HP Vectra VL5 4, Vectra VL 5/00, Vectra VL 5/xx MT Technical Reference Manual

Technical Reference
Manual
Hardware and BIOS
HP Vectra VL 5/xx series 4 PC
and
HP Vectra VL 5/xx MT series 4 PC
December 1995

NOTICE
Information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
Hewlett-Packard makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including,
but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular
purpose. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental
or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of
this material.
Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential
damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
Hewlett-Packard assumes no responsibility for the use or reliability of its software on equipment
that is not furnished by Hewlett-Packard.
This document contains proprietary information which is protected by copyright. All rights are
reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another
language without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard Company.
Centronics® is a U.S. registered trademark of Centronics Data Computer Corporation.
LANManager, Microsoft Windows, Windows 95 and OS/2 are products of Microsoft
Corporation.
Microsoft® and MS-DOS® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Novell® and Netware® are registered trademarks of Novell Inc.
Pentium™ is a trademark of Intel Corporation.
©1995 Hewlett-Packard Company

Table of Contents
NOTICE 2
PREFACE 5
ORDERING INFORMATION FOR THE PHOENIX BIOS MANUAL 5
CONVENTIONS 5
BIBLIOGRAPHY 6
1 SYSTEM OVERVIEW 7
SYSTEM OVERVIEW 7
HP VECTRA VL 5/XX SERIES 3 – VL 5/XX SERIES 4 COMPARISON 7
HP VECTRA VL 5/XX SERIES 4 DESKTOP – MINI-TOWER
COMPARISON 8
VL 5/XX SERIES 4 PC BLOCK DIAGRAM 9
PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS AND FEATURES 9
VL 5/XX SERIES 4 SYSTEM BOARD 10
VL 5/XX MT SERIES 4 DESKTOP BACKPLANE 11
VL 5/XX MT SERIES 4 MINI-TOWER BACKPLANE 11
PROCESSOR 11
SUPERSCALAR ARCHITECTURE 12
FLOATING POINT UNIT (FPU) 12
DYNAMIC BRANCH PREDICTION 12
INSTRUCTION AND DATA CACHE 12
DATA INTEGRITY 13
PCI CHIP SET 13
PCI, CACHE AND MEMORY CONTROLLER (82437FX) 14
DATA PATH UNIT (82438FX) 15
THE PCI/ISA BRIDGE AND IDE CONTROLLER (82371FB) 15
THE 82438FX AND 82371FB FEATURE SUMMARY 16
SUPER I/O CHIP 1 7
NS PC87332VF FEATURE SUMMARY 17
FLEXIBLE DRIVE CONTROLLER (FDC) 17
SERIAL/PARALLEL PORTS 18
GRAPHICS/INTEGRATED VIDEO 18
IDE TO PCI CONTROLLER 19
FLASH ROM 19
SECURITY FEATURES 19
PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS 19
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS 20
POWER AVAILABILITY (CONTINUOUS OPERATION): 20
ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATIONS 21
2 SUMMARY OF THE HP/PHOENIX BIOS 22
HP/PHOENIX BIOS DESCRIPTION 22
OVERVIEW OF ADDRESS SPACE 22
I/O ADDRESSES USED BY THE SYSTEM* 22
BIOS I/O PORT MAP 23

ADDRESSING SYSTEM BOARD COMPONENTS 24
3 DESKTOP MANAGEMENT INTERFACE 26
DMI INFORMATION STRUCTURE 26
ACCESSING BIOS DMI INFORMATION 27
THE DMI HEADER 28
VERIFYING THE DMI INFORMATION STRUCTURE 28
DMI SUB-STRUCTURE TABLES 2 9
4 POWER-ON SELF-TESTS AND ERROR MESSAGES 32
POWER-ON SELF TEST (POST) 32
SHADOW RAM 32
ERROR MESSAGES 34
BEEP CODES 36
5 THE ULTRA VGA VIDEO CONTROLLERS 37
THE MATROX MGA MILLENNIUM VIDEO ADAPTER BOARD 37
VIDEO MEMORY 37
AVAILABLE VIDEO RESOLUTIONS 37
VESA CONNECTOR 38
FURTHER INFORMATION 38
THE INTEGRATED ULTRA VGA VIDEO CONTROLLER 38
VIDEO MEMORY 39
VIDEO MODES 39
AVAILABLE BIOS VIDEO RESOLUTIONS 42
VESA CONNECTOR 43
DB15 CONNECTOR PINOUT 43
VIDEO CONTROLLER SUMMARY 43

PREFACE
This manual is a technical reference and BIOS document for engineers and technicians
providing system level support. It is assumed that the reader possesses a detailed
understanding of AT-compatible microprocessor functions and digital addressing techniques.
Technical information that is readily available from other sources, such as manufacturer’s
proprietary publications, has not been reproduced.
This manual contains summary information only. For additional reference material, refer to the
bibliography.
ORDERING INFORMATION FOR THE PHOENIX BIOS MANUAL
System BIOS for IBM PCs, Compatibles, and EISA Computers
Phoenix Technologies is available in many bookstores. It can also be ordered directly from the
publisher as follows:
In the U.S.A.
Call Addison-Wesley in Massachusetts at +1-800-447-2226, and be prepared to give a credit
card number and expiry date.
In Europe
Send your request to Addison-Wesley at the address given below, and be prepared to give a
credit card number and expiry date.
Addison-Wesley
Concertgebouwplein 25
1071 LM Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Tel: +31 (20) 671 72 96
Fax: +31 (20) 675 21 41
(ISBN 0-201-57760-7) by
CONVENTIONS
The following conventions are used throughout this manual to identify specific elements:
• Hexadecimal numbers are identified by a lower case h.
For example, 0FFFFFFFh or 32F5h
• Binary numbers and bit patterns are identified by a lower case b.
For example, 1101b or 10011011b

BIBLIOGRAPHY
•
System BIOS for IBM PCs, Compatibles, and EISA Computers
Phoenix Technologies. Addison-Wesley (publisher).
The following Hewlett-Packard publications may also assist the reader of this manual.
(ISBN 0-201-57760-7) by
• HP Vectra VL 5/xx series 4 PC
• HP Vectra VL 5/xx MT series 4 PC
• HP Vectra VL 5/xx series 4 PC and HP Vectra VL 5/xx MT series 4 PC
(D3645-90901)
Guide
HP Vectra PC Service Handbook - 9th edition
•
The following Intel® publication provides more detailed information:
Pentium Processor
•
(241595-1)
User’s Guide
User’s Guide
(supplied with PC).
(supplied with PC).
(Available January 1996)
Familiarization
1 SYSTEM OVERVIEW
This chapter provides a description of the HP Vectra VL 5/xx series 4 desktop and HP Vectra
VL 5/xx MT series 4 mini-tower PC with detailed system specifications.
SYSTEM OVERVIEW
The HP Vectra VL 5/xx series 4 PC is a Pentium processor, ISA/PCI-based PC and features
the Intel Triton chip set.
HP VECTRA VL 5/XX SERIES 3 – VL 5/XX SERIES 4 COMPARISON
Vectra VL 5/xx series 3 Vectra VL 5/xx series 4
Processor Pentium 75 (VL 5/75)
Pentium 90 (VL 5/90)
Pentium 100 (VL 5/100)
Pentium 120 (VL 5/120)
Level-two cache memory 256 KB asynchronous cache 256 KB synchronous cache
Main memory 8 MB or 16 MB standard
192 MB maximum
Video controller Cirrus Logic GD 5434
integrated on PCI bus
Video memory 1 MB standard
upgradable to 2 MB
Enhanced IDE hard disk controller CMD PCI0640B
Integrated on PCI bus
dedicated for hard disk drives
Secondary IDE controller Integrated in NS 87332 Super I/O
chip on ISA bus
dedicated for CD-ROM drives
Flexible disk controller Integrated in NS 87332 Super I/O
chip on ISA bus
Serial / parallel port controller Integrated in NS 87332 Super I/O
chip on ISA bus
Pentium 90
Pentium 100
Pentium 120
Pentium 133
Pentium 150
Pentium 166
8 MB or 16 MB standard
128 MB maximum
Trio 765 64V+ or 764 integrated on
PCI bus or
Matrox MGA Millennium video card
1 MB standard
upgradable to 2 MB
Matrox Models
2 MB standard
upgradable to 4 MB or 8 MB*
Integrated in chip set (part of
82371FB multipurpose chip)
Integrated on PCI bus
Primary channel dedicated for hard
disk drives
Secondary channel recommended for
CD-ROM drives
No secondary IDE controller
(Two channels on enhanced IDE
controller - see above)
Integrated in SMC 932 Super I/O chip
on ISA bus
Integrated in SMC 932 Super I/O chip
on ISA bus
*The 6 MB video upgrade module is available only from Matrox Electronic Systems Limited.
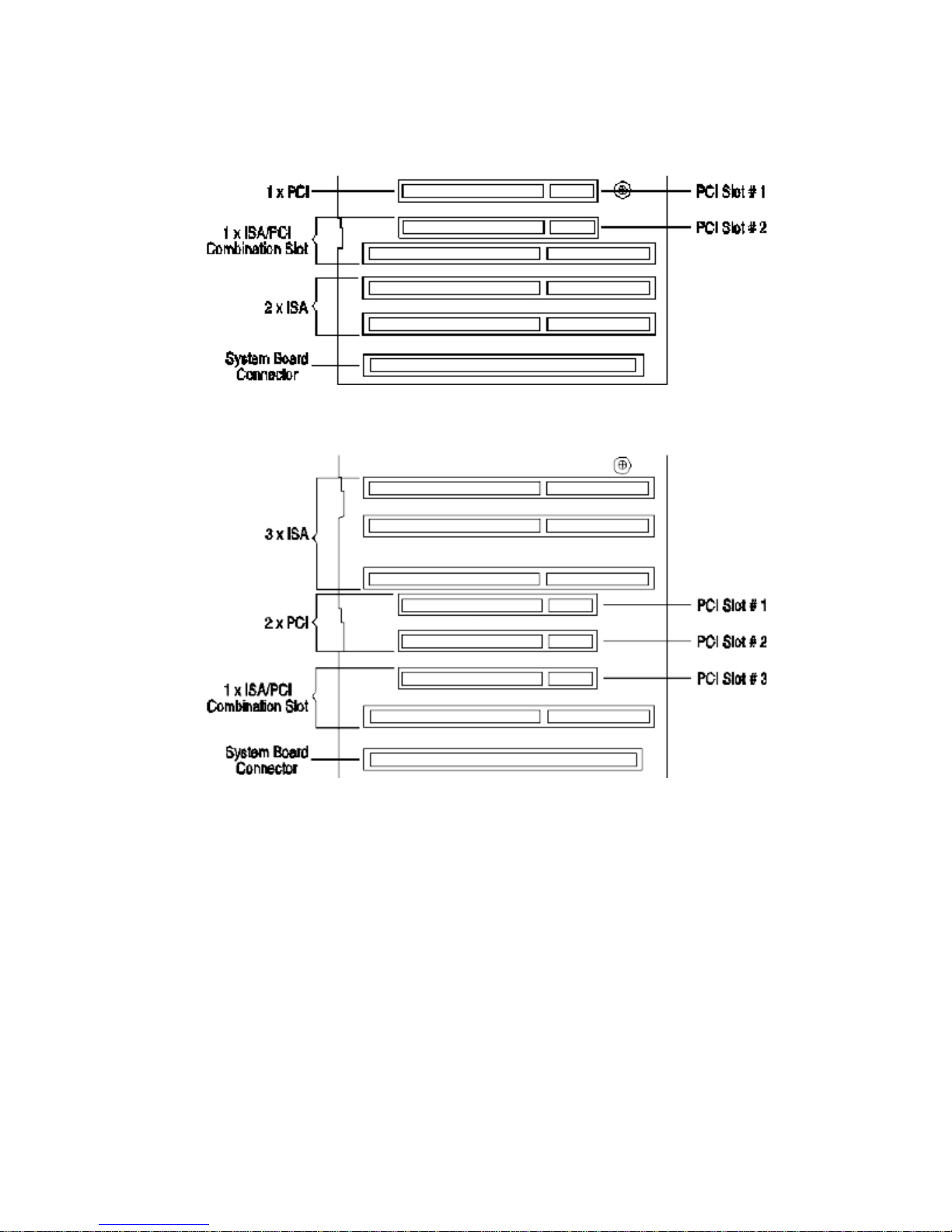
HP VECTRA VL 5/XX SERIES 4 DESKTOP – MINI-TOWER COMPARISON
Desktop Mini-Tower
IDE Controller
Primary channel connectors
IDE Controller
Secondary channel connectors
Flexible disk controller connectors Two connectors for 3.5-inch
Accessory board slots (on
backplane)
Internal device shelves One for hard disk drive Two for hard disk drives
Front-access device shelves One 3.5-inch
Two connectors for hard disk
drives
One red connector recommended
for CD-ROM
flexible disk drive or tape drive
One 16-bit ISA (short 16cm/
6.3-inch)
One 16-bit ISA (full-length)
One 32-bit PCI/16-bit ISA
Combination (full-length)
One 32-bit PCI (full-length)
One 5.25-inch
One 5.25-inch, 1-inch high
Two connectors for hard disk drives
Two red connectors recommended for
CD-ROM and supplementary hard
disk drive
Two connectors for 3.5-inch flexible
disk drive or tape drive
One connector for 5.25-inch flexible
disk drive
Maximum two devices connected
simultaneously
Three 16-bit ISA (full-length)
One 32-bit PCI/16-bit ISA
Combination (short 16cm/ 6.3-inch)
Two 32-bit PCI (full-length)
One 3.5-inch
Three 5.25-inch
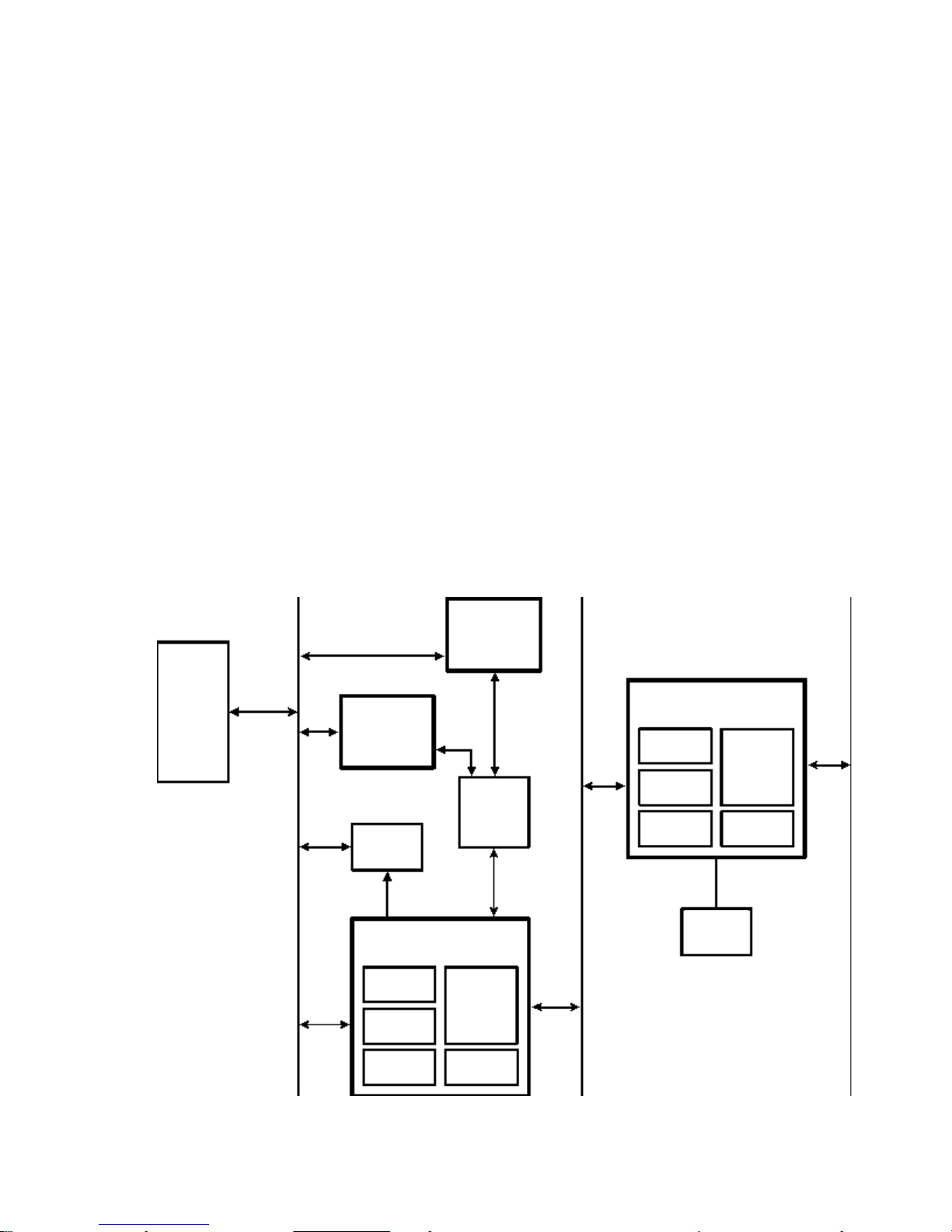
VL 5/XX SERIES 4 PC BLOCK DIAGRAM
ISA
Accessory
Board Slots
Keyboard
Mouse
Pentium
Processor
Intel Triton
82437/8FX
Chipset
Intel
82371FB
PCI/ISA
Bridge
SMC932
Super I/O
Controller
256 KB
Level-Two
Host Bus
Memory
(8 MB -
128 MB)
PCI Bus
IDE Controller Channel 1
IDE Controller Channel 2
ISA Bus
I/O
Decode
Logic
Cache
Flash
Support
PCI
Accessory
Board Slots
S3 Trio
Video
Controller
BIOS
Flash
ROM
FDD
Parallel
Serial 2
Serial 1
PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS AND FEATURES
The main features of the system board are:
• supports Pentium processors of several different clock speeds (90, 100, 120 or 133 MHz,
and 150 and 166 MHz when available) with accompanying voltage regulator module
(VRM)
• a PCI bus video controller: most models of the Vectra VL 5/xx series 4 have an integrated
64-bit Ultra VGA controller on the PCI bus (S3 Trio 765 64V+ on D3xxxA models and S3
Trio 764 on D3xxxB models)
• an Enhanced IDE controller with two channels on the PCI bus
• a primary IDE channel for two IDE hard disk drives
• a secondary IDE channel for an IDE CD-ROM drive and, in the mini-tower models, a
fourth IDE device (such as a third IDE hard disk drive)
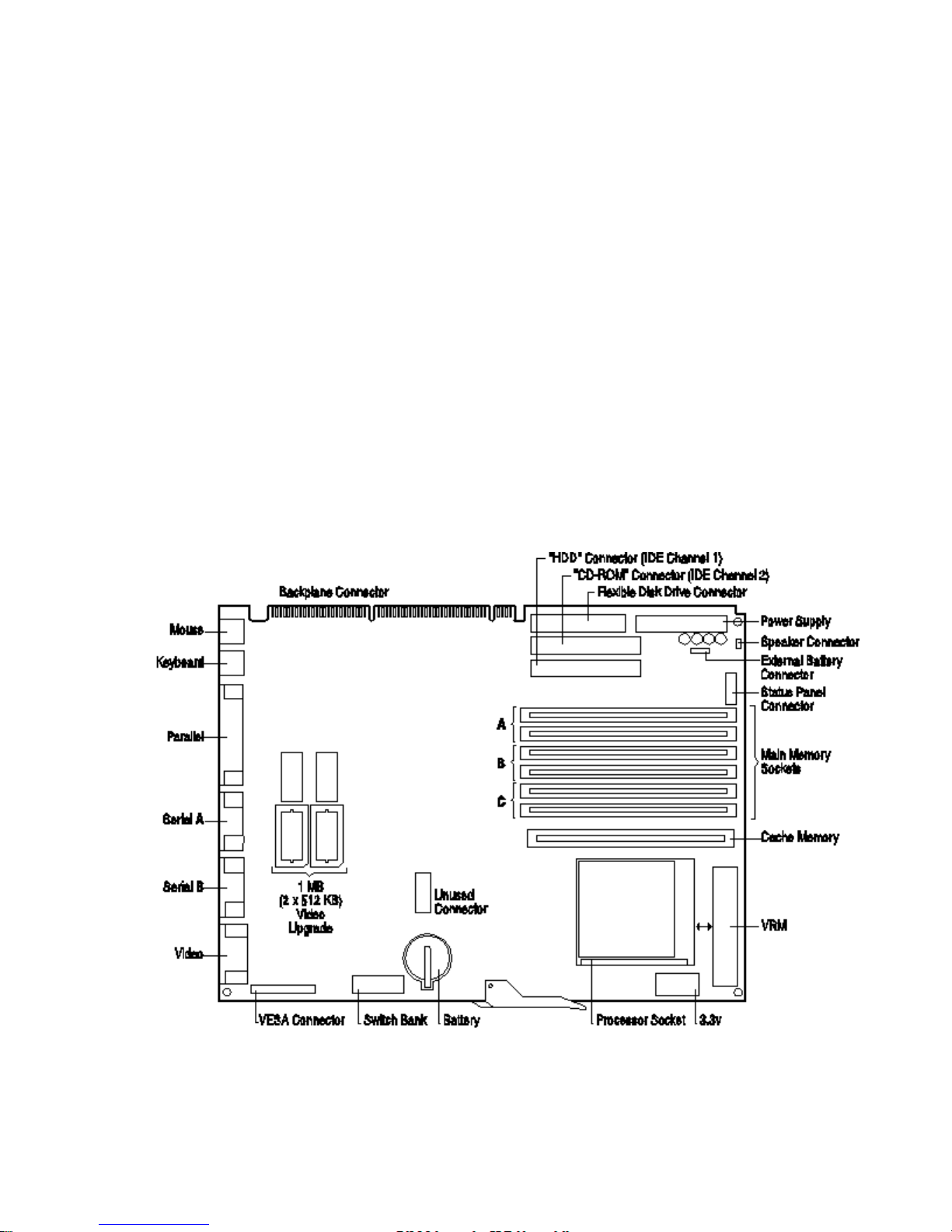
• a combined controller on the ISA bus for
• 2 flexible disk drives and/or tape drives
• 2 serial ports
• 1 parallel port
• sockets for DRAM main memory: the Vectra VL 5/xx series 4 PCs provide six sockets for
main memory, allowing installation of up to 128 MB
• a system ROM (using flash ROM technology) that can be easily updated with the latest
firmware, using the
Phlash.exe
program supplied with the firmware upgrade. The system
ROM contains:
• the BIOS (system BIOS, video BIOS and low option ROM)
• a power-on hardware test that allows you to view the results of the diagnostics as well
as a corrective action message (error message utility)
• menu-driven SETUP with context-sensitive help (in US English only)
• a keyboard/mouse controller and interface.
VL 5/XX SERIES 4 SYSTEM BOARD
*This video upgrade applieso nly to themodels with integrated video controller.
VL 5/XX MT SERIES 4 DESKTOP BACKPLANE
VL 5/XX MT SERIES 4 MINI-TOWER BACKPLANE
PROCESSOR
The Pentium processor uses 64-bit architecture and is 100% compatible with Intel’s family of
x86 processors. All application software written for Intel386 and Intel486 processors can run on
the Pentium without modification. The Pentium processor contains all the features of the Intel
486 processor, with the following added features which enhance performance:
• Superscalar Architecture
• Floating Point Unit
• Dynamic Branch Prediction
• Instruction and Data cache
• Data Integrity
• Supports MultiProcessor Specification (MPS) 1.1
• PCI bus architecture
• Advanced Power Management capability for reducing power consumption
The processor is seated in a Zero Insertion Force (ZIF) socket.

SUPERSCALAR ARCHITECTURE
The Pentium processor’s superscalar architecture has two instructions pipelines and a floatingpoint unit, each capable of independent operation. The two pipelines allow the Pentium to
execute two integer instructions in parallel, in a single clock cycle. Using the pipelines halves
the instruction execution time and almost doubles the performance of the processor, compared
with an Intel486 microprocessor of the same frequency.
Frequently, the microprocessor can issue two instructions at once (one instruction to each
pipeline). This is called instruction pairing. Each instruction must be simple. One pipeline will
always receive the next sequential instruction of the one issued to the other pipeline.
FLOATING POINT UNIT (FPU)
The Floating Point Unit incorporates optimized algorithms and dedicated hardware for multiply,
divide, and add functions. This increases the processing speed of common operations by a
factor of three.
DYNAMIC BRANCH PREDICTION
The Pentium processor uses dynamic branch prediction. To dynamically predict instruction
branches, the processor uses two prefetch buffers. One buffer is used to prefetch code in a
linear way, and one to prefetch code depending on the contents of the Branch Target Buffer
(BTB). The BTB is a small cache which keeps a record of the last instruction and address used.
It uses this information to predict the way that the instruction will branch the next time it is used.
When it has made a correct prediction, the branch is executed without delay, thereby
enhancing performance.
INSTRUCTION AND DATA CACHE
The Pentium processor has separate code and data caches on-chip. Each cache is 8 KB in size
with a 32-bit line. The cache acts as temporary storage for data and instructions from the main
memory. As the system is likely to use the same data several times, it is faster to get it from
the on-chip cache than from the main memory.
Each cache has a dedicated Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB). The TLB is a cache of the
most recently accessed memory pages. The data cache is configured to be Write-Back on a
line-by-line basis (a line is an area of memory of a fixed size).
The data cache tags (directory entries used to reference cached memory pages) are triple
ported to support two data transfers and an inquire cycle in the same clock cycle. The code
cache tags are also triple ported to support snooping (a way of tracking accesses to main
memory by other devices) and split line accesses.
Individual pages of memory can be configured as cacheable or non-cacheable by software or
hardware. They can also be enabled and disabled by hardware or software.
DATA INTEGRITY
PCI
Slave
The processor uses a number of techniques to maintain data integrity. It employs two methods
of error detection:
• Data Parity Checking
This is supported on a byte-by-byte basis, generating parity bits for data addresses sent
out of the microprocessor. These parity bits are not used by the external subsystems.
• Internally
The processor uses functional redundancy checking to provide maximum error detection
of the processor and its interface.
PCI CHIP SET
The chip set consists of three devices:
• The PCI, Cache, and Memory Controller (82437FX)
• Two Data Path Units (82438FX)
• The PCI/ISA bridge and IDE controller (82371FB)
The 82437FX and 82438FX2 devices provide the core cache and memory system architecture,
and the PCI interface.
Pentium
Processor
Host Bus
82438FX
Data Path Unit
Level-Two
Cache
82437FX PCI, Cache and
Memory Controller
Cache
Controller
Write
Buffer
82438FX
Data Path Unit
Main
Memory
Main
Memory
Controller
PCI Bus
82371Fb
PCI/ISA Bridge
PCI
Master
APIC
ISA Bus
ISA Bus
Controller
IDE
Controller
BIOS
PCI
Master
PCI
Slave
 Loading...
Loading...