Page 1

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide
Issue 01
Date 2021-03-11
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Page 2

Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2021. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specied in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees
or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every eort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i
Page 3

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide Contents
Contents
1 HUAWEI CLOUD Provider Authentication......................................................................... 1
2 Elastic Cloud Server (ECS)..................................................................................................... 3
2.1 Creating an ECS....................................................................................................................................................................... 3
2.2 Adding an EVS Disk................................................................................................................................................................ 4
2.3 Binding an EIP.......................................................................................................................................................................... 5
3 Auto Scaling (AS).................................................................................................................... 6
4 Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)................................................................................................10
4.1
Conguring the Network................................................................................................................................................... 10
4.2 Binding a Virtual IP Address..............................................................................................................................................12
5 NAT Gateway......................................................................................................................... 15
6 Object Storage Service (OBS).............................................................................................18
6.1 Performing Basic Operations............................................................................................................................................ 18
Conguring Static Website Hosting............................................................................................................................... 20
6.2
7 Cloud Container Engine (CCE)........................................................................................... 23
7.1 Creating a CCE Cluster........................................................................................................................................................ 23
7.2 Creating a CCE Node........................................................................................................................................................... 26
8 Relational Database Service (RDS)...................................................................................28
8.1 Creating an RDS MySQL DB Instance............................................................................................................................ 28
8.2 Binding an EIP to an RDS DB Instance.......................................................................................................................... 31
8.3 Adding a Read Replica........................................................................................................................................................ 33
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
Page 4

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 1 HUAWEI CLOUD Provider Authentication
1 HUAWEI CLOUD Provider Authentication
HUAWEI CLOUD Provider uses AK/SK for authentication. You can provide
credentials as either static credentials or environment variables.
Static Credentials
Congure parameters region, access_key, and secret_key in the provider block.
For example:
provider "huaweicloud" {
region = "cn-north-1"
access_key = "my-access-key"
secret_key = "my-secret-key"
}
Static credentials are simple to use. However, they require AKs and SKs to be
stored in
recommended that you provide credentials as environment variables.
conguration les in plaintext, which risks secret leakage. It is
Environment Variables
Congure the region, AK, and SK as environment variables. For example:
$ export HW_REGION_NAME="cn-north-1"
$ export HW_ACCESS_KEY="my-access-key"
$ export HW_SECRET_KEY="my-secret-key"
After setting the environment variables, declare the HUAWEI CLOUD provider.
provider "huaweicloud" {}
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1
Page 5
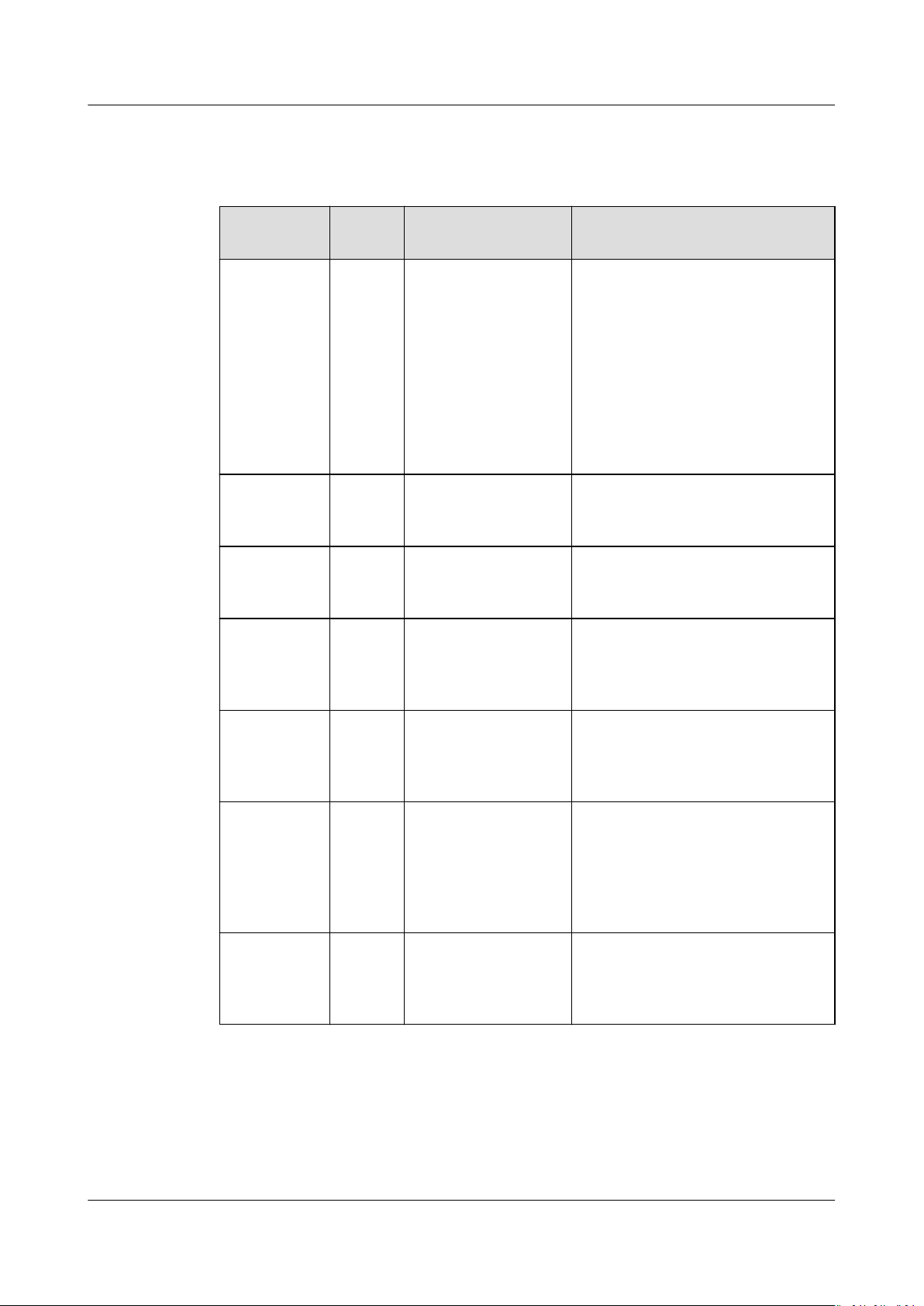
HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 1 HUAWEI CLOUD Provider Authentication
Parameter Description
Table 1-1 Provider authentication parameters
Parameter Manda
tory
region Yes HW_REGION_NAME Region where the HUAWEI
access_key Yes HW_ACCESS_KEY Access key ID of a user. For
secret_key Yes HW_SECRET_KEY Secret access key of a user. For
domain_nameNo HW_DOMAIN_NAMEHUAWEI CLOUD account name.
Environment
Variable
Description
CLOUD service is located. For
details, see Regions and
Endpoints.
If you want to create cloud
services in
congure parameter alias or
region for the resource
corresponding to the cloud
service.
details on how to obtain an
access key ID, see Access Keys.
details on how to obtain a secret
access key, see Access Keys.
For details on how to obtain an
account name, see API
Credentials.
dierent regions,
project_nameNo HW_PROJECT_NAMEHUAWEI CLOUD project name.
For details on how to obtain a
project name, see API
Credentials.
enterprise_p
roject_id
max_retries No HW_MAX_RETRIES Maximum number of retries
No HW_ENTERPRISE_P
ROJECT_ID
Enterprise project ID. For more
information about enterprise
projects and how to obtain
enterprise project IDs, see
Enterprise Management User
Guide.
allowed when a network
transmission problem occurs.
The default value is 5.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
Page 6

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 2 Elastic Cloud Server (ECS)
2 Elastic Cloud Server (ECS)
2.1 Creating an ECS
Application Scenario
An Elastic Cloud Server (ECS) is a basic computing unit that consists of vCPUs,
memory, OS, and Elastic Volume Service (EVS) disks. After creating an ECS, you
can use it like using your local computer or physical server. HUAWEI CLOUD
provides a variety of ECS types for
an ECS, select specications, image type, and disk type and congure network
parameters and security group rules based on your scenario requirements.
Related Resources
huaweicloud_compute_instance
Procedure
Step 1 Use data source to query the AZ, ECS
parameters.
Create the main.tf le, enter the following information, and save the le:
data "huaweicloud_availability_zones" "myaz" {}
data "huaweicloud_compute_avors" "myavor" {
availability_zone = data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[0]
performance_type = "normal"
cpu_core_count = 2
memory_size = 4
}
dierent scenario requirements. When creating
specications, image, and network
data "huaweicloud_images_image" "myimage" {
name = "Ubuntu 18.04 server 64bit"
most_recent = true
}
data "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet" "mynet" {
name = "subnet-default"
}
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
Page 7

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 2 Elastic Cloud Server (ECS)
Step 2 Create an ECS that supports login with a random password.
1. Add the following information to the main.tf le:
resource "random_password" "password" {
length = 16
special = true
override_special = "!@#$%*"
}
resource "huaweicloud_compute_instance" "basic" {
name = "basic"
admin_pass = random_password.password.result
image_id = data.huaweicloud_images_image.myimage.id
avor_id = data.huaweicloud_compute_avors.myavor.ids[0]
availability_zone = data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[0]
security_groups = ["default"]
network {
uuid = data.huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.mynet.id
}
}
2. Run terraform init to initialize the environment.
3. Run terraform plan to view resources.
4. After you conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start ECS creation.
5. Run terraform show to view the created ECS.
----End
Sample Code
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/blob/
master/examples/ecs/basic/main.tf
2.2 Adding an EVS Disk
Application Scenario
Create an EVS disk and attach it to the ECS.
Related Resources
● huaweicloud_evs_volume
● huaweicloud_compute_volume_attach
Procedure
Step 1 Add the following information to the main.tf
resource "huaweicloud_evs_volume" "myvolume" {
name = "myvolume"
availability_zone = data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[0]
volume_type = "SAS"
size = 10
}
resource "huaweicloud_compute_volume_attach" "attached" {
instance_id = huaweicloud_compute_instance.myinstance.id
volume_id = huaweicloud_evs_volume.myvolume.id
}
le:
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
Page 8

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 2 Elastic Cloud Server (ECS)
Step 2 Run terraform plan to view resources.
Step 3 After you conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform apply to
start EVS creation.
Step 4 After the EVS disk is attached to the ECS, you need to initialize the disk before you
use it.
----End
Sample Code
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/blob/
master/examples/ecs/attached-volume/main.tf
2.3 Binding an EIP
Application Scenario
Purchase an EIP and bind it to the ECS.
Related Resources
● huaweicloud_vpc_eip
● huaweicloud_compute_eip_associate
Procedure
Step 1 Add the following information to the main.tf
resource "huaweicloud_vpc_eip" "myeip" {
publicip {
type = "5_bgp"
}
bandwidth {
name = "mybandwidth"
size = 8
share_type = "PER"
charge_mode =
}
}
resource "huaweicloud_compute_eip_associate" "associated" {
public_ip = huaweicloud_vpc_eip.myeip.address
instance_id = huaweicloud_compute_instance.myinstance.id
}
Step 2 Run terraform plan to view resources.
le:
"trac"
Step 3 After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform apply to
purchase the EIP and bind the EIP to the ECS.
----End
Sample Code
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/blob/
master/examples/ecs/associated-eip/main.tf
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
Page 9

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 3 Auto Scaling (AS)
3 Auto Scaling (AS)
Application Scenarios
AS automatically adjusts service resources to keep up with your demand based on
pre-congured AS policies. With automatic resource adjustment, you can enjoy
reduced costs, improved availability, and high fault tolerance. AS applies to the
following scenarios:
●
● E-commerce: Large-scale e-commerce promotions can attract visits that may
● Live streaming: A live streaming website broadcasts popular programs from
Related Resources
●
● huaweicloud_as_group
● huaweicloud_as_policy
● huaweicloud_ces_alarmrule
Procedure
Step 1 Create an AS conguration.
Create the main.tf le, enter the following information, and save the le:
data "huaweicloud_availability_zones" "myaz" {}
Heavy-trac forums: Service load changes of a heavy-trac forum website
are dicult to predict. AS dynamically adjusts the number of cloud servers
based on monitored ECS metrics, such as vCPU Usage and Memory Usage.
break your website. AS automatically adds ECSs and increases bandwidth to
ensure that promotions will go smoothly.
14:00 to 16:00 every day. AS automatically adds ECSs and increases
bandwidth during this period to ensure smooth viewer experience.
huaweicloud_as_conguration
data "huaweicloud_compute_avors" "myavor" {
availability_zone = data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[0]
performance_type = "normal"
cpu_core_count = 2
memory_size = 4
}
data "huaweicloud_images_image" "myimage" {
name = "Ubuntu 18.04 server 64bit"
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
Page 10

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 3 Auto Scaling (AS)
most_recent = true
}
resource "huaweicloud_as_conguration" "my_as_cong" {
scaling_conguration_name = "my_as_cong"
instance_cong {
avor = data.huaweicloud_compute_avors.myavor.ids[0]
image = data.huaweicloud_images_image.myimage.id
key_name = var.my_keypair
disk {
size = 40
volume_type = "SSD"
disk_type = "SYS"
}
}
}
Step 2 Create an AS group.
Add the following information to the main.tf
data "huaweicloud_vpc" "vpc_1" {
name = var.vpc_name
}
data "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet" "subnet_1" {
name = var.subnet_name
vpc_id = data.huaweicloud_vpc.vpc_1.id
}
data "huaweicloud_networking_secgroup" "secgroup_1" {
name = var.secgroup_name
}
resource "huaweicloud_as_group" "my_as_group" {
scaling_group_name = "my_as_group"
scaling_conguration_id = huaweicloud_as_conguration.my_as_cong.id
desire_instance_number = 2
min_instance_number = 0
max_instance_number = 10
vpc_id = data.huaweicloud_vpc.vpc_1.id
delete_publicip = true
delete_instances = "yes"
networks {
id = data.huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.subnet_1.id
}
security_groups {
id = data.huaweicloud_networking_secgroup.secgroup_1.id
}
tags = {
owner = "AutoScaling"
}
}
le:
Step 3 Add a scale-out policy.
In this example, add a metric-based policy. The following content that you will add
to the main.tf
le indicates that when the average CPU usage is greater than or
equal to 80%, an ECS is automatically added.
resource "huaweicloud_ces_alarmrule" "scaling_up_rule" {
alarm_name = "scaling_up_rule"
metric {
namespace = "SYS.AS"
metric_name = "cpu_util"
dimensions {
name = "AutoScalingGroup"
value = huaweicloud_as_group.my_as_group.id
}
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
Page 11

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 3 Auto Scaling (AS)
}
condition {
period = 300
lter = "average"
comparison_operator = ">="
value = 80
unit = "%"
count = 1
}
alarm_actions {
type = "autoscaling"
notication_list = []
}
}
resource "huaweicloud_as_policy" "scaling_up_policy" {
scaling_policy_name = "scaling_up_policy"
scaling_policy_type = "ALARM"
scaling_group_id = huaweicloud_as_group.my_as_group.id
alarm_id = huaweicloud_ces_alarmrule.scaling_up_rule.id
cool_down_time = 300
scaling_policy_action {
operation = "ADD"
instance_number = 1
}
}
Step 4 Add a scale-in policy.
In this example, add a metric-based policy. The following content that you will add
to the main.tf
le indicates that when the average CPU usage is equal to or lower
than 20%, an ECS is automatically reduced.
resource "huaweicloud_ces_alarmrule" "scaling_down_rule" {
alarm_name = "scaling_down_rule"
metric {
namespace = "SYS.AS"
metric_name = "cpu_util"
dimensions {
name = "AutoScalingGroup"
value = huaweicloud_as_group.my_as_group.id
}
}
condition {
period = 300
lter = "average"
comparison_operator = "<="
value = 20
unit = "%"
count = 1
}
alarm_actions {
type = "autoscaling"
notication_list = []
}
}
resource "huaweicloud_as_policy" "scaling_down_policy" {
scaling_policy_name = "scaling_down_policy"
scaling_policy_type = "ALARM"
scaling_group_id = huaweicloud_as_group.my_as_group.id
alarm_id = huaweicloud_ces_alarmrule.scaling_down_rule.id
cool_down_time = 300
scaling_policy_action {
operation = "REMOVE"
instance_number = 1
}
}
Step 5
Congure variables.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
Page 12

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 3 Auto Scaling (AS)
Create the variables.tf le, enter the following information, and save the le. You
can change the variable values based on your needs.
variable "my_keypair" {
default = "default"
}
variable "vpc_name" {
default = "vpc-default"
}
variable "subnet_name" {
default = "subnet-default"
}
variable "secgroup_name" {
default = "default"
}
Step 6 Create resources.
1. Run terraform init to initialize the environment.
2. Run terraform plan to view resources.
3. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start resource creation.
4. Run terraform show to view the created resources.
Sample Code
----End
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/auto-scaling/alarm_policy
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
Page 13

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 4 Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
4 Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
4.1 Conguring the Network
Application Scenario
Before creating your VPCs, determine how many VPCs, the number of subnets,
and what IP address ranges or connectivity options you will need. For details
about network planning, see VPC Best Practices.
In this topic, you will create a VPC to host web applications or websites. This VPC
uses the private CIDR block 192.168.0.0/16 and is divided into three subnets for
web, application, and database servers. In addition, servers are arranged into
dierent security groups with targeted access control rules congured.
Related Resources
● huaweicloud_vpc
● huaweicloud_vpc_subnet
● huaweicloud_networking_secgroup
● huaweicloud_networking_secgroup_rule
Procedure
Step 1 Create a VPC and three subnets.
1. Create the network.tf le, enter the following information, and save the le:
resource "huaweicloud_vpc" "vpc" {
name = "vpc-web"
cidr = "192.168.0.0/16"
}
resource "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet" "subnet1" {
name = "subnet-web"
cidr = "192.168.10.0/24"
gateway_ip = "192.168.10.1"
vpc_id = huaweicloud_vpc.vpc.id
dns_list = ["100.125.1.250", "100.125.129.250"]
}
resource "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet" "subnet2" {
name = "subnet-app"
cidr = "192.168.20.0/24"
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10
Page 14

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 4 Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
gateway_ip = "192.168.20.1"
vpc_id = huaweicloud_vpc.vpc.id
dns_list = ["100.125.1.250", "100.125.129.250"]
}
resource "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet" "subnet3" {
name = "subnet-db"
cidr = "192.168.30.0/24"
gateway_ip = "192.168.30.1"
vpc_id = huaweicloud_vpc.vpc.id
dns_list = ["100.125.1.250", "100.125.129.250"]
}
Table 4-1 Parameter description
Resource
Name
huaweicloud_
vpc
huaweicloud_
vpc_subnet
Param
Description
eter
name VPC name.
– Value: a string of 1 to 64 characters that can
contain letters, digits, underscores (_),
hyphens (-), and periods (.)
– Constraints: A VPC name must be unique
under a tenant.
cidr Available subnets in the VPC. The value must be
in CIDR format, for example, 192.168.0.0/16.
name Subnet name.
– Value: a string of 1 to 64 characters that can
contain letters, digits, underscores (_),
hyphens (-), and periods (.)
cidr CIDR block of the subnet.
– Value: a CIDR block in the range allowed in
the VPC
– Constraints: The value must be in CIDR
format. The subnet mask length cannot be
greater than 28 bits.
gatew
Subnet gateway address.
ay_ip
vpc_id ID of the VPC to which the subnet belongs. The
value is referenced from
huaweicloud_vpc.vpc.id.
dns_listAddresses of DNS servers on the subnet. If this
parameter is not specied, the value is left blank
by default. For details about private DNS server
addresses, see What Are the Private DNS Server
Addresses Provided by the DNS Service?
2. Run terraform init to initialize the environment.
3. Run terraform plan to view resources.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
Page 15

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 4 Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
4. After you conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start VPC and subnet creation.
5. Run terraform show to view the created VPC and subnets.
Step 2 Create a security group and add a rule to it.
Sample Code
1. Add the following information to the network.tf
resource "huaweicloud_networking_secgroup" "mysecgroup" {
name = "secgroup"
description = "My security group"
delete_default_rules = true
}
resource "huaweicloud_networking_secgroup_rule" "secgroup_rule" {
direction = "ingress"
ethertype = "IPv4"
protocol = "tcp"
port_range_min = 22
port_range_max = 22
remote_ip_prex = "0.0.0.0/0"
security_group_id = huaweicloud_networking_secgroup.mysecgroup.id
}
le:
2. Run terraform plan to view resources.
3. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start security group and rule creation.
4. Run terraform show to view the created security group and rule.
----End
● https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/vpc/basic
● https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/blob/
master/examples/vpc/secgroup/main.tf
4.2 Binding a Virtual IP Address
Application Scenario
Virtual IP addresses are used for high availability (HA) as they make active/
standby ECS switchover possible. If the active ECS becomes faulty and cannot
provide services, the virtual IP address is dynamically re-assigned to the standby
ECS so services can continue uninterrupted.
Related Resources
● huaweicloud_networking_vip
● huaweicloud_networking_vip_associate
Procedure
Step 1
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
Congure the network.
Create the main.tf le, enter the following information, and save the le:
Page 16

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 4 Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
resource "huaweicloud_vpc" "vpc_1" {
name = var.vpc_name
cidr = var.vpc_cidr
}
resource "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet" "subnet_1" {
vpc_id = huaweicloud_vpc.vpc_1.id
name = var.subnet_name
cidr = var.subnet_cidr
gateway_ip = var.subnet_gateway
primary_dns = var.primary_dns
}
Step 2 Create two ECSs.
Add the following information to the main.tf
data "huaweicloud_availability_zones" "myaz" {}
data "huaweicloud_compute_avors" "myavor" {
availability_zone = data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[0]
performance_type = "normal"
cpu_core_count = 2
memory_size = 4
}
data "huaweicloud_images_image" "myimage" {
name = "Ubuntu 18.04 server 64bit"
most_recent = true
}
resource "huaweicloud_compute_instance" "mycompute" {
name = "mycompute_${count.index}"
image_id = data.huaweicloud_images_image.myimage.id
avor_id = data.huaweicloud_compute_avors.myavor.ids[0]
security_groups = ["default"]
availability_zone = data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[0]
network {
uuid = huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.subnet_1.id
}
count = 2
}
le:
Step 3 Apply for a virtual IP address and bind it to the ECS ports.
le:
Step 4
Add the following information to the main.tf
resource "huaweicloud_networking_vip" "vip_1" {
network_id = huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.subnet_1.id
}
# associate ports to the vip
resource "huaweicloud_networking_vip_associate" "vip_associated" {
vip_id = huaweicloud_networking_vip.vip_1.id
port_ids = [
huaweicloud_compute_instance.mycompute[0].network.0.port,
huaweicloud_compute_instance.mycompute[1].network.0.port
]
}
Congure variables.
Create the variables.tf
le, enter the following information, and save the le. You
can change the variable values based on your needs.
variable "vpc_name" {
default = "vpc-basic"
}
variable "vpc_cidr" {
default = "172.16.0.0/16"
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
Page 17

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 4 Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
}
variable "subnet_name" {
default = "subent-basic"
}
variable "subnet_cidr" {
default = "172.16.10.0/24"
}
variable "subnet_gateway" {
default = "172.16.10.1"
}
variable "primary_dns" {
default = "100.125.1.250"
}
Step 5 Create resources.
1. Run terraform init to initialize the environment.
2. Run terraform plan to view resources.
3. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start resource creation.
4. Run terraform show to view the created resources.
----End
Sample Code
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/vpc/vip
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
Page 18

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 5 NAT Gateway
5 NAT Gateway
Application Scenario
If multiple cloud servers need to access the Internet without binding EIPs, you can
use a NAT gateway to share EIPs and prevent the IP addresses of the servers from
being exposed to the Internet.
Related Resources
huaweicloud_vpc_eip
huaweicloud_nat_gateway
huaweicloud_nat_snat_rule
Procedure
Step 1 Apply for an EIP.
Create the main.tf le, enter the following information, and save the le:
resource "huaweicloud_vpc_eip" "eip_1" {
publicip {
type = "5_bgp"
}
bandwidth {
name = "test"
size = 5
share_type = "PER"
charge_mode =
}
}
Step 2 Apply for a NAT gateway and congure SNAT rules.
"trac"
Add the following information to the main.tf le:
data "huaweicloud_vpc" "vpc_1" {
name = "vpc-default"
}
data "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet" "subnet_1" {
name = "subnet-default"
vpc_id = data.huaweicloud_vpc.vpc_1.id
}
resource "huaweicloud_nat_gateway" "nat_1" {
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15
Page 19

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 5 NAT Gateway
name = "nat-gateway-basic"
description = "test for terraform examples"
spec = "1"
internal_network_id = data.huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.subnet_1.id
router_id = data.huaweicloud_vpc.vpc_1.id
}
resource "huaweicloud_nat_snat_rule" "snat_1" {
oating_ip_id = huaweicloud_vpc_eip.eip_1.id
nat_gateway_id = huaweicloud_nat_gateway.nat_1.id
network_id = data.huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.subnet_1.id
}
Table 5-1 Parameter description
Resource
Name
huaweicloud_n
at_gateway
Parameter Description
name NAT gateway name, which can contain digits,
letters, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
description Supplementary information about the NAT
gateway.
spec Type of the NAT gateway. The value can be:
● 1: small type, which supports up to 10,000
SNAT connections.
● 2: medium type, which supports up to
50,000 SNAT connections.
● 3: large type, which supports up to 200,000
SNAT connections.
● 4: extra-large type, which supports up to
1,000,000 SNAT connections.
internal_net
Network ID of the subnet.
work_id
router_id VPC ID.
huaweicloud_n
at_snat_rule
oating_ip_idEIP ID. Separate multiple EIPs with commas (,).
● The number of EIP IDs cannot exceed 20.
nat_gateway
ID of the NAT gateway.
_id
network_id Network ID used by the SNAT rule.
Step 3 Create resources.
1. Run terraform init to initialize the environment.
2. Run terraform plan to view resources.
3. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start resource creation.
----End
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16
Page 20

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 5 NAT Gateway
Sample Code
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/nat/snat-basic
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
Page 21

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 6 Object Storage Service (OBS)
6 Object Storage Service (OBS)
6.1 Performing Basic Operations
Application Scenario
Object Storage Service (OBS) is a cloud storage service optimized for storing data
of any type and size. It provides unlimited, secure, and highly reliable storage
capabilities at a low cost. It is suitable for various data storage scenarios, such as
enterprise-level backup/archiving, video on demand (VoD), and video surveillance.
Related Resources
● huaweicloud_obs_bucket
● huaweicloud_obs_bucket_object
Procedure
Step 1 Create an OBS bucket.
1. Create the main.tf
resource "huaweicloud_obs_bucket" "myexample" {
bucket = "myexample-bucket"
acl = "private"
tags = {
type = "bucket"
env = "Test"
}
}
2. Run terraform init to initialize the environment.
3. Run terraform plan to view resources.
4. After you
apply to start OBS bucket creation.
5. Run terraform show to view the created OBS bucket.
le, enter the following information, and save the le:
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
Step 2 Upload objects.
1. Objects can be uploaded through data ows or source les. Add the following
information to the main.tf le:
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 18
Page 22

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 6 Object Storage Service (OBS)
# Upload an object through data ows.
resource "huaweicloud_obs_bucket_object" "myobject1" {
bucket = huaweicloud_obs_bucket.myexample.bucket
key = "myobject1"
content = "content of myobject1"
content_type = "application/xml"
}
# Upload an object through a source
resource "huaweicloud_obs_bucket_object" "myobject2" {
bucket = huaweicloud_obs_bucket.myexample.bucket
key = "myobject2"
source = "hello.txt"
}
# Upload an object through a source
resource "huaweicloud_obs_bucket_object" "myobject3" {
bucket = huaweicloud_obs_bucket.myexample.bucket
key = "myobject3"
source = "hello.txt"
encryption = true
}
le.
le and enable server-side encryption.
2. Run terraform plan to view resources.
3. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start resource creation.
4. Run terraform show to view the uploaded objects.
----End
Table 6-1 Parameter description
Resource Name
huaweicloud_obs_bu
Parameter Description
bucket (Mandatory) OBS bucket name.
cket
acl (Optional) OBS bucket access control policy.
An OBS bucket name:
● Must be globally unique in OBS.
● Contains 3 to 63 characters, including lowercase letters,
digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.).
● Cannot start or end with a period (.) or hyphen (-).
● Cannot contain two consecutive periods (..) or adjacent
periods and hyphens (.- or -.).
● Cannot be an IP address.
● Value:
private (default value): No access permission beyond
the bucket ACL settings is granted.
public-read: Any user can read objects in the bucket.
public-read-write: Any user can read, write, and delete
objects in the bucket.
tags (Optional) Bucket tag.
huaweicloud_obs_bu
bucket (Mandatory) Bucket name.
cket_object
key (Mandatory) Object name.
source (Optional) Path to the source le of the object.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 19
Page 23

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 6 Object Storage Service (OBS)
Resource Name Parameter Description
content (Optional) Data ow of the object.
content_type (Optional) MIME type of the object.
encryption (Optional) Whether to enable server-side encryption using
keys hosted by KMS (SSE-KMS).
Sample Code
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/blob/
master/examples/obs/basic/main.tf
6.2
Conguring Static Website Hosting
Application Scenario
OBS allows static websites to be hosted on buckets and supports index page, error
page display, and page redirection. You can upload the content les of the static
website to your bucket on OBS and
users for these les, and then congure the static website hosting mode for your
bucket to host your static websites on OBS.
Related Resources
● huaweicloud_obs_bucket
● huaweicloud_obs_bucket_object
● huaweicloud_obs_bucket_policy
Procedure
Step 1 Create an OBS bucket and congure static website hosting.
1. Create the main.tf le, enter the following information, and save the le:
resource "huaweicloud_obs_bucket" "mywebsite" {
bucket = "mywebsite"
website {
index_document = "index.html"
error_document = "error.html"
}
}
2. Run terraform init to initialize the environment.
3. Run terraform plan to view resources.
4. After you
apply to start OBS bucket creation.
5. Run terraform show to view the created OBS bucket.
congure a read permission to anonymous
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
Step 2 Congure a bucket policy to allow anonymous users to access objects in the
bucket.
Add the following information to the main.tf le:
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 20
Page 24

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 6 Object Storage Service (OBS)
# Grant the Read-Only permission to anonymous users.
resource "huaweicloud_obs_bucket_policy" "policy" {
bucket = huaweicloud_obs_bucket.mywebsite.bucket
policy = <<POLICY
{
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AddPerm",
"Eect": "Allow",
"Principal": {"ID": "*"},
"Action": ["GetObject"],
"Resource": "mywebsite/*"
}
]
}
POLICY
}
Step 3 Upload static website
1. Edit the index.html and error.html les in the current directory.
2. Add the following information to the main.tf
OBS bucket:
# put index.html
resource "huaweicloud_obs_bucket_object" "index" {
bucket = huaweicloud_obs_bucket.mywebsite.bucket
key = "index.html"
source = "index.html"
}
# put error.html
resource "huaweicloud_obs_bucket_object" "error" {
bucket = huaweicloud_obs_bucket.mywebsite.bucket
key = "error.html"
source = "error.html"
}
3. Run terraform plan to view resources.
4. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start le uploading.
Step 4 Verify the
conguration.
Use a browser to access https://
north-4
.myhuaweicloud.com, that is, to access index.html.
the OBS bucket name, and
belongs.
les.
mywebsite
cn-north-4
le and upload the les to the
.obs-website.
cn-
mywebsite
indicates
indicates the region to which the bucket
----End
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 21
Page 25

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 6 Object Storage Service (OBS)
Table 6-2 Parameter description
Resource Name Parameter Description
huaweicloud_obs_bu
cket
huaweicloud_obs_bu
cket_policy
bucket (Mandatory) OBS bucket name.
An OBS bucket name:
● Must be globally unique in OBS.
● Contains 3 to 63 characters, including lowercase
letters, digits, hyphens (-), and periods (.).
● Cannot start or end with a period (.) or hyphen (-).
● Cannot contain two consecutive periods (.) or
adjacent periods and hyphens (.- or -.).
● Cannot be an IP address.
webs
ite
bucket (Mandatory) Bucket name.
policy_format (Optional) Policy format. The value can be obs or s3.
index_doc
ument
error_doc
ument
routing_ru
les
(Mandatory) The index page that is returned when
you access a static website, that is, the homepage.
(Optional) The 404 error page that is returned when
an incorrect static website path is accessed.
(Optional) Rule for redirecting the static website.
The default value is obs.
policy (Mandatory) Policy content. For details, see Policy
huaweicloud_obs_bu
cket_object
bucket (Mandatory) Bucket name.
key (Mandatory) Object name.
source (Optional) Path to the source le of the object.
Follow-up Operation
You can bind a user-dened domain name to the access domain name of an OBS
bucket so that you can access les stored in OBS through the user-dened domain
name. With the domain name management of OBS, you can also use CDN for
service acceleration. For details, see Using a
Host a Static Website.
Sample Code
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/obs/website
Format.
User-Dened Domain Name to
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 22
Page 26

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 7 Cloud Container Engine (CCE)
7 Cloud Container Engine (CCE)
HUAWEI CLOUD CCE allows you to easily deploy, manage, and scale containerized
applications in the cloud by providing support for you to use Kubernetes. This
chapter describes how to create a CCE cluster and node using Terraform scripts.
7.1 Creating a CCE Cluster
Related Resources
● huaweicloud_vpc
● huaweicloud_vpc_subnet
● huaweicloud_vpc_eip
● huaweicloud_cce_cluster
Procedure
Step 1 Create a VPC and subnet. For details, see 4.1 Conguring the Network.
1. Create the cce.tf le, enter the following information, and save the le:
resource "huaweicloud_vpc" "myvpc" {
name = "myvpc"
cidr = "192.168.0.0/16"
}
resource "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet" "mysubnet" {
name = "mysubnet"
cidr = "192.168.0.0/16"
gateway_ip = "192.168.0.1"
//dns is required for cce node installing
primary_dns = "100.125.1.250"
secondary_dns = "100.125.21.250"
vpc_id = huaweicloud_vpc.myvpc.id
}
2. Run terraform init to initialize the environment.
3. Run terraform plan to view resources.
4. After you
apply to start resource creation.
5. Run terraform show to view the created VPC and subnet.
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 23
Page 27

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 7 Cloud Container Engine (CCE)
Step 2 Assign an EIP. If the cluster does not use the public network, skip this step.
1. Add the following information to the cce.tf le:
resource "huaweicloud_vpc_eip" "myeip" {
publicip {
type = "5_bgp"
}
bandwidth {
name = "mybandwidth"
size = 8
share_type = "PER"
charge_mode =
}
}
"trac"
2. Run terraform plan to view resources.
3. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start resource creation.
4. Run terraform show to view the created EIP.
Step 3 Create a CCE cluster.
1. Add the following information to the cce.tf
resource "huaweicloud_cce_cluster" "mycce" {
name = "mycce"
avor_id = "cce.s1.small"
vpc_id = huaweicloud_vpc.myvpc.id
subnet_id = huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.mysubnet.id
container_network_type = "overlay_l2"
eip = huaweicloud_vpc_eip.myeip.address // If you choose not to use EIP, skip this line.
}
le:
2. Run terraform plan to view resources.
3. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start resource creation.
4. Run terraform show to view the created CCE cluster.
----End
Table 7-1 Parameter description
Resource
Parameter Description
Name
huaweiclou
d_cce_cluste
r
name (Mandatory) Cluster name.
● Enter 4 to 128 characters, starting with a
lowercase letter and not ending with a
hyphen (-). Only lowercase letters, digits,
and hyphens (-) are allowed.
● Clusters under a tenant must have unique
names.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 24
Page 28

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 7 Cloud Container Engine (CCE)
Resource
Name
Parameter Description
avor_id (Mandatory) Cluster avor.
● Options:
– cce.s1.small: small-scale, single-master
hybrid cluster (≤ 50 nodes)
– cce.s1.medium: medium-scale, single-
master hybrid cluster (≤ 200 nodes)
– cce.s2.small: small-scale, multi-master
hybrid cluster (≤ 50 nodes)
– cce.s2.medium: medium-scale, multi-
master hybrid cluster (≤ 200 nodes)
– cce.s2.large: large-scale, multi-master
hybrid cluster (≤ 1,000 nodes)
– cce.s2.xlarge: ultra-large-scale, multi-
master hybrid cluster (≤ 2,000 nodes)
● Cluster
avor cannot be changed after the
cluster is created.
vpc_id (Mandatory) ID of the VPC used to create a
master node.
subnet_id (Mandatory) Network ID of the subnet used to
create a master node.
container_netw
ork_type
(Mandatory) Container network type.
● Options:
– overlay_l2: an overlay_l2 network built
for containers by using Open vSwitch
(OVS).
– underlay_ipvlan: an underlay_l2 network
built for BMS nodes by using IPVlan.
– vpc-router: an underlay_l2 network built
for containers by using IPVlan and custom
VPC routes.
– eni: The Yangtse network model, which
deeply integrates the native ENI capability
of VPC, uses the VPC CIDR block to
allocate container addresses and supports
data passthrough from a load balancer to
containers. This option is available when
you are creating a CCE Turbo cluster (in
OBT).
eip (Optional) EIP.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 25
Page 29

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 7 Cloud Container Engine (CCE)
Sample Code
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/cce/basic
7.2 Creating a CCE Node
Related Resources
● huaweicloud_availability_zones
● huaweicloud_compute_keypair
● huaweicloud_cce_cluster
● huaweicloud_cce_node
Procedure
Step 1 Create a CCE cluster. For details, see 7.1 Creating a CCE Cluster.
Step 2 Create a CCE node.
1. Add the following content to the cce.tf
le created in 7.1 Creating a CCE
Cluster.
data "huaweicloud_availability_zones" "myaz" {}
resource "huaweicloud_compute_keypair" "mykeypair" {
name = "mykeypair"
}
resource "huaweicloud_cce_node" "mynode" {
cluster_id = huaweicloud_cce_cluster.mycce.id
name = "mynode"
avor_id = "t6.large.2"
availability_zone = data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[0]
key_pair = huaweicloud_compute_keypair.mykeypair.name
root_volume {
size = 40
volumetype = "SAS"
}
data_volumes {
size = 100
volumetype = "SAS"
}
}
2. Run terraform plan to view resources.
3. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start resource creation.
4. Run terraform show to view the created CCE node.
----End
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 26
Page 30

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 7 Cloud Container Engine (CCE)
Table 7-2 Parameter description
Resource
Name
huaweiclou
d_cce_node
Parameter Description
cluster_id (Mandatory) Cluster ID.
name (Optional) Node name.
● Enter 1 to 56 characters, starting with a
lowercase letter and not ending with a
hyphen (-). Only lowercase letters, digits,
and hyphens (-) are allowed.
avor_id (Mandatory) Node avor.
availability_zone(Mandatory) Name of the AZ to which a node
belongs.
● Select an AZ that exists at the underlying
layer and is in the physical AZ group of the
user.
key_pair (Optional) Key pair used for login.
● You must select either key pair or password
for login.
root_vo
lume
size (Mandatory) Disk size in GB.
● For the system disk, the value ranges from
40 to 1024.
Sample Code
volum
etype
data_v
olume
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/cce/basic
size (Mandatory) Disk size in GB.
volum
etype
(Mandatory) Disk type.
● Options:
– SATA: common I/O disk type
– SATA: high I/O disk type
– SSD: ultra-high I/O disk type
● For a data disk, the value ranges from 100
to 32768.
(Mandatory) Disk type.
● Options:
– SATA: common I/O disk type
– SATA: high I/O disk type
– SSD: ultra-high I/O disk type
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 27
Page 31

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 8 Relational Database Service (RDS)
8 Relational Database Service (RDS)
RDS is a cloud-based web service that is reliable, scalable, easy to manage, and
immediately ready for use.
8.1 Creating an RDS MySQL DB Instance
Application Scenario
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system. The LAMP
solution (Linux + Apache + MySQL + Perl/PHP/Python) makes it much
develop web applications. This section describes how to create an RDS MySQL DB
instance by using Terraform scripts.
Related Resources
huaweicloud_rds_instance
Procedure
Step 1 Plan and create a VPC, subnet, and security group.
1. For details about how to create a network resource, see 4.1
Network.
2. If you want to use a created network resource, use data source to obtain the
corresponding resource ID. The following is an example:
data "huaweicloud_vpc" "myvpc" {
name = var.vpc_name
}
data "huaweicloud_vpc_subnet" "mysubnet" {
vpc_id = data.huaweicloud_vpc.myvpc.id
name = var.subnet_name
}
data "huaweicloud_networking_secgroup" "mysecgroup" {
name = var.secgroup_name
}
ecient to
Conguring the
Step 2 Create an RDS MySQL DB instance.
Example 1: Using new network resources and a random password
data "huaweicloud_availability_zones" "myaz" {}
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 28
Page 32

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 8 Relational Database Service (RDS)
resource "random_password" "mypassword" {
length = 12
special = true
override_special = "!@#%^*-_=+"
}
resource "huaweicloud_rds_instance" "myinstance" {
name = "mysql_instance"
avor = "rds.mysql.c2.large.ha"
ha_replication_mode = "async"
vpc_id = huaweicloud_vpc.myvpc.id
subnet_id = huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.mysubnet.id
security_group_id = huaweicloud_networking_secgroup.mysecgroup.id
availability_zone = [
data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[0],
data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[1]
]
db {
type = "MySQL"
version = "8.0"
password = random_password.mypassword.result
}
volume {
type = "ULTRAHIGH"
size = 40
}
}
Step 3
Example 2: Using existing network resources
data "huaweicloud_availability_zones" "myaz" {}
resource "huaweicloud_rds_instance" "myinstance" {
name = "mysql_instance"
avor = "rds.mysql.c2.large.ha"
ha_replication_mode = "async"
vpc_id = data.huaweicloud_vpc.myvpc.id
subnet_id = data.huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.mysubnet.id
security_group_id = data.huaweicloud_networking_secgroup.mysecgroup.id
availability_zone = [
data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[0],
data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[1]
]
db {
type = "MySQL"
version = "8.0"
password = var.rds_password
}
volume {
type = "ULTRAHIGH"
size = 40
}
}
Congure variables.
Create the variables.tf le, enter the following information, and save the le. You
can change the variable values based on your needs.
variable "vpc_name" {
default = "vpc-basic"
}
variable "vpc_cidr" {
default = "172.16.0.0/16"
}
variable "subnet_name" {
default = "subent-basic"
}
variable "subnet_cidr" {
default = "172.16.10.0/24"
}
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 29
Page 33

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 8 Relational Database Service (RDS)
variable "subnet_gateway" {
default = "172.16.10.1"
}
variable "primary_dns" {
default = "100.125.1.250"
}
Step 4 Create resources.
1. Run terraform init to initialize the environment.
2. Run terraform plan to view resources.
3. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start resource creation.
4. Run terraform show to view information about the created RDS instance.
----End
Table 8-1 Parameter description
Resource
Name
huaweicloud_rd
s_instance
Parameter Description
name (Mandatory) Database instance name. Under the same
tenant, database instances of the same type can have the
same name.
● The value must be 4 to 64 characters in length and start
with a letter. It is case-sensitive and can contain only
letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
avor (Mandatory) DB instance avor. In this example,
rds.mysql.c2.large.ha is used. You can query the instance
avor via huaweicloud_rds_avors.
ha_replication_mode(Optional) Replication mode for the standby DB instance.
For MySQL, the value can be async or semisync.
availability_zone (Mandatory) AZ where the instance is located. Multiple AZs
are supported for master/standby instances. For details, see
Regions and Endpoints.
vpc_id (Mandatory) ID of the VPC to which the instance belongs.
subnet_id (Mandatory) ID of the subnet to which the instance
belongs.
security_group_id (Mandatory) ID of the security group to which the instance
belongs.
db type (Mandatory) Database engine type.
● Value options: MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLServer
version(Mandatory) Database engine version. For MySQL, versions
5.6, 5.7, and 8.0 are supported.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 30
Page 34

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 8 Relational Database Service (RDS)
Resource
Name
Parameter Description
passw
ord
port (Optional) Database port.
volume type (Mandatory) Disk type of the database instance.
size (Mandatory) Disk space of the database instance.
(Mandatory) Database password.
The value contains 8 to 32 characters. Only letters, digits,
and the following special characters are supported: ~!@#
%^*-_=+?
Enter a strong password to prevent security risks such as
brute force cracking.
● The MySQL database port ranges from 1024 to 65535
(excluding 12017 and 33071, which are occupied by the
RDS system). The default value is 3306.
● Options:
ULTRAHIGH: SSD type
ULTRAHIGHPRO: ultra-high I/O (advanced), which
supports ultra-high performance (advanced) DB
instances.
● The value must be a multiple of 10 and range from 40
GB to 4,000 GB.
Sample Code
● https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/rds/mysql
● https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/rds/mysql-with-network
8.2 Binding an EIP to an RDS DB Instance
Application Scenario
After an RDS DB instance is created, you can bind an EIP to it so that you can
access the DB instance through the public network. This section describes how to
use the Terraform scripts to bind or unbind an EIP from an RDS DB instance.
An EIP cannot be bound to or unbound from a DB instance that is being created,
modied, restored, frozen, or rebooted.
Related Resources
● huaweicloud_rds_instance
● huaweicloud_vpc_eip
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 31
Page 35

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 8 Relational Database Service (RDS)
● huaweicloud_networking_eip_associate
Procedure
Step 1 For details about how to create a MySQL database instance, see 8.1 Creating an
RDS MySQL DB Instance.
Step 2 Add a security group rule to allow the
specied network to access the port of the
RDS DB instance.
resource "huaweicloud_networking_secgroup_rule" "allow_rds" {
direction = "ingress"
ethertype = "IPv4"
protocol = "tcp"
port_range_min = 3306
port_range_max = 3306
remote_ip_prex = var.allow_cidr
security_group_id = huaweicloud_networking_secgroup.mysecgroup.id
}
Step 3 Create an EIP and bind it to the private IP address of the RDS DB instance.
# Creating an EIP
resource "huaweicloud_vpc_eip" "myeip" {
publicip {
type = "5_bgp"
}
bandwidth {
name = "test"
size = 5
share_type = "PER"
charge_mode =
}
}
# Querying the private network port of the RDS DB instance
data "huaweicloud_networking_port" "rds_port" {
network_id = huaweicloud_vpc_subnet.mysubnet.id
xed_ip = huaweicloud_rds_instance.myinstance.private_ips[0]
}
# Binding an EIP
resource "huaweicloud_networking_eip_associate" "associated" {
public_ip = huaweicloud_vpc_eip.myeip.address
port_id = data.huaweicloud_networking_port.rds_port.id
}
"trac"
1. Run terraform plan to view resources.
2. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start resource creation.
3. Run terraform show to view binding information about the created EIP.
----End
Table 8-2 Parameter description
Resource Name
Para
Description
mete
r
huaweicloud_vpc_eippubliciptype (Mandatory) IP address type. Currently,
only 5_bgp is supported.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 32
Page 36

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 8 Relational Database Service (RDS)
Resource Name Para
mete
r
band
width
huaweicloud_netw
orking_port
huaweicloud_netw
orking_eip_associat
e
xed_ip (Mandatory) Private IP address of the
network_id (Mandatory) Network ID of the subnet
public_ip (Mandatory) EIP.
port_id (Mandatory) ID of the port
Description
name (Optional) Bandwidth conguration
name.
size (Optional) IP bandwidth. The value
ranges from 1 to 300 Mbit/s.
share_
type
(Mandatory) Add the IP address to a
shared bandwidth or an exclusive
bandwidth.
RDS DB instance.
to which the RDS instance belongs.
corresponding to the RDS DB instance.
Sample Code
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/rds/mysql-with-eip
8.3 Adding a Read Replica
Application Scenario
In read-intensive scenarios, a single DB instance may be unable to handle the read
pressure and service performance may be
database, you can create read replicas in a region. These read replicas can process
a large number of read requests and increase application throughput. Data
synchronization between the primary DB instance and read replicas is not
by network latency. Read replicas and the primary DB instance must be in the
same region but can be in dierent AZs. This section describes how to use
Terraform scripts to create an RDS read replica.
Related Resources
huaweicloud_rds_read_replica_instance
aected. To ooad read pressure on the
aected
Procedure
Step 1 For details about how to create a MySQL database, see 8.1 Creating an RDS
MySQL DB Instance.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 33
Page 37

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 8 Relational Database Service (RDS)
Step 2 Create an RDS read replica. The following uses MySQL as an example.
data "huaweicloud_availability_zones" "myaz" {}
resource "huaweicloud_rds_read_replica_instance" "myreplica" {
name = "myreplica"
avor = "rds.mysql.c2.large.rr"
primary_instance_id = huaweicloud_rds_instance.myinstance.id
availability_zone = data.huaweicloud_availability_zones.myaz.names[1]
volume {
type = "ULTRAHIGH"
}
tags = {
type = "readonly"
}
}
1. Run terraform plan to view resources.
2. After you
conrm that the resource information is correct, run terraform
apply to start resource creation.
3. Run terraform show to view information about the created RDS read replica.
----End
Table 8-3 Parameter description
Resource Name
huaweicloud_rds_
Parameter Description
name (Mandatory) Read replica name.
read_replica_insta
nce
avor (Mandatory) Read replica avor. In this
primary_inst
ance_id
availability_z
one
tags (Optional) Instance tags.
volume ty
● The value must be 4 to 64 characters in
length and start with a letter. It is casesensitive and can contain only letters,
digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_).
example, rds.mysql.c2.large.rr is used. You
can query the instance avor via
huaweicloud_rds_avors.
(Mandatory) Primary DB instance ID.
(Mandatory) AZ where the read replica is
located. For details, see Regions and
Endpoints.
(Mandatory) Disk type of the read replica.
p
● Options:
e
ULTRAHIGH: SSD type
ULTRAHIGHPRO: ultra-high I/O
(advanced), which supports ultra-high
performance (advanced) DB instances.
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 34
Page 38

HuaweiCloud Terraform Provider
User Guide 8 Relational Database Service (RDS)
Sample Code
https://github.com/huaweicloud/terraform-provider-huaweicloud/tree/
master/examples/rds/read-replica
Issue 01 (2021-03-11) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 35
 Loading...
Loading...