Page 1

OPERATION INSTRUCTIONS Form 5473-T, 01-10
Supersedes Form 5473-T, 09-08
DSP9200 Series
Wheel Balancer
© Copyright 2006 -2010 Hunter Engineering Company
Page 2

OWNER INFORMATION
Model Number ____________________________________________________________________
Serial Number ____________________________________________________________________
Date Installed _____________________________________________________________________
Software Version Number ___________________________________________________________
Service and Parts Representative _____________________________________________________
Phone Number ____________________________________________________________________
Sales Representative _______________________________________________________________
Phone Number ____________________________________________________________________
Operation
Trained Declined
Safety and Maintenance
Equipment Components
Basic Operation
Static vs. Dynamic Balancing
Calibration and Quick Calibration Check
Split Weight Feature
Adhesive Weight (ALU) Procedures
Optimizing Procedures
Patch Balance
®
Procedures
Inflation Station™/Wheel Lift
Split Spoke
®
Servo-Aided Weight Placement
CenteringCheck™
Individuals and Date Trained
___________________________________ ___________________________________
___________________________________ ___________________________________
___________________________________ ___________________________________
___________________________________ ___________________________________
___________________________________ ___________________________________
___________________________________ ___________________________________
___________________________________ ___________________________________
Page 3

CONTENTS
1. GETTING STARTED ........................................................................................ 1
1.1 Introduction............................................................................................................. 1
References............................................................................................................. 1
1.2 For Your Safety ...................................................................................................... 1
Hazard Definitions.................................................................................................. 1
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS............................................................... 2
Electrical................................................................................................................. 3
Decal Information and Placement.......................................................................... 4
Right Side View ............................................................................................... 4
Left Side View.................................................................................................. 5
Back View........................................................................................................ 6
Specific Precautions/Power Source....................................................................... 7
Turning Power ON/OFF ......................................................................................... 7
Equipment Installation and Service ....................................................................... 7
Equipment Specifications....................................................................................... 8
Safety Summary .................................................................................................... 8
Explanation of Symbols................................................................................... 8
1.3 DSP9200 Components........................................................................................... 9
Standard Accessories .......................................................................................... 10
1.4 Operating the Control Panel................................................................................. 11
Control Panel ....................................................................................................... 11
Using the Control Panel ....................................................................................... 11
Using Wheel Dimension Control Knobs............................................................... 12
2. BALANCING OVERVIEW .............................................................................. 13
2.1 Balancing Modes.................................................................................................. 13
Static Balance ...................................................................................................... 13
Dynamic Imbalance ............................................................................................. 14
Static and Dynamic Imbalance Sensitivity ........................................................... 15
2.2 Identifying the Static Balance Weight Plane ........................................................ 15
2.3 Identifying the Dynamic Balance Weight Planes.................................................. 16
2.4 On-Vehicle Wheel Mounting Methods.................................................................. 18
Hub Centric .......................................................................................................... 18
Lug Centric........................................................................................................... 18
3. BALANCING A WHEEL................................................................................. 19
3.1 Mount the Wheel on the Spindle Shaft................................................................. 19
Front/Back Cone Mounting .................................................................................. 20
Using Plastic Wheel Mounting Washer................................................................ 21
Cone/Flange Plate Mounting ............................................................................... 23
Using the Pressure Ring and Spacers................................................................. 24
Pressure Ring................................................................................................ 24
Spacers ......................................................................................................... 24
CenteringCheck
3.2 Measuring the Wheel with Inner and Outer Auto Dataset
Measuring Dimensions for Clip-On Weights: ................................................ 26
Mixed Weights and Two Adhesive Weights (Inputting Distance and Diameter for
Both Planes): ....................................................................................................... 27
3.3 Manually Setting Wheel Dimensions.................................................................... 28
Measuring the Wheel at the Inner Rim Lip (Clip-On Weight) .............................. 29
Measuring Wheel Width with Rim Width Calipers ...............................................30
Measuring the Inside Wheel Surface with the Pointer Disk Edge (Adhesive Tape-
On Weights) ......................................................................................................... 30
®
.................................................................................................. 25
®
Arms......................... 26
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions Contents x i
Page 4

Measuring the Inside Wheel Diameters (For Adhesive Weights) ........................ 31
3.4 Locating the Wheel Weights at the Top Dead Center (“TDC”) and Bottom Dead
Center (“BDC”) ........................................................................................................... 32
3.5 Standard Balancing Procedure (Clip-on Weights) ............................................... 33
3.6 Static / Standard Balancing Procedure (Clip-on Weight) ..................................... 35
3.7 Adhesive Weight Procedures (Combination of Clip-on & Adhesive Weights, or
Two Adhesive)............................................................................................................ 36
3.8 Static / ALU Balancing Procedure (Adhesive Weight) ......................................... 41
3.9 OPT-1 Optimizing Tire & Wheel Imbalances (Wheel with the Tire Mounted
Procedure).................................................................................................................. 42
3.10 OPT-2 Optimizing Tire & Wheel Imbalances (Tire Not Mounted Procedure) ....43
3.11 Patch Balance
Static Patch Balance
Dynamic Patch Balance
®
Procedures ............................................................................... 44
®
(Single Weighted Balance Patch) .................................... 44
®
(Two Weighted Balance Patches) ..............................45
4. BALANCING FEATURES AND OPTIONS.................................................... 47
4.1 Servo-Stop............................................................................................................ 47
Servo-Stop Wheel Weight Positioning................................................................. 47
Disabling Servo-Stop..................................................................................... 47
Turning On Servo-Stop.................................................................................. 47
Servo-Stop Aided Clip-On Weight Placement ..................................................... 47
Servo-Stop Aided Adhesive Weight Placement................................................... 47
4.2 Locate the Adhesive Wheel Weights Using the Dataset£ Arm Pointer Disk Edge48
Inside of Wheel (Single Row of Adhesive Weights)............................................. 48
Inside of Wheel (Double Row of Adhesive Weights) ........................................... 48
4.3 Quick-Thread™ Feature....................................................................................... 49
4.4 Motor Drive/Servo-Stop........................................................................................ 49
Servo-Stop/Servo-Push ....................................................................................... 49
4.5 Spindle-Lok
4.6 Hood Close Autostart Feature.............................................................................. 50
4.7 Loose Hub Detect Feature ................................................................................... 50
4.8 Blinding and Rounding .........................................................................................51
4.9 Split Weight
Split Weight
Correcting Large Imbalances............................................................................... 52
4.10 Split Spoke
Re-entering Similar Wheel after Split Spoke® is Enabled................................... 53
Placing Hidden Weight Forward of Obstructions................................................. 54
4.11 Automatic Weight Recalculation and Dimension Preservation .......................... 55
4.12 Storing and Recalling Wheels ............................................................................ 55
Storing a Wheel into Memory............................................................................... 55
Recalling a Wheel from Memory.......................................................................... 55
®
Feature ........................................................................................... 50
®
Feature ........................................................................................... 51
®
Operation .......................................................................................52
®
Feature .......................................................................................... 53
5. MAINTENANCE AND CALIBRATION........................................................... 57
5.1 Cleaning the Unit .................................................................................................. 57
5.2 Spindle Hub Face and Shaft Maintenance........................................................... 57
5.3 Mounting Cone Maintenance ............................................................................... 57
5.4 Identifying Software Version and Serial Number ................................................. 57
5.5 Calibration Procedures......................................................................................... 58
Quick Cal Check ..................................................................................................58
Balancer Calibration............................................................................................. 59
Inner Dataset
Outer Dataset
6. GLOSSARY ................................................................................................... 63
iix Contents DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
®
Arm (Calibration Tool, 221-672-1, Required) .............................. 60
®
Arm (Calibration Tool, 221-672-1, Required) .............................62
Page 5

1. GETTING STARTED
1.1 Introduction
This manual provides operation instructions and information required to operate the
DSP9200 Wheel Balancer. Read and become familiar with the contents of this
manual prior to operating the DSP9200.
The owner of the DSP9200 is solely responsible for arranging technical training. The
DSP9200 is to be operated only by a qualified, trained technician. Maintaining
records of personnel trained is solely the responsibility of the owner and
management.
References
This manual assumes that you are already familiar with the basics of tire balancing.
The first section provides the basic information needed to operate the DSP9200. The
following sections contain detailed information about equipment operation and
procedures. “Italics” are used to refer to specific parts of this manual that provide
additional information or explanation. For example, Refer to “Equipment
Components,” page 9. These references should be read for additional information to
the instructions being presented.
1.2 For Your Safety
Hazard Definitions
Watch for these symbols:
CAUTION: Hazards or unsafe practices, which could result in minor
WARNING: Hazards or unsafe practices, which could result in
DANGER: Immediate hazards, which will result in severe personal
These symbols identify situations that could be detrimental to your safety and/or
cause equipment damage.
personal injury or product or property damage.
severe personal injury or death.
injury or death.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 1. Getting Started x 1
Page 6

IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Read all instructions before operating the DSP9200.
Do not operate equipment with a damaged cord or equipment that has been dropped
or damaged until a Hunter Service Representative has examined it.
Always unplug equipment from electrical outlet when not in use. Never use the cord
to pull the plug from the outlet. Grasp plug and pull to disconnect.
If an extension cord is necessary, a cord with a current rating equal to or more than
that of the equipment should be used. Cords rated for less current than the
equipment may overheat. Care should be taken to arrange the cord so that it will not
be tripped over or pulled.
Verify that the electrical supply circuit and the receptacle are properly grounded.
To reduce the risk of electrical shock, do not use on wet surfaces or expose to rain.
Never direct a hose stream at equipment when cleaning.
Verify the appropriate electrical supply circuit is the same voltage and amperage
ratings as marked on the balancer before operating.
WARNING: DO NOT ALTER THE ELECTRICAL PLUG. Plugging the
electrical plug into an unsuitable supply circuit will
damage the equipment and may result in personal
injury.
To reduce the risk of fire, do not operate equipment near open containers of
flammable liquids or sprays (gasoline, cleaners, fluids, etc.).
Read and follow all caution and warning labels affixed to your equipment and tools.
Misuse of this equipment can cause personal injury and shorten the life of the
balancer.
Keep all instructions permanently with the unit.
Keep all decals, labels, and notices clean and visible.
To prevent accidents and/or damage to the balancer, use only Hunter DSP9200
recommended accessories.
Use equipment only as described in this manual.
Never stand on the balancer.
Wear non-slip safety footwear when operating the balancer.
Keep hair, loose clothing, neckties, jewelry, fingers, and all parts of body away from
all moving parts.
Do not place any tools, weights, or other objects on the safety hood while operating
the balancer.
ALWAYS WEAR OSHA APPROVED SAFETY GLASSES. Eyeglasses that have only
impact resistant lenses are not safety glasses.
Keep the safety hood and its safety interlock system in good working order.
Verify that the wheel is mounted properly and that the wing nut is firmly tightened
before spinning the wheel.
Hood Autostart will cause the balancer shaft to spin automatically upon hood closure.
For the next Autostart, the safety hood has to be lifted to the full up position and then
closed.
Raise safety hood only after wheel has come to a complete stop. If safety hood is
raised before the spin is completed, the weight values will not be displayed.
Do not let cord hang over any edge or contact fan blades or hot manifolds.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
2x 1. Getting Started DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 7

Electrical
The DSP9200 is manufactured to operate at a specific voltage and amperage rating.
Make sure that the appropriate electrical supply circuit is of the same voltage and
amperage ratings as marked on the balancer.
Make sure that the electrical supply circuit and the appropriate receptacle is installed
with proper grounding.
To prevent the possibility of electrical shock injury or damage to the equipment when
servicing the balancer, power must be disconnected by removing the power cord
from the electrical power outlet.
After servicing, be sure the balancer ON/OFF switch is in the “O” (off) position before
plugging the power cord into the electrical power outlet.
WARNING: DO NOT ALTER THE ELECTRICAL PLUG. Plugging the
electrical plug into an unsuitable supply circuit will
damage the equipment.
This device is rated as Class A for radiated emissions.
In the event of radio interference, the display read out may flicker - this is normal.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 1. Getting Started x 3
Page 8
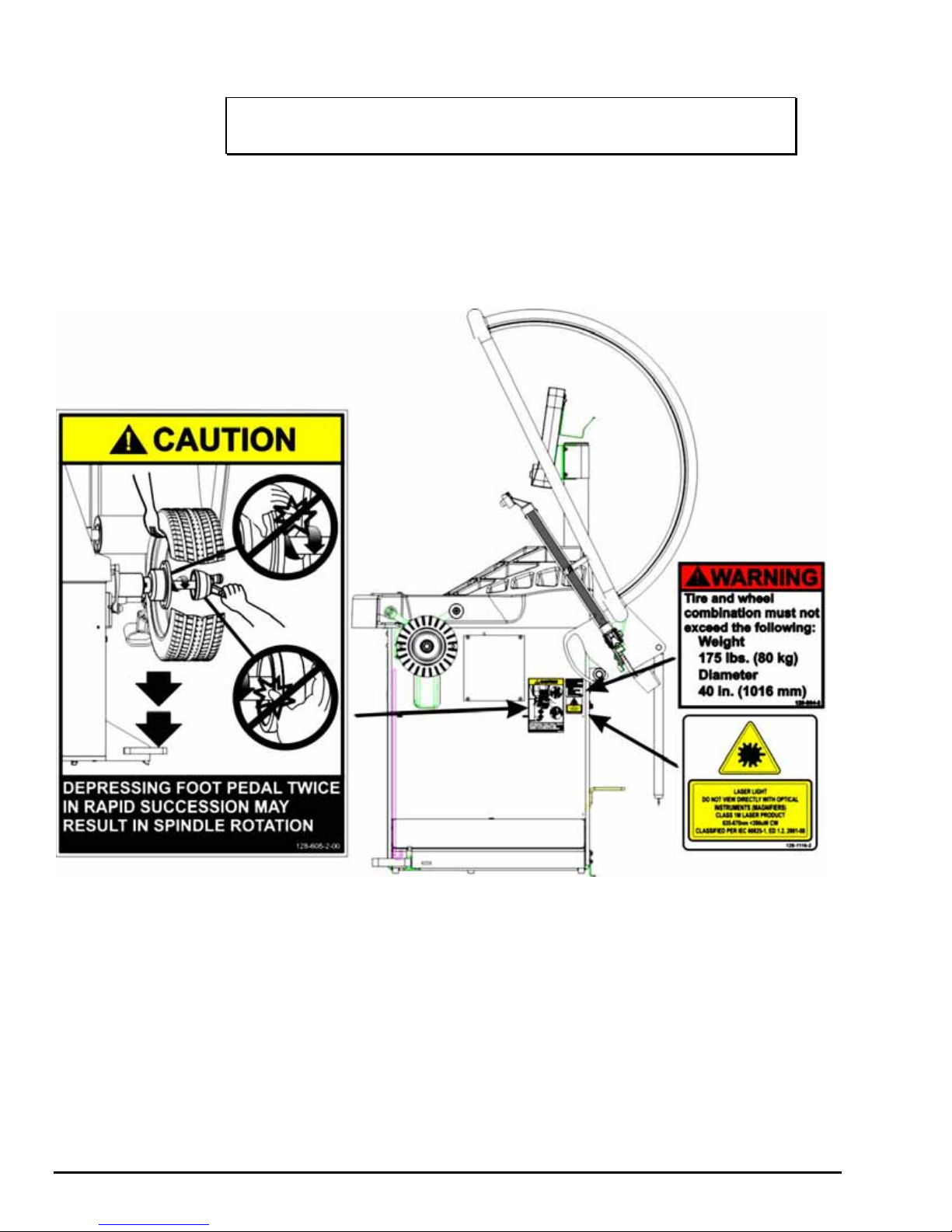
Decal Information and Placement
NOTE: Decals and their placement may vary due to balancer
configuration and options.
Right Side View
Decal 128-963-2 gives the maximum wheel diameter, maximum wheel weight, and
maximum rotational frequency for the DSP9200.
Decal 128-605-2-00 cautions the user that spindle rotation may occur with foot pedal
depression and to keep clear of clamping components during Quick-Thread™ shaft
rotation.
4x 1. Getting Started DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 9

Left Side View
Decal 128-391-2-00 cautions that the unit may automatically start upon closing of the
hood when hood Autostart is enabled.
Decal 128-229-2 and decal 128-905-2 work in conjunction to caution the user to not
remove the screw because of the risk of electrical shock.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 1. Getting Started x 5
Page 10
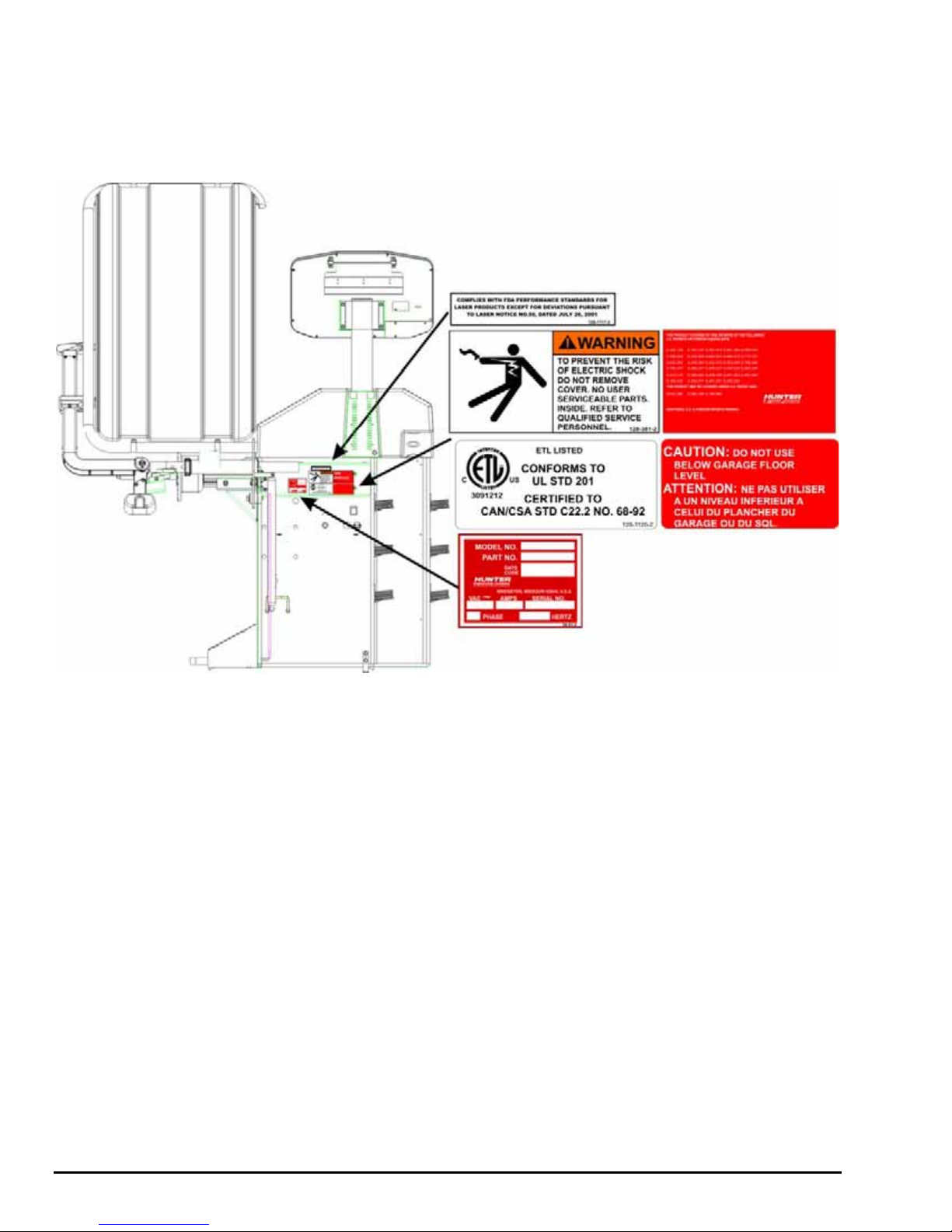
Back View
Decal 128-907-2 warns the user to place the DSP9200 at garage floor level, and not
in a recessed area, to avoid the possibility of flammable fume ignition.
Decal 128-229-2 and decal 128-905-2 work in conjunction to caution the user to not
remove the screw because of the risk of electrical shock.
6x 1. Getting Started DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 11

Specific Precautions/Power Source
The DSP9200 is intended to operate from a power source that will apply 230VAC
+10% / -15%, 1 phase, 3 amp 50/60 Hz, power cable includes NEMA 20 amp plug,
L6-20P, between the supply conductors of the power cord. The power cord supplied
utilizes a twist lock connector, NEMA L6-20P. This machine must be connected to a
20 amp branch circuit. Please refer all power source issues to a certified electrician.
Refer to Form 5467T, “Installation Instructions for DSP9200 Wheel Balancer.”
CAUTION: A protective ground connection, through the grounding
conductor in the power cord, is essential for safe operation.
Use only a power cord that is in good condition.
NOTE: For information on converting from single phase NEMA
L6-20P plug to thee phase NEMA L15-20P plug refer to
Form 5350T, “NEMA L6-20P to NEMA L15-20P Power Plug
Conversion Instructions.”
or
Turning Power ON/OFF
The ON/OFF switch is located on the back of the balancer cabinet. To turn the
balancer “ON,” press the “I” side of the ON/OFF switch. To turn the balancer “OFF,”
press the “O” side of the ON/OFF switch.
ON
OFF
When the ON/OFF switch is turned “ON,” the display panel segments will begin
lighting individually from left to right presenting a merchandising display. This also
indicates that power is on, the unit has self-checked, and that all displays are
functioning. Pressing any button on the control panel or moving the spindle shaft will
exit the merchandising display and advance the balancer to the default settings:
STANDARD procedure / DYNAMIC mode with the “Blind” and “Rounding” enabled.
Refer to “Blinding and Rounding,” page 51.
Equipment Installation and Service
Installation should be performed by a factory-authorized representative.
This equipment contains no user serviceable parts. All repairs must be referred to a
qualified Hunter Service Representative.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 1. Getting Started x 7
Page 12

Equipment Specifications
Electrical
Voltage: 230VAC +10% / -15%, 1 phase, 50/60 Hz, power
cable includes NEMA 20 amp plug, L6-20P
Amperage: 3 amperes
Wattage: 920 watts (peak)
Atmospherics
Temperature:
Relative Humidity: Up to 95% Non-condensing
Altitude: Up to 6000 ft. (1829 m)
Sound Pressure Level Equivalent continuous A-weighted sound pressure
+32qF to +122qF (0qC to +50qC)
at operator’s position does not exceed 70 dB (A).
Safety Summary
Explanation of Symbols
These symbols may appear on the equipment.
Alternating current.
Earth ground terminal.
Protective conductor terminal.
l ON (supply) condition.
OFF (supply) condition.
8x 1. Getting Started DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Risk of electrical shock.
Stand-by switch.
Not intended for connection to public
telecommunications network.
Page 13

1.3 DSP9200 Components
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 1. Getting Started x 9
Page 14

Standard Accessories
1. 106-82-2 Sleeve, Scratch Guard for Small Cup
2. 175-353-1 Polymer Cup (4.5” O.D.)
3. 76-433-3 Quick Take-Up Wing Nut with Handles
4. 221-658-2 Hammer Heads (4)
5. 46-320-2 Spacer
6. 221-589-2 Weight Hammer/Pliers
7. 221-659-2 Adhesive Weight Scraper
8. 223-68-1 Pressure Ring
9. 65-72-2 Calibration Weight
NOTE: Hunter wheel balancers do not include a standardized set of
mounting adaptors.
For optional accessories, refer to Wheel Balancer Brochure, Form 3203T.
10x 1. Getting Started DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 15

1.4 Operating the Control Panel
Control Panel
Using the Control Panel
Press the “Standard/ALU” button to select a STANDARD or ALU procedure.
Refer to “Standard Balancing Procedure (Using Clip-on Weights),” page 19 or
“Adhesive Weight Procedures (Combination Of Clip-on & Adhesive Weights, or Two
Adhesive),” page 36.
Press the
Optimizing Tire & Wheel Imbalances (Wheel with the Tire Mounted Procedure),”
page 42 or “OPT-2 Optimizing Tire & Wheel Imbalances (Tire Not Mounted
Procedure),” page 43.
Press the
“Static / Standard Balancing Procedure (Clip-on Weight),” page 35 or “Static / ALU
Balancing Procedure (Adhesive Weight),” page 41.
Press the
Refer to “Calibration Procedures,” page 58.
Press the
plane selected) or scroll through menus, or to select wheel to store/recall.
Press the
been selected, or to “Store/Recall” wheels. Refer to “Storing and Recalling Wheels,”
page 55.
“Optimize” button to select an Optimize procedure. Refer to “OPT-1
“Static/Dynamic” button to select the balancing mode. Refer to
“Setup/Cal” button to select from the Setup or Calibration options.
“Next” button to change planes (green “weight” will indicate current
“Enter” button to enter information and to begin a procedure that has
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 1. Getting Started x 11
Page 16

Press the “Left Plane Split Weight®” button to split weights on the Left Plane.
Refer to “Split Weight
®
Feature,” page 51.
Press the
Press the
Plane. Refer to “Split Weight
Press the
“Oz/Gm” button to view balancing weights in ounces or grams.
“Right Plane Split Weight®” button to split weights on the Right
®
Feature,” page 51.
“CenteringCheck®” button to check the accuracy of the mounting of
the tire/wheel assembly on the balancer shaft. Refer to “CenteringCheck
Using Wheel Dimension Control Knobs
The control knobs are located to the left of the control panel. The control knobs are
used to manually input wheel dimension data. The control knobs are identified as the
distance, width, and diameter control knobs.
Wheel dimension control knobs are used for manual data entry when required.
Changes to wheel dimensions are made by rotating the knobs. The control knobs are
digital encoder design and variable speed. Rotating slowly will change increments in
single digits. Rotating quickly will advance and move increments at an increased rate.
®
,” page 25.
12x 1. Getting Started DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 17

2. BALANCING OVERVIEW
2.1 Balancing Modes
Static Balance
As the word static implies, the tire will be balanced when at rest. For example, if an
unmoving assembly was centered on a cone and was balanced, it would be statically
balanced. A “bubble balancer” is designed to statically balance a tire/wheel
assembly.
IMBALANCE
FORCE
FRONT VIEW
CUPPING
STATIC IMBALANCE
Static imbalance is where there is one amount of weight located in the center of the
tire/wheel assembly causing an imbalance. As the weight rotates, centrifugal forces
are created causing the wheel to lift as the weight reaches top dead center. This
lifting motion causes the tire/wheel assembly to move “up and down” creating a
bounce to be felt. This static imbalance condition is evident by a “jiggle” or up-down
movement of the steering wheel. These vibrations may also be apparent in the body,
with or without steering wheel shake.
A statically imbalanced tire driven for an extended period may cause “cupping” in the
tire’s tread, create vibration, and adversely effect handling.
Static balancing alone is a seldom-recommended procedure that balances the
assembly using only a single weight plane. For example, a single weight is commonly
placed on the inner clip weight position for cosmetic purposes. This is not a
recommended practice and usually insures the assembly is not properly dynamically
balanced. The assembly may then experience side-to-side imbalance while in
motion, causing a shimmy condition and objectionable vibration.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 2. Balancing Overview x 13
Page 18

Dynamic Imbalance
x
In general terms, dynamic imbalance is defined as where one or more locations of
the tire/wheel assembly are heavier causing an imbalance force and/or an imbalance
wobble. Shown below is a tire/wheel assembly with two heavy spots of equal weight
which are located 180 degrees radially from each other on opposite sides. As this
assembly rotates, centrifugal forces cause a large imbalance wobble to be created,
but the imbalance force (as well as the static imbalance) will be zero. A wheel with
this condition will cause a wobble or shimmy to be felt in the steering wheel.
Excessive dynamic imbalance of this type creates a shimmy that transfers through
the suspension components to the occupants of the vehicle, especially at higher
speeds.
IMBALANCE WOBBLE
(LATERAL TWIST OR TORQUE)
FRONT VIEW
ZERO STATIC IMBALANCE WITH LARGE
DYNAMIC (COUPLE) IMBALANCE
Modern “dynamic” balancers spin the wheel in order to measure both the up and
down imbalance force and the wobble or shimmy related imbalance (side-to-side).
Dynamic balancers direct the operator to place correction weights on the inside and
outside correction locations of the rim so that both imbalance force and imbalance
wobble will be eliminated.
TOP VIEW
IMBALANCE WOBBLE
(LATERAL TWIST OR TORQUE)
IMBALANCE FORCE
(UP & DOWN)
ZERO STATIC IMBALANCE (UP & DOWN)
+ ZERO COUPLE IMBALANCE (WOBBLE)
_____________________________________
= ZERO DYNAMIC BALANCE
2. Balancing Overview DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
14
Page 19

Static and Dynamic Imbalance Sensitivity
As a general rule of thumb, to achieve the best balance on an average sized tire and
wheel assembly:
Residual static imbalance should be less than 1/2 ounce.
Residual dynamic imbalance should be less than 1/4 ounce per plane.
A small amount of residual dynamic imbalance is preferred over a similar amount of
remaining static imbalance.
In general, it takes much more residual dynamic imbalance to cause a vibration than
the same amount of static imbalance.
The larger the diameter used for weight placement, the smaller the amount of
correction weight is required.
The wider the distance between the two weight placement locations, the smaller the
amount of correction weight is required.
If static balance is the only option, always verify that the remaining dynamic residual
imbalance is within acceptable tolerance.
2.2 Identifying the Static Balance Weight Plane
In “STANDARD BALANCE” mode, using only a clip-on weight, the plane is input as
follows:
For static balancing, it is recommended that you place half of the correctional weight
value on each side of the tire to reduce residual dynamic imbalance.
In “MIXED WEIGHTS BALANCE” mode and “ADHESIVE WEIGHTS BALANCE”
mode, using an adhesive weight, the plane is input as follows:
DIAMETER
For static balancing, it is recommended that the adhesive weight be placed as close
to the center of the wheel as possible to reduce residual dynamic imbalance.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 2. Balancing Overview x 15
Page 20

In “PATCH BALANCE” mode, using a patch weight, the plane is input as follows:
x
DIAMETER
For static balancing, it is recommended that the patch weight be placed as close to
the center of the tread as possible to reduce residual dynamic imbalance.
2.3 Identifying the Dynamic Balance Weight Planes
The balancer must know the location of the two weight circle planes for placement of
correction weights on the wheel assembly.
Each plane is described by a distance from the balancer and a diameter.
MIXED WEIGHTSSTANDARD PATCHADHESIVE WEIGHTS
RIM LIP / RIM LIP RIM LIP / INNER RIM SURFACE
In “STANDARD BALANCE” mode, using only clip-on weights, left and right planes
are input as follows:
INNER RIM SURFACE /
INNER RIM SURFACE
INNER TIRE SURFACE /
INNER TIRE SURFACE
2. Balancing Overview DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
16
Page 21
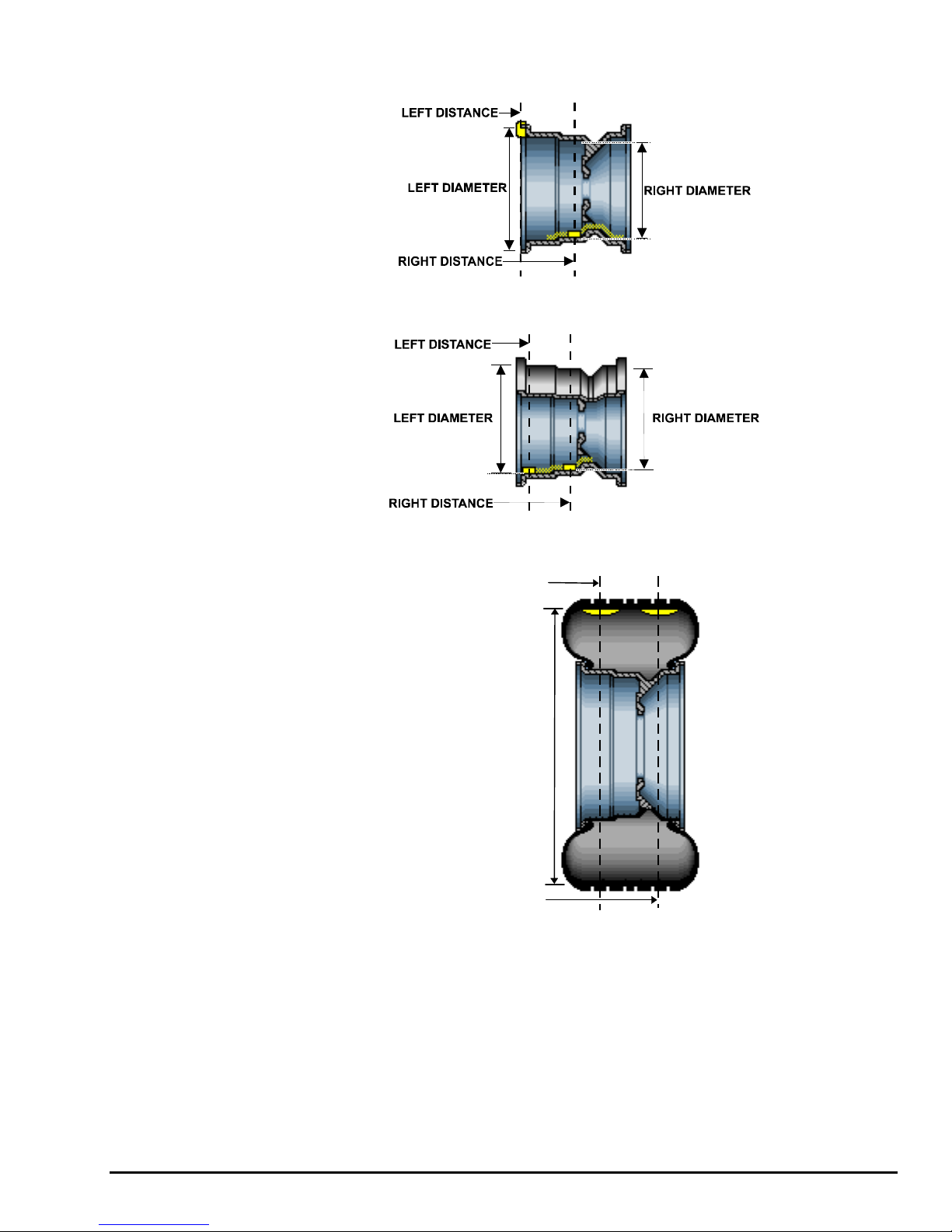
In “MIXED WEIGHTS BALANCE” mode, using clip-on and adhesive weights, the left
x
and right planes are input as follows:
In “ADHESIVE WEIGHTS BALANCE” mode, left and right planes are input as
follows:
In “PATCH BALANCE” mode, using patch weights, left and right planes are input as
follows:
LEFT DISTANCE
DIAMETER
RIGHT DISTANCE
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 2. Balancing Overview
17
Page 22

2.4 On-Vehicle Wheel Mounting Methods
x
Hub Centric
A hub centric wheel is aligned to the hub by the center bore of the wheel. The vehicle
weight rests on the hub bore. The clearance between the hub bore and the hub on a
hub centric wheel is between 0.003 and 0.004 of an inch. A hub centric wheel is
identified by removing the lug nuts (or bolts) and moving the wheel up, down, and
side-to-side. If there is little or no movement, the wheel is centered by the hub.
To verify if the wheel is hub centric:
Remove the lug nuts (or bolts) and try to move the wheel up/down and
side/side on the hub.
If the wheel has no appreciable movement around or about the
centerline of the hub, it should be considered hub centric.
A hub centric wheel will have very little (0.003 – 0.004”) clearance or a
slip fit to the hub.
Lug Centric
A lug centric wheel is identified by removing the lug nuts (or bolts) and moving the
wheel up, down, and side-to-side. If movement around the hub is apparent, the wheel
is centered on the vehicle by the lugs or studs of the axle flange.
TIP: When mounting a lug centric wheel to a vehicle, extreme
centering care must be taken by ensuring the lug nuts (bolts)
are tightened equally, while rotating the wheel.
“Step-torque” star pattern to proper torque specification.
To verify if the wheel is lug centric:
Remove the lug nuts (or bolts) and try to move the wheel up/down and
side/side on the hub.
A lug centric wheel will display noticeable movement.
18
2. Balancing Overview DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 23

3. BALANCING A WHEEL
x
3.1 Mount the Wheel on the Spindle Shaft
Remove any existing wheel weights, rocks, and debris from the tire tread, and clean
the center hole of the wheel. Inspect inside of wheel for excessive accumulation of
dirt and debris. Remove if necessary before balancing.
Accurate balancing depends on accurately centering the wheel. Choose the proper
wheel mounting cone by placing it in the center hole of the wheel to be balanced.
Refer to “CenteringCheck
®
,” page 25.
NOTE: If the basic cone and adaptors do not fit the wheel, additional
centering adaptors will be necessary. A wheel that cannot be
properly centered, cannot be properly balanced. All
balancers require additional centering adaptors to properly
center certain types of wheels. For additonal information,
refer to Form 3203T for optional accessories.
With the safety hood open, place the wheel mounting cone on the spindle shaft
against the captivated spring. Position the wheel with the inside surface facing the
balancer, centered on the cone.
Install the plastic clamping cup and wing nut on the spindle shaft against the wheel
and secure the entire assembly by firmly tightening the wing nut.
If equipped with optional Spindle-Lok
tightening the wing nut. Holding the shaft locked while tightening the wing nut
improves centering accuracy.
Slowly roll the wheel towards you while tightening the wing nut. This improves
accurate wheel centering, since the wheel is allowed to roll up the taper of the cone
as opposed to forcing it to slide up the cone.
®
foot pedal, depress and hold down while
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
19
Page 24

Front/Back Cone Mounting
x
Cone mounting is one of the most common and reliable ways to mount wheels on
balancers.
Select the proper wheel mounting cone by placing it in the center bore of the wheel to
be balanced. Select the cone that contacts the wheel nearest the center of the cone.
Place the wheel mounting cone on the spindle against the spring plate. Mount the
wheel with the inner rim facing the balancer and centered on the cone.
Install the clamping cup and wing nut on the spindle shaft against the wheel and
secure the entire assembly by firmly tightening the wing nut, while depressing the
foot pedal to hold the spindle in place.
NOTE: If equipped with optional Spindle-Lok
and hold down while tightening the wing nut. Holding the
shaft locked while tightening the wing nut improves centering
accuracy.
Slowly roll the wheel toward you during the initial tightening
of the wing nut. This aids in accurate wheel centering and
increased repeatability, since the wheel is allowed to roll up
the taper of the cone as opposed to forcing it to slide up the
cone.
®
foot pedal, depress
20
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
WHEEL
MOUNTING
CONE
CAPTIVATED
SPRING
INSIDE
SURFACE
STANDARD
WHEEL
SPINDLE
SHAFT
WING NUT
PLASTIC
CLAMPING
CUP
STANDARD STEEL
WHEEL RIM
Page 25

Wheels with center holes over 3 9/16 inch diameter require the light truck cone. The
R
x
light truck cone can be installed from the outside of the wheel. (When using the light
truck cone, the plastic clamping cup is not used.)
LIGHT TRUCK
WHEEL
LIGHT
TRUCK CONE
CAPTIVATED
SPRING
Using Plastic Wheel Mounting Washer
The plastic wheel mounting washer, 46-320-2, is used to prevent scratches on
wheels where the standard plastic cup and scratch guard cannot be used.
The plastic wheel mounting washer can also be used when mounting a wheel with a
large offset that is between cone sizes. Use of the washer as shown below can
improve centering ability by increasing cone pressure against the wheel.
For example: One cone size is too small because the captivated spring is not
pressing the cone against the inner wheel opening, but the next larger cone size is
too big and will not fit the opening. Use the smaller cone size with the plastic wheel
mounting washer to “extend” the captivated spring to hold the mounting cone against
the wheel opening with greater pressure.
PLASTIC
WASHE
LARGE OFFSET
MOUNTING
CONE
PLASTIC
CLAMPING
CUP
NOT USED
WHEEL
SPINDLE
SHAFT
CAPTIVATED
SPRING
WING NUT
PLASTIC
CUP
The scratch guard may be installed on the clamping cup to protect aluminum rims
from being marred, but should not be used on steel wheels.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
21
Page 26

NOTE: Use only the wing nut supplied with the DSP9200.
x
In some cases, the mounting pad of the wheel may be extremely wide, and the
standard clamp cup will not properly contact the wheel hub area. In these cases, the
optional nine inch alloy wheel pressure cup may be used in place of the clamping
cup.
Wheels with center bores over 3 9/16 inch diameter require one of the light truck
cones. The light truck cones must be mounted from the outside of the wheel.
NOTE: When using the light truck cones, the pressure ring is used
in place of the clamping cup.
This procedure utilizes a tapered cone inserted from the front side of the wheel
instead of the backside as previously described.
Select the proper wheel mounting cone by placing it in the center bore of the wheel to
be balanced. Choose the cone that contacts the wheel nearest the center of the
cone.
Mount the wheel with the inner rim facing the balancer. Place the wheel mounting
cone on the spindle with the small end of the cone facing the front of the wheel.
Install the wing nut and pressure ring assembly onto the spindle shaft against the
wheel and secure the entire assembly by firmly tightening the wing nut.
Heavy wheel centering may benefit by (1) pulling the tire away from the hub face at
top dead center while tightening the wing nut or (2) use of optional wheel lift to
position heavy wheel onto shaft and cone. This helps the wheel to overcome gravity
against the hub or spacer.
22
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 27

Cone/Flange Plate Mounting
x
Wheels may be centered using the lugholes and center bore with a flange plate and
centering cone. It is important that a back mounted cone be used to support and
center the wheel when using flange plates.
The correct flange adaptor setup is determined by:
1. Measure and set the bolt circle diameter and number of studs to use
against the lug holes.
Set the number of lugholes as follows:
A three-lug wheel uses three studs.
A four-lug wheel uses four studs.
A five-lug wheel uses five studs.
A six-lug wheel uses three studs.
A seven-lug wheel uses seven studs.
An eight-lug wheel uses four studs.
2. Choose the correct taper design of flange studs to fit the wheel lug
seats. The mounting area of the flange stud must match the design
of the wheel’s lughole seat or depression.
The flange plate must be able to apply pressure to the center of the wheel while
maintaining perpendicularity to the shaft.
NOTE: If the lug seats are unevenly machined or worn, an optional
universal flange adaptor with compressible studs or bolt on
lugs may be used to more accurately mount the wheel with
the cone.
Flange plates are useful when the wheel cannot be properly centered off the hub
bore with a tapered cone alone because of improper fit, interference, or lack of a
center hole.
A flange plate in many cases adds value because it aids in more effective centering
than a tapered cone alone. This statement is true for many wheels including hub
centric wheels. That is why a flange plate and back cone may be more accurate and
repeatable, regardless of whether the wheel is lug centric or hub centric.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
23
Page 28

Using the Pressure Ring and Spacers
x
Pressure Ring
The pressure ring clips on to the wing nut. It is used in lieu of the clamping cup.
It may also be used in place of a clamping cup if space is limited between the wheel
and the end of the spindle.
The pressure ring should be used to prevent the wing nut from directly contacting an
adaptor or a cone. It will act as a bearing to enable higher clamping forces.
Spacers
There are two types of spacers:
x Hub Ring Spacers
x Shaft Spacers
Hub Ring Spacers
These light truck spacers are designed to build a larger pocket when using extra
large truck cones. It also provides a location for the centering pins found on some
dual wheel configurations.
24
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 29

Shaft Spacers
x
The shaft spacer can be used to make the cone contact the hub bore more firmly.
For example, one cone size is too small because the captivated spring is not
pressing the cone against the inner wheel opening, but the next larger cone size is
too large and will not fit the opening. Use the smaller cone size, with the spacer, to
extend the captivated spring and hold the smaller mounting cone against the wheel
opening with greater pressure.
CenteringCheck
After mounting the wheel on the spindle and securing with the wing nut, press the
“CenteringCheck®” button.
Display shows “Rdy” “Spn.”
Press
“Top,” and valve stem flashes.
Rotate wheel until valve stem is at TDC and press
Display shows “rot” “180.”
Step on foot pedal to lock spindle. Loosen wing nut and rotate wheel and adaptors
about 180 degrees. Tighten wing nut. (Press
shows “Rdy” “Spn.”
Press
at TDC, and press
If centering of the assembly repeats balance weight magnitude and phase angle to
within programmed limits, the assembly is assumed to be centered. The display
momentarily flashes “PASS,” then shows correction weights.
If centering of the assembly does not repeat balance weight magnitude and phase
angle to within programmed limits, the assembly is likely not centered. The display
momentarily flashes “FAIL” then shows “---” instead of weights. Check wheel to
adaptor fitment and centering. Retry.
®
“Start” or lower hood to spin. When spin ends, display shows “Put”
“Enter” or step on foot pedal.
“Enter” if no foot pedal.) Display
“Start” or lower hood. When spin ends, rotate wheel until valve stem is
“Enter” or step on foot pedal.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
25
Page 30

3.2 Measuring the Wheel with Inner and Outer Auto Dataset® Arms
x
Auto Dataset® is a faster and more accurate method to take rim measurements than
traditional manual wheel data entry methods. Auto Dataset
distance, rim width, and weight plane location automatically. The Dataset
the DSP9200 are positioned at the weight plane and data is entered by depressing
the foot pedal.
Measuring Dimensions for Clip-On Weights:
Lift or pull the inner Dataset® arm away from the weight tray to trigger a new left
plane reading. A beep will occur and the green LED left rim lip “weight” will blink to
prompt for the input of the left plane weight. When the arm is steady, step on the foot
pedal, a confirmation beep occurs, the inner distance and rim diameter readouts are
updated, and the prompt stops blinking.
Lift or push the outer Dataset
reading. A beep will occur and the green LED right rim lip “weight” will blink to prompt
for the input of the right plane weight. When the arm is steady, step on the foot pedal,
a confirmation beep occurs, the wheel width readout updates and the prompt stops
blinking.
®
arm toward the weight tray to trigger a new right plane
®
is used to input rim
®
arms of
TIPS:
®
1. Both Dataset
arms may be used simultaneously.
2. If the balancer determines that the weight planes are too close together, the
weight digits will be turned off and the distance and the width digits will start
blinking. Re-enter the planes to correct this condition.
®
3. If the Dataset
arm is not steady when the foot pedal is depressed, there will be a
long error beep.
®
4. If the Dataset
arm is returned to the storage position before a reading is taken,
the trigger is canceled and the prompt stops blinking.
®
5. After taking a reading, the Dataset
arm must be returned to the storage position
to trigger a new reading.
6. If STATIC mode is in effect, distance readouts will not be updated. Distance
readouts are not used in STATIC mode.
NOTE: The wheel diameter input by the inner auto Dataset
26
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
®
arm
might be slightly different from the known nominal wheel (tire
bead seat) diameter. The auto Dataset® arm measures the
actual weight circle instead for the rim lip configuration of the
wheel. A more accurate wheel balance will result if the
reading is not manually (knob) adjusted to the nominal wheel
diameter.
Page 31

Mixed Weights and Two Adhesive Weights (Inputting Distance and
x
Diameter for Both Planes):
The inner Dataset® arm will trigger as it is raised from the home resting position (left
plane green LED “weight” will blink as a prompt). Place the pointer tip or pointer disc
edge at the desired left plane weight location, and step on the foot pedal. The
reading will be taken and the display will update the left plane weight position.
Mixed Weights Two Adhesive Weights
Right plane green LED will now blink as a prompt for the right plane weight to be input.
Before returning the inner Dataset
at the desired right plane weight location and step on the foot pedal. The weight
position will be taken and the display will automatically change to show the right
weight LED and the new right plane weight dimensions.
®
arm to the storage position, place the disc edge
A confirmation beep occurs, the readouts change to the newly acquired values and
the prompt stops flashing.
The dimension digits will now blink a prompt for optional “Split Spoke
to “Split Spoke® Feature,” page 53, or return the arm to the home position.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
®
” mode. Refer
27
Page 32

3.3 Manually Setting Wheel Dimensions
x
12
3
The distance knob (1) is used to input the distance from the balancer to a weight
plane.
The width knob (2) is used to input the distance from the left weight plane to the right
weight plane.
28
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 33

The diameter knob (3) is used to input the weight circle diameter of a weight plane.
x
“P195/75R-14”
ADHESIVE WEIGHT CLIP ON WEIGHT
The optional inner auto Dataset® arm can be used to automatically measure distance
and diameter. Refer to “Measuring the Wheel with Inner and Outer Auto Dataset
Arm(s),” page 26.
The optional outer auto Dataset
®
arm can be used to automatically measure wheel
width. Refer to “Measuring the Wheel with Inner and Outer Auto Dataset
page 26.
Measuring the Wheel at the Inner Rim Lip (Clip-On Weight)
Measure the distance to the wheel inner rim lip by pulling the sliding Dataset® arm
pointer outward until it is touching the wheel inner rim lip. Read the Dataset
scale and set the distance knob to the reference number on the scale.
®
Arm(s),”
®
arm
®
Most of the time, the Dataset® arm pointer will contact the rim lip as shown in
illustration (A) below. In some cases, the rim lip may be so wide that the pointer disk
touches the rim as shown in illustration (B) below. In either case, the balancer will
compensate for this and provide accurate weight locations.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
TIRE
WHEEL
RIM LIP
DATASET£ ARM
POINTER DISK
29
Page 34

Measuring Wheel Width with Rim Width Calipers
x
The rim width calipers are used to measure the distance between the wheel rim lips
(tire bead seats).
Apply the rim width calipers as shown below.
Read the scale imprinted on the rim width calipers and set the rim width knob to the
rim width reference number on the scale.
Measuring the Inside Wheel Surface with the Pointer Disk Edge
(Adhesive Tape-On Weights)
Place edge of manual Dataset® arm disk against the inside surface of the wheel at
the location where the right edge of the adhesive weight is to be placed. Set Dataset
arm distance knob to the reference number on the Dataset
NOTE: The Dataset
®
arm is used in the position as shown in the
®
arm scale.
photo below.
TIP:
®
When using Adhesive Weight programs, the greater the distance between the two
weights, the less weight it takes to perform a dynamic balance. The balancer
prevents the operator from locating the two wheel weights too close together to
provide a correct dynamic balance.
30
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 35

For example: The illustration below shows the installation of two adhesive weights.
x
The weight locations are at the minimum allowed distance.
If the weight locations are moved any closer together using the Dataset® distance
knob or auto Dataset
®
arm, the distance digits will blink and the weight amount
display will change to - - - - - -. Move either weight location away from the other
weight location to resolve this situation before proceeding.
*An optimum chosen position by the operator would be at the extreme left edge of
the wheel and extreme inside right edge (280 and 400 as shown). This would lessen
the total amount of weight required in order to perform a correct dynamic balance.
Measuring the Inside Wheel Diameters (For Adhesive Weights)
If other wheels have been removed from the vehicle, it will be easier to measure
inside rim diameters on an unmounted wheel. Use rim width calipers or a tape
measure to make the measurements for both the plane right and left plane adhesive
weight location internal wheel diameters as shown below.
Measure the rim inside diameters at the same location where the wheel weight is to
be placed and set the wheel diameter knob to the measurement:
OR
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
31
Page 36

3.4 Locating the Wheel Weights at the Top Dead Center (“TDC”)
x
and Bottom Dead Center (“BDC”)
Clip-on weights are always located at TDC and adhesive tape-on weights are always
located at BDC as shown on the weight indicator display.
Find TDC by turning the wheel until the Green Arrow and the Center LED on the
weight indicator are both “ON” (see the left plane weight indicator in the illustration
below). In this position, a balance weight has to be attached at top dead center. To
automatically position weights at TDC or BDC, refer to “Motor Drive/Servo-Stop,”
page 49.
To apply wheel balancing weights at TDC (12 o’clock position), align the weights with
the white line on the spindle housing. The line is used to accurately locate the TDC
position.
When the weight indicator LED bar is blinking, it indicates that the weight location is
more than 90 degrees from TDC (on the hidden side of the wheel). When the green
arrow is blinking, it indicates that the weight location is at BDC. The illustration below
shows the wheel positioned at TDC for placement of the left plane weight, while the
right plane weight position is 180 degrees from TDC (Bottom Dead Center - BDC).
(TDC) ON
ON
BLINKING
BLINKING (BDC)
LEFT PLANE
WEIGHT AT TDC
(APPLIED)
32
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
RIGHT PLANE
WEIGHT (APPLIED)
Page 37

3.5 Standard Balancing Procedure (Clip-on Weights)
x
Mount wheel.
Press the
Press the
“Static/Dynamic” button to select DYNAMIC .
“Standard/ALU” button until both clip-on weights are blinking.
Measure and enter the distance to the wheel inner rim lip and rim diameter as shown
below:
Measurement can be input automatically, if the DSP9200 is equipped with the
optional auto inner and/or outer Dataset
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
®
arms.
“P195/75R-15”
33
Page 38

Measure and enter the wheel width as shown below:
x
OR
RIM WIDTH
This measurement can be input automatically, if the DSP9200 is equipped with the
optional auto inner and/or outer Dataset
Inner and Outer Auto Dataset
®
Arm(s),” page 26.
®
arms. Refer to “Measuring the Wheel with
Close safety hood and spin wheel.
After wheel stops, raise safety hood.
Find TDC for left plane and attach weight.
LEFT PLANE TDC
If necessary, use the “Left Plane Split Weight®” button to split weight.
Find TDC for right plane and attach weight.
RIGHT PLANE TDC
If necessary, use the “Right Plane Split Weight®” button to split weight.
34
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 39

Verify balance condition by spinning again. Display should show “zero.”
x
“Standard” balancing procedure is complete.
NOTE: Weight digits blink if the force signals are larger than the
measurement range of the balancer. If this occurs, check for
wheel not being properly centered on spindle shaft. If wheel
is centered, apply the displayed weights. The blinking
weights indicate that a second spin and additional weight(s)
may be required to get zero imbalance. Refer to “Correcting
Large Imbalances,” page 52.
3.6 Static / Standard Balancing Procedure (Clip-on Weight)
Use STATIC / STANDARD balancing procedure for “static” (single-plane) balancing
using a clip-on weight.
Mount wheel.
Press the
Press the
“Static/Dynamic” button to select STATIC .
“Standard/ALU” button until both clip-on weights are blinking.
Measure and enter the rim diameter of static plane weight location as shown below:
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
35
Page 40

This measurement can be input automatically, if the DSP9200 is equipped with the
x
optional auto inner and/or outer Dataset
®
arms.
Close safety hood and spin wheel.
After wheel stops, raise the safety hood.
Find TDC for static plane and attach clip-on weight on either rim lip.
NOTE: It is recommended that the weight be distributed equally
between the left and right rim lips to provide minimum
residual dynamic imbalance.
For example: In the illustration above, place a 0.25 oz.
weight amount on each rim lip at the TDC position.
If necessary, use the “Right Plane Split Weight®” button to split weight.
Verify balance condition by spinning again. Display should show “zero.”
The STATIC / STANDARD balancing procedure is complete.
3.7 Adhesive Weight Procedures (Combination of Clip-on &
Adhesive Weights, or Two Adhesive)
LEFT PLANE
CLIP-ON/ADH
RIGHT PLANE
LEFT PLANE
ADH/ADH
The following combinations of weight placements are available:
Adhesive Weight Placement (Types and Locations)
Left Plane Right Plane
Dynamic Balancing
Clip-On (TDC) Adhesive inner (backside of wheel, BDC)
Clip-On (TDC) * Adhesive outer (front side of wheel, BDC)
Adhesive (BDC) Adhesive inner (backside of wheel, BDC)
Adhesive (BDC) * Adhesive outer (front side of wheel, BDC)
Static Balancing
N/A Adhesive inner (backside of wheel, BDC)
* Select front side weight placement mode by entering either clip-on/adhesive or
adhesive/adhesive mode, then move the optional outer Dataset
home position.
®
arm away from the
36
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 41

Mount wheel.
x
Press the
“Standard/ALU” button repeatedly until the desired combination of
weight placements are lit on the display.
Measure and enter the dimensions of the left plane weight location as shown below:
CLIP-ON/ADHESIVE
ADHESIVE/ADHESIVE
Press the “Next” button to change display to show right plane weight
dimensions.
Measure and enter the dimensions of right plane weight location as shown below:
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
37
Page 42

CLIP-ON/ADHESIVE
x
LEFT PLANE TDC
If using the optional inner Dataset® arm, refer to “Split Spoke Feature,” page 53. This
measurement can be input automatically, if the DSP9200 is equipped with the
optional auto inner and/or outer Dataset
Inner and Outer Auto Dataset
®
Arm(s),” page 26.
®
arms. Refer to “Measure the Wheel with
Close safety hood and spin wheel.
After wheel stops, raise safety hood.
Find TDC for left plane and attach clip-on weight, or find BDC for left plane and
attach adhesive weight.
ADHESIVE/ADHESIVE
LEFT PLANE BDC
(BLINKING)
If necessary, use the “Left Plane Split Weight®” to split weight.
The 360 degree weight angle display can be used to place the adhesive weight at
Bottom Dead Center (BDC) for easier and more accurate placement than the
conventional TDC method. If TDC placement is desired, press the
button to disable Servo Stop. Rotate the wheel to TDC and attach weight.
The Dataset
®
arm may be used as a reference device for locating previously input
placement position of adhesive weight on left or right plane. If equipped with an
optional inner auto Dataset
trigger the Dataset
Aided Weight Placement,” page 47.
38
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
“Stop”
®
®
arm to begin Servo Aided Weight Placement. Refer to “Servo
arm, servo to locate an adhesive weight at BDC, then
Page 43

If using a manual Dataset® arm, press the “Next” button (if
x
necessary) to change display to show distance to the weight plane (right
or left) for the weight being placed.
®
Pull Dataset
arm out until the scale reading and the display right plane
distance reading are the same.
Find BDC for right plane as shown below.
Attach adhesive weight at BDC in-line with the Dataset
Aided Weight Placement or manual Dataset
RIGHT PLANE BDC
(BLINKING)
®
arm as described above.
®
arm disc edge, using Servo
If necessary, use the “Right Plane Split Weight®” to split weight.
Verify balance condition by spinning again. Display should show “zero.”
Balancing procedure is complete.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
39
Page 44

LEFT PLANE
x
WHEN RIGHT WEIGHT IS TO BE PLACED AS ILLUSTRATED,
I
NPUT RIGHT PLANE DIMENSIONS AS FOLLOWS:
RIGHT PLANE
40
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 45

3.8 Static / ALU Balancing Procedure (Adhesive Weight)
x
Use STATIC / ALU procedure for “static” (single-plane) balancing using an adhesive
weight. Because “static” balancing depends on the placement of only one weight, in
this procedure only one adhesive weight is shown, not an additional clip-on or
adhesive weight.
Mount wheel.
Press the
Press the
“Static/Dynamic” button to select STATIC .
“Standard/ALU” button to select one adhesive weight.
Measure and enter the internal diameter and distance near the center of wheel as
shown below:
This measurement can be input automatically, if the DSP9200 is equipped with the
optional auto inner and/or outer Dataset
If necessary, use the “Split Spoke” feature. Refer to “Split Spoke Feature,” page 53.
Close safety hood and spin wheel. After wheel stops, raise safety hood.
The 360 degree weight angle display can be used to place the adhesive weight at
Bottom Dead Center (BDC) for easier and more accurate placement than the
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
®
arms.
41
Page 46

conventional TDC method. If TDC placement is desired, press the “Stop”
x
button to disable servo and rotate the wheel to TDC and attach weight.
Find BDC for static plane as shown below.
®
Attach adhesive weight at BDC in-line with the Dataset
BDC
(BLINKING)
PLACE WEIGHT NEAR
CENTER OF RIM
arm disc edge.
NOTE: It is recommended that the weight be attached near the
center of the wheel to provide minimum residual dynamic
imbalance.
If necessary, use the “Right Plane Split Weight®” to split weight.
Verify balance condition by spinning again. Display should show “zero.”
The STATIC / ALU balancing procedure is complete.
3.9 OPT-1 Optimizing Tire & Wheel Imbalances (Wheel with the Tire
Mounted Procedure)
“Optimizing” positions the wheel with respect to the tire, minimizing the amount of
correction weight required.
Use OPT-1 when the tire is already mounted on the wheel.
Mount the tire/wheel assembly on the spindle shaft with the valve stem at TDC.
Enter Standard wheel dimensions.
Press the
Press the
Display shows “Put” “Top,” and the valve stem is flashing. Rotate the wheel until the
valve stem is at TDC and press “Enter.”
Close safety hood and spin wheel.
After wheel stops, raise the safety hood.
Remove tire/wheel assembly from balancer, deflate tire and loosen the tire beads
from the wheel, then rotate tire 180 degrees on the wheel.
Remount the tire/wheel assembly on the balancer with valve stem at TDC and press
“Enter.”
Close safety hood and spin wheel.
After wheel stops, raise the safety hood.
“Optimize” button once.
“Enter” button to begin procedure.
42
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 47

With green arrows lit respectively, mark wheel when flashing “r” is at TDC, and mark
x
tire when flashing “t” is at TDC.
If imbalance is less than 0.25 oz. for wheel or tire there will be no benefit
in proceeding.
If imbalance is excessive in tire or wheel only, replace unit and
rebalance.
Remove wheel from balancer.
Deflate tire, loosen the tire beads from the wheel, and rotate tire on the wheel to
lineup the two marks.
OPT-1 balancing procedure is complete.
Balance the wheel. Refer to the desired balance procedure.
3.10 OPT-2 Optimizing Tire & Wheel Imbalances (Tire Not Mounted
Procedure)
OPTimizing positions the wheel with respect to the tire, minimizing the amount of
correction weight required. Use OPT-2 when tire has not been mounted on wheel.
Mount bare wheel on spindle shaft with the valve stem at TDC.
Enter Standard wheel dimensions.
Press the
Press the
“Optimize” button twice.
“Enter” button to begin procedure.
Display shows “Put” “Top,” and the valve stem is flashing. Rotate the wheel until the
valve stem is at TDC and press the “Enter” button.
Close safety hood and spin wheel.
After the wheel stops, raise the safety hood.
Remove wheel from balancer and mount tire on wheel.
Remount the tire/wheel assembly on the balancer with the valve stem at TDC and
press the “Enter” button.
Close safety hood and spin wheel.
After wheel stops, raise safety hood.
With green arrows lit respectively, mark wheel when flashing “r” is at TDC, and mark
tire when flashing “t” is at TDC.
If imbalance is less than 0.25 oz. for wheel or tire there will be no benefit
in proceeding.
If imbalance is excessive in tire or wheel only, replace unit and
rebalance.
Remove tire/wheel assembly from balancer.
Deflate tire, loosen the tire beads from the wheel, and rotate tire on the wheel to
lineup the two marks.
OPT-2 balancing procedure is complete.
Balance the tire/wheel assembly. Refer to the desired balance procedure.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
43
Page 48

3.11 Patch Balance® Procedures
x
Use Patch Balance® procedure when weighted balance patches are to be cemented
to the inside of the tire. Weight balance patches are recommended for oversize light
truck tires that require excessive weight on the rim.
Before performing Patch Balance
and spin steps to determine which patch balancing procedure should be used:
Find TDC for the left plane.
If the right plane weight position indicator is lit solid and not blinking,
perform a Static Patch Balance.
If the right plane weight position indicator is blinking, perform a Dynamic
Patch Balance.
Static Patch Balance® (Single Weighted Balance Patch)
A weighted balance patch will be placed in the center of the tread area inside of the
tire as shown below:
SINGLE PLANE
®
procedure, perform Standard Dynamic rim entry
Mount wheel.
Enter Standard wheel dimensions.
Press the
Press the
“Static/Dynamic” button to select STATIC mode.
“Standard/ALU” button twice to select adhesive weight mode.
Measure inside tire diameter using a tape measure or tool, 221-527-1, just below
tread depth as shown below:
44
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 49

Enter inside tire diameter using the diameter knob.
x
Close safety hood and spin wheel.
After wheel stops, raise the safety hood.
Rotate wheel to TDC and mark tire and wheel for weighted patch(es) at location as
shown below:
If necessary, use “Left Plane Split Weight®” or “Right Plane Split
Weight£” to split weight.
Remove wheel from balancer and dismount tire from wheel.
Install weighted balance patch centered on inside of tire at mark as instructed by
manufacturer’s instructions.
Mount the tire onto wheel and align marks.
Press the
“Standard/ALU” button twice to select standard clip-on weight mode.
Balance. Verify balance condition by spinning again.
NOTE: Weight digits blink if the force signals are larger than the
measurement range of the balancer. If this occurs, check for
wheel being not properly centered on spindle shaft. If wheel
is centered, apply the displayed weights. The blinking
weights indicate that a second spin and additional weight(s)
may be required to get zero imbalance. Refer to “Correcting
Large Imbalances,” page 52.
Dynamic Patch Balance® (Two Weighted Balance Patches)
Weighted balance patches will be placed on the inside of the tire at the edge of the
tread area beside the sidewall as shown below:
LEFT PLANE RIGHT PLANE
NOTE: Weighted balance patches should be installed only in tread
Mount wheel.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 3. Balancing a Wheel
area. Do not install weighted balance patches near sidewall
or shoulder of tire.
45
Page 50

Press the “Static/Dynamic” button to select DYNAMIC mode.
x
Press the
Place inner Dataset
“Standard/ALU” button to select two adhesive weights mode.
®
arm on rim under the desired left patch location and tap foot pedal.
Place inner arm on rim under the desired right patch location and tap foot pedal.
Measure inside tire diameter using a tape measure or tool, 221-527-1, just below
tread depth, and enter reading as inside tire diameter for the left plane using the
diameter knob. Refer to illustration on page 44.
Close safety hood and spin wheel.
After wheel stops, raise the safety hood.
If necessary, use
“Left Plane Split Weight®” to split weight(s).
Find TDC for left plane weighted balance patch(es) and mark tire for patch
placement.
Find TDC for right plane weighted balance patch(es) and mark tire and wheel for
patch placement and reassembling.
Remove wheel from balancer and dismount tire from wheel.
Install left weighted balance patch(es) at mark(s) as instructed by manufacturer’s
instructions.
Install right weighted balance patch(s) at mark(s) as instructed by manufacturer’s
instructions.
Mount tire onto wheel and align marks.
Verify balance condition by spinning again.
Balance the wheel. Refer to the desired balance procedure.
NOTE: Weight digits blink if the force signals are larger than the
measurement range of the balancer. If this occurs, check for
wheel being not properly centered on spindle shaft. If wheel
is centered, apply the displayed weights. The blinking
weights indicate that a second spin and additional weight(s)
may be required to get zero imbalance. Refer to “Correcting
Large Imbalances,” page 52.
46
3. Balancing a Wheel DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 51

4. BALANCING FEATURES AND OPTIONS
x
4.1 Servo-Stop
Servo-Stop Wheel Weight Positioning
After the balance spin, the wheel assembly will automatically locate, brake, and hold
the wheel assembly in the correct weight installation location.
Disabling Servo-Stop
Press the red “Stop” button to disable servo-stop.
Turning On Servo-Stop
Press the green “Start” button, or step on the foot pedal with the safety hood
in the raised position to turn on servo-stop.
Servo-Stop Aided Clip-On Weight Placement
Spin the wheel using Clip-On Weights selection. The wheel will stop with the clip-on
weight location at TDC.
Pressing the green
automatically rotate the wheel to place the next weight location at TDC.
“Start” button or stepping on the foot pedal will
Servo-Stop Aided Adhesive Weight Placement
The inner Dataset® arm can be used to assist in proper placement of adhesive
weights. Using dimensional information previously obtained, the display identifies the
exact location of the weight plane and the current position of the inner Dataset
Wheel dimensions must be entered using the inner automatic Dataset
the desired balance mode. Servo aided weight placement is not allowed if wheel
dimensions were changed by turning the knobs, or if dimensions were entered using
the automatic inner Dataset
from clip-on mode to clip-on/adhesive mode).
Spin the wheel using Mixed Weights or Adhesive Weights selection. The wheel will
stop with one of the adhesive weight locations at BDC.
Shape the weight to a contour similar to the curve of the rim.
With one of the weight locations at BDC and servo on, pull the inner Dataset
out from the base.
The wheel will automatically rotate to place the weight location where the inner arm
will contact the rim.
The “target” inner arm distance will be shown on the rim distance dimension.
If a weight is being placed on the left plane, the live inner arm distance will be
flashing on the right weight display and the amount of weight to be placed is shown
on the left weight display. The displays are reversed if a weight is being placed on the
right plane.
Continue to pull out the inner arm until the “live” distance equals the target distance.
Maintaining that distance, rotate the Dataset
then apply the adhesive weights to the rim by pressing the adhesive weight release tab.
®
arm before changing the balance mode (i.e. changing
®
arm toward the inner rim surface, and
®
®
arm
arm.
®
arm while in
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 4. Balancing Features and Options
47
Page 52

Return the inner Dataset® arm to the home position. The wheel will automatically
x
rotate to return the weight location back to BDC.
Press
“Start” to advance to the other weight locations, and place all adhesive
weights similarly.
NOTE: The balancer assumes that the weight being placed is the
one located at BDC when the inner arm is lifted. If there is a
weight located at BDC on both the right and left planes, lift
the inner arm to enter weight placement mode, then press
“Next” to select the plane that you wish to display.
NOTE: To cancel weight placement mode and use the inner
Dataset® arm for wheel dimension entry, return the inner arm
to home position and press the “Stop” button to
disable servo.
4.2 Locate the Adhesive Wheel Weights Using the Dataset£ Arm
Pointer Disk Edge
Find BDC (6 o’clock position) by turning the wheel until the Green Arrow of the TDC
indicator is blinking and the center LED is blinking on the weight indicator. In this
position, an adhesive weight has to be attached at BDC.
Inside of Wheel (Single Row of Adhesive Weights)
When using a single row of adhesive weights, place them so they are at the right
edge of the pointer disk edge as illustrated below.
WEIGHTS ON
RIGHT EDGE OF
WEIGHT PLANE
AS MEASURED
BY DATASET®
Inside of Wheel (Double Row of Adhesive Weights)
When using a double row of weights, place them so they are at the right edge of the
pointer disk edge as shown below. Two rows are recommended when the required
weight is more than 3 ounces. Make each strip of weights as close as possible to
one-half the required amount of weight.
WEIGHTS ON
RIGHT EDGE OF
WEIGHT PLANE
AS MEASURED
BY DATASET®
AR M
AR M
48
4. Balancing Features and Options DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 53

4.3 Quick-Thread™ Feature
x
Quick-Thread™ is an “intelligent” DC drive motor control feature that allows motor
assisted threading for fast installation and removal of the DSP9200 wing nut.
WARNING: Keep clear of clamping components during Quick-
Thread® shaft rotation.
Lift the wheel assembly onto the shaft as normal without threading on the wing nut.
With your left hand, hold the rim over the cone to remove the weight of the rim from
the spindle and to allow maximum Quick-Thread
Place the wing nut on the spindle and rotate one full turn onto the spindle threads.
With your right hand, hold one handle of the wing nut while you are still lifting the rim.
NOTE: Heavier wheel assemblies may require extra lifting to
prevent the software limited motor torque control from
stopping the rotation of the spindle.
Tap the foot pedal twice and the spindle will rotate to install the wing nut to save
threading time.
The direction of spindle rotation toggles each time it is used. For normal operation,
spindle rotation will begin in the correct direction for wing nut installation. A single tap
within the first three seconds of rotation will reverse the direction of rotation. A single
tap after the first three seconds of rotation will stop rotation.
Quick-Thread
wheel, or when the foot brake (refer to “Spindle-Lok® Feature,” page 50) is applied
for more than half of a second.
®
spindle rotation will stop when the clamping components contact the
®
wing nut travel.
CAUTION: Quick-Thread® does not tighten the wing nut! In Quick-
Thread® rotation, torque allowed is minimal. Therefore, you
must still perform the final tightening of the wing nut.
NOTE: Also because of the software limited torque control, you
must loosen the wing nut before Quick-Thread® will remove
it.
Quick-Thread® will not operate if:
You are in “Diagnostics,” “Setup,” or all calibration procedures except
“Servo-Stop.”
Either Dataset
®
Inflation Station hose is out of its “home position.”
4.4 Motor Drive/Servo-Stop
The intelligent DC motor drive on the DSP9200 is able to position and hold the tire
assembly in position for weight application, apply different amounts of torque, and
control the speed and direction of the spindle.
Servo-Stop/Servo-Push
With Servo-Stop, when the “Start” button is pushed with the hood in the raised
position, while weights are showing, the motor will automatically rotate the wheel to
the next weight plane and hold the assembly in position for weight application.
arm is out of its “home position.”
Servo-Push allows pushing the wheel (approximately 1/8 of a revolution) to cause the
intelligent DC motor drive to automatically rotate the wheel to the next weight
placement position. Pressing the “START” key may still be used for this function.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 4. Balancing Features and Options
49
Page 54

4.5 Spindle-Lok® Feature
x
If the balancer is equipped with the Spindle-Lok®, depressing the foot pedal will lock
the spindle. Locking the spindle will stabilize the wheel for attaching weights at
precise locations, and for tightening and loosening of the wing nut. Do not use the
Spindle-Lok
®
as a brake to stop a spinning wheel.
CAUTION: Using the Spindle-Lok® to stop a spinning wheel
may result in personal injury or damage to the
balancer.
4.6 Hood Close Autostart Feature
The balancer can be set to automatically spin the wheel when the safety hood is
closed. After a spin, the hood must be lifted completely before the balancer will
autostart again.
Hood Close Autostart feature can be enabled or disabled in the setup procedure.
4.7 Loose Hub Detect Feature
If the wheel slips on the spindle shaft during the spin, the balancer automatically
brakes the shaft to a stop and displays “LOO SE” on the weight amount indicators.
If the “LOO SE” hub error occurs:
Lift the safety hood.
Retighten the wing nut.
Spin the wheel again.
If the wing nut feels like it is already tight, the shaft braking to a stop
caused the wing nut to retighten. Make sure that the wing nut is fully
tightened and then re-spin the wheel.
To override the loose hub detect feature:
Decrease the wheel diameter knob setting to the minimum value allowed
while in the STANDARD procedure, then continue to turn the wheel
diameter knob counterclockwise until the wheel diameter digits change to
zero. It will take approximately one full turn of the knob while the
“ratcheting” sound is occurring (at minimum value) for this to occur.
When the balancer is first turned “ON,” the diameter digits will default to zero (the
loose hub detect feature is overridden).
50
4. Balancing Features and Options DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 55

4.8 Blinding and Rounding
x
The balancer can display either an “actual” or “blinded and rounded” amount of
imbalance.
“Blind” is a tolerance or amount of imbalance required before an imbalance amount is
displayed. “Rounded” allows the balancer to display weight imbalance to the closest
increment. The blinded and rounded values can be changed by the service
representative.
Blind Settings Rounding Settings
oz gm oz gm
0.00 0.0 0.00 0.0
0.15 4.0 0.05 1.0
*0.29 8.0 *0.25 5.0
0.58 16.0
* Factory settings
When using the
to include the middle display LED (as shown below). When the middle display LED is
on, the blind and rounding are disabled. The actual amounts of imbalance, for the
selected mode, will be displayed. (The blind and rounding are disabled.)
For example: Pressing the “Static/Dynamic” button from DYNAMIC LED lit to
the DYNAMIC plus the middle position LED lit, will display the actual imbalance
amounts on the inner plane and outer plane weight amount indicators.
4.9 Split Weight® Feature
Pressing either the “Left Plane Split Weight®” or the “Right Plane Split
Weight
two smaller size weights. The angle is adjusted by the balancer to produce the nonrounded correction called for by the single weight before the split. This provides exact
imbalance correction without weight trimming. The non-rounded imbalance is split
regardless of whether blind and rounding are enabled. For this reason, Split Weight
is more accurate than applying a single weight with the blind and rounding enabled.
Split Weight
such as 6.0 ounces. Split Weight
ounce weights side-by-side, which would leave a substantial residual imbalance:
®
” button will change the required imbalance correction weight amount into
®
is especially useful when the imbalance amount is large or unavailable,
6.0 oz
“Static/Dynamic” button, STATIC or DYNAMIC can be selected
®
®
eliminates the error caused by placing two 3.0
3.0 oz 3.0 oz
6.0 oz
3.50 oz3.50 oz
Use the “Left Plane Split Weight®” or “Right Plane Split Weight®” when the weight
location interferes with a hubcap or trim ring, when one weight is too large, to avoid
weight trimming, or to substitute for a weight size that is out of stock.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 4. Balancing Features and Options
BY HAND
USING SPLIT WEIGHT
51
Page 56

Split Weight® Operation
x
Press either the left or the right “Split Weight®” button to divide that plane’s required
weight into two smaller weights.
Press the left or right
“Split Weight®” button repeatedly to gain additional size
and location choices. Continued presses will return display to single weight amount
and angle.
®
Each time a “Split Weight
” button is pressed, the two weights are increased to the
next largest weight size and are placed (fanned-out) further down the rim. The
display shows the amount and placement angle for both weights at the same time.
After all Split Weight
®
choices have been displayed, pressing the “Split Weight®”
button returns the display to the original single weight amount and angle.
6.0 oz
Correcting Large Imbalances
“Split Weight®” can also be used to apply three weights when needed. For example,
a large wheel may require 6.75 ounces. Not only is this size unlikely to be in the
weight tray, but splitting 6.75 ounces would likewise result in large weights. In this
case, apply one-third of the called for weight (in this case 2.25 ounces) at the 6.75
ounce weight location and spin again. The display will now call for a 4.5 ounce weight
to be placed on top of the 2.25 ounce weight. Press the
(to fan out the two weights) until they clear the previously applied 2.25 ounce weight.
Then place the two indicated ounce weights on either side of the 2.25 ounce weight
(as illustrated below) using the TDC display indicators.
3.50 oz3.50 oz 3.75 oz3.75 oz
“Split Weight®” button
Splitting 1 Large Weight into 3 Smaller Weights
REQUIRED
SINGLE WEIGHT
6.75 oz
(3) WEIGHTS
EQUIVALENT TO 6.75 OZ
2.25 oz
2.75 oz 2.75 oz
52
4. Balancing Features and Options DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 57

4.10 Split Spoke® Feature
Split Spoke® requires the optional inner Dataset® arm.
When in “mixed weight” or “adhesive weight modes,” (dynamic or static), correction
weights can be hidden behind the spokes of a wheel.
Move the optional inner Dataset
pressing the foot pedal.
Move the optional inner Dataset
downward arm position. Enter the data by pressing the foot pedal.
The display is now flashing “SPO -1-.” Without returning the optional inner Dataset
arm to the home position, rotate the wheel and place the arm so that it is centered
behind a spoke. Enter the data by pressing the foot pedal.
®
arm to left weight plane position. Enter the data by
®
arm to the far right weight position, using the
®
The display is now flashing “SPO -2-.” Rotate the wheel to position the optional inner
Dataset
®
arm behind an adjacent spoke (nearest spoke in either direction). Enter the
data by pressing the foot pedal.
Return the optional inner Dataset
Press the green
“Start” button if “Hood Autostart” is disabled.
®
arm to the home position. Close safety hood.
After wheel comes to a complete stop, raise the safety hood.
Place left plane weight (if in DYNAMIC mode) per the balance procedure being
performed.
Notice that there are two weights on the right plane bar graph. The amount shown
depends upon which weight is currently located at the correct position to place the
weight. If the wheel is not positioned to locate either weight, no amount is shown “---.”
NOTE: There will be only one weight on the right plane if all of the
correction weight can be placed behind one spoke.
With the servo enabled, attach the adhesive weight behind the first spoke using the
weight amount shown.
Press the “Start” button with the hood raised to servo to the location for the second
spoke. The display automatically changes to the amount of the second weight.
Attach the adhesive weight behind the second spoke.
Verify by spinning again. Both planes should be zero.
Re-entering Similar Wheel after Split Spoke® is Enabled
Once Split Spoke® mode is enabled, use the “Next” button to input the spoke
orientation of the other three wheels from a set to avoid re-measuring the weight plane
dimensions each time.
Press the
placement mode. Mount the next wheel.
Move the optional inner Dataset
downward arm position to align the spoke location.
Press the
Enter the spoke location by pressing the foot pedal (no need to enter a second spoke).
Return the optional inner Dataset
the green
procedure.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 4. Balancing Features and Options x 53
“Stop” button to disable servo and avoid starting servo aided weight
®
arm to a position centered behind a spoke, using the
“Next” button. The display flashes “Put SPO.”
®
arm to the home position. Close safety hood. Press
“Start” button if “Hood Autostart” is disabled. Continue the balancing
Page 58

Placing Hidden Weight Forward of Obstructions
On some wheels, it may be possible to hide right weight plane adhesive weights inside
of the hollow spoke. However, wheel construction may make it impossible to enter the
right weight plane to the desired location with the optional inner Dataset
The following example is in the mixed weight mode.
Move the optional inner Dataset
pressing the foot pedal.
Enter the left weight plane to the best possible position, using a tape measure. This
distance must be in millimeters (convert inches to millimeters by multiplying by 25.4).
Measure the weight plane diameter manually, using caliper.
®
arm to left plane position. Enter the data by
®
arm.
NOTE: This may need to be done before the wheel is mounted on
the DSP9200.
Add the measurement from the left weight plane to the desired right weight plane to
the distance to the inner rim lip and enter this new dimension manually.
Enter the weight plane distance (mm) and diameter (in) manually. Close safety hood.
Press the green
“Start” button if “Hood Autostart” is disabled.
After wheel comes to a complete stop, raise the safety hood.
Place left plane weight (if in DYNAMIC mode) per the balance procedure being
performed. Refer to “Balancing a Wheel,” page 19.
Press the green
“Start” button with the safety hood in the raised position and
the DSP9200 will servo to the location for the right adhesive weight plane (dynamic)
or the static adhesive weight plane (static), aligned with the first spoke.
With the servo enabled, attach the adhesive weight behind the first spoke using the
weight amount shown on the CRT.
Press the green
“Start” button with the safety hood in the raised position and
the DSP9200 will servo to the location for the second spoke.
Attach the appropriate weight as displayed on the console.
Verify balance condition by spinning again.
54x 4. Balancing Features and Options DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 59

All weight plane displays should show “zero.” Split Spoke® balancing procedure is
complete.
4.11 Automatic Weight Recalculation and Dimension Preservation
When dialing a rotary encoder knob, each click of the knob (changing a dimension)
causes the weights to be recalculated. The benefit is that without re-spinning, you
have the unique ability to relocate the desired weight locations and see the resulting
weights and placement angles updated in real-time.
When attempting to dial in a value not allowed or exceeding a limit, the rotary
encoder knob will make a “ratcheting” sound. For example: Trying to dial in a wheel
width under 1.5 inches, will cause a “ratcheting” sound.
When entering STANDARD, MIXED WEIGHTS, or TWO ADHESIVE WEIGHTS
MODE, the last dialed in dimensions for that procedure are recalled and displayed.
The weight amounts and angles for these dimensions are recalculated and
displayed. The benefit is that without re-spinning the wheel, you have the unique
ability to switch between balancing procedures to determine the best combination of
weight types for the tire/wheel assembly.
NOTE: The exception to this rule is when changing a dimension in
STANDARD and then entering an ALU mode. The last ALU
dimensions used are replaced by new dimensions based on
the new STANDARD dimensions.
Any change between STATIC and DYNAMIC, or Enabling/Disabling the “blind” and
“rounding” also preserves dimension information and recalculates the weights.
4.12 Storing and Recalling Wheels
The balancer can store and recall SETUP information, balance procedure, and wheel
dimensions for up to four specific wheels. Storing and recalling can also be used to
allow up to four technicians to use the wheel balancer at the same time.
Storing a Wheel into Memory
Enter SETUP information (oz/gm, diameter in/mm, and width in/mm), balance
procedure, and wheel dimensions for a specific wheel.
Press the
activated, but no wheel has been selected.
Press the
Press and hold the
A confirmation beep will confirm that the wheel has been stored into memory and
wheel index turns into weights for the recalled wheel.
Recalling a Wheel from Memory
“Enter” button. -0- appears indicating that the store/recall mode is
“Next” button until wheel 1, 2, 3, or 4 is selected.
“Enter” button for a minimum of two seconds to store wheel.
Press the “Enter” button. -0- appears indicating that the store/recall mode is
activated, but no wheel has been selected.
Press the
Press the
dimensions and SETUP information.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 4. Balancing Features and Options x 55
“Next” button until stored wheel 1, 2, 3, or 4 is selected.
“Enter” button briefly (less than two seconds) to recall stored wheel
Page 60

56x 4. Balancing Features and Options DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 61

5. MAINTENANCE AND CALIBRATION
5.1 Cleaning the Unit
When cleaning the unit, use window cleaning solution to wipe off the display console
and cabinet. Do not spray window cleaning solution directly onto control panel. Do
not hose down the unit. This could damage the electrical system.
5.2 Spindle Hub Face and Shaft Maintenance
Keep the spindle shaft and wing nut threads clean and lubricated. Lubricate the shaft
without contaminating the hub face. Run the edge of a rag between the threads while
the spindle is slowly turned by the motor drive. If any signs of dirt or debris appear on
the spindle threads, the spindle should be cleaned immediately prior to mounting a
wheel.
CAUTION: Failure to clean spindle properly will result in a loss of
clamping force.
Lubricate the shaft with a coating of light lubricant with Teflon® such as Super Lube
by Loctite
This could cause slipping between the wheel and the hub face. Keep the hub face
mounting surface clean and dry.
®
after cleaning. Do not lubricate the spindle hub face mounting surface.
5.3 Mounting Cone Maintenance
Keep the mounting cones clean and lubricated. Periodically lubricate with a coating
of rust preventative to minimize corrosion. Spray lubricants, such as PS/2 or WD-40,
are recommended.
Do not use cones in any way that is not described in this operation manual. This
could cause damage to the mounting cone and not allow for proper mounting of the
wheel. Refer to “Mount the Wheel on the Spindle Shaft,” page 19.
5.4 Identifying Software Version and Serial Number
If a problem arises, have your software version number and the balancer serial
number at hand before calling for service. This will prevent the need for a second
phone call.
The serial number is located on the serial plate label on the back of the balancer
cabinet.
To access the software version number, press and hold the
turning the machine “ON.” The left weight digits display the balancer model as
determined by the configuration jumpers.
“920” Indicates a DSP9200 (No Auto Dataset
“92d” Indicates a DSP9200 (Inner Auto Dataset
“2dd” Indicates a DSP9200 (Inner and Outer Auto Dataset
“Enter” button while
®
arms)
®
arm only)
®
arms)
®
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 5. Maintenance and Calibration x 57
Page 62

The right weight digits display the software version number.
This manual provides operating instructions for the DSP9200 wheel balancer with
software revision 1.0 and higher.
5.5 Calibration Procedures
“Calibration” can be selected by pressing the “Setup/Cal” button.
Store the calibration weight, 65-72-2, in the threaded hole on the back of the control
panel support.
Dataset® arm calibration requires the optional calibration tool, 221-602-1.
Quick Cal Check
Begin with balancer “OFF,” then turn “ON.”
Attach cal weight to either side of one of the two holes in the hub faceplate.
Lower hood and press the
“CAL ERR.”
NOTE: If “CAL ERR” is displayed, the balancer needs to be
Whichever side the cal weight was installed, a plane weight position indicator will be
displayed.
Check angle accuracy by verifying that the cal weight stops at TDC (12 o’clock
position). If cal weight is in a position other than TDC, perform calibration procedure.
Press the
The Quick Cal™ Check is complete.
“Start” button to spin. Display shows “CAL RDY” or
recalibrated.
“Next” button to show weights.
58x 5. Maintenance and Calibration DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 63

Balancer Calibration
Press the “Setup/Cal” button once. “CAL” is displayed.
Press the “Enter” button to begin calibration.
Do not install cal weight. Lower the hood and press the “Start” button to spin (if “Hood
Autostart” is disabled).
Install cal weight on left side of hub faceplate in either hole, align cal weight at TDC,
and press the
“Enter” button. Spin.
Move cal weight to right side of hub faceplate in same hole.
Spin, display reads “CAL RDY.”
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 5. Maintenance and Calibration x 59
Page 64

Inner Dataset® Arm (Calibration Tool, 221-672-1, Required)
Press “Setup/Cal” button once. “CAL” is displayed.
Press
is displayed if equipped with outer Dataset
Press
“Next” button. “CAL” is displayed at inner Dataset® arm location, and “---]”
®
arm.
“Enter” to begin calibration. The step numbers are shown on the display,
starting with “Stp -1-.” Each step is described below.
NOTE: Turn the distance dimension knob to backup to a previous
cal step.
Verify that the inner arm is not extended, is in the “home” position, and is
not moving. Tap the foot pedal once or press “Enter.”
Place the calibration tool on the shaft, using the spindle shaft slot located
closest to the middle of the calibration tool, as shown. Rotate the
calibration tool slowly by hand, clockwise until there is a beep, and the
step number changes to “-3-.”
Position the calibration tool parallel to the floor. Tap the foot pedal once
or press “Enter.”
®
Place the inner Dataset
arm at upward position “1” as shown. Tap the
foot pedal once or press “Enter.”
Move the inner Dataset® arm to upward position “2.” Tap the foot pedal
once or press “Enter.”
Move the inner Dataset
once or press “Enter.”
60x 5. Maintenance and Calibration DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
®
arm to upward position “3.” Tap the foot pedal
Page 65

Place the inner Dataset® arm at downward position “4.” Tap the foot
pedal once or press “Enter.”
Move the inner Dataset® arm to downward position “5.” Tap the foot
pedal once or press “Enter.”
®
Move the inner Dataset
arm to downward position “6.” Tap the foot
pedal once or press “Enter.”
®
Remove the metal plug from the inner Dataset
arm and thread it back
onto the calibration tool. Reinstall the black roller onto the inner Dataset
arm using the 1/8 inch Allen wrench.
Position the calibration tool parallel to the spindle shaft on the hub using
the hub mounting slot as shown.
®
Place the inner Dataset® arm at the position “7.” Tap the foot pedal once
or press "Enter.”
Move the inner Dataset
press “Enter.”
Move the inner Dataset
press “Enter.”
If optional outer Dataset
Dataset
®
arm is installed, refer to “Outer Dataset® Arm,” page 62.
®
arm to position “8.” Tap the foot pedal once or
®
arm to position “9.” Tap the foot pedal once or
®
arm is not installed, calibration is complete. If optional outer
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 5. Maintenance and Calibration x 61
Page 66

Outer Dataset® Arm (Calibration Tool, 221-672-1, Required)
With the hood in the raised position, verify that the outer arm is in the “home” position
and that the arm and hood are not moving. Tap the foot pedal once or press “Enter.”
Place the calibration tool on the hub using the hub mounting slot as shown.
Place the outer Dataset® arm ball in hole position “1.” Tap the foot pedal once or
press “Enter.”
Place the outer Dataset
press “Enter.”
Place the outer Dataset
press “Enter.”
Dataset
®
arm calibration is complete. “RDY” is displayed near the inner arm graphic
to indicate that the inner Dataset
weight digits to indicate that the outer Dataset
®
arm ball in hole position “2.” Tap the foot pedal once or
®
arm ball in hole position “3.” Tap the foot pedal once or
®
calibration passed. “RDY --]” is displayed on the
®
calibration passed.
62x 5. Maintenance and Calibration DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 67

6. GLOSSARY
Amplitude (Magnitude)
The amount of force or the intensity of the vibration.
Back Coning
When the wheel requires the cone to center the wheel on the balancer’s shaft from the
backside, primarily due to the chamfer of the wheel. Also referred to as Back-Cone
Mounting.
Backspacing
The distance measured from the mounting face to the back edge of the wheel.
BDC
The abbreviation for bottom dead center also referred to as 6 o’clock.
Bead seating
The process of seating the tire to the rim bead seats. Bead seating preferably occurs just
after the tire and rim have been assembled, but may gradually change and optimize over
a longer period. If loaded with the GSP9200 load roller or driven, the position of the bead
may optimize or always remain seated improperly, unless the tire is demounted,
lubricated, and remounted. However, the load force and its’ relatively short duration will
not necessarily solve defective mounting of the tire bead seat to the rim seat.
Bolt Pattern Circle
The diameter of an imaginary circle drawn through the center of each lughole, and
virtually always on the same centerline as the hub bore of the wheel.
Computerized Vibration Analyzer
A device used to determine the frequency of the vibration by isolating the vibrations with
the greatest magnitude.
Cycle
One complete disturbance.
Dampen
To decrease the magnitude of a vibration or sound.
Dampers
Used to reduce the magnitude of a given vibration. Rubber is commonly used to isolate
and dampen vibrations.
Dataset
Dynamic Balance
Electro-Mechanical Ear
Forced Vibration
Free Vibration
®
The inner and outer electronic arms on the GSP9200. By positioning the Dataset arms
and entering data using the foot pedal, rim dimensions can be recorded for balancing.
A procedure that balances the wheel assembly by applying correction weights in two
planes so that up and down imbalance and side to side imbalance are eliminated.
A device used much like a doctor’s stethoscope and is for noise diagnosis problems only.
Vibrates when energy is applied.
Continues to vibrate after the outside energy stops.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 6. Glossary x 63
Page 68

Frequency
The number of disturbances that occur per unit of time.
Front Coning
When the wheel requires the cone to center the wheel on the balancer’s shaft from the
front. Also referred to as Front-Cone Mounting.
Harmonic
A vibration that is identified by the number of occurrences per revolution. For example, a
1st harmonic vibration has a once per revolution vibration component.
Hertz
A unit of frequency: one disturbance per second.
Hub Centric
The wheel is centered using the center hole of the wheel.
Lateral Runout
The amount of side-to-side movement as the tire/wheel assembly rotates.
Lug Centric
The wheel is centered using the lugholes rather than the wheel center hole.
Magnitude (Amplitude)
The amount of force or the intensity of the vibration.
MatchMaker™
Allows the operator to match up four identical tires on identical rims, to achieve the
optimal combination of match mounting.
Natural Frequency
The point at which an object will vibrate the easiest.
Order
The number of disturbances per cycle (rotation). For example, a 1st order vibration
occurs once per cycle, and a 2nd order vibration occurs twice per cycle.
P, P/SUV, LT
“P Tires” refers to passenger tires, “LT Tires” refers to light truck tires, and “P/SUV Tires”
refers to P-Rated sport utility vehicle tires.
Phase
The position of a vibration cycle relative to another vibration cycle in the same time
reference.
Phasing
The cycle pattern of two or more vibrations that overlap and combine to increase the
overall magnitude.
Pressure Ring
The accessory used to prevent the wing nut from contacting the wheel when on the
balancer shaft.
Quick-Thread™
Motor assisted threading of the wing nut for quick installation and removal.
Radial Force Variation (RFV)
A term describing a measurement of the tire uniformity, under load, measuring the
variation of the load acting toward the tire center.
Radial Runout
A condition where the tire and wheel assembly is slightly out of round forcing the spindle
to move up and down as the vehicle rolls along a smooth surface.
64x 6. Glossary DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions
Page 69

x
Reed Tachometer
A mechanical device that uses reeds to indicate the frequency and magnitude of the
vibration.
Resonance
The point where a vibrating component’s frequency matches the natural frequency of
another component.
Responding Component
The noticeable component that is vibrating.
Servo-Stop
The ability to locate varying positions of the tire/wheel assemblies and hold the position in
place while correctional weights or OE-Matching marks are applied.
Source Component
A component causing another object to vibrate, such as a tire/wheel assembly.
Spindle-Lok
A feature that locks the spindle in place by depressing the foot pedal.
®
Static Balance
A procedure that balances the wheel assembly using only a single weight plane.
TDC
An abbreviation for top dead center. Also referred to as 12 o’clock.
Torque Sensitive Vibration
The vibration occurs when accelerating, decelerating, or applying the throttle.
Total Indicated Reading (T.I.R.)
Data measurements taken by the load roller (measured in lbs. or kg) or Dataset® Arms
(measured in inches or millimeters) representing the actual runout measured. The T.I.R.
data represents the difference in value between the highest and lowest value measured.
Transference Path
The object(s) that transfer the frequency.
Vibration
A shaking or trembling, which may be heard or felt.
Wheel Diameter
Dimension measured on the inside of the rim at the bead seats.
Wheel Offset
The measured distance between the mounting face of the wheel and the centerline of the
rim.
Wheel Width
Dimension measured on the inside of the rim between the bead seats.
DSP9200 Series Balancer Operation Instructions 6. Glossary
65
Page 70

HUNTER RESEARCH AND TRAINING
CENTER
HUNTER . . . dedicated to service excellence through professional training
HUNTER TRAINING - Hunter operates the most advanced, up-to-date
Training Center in the industry today.
The courses have been designed to meet the needs of new and
experienced technicians who want to increase their mechanical and
diagnostic capabilities. The low student-teacher ratio (average 7 to 1)
and the emphasis on “hands-on” training (80% time in shop) create an
excellent learning environment.
Align 1 (Basic Alignment Theory and Practice) 3 day / 24 hrs
Students will learn basic wheel alignment service through classroom and
hands-on practice. Pre-alignment services, wheel alignment angle theory
and wheel alignment equipment operation are the focus of this course.
Basic wheel alignment adjustments will be demonstrated and students
will practice on vehicles in a shop environment.
Align 3 (Advanced Diagnostics and OE Procedures) 2-day / 16 hrs
This class focuses on using advanced diagnostic angles and
measurements to determine damaged suspension and steering
components. Techniques used in finding damaged parts are reinforced
with classroom scenarios and hands-on labs designed to both challenge
and further embed these much needed skills.
GSP9700 Certification 2-days / 16 hrs
This course combines the Rolling Smooth course with a certification
program for Hunter Engineering’s GSP9700 Road Force Measurement
system. Students use hands-on practice with the GSP9700 to gain a
proficiency level acceptable to be deemed certified.
HDT Alignment 1 (Fundamental Alignment) 3-day / 24 hrs
Classroom and shop practice is used to teach the basic elements of
Class 8 truck wheel alignment. Students will learn the proper method to
measure and correct the required basic alignment angles using state of
the art equipment. Trailer alignment is included.
Hunter University’s eLearning courses are designed for all student levels and can be used
as an integral supplement to instructor-led training courses. In-depth information, detailed
graphics, video and modular segments assist the participant in expanding their knowledge
For further information about other classes offered or to schedule into a class,
simply call the Hunter Research and Training Center at 1-800-448-6848.
base at a self-determined level. Go to www.hunter.com and click on TRAINING.
Highlights of the Hunter Training Center include:
An instruction staff with over 100 years of shop, field, and teaching
experience.
Fully-equipped service bays.
Classrooms equipped with modern teaching aids.
The most up-to-date wheel alignment, balancing service and brake
equipment on the market today.
Align 2 (Advanced theory / Aftermarket Adjustment) 2-day / 16 hrs
Modified vehicle wheel alignment is the focus of this course. Students
learn how to use alignment angles to achieve vehicle handling
performance in conjunction with ride height kits and modified tire/wheel
packages. Aftermarket alignment adjustment kits are discussed and
demonstrated.
Performance Tire (Basic and Advanced Tire Changing) 1-day 8 hrs
Students will learn basic terminology and theory related to servicing tires
and wheels. Students learn the proper techniques for changing tires on
tulip clamp and table top tire changer designs. This course covers the
proper tire changing techniques for low profile tires, run flat designs, and
tire/wheel assemblies using TPMS.
Rolling Smooth (Basic & Advanced vibration theory) 1-day / 8 hrs
This course offers a study of vehicle vibration specific to wheel speed.
The student will learn basic vibration terminology and vibration theory,
Shop activities include the measurement of Road Force Variation, wheel
runout and balance. Additional diagnostic tools are discussed.
HDT Alignment 2 (Advanced Alignment) 2-day / 16hrs
The student will understand the cause and affect of basic alignment
angles relative to ride quality, performance and tire life. Classroom and
shop practice are used to learn the proper use of diagnostic alignment
angles. Additional adjustment techniques and alignment system
operation are explored in both the classroom and lab environment.
Busses and RVs are discussed.
 Loading...
Loading...