HP ProCurve J8162A, ProCurve 6400cl, ProCurve 5300xl, ProCurve 3400cl, xl Module Supplementary Manual
Page 1

Access Controller xl Module Supplement
to the HP ProCurve 6400cl/5300xl/3400cl
Management and Configuration Guide.
This supplement describes the configuration, operation, and monitoring of the ProCurve Access
Controller xl Module (J8162A) on the HP ProCurve Series 5300xl switches.
Related HP ProCurve Switch 5300xl Series publications include:
■ HP ProCurve xl Modules Installation Guide
■ HP ProCurve Secure Access 700wl Series Management and Configuration Guide
HP periodically updates switch software and product manuals, and posts them on the world wide
Web. For the latest software release and publications for your HP networking product, visit
http://www.hp.com/go/procurve. Click on Software updates to check on the latest software releases.
Click on Technical support, then Product manuals (all) to check on the latest publications.
Page 2

© Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Company, LP. The
information contained herein is subject to change without
notice.
Publication Number
5991-2136
March, 2005
Applicable Products
HP ProCurve Switch 5304xl (J4850A)
HP ProCurve Switch 5308xl (J4819A)
HP ProCurve Switch 5348xl (J4849A)
HP ProCurve Switch 5372xl (J4848A)
HP ProCurve Switch 5304xl-G32 (J8166A)
HP ProCurve Switch 5308xl-G48 (J8167A)
ProCurve Access Controller xl Module (J8162A)
HP ProCurve Access Control Server 740wl (J8154A)
HP ProCurve Integrated Access Manager 760wl (J8155A)
Trademark Credits
Microsoft®, Windows®, and Windows NT® are US
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Adobe® and Acrobat® are trademarks of Adobe Systems
Incorporated.
Disclaimer
The information contained in this document is subject to
change without notice.
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Hewlett-Packard shall not
be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing,
performance, or use of this material.
The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying
such products and services. Nothing herein should be
construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions
contained herein.
Hewlett-Packard assumes no responsibility for the use or
reliability of its software on equipment that is not furnished
by Hewlett-Packard.
Warranty
See the Customer Support/Warranty booklet included with
the product.
A copy of the specific warranty terms applicable to your
Hewlett-Packard products and replacement parts can be
obtained from your HP Sales and Service Office or
authorized dealer.
Hewlett-Packard Company
8000 Foothills Boulevard, m/s 5551
Roseville, California 95747-5551
http://www.hp.com/go/procurve
ii
Page 3

Contents
Contents
Applicable Switch Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Applicable Secure Access 700wl Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
General Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Related Publications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Access Controller xl Module Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Module Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
Using 5300xl Features with the Access Controller xl Module . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Routing Infrastructure Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Using 5300xl Switch Network Address Translation with the ACM . . 11
The Role of VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Client VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Static VLAN Features Supported on Client VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
General Operating Rules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Configuring the ACM on the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Configuring the Access Controller xl Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Configuring Downlink Client Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Changing the VLAN-Base . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Configuring Client VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Configuring Uplink Network Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Configuring the Uplink VLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
ACM Configuration Commands Summary and Syntax . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Configuration Context Command Syntax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Access Controller Context Command Syntax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Displaying Access Controller xl Status from the 5300xl CLI . . . . . . . . . . . 24
ACM Display Commands Summary and Syntax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Configuration Context Command Syntax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Access Controller Context Command Syntax . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Managing the ACM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Using the ACM’s Extended CLI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Downloading New Software to the Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
iii
Page 4

Resetting the Module to Factory Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Operating Notes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
BIOS POST Event Log Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Page 5
Applicable Switch Models
Applicable Switch Models
The Access Controller xl Module (J8162A) described in this supplement
operates on the HP ProCurve Series 5300xl switches.
The 5300xl switch software must be updated to version E.09.21 or later.
Applicable Secure Access 700wl Models
The Access Control Server 740wl or the Integrated Access Manager 760wl
must use software version 4.1.3.93 or later.
Introduction
The ProCurve Access Controller xl Module (ACM) enables secure, mobile user
access to appropriate network services on any ProCurve Series 5300xl switch.
This modular addition to the 5300xl switch offers a unique approach to
integrating identity-based user access control, wireless data privacy and
secure roaming with the flexibility of a full-featured intelligent edge switch.
Centrally configured and managed access policies provide identity-based
access control to wired and wireless users.
General Operation
The Access Controller xl Module (J8162A) uses ports on a 5300xl switch to
pass wired and wireless traffic to and from the network using authentication
and rights administration policies from an Access Control Server 740wl or an
Integrated Access Manager 760wl. Up to two ACMs may be used in a single
5300xl switch. Once the ACM is installed in the switch, connected to the
Access Control Server (740wl or 760wl), and configured for operation, it is
managed from the Administrative Console of the Secure Access 740wl or
760wl products.
1
Page 6

Introduction
Related Publications
This supplement introduces Access Controller xl Module operation, configuration, and monitoring. The following two manuals provide further information:
■ For information on installing the ACM, refer to the HP ProCurve xl
Modules Installation Guide provided with the module.
■ To help you manage and configure the ACM in your network, refer to
the HP ProCurve Secure Access 700wl Series Management and
Configuration Guide, which is available from either of the following
sources:
• The Documentation CD-ROM shipped with your module
• The ProCurve Networking Web site at
http://www.hp.com/go/procurve. (Click on Technical support, then Product manuals (all).)
Terminology
Term Use in this Manual
Access Control
Server
Client A device looking to access the network.
Client VLAN A special VLAN created to handle downlink client port traffic for the ACM.
Downlink Client
Ports
Downlink Port The internal port that carries client traffic to and from the ACM. This port
A centralized resource on the network that provides services, such as
authentication management, mobility management (roaming support),
policy management, and system monitoring and reporting, to the
connected Access Controllers.
The Access Control Server is deployed as a dedicated control function
and does not sit in the user data path. The Secure Access 700wl Series
has two products that provide this capability: the ProCurve Access
Control Server 740wl and the Integrated Access Manager 760wl.
Includes the downlink client port (with untagged VLAN membership) and
the downlink port (
Series 5300xl switch ports assigned as an untagged member to a client
VLAN to supply client connectivity.
is identified by the slot ID where the module is installed, combined with
‘DP’. For example, CDP is the downlink port for an ACM installed in slot
C of a 5300xl switch.
<slot-id>DP) (with tagged VLAN membership).
2
Page 7

Term Use in this Manual
Access Controller xl Module Overview
Integrated
Access
Manager 760wl
Uplink Port The internal port that carries ACM traffic to and from the network. Must
Uplink Network
Ports
Uplink VLAN The VLAN containing the uplink port as an untagged member. By default,
Combines the functionality of the ProCurve Access Controller 720wl and
the ProCurve Access Control Server 740wl in a single device.
be an untagged member of a non-client VLAN. This port is identified by
the slot ID where the module is installed, combined with ‘UP.’ For example,
CUP is the uplink port for an ACM installed in slot C of a 5300xl switch.
Any 5300xl port that is a member of the uplink VLAN.
this is the DEFAULT_VLAN on the 5300xl switch.
Access Controller xl Module Overview
The Access Controller xl Module adds new wireless security and access
control capabilities to the 5300xl switch. The module supplies identity-based
user access control to specific network services, wireless data privacy with
VPN services, and application persistence across subnet boundaries at the
edge of the network, where users connect. Centrally managed from the
ProCurve Secure Access Control Server 740wl or Integrated Access Manager
760wl, the Access Controller xl Module provides hassle-free access while
maintaining a high level of security.
3
Page 8
Access Controller xl Module Overview
Module Operation
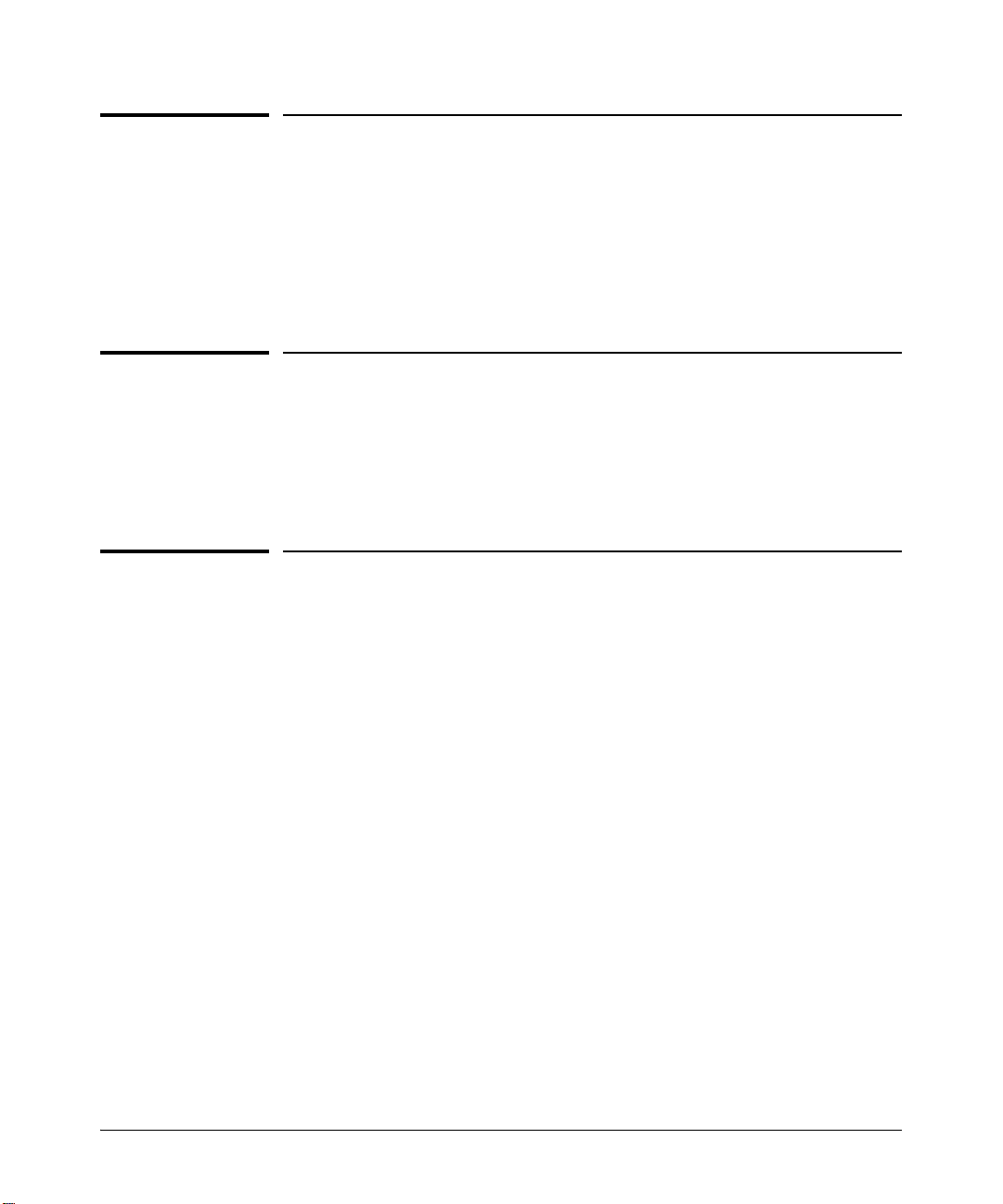
Figure 1 below presents the module’s key components. Each component is
then discussed.
Figure 1. The Access Controller xl Module Conceptual View
The Access Controller xl Module has no external ports, as shown in Figure 1.
The module uses ports on the 5300xl switch through two internal ports, the
uplink port and the downlink port. Clients, typically connecting through an
access point, connect to 5300xl ports defined as downlink client ports. The
internal uplink port passes network traffic through other 5300xl ports, which
are external uplink network ports. VLANs are used to direct traffic to and from
the ACM.
For an explanation of the module’s features and LEDs, see the HP ProCurve
xl Modules Installation Guide.
4
Page 9

Access Controller xl Module Overview
Note Uplink and downlink port names depend on the switch slot where the module
is installed. When the module is in switch slot A, ‘N’ is ‘A’ in Figure 1. The uplink
port for the module is AUP; the downlink port is ADP.
The following steps are required to add an ACM to your network:
1. Install an Access Control Server 740wl or Integrated Access Manager
760wl in the network, or identify an existing 740wl or 760wl to be used
with the ACM.
2. Having identified the Access Control Server 740wl or Integrated Access
Manager 760wl to be used with the ACM, note its IP address. To operate,
the ACM must establish secure communications with the Access Control
Server or Integrated Access Manager.
The shared secret configured on the 740wl/760wl’s is also needed. If you
are already using a 760wl, you may not have configured a shared secret.
See “Editing the Access Control Server Configuration” in the HP ProCurve
Secure Access 700wl Series Management and Configuration Guide,
available on the Documentation CD-ROM shipped with your module or
from the ProCurve Networking Web site at
http://www.hp.com/go/procurve
manuals (all)).
(Click on Technical support, then Product
3. Install the ACM in a slot on the 5300xl switch. Once the Module Ready
LED is on, the ACM requires an IP address. By default, the ACM uses
DHCP. The IP address also can be set manually. The uplink port must be
an untagged member of a VLAN that can communicate with the 740wl or
760wl. The ACM establishes communication with the 740wl/760wl, using
the IP address and the shared secret from step 2 above. See the HP
ProCurve xl Modules Installation Guide for details.
4. Configure downlink client ports, client VLANs, uplink network ports, and
the uplink VLAN on the 5300xl switch. Configure access and user/group
policy rights on the 740wl/760wl to support and manage clients and client
traffic through the ACM.
5. Manage and monitor the ACM using the Administrative Console on a
740wl or 760wl.
There are specific installation and operational requirements for this device as
a module in a Series 5300xl switch. The following sections describe how the
module operates and how it is configured for use.
5
Page 10
Using 5300xl Features with the Access Controller xl Module
Using 5300xl Features with the Access
Controller xl Module
As the ACM uses special ports and VLANs to provide access security to
wireless devices, not all of the features of the 5300xl switch are applicable.
For example, features that provide an alternative means of authentication are
not supported on ACM downlink client ports.
Some 5300xl configurations are not allowed by the Command Line Interface
(CLI). When a CLI command fails, a message is displayed explaining why.
Warning messages are issued when an operation could potentially cause
problems managing traffic through the ACM. For example, if a downlink client
port is assigned to a non-client VLAN, traffic could enter the network without
first being authenticated and assigned specific access rights by the ACM. In
this case, a warning message is issued stating that the port is a member of a
client VLAN. In some cases Log messages are also created when an operation
is done, noting the potential conflict with ACM operation.
Note 5300xl switch ports that are not used by the Access Controller xl Module (that
is, they are not downlink client ports, or members of client VLANs) continue
to operate as regular 5300xl ports. Their operation is not affected.
The table below presents the 5300xl switch features that are not supported
for use with an ACM module.
Table 1. 5300xl Switch Features Not Supported on an ACM
Feature Explanation
802.1X
ACL
CDP
‘x’ indicates that the feature is not supported.
6
Uplink Port
x x x Not allowed.
x x Set to off for these ports.
Downlink Client Ports
Downlink Port
Client VLANs
x Has no effect if assigned. Warning issued
Page 11

Using 5300xl Features with the Access Controller xl Module
Table 1. 5300xl Switch Features Not Supported on an ACM (Continued)
Feature Explanation
Uplink Port
Configuring IP
Downlink Client Ports
Downlink Port
Client VLANs
x Not allowed.
Addresses
DHCP/DHCP Relay
IP Helper Address
Flow Control
GVRP
IGMP
Interface Monitoring
x x x x 1. GVRP cannot be enabled on an uplink,
x x x IGMP cannot be enabled on client
x x x Cannot be used as a monitoring port.
x Not allowed.
x Not allowed.
Not supported across an ACM.
downlink, or downlink client port.
2. A port in a GVRP VLAN cannot be added
to a client VLAN.
3. If GVRP is enabled on a port when it is
added to a client VLAN, it is disabled.
VLANs.As a result, it cannot be enabled on
downlink client ports.
(Port Mirroring)
Interface Provisioning:
Speed
Duplex
Flow-Control
Auto-MDIX mode
x x Fixed at 1000Mbps.
x x Fixed at Full-Duplex.
x x Not allowed.
x x Not allowed.
IP Routing/
Multicast Routing
IP Stacking
IRDP
Link Test
LLDP
‘x’ indicates that the feature is not supported.
x x Test packets not supported across an ACM.
x x Set to off.
x x No routing is done.
Not allowed.
Not supported across an ACM.
x Not allowed.
7
Page 12

Using 5300xl Features with the Access Controller xl Module
Table 1. 5300xl Switch Features Not Supported on an ACM (Continued)
Feature Explanation
MAC Auth
Meshing
Uplink Port
x x x Not allowed.
x x x Not allowed
MSTP (802.1s)
OSPF
PIM
RIP
Static VLANs
Downlink Client Ports
Downlink Port
Client VLANs
x Mesh ports cannot be a member of a client
VLAN.
An MSTP region may not span across an
ACM.
x Not allowed.
x Not allowed.
x Not allowed.
See table 2 below.
Trunkinga:
LACP
FEC
Virus Throttling
Web Auth
XRRP
‘x’ indicates that the feature is not supported.
x x x x Not allowed.
x x x x Not allowed.
x x x Not supported.
x x x Not allowed.
x Not allowed.
a. A 5300xl switch trunk group that is configured using the trunk option, can
be added to a client VLAN.
8
Page 13

Using 5300xl Features with the Access Controller xl Module
Routing Infrastructure Support
The ACM uses IP to communicate with Access Control Server 740wls, Integrated Access Managers 760wls and Access Controller 720wls. The default
gateway must be set up correctly if there is a router in the communications
path. Figure
router.
Figure 2. Accessing a 740wl or 760wl Through a Router
2 shows an ACM communicating with its 740wl/760wl through a
9
Page 14

Using 5300xl Features with the Access Controller xl Module
The ACM does not support any routing infrastructure attached to a downlink
client port. Figure 3 below shows how an ACM can be used to communicate
with a lower-level, non-routed network structure through a downlink client
port.
Figure 3. A Downlink Client Port with a Non-Routed Network Structure
10
Page 15

Using 5300xl Features with the Access Controller xl Module
Using 5300xl Switch Network Address Translation with the ACM
The Secure Access 700wl series products and the ACM provide network
address translation for client traffic. The 5300xl switch’s network address
translation feature is not recommended for use with the ACM.
The Role of VLANs
VLANs are used by the Access Controller xl Module to manage client traffic
through the switch. Downlink client ports, connecting to access points, either
directly or through an intermediate network, are assigned as untagged members to a unique VLAN that also includes the downlink port as a tagged
member. Traffic from the downlink client port, passing inbound through the
downlink port on its way to the Access Controller xl Module, is normally
tagged with the downlink client port’s VLAN ID (VID), except when traffic is
being bridged (see
policies and access policies are applied to this inbound client traffic by the
Access Controller xl Module, based, in part, on the VLAN tag the traffic carries.
In a similar fashion, ACM traffic outbound to the network uses a VLAN to
connect to the correct switch port. The uplink network port is an untagged
member of the uplink VLAN, which by default is the 5300xl DEFAULT_VLAN.
All switch ports that belong to the uplink VLAN are uplink network ports. The
uplink VLAN may be changed by creating a new VLAN and assigning the uplink
port to it as an untagged member. Any ports that belong to the new VLAN are
uplink network ports, carrying ACM traffic to and from the network.
“Operating Notes” on page 31). The correct authentication
Client VLANs
Client VLANs are special VLANs used by the module for client traffic. They
have the following characteristics:
■ Up to 24 client VLANs, depending on your configuration, may be used
on a 5300xl switch. If two Access Controller xl Modules are installed
in a 5300xl switch, the total number of VLANs used by the two
modules may not exceed 24.
■ Uplink network ports may not be members of a client VLAN.
11
Page 16

Using 5300xl Features with the Access Controller xl Module
When a port is added to a client VLAN the following changes are made to the
port:
■ Information used for ARP and MAC address processing is flushed.
■ If GVRP is enabled, it is disabled and a message is displayed.
■ If LACP passive is configured, it is disabled and a message is
displayed.
Downlink client ports must be members of some other VLAN before they can
be removed from a client VLAN. If you use the no access-controller <slot-id>
client-ports [e] <port-list> command to remove an untagged downlink client
port with no other VLAN memberships from a client VLAN, the port is
automatically placed in the DEFAULT-VLAN as an untagged member. If you
attempt to remove a tagged downlink client port that belongs to no other
VLAN, the removal fails. Add the port to another VLAN, then delete it from the
client VLAN.
Client VLANs can be configured without specifying any switch ports using the
access-controller <slot-id> client-ports vlan <vlan-list> command from the configuration context. The VLANs are created with only the downlink port,
<slot-id>DP, as a tagged member. Later you can use VLAN commands from the
5300xl CLI to add switch ports to this VLAN as downlink client ports.
12
Page 17

Using 5300xl Features with the Access Controller xl Module
Static VLAN Features Supported on Client VLANs
Client VLANs are special and they don’t support all of the features of a regular
5300xl static VLAN. Table 2 below outlines the feature limitations of client
VLANs.
Table 2. 5300xl Static VLAN Features on Client VLANs
5300xl Static VLAN Feature Client VLAN Support
ACLs
IGMP
IP Address
IP Helper Address
IRDP
Management VLAN
Multicast routing
OSPF
PIM
Primary VLAN
Protocol VLAN
RIP
XRRP
Do not work. A warning issued.
Not allowed.
Not allowed.
Not allowed.
Not allowed.
A client VLAN may not be used.
Not allowed.
Not allowed.
Not allowed.
A client VLAN may not be used.
A client VLAN may not be used.
Not allowed.
Not allowed.
13
Page 18

General Operating Rules
General Operating Rules
■ Uplink and downlink ports cannot be members of the same VLAN.
■ Switch 5300xl features used to manage ports that are connected to
bridges don’t apply, as the ACM is not a bridge.
■ A client VLAN containing the downlink port, <slot-id>DP, is automat-
ically created when the ACM is installed in a 5300xl switch. The VID
for this VLAN is the vlan-base (default: 2000). You cannot remove a
client VLAN if it is the only remaining VLAN with the downlink port
as a member.
■ Client VLANs may not be configured as the Management or Primary
VLAN on the 5300xl switch.
■ Multiple subnets on a downlink client port are not supported.
■ Shut down the ACM
• before resetting or reloading the 5300xl chassis
• before turning off the 5300xl chassis.
• before removing the module from the 5300xl chassis.
See the shutdown command in “ACM Configuration Commands Summary
and Syntax” on page 20.
Configuring the ACM on the Network
By default, the ACM uses DHCP to get an IP address. The uplink port of the
ACM must be an untagged member of a VLAN that can communicate with the
740wl/760wl. If that communication is routed, the Default gateway: needs to be
present in the IP address configuration. When the IP address is assigned
manually be sure to configure the Default gateway: if it is needed. (See
the ACM’s Extended CLI” on page 27.)
Use the following commands to configure an IP address manually.
Note ‘HPswitch’ is used as a generic prompt for all 5300xl switches. The term ‘id’ is
used below for ‘slot-id’ to shorten the command prompt.
14
“Using
Page 19

Configuring the ACM on the Network
HPswitch (config)# access-controller <slot-id>
where <slot-id> is the slot in the 5300xl where the ACM is installed.
HPswitch (access-controller-id)# ip address <<ip-addr>/<1-32> |<ip-addr> <mask>>
where <ip-addr>/<1...32> is the selected address in CIDR notation (/mask
bit number), for example 10.1.2.3/24.
<ip-addr> <mask> provides the selected address and the mask.
If necessary, use the following command to set or change the default gateway:
HPswitch (access-controller-id)# ip default-gateway <ip-addr>
where <ip-addr> is the numeric IP address of the default gateway, for
example 10.1.2.3.
Use the IP address of the 740wl/760wl and its shared secret to establish
communications with the ACM.
HPswitch (access-controller-id)# access-control-server ip <ip-addr> secret
<secret> <secret>
where <ip-addr> is the address of the 740wl/760wl
<secret> is the shared secret configured on the 740wl/760wl.
In the following example, an ACM establishes communications with an access
control server with IP address 13.13.13.8. The access control server has a
shared secret of 7734Oh. The show status command is used to confirm that
communications has been established, indicated by a time value displayed
(2 secs) in the Connected: field.
15
Page 20

Configuring the Access Controller xl Module
Configuring the Access Controller xl
Module
Once the module has an IP address and is communicating with its Access
Control Server or Integrated Access Manager, configure downlink client ports,
client VLANs, uplink network ports, and the uplink VLANs on the 5300xl
switch.
Configuring Downlink Client Ports
Each downlink client port is automatically assigned to a unique client VLAN.
The VID of the first client VLAN configured is specified by the vlan-base
(default: 2000). Additional client VLANs use the next available sequential VID
(2001, 2002, 2003, ...). If two Access Controller xl Modules are installed in the
5300xl switch, the vlan-base is the VID of the first client VLAN configured by
either ACM. The next client VLAN configured on either ACM uses the next
available sequential VID. Switch ports become untagged members of the client
VLAN. The downlink port also becomes a tagged member of the client VLAN.
16
From the CLI command prompt at the global configuration level, enter
HPswitch (config) #access-controller <slot-id> client-ports <port list>
where
<slot-id> is the slot letter where the module is installed.
<port list> is the switch port(s) to be used as downlink client ports.
For example:
HPswitch (config)# access-controller b client-ports a2,a6
assigns two downlink client ports and two new client VLANs (see Figure 4).
BDP, the downlink port for the module in slot B, is a tagged member of both
client VLANs.
Page 21

Configuring the Access Controller xl Module
HP ProCurve Switch 5308xl(config)# access-controller b client-ports a2,a6
HP ProCurve Switch 5308xl(config)# access-controller b
HP ProCurve Switch 5308xl(access-controller-B)# show vlans
Downlink:
VLAN ID VLAN Name Ports
2000 VLAN2000 A2,BDP
2001 VLAN2001 A6,BDP
Uplink:
VLAN ID VLAN Name Ports
1 DEFAULT_VLAN A1,A3-A5,A7-A24,BUP
HP ProCurve Switch 5308xl(config)# show vlans 2000
Status and Counters - VLAN Information - Ports - VLAN 2000
802.1 Q VLAN ID : 2000
Name : VLAN2000
Statu s : Port-based
Voice : No
Port Information Mode Unknown VLAN Status
----- ----------- -------A2 Untagged Disable Down
BDP Tagged Disable Up
------------ ----------
Figure 4. Configuring A Downlink Client Port
Notes on Depending on how many VLANs are already configured in the 5300xl switch,
Creating
Downlink Client
Ports
the following messages may occur:
■ Maximum Number of VLANs (X) has already been reached
Increase the maximum number of VLANs allowed on the switch.
■ Command will take effect after saving configuration
and reboot.
The switch requires a reboot to incorporate the new client VLANs into
the system. If downlink client ports are added over a period of time,
a reboot may be required after each addition to make the client VLAN
available.
17
Page 22

Configuring the Access Controller xl Module
■ Maximum number of client VLANs have been configured.
Operation failed.
The maximum number of client VLANs for this configuration has been
reached. An existing client VLAN must be removed before the
requested VLAN can be added.
Changing the VLAN-Base
When the ACM is installed in the 5300xl switch, a VLAN is created for the
internal downlink port (<slot-id>DP). By default, this client VLAN is VLAN ID
2000, the vlan-base. You may change this using the following command.
HPswitch (Config)# access-controller vlan-base <2-4094>
where <2-4094> is the starting VLAN ID (VID) used when a client VLAN is
configured.
The vlan-base is used by the [no] access-controller <slot-id> client-ports [ether-
net] < port-list > command when it configures client VLANs for the specified
switch ports. The very first port specified for use as a downlink client port
becomes an untagged member of the vlan-base VID. Subsequent downlink
client ports are assigned as untagged members of the next available sequential
VID, beginning at the vlan-base.
18
Configuring Client VLANs
You may configure a client VLAN with a specific VID, containing just the
downlink port as a tagged member. Later, you can add an untagged 5300xl port
as a downlink client port to carry client traffic.
Use the following command to configure a client VLAN:
HPswitch (Config)# access-controller <slot-id> client-ports vlan <vlan-list>
where <slot-id> is the slot letter where the module is installed.
<vlan-list> is the VID for the desired client VLAN.
Configuring Uplink Network Ports
Uplink network ports are any switch ports that are members of the uplink
VLAN, that is, the VLAN where the ACM’s internal uplink port is an untagged
member. By default, the uplink port (<slot-id>UP) is an untagged member of
the DEFAULT-VLAN on the 5300xl switch. In this default configuration, all
members of the DEFAULT-VLAN are uplink network ports.
Page 23

Configuring the Access Controller xl Module
Configuring the Uplink VLAN
To change the uplink VLAN, make the internal uplink port an untagged member
of a new VLAN. Be sure that the new VLAN allows communication with the
740wl/760wl, or communications is lost.
HPswitch (Config)# vlan 25 untagged <slot-id>up
where slot-id is the 5300xl switch slot where the ACM module is installed.
This command configures a new uplink VLAN, VID 25, for the ACM module
installed in slot n.
19
Page 24

Configuring the Access Controller xl Module
ACM Configuration Commands Summary and Syntax
Command Page
Configuration Context
access-controller <slot-id> 20
[no] access-controller <slot-id> client-ports [e] < port-list > 21
[no] access-controller <slot-id> client-ports vlan < vlan-list > 22
access-controller <slot-id> reload 22
access-controller <slot-id> shutdown 22
access-controller vlan-base <2-4094> 22
Access Controller Context
access-control-server ip <ip addr> secret <secret> <secret> 22
enable extended-commands 23
exit 23
ip address <<ip-addr>/<1-32> | <ip addr> <mask>> 23
[no]
ip default-gateway <ip-addr> 23
[no]
[no] page 23
terminal <length <2-1000> | width <61-1920>> 23
20
Configuration Context Command Syntax
Syntax:
access-controller <slot-id>
Changes the CLI to the access controller context for the
access controller in slot-id (a - h). The exit command
returns the CLI to the configuration context.
Page 25

Configuring the Access Controller xl Module
Syntax: [no] access-controller <slot-id> client-ports [ethernet] < port-list >
Assigns switch ports (port-list) to separate client VLANs
for the access controller in slot-id (a - h). The ports are
removed from all other VLANs. GVRP and LACP port
provisioning are disabled.
The client VLAN has the following port membership:
the switch port, as an untagged member, and the ACM’s
downlink port (<slot-id>DP), as a tagged member.
The vlan-base VID is configured when the ACM is
installed in the switch. By default, this is VLAN 2000,
whose only member is the downlink port. The very first
time this command is used, the first switch port configured becomes a member of client VLAN vlan-base
VID. For example, by default, the first time this command is used to assign a switch port to a client VLAN
it becomes an untagged member of VLAN 2000. The
next client VLAN configured takes the next available
sequential VID, starting from the vlan-base.
Use the no form of the command to remove downlink
client ports from ALL client VLANs associated with
the module in <slot-id>. If the removed port has no other
VLAN memberships it is automatically placed in the
DEFAULT VLAN as an untagged member.
If a client VLAN that contained the removed port was
configured using an access-controller <slot-id> client-
ports [ethernet] < port-list > command and the ACM’s
downlink port is the only remaining member, the client
VLAN is also removed.
The no form of this command does not remove a client
VLAN configured using the access-controller <slot-id>
client-ports vlan < vlan-list > command.
21
Page 26

Configuring the Access Controller xl Module
Syntax: [no] access-controller <slot-id> client-ports vlan < vlan-list >
Syntax: access-controller <slot-id> reload]
Syntax: access-controller <slot-id> shutdown]
Syntax: access-controller vlan-base <2-4094>]
Configures client VLANs with the VIDs given, containing only the downlink port, (<slot-id>DP), as a tagged
member.
The no form can be used to remove client VLANs that
were configured using the access-controller <slot-id>
client-ports vlan < vlan-list > command and contain only
the downlink port.
Reboots the access controller in slot-id with the current
software version.
Halts the access controller in slot-id.
Sets the starting VLAN ID (VID) for client VLANs
configured by the access-controller <slot-id> client-ports
< port-list > or the access-controller <slot-id> client-ports
vlan < vlan-list> commands. Valid VIDs are 2 - 4094.
22
Access Controller Context Command Syntax
Syntax: access-control-server ip <ip addr> secret <secret> <secret>]
Specifies the numeric ip address and shared secret for
the access control server (740wl or 760wl) that provides services to the ACM.
The secret must match the shared secret configured on
the 740wl/760wl. If the shared secret contains spaces,
enclose the secret in double quotes (“ ”). The secret must
be entered twice, identically.
Page 27

Configuring the Access Controller xl Module
Syntax: enable extended-commands
Changes the CLI to the access controller extended commands context. A limited set of commands from the
720wl CLI is provided here. See “Using the ACM’s
Extended CLI” for more information.
Syntax: exit
Leaves the access controller context and returns the CLI
to the global configuration context.
Syntax: [no] ip address <<ip-addr>/<1-32> | <ip addr> <mask>>
Statically configures the ip address and subnet mask
for the ACM. The no form removes the fixed ip address
and enables DHCP. (Default: DHCP)
Syntax: [no] ip default-gateway <ip-addr>
Statically configures the numeric ip-addr of the default
gateway. If DHCP is enabled, this command overrides
the default gateway supplied by DHCP.
Syntax: [no] page
Turns on or off paging of the CLI command responses
and CLI command stack replay (the up arrow function).
Syntax: terminal <length <2-1000> | width <61-1920>>
length <2-1000> Sets the number of lines that are displayed between pauses when page is on. The initial
setting is inherited from the previous context. This
setting remains in effect when this context is exited.
width <61-1920> Sets the maximum line width to be used
for CLI output or CLI input. Lines longer than the
specified value wrap to the next line. The initial setting
is inherited from the previous context. This setting
remains in effect when this context is exited.
23
Page 28

Displaying Access Controller xl Status from the 5300xl CLI
Displaying Access Controller xl Status
from the 5300xl CLI
Show commands are available in both the configuration context and the
access controller context of the 5300xl CLI. These commands display ACM
status and configuration.
ACM Display Commands Summary and Syntax
Command Page
Configuration Context
show access-controller <slot-id> 25
[client-ports] 25
[uplinks] 25
show access-controller vlans 25
show access-controller vlan-base 26
24
Access Controller Context
show ip 26
show status 26
show temperature 27
show vlans 25
Page 29

Displaying Access Controller xl Status from the 5300xl CLI
Configuration Context Command Syntax
Syntax: show access-controller <slot-id>
Displays the following for the access controller in slot-id (a - h).
Versions
Current status
Uplink MAC Address
ACM version information for
support staff.
BIOS error
booted
booting
booting timed out
configuration fault
failed to boot
halted
initializing
not responding
performing self-test
rebooting
running
self-test failed
shutting down
shut down (safe for removal)
ACM MAC address that appears in
the 740wl/760wl Administrative
Console as the System ID.
Syntax: show access-controller <slot-id> [client-ports]
Displays the downlink client ports for each client VLAN
configured on the access controller in slot-id (a - h)
Syntax: show access-controller <slot-id>
Displays the uplink network ports configured on the
access controller in slot-id (a - h)
Syntax: show access-controller vlans
Displays the 802.1Q VID and Name of all configured
client VLANs on the 5300xl switch. If two ACMs are
installed, their client VLANs are presented in the list.
[uplinks]
25
Page 30

Displaying Access Controller xl Status from the 5300xl CLI
Syntax: show access-controller vlan-base
Displays the starting VLAN ID (VID) for client VLANs
configured by the access-controller <slot-id> client-ports
< port-list > or the access-controller <slot-id> client-ports
vlan < vlan-list> commands.
Access Controller Context Command Syntax
Syntax:
Syntax: show status
show ip
Displays the current IP configuration for the ACM,
including:
Hostname:
Domain Name:
IP Address:
DHCP enabled:
Default gateway:
DHCP server:
DNS servers:
WINS servers:
Displays an overview of the ACM’s status, including:
Uptime:
Access Control
Server:
Connected:
Active Clients:
26
Page 31

Managing the ACM
Syntax: show temperature
Displays the current temperature in degrees Celsius of
the main processor of the ACM module.
Syntax: show vlans
Displays the VLAN ID, VLAN Name, and Ports for all
VLANs associated with the ACM’s uplink and downlink
ports.
Managing the ACM
Once the module is installed and configured, most management tasks are done
on the Access Control Server 740wl or Integrated Access Manager 760wl, using
the Administrative Console. The Access Controller Module is managed in the
same manner as a 720wl. For more information, see the HP ProCurve Secure
Access 700wl Series Management and Configuration Guide, available on the
CD shipped with the ACM, or from the ProCurve Networking Web site at
http://www.hp.com/go/procurve. (Click on Technical support, then Product manuals (all)).
Using the ACM’s Extended CLI
A set of extended commands, available from the Access-Controller context,
may be used to configure an ACM or display its status. These commands are
a subset of the 720wl CLI commands. They are documented in the HP
ProCurve Secure Access 700wl Series Management and Configuration
Guide, available on the CD shipped with the ACM, or from the ProCurve
Networking Web site at http://www.hp.com/go/procurve. (Click on Technical
support, then Product manuals (all)).
To access this context, type the following in the ACM context:
HPswitch(access-controller-id) # enable extended-commands
The command line prompt for the extended context is:
27
Page 32

Managing the ACM
HPswitch(access-controller-id-ext)#
The available commands are listed below. Detailed descriptions are found in
Appendix A, “Command Line Interface” in the HP ProCurve Secure Access
700wl Series Management and Configuration Guide.
Command
[no] ip address <<ip-addr>/<1-32> | <ip-addr> <mask>>
[no] ip default-gateway <ip-addr>
[no] page
access-control-server ip <ip-addr> secret <secret> <secret>
add bridging <atalk | cdp | wnmp> | <custom-bridging-string>
cancel upgrade
Clear Commands
clear accesscontrolserver
clear dhcpserver
clear dns
clear domainname
clear gateway
clear hostname
clear logs
clear sharedsecret
clear upgradeproxy
delete bridging <atalk | cdp | wnmp> | <custom-bridging-string>
enable extended-commands
exit
factoryreset
get upgrade <url> <key> [mindowngrade | reboot | version]
help
logoff client <all | mac <mac-addr>>
reboot [downgrade | same | upgrade]
Set Commands
set accesscontrolserver <ip-addr>
set bridging <on | off>
set clientprobes <interval> <timeout>
28
Page 33

Managing the ACM
Command
set dhcp <on | off>
set dhcpserver <ip-addr>
set dns <primary-ip-addr> [<secondary-ip-addr>]
set domainname <domain>
set forwardipbroadcasts <all | none | on <port> | off <port> | <port>>
set gateway <ip-addr>
set hostname <host>
set ip <ip-addr> [<mask>] | <ip-addr>/<1-32>
set logopt addcat <all | error | info | none | session>
set logopt catlevel <error | info | none | session> <critical | major | minor | trivial | never>
set logopt cats <mask>
set logopt delcat <all | error | info | none | session>
set logopt level <critical | major | minor | trivial | never>
set logopt nofuncs <on | off>
set logopt noids <on | off>
set logopt oflags <mask>
set logopt shorttrace <on | off>
set logopt string <logparam>
set sharedsecret <secret> <secret>
set upgradeproxy [<on | off>] [host <ip-addr> [<port> ]] [user <user> [<password>]]
Show Commands
show accesscontrolserver
show bridging
show client mac <mac-addr> [ rights ]
show clientprobes
show clients [mac <mac-addr>]
[sort <mac | ip | user | machine | port | sessions | idle>] [reverse]
show dhcpserver
show forwardipbroadcasts
show id
show ip
show logopt [level | cats | oflags | catlevel]
show logs [<critical | major | minor | trivial | never>] [cat <all | error | info>] [max <lines>]
[for <count> <seconds | minutes | hours | days | weeks | months>]
[search <quoted-text>] [reverse]
29
Page 34

Command
show natdhcp
show product
show serial
show sharedsecret
show status
show syslogserver
show temperature
show time
show upgrade
show upgradeproxy
show version
show vlans
show vpn
terminal length <2..1000>
terminal width <61…1920>
Downloading New Software to the Module
New software is loaded through the Access Control Server or Integrated
Access Manager using the Administrative Console.
Resetting the Module to Factory Defaults
The ACM may be returned to the factory default configuration using one of
the following methods.
■ Using the factoryreset command in the ACM’s extended command
context in the 5300xl CLI.
■ Boot another, non-ACM module in the slot. This also removes the
encoded ACM configuration information from the show running or
show config command output.
■ Use the erase startup-config command in the 5300xl CLI.
■ Return the 5300xl chassis to its factory default configuration using
the Reset and Clear keys on the front panel. (Refer to “Clear/Reset:
Resetting to the Factory Default Configuration” in the Troubleshooting appendix of the Management and Configuration Guide for
your switch.) This also resets the ACM.
Page 35

Operating Notes
Operating Notes
■ Bridged protocols, such as Appletalk, are supported through a single
downlink client port, whose client VLAN contains the downlink port
as an untagged member. This must be configured manually on the
switch. Each ACM may have one downlink client port configured to
support bridged protocols.
■ HP recommends that a downlink client port be a member of only one
client VLAN. Downlink client ports should not be members of any
other VLANs, as this would allow access to unauthorized clients. If a
downlink client port must be a member of another VLAN, configure
filtering on the 740wl or 760wl to remove network traffic that might
be sent to unauthorized ports.
■ HP recommends that you create a Management VLAN on your 5300xl
switch. This secures the management of the 5300xl switch, allowing
it to be managed only by members of the Management VLAN.
■ Client-to-client communications is not possible through an ACM.
■ ProCurve Manager does not support the ACM at this time. Support is
expected later in 2005.
BIOS POST Event Log Messages
If a critical BIOS power on self test (POST) failure occurs when the ACM is
inserted into a slot in a 5300xl chassis, the message below is posted to the
Event Log. The 5300xl switch resets the ACM, up to two times (a total of three
attempts to pass the POST). If the ACM fails three consecutive times, the
module does not power on. The 5300xl switch can operate successfully if this
occurs.
31
Page 36

BIOS POST Event Log Messages
Slot <slot-id> Access Control Module Bios POST tests failed,
Post bitmap = 0xXXXX
The POST error bitmap values are explained below.
0x0001 IDE failure.
0x0002 System memory failure.
0x0004 Shadow memory failure.
0x0020 Protected memory failure.
0x0040 CMOS not ready error.
0x0100 Periodic timer failure.
0x0800 Device configuration error.
0x1000 Memory configuration error.
0x2000 Non-volatile RAM failure.
0x4000 External or CPU cache failure.
0x8000 Level2 cache failure.
32
Page 37

BIOS POST Event Log Messages
— This page is intentionally unused. —
33
Page 38

© 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development
Company, LP. The information contained
herein is subject to change without notice.
March 2005
Manual Part Number
5991-2136
 Loading...
Loading...