Page 1

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide
Issue 04
Date 2020-04-08
HUAWEI TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD.
Page 2

Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2021. All rights reserved.
No part of this document may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
Trademarks and Permissions
and other Huawei trademarks are trademarks of Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
All other trademarks and trade names mentioned in this document are the property of their respective
holders.
Notice
The purchased products, services and features are stipulated by the contract made between Huawei and
the customer. All or part of the products, services and features described in this document may not be
within the purchase scope or the usage scope. Unless otherwise specied in the contract, all statements,
information, and recommendations in this document are provided "AS IS" without warranties, guarantees
or representations of any kind, either express or implied.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Every eort has been made in the
preparation of this document to ensure accuracy of the contents, but all statements, information, and
recommendations in this document do not constitute a warranty of any kind, express or implied.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. i
Page 3

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide Contents
Contents
1 Vault Management................................................................................................................. 1
1.1 Querying a Vault..................................................................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Deleting a Vault....................................................................................................................................................................... 4
1.3 Dissociating a Resource.........................................................................................................................................................5
1.4 Migrating a Resource............................................................................................................................................................. 6
1.5 Expanding Vault Capacity.................................................................................................................................................... 7
1.6 Changing the Billing Mode from Pay-per-Use to Yearly/Monthly..........................................................................8
1.7 Changing Vault
1.8 Replicating a Vault............................................................................................................................................................... 10
1.9 Managing Vault Tags........................................................................................................................................................... 12
1.10 Managing the Enterprise Projects of Vaults..............................................................................................................13
Specications............................................................................................................................................ 9
2 Backup Management........................................................................................................... 14
2.1 Querying a Backup............................................................................................................................................................... 14
2.2 Sharing a Backup.................................................................................................................................................................. 16
2.3 Deleting a Backup................................................................................................................................................................ 18
2.4 Using a Backup to Create an Image.............................................................................................................................. 19
2.5 Using a Backup to Create a Disk..................................................................................................................................... 20
2.6 Using a Backup to Create a File System....................................................................................................................... 21
2.7 Replicating a Backup (Across Regions)......................................................................................................................... 22
2.8 Enabling Application-Consistent Backup...................................................................................................................... 25
2.8.1 Overview............................................................................................................................................................................... 25
2.8.2 Changing a Security Group............................................................................................................................................ 27
2.8.3 Installing the Agent.......................................................................................................................................................... 28
2.8.4 Creating an Application-Consistent Backup.............................................................................................................35
2.8.5 Uninstalling the Agent.....................................................................................................................................................36
3 Policy Management.............................................................................................................. 38
3.1 Creating a Backup Policy....................................................................................................................................................38
3.2 Modifying a Policy................................................................................................................................................................ 44
3.3 Deleting a Policy................................................................................................................................................................... 45
3.4 Applying a Policy to a Vault.............................................................................................................................................. 45
3.5 Removing a Policy from a Vault...................................................................................................................................... 46
4 Restoring Data....................................................................................................................... 48
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. ii
Page 4

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide Contents
4.1 Restoring Data Using a Cloud Server Backup.............................................................................................................48
4.2 Restoring Data Using a Cloud Disk Backup.................................................................................................................50
4.3 Restoring Data Using a Hybrid Cloud Backup............................................................................................................ 51
5 (Optional) Migrating Resources from CSBS/VBS.......................................................... 53
6 Managing Tasks..................................................................................................................... 56
7 Auditing................................................................................................................................... 57
8 Quotas......................................................................................................................................59
A Appendix................................................................................................................................. 61
A.1 Agent Security Maintenance............................................................................................................................................ 61
A.1.1 Changing the Password of User rdadmin.................................................................................................................61
A.1.2 Changing the Password of the Account for Reporting Alarms (SNMP v3).................................................. 62
A.1.3 Replacing the Server
A.1.4 Replacing CA Certicates............................................................................................................................................... 66
A.2 Change History...................................................................................................................................................................... 68
Certicate...................................................................................................................................64
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. iii
Page 5
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
1 Vault Management
1.1 Querying a Vault
You can set search criteria for querying desired vaults in the vault list.
Prerequisites
A vault has been created.
Viewing Vault Details
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 View the basic information about vaults. Related parameters are described in the
following table.
Table 1-1 Basic information parameters
Parameter
Name/ID Name and ID of the vault. Click the vault name to view
Type Vault type
Description
details about the vault.
Status Vault status. Table 1-2 describes the vault statuses.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 1
Page 6
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
Parameter Description
Specications Vault specications, which can be server backup and
application-consistent backup
● A server backup vault stores backups of common
servers.
● An application-consistent backup vault stores backups
of database servers.
Vault Capacity
(GB)
Vault capacity, which displays the capacity of the vault and
the capacity used by backups in the vault.
For example: If 20/100 is displayed, 20 GB has been used
out of the 100 GB vault capacity.
Associated Servers/
File Systems/Disks
Number of servers/le systems/disks associated with the
vault. You can click the number to view details of an
associated resource.
Step 3 On any backup page, click the Vaults tab and set lter criteria to view the vaults.
● Select a value from the status drop-down list to query vaults by status. Table
1-2 describes the vault statuses.
Table 1-2 Vault statuses
Status
Status
Description
Attribute
All
-- All vaults are displayed if this value is selected.
statuses
Available A stable
state
A stable state after a vault task is complete.
This state allows various operations.
Locked An
intermediat
e state
An intermediate state when a capacity
expansion, billing mode change, or specications
change operation is in progress.
In this state, you cannot expand the vault
capacity, change the billing mode, or change the
specications. However, you can perform
vault
other operations, such as applying a policy and
associating servers, le systems, or disks. After
the capacity expansion, billing mode change, or
specications change operation is complete, the
vault status becomes Available.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 2
Page 7
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
Status Status
Attribute
Deleting An
intermediat
e state
Frozen A stable
state
Description
An intermediate state when a vault is being
deleted.
In this state, a progress bar is displayed
indicating the deletion progress. If the progress
bar remains unchanged for an extended time, an
exception has occurred. Contact customer
service.
If your resources enter a pending deletion period
in the case that your subscription has expired or
your account is in arrears, or if the resources do
not meet security requirements, your vault is put
in the Frozen state.
If the resources are frozen due to arrears, the
state will become Available after your account is
topped up. Resources can then be used normally.
If you do not top up your account in time, the
system automatically deletes the frozen
resources after the retention period expires. If the
resources are frozen due to security reasons,
contact customer service.
Error A stable
state
A vault enters the Error state when an exception
occurs during task execution.
You can click Tasks in the navigation tree on the
left to view the error cause. If the error persists,
contact customer service.
● Search the vault by its name or ID.
● Click Search by Tag in the upper right corner to search for vaults by tag.
– On the Search by Tag tab page that is displayed, enter an existing tag
key and value and click
. The added tag search criteria are displayed
under the text boxes. Click Search in the lower right corner.
– You can use more than one tag for a combination search. Each time after
a key and a value are entered, click . The added tag search criteria are
displayed under the text boxes. When more than one tag is added, the
tags will be applied together for a combination search. A maximum of 10
tags can be added at a time.
– You can click Reset in the lower right corner to reset the search criteria.
Step 4 Click the vault name to view details about the vault.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 3
Page 8
NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
For the values of used capacity and backup space, only the integer part is maintained, and
the decimal part is rounded o. For example, the used backup space is displayed as 0 GB,
but the backup space that has actually been used might be 0.2 GB.
----End
1.2 Deleting a Vault
You can delete unwanted vaults to reduce storage space usage and costs.
All backups stored in the vault will be deleted once you delete a vault.
Only pay-per-use vaults can be deleted. Yearly/monthly vaults need to be
unsubscribed by following instructions in How Do I Unsubscribe from a Vault?.
Prerequisites
● At least one vault exists.
● The vault is in the Available or Error state.
● A hybrid cloud backup vault can be deleted only after you clear the
corresponding backups both on-premises and in the cloud.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
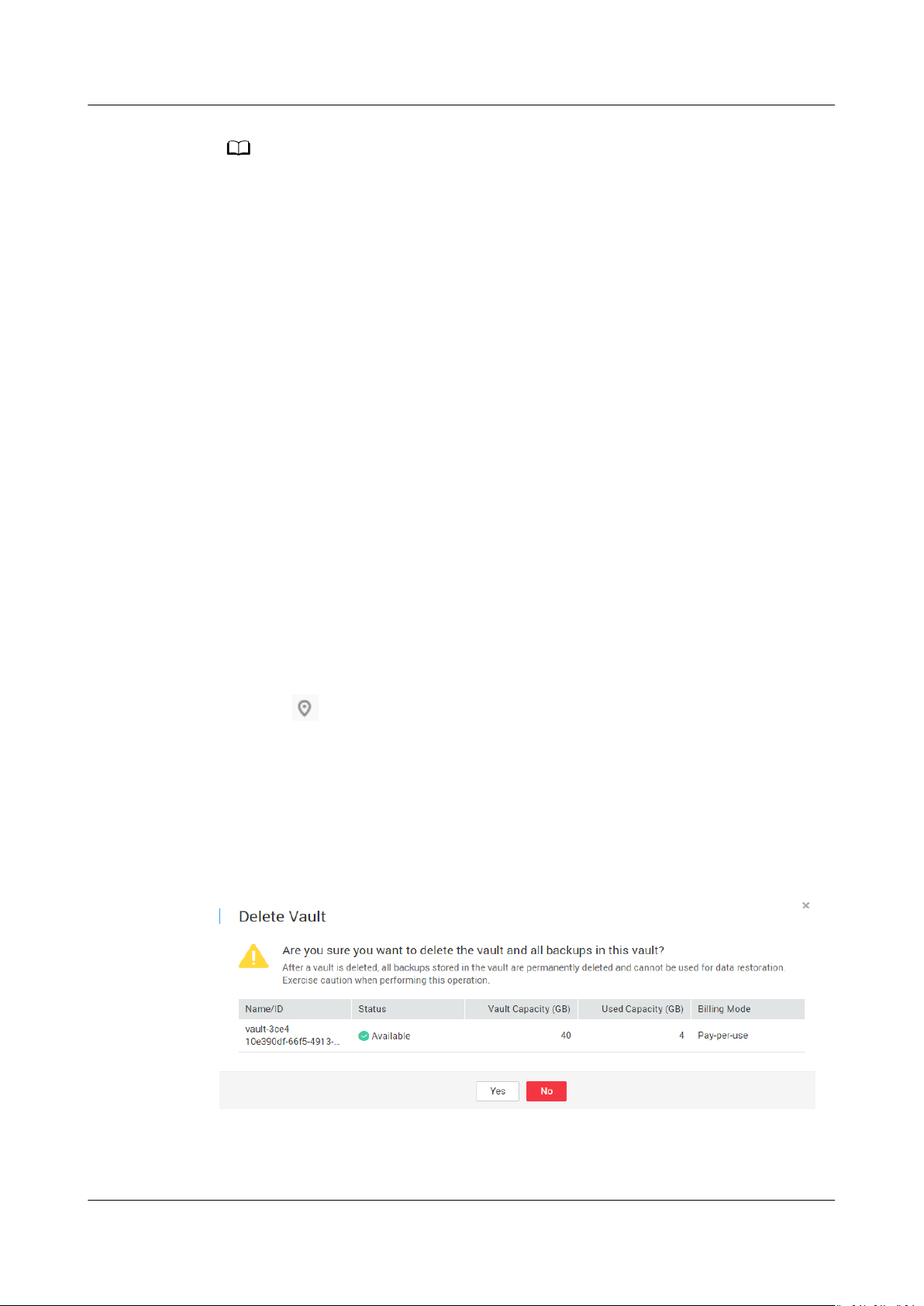
Step 2 On any backup page, locate the vault to be deleted and choose More > Delete in
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
the Operation column. See Figure 1-1. All backups stored in the vault will be
deleted once you delete a vault. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
Figure 1-1 Deleting a vault
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 4
Page 9
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
Step 3 Click Yes.
----End
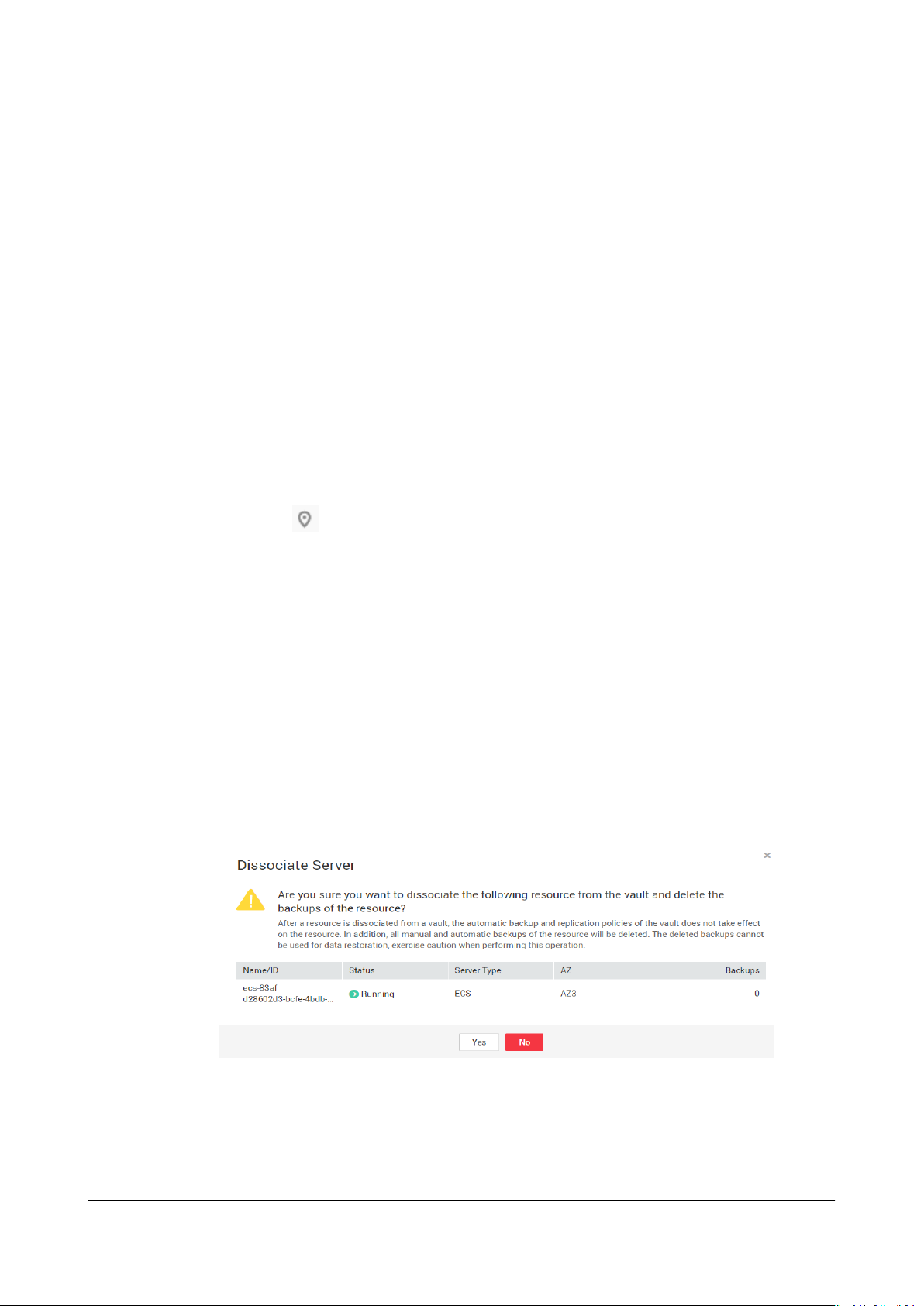
1.3 Dissociating a Resource
If you no longer need to back up an associated resource, dissociate it from the
vault.
After a resource is dissociated from a vault, the automatic backup policies of the
vault no longer have any
automatic backups of the resource will be deleted. The deleted backup cannot be
used for data restoration. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
eect on the resource. In addition, all manual and
Step 2 On any backup page, locate the target vault and click the vault name.
Step 3 In this example, we will be using the Cloud Server Backup page to illustrate the
process. Click the Associated Servers tab. Find the target server and click
Dissociate in the Operation column. See Figure 1-2.
After a resource is dissociated from a vault, the automatic backup and replication
policies of the vault no longer have any
manual and automatic backups of the resource will be deleted. The deleted
backup cannot be used for data restoration. Exercise caution when performing this
operation.
Figure 1-2 Dissociating a server
eect on the resource. In addition, all
Step 4 Conrm the information and click Yes.
----End
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 5
Page 10
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
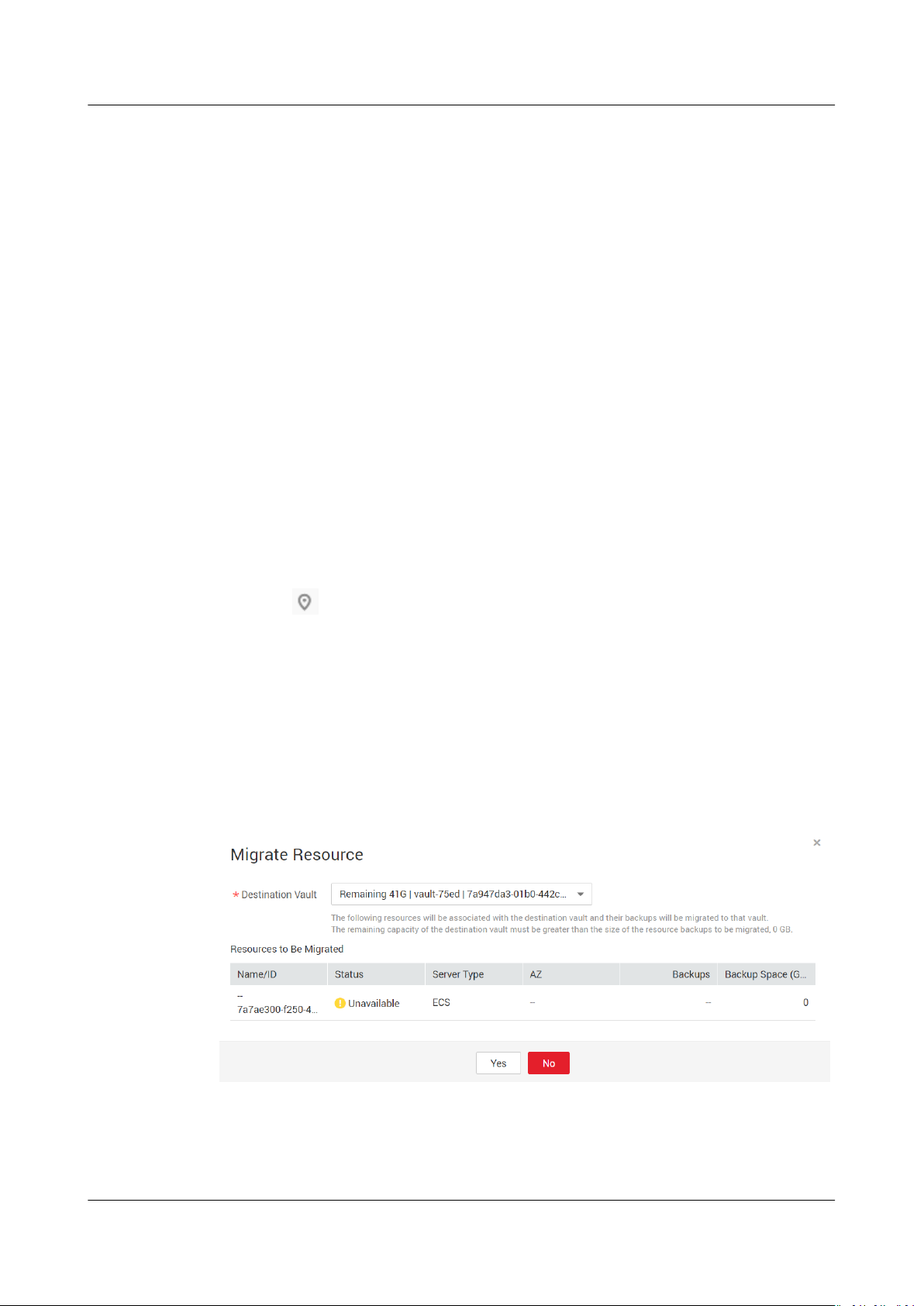
1.4 Migrating a Resource
Migrating a resource means that you dissociate a resource from a vault and then
associate it to another vault. All backups of the resource will be migrated to the
destination vault.
Constraints and Limitations
● The source and destination vaults for resource migration must be in the
Available state.
● The source and destination vaults for resource migration must be of the same
specications.
● The remaining capacity of the destination vault must be greater than the size
of resource backups to be migrated.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 On any backup page, locate the destination vault and click the vault name. In this
example, we will be using the Cloud Server Backup page to illustrate the process.
Step 3 Click the Associated Servers tab. Find the target server and click Migrate in the
Operation column. See Figure 1-3.
Figure 1-3 Migrating a resource
Step 4 Select the destination vault and click Yes.
Step 5 View the migration progress on the Tasks page. If Status changes to Successful,
the resource has been migrated.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 6
Page 11

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
Step 6 Go to the destination vault to conrm that the resource has been associated with
the vault and all its backups have been migrated to that vault.
----End
1.5 Expanding Vault Capacity
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
Step 2 On any backup page, locate the target vault and choose More > Expand Capacity
You can expand the size of a vault if its total capacity is
can be expanded only, but cannot be reduced.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
in the Operation column. See Figure 1-4.
Figure 1-4 Expanding the capacity of a vault
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
insucient. Vault capacity
Step 3 Enter the capacity to be added. The minimum value is 1.
Step 4 Click Next. Conrm the settings and click Submit.
Step 5 Return to the vault list and check that the capacity of the vault has been
expanded.
----End
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 7
Page 12

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
Auto Capacity Expansion
If you want a vault to be automatically expanded when its capacity is used up,
enable auto capacity expansion.
If this function is enabled, the vault size will be automatically expanded to 1.25x
the capacity of the original vault when the maximum size limit has been reached.
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 On any backup page, click the name of the vault you wish to expand.
Step 3 On the vault details page, enable Auto Capacity Expansion.
Step 4 (Optional) Disable Auto Capacity Expansion if you no longer need this.
----End
1.6 Changing the Billing Mode from Pay-per-Use to Yearly/Monthly
● Yearly/monthly is a prepaid billing mode. You are billed based on the
subscription duration you specify. This mode provides lower prices and is ideal
when the resource use duration is predictable.
● Pay-per-use is a postpaid billing mode. You are billed based on your resource
usage. With this mode, you can increase or delete resources at any time. Fees
are deducted from your account balance.
If you want to use a vault for a long time, you can change its billing mode from
pay-per-use to yearly/monthly to reduce cost. For details about the operations, see
this section.
Prerequisites
A vault is in the pay-per-use billing mode.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 On any backup page, nd the target vault. Choose More > Change Billing Mode
in the Operation column of the vault.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 8
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
Page 13
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
Step 3 Select the renewal duration of the vault, conrm the information, and click
Submit and Pay.
Step 4 Return to the vaults page. You can see that the value of the vault in the Billing
Mode column is changed to Yearly/Monthly.
----End
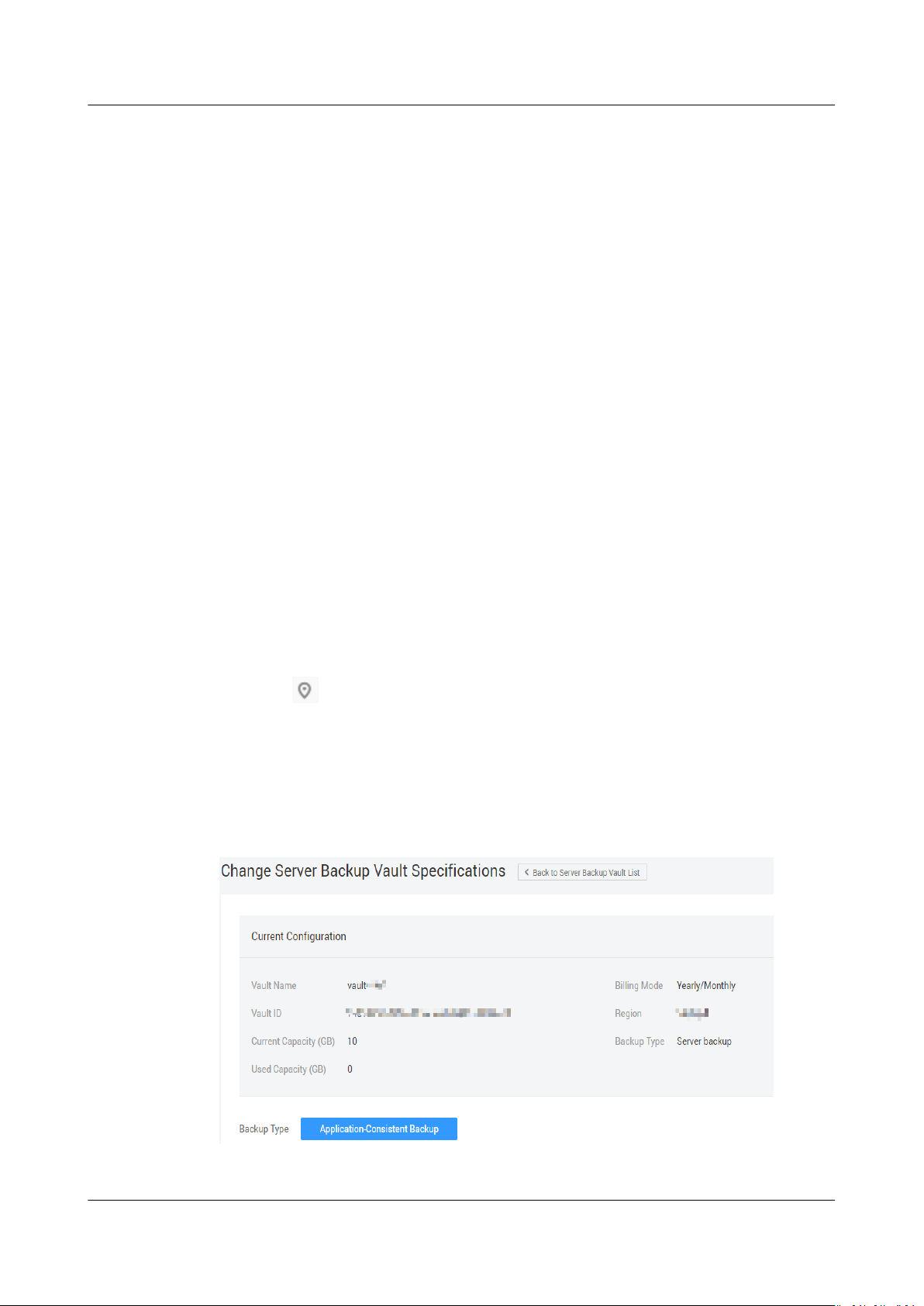
1.7 Changing Vault
Server backup vaults have two specications: those for server backups and those
for application-consistent backups.
● Server backups are backups of common servers.
● Application-consistent backups are backups of servers with databases.
If you need to back up a server that contains a database, change the
of the associated vault from server backup to application-consistent backup. This
section describes the detailed operations.
You can change the specications of a vault from server backup to applicationconsistent backup, but not the other way around.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
Specications
specications
Step 2 On the Cloud Server Backup page, locate the target vault. Choose More >
Change
Figure 1-5 Changing specications
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 9
Specications in the Operation column of the vault. See Figure 1-5.
Page 14

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
Step 3 Set Backup Type to Application-Consistent Backup. Click Next.
Step 4 Click Submit and complete the payment. The system automatically changes the
vault specications.
----End
1.8 Replicating a Vault
CBR allows you to replicate a server backup vault, a hybrid cloud backup vault, or
a le system backup vault entirely to a replication vault in another region. Replicas
of server backups in the destination region can be used to create images and
provision servers. Replicas of le system backups in the destination region can be
used to create
Two replication modes are available for replicating a vault.
● Select a backup vault and manually replicate it.
● Congure a replication policy to periodically replicate backups that have not
been replicated or failed to be replicated to the destination region.
le systems.
Constraints
● The replication rate of a single backup is about 80 MB/s. A maximum of eight
backups can be replicated at a time.
● Data can be replicated to vaults in
replica will replicate all backups in the source vault to the destination vault.
● A server backup vault can be replicated only when it contains at least one
backup that meets all the following conditions:
a. The backup is an ECS backup.
b. The backup contains system disk data.
c. The backup is in the Available state.
● Only vaults in the current region can be replicated. Replicas cannot be
replicated again but can be used to create images or
● A backup vault can be replicated to
replication rule varies with the replication method:
– Manual replication: Backups can be replicated to the destination region
as long as its replica is deleted from that region.
– Policy-driven replication: Once a backup has been successfully replicated
to the destination region, it cannot be replicated to that region again,
even if its replica has been deleted.
● Only regions with replication capabilities can be selected as destination
regions.
dierent destination regions. Creating
le systems.
dierent destination regions. The
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 10
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
Page 15
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click the Vaults tab and nd the target backup vault.
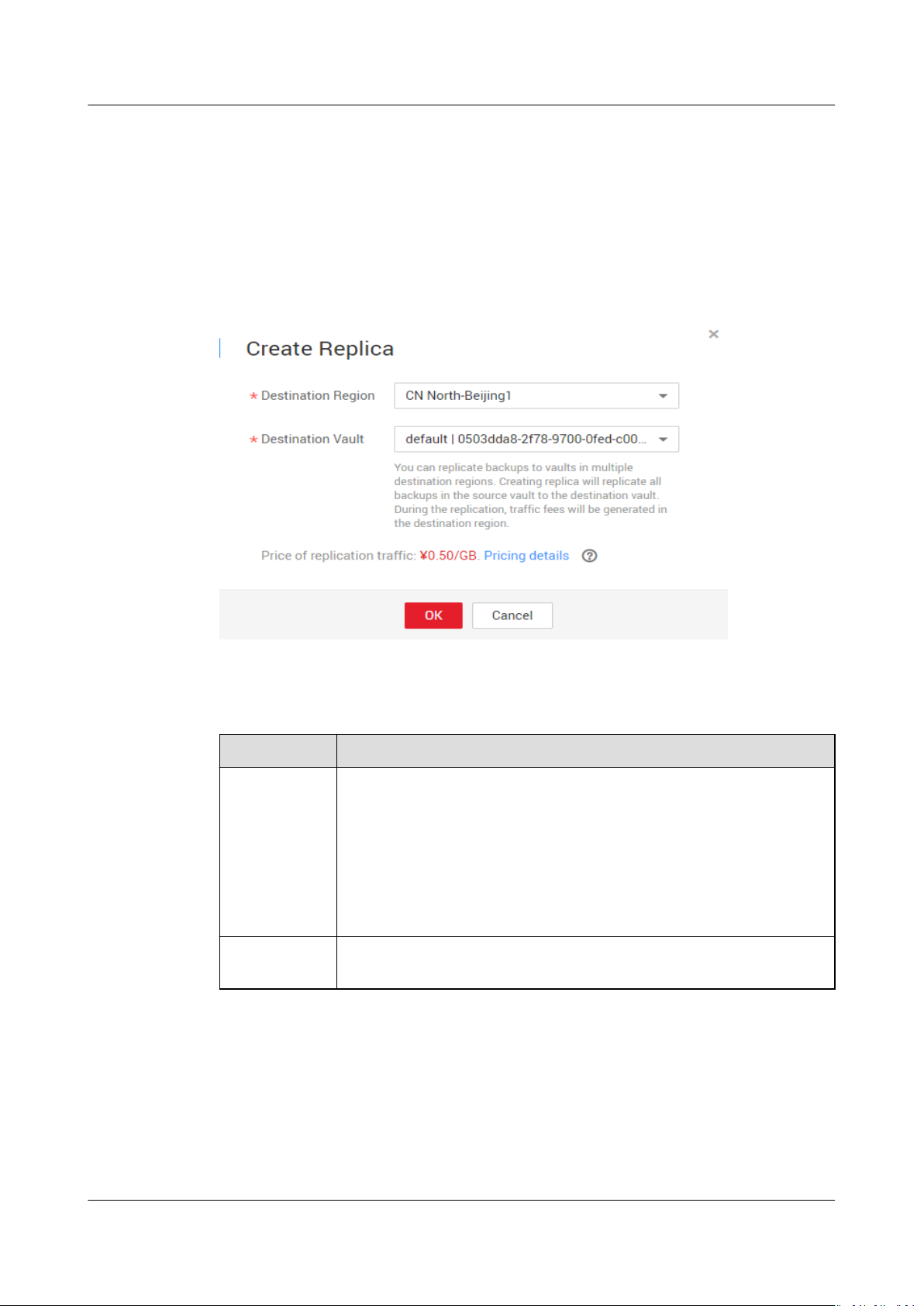
Step 3 Click More > Create Replica in the Operation column of the vault. See Figure
1-6.
Figure 1-6 Creating a replica
Step 4 In the displayed dialog box, set the parameters as described in Table 1-3.
Table 1-3 Parameter description
Parameter
Destination
Region
Description
Region to which the vault is replicated
Only regions that support replication will be displayed.
● If the selected region contains only one project, you can
directly select the region name.
● If the selected region has multiple projects, the master
project of the region is selected by default. You can select
another project if needed.
Destination
A replication vault in the destination region
Vault
Step 5 Click OK.
Step 6 After the replication is complete, you can switch to the destination region to view
generated replicas. For details, see Querying a Vault. You can then use replicas to
create images.
----End
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 11
Page 16
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
1.9 Managing Vault Tags
You can add tags to a vault as well as edit and delete these tags. Vault tags are
used to lter and manage vaults only.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click the name of a vault and select the Tag tab in the displayed vault information
page.
● Adding a tag
a. Click Add Tag in the upper left corner.
b. In the dialog box that is displayed, set the key and value of the new tag.
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
A tag is represented in the form of a key-value pair. Tags are used to
identify, classify, and search for cloud resources. Vault tags are used to
lter and manage vaults only. A vault can have a maximum of 10 tags.
Table 1-4 describes parameters of a tag.
Table 1-4 Tag parameter description
Parameter
Key Tag key. Each tag of a vault has a unique
Description Example
Value
Key_0001
key. You can customize the key or select the
key of an existing tag created in TMS.
The naming rules for a tag key are as
follows:
▪ It contains 1 to 36 Unicode characters.
▪ It can contain only letters, digits, hyphens
(-), and underscores (_).
Value A tag value can be repetitive or left blank.
The naming rules for a tag value are as
follows:
Value_000
1
▪ It contains 0 to 43 Unicode characters.
▪ It can contain only letters, digits, hyphens
(-), and underscores (_).
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 12
Page 17

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 1 Vault Management
c. Click OK.
● Editing a tag
a. In the Operation column of the tag that you want to edit, click Edit.
b. In the Edit Tag dialog box that is displayed, modify the tag value. Table
1-4 describes the parameters.
c. Click OK.
● Deleting a tag
a. In the Operation column of the tag that you want to delete, click Delete.
b. In the dialog box that is displayed,
c. Click OK.
----End
conrm the deletion information.
1.10 Managing the Enterprise Projects of Vaults
If you need to modify the enterprise project of a vault, go to the Enterprise
Management page to move the vault from the original enterprise project to a
new one.
Procedure
Step 1 Click Enterprise on the upper right of console page. By default, the Overview
Step 2 In the navigation pane of the Enterprise Management page, choose Enterprise
Step 3 Locate the enterprise project from which the vault will be removed. Click View
Step 4 Select Single Resource for the removal mode.
Step 5 Select the destination enterprise project to which the vault is to be added and click
page of Enterprise Management is displayed.
Project Management.
Resources in the Operation column. The Resources tab page is displayed. You
can view resources in the current enterprise project.
OK.
After the vault is removed from the enterprise project, you can view it in the
resource list of the destination enterprise project.
----End
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 13
Page 18
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
2 Backup Management
2.1 Querying a Backup
On the backup list, you can set search criteria to lter backups and view backup
details. The results contain backup tasks that are running or have completed.
Prerequisites
A backup task has been created.
Viewing Backup Details
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 On any backup page, click the Backups tab and set
backups.
● You can search for backups by selecting a status from the All statuses dropdown list in the upper right corner of the backup list. Table 2-1 describes the
backup statuses.
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
lter criteria to view the
Table 2-1 Backup statuses
Status
All
statuses
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 14
Status
Attribute
-- All backups are displayed if this value is
Description
selected.
Page 19
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Status Status
Attribute
Available A stable
state
Creating An
intermediat
e state
Restoring An
intermediat
e state
Description
A stable state of a backup after the backup is
created, indicating that the backup is available
and currently not being used.
This state allows most of the operations.
An intermediate state of a backup from the
start of a backup job to the completion of this
job.
In the Tasks list, a progress bar is displayed for
a backup task in this state. If the progress bar
remains unchanged for an extended time, an
exception has occurred. Contact customer
service.
An intermediate state when using the backup to
restore data.
In the Tasks list, a progress bar is displayed for
a backup task in this state. If the progress bar
remains unchanged for an extended time, an
exception has occurred. Contact customer
service.
Deleting An
intermediat
e state
An intermediate state from the start of deleting
the backup to the completion of deleting the
backup.
In the Tasks list, a progress bar is displayed for
a backup task in this state. If the progress bar
remains unchanged for an extended time, an
exception has occurred. Contact customer
service.
Error A stable
state
A backup enters the Error state when an
exception occurs.
A backup in this state cannot be used for
restoration, and must be deleted manually. If
manual deletion fails, contact customer service.
● You can search for backups by clicking Advanced Search in the upper right
corner of the backup list.
You can search by specifying a backup status, backup name, backup ID, server
name, server ID, server type, or the creation date.
● You can search for backups by selecting a project from the All projects dropdown list in the upper right corner of the backup list.
Step 3 Click the backup name to view details about the backup.
----End
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 15
Page 20

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
2.2 Sharing a Backup
You can share a server or disk backup with other accounts. The shared backups
can be used to create servers or disks.
Context
● You can only share backups among accounts in the same region.
● A backup recipient can choose whether to accept the backup. After accepting
the backup, the recipient can use the backup to create a new server or disk.
● Encrypted backups cannot be shared. Backups cannot be shared across
regions. Account to which a backup is shared must be in the same region as
the backup.
● Accepted shared backups will be deleted once the sharer deletes the original
backup.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 On the cloud server backup page, click the Backups tab and set
view the backups.
Step 3 Choose More > Share Backup in the Operation column of the target backup.
The backup name, server name, backup ID, and backup type are displayed.
● Adding a share
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
lter criteria to
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 16
Page 21
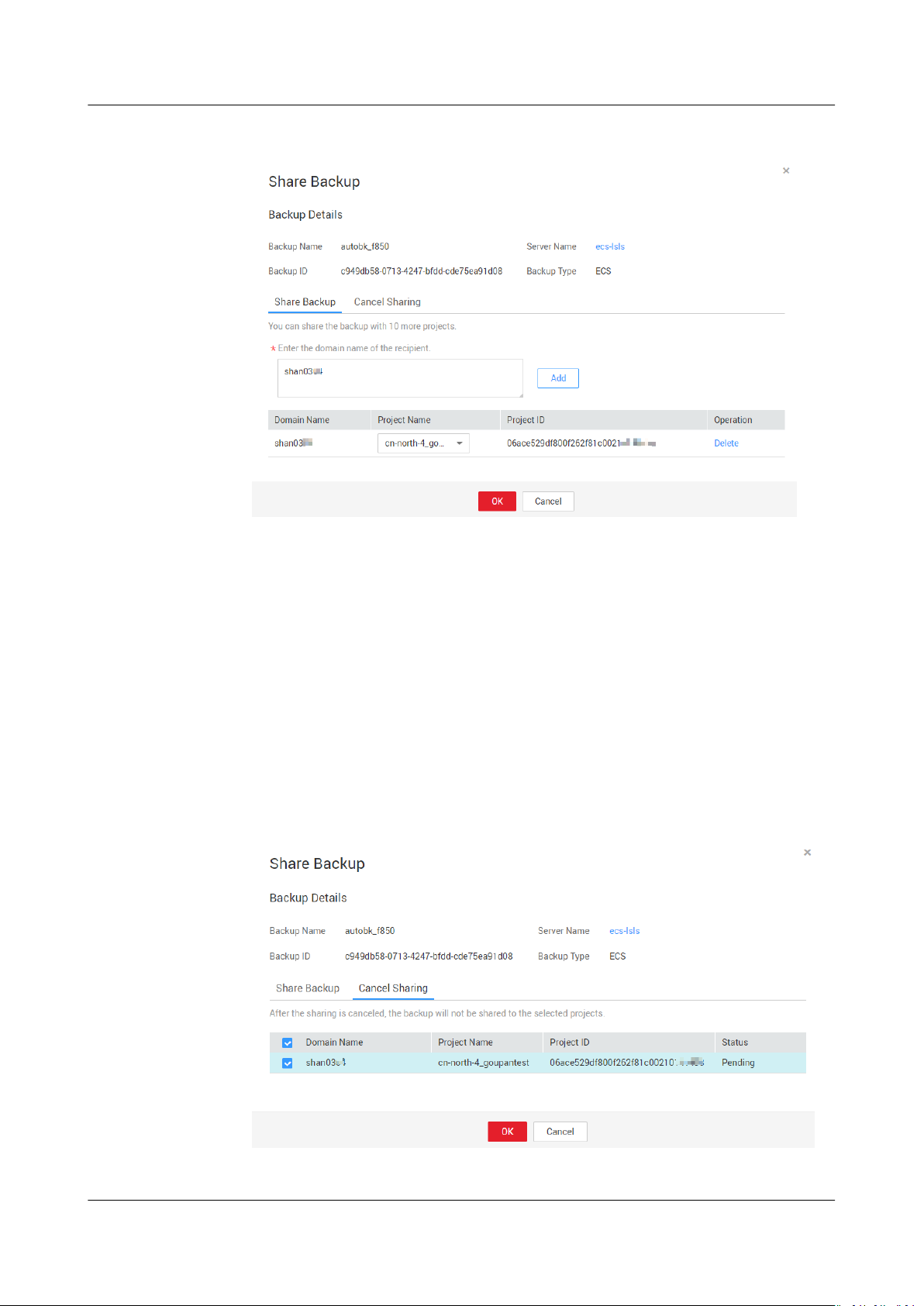
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Figure 2-1 Sharing a backup
1. Click the Share Backup tab.
2. Enter the account name of the tenant to whom the backup is to be shared.
3. Click Add in the dialog box. The account name and project to be added are
displayed on the list. You can continue to add accounts. A backup can be
shared to a maximum of ten projects.
4. Click OK.
● Canceling a share
1. Choose More > Share Backup in the Operation column of the target backup.
2. On the displayed dialog box, click the Cancel Sharing tab and select the
backup that no longer needs to be shared. Then, click OK. See Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2 Canceling a share
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 17
Page 22
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
----End
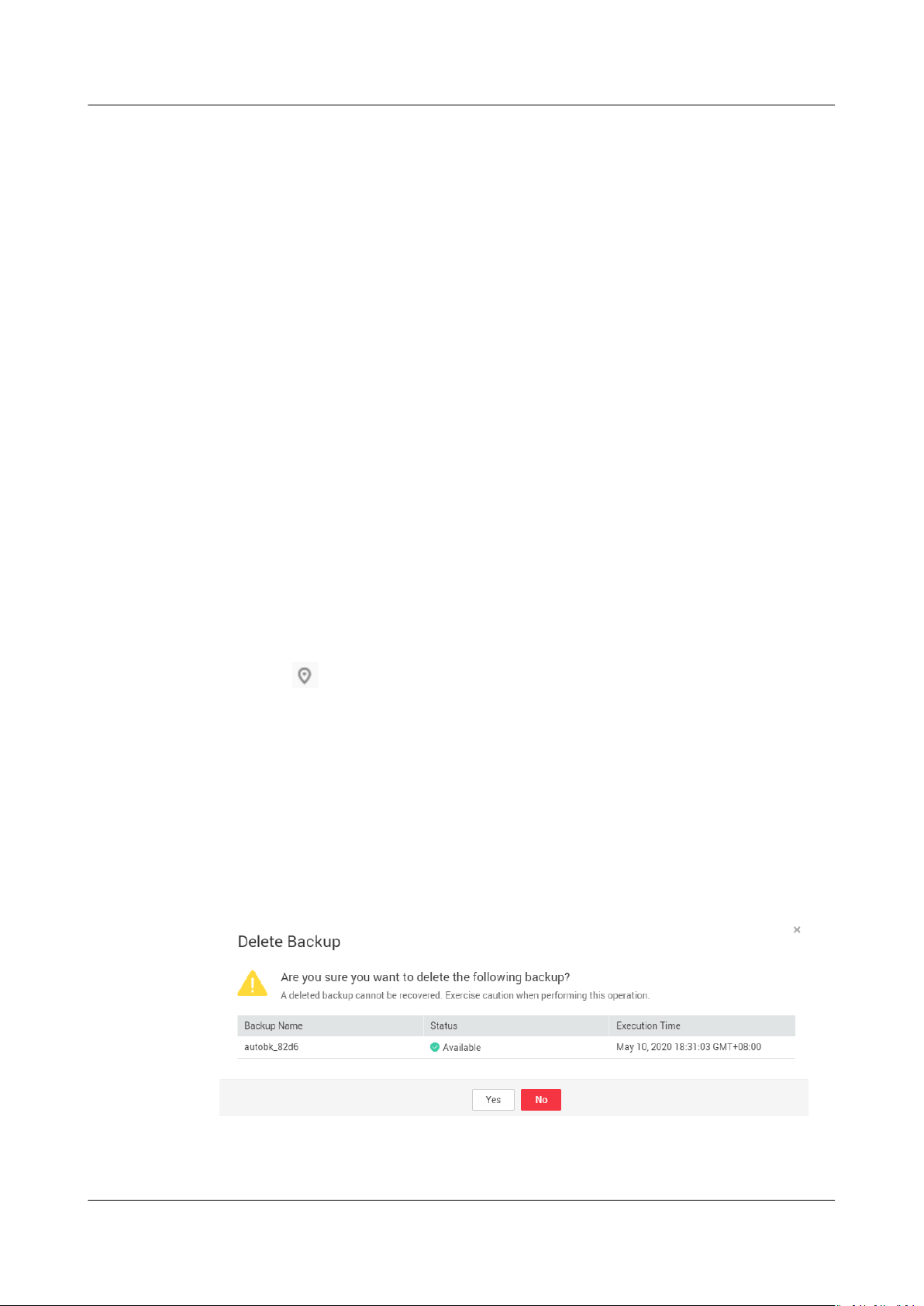
2.3 Deleting a Backup
You can delete unwanted backups to reduce space usage and costs.
Deleting a backup from a hybrid cloud backup vault does not aect the
corresponding backup on-premises, and vice versa.
Context
CBR supports manual deletion of backups and automatic deletion of expired
backups. The latter is implemented based on the backup retention rule in the
backup policy. For details, see Creating a Backup Policy.
Prerequisites
● At least one backup exists.
● The backup to be deleted is in the Available or Error state.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
Step 2 On any backup page, click the Backups tab and locate the desired backup. For
Step 3 In the row of the backup, choose More > Delete. See Figure 2-3. Alternatively,
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
details, see Querying a Backup.
select the backups you want to delete and click Delete in the upper left corner to
delete them in a batch.
Figure 2-3 Deleting a backup
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 18
Page 23

NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Step 4 Click Yes.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
When you use CBR to back up a disk, all data, including those invisible data, on
the disk, will be backed up. If frequent addition, deletion, and modication
operations have been performed on the disk before each backup task, a large
amount of vault space will still be occupied even after some backups are deleted.
For details on how to reduce occupied vault space, see How Do I Reduce the
Vault Space Occupied by Backups?.
2.4 Using a Backup to Create an Image
CBR allows you to create images using ECS backups. You can use the images to
provision ECSs to rapidly restore service operating environments.
Prerequisites
Conrm that the following operations have been performed before you use
●
an ECS's backup to create an image:
– You have optimized the Linux ECS (referring to Optimizing a Linux
Private Image) and installed Cloud-Init (referring to Installing CloudInit).
– You have optimized the Windows ECS (referring to Optimizing a
Windows Private Image) and installed Cloudbase-Init (referring to
Installing Cloudbase-Init).
● A backup can be used to create an image in either of the following scenarios:
1. The backup is in the Available state. 2. The backup is in the Creating state
which is marked with Image can be created.
Once a backup creation starts, the backup enters the Creating state. After a period of
time, a message stating "Image can be created" is displayed under Creating. In this
case, the backup can be used for creating an image, even though it is still being
created and cannot be used for restoration.
● The backup you want to use to create an image contains the system disk
data.
● Only ECS backups can be used for creating images.
Function Description
● Images created using a backup are the same, so CBR allows you to use a
backup to create only one full-ECS image that contains the whole data of the
ECS's system disk and data disks, in order to save the image quota. After an
image is created, you can use the image to provision multiple ECSs in a batch.
● A backup with an image created cannot be directly deleted. If you want to
delete such a backup, delete its image
generated based on a backup policy and the backup has been used to create
an image, the backup will not be counted as a retained backup and will not
be deleted automatically.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 19
rst. If a backup is automatically
Page 24

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
● A backup is compressed when it is used to create an image. Therefore, the
size of the generated image is smaller than that of the backup.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click the Backups tab. Locate the desired backup. For details, see Querying a
Backup.
Step 3 In the row of the backup, choose More > Create Image.
Step 4 Create an image by referring to Creating a Full-ECS Image Using a Cloud Server
Backup in the
Image Management Service User Guide
.
Step 5 If you want to use an image to provision ECSs, see Creating ECSs Using an Image
in the
----End
Image Management Service User Guide
2.5 Using a Backup to Create a Disk
You can use a disk backup to create a disk. After the disk is created, data on the
new disk is the same as that in the disk backup.
After a new disk is created using the backup data of a system disk, the new disk
can only be mounted to the cloud server as a data disk and cannot be mounted as
a system disk.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
.
Step 2 Click the Backups tab. Locate the desired backup. For details, see Querying a
Backup.
Step 3 If the status of the target backup is Available, click Create Disk in the Operation
column of the backup.
Step 4 Set the disk parameters.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 20
Page 25

NO TE
NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
For details about these parameters, see the parameter description table in the section
"Purchasing an EVS Disk" of the
Note the following items when setting disk parameters:
● You can choose the AZ to which the backup source disk belongs, or you can choose a
dierent AZ.
● The newly created disk must be at least as large as the backup source disk.
If the capacity of the new disk is greater than that of the backup source disk, initialize
the disk by following the steps provided in section "Extending Disk Partitions and File
Systems" of the
● You can create a disk of any type regardless of the backup's disk type.
● If disks are created from a backup, batch creation is not supported. You can create only
one EVS disk at a time.
Elastic Volume Service User Guide
Elastic Volume Service User Guide
.
.
Step 5 Click Next.
You can choose Pay-per-use or Yearly/Monthly as your Billing Mode. The fees you pay
depends on the billing mode you choose. The following steps use the Yearly/Monthly
billing mode as an example.
Step 6 Conrm the disk information and click Submit.
Step 7 Pay the fees as prompted and click OK.
Step 8 Go back to the disk list. Check whether the disk is successfully created.
This disk status changes in the sequence of Creating, Available, Restoring, and
Available. If Instant Restore is enabled, you may not notice the Restoring state
because the restoration is so fast. After the state has changed from Creating to
Available, the disk has been successfully created. After the state has changed
from Restoring to Available, backup data has been successfully restored to the
created disk.
----End
2.6 Using a Backup to Create a File System
You can use a
data on the new le system is the same as that in the backup.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
le system backup to create a new le system. After it is created,
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click the Backups tab. Locate the desired backup. For details, see Querying a
Backup.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 21
Page 26

NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Step 3 If the status of the target backup is Available, click Create File System in the
Operation column of the backup.
Step 4 Set the le system parameters.
For details about these parameters, see the parameter description table under "Creating an
SFS Turbo File System" in section "Creating a File System" of
Guide
.
Scalable File System User
Step 5 Click Next.
You can choose Pay-per-use or Yearly/Monthly as your Billing Mode. The fees you pay
will depend on the billing mode you choose. The following steps use the Yearly/Monthly
billing mode as an example.
Step 6 Conrm the le system information and click Submit.
Step 7 Pay the fees as prompted and click OK.
Step 8 Go back to the le system list and check whether the le system is successfully
created.
This le system status changes in the sequence of Creating, Available, Restoring,
and Available. If Instant Restore is enabled, you may not notice the Restoring
state because the restoration is so fast. After the state has changed from Creating
to Available, the
le system has been successfully created. After the state has
changed from Restoring to Available, backup data has been successfully restored
to the created
le system.
----End
2.7 Replicating a Backup (Across Regions)
CBR enables you to replicate server backups and le system backups from one
region to another. Replicas of server backups in the destination region can be used
to create images and provision servers. Replicas of
destination region can be used to create le systems. With backup replication, you
can quickly deploy services in a
dierent region. The state of the new resource in
the destination region is the same as that of the source resource at the backup
time point in the source region.
CBR Console provides the following methods for replication:
● Select a backup from the backup list and perform one-o replication
manually.
● Select a backup vault and manually replicate it. Alternatively, you can
congure a replication policy to periodically replicate backups that have not
been replicated or failed to be replicated to the destination region.
le system backups in the
This section uses the rst way to describe how to replicate a backup. For details
about the second method, see Replicating a Vault.
The following constraints apply to both replication methods.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 22
Page 27

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Constraints
● The replication rate of a single backup is about 80 MB/s. A maximum of eight
backups can be replicated at a time.
● A server backup can be replicated only when it meets all the following
conditions:
a. It is an ECS backup.
b. It contains system disk data.
c. It is in the Available state.
● Only backups and vaults in the current region can be replicated. Replicas
cannot be replicated again but can be used to create images or
● A backup can be replicated to multiple destination regions but can have only
one replica in each destination region. The replication rule varies with the
replication method:
– Manual replication: A backup can be replicated to the destination region
as long as it has no replica in the destination region. A backup can be
replicated again if its replica has been deleted in the destination region.
– Policy-driven replication: Once a backup has been successfully replicated
to the destination region, it cannot be replicated to that region again,
even if its replica has been deleted.
● Only regions with replication capabilities can be selected as destination
regions.
le systems.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
Step 2 Click the Backups tab. Locate the desired backup. For details, see Querying a
Step 3 Choose More > Create Replica in the row of the desired backup. See Figure 2-4.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Backup.
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 23
Page 28

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Figure 2-4 Creating a replica
Step 4 In the displayed dialog box, set the parameters as described in Table 2-2.
Table 2-2 Parameter description
Parameter
Description
Name Replica name
A name must contain 1 to 255 characters including digits,
letters, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
Description Replica description
Cannot exceed 255 characters.
Destination
Region
Region to which the vault is replicated
Only regions that support replication will be displayed.
● If the selected region contains only one project, you can
directly select the region name.
● If the selected region has multiple projects, the master
project of the region is selected by default. You can select
another project if needed.
Destination
Vault
A replication vault in the destination region.
You can replicate backups to vaults in multiple destination
regions. Creating replica will replicate all backups in the source
vault to the destination vault.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 24
Page 29

NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
The trac for cross-region replication is the size of the replicated backup.
Step 5 Click OK.
Step 6 After the replication is complete, you can switch to the destination region to view
generated replicas. For details, see Querying a Backup. You can then use replicas
to create images.
----End
2.8 Enabling Application-Consistent Backup
2.8.1 Overview
There are three backup types in terms of backup consistency:
● Inconsistent backup: Files in an inconsistent backup contain data taken from
dierent points in time. This typically occurs if changes are made to your les
or the data on your disks while backup is running. CBR's server backup uses
the consistency snapshot technology for disks to protect data of ECSs and
BMSs. If you back up multiple EVS disks separately, the backup time points of
the EVS disks are
inconsistent.
● Crash-consistent backup: A crash-consistent backup captures data that exists
on disks as of the backup time, without backing up memory data or quiescing
application systems. Backup consistency of application systems is not ensured.
To complete this, disks are checked upon operating system restart to restore
damaged data, for example, by using chkdsk, and log rollback is performed
on databases to keep data consistent.
● Application-consistent backup: An application-consistent backup is a backup
of application data that allows applications to achieve a quiescent and
consistent state. This type of backup captures the contents of the memory
and any pending writes that occurred during the backup process.
dierent. As a result, the backup data of the EVS disks is
CBR supports both crash-consistent backup and application-consistent backup
(also called database backup).
If a MySQL or SAP HANA database is deployed on a server, you can use the
application-consistent backup function of CBR to back up the server data and
application cache. Crash-consistent backup backs up only data and some
application caches without interrupting services. When a system fails or data loss
occurs, you can use an application-consistent backup to quickly restart services. A
crash-consistent backup, however, may fail to restore some application
congurations.
Figure 2-5 shows the application-consistent backup process.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 25
Page 30

NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Figure 2-5 Application-consistent backup owchart
● Change the security group: Before performing an application-consistent backup task,
change the security group of the server you want to back up. For details, see Changing
a Security Group.
● Install the agent: Change the security group and install the agent in any sequence. Just
make sure that the two operations are completed before backing up the desired server.
For details, see Installing the Agent.
● Creating an application-consistent backup: After creating a server backup vault for
storing application-consistent backups, associate it with the desired database server and
then create an application-consistent backup. For details, see Creating an Application-
Consistent Backup.
● Modify or compile a custom script: After backing up a database server on CBR Console,
modify or compile a custom script on the database of the server. For details, see Using a
Custom Script to Implement Application-Consistent Backup.
● Verify the backup result after the application-consistent backup is implemented by using
a custom script. For details, see Verifying the Application-Consistent Backup Result.
● Use the backup to restore server data: Use the application-consistent backup to restore
server data. The restored database applications and data are the same as those at the
backup point in time. For details, see Restoring Data Using a Cloud Server Backup.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 26
Page 31

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
2.8.2 Changing a Security Group
Context
A security group is a collection of access control rules for ECSs that have the same
security protection requirements and are mutually trusted in a VPC. After a
security group is created, you can create
group to protect the ECSs that are added to this security group. The default
security group rule allows all outgoing data packets. ECSs in a security group can
access each other without the need to add rules. The system creates a security
group for each cloud account by default. You can also create custom security
groups by yourself.
When creating a security group, you must add the inbound and outbound access
rules and enable the ports required for application-consistent backup to prevent
application-consistent backup failures.
Procedure
dierent access rules for the security
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to the ECS console.
Step 2 In the navigation tree on the left, choose Elastic Cloud Server or Bare Metal
Before using the application-consistent backup function, you need to change the
security group. To ensure network security, CBR has not set the inbound direction
of a security group, so you need to manually
In the outbound direction of the security group, ports 1 to 65535 on the
100.125.0.0/16 network segment must be congured. In the inbound direction,
ports 59526 to 59528 on the 100.125.0.0/16 network segment must be
The default outbound rule is 0.0.0.0/0, that is, all data packets are permitted. If
the default rule in the outbound direction is not
congure the outbound direction.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Under Computing, click Elastic Cloud Server.
Server. On the page displayed, select the target server. Go to the target server
details page.
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
congure it.
congured.
modied, you do not need to
Step 3 Click the Security Groups tab and select the target security group. On the right of
the ECS page, click Modify Security Group Rule for an ECS. Click Change
Security Group for a BMS. In the dialog box displayed, click Manage Security
Group.
Step 4 On the Security Groups page, click the Inbound Rules tab, and then click Add
Rule. The Add Inbound Rule dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 2-6.
Select TCP for Protocol/Application, enter 59526-59528 in Port & Source, select
IP address for Source and enter 100.125.0.0/16. After supplementing the
description, click OK to complete the setting of the inbound rule.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 27
Page 32

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Figure 2-6 Adding an inbound rule
Step 5 Click the Outbound Rules tab, and then click Add Rule. The Add Outbound Rule
dialog box is displayed, as shown in Figure 2-7. Select TCP for Protocol/
Application, enter 1-65535 in Port & Source, select IP address for Destination
and enter 100.125.0.0/16. After supplementing the description, click OK to
complete the setting of the outbound rule.
Figure 2-7 Adding an outbound rule
----End
2.8.3 Installing the Agent
Procedure
● Application-consistent backup supports only x86-based ECSs, not Kunpengbased ECSs.
● Before enabling application-consistent backup, change the security group and
install the Agent on your ECSs. This section guides you on how to download
and install the Agent.
● During the Agent installation, the system requires the rdadmin user's
permissions to run the installation program. To improve O&M security, change
the user rdadmin's password of the Agent OS regularly and disable this user's
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 28
Page 33

NO TICE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
remote login permission. For details, see Changing the Password of User
rdadmin.
● Table 2-3 lists OSs that support installation of the Agent.
Table 2-3 OSs that support installation of the Agent
Database
Name
SQL Server
2008/2012
SQL Server
2014/2016/
EE
MySQL
5.5/5.6/5.7
HANA
1.0/2.0
OS Version
Windows Windows Server 2008, 2008 r2, 2012, 2012 r2
for x86_64
Windows Windows Server 2012, 2012 R2, and 2016
Datacenter for x86_64
Red Hat Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 and 7 for x86_64
SUSE SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 11 and 12 for
x86_64
CentOS CentOS 6 and 7 for x86_64
EulerOS EulerOS 2.2 and 2.3 for x86_64
SUSE SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 12 for x86_64
To install the Agent, the system will open the rewall of a port from 59526 to
59528 of the ECS. When port 59526 is occupied, the
enabled, and so on.
Prerequisites
● You have obtained a username and its password for logging in to the
management console.
● The security group has been congured.
● The Agent Status of the ECS is Not installed.
● If you use Internet Explorer, you need to add the websites you will use to
trusted sites.
Installing the Agent for a Linux OS (Method 1)
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
rewall of port 59527 is
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 29
Page 34

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Step 2 Click the Agent Installation tab.
Figure 2-8 Installation page for Linux
Step 3 In method 1, select the corresponding Agent version as required, and copy the
installation command in step 2.
Step 4 On the ECS page, select the target server and click Remote Login in the
Operation column to log in to the ECS.
Step 5 Paste the installation command in step 2 to the server and run the command as
the root user. If the execution fails, run the yum install -y bind-utils command to
install the dig module. If the installation still fails, use method 2 to install the
Agent for a Linux OS.
Step 6 After the Agent for Linux is installed, see the best practices of application-
consistent backup to modify or compile a custom script to implement consistent
backup for MySQL, SAP HANA, or other database types.
----End
Installing the Agent for a Linux OS (Method 2)
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click the Agent Installation tab.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 30
Page 35

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Figure 2-9 Installation page for Linux
Step 3 In method 2, click Download. On the displayed download client dialog box, select
the version to be downloaded based on the operating system type of the target
ECS, and click OK. See Figure 2-10.
Figure 2-10 Downloading the Agent
Step 4 After downloading the Agent, use a le transfer tool, such as Xftp, SecureFX, or
WinSCP, to upload the Agent installation package to your ECS.
Step 5 After the upload, go to the ECS page. Select the target server and click Remote
Login in the Operation column to log in to the ECS.
Step 6 Run the tar -zxvf command to decompress the Agent installation package to any
directory and run the following command to go to the bin directory:
save directory of the installation package
cd
Step 7 Run the following command to run the installation script:
sh agent_install_ebk.sh
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 31
Page 36

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Step 8 The system displays a message indicating that the client is installed successfully.
See Figure 2-11.
Figure 2-11 Successful client installation for Linux
Step 9 If the MySQL or SAP HANA database has been installed on the ECS, run the
following command to encrypt the password for logging in to the MySQL or SAP
HANA database:
/home/rdadmin/Agent/bin/agentcli encpwd
Step 10 Use the encrypted password in Step 9 to replace the database login password in
the script in /home/rdadmin/Agent/bin/thirdparty/ebk_user/.
Step 11 After the Agent for Linux is installed, see the best practices of application-
consistent backup to modify or compile a custom script to implement consistent
backup for MySQL, SAP HANA, or other database types.
----End
Installing the Agent for a Windows OS (Method 1)
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click the Agent Installation tab.
Figure 2-12 Installation page for Windows
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 32
Page 37

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Step 3 In method 1, click Download. Save the downloaded installation package to a local
directory.
Step 4 After downloading the Agent, use a le transfer tool, such as Xftp, SecureFX, or
WinSCP, to upload the Agent installation package to your ECS.
Step 5 Log in to the console and then log in to the ECS as the administrator.
Step 6 Decompress the installation package to any directory and go to the
path
\bin directory.
Step 7 Double-click the agent_install_ebk.bat script to start the installation.
Step 8 The system displays a message indicating that the client is installed successfully.
See Figure 2-13.
Figure 2-13 Successful client installation for Windows
Installation
----End
Installing the Agent for a Windows OS (Method 2)
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click the Agent Installation tab.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 33
Page 38

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Figure 2-14 Installation page for Windows
Step 3 On the ECS page, select the target server and click Remote Login in the
Operation column to log in to the ECS as the administrator.
Step 4 Copy the installation commands in step 2 of method 2 to the server and run the
command in the CMD window.
Step 5 Copy any IP address in the response name, paste it in the address box of the
browser, and replace 0.0.0.0 in the following address with the address. Replace
southeast-1
as an example. Then, press Enter in the browser to download the installation
package.
http://
WIN64.zip
Step 6 Decompress the
package to any directory and go to the
Step 7 Double-click the agent_install_ebk.bat script to start the installation.
Step 8 The system displays a message indicating that the client is installed successfully.
See Figure 2-15.
with the actual region. The following command uses
0.0.0.0
/csbs-agent-
le to obtain the installation le. Decompress the installation
ap-southeast-1
/Cloud Server Backup Agent-
Installation path
\bin directory.
ap-southeast-1
ap-
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 34
Page 39

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Figure 2-15 Successful client installation for Windows
----End
2.8.4 Creating an Application-Consistent Backup
CBR supports application-consistent backup in addition to crash-consistent
backup. Application-consistent backup ensures the consistency of application data
by backing up
for scenarios such as backing up ECSs that run MySQL or SAP HANA databases.
Constraints
● Application-consistent backup for clusters, for example, MySQL clusters, is not
supported. Application-consistent backup is supported only for a single server.
● You are advised to perform application-consistent backup in
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
les and disks at the exact same time. This backup mode is suitable
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
o-peak hours.
Step 2 Create a vault for application-consistent backups by referring to Purchasing a
Cloud Server Backup Vault.
Step 3 Create a cloud server backup by referring to Creating a Cloud Server Backup.
Before creating a cloud server backup, you need to install the Agent. If an
application-consistent backup fails to be created, the system automatically creates
a server backup and stores the backup in the vault.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 35
Page 40

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Step 4 Return to the cloud server backup page as prompted. If the execution fails, rectify
the fault based on the failure details on the creation result page.
----End
Follow-up Procedure
If data is lost due to virus attacks or database faults, you can restore the data by
following instructions in Restoring Data Using a Cloud Server Backup and Using
a Backup to Create an Image.
2.8.5 Uninstalling the Agent
Scenarios
This section describes how to uninstall the Agent when application-consistent
backup is no longer needed.
Prerequisites
The username and password for logging in to an ECS have been obtained.
Uninstalling the Agent for Linux
Step 1 Log in to the ECS and run the su -root command to switch to user root.
Step 2 In the home/rdadmin/Agent/bin directory, run the following command to
uninstall the Agent. Figure 2-16 displays an example. If the word successfully in
green is displayed, the Agent is uninstalled successfully.
sh agent_uninstall_ebk.sh
Figure 2-16 Agent uninstalled successfully from Linux
----End
Uninstalling the Agent for Windows
Step 1 Log in to the ECS.
Step 2 In the
window for uninstalling the Agent is displayed.
After the uninstallation is complete and successful, the window will be
automatically closed. See Figure 2-17.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 36
Installation path
/bin directory, double-click agent_uninstall_ebk.bat. The
Page 41

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 2 Backup Management
Figure 2-17 Agent uninstalled successfully from Windows
----End
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 37
Page 42

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 3 Policy Management
3 Policy Management
3.1 Creating a Backup Policy
A backup policy allows the vault to automatically execute backup tasks at
specied times or intervals. Periodic backups can be used to restore data quickly
against data corruption or loss.
Context
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
To implement periodic backup, you need to create a backup policy rst. CBR will
then periodically perform backups according to the execution time
backup policy. You can choose to use the default backup policy provided by CBR or
create one as needed.
You can set backup policies for server backup vaults, le system backup vaults,
and disk backup vaults.
● After a backup policy is enabled, CBR automatically backs up resources
associated with the vaults that have been associated with the policy and
periodically deletes expired backups.
● Each account can create a maximum of 32 backup policies.
● Automatic deletion of expired backups does not apply to manual backups.
● Only servers in the Running or Stopped state can be backed up.
● Only disks in the Available or In-use state can be backed up.
1. Log in to the management console.
specied in the
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click the Backup Policies tab and then Create Policy in the upper right corner to
create a user-dened policy. See Figure 3-1.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 38
Page 43

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 3 Policy Management
Figure 3-1 Creating a backup policy
Step 3 Set the backup policy parameters. Table 3-1 describes the parameters.
Table 3-1 Backup policy parameter description
Parameter
Type Select a policy type. This section uses
Description Example Value
Backup policy
creating a backup policy as an
example.
Name Backup policy name
backup_policy
A name must contain 1 to 64
characters including digits, letters,
underscores (_), or hyphens (-).
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 39
Page 44

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 3 Policy Management
Parameter Description Example Value
Status Whether to enable the backup policy.
● Enabled:
● Disabled:
Execution
Time
Execution time
Backups can be scheduled at the
beginning of each hour. Multiple
selections are supported.
NOTICE
If you want to back up a large amount of
data, you are advised to set a less frequent
backup schedule. If a backup task takes
longer than the backup interval, the system
will skip the next backup execution time.
For example, as scheduled in a backup
policy, a disk needs to backed up at 00:00,
01:00, and 02:00. At 00:00, the disk starts
being backed up. Because the high-volume
incremental data needs to be backed up or
a heap of backup tasks are executed at the
same time, this backup task takes 90
minutes and completes at 01:30. In this
case, the system performs the next backup
at 02:00. Therefore, only two backups will
be generated in total, one at 00:00, and the
other at 02:00.
Only after a backup
policy is enabled will
CBR automatically back
up servers and disks
associated with the
vaults that have been
associated with the
policy and delete expired
backups.
00:00, 02:00
It is recommended that
backups be performed
during o-peak hours or
when there are no
services running.
Time zone Species the time zone for the backup
UTC+08:00
execution time. By default, the time
zone where you are located is selected.
You can select a dierent one from the
drop-down list.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 40
Page 45

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 3 Policy Management
Parameter Description Example Value
Backup
Cycle
Dates for performing backups
● Week-based cycle
Species on which days of each
week the backup task will be
executed. You can select multiple
days.
● Custom cycle
Species the interval (every 1 to 30
days) for executing the backup task.
Every day
If you select Custom
cycle, the rst backup
time is supposed to be
on the day the backup
policy is created. If the
creation time of the
backup policy is later
than the latest execution
time, the initial backup
will be performed in the
next backup cycle.
It is recommended that
backups be performed
during
o-peak hours or
when there are no
services running.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 41
Page 46

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 3 Policy Management
Parameter Description Example Value
Retention
Rule
Rule that species how backups will be
retained
● Time period
You can choose to retain backups
for one month, three months, six
months, one year, or for any desired
number (2 to 99999) of days.
● Backup quantity
Species the maximum allowed
number of backups for a single ECS.
The value ranges from 2 to 99999.
You can also set long-term retention
rules. Long-term retention rules can
eective together with quantity-
be
based retention rules.
– The value range for daily backup
retention is 0 to 100.
– The value range for weekly
backup retention is 0 to 100.
– The value range for monthly
backup retention is 0 to 100.
6 months
– The value range for yearly
backup retention is 0 to 100.
For example, if you select daily
backup, the system retains the latest
backup every day. Although the disk
is backed up for multiple times in a
day, only the last backup of the
current day is retained. If you set
the retention number to 5, the
ve daily backups are
latest
retained. If there are more than
ve
backup les, the system
automatically deletes the earliest
backups. If the daily backup, weekly
backup, monthly backup, and yearly
backup are all
congured, the union
backups are selected for retention.
For example, if the number of
retained daily backups is set to 5
and the number of retained weekly
backups is set to 1,
ve backups will
be retained. The long-term retention
rule and the quantity-based
retention rule can be
eective at the
same time.
● Permanent
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 42
Page 47

NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 3 Policy Management
Parameter Description Example Value
NOTE
– When the number of retained
backups exceeds the preset value,
the system automatically deletes the
earliest backups. When the retention
periods of retained backups exceed
the preset value, the system
automatically deletes all expired
backups. By default, the system
automatically clears data every
other day. The deleted backup does
not
aect other backups for
restoration.
– This parameter applies only to
backups generated based on a
scheduled backup policy. Manual
backups are not
parameter and will not be
automatically deleted. You can
manually delete them from the
backup list.
– After a backup is used to create an
image, the backup will not be
counted as a retained backup and
will not be deleted automatically.
– A maximum of 10 backups are
retained for failed periodic backup
tasks. They are retained for one
month and can be manually deleted.
aected by this
Example
More frequent backup intervals create more backups or retain backups for a longer time,
protecting data to a greater extent but occupying more storage space. Set an appropriate
backup cycle as needed.
Step 4 Click OK.
Step 5 Locate the desired vault and choose More > Bind Backup Policy to apply the
created backup policy to the vault. You can view the
congured backup policy in
the vault details.
After the setting is successful, data is periodically backed up to the vault based on
the backup policy.
----End
A user has a vault associated with one disk. At 10:00 a.m. on Monday, the user
sets a backup policy for the vault, that is, executing a backup task at 02:00 a.m.
every day and retaining a maximum of three backups. At 11:00 a.m. on Saturday,
three backups are retained, which are generated on Wednesday, Thursday, and
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 43
Page 48

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 3 Policy Management
Friday. The backup generated at 2:00 a.m. on Tuesday has been automatically
deleted.
3.2 Modifying a Policy
This section describes how to modify a policy.
Prerequisites
You have created at least one policy.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 On any backup page,
vault details.
Step 3 In the Policies area, click Edit in the row of a policy to open the policy editing
page. See Figure 3-2.
Figure 3-2 Editing a backup policy
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
nd the target vault and click the vault name to view the
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 44
Page 49

NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 3 Policy Management
Related parameters are described in Table 3-1.
Step 4 Click OK.
After the policy is modied, the retention rule takes eect only for new backups.
For details, see Why Does the Retention Rule Not Take
Modied?.
Step 5 Alternatively, you can select Policies from the navigation tree on the left and edit
the desired policy.
----End
Eect After Being
3.3 Deleting a Policy
You can delete backup and replication policies if needed.
Prerequisites
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
Step 2 Click the Backup Policies tab, and then click Delete in the row where the policy
Step 3
You have created at least one policy.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
you want to delete is located.
Deleting a policy will not delete backups generated based on the policy. You can manually
delete unwanted backups.
Conrm the information and click Yes.
----End
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3.4 Applying a Policy to a Vault
A backup policy allows the vault to automatically execute backup tasks at
specied times or intervals. Periodic backups can be used to restore data quickly
against data corruption or loss.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 45
Page 50

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 3 Policy Management
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 On any backup page, nd the target vault and choose More > Bind Backup
Policy. See Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 Setting a backup policy
Step 3 You can select an existing backup policy from the drop-down list or create a new
one. For details about how to create a policy, see Creating a Backup Policy.
Step 4 After the policy is successfully applied, you can view the details in the Policies
area on the vault details page.
----End
3.5 Removing a Policy from a Vault
If you no longer need automatic backup for a vault that have been set with a
policy, remove the policy.
Prerequisites
A policy has been applied to the vault.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 On any backup page, nd the target vault and click the vault name to view the
vault details.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 46
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
Page 51

NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 3 Policy Management
Step 3 In the Policies area, click Unbind Policy. See Figure 3-4.
Figure 3-4 Removing a policy
● If a backup task is being executed for a resource in the vault, the policy can be removed
normally. However, the backup task will continue and backups will be generated.
● After the policy is unbound, backups generated based on the policy will not be deleted.
You can manually delete unwanted backups.
Step 4 Click Yes. The vault will no longer execute tasks as specied in this policy.
----End
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 47
Page 52

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 4 Restoring Data
4 Restoring Data
4.1 Restoring Data Using a Cloud Server Backup
Context
Prerequisites
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
When disks on a server are faulty or server data is lost due to misoperations, you
can use a backup to restore the server.
To restore data to another server, see How Do I Restore Data on the Original
Server to a New Server?.
● Data on data disks cannot be restored to system disks.
● Data cannot be restored to servers in the Faulty state.
● Disks on the server whose data needs to be restored are running properly.
● The server whose data needs to be restored has at least one Available
backup.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click the Backups tab. Locate the desired backup. For details, see Querying a
Backup.
Step 3 In the row of the backup, click Restore Server. See Figure 4-1.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 48
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
Page 53

NO TICE
NO TICE
NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 4 Restoring Data
The historical data at the backup point in time will overwrite the current server
data. The restoration cannot be undone.
Figure 4-1 Restoring a server
Step 4 (Optional) Deselect Start the server immediately after restoration.
If you deselect Start the server immediately after restoration, manually start
the server after the restoration is complete.
Servers are shut down during restoration. It is therefore recommended that you
perform restoration operations during
o-peak hours.
Step 5 In the Specied Disk drop-down list, select the target disk to which the backup
will be restored.
● If the server has only one disk, the backup is restored to the disk by default.
● If the server has multiple disks, the backup is respectively restored to the original disks
by default. You can also restore the backup to another disk on the backup server by
selecting the disk from the drop-down list. However, the capacity of the
must not be smaller than that of the backup source disk.
● Data on data disks cannot be restored to system disks.
specied disk
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 49
Page 54

NO TICE
NO TICE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 4 Restoring Data
If the number of disks to be restored is greater than the number of disks that are
backed up, restoration may cause data inconsistency.
For example, if the data of Oracle is scattered across multiple disks and only some
of them are restored, data inconsistency occurs after the restoration and the
application may unable to start.
Step 6 Click Yes and conrm the restoration is successful.
In the backup list, view the restoration status. When the backup enters the
Available state and no new failed restoration tasks exist in Tasks, the restoration
is successful. The resource data that is successfully restored is the same as that at
the backup time point.
For details about how to view failed restoration tasks, see Managing Tasks.
If a Windows server is restored, data disks may fail to be displayed due to
Windows limitations.
After you use a cloud server backup to restore a logical volume group, the logical
volume group needs to be attached again.
You need to manually set these data disks to be online. For details, see Data Disks
Are Not Displayed After a Windows Server Is Restored.
----End
4.2 Restoring Data Using a Cloud Disk Backup
You can use a disk backup to restore a disk to the time when the backup was
created.
To restore the backup of a data disk to the system disk, see How Do I Restore a
Data Disk Backup to a System Disk?.
Prerequisites
● The status of the disk to be restored must be Available.
● Before restoring the disk data, stop the server to which the disk is attached
and detach the disk from the server. After the disk data is restored, attach the
disk to the server and start the server.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 50
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
Page 55

NO TICE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 4 Restoring Data
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click the Backups tab. Locate the desired backup. For details, see Querying a
Backup.
Step 3 In the row of the backup, click Restore Disk. See Figure 4-2.
The historical data at the backup point in time will overwrite the current disk data.
The restoration cannot be undone.
Figure 4-2 Restoring a disk
Step 4 Click Yes. You can check whether the data is successfully restored on the Backups
tab page of disk backup.
When the status of the backup changes to Available, the restoration is successful.
The resource data that is successfully restored is the same as that at the backup
time point.
Step 5 After the restoration is complete, re-attach the disk to the server. For details, see
Attaching an Existing Non-Shared Disk.
----End
4.3 Restoring Data Using a Hybrid Cloud Backup
After backups are successfully synchronized to a hybrid cloud backup vault, you
can use the backups to restore to servers on the cloud for disaster recovery, service
migration, development, and testing.
Restoring Data Using a Storage Backup
You can synchronize the backups of on-premises OceanStor Dorado storage
systems to the cloud and then restore to cloud servers using the backups. For
details, see Restoring Data Using a Storage Backup.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 51
Page 56

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 4 Restoring Data
Restoring Data Using a VMware Backup
You can synchronize the backups of on-premises VMware VMs to the cloud and
restore to cloud servers using the backups. Congure security groups before the
restoration. Otherwise, the restoration may fail. For details, see Restoring to
Cloud Servers Using VMware Backups.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 52
Page 57

Cloud Backup and Recovery User Guide 5 (Optional) Migrating Resources from CSBS/VBS
5 (Optional) Migrating Resources from
CSBS/VBS
Context
HUAWEI CLOUD has launched the next-generation backup service Cloud Backup
and Recovery. If you have backup resources in CSBS or VBS but want to switch to
CBR for the management of these historical backups, you can migrate the backup
resources to CBR in a few clicks.
If you have never used CSBS or VBS or do not need the historical backup resources
anymore, skip this section.
Migration Rule Description
During migration, the system automatically creates vaults based on your historical
resources.
1. If a server or disk has been associated with a backup policy and has been
backed up, during the migration, the system creates a vault with the same
name as the backup policy (containing a maximum of 64 characters),
regardless of whether the policy is enabled. After the vault is created, it is
associated with the policy.
2. If a server or disk has been associated with a backup policy but no backup
has been generated, during the migration, the system creates a vault only
when the policy is enabled. After the vault is created, it is associated with the
policy. The rule for naming the vault is the same as that in the preceding
item.
3. If a server or disk has been associated with a backup or replication policy but
no backup or replica has been generated, and the policy is not enabled, then
only the policy is migrated.
4. The system migrates the backup and replication policies regardless of whether
they are associated with servers or disks.
5. If application-consistent backup is enabled in a backup policy, the system
creates a vault named default for storing generated application-consistent
backups.
6. The generated replicas of backups are stored in a replication vault named
default.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 53
Page 58

NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 5 (Optional) Migrating Resources from CSBS/VBS
7. Other backups, such as manual backups, are stored in a server backup vault
named default. Dierent vaults are automatically created based on dierent
types of resources. For example, the system creates a disk backup vault during
the migration of disk backups.
8. After the migration, backups created using CBR will also be displayed on the
VBS console, but you will be billed only once.
9. If an image has been created using a backup before the migration and a tag
has been added to the image, the backup migration may fail. In this case, go
to the IMS console page, delete the tag of the image, and then perform the
migration again. After the migration is complete, re-add the tag if needed.
10. If backups are migrated from any of the following regions, all backups in
these regions will be migrated: CN East-Shanghai1, CN East-Shanghai 2, CN
North-Beijing1, CN North-Beijing4, CN South-Guangzhou, AP-Singapore, APHong Kong, and AP-Bangkok. To migrate backups in other regions, go to the
corresponding region and proceed with migration separately.
Base on the preceding rules, the capacity of each vault created by the system is
predened as follows:
● If the total server/disk capacity is greater than the backup size multiplied by
1.2, the vault capacity is equal to the total disk capacity.
Constraints
● If the total server/disk capacity is smaller than the backup size multiplied by
1.2, the vault capacity is equal to the backup size multiplied by 1.2.
Total server/disk capacity indicates the total capacity of the servers or disks to be
associated with the vault.
For example, a user has a 100 GB ECS and a 50 GB ECS. The used storage capacity
of the two ECSs is 20 GB and 10 GB, respectively. The user manually has backed
up the two entire ECSs using the cloud server backup function. During the
migration, the system automatically compares the total server/disk capacity with
the backup size multiplied by 1.2. In this example, the total server capacity is 150
GB, and the backup size multiplied by 1.2 is 36 GB. Therefore, the system
automatically creates a 150 GB vault.
● By default, a vault created by the system is billed on pay-per-use basis. If you
want to switch to the yearly/monthly billing mode, refer to instructions in
Changing the Billing Mode from Pay-per-Use to Yearly/Monthly.
● After the migration, VBS and CSBS will be unavailable. CBR is billed in the
new billing mode. For details, see How Is CBR Billed?.
● During migration, purchased vaults cannot be used. The system automatically
migrates resources to the vaults created by the system.
● Before the migration, remove the policies from the servers or disks. Otherwise,
the servers or disks may fail to be associated with a CBR vault later.
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 54
Page 59

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 5 (Optional) Migrating Resources from CSBS/VBS
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery. Select a backup tab from the
left navigation pane.
Step 2 Click Migrate to CBR in the upper right corner. Read the content in the displayed
dialog box and click OK. See Figure 5-1.
Figure 5-1 Migrating resources
Step 3 The system automatically migrates resources. After the migration, a vault named
default is created and a message is displayed in the upper part of the page
indicating that the migration is successful.
----End
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 55
Page 60

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 6 Managing Tasks
6 Managing Tasks
This section describes how to view tasks. The Tasks list can show policy-driven
backup tasks that have been executed in the past 30 days.
Prerequisites
Procedure
Step 1 Log in to CBR Console.
Step 2 You can
Step 3 Click
At least one failed task exists.
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. Choose Storage > Cloud Backup and Recovery > Tasks.
name, vault ID, vault name, and time.
If a task fails, you can view the failure cause in the task details.
----End
in the upper left corner and select your region and project.
lter tasks by project, task type, task status, task ID, resource ID, resource
in front of the task to view the task details.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 56
Page 61

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 7 Auditing
7 Auditing
You can use Cloud Trace Service (CTS) to trace operations in CBR.
Prerequisites
CTS has been enabled.
Key Operations Recorded by CTS
Table 7-1 CBR operations that can be recorded by CTS
Operation
Creating a policy policy createPolicy
Updating a policy policy updatePolicy
Deleting a policy policy deletePolicy
Setting a vault policy vault associatePolicy
Removing a policy from
a vault
Creating a vault vault createVault
Modifying a vault vault updateVault
Deleting a vault vault deleteVault
Resource Type Trace Name
vault dissociatePolicy
Removing resources vault removeResources
Adding resources vault addResources
Performing a backup vault createVaultBackup
Creating a backup backup createBackup
Deleting a backup backup deleteBackup
Synchronizing a backup backup syncBackup
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 57
Page 62

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 7 Auditing
Operation Resource Type Trace Name
Restoring a backup backup restoreBackup
Viewing Audit Logs
To view audit logs, see section "Querying Real-Time Traces" in the
Service User Guide.
Disabling or Enabling a Tracker
The following procedure illustrates how to disable an existing tracker on the CTS
console. After the tracker is disabled, the system will stop recording operations,
but you can still view existing operation records.
Step 1 Log in to the management console.
Step 2 In the upper left corner of the page, click
Step 3 Click Service List and choose Management & Deployment > Cloud Trace
Service.
Step 4 Click Trackers in the left navigation pane.
Step 5 In the tracker list, click Disable in the Operation column.
Step 6 Click Yes.
Step 7 After the tracker is disabled, the available operation changes from Disable to
Enable. To enable the tracker again, click Enable and then click Yes. The system
will start recording operations again.
Cloud Trace
and select your region and project.
----End
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 58
Page 63

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 8 Quotas
8 Quotas
What Is Quota?
Quotas are enforced for service resources on the platform to prevent unforeseen
spikes in resource usage. Quotas can limit the number or amount of resources
available to users, such as the maximum number of ECSs or EVS disks that can be
created.
If the existing resource quota cannot meet your service requirements, you can
apply for a higher quota.
How Do I View My Quotas?
1. Log in to the management console.
2. Click
3. In the upper right corner of the page, choose Resources > My Quotas.
The Service Quota page is displayed.
Figure 8-1 My Quotas
in the upper left corner and select the desired region and project.
4. View the used and total quota of each type of resources on the displayed
page.
If a quota cannot meet service requirements, apply for a higher quota.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 59
Page 64

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide 8 Quotas
How Do I Apply for a Higher Quota?
1. Log in to the management console.
2. In the upper right corner of the page, choose Resources > My Quotas.
The Service Quota page is displayed.
Figure 8-2 My Quotas
3. Click Increase Quota.
4. On the Create Service Ticket page,
In Problem Description area, ll in the content and reason for adjustment.
5. After all necessary parameters are
to the Tenant Authorization Letter and Privacy Statement and click
Submit.
congure parameters as required.
congured, select I have read and agree
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 60
Page 65

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide A Appendix
A Appendix
A.1 Agent Security Maintenance
A.1.1 Changing the Password of User rdadmin
Procedure
● For O&M security purposes, you are advised to change the user rdadmin's
password of the Agent OS regularly and disable this user's remote login
permission.
● In Linux, user rdadmin has no password; in Windows, the default password of
user rdadmin is Huawei@123.
● This section describes how to change the password of user rdadmin in
Windows 2012. For other versions, change the password according to actual
situation.
Prerequisites
● You have obtained a username and its password for logging in to the
management console.
● The username and password for logging in to a Windows ECS have been
obtained.
Procedure
Step 1 Go to the ECS console and log in to the Windows ECS.
Step 2 Choose Start > Control Panel. In the Control Panel window, click User Accounts.
Step 3 Click User Accounts. The User Account Control dialog box is displayed. Select
rdadmin and click Reset Password.
Step 4 Enter the new password and click OK.
Step 5 In Task Manager, click the Services tab and then click Open Service.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 61
Page 66

NO TICE
NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide A Appendix
Step 6 Select RdMonitor and RdNginx respectively. In the displayed dialog box, select
Login, change the password to the one entered in Step 4, and click OK.
----End
A.1.2 Changing the Password of the Account for Reporting Alarms (SNMP v3)
To enhance the system O&M security, you are advised to change the password of
the account for reporting alarms.
Prerequisites
● You have obtained a username and its password for logging in to the
management console.
● The username and password for logging in to a server have been obtained.
Context
This section introduces the procedures in Windows and Linux.
If the authentication password and data encryption password for SNMP v3 of the
Agent are the same, security risks exist. To ensure system security, you are advised
to set
dierent passwords for authentication and data encryption.
The initial authentication password is BCM@DataProtect6 and the initial data
encryption password is BCM@DataProtect8.
The password must meet the following complexity requirements:
● Contains 8 to 16 characters.
● Contains at least one of the following special characters: `~!@#$%^&*()-_=+\|
[{}];:'",<.>/?
● Contains at least two of the following types of characters:
● Uppercase letters
● Lowercase letters
● Numeric characters
● Cannot be the same as the username or the username in reverse order.
● Cannot be the same as the old passwords.
● Cannot contain spaces.
Procedure (Windows)
Step 1 Log in to the server where the Agent is installed.
Step 2 Open the CLI and go to the
installation path
\bin directory.
Step 3 Run the agentcli.exe chgsnmp command. Type the login password of the Agent
and press Enter.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 62
Page 67

NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide A Appendix
Please choose operation:
1: Change authentication password
2: Change private password
3: Change authentication protocol
4: Change private protocol
5: Change security name
6: Change security Level
7: Change security model
8: Change context engine ID
9: Change context name
Other: Quit
Please choose:
admin is the username congured during the Agent installation.
Step 4 Select the SN of the authorization password or data encryption password that you
want to change and press Enter.
Step 5 Type the old password and press Enter.
Step 6 Type a new password and press Enter.
Step 7 Type the new password again and press Enter. The password is changed.
----End
Procedure (Linux)
Step 1 Log in to the Linux server using the server password.
Step 2 Run the TMOUT=0 command to prevent PuTTY from exiting due to session
timeout.
After the preceding command is executed, the system remains running even when no
operation is performed, which results in security risks. For security purposes, run the exit
command to exit the system after you
Step 3 Run the su - rdadmin command to switch to user rdadmin.
Step 4 Run the /home/rdadmin/Agent/bin/agentcli chgsnmp command. Type the login
password of the Agent and press Enter.
The installation path of the Agent is /home/rdadmin/Agent.
Please choose operation:
1: Change authentication password
2: Change private password
3: Change authentication protocol
4: Change private protocol
5: Change security name
6: Change security Level
7: Change security model
8: Change context engine ID
9: Change context name
Other: Quit
Please choose:
nish performing operations.
Step 5 Select the SN of the authorization password or data encryption password that you
want to change and press Enter.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 63
Page 68

NO TE
NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide A Appendix
Step 6 Type the old password and press Enter.
Step 7 Type a new password and press Enter.
Step 8 Type the new password again and press Enter. The password is changed.
----End
A.1.3 Replacing the Server
For security purposes, you may want to use a Secure Socket Layer (SSL) certicate
issued by a third-party certication authority. The Agent allows you to replace
authentication certicates and private key les as long as you provide the
certicates and private-public key pairs. The update to the
certicate during o-peak hours.
certicates in the X.509v3 format have been obtained.
Prerequisites
Context
authentication
certicate can take eect only after the Agent is restarted, hence you are advised
to update the
● You have obtained a username and its password for logging in to the
management console.
● The username and password for logging in to a server have been obtained.
● New
● The Agent is pre-deployed with the Agent AC certicate bcmagentca, private
le of the CA certicate server.key (), and authentication certicate
key
server.crt. All these les are saved in /home/rdadmin/Agent/bin/nginx/conf
(if you use Linux) or \bin\nginx\conf (if you use Windows).
● You need to restart the Agent after replacing a
certicate eective.
Certicate
certicate to make the
Procedure (Linux)
Step 1 Log in the Linux server with the Agent installed.
Step 2 Run the TMOUT=0 command to prevent PuTTY from exiting due to session
timeout.
After the preceding command is executed, the system remains running even when no
operation is performed, which results in security risks. For security purposes, run the exit
command to exit the system after you nish performing operations.
Step 3 Run the su - rdadmin command to switch to user rdadmin.
Step 4 Run the cd /home/rdadmin/Agent/bin command to go to the script path.
The installation path of the Agent is /home/rdadmin/Agent.
Step 5 Run the sh agent_stop.sh command to stop the Agent running.
Step 6 Place the new certicates and private key les in the specied directory.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 64
Page 69

NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide A Appendix
Place new certicates in the /home/rdadmin/Agent/bin/nginx/conf directory.
Step 7 Run the /home/rdadmin/Agent/bin/agentcli chgkey command.
The following information is displayed:
Enter password of admin:
admin is the username congured during the Agent installation.
Step 8 Type the login password of the Agent and press Enter.
The following information is displayed:
Change certicate le name:
Step 9 Enter a name for the new certicate and press Enter.
If the private key and the certicate are the same le, names of the private key and the
certicate are identical.
The following information is displayed:
Change certicate key le name:
Step 10 Enter a name for the new private key le and press Enter.
The following information is displayed:
Enter new password:
Enter the new password again:
Step 11 Enter the protection password of the private key le twice. The certicate is then
successfully replaced.
Step 12 Run the sh agent_start.sh command to start the Agent.
----End
Procedure (Windows)
Step 1 Log in to the Windows server with the Agent installed.
Step 2 Open the CLI and go to the
Step 3 Run the agent_stop.bat command to stop the Agent running.
Step 4 Place the new certicates and private key les in the specied directory.
installation path
\bin directory.
Place new certicates in the
installation path
\bin\nginx\conf directory.
Step 5 Run the agentcli.exe chgkey command.
The following information is displayed:
Enter password of admin:
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 65
Page 70

NO TE
NO TE
Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide A Appendix
admin is the username congured during the Agent installation.
Step 6 Enter a name for the new certicate and press Enter.
If the private key and the certicate are the same le, names of the private key and the
certicate are identical.
The following information is displayed:
Change certicate key le name:
Step 7 Enter a name for the new private key le and press Enter.
The following information is displayed:
Enter new password:
Enter the new password again:
Step 8 Enter the protection password of the private key le twice. The certicate is then
successfully replaced.
Step 9 Run the agent_start.bat command to start the Agent.
----End
A.1.4 Replacing CA
Scenarios
A CA certicate is a digital le signed and issued by an authentication authority. It
contains the public key, information about the owner of the public key,
information about the issuer, validity period, and certain extension information. It
is used to set up a secure information transfer channel between the Agent and the
server.
If the CA
expired, replace it for security purposes.
Prerequisites
● The username and password for logging in to an ECS have been obtained.
● A new CA
Procedure (Linux)
certicate does not comply with the security requirements or has
Certicates
certicate is ready.
Step 1 Log in the Linux server with the Agent installed.
Step 2 Run the following command to prevent logout due to system timeout:
TMOUT=0
Step 3 Run the following command to switch to user rdadmin:
su - rdadmin
Step 4 Run the following command to go to the path to the Agent start/stop script:
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 66
Page 71

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide A Appendix
cd /home/rdadmin/Agent/bin
Step 5 Run the following command to stop the Agent running:
sh agent_stop.sh
Step 6 Run the following command to go to the path to the CA certicate:
cd /home/rdadmin/Agent/bin/nginx/conf
Step 7 Run the following command to delete the existing CA
rm bcmagentca.crt
Step 8 Copy the new CA certicate le into the /home/rdadmin/Agent/bin/nginx/conf
directory and rename the
Step 9 Run the following command to change the owner of the CA certicate:
chown rdadmin:rdadmin bcmagentca.crt
Step 10 Run the following command to modify the permissions on the CA certicate:
chmod 400 bcmagentca.crt
Step 11 Run the following command to go to the path to the Agent start/stop script:
cd /home/rdadmin/Agent/bin
Step 12 Run the following command to start the Agent:
sh agent_start.sh
----End
le bcmagentca.crt.
certicate:
Procedure (Windows)
Step 1 Log in to the ECS with the Agent installed.
Step 2 Go to the
Step 3 Run the agent_stop.bat script to stop the Agent.
Step 4 Go to the
Step 5 Delete the bcmagentca.crt
Step 6 Copy the new CA certicate le into the
and rename the
Step 7 Go to the
Step 8 Run the agent_stop.bat script to service.
----End
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 67
Installation path
Installation path
le bcmagentca.crt.
Installation path
\bin directory.
\nginx\conf directory.
certicate le.
Installation path
\bin directory.
\nginx\conf directory
Page 72

Cloud Backup and Recovery
User Guide A Appendix
A.2 Change History
Released
On
2020-04-08 This issue is the fourth ocial release.
2020-02-25 This issue is the third ocial release.
2019-08-27 This issue is the second ocial release.
2019-07-31 This issue is the rst ocial release.
Description
This issue incorporates the following changes:
Added the content of le system backup.
This issue incorporates the following changes:
Moved section "Hybrid Cloud Backup" into a new documentation
titled
Hybrid Cloud Backup Feature Guide
This issue incorporates the following changes:
● Deleted description about cross-region replication and BMS
backup.
.
Issue 04 (2020-04-08) Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd. 68
 Loading...
Loading...