HP Vectra VT6, Vectra XU6 Technical Reference Manual

Technical Reference
Manual
Hardware and BIOS
HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
and
HP Vectra VT 6/xxx PC
January 1996

Table of Contents
NOTICE 3
PREFACE 4
CONVENTIONS 5
BIBLIOGRAPHY 5
1 SYSTEM OVERVIEW 6
EXTERNAL FEATURES 6
INTERNAL FEATURES 7
SPECIFICATIONS AND CHARACTERISTIC DATA 7
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS 8
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION 8
ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATIONS 9
DOCUMENTATION 9
WHERE TO FIND THE INFORMATION 10
2 SYSTEM BOARD 12
PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS AND FEATURES 12
DEVICES ON THE PROCESSOR-LOCAL BUS 15
INTEL PENTIUM PRO (P6) MICROPROCESSOR 15
CACHE MEMORY 16
PROCESSOR-LOCAL BUS 17
OPTIONAL SECOND MICROPROCESSOR 17
MAIN MEMORY 18
DEVICES ON THE PCI BUS 19
SMALL COMPUTER SYSTEM INTERFACE (SCSI) 19
INTEGRATED DRIVE ELECTRONICS (IDE) 19
OTHER PCI ACCESSORY DEVICES 20
DEVICES ON THE ISA BUS 21
ULTRA I/O CONTROLLER 21
LITTLE BEN 22
AUDIO CONTROLLER 2 2
SYSTEM ROM 23
OTHER ISA ACCESSORY DEVICES 23
3 INTERFACE BOARDS AND MASS-STORAGE DRIVES 25
AVAILABLE VIDEO RESOLUTIONS 25
VESA CONNECTOR 27
VIDEO BIOS 27
ERROR DIAGNOSTICS AND SUGGESTED CORRECTIVE ACTIONS 27
HP PCI INTEGRATED 10/100 VG INTERFACE 28
ERROR DIAGNOSTICS AND SUGGESTED CORRECTIVE ACTIONS 29
MASS-STORAGE DRIVES 29
HARD DISK DRIVES 29
FLEXIBLE DISK DRIVES 30

CD-ROM DRIVES 30
4 HP BIOS 31
SETUP
BIOS 36
PROGRAM 31
I/O ADDRESSES USED BY THE SYSTEM* 36
SYSTEM MEMORY MAP 37
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION 37
BIOS VERSION NUMBER 37
YEAR OF THE ROM BIOS RELEASE 38
WEEK OF THE ROM BIOS RELEASE 38
HP BIOS I/O PORT MAP 39
ADDRESSING SYSTEM BOARD COMPONENTS 40
5 POWER-ON SELF-TEST ROUTINES 42
VIEWED ON THE SCREEN 42
ERROR CODES 44
SUGGESTIONS FOR CORRECTIVE ACTION 47

NOTICE
Information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
Hewlett-Packard makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but
not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular
purpose. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this
material.
Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential
damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
Hewlett-Packard assumes no responsibility for the use or reliability of its software on equipment
that is not furnished by Hewlett-Packard.
This document contains proprietary information which is protected by copyright. All rights are
reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another
language without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard Company.
Centronics® is a U.S. registered trademark of Centronics Data Computer Corporation.
Microsoft®, Windows® and MS-DOS® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Novell® and Netware® are registered trademarks of Novell Inc.
O/S2™ is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
NextStep™ is a trademark of Next Incorporated.
Pentium™ is a trademark of Intel Cor[oration.
SCO UNIX® is a registered trademark of the Santa Cruz Operation.
Solaris™ is a trademark of Sun Microsystems Incorporated.
SoundBlaster™ is a trademark of Creative Technology Limited.
©1996 Hewlett-Packard Company
PREFACE
This manual is a technical reference and BIOS document for engineers and technicians providing
system level support. It is assumed that the reader possesses a detailed understanding of ATcompatible microprocessor functions and digital addressing techniques.
Technical information that is readily available from other sources, such as manufacturer’s
proprietary publications, has not been reproduced.
This manual contains summary information only. For additional reference material, refer to the
bibliography.

CONVENTIONS
The following conventions are used throughout this manual to identify specific elements:
• Hexadecimal numbers are identified by a lower case h.
For example, 0FFFFFFFh or 32F5h
• Binary numbers and bit patterns are identified by a lower case b.
For example, 1101b or 10011011b
BIBLIOGRAPHY
• HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
• HP Vectra VT 6/xxx PC
• HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC and HP Vectra VT 6/xxx PC
• HP Vectra
• HP Vectra
Accessories Service Handbook - 5th edition
PC Service Handbook (Volume 1) - 9th edition
User’s Guide
User’s Guide
manual kit (D3538A).
manual kit (D3539A).
Familiarization Guide
(5963-8034).
(5963-8033).
• HP 10/100 VG Selectable PC LAN Adapters Installation Guide
• XU/VT Drivers and Documentation
• Support Assistant
The following Intel® publication provides more detailed information:
•
Pentium Pro Processor Data Sheet
CD-ROM.
CD-ROM (5063-7925).
(242769-001)
(D3538-90901).
(5963-2665).
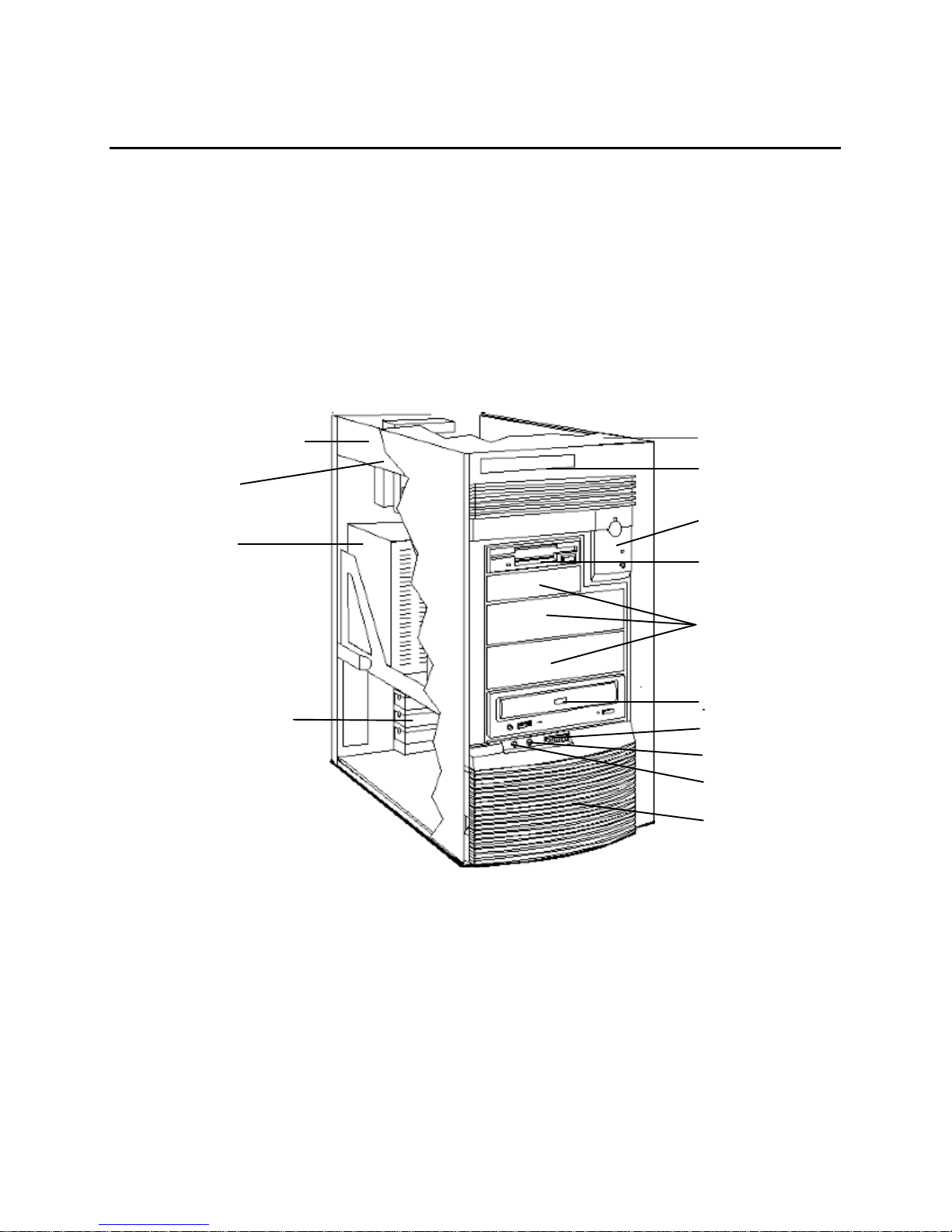
1 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
Hard disk drive
Power supply
This manual describes the
HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
and
HP Vectra VT 6/xxx PC
, and provides
detailed system specifications.
This chapter introduces the external features, and lists the specifications and characteristic data of
the system. It also summarizes the documentation which is available.
EXTERNAL FEATURES
The following two diagrams show the front and rear views of the
“A” model network board. The
HP Vectra VT 6/xxx PC
is similar, but has no SCSI or LAN
connectors.
Empty internal drive shelf
HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
Main memory
Logo
Status panel
Flexible disk drive
Empty front access
drive shelves
with an
Up to six accessory
boards can be installed
CD-ROM drive
Volume control
Headphone jack
Microphone jack
Internal speaker grill
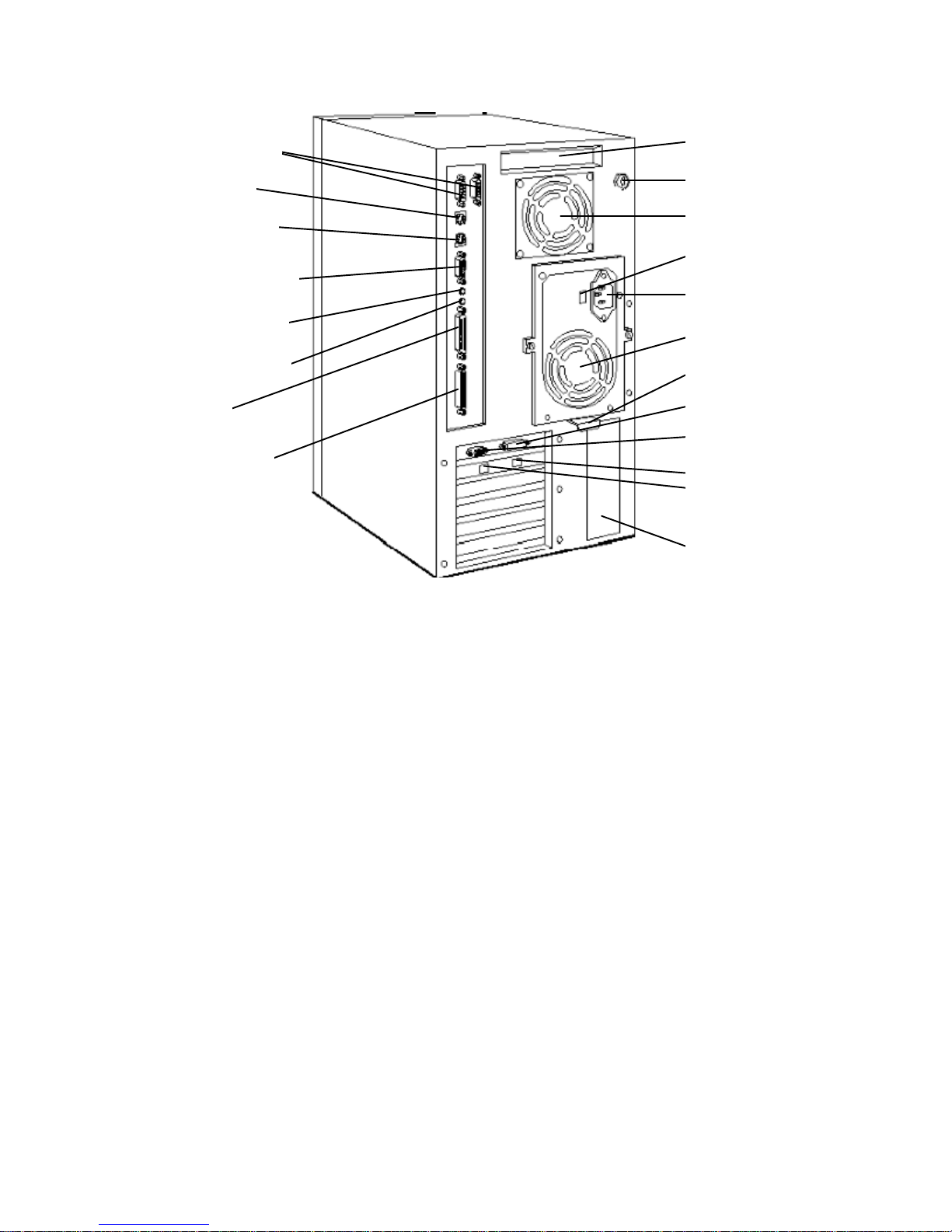
Mouse connector
Serial ports B and A
Hand-hold recess
Key lock
Keyboard connector
MIDI/joystick connector
Stereo-in (audio) jack
Stereo-out (audio) jack
Parallel port
Fast-20 SCSI-2
connector (XU only)
INTERNAL FEATURES
Processor fan
Voltage selection
switch
Power connector
Power supply fan
Power supply handle
VESA connector
Display connector
100 Mb/s LAN
10 Mb/s LAN
(XU with "A" model
network board only)
Identification label
Both models of PC are constructed around the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus and
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) bus. They are the first members of the HP Vectra PC family
to use the Intel Pentium Pro (P6) processor.
Since there is no back-plane, the system board diagram, at the beginning of the next chapter,
shows the locations of all the PC’s main field-serviceable components. The components of the
system board are described in Chapter 2; the characteristics of the PC’s video, disk and
networking devices are described in Chapter 3. The HP BIOS routines are described in Chapter 4;
and the Power-On Self-Test routines are summarized in Chapter 5.
SPECIFICATIONS AND CHARACTERISTIC DATA
Status (Control) Panel
The status (control) panels of the
HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
following features:
• a power on/off button with integrated on/error status light
press-and-hold
• a
RESET button
• a hard disk activity light.
and
HP Vectra VT 6/xxx PC
have the
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS
System Processing Unit
Weight: 33 lbs (15 kg)
Dimensions: 15.95 inches (D) by 8.27 inches (W) by 16.34 inches (H)
(40.5 cm by 21 cm by 41.5 cm)
Footprint: 0.91 sq ft (0.085 m2)
Keyboard: 18 inches (W) by 7 inches (D) by 1.3 inches (H), when flat, or
18 inches (W) by 7 inches (D) by 2 inches (H), when standing
(464mm by 178mm by 33mm when flat, or
464mm by 178mm by 51mm, when standing)
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATION
Parameter Total Rating Notes
Input voltage 100-127
Vac
Input current (max) 6 A 3.15 A
Input power (max) 280 W Less than 5 W
Input frequency 47 Hz to 63 Hz
Heat dissipation 280 W
Available power 200 W 15 W (max) 15 W (max)
Max current at +12 V 4 A — 0.2 A 0.2 A
Max current at -12 V 0.5 A — 0.2 A 0.5 A
Max current at +3.3 V 16 A Together, these two
Max current at +5V 29 A 1 A
Max current at -5V 0.2 A — — 0.2 A
Max current at +5Vst 70 mA — — —
200-240
Vac
Switch selectable
when turned off
must not exceed
145 W*
Typical per PCI
Accessory Slot
These must not
exceed 2.5 A
per slot
Typical per ISA
Accessory Slot
—
*Since 29 A at 5 V equates to 145 W, it follows that for every 1 A that is required from the 3.3V
supply, it is necessasry to reduce the 29 A limit on the 5 V supply by 0.66 A. For example, 3A
at 3.3 V plus a maximum of 27 A at 5 V, or 6 A at 3.3 V plus a maximum of 25 A at 5 V.
An attempt to draw too much current (such as a short circuit across edge-connector pins, or an
accessory board that is not suitable for these PCs), will cause the overload protection in the power
supply to be triggered, and the PC could fail to boot.
ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATIONS
Environmental Specifications (System Processing Unit, with Hard Disk)
Operating Temperature + 40°F to 104° F (+5°C to +40°C)
Recommended
+59°F to +158°F (+15°C to +30°C)
Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature -40°F to +158°F (-40°C to +70°C)
Over Temperature
+122°F (+50°C)
Shutdown
Operating Humidity 15% to 80% (relative)
Storage Humidity 8% to 80% (relative)
Acoustic noise emission less than 40 dB in the workplace under normal
conditions as defined by DIN 45635 T.19 and ISO
7779
Operating Altitude 10000 ft (3100m) max
Storage Altitude 15000ft (4600m) max
Operating temperature and humidity ranges may vary depending upon the mass storage devices
installed. High humidity levels can cause improper operation of disk drives. Low humidity levels
can aggravate static electricity problems and cause excessive wear of the disk surface.
DOCUMENTATION
The table below summarizes the availability of the documentation that is appropriate to the
and
Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
HP Vectra VT 6/xxx PC
. Three dots, ‘...’, are used to indicate ‘XU’ or ‘VT’,
HP
as appropriate.
Only selected publications are available in paper-based form. Most are available as printable files
from the HP regional support servers, or from the
Title
Line of HPVectra 6/xxx PC: X U VT XU VT XU VT
HP Vectra ... 6/xxx User’s Guide yes yes yes yes D3538A D3539A
Optimizing Performance Guide yes no yes no no
HP Vectra XU/VT 6/xxx
Familiarization Guide
HP Vectra XU/VT 6/xxx Technical
Reference Manual
HPVectra PC Service Handbook
(9th Edition)
HPVectra Accessory Service
Handbook (5th Edition)
Network Administrators Guide WinHelp,
HP 10/100 VG Selectable PC LAN
Adapters
Matrox MGA Millennium no no* no
Regional Support
Servers
yes yes D3538-90901
yes yes no
yes yes yes yes 5963-8033
yes yes 5963-8034
HTML and
text
formats
yes not
Support Assistant
not
applicable
applicable
Support Assistant
yes not
yes not
CD-ROM.
CD-ROM Paper-based
applicable
applicable
no not
applicable
5963-2665 not
applicable
*Available on the XU/VT Drivers and Documentation CD-ROM
WHERE TO FIND THE INFORMATION
Introducing the PC
Product features
Product model
numbers
Using the PC
Connecting cables
and turning on
Finding on-line
information
Environmental
Formal documents
Upgrading the PC
Opening the PC
Supported
accessories
Installing
accessories
Configuring
devices
Fields and their
options within
Setup
Repairing the PC
Troubleshooting
Technical
information
System board
BIOS
The table below summarizes the availability of information within the documentation:
User Guide User Online
Key features Exploring New features
Keyboard, mouse,
display, network,
printer, power
Finding READ.MEs
and on-line
documentation
Setting up the PC Working in
License agreement
Warranty information
Full details
Full PN details Full PN details Full PN
How to install Why to install New procedures
comfort
License
agreement
Performance
Guide
Familiarization
Guide
Vectra PC
comparison
Product range Product
Service
Handbook
Exploded
view
Parts list
range
CPL dates
details
Technical
Reference
Manual
Key features
Product
range
Installing drivers Configuring
Key fields New fields Complete
Basic Repair policy Service
Basic Advanced Basic Advanced
Jumpers, switches
and connectors
Basic details New features Technical
peripherals
Jumpers,
switches and
connectors
How to replace
notes
Jumpers,
switches
and
connectors
list
Advanced
Jumpers,
switches
and
connectors
Chip-set
details
details
Memory
maps
Power-On Self-
Test routines
(POST)
Key error codes and
Vectra diagnostic
utility
Peripheral Devices
Display User’s
Guide
Disk drive User’s
Guide
Audio User’s
Guide
LAN
Administrator’s
Guide
suggestions for
corrective action
Setting up and
configuring
Setting up and
configuring
Setting up and
configuring
Setting up and
configuring
New features Error codes
and
suggestions
for
corrective
action
Order of
tests
New features Technical
details
2 SYSTEM BOARD
The next chapter describes the video, disk and network devices which are supplied with the PC.
This chapter describes the components of the system board. An overview of the system board is
first given. Then the components of the Processor-Local Bus, the PCI Bus and the ISA Bus are
described in more detail.
PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS AND FEATURES
The system board contains the following components:
PGA ZIF sockets
Each processor is packaged in a 387-way
board in a
zero-insertion-force
(ZIF)
socket
pin-grid-array
. The
HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
(PGA), which is seated on the system
has two such sockets: the
top one is occupied by the Pentium Pro (P6) processor; the bottom one is empty, and can be filled
with an optional second Pentium Pro processor. The
HP Vectra VT 6/xxx PC
has one socket,
occupied by the Pentium Pro processor, with no option for fitting a second Pentium Pro processor.
VRM sockets
voltage regulator module
The
(VRM) is capable of supplying a voltage of 1.5 V to 3.5 V. This
voltage is selected automatically, and depends on the needs of each processor. For instance, the
150 MHz Pentium Pro requires 3.1 V, whilst the 200 MHz version requires 3.3 V. There are two
VRM sockets on the
HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
HP Vectra VT 6/xxx PC
.
(one of which is already occupied), and one on the
Accessory Slots
There are three
accessory slots
on the PCI bus, two on the ISA bus, and one that lies on either
bus. Thus there are four PCI accessory sockets, and three ISA bus accessory sockets. The top
PCI bus slot is already occupied by the Matrox MGA Millennium video controller. On the
HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
, the second PCI slot is also already occupied, by the HP PCI Integrated
10/ 100 VG Interface. (These two boards are described in the next chapter).
System Board Switches
The first three of the
system board switches
set the configuration for the PC, as summarized in the
table below. The next two set the frequency of the Processor-Local bus, and the last three the ratio
of processor-frequency to Processor-Local-bus-frequency.
Switch: Function: OFF (default) ON
1 - CONFG Retain or clear the configuration which is stored in EEPROM Retain Clear
2 - PSWRD Enable or clear the User and System Administrator Passwords
3 - SECURE Security mode prevents changes to the PC’s configuration with
4, 5, 6, 7, 8 Processor bus frequencies (see the table on page 15)
which are stored in EEPROM
Setup
the
program
Enable Clear
Disable Enable
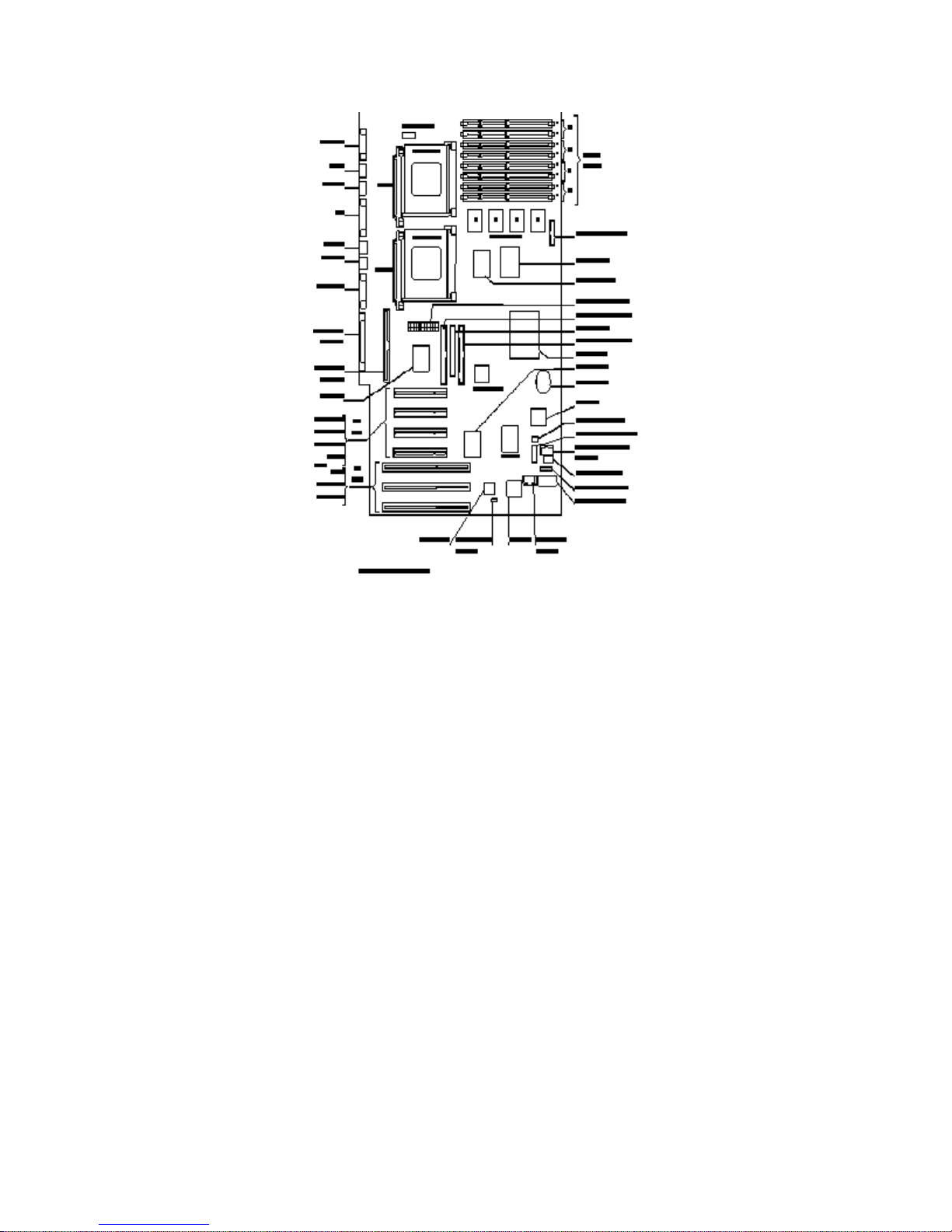
Wavetable Interface Connector
This is used when installing a Creative Labs wavetable accessory board that operates with the
integrated SoundBlaster audio interface.
Main Memory Module Sockets
There are eight
main memory module sockets
already occupied by the pair of
double interline memory modules
, arranged in four banks(A to D). One bank is
(DIMMs) that contain the 16 MB
of memory that is fitted as standard on all models of the PC.
SCSI Controller and Connector
Ultra SCSI controller
An
, on PCI bus of the
HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
, supports
Fast-20 SCSI-2
.
Internal and external connectors are provided.
IDE Controller and Connector
The Enhanced IDE (EIDE) controller chip can be found next to the IDE connectors. Connected to
the PCI bus, it has IDE-Master capability. It has two channels, each capable of supporting two
devices: a primary channel (recommended for EIDE, or IDE, hard disk drives, using the grey
connectors); a secondary channel (recommended for EIDE, or IDE, CD-ROM drives, using the red
connectors).

Ultra I/O Chip
The
Ultra I/O
chip is located just slightly above and to the right of the ISA slots. It is a combined
controller on the ISA bus for the flexible disk drive connector, and for the one parallel and two
serial communications ports.
Audio Chip
SoundBlaster 16
The
chip is located to the right of the Ultra I/O chip, near the bottom right hand
edge of the board. This provides the audio interface, and is driven from the ISA bus.
Chip-Set
Intel 82450KX chip-set
The
comprises eight chips. Six of them are concerned with controlling
memory accesses, and are located below the memory module sockets. These are the four
datapath units, the memory controller chip, and the Mem/PL bridge chip. They are described in the
sub-section of this chapter entitled “Main Memory”. The remaining two chips are the PL/PCI bridge
chip, which is described in the section entitled “Devices on the PCI Bus”, and the PCI/ISA bridge
chip, which is described in the section entitled “Devices on the ISA Bus”.
Gold Capacitor
Gold Capacitor
A
is provided instead of a battery, and can store enough energy to power the
CMOS configuration memory for over a week after the mains power has been disconnected.
Architectural View
The following block diagram gives an architectural view of the
HP VectraXU 6/150 PC
. The next
section describes the devices on the system board which are associated with the Processor-Local
(PL) bus. The section after describes the devices on the system board that are associated with the
Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) bus. The final section describes the devices on the
system board that are associated with the Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) bus.
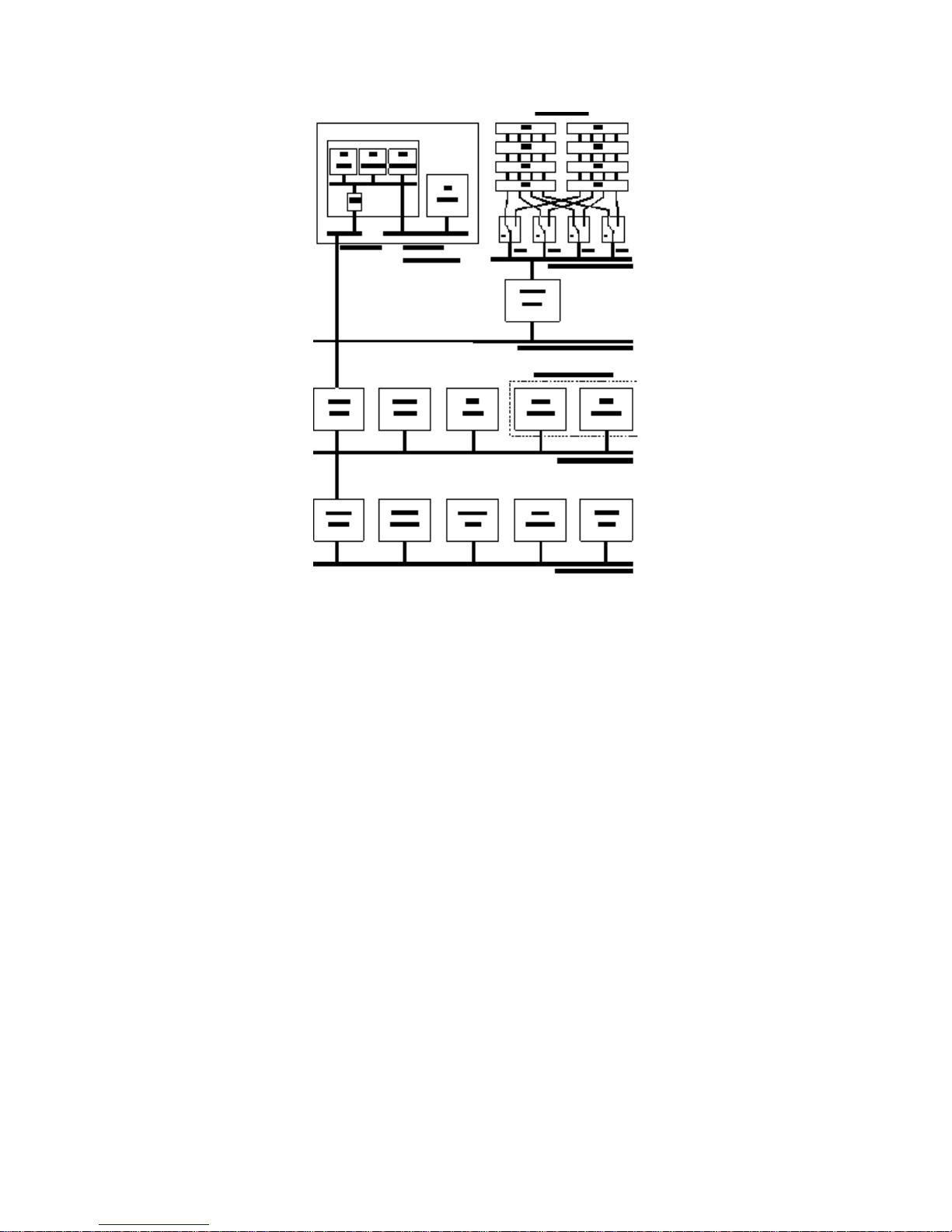
DEVICES ON THE PROCESSOR-LOCAL BUS
The following subsystems are associated with the Processor-Local bus:
• Intel Pentium Pro (P6) microprocessor
• cache memory
• optional second microprocessor (
• main memory.
HP Vectra XU 6/xxx PC
only)
INTEL PENTIUM PRO (P6) MICROPROCESSOR
Apart from the two levels of cache memory, contained within the processor’s single integrated
package, the other new features of the Pentium Pro are:
• three-way super-scalar pipeline (versus two for the Pentium)
• five execution units (versus three for the Pentium)
• 12 stage super-pipeline (versus 5 stage pipeline for the Pentium)
• dynamic, out-of-order, speculative execution
• 16-state, dynamic multiple branch prediction
• split-transaction bus
• register renaming.
Although it is not pin compatible with the Pentium, the Pentium Pro is backward code-compatible.
Software written for previous HP Vectra models will run on the Pentium Pro-based HP Vectras.
However, only 32-bit programs execute faster. 16-bit programs might even only execute at the
speed that would have been attained by an equivalent 80486-based system.
Many techniques have been adopted to accelerate the throughput of the instruction-pipeline of the
Pentium Pro over that of the Pentium. Firstly, it is
super-pipelined
: the individual operations of the
Pentium pipeline have been broken down into many sub-operations, leading to a much longer
pipeline of smaller operations. Secondly, it is
super-scalar
: the five execution units are completely
independent; not only can they have instructions issued to them asynchronously of each other, but
they can complete their execution asynchronously of each other, too.
Since instructions can complete asynchronously, it is possible for a simple instruction to complete
before a complex one which precedes it. This is the first of two ways in which the Pentium Pro
manifests
out-of-order instruction execution
speculative execution
feature: whilst a time-consuming instruction is still awaiting completion, the
. The second way follows as a direct result of the
processor gets on with executing instructions that were fetched after it, on the speculation that they
will probably be needed next.
Related to this, the Pentium Pro incorporates an even more elaborate (and more accurate) 16-
dynamic branch prediction
state
mechanism than the one which is used on the Pentium. This
allows the processor to speculate as to which instructions will be needed following a conditional
branch, based on past behavior at the branch.
A module, known as the
re-order buffer
(ROB), handles the out-of-order completion of instructions,
and the cases where speculative execution proves to have been wrong (a misprediction by the
branch prediction unit, for example).
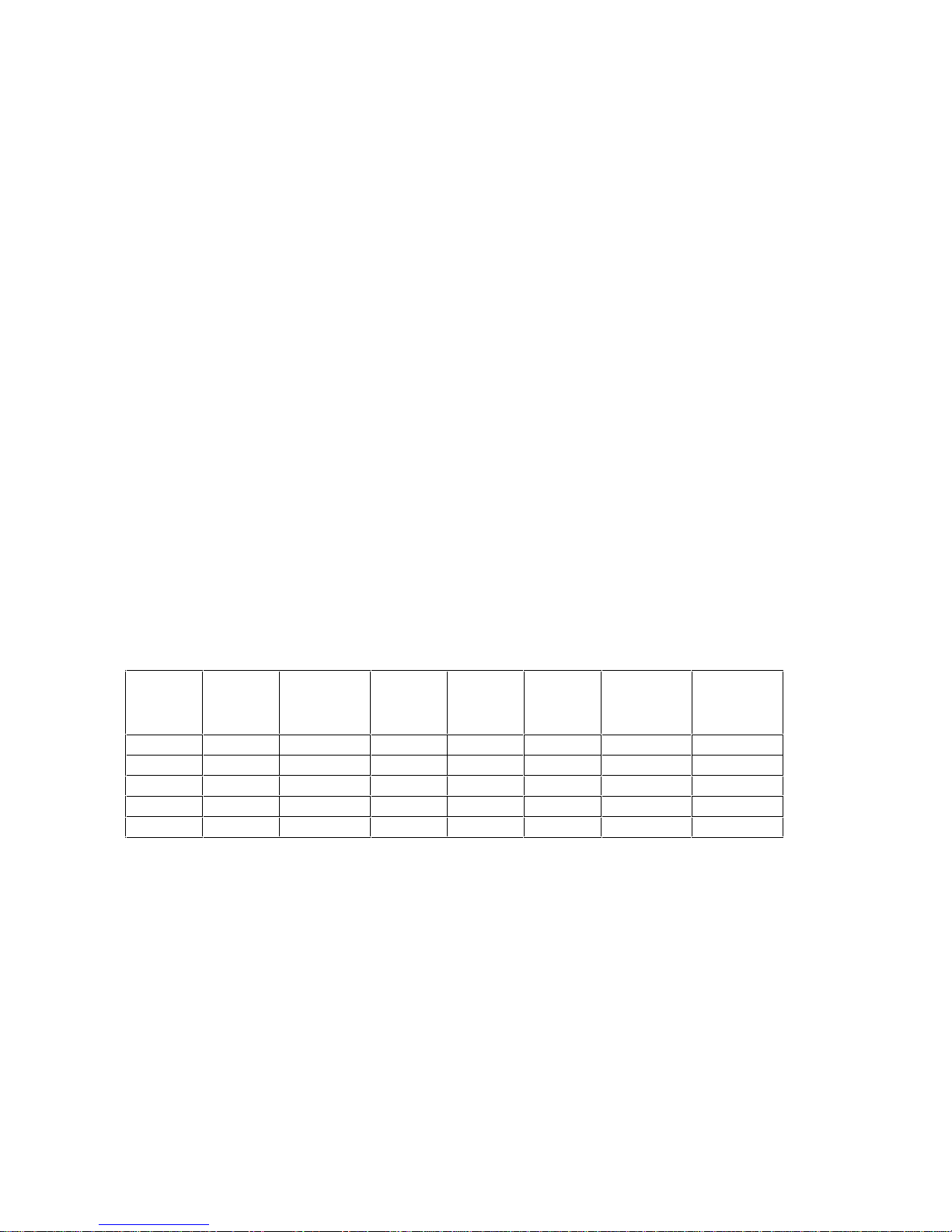
System Board Switch Speed Settings
Like the Pentium and 80486 DX2 processors, the Pentium Pro uses internal clock multiplication.
For example, the Pentium Pro 150 MHz processor multiplies the 60 MHz system clock by 2.5.
Switches 4 and 5 on the system board switch bank set the frequency of the Processor-Local bus.
Switches 6, 7 and 8 set the clock multiplier ratio. The relationship of the switch settings to
Processor-Local bus and processor frequencies is summarized in the following table:
Switch 4 Switch 5 Processor
Local Bus
Frequency
Off Off 66 MHz Off Off Off 2 : 1 133 MHz*
On Off 60 MHz On Off Off 2.5 : 1 150 MHz
Off Off 66 MHz On Off Off 2.5 : 1 166 MHz
On Off 60 MHz Off On Off 3 : 1 180 MHz
Off Off 66 MHz Off On Off 3 : 1 200 MHz
*The 133 MHz PentiumPro processor is not supplied in any of the Vectra models. This information is
provided for completeness only.
Switch 6 Switch 7 Switch 8 Frequency
Ratio
Processor :
Local Bus
Processor
Frequency
CACHE MEMORY
There are two integrated circuits sealed within a single Pentium Pro package. One of these
contains the Level-2 (L2) cache memory chip; the other contains the processor, which includes two
banks of Level-1 (L1) cache memory.
Each L1 cache memory has a capacity of 8 KB, and is set-associative. The L2 cache memory has
a capacity 256 KB, and is four-way set-associative.
Data is stored in the cache memories in lines of 32-bytes (256 bits). This involves two consecutive
transfers of 128-bits with the main memory.
 Loading...
Loading...