Page 1
eBIMS
V100R001C00
Product Description
Issue
01
Date
2013-04-30
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Page 2

Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
i
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2013. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specified in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees or
representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every effort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Address:
Huawei Industrial Base
Bantian, Longgang
Shenzhen 518129
People's Republic of China
Website:
http://www.huawei.com
Email:
support@huawei.com
Page 3

eBIMS
Product Description
About This Document
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
ii
Intended Audience
Symbol
Remarks
Indicates a hazard with a high level of risk that, if not
avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a hazard with a medium or low level of risk
that, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate
injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that, if not
avoided, could cause equipment damage, data loss, and
performance degradation, or unexpected results.
Provides a tip that may help you solve a problem or save
time.
Provides additional information to emphasize or
supplement important points of the main text.
This document is intended for:
Sales specialist
Technical support personnel
Maintenance personnel
Symbol Conventions
About This Document
The symbols that may be found in this document are defined as follows.
Change History
Changes between document issues are cumulative. The latest document issue contains all the
changes made in previous issues.
Page 4

eBIMS
Product Description
About This Document
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iii
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
This issue is the first official release.
Page 5

eBIMS
Product Description
Contents
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
iv
Contents
About This Document .................................................................................................................... ii
1 Positioning and Characteristics .................................................................................................. 1
1.1 Positioning .................................................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Characteristics............................................................................................................................................................... 2
2 Architecture .................................................................................................................................... 4
2.1 Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................... 4
2.2 Hardware ...................................................................................................................................................................... 4
2.3 Software ................................................................................................................................ ........................................ 7
3 Functions and Features ................................................................................................................ 8
3.1 Overview ...................................................................................................................................................................... 8
3.2 Resource Management .................................................................................................................................................. 9
3.3 Monitoring Management .............................................................................................................................................. 9
3.4 Report Management .................................................................................................................................................... 12
3.5 System Management ................................................................................................ ................................................... 13
4 Application Scenarios ................................................................................................................ 14
4.1 Overview .................................................................................................................................................................... 14
4.2 Application Scenarios ................................................................................................................................................. 14
5 Configuration ............................................................................................................................... 18
5.1 Overview .................................................................................................................................................................... 18
5.2 Typical Configuration ................................................................................................................................................. 18
6 Technical Specifications ............................................................................................................ 21
7 Acronyms and Abbreviations ................................................................................................... 24
8 Safety Precautions ....................................................................................................................... 25
Page 6

eBIMS
Product Description
1 Positioning and Characteristics
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
1
1 Positioning and Characteristics
About This Chapter
1.1 Positioning
This product description is oriented to the battery intelligent management system (eBIMS)
V100R001.
1.2 Characteristics
The eBIMS supports client-free fast deployment, comprehensively monitors the battery
temperature, voltage, and impedance, and achieves simple and fast operation.
1.1 Positioning
This product description is oriented to the battery intelligent management system (eBIMS)
V100R001.
Batteries, an indispensable part of sites, are the O&M focus. The correctness of battery
performance management, timeliness of battery fault rectification, and fix rate of network
problems caused by battery faults have a large impact on network status. Therefore, low-cost
automatic detection and analysis for batteries become key requirements of the management
service center. The Huawei eBIMS fully meets battery maintenance requirements by remotely
monitoring real-time battery status, detecting, predicting, and reporting battery faults, and
identifying batteries reaching their replacement thresholds and guiding the battery
replacement. Figure 1-1 shows the eBIMS solution.
Page 7

eBIMS
Product Description
1 Positioning and Characteristics
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
2
Figure 1-1 eBIMS solution
1.2 Characteristics
The eBIMS supports client-free fast deployment, comprehensively monitors the battery
temperature, voltage, and impedance, and achieves simple and fast operation.
Simple Structure, Achieving Fast Deployment
The eBIMS uses the modular design. Wireless connection is used between the eBat and
eBox, reducing cables and simplifying installation.
The eBat connects to a battery using OT terminals. The eBox deployment is flexible and
convenient because the eBox can be installed on a wall or by using hook-and-loop
fasteners.
The eBIMS supports client-free installation and has a built-in database.
Simple Operation, Improving User Experience
The eBIMS uses the lightweight browser/server (B/S) architecture, uses the Web 2.0
technology, and allows users to perform access and operation using the Internet Explorer.
The intelligent report analysis function displays the battery temperature, impedance, and
voltage performance parameters using diversified graphs.
The configuration management function allows batch processing, achieving fast setting
of battery parameters.
Users can customize the home page to know the information to be concerned.
Real-Time Fault Monitoring, Reducing Battery Maintenance Costs Effectively
The eBIMS real-timely monitors and reports the temperature, voltage, and impedance
alarms of all batteries, preventing network accidents caused by battery faults.
The eBIMS monitors faults 24/7 and provides fault reminders in a timely manner, saving
the routine onsite maintenance costs of batteries.
Page 8

eBIMS
Product Description
1 Positioning and Characteristics
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
3
The eBIMS identifies single batteries that reach their replacement thresholds, avoiding
replacement of an entire battery string, reducing abnormal battery retirement from
networks, and saving costs.
Page 9

eBIMS
Product Description
2 Architecture
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
4
About This Chapter
2.1 Overview
This chapter briefly describes the eBIMS hardware and software architecture.
2.2 Hardware
2 Architecture
The eBIMS hardware includes the eBat and eBox.
2.3 Software
The eBIMS software architecture includes three parts: data collection, data exchange, and
application management.
2.1 Overview
This chapter briefly describes the eBIMS hardware and software architecture.
The eBIMS uses the modular design and includes the following basic function modules:
The eBIMS software management system includes auxiliary facilities like the server hardware system
and operating system.
2.2 Hardware
Battery detection module (eBat)
Battery module data collection unit (eBox)
eBIMS software management system
The eBIMS hardware includes the eBat and eBox.
eBat
The eBat is a battery detection module and communicates with the eBox using wireless
connection. The eBat has the following functions:
Page 10
eBIMS
Product Description
2 Architecture
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
5
No.
Item
Parameter
Remarks
—
Dimensions
48.5 mm (L) x 35 mm
(W) x 17 mm (H)
—
1
Radio
frequency (RF)
2.4 GHz
IEEE 802.15.4
The eBat communicates
wirelessly with the eBox
using RF 2.4 GHz.
2
Port
—
The eBat leads out four
cables from the port. Two
red cables and two black
cables are connected to
positive and negative
ends of a battery.
Detects the battery voltage.
Detects the battery impedance.
Detects the battery temperature.
Transmits detected battery information to the eBox.
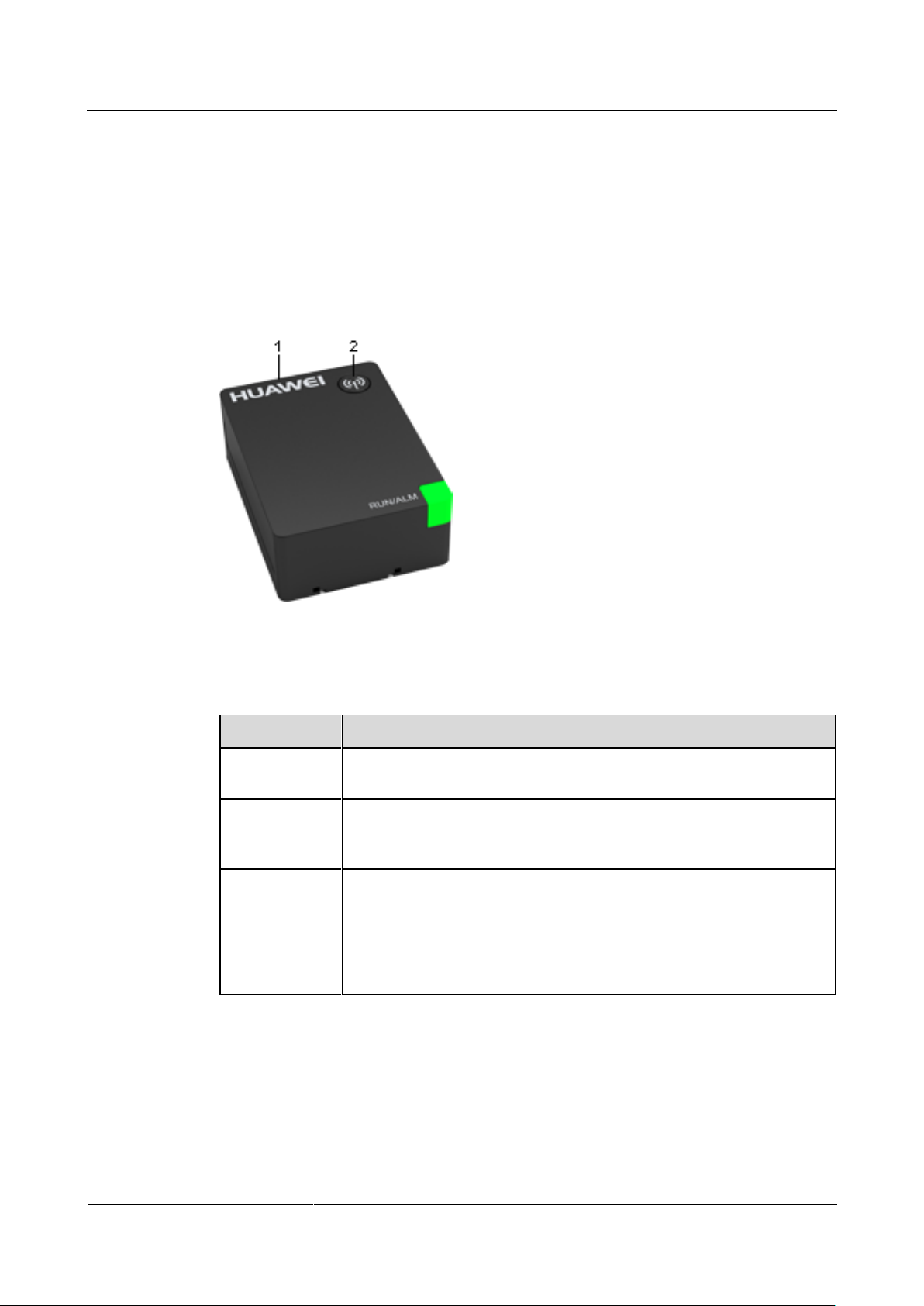
The eBat is connected to the positive and negative ends of a battery using cables. Figure 2-1
shows the eBat appearance.
Figure 2-1 eBat appearance
Table 2-1 lists relevant parameters of the eBat.
Table 2-1 Technical specifications of the eBat
eBox
The eBox is a battery module data collection unit for collecting the battery
voltage/impedance/temperature data, and providing collected data to the eBIMS. The eBox
has the following functions:
Page 11

eBIMS
Product Description
2 Architecture
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
6
No.
Item
Parameter
Remarks
—
Dimensions
145 mm (L) x 95 mm
(W) x 33 mm (H)
-
1
RF 2.4 GHz
IEEE 802.15.4
The eBox communicates
wirelessly with the eBat
using RF 2.4 GHz.
2
GPRS antenna
-
The eBox communicates
with the upstream device
using GPRS wireless
connection.
3
Universal
Serial Bus
(USB) port
One
Used for device
debugging.
4
FE port
One
Using an RJ45 network
cable to communicate
with the upstream device.
5
SIM card
One
Allowing GPRS wireless
Collects the battery voltage.
Collects the battery impedance.
Collects the battery temperature.
Transmits battery parameters to the server.
Figure 2-2 shows the eBox appearance.
Figure 2-2 eBox appearance
Table 2-2 lists relevant parameters of the eBox.
Table 2-2 Technical specifications of the eBox
Page 12

eBIMS
Product Description
2 Architecture
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
7
No.
Item
Parameter
Remarks
connector
communication using a
SIM card.
6
Power port
One
Supplies power to the
eBox.
2.3 Software
The eBIMS software architecture includes three parts: data collection, data exchange, and
application management.
Figure 2-3 shows the basic architecture.
The eBox provides two types of upstream ports:
GPRS wireless port
FE port
Figure 2-3 Software architecture of the eBIMS
Page 13

eBIMS
Product Description
3 Functions and Features
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
8
About This Chapter
3.1 Overview
The eBIMS provides comprehensive battery management functions. The eBIMS real-timely
monitors and collects the battery temperature, impedance, and voltage to identify batteries
reaching their replacement thresholds, report alarms, guide replacement, and output relevant
reports.
3 Functions and Features
3.2 Resource Management
The eBIMS resource management covers management domains and physical resources
connected to the eBIMS.
3.3 Monitoring Management
Monitoring management includes functions like monitoring, collecting, displaying,
confirming, clearing, and shielding device alarms, and querying historical events and alarms.
These functions facilitate fast discovery, location, and handling of network or device faults.
3.4 Report Management
The eBIMS allows users to view and download basic report information, or output reports in
the Word, Excel, or PDF format.
3.5 System Management
System management includes user management, log management, and system configuration.
3.1 Overview
The eBIMS provides comprehensive battery management functions. The eBIMS real-timely
monitors and collects the battery temperature, impedance, and voltage to identify batteries
reaching their replacement thresholds, report alarms, guide replacement, and output relevant
reports.
Page 14

eBIMS
Product Description
3 Functions and Features
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
9
3.2 Resource Management
The eBIMS resource management covers management domains and physical resources
connected to the eBIMS.
Physical resources refer to all the devices connected to the eBIMS.
Management domain refers to a small network separated from a larger network by a
certain principle (region or device type) for easy network management. In resource
management, this type of small network is called a management domain. The eBIMS
management domains are classified by region, site, and equipment room.
Resource Management
Supports creation of a single management domain.
Supports creation of a single device or devices in batches.
Supports modification of management domain and device information.
Supports display of complete information of every battery as shown in Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 Battery information list
3.3 Monitoring Management
Monitoring management includes functions like monitoring, collecting, displaying,
confirming, clearing, and shielding device alarms, and querying historical events and alarms.
These functions facilitate fast discovery, location, and handling of network or device faults.
Alarms are classified into critical, major, minor, and warning alarms.
Critical alarm: indicates that services have been affected and requires immediate
rectification measures.
Major alarm: indicates that services have been affected and severe results may occur if
the alarm is not handled in a timely manner.
Minor alarm: indicates that services have not been affected but requires rectification
measures to prevent more severe faults.
Warning: indicates that services have not been affected, but potential faults that will
affect services have been detected.
Page 15

eBIMS
Product Description
3 Functions and Features
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
10
Displaying and Collecting Statistics on Alarms
The eBIMS real-timely monitors and receives alarms generated by managed devices, and
displays and collects statistics on alarms in various modes.
Alarm panel
− The alarm panel displays the alarm quantity and cleared alarms in the current alarm
list by severity.
Alarm histogram
− The alarm histogram is an eBIMS window displaying alarms. The alarm histogram
displays alarms of the managed objects by severity in graphs and numbers.
Querying Alarms
The eBIMS supports view of current alarms and query of historical alarms, events, and
performance statistics. Alarms that users need to pay attention to and handle are displayed in
the current alarm list.
Acknowledging an Alarm
Acknowledging an alarm indicates that a user has handled this alarm, which does not need to
be concerned. If needing to pay attention to this alarm again, unacknowledge this alarm and
take corresponding measures.
Clearing Alarms
Clearing alarms in a timely manner can effectively prevent service exceptions caused by
device malfunctions. The eBIMS supports automatic and manual clearing of alarms.
Shielding Alarms
Shielding rules can be set to shield the alarms that comply with the shielding rules. Shielded
alarms can be viewed in the list of shielded alarms.
Page 16

eBIMS
Product Description
3 Functions and Features
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
11
Supports graphic display of the battery impedance
Figure 3-2 Battery impedance comparison
Supports graphic display of the battery temperature
Figure 3-3 Battery temperature comparison
Page 17

eBIMS
Product Description
3 Functions and Features
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
12
Supports graphic display of the battery voltage
Figure 3-4 Battery voltage comparison
3.4 Report Management
The eBIMS allows users to view and download basic report information, or output reports in
the Word, Excel, or PDF format.
By default, the eBIMS outputs the following types of reports:
Site battery statistics report
Battery analysis report
Report Management
Report management includes generating, viewing, enabling, disabling, modifying, and
deleting a report.
Generating a report
− Users can create a report task to generate a report. After a report is generated, the
report is saved in the storage area and sent by e-mail if configured.
Viewing a report
− After a report is generated, users can view all report contents.
Enabling a report
− Users start a report task.
Disabling a report
− Users stop a report task.
Page 18

eBIMS
Product Description
3 Functions and Features
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
13
Modifying a report
− Users modify a report task based on needs.
Deleting a report
− Users delete an unnecessary report task.
3.5 System Management
System management includes user management, log management, and system configuration.
User Management
The eBIMS supports user information management and system security configuration.
Creating and modifying users
Creating and modifying roles
Changing user passwords
Setting account policies
Controlling login IP addresses
Controlling login time
Managing user sessions
Setting idle timeout
Log Management
The eBIMS allows users to view logs to learn about the eBIMS operating status and
operations. The eBIMS logs include security logs, system logs, and operation logs.
Security logs record security operations for the eBIMS, such as user login, changing a
password, creating a user, and user logout.
System logs record events for the eBIMS such as abnormal running, device faults,
periodical operations, and database dump.
Operation logs record user operations on the eBIMS such as adding a device.
System Configuration
System configuration includes component upgrade, database setting, and e-mail server setting.
Component upgrade
Setting database dump
Setting the notification e-mail server
Database dump settings are as follows:
Setting log database dump
Setting alarm database dump
Setting performance database dump
Page 19

eBIMS
Product Description
4 Application Scenarios
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
14
About This Chapter
4.1 Overview
The eBIMS can be deployed inside an outdoor cabinet or indoor equipment room. An
equipment room can be a data center power battery room or a site equipment room.
4.2 Application Scenarios
4 Application Scenarios
This section briefly describes the scenarios requiring the eBIMS and typical eBIMS
deployment scenarios.
4.1 Overview
The eBIMS can be deployed inside an outdoor cabinet or indoor equipment room. An
equipment room can be a data center power battery room or a site equipment room.
Deployment inside an outdoor cabinet
− Both the eBats and eBox are installed inside the outdoor cabinet. The eBats are
connected to batteries and the eBox is installed inside the cabinet using
hook-and-loop fasteners. One eBox is installed for each cabinet.
Deployment inside a data center power battery room
− Both the eBats and eBox are installed inside the indoor equipment room. The eBats
are connected to batteries and multiple eBoxes are installed on a wall using screws.
One eBox manages 250 eBats.
Deployment inside a site equipment room
− Both the eBats and eBox are installed inside the indoor equipment room. The eBats
are connected to batteries and the eBox is installed on a wall using screws. One eBox
manages 250 eBats.
4.2 Application Scenarios
This section briefly describes the scenarios requiring the eBIMS and typical eBIMS
deployment scenarios.
Page 20

eBIMS
Product Description
4 Application Scenarios
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
15
Scenarios Requiring the eBIMS
Typical scenarios:
1. Outdoor sites encounter network problems because battery aging due to
overcharge/overdischarge/undercharge/underdischarge deteriorates backup time. In this
case, maintenance costs are increased because multiple site visits are required to confirm
the battery location and quantity, check battery performance, and determine whether to
replace batteries.
2. Routine testing and inspection of batteries inside equipment rooms require much human
power. Moreover, one-by-one battery check cannot accurately determine the battery
status, causing much waste.
Deployment Inside an Outdoor Cabinet
The eBats and eBox are deployed in an outdoor cabinet. They communicate with each other
wirelessly. The eBox transmits collected battery data to the server. Users log in to the server to
perform real-time monitoring and operations. This solution achieves real-time monitoring and
detection of battery status, predicts fault risks, and avoids futile site visits. Maintenance costs
are reduced. Figure 4-1 shows details of this scenario.
Figure 4-1 Deployment inside an outdoor cabinet
Page 21

eBIMS
Product Description
4 Application Scenarios
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
16
Deployment Inside a Data Center Power Battery Room
The eBats and eBoxes are deployed in a data center power battery room. They communicate
with each other wirelessly. Multiple eBoxes transmit collected battery data to the server. Users
log in to the server to perform real-time monitoring and operations. This solution achieves
real-time detection of battery status and avoids onsite tests, saving costs. Moreover, this
solution accurately identifies batteries reaching their replacement thresholds, avoiding waste.
Figure 4-2 shows details of this scenario.
Figure 4-2 Deployment inside a data center power battery room
Deployment Inside a Site Equipment Room
The eBats and eBox are deployed in a site equipment room. They communicate with each
other wirelessly. The eBox transmits collected battery data to the server. Users log in to the
server to perform real-time monitoring and operations. This solution achieves real-time
detection of battery status and avoids onsite tests, saving costs. Moreover, this solution
accurately identifies batteries reaching their replacement thresholds, avoiding waste. Figure
4-3 shows details of this scenario.
Page 22

eBIMS
Product Description
4 Application Scenarios
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
17
Figure 4-3 Deployment inside a site equipment room
Page 23

eBIMS
Product Description
5 Configuration
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
18
About This Chapter
Configuration Item
Configuration Description
eBIMS software
eBIMS
eBat
Multiple
5.1 Overview
5.2 Typical Configuration
5 Configuration
5.1 Overview
The eBIMS uses modular deployment. The typical configuration includes the software system,
a set of matched hardware, multiple eBats, and one eBox.
The eBats, connected to batteries using cables, real-timely monitor the battery voltage,
current, and impedance, and wirelessly communicate with the eBox.
The eBox manages the eBats and transmits collected battery data to the server of the
software system.
Users log in to the eBIMS client to real-timely monitor battery status and take
corresponding measures based on actual situations.
5.2 Typical Configuration
The typical eBIMS configuration includes the software system, matched hardware facilities,
eBats, and eBox as shown in Table 5-1.
The software system requires matched facilities on both the server and client sides.
Typical eBIMS Configuration
Table 5-1 Typical eBIMS configuration
Page 24

eBIMS
Product Description
5 Configuration
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
19
Configuration Item
Configuration Description
NOTE
The number of eBats is determined by the
eBox management capacity and the battery
quantity. One eBox manages a maximum of
250 eBats and one eBat is used for each
battery.
There are 2 V and 12 V batteries.
eBox
One. The eBox quantity varies with
management scenarios.
Matched facilities of the software system
Refer to Table 5-2 and Table 5-3.
Configuration Item
Configuration Description
Basic hardware configuration
CPU: 2 x four-core, 2.4 GHz or above
Memory: 32 GB or above
Disk: 2 TB or above
Operating system
Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2
Standard
Database
MySQL 5.5
Configuration Item
Configuration Description
Hardware configuration
CPU: Intel(R) Pentium(R) dual CPU
E2180 @ 2.00 GHz
Memory: 2 GB or above
Operating system
Windows XP, Windows 7, or Windows
Server 2008
Browser
Internet Explorer 8.0 or later
NOTE
Ensure that the Internet Explorer 8.0 works in
standard browsing mode. Perform the
following steps to check whether the Internet
Explorer 8 is in standard browsing mode:
1. Open Internet Explorer 8.0 and
choose Tools > Compatibility View.
Matched Facilities of the Software System on the Server Side
Table 5-2 Matched facilities of the software system on the server side
Matched Facilities of the Software System on the Client Side
Table 5-3 Matched facilities of the software system on the client side
Page 25

eBIMS
Product Description
5 Configuration
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
20
Configuration Item
Configuration Description
In the Compatibility View dialog box, check
Display intranet sites in Compatibility View
and Display all websites in Compatibility
View and ensure that they are not selected.
Windows 2008 has a strict security policy.
Contact the operating system administrator to
modify the security policy before using
Internet Explorer 8.0 to log in to the client that
runs on Windows 2008.
Monitor resolution
1024 x 768 or higher
Page 26

eBIMS
Product Description
6 Technical Specifications
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
21
6 Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications
Description
Maximum eBoxes managed by the eBIMS
The eBIMS supports a maximum of 3000
eBoxes.
Maximum eBats managed by an eBox
One eBox supports a maximum of 250
eBats.
Maximum clients connected to a server
A maximum of 100 clients can visit one
server at the same time.
Effective transmission distance between the
eBat and eBox
50 meters to 100 meters
Wireless transmission frequency band
between the eBat and eBox
2.4 GHz
Technical Specifications
Description
Working voltage
1.5 V DC to 3.3 V DC
Working temperature range
-20°C to 65°C
Voltage detection range
1.5 V DC to 3.3 V DC
Temperature detection range
-20°C to 65°C
impedance detection range
0.1 Mohms to 20 Mohms
Voltage detection precision
2%
Temperature detection precision
The temperature difference is ±2°C in an
environment with the temperature range of
-25°C to 70°C.
The eBIMS involves eBIMS, eBat, and eBox technical specifications.
Table 6-1 Key technical specifications of the eBIMS
Table 6-2 Key technical specifications when an eBat monitors a 2 V DC battery
Page 27

eBIMS
Product Description
6 Technical Specifications
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
22
Technical Specifications
Description
impedance detection precision
0.01 Mohms
Quiescent Current
21 mA
Technical Specifications
Description
Working voltage
11 V DC to 17 V DC
Working temperature range
-20°C to 65°C
Voltage detection range
11 V DC to 17 V DC
Temperature detection range
-20°C to 65°C
impedance detection range
1.5 Mohms to 60 Mohms
Voltage detection precision
2%
Temperature detection precision
The temperature difference is ±2°C in an
environment with the temperature range of
-25°C to 70°C.
impedance detection precision
0.1 Mohms
Quiescent Current
7 mA
Technical Specifications
Description
Frequency band supported by GPRS
communication
850 MHz/900 MHz/1800 MHz/1900 MHz
Working voltage
-36 V DC to -72 V DC
Working current
300 mA DC Max.
Working temperature range
-20°C to 65°C
Working relative humidity (RH)
5% to 95% RH
Working altitude
-60 meters to 4000 meters
Table 6-3 Key technical specifications when an eBat monitors a 12 V DC battery
An eBat can monitor a 2 V or 12 V DC battery.
Table 6-4 Key technical specifications of the eBox with GPRS
Page 28

eBIMS
Product Description
6 Technical Specifications
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
23
Technical Specifications
Description
Working voltage
-36 V DC to -72 V DC
Working current
200 mA DC Max.
Working temperature range
-20°C to 65°C
Working relative humidity (RH)
5% to 95% RH
Working altitude
-60 meters to 4000 meters
Table 6-5 Key technical specifications of the eBox with FE
Page 29

eBIMS
Product Description
7 Acronyms and Abbreviations
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
24
7 Acronyms and Abbreviations
Acronym or Abbreviation
Full Name
eBIMS
Battery intelligent management system
eBox
Battery module data collection unit
eBat
Battery detection module
B/S
Browser/Server
FE
Fast Ethernet
RF
Radio frequency
Page 30

eBIMS
Product Description
8 Safety Precautions
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
25
FCC Part 15
8 Safety Precautions
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
This device does not cause harmful interference.
This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
If this device is modified without authorization from Huawei, the device may no longer
comply with FCC requirements for Class B digital devices. In that a case, your right to use the
device may be limited by FCC regulations. Moreover, you may be required to correct any
interference to radio or television communications at your own expense.
This device has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation.
This device generates, uses and radiates radio frequency energy. If it is not installed and used
in accordance with the instructions, it may cause harmful interference to radio
communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If
this device does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the device off and on, the user may take one or more of the following
measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Reinforce the separation between the device and receiver.
Connect the device into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio or TV technician for assistance.
This equipment complies with FCC RF radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any
other antenna or transmitter. This equipment should be installed and operated with a minimum
distance of 20 centimeters between the radiator and your body.
The manufacturer is not responsible for any radio or TV interference caused by unauthorized
modifications to this equipment. Such modifications could void the user authority to operate
Page 31

eBIMS
Product Description
8 Safety Precautions
Issue 01 (2013-04-30)
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
26
the equipment.
Canada Regulatory Compliance
RSS-Gen statement
This device complies with Industry Canada licence-exempt RSS standard(s).
Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device may not cause
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference, including interference that may
cause undesired operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
exempts de licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil
ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et (2) l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage
radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le
fonctionnement.
RSS-210 statement:
This device complies with Industry Canada RSS-210. Operation is subject to the following
two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and(2) this device must accept any
interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio
RSS-210. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil ne doit pas
produire de brouillage, et (2) l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioé
lectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
 Loading...
Loading...