Page 1
Command Line
Interface
User’s Guide
hp surestore director fc-64
Page 2

Page 3

hp surestore director fc-64
Command Line Interface
User’ s Guide
KS+
Edition E0102
Orde r No. A6534-90909
Printed in U.S.A.
Page 4

Notice
Format Conventions
© Hewlett-Pac kard Co mpany, 2002. All rights
reserved.
Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty o f
any kind with regard to this material, including, but
not limited to, the implied warranties o f merchantability and fitness fo r a partic ular purpose. HewlettPackard shall not be liable fo r erro rs contained
herein or for incidental or c onsequential damages in
connection with the f urnishing, performanc e, or use
of this material.
This do c ument c ontains pro prietary info rmation,
which is protected by co pyright. No part of this
document may be photocopied, reproduced, or
translated into another language witho ut the prior
written consent o f Hew lett-Pac kard. The informatio n contained in this do cument is subje ct to c hange
witho ut notic e.
Warranty
If yo u have any questions abo ut the warranty fo r
this product, contac t yo ur de aler o r lo c al HewlettPackard sales representative.
Denotes
Note Signific ant concepts or o perating
instructions
this font Text to be typed verbatim: all
commands, path names, file
names, and direc to ry names
this font Text displayed on the screen
<this font> Keys to be pressed, for example,
the <Return> key
Safety Instructions
Service
Any servic ing, adjustment, maintenance, or repair
must be performed o nly by authorized servicetrained perso nnel.
ii
Page 5

CONTENTS
1 Introduction
Command Line Interface Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Entering Command Line Interface Commands. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Doc umentation Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Navigation Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Command Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
Navigation of the CLI Command Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Limitation on Movements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Output. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Logging In and Logging Out. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
User Access Rights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
login. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
logo ut . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Using the commaDelim Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
commaDelim . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Handling Command Line Interface Errors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Using the Command Line Interface Help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
Telnet Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Ethernet Connection Loss . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Contents
2 CLI Commands
Co mmand Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
config . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
iii
Page 6

config.ip.ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
config.ip.show . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
config.port.blocked. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
config.port.extDist . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
config.port.name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
config.port.type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
config.port.show . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
config.sec urity.portBinding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
config.sec urity.portBinding.bound . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
config.sec urity.portBinding.wwn . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
config.sec urity.portBinding.show . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
config.sec urity.userRights . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
config.sec urity.userRights.administrator. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
config.sec urity.userRights.operator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
config.sec urity.userRights.show . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
config.snmp.addCommunity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
config.snmp.authTraps. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
config.snmp.deleteCommunity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
config.snmp.show . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
config.switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
config.switch.bbCredit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
config.switch.edTOV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
config.switch.interopMode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
config.switch.prefDomainId . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
config.switch.priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
config.switch.raTOV. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
config.switch.rerouteDelay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
config.switch.show . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
config.system.contact. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
iv
Page 7

config.system.date. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
config.system.description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
config.system.loc ation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
config.system.name. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
config.system.show . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
config.zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
config.zoning.setDefZoneState . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
config.zoning.activateZoneSet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
config.zoning.deactivateZoneSet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
config.zoning.replaceZoneSet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
config.zoning.clearZoneSet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
config.zoning.addZone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
config.zoning.deleteZone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
config.zoning.renameZoneSet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
config.zoning.addWwnMem. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
config.zoning.addPortMem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
config.zoning.clearZone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
config.zoning.deleteWwnMem. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
config.zoning.deletePortMem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
config.zoning.renameZone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
config.zoning.showPending . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
config.zoning.showActive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
maint. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
maint.port.beacon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
maint.port.reset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
maint.system.beacon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
maint.system.clearSysError. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .66
maint.system.ipl. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
maint.system.resetConfig . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Contents
v
Page 8

maint.system.setOnlineState . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
perf . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
perf.class2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
perf.class3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
perf.clearStats . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
perf.errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
perf.link . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
perf.traffic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
show . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
show.eventLo g. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
show.frus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
show.ip.ethernet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
show.loginServer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
show.nameServer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
show.port.co nfig . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
show.port.info . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
show.port.status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
show.port.technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
show.security.portBinding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
show.switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
show.system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
show.zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Error Messages
Glossary
A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
B . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .111
vi
Page 9

C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .112
D . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
E. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
F. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
G . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
H . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .118
I . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
L. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120
M . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120
N . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .121
O . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .121
P. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
R. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .124
S. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .124
T. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
W . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
Z. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
Contents
Index
vii
Page 10

viii
Page 11

TABLES
1 CLI Command Tree Navigation Conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
2 Command Line Interface Command Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Tables
ix
Page 12

x
Page 13

1 INTRODUCTION
Command Line Interface Overview
Entering Command Line Interface Commands
Logging In and Logging Out
Using the commaDelim Command
Handling Command Line Interface Errors
Using the Command Line Interface Help
Telnet Session
This c hapter introduc es the Co mmand Line Interfac e and describes the essentials for using
the Co mmand Line Interface c o mmands.
Introduction
1
Page 14

Command Line Interface Overview
The Co mmand Line Interface ( CLI) is a feature that pro vides an alternative to HP EFC
Manager and HP Embedded Web Server (HP EWS) produc ts fo r direc to r and switc h
management capabilities.
The CLI can only be used through a Telnet c lient session in an o ut-o f-band management
environment, using the Ethernet port in the directo r o r switc h. Although the primary use o f
the CLI is in ho st-based scripting environments, the CLI commands can also be entered
directly at a co mmand line. Any hardware platfo rm that supports the Telnet c lient software
can be used.
The primary purpo se o f the CLI is to auto mate management o f a large number o f switc hes
with the use of scripts.
Bec ause the CLI is not an interactive interface, no checking is done fo r pre-existing
conditions and no prompts are displayed to guide the user through a task. If an interactive
interface is needed, the HP EFC Manager or HP EWS products should be used instead of
the CLI.
2 Command Line Interface Overview
Page 15

Entering Command Line Interface Commands
The Command Line Interface (CLI) commands can be entered directly at the command line
of a terminal or coded in a script.
Note that the CLI co mmands are not case sensitive.
Documentation Conventions
Throughout this public atio n, perio ds are used to separate the compo nents of a c o mmand
name. However, the periods cannot be included when the command is actually entered at
the terminal or coded in a sc ript. (Ho w to enter the commands is explained in Navigatio n of
the CLI Command Tree on page 8.)
Even though the commands cannot be entered with the periods, the command line
prompts do include the periods.
Config.Port>
Navigation Conventions
Basic command line navigatio n c o nventio ns are suppo rted. The fo llowing table inc ludes
the asynchrono us co mmands that are rec o gnized by the Co mmand Line Interface.
Table 1
CLI Co mmand Tree Navigatio n Co nventions
Introduction
Character Sequence Common Name Action or Description
<CR> Carriage Return Pass a completed line to the parser.
<DEL> Delete Backspace one character and delete the
character.
<NL> New Line Pass a completed line to the parser.
<SP> Space Used to separate keywords.
? Question Mark Provide help information. (No <CR> required)
“ Quotation Mark Used to surround a single token.
Entering Command Line Interface Commands 3
Page 16
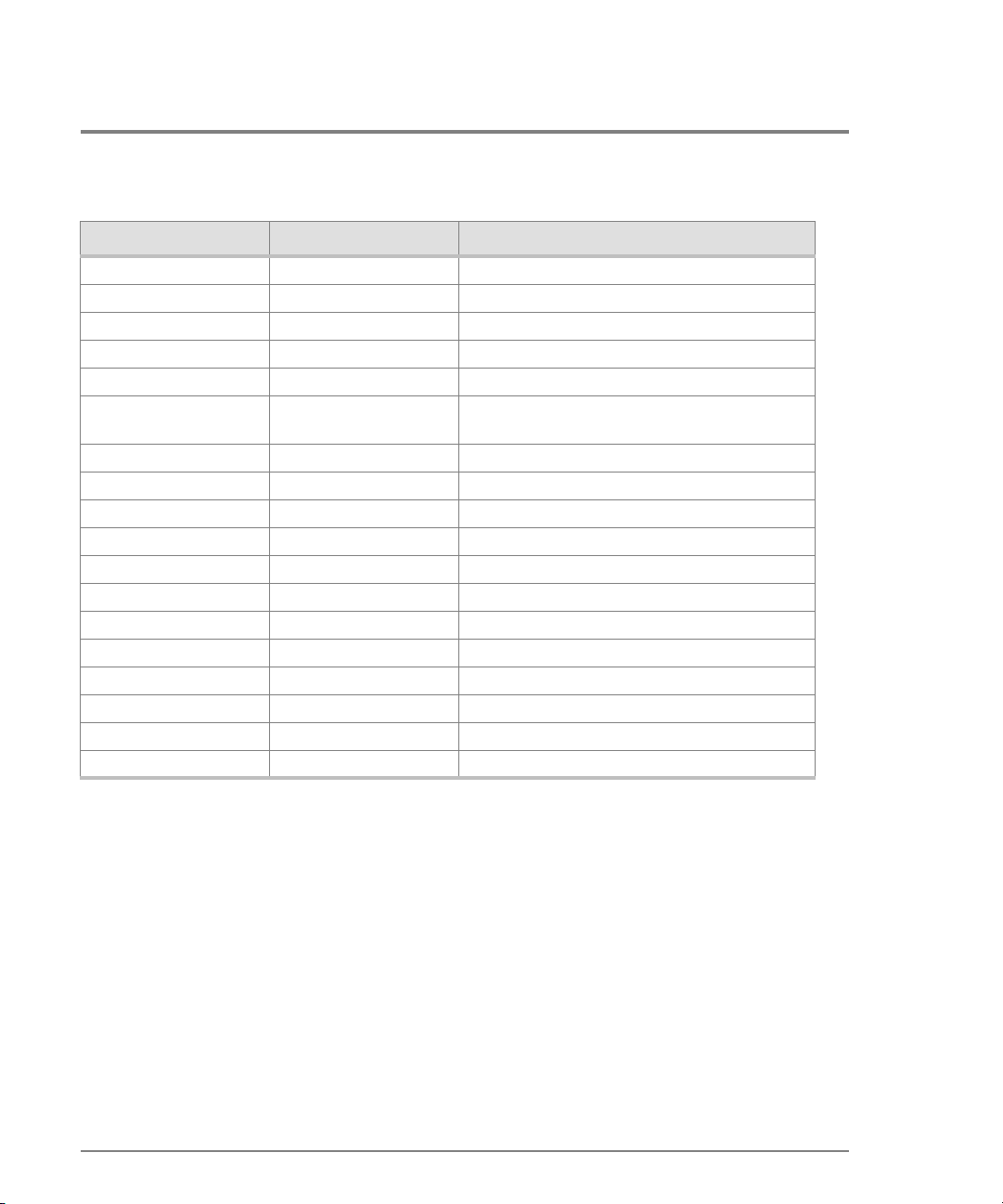
Table 1 CLI Command Tree Navigation Conventio ns ( c o nt’d)
Character Sequence Common Name Action or Description
^A Control-A Position the cursor to the start of the line.
^B Control-B Position the cursor left one character.
^D Control-D Delete the current character.
^E Control-E Position the cursor to the end of the line.
^F Control-F Position the cursor right one character.
^H Control-H Backspace one character and delete the
character.
^I Tab Complete the current keyword.
^K Control-K Delete to the end of the line.
^L Control-L Redraw the line.
^N Control-N Move down one line in the command history.
^P Control-P Move up one line in the command history.
^R Control-R Redraw the line.
^U Control-U Clear the input and reset the line buffer.
^X Control-X Clear the input and reset the line buffer.
<ESC>[A Up Arrow Move up one line in the command history.
<ESC>[B Down Arrow Move down one line in the command history.
<ESC>[C Right Arrow Position the cursor right one character.
<ESC>[D Left Arrow Position the cursor left one character.
Command Tree
The command tree of the Command Line Interface begins from the root. The commands in
the fo ur extended branches (co nfig, maint, perf, and show) are described in Chapter 2, CLI
Co mmands.
There are three additio nal commands (login, logo ut, and c o mmaDelim) that are glo bally
available commands. These c ommands are described in this chapter.
4 Entering Command Line Interface Commands
Page 17
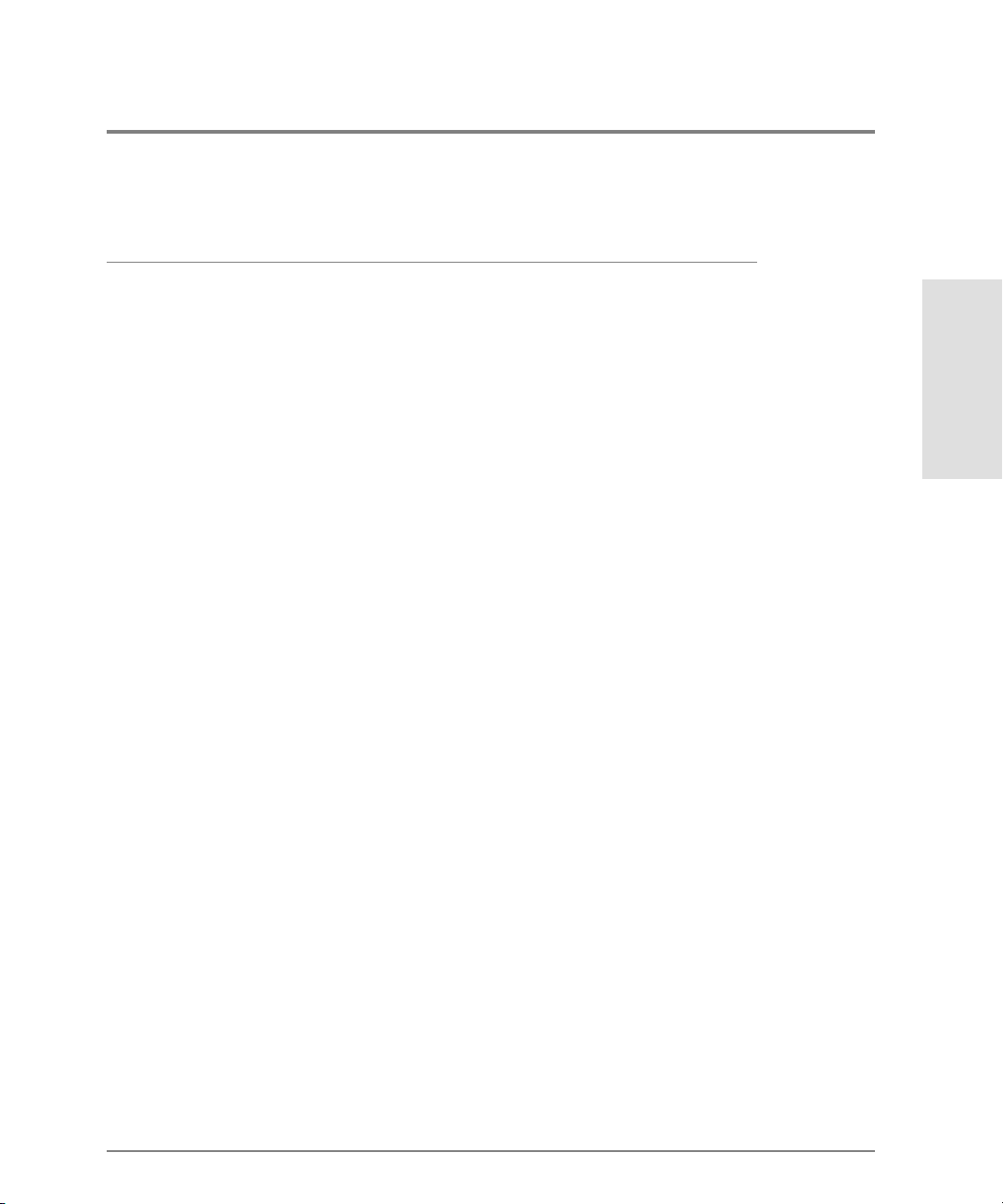
The hierarchy from the root, reading from left to right, is as follows.
Table 2
config -------------------- ip -------------------------- ethernet
Command Line Interface Co mmand Tree
show
port ----------------------- blocked
extDist
name
type
show
security ----------------- portBinding ------------- bound
userRights -------------- administrator
snmp --------------------- addCommunity
authTraps
deleteCommunity
show
Introduction
wwn
show
operator
show
switch -------------------- bbCredit
edTOV
interopMode
prefDomainId
priority
raTOV
rerouteDelay
show
Entering Command Line Interface Commands 5
Page 18

Table 2 Command Line Interface Co mmand Tree
system ------------------ contact
date
description
location
name
show
zoning ------------------- setDefZoneState
activateZoneSet
deactivateZoneSet
replaceZoneSet
clearZoneSet
addZone
deleteZone
renameZoneSet
addWwnMem
addPortMem
clearZone
deleteWwnMem
deletePortMem
renameZone
showPending
showActive
maint --------------------- port ----------------------- beacon
reset
system ------------------ beacon
clearSysError
6 Entering Command Line Interface Commands
Page 19
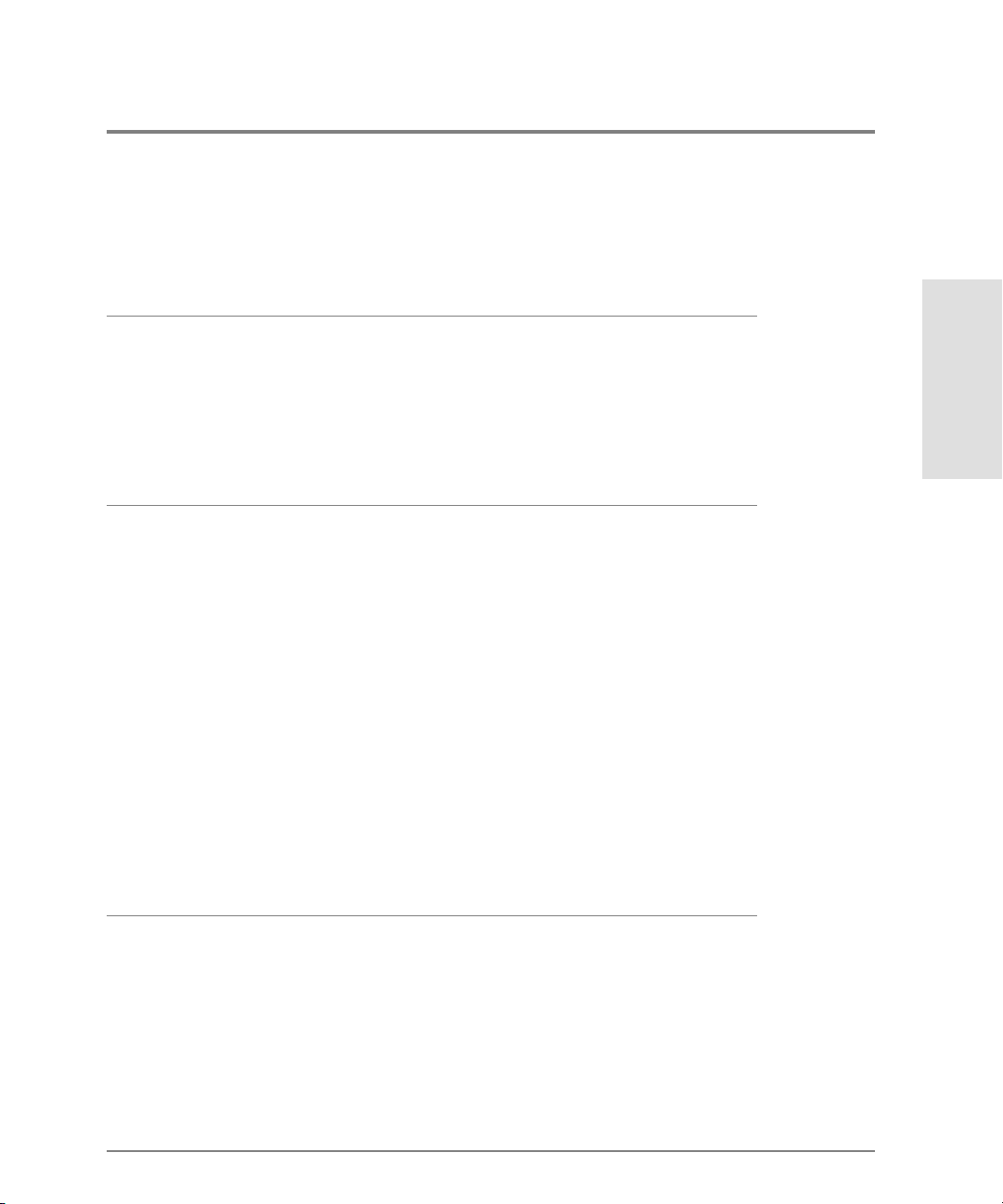
Table 2 Command Line Interface Co mmand Tree
ipl
resetConfig
setOnlineState
perf ----------------------- class2
class3
clearStats
errors
link
traffic
show --------------------- eventLog
frus
ip -------------------------- ethernet
loginServer
nameServer
port ----------------------- config
info
status
technology
Introduction
security ----------------- portBinding
switch
system
zoning
Note that the c o mmands are sho wn, with the exception of the zo ning commands, in
alphabetical order to make them easier to locate. Although the commands can be entered
in any order, depending on the results desired, the order shown in Table 2, Command Line
Interfac e Command Tree for the zo ning commands is a typical order in which the zo ning
commands are e ntered.
Entering Command Line Interface Commands 7
Page 20

Note that the o rder in which c o mmands are entered determines the o rder in which the
show c ommands display the values. Refer to Chapter 2, CLI Commands for examples of
show commands output.
Navigation of the CLI Command Tree
Once the Administrator or Operator logs in and receives the Root> prompt, the CLI
commands are ac c essed by navigating up and do wn the CLI command tree.
To move from the ro o t through the any o f the four extended branches, enter the name o f
the next branch as shown in Table 2, Command Line Interface Command Tree. For
ex ample, to use the co nfig.port.name c o mmand to configure the name fo r po rt 4 on the
switc h, this series of commands is entered:
config
Ro ot >
Config> port
Config.Port> name 4 "Sam’s Tape Drive"
At this po int, to enter the maint.po rt.beac o n c o mmand to set the be aconing state of po rt 4,
the fo llo wing series o f c ommands is entered:
Config.Port>
Config> ..
Ro ot > maint
Maint> port
Maint.Port> beacon 4 true
Note that you must return all the way to the root of the tree to transition to another
extended branch. When traversing back to the root, the name of each branch cannot be
used. Instead use the double-dot command (two periods) to move back towards the root.
Note that only one double-do t command may be entered at a time.
One approach to making the navigatio n mo re c o nc ise is to use the root command to jump
directly to the roo t of the CLI command tree. The previous example, which shows stepping
back to the ro ot with the double-do t c ommand, is simplified as follows:
8 Entering Command Line Interface Commands
..
Page 21

Config.Port> root
Ro ot > maint
Maint> port
Maint.Port> beacon 4 true
Ano ther appro ac h to making the navigation more c o nc ise is to use the complete c o mmand
syntax from the Roo t> prompt each time. For example, to issue the config.port.name
command and then the maint.port.beacon command, the co mmands are entered as
fo llows:
config port name 4 "Sam’s Tape Drive"
Ro ot >
Ro ot > maint port beacon 4 true
As shown in this example, use o f the c o mplete c o mmand syntax avo ids navigating up and
down the branches of the CLI command tree, and the prompt stays at the root. The use of
complete c ommand syntax is particularly useful when writing scripts.
When coding a script, remember to code the appropriate character sequences, which are
described in Navigation Conventions.
config port name 4 "Sam’s Tape Drive"<CR>
Ro ot >
Ro ot > maint port beacon 4 true<CR>
Introduction
Limitation on Movements
As the co mmands are entered, they are rec o rded in a history log. Note these limitatio ns on
movement that result f ro m use of the history lo g:
• If a c o mmand has more than 60 characters, the command runs, but the c ommand is not
rec orded in the histo ry log, and the positio n in the tree does not change , as shown in the
fo llo wing example. Because the c o mmand is no t rec o rded in the histo ry, a subsequent
async hronous co mmand ( navigatio n c o mmand) cannot depend on it.
config zoning addWwnMem TheUltimateZone 10:00:00:00:C9:22:9B:
Ro ot >
64
Entering Command Line Interface Commands 9
Page 22

Ro ot >
• Whenever the position in the CLI command tree moves to a new branch (for example,
config to maint, config to c onfig.port, or c onfig.po rt to co nfig), the history lo g is cleared.
In this case, any asynchronous commands (fo r example, the up-arrow command
<ESC>[A) or the up-arrow keyboard symbol) cannot move the position back towards
the root, as shown in this example:
config
Ro ot >
Ro ot . Co nf ig> port
Ro ot . Co nf ig. Po rt > <ESC>[A
Ro ot . Co nf ig. Po rt >
Parameters
Some command parameters ac cept character strings that inc lude spac es. Quo tatio n marks
are required when a string includes spaces.
Config.System>
Config.System> location "Building 24 Room 16"
If spac es are no t inc luded in a parameter that accepts a string, the quotatio n marks are not
required around that string.
A null string can be created by using the quo tation marks witho ut any spac e between them.
Config.System>
location Building_24_Room_16
location ""
Output
All o utput fro m the CLI commands is limited to the standard 80 c olumns supported b y mo st
Telnet interfaces. The output is left-justified.
10 Entering Command Line Interface Commands
Page 23

Logging In and Logging Out
The Command Line Interface allo ws a single Telnet c lient to be c o nnected to the switc h. If
a Telnet client logs o ut, o r if after 15 minutes o f inactivity the client’s access times out,
another Telnet client may log in. Also note that the Telnet c lient ( user) must log in any time
the direc to r o r switch is restarted bec ause the current user’s access is lost. Examples of a
restart include an IPL and any po wer-off situatio n.
User Access Rights
The Command Line Interfac e suppo rts two use r ac c ess rights: Administrator and Operato r.
A user who logs in with Administrator acc ess rights can use all of the commands described
in this publication. However, Operator acc ess rights grant permissio n to use only the perf
and show branc hes o f the CLI command tree (fo r example , the perf.traffic and
show.system c o mmands), as well as the globally available co mmands (login, logout, and
commaDelim).
login
Syntax
login
Purpose
This command allows a Telnet client to co nnec t to the switch.
Introduction
Description
This command allows the user to lo g in with either Administrator or Operator acc ess
rights. The default passwords are password.
After the lo gin co mmand is issued, the Username: pro mpt automatic ally displays. After a
valid user name is entered, the Password: prompt automatically displays. After the
corresponding valid password is entered, the Root> prompt displays. At this prompt the
Logging In and Logging Out 11
Page 24

user enters any of the commands included in Table 2, Command Line Interface Command
Tre e .
A user name and passwo rd can be set by the Administrato r thro ugh the
config.sec urity.userRights.administrator c ommand o r through the
config.se c urity.userRights.o perato r c o mmand.
The ac c ess rights chosen for the CLI are c o mpletely independent o f the o ther product
interfaces, fo r example, SNMP or HP pro duct interfac e s.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x amples
login
User name : Administrator
Pas swo rd: password
login
User name : Operator
Pas swo rd: password
12 Logging In and Logging Out
Page 25

logout
Syntax
logout
Purpose
This command allows a Telnet client to disconnec t fro m the switch.
Description
This command logs out the single Telnet client co nnec ted to the switch. This c ommand c an
be entered at any point in the command tree.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x amples
Ro ot >
logout
Config> logout
Config.Port> logout
Introduction
Logging In and Logging Out 13
Page 26

Using the commaDelim Command
Note that the o utput examples sho wn in the other sections of this publication presume that
commaDelim is off.
commaDelim
Syntax
commaDelim enable
Purpose
This command enables the user to obtain displayed information ( fro m a show c ommand)
in comma-delimited, rather than tabular, format. Tabular fo rmat is the default.
Description
This c o mmand c an be entered at any po int in the command tree.
Parame ter
This command has one parameter.
enable
Co mmand E x amples
Ro ot >
commaDelim true
Config> commaDelim true
Config.Port> commaDelim true
14 Using the commaDelim Co mmand
Specifies the comma-delineated state for output. Valid values are
and
false. Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
true
Page 27

Output Example
Output displayed in c ommaDelim mode is as fo llo ws:
Ro ot >
show eventLog
Date/Time,Code,Severity,FRU,Event Data,
04/12/01 10:58A,375,Major,CTP-0,00010203 04050607 08090A0B 0C0D0E0F,
04/12/01 10:58A,375,Major,CTP-0,00010203 04050607 08090A0B 0C0D0E0F,
04/12/01 09:58A,385,Severe,CTP-0,00010203 04050607 08090A0B 0C0D0E0F,
04/11/01 07:18P,395,Severe,CTP-0,00010203 04050607 08090A0B 0C0D0E0F,
Introduction
Using the c ommaDelim Command 15
Page 28

Handling Command Line Interface Errors
Two types o f erro rs detec ted by the Co mmand Line Interfac e are:
• An error associated with the interface. For example, a keyword is misspelled or does
not exist.
confg
Ro ot >
Error 234: Invalid Command
• An error associated with fabric or switch issues. For example, a parameter error is
detected by the switch, where port 24 is entered for a switch that supports only 16 ports.
Ro ot >
config port name 24 "Port 24"
Error 13: Invalid Port Number
In either case, the command is ignored. The Command Line Interface remains at the po int
it was before the command was entered.
The erro r messages, inc luding error number and error, are listed in Appendix, Erro r
Messages.
16 Handling Command Line Interface Errors
Page 29

Using the Command Line Interface Help
The question mark (?) c an be used within a command to obtain certain information:
• If the questio n mark is used in place o f a c o mmand keywo rd, all the ke ywords at that
level of the CLI co mmand tree display.
config system ?
Ro ot >
Command identified
contact - sets the system contact attribute
date - sets the system date and time
description - sets the system information string
location - sets the system location attribute
name - sets the system name attribute
show - displays the system configuration
• If the question mark is used at the end of a rec ognized command, any parameters for
that c o mmand display.
config port name ?
Ro ot >
- name <portNumber> <portName>
• If the question mark is used after one or more characters of a keyword, any keywords
at that level o f the CLI command tree display.
Introduction
config s?
Ro ot >
security snmp switch system
Using the Command Line Interface Help 17
Page 30

Telnet Session
The CLI can only be used through a Telnet c lient session in an o ut-o f-band management
environment, using the Ethernet port in the directo r o r switc h. Although the primary use o f
the CLI is in ho st-based scripting environments, the CLI commands can also be entered
directly at a co mmand line. Any hardware platfo rm that supports the Telnet c lient software
can be used.
Ethernet Connection Loss
If the Ethernet cable is disco nnected from the director or switch during a Telnet sessio n,
one of three scenarios is possible:
• Replace the Ethernet c able before the c lient c onnec tio n times o ut, and the Telnet
session will continue.
• Wait 10 minutes fo r the client connection times out; then replac e the Ethernet c able and
restart the c o nne c tio n.
• If the client c o nnec tion has already timed o ut, open an HP Embedded Web Server (HP
EWS) or HP Surestore Director FC-64 Product Manager window. Toggle the enabled
state of the Command Line Interface (CLI), thereby clearing the client connection.
Restart the c lient connection.
Once the client connectio n is reestablished, verify your co nfiguration’s completeness and
accuracy.
18 Telnet Session
Page 31

2 CLI COMMANDS
Command Overview
config
maint
perf
show
This chapter describes the Command Line Interface co mmands, including their syntax,
purpose, and parameters, as well as examples o f their usage and any o utput that they
generate.
CLI Commands
19
Page 32

Command Overview
Note that most of the commands in this chapter are listed in alphabetic al o rder to make
them easier to lo cate. Although the co mmands can be entered in any order, depending on
the results desired (so long as the tree structure is followed), the o rder used herein fo r the
zo ning commands fo llo ws a typic al o rder of entry. The various show c o mmands are usually
entered at the end of a group of other co mmands.
Note The order in whic h commands are entered determines the o rder in which the
show commands display the values. Therefore, the examples of the output from
the show commands may no t match the order o f the o utput parameters in your
output.
20 Command Overview
Page 33

config
The c onf ig branc h o f the CLI command tree c ontains c o mmands that set parameter values.
These values are no t tempo rary ( sessio n) values, b ut are retained across po wer c yc les.
The commands in the config branch can by used only by the Administrator.
Note that the c o nfig.zo ning c o mmands func tio n in a different way fro m the o ther CLI
commands, which are single ac tio n c o mmands that take effect immediately. A zoning
configuration is typically too complicated to be described by a single command, so the first
zoning co mmand entered invokes a work area editor. The co mmands take effect on a
temporary copy o f a zone set in the work area until the tempo rary c o py in the work area is
activated to the fabric--or is discarded.
Because not all the verification of the zone set can occur on the temporary copy in the
work area, it is possible, however unlikely, that the co py of the zone set encounters no
erro rs until the zo ne set is activated to the fabric.
config.ip.ethernet
Syntax
CLI Commands
ethernet ipAddress gatewayAddress subnetMask
Purpose
This c o mmand sets the Ethernet netwo rk settings.
Description
Note The Telnet c o nnection can be lo st when these Etherne t netwo rk settings are
changed.
config 21
Page 34

Note If the IP address is rec o nfigured, your Telnet client must be rec o nnec ted to the
new IP address. A new login will be requested.
Parameters
This command has three parameters.
ipAddress Specifies the new IP address for the director or switch. The address must be
entered in dotted decimal format (for example, 10.0.0.0).
gatewayAddress Specifies the new gateway address for the Ethernet interface. The address
must be entered in dotted decimal format (for example, 0.0.0.0).
subnetMask Specifies the new subnet mask for the Ethernet interface. The address must
be entered in dotted decimal format (for example, 255.0.0.0).
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config ip ethernet 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.0.0.0
config.ip.show
Syntax
show
Purpose
This command shows the LAN configuration.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config ip show
22 config
Page 35

Output
The LAN co nfiguration data is displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing properties.
IP Address The IP address.
Gateway Address The gateway address.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask.
Output Example
The output from the co nfig.ip.show c ommand displays as follows.
IP Address: 10.0.0.0
Gateway Address: 0.0.0.0
Subnet Mask: 255.0.0.0
config.port.blocked
Syntax
blocked portNumber blockedState
Purpose
This command sets the bloc ked state for a po rt.
Parameters
This command has two required parameters.
portNumber Specifies the port number. Valid values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
blockedState
Specifies the blocked state for the port. Valid values are
Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
CLI Commands
true and false.
config 23
Page 36

Co mmand E x amples
config port blocked 4 false
Ro ot >
Ro ot > config port blocked 4 0
config.port.extDist
Syntax
extDist portNumber extDistOn
Purpose
This c o mmand sets the extended distance state fo r a port.
Description
When the extended distance field is true, the port is configured fo r 60 buffer credits, whic h
supports a distance of up to 100 km for a 1 GB port.
Parameters
This command has two required parameters.
portNumber Specifies the port number. Valid values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
extDistOn
Specifies the extended distance state for the port. Valid values are true and
false. Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
Co mmand E x amples
Ro ot >
config port extDist 4 false
Ro ot > config port extDist 4 0
24 config
Page 37

config.port.name
Syntax
name portNumber “portName”
Purpose
This c o mmand sets the name for a port.
Parameters
This command has two required parameters.
portNumber Specifies the port number. Valid values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
portName Specifies the name for the port. The port name must not exceed 24
characters in length.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config port name 4 “Sam’s tape drive”
config.port.type
CLI Commands
Syntax
type portNumber portType
Purpose
This command sets the allowed type for a port.
Description
A port can be co nfigured as an F_Port, an E_Port, or a G_Port. If a port is configured as an
F_Po rt, that port canno t be used as an interswitch link, but may attach to a devic e with an
N_Port. If a port is co nfigured as an E_Port, only other switches may attach to that port. If
a port is configured as a G_Port, either a device or another switch may attach.
config 25
Page 38

Parameters
This command has two required parameters.
portNumber Specifies the port number. Valid values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
portType
Specifies the type of the port. Valid values are
eport, fport, and gport.
Co mmand E x ample
config port type 4 fport
Ro ot >
config.port.show
Syntax
show portNumber
Purpose
This c o mmand displays the port configuratio n for a single po rt.
Description
This show command, on the config.port branch, displays the current configuration fo r the
specified port.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
portNumber Specifies the port number. Valid values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
26 config
Page 39

Co mmand E x ample
config port show 4
Ro ot >
Output
The po rt configuration is displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing pro perties.
Port Number The port number.
Name The port name.
Blocked
Extended Distance
Typ e
The blocked state. Valid values are
The extended distance configuration state. Valid values are true and false.
The port type. Valid values are FPort, EPort, and GPort.
true and false.
Output Example
The output from the c o nfig.po rt.sho w c o mmand displays as follo ws.
Port Number: 4
Name: Sam’s tape drive
Blocked: false
Extended distance: false
Type: F Port
config.security.portBinding
config.security.portBinding.bound
Syntax
bound portNumber portBindingState
CLI Commands
Purpose
This command sets the port binding state fo r a given port.
config 27
Page 40

Parameters
This command has two parameters.
portNumber Specifies the port number for which the port binding state is being set. Valid
port number values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
portBindingState
Specifies the port binding state as active or inactive. Valid values are
and
false.
true sets the port binding to active. The specified port will be bound to the
WWN configured with the config.security.portBinding.wwn command. If no
WWN has been configured, no devices can log in to that port.
false sets the port binding to inactive. Any device is free to connect to the
specified port in this state, regardless of the WWN setting.
Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
Co mmand E x amples
Ro ot >
config security portBinding bound 4 true
Ro ot > config security portBinding bound 4 1
config.security.port Binding.wwn
Syntax
wwn portNumber boundWwn
Purpose
This command configures the single devic e WWN to which a po rt is bo und.
true
28 config
Page 41

Parameters
This command has two parameters.
portNumber Specified the port number for which the bound WWN is being set. Valid port
number values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
boundWwn Specifies the WWN of the device that is being bound to the specified port.
The value must be entered in colon-delimited hexidecimal notation (for
example, 11:22:33:44:55:66:AA:BB).
If the boundWwn is configured and the portBindState is:
Active—only the device described by boundWwn will be able to connect to
the specified port.
Inactive—the WWN is retained, but any device can connect to the specified
port.
Instead of the WWN, either of two values can be entered in this parameter:
attached automatically configures the currently attached device WWN as the
bound WWN.
remove changes the WWN to the default value, 00:00:00:00:00:00:00:00.
Even though this removes the WWN-port association, if the portBindingState
value set with the config.security.portBinding.bound command is still
(the port binding is active), other devices are prevented from logging in to this
port. To allow other devices to log in to this port, use the
config.security.portBinding.bound command to set the portBindingState
parameter to false.
true
CLI Commands
Co mmand E x amples
config security portBinding wwn 4 AA:99:23:23:08:14 :88:C1
Ro ot >
Ro ot > config security portBinding wwn 4 attached
Ro ot > config security portBinding wwn 4 remove
config 29
Page 42

config.security.port Binding.show
Syntax
show portNumber
Purpose
This command shows the po rt binding c o nfiguration for a single port.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
portNumber Specifies the port number for which the port binding configuration will be
shown. Valid values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config security portBinding show 4
Output
The po rt binding configuration date is displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing
properties.
Port Number The port number.
WWN Binding The state of port binding for the specified port, either active or inactive.
Bound WWN The WWN of the device that is bound to the specified port. If this field is
blank, no device has been bound to the specified port.
30 config
Page 43

Output Example
The output from the c o nfig.security.portBinding.show c ommand displays as fo llows.
Port Number: 4
WWN Binding: Active
Bound WWN: AA:99:23:23:08:14:88:C1
config.security.userRights
config.security.userRights.administrator
Syntax
administrator “username” “password”
Purpose
This command sets the name and password for administrator-level access.
Description
Immediately after the name and password fo r the administrator is set, yo u will be
pro mpted to lo g in with the new ac c ess rights.
CLI Commands
Parameters
This command has two parameters.
username Specifies the new user name for administrator-level login. Default is set to
Administrator. This parameter is 1–15 characters. Valid characters include
all characters in the USASCII character set, excluding control characters and
spaces. Spaces are not valid even though quotation marks are used.
password Specifies the password for administrator-level login. Default is set to
password. This parameter is 1–15 characters. Valid characters include all
characters in the USASCII character set, excluding control characters and
spaces. Spaces are not valid even though quotation marks are used.
config 31
Page 44

Co mmand E x ample
config security userRights administrator “Administrator” “new
Ro ot >
password”
config.security.userRights.operator
Syntax
operator “username” “password”
Purpose
This command sets the name and password for operator-level acc ess.
Parameters
This command has two parameters.
username Specifies the new user name for operator-level login. Default is set to
Operator. This parameter is 1–15 characters. Valid characters include all
characters in the USASCII character set, excluding control characters and
spaces. Spaces are not valid even though quotation marks are used.
password
Specifies the password for operator-level login. Default is set to
This parameter is 1–15 characters. Valid characters include all characters in
the USASCII character set, excluding control characters and spaces. Spaces
are not valid even though quotation marks are used.
password.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config security userRights operator “Operator” “newpassword”
32 config
Page 45

config.security.userRights.show
Syntax
show
Purpose
This c o mmand shows the user rights fo r the command line interfac e access levels.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config security userRights show
Output
The user rights configuration data is displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing
properties.
Operator Username The username for operator privileges.
Operator Password The password for operator privileges.
Administrator
Username
Administrator
Password
The username for administrator privileges.
The password for administrator privileges.
CLI Commands
config 33
Page 46

Output Example
The o utput fro m the config.security.use rRights.sho w command displays as fo llo ws.
Operator Username: Operator
Operator Password: **************
Administrator Username: Administrator
Administrator Password: ***************
config.snmp.addCommunity
Syntax
addCommunity commIndex "commName" writeAuthorization trapRecipient
udpPortNum
Purpose
This c o mmand adds an SNMP community to the SNMP co nfiguration.
Parameters
This c ommand has five parameters. Up to six community names and trap recipients may be
defined.
commIndex Specifies the community to be created or edited. Valid values are integers in
the range 1–6.
commName Specifies the community name of the community specified by commIndex.
The community name must not exceed 32 characters in length. Valid
characters include all those in the ISO Latin-1 character set. Duplicate
community names are allowed, but the corresponding writeAuthorization
values must match.
writeAuthorization Specifies the write authorization state of the community. Valid values are
enabled and disabled. Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
34 config
Page 47

trapRecipient Specifies the trap recipient. Values must be 4 bytes in dotted-decimal format.
udpPortNum Specifies the UDP port number to which the director will send traps for each
recipient. The values must be a decimal number; the default value is 162.
Valid values include all legal UDP port numbers.
Co mmand E x ample
config snmp addCommunity 1 "CommunityName1" enabled 123.123.1
Ro ot >
23.123 162
config.snmp.authTraps
Syntax
authTraps enabledState
Purpose
This co mmand enables or disables the authorization traps to be sent to SNMP management
stations when unauthorized stations try to acc ess SNMP information from the directo r or
switch.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
enabledState
Specifies whether the authorization traps are enabled. Valid values are
and
false. Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
true
Co mmand E x amples
Ro ot >
config snmp authTraps true
Ro ot > config snmp authTraps 1
CLI Commands
config 35
Page 48

config.snmp.deleteCommunity
Syntax
deleteCommunity commIndex
Purpose
This command entirely deletes a co mmunity from the SNMP
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
commIndex Specifies the community to be deleted. Valid values are integers in the range
1–6. This value was set in the commIndex parameter of the
config.snmp.addCommunity command. Valid values are integers in the range
1–6.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config snmp deleteCommunity 5
config.snmp.show
Syntax
show
Purpose
This command shows the switch SNMP configuration.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
36 config
Page 49

Co mmand E x ample
config snmp show
Ro ot >
Output
The switch configuration data is displayed as a table that includes the follo wing properties
commIndex The community index number.
commName The name of the community.
writeAuthorization The write authorization state.
trapRecipient The address of the trap recipient.
udpPortNum The UDP port number to which the director will send traps for each recipient.
Output Example
The output from the co nfig.snmp.show command displays as follows.
Authorization Traps: Enabled
Index Community Name WriteAuth Trap Recipient UDP Port
----- -------------------------------- --------- --------------- -------1 CommunityName1 Enabled 123.123.123.123 162
2 CommunityName2 Enabled 10.25.25.10 144
3 CommunityName3 Disabled 132.44.85.224 162
4 public Enabled 162
5
6
CLI Commands
config 37
Page 50

config.switch
All of the config.switch commands, exc ept fo r the co nfig.switch.show command, require
that the switc h first be set of fline. ( Use the maint.system.setOnlineState to set the switc h
offline.) If these commands are entered while the switc h is online, an error message
results.
config.switch.bbCredit
Syntax
bbCredit bbCreditValue
Purpose
This command sets the buffer-to-buffer c redit value for all po rts, except those po rts
configured fo r extended distanc e.
Description
The switc h must be set offline before this co mmand is entered.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
bbCreditValue Specifies the new buffer-to-buffer credit value. This parameter must be an
integer in the range 1–60.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config switch bbCredit 2
38 config
Page 51

config.switch.edTOV
Syntax
edTOV timeoutValue
Purpose
This c o mmand sets the E_D_TOV fo r the switch.
Description
The switc h must be set offline before this co mmand is entered.
Spec ial care should be used when scripting this command due to its relationship with
R_A_TOV.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
timeoutValue Specifies the new E_D_TOV value. The units for this value are tenths of a
second. This parameter must be an integer in the range 2–600 (0.2 second to
60 seconds), and it must be smaller than the R_A_TOV.
CLI Commands
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config switch edTOV 4
config.switch.interopMode
Syntax
interopMode interopMode
Purpose
This command sets the Interoperability mo de for the switch.
config 39
Page 52

Description
The switc h must be set offline before this co mmand is entered.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
interopMode
Specifies the interoperability mode. Valid values are
mcdata — McDATA Fabric 1.0
open — Open Fabric 1.0
Co mmand E x ample
config switch interopMode open
Ro ot >
config.switch.prefDomainId
Syntax
prefDomainId domainId
Purpose
This command sets the preferred domain ID for the switch.
Description
The switc h must be set offline before this co mmand is entered.
Parameters
mcdata and open:
This command has one parameter.
domainId Specifies the new preferred domain ID value. This parameter must be an
integer in the range 1–31.
40 config
Page 53

Co mmand E x ample
config switch prefDomainId 1
Ro ot >
config.switch.priority
Syntax
priority switchPriority
Purpose
This command sets the switch priority.
Description
The switc h must be set offline before this co mmand is entered.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
switchPriority
Specifies the switch priority. Valid values are: pri nci pal, default, or
neverprincipal.
principal — sets the numerical switch priority to 1. The switch with a priority
of 1 becomes the principal switch; however, if two or more switches have a
priority of 1, the switch with the lowest WWN becomes the principal switch.
def ault — sets the numerical switch priority to 254. If no switch is set to
principal, the switch with a priority 254 becomes the principal switch;
however, if two or more switches have a priority of 254, the switch with the
lowest WWN becomes the principal switch.
neverprincipal — sets the numerical switch priority to 255. This switch is
not able to become the principal switch.
Note that at least one switch in a multiswitch fabric must have a switch
priority value of principal or default.
Note that the number codes 2–253 are not now in use.
CLI Commands
config 41
Page 54

Co mmand E x ample
config switch priority principal
Ro ot >
config.switch.raTOV
Syntax
raTOV timeoutValue
Purpose
This c o mmand sets the R_A_TOV fo r the switch.
Description
The switc h must be set offline before this co mmand is entered.
Spec ial care should be used when scripting this command due to its relationship with
E_D_ TOV.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
timeoutValue Specifies the new R_A_TOV value. The units for this value are tenths of a
second. This parameter must be an integer in the range 10–1200 (1 second
to 120 seconds), and it must be larger than the E_D_TOV.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config switch raTOV 20
42 config
Page 55

config.switch.rerouteDelay
Syntax
rerouteDelay rerouteDelayState
Purpose
This command enables or disables rerouting delay fo r the switc h.
Description
The switc h must be set offline before this co mmand is entered.
This command is o nly applic able if the configured switch is in a multiswitc h fabric .
Enabling the rerouting delay ensures that frames are delivered in order through the fabric
to their destination.
If there is a c hange to the fabric topo lo gy that creates a new path (for ex ample, a new
switc h is added to the fabric), frames may be ro uted o ver this new path if its hop count is
less than a previous path with a minimum hop c o unt. This may result in frames being
delivered to a destination out of order because frames sent over the new, shorter path may
arrive ahead of older frames still in route over the older path.
If rerouting delay is enabled, traffic ceases in the fabric fo r the time specified in the
config.switch.edTOV command. This delay allows frames sent o n the old path to exit to
their destinatio n bef ore ne w frames be gin traversing the new path. Note that during this
delay period, frames addressed to the destinations that are being rerouted are discarded if
they are Class 3 frames and rejected if they are Class 2 or Class F frames.
CLI Commands
Parame ter
This command has one parameter.
rerouteDelayState
Specifies whether Rerouting Delay is enabled. Valid values are
false. Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
true and
config 43
Page 56

Co mmand E x amples
config switch rerouteDelay true
Ro ot >
Ro ot > config switch rerouteDelay 1
config.switch.show
Syntax
show
Purpose
This command shows the switch co nfiguration.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config switch show
Output
The switch configuration data is displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing properties.
BB Credit The maximum number of outstanding frames that can be transmitted without
causing a buffer overrun condition at the receiver.
R_A_TOV Resource Allocation Time Out Value.
This value is set in tenths of a second.
E_D_TOV Error Detect Time Out Value.
This value is set in tenths of a second.
Preferred Domain Id The preferred domain ID of the switch.
Switch Priority The switch priority. Values are Principal, Default, or Never Principal.
44 config
Page 57

Rerouting Delay The rerouting delay that ensures that frames are delivered in order through
the fabric to their destination. Values are Enabled or Disabled.
Interop Mode Interoperability mode for the switch.
Output Example
The output from the c o nfig.switch.show command displays as follows.
BB Credit: 2
R_A_TOV: 20
E_D_TOV: 4
Preferred Domain Id: 1
Switch Priority: Principal
Rerouting Delay: Enabled
Interop Mode: Open Fabric 1.0
config.system.contact
Syntax
contact “systemContact”
Purpose
CLI Commands
This c o mmand sets the system contact attribute.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
systemContact Specifies the new system contact string for the director or switch. The contact
can contain 0–255 characters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config system contact “Joe”
config 45
Page 58

config.system.date
Syntax
date sysDate sysTime
Purpose
This command sets the system date and time.
Parameters
This command has two required parameters.
sysDate Specifies the new system date. The format of the date parameter must be
mm:dd:yyyy or mm/dd/yyyy. Valid date values include:
mm: 1–12
dd: 1–31
yyyy: >1980
sysTime Specifies the new system time. The format of the time parameter must be
hh:mm:ss. Valid time values include:
hh: 0–23
mm: 0–59
ss: 0–59
Co mmand E x amples
Ro ot >
config system date 04:16:2001 10:34:01
Ro ot > config system date 10/09/2001 14:07:55
46 config
Page 59

config.system.description
Syntax
description “systemDescription”
Purpose
This command sets the system description string.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
systemDescription Specifies the new system description string for the director or switch. The
name can contain 0–255 characters.
Co mmand E x ample
config system description “HP Surestore Director FC-64”
Ro ot >
Note The value “HP Suresto re Director FC-64” in the command example can be any
user specified value.
CLI Commands
config.system.location
Syntax
location “systemLocation”
Purpose
This c o mmand sets the system lo c atio n attribute.
config 47
Page 60

Parameters
This command has one parameter.
systemLocation Specifies the new system location for the director or switch. The location can
contain 0–255 characters.
Co mmand E x ample
config system location “Everywhere”
Ro ot >
config.system.name
Syntax
name “systemName”
Purpose
This c o mmand sets the system name attribute.
Parameters
This command has one required parameter.
systemName Specifies the new system name for the director or switch. The name can
contain 0–24 characters.
Co mmand E x ample
config system name “Joe’s Switch”
Ro ot >
config.system.show
Syntax
show
48 config
Page 61

Purpose
This command shows the system configuration.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
config system show
Ro ot >
Output
The system c o nfiguration is displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing properties.
Name The system name.
Description The system description.
Contact The system contact.
Location The system location.
Date/Time The system date and time.
CLI Commands
Output Examples
The output from the co nfig.system.show c ommand displays as follows.
Name: Joe’s Switch
Description: HP Surestore Director FC-64
Contact: Joe
Location: Everywhere
Date/Time: 04/16/2001 10:34:01
config 49
Page 62

config.zoning
Note that the c o nfig.zo ning c o mmands func tio n in a different way fro m the o ther CLI
commands, which are single actio n c o mmands that take effect immediately. A zo ning
configuration is typically too complicated to be described by a single command, so the first
zoning command entered invokes a work area editor. The commands take effect on a
temporary copy o f a zone set in the wo rk area until the tempo rary c o py in the work area is
activated to the fabric--or is discarded.
Because not all the verification of the zone set can occur on the temporary copy in the
work area, it is possible, however unlikely, that the co py of the zone set encounters no
erro rs until the zo ne set is activated to the fabric.
config.zoning.setDefZoneState
Syntax
setDefZoneState defaultZoneState
Purpose
This command enables or disables the default zone and takes effec t immediately fabric
wide.
Description
Note This command takes effect immediately in the fabric.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
defaultZoneState
50 config
Specifies whether the default zone is enabled. Valid values are
false. Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
true and
Page 63

Co mmand E x amples
config zoning setDefZoneState false
Ro ot >
Ro ot > config zoning setDefZoneState 0
config.zoning.activateZoneSet
Syntax
activateZoneSet
Purpose
This c o mmand ac tivates the zone se t contained in the work area to the fabric and takes
effect immediately.
Description
Note This command takes effect immediately in the fabric.
Parameters
CLI Commands
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config zoning activateZoneSet
config 51
Page 64

config.zoning.deactivateZoneSet
Syntax
deactivateZoneSet
Purpose
This command places all attached devices in the default zone and takes effec t immediately
fabric wide.
Description
The default zone must be ac tivated independently of this command.
Note This command takes effect immediately in the fabric.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config zoning deactiveZoneSet
config.zoning.replaceZoneSet
Syntax
replaceZoneSet
Purpose
This c o mmand replac es the work area with the ac tive zone set that is c urrently loaded on
the fabric .
52 config
Page 65

Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
config zoning replaceZoneSet
Ro ot >
config.zoning.clearZoneSet
Syntax
clearZoneSet
Purpose
This c o mmand clears the zone set c o ntaine d in the wo rk area, removing all zo nes, and
takes effect immediately.
Description
This c o mmand does no t c hange the zo ne set name.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config zoning clearZoneSet
CLI Commands
config 53
Page 66

config.zoning.addZone
Syntax
addZone “zoneName”
Purpose
This c o mmand adds a new ( empty) zone to the zone set in the work area.
Description
Changes are no t activated on the switc h until the co nfig.zo ning.activateZo neSet c o mmand
is issued. The CLI supports the number of zones per zone set specified for a given product.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
zoneName Specifies the name of the new zone. The zoneName must contain 1–64
characters. Valid characters are:
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz012345
6789$-^_
Spaces are not permitted, and the first character must be alphabetical.
Co mmand E x ample
config zoning addZone TheUltimateZone
Ro ot >
config.zoning.deleteZone
Syntax
deleteZone “zoneName”
Purpose
This c o mmand deletes a zone fro m the zone set in the wo rk area.
54 config
Page 67

Description
Changes are not activated on the switch until the config.zoning.activeZoneSet c ommand is
issued.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
zoneName Specifies the name of the zone to be deleted.
Co mmand E x ample
config zoning deleteZone TheLeastUltimateZone
Ro ot >
config.zoning.renameZoneSet
Syntax
renameZoneSet “zoneSetName”
Purpose
This c o mmand c hanges the name of the zone set in the wo rk area.
CLI Commands
Description
Changes are no t activated on the switc h until the co nfig.zo ning.activateZo neSet c o mmand
is issued.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
zoneSetName Specifies the new name for the zone set. The zoneSetName must contain
1-64 characters. Valid characters are:
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz012345
6789$-^_
Spaces are not permitted, and the first character must be alphabetical.
config 55
Page 68

Co mmand E x ample
config zoning renameZoneSet TheUltimateZoneSet
Ro ot >
config.zoning.addWwnMem
Syntax
addWwnMem “zoneName” wwn
Purpose
This command adds a world-wide name zo ne member to the spec ified zo ne in the wo rk
area.
Description
The CLI supports the number o f zones members per zone spec if ied for a given pro duc t.
Parameters
This command has two parameters.
zoneName Specifies the name of the zone.
wwn The world-wide name of the member to be added to the zone. The value of
the WWN must be in colon-delimited hexidecimal notation (for example,
AA:00:AA:00:AA:00:AA:00).
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config zoning addWwnMem TheUltimateZone 10:00:00:00:C9:22:9B:
64
56 config
Page 69

config.zoning.addPortMem
Syntax
addPortMem “zoneName” domainId portNumber
Purpose
This command adds the domain ID and port number of a zone member to the spec ified
zone in the work area.
Description
The CLI supports the number o f zones members per zone spec if ied for a given pro duc t.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
zoneName Specifies the name of the zone.
domainId Specifies the domain ID of the member to be added to the zone. Valid values
are in the range 1–31.
portNumber Specifies the port number of the member to be added to the zone. Valid port
number values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config zoning addPortMem TheUltimateZone 10 6
CLI Commands
config 57
Page 70

config.zoning.clearZone
Syntax
clearZone “zoneName”
Purpose
This command clears all zone members for the spec ified zo ne in the wo rk area.
Description
This c o mmand do es no t c hange the zone name.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
zoneName Specifies the name of the zone to be cleared.
Co mmand E x ample
config zoning clearZone TheNotUltimateAtAllZone
Ro ot >
config.zoning.deleteWwnMem
Syntax
deleteWwnMem “zoneName” wwn
Purpose
This command removes a WWN memb er fro m a zo ne that is in the w o rk area.
58 config
Page 71

Parameters
This command has two parameters.
zoneName Specifies the name of the zone that contains the member to be deleted.
wwn Specifies the world-wide name of the member to be deleted from the zone.
The value of the WWN must be in colon-delimited hexidecimal notation (for
example, AA:00:AA:00:AA:00:AA:00).
Co mmand E x ample
config zoning deleteWwnMem TheNotSoUltimateZone 10:00:00:00:C
Ro ot >
9:22:9B:AB
config.zoning.deletePortMem
Syntax
deletePortMem “zoneName” domainId portNumber
Purpose
This command deletes a domain ID and port number for a zone member in the spec ified
zone in the work area.
CLI Commands
Parameters
This command has three parameters.
zoneName Specifies the name of the zone that contains the member to be deleted.
domainId Specifies the domain ID of the member that to be deleted from the zone. Valid
domain IDs are in the range 1–31.
portNumber Specifies the port number of the member to be deleted from the zone. Valid
port numbers values are:
0–64 for the FC-64
config 59
Page 72

Co mmand E x ample
config zoning deletePortMem TheUltimateZone 10 5
Ro ot >
config.zoning.renameZone
Syntax
renameZone “oldZoneName” “newZoneName”
Purpose
This command renames a zo ne in the wo rk are a.
Parameters
This command has two parameters.
oldZoneName Specifies the current zone name of the zone to be renamed.
newZoneName Specifies the new zone name.
Co mmand E x ample
config zoning renameZone TheOldUltimateZone TheUltimateZone
Ro ot >
config.zoning.showPending
Syntax
showPending
Purpose
This c ommand sho ws the zoning c o nfiguratio n in the work area o f the zone set that has no t
yet been ac tivated.
60 config
Page 73

Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
config zoning showPending
Ro ot >
Output
The zoning co nfiguration data is displayed as a table that includes the following properties.
Local ZoneSet The enabled status, name, and member zones of the zone set.
Output Example
The output from the c o nfig.zo ning.sho wPending co mmand displays as follows.
Pending Zone Set
Default Zone Enabled: False
ZoneSet: TheNewUltimateZoneSet
Zone: TheNewUltimateZone
ZoneMember: Domain 10, Port 6
ZoneMember: Domain 15, Port 2
Zone: TheNewNotSoUltimateZone
ZoneMember: 10:00:00:00:C9:22:9B:AB
ZoneMember: 10:00:00:00:C9:22:9B:C6
ZoneMember: 10:00:00:00:C9:22:9B:AB
Zone: TheNewNotUltimateAtAllZone
ZoneMember: Domain 2, Port 63
CLI Commands
config 61
Page 74

config.zoning.showActive
Syntax
showActive
Purpose
This command shows the zoning configuration saved on the fabric.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
config zoning showActive
Output
The zoning co nfiguration data is displayed as a table that includes the following properties.
Active ZoneSet The enabled status, name, and member zones of the zone set.
62 config
Page 75

Output Example
The output from the config.zoning.showActive command displays as follows.
Active Zone Set
Default Zone Enabled: False
ZoneSet: TheUltimateZoneSet
Zone: TheUltimateZone
ZoneMember: Domain 10, Port 6
ZoneMember: Domain 15, Port 2
ZoneMember: Domain 2, Port 63
ZoneMember: 10:00:00:00:C9:22:9B:64
ZoneMember: 10:00:00:00:C9:22:9B:BD
Zone: TheNotSoUltimateZone
ZoneMember: 10:00:00:00:C9:22:9B:AB
ZoneMember: 10:00:00:00:C9:22:9B:C6
ZoneMember: 10:00:00:00:C9:22:9B:AB
Zone: TheNotUltimateAtAllZone
ZoneMember: Domain 2, Port 63
CLI Commands
config 63
Page 76

maint
The maint branch of the CLI command tree contains commands that relate to maintenanc e
ac tivities.
The co mmands in the maint branch c an be used only by the Administrator.
Note that the maint.system.resetCo nfig c o mmand resets all configuratio n data and no nvolatile settings, inc luding netwo rk info rmation, to their default values ( facto ry settings) .
Management access may be lo st until the network informatio n is resto red.
maint.port.beacon
Syntax
beacon portNumber beaconState
Purpose
This command enables or disables port beaconing for a particular port.
Parameters
This command has two required parameters.
portNumber Specifies the port number. Valid values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
beaconState
Co mmand E x amples
Ro ot >
Ro ot > maint port beacon 4 0
64 maint
Specifies whether unit beaconing is enabled. Valid values are
Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
maint port beacon 4 false
true and false.
Page 77

maint. port.reset
Syntax
reset portNumber
Purpose
This command resets an individual port.
Description
This command resets an individual port without affecting any other ports. Ho wever, if a
device is attached to the po rt and the device is online, the reset c auses a link reset to o ccur.
If the port is in a failed state ( that is, after failing a loopback test) , the reset restores the
port to an operational state. The reset also clears all statistics counters and disables port
beaco ning fo r the specified port.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
portNumber Specifies the port number to be reset. Valid values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
CLI Commands
Co mmand E x ample
maint port reset 4
Ro ot >
maint.system.beacon
Syntax
beacon beaconState
Purpose
This command enables or disables unit beaconing.
maint 65
Page 78

Parameters
This command has one parameter.
beaconState
Specifies whether unit beaconing is enabled. Valid values are
Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
Co mmand E x amples
maint system beacon false
Ro ot >
Ro ot > maint system beacon 0
maint.system.clearSysError
Syntax
clearSysError
Purpose
This command clears the system error light.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
true and false.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
maint system clearSysError
66 maint
Page 79

maint.system.ipl
Syntax
ipl
Purpose
This command IPLs the switc h.
Description
Note Connec tio n to the c o mmand line interfac e is lost when this co mmand runs.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
maint system ipl
maint.system.resetConfig
Syntax
resetConfig
Purpose
This command resets all NV-RAM co nfiguration parameters to their default values.
Description
This c o mmand IPLs the switc h. Co nnection fro m the c o mmand line interfac e to the switch
is lost when this c ommand runs.
CLI Commands
maint 67
Page 80

Note This command resets all configuration data and non-volatile settings, including
network info rmatio n, to their default values ( factory settings). Management
access may be lost until the netwo rk information is resto red.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
maint system resetConfig
maint.system.setOnlineState
Syntax
setOnlineState onlineState
Purpose
This command sets the switch online or offline.
Parameters
This command has one parameter.
onlineState
Specifies whether the switch is online. Valid values are
Boolean 1 and 0 may be substituted as values.
Co mmand E x amples
Ro ot >
maint system setOnlineState true|
Ro ot > maint system setOnlineState 1
68 maint
true and false.
Page 81

perf
The perf branch of the CLI co mmand tree c ontains co mmands that relate to performance
services.
The c o mmands in the perf branch can by used by either the Administrato r o r the Operato r.
perf.class2
Syntax
class2
Purpose
This command displays port Class 2 counters for all ports.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
perf class2
Output
The po rt Class 2 co unter data is displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing pro perties.
Port The port number.
Rx Frames The number of Fibre Channel Class 2 frames that the port has received.
Tx Frames The number of Fibre Channel Class 2 frames that the port has transmitted.
Rx Words The number of Class 2 4-byte words within frames that the port has received.
TX Words The number of Class 2 4-byte words within frames that the port has
transmitted.
CLI Commands
perf 69
Page 82

Busied Frms The number of times that FBSY was returned to this port as a result of a
Class 2 frame that could not be delivered to the other end of the link. This
occurs if either the fabric or the destination port is temporarily busy.
Rjct Frames The number of times that FRJT was returned to this port as the result of a
Class 2 frame that was rejected by the fabric.
Output Example
The output from the perf.class2 command displays as follows.
Port Rx Frames Tx Frames Rx Words Tx Words Busied Frms Rjct Frames
---- --------- --------- -------- -------- ----------- ----------0 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
1 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
2 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
3 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
4 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
5 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
6 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
7 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
8 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
9 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
10 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
11 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
12 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
13 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
14 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4 5
15 134285 289355 890422 18483277 4 5
perf.class3
Syntax
class3
Purpose
This command displays port Class 3 counters for all ports.
70 perf
Page 83

Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
perf class3
Ro ot >
Output
The po rt Class 3 co unter data is displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing pro perties.
Port The port number.
Rx Frames The number of Fibre Channel Class 3 frames that the port has received.
Tx Frames The number of Fibre Channel Class 3 frames that the port has transmitted.
Rx Words The number of Class 3 4-byte words within frames that the port has received.
TX Words The number of Class 3 4-byte words within frames that the port has
transmitted.
Disc Frames The number of Class 3 frames that have been discarded upon receipt by this
port. There are no FBSYs or FRJTs generated for Class 3 frames.
CLI Commands
perf 71
Page 84

Output Example
The output from the perf.class3 command displays as follows.
Port Rx Frames Tx Frames Rx Words Tx Words Disc Frames
---- --------- --------- -------- -------- ----------0 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
1 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
2 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
3 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
4 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
5 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
6 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
7 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
8 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
9 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
10 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
11 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
12 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
13 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
14 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
15 134285 289355 890442 18483277 4
perf.clearStats
Syntax
clearStats portNumber
Purpose
This command resets all port statistics fo r an individual port or fo r all po rts.
Parameters
This c o mmand has to ne parameter.
portNumber Specifies the port number. Valid values are:
0–63 for the FC-64
all for every port on the director or switch
72 perf
Page 85

Co mmand E x ample
perf clearStats 4
Ro ot >
Ro ot > perf clearStats all
perf.errors
Syntax
errors
Purpose
This command displays port error co unters for all ports.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
perf errors
CLI Commands
Output
The port error counter data is displayed as a table that includes the following properties.
Port The port number.
Prim Seq Err The number of state machine protocol errors detected by the port hardware.
Disc Frms The number of received frames discarded due to a frame size of less than
size words or to frames dropped because the BB credit was zero. This
number is counted during the first round of frame verification and applies to
both Class 2 and Class 3 traffic.
Inv Tx Wrds The number of 10-bit transmission words that the port is unable to map to 8-
bit bytes because of disparity errors or misaligned K characters while in the
OL2 or OL3 state.
perf 73
Page 86

CRC Errs The number of frame CRC errors detected by the port.
Dlim Errs The number of invalid frame delimiters (SOF or EOF) received by the port.
Addr Id Errs The number of frames received with unknown addressing.
Output Example
The output from the perf.errors c o mmand displays as follo ws.
Port Prim Seq Err Disc Frms Inv Tx Wrds CRC Errs Delim Errs Addr Id Errs
---- ------------ --------- ----------- -------- ---------- -----------0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 1284899 1 0 0
2 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 8 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0 0 0
6 0 0 305233444 0 0 0
7 0 0 0 0 0 0
8 0 0 456 0 0 0
9 0 0 0 0 0 0
10 0 0 0 0 0 0
11 0 0 0 0 0 0
12 0 0 0 0 0 0
13 0 0 0 0 0 0
14 0 0 123527 21 0 0
15 0 0 0 0 0 0
74 perf
Page 87

perf.link
Syntax
link
Purpose
This command displays port link co unters fo r all ports.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
perf link
Output
The po rt link co unter data is displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing pro perties.
Port The port number.
OLS In The number of offline sequences initiated by the attached N_Port.
OLS Out The number of offline sequences initiated by this director or switch port.
CLI Commands
Reset In The number of link resets initiated by the attached N_Port.
Reset Out The number of link resets initiated by this director or switch.
Link Flrs The number of times the port has detected a link error resulting from an
invalid link state transition or timeout.
Sync Losses The number of times the port has detected a loss of synchronization timeout
while not in an offline or LF2 state.
Sig Losses The number of times the port has detected a loss of signal while not in an
offline or LF2 state.
perf 75
Page 88

Output Example
The output from the perf.link command displays as fo llows.
Port OLS In OLS Out Reset In Reset Out Link Flrs Sync Losses Sig Losses
---- ------ ------- -------- --------- --------- ----------- ---------0 0 0 13 21 0 0 0
1 2 0 16 30 6 0 9
2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
6 0 0 0 0 0 0 3
7 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
8 0 0 0 0 0 0 3
9 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
10 0 0 0 4 4 0 0
11 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
12 0 0 0 1 1 0 0
13 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
14 0 0 0 0 0 0 3
15 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
perf.traffic
Syntax
traffic
Purpose
This command displays port traffic c ounters for all ports.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
perf traffic
76 perf
Page 89

Output
The port traffic c o unter data is displayed as a table that includes the fo llowing properties.
Port The port number.
Rx% The received link utilization percentage.
Tx% The transmitted link utilization percentage.
Rx Frames The number of Fibre Channel Class 2 and Class 3 frames that the port has
received.
Tx Frames The number of Fibre Channel Class 2 and Class 3 frames that the port has
transmitted.
Rx Words The number of 4-byte words in Class 2 and Class 3 frames that the port has
received.
Tx Words The number of 4-byte words in Class 2 and Class 3 frames that the port has
transmitted.
Output Example
The output from the perf.traffic command displays as follows.
Port Rx% Tx% Rx Frames Tx Frames Rx Words Tx Words
---- --- --- --------- --------- -------- -------0 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
1 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
2 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
3 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
4 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
5 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
6 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
7 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
8 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
9 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
10 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
11 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
12 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
13 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
14 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
15 75 30 2953184 890442 18483277 9386156
CLI Commands
perf 77
Page 90

show
The show branch of the CLI command tree contains commands that display, but do not
change, stored data values. Note that the displayed o utput that results from these
commands is not identical with the output fro m the show c o mmands that are within the
other CLI command tree branches, for example, config.port.show.
The co mmands in the show branch can by used by either the Administrator or the
Operator.
show.eventLog
Syntax
eventLog
Purpose
This c o mmand shows the contents o f the event lo g as maintained in NV-RAM on the
director or switch.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
show eventLog
Ro ot >
78 show
Page 91

Output
The event log data are displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing properties.
Date/Time The date and time when the event occurred.
Code The event reason code.
Severity The severity of the event. The values are:
Major—Unit operational (major failure).
Minor—Unit operational (minor failure).
Severe—Unit not operational. The causes are either the switch contains no
operational SBAR cards or the system shutdowns due to CTP thermal
threshold violations.
Info—Unit operational (information only).
FRU The FRU and FRU position, where applicable.
Event Data The 32-byte hexidecimal description of the event in words.
Output Example
The output from the show.eventLog command displays as follows.
Date/Time Code Severity FRU Event Data
---------------- ---- -------- ----- ----------------------------------04/12/01 10:58A 375 Major CTP-0 00010203 04050607 08090A0B 0C0D0E0F
04/12/01 09:58A 385 Severe CTP-0 00010203 04050607 08090A0B 0C0D0E0F
04/11/01 07:18P 395 Severe CTP-0 00010203 04050607 08090A0B 0C0D0E0F
CLI Commands
show 79
Page 92

show.frus
Syntax
frus
Purpose
This command displays information about all FRUs.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
show frus
Output
The FRU information is displayed as a table that includes the follo wing properties.
FRU The FRU name. NotInstalled means the FRU is not installed.
Position The relative position of the FRU, that is, its slot.
State
The state of the FRU. Values are:
Active—the current module is active.
Backup—this module is not currently being used, but it is available for
immediate failover.
Failed—the current module is failed.
Serial Num The serial number of the FRU.
Part Num The part number of the FRU.
Beaconing The beaconing state of the FRU (true or false).
Pwr On Hrs The power-on hours value for the FRU.
80 show
Page 93

Output Example
The output from the show.frus command displays as follows.
FRU Position State Serial Num Part Num Beaconing Pwr On Hrs
-------- -------- ------ ---------- -------------- --------- ---------CTP 1 Active 21234560 A6534-67005 false 892
CTP 0 Backup 21234561 A6534-67005 false 766
SBAR 1 Active 31234560 A6534-67007 false 890
SBAR 0 Backup 31234561 A6534-67007 false 891
NotInst 13
NotInst 14
NotInst 15
Power 0 Active 61234560 A6534-67008 false 799
Power 1 Active 61234561 A6534-67008 false 799
Fan 0 Active 51234560 A6534-67004 false 0
Fan 1 Active 51234561 A6534-67004 false 0
Backplane 0 Active 11234560 A6534-67006 false 891
show.ip.ethernet
Syntax
ethernet
Purpose
CLI Commands
This command displays ethernet attributes.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
show ip ethernet
show 81
Page 94

Output
The Ethernet attributes data is displayed as a table that inc ludes the fo llo wing pro pe rties.
IP Address The IP address for the Ethernet adapter as set in the config.ip.ethernet
command.
Gateway Address The gateway address for the Ethernet adapter as set in the config.ip.ethernet
command.
Subnet Mask The subnet mask for the Ethernet adapter as set in the config.ip.ethernet
command.
Output Example
The o utput fro m the sho w.ip.e thernet c o mmand displays as fo llows.
LAN Information
IP Address: 144.49.10.15
Gateway Address: 144.49.10.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
show.loginServer
Syntax
loginServer
Purpose
This command displays information fro m the lo gin server database for devic es attached to
this switc h.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
82 show
Page 95

Co mmand E x ample
show loginServer
Ro ot >
Output
The devic e information is displayed as a table that includes the follo wing properties.
Port The port number where the device is attached.
BB Crdt The maximum number of remaining frames that can be transmitted without
causing a buffer overrun condition at the receiver.
RxFldSz The buffer-to-buffer receive data field size from the FLOGI received from the
attached N_Port.
COS The class of service (for example, 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; F; 1,2; 2,3).
Port Name The port world-wide name of the attached device.
Node Name The node world-wide name of the attached device.
Output Example
The output from the sho w.lo ginServer c ommand displays as fo llows.
Port BB Crdt RxFldSz COS Port Name Node Name
---- ------- ------- --- ----------------------- -----------------------
0 10 2,3 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77
1 10 2 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77
4 10 2,3 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77
7 10 2,3 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77
8 10 2 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77
10 10 2,3 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77
11 10 2,3 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77
12 10 3 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77
13 10 2,3 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77
15 10 2,3 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77
CLI Commands
show 83
Page 96

show.nameServer
Syntax
nameServer
Purpose
This command displays information from the name server database for devices attached to
this switc h.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
show nameServer
Output
The devic e information data is displayed as a table that includes the follo wing properties.
Type The type (N, NL, F/NL, F, FL, E, B).
Port Id The 24-bit Fibre Channel address.
Port Name The port world-wide name of the attached device.
Node Name The node world-wide name of the attached device.
COS The class of service (for example, 1; 2; 3; 4; 5; 6; F; 1,2; 2,3).
FC4 Types The FC4 types registered for this device. The numbers in this field
correspond to the list at the bottom of the table.
84 show
Page 97

Output Example
The output from the show.nameServer co mmand displays as follo ws.
Type Port Id Port Name Node Name COS FC4 Types
---- ------- ----------------------- ----------------------- --- --------N 010400 00:11:22:33:44:55:00:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 2,3 2
N 010500 00:11:22:33:44:55:01:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 2,3 0
N 010600 00:11:22:33:44:55:66:02 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 2,3 2
N 010700 00:11:22:33:44:55:66:03 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 2 2
N 010800 00:11:22:33:44:55:66:04 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 3 2
N 010900 00:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 3 2
N 010C00 00:11:22:33:44:55:66:07 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 2,3 2
N 010D00 00:11:22:33:44:55:66:08 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 2,3 2
N 010E00 00:11:22:33:44:55:66:09 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 2 5
N 010F00 00:11:22:33:44:55:66:0A 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 2 4
N 011200 00:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 20:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 2,3 2
N 011300 00:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 10:11:22:33:44:55:66:77 2,3 2
FC4 Types
0: ISO/IEC 8802-2 LLC/SNAP (in order)
1: ISO/IEC 8802-2 LLC/SNAP (misordered)
2: SCSI-FCP
3: SCSI-GPP
4: IPI-3 Master
5: IPI-3 Slave
6: IPI-3 Peer
7: CP IPI-3 Master
8: CP IPI-3 Slave
9: CP IPI-3 Peer
10: SBCCS-Channel
11: SBCCS-Control Unit
12: FC-SB-2 Channel to Control Unit
13: FC-SB-2 Control Unit to Channel
14: Fibre Channel Service
15: FC-FG
16: FC-SW
17: FC-AL
18: SNMP
19: HIPPI-FP
20: Vendor Unique
CLI Commands
show 85
Page 98

show.port.config
Syntax
config
Purpose
This command shows the po rt configuration fo r all ports.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
show port config
Output
The po rt configuration attributes are displayed as a table that includes the follo wing
properties.
Port The port number.
Name The name of the port as set in the config.port.name command.
Blocked The blocked state of the port as set in the config.port.blocked command.
Ext Dist The extended distance state as set in the config.port.extDist command.
Type The port type as set in the config.port.type command.
86 show
Page 99

Output Example
The output from the sho w.po rt.config command displays as follows.
Port Name Blocked Ext Dist Type
---- ------------------------ ------- -------- ----0 Port 1 false false fPort
1 Port 2 true true fPort
2 Port 3 false false gPort
3 Port 4 false false fPort
4 Port 5 true true fPort
5 Port 6 false false fPort
6 Port 7 true true fPort
7 Port 8 false false fPort
8 Port 9 false true fPort
9 Port A false false fPort
10 Port B false false fPort
11 Port C false false fPort
12 Port D false false fPort
13 Port E false false fPort
14 Port F false false fPort
15 Port X false false fPort
show.port.info
Syntax
CLI Commands
info
Purpose
This command displays port information for all po rts.
Parameters
This command has no parameters.
Co mmand E x ample
Ro ot >
show port info
show 87
Page 100

Output
The po rt information data is displayed as a table that includes the fo llo wing properties.
Port The port number.
WWN The world-wide name of the port.
OpSpeed The current operating speed (1G, where G represents gigabits).
SpeedCap The current transceiver capability speed (1G or 2G, where G represents
gigabits).
Output Example
The output from the show.port.info co mmand displays as fo llows.
Port WWN OpSpeed SpeedCap
---- ----------------------- ------- -------0 10:00:80:00:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
1 10:00:80:01:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
2 10:00:80:02:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
3 10:00:80:03:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
4 10:00:80:04:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
5 10:00:80:05:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
6 10:00:80:06:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
7 10:00:80:07:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
8 10:00:80:08:11:22:33:44 1G 2G
9 10:00:80:09:11:22:33:44 1G 2G
10 10:00:80:10:11:22:33:44 1G 2G
11 10:00:80:11:11:22:33:44 1G 2G
12 10:00:80:12:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
13 10:00:80:13:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
14 10:00:80:14:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
15 10:00:80:15:11:22:33:44 1G 1G
88 show
 Loading...
Loading...