Page 1

Windows Server 2003
HP StorageWorks EVA
Fast Recovery Solution
administration guide
EVA4000
EVA6000
EVA8000
product version: 02.01.00
first edition (July 2005)
part number: B9552-96006
This guide describes how to use the fast recovery solution with Microsoft Exchange 2003
Page 2

© Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. All rights reserved.
Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but not limited to,
the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for
errors contained herein or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance,
or use of this material.
This document contains proprietary information, which is protected by copyright. No part of this document may be
photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard.
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
Product names mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective companies.
Hewlett-Packard Company shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein. The
information is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind and is subject to change without notice. The warranties
for Hewlett-Packard Company products are set forth in the express limited warranty statements accompanying such
products. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.
Printed in the U.S.A.
HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
first edition (July 2005)
part number: B9552-96006
2 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 3

About this guide 7
IMPORTANT: firmware and software dependencies 7
Prerequisite information 8
HP storage web site 8
Helpful web sites 8
HP technical support 9
HP sales and authorized resellers 9
Document conventions and symbols 10
Revision history 11
Warranty statement 12
1Overview 15
FRS feature summary 16
High availability using FRS 16
FRS overview 17
Additional FRS capabilities 18
Functional components 18
Exchange 20
FRS 20
Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) 21
HP VDS/VSS Hardware Providers 23
HP disk arrays 23
Contents
Contents 3
Page 4

2Configuration 25
Typical FRS server configuration 26
Required hardware components 27
Required software components 28
Important limitations 29
Important general configuration notes 29
Important performance issues 30
Important Exchange 2003 configuration notes 30
Configuration summary 31
Configuration details 32
Configuring the Command View workstation and software 32
Configure production and recovery servers 33
Configuring the EVA disk array 34
3 Installation 39
Installing HP VSS HWP 40
Installing FRS on recovery and production servers 41
Installing integrity checking components 43
Enabling the FRS license using AutoPass 44
Installing a permanent license before trial expiration 44
Installing a permanent license after trial expiration 44
Permanent license installation 45
Instance count check 47
Recovery server XML files 48
Uninstalling FRS 49
4 Using FRS 51
Using FRS 52
Opening FRS 52
Using the main window 53
Adding server instances 55
Deleting server instances 56
Creating shadow copies 57
Executing an FRS recovery 60
Deleting old point-in-time copies 64
Recovery log analysis 65
Command line interface 66
Available commands 67
Example commands 70
Command line error codes 72
4 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 5

5Troubleshooting 75
Troubleshooting 76
Checking logs 76
Troubleshooting checks 76
FRS error messages 78
Maintenance 78
Recovery 79
Terminating processes 80
Glossary 81
Index 85
Contents 5
Page 6

6 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 7

About this guide
This guide provides information about configuring and using HP
StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solutions (FRS) in a Microsoft
Windows Server 2003 environment running Exchange 2003. FRS enables
quick recovery of Exchange storage groups.
FRS combines LUN copy creation and database recovery features for use
with HP StorageWorks EVA disk arrays. Using the Microsoft VSS
(Volume Shadow Copy Service), FRS creates and manages recovery-ready
copies of the production Exchange 2003 storage groups to be used in the
event of a disaster. FRS allows you to recover storage groups in minutes
rather than the hours typically required for a conventional restore from
backup.
Unless otherwise noted, the term disk array refers to the disk arrays listed
on the front cover of this guide.
Related information
For information about the disk arrays, please refer to the owner’s manuals.
IMPORTANT: firmware and software dependencies
This guide describes FRS behavior based on features implemented in the
latest disk array firmware and software versions. FRS may not work if
incompatible software versions are used. Check the Readme file to verify
that you have the correct versions.
About this guide 7
Page 8
Prerequisite information
The instructions in this guide are intended for system administrators who
have the following skills and knowledge:
• A background in direct access storage device subsystems and their
• Familiarity with EVA and related disk array management software
• An understanding of VSS installation and configuration of the
• Familiarity with the Windows Server 2003 operating system
• Familiarity with Exchange 2003 administration
HP storage web site
For the most current information about HP StorageWorks products, visit:
http://h18006.www1.hp.com/storage/enterprisestorage.html
For information about product availability, configuration, and connectivity,
contact your HP support representative.
basic functions
such as CommandView EVA
recovery volumes within VSS
.
Helpful web sites
For third party product information, see the following web sites:
http://www.hp.com/go/storage
http://www.hp.com/support
8 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003:
Page 9
HP technical support
In North America, call technical support at 1-800-633-3600, available 24
hours a day, 7 days a week.
Outside North America, call technical support at the location nearest you.
The HP web site lists telephone numbers for worldwide technical support
at:
Collect the following information before calling:
For continuous quality improvement, calls may be recorded or monitored.
HP strongly recommends that customers sign up online using the
Subscriber’s choice web site at
Subscribing to this service provides you with email updates on the latest
product enhancements, newest drivers, and firmware documentation
updates as well as instant access to numerous other product resources.
http://www.hp.com/support
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Product model names and numbers
• Applicable error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed questions
. From this web site, select your country.
http://www.hp.com/go/e-updates
.
HP sales and authorized resellers
To reach HP sales or find a local authorized reseller of HP products, call
1-800-282-6672 or visit the HP How To Buy web site:
http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/howtobuy.html
You can also find HP sales and resellers at
Contact HP.
About this guide 9
http://www.hp.com
. Click
Page 10

Document conventions and symbols
Table 1. Document conventions
Convention Element
Blue text (Figure 1) Cross-reference links
Bold Menu items, button names, key names, tab names, and group box names
Italics Text emphasis and document titles
Blue underlined sans serif
font (www.hp.com
)
Caution Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to
Web site addresses
equipment or data.
Warning
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or
death.
10 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003:
Page 11

Revision history
July 2005 New EVA FRS manual
About this guide 11
Page 12

Warranty statement
HP warrants that for a period of ninety calendar days from the date of
purchase, as evidenced by a copy of the invoice, the media on which the
Software is furnished (if any) will be free of defects in materials and
workmanship under normal use.
DISCLAIMER
EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW, THIS SOFTWARE IS
PROVIDED TO YOU “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTIES OF ANY
KIND, WHETHER ORAL OR WRITTEN, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED.
HP SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY, SATISFACTORY
QUALITY, NON-INFRINGEMENT, TITLE, ACCURACY OF
INFORMATIONAL CONTENT, AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Some jurisdictions do not allow exclusions
of implied warranties or conditions, so the above exclusion may not apply
to you to the extent prohibited by such local laws. You may have other
rights that vary from country to country, state to state, or province to
province.
WA R NI N G
THAT USE OF THE SOFTWARE IS AT YOUR SOLE RISK. HP
DOES NOT WARRANT THAT THE FUNCTIONS CONTAINED IN
THE SOFTWARE WILL MEET YOUR REQUIREMENTS, OR THAT
THE OPERATION OF THE SOFTWARE WILL BE UNINTERRUPTED,
VIRUS-FREE OR ERROR-FREE, OR THAT DEFECTS IN THE
SOFTWARE WILL BE CORRECTED. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE
RESULTS AND PERFORMANCE OF THE SOFTWARE IS ASSUMED
BY YOU. HP DOES NOT WARRANT OR MAKE ANY
REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OR THE RESULTS OF
THE USE OF THE SOFTWARE OR RELATED DOCUMENTATION IN
TERMS OF THEIR CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY,
CURRENTNESS, OR OTHERWISE. NO ORAL OR WRITTEN
INFORMATION OR ADVICE GIVEN BY HP OR HP’S AUTHORIZED
REPRESENTATIVES SHALL CREATE A WARRANTY.
. EXCEPT FOR THE FOREGOING AND TO THE
! YOU EXPRESSLY ACKNOWLEDGE AND AGREE
12 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003:
Page 13
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY. EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT
PROHIBITED BY LOCAL LAW, IN NO EVENT INCLUDING
NEGLIGENCE WILL HP OR ITS SUBSIDIARIES, AFFILIATES,
DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, EMPLOYEES, AGENTS OR
SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL,
INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR OTHER
DAMAGES (INCLUDING LOST PROFIT, LOST DATA, OR
DOWNTIME COSTS), ARISING OUT OF THE USE, INABILITY
TO USE, OR THE RESULTS OF USE OF THE SOFTWARE,
WHETHER BASED IN WARRANTY, CONTRACT, TORT OR
OTHER LEGAL THEORY, AND WHETHER OR NOT ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. Your use of the
Software is entirely at your own risk. Should the Software prove defective,
you assume the entire cost of all service, repair or correction. Some
jurisdictions do not allow the exclusion or limitation of liability for
incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitation may not apply
to you to the extent prohibited by such local laws.
NOTE
. EXCEPT TO THE EXTENT ALLOWED BY LOCAL LAW,
THESE WARRANTY TERMS DO NOT EXCLUDE, RESTRICT OR
MODIFY, AND ARE IN ADDITION TO, THE MANDATORY
STATUTORY RIGHTS APPLICABLE TO THE LICENSE OF THE
SOFTWARE TO YOU; PROVIDED
, HOWEVER, THAT THE
CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL
SALE OF GOODS IS SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMED AND SHALL
NOT GOVERN OR APPLY TO THE SOFTWARE PROVIDED IN
CONNECTION WITH THIS WARRANTY STATEMENT.
About this guide 13
Page 14

14 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003:
Page 15

1
Overview
This chapter presents a technical overview of the HP StorageWorks Fast
Recovery Solution (FRS) and explains how it operates with Microsoft’s
operating system, VSS service, and applications as well as HP
StorageWorks Hardware Providers.
When you have read this chapter, you should have a functional
understanding of FRS that will prepare you to install it and get it working.
Overview 15
Page 16

FRS feature summary
HP StorageWorks FRS provides these features:
• Supports HP StorageWorks EVA disk arrays
• Provides fast recovery of large Microsoft Exchange 2003 storage
groups
• Minimizes downtime from an Exchange corruption
• Independently recovers Exchange storage groups
• Supports multiple instances of production Exchange 2003 servers
from a single FRS server (and a single Command View workstation)
• Supports Microsoft Cluster Services
• Includes Command Line Interface (CLI) feature for FRS copy creation
and deletion of point-in-time copies
• Creates and maintains multiple point-in-time recovery LUNs
High availability using FRS
HP provides a total high-availability solution package from high-end
storage to software and support. Fast Recovery Solutions is part of the
high-availability offering, which includes:
• Servers and software
• Disk arrays
• HP StorageWorks Business Copy EVA
• CommandView EVA
• Fast Recovery Solutions for EVA
• Storage consulting services and post-sales total solution support
16 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 17
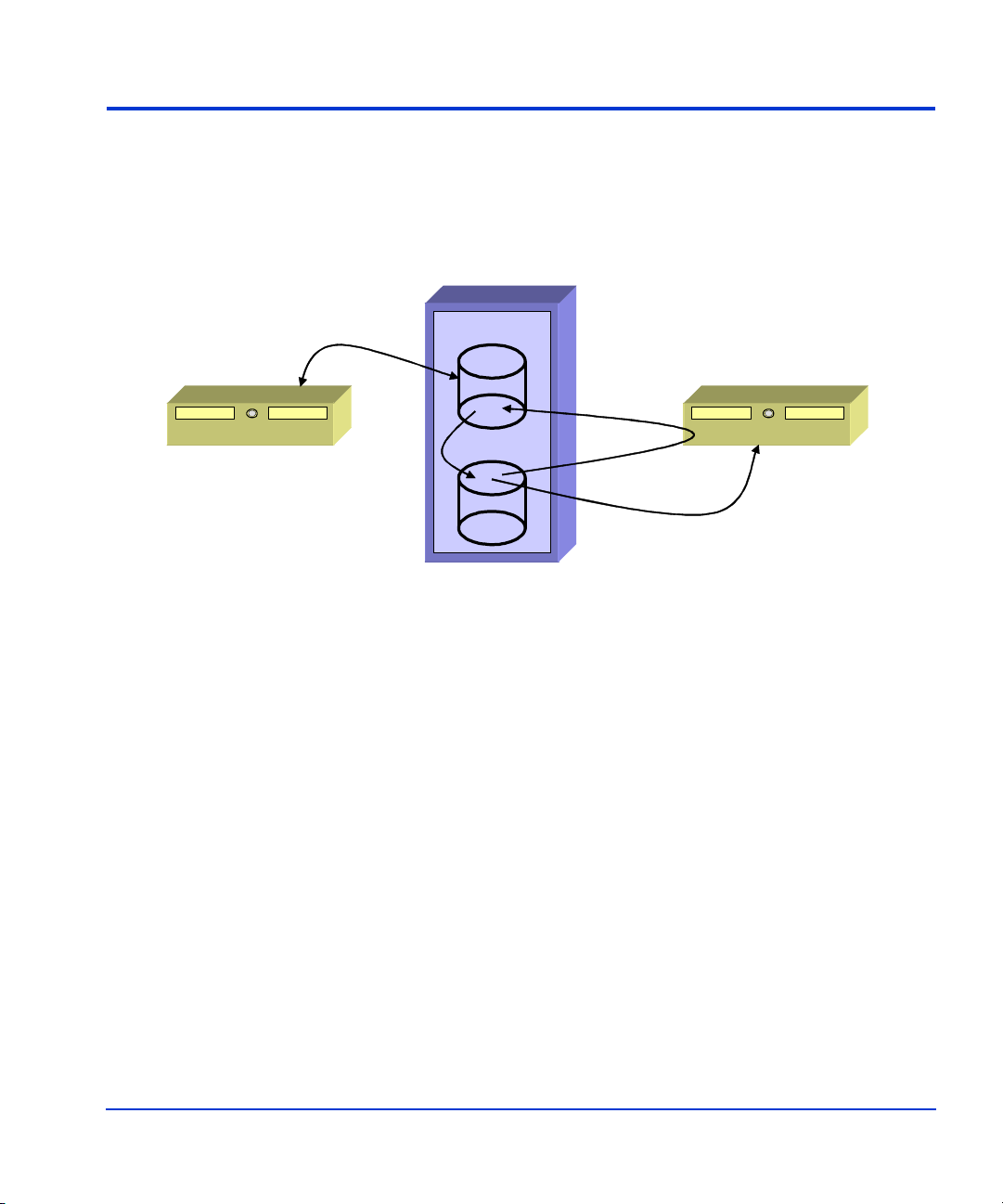
FRS overview
FRS is a Windows server tool designed to enable fast recovery when an
Exchange storage group maintained on an HP disk array becomes
damaged.
(1) Use Production Server to store
production data on array primary
volume.
Store
Production Server w/FRS FRS Recovery Server
(2) Use FRS GUI on Recovery Server
to copy production data to secondary
array volume.
Disk Array
Primary
Copy
Secondary
(3) In the event of production data damage,
restore primary data from the seconda ry data
using the FRS GUI on t he Recovery Server.
Restore
Recovery Data (read-only) is routinely available on
the secondary disk for data mining or transport.
The FRS life cycle can be summarized as follows:
• (1) The production server maintains production storage groups or
databases on specified production volumes of the disk array.
• (2) The FRS GUI runs on the recovery server. It captures copies of the
Exchange storage groups from the production volumes and stores
them on recovery volumes of the array. FRS creates, maintains, and
manages these “recovery-ready” copies.
• (3) When a data corruption occurs, the administrator uses the FRS
graphical user interface to replace the damaged storage group or
database with the most recent known good recovery-ready copy.
Overview 17
Page 18

Additional FRS capabilities
FRS can create and maintain copies of storage groups or databases for
multiple production servers. The FRS user interface allows Exchange
instances to be added or deleted from FRS management at will.
FRS supports Microsoft clustering. Without compromising the cluster or
taking it offline, FRS provides quick database recovery.
Database integrity checking is included in FRS. FRS interacts with the
Microsoft Exchange eseutil integrity checking tool for Exchange to check
database copies and recovered databases, ensuring they are free of logical
and physical corruption.
FRS performs both point-in-time and roll-forward recovery.
Functional components
The process of creating and managing recovery copies on the disk array
using FRS involves the following components:
• Exchange
• HP FRS
• Windows VSS Service
• HP VSS Hardware Provider
• HP Disk Array System
18 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 19
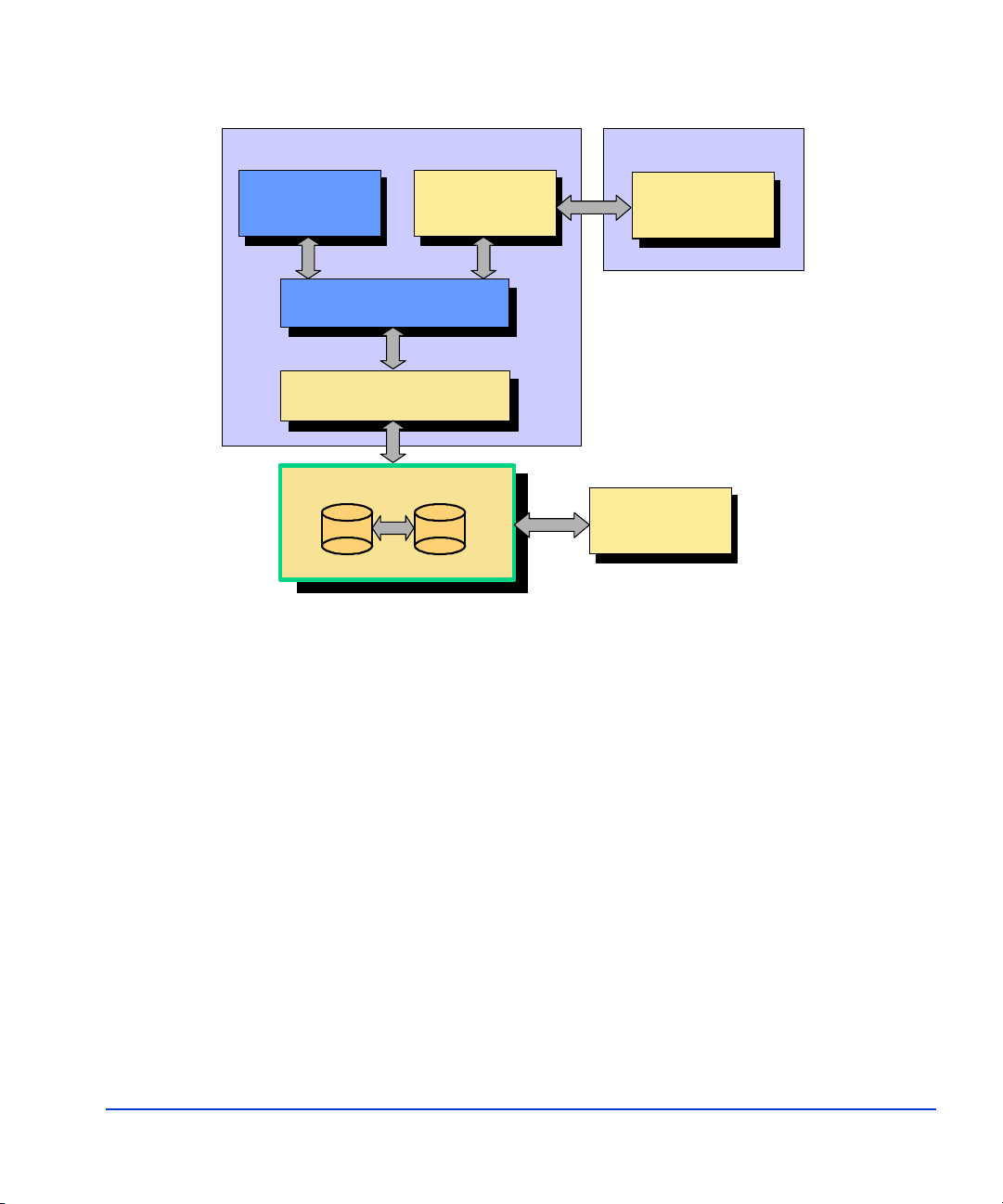
Production Server
Management
MS Exchange
Application(s)
Microsoft Volume
Shadow Copy Service
HP EVA VSS
Hardware Provider(s)
Hardware Provider
Disk Array
HP FRS
Management
Provider
Application(s)
Recovery Server
Management
HP FRS GUI
Application(s)
Array
Management
Command
Application(s)
Device
Overview 19
Page 20

Exchange
FRS
Exchange runs on the Producton Server and writes data to primary disk
array volumes. FRS protects Exchange by creating and managing shadow
copies of Exchange storage groups.
Software components called “writers” interface with Exchange to
coordinate volume shadow copy creation. Some operating system writers
come with Windows, while others, such as the Exchange writer, come with
the application software.
Upon request from FRS for a shadow copy, the writer flushes the
application buffers and holds I/O to the application. It then notifies the VSS
hardware provider that it is ready for a shadow copy, and the VSS HWP
copies the production volume to a recovery volume. When the copy is
complete, VSS releases the application to resume normal operation. This
process ensures consistent data even though the application is still running.
FRS consists of two sets of components: one set of production server
components, and a separate set of recovery server components, including a
graphical user interface. FRS as a whole is referred to by Microsoft as a
“requestor” application that requests service from VSS.
The FRS GUI runs on the recovery server and provides user control of FRS
on the production server. You can use the FRS GUI to make shadow copies
of the data on the production LUNs, and use the GUI to recover the
complete dataset from a copy on the recovery LUNs.
FRS on the production server interacts with the Windows VSS service and
HP Hardware Provider (HWP). When FRS requests it, this service and
provider combination coordinates with the writer and application to create a
volume shadow copy of the production data on the production array LUNs.
The complete recovery-ready copy is placed on recovery array volumes.
FRS presents the recovery volumes to the recovery server through VSS.
This enables you to use the recovery server to archive the recovery data to
backup tapes at any time. In the event of production data corruption, you
20 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 21

can use the FRS GUI to restore the production volumes from the most
recent data copy or another point-in-time copy on the recovery volumes.
Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS)
Microsoft’s VSS manages creation and maintenance of shadow copies of
production data for backup and recovery. This service works under the
control of the FRS interface and the Windows OS file system services.
When requested by FRS, VSS coordinates with the writer and hardware
providers to perform shadow copying of production data to the recovery
volumes. The shadow copies contain static copies of all files, such as
databases, transaction logs, and checkpoint files.
Copy terminology
Understanding how Microsoft VSS terminology corresponds to standard IT
industry terms for data copying makes it easier to understand what VSS
does. The following paragraphs explain the terminology.
Microsoft generally refers to a VSS copy as a “volume shadow copy.”
When created using HP FRS and HWP, this type of copy is a static replica
of an original volume’s contents. It is keyed with a GUID to allow
identification of the parts of a shadow copy set that span multiple volumes.
Microsoft also refers to a VSS copy as a “plex,” commonly known in the IT
industry as a “split mirror.”
When you use an EVA array to make the shadow copy, the array makes
what is known as a “snapclone.” An EVA Snapclone is a complete clone
copy of a specified Virtual Disk (LUN). EVA snapclones are available
almost immediately. This is accomplished by creating a point-in-time copy
and making it immediately available by pointing to data on the original
volume while continuing to copy data to a secondary volume in the
background. When copying is complete, the snapclone is a static
point-in-time copy of the original.
The shadow copies made on the EVA array using VSS, FRS, and HWP are
always static, point-in-time copies.
Overview 21
Page 22

VSS process flow
The following steps show the VSS process flow:
1. A Requestor application (FRS) initiates a Volume Shadow Copy.
2. FRS requests that the Volume Shadow Copy service create a shadow
copy of a selected set of storage groups.
3. VSS tells the Writer and application to prepare for a shadow copy. The
Writer reports which LUNs to copy, flushes cache, and holds I/O.
4. VSS tells the disk array through HP HWP to create a shadow copy of
the production storage volume.
5. VSS releases the writer application to resume normal operations.
6. The Requestor (FRS) presents the recovery LUNs to the recovery server
using VSS, waits for normalization, runs integrity checking, verifies
backup integrity, truncates logs upon success, and tells the writer that
the backup was successful.
Application
(Exchange)
and Writer
Requestor
(FRS)
Virtual Disk Service
22 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
VSS Service
HP HWP
Disk Array
Page 23

HP VDS/VSS Hardware Providers
Windows Server 2003 sees, partitions, mounts, and manages file systems
on the disk array using its own software providers. HP’s Hardware
Providers extend the array management capabilities of Windows and its
applications to include functions normally performed using the disk array’s
proprietary control software. These functions include managing disk array
LUNs and ports and performing volume copy operations.
HP’s Business Copy (BC) application, which resides on the disk array and
is licensed in Command View, works with the VSS and the HP HWP
components to enable the array to make VSS shadow copies. For functional
purposes, you can think of BC as a part of the hardware providers, even
though it is installed separately.
For more information about the HP Hardware Providers, refer to the HP
EVA Hardware Providers Administration Guide.
HP disk arrays
The HP EVA array works with FRS, Microsoft VSS, and HP VSS HWP to
perform snapclone creation, storage, and management. FRS takes
advantage of the many advanced capabilities of the EVA disk array to
provide multiple recovery options.
Overview 23
Page 24

24 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 25

2
Configuration
This chapter explains how to configure the servers and the disk array before
you install FRS.
If you have not read Chapter 1 Overview to understand how FRS works,
HP recommends that you do so before attempting to install and use FRS.
Configuration 25
Page 26

Typical FRS server configuration
The following figure shows a typical FRS configuration.
Note that any firewall must be open between the FRS servers and the
Command View server. Anything that slows down access to the CV server
will cause VSS timeout failures.
Corporate LAN (TCP/IP)
DCOM/RPC (servers in same domain)
FRS
Production
Server
FC SAN
FC Switch
PRODUCTION SERVER S/W:
Windows 2003 Server
MS Exchange
HP VSS HWP
HP FRS
HP MPIO FF
FC SAN
Optional Firewall
(open between CV and servers)
CV Workstation
BC License
HP MPIO FF
EVA
Disk Array
FC SAN
DCOM/RPC
FRS
Recovery
Server
FC SAN
FC Switch
RECOVERY SERVER S/W:
Windows 2003 Server
HP VSS HWP
HP FRS (GUI included)
HP MPIO FF
eseutil.exe
ese.dll
26 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 27

Required hardware components
• HP StorageWorks Disk Array: EVA disk array 4000/6000/8000
with a Windows workstation running Command View EVA.
• Production Server with Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition.
This server runs Exchange and manages storage and retrieval of
application data on the production volumes of the array. Server
specifications must meet minimum Microsoft OS requirements.
• Recovery Server with Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition. The
recovery server contains the FRS GUI and manages the array recovery
volumes and recovery administration. Server specifications must meet
minimum Microsoft OS requirements.
• Fibre Channel Host Bus Adapters (HBAs) in each server for
connecting to the disk array via a Fibre Channel SAN.
• Fiber cables and fabric switches to connect the hosts to the array.
• Ethernet Network Interface Cards or available network interface
port in each server for connecting to Ethernet LAN.
Important: The Windows Network Connections control panel
Advanced Settings must be set to list first the network that provides
communication between the FRS servers and the CV server.
Configuration 27
Page 28

Required software components
IMPORTANT NOTE: The right combination of software versions is
crucial to configuring a working system. Refer to the README file
accompanying FRS for information about compatible software versions.
EVA 4000/6000/8000 Disk array with CV Workstation:
• Command View EVA
• Business Copy EVA license
• HP MPIO Full Featured Failover Software and Manager for EVA
arrays (if multipathing is desired)
Production Server
• Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition with SP1 and QFEs
• MS Exchange 2003 with SP1
• HP MPIO Full Featured Failover Software and Manager for EVA
arrays (if multipathing is desired)
• HP VSS HWP
• HP FRS
Recovery Server
• Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition with SP1 and QFEs
• Java Runtime Environment 1.4.2 or later from Sun Microsystems
• HP MPIO Full Featured Failover Software and Manager for EVA
arrays (if multipathing is desired)
• HP VSS HWP
• HP FRS
• Exchange eseutil.exe and ese.dll copied to c:\hpfrs directory
Required Microsoft quick fixes (QFEs) for FRS servers
The following list of QFEs (also called “hotfixes”) is subject to change;
check the README file or contact HP Support for the latest list of QFEs
required for FRS. QFEs must be obtained by downloading from Microsoft.
For QFEs not available on the Microsoft web site, contact Microsoft
support:
28 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
http://support.microsoft.com/contactus/?ws=support
.
Page 29

• KB903650 Extended maintenance mode fix for clusters
Important limitations
• KB831112 VDS update
• KB887827 VSS update 2
• KB891957 VSS hotfix
• KB892514 Exchange hotfix
http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=892514
• KB898790 Volume mount point hotfix for clusters
http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=898790
• FRS supports only basic disk configuration, not dynamic disks.
• Only one instance of FRS can be running at one time on a server. Run
FRS only from one management console to prevent simultaneous
commands to FRS from different sources.
• FRS supports only a homogeneous disk array solution. If you want to
run FRS on an XP1024 and an EVA6000 disk array, for example, you
will need two mutually exclusive recovery servers—one per disk array
with no shared components.
• FRS supports multiple arrays of the same model, but all arrays must
managed using the same Command View workstation.
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/831112
http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=887827
http://support.microsoft.com/?kbid=891957
Important general configuration notes
The following notes will help ensure a successful configuration:
• Production and recovery servers must be in the same Ethernet domain
so that the DCOM communication process works between servers.
• Administrator privileges are required for all devices and software. If
you do not have administrator privileges, the software and hardware
will not communicate properly.
Configuration 29
Page 30

Important performance issues
Take steps to prevent these issues which can affect FRS performance:
• Excessive traffic on the Ethernet LAN.
• Viruses that slow down network traffic.
• A firewall that slows traffic between the servers hosting FRS and the
CV server. Any firewall must be open between these systems.
Important Exchange 2003 configuration notes
FRS works within the limits of Exchange 2003. No more than five
databases per storage group and no more than four storage groups per
Exchange instance are supported.
FRS manages Exchange 2003 at the storage group level. The following
configuration rules apply:
• All databases within a storage group must reside on one LUN of the
HP disk array. Databases cannot be separated onto different storage
LUNs.
• The logs for each storage group must also reside on an HP disk array
LUN, and the logs and the checkpoint file must remain together on the
same LUN.
• The LUN that the databases reside on and the LUN that the logs reside
on must NOT be the same LUN.
FRS requires that a copy of the MS Exchange eseutil.exe and ese.dll
utilities be placed in the installation directory (c:\hpfrs) on the recovery
server.
30 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 31

Configuration summary
Before you install FRS as explained in the next chapter, you must configure
the Exchange production server(s) the FRS recovery server(s), and the
array as follows:
• Install and configure production server(s) and recovery server(s) with
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition with SP1. Install
any required Microsoft quick fixes (QFEs) also.
• Download JRE 1.4.2 or later from Sun and install on all FRS servers.
• Install HP MPIO Full Featured Failover Software on production and
recovery servers if high availability multipathing is desired.
• Install HBAs and NICs as required, and establish SAN and LAN
connectivity between all servers and the array as shown in the
preceding FRS configuration diagram.
• Install and configure Exchange on the production server(s).
• You may use a firewall between the servers and the corporate LAN,
but the firewall must be open between all FRS servers and the EVA
CV workstation. If VSS times out, the firewall may be the problem.
• On the CV station, ensure the Network Connections control panel
Advanced Settings window lists the FRS network first.
• In Command View, add a license for Business Copy.
• On the Command View station, install HP MPIO Full Featured
Failover Software and Manager if high availability multipathing is
desired.
• On the array, add hosts and add a snapclone disk group. Depending on
your application, you may also need to add other disk groups for data,
logs, etc.
• On the production server, ensure databases or mailboxes within a
given storage group all reside on the same LUN.
• After FRS installation, copy Exchange eseutil.exe and ese.dll files to
the c:\hpfrs directory on the recovery server.
Configuration 31
Page 32

Configuration details
Configuring the Command View workstation and software
Configure the Command View workstation as explained below:
1. Ensure an ethernet LAN connects the FRS servers to the CV station. If
you use a firewall, make sure it is open between the CV and FRS servers.
Important: Ensure this network is listed first in the Network
Connections control panel Advanced Settings window. If you change
settings in this panel, reboot the CV station so they take effect.
2. Ensure an FC SAN connection exists between the CV station and the
disk array.
3. Log into the CV station and launch Command View EVA.
4. Click Agent Options>Licensing options to display the Licensing
Options page.
5. Click View previously entered license keys to see if a Business Copy
license is already installed. Click Cancel if you need to install the
license.
6. Click Enter new license key and type or paste the license key in the
Add a License dialog box. The key comes by email from the HP License
Key Retrieval website:
http://h18000.www1.hp.com/products/software/softwarekeys/index.html
.
7. Click Add License to save the license key. Repeat for the next license.
8. Install HP MPIO Full Featured Failover Software and Manager if you
plan to use multipathing.
32 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 33

Configure production and recovery servers
The production server hosts Exchange and manages the production
volumes on the disk array where production data is stored. The recovery
server hosts the FRS GUI and manages the array recovery volumes where
snapclones are stored. Configure the servers as follows:
Install Windows OS and Microsoft quick fixes
1. If it is not already present, install the Windows Server 2003 OS with
SP1 on the host according to Microsoft’s installation instructions. Be
sure to install any required Microsoft quick fixes (QFEs) also.
Install Java Runtime Environment 1.4.2 or later
2. Download JRE from Sun Microsystems and install it on all FRS servers.
Install HP MPIO software
3. Install the HP MPIO Full Featured Failover Software.
Make SAN and LAN connections
4. Install a NIC if needed, and connect the servers to an ethernet LAN. If
you use a firewall, it must be open between the CV station and the FRS
servers. Set Network control panel Advanced Settings to give this
network priority. Use a ping command to test communication.
5. Install a Fibre Channel host bus adapter (HBA) card into the servers
according to the HBA manufacturer’s instructions.
6. Install the HBA driver and utility software onto the servers according
to the HBA manufacturer’s instructions. HP tested drivers are available
by searching
7. Connect the server to the disk array, either via FC direct-connect or
through a fabric switch and SAN topology. If you use a switch, configure
it according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Install Exchange software
8. Install Microsoft Exchange on the production server according to
Microsoft’s instructions. Exchange is not required on the recovery
server; however, after you install FRS, copy the Exchange eseutil.exe
and ese.dll files to the recovery server FRS c:\hpfrs directory. If these
files are not copied to c:\hpfrs, integrity checking and copying fails.
Configuration 33
hp.com; follow the README file for installation.
Page 34

Configuring the EVA disk array
The following configuration steps are required in order for the disk array to
recognize the FRS production and recovery servers. This procedure also
explains how to create disk groups for the recovery snapclones.
1. Log into Command View as an administrator (the default administrator
user name and password is administrator).
Adding FRS production and recovery hosts
2. Click the + symbol next to the EVA disk array in the left panel to expand
the contents of the array and begin configuration.
3. Click the Hosts folder in the left panel. The Host Folder Properties
window displays. Click Add Host and fill in the host characteristics for
the FRS production server. Click Save Changes to save the new host
information. Repeat for additional production servers (if present) and
for the FRS recovery server.
34 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 35

Adding disk groups
Add a snapclone disk group using the steps below. Exchange also requires
separate disk groups for data and logs.
4. Click the Disk Groups folder in the left panel. The Disk Groups
Properties window displays.
5. Select the + next to the Disk Groups folder to expand Disk Groups.
Configuration 35
Page 36

6. Click Create disk group to begin creating a new disk group.
7. Enter a name for the new disk group, and click Advanced options.
36 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 37

8. Select a disk type, enter the number of disks to use for this disk group,
and click Next step.
9. Select a drive failure protection level, and click Next step.
Configuration 37
Page 38

10. Accept the occupancy alarm level and select Finish.
11. A message indicates the disk group was added, and the new group
appears in the left panel. Click OK.
12. Repeat the previous steps as required to add the data and log disk groups.
38 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 39

3
Installation
This chapter covers installing, uninstalling, and licensing FRS. You m ust
use Administrator privileges for all hardware and software to perform
these tasks.
Before you install FRS, you must complete the server and array
configuration tasks presented in Chapter 2. If you have not yet done so,
go to Chapter 2 and complete those tasks now. Then return to this chapter
and follow the installation instructions.
Installation 39
Page 40

Installing HP VSS HWP
Install HP’s VSS Hardware Provider on each production and recovery
server according to the HP StorageWorks HWP Administration Guide.
40 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 41

Installing FRS on recovery and production servers
FRS is required on all servers participating in FRS. This includes the
recovery server and all production servers. For example, if one FRS
recovery server will host two Exchange 2003 servers, you must install FRS
on all three servers.
The installation steps for each production or recovery server are nearly
identical, except for the Custom Setup window:
1. Download FRS from the hp.com web site or open the FRS CD and
launch the ISScript8.Msi file. This will ensure that a script engine is
available for the installation process.
2. Click Next and read the license agreement.
3. Click “I accept” and click Next.
4. Click Install to install ISScript on the server.
5. When ISScript installation completes, click Finish.
Installation 41
Page 42

6. Launch the HP StorageWorks Fast Recovery Solution.msi file. The
installation wizard opens.
7. Click Next. The Custom Setup window opens.
8. Choose Change... to select a directory where the program will be
installed, or use the default location shown under Install to:.
9. Select the type of server software you want to install:
To install on a PRODUCTION server: Click the Production
Server drop down menu, and select “This feature will be installed on
local hard drive”. Then click the Recovery Server drop down menu
and select “This feature will not be available.” The recovery server
icon is marked with an “X”, which means it is NOT being installed.
To install on a RECOVERY server: Click the Recovery Server
drop down menu, and select “This feature will be installed on local
hard drive”. Then click the Production Server drop down menu and
select “This feature will not be available.” The production server
icon is marked with an “X”, which means it is NOT being installed.
42 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 43

10. Click Next.
11. Click Install. Installation begins.
12. When installation completes, click Finish.
13. Repeat the installation on all additional servers participating in FRS. Be
sure to select the correct server icon each time and to deselect the
unwanted icon so that it is marked with an “X”.
Installing integrity checking components
For Exchange integrity checking to work, you must copy the Exchange
eseutil.exe and ese.dll files to the c:\hpfrs directory on the recovery server.
These files are located in the Exchange directory: c:\program
files\exchsrvr\bin. If these files are not present in the FRS directory on the
recovery server, copying will fail.
Installation 43
Page 44

Enabling the FRS license using AutoPass
FRS offers a free trial license period of 60 days. When the trial period is
over, you must install a permanent license using AutoPass within the FRS
GUI in order to continue using FRS. The procedure for starting the
permanent licensing process is different depending on whether your trial
license has already expired or not. Use one of the two procedures below to
install the permanent license.
Installing a permanent license before trial expiration
If you are installing a permanent license before the trial license expires, a
command line application called ImportLicense.exe allows you to install
the license:
1. Locate and double click the ImportLicense.exe executable file to run
it. The path to this file is Start>Programs>Hewlett-Packard>HP
StorageWorks Fast Recovery Solution>Import Permanent License.
The AutoPass: Import Passwords screen displays.
2. Follow the procedure for “Permanent license installation” on page 45.
Installing a permanent license after trial expiration
When you start the FRS GUI, a window notifies you how many days
remain before your trial version of the software expires.
If your AutoPass trial version license has expired, this message appears:
1. Click Ye s to install the license (or click No to exit FRS).
2. Follow the procedure for “Permanent license installation” on page 45.
44 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 45
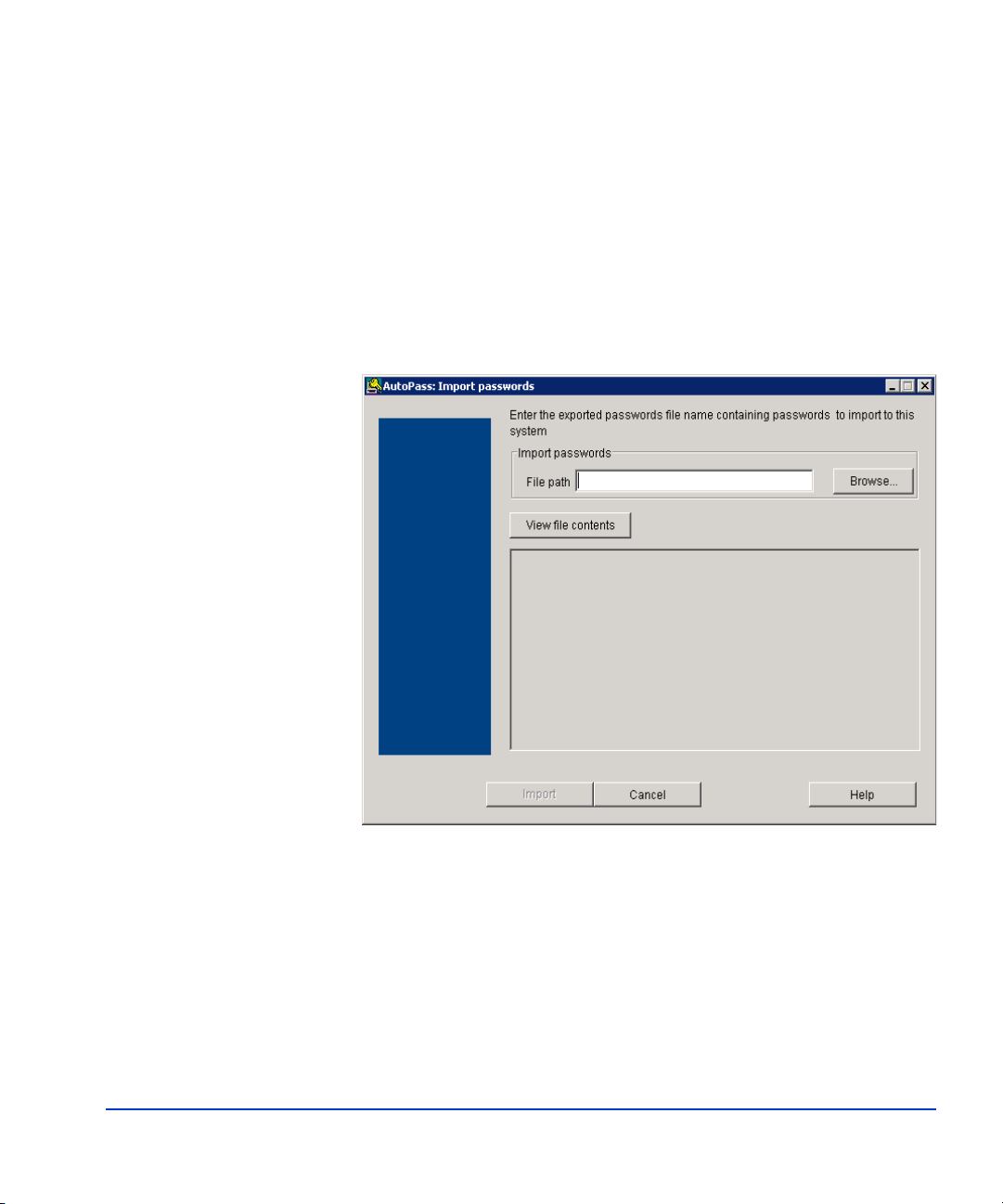
Permanent license installation
Important: If you have multiple FRS instances, be ready to import all
license passwords for all instances in one session. If you quit AutoPass
while some licenses are still without passwords, all licenses will fail, and
AutoPass will have been overwritten and disabled by the partial license file.
Use the following procedure to install the permanent license(s):
1. When you click Ye s on one of the preceding license notification
windows, the AutoPass: Import passwords window opens.
2. Click the Browse button to locate the license password file. The file
path shows in the file path text entry box.
3. Click the View file contents button to display the license passwords
stored in the file.
Installation 45
Page 46
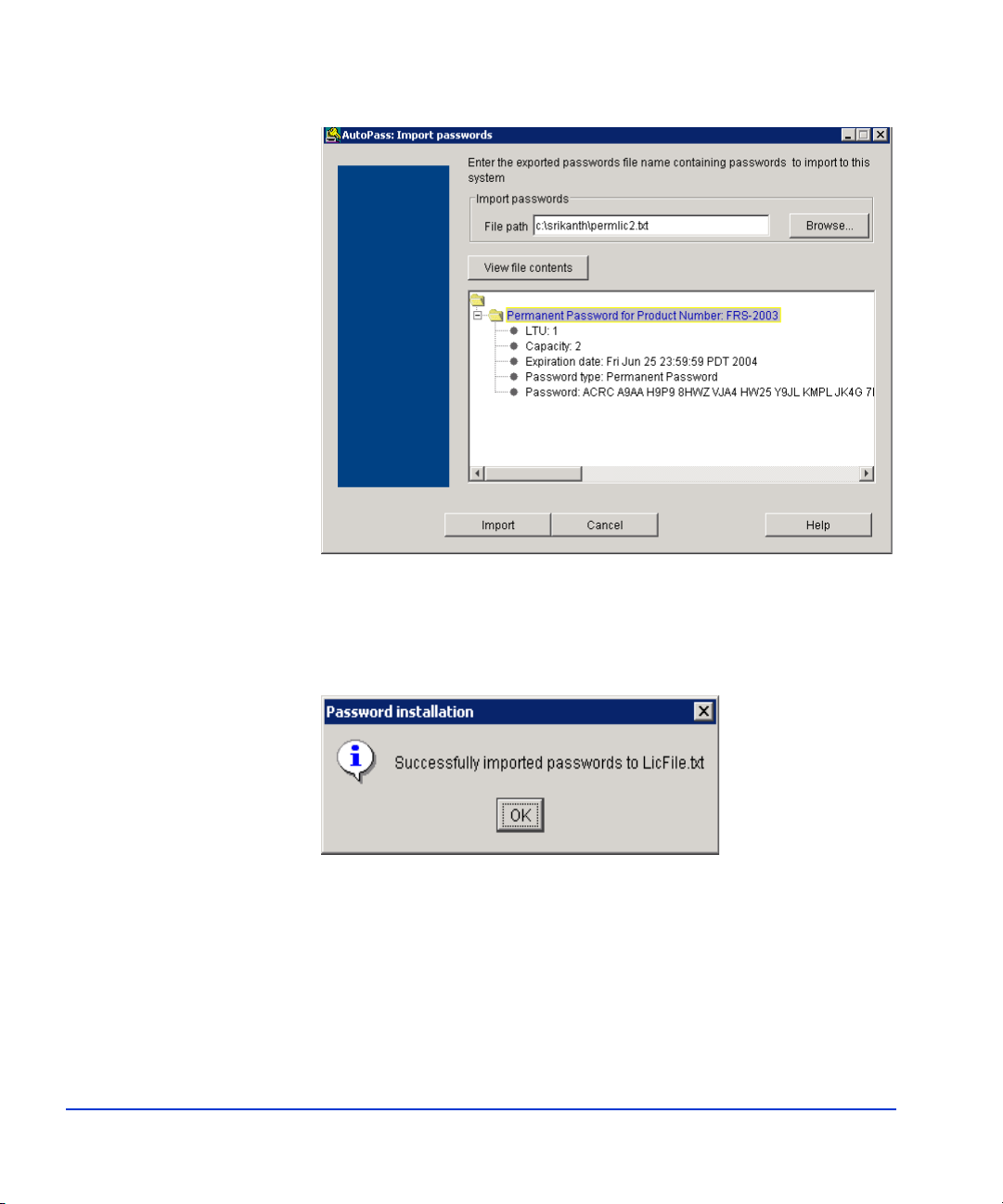
4. Click the password file in the display to highlight it (as shown above).
5. Click Import to import the selected password file.
The message below indicates a successful password import.
46 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 47

Instance count check
If you are running too many instances of FRS for the license you own, you
may receive a warning message. This message appears under the following
conditions:
6. Click OK. This completes installation of the license password.
Important: If you need to install multiple licenses, you must repeat
this process for each license password. It is not possible to import
multiple passwords at one time.
Also, be sure you have imported all licenses before closing AutoPass.
If some licenses are left without passwords, all licenses will fail.
• The recovery server is connected to a production server running more
than the licensed number of instances.
• A recovery server is connected to multiple production servers and the
total number of Exchange instances running are more than the licensed
capacity.
• The product is already running the maximum number of instances
when you try to add another instance by clicking Add Exchange
Server Instance from the File menu.
Contact HP if you need to add more instances to your license.
Installation 47
Page 48

Recovery server XML files
FRS stores the recovery volume information in the form of XML files. By
default these files are created in the install directory. It is not necessary to
change the location of the XML files, but should you wish to do so, you can
place these files in a different directory.
Important: If you change the location of the XML files after snapclones
have already been created, the FRS GUI will not be able to find them, so
HP recommends changing the location before you create any snapclones.
The following procedure explains how to change the location of this
directory:
1. Start FRS on the recovery server by clicking
Sta rt>Programs>Hewlett-Packard>HP StorageWorks Fast
Recovery Solution>FRS GUI.
2. Click the ShadowCopy menu and click Options.
The Options window containing the default location appears.
3. Click Browse, browse to a directory of your choice, and click OK.
4. Click OK in the Options window to change the default XML file path.
48 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 49

Uninstalling FRS
You can uninstall FRS in one of three ways: by using the FRS CD, by using
the Uninstall FRS shortcut, or by using the Windows Add/Remove
Programs feature in the Control Panel.
With each method, the uninstall script prompts you to remove FRS.
To uninstall FRS with the CD:
Open the FRS CD. Click setup.exe to launch the uninstall script and follow
the prompts.
To uninstall using the Uninstall FRS shortcut:
Click Start>Programs>Hewlett-Packard>HP StorageWorks Fast
Recovery Solution>Uninstall FRS, and follow the prompts.
To uninstall using Add/Remove Programs:
1. Click the Start menu, click Settings, click Control Panels.
2. Open Add/Remove Programs.
3. Find the HP StorageWorks Fast Recovery Solution entry and select it.
Installation 49
Page 50

4. Click Remove to launch the uninstall script.
A confirmation window asks “Are you sure...”
5. Click Yes to remove FRS from the server. The removal process takes a
few minutes.
50 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 51

The following items are explained in this chapter:
• Using FRS
• Creating shadow copies
• Executing an FRS recovery
• Using the command line interface
4
Using FRS
Using FRS 51
Page 52

Using FRS
Opening FRS
You operate FRS from the graphical user interface that was installed on the
recovery server when you installed FRS. The following pages explain how
to open and use the FRS GUI to add and delete servers, make shadow
copies of production storage groups and restore production storage groups
and databases from shadow copies.
1. On the recovery server, click Windows Start, and select Programs.
2. Click Hewlett-Packard, click HP StorageWorks Fast Recovery
Solution, and click HP FRS GUI.
The FRS main window opens.
52 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 53

Using the main window
The following example shows the FRS main window after two Exchange
2003 server instances have been added. Adding server instances is
explained later in this chapter.
Using FRS 53
Page 54

To expand a server instance:
1. Click the plus symbol (+) next to a server instance in the left panel of
the main window. This displays the detail views of the production
storage groups and/or databases associated with that server instance.
2. Click a storage group or database to display the location and path of the
LUN where it is stored in the right panel of the main window.
54 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 55

Adding server instances
Add Exchange production server instances whose storage groups or
databases you want FRS to be able to copy and restore. The servers must
have FRS installed on them for the GUI to recognize them:
1. On the FRS main window, click the File pulldown menu and click
2. Enter the instance name in the “Enter Server Instance” box and click OK.
Add Exchange Server Instance.
The Add Server Instance window opens.
The FRS main window opens and shows the new server instance.
Using FRS 55
Page 56

Deleting server instances
If you no longer need to use FRS with a particular server, you can delete it
from the FRS GUI. This does not affect the server itself but only removes it
from the list of servers available in the FRS main window.
1. Click the server instance to highlight it.
2. Click File and click Delete Server Instance. A confirmation window
opens.
3. Click Ye s to confirm your choice.
56 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 57

Creating shadow copies
The primary feature of FRS is creating shadow copies of production LUNs.
FRS then manages these copies. If a production database is lost because of
a failure or catastrophic event, FRS restores the production database from a
shadow copy.
To create shadow copies of production LUNs:
1. Click the production server instance, storage group, or database you
want to copy. The example below shows Exchange 2003 Server “N03”
selected.
2. Click ShadowCopy in the menu bar, and select Create Shadow Copy.
The Create shadow copy window opens.
Using FRS 57
Page 58

3. Select the storage group to be copied and click Add. Repeat as needed.
The storage group to be copied appears in the “Selected for shadow
copy” list, and the associated databases appear in the “Files/Volumes
selected for shadow copy” list.
58 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 59

4. Click Create at the bottom of the Create shadow copy window. Storage
group copying begins. The copy is placed on a volume in the recovery
storage group you identified when you installed FRS.
The Activity Log shows the stages of copying and their success or
failure, ending with a completion message.
5. When copying ends, click Close to close the window. FRS now has a
recovery-ready LUN containing the shadow copy of the storage group
or database. You can create shadow copies as often as needed.
Troubleshooting copy failures:
If a copy fails, you may be able to troubleshoot the cause by examining the
copy activities shown in the Activity Log to see which activities failed.
Failed Exchange copies can often traced to a failed integrity check
performed automatically on the storage group by the Microsoft Exchange
eseutil.exe utility. Integrity check failure typically indicates physical file or
page damage in the production storage group.
Using FRS 59
Page 60

Executing an FRS recovery
Use the Recovery feature to restore a production storage group from an
FRS shadow copy.
1. Click Recovery on the main window menu bar, and select
Roll-Forward Recovery or Point-in-Time Recovery.
Roll Forward Recovery
Use Roll Forward Recovery if the production storage group's
database(s) becomes damaged but the storage group's transaction logs
are known to be unaffected. This recovery method replaces the
production storage group's database LUN with the latest known-good
shadow copy but does not replace the production transaction log LUN.
During the recovery, Exchange replays the production logs to fully
restore the production databases up to the last logged transaction prior
to the point of failure. A Roll Forward Recovery only works with the
most recent Point-in-Time shadow copy.
Point-in-Time Recovery
Use Point-in-Time recovery if the production storage group's
transaction logs are damaged. This recovery method replaces the
production storage group and production logs with the point-in-time
copy that you select. A Point-in-Time recovery will cause you to lose
60 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 61

all data created after the Copy Date and Copy Time of the selected
shadow copy.
After you select a recovery method, the Recover Storage Group
window opens and indicates the type of recovery in the window name.
The copies available for selection differ in this window depending on
whether you selected Roll Forward or Point-in-Time.
Using FRS 61
Page 62

2. Click on the production storage group you want to recover in the Select
Storage Group panel.
A list of point-in-time shadow copies displays in the Point-in-Time
copies panel. The contents of the list depends on whether you selected
Roll Forward or Point-in-Time.
3. Click the point-in-time copy you want to use to restore the production
storage group.
Note: The point-in-time recovery dialog shows only the point-in-time
copies residing in the user specified xml file path. If you want to see
the point-in-time copies in other directories you must change the xml
file path to point to those directories.
4. Select LUN Swap or Full Resync. (These are grayed out for PIT.)
Full Resync replaces the production data on the production LUN with
the most recent copy from the recovery LUN by copying the data back
to its original location. For servers in a cluster, only Full Resync is
allowed.
LUN Swap reverses roles of the LUNs and turns the recovery LUN
into the production LUN, and the production LUN into a recovery
LUN. This is the fastest option, producing almost immediate results.
After a swap, you may need to create additional recovery LUNs before
you can make new shadow copies. For servers in a cluster, LUN Swap
is not allowed.
Caution When you select LUN Swap, the Delete Production Volumes after swap
checkbox is selected. Selecting this checkbox deletes the production
volumes after the swap, which irreversibly deletes your production data.
Important: Use swap only temporarily if your recovery LUNs reside
on less reliable external storage disks because these less reliable disks
become the production LUNs. To swap disks back again, use Business
Copy within Command View to create copies of the current
production LUNs in the original production disk group. Then present
the copied LUNs to the production server, assign drive letters, and
update the database and log path within Exchange.
Delete Selected Copy deletes the selected point-in-time copy without
waiting until after the recovery.
62 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 63

5. Click Start Recovery. The recovery process begins.
Progress of the recovery displays in the Activity Log panel.
6. When the log panel shows the recovery is finished, click Close to close
the window. Your recovered production LUN should now be ready to
use again.
Using FRS 63
Page 64

Deleting old point-in-time copies
Using the procedure below, you can delete old point-in-time copies any
time your pool of Point-In-Time copies grows too large. HP recommends
you delete the oldest copy first, followed by the next oldest, and so on.
1. Click Recovery on the main window menu bar, and select
Point-in-Time Recovery.
2. Click on a production storage group in the Select Storage Group panel.
A list of point-in-time shadow copies displays in the Point-in-Time
copies panel.
64 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 65

3. Click the point-in-time copy you want to delete, and click Delete
4. Click Close when copy deletion is finished.
Recovery log analysis
If a recovery fails, analyze the Activity Log in the FRS GUI for any failed
activities.
Selected Copy. FRS deletes the copy immediately.
Using FRS 65
Page 66

Command line interface
The following pages describe the FRS command line interface.
1. Change to the directory (cd) where FRS is installed. The default location
is c:\hpfrs.
2. Type this command, and press Enter:
dir
A list of files and subdirectories in the 'hpfrs' directory is presented.
66 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 67

Available commands
Type C:\hpfrs>hpfrscli /? to see a listing of available FRS commands.
Using FRS 67
Page 68

Command usage
hpfrscli.exe <operation> <operation specific parameters>
Microsoft Exchange Server:
<operation>
addcopy Create a point-in-time copy
delcopy Delete a point-in-time copy
listcopy List all point-in-time copies
/? Displays the current usage screen
Creating a point-in-time copy:
hpfrscli addcopy
/EXCHANGE
/SERVER=<Exchange Server Instance>
/SG=<Storage Group1, Storage Group2,...>
[/AUTOCLOSE={ON|OFF}]
[/OUTPUT=<Filename with path>]
Deleting a point-in-time copy:
hpfrscli delcopy
/EXCHANGE
/SERVER=<Exchange Server Instance>
/XMLFILE=<Filename with path>
[/AUTOCLOSE={ON|OFF}]
[/OUTPUT=<Filename with path>]
68 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 69

Listing the point-in-time copies:
hpfrscli listcopy
/EXCHANGE
/SERVER=<Exchange Server Instance>
/SG=<Storage Group1, Storage Group2,...>
[/AUTOCLOSE={ON|OFF}]
[/OUTPUT=<Filename with path>]
/EXCHANGE: Connect to an Exchange Server Instance
/SERVER: Specifies the Server Instance name to be connected to
/SG: Specifies the list of Exchange storage groups separated
by a comma
/XMLFILE: Specifies the XML filename (with path) of the
point-in-time copy
/AUTOCLOSE: If set to ON, automatically closes the activity window
on task completion. The default value is OFF. If set to
OFF, press Enter to close the activity window
/OUTPUT: [drive:][path] filename. Specifies the filename to save
the activity log
Using FRS 69
Page 70

Example commands
Three examples follow to demonstrate the addcopy, listcopy, and delcopy
commands.
Creating a copy
The following command creates a point-in-time copy of a storage group
(sg1) on a selected Exchange server instance (evs1).
C:\hpfrs>hpfrscli addcopy /exchange /server=evs1 /sg=sg1
The screen displays progress as the copy is made.
70 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 71

Listing copies
The following command lists point-in-time copies of a storage group (sg1)
on a selected Exchange instance (evs1).
C:\hpfrs>hpfrscli listcopy /exchange /server=evs1 /sg=sg1
The following example lists the point-in-time copies of storage group “sg1”
on selected Exchange instance “evs1.”
Using FRS 71
Page 72

Deleting a copy
The following command deletes a copy of a selected XML file
(evs1_sg1_07-26-2005_09-20-31.xml):
C:\hpfrs>hpfrscli delcopy /exchange /server=evs1
/xmlfile=C:\hpfrs\evs1_sg1_07-26-2005_09-20-31.xml
The figure shows the deletion in progress.
Command line error codes
FRS CLI issues a return code indicating success or failure of the operation
performed. Upon failure, error codes are returned indicating the type of
72 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 73

failure. The following example shows a 0 code being returned, indicating a
successful operation.
The return codes for the supported operations are:
[0] The operation displayed in the usage screen (create
shadow copy, delete point-in-time copy or listcopy)
succeeded.
[1] The specified operations failed with a win32 error
[1001] Incorrect command line parameter entered by the user
[1002] Missing command line parameter entered by the user
[1003] Create shadow copy operation failed.
[1004] Delete point-in-time copy operation failed.
[1005] Listcopy operation failed.
Using FRS 73
Page 74

74 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 75

5
Troubleshooting
This chapter explains how to maintain Fast Recovery Solutions (FRS) on
an EVA disk array and troubleshoot problems or error messages.
Troubleshooting 75
Page 76

Troubleshooting
The following pages present typical problems and solutions as well as
suggested testing methods.
Checking logs
Checking event logs is often the first step when trying to identify problems.
Error messages in the logs may indicate the problem.
• Check application event logs associated with Exchange, FRS, and HP
• Check Windows system event logs.
Common problems and solutions are also listed below.
Troubleshooting checks
The following checks may help you isolate and resolve issues with FRS or
associated systems and software.
1. Ensure the HP Business Copy license and the HP VSS Hardware
VSS Hardware Provider.
Provider were installed and correctly configured.
A simple way to verify the HP VSS HWP is installed correctly, is to
see if it is running. At the command line, enter:
vssadmin list providers
Look for the HP VSS HWP in the resulting list.
2. In order for the production and recovery servers and their applications
to communicate, the Windows DCOM distributed communication
process must be able to communicate among all FRS servers. This
requires that you be logged into all FRS-related applications and all FRS
servers (including Command View) as an administrator and requires
connectivity without a firewall between servers. You can check for
DCOM errors in the system event logs.
3. Check that the Exchange server is online.
76 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 77

4. Check Cluster administrator and verify resources are online.
5. Check the Command View server for errors associated with the storage
system.
6. Check that the Exchange server can access the data LUNs via My
Computer.
7. Check for mount points found under the FRS directory.
8. If Exchange copies fail because of a failed integrity check, verify that
eseutil.exe and ese.dll are installed on the recovery server. Integrity
checks will not work without them, and a failed integrity check causes
a failed copy.
9. The VSS Hardware Provider may not be able to make the copy because
it has run out of copy space. Return to the disk array and the HP VSS
Hardware Provider Configuration Utility (in Windows
Start/Programs/Hewlett-Packard) to create more shadow copy LUNs
and then re-populate the configuration utility.
10. Bypass FRS and test VSS, HWP, and the array by using the Microsoft
vshadow utility available in the Microsoft VSS Software Developer’s
Kit to create snapshots. See the Microsoft documentation for
instructions. If you can create snapshots without FRS, FRS may not be
properly installed or configured.
FRS does not recognize storage groups
1. Storage groups are not properly set up. See “Chapter 2 Configuration”
page 34 to correctly set up production and recovery storage groups.
Troubleshooting 77
Page 78

FRS error messages
The following text explains FRS error messages.
Maintenance
Error:
Dismounting the local/remote drive failed. Please close any open files on
that drive and select retry to try again, select ignore to ignore the error and
continue, or select abort to cancel the operation.
Explanation:
FRS cannot dismount any file system drive if it sees any activity on the
drive. This could cause corruption, so FRS waits until all files on that drive
are closed before dismounting the drive. Confirm that all files are closed
and select retry.
If the problem is with the remote drive, confirm that all connectivity to the
remote machine is intact and that there are no network issues preventing
FRS from communicating with the remote server.
Error:
Mounting the remote drive failed. Please select retry to try again, select
ignore to ignore and continue, or select abort to cancel the operation.
Explanation:
If FRS was able to dismount a drive, there should be no problem
re-mounting it unless FRS has lost connection to the production server.
Confirm that all connections are intact and that the recovery server can ping
the production server. Then retry.
78 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 79

Recovery
Error:
Extended maintenance mode fix (for clusters) is not installed on node
[production server name].
Explanation:
Before installing HP StorageWorks Fast Recovery Solution (FRS) on a
Microsoft cluster node, Microsoft hot fix KB903650 must be installed on
the cluster node. This hot fix is required on Windows Server 2003 systems
to support the cluster extended maintenance mode.
During recovery, FRS inspects the cluster configuration to check whether
the above hot fix is installed on the production servers. If the hot fix is
installed, the recovery operation proceeds normally. Otherwise the recovery
operation is terminated and the error message above is displayed in the
recovery activity log window and also in the application event log.
Error:
Failure setting the database restore flag. Please select retry to try again.
Explanation:
If FRS cannot reach the exchange server, it cannot manipulate the restore
flag. Check connectivity and network to the production server. Confirm that
all Microsoft services are online.
Error:
This operation cannot be completed, no recovery LUN available.
Explanation:
The recovery button will only be enabled if a split mirror backup has been
done in the past and the pair has been created using FRS. However, if
someone goes into the disk array and manually deletes a pair which was
Troubleshooting 79
Page 80

being managed by FRS, and then a recovery is attempted, this error will be
given.
Error:
Are you sure you want to continue with a recovery?
Explanation:
Once a recovery is started, it cannot be cancelled until the recovery is
complete. The production database will be replaced by the recovery-ready
database and there is no going back to the original if this was not the
intended action.
Terminating processes
Message:
Operation cannot be cancelled…
Explanation:
Closing either the GUI or the progress window for a split mirror backup or
a recovery causes FRS to leave the database in an unknown state. For this
reason, FRS does not allow windows to be closed while an action is in
progress. If the process is forcibly closed through the use of “task
manager,” the integrity of the database cannot be guaranteed, and FRS and
the disk array may have conflicting information about the databases.
80 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 81

Glossary
This glossary defines acronyms and terms used in this guide or related to
this product and is not a comprehensive glossary of computer terms.
API Application Programming Interface, an interface that allows a software
application to connect to and work with a third party software application.
BC HP StorageWorks Business Copy EVA. Software that creates and
maintains local copies of data stored on the disk array. The copies can be
used for data duplication, backup, and local disaster recovery.
clone A full copy of a volume, usable by an application.
cluster The concept of linking individual servers physically and programmatically
and coordinating communication between them so they can perform
common tasks.
CV HP StorageWorks CommandView, a browser-based interface that allows
management of an HP disk array.
differential copy A copy of a database consisting only of the differences in the database since
the last full copy.
disk array A RAID. A collection of disk drives within a cabinet or multiple cabinets
and including a controller and software allowing drives to be ganged together
in various configurations to create virtual drives (LUNs).
EVA HP StorageWorks Enterprise Virtual Array.
Glossary 81
Page 82

failover Process that automatically shifts the workload from one server in a cluster
to another server in the event of a failure.
FC Fibre Channel, a fiber optic interconnection standard commonly used for
storage area networks.
FRS HP StorageWorks Fast Recovery Solution.
FRS server The server where copies of the production database are staged and
managed. The FRS server runs the FRS GUI. Also known as the recovery
server.
GUI Graphical User Interface.
HBA Host bus adapter. The FC interface card that installs in a host to connect the
host to a fabric SAN.
HWP Hardware Providers. A collection of software that executes on the host, a bus
adapter, and the disk array to enable managing and/or copying of array LUNs
through the Windows OS and applications.
LDEV Logical device. An LDEV is created when a RAID group is divided into
pieces according to a selected host emulation mode (that is, OPEN-3,
OPEN-8, OPEN-9, etc.). The number of resulting LDEVs depends on the
selected emulation mode. The term LDEV is often used synonymously
with the term volume.
LUN Logical unit number. A LUN results from mapping a SCSI logical unit
number, port ID, and LDEV ID to a RAID group. The size of the LUN is
determined by the emulation mode of the LDEV, and the number of
LDEVs associated with the LUN. For example, a LUN associated with two
OPEN-3 LDEVs has a size of 4,693 MB.
mirror Synonymous with “clone.”
MSA HP StorageWorks Modular Smart Array.
online backup Backup while Exchange services are still running. There is no interruption
in services for backup.
82 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 83

production server Exchange 2003 server.
plex A Microsoft term denoting a full copy of data that has been split off from the
original and is no longer being updated. Synonymous with “split mirror.”
production LUN The volume containing the active application database. Known to Business
Copy as a P-VOL.
P-VOL Primary volume. Typically the volume where application data is stored.
RAID Redundant array of independent disks.
recovery LUN The volume containing the data copies used for recovery. Known to Business
Copy as an S-VOL.
recovery server FRS server. The server where copies of the production database are
managed.
SAN fabric The Fibre Channel hardware and cabling that connects servers to storage
devices in a Storage Area Network (SAN) is referred to as a “fabric.” A fabric
switch provides automatically-switched connectivity between servers and
storage in the fabric.
shadow copy A Microsoft term describing a point-in-time copy of an original volume. The
original volume continues to change as the process continues, but the shadow
copy of the volume remains constant.
SMA Storage Management Appliance. A PC built into the EVA Disk Array. The
SMA provides a direct interface into the disk array. Some EVA arrays do not
have an SMA but use a Command View server instead.
snapclone An HP EVA disk array term denoting a full copy of a volume that becomes
immediately usable by an application. Created much faster than ordinary
clones by taking a snapshot and updating to a full copy in the background.
snapshot A generic term meaning a static point-in-time copy of a volume, typically
used for backup.
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol.
Glossary 83
Page 84

split mirror A full copy of data that has been split off from the original and is no longer
being updated.
subsystem Synonym for “disk array” or “RAID.”
S-VOL Secondary volume. The volume that receives copies of data.
SVP Service processor. A laptop PC built into the HP XP Disk Array. The SVP
provides a direct interface into the disk array, and is used by the HP service
representative only.
volume Generic term for a number of physical disks or portions of disks logically
bound together as a virtual disk containing contiguous logical blocks.
Volume can also be software shorthand for a mapped volume (Windows
drive letter or mount point).
VDS Microsoft Virtual Disk Service, the Windows service that manages storage
through hardware providers.
volume shadow copy See “shadow copy.”
VSC Volume Size Configuration, a feature of HP disk arrays that allows creation
of logical volumes custom-sized according to user requirements.
VSS Microsoft Volume Shadow Copy Service, the Windows service that creates
data copies. Works through HP HWP to make copies of disk array volumes.
84 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 85

Index
A
addcopy command 68, 70
adding server instances 55
architecture
Fast Recovery 26
authorized resellers 9
B
Business Copy 28
C
command line 66
addcopy 68, 70
available commands 67
delcopy 68, 72
error codes 72
examples 70
listcopy 69, 71
Command View 28
Command View management station 27
components 18
hardware 27
software 28
conceptual overview, FRS 17
configuration
disk array 34
important notes 29
conventions, document 10
copy terminology 21
creating shadow copies 57
D
deinstallation
FRS 49
delcopy command 68, 72
disk array 27
configuring 34
overview 23
disk arrays
requirements 7
supported 7
documentation
conventions 10
related products 7
E
error codes, command line 72
error messages 75, 78
F
fabric switch 27
features, FRS 16
fibre cables 27
Index 85
Page 86

firmware
required 7
FRS
adding servers 55
creating shadow copies 57
installing 41
main window 53
overview 20
recovery 60
starting 52
functional components 18
G
glossary 81
H
hardware components 27
HBAs 27
hot fixes 28
HWP 28
HWP overview 23
O
opening FRS 52
overview
components 18
disk array 23
FRS conceptual 17
HWP 23
VSS 21
P
performance issues 30
production server
installing FRS 41
Q
QFEs 28
QFEs (See "quick fixes") 28
quick fixes 28
R
recovery 60
resellers, authorized 9
I
Installation 39
S
Secure Path 28
J
Java Runtime Environment 28
server, adding instances 55
shadow copies 57
SMA
L
licensing FRS 44
listcopy command 69, 71
configuration for FRS 32
software
licensing 44
software components 28
M
main window, FRS 53
maintenance 75
Microsoft quick fixes 28
solutions
high availability 16
system administrator
prerequisite knowledge 8
N
network interface cards 27
86 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
Page 87

T
technical support 9
terminology 21
troubleshooting 75, 76
V
VDS/VSS server 27
VSS
overview 21
VSS process flow 21
W
web site
HP storage 8
HP support 9
Index 87
Page 88

88 HP StorageWorks EVA Fast Recovery Solution for Windows Server 2003: Administration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...