Page 1

HP
XP 9000 Cache Partition User Guide
Abstract
This guide describes how to use the HP XP P9000 Cache Partition Software on HP XP P9000 disk arrays. The intended audience
is a storage administrator or authorized service provider with independent knowledge of HP XP P9000 disk arrays and HP XP
P9000 software.
HP Part Number: AV400-96477
Published: August 2012
Edition: Eighth
Page 2
© Copyright 2011, 2012 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial
Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under
vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
This document is intended for system administrators and HP representatives who are involved in installing, configuring, and operating the P9500
storage system.
Readers of this document should meet the following requirements:
• Understand RAID storage systems and their basic functions.
• Be familiar with the HP XP P9000 Owner Guide.
• Be familiar with the Remote Web Console software.
Acknowledgements
Microsoft®, Windows®, Windows® XP, and Windows NT® are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Export Requirements
You may not export or re-export this document or any copy or adaptation in violation of export laws or regulations.
Without limiting the foregoing, this document may not be exported, re-exported, transferred or downloaded to or within (or to a national resident
of) countries under U.S. economic embargo, including Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Sudan, and Syria. This list is subject to change.
This document may not be exported, re-exported, transferred, or downloaded to persons or entities listed on the U.S. Department of Commerce
Denied Persons List, Entity List of proliferation concern or on any U.S. Treasury Department Designated Nationals exclusion list, or to parties directly
or indirectly involved in the development or production of nuclear, chemical, biological weapons, or in missile technology programs as specified
in the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (15 CFR 744).
Revision History
DescriptionDateEdition
Applies to microcode version 70-01-01-00/00 or later.October 2010First
Applies to microcode version 70-01-24-00/00 or later.November 2010Second
Applies to microcode version 70-01-62-00/00 or later.January 2011Third
Applies to microcode version 70-02-01-00/00 or later.May 2011Fourth
Applies to microcode version 70-02-7x-00/00 or laterSeptember 2011Fifth
Applies to microcode version 70-03-00-00/00 or later.November 2011Sixth
Applies to microcode version 70-03-3x-00/00 or later.April 2012Seventh
Applies to microcode version 70-04-00-00/00 or later.August 2012Eighth
Page 3

Contents
1 Creating virtual cache partitions...................................................................4
About virtual cache partitions.....................................................................................................4
Cache capacity for a CLPR........................................................................................................4
Cache partitioning rules and guidelines.......................................................................................7
Partitioning cache.....................................................................................................................9
Cache partition work flows....................................................................................................9
Creating a CLPR..................................................................................................................9
Migrating resources to and from a CLPR................................................................................10
Deleting a CLPR ................................................................................................................11
2 Troubleshooting........................................................................................12
Troubleshooting Cache Partition................................................................................................12
3 Support and other resources......................................................................13
Contacting HP........................................................................................................................13
Subscription service............................................................................................................13
Documentation feedback....................................................................................................13
Related information.................................................................................................................13
HP websites......................................................................................................................13
Conventions for storage capacity values....................................................................................14
Typographic conventions.........................................................................................................14
A Cache Partition GUI reference....................................................................16
Partition Definition tab (Storage System selected).........................................................................16
Partition Definition tab, Cache Logical Partition window (CLPR selected).........................................17
Partition Definition tab, Cache Logical Partition window (each CLPR information).............................17
Select CU dialog box..............................................................................................................19
Glossary....................................................................................................21
Index.........................................................................................................22
Contents 3
Page 4
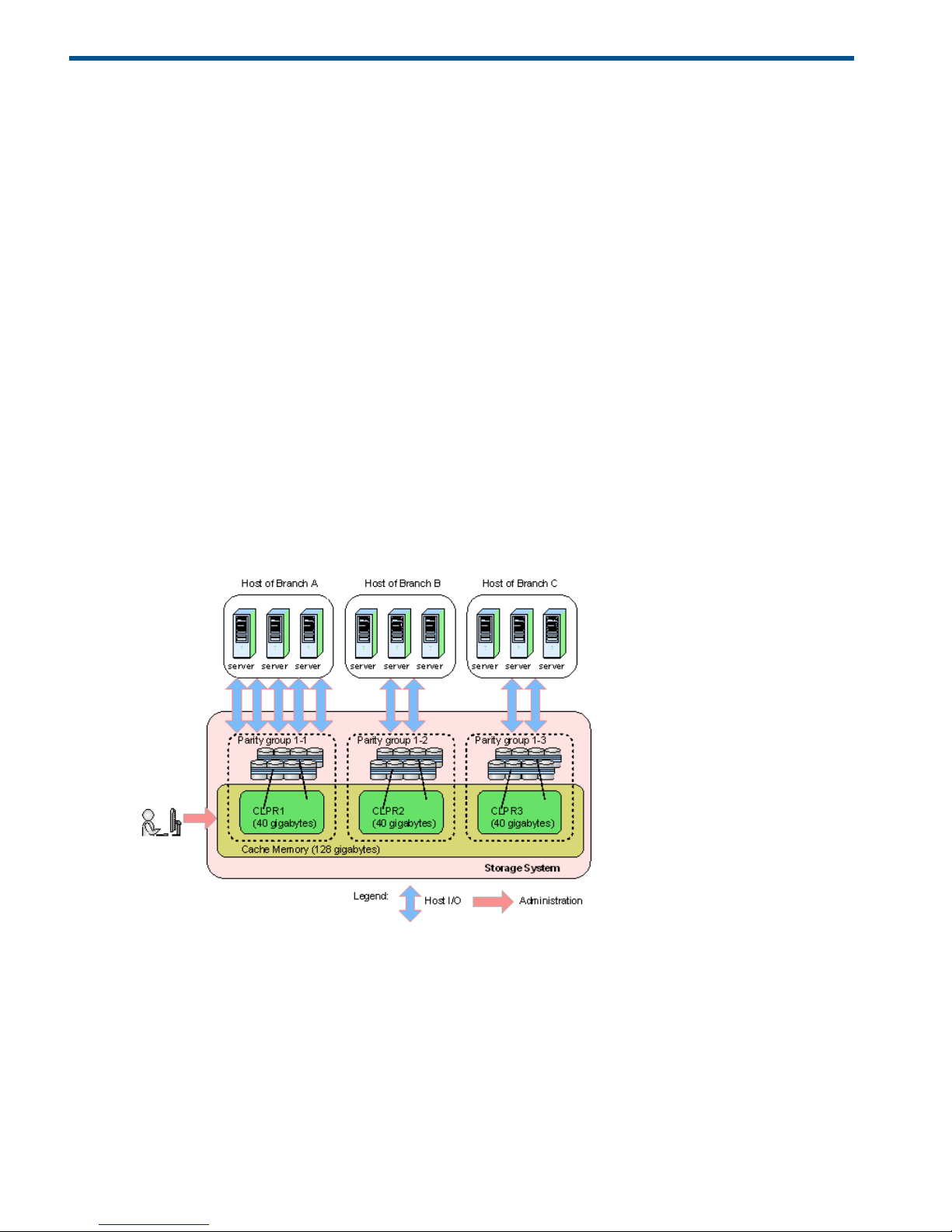
1 Creating virtual cache partitions
This topic provides detailed instructions for dividing storage system cache memory into virtual
cache logical partitions (CLPRs) using Cache Partition software.
About virtual cache partitions
If one storage system is shared with multiple hosts, one host reading or writing a large amount of
data can require enough of the storage system’s cache memory to affect other users. The Cache
Partition function allows improved I/O performance by dividing storage system cache memory
into multiple virtual cache memories (cache logical partitions or CLPRs).
Partitioning cache matches data to appropriate storage resources based on availability,
performance, capacity, and cost. It improves flexibility by allowing dynamic changes to cache
partitions while in use.
Partitioning cache dedicates cache resources for exclusive use by specific applications to maintain
priority and quality of service for business-critical applications. Storage administrators can secure
and/or restrict access to storage resources to ensure confidentiality for specific applications. By
dedicating resources to each partition as needed, a high quality of service can be maintained for
all users.
The following illustrates the use of cache memory within a corporation. In this example, cache
memory is partitioned into three segments of 40 GB, each of which is allocated to a branch office.
The host of branch A has a heavy I/O load. Because the cache memory is partitioned, that heavy
I/O load does not impact the cache memory for the other two branches.
Cache capacity for a CLPR
A CLPR is a pool of the cache and parity groups in the storage system. Partitioning cache into one
or more CLPRs allows storage administrators to dedicate individual CLPRs to a different host,
preventing I/O contention for cache memory.
Before you partition cache memory into CLPRs, calculate the cache capacity that will be needed
on your storage system. If necessary, install additional cache memory.
When you create a CLPR, the recommended cache capacity is determined by the conditions such
as: the number of mounted processor blades, RAID level, the number of drives that are installed
4 Creating virtual cache partitions
Page 5
on the storage system, and whether Thin Provisioning, Smart Tiers, Cache Residency, Compatible
XRC, or External Storage is used or not (enabled or disabled).
Calculate the recommended cache capacity for a CLPR using the formula below:
Recommended cache capacity (GB) for a CLPR = (CLPR capacity (GB) – ceiling (Cache Residency
extents (MB)/ 2,048) × 2 GB)
(i) When Thin Provisioning, Smart Tiers, Cache Residency or Compatible XRC
is not used:
When you do not use any of Thin Provisioning, Smart Tiers, Cache Residency, or Compatible XRC
for a CLPR, see the table below for the recommended cache capacity.
Recommended cache capacity for a CLPRNumber of processor bladesTotal capacity of internal VOL* and
external VOL for a CLPR
7 GB or more2Less than 1,500 GB
15 GB or more4
22 GB or more6
30 GB or more8
8 GB or more21,500 GB or more
15 GB or more4
22 GB or more6
30 GB or more8
16 GB or more2 or 42,900 GB or more
22 GB or more6
30 GB or more8
22 GB or more2, 4 or 611,500 GB or more
30 GB or more8
24 GB or more2, 4 or 614,400 GB or more
30 GB or more8
30 GB or more2, 4, 6 or 8100,000 GB or more
32 GB or more128,000 GB or more
40 GB or more182,000 GB or more
48 GB or more218,000 GB or more
56 GB or more254,000 GB or more
64 GB or more290,000 GB or more
72 GB or more326,000 GB or more
* Calculate the internal volume capacity for a CLPR using the formula below.
Internal volume capacity = number of (3D+1P) parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 3 + number of (6D+2P) parity
groups x capacity of one HDD x 6 + number of (7D+1P) parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 7 + number of
(14D+2P) parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 14 + number of (2D+2D) parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 2
When you use an external volume or a virtual volume, you cannot use the above formula. If you
use an external volume, calculate the total capacity of parity groups that are associated with the
CLPR. If you use a virtual volume, calculate the total LDEV capacity of the virtual volume that is
Cache capacity for a CLPR 5
Page 6

associated with the CLPR. To check the LDEV capacity of the virtual volume, see the LDEV dialog
box in the Basic Information Display dialog box of the Remote Web Console subwindow. For
further information about Remote Web Console subwindow, see the HP XP P9000 Remote Web
Console User Guide.
(ii) When Thin Provisioning or Smart Tiers is used:
When you use Thin Provisioning or Smart Tiers for a CLPR, see the table below for the recommended
cache capacity.
Recommended cache capacity for a CLPRNumber of processor bladesTotal capacity of internal VOL* and
external VOL for a CLPR
12 GB or more2Less than 2,900 GB or more
22 GB or more4
22 GB or more6
42 GB or more8
16 GB or more22,900 GB or more
22 GB or more4
32 GB or more6
42 GB or more8
22 GB or more2 or 411,500 GB or more
32 GB or more6
42 GB or more8
24 GB or more2 or 414,400 GB or more
32 GB or more6
42 GB or more8
32 GB or more2, 4, or 6100,000 GB or more
42 GB or more8
32 GB or more2, 4, or 6128,000 GB or more
42 GB or more8
42 GB or more2, 4, 6, or 8182,000 GB or more
48 GB or more218,000 GB or more
56 GB or more254,000 GB or more
64 GB or more290,000 GB or more
72 GB or more326,000 GB or more
* Calculate the internal volume capacity for a CLPR using the formula below.
Internal volume capacity = number of (3D+1P) parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 3 + number of (6D+2P) parity
groups x capacity of one HDD x 6 + number of (7D+1P) parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 7 + number of
(14D+2P) parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 14 + number of (2D+2D) parity groups x capacity of one HDD x 2
(iii) When Cache Residency is used:
When you use the Priority mode by using Cache Residency for a CLPR, you may want to add
cache capacity depending on the number of areas in which the priority mode is set in addition to
the cache used for Cache Residency. For further information, see the Priority mode section of the
HP XP P9000 Performance for Open and Mainframe Systems User Guide.
6 Creating virtual cache partitions
Page 7
(iv) When Compatible XRC is used:
When you use Compatible XRC for a CLPR, cache capacity for administrative information called
sidefile is needed. Therefore, you may want to add larger cache capacity than the recommended
cache capacity calculated from (i), (ii), or (iii) with sleep wait threshold in mind.
Calculate the recommended capacity using the formula below:
Recommended cache capacity = (Recommended cache capacity calculated from (i)-(iii)) × 100 /
(100 - (Sleep wait threshold))
(v) When only External Storage is used:
If the CLPR to be created meets the following conditions, the recommended cache memory capacity
in the table below can be applied.
• The CLPR uses only external volumes.
• The transfer speed is not emphasized.
• The cache mode of the mapped volume is Disable.
• The CLPR uses only volumes that are for Open systems.
Recommended cache capacity for a
CLPR
Number of processor
blades
Total capacity of external volume of CLPR in which
only Ext Stor is used
4 GB2 or 4Less than 128,000
8 GB6 or 8
8 GB2 or 4128,000 or more
16 GB6 or 8
When adding cache memory, use either the Standard Cache Access Model mode or the High
Performance Cache Access Model mode. If your storage system has any additional printed circuit
boards (PCBs), you must use the High Performance Cache Access Model mode. For more information
about adding cache memory, contact the HP Technical Support.
Cache partitioning rules and guidelines
Observe the following rules, restrictions, and guidelines when creating cache logical partitions:
For the priority mode cache requirements, see the HP XP P9000 Performance for Open and
Mainframe Systems User Guide.
You can operate Cache Partition from Remote Web Console or RAID Manager. To use RAID
Manager, see the HP XP P9000 RAID Manager User Guide.
Rules
• Cache Partition must be enabled on your system.
• CLPR0 is the default CLPR in a storage system. If you have not yet created any cache logical
partitions, all cache belongs to CLPR0.
• Usually, you can create a CLPR if the storage system has 4 GB cache. However, when creating
a CLPR while using Cache Residency, the remaining cache size, which is calculated by
subtracting Cache Residency size from the cache size of CLPR0, must be 8 GB or more.
• Adding or changing CLPR definitions or configurations may take hours to implement and
cannot be canceled or modified until all changes are complete. For assistance or for more
information, contact your HP account team.
Cache partitioning rules and guidelines 7
Page 8

Restrictions
The following operations are not allowed when multiple CLPRs are involved:
• Creating LUSE volumes across multiple CLPRs. If you forcibly perform this operation and create
a LUSE across multiple CLPRs, the LUSE volumes cannot be used for Continuous Access
Synchronous or Continuous Access Synchronous Z pair volumes.
• Business Copy Quick Restore operations that affect multiple CLPRs.
• Auto LUN manual migration operations that affect multiple CLPRs.
• A parity group containing LDEVs assigned to Cache Residency cache extents (cache areas)
cannot be migrated to another CLPR. See the HP XP P9000 Performance for Open and
Mainframe Systems User Guide for more information about cache extents.
• If you are using Continuous Access Journal, Continuous Access Journal data volumes and
journal volumes can belong to different CLPRs. All journal volumes in the same journal must
belong to the same CLPR. If not, an error occurs.
Guidelines
• Install any needed additional cache memory before partitioning cache. It will be difficult to
add additional cache memory after partitioning cache into CLPRs.
• If the cache capacity of defined CLPR is decreased by the Cache Residency cache area, cancel
Cache Residency bind mode setting, change the cache capacity of CLPR, and then set the
bind mode or priority mode again.
• Best practice is to create cache logical partitions either during the initial installation and setup
or during a maintenance window, because cache logical partition operations can significantly
degrade host performance. If you must perform such operations on a production machine,
use Performance Monitor to verify that the write pending rate, including spikes, is well below
30%.
The table below shows CLPR names set by default to associated CLPR numbers. Because CLPR
names are reserved, they cannot be set to alternative CLPR numbers. For example, "CLPR2" cannot
be set to the CLPR number 1.
CLPR nameCLPR numberCLPR nameCLPR number
CLPR1616CLPR00
CLPR1717CLPR11
CLPR1818CLPR22
CLPR1919CLPR33
CLPR2020CLPR44
CLPR2121CLPR55
CLPR2222CLPR66
CLPR2323CLPR77
CLPR2424CLPR88
CLPR2525CLPR99
CLPR2626CLPR1010
CLPR2727CLPR1111
CLPR2828CLPR1212
CLPR2929CLPR1313
8 Creating virtual cache partitions
Page 9

CLPR nameCLPR numberCLPR nameCLPR number
CLPR3030CLPR1414
CLPR3131CLPR1515
Partitioning cache
Cache partition work flows
Creating a CLPR
1. Create a CLPR (see “Creating a CLPR” (page 9)).
2. Migrate resources to the new CLPR (see “Migrating resources to and from a CLPR” (page 10)).
Removing a CLPR
1. Migrate resources from the CLPR that is to be removed (see “Migrating resources to and from
a CLPR” (page 10)).
2. Delete the CLPR (see “Deleting a CLPR ” (page 11)).
Creating a CLPR
Before creating a CLPR, review “Cache partitioning rules and guidelines” (page 7).
1. Click Settings > Environmental Setting > Partition Definition on the menu bar of the Remote
Web Console main window.
2. Click to change the mode from View to Modify.
3. In Cache Partition, open the Partition Definition window, and select a CLPR in the Partition
Definition tree.
4. In the Cache Logical Partition window, right-click a CLPR from the Partition Definition tree and
select Create CLPR. This adds a cache logical partition to the Partition Definition tree. The
maximum number of CLPRs that can be manually created is 31 (not including CLPR0).
5. Select the newly created CLPR to open the Cache Logical Partition window.
Partitioning cache 9
Page 10

6. In the Detail for CLPR in Storage System section, do the following:
• In CLPR Name field, type the name of the cache logical partition, in up to 16 alphanumeric
characters. However, it cannot be changed to the CLPR name that is reserved for the
storage system. See “Cache partitioning rules and guidelines” (page 7).
• In Cache Size, select the cache capacity. You may select from 4 to 508 GB, in 2 GB
increments. The default value is 4 GB. The size of the cache is allocated from CLPR 0,
but you must leave at least 8 GB remaining in CLPR 0.
• In Cache Residency Size, select the cache capacity. You may select from 4 to 508 GB,
in 2 GB increments. The default value is 4 GB. The size of the cache is allocated from
CLPR0, but you must leave at least 8 GB remaining in CLPR0.
• In Num of Cache Residency Areas, type the desired capacity for the Cache Residency
area. The range of values is 0 to 16384 and the default value is 0.
7. Click Apply. The progress bar appears. The change in cache capacity is reflected in this cache
logical partition and in the CLPR0.
8. To change the settings of an existing CLPR, repeat steps 5 through 7.
At this point, the CLPR has no parity groups. You can now migrate resources to the new CLPR (see
“Migrating resources to and from a CLPR” (page 10)).
Migrating resources to and from a CLPR
After adding a CLPR, you must migrate resources (parity groups) from existing CLPRs to the new
CLPR. Before deleting a CLPR, you must first migrate resources from that CLPR to CLPRs that will
not be deleted.
When migrating resources to and from cache logical partitions:
• You can migrate resources only within the same CU.
• All interleaved parity groups must be in the same CLPR.
• LUSE volumes cannot be set across more than one CLPR.
• If a parity group contains one or more LDEVs that have defined Cache Residency extents, you
cannot migrate that parity group to another CLPR.
To migrate resources to and from a CLPR:
1. Click Settings > Environmental Setting > Partition Definition on the menu bar of the Remote
Web Console main window.
2. Click to change the mode from View to Modify.
3. Access the Logical Partition window, then select a CLPR from the Partition Definition tree.
4. In the Cache Logical Partition window, click Select CU to choose a CU.
5. Specify how you want to view information the CLPR resource list. In the Select CU dialog box,
choose one of the following:
• All CUs: Shows the information about all CUs on the CLPR resource list.
• Choose Specific CU, then specify the LDKC and the CU. This shows only CLPRs from the
selected CU.
• Unallocated: Shows information about only the CUs unallocated to CLPR on the CLPR
resource list.
10 Creating virtual cache partitions
Page 11

6. Click Set to close the dialog box.
7. From the Cache Logical Partition Resource List, select one or more parity groups to be migrated,
then select Cut.
8. On the Partition Definition tree, right-click the CLPR to which you want to migrate resources,
and then select Paste Resources.
9. Click Apply. The progress bar appears.
Deleting a CLPR
Before deleting a CLPR, be sure to migrate any resources (for example, parity groups) to the CLPR
that will not be deleted (see “Migrating resources to and from a CLPR” (page 10) for more
information).
Unnecessary CLPRs may be deleted, but CLPR0 cannot be deleted.
To delete a CLPR:
1. Click Settings > Environmental Setting > Partition Definition on the menu bar of the Remote
Web Console main window.
2. Click to change the mode from View to Modify.
3. Select a CLPR in the Partition Definition tree to open the Cache Logical Partition window.
4. Right-click the CLPR that you want to delete and select Delete CLPR.
5. Click Apply. The progress bar appears.
Partitioning cache 11
Page 12

2 Troubleshooting
This topic provides troubleshooting information for Cache Partition software.
Troubleshooting Cache Partition
Displaying an error message
If the settings contain a discrepancy after you click Apply, an error message appears.
To display an error message:
1. Right-click a CLPR on the Partition Definition tree, then select Error Detail to open the message.
2. Review the message and click OK to close the message.
General troubleshooting
The following table provides general troubleshooting instructions for Cache Partition operations.
Table 1 General troubleshooting for Cache Partition operations
CauseError
LUSE volumes cannot be set across more than one CLPR.When you attempt to migrate a parity group
to another CLPR, an LU warning message
appears.
You cannot assign the same name to more than one CLPR. The name you
entered is already being used or is reserved by a system. Enter another
The CLPR name cannot be changed.
name. For more information, see the table in the “Guidelines” (page 8)
section.
The parity group in a CLPR cannot be
migrated to another CLPR.
• Only open-system parity groups can be migrated.
• Make sure that all interleaved parity groups belong to the same CLPR.
• Make sure to click Apply when creating a new CLPR.
12 Troubleshooting
Page 13

3 Support and other resources
Contacting HP
For worldwide technical support information, see the HP support website:
http://www.hp.com/support
Before contacting HP, collect the following information:
• Product model names and numbers
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed questions
Subscription service
HP recommends that you register your product at the Subscriber's Choice for Business website:
http://www.hp.com/go/e-updates
After registering, you will receive e-mail notification of product enhancements, new driver versions,
firmware updates, and other product resources.
Documentation feedback
HP welcomes your feedback.
To make comments and suggestions about product documentation, please send a message to
storagedocsfeedback@hp.com. Include the document title and manufacturing part number. All
submissions become the property of HP.
Related information
The following documents [and websites] provide related information:
• HP XP P9000 Performance for Open and Mainframe Systems User Guide
• HP XP P9000 Remote Web Console User Guide
You can find these documents on the Manuals page of the HP Business Support Center website:
http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
In the Storage section, click Disk Storage Systems for hardware or Storage Software for software,
and then select your product.
HP websites
For additional information, see the following HP websites:
• http://www.hp.com
• http://www.hp.com/go/storage
• http://www.hp.com/service_locator
• http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
Contacting HP 13
Page 14

• http://www.hp.com/support/downloads
• http://www.hp.com/storage/whitepapers
Conventions for storage capacity values
HP XP P9000 disk arrays use the following values to calculate physical storage capacity values
(hard disk drives):
• 1 KB (kilobyte) = 1,000 bytes
• 1 MB (megabyte) = 1,0002bytes
• 1 GB (gigabyte) = 1,0003bytes
• 1 TB (terabyte) = 1,0004bytes
• 1 PB (petabyte) = 1,0005bytes
• 1 EB (exabyte) = 1,0006bytes
HP XP P9000 disk arrays use the following values to calculate logical storage capacity values
(logical devices):
• 1 KB (kilobyte) = 1,024 bytes
• 1 MB (megabyte) = 1,0242bytes
• 1 GB (gigabyte) = 1,0243bytes
• 1 TB (terabyte) = 1,0244bytes
• 1 PB (petabyte) = 1,0245bytes
• 1 EB (exabyte) = 1,0246bytes
Typographic conventions
Table 2 Document conventions
ElementConvention
Cross-reference linksBlue text: Table 2 (page 14)
email addressesBlue, bold, underlined text
Website addressesBlue, underlined text: http://www.hp.com
Bold text
• Keys that are pressed
• Text typed into a GUI element, such as a box
• GUI elements that are clicked or selected, such as menu
and list items, buttons, tabs, and check boxes
Text emphasisItalic text
Monospace text
• File and directory names
• System output
• Code
• Commands, their arguments, and argument values
Monospace, italic text
• Code variables
• Command variables
Emphasized monospace textMonospace, bold text
WARNING! Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or death.
14 Support and other resources
Page 15

CAUTION: Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
IMPORTANT: Provides clarifying information or specific instructions.
NOTE: Provides additional information.
TIP: Provides helpful hints and shortcuts.
Typographic conventions 15
Page 16

A Cache Partition GUI reference
This topic describes the windows that comprise the Cache Partition GUI.
Partition Definition tab (Storage System selected)
Use this tab to view detail about all of the cache logical partitions in the storage system. Information
appearing in this tab differs depending on what is selected in the Logical Partition tree.
• When Storage System is selected, information about the selected storage system appears in
the resource list.
• When CLPR is selected, information about cache partition appears in the resource list.
• When a specific CLPR is selected, information about that CLPR appears in the resource list,
and the CLPR detail appears below the list.
To access this tab, from the Remote Web Console main window click Go, then Environmental
Setting, and then select the Partition Definition tab.
DescriptionItem
A hierarchical list of storage system and cache logical partitions. CLPRs defined in the storage
system are indicated by an icon and a unique CLPR number.
Logical Partition tree
Provides information about the item selected in the Logical Partition tree. When Storage System
is selected, the resource list provides the following information:
Resource list
• No.: The storage system resource list number.
• Item: The resource type, for example, Storage Partition.
• Cache (Num. of CLPRs): The cache capacity, in GM, and number of cache logical partitions.
• Num. of Resources: Number of parity groups.
See also:
• “Partition Definition tab, Cache Logical Partition window (CLPR selected)” (page 17)
• “Partition Definition tab, Cache Logical Partition window (each CLPR information)” (page 17)
Implements the Storage System settings made in this window.Apply
Cancels any settings that were made in this window.Cancel
16 Cache Partition GUI reference
Page 17

Partition Definition tab, Cache Logical Partition window (CLPR selected)
Use this window to view information about all of the cache logical partitions in the storage system.
This window opens when you select a CLPR in the Partition Definition tree of the Partition Definition
tab.
DescriptionItem
A hierarchical list of the cache logical partitions in the selected storage system. The CLPR
identifier, for example CLPR0, appears to the right of the CLPR icon ( ).
Partition Definition
tree
Information about the CLPR. When a CLPR is selected, the list provides the following information:Cache Logical
Partition resource list
• No.: Line number.
• Resource Type: Resource type, for example, Cache Partition or Port.
• Name: Resource name. If the resource type is Cache Partition, the CLPR number and CLPR
ID appear.
• Properties: Capacity, in GB, and number of resources allocated to the selected CLPR.
• Information: Status of the selected CLPR. When the CLPR is created, Create appears. When
the CLPR is deleted, Delete appears.
Implements settings made in this window.Apply
Cancels any settings made in this window.Cancel
Partition Definition tab, Cache Logical Partition window (each CLPR
information)
The Cache Logical Partition window appears below the resource list when you select a specific
CLPR in the Partition Definition tree of the Partition Definition tab. Use this window to view and
update CLPR resources. Parity groups, external volume groups, virtual volumes, the cache size, the
Cache Residency size and the number of Cache Residency areas are configured to CLPR.
Before changing cache size or cache residency size, verify that CLPR0 has at least 4 GB remaining
after subtracting cache residency size from the cache size.
Partition Definition tab, Cache Logical Partition window (CLPR selected) 17
Page 18

DescriptionItem
Indicates either All CUs or the selected CU number.CU
Opens the Select CU dialog box.Select CU
A hierarchical list of all of the cache logical partitions in the storage system. The cache logical
partition number and name appear to the right of the CLPR icon ( ).
Partition Definition
tree
When a CLPR is selected in the Partition Definition tree, the Cache Logical Partition resource list
show the resource information for the selected CU and CLPR.
Cache Logical
Partition resource list
When CLPR0 is selected in the Cache Logical Partition tree, this list shows all resources not
already assigned to other partitions.
The resource list provides the following information:
• No.: Row number.
• Resource Type: Type of CLPR resources. Parity Group or V-VOL appears in this column.
• Address: Resource address.
An address with E (for example, E1-1) indicates that the parity group contains external
volumes.
An address with M (for example, M1-1) indicates that the parity group contains migration
volumes.
An address with V (for example, V1-1) indicates that the parity group contains Snapshot
virtual volumes.
An address with X (for example, X1-1) indicates that the parity group contains Thin
Provisioning virtual volumes.
An address with [1-1(Couple)] indicates that parity group 1-1 is connected to another parity
group and the top parity group is 1-1.
An address with [1-2(1-1)] indicates that parity group 1-2 is connected to another parity
group and the top parity group is 1-1.
• Properties: Properties of the parity group.
If a parity group contains internal volumes, the parity group and RAID configuration are
shown.
If a parity group contains external volumes, the volume capacity is shown, but the RAID
configuration is not shown.
18 Cache Partition GUI reference
Page 19

DescriptionItem
For virtual volumes (for example, Snapshot or Thin Provisioning), the logical volume capacity
is shown, but the RAID configuration is not shown.
• Emulation: Emulation type of the resource.
When a CLPR is selected in the Partition Definition tree, the CLPR detail appears below the
resource list. Use this area to set or change the settings of the specified cache logical partition.
Detail For CLPR in
Storage System
You cannot directly change the capacity value of CLPR0. Any changes in the capacity of the
other CLPRs are reflected as an opposite change in the capacity of CLPR0.
The maximum available cache capacity (installed cache capacity less the cache assigned to
other cache logical partitions) is shown for the upper limit of Cache Size, Cache Residency
Size, and Num. of Cache Residency Areas. For more information on cache residency, see the
HP XP P9000 Performance for Open and Mainframe Systems User Guide.
• CLPR Name: Allows you to set or change the name of the cache logical partition, provided
that it is within the selected CU. You can use up to 16 alphanumeric characters.
• Cache Size: Allows you to set or change the cache capacity of each cache logical partition.
You may select 4 GB or more up to a maximum size of 508 GB, which is 4 GB smaller than
the cache size of the whole storage system. From a default value of 4 GB you may increase
the size in 2 GB increments.
• Cache Residency Size: Allows you to set or change the capacity of the Cache Residency
cache. You may select nothing (0 GB) to a maximum of 504 GB, which is the Cache
Residency size of the entire storage system. The default value is 0 GB to which you may add
capacity in 0.5 GB increments.
If you have previously defined cache residency size for this cache logical partition using
Cache Residency, the cache residency size selected for this cache logical partition must be
greater than that which was previously defined. Use Cache Residency to verify the size before
you set the value for this field.
• Num. of Cache Residency Areas: Allows you to set or change the number of cache residency
areas, from 0 to 16,384. The default value is zero (0).
If you have previously defined cache residency areas for this cache logical partition using
Cache Residency, the number of cache residency areas selected for this cache logical partition
must be more than that which was previously defined. Use Cache Residency to verify the
number of areas before you set the value for this field.
Implements settings made in this window.Apply
Cancels settings made in this window.Cancel
Select CU dialog box
Use this dialog box to select how you want CU information to appear on the CLPR resource list.
Open the Select CU Dialog box by clicking Select CU on the Cache Logical Partition Window.
Select CU dialog box 19
Page 20

DescriptionItem
When selected, only information about resources of all CUs appears on the CLPR resource list.All CUs
When selected, only information about resources that are associated with the specified CU
appears on the CLPR resource list.
Specific CU
• Use the LDKC list to specify LDKC.
• Use the CU list to specify CU.
When selected, only information about resources that are not assigned with any CU appears
on the CLPR resource list.
Unallocated
Implements the settings in the storage system.Set
Cancels any settings made in this window.Cancel
20 Cache Partition GUI reference
Page 21

Glossary
BC HP XP P9000 or XP Business Copy. An HP application that provides volume-level, point-in-time
copies in the disk array.
CLPR Cache logical partition.
Cnt Ac-J HP XP P9000 or XP Continuous Access Journal software.
Cnt Ac-J Z The version of Continuous Access Journal that supports mainframe volumes.
Cnt Ac-S HP XP P9000 or XP Continuous Access Synchronous software.
Cnt Ac-S Z The version of Continuous Access Synchronous that supports mainframe volumes.
CU Control Unit. Used to organize the storage space attached to the disk controller ( DKC). You can
group similarly configured logical devices (LDEVs) with unique control unit images (CUs). CUs
are numbered sequentially. The disk array supports a certain number of CUs, depending on the
disk array model. Each CU can manage multiple LDEVs; therefore, both the CU number and the
LDEV number are required to identify an LDEV.
DKC Disk controller.
DKU Disk Unit.
emulation mode The LDEVs associated with each RAID group are assigned an emulation mode that makes them
operate like OPEN system disk drives. The emulation mode determines the size of an LDEV or
volume.
OPEN-V: User-defined custom size
3390-3/3R: 2.838 GB
3390-9: 8.514 GB
3390-L: 27.844 GB
3390-M: 55.689 GB
3380-3 2.377 GB
HDD Hard disk drive.
LDKC Logical disk controller.
local disk A disk in the local array. Sometimes refers to a disk in a local host.
LUN Logical unit number. A LUN results from mapping a logical unit number, port ID, and LDEV ID to
a RAID group. The size of the LUN is determined by the emulation mode of the LDEV and the
number of LDEVs associated with the LUN.
parity group A set of hard disk drives that have the same capacity and that are treated as one group. A parity
group contains both user data and parity information, which enables user data to be accessed
if one or more drives in the group is not available.
PCB Printed circuit board.
remote instance The instance with which the local instance communicates, as configured in the HORCM_INST
section of the RAID Manager instance configuration file.
Remote Web
Console
A browser-based program installed on the SVP that allows you to configure and manage the disk
array.
synchronous Describes computing models that perform tasks in chronological order without interruption. In
synchronous replication, the source waits for data to be copied at the destination before
acknowledging that it has been written at the source.
V-VOL Virtual Volume.
VOL, vol Volume.
volume Volume on disk. An accessible storage area on disk, either physical or virtual.
XDF Extended distance feature (for ExSA channels).
21
Page 22

Index
A
Auto LUN
restrictions on manual migration across multiple CLPRs,
8
B
Business Copy
restrictions on quick restore operations across multiple
CLPRs, 8
C
cache
capacity recommendations, 4
partitioning, 4
partitioning example, 4
partitions, 4
CLPR
creating, 9
CLPRs
creating, 9
deleting, 11
migrating resources, 10
restrictions, 8
contacting HP, 13
conventions
document, 14
storage capacity values, 14
text symbols, 14
creating a CLPR, 9
D
deleting a CLPR, 9, 11
document
conventions, 14
related information, 13
documentation
HP website, 13
providing feedback, 13
H
help
obtaining, 13
HP
technical support, 13
I
interleaved parity groups in CLPRs, 10
M
migrating resources, 10
O
operations not allowed with multiple CLPRs
restrictions, 8
P
partitioning cache, 4
R
related documentation, 13
restrictions
Auto LUN manual migration across multiple CLPRs, 8
Business Copy quick restore operations across multiple
CLPRs, 8
operations not allowed with multiple CLPRs, 8
S
storage capacity values
conventions, 14
Subscriber's Choice, HP, 13
symbols in text, 14
T
technical support
HP, 13
service locator website, 13
text symbols, 14
troubleshooting
Cache Partition, 12
typographic conventions, 14
V
virtual cache partitions, 4
W
websites
HP , 13
HP Subscriber's Choice for Business, 13
product manuals, 13
22 Index
 Loading...
Loading...