇒ Gateway Unit ⇒ Input to PLC
Upper byte Lower byte
Gateway control signal 0
Gateway control signal 1
Command position
number (0)
Command position
number (1)
Command position
number (2)
Command position
number (3)
Command position
number (4)
Command position
number (5)
Command position
number
(6)
Command position
number (7)
Command position
number (8)
Command position
number (9)
Command position
number (10)
Command position
number (11)
Command position
number (12)
Command position
number (13)
Command position
number (14)
Command position
number (15)
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Control signal (0)
Control signal (1)
Control signal (2)
Control signal (3)
Control signal (4)
Control signal (5)
Control signal (6)
Control signal (7)
Control signal (8)
Control signal (9)
Control signal (10)
Control signal (11)
Control signal (12)
Control signal (13)
Control signal (14)
Control signal (15)
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte
1 byte
* The byte address is indicated as a relative byt e ad dress from the initial byte-address byte of the
gateway.
*
Byte address
Upper byte Lower byte
Gateway status signal 0
Gateway status signal 1
Completed position
number (0)
Completed position
number (1)
Completed position
number (2)
Completed position
number (3)
Completed position
number (4)
Completed position
number (5)
Completed position
number (6)
Completed position
number (7)
Completed position
number (8)
Completed position
number (9)
Completed position
number (10)
Completed position
number (11)
Completed position
number (12)
Completed position
number (13)
Completed position
number (14)
Completed position
number (15)
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Status signal (0)
Status signal (1)
Status signal (2)
Status signal (3)
Status signal (4)
Status signal (5)
Status signal (6)
Status signal (7)
Status signal (8)
Status signal (9)
Status signal (10)
Status signal (11)
Status signal (12)
Status signal (13)
Status signal (14)
Status signal (15)
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
Cannot be used.
36
Page 43

PfofiBus Gateway
5.1.2 Gateway Control/Status Signals
The initial fixed area in the address configuration is used by signals that control the gat eway unit, and
consists of four input bytes and four output bytes.
These signals are used to control the ON/OFF of SIO communication and monitor the SIO communication
status and gateway unit status.
PLC output
Gateway
control signal 0
Gateway
control signal 1
PLC input
Gateway
status signal 0
Gateway
status signal 1
* The byte address is indicated as a relative byt e ad dress from the initial byte-address byte of the
gateway.
Byte address
37
Page 44

PfofiBus Gateway
I/O Signal List
Signal type Byte Bit
Signal
name
SIO link communication will start when this signal is turned ON,
and stop when it is turned OFF.
Do not turn the MON signal ON when CFG15 to 0 (linked axis
connection) are all OFF.
7 MON
+0
Also, do not turn all of CFG15 to 0 OFF when the MON signal
is ON.
If CFG15 to 0 are all turned OFF and the MON signal turned
ON, the Gateway Unit will generate a SIO link error and the
LED (T.ER) on the front face of the unit will illuminate.
These bits cannot be used.
Always set them to OFF (0).
In all other modes, always set these bits to OFF (”0”).
Set the axis number (0 to 16) corresponding to each axis
operated by positioner operation, using a 5-bit binary code. *1
These bits are used in the command specification mode.
In all other modes, always set these bits to OFF (”0”).
Set the I/O pattern (pattern 0 to 4) of the axis using a 3-bit binary code.
*2
PLC output
Control
signal 0
+1
6-0 -
7 NPS4 These bits are used in the command specification mode.
6 NPS3
5 NPS2
4 NPS1
3 NPS0
2 PPS2
1 PPS1
0 PPS0
7 CFG15 Link ON Axis No. 15 Specify the axis number
6 CFG14 14
5 CFG13 13
+2
4 CFG12 12
3 CFG11 11
2 CFG10 10
1 CFG9 9
Control
signal 1
0 CFG8 8
7 CFG7 7
6 CFG6 6
5 CFG5 5
+3
4 CFG4 4
3 CFG3 3
2 CFG2 2
1 CFG1 1
0 CFG0 0
*1 If the mode setting switch (SW1) specifies the command specification mode and NPS0 to NPS4 are
set to 0, all axes will become simple direct operation axes.
*2 For positioner operation axes, only one I/O pattern of 0 to 4 can be specified.
Description
corresponding to each axis to be
linked.
The axis will be connected when the
signal is turned ON (1), and
disconnected when it is turned OFF (0).
ON/OFF switching is permitted even
when the MON signal is ON.
(Cautions)
z Do not turn ON the axis number
signal corresponding to any axis not
physically connected.
z Do not turn ON any axis number
signal other than the specifiable
number selected by the mode
setting switch.
If either of the above conditions is
breached, a SIO link error will occur.
38
Page 45

Signal type Byte Bit
+0
Status
signal 0
PLC input
+1
+2
Status
signal 1
+3
Signal
name
7 RUN
6 G.ER
Gateway Unit normal
output
Gateway Unit error
detection output
SIO-link
5 T.ER
communication error
detection output
4 TPC Port switch ON output
3 MOD4
2 MOD3
1 MOD2
0 MOD1
7 Major V.4
6 Major V.2
5 Major V.1
Mode setting switch 4
ON output
Mode setting switch 3
ON output
Mode setting switch 2
ON output
Mode setting switch 1
ON output
The major version
number is output as a
three-bit binary value.
4 Minor V.16
3 Minor V.8
2 Minor V.4
1 Minor V.2
The major version
number is output as a
five-bit binary value.
0 Minor V.1
7 LNK15 Linked Axis No. 15
6 LNK14 14
5 LNK13 13
4 LNK12 12
3 LNK11 11
2 LNK10 10
1 LNK9 9
0 LNK8 8
7 LNK7 7
6 LNK6 6
5 LNK5 5
4 LNK4 4
3 LNK3 3
2 LNK2 2
1 LNK1 1
0 LNK0 0
PfofiBus Gateway
Description
This signal remains ON while the Gateway
Unit is operating normally.
The signal is synchronized with the
illumination of the LED (RUN) on the front
face of the unit.
This signal turns ON when a major
shutdown failure has been detected.
The signal is synchronized with the
illumination of the LED (G.ER) on the front
face of the unit.
This signal turns ON when a SIO link
communication error has been detected.
The signal is synchronized with the
illumination of the LED (T.ER) on the front
face of the unit.
The status of the port switch on the front
face of the unit is output.
This signal is ON wh ile the por t swi tch i s ON .
The setting status of each pin of the
mode setting switch is output.
When the switch is turned ON, the
applicable bit will turn ON (“1”).
The Gateway version information is output.
You may need to check this information in
certain situations, such as when the
Gateway encountered a problem. Provide
the necessary wiring so that these signals
can be read by the PLC.
Example) If the version is 1.03, the major
version number is “1” (data:
001), while the minor version
number is “3” (data: 00011).
Link connection of an axis selected for
link connection by any one of CFG15
to 0 will become enabled when the
MON signal is turned ON. The signal
corresponding to each axis whose link
connection is enabled turns ON.
39
Page 46

PfofiBus Gateway
5.1.3 Assignment for Each Axis
The input signal and output signal of each axis consist of two bytes each in the PLC I/O area.
Control signals and status signals are ON/OFF signals defined in units of bits.
The command position number or completed position number is handled as a 1-byte (8-bit) binary
data. Specify each command position number within the range of position numbers set by the
controller of each axis.
PLC output
PLC input
Byte address*
Control signal
Command position number
Byte address
Status signal
Completed position number
* Byte: Initial gateway address
n: Axis number (0 to 15)
40
Page 47

PfofiBus Gateway
I/O Signal Details
Signal type Bit
Signal
name
b7 - Cannot be used. b6 - Cannot be used. b5 - Cannot be used. -
Control
signal
b4 SON Servo on command 6.2 (7)
b3 STP Pause command 6.2 (5)
b2 HOME Home return command 6.2 (8)
PLC output
b1 CSTR Start command 6.2 (9)
b0 RES Reset command 6.2 (4)
Command
position
number
6-bit
data
(b5-0)
RC 32
~
PC1
Specify the command position number using a
binary value.*1
b7 EMGS Emergency stop 6.2 (2)
b6 - Cannot be used. b5 PWR Controller ready 6.2 (1)
Status
signal
b4 SV Ready (servo is on) 6.2 (7)
b3 MOVE Moving 6.2 (6)
b2 HEND Home return complete 6.2 (8)
b1 PEND Positioning complete 6.2 (10)
b0 ALM Alarm 6.2 (3)
Zone signal
PLC input
output 2
Zone signal
output 1
Completed
position
number
(alarm
output)
b7
ZONE2
*2
b6 ZONE1
6-bit
data
(b5-0)
PM32
~
PM1
The completed position number and zone signal
status are output. Read the completed position
number as a six-bit binary value.
While an alarm is present (= the ALM signal is ON),
the content of the alarm is output to the completed
position number.
(For the contents of alarms that may be output ,
refer to the table entitled “Alarm List” on the next
page.)
*1 With the ERC2-NP/PN, up to 16 positioning points are supported in PIO control. If the gateway unit is
connected, however, up to 64 points can be specified.
*2 [ZONE2] is not supported by the ERC2-NP/PN.
Description Details
6.2 (11)
6.2 (13)
6.2 (12)
41
Page 48

PfofiBus Gateway
[Alarm List]
The table below summarizes the content of each alarm that may be output by PM8 to PM1 (as a binary
code) while the alarm is present. For details on each alarm, refer to the operation manual for the
controller.
{: ON X: OFF
ALM PM8 PM4 PM2 PM1
Output
code
X - - - - - Normal
{
X X X
{
X X
{
{
X 2 For manufacturer’s use *1
1 For manufacturer’s use *1
Movement command issued with servo off (80)
Position command issued before completion of home
{
X X
{ {
return (82)
3
Absolute position movement command issued before
completion of home return (83)
Movement command issued during home return (84)
{
{
X
X
{
X X 4 PCB inconsistency error (F4)
{
X
{
5 Non-volatile memory write error (F7) *1
Parameter data er ror (A1)
{
X
{ {
X 6
Position data error (A2)
Position command information data error (A3)
{
X
{ {
{ { {
X X X 8 Excessive actual speed (C0)
Excitation detection error (B8)
7
Operation timeout during home return operation (BE)
Overvoltage (C9)
{ {
X X
{
Overheat (CA)
9
Control power-supply voltage error (CC)
Control power-supply voltage low (CE)
{ {
{ {
{ { {
{
X
X
X A For manufacturer’s use *1
{ {
B Position deviation counter overflow (D8)
X X C Servo error (C1)
Open phase A, B (E8)
Open phase A (E9)
{ { {
X
{
Open phase B (EA)
D
RCP2 absolute encoder error detection 1 (ED)
RCP2 absolute encoder error detection 2 (ED)
RCP2 absolute encoder error detection 3 (ED)
{ { { {
X E
CPU error (FA)
FPGA error (FB)
Non-volatile memory write count over (F5)
{ { { { {
F
Non-volatile memory writing timeout (F6)
Non-volatile memory data corrupted (F8)
*1 This error will not generate when the gateway unit is used.
*2 The corresponding alarm code displayed on the PC software or teaching pendant is shown in
parentheses ( ).
Description *2 Remarks
42
Page 49

PfofiBus Gateway
5.2 Direct Numerical Specification Mode
In the direct numerical specification mode, the position data, speed, acceleration/deceleration, positioning
band (push band) and push-current limiting value are specified directly as numerical values to operate the
actuator.
One of five patters can be set according to the maximum number of connected axes. (Mode setting switch
SW1)
Also, the current position data can be read at any time.
The position table need not be set for each axis.
The key functions that can be controlled in this mode are summarized in the table below.
{: Direct control
Key function
∆: Indirect control
X: Disabled
Home return operation
Positioning operation
Speed/acceleration setting
{
{
{
Pitch (incremental) feed X Pitch feed data cannot be processed direc tly.
The host PLC must issue each command by
adding/subtracting the pitch-feed distance
data to/from the current position.
Push-motion operation
Speed change during movement
{
{
Speed data is accepted at the start of
positioning. To change the speed during
movement, therefore, change the speed data
during movement and then restart the
positioning operation.
Operation with acceleration and
deceleration set differently
{
Acceleration/deceleration data is accepted at
the start of positioning. To specify a
deceleration different from the acceleration,
therefore, change the deceleration data during
movement and then restart the pos itio nin g
operation.
Pause
{
Zone signal output X Monitor the current position using the PLC. *1
PIO pattern selection X *2
*1 The current position data does not use strobe signals. Accordingly, to check the current position
using the PLC while the actuator is moving, set a zone and confirm that the data has remained in the
specified zone for at least two scan periods.
*2 Set the PIO pattern selection parameter (No. 25) of the connected controller to 0 (standard type).
(PCON-C/CG, ACON-C/CG, SCON-C, ERC-2NP/PN)
Remarks
43
Page 50

PfofiBus Gateway
5.2.1 Overall Address Configuration
Four bytes are used by the gateway control signals, and also by the status signals, to be input/output.
In the direct numerical specification mode, the control signals of each axis consist of 12 bytes in the
PLC output area (gateway input area) and six bytes in the PLC input area (gateway output area).
The number of controlled axes is set by the mode setting switch (SW1), and the applicable data
areas vary depending on the setting of this switch. The switch settings and corresponding data areas
are shown below.
No.
4 3 2 1 Description Output Input
1 X X X X
2 X
{
3
{ {
4
{ {
5
{: ON X: OFF
SW1 I/O bytes
{
X X
X X X
{
X
X X
Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 4
axes can be connected
Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 6
axes can be connected
Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 8
axes can be connected
Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 10
axes can be connected
Direct numerical specification mode/Up to 16
axes can be connected
52 28
76 40
100 52
124 64
196 100
44
Page 51

)
)
)
)
)
A
The overall address configuration is shown below.
The byte address indicates the initial address of the assigned area in the master.
The values in parentheses ( ) indicate axis numbers.
Byte address
Byte+
Output from PLC ⇒ Gateway Unit
⇒ Input to each axis
Gateway control 0
Gateway control 1
Axis control (0)
Axis control (1)
Axis control (2)
Axis control (3)
Axis control (4)
Axis control (5)
Axis control (6)
Axis control (7)
Axis control (8)
Output from each axis ⇒ Gateway Unit ⇒
Byte+
Input to PLC
Gateway status 0
Gateway status 1
Axis status (0)
Axis status (1)
Axis status (2)
Axis status (3)
Axis status (4)
Axis status (5)
Axis status (6)
Axis status (7)
Axis status (8)
Axis status (9)
Axis status (10)
Axis status (11)
Axis status (12)
Axis status (13)
Axis status (14)
Axis status (15)
Axis control (9)
Axis control (10)
Axis control (11)
Status signal (11
Status signal (11
Current position data (11
Current position data (11
Current position data (11
Cannot be used.
Axis control (12)
Axis control (13)
Axis control (14)
Axis control (15)
Position data specification
(11)
Position data specification
(11)
Position data specification
(11)
Current-limiting value for
push motion
Speed specification
(11)
Speed specification
(11)
(11)
Speed specification
cceleration/deceleration
specification
(11)
Positioning band specification
Positioning band specification
(11)
Positioning band specification
(11)
Control signal (11)
PfofiBus Gateway
Mode No. 1
Mode No. 2
Mode No. 3
Mode No. 4
Mode No. 5
Byte data
Byte data
(11)
(11)
45
Page 52

PfofiBus Gateway
5.2.2 Gateway Control/Status Signals
The initial fixed area in the address configuration is used by signals that control the gat eway unit, and
consists of four input bytes and four output bytes.
These signals are used to control the ON/OFF of SIO communication and monitor the SIO communication
status and gateway unit status.
PLC output
Gateway
control signal 0
Gateway
control signal 1
PLC input
Gateway
status signal 0
Gateway
status signal 1
* The byte address is indicated as a relative byt e ad dress from the initial byte-address byte of the
gateway.
Byte address
46
Page 53

PfofiBus Gateway
I/O Signal List
Signal type Byte Bit
Signal
name
SIO link communication will start when this signal is turned ON,
and stop when it is turned OFF.
Do not turn the MON signal ON when CFG15 to 0 (linked axis
connection) are all OFF.
7 MON
+0
Also, do not turn all of CFG15 to 0 OFF when the MON signal
is ON.
If CFG15 to 0 are all turned OFF and the MON signal turned
ON, the Gateway Unit will generate a SIO link error and the
LED (T.ER) on the front face of the unit will illuminate.
These bits cannot be used.
Always set them to OFF (0).
In all other modes, always set these bits to OFF (”0”).
Set the axis number (0 to 16) corresponding to each axis
operated by positioner operation, using a 5-bit binary code. *1
These bits are used in the command specification mode.
In all other modes, always set these bits to OFF (”0”).
Set the I/O pattern (pattern 0 to 4) of the axis using a 3-bit binary code.
*2
signal 0
PLC output
Control
+1
6-0 -
7 NPS4 These bits are used in the command specification mode.
6 NPS3
5 NPS2
4 NPS1
3 NPS0
2 PPS2
1 PPS1
0 PPS0
7 CFG15 Link ON Axis No. 15 Specify the axis number
6 CFG14 14
5 CFG13 13
+2
4 CFG12 12
3 CFG11 11
2 CFG10 10
1 CFG9 9
Control
signal 1
0 CFG8 8
7 CFG7 7
6 CFG6 6
5 CFG5 5
+3
4 CFG4 4
3 CFG3 3
2 CFG2 2
1 CFG1 1
0 CFG0 0
*1 If the mode setting switch (SW1) specifies the command specification mode and NPS0 to NPS4 are
set to 0, all axes will become simple direct operation axes.
*2 For positioner operation axes, only one I/O pattern of 0 to 4 can be specified.
Description
corresponding to each axis to be
linked.
The axis will be connected when the
signal is turned ON (1), and
disconnected when it is turned OFF (0).
ON/OFF switching is permitted even
when the MON signal is ON.
(Cautions)
z Do not turn ON the axis number
signal corresponding to any axis not
physically connected.
z Do not turn ON any axis number
signal other than the specifiable
number selected by the mode
setting switch.
If either of the above conditions is
breached, a SIO link error will occur.
47
Page 54

Signal type Byte Bit
+0
Status
signal 0
PLC input
+1
+2
Status
signal 1
+3
Signal
name
7 RUN
6 G.ER
Gateway Unit normal
output
Gateway Unit error
detection output
SIO-link
5 T.ER
communication error
detection output
4 TPC Port switch ON output
3 MOD4
2 MOD3
1 MOD2
0 MOD1
7 Major V.4
6 Major V.2
5 Major V.1
Mode setting switch 4
ON output
Mode setting switch 3
ON output
Mode setting switch 2
ON output
Mode setting switch 1
ON output
The major version
number is output as a
three-bit binary value.
4 Minor V.16
3 Minor V.8
2 Minor V.4
1 Minor V.2
The major version
number is output as a
five-bit binary value.
0 Minor V.1
7 LNK15 Linked Axis No. 15
6 LNK14 14
5 LNK13 13
4 LNK12 12
3 LNK11 11
2 LNK10 10
1 LNK9 9
0 LNK8 8
7 LNK7 7
6 LNK6 6
5 LNK5 5
4 LNK4 4
3 LNK3 3
2 LNK2 2
1 LNK1 1
0 LNK0 0
PfofiBus Gateway
Description
This signal remains ON while the Gateway
Unit is operating normally.
The signal is synchronized with the
illumination of the LED (RUN) on the front
face of the unit.
This signal turns ON when a major
shutdown failure has been detected.
The signal is synchronized with the
illumination of the LED (G.ER) on the front
face of the unit.
This signal turns ON when a SIO link
communication error has been detected.
The signal is synchronized with the
illumination of the LED (T.ER) on the front
face of the unit.
The status of the port switch on the front
face of the unit is output.
This signal is ON wh ile the por t swi tch i s ON .
The setting status of each pin of the
mode setting switch is output.
When the switch is turned ON, the
applicable bit will turn ON (“1”).
The Gateway version information is output.
You may need to check this information in
certain situations, such as when the
Gateway encountered a problem. Provide
the necessary wiring so that these signals
can be read by the PLC.
Example) If the version is 1.03, the major
version number is “1” (data:
001), while the minor version
number is “3” (data: 00011).
Link connection of an axis selected for
link connection by any one of CFG15
to 0 will become enabled when the
MON signal is turned ON. The signal
corresponding to each axis whose link
connection is enabled turns ON.
48
Page 55

PfofiBus Gateway
5.2.3 Assignment for each axis
Control and status signals are set using ON (1)/OFF (0) signal bits, while current-limiting value for
push-mode operation and acceleration/deceleration are set using one-byte (eight-bit) hexadecimal
data. Speed, target position data, in-position band and current position data are three-byte (24-bit)
hexadecimal data.
It is recommended that control and status signals be transferred to, and used in, bit registers.
Set a desired current-limiting value for push motion, acceleration/deceleration or speed within the
corresponding range specified for the applicable actuator, while target position data must be inside
the soft stroke limits.
Units: Push-current limiting value = 1%, Acceleration/deceleration = 0.01 G,
Speed = 1/100 mm/sec, Position data/in-position band = 1/100 mm
PLC output = Axis control signal
Byte address
* “Byte+” indicates the Gateway head address,
while n indicates an axis number (0 to 15).
(Sign)
Position data specification (signed 24-bit integer)
Current-limiting value for push motion
Speed specification (24-bit integer)
Acceleration/deceleration specification
Positioning band specification (24-bit integer)
Control signal
49
Page 56

PLC input = Axis status signal
Byte address
* “Byte+” indicates the Gateway head address,
while n indicates an axis number (0 to 15).
Sign
(Sign)
Current position data (signed 24-bit integer)
PfofiBus Gateway
Status signal
Caution
1. Signed 24-bit hexadecimal data output or input from/to the PLC is treated as a negative value when
the most significant bit is “1.” Take note that all these data are treated as normal numerical data
within the PLC.
50
Page 57

I/O Signal Details
Signal type Bit
Target
position
data
Current-
limiting
value for
push
motion
PLC output
Speed
Acceleration/
deceleration
24-bit
24-bit
data
8-bit
data
data
8-bit
data
Signal
name
-
-
-
-
PfofiBus Gateway
Description Details
Set a signed 24-bit integer (unit: 0.01 mm) based on
hexadecimal notation.
Example) To specify +25.4 mm, set “0009ECH”
(“2540” in decimal notation).
z The maximum value that can be set is +9999.99
mm = 999999 (decimal) = 0F423FH (hexadecimal).
z A negative value is indicated by a 2’s complement,
which means that the most significant bit becomes
“1.”
z Set position data within the soft stroke limits.
To set the push force, set the current-limiting value for
push motion as a hexadecimal value (unit: %).
The setting range is from “00H” to “FFH,” with FFH
corresponding to 100%.
Example) To specify 50%, set “7FH” (corresponding
to the decimal value of 127 obtained by
FFH (255) x 50%).
Set a 24-bit integer (unit: 0.01 mm/sec) based on
hexadecimal notation. The maximum value is
“0F423FH” (“999999” in decimal notation).
Example) To specify 200 mm/sec, set “004E20H”
(“20000” in decimal notation).
(Cautions)
If speed is not set or the set speed is “0,” the actuator
will remain stopped. No alarm will generate.
If the set speed is changed to “0” during movement, the
actuator will decelerate to a stop.
Set an eight-bit integer (unit: 0.01 G) based on
hexadecimal notation.
Example) To specify 0.2 G, set “14H” (“20” in decimal
notation).
The maximum value is “C8H” (“200” in decimal
notation) corresponding to 2 G.
(Cautions)
Even if acceleration/deceleration is not set, the setting
of parameter No. 9, “Default acceleration/deceleration”
will not be applied.
6.3 (4)
6.3 (4)
6.3 (4)
6.3 (4)
51
Page 58
Signal type Bit
In-position
band
PLC output
Control
signal
Status
signal
PLC input
Current
position
data
- b7-b0 - Cannot be used. -
PfofiBus Gateway
Signal
name
Set a 24-bit integer (unit: 0.01 mm) based on
Description Details
6.3 (4)
hexadecimal notation.
Example) To specify +25.4 mm, set “0009ECH”
(“2540” in decimal notation).
24-bit
data
-
(Notes)
z Set position data within the soft stroke limits.
z Specify the direction of push-motion operation using
DIR.
z Even if in-position band is not set, the setting of
parameter No. 10, “Default in-position band” will not
be applied.
b7 - Cannot be used. -
Push direction specification
b6 DIR
(0 = Home return direction,
6.3 (4)
1 = Opposite to home return direction)
b5 PUSH Push-motion operation mode specification 6.3 (4)
b4 SON Servo on command 6.2 (7)
b3 STP Pause command 6.2 (5)
b2 HOME Home return command 6.2 (8)
b1 CSTR Start command 6.2 (9)
b0 RES Reset command 6.2 (4)
b7 EMGS Emergency stop status 6.2 (2)
b6 PSFL Missed work 6.3 (4)
b5 PWR Controller ready 6.2 (1)
b4 SV Ready (servo is on) 6.2 (7)
b3 MOVE Moving 6.2 (6)
b2 HEND Home return complete 6.2 (8)
b1 PEND Positioning complete 6.2 (10)
b0 ALM Alarm 6.2 (3)
b7-b0 - Cannot be used. -
The current position data is output as a signed 24-bit
6.3 (4)
integer (unit: 0.01 mm) based on hexadecimal
24-bit
data
-
notation.
Example) To specify +25.4 mm, set “0009ECH”
(“2540” in decimal notation).
A negative value is indicated by a 2’s complement,
which means that the most significant bit becomes “1.”
52
Page 59

PfofiBus Gateway
5.3 Command Specification Mode
In this operation mode, one of two patterns can be combined including one (simple direct operation) where
only the target position data is specified as a numerical value and all other position data are specified via a
position number to operate the actuator, and the other (positioner operation) where the actuator is
operated only by specifying a position number.
You can also use request commands to read/write the position table, monitor the current value, and
broadcast, among others.
Two operation patterns are available: “positioner operation” where the actuator is operated by specifying a
position number, and “simple direct operation” where only the target position data is specified as a
numerical value and all other position data such as the speed, acceleration/deceleration, positioning band
and push-current limiting value are specified via a position number to operate the actuator.
As for the axis configuration, these two operation patterns can be used separately or in combination.
If the two patterns are combined, the axis numbers must be assigned sequentially from the axes used in
positioner operation, followed by the axes used in simple direct operation.
You can select the Large mode (160 input bytes, 160 output bytes), Middle mode (128 input bytes, 128
output bytes) or Small mode (64 input bytes, 64 output bytes) depending on the size of the assigned
areas, and up to 16 axes can be connected.
It is also possible to use request commands to read/write the position table (only in positioner operation),
read the current position, and broadcast (only in positioner operation), among others.
Caution
Although the position table can be rewritten only in positioner operation, remember that the position
table can be rewritten by up to 100,000 times or so.
If the stored positions are not enough, the position table rewrite function can be used to specify
additional positions indirectly as numerical values.
53
Page 60

∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
∆
PfofiBus Gateway
For all items, the top row indicates positioner operation, while the bottom row indicates simple direct
operation.
{: Direct control
Key function
∆: Indirect control
Remarks
X: Disabled
Home return operation
Positioning operation
{
{
Specify the position table number. *1
Specify all positioning data other than the
{ ∆
position in the position table, and specify the
position data and position table number at the
same time.
Speed/acceleration setting
Pitch (incremental) feed
Set in the position table. *1
Set in the position table.
Set in the position table. *1
This operation cannot be processed directly.
X
Issue a command from the host PLC by
adding or subtracting an equal pitch data
to/from the current position.
Push-motion operation
Speed change during movement
Operation with acceleration and
deceleration set differently
Pause
Zone signal output
∆
∆
{
{
{
Set in the position table. *1
Set in the position table.
This operation is performed by combining two
or more position table numbers. (Refer to the
operation manual for the controller.)
Set in the position table. *1
Set in the position table.
A zone is set in the position table or using
parameters. *2
The current position data is constantly output
X
from the gateway, so have the PLC monitor
the current position data. *3
PIO pattern selection
{
*4
X *5
*1 You can use request commands (position table data write commands) to write (rewrite) data in the
position table from the PLC. In this case, you must write the necessary data in the position table
beforehand.
*2 The current position data can be read via request commands, but it is not constantly output.
*3. The current position data does not use strobe signals. Accordingly, to check the current position
using the PLC while the actuator is moving, set a zone and confirm that the data has remained in the
specified zone for at least two scan periods.
*4 The PCON-SE, ACON-SE and ERC2-SE do not provide the PIO pattern selection parameter (No.
25).
54
Page 61

PfofiBus Gateway
5.3.1 Overall Address Configuration
Input/output Gateway control signals consist of four bytes each. Only in this mode, PPS0 to PPS2
and NPS0 to NPS4 of control signal 0 are used to set the pattern and number of position-number
specification axes. The subsequent 14 bytes constitute the command input/output area, and a total of
18 bytes each for input and output, including the Gateway control signals and command area,
constitute the fixed area.
The control area is assigned after the fixed area for each axis. Address assignment is performed from
position-number specification axes first, followed by simple direct mode axes.
Assign the signals so that no gaps remain between the areas of adjacent axes.
The total I/O area size of the Gateway varies in accordance with the setting of the mode setting
switch SW1, as shown in the table below.
Mode
No.
4 3 2 1
7 X X X
8 X
{
9
Up to 16 axes, including positioner operation axes and simple direct operation axes, can be assigned
within the range specified in the table above.
The control signals of each axis occupy two input bytes and two output bytes in the case of a
positioner operation axis, or six PLC input bytes and eight PLC output bytes in the case of a simple
direct operation axis.
An example of assigning four positioner operation axes and four simple direct operation axes to be
operated in the Small mode is shown on the following page.
SW1
{
X
X X
- Total I/O area Fixed area
{
Large mode 160 bytes each
{
Middle mode 128 bytes each 110 bytes each
{
Small mode 64 bytes each 46 bytes each
18 bytes each
142 bytes each
Axis control
area
55
Page 62

A
PfofiBus Gateway
Example of Address Configuration
Gateway
control
area
Command
Command
I/O area
I/O area
2 bytes
8 bytes
Small mode
(64 bytes)
Output from PLC ⇒ Gateway Unit
⇒ Input to each axis
Byte
address
Upper byte Lower byte
Gateway control signal 0
Gateway control signal 1
Request command
Data 0
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
Data 4
Data 5
Positioner operation axis (0) control signal
Positioner operation axis (1) control signal
Positioner operation axis (2) control signal
Positioner operation axis (3) control signal
Simp l e d i r ec t o p er a t i on axis (4)*2 control signal
Simple direct operation axis (5) c o n t r o l s i gnal
Simple direct operation axis (6) c o n t r o l s i gnal
Simple direct operation axis (7) c o n t r o l s i gnal
Cannot be used.
Output from each axis ⇒ Gateway Unit
Positioner operation axis (0) status signal
Positioner operation axis (1) status signal
Positioner operation axis (2) status signal
Positioner operation axis (3) status signal
Simple direct oper at ion axis (4) status signal
Simple direct operation axis (5) status signal
Simple direct operation axis (6) status signal
Simple direct operation axis (7) status signal
⇒ Input to PLC
Upper byte Lower byte
Gateway status signal 0
Gateway status signal 1
Response command
Data 0
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
Data 4
Data 5
Cannot be used.
Fixed
area
2 bytes
6 bytes
xis control
area
Middle mode
(128 bytes)
Large mode
(160 bytes)
*1 The byte address Byte+ indicates a relative address from the initial byte address of the gateway.
*2 The numbers in parentheses ( ) indicate axis numbers on the SIO communication network.
56
Page 63

PfofiBus Gateway
5.3.2 Gateway Control/Status Signals
The initial fixed area in the address configuration is used by signals that control the gateway unit, and
consists of four input bytes and four output bytes.
These signals are used to control the ON/OFF of SIO communication and monitor the SIO communication
status and gateway unit status.
PLC output
Gateway
control signal 0
Gateway
control signal 1
PLC input
Gateway
status signal 0
Gateway
status signal 1
* The byte address is indicated as a relative byt e ad dress from the initial byte-address byte of the
gateway.
Byte address
57
Page 64

PfofiBus Gateway
I/O Signal List
Signal type Byte Bit
Signal
name
SIO link communication will start when this signal is turned ON,
and stop when it is turned OFF.
Do not turn the MON signal ON when CFG15 to 0 (linked axis
connection) are all OFF.
7 MON
+0
Also, do not turn all of CFG15 to 0 OFF when the MON signal
is ON.
If CFG15 to 0 are all turned OFF and the MON signal turned
ON, the Gateway Unit will generate a SIO link error and the
LED (T.ER) on the front face of the unit will illuminate.
These bits cannot be used.
Always set them to OFF (0).
In all other modes, always set these bits to OFF (”0”).
Set the axis number (0 to 16) corresponding to each axis
operated by positioner operation, using a 5-bit binary code. *1
These bits are used in the command specification mode.
In all other modes, always set these bits to OFF (”0”).
Set the I/O pattern (pattern 0 to 4) of the axis using a 3-bit binary code.
*2
signal 0
PLC output
Control
+1
6-0 -
7 NPS4 These bits are used in the command specification mode.
6 NPS3
5 NPS2
4 NPS1
3 NPS0
2 PPS2
1 PPS1
0 PPS0
7 CFG15 Link ON Axis No. 15 Specify the axis number
6 CFG14 14
5 CFG13 13
+2
4 CFG12 12
3 CFG11 11
2 CFG10 10
1 CFG9 9
Control
signal 1
0 CFG8 8
7 CFG7 7
6 CFG6 6
5 CFG5 5
+3
4 CFG4 4
3 CFG3 3
2 CFG2 2
1 CFG1 1
0 CFG0 0
*1 If the mode setting switch (SW1) specifies the command specification mode and NPS0 to NPS4 are
set to 0, all axes will become simple direct operation axes.
*2 For positioner operation axes, only one I/O pattern of 0 to 4 can be specified.
Description
corresponding to each axis to be
linked.
The axis will be connected when the
signal is turned ON (1), and
disconnected when it is turned OFF (0).
ON/OFF switching is permitted even
when the MON signal is ON.
(Cautions)
z Do not turn ON the axis number
signal corresponding to any axis not
physically connected.
z Do not turn ON any axis number
signal other than the specifiable
number selected by the mode
setting switch.
If either of the above conditions is
breached, a SIO link error will occur.
58
Page 65

Signal type Byte Bit
+0
Status
signal 0
PLC input
+1
+2
Status
signal 1
+3
Signal
name
7 RUN
6 G.ER
Gateway Unit normal
output
Gateway Unit error
detection output
SIO-link
5 T.ER
communication error
detection output
4 TPC Port switch ON output
3 MOD4
2 MOD3
1 MOD2
0 MOD1
7 Major V.4
6 Major V.2
5 Major V.1
Mode setting switch 4
ON output
Mode setting switch 3
ON output
Mode setting switch 2
ON output
Mode setting switch 1
ON output
The major version
number is output as a
three-bit binary value.
4 Minor V.16
3 Minor V.8
2 Minor V.4
1 Minor V.2
The major version
number is output as a
five-bit binary value.
0 Minor V.1
7 LNK15 Linked Axis No. 15
6 LNK14 14
5 LNK13 13
4 LNK12 12
3 LNK11 11
2 LNK10 10
1 LNK9 9
0 LNK8 8
7 LNK7 7
6 LNK6 6
5 LNK5 5
4 LNK4 4
3 LNK3 3
2 LNK2 2
1 LNK1 1
0 LNK0 0
PfofiBus Gateway
Description
This signal remains ON while the Gateway
Unit is operating normally.
The signal is synchronized with the
illumination of the LED (RUN) on the front
face of the unit.
This signal turns ON when a major
shutdown failure has been detected.
The signal is synchronized with the
illumination of the LED (G.ER) on the front
face of the unit.
This signal turns ON when a SIO link
communication error has been detected.
The signal is synchronized with the
illumination of the LED (T.ER) on the front
face of the unit.
The status of the port switch on the front
face of the unit is output.
This signal is ON wh ile the por t swi tch i s ON .
The setting status of each pin of the
mode setting switch is output.
When the switch is turned ON, the
applicable bit will turn ON (“1”).
The Gateway version information is output.
You may need to check this information in
certain situations, such as when the
Gateway encountered a problem. Provide
the necessary wiring so that these signals
can be read by the PLC.
Example) If the version is 1.03, the major
version number is “1” (data:
001), while the minor version
number is “3” (data: 00011).
Link connection of an axis selected for
link connection by any one of CFG15
to 0 will become enabled when the
MON signal is turned ON. The signal
corresponding to each axis whose link
connection is enabled turns ON.
59
Page 66

PfofiBus Gateway
5.3.3 Assignment for Each Axis
The I/O signals of each axis vary in terms of the size and content of each applicable area depending
on whether the axis is a positioner operation axis or simple direct operation axis.
(1) Control/status signals for positioner operation axis
Each axis consists of two PLC output (control signal) bytes and two PLC input (status signal) bytes,
as shown below. Five patterns are available depending on the PIO pattern set by the gateway control
signal PPS.
Pattern 0
(standard mode)
Pattern 1
(teaching mode)
Pattern 2
(256 positioning
points)
PLC output PLC input
Pattern 3
(512 positioning
points)
Pattern 4
(solenoid mode
1)
Pattern 0
(standard mode)
Pattern 1
(teaching mode)
Pattern 2
(256 positioning
points)
Pattern 3
(512 positioning
points)
Pattern 4
(solenoid mode
1)
* Byte address A: Gateway head address + 18 + 2n
n: Axis number assigned to a positioner operation axis (0 or greater)
Byte address
60
Page 67
I/O Signal Details
Signal type Bit
Control
signal
PLC output
Command
position
number
Status
signal
PLC input
Completed
position
number
b7-b0 PC*** 0 to 3
b6-b0 ST0-ST6 4
b7 to b0 PM*** 0 to 3
b6 to b0
PfofiBus Gateway
Signal
name
Pattern No. Description Details
b7 SON 0 to 4 Servo on command 6.2 (7)
b6 RES 0 to 4 Reset command 6.2 (4)
b5
CSTR 0, 2, 3 Start command 6.2 (9)
PWRT 1 Position data load command TEAC 6.2 (17)
b4 STP 0 to 4 Pause command 6.2 (5)
b3 HOME 0 to 4 Home return command 6.2 (8)
b1 BKRL 0, 2 to 4 Forced brake release 6.2 (18)
b1 JOG- 1 Jog- command 6.2 (14)
b0 JOG+ 1 Jog+ command 6.2 (14)
b7 JISL 1 Jog/inching switching 6.2 (15)
b6 MOD 1 Teaching mode command 6.2 (16)
Specify the command position number
using a binary value.
Specify the start position using a bit
pattern.
6.2 (11)
b7 BALM 0 to 4 Battery voltage low alarm
b6 ALM 0 to 4 Alarm 6.2 (3)
b5 EMGS 0 to 4 Emergency stop 6.2 (2)
b4 SV 0 to 4 Ready (servo is on) 6.2 (7)
b3 PEND 0, 2 to 4 Positioning complete 6.2 (10)
b3 WEND 1
Position data load command status
TEAC
6.2 (17)
b2 HEND 0 to 4 Home return complete 6.2 (8)
b1 RMDS 0 to 4 Operation mode status
b0 PZONE 0 to 2, 4 Position zone output monitor
b7 ZONE1 0, 4 Zone output monitor 1
6.2 (13)
b7 MODS 1 Teaching mode status 6.2 (16)
b6 MOVE 0, 1 Moving 6.2 (6)
PE0 to
PE6
4
The completed position number is read
as a binary value.
The completed position is read as a bit
pattern.
6.2 (12)
61
Page 68

PfofiBus Gateway
(2) Control/status signals for simple direct operation axis
Each axis consists of eight PLC output (control signal) bytes and six PLC input (status signal) bytes,
as shown below.
The position data specification and current position data signals use singed 32-bit hexadecimals
based on integers that are multiples of 0.01 mm.
PLC output = Control signal
Byte address*
PLC input = Status signal
Byte address
* Byte address
B: Initial address of simple direct operation axis
m: Axis number assigned only to a simple direct operation axis (0 or greater), indicating each axis as the
nth axis from the first simple direct operation axis.
(Sign)
Position data specification (signed 32-bit integer)
Movement data position number
Control signal
(Cannot be used)
(Sign)
Current position data (signe d 32-bit integer)
Status signal
Status signal
62
Page 69

I/O Signal Details
Signal type Bit
Movement
PLC output
PLC input
Target
position
data
data
position
number
Control
signal
Current
position
data
Status
signal
32-bit
16-bit
B6-b5 - Cannot be used.
b7-b0 - Cannot be used.
32-bit
b7-b1 - Cannot be used.
PfofiBus Gateway
Signal
name
Description Details
Set a signed 32-bit integer (unit: 0.01 mm) based on
hexadecimal notation.
Example) To specify +25.4 mm, set “0009ECH”
(“2540” in decimal notation).
z The maximum value that can be set is +9999.99
data
-
mm = 999999 (decimal) = 0F423FH
(hexadecimal).
6.3 (5)
z A negative value is indicated by a 2’s complement,
which means that the most significant bit becomes
“1.”
z Set position data within the soft stroke limits.
All movement data, other than the position data to be
specified, must set in the position table. Specify a
desired position number as a hexadecimal code.
6.3 (5)
data
PC1 to
PC32768
B7 BKRL Forced brake release 6.2 (18)
b4 SON Servo on command 6.2 (7)
b3 STP Pause command 6.2 (5)
b2 HOME Home return command 6.2 (8)
b1 CSTR Start command 6.2 (9)
b0 RES Reset command 6.2 (4)
The current position data is output as a signed 32-bit
data
-
integer (unit: 0.01 mm) based on hexadecimal
notation.
6.3 (5)
PIO/Modbus switching status
b0 PMSS
0: PIO, 1: Modbus
A PIO/Modbus switching command is used to switch
between the two modes.
b7 EMGS Emergency stop status 6.2 (2)
b6 PSEL Missed work (6.3 (4))
b5 PWR Controller ready 6.2 (1)
b4 SV Ready (servo is on) 6.7 (7)
b3 MOVE Moving 6.2 (6)
b2 HEND Home return complete 6.2 (8)
b1 PEND Positioning complete 6. 2 (10)
b0 ALM Alarm 6.2 (3)
63
Page 70

PfofiBus Gateway
Caution
The corresponding “default parameter value” will not be applied to any movement data that must be
specified directly as a numerical value from the PLC. Accordingly, take note that the actuator will not
operate or an alarm will generate when any such movement data is not specified as a numerical value.
The table below summarizes the method for specifying movement data in each operation mode.
Specified data
Mode
Position number
specification
Position Position table
Speed
Acceleration/
deceleration
Positioning band
Push-current
limiting value
Position table
(Parameter) *1
Position table
(Parameter) *1
Position table
(Parameter) *1
Position table
Direct numerical
specification
PLC numerical
specification
PLC numerical
specification
PLC numerical
specification
PLC numerical
specification
PLC numerical
specification
Positioner operation
*1 (Parameter) indicates that the default parameter value will be applied when the applicable data is not
set in the position table.
Command specification
Simple direct
operation
Position table
Position table
(Parameter) *1
Position table
(Parameter) *1
Position table
(Parameter) *1
PLC numerical
specification
Position table
(Parameter) * 1
Position table
(Parameter) * 1
Position table
(Parameter) * 1
Position table Position table
64
Page 71

PfofiBus Gateway
5.3.4 Command Area
In the command specification mode, command areas are provided to let you use the various
commands explained below to read/write the position table, among others.
(1) Address configuration
The request command area and response command area consist of 14 bytes each in the range of
(Byte+ 04) to (Byte+ 17).
Output from PLC ⇒ Gateway Unit
⇒ Input to each axis
Upper byte Lower byte Upper byte Lower byte
Request command
Data 0
Data 1
Data 2
Data 3
Data 4 (RSV)*2
Data 5 (RSV)*2
Output from each axis ⇒ Gateway Unit
⇒ Input to PLC
Response command
Data 0
Data 1*3 (Error code)
Data 2
Data 3
Data 4 (RSV)*2
Data 5 (RSV)*2
Caution
If a command code is not synchronized with related data, the command does not function properly.
With Siemens’s S7 Series PLC, synchronicity (consistency) of ProfiBus I/Os is normally guaranteed
only in units of bytes and words. To handle data spanning multiple words synchronously, an applicable
item must be set to ensure data consistency in the STEP 7’s HW Config screen (refer to7.4 (5),
“Setting for I/O data consistency) and the SFC14 and SFC15 must be used (used in the command
function blocks explained in 8).
*1 Byte+ indicates a relative byte address from the initial byte address of the gatew ay.
*2 Data 4 (RSV) and data 5 (RSV) are not currently used.
*3 If a command error occurs, the most significant bit (b7) of the upper byte of the response command
will turn ON and the applicable error code specified in (4) will be set in response data 1.
65
Page 72

(2) Command list
The available commands and commands are listed below.
Function category Code Description
Handshake 0000H Clear a request command.
Position table data
write
Position table data
read
Writing of position
table data to ROM
Present alarm code
read
Current value monitor 0440H Monitor the current position of a specified
Group broadcast
operation
PIO/Modbus control
authority switching
{: Available X: Not available
1000H Write a target position.
1001H Write an in-position band.
1002H Write a speed.
1003H Write a positive boundary for each zone.
1004H Write a negative boundary for each zone.
1005H Write an acceleration.
1006H Write a deceleration.
1007H Write a current-limiting value for push
motion.
1008H Write a load current threshold.
1040H Read a target position.
1041H Read an in-position band.
1042H Read a speed.
1043H Read a positive boundary for each zone.
1044H Read a negative boundary for each zone.
1045H Read an acceleration.
1046H Read a deceleration.
1047H Read a current-limiting value for push
motion.
1048H Read a load current threshold.
0DA0H POS writing coil write
02E0H POS writing complete coil read
0342H
Read an alarm code currently present.
axis.
0D03H Cause all axes in a group to start moving to
the same POS number.
0DA1H
Switch between PIO and Modbus. x
Positioner
operation
axis
{ {
{
{
{
{ {
{ {
{
PfofiBus Gateway
Positioner
operation
axis
x
x
X
X
{
66
Page 73

(3) Each command and data format
[1] Position table data write commands
Command name Byte+*1 PLC output (request) PLC input (response)
Target position write +4 1000H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
8 Position data *2
10
12 Axis number 0 to FH *3
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
In-position write +4 1001H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
8 In-position band data *4
10
12 Axis number 0 to FH *3
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
Speed write +4 1002H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
8 Speed data *4
10
12 Axis number 0 to FH *3
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
Each zone positive
boundary write
+4 1003H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
8 Position data *2
10
12 Axis number 0 to FH *3
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
Each zone negative
boundary write
+4 1004H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
8 Position data *2
10
12 Axis number 0 to FH *3
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
Acceleration write +4 1005H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
8 Acceleration data *5
10 0
12 Axis number 0 to FH *3
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
request command if normal.
request command if normal.
request command if normal.
request command if normal.
request command if normal.
request command if normal.
PfofiBus Gateway
67
Page 74

PfofiBus Gateway
Command name Byte+*1 PLC output (request) PLC input (response)
Deceleration write +4 1006H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
request command if normal.
8 Deceleration data *5
10 0
12 Axis number 0 to FH *3
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
Push motion currentlimiting value write
+4 1007H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
0000 to 00FFH
8
(00FFH: maximum current)
request command if normal.
10 0
12 Axis number 0 to FH *3
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
Load current threshold
write
+4 1008H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
0000 to 00FFH
8
(00FFH: maximum current)
request command if normal.
10 0
12 Axis number 0 to FH *3
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
*1 Relative byte address recognized with respect to the Gateway head address
*2 Signed 32-bit integer data
*3 Data 00 to 0FH correspond to axis numbers (0) to (15), respectively.
*4 32-bit integer data
*5 Eight-bit integer data
*6 This command is effective only with those position table numbers for which a push-current
limiting value (push-motion operation setting) other than 0 has been set.
68
Page 75

[2] Position table data read commands
Command name Byte+*1 PLC output (request) PLC input (response)
Target position read +4 1040H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
request command if normal.
8 0 Target position data *3
10 0
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2 Same as the value in the
14 (RSV)
request command if normal.
16 (RSV)
In-position band read +4 1041H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
request command if normal.
8 0 In-position band data *4
10 0
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2 Same as the value in the
14 (RSV)
request command if normal.
16 (RSV)
Speed read +4 1042H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
request command if normal.
8 0 Speed data *4
10 0
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2 Same as the value in the
14 (RSV)
request command if normal.
16 (RSV)
Each zone positive
boundary read
+4 1043H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
request command if normal.
8 0 Positive boundary data for
10 0
each zone *3
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2 Same as the value in the
14 (RSV)
request command if normal.
16 (RSV)
Each zone negative
boundary read
+4 1044H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
request command if normal.
8 0 Negative boundary data for
10 0
each zone *3
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2 Same as the value in the
14 (RSV)
request command if normal.
16 (RSV)
Acceleration read +4 1045H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
request command if normal.
8 0 Acceleration data *5
10 0 Same as the value in the
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2
request command if normal.
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
PfofiBus Gateway
69
Page 76

PfofiBus Gateway
Command name Byte+*1 PLC output (request) PLC input (response)
Deceleration read +4 1046H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
request command if normal.
8 0 Deceleration data *5
10 0 Same as the value in the
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2
request command if normal.
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
Current-limiting value
read *6
+4 1047H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
8 0
request command if normal.
0000 to 00FFH
(00FFH: maximum current)
10 0 Same as the value in the
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2
request command if normal.
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
Load current threshold
read
+4 1048H Same as the value in the
6 Position number
8 0
request command if normal.
0000 to 00FFH
(00FFH: maximum current)
10 0 Same as the value in the
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2
request command if normal.
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
*1 Relative byte address recognized with respect to the Gateway head address
*2 Data 00 to 0FH correspond to axis numbers (0) to (15), respectively.
*3 Signed 32-bit integer data
*4 32-bit integer data
*5 8-bit integer data
*6 This command is effective only with those position table numbers for which a push-current
limiting value (push-motion operation setting) other than 0 has been set.
70
Page 77

[3] Position table data ROM write command
Command name Byte+*1 PLC output (request) PLC input (response)
Position table data
ROM writing coil write
+4 0DA0H Same as the value in the
6 0
request command if normal.
8 0
10 0
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
Position table data
ROM writing complete
coil read
+4 02E0H Same as the value in the
6 0
request command if normal.
8 0 00FFH = Writing ROM
0000H = ROM writing
complete
10 0 Same as the value in the
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2
request command if normal.
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
*1 Relative byte address recognized with respect to the Gateway head address
*2 Data 00 to 0FH correspond to axis numbers (0) to (15), respectively.
[4] Present alarm code read command
Command name Byte+*1 PLC output (request) PLC input (response)
Alarm code currently
present read
+4 0342H Same as the value in the
6 0
request command if normal.
8 0 Alarm code
10 0 Same as the value in the
12 Axis number 0 to FH *2
request command if normal.
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
*1 Relative byte address recognized with respect to the Gateway head address
*2 Data 00 to 0FH correspond to axis numbers (0) to (15), respectively.
PfofiBus Gateway
71
Page 78

[5] Current position read command
Command name Byte+*1 PLC output (request) PLC input (r esponse)
Monitor the current
position of a specified
axis.
+2 0440H Same as the value in the
3 0
request command if normal.
4 0 Current position of the
5 0
specified axis*3
(32-bit signed integer)
6 Axis number 0 to FH *2
7 (RSV)
8 (RSV)
*1 Relative byte address recognized with respect to the Gateway head address
*2 Data 00 to 0FH correspond to axis numbers (0) to (15), respectively.
*3 Signed 32-bit integer data set in units of 0.01 mm
PfofiBus Gateway
72
Page 79

PfofiBus Gateway
[6] Group specification broadcast command
The axes specified by the group number are started simultaneously to the position specified by the
position number.
When this command is issued, the Gateway and each controller communicate in the broadcast
mode, meaning that the controller does not return any response.
The response result indicated by the PLC input only means that the command has been sent
successfully to the applicable controllers; it does not indicate the status of each controller. Check the
status signal of each axis to determine if the command was executed successfully.
Byte+ PLC output (request) PLC input (response)
+4 0D03H Same as the value in the request
6 Position number *1
command if normal.
8 Group ID number *2
10 0
12 0
14 (RSV)
16 (RSV)
*1 Values that can be specified vary depending on the type and settings of the applicable ROBO
Cylinder controller.
*2 If this number is “0,” all linked axes will move regardless of the group specification.
A desired group number can be set using the applicable system parameter in the PC software.
Caution
1. If a movement command is issued to each axis via a control signal while the movement specified
by this command is still in progress, the movement by this command will be cancelled and the
operation corresponding to the latest movement command will take place. Since each axis
effectively has two movement c omm and inte rfac es, make sure the two interfaces are used
exclusively to each other.
2. Even when the link was cancelled by turning OFF the CFG bit of the gateway control signal, once
the link is established again the controller will always receive this command to perform the
specified operation.
[7] PIO/Modbus switching command
Byte+ PLC output (request) PLC input (response)
+4 0DA1H Same as the value in the request
6 0
8 Coil ON/OFF
00FFH = ON: Modbus (Disable PIO command)
0000H = OFF: PIO (Enable PIO command)
*1 to *3
10 0
12 Axis number 0 to FH
14 0
16 0
*1 The PIO/Modbus switching status is reflected in the status signal PMSS. Also note that this
command cannot be set for position number specification axes (if issued, the command will
generate an invalid request command error (0103H)).
*2 Even if the coil is set to OFF (Enable PIO command), axis position data can still be changed
from the PLC via Modbus communication (although the link must be retained).
*3 The controller will still accept and execute movement commands via Modbus communication
even after the control authority is switched to PIO.
command if normal.
73
Page 80

PfofiBus Gateway
(4) Error response
If a command error occurs, the most significant bit (b7) of the response command will turn ON. In
addition, one of the following error codes will be set in response data 1.
If no link is currently formed, nothing will be shown in the response command.
Code Description
0101H Invalid address *1
0102H Invalid position number *1
0103H Invalid request command *1
0201H Communication failed
0202H Not executable by the controller
*1) If any of these conditions is found as a result of data check from the PLC, an applicable error
code will be set in the response data without the data being sent to the controller.
(5) How to use commands
To use various commands, proces s the da ta in ea ch c omm a nd a re a according to the flow shown
below. This flow assumes that only one command is processed.
Clear the request command area.
Use a command
Response
command area 0?
Write the command code in the
request command area.
Write the necessary data in data
areas 0 to 3.
Response command
= Request command?
Clear data areas 0 to 3.
Clear the request command area
and data areas 0 to 3.
74
Page 81

r
PfofiBus Gateway
6 Communication Signal Details
6.1 Overview of Communication Signal Timings
When a given control signal is turned ON to operate the ROBO Cylinder using the sequence program in
the PLC, the maximum response time before a response (status) signal will be received is expressed by
the formula below:
Maximum response time (mse c) = Yt + Xt + 2 x Mt + Command processing time (operation time, etc.)
Mt = 10 (msec) x (n+1): SIO link (Modbus) cycle time
n: Number of controlled axes
Yt: Master → remote I/O station transmission delay
Xt: Remote I/O → master station transmission delay
For the master → remote I/O station transmission delay (Yt) and remote I/O → master station
transmission delay (Xt), refer to the operation manuals for your ProfiBus master unit and PLC.
PLC sequence program
Control signal
Status signal
Master → remote I/O station
transmission delay (Yt)
Remote I/O → master station
transmission delay (Xt)
Gateway
Control signal
Status signal
SIO link cycle time SIO link cycle time
Controlle
Control signal
Response
processing time
Status signal
(Note) If a communication error occurs due to a problem along the transmission path, etc.,
a communication retry or retries (up to three times) may occur, in which case the SIO link cycle
time (Mt) will be extended.
ProfiBus
transmission delay
75
Page 82

PfofiBus Gateway
76
Page 83

PfofiBus Gateway
6.2 Communication Signals and Operation Timings
(1) Controller ready (PWR) PLC input signal
This signal turns “1” (ON) when the controller becomes ready following the power on.
Function
This signal turns “1” (ON) when the controller has been initialized properly following the power
on and becomes ready, regardless of the alarm condition, servo status, etc.
Even when an alarm is present, the PWR signal still turns “1” (ON) as long as the controller
becomes ready.
This signal is synchronized with the status indicator LED (green) on the front panel of the
controller.
(2) Emergency stop (EMGS) PLC input signal
This signal turns “1” (ON) when the controller actuates an emergency stop.
Function
This signal turns “1” (ON) when a controller alarm generates, an emergency stop is actuated by
the emergency stop circuit (refer to 4.3.1), or the motor drive power is cut off. It will turn “0”
(OFF) once the emergency stop is cancelled.
(3) Alarm (ALM) PLC input signal
This signal turns “1” (ON) when the controller’s protective circuit (function) detects an error.
Function
This signal turns “1” (ON) when the controller’s protective circuit (function) is actuated.
It will turn “0” (OFF) when the reset (RES) signal is turned “1” (ON) after removing the cause of
the problem. (This is not the case with cold-sta rt ala r ms . )
When an alarm is detected, the ALM LED (red) on the front panel of the controller illuminates.
This LED remains unlit while the controller is normal.
With the ERC2-NP/PN/SE, the LED at the top of the motor unit illuminates in red. When the
servo turns on, the LED changes to a steady green light.
(4) Reset (RES) PLC output signal
This signal has two functions. It can be used to reset controller alarms or cancel the remaining travel
distance while the actuator is paused.
Function
[1] When an alarm is present, you can reset the alarm by removing the cause of the alarm and
then turning this signal from “0” (OFF) to “1” (ON). (This is not the case with cold-start
alarms.)
[2] While the actuator is paused, you can cancel the remaining travel by turning this signal from
“0” (OFF) to “1” (ON).
77
Page 84

PfofiBus Gateway
(5) Pause (STP) PLC output signal
Turning this signal “1” (ON) causes the axis to stop temporarily (decelerate to a stop). Turning it “0”
(OFF) resumes the axis movement.
The relationship of the STP signal and MOVE (moving) signal is shown below.
tdicm ≤ Acceleration/deceleration
tdicp ≤ Yt + 2Mt + Xt + 6 (msec)
(6) Moving (MOVE) PLC input signal
This signal turns “1” (ON) while the actuator is moving with the servo turned on (and also during
home return, push-motion operation and jogging).
Use the MOVE signal along with PEND for status discrimination on the PLC side.
The MOVE signal turns “0” (OFF) upon completion of positioning, home return or push-motion
operation, and also while the actuator is paused.
(7) Servo ON command (SON) PLC output signal
Ready (SV) PLC input signal
Turning the SON signal “1” (ON) turns on the servo.
Once the servo turns on, the SV LED (green) on the front panel of the controller illuminates. With the
ERC2, the LED at the top of the motor unit illuminates in green.
The SV signal is synchronized with this LED indicator.
Function
The controller servo can be turned on/off using the SON (servo ON) signal.
While the SV signal is “1” (ON), the controller servo remains on and therefore the controller is
operational.
The relationship of the SON signal and SV signal is shown below.
78
Page 85

A
PfofiBus Gateway
(8) Home return command (HOME) PLC output signal
Home return complete (HEND) PLC input signal
Home return operation starts at the leading edge of the HOME signal from “0” (OFF) to “1” (ON).
When the home return is complete, the HEND (home return complete) signal turns “1” (ON).
Turn the HOME signal “0” (OFF) after the HEND signal has turned “1” (ON). Once tur n ed “1” (ON),
the HEND signal will not turn “0” (OFF) unless the power is turned off or the HOME signal is input
again. Accordingly, even after the initial home return is completed you can still perform home return
as many times as desired using the HOME signal.
ctuator operation
Mechanical end Stops at the home position.
Caution
1. In the case of a positioner operation axis operating in the position number specification mode or
command specification mode, issuing a positioning command to a given position immediately after
the power was turned on, without performing the home return first, will cause the actuator to
automatically return to its home and then execute the positioning, provided that this is the first
operation after the power on.
2. Take note that in any other mode, an alarm “Error code 83: ALARM HOME ABS (absolute position
movement command issued before completion of home return)” will generate.
79
Page 86

PfofiBus Gateway
(9) Positioning start (CSTR) PLC output signal
Upon detecting the leading edge of this signal from “0” (OFF) to “1” (ON), the controller reads the
target position number specified by the binary code of PC1 to PC32768 (the signal varies according
to the operation mode), and then performs positioning to the target position corresponding to the
applicable position data. The same applies when a numerical value is specified directly in the position
data specification area.
Before positioning is performed, the target position, speed and other operation data must be set in
the position table using a PC/teaching pendant.
If this command is issued before the home return operation is performed following the power on (=
while the HEND output signal is “0” (OFF)), the actuator will automatically perform the home return
operation and then position itself to the target position.
Turn this signal “0” (OFF) after confirming that the PEND signal has turned “0” (OFF).
(10) Positioning complete (PEND) PLC input signal
This signal turns “1” (ON) when the actuator has moved to the target position and entered the
positioning band, or when the p ush-motion operation has c ompleted (without missing the load).
If the servo has turned ON, the applicable position is set as the target position and accordingly this
signal turns “1” (ON). When positioning operation is started using the HOME signal or CSTR signal
thereafter, this signal will become “0” (OFF).
Speed
Travel distance
Timing at which the positioning
complete signal turns ON
Target position
Time
Positioning band
Caution
If the servo is turned off or an emergency stop is actuated while the actuator is stopped at the target
position, the PEND signal turns “0” (OFF).
When the servo subsequently turns ON, the signal will turn “1” (ON) again if the actuator is inside the
positioning band.
If CSTR remains “1” (ON), the PEND signal will not become “1” (ON) even when the current actuator
position is inside the positioning band. The PEND signal will turn “1” (ON) when the CSTR signal turns
“0” (OFF).
80
Page 87

A
PfofiBus Gateway
(11) Command position number (PC1 to PC512) PLC output signal
A command position number is read as a binary code.
The number of command positions varies as follows according to the operation mode:
• Position number specification mode PC1 to PC32 64 points
• Command specification mode, positioner operation PC1 to PC256 512 points
• Command specification mode, simple direct operation PC1 to PC32768
The controller unit reads the PC signal as a binary command position number at the “0” (OFF) Æ “1”
(ON) edge of the CSTR si gnal.
(12) Completed position number (PM1 to PM256) PLC input signal
These signals are effective in simple direct operation in the position number specification mode and
command specification mode. A completed position number is output as a binary code.
When the power is turned on or the actuator is moving, all PM signals from 1 to 256 turn “0” (OFF).
When the servo turns off or an emergency stop is actuated, all signals turn "0" (O FF). However, the
applicable signal will turn “1” (ON)” again when the servo subsequently turns on, if the actuator is
inside the positioning band (INP) relative to the target position. If the actuator has exceeded the
positioning band (INP), the signals will remain “0” (OFF).
The applicable PM signal will also turn “1” (ON) when the push-motion operation has completed or
the actuator has missed the load.
(13) Zone (PZONE, ZONE1, ZONE2) PLC input signal
Each of these signals turns “1” (ON) when the current actuator position is ins ide the specified zone. *1
A desired zone can be set in the position table or using user parameters.
Individual zone boundary fields in position
table
User parameter “Zone bou ndary 1”
(Parameter No. 1 = + side, No. 2 = - si de )
User parameter “Zone bou ndary 2”
(Parameter No. 23 = + side, No. 24 = - side)
*1 This signal becomes effective when the home return has completed. As long as the home return
has completed once, this signal remains effective even when the servo is off.
*2 PIO pattern 3 is not supported.
*3 PIO patterns 1 to 3 are not supported.
Zone signal
ctuator operation
Home
Setting Zone signal
Zone setting- Zone setting+
Position zone
output
PZONE
Zone output 1
ZONE1
Zone output 2
ZONE2
+ direction
Position number
specification
mode
X { *2
{
{
Command
specification
mode, positioner
operation
{ *3
X
81
Page 88

PfofiBus Gateway
(14) Jog+ command/jog- command (JOG+ / JOG-) PLC output signal
These signals are used to operate a positioner operation axis in the command specification mode
under PIO pattern 1 (teaching mode).
These signals are used to start jogging or inching.
When the + command is issued, the actuator moves in the direction opposite home. When the –
command is issued, the actuator moves in the direction of home.
Jogging or inching is specified by a combination of the JOG signal and JISL signal (jogging/inching
switching signal).
[1] Jogging
Jogging is enabled when the jog/inch switching signal (JISL) is “0” (O FF).
While JOG+ is “1” (ON), the actuator moves in the direction opposite home. When the signal
turns “0” (OFF), the actuator decelerates to a stop.
While JOG- is “1” (ON), the actuator moves in the direction of home. When the signal turns “0”
(OFF), the actuator decelerates to a stop.
The operation is set using the following parameter settings:
• Speed: Defined by parameter No. 26 (PIO jog speed)
• Acceleration/deceleration: Rated acceleration/deceleration (varies according to the actuator)
To stop jogging (cause the actuator to decelerate to a stop), turn the current JOG signal from “1”
(ON) to “0” (OFF) or cause both JOG+ and JOG- to turn “1” (ON).
[2] Inching
Inching is enabled when the jog/inch switching signal (JISL) is “1” (ON).
The actuator moves by the inching distanc e eve ry time the JO G si gn al turns from “0 ” (O FF) to
“1” (ON).
The actuator inches in the direction opposite home when JOG+ is issued, or in the direction of
home if JOG- is issued.
The operation is set using the following parameter settings:
• Speed: Defined by parameter No. 26 (PIO jog speed)
• Travel distance: Defined by parameter No. 48 (PIO inching distance)
• Acceleration/deceleration: Rated acceleration/deceleration (varies according to the actuator)
During normal operation, the actuator will continue with the normal operation even after the
JOG+ or JOG- signal is turned “1” (ON) (= the JOG signal will be ignored). Also while the
actuator is paused, the actuator will not operate even after the JOG+ or JOG- signal is turned “1”
(ON) (= the JOG signal will be ignored).
Caution
Exercise caution that the actuator may collide with a mechanical end before the home return is
completed, because the software stroke limits are still not effective during this period.
82
Page 89

PfofiBus Gateway
(15) Jog/inch switching (JISL) PLC output signal
This signal is used to switch between jogging and inching.
JISL = “0” (OFF): Jogging
JISL = “1” (ON): Inching
If the JISL signal switches to “1” (ON) during jogging, the accelerator will decelerate to a stop and the
inching function will be enabled. If the JISL signal switches to “0” (OFF) during inching, the actuator
will complete the inching and then the jogging function will be enabled.
Jogging and inching commands are issued by a combination of the JISL signal and the JOG+/JOGsignal. The relationships of these signals are summariz ed in the table below.
Jogging Inching
JISL “0” (OFF) “1” (ON)
Speed Parameter No. 26 (jog speed) Parameter No. 26 (jog speed)
Travel distance - Parameter No. 48 (inch distance)
Acceleration/
deceleration
Rated value (varies according to the
actuator)
Rated value (varies according to the
actuator)
(16) Teaching mode command (MOD) PLC output signal
Teaching mode status (MODS) PLC input signal
These signals are used when a positioner operation axis is operated in the command specification
mode under PIO pattern 1 (teaching mode).
When the MOD signal is turned “1” (ON), the actuator switches from the normal operation mode to
the teaching mode. The controller of each axis turns the MODS signal “1” (ON) upon switching to the
teaching mode. Be sure to perform teaching operation after confirming on the PLC side that the
MODS signal has turned “1” (ON).
*1 The following conditions must be satisfied before the actuator can be switched from the normal
operation mode to the teaching mode:
• The actuator (motor) is stop ped
• The JOG+ signal and JOG- signal are “0” (OFF)
• The position data read command (PWRT) signal and positioning start (CSTR) signal are “0”
(OFF)
The PWRT signal must also be “0” (OFF) when switching from the teaching mode to the normal
operation mode.
83
Page 90

PfofiBus Gateway
(17) Position data read command (PWRT) PLC output signal
Position data read complete (WEND) PLC input signal
These signals are used when a positioner operation axis is operated in the command specification
mode under PIO pattern 1 (teaching mode).
The PWRT signal is effective when the MODS signal is “1” (ON).
When the PWRT signal is turned “1” (ON) for 20 msec or more (*1), the current position data will be
written to the “Position” field under the position number currently specified by the PLC command. (*2)
When the writing is complete, the WEND signal turns “1” (ON).
The host PLC should turn the PWRT signal “0” (OFF) after the WEND signal has turned “1” (ON).
If the PWRT signal is turned “0” (OFF) before the WEND signal turns “1” (ON), the WEND signal will
not turn “1” (ON).
When the PWRT signal is turned “0” (OFF), the WEND signal turns “0” (OFF).
*1 Make sure the signal remains “1” (ON) for 20 msec or more. If the signal is turned “1” (ON) for
less than 20 msec, the data may not be written.
*2 If any data other than position is not yet defined, the default value of the applicable parameter
will be written.
20 msec or more
(18) Forced brake release (BKRL) PLC output signal
You can forcibly release the brake by turning this signal “1” (ON).
84
Page 91

PfofiBus Gateway
6.3 Basic Operation Timings
(1) Preparation
After confirming that the slider or rod is not colliding with a mechanical end or the load is not
contacting any surrounding equipment, start the system by following the procedure below:
[1] Cancel the emergency stop or enable the motor drive power supply.
[2] Turn on the 24-VDC controller power via the 24-V terminal and 0-V terminal on the power-supply
terminal block.
[3] Set the minimum required parameters.
(Example) • To change the feed speed during teaching:
Change the value of parameter No. 35 (Safety speed).
[4] In the positioner mode or simple direct mode, set appropriate values in the “Position,” “Speed,”
“Acceleration” and “Decele ration” fields, etc., in the position table.
Safety circuit status
24-VDC controller
power supply
SV lamp
(front panel)
Controller ready
Pause
Servo ON
Ready
Positioning complete
Emergency stop cancelled
Illuminates in orange for 2 seconds, and then turns off.
Default parameter
setting
1.6 sec or less
Green
Pause cancelled
Caution
When the power is turned on while an emergency st op is ac tua te d and the n the e mergency stop is
cancelled (= the SON signal is turned “1” (ON)), the servo will turn on up to 1.6 sec after the
cancellation of the emergency stop.
1.6 sec or less
Emergency stop cancelled
Servo on
85
Page 92

PfofiBus Gateway
Warning
With the ACON, excited-phase detection operation is performed when the servo is turned on for the
first time following the power on. Because of this detection operation, the actuator normally moves by
approx. 0.5 to 2 mm, although the specific dimension varies according to the ball screw lead.
(On rare occasions, the actuator may move by up to around a half of the ball screw lead depending on
the actuator position when the power is turned on.)
Also note that if the power is turned on while the actuator is near a mechanical end, the actuator may
contact the mechanical end during the detection operation and reverse its direction as a result.
Exercise due caution not to cause the load or robot hand to get damaged as a result of contact with
surrounding objects during this detection operation.
86
Page 93

t
PfofiBus Gateway
(2) Home return operation
The controller unit uses an incremental position detector (encoder), which means that once the power
is cut off, the mechanical coordinates will be lost.
Accordingly, home return must be performed after the power is turned on to establish the mechanical
coordinates.
To perform home return operation, input the home return command (HOME) signal.
For your information, home return operation is not required if the simple absolute R unit is connected
to the controller unit to convert the axes into absolute axes.
Operation timings
PLC process 1: The home return command (HOME) signal turns “1” (ON) when the start button is
pressed.
Operation: [1] The actuator starts moving toward the mechanical end on the home s ide .
[2] After contacting the mechanical end, the actuator reverses its direction and then
stops at the home position → The home return complete (HEND) signal turns “1”
(ON).
PLC process 2: The home return command (HOME) signal is turned “0” (OFF) after confirmation of the
HEND signal turning “1” (ON).
PLC process 3: The actuator starts continuous operation.
Home return command
Home return complete
Positioning complete
Moving
1 msec or less
Actuator movement
[1] [2]
position
Power inpu
Home position
Mechanical end
Caution
Pay attention to the following points when performing home return:
[1] Confirm that no obstacle exists in the direction of home return.
[2] Should an obstacle be found in the direction of home return, tentatively move the actuator in the
direction opposite home and remove the obstacle.
[3] Turning the HOME signal “1” (ON) turns the PEND signal “0” (OFF) and MOVE signal “1” (ON).
Turn the HOME signal “0” (OFF) again after confirming that the HEND signal has turned “1” (ON) while
the HOME signal is still “1” (ON).
87
Page 94

A
PfofiBus Gateway
(3) Operation by position number specification
Positioner operation in the position number specification mode or command specification mode is
explained.
Operation
The actuator is operated by specifying position data in the controller’s position table beforehand, and
specifying a desired position number using the link register in the PLC.
The push-motion operation, speed change during movement, pitch feed by incremental coordinate
specification, etc., are the same in PIO (I/O cable) operation. Refer to the operation manual for your
PCON, ACON, SCON or ERC2.
[1] Set the position number in the command position number register.
[2] Next, turn the start command (CSTR) signal “1” (ON) after confirming that the positioning
complete (PEND) signal is “1” (ON).
[3] PEND turns “0” (OFF) tdpf after CSTR has turned “1” (ON).
[4] Turn CSTR “0” (OFF) after confirming that PEND has turned “0” (OFF).
[5] MOVE turns “1” (ON) simultaneously as PEND turns “0” (OFF) or within 1 Mt thereafter.
[6] When the remaining travel falls within the positioning band (INP), PEND turns “1” (ON) if CSTR
is “0” (OFF), and then the completed position number is output.
Accordingly, when reading the completed position number upon completion of positioning, check
the position number after waiting for an appropriate period (time needed to complete the
remaining travel) after PEND has turned “1” (ON).
Caution
• When the start (CSTR) signal turns “1” (ON), the positioning complete (PEND) signal turns “0”
(OFF) and moving (MOVE) signal turns “1” (ON).
Be sure to turn the CSTR signal OFF after confirming that PEND has turned OFF while the CSTR
signal is still ON.
If CSTR remain ON, PEND will not turn ON even after the actuator completes its movement,
shown below.
Start
Positioning
complete
Moving
ctuator
Movement complete
• If a movement command is issued to the same position, the positioning complete output will turn
OFF, but the moving output will not turn ON.
• The moving output turns OFF the moment the positioning complete output turns ON, even when
the actuator is still moving. Accordingly, increasing the positioning band specified by the position
data may result in a situation where the moving signal turns OFF the moment the positioning
complete output turns ON, but the actuator may be still moving.
• When a soft limit is reached after continuous incremental moves, the actuator will stop at that
position and then the positioning complete signal will be output.
as
88
Page 95

[1]
Command position number
Positioning complete
Completed pos i tion
Start command
number
Moving
[2]
[3]
[4]
[6]
[5]
*1 T1: Set T1 to 0 ms or more by considering the scan time of the host controller.
*2 Yt+2Mt+Xt≤tdpf≤Yt+2Mt+Xt+7 (ms)
PfofiBus Gateway
89
Page 96

PfofiBus Gateway
(4) Operation in the direct numerical specification mode
The actuator is operated not by using the position table of the controller, but by writing the target
position data, acceleration/deceleration data, speed data, push-current limiting value data and
positioning band data to the link registers in the PLC.
All these data must be set in the case of push-motion operation.
In the case of normal positioning operation, the push-current limiting value data, PUSH signal and
DIR signal are not required.
Take note that in either operation, the actuator will not move unless all necessary data is set.
Operation
[Push-motion operation]
[1] Set the push start position data in the target position data specification register.
[2] Set the speed data until the push start position in the speed specification register, and set the
corresponding acceleration/deceleration data in the acceleration/deceleration register. Take note
that even if acceleration/de celeration is not set, the setting of parameter No. 9, “Def ault
acceleration/deceleration” will not be applied.
[3] Set the push-motion travel in the positioning band specification register. (*)
[4] Set the push-current limiting value data in the push-current limiting value register in order to set
the push force.
[5] Turn the PUSH (push-motion operation mode specification) signal “1” (ON).
[6] Use the DIR (push direction specification) signal to select the push direction.
When the DIR signal is set to “1” (ON), push-motion operation is performed in the direction
opposite home. When the signal is set to “0” (OFF), push-motion operation is performed in the
direction of home.
[7] Next, turn the start command (CSTR) signal “1” (ON) after confirming that the positioning
complete (PEND) signal is “1” (ON).
The data set in [1] to [4] will be read by the controller at the “0” (OFF) Æ “1” (ON) edge of CSTR
(leading edge of the signal).
[8] PEND turns “0” (OFF) tdpf after CSTR has turned “1” (ON).
[9] Turn CSTR “0” (OFF) after confirming that the PEND signal has turned “0” (OFF) or MOVE
signal has turned “1” (ON).
[10] MOVE turns “1” (ON) simultaneously as PEND turns “0” (OFF) or within 1 Mt thereafter.
[11] PEND turns “1” (ON) when the motor current reaches the push-current limiting value set in [4]
while CSTR is “0” (OFF). (The push operation has completed.)
If the motor current does not reach the push-current limiting value set in [4] even after the
positioning band set in [3] has been reached, the PSFL (missed load in push operation) signal
turns “1” (ON). In this case, PEND will not turn “1” (ON). (The actuator has missed the load.)
[12] The current position data is constantly refreshed.
[13] Turn PUSH “0” (OFF) after PEND or PSFL has turned “1” (ON).
* Take note that even if positioning band specification data is not set, the value of parameter
No. 10, “Default positioning band” will not be applied.
[Normal positioning operation]
In the case of normal operation, the operation continues while the PUSH signal is still “0” (OFF)
in [5] above. Setting of push-current limiting value data in [4] is not required. PEND turns “1”
(ON) when the remaining travel falls within the range of positioning band specification data set in
[3], while CSTR is “0” (OFF).
90
Page 97

PfofiBus Gateway
Set value of target
position data
Set value of speed and
acceleration/deceleration
data
Set value of positioning
band data
Set value of push-current
limiting value data
Push mode
Push direction
Start command
Positioning complete/missed
load in push operation
Current position
Moving
[1]
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[13]
[8]
[10]
[9]
[11]
[12]
*1 T1: Set T1 to 0 ms or more by considering the scan time
of the host controller.
*2 Yt+2Mt+Xt≤tdpf≤Yt+2Mt+Xt+7 (ms)
91
Page 98

PfofiBus Gateway
The target position data, acceleration/deceleration data, speed data, positioning band data and pushcurrent limiting value data can be changed while the actuator is moving. After a given data has been
changed, turn CSTR “1” (ON) for at least tdpf.
Also, after CSTR is turned “0” (OFF), wait for at least 1 Mt before turning it “1” (ON).
An example of changing the speed and acceleration/deceleration data is given below.
Set value of speed and
acceleration/
deceleration data
[1]
[2]
[3]
Actuator
speed
Speed n2
Speed n3
Caution
1. If speed data is not set or the set speed is zero, the actuator will remain standstill and no alarm will
generate.
2. If the speed data setting is changed to zero while the actuator is moving, the actuator will
decelerate to a stop and no alarm will generate.
3. Even when only the acceleration/deceleration data or speed data is changed while the actuator is
moving, the target position data must still be set.
4. Even when only the target position data is changed while the actuator is moving, the
acceleration/deceleration data and speed data must still be set.
92
Page 99

PfofiBus Gateway
(5) Simple direct operation (command specification mode)
The actuator is operated by writing the target position data to the link register in the PLC and
specifying other data such as the speed, acceleration/deceleration, positioning band and pushcurrent limiting value in the position table.
Preparation
Set all position data other than the target position (speed, acceleration/deceleration, positioning
band, push-current limiting value, etc.) in the position table.
Operation
[Normal positioning operation]
[1] Set the target position data in the position data specification register.
[2] Set the position number in the command position number register.
[3] Turn the start command (CSTR) signal “1” (ON) after confirming that the positioning complete
(PEND) signal is “1” (ON) or moving (MOVE) signal is “0” (OFF).
The target position data will be read by the controller at the “0” (OFF) Æ “1” (ON) edge of CSTR
(leading edge of the signal).
[4] PEND turns “0” (OFF) tdpf after CSTR has turned “1” (ON).
[5] Turn CSTR “0” (OFF) after confirming that the PEND signal has turned “0” (OFF) or MOVE
signal has turned “1” (ON).
Do not change the target position data until CSTR turns “0” (OFF).
[6] MOVE turns “1” (ON) simultaneously as PEND turns “0” (OFF) or within 1 Mt thereafter.
[7] The current position data is constantly refreshed. When the remaining travel falls within the
specified positioning band (INP), PEND turns “1” (ON) if CSTR is “0” (OFF).
Accordingly, when reading the completed position number upon completion of positioning, check
the position number after waiting for an appropriate period (time needed to complete the
remaining travel) after PEND has turned “1” (ON).
Also note that the current position data may shift somewhat due to vibration, etc., even while the
actuator is stopped.
[8] MOVE turns “0” (OFF) simultaneously as PEND turns “1” (ON) or within 1 Mt thereafter.
[9] The target position data can be changed while the actuator is moving.
To change the target position while the actuator is moving, change the target position data, wait
for the PLC scan time, and then turn CSTR “1” (ON).
In this case, turn CSTR “1” (ON) for at least tdpf. Also, after CSTR is turned “0” (OFF), wait for at
least 1 Mt before turning it “1” (ON).
[Push-motion operation]
Push-motion operation is performed by setting a push-current limiting value in the Push field of
the position table in the preparation stage, and then performing positioning to the applicable
position number.
93
Page 100

PfofiBus Gateway
[1]
Set value of target
position data
Command position
number
Start command
Positioning
complete
Current position
Moving
[2]
[3]
[4]
[5]
[7]
[8]
[6]
*1 T1: Set T1 to 0 ms or more by considering the scan time
of the host controller.
*2 Yt+2Mt+Xt≤tdpf≤Yt+2Mt+Xt+7 (ms)
*3 twcsON1≥Mt
*4 twcsOFF≥1Mt
94
 Loading...
Loading...