Page 1

HP VMware ESXi 4.0
Getting Started guide
Page 2

Overview
Thank you for downloading HP VMware ESXi 4.0. HP has seamlessly integrated
VMware ESXi, delivering active HP ProLiant management and consolidated lifecycle
management for a consistent, reliable ProLiant experience.
HP CIM (Common Information Module) providers proactively surface hardware
monitoring data to deliver the most up-to-date server state information possible. HP
CIM providers and VMware ESXi provide active hardware management using HP SIM
(Systems Insight Manager).
You can update VMware ESXi using the standard VMware update tools. The
integrated hypervisor installation is partitioned with redundant images, enabling a
robust upgrade and recovery process.
The
HP VMware ESXi 4.0 Getting Started Guide is for ESXi 4.0 Standalone Edition or
as a part of a HP VMware vSphere full licensed product.
The ESXi Stand-Alone Edition is well suited for single server virtualization installations
and is managed using the free VMware vSphere Client management console. HP
Technical Software Support and Update Service is optional and can be purchased as
a support pack.
If downloaded from HP, the installation ISO includes a trial license for standalone
edition. To obtain a permanent license for standalone edition, go to the
VMware
website
(https://www.vmware.com/tryvmware/?p=esxi) and register to obtain the
serial number license.
You can also upgrade HP VMware ESXi Stand-Alone Edition to any of the fully
licensed products for VMware vSphere including Essentials, Essentials Plus, Standard,
Advanced, Enterprise and Enterprise Plus editions. HP VMware vSphere products
includes one-year, 9x5 unlimited HP Technical Software Support and Update Service
and are upgradeable to a 3, 4, or 5 year Technical Software Support and Update
Service.
To learn more about license delivery and enabling enterprise entitlement, see
Activating standalone license ("Activating stand-alone license" on page 7) or
Upgrading to a full license (on page 7).
Page 3
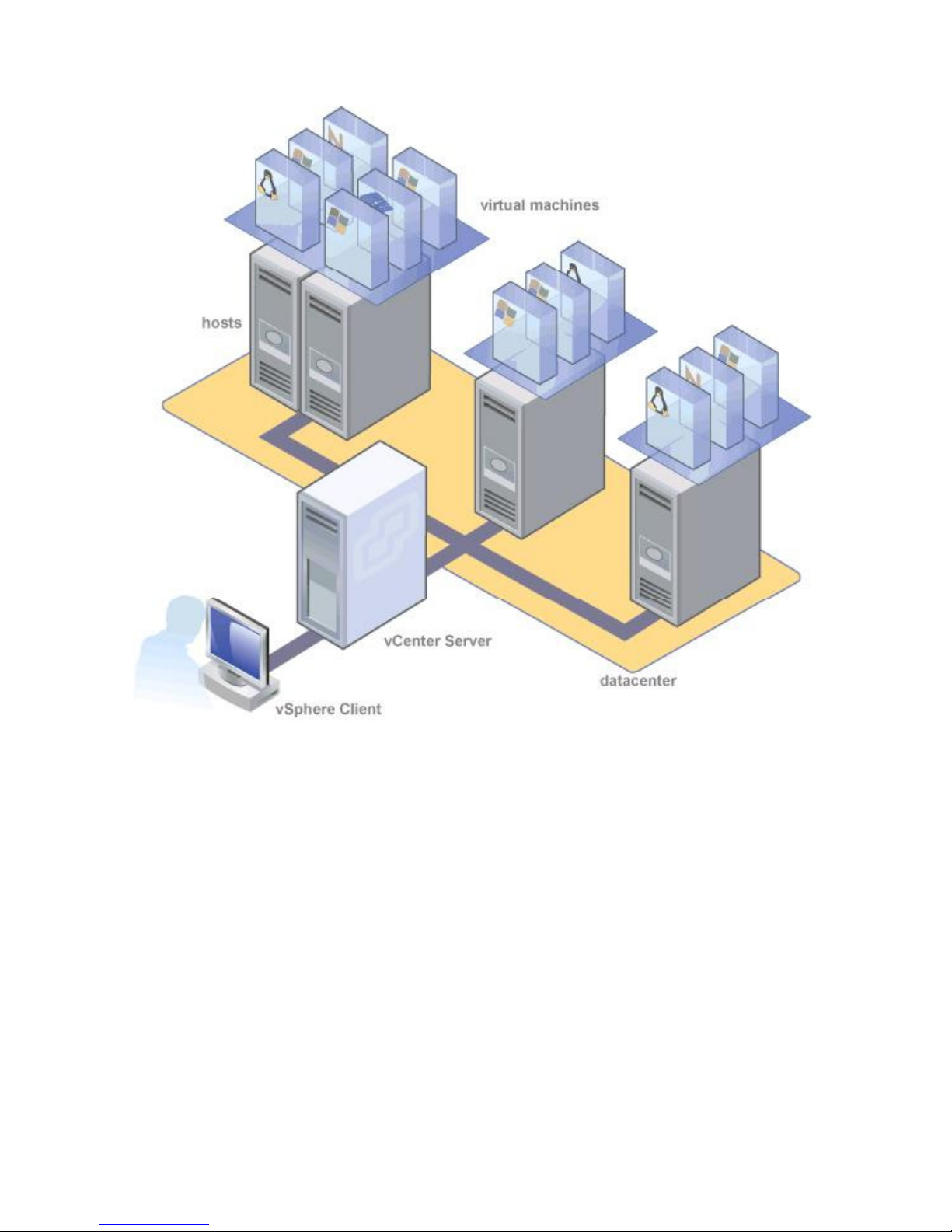
Understanding VMware infrastructure
VMware vSphere includes the following components:
Virtual machine—A virtual machine is a software-based computer capable of running
an operating system such as Microsoft® Windows® or GNU/Linux just as if the
operating system is installed on a physical machine.
Host—A host is a physical machine running platform virtualization software such as
ESXi. Hosts provide processor, memory, storage, and network resources for one or
more virtual machines.
vCenter Server—vCenter Server continuously monitors your virtual infrastructure,
automates system administration tasks, and centralizes remote management sessions. It
coordinates the resources and activities of individual hosts to efficiently distribute
virtual machines and tolerate hardware downtime across a data center.
vSphere Client—vSphere Client is the primary interface for interacting with hosts and
virtual machines. vSphere Client can manage a standalone host by connecting directly
to the host, or manage multiple hosts by connecting to a vCenter Server machine.
Page 4

Additional HP components that complete your
virtualization infrastructure
Management network—A management network enables the server administrator to
manage discrete, physical servers without relying on a general purpose
communications network. This dedicated network enables a reliable connection to the
hardware in the event of a network failure.
Virtual machine communication network—A virtual machine communication network is
built on the traditional, general-purpose communication network. As with physical
servers, virtual machine traffic is brokered through a general-purpose network if the
virtual machines are on different, discrete servers. Virtual machine communication on
the same physical server is handled by a virtual switch within the server.
HP storage network—A storage network enables virtual machines to access Storage
Area Network (SAN) devices similarly to physical servers. The medium for a storage
network can be Fibre Channel or Ethernet. HP recommends HP StorageWorks SAN
solutions.
Configuring your HP ProLiant server to use
VMware ESXi
HP recommends upgrading to the latest ProLiant firmware revisions. For more
information, see your server documentation.
VMware ESXi 4.0 only supports the following installation destinations:
• Any HP supported hard drive
• Secure Digital (SD) memory card
o HP 4GB SD flash media
o HP part number 580387-B21
o HP spare kit part number 583306-001
• Flash media (USB flash drive)
o HP 4GB USB flash media drive key
o HP part number 580385-B21
o HP spare kit part number 583307-001
To configure your ProLiant server using VMware ESXi:
1. Download the installation ISO from the
HP website
(
http://h20392.www2.hp.com/portal/swdepot/index.do) or VMware's website
(
https://www.vmware.com/tryvmware/?p=esxi).
2. Burn the installation ISO to a CD, or move the ISO image to a location
accessible using the virtual media capabilities of HP iLO 2.
Page 5

NOTE: The CD-is bootable. Boot the server and choose to install
the HP VMware ESXi product either to the hard drive or to flash
media (USB key or SD card). You must install the flash media into
the internal port on your ProLiant server.
3. Set up the server hardware, and if desired, connect the server to your network.
4. If you install to flash media (USB or SD card), you must install the flash media
into the internal port on your ProLiant server.
For instructions on how to access the internal flash media (USB or SD card) port,
see the server documentation included with your server.
For hardware requirements, see the server documentation included with your
server.
5. Access the server console in one of the following ways:
o Locally—Use your local keyboard and monitor.
o Remotely—Use iLO Integrated Remote Console remotely from a network
client using a web browser.
Remote setup requires HP iLO2 Advanced Pack, which is sold separately for
HP ProLiant ML and DL servers. The remote graphics capability is included
with BL servers.
IMPORTANT: After you boot up the server, you must press the
correct function key when prompted to enter setup mode to
configure boot order, configure hardware virtualization, and
configure iLO and the Smart Array controller. Familiarize yourself
with the following steps and prompts; each prompt is available
for only a few seconds during the boot process.
If you are installing to the hard drive, proceed to step 8.
6. To enable flash media (USB flash drive or SD card):
a. Configure your flash device to boot before the hard drive. By default, flash
media is configured to boot before the hard drive.
b. Boot the server, and then press
F9 to enter ROM Based Setup Utility (RBSU).
c. Scroll down to Standard Boot Order (IPL), and press
Enter.
d. To modify the boot order, select the device you want to move, and press
Enter. A menu appears to change the device boot order.
e. Ensure the flash media is set to boot before the hard drive.
7. Enable CPU virtualization.
For CPU-specific virtualization capabilities, you can select
Intel® Virtualization
Technology
or AMD® Virtualization. You must perform this step for supporting
Windows® 64 bit operating systems and all guest 64 bit operating systems such
as Linux.
Page 6

a. If you are not in RBSU, boot the server, and then press F9 to enter ROM
Based Setup Utility (RBSU).
b. Scroll down to Advanced Options, and press
Enter.
c. Scroll down to Processor Options, and press
Enter.
d. Scroll down to the servers supported processor (either Intel® Virtualization
Technology or AMD® Virtualization), and press
Enter.
e. At the next screen select
Enable, and press Enter.
f. Save configuration changes, and then exit. The server reboots.
8. To configure iLO network parameters, directory settings, global settings, and user
accounts, when prompted at POST, press
F8.
For more information, see the
HP Integrated Lights-Out 2 User Guide.
9. To create, view, or delete a logical drive for the Smart Array Controller using
local storage, press
F8 when prompted.
For more information, see
Configuring Arrays on HP Smart Array Controllers
Reference Guide
.
Installing HP VMware ESXi 4.0
Installing the software image locally
1. Place the installation CD into the CD-ROM drive, and then boot the server.
2. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Installing the software image remotely using iLO 2
1. Verify that the server has the appropriate iLO license to use Virtual Media, open
a web browser on your local machine, and then log in to iLO.
HP c-Class servers include a license for Virtual Media. For other servers, the HP
iLO2 Advanced Pack license is required and is sold separately.
2. Select the Virtual Media tab, and then select the
Virtual Media Applet.
3. Choose one of the following options:
o Local Media Drive
i. Under the Virtual CD/DVD-Rom section, select
Local Media Drive.
ii. From the menu, select the drive letter of the desired physical CD/DVD-
ROM drive on your client computer.
iii. Click
Connect. The connected drive icon turns green.
o Local Image File
i. Under the Virtual CD/DVD-ROM section, select
Local Image File.
ii. Enter the path or file name of the image (ISO file) in the text box or click
Browse to locate the image file.
iii. Click
Connect. The connected drive icon turns green.
Page 7

4. Follow the prompts generated by the installation CD to complete the installation.
If performing restoration or recovery, when installation is complete, restore from
backup files.
5. (Optional) To discover and manage this server, configure HP SIM.
For more information about hosting and managing a VMware ESXi virtualization
environment on ProLiant servers, see the
HP website
(
http://www.hp.com/go/VMware).
For more information about VMware and setting up your virtualized environment,
see the
VMware website (http://www.vmware.com/products/vi/esx/).
Activating stand-alone license
When downloading the ESXi image from HP or VMware, the installation ISO includes
a trial serial number. To obtain a permanent license serial number:
1. Register at the
VMware website
(
https://www.vmware.com/tryvmware/?p=esxi).
2. Download the serial number.
3. Use the vSphere Client to insert the license serial number.
Upgrading to a full license
If you purchased a license for VMware vSphere Essentials, Essentials Plus, Standard,
Advanced, Enterprise or Enterprise Plus versions, follow the instructions included in
your package to redeem and apply the license.
Updating VMware ESXi 4.0
Updates and patches for VMware ESXi are provided and delivered by VMware. These
updates and patches include the latest ESXi software from VMware as well as updated
CIM providers from HP.
The updates and patches are delivered and installed by VMware Update Manager
(VUM). For more information on this process, consult the
VUM Administration Guide
(
http://www.vmware.com/pdf/vi3_vum_10_admin_guide.pdf).
Recovering from a system failure
If you encounter a system failure and need to reinstall the software, see Installing HP
VMware ESXi.
IMPORTANT: Using the installation CD completely erases all
existing data and user configuration. All preconfigured settings,
user data and license information is lost. After reinstalling the
software you must reapply your licenses.
Page 8

© Copyright 2008, 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP
products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such
products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.
HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying.
Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software
Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government
under vendor’s standard commercial license.
Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Intel is a trademark or registered trademark of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and other countries.
AMD is a trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Part Number 509678-004
December 2009 (Second Edition)
 Loading...
Loading...