Page 1

HP StorageWorks
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools
administrator guide
Part number: AA–RVHYB–TE
Second edition: September 2005
Page 2

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2005 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
© Copyright 2005 Brocade Communications Systems, Incorporated.
Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Hewlett-Packard shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this material.
This document contains proprietary information, which is protected by copyright. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or
translated into another language without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard. The information is provided “as is” without warranty of any
kind and is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express warranty statements
accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for
technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Windows and Windows XP are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Java is a U.S. trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide
Page 3

Contents
About this guide. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Intended audience . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Related documentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x master glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Document conventions and symbols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
HP technical support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
HP-authorized reseller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Helpful web sites . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
1 Introducing Advanced Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
What’s New in This Document . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Requirements, installation, and support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Requirements. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Configuring Internet Explorer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Setting the refresh frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Installing Java on the workstation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Installing the JRE on your Solaris or Linux client workstation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Installing patches on Solaris . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Installing the Java Plug-in on Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Installing an Advanced Web Tools license . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Installing an Advanced Web Tools license through telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Installing an Advanced Web Tools license through telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Installing an Advanced Web Tools license through the web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Installing the first license through the web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Installing additional licenses through the web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Value line licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Switch support. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Launching Advanced Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Launching Advanced Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Advanced Web Tools. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Logging in . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Upfront login . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Role-based access control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Logging in. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Logging out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Ending an Advanced Web Tools session with upfront login enabled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Session management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2 Using Advanced Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Viewing the Switch Explorer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Core Switch 2/64 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
SAN Director 2/128 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4/256 SAN Director . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
SAN Switch 2/8V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Refresh rates . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Fabric Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Fabric toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Switch View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Switch View button menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Switch Information View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Status Legend . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Displaying switches in the fabric. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Accessing the Switch Explorer for a particular switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Ending the Advanced Web Tools session. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 3
Page 4

Ending the Advanced Web Tools session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Using Advanced Web Tools and secure mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Advanced Web Tools access and HTTP_POLICY . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Opening modules in a secure fabric . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Primary-FCS-only functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Disabled functionality. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Recommendations for working with Advanced Web Tools. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
3 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Managing fabrics, switches, and ports using Advanced Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Launching the switch Admin Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Accessing the Switch Admin module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Refreshing the switch Admin Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Launching the telnet window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Accessing telnet through Advanced Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Configuring IP and netmask information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Configuring IP and netmask information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Configuring a syslog IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Configuring the syslog IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Removing a syslog IP address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Configuring a switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Enabling and disabling a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Enabling or disabling a switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Changing the switch name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Changing the switch name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Changing the switch domain ID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Viewing and printing a switch report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Viewing or printing a switch report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Rebooting a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Performing a fast boot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Performing a switch reboot . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Changing system configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Configuring fabric parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Configuring fabric parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Enabling insistent domain ID mode (FICON only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Configuring virtual channel settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Configuring system services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Configuring arbitrated loop parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Configuring arbitrated loop parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Configuring system services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Configuring system services. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Configuring ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Configuring port type. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Configuring the port type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Configuring port speed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Assigning a name to a port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Naming a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Disabling a port over reboots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Disabling a port so that it remains disabled over reboots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Enabling and disabling a port. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Enabling or disabling a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Activating Ports on Demand . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Enabling a Port Upgrade License . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Maintaining licensed features. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Activating a license on a switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Removing a license from a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Administering high availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Launching the High Availability module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
To launch the High Availability module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
4
Page 5

Synchronizing services on the CP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Initiating a CP failover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
To initiate a CP failover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Monitoring events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Displaying fabric events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
To display fabric events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Displaying switch events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Displaying switch events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Filtering fabric and switch events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Filtering events by time intervals. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Filtering events by event severity levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Filtering events by message ID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Filtering events by service component . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Displaying a fabric topology report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Viewing a fabric topology report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Displaying the Name Server entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Viewing a list of the switches in the Name Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Printing the Name Server entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Displaying detailed Name Server information for a particular device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Displaying the zone members of a particular device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Physically locating a switch using beaconing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Enabling beaconing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Displaying swapped port area IDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Determining whether a port area ID has been swapped with another switch port . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
4 Maintaining configurations and firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Maintaining configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Backing up a configuration file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
To back up a configuration file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Restoring a configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Downloading a configuration to the switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Performing a firmware download . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Downloading a new version of the firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
5 Configuring standard security features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Creating and maintaining user-defined accounts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Displaying account information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Creating a user-defined account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Deleting a user-defined account . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Changing account parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Changing an account password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Configuring SNMP information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Setting SNMP trap levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Setting trap levels. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Configuring SNMP information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Changing the systemGroup configuration parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Setting SNMPv1 configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Setting SNMPv3 configuration parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Changing the accessControl configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Managing the RADIUS server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Enabling and disabling RADIUS service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Configuring the RADIUS server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
To configure the RADIUS server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Modifying the RADIUS server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Modifying the RADIUS server order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Modifying the order in which the RADIUS servers are contacted . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Removing a RADIUS server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
6 Routing traffic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Introducing routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 5
Page 6

Displaying FSPF routing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Viewing FSPF routing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Configuring a static route . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
To configure a static route. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
Enabling and disabling dynamic load sharing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Configuring the DLS setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Specifying frame order delivery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Configuring the IOD setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Configuring link cost . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Configuring the link cost for a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
7 Administering extended fabrics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
About extended link buffer allocation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Configuring for long distance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Configuring a port for long-distance connection. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
8 Administering ISL trunking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Displaying trunk group information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Viewing information on a trunk group . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Disabling or reenabling trunking mode on a port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
9 Administering zoning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Introducing zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Managing zoning with Advanced Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Launching the Zone Admin module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Refreshing the fabric information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
To refresh the fabric information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Refreshing the Zone Admin module information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Refreshing the local Zone Admin buffer from the fabric zoning database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Saving local zoning changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Saving Zone Admin module changes to the switch zoning database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Closing the Zone Admin module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Safely closing the Zone Admin module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Zoning views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Selecting a zoning view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Managing zone aliases. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Creating and populating a zone alias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Creating an alias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Adding and removing members of a zone alias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Modifying the members of an alias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Renaming a zone alias. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Deleting a zone alias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Managing zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Creating and populating a zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Creating a zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Adding and removing the members of a zone. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Modifying the members of a zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Renaming a zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Deleting a zone. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Managing QuickLoops . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Creating a QuickLoop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Adding and removing members of a QuickLoop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Modifying the members of a QuickLoop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Renaming a QuickLoop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Deleting a QuickLoop. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Managing Fabric Assist zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Creating a Fabric Assist zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Adding and removing Fabric Assist zone members . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Modifying the members of a Fabric Assist zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Renaming a Fabric Assist zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
6
Page 7

Deleting a Fabric Assist zone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Managing zone configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Creating a zone configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Adding or removing zone configuration members . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Modifying the members of a zone configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Renaming a zone configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Deleting a zone configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Deleting a disabled configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Enabling a zone configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
To enable a zone configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Disabling a zone configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
To disable a zone configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Displaying the enabled zone configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Viewing the enabled zone configuration name without launching the Zone Admin module . . . . . 95
Viewing detailed information about the enabled zone configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Displaying the zone configuration summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Viewing a zone configuration summary report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Creating a configuration analysis report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
To create a configuration analysis report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Displaying Initiator/Target Accessibility Matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Managing the zoning database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Adding a WWN to multiple aliases, zones, and Fabric Assist zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Adding a WWN to the Zone Admin buffer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Removing a WWN from multiple aliases, zones, and Fabric Assist zones. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Deleting a WWN from the Zone Admin buffer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Replacing a WWN in multiple aliases, Fabric Assist zones, and zones . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
Replacing a WWN in the Zone Admin buffer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Searching for a zone member . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
To search for a zone member . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Clearing the zoning database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Disabling any active configuration and deleting the entire zoning database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Using zoning wizards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Adding unzoned online devices to a zone or alias . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Removing offline devices from the zoning database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Replacing offline devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Defining device aliases . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Assigning aliases to devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Best practices for zoning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
10Working with diagnostic features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Managing trace dumps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
How a trace dump is used . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Setting up automatic trace dump transfers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
Specifying a remote server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Enabling automatic transfer of trace dumps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Disabling automatic trace uploads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Disabling automatic uploading of the trace dump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Uploading a trace dump manually . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Uploading a trace dump . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Displaying switch information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Displaying detailed fan hardware status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Displaying the fan status detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Displaying the temperature status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Displaying the temperature status detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Displaying the power supply status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Displaying the power supply status detail . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Checking the physical health of a switch. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Displaying a detailed switch status report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Interpreting port LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 7
Page 8

Displaying port information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Accessing the Port Information screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
11Administering FICON CUP fabrics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Enabling or disabling FMS mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
To enable or disable FMS mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Configuring FMS parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Configuring FMS mode parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Displaying the code page information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Displaying the Control Device state. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Displaying the Control Device state . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Configuring CUP port connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Displaying CUP port connectivity configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
Displaying the CUP port connectivity configurations list. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Creating or editing CUP port connectivity configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Activating a CUP port connectivity configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Activating a saved CUP port connectivity configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Copying a CUP port connectivity configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Deleting a CUP port connectivity configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Deleting a saved CUP port connectivity configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
12Administering Fabric Watch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Introduction to Fabric Watch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Using Fabric Watch with Advanced Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Launching the Fabric Watch module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Configuring Fabric Watch thresholds . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Configuring threshold traits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
To configure threshold traits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Configuring threshold alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Enabling or disabling threshold alarms for individual elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Enabling or disabling threshold alarms for an element . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Configuring alarms for FRUs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Displaying Fabric Watch alarm information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Displaying an alarm configuration report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Viewing an alarm configuration report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
Displaying alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Viewing alarms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Configuring e-mail notifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Configuring the e-mail server on a switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Configuring the e-mail server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
Configuring the e-mail alert recipient . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Configuring the e-mail alert alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
13Monitoring performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Monitoring performance using Advanced Web Tools . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Predefined performance graphs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
User-defined graphs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Canvas configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Launching the Performance Monitor module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Creating a basic Performance Monitor graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Customizing basic Performance Monitor graphs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Customizing a basic Performance Monitor graph. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Creating advanced Performance Monitor graphs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Creating an SID/DID performance graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Creating an SID/DID performance graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Creating a SCSI vs. IP traffic graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
To create a SCSI vs. IP traffic graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Creating a SCSI command graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Creating an AL_PA error graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Managing performance graphs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
8
Page 9

Saving graphs to a canvas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Saving graphs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Adding a graph to an existing canvas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Adding a graph. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Printing graphs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Printing a single graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Printing all graphs in a canvas. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Modifying an existing graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
14Limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
General Advanced Web Tools limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Platform-specific limitations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Limitations when using the Mozilla browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Figures
1 Configuring Internet Explorer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2 Advanced Web Tools interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
3 Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a Core Switch 2/64 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
4 Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a SAN Director 2/128 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
5 Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a 4/256 SAN Director . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6 Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a SAN Switch 2/8V . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
7 Switch Admin Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8 Network tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
9 Configure tab, Fabric subtab. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
10 Ports tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
11 License tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
12 High availability mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
13 Fabric Events window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
14 Switch Events window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
15 Event Filter dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
16 Fabric topology report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
17 Name server window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
18 Configure tab, Upload/Download Subtab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
19 Firmware tab. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
20 User tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
21 SNMP tab. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
22 AAA Service tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
23 Routing tab for port-based routing policy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
24 Extended Fabric tab. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
25 Trunking tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
26 Zone Admin Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
27 Device detail example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
28 Sample zoning database . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
29 Effective Configuration window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
30 Zone Configuration summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
31 Initiator/Target Accessibility Matrix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
32 Add Un-zoned Devices wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
33 Entering a zone alias in the Define Device Alias wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
34 Trace tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 104
35 Fan status window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
36 Temperature status window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
37 Switch report. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
38 Switch report action menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
39 Port and LED status color-coded information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
40 Port LEDs for the FC4-32 port blade in the 4/256 SAN Director . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
41 Port information screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
42 FICON CUP management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
43 FICON CUP busy error. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 9
Page 10

44 Configuring CUP port connectivity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
45 Port CUP Connectivity Configuration dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
46 Activate CUP Port Connectivity configuration dialog box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
47 Fabric Watch module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
48 Threshold configuration for Fabric Watch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
49 Fabric Watch e-mail configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
50 Accessing performance graphs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
51 Canvas of eight performance monitoring graphs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
52 Creating a port throughput graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
53 Switch Throughput Utilization Setup dialog box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
54 Creating an SID/DID performance graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
55 Creating a SCSI command graph . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
56 Creating an ALPA error graph. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Tables
1 Document conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2 Certified and tested platforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
3 Tested platforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4 Comparison of login modes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
5 Key to Figure 3 through Figure 6. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
6 Polling rate in the Switch Explorer window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
7 Ports enabled with Ports on Demand licenses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
8 Event severity levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
9 Long-distance settings and license requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .76
10 FMS mode paramenter descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
11 Alarm notification table fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 126
12 Basic performance graphs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
13 Advanced performance monitoring graphs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
14 Advanced Web Tools limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
15 Platform-specific limitations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
16 Advanced Web Tools limitations when using the Mozilla browser . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
10
Page 11

About this guide
This guide provides information about:
• Using Advanced Web Tools
• Managing fabrics, switches, and ports
• Routing traffic
• Extended fabrics
• ISL trunking
• Zoning
• Diagnostics
• Fabric Watch
NOTE: FICON is not supported on HP B-Series Fibre Channel switches. The FICON information in this
document is included for reference only.
Intended audience
This guide is intended for:
• System administrators responsible for setting up HP StorageWorks Fibre Channel Storage Area
Network (SAN) switches
• Technicians responsible for maintaining the Fabric Operating System (OS)
Related documentation
Documentation, including white papers and best practices documents, is available on the HP web site:
http://www.hp.com/country/us/eng/prodserv/storage.html
IMPORTANT: For late breaking, supplemental information, access the latest version of the HP
StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x release notes using the following steps.
To access current Fabric OS related documents:
1. Locate the IT storage products section of the web page.
2. Under Networked storage, click SAN infrastructure.
3. From the SAN Infrastructure web page, locate the SAN Infrastructure products section.
4. Click Fibre Channel Switches.
5. Locate the B-Series Fabric-Enterprise Class section. Click 4/256 SAN Director and 4/256 SAN Director
power pack, to access Fabric OS 5.x documents (such as this document).
The switch overview page displays.
6. Go to the Product Information section, located on the right side of the web page.
7. Click Technical documents.
8. Follow the onscreen instructions to download the applicable documents.
.
HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x master glossary
This guide uses industry standard SAN terminology. However, some terms are intrinsic to Fabric OS 5.x.
See the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x master glossary for a complete list of terms and definitions.
Access the master glossary from the HP StorageWorks SAN Switch Documentation CD that shipped with
your switch. Also, access from the HP web site using the procedure outlined in Related documentation.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 11
Page 12

Document conventions and symbols
Table 1 Document conventions
Convention Element
Medium blue text: Figure 1 Cross-reference links and e-mail addresses
Medium blue, underlined text
(http://www.hp.com)
Bold font • Key names
Italics font Text emphasis
Monospace font • File and directory names
Monospace, italic font • Code variables
Monospace, bold font Emphasis of file and directory names, system output, code, and text
Web site addresses
• Text typed into a GUI element, such as into a box
• GUI elements that are clicked or selected, such as menu and list
items, buttons, and check boxes
• System output
• Code
• Text typed at the command-line
• Command line variables
typed at the command line
WARNING! Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or death.
CAUTION: Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
IMPORTANT: Provides clarifying information or specific instructions.
NOTE: Provides additional information.
TIP: Provides helpful hints and shortcuts.
HP technical support
Telephone numbers for worldwide technical support are listed on the HP support web site:
http://www.hp.com/support/
Collect the following information before calling:
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Product model names and numbers
• Applicable error messages
.
12
Page 13

• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed, specific questions
For continuous quality improvement, calls may be recorded or monitored.
HP strongly recommends that customers sign up online using the Subscriber's choice web site:
http://www.hp.com/go/e-updates
• Subscribing to this service provides you with e-mail updates on the latest product enhancements,
newest versions of drivers, and firmware documentation updates as well as instant access to numerous
other product resources.
• After signing up, you can quickly locate your products by selecting Business support and then Storage
under Product Category.
HP-authorized reseller
For the name of your nearest HP-authorized reseller:
• In the United States, call 1-800-282-6672.
• Elsewhere, visit the HP web site: http://www.hp.com
telephone numbers.
Helpful web sites
For other product information, see the following HP web sites:
.
. Then click Contact HP to find locations and
• http://www.hp.com
• http://www.hp.com/go/storage
• http://www.hp.com/support/
• http://www.docs.hp.com
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 13
Page 14

14
Page 15

1 Introducing Advanced Web Tools
HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools is a GUI that enables administrators to monitor
and manage single or small fabrics, switches, and ports from a standard workstation. It is an optionally
licensed product that runs on HP Fabric OS.
Advanced Web Tools provides the administrative control point for HP Advanced Fabric Services,
including Advanced Zoning, Interswitch Link (ISL) Trunking, Advanced Performance Monitoring, and
Fabric Watch. Advanced Web Tools also provides an interface to telnet commands to perform special
switch functions and diagnostics that are available only through the telnet interface.
This chapter contains the following sections:
• What’s New in This Document, next
• Requirements, installation, and support, page 15
• Launching Advanced Web Tools, page 20
• Logging in, page 21
• Logging out, page 22
• Session management, page 22
What’s New in This Document
The following changes have been made since this document was last released:
• Information that was added:
• Upfront login and the switchAdmin role are described in ”Logging in” on page 21.
• Support for the 4/256 SAN Director and the 4/16 SAN Switch is added throughout.
• Information that was changed:
• Changes to the FICON CUP tab are described in ”Configuring CUP port connectivity” on
page 117.
For further information, see the release notes.
Requirements, installation, and support
Before you install Advanced Web Tools on your workstation, verify that your switches and workstation
meet the Advanced Web Tools requirements listed in this chapter.
This section contains the following subsections:
• Requirements, page 15
• Installing an Advanced Web Tools license, page 18
• Value line licenses, page 19
• Switch support, page 19
• Launching Advanced Web Tools, page 20
Requirements
Advanced Web Tools requires a browser that conforms to HTML version 4.0, JavaScript version 1.0, and
TM
Java
Plug-in 1.4.2_06 or later.
HP has certified and tested Advanced Web Tools on the platforms shown in Table 2.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 15
Page 16
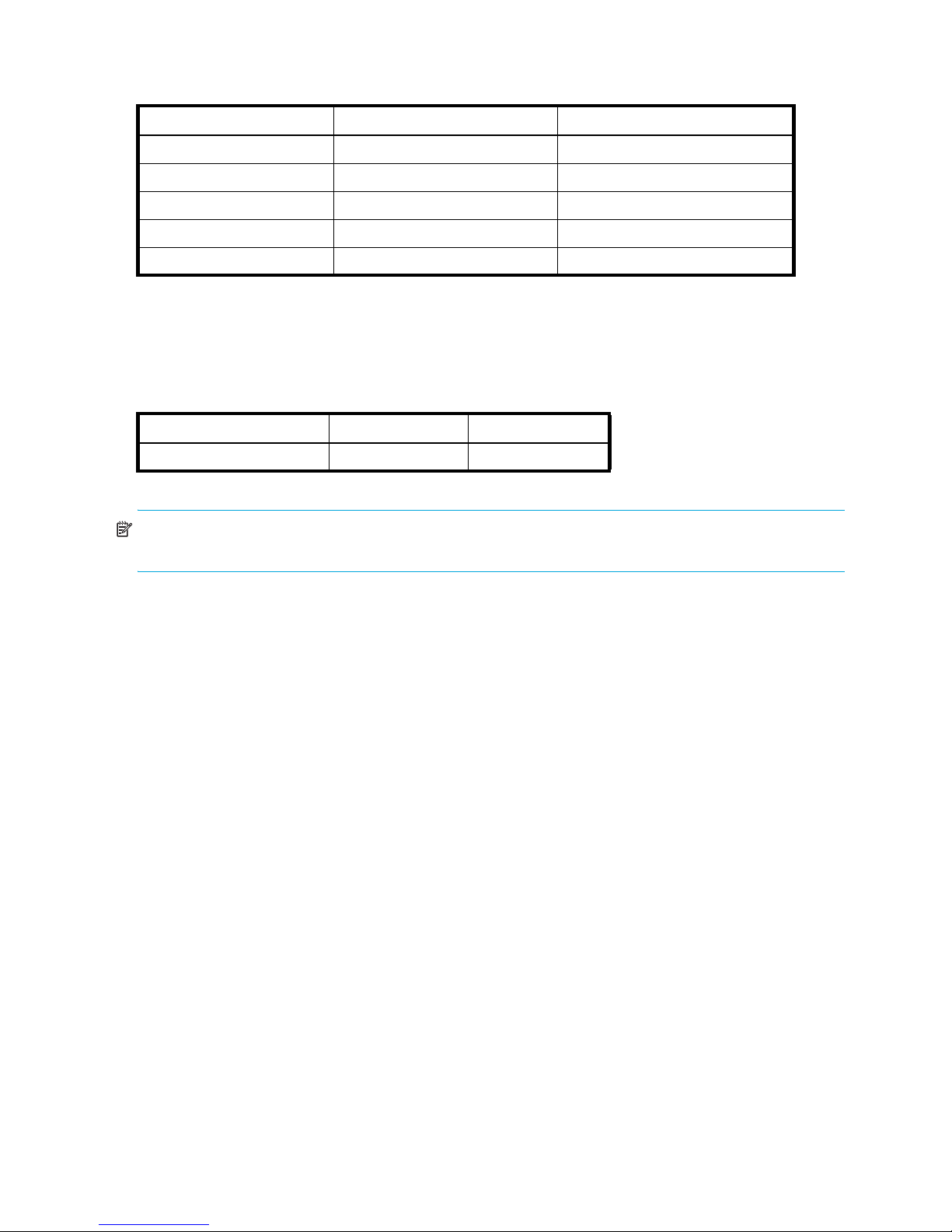
Table 2 Certified and tested platforms
Operating system Browser Java Plug-in
Solaris 2.8 Mozilla 1.6 1.4.2_06
Solaris 2.9 Mozilla 1.6 1.4.2_06
Windows® 2000 Internet Explorer 6.0 1.4.2_06
Windows 2003 Internet Explorer 6.0 1.4.2_06
Windows XP® Internet Explorer 6.0 1.4.2_06
In addition, HP has tested Advanced Web Tools on the platforms shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Tested platforms
Operating system Browser Java Plug-in
Red Hat Linux® 9.0 Mozilla 1.6 1.4.2_06
NOTE: Some browsers must be configured to work with Advanced Web Tools. For information about
how to do this, see the section “Configuring Internet Explorer,” n ext.
Adequate RAM is required on Windows systems:
• 256 MB or more RAM for fabrics comprising 15 switches or less
• 512 MB or more RAM for fabrics comprising more than 15 switches
HP recommends a minimum of 8 MB of video RAM.
Configuring Internet Explorer
Correct operation of Advanced Web Tools with Internet Explorer requires specifying the appropriate
settings for browser refresh frequency and process model. Browser pages should be refreshed frequently
to ensure the correct operation of Advanced Web Tools.
Setting the refresh frequency
1. Select Tools > Internet Options in the browser.
2. Select the General tab and click Settings (under Temporary Internet Files).
3. Click Every visit to the page under Check for newer versions of stored pages, as shown in Figure 1.
16 Introducing Advanced Web Tools
Page 17
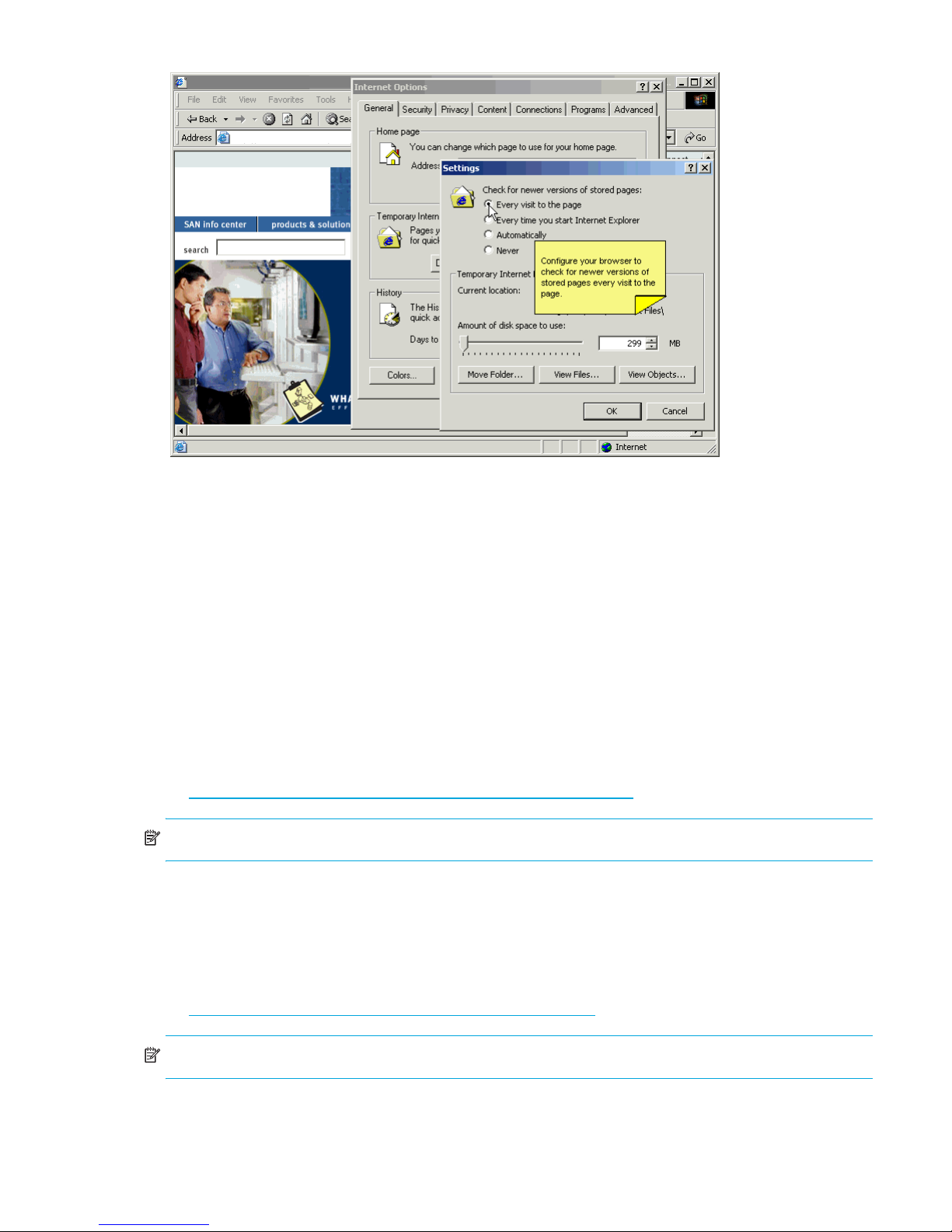
Figure 1 Configuring Internet Explorer
Installing Java on the workstation
Java Plug-in version 1.4.2_06 must be installed on the workstation for the correct operation of Advanced
Web Tools.
If you try to launch Advanced Web Tools without any Java Plug-in installed:
• Internet Explorer prompts and downloads the proper Java Plug-in.
• Mozilla downloads the most recently released Java Plug-in.
If you try to launch Advanced Web Tools with an earlier version Java Plug-in installed,
• Internet Explorer might prompt you for an upgrade, depending on the existing Java Plug-in version.
• Mozilla uses the existing Java Plug-in.
Installing the JRE on your Solaris or Linux client workstation
1. Locate the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) on the Internet, at the following URL:
http://java.sun.com/products/archive/j2se/1.4.2_06/index.html
NOTE: This URL points to a non-HP web site and is subject to change without notice.
2. Follow the instructions to install the JRE.
3. Create a symbolic link from $MOZILLA/plugins/libjavaplugin_oji.so to
$JRE/plugin/$ARCH/ns600/libjavaplugin_oji.so
Installing patches on Solaris
1. Search for any required patches for your current version of the JRE at the following web site:
http://sunsolve.sun.com/pub-cgi/show.pl?target=patchpage
NOTE: This URL points to a non-HP web site and is subject to change without notice.
2. Follow the link to download the patch, and exit the browser when you are done.
3. Install the patch and reboot the system.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 17
Page 18
Installing the Java Plug-in on Windows
1. Select Start Menu > Settings > Control Panel and then select the Java Plug-in Control Panel.
2. Select the About tab.
3. Determine whether the correct Java Plug-in version is installed:
• If the correct version is installed, Advanced Web Tools is ready to use.
• If no Java Plug-in is installed, point the browser toward a switch running Fabric OS 4.x or later,
follow the link to the Sun Microsystems web site, download the correct Java Plug-in, and
double-click the downloaded file to install the plug-in.
• If an outdated version is currently installed, uninstall it, relaunch the browser, and enter the address
of a switch running Fabric OS 4.4.0 or later. Advanced Web Tools guides you through the steps to
download the proper Java Plug-in.
Installing an Advanced Web Tools license
You can install an Advanced Web Tools license either through telnet or over the Web.
All licenses, including Advanced Web Tools licenses, are installed on a chassis basis. For example, if you
install an Advanced Web Tools license on logical switch 0 in a Core Switch 2/64, you do not need to
install an additional Advanced Web Tools license on logical switch 1 of that Core Switch 2/64, because
both are in the same chassis.
To determine whether a license is already installed on a switch, follow the instructions provided in the
section “Installing an Advanced Web Tools license through telnet,” next. If a license is not installed,
contact your switch supplier to obtain a license key.
Installing an Advanced Web Tools license through telnet
Use the following procedure to determine whether an Advanced Web Tools license is installed on your
switch and, if not, install it.
Installing an Advanced Web Tools license through telnet
1. Log in to the switch via telnet (see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide for more
information), using an account that has administrative privileges.
2. To determine whether an Advanced Web Tools license is already installed on the switch, enter
licenseShow on the telnet command line.
A list is displayed, showing all the licenses currently installed on the switch:
switch:admin> licenseshow
1A1AaAaaaAAAA1a: ]-- This is the license key. The installed feature is
listed below.
Zoning license
1A3AaAbcbBBCC1d:
QuickLoop license
If the Advanced Web Tools license is not included in the list or is incorrect, continue with step 3.
3. On the command line, enter:
licenseadd key
where key is the license key. The license key value is case-sensitive and must be entered exactly as
given.
4. Verify that the license was added by typing the following command:
licenseshow
If the Advanced Web Tools license is listed, the feature is available. If the license is not listed, repeat
step 3.
Installing an Advanced Web Tools license through the web
Launching Advanced Web Tools from any nonlicensed switch opens the license dialog box. If the fabric
already contains at least one licensed switch, you can use Advanced Web Tools to view and license other
switches from the licensed switch.
18 Introducing Advanced Web Tools
Page 19

Installing the first license through the web
1. Launch the web browser and enter the IP address of the switch in the Location/Address field:
http://10.77.77.77
2. Press Enter.
If an Advanced Web Tools license is already installed on the switch, Advanced Web Tools launches.
If no license is installed, a license dialog box opens.
3. If the license dialog box opens, follow the instructions provided.
Installing additional licenses through the web
1. Launch the Web browser and enter the IP address of the licensed switch in the Location/Address field:
http://10.77.77.77
2. Press Enter.
Advanced Web Tools opens, displaying the Switch Explorer.
3. Click the icon for the switch to which you want to add a license.
A licensing window opens.
4. Follow the instructions provided.
Value line licenses
If your fabric includes a switch with a limited switch license and you are launching Advanced Web Tools
using that switch, and if the fabric exceeds the switch limit indicated in the license, Advanced Web Tools
allows a 45-day grace period in which you can still monitor the switch through Advanced Web Tools.
However, Advanced Web Tools displays warning messages periodically.
These messages warn you that your fabric size exceeds the supported switch configuration limit and tells
you how long you have before Advanced Web Tools will be disabled. After the 45-day grace period,
you will no longer be able to launch Advanced Web Tools from the switch with the limited switch license
if that switch is still exceeding the switch limit.
Value line fabric licensing is applicable only to the SAN Switch 2/8V and SAN Switch 2/16V. These
licenses are indicated by 2 Domain Fabric and 4 Domain Fabric in the License tab of the Switch
Admin module. See ”Maintaining licensed features” on page 47 for more information.
Switch support
You can use Advanced Web Tools 5.x with the following HP StorageWorks switches and directors:
• 4/8 SAN Switch
• SAN Switch 2/16
• SAN Switch 2/8V
• SAN Switch 2/16V
• SAN Switch 2/32
• 4/16 SAN Switch
• SAN Switch 4/32
• Core Switch 2/64
• SAN Director 2/128
• 4/256 SAN Director
• Brocade 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem
Advanced Web Tools is part of the Fabric OS of a switch. When you launch Advanced Web Tools on a
switch, you can manage other switches in the fabric that have lower or higher firmware versions. It is
important to note that when accessing these switches you are opening the remote switch’s version of
Advanced Web Tools, and the functionality available for those switches might vary.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 19
Page 20
Launching Advanced Web Tools
You can launch Advanced Web Tools on any workstation with a compatible web browser installed. For a
list of web browsers compatible with Fabric OS 5.x, see Table 2 on page 16 and Table 3 on page 16.
Advanced Web Tools also supports HTTPS protocol, if that protocol is enabled for the switch. For more
information on enabling the HTTPS protocol on your switch, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x
administrator guide.
Launching Advanced Web Tools
1. Launch the web browser and enter the IP address of the licensed switch in the Address field:
http://10.77.77.77 or https://10.77.77.77
2. Press Enter.
Depending on the switch is configuration, you might be prompted to log in to the switch at this time.
See ”Advanced Web Tools interface” on page 20 for more information.
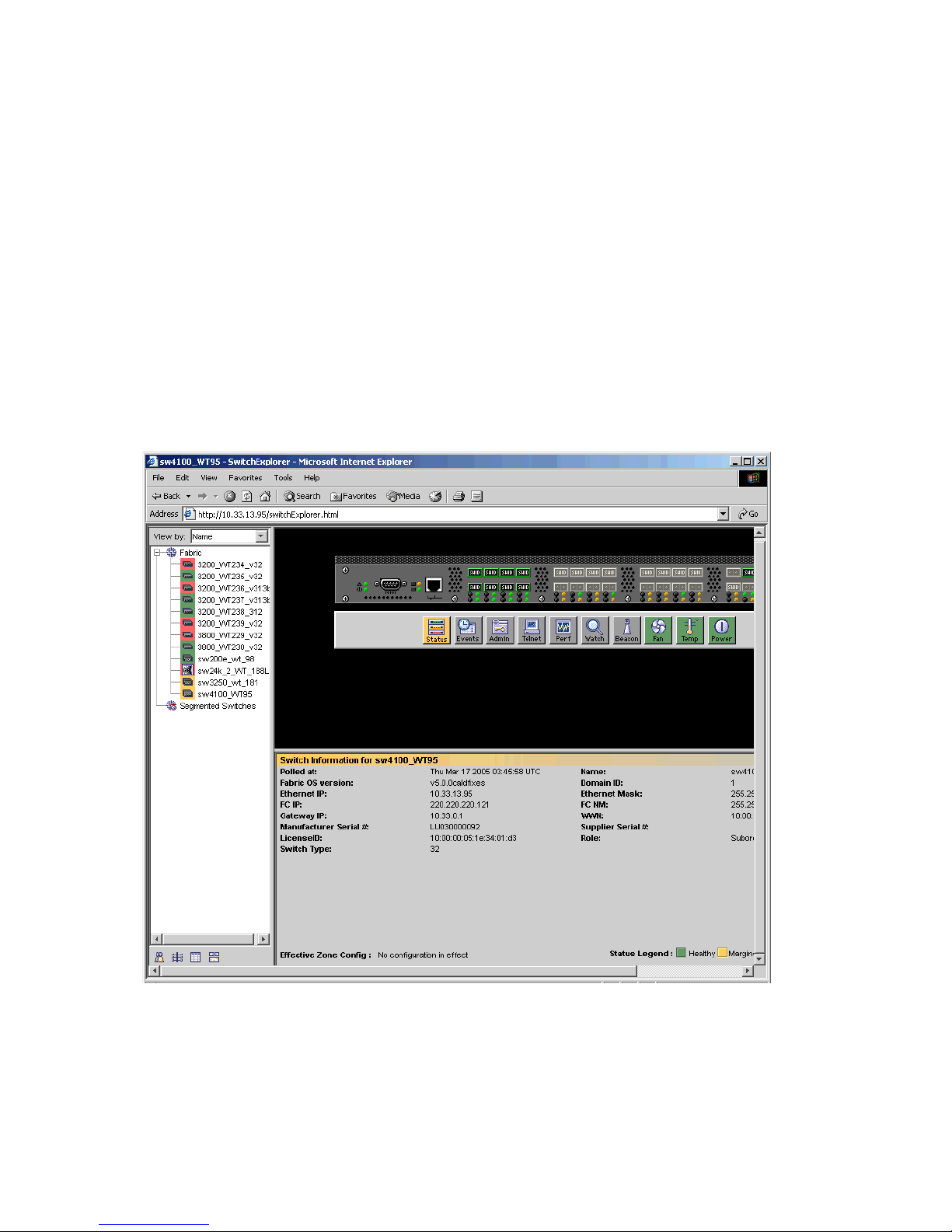
Advanced Web Tools
Advanced Web Tools launches, as shown in Figure 2. Go to Chapter 3, Using Advanced Web Tools for
instructions on using this interface.
Figure 2 Advanced Web Tools interface
20 Introducing Advanced Web Tools
Page 21
Logging in
When you use Advanced Web Tools, you must log in before you can modify any switch information. This
section describes upfront login, which determines when you log in, and role-based access control, which
is determined by how you log in.
Prior to displaying the login window, Advanced Web Tools displays a security banner (if one is
configured for your switch), which you must accept before logging in. The security banner is displayed
every time you log in, regardless of whether upfront login is enabled.
Upfront login
Depending on how your switch is configured, you are either prompted to log in once, when you launch
Advanced Web Tools (upfront login), or you are prompted to log in whenever you launch a switch
administration module, such as the Switch Admin or Zoning module.
By default, upfront login is disabled. Use the configure telnet command to enable or disable upfront
login. See the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command reference guide for information.
Table 4 lists different behaviors, depending on whether upfront login is enabled.
Table 4 Comparison of login modes
Upfront login enabled Upfront login not enabled
You must log in before you see the Switch Explorer
(shown in Figure 2 on page 20).
A single session is shared by the Switch Explorer
and all child windows launched from it. (See
”Session management” on page 22 for more
information on sessions.)
Role-based access control is enforced across the
entire session. (See Role-based access control next,
for more information.)
When you log out or close Switch Explorer, all
windows belonging to the session are invalided.
(See ”Logging out” on page 22 for more
information.)
If you refresh the Switch Explorer window, all
windows belonging to the session are invalidated.
Inactivity timeout (two hours) invalidates the Switch
Explorer and all windows opened from it.
Switch Explorer launches with no login.
Switch Admin, Zone Admin, and other protected
modules require separate login. (These modules
are described in subsequent chapters.)
Role-based access control is enforced on a
per-module basis.
There is no Logout button in Switch Explorer.
Closing the Switch Explorer window does not
invalidate other windows that were opened from it.
Refreshing the Switch Explorer window does not
affect other windows that were opened from it.
Inactivity timeout applies only to protected
modules, and each module has its own session.
This means that if the Switch Admin module times
out, the Zone Admin module could still be left
open. Conversely, recent activity in the Switch
Admin module does not prevent the Zone Admin
module from timing out if there is no activity in that
module.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 21
Page 22

Role-based access control
You can log in at the admin, switchAdmin, or user level. Each role gives you a different access level:
admin You have full access to all of the Advanced Web Tools functionality.
switchAdmin You can do everything the admin role can do, except for the following:
user You can view switch information but cannot access any of the switch administration modules.
When upfront login is enabled and the security banner is set on a switch, users are required to log in at
user level or higher to launch individual modules.
When upfront login is disabled and the security banner is set on a switch, users are required to log in at
admin level to launch individual modules.
Logging in
1. Click OK in the security banner window, if one appears.
The login window opens.
2. Enter the user name of an account with the admin, switchAdmin, or user role.
3. Enter the password.
4. Click OK.
• You cannot modify zoning configurations.
• You cannot create new accounts.
You cannot view or change account information for any accounts. You can view only your
own account and change your account password.
Logging out
If upfront login is enabled, you can end your Advanced Web Tools session either by logging out or by
closing the Switch Explorer browser window. All windows belonging to the session are invalidated (after
a short delay they become grayed out and unusable, but you must close them manually).
If upfront login is not enabled, each module that you have logged in to is a separate session. You need to
close each module to end each session. Closing the Switch Explorer does not invalidate these other
sessions.
Ending an Advanced Web Tools session with upfront login enabled
Click Logout in the Switch Explorer or click the X in the upper right corner of the Switch Explorer browser
window to close it.
Session management
A Web Tools session is defined as the connection between the Advanced Web Tools client and its
managed switch.
A session is established when you log in to a switch through Advanced Web Tools. The scope of the
session depends on whether upfront login is enabled:
• If upfront login is enabled, a single session is shared by the Switch Explorer and all child windows
launched from it. Closing or navigating away from the Switch Explorer ends the session and
invalidates all related child windows. Closing the child windows, however, does not end the session.
• If upfront login is not enabled, a session encompasses only the child window to which you are logged
in (such as the Switch Admin, Zone Admin, and other protected modules). You can open multiple
sessions from the same Switch Explorer window. Closing or navigating away from the Switch Explorer
does not close the session or affect the child windows.
22 Introducing Advanced Web Tools
Page 23

A session remains in effect until one of the following happens:
• You log out.
• You close or navigate away from the Switch Explorer window (if upfront login is enabled).
• You refresh the Switch Explorer window (if upfront login is enabled).
• You close the child window (if upfront login is disabled).
• The session times out due to inactivity.
A session times out if it has been inactive for longer than two hours. Inactivity does not mean that there is
no user activity (such as keystrokes or mouse movements); it means that no information is sent to the switch
(by clicking Apply or Save buttons). For example, in the Zoning module you can spend a lot of time
setting up a zoning scheme without actually sending information to the switch. Advanced Web Tools does
not display a warning when the session is about to time out. If the session times out, you must restart
Advanced Web Tools and log in again.
Advanced Web Tools enables sessions to both secure and nonsecure switches.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 23
Page 24

24 Introducing Advanced Web Tools
Page 25
2 Using Advanced Web Tools
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Viewing the Switch Explorer, page 25
• Displaying switches in the fabric, page 32
• Ending the Advanced Web Tools session, page 32
• Using Advanced Web Tools and secure mode, page 32
• Recommendations for working with Advanced Web Tools, page 33
Viewing the Switch Explorer
The first thing you see when you log in to a switch with Advanced Web Tools is the Switch Explorer (see
Figure 3). The Switch Explorer is divided into several areas that provide access to and information about
the switch and fabric. You should familiarize yourself with these areas, as the procedures in this guide
refer to them as follows:
• Fabric Tree, which displays a list of all the switches in the fabric
• Fabric Toolbar, which provides access to fabric-wide management interfaces, such as Name Server,
zoning, and events
• Switch View, which displays an interactive graphical representation of the switch
• Switch View Button Menu, which displays buttons providing switch information such as status, event
information, access to telnet, switch administration, switch performance, beaconing, and much more
• Switch Information View, which displays information about the switch such as name, status, Fabric OS
version, domain ID, IP address, and WWN
• Status Legend, which defines the meaning of the colors visible in the background of various icons in
the Switch Explorer
These areas are described further in the sections that follow.
Clicking some of the buttons and icons in the Switch Explorer opens up a separate module, from which
you can perform management tasks. In this document, a module is a collection of related tabs or views
that are displayed in a single browser window. The zoning module and the Switch Admin module require
you to log in, if upfront login is not enabled.
The format of the Switch Explorer varies, depending on the hardware type. Figure 3 through Figure 6 on
page 29 show Switch Explorer examples for several HP StorageWorks switches.
Note that the figures are grayed out so that you can more easily see the areas of the Switch Explorer.
In Figure 3 through Figure 6 on page 29, the letters A through F call out the different areas within the
Switch Explorer. Table 5 is a key for these callouts.
Table 5 Key to Figure 3 through Figure 6
Callout Area of Switch Explorer view
A Fabric tree
B Fabric toolbar
CSwitch view
D Switch view button menu
E Switch information view
FStatus legend
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 25
Page 26
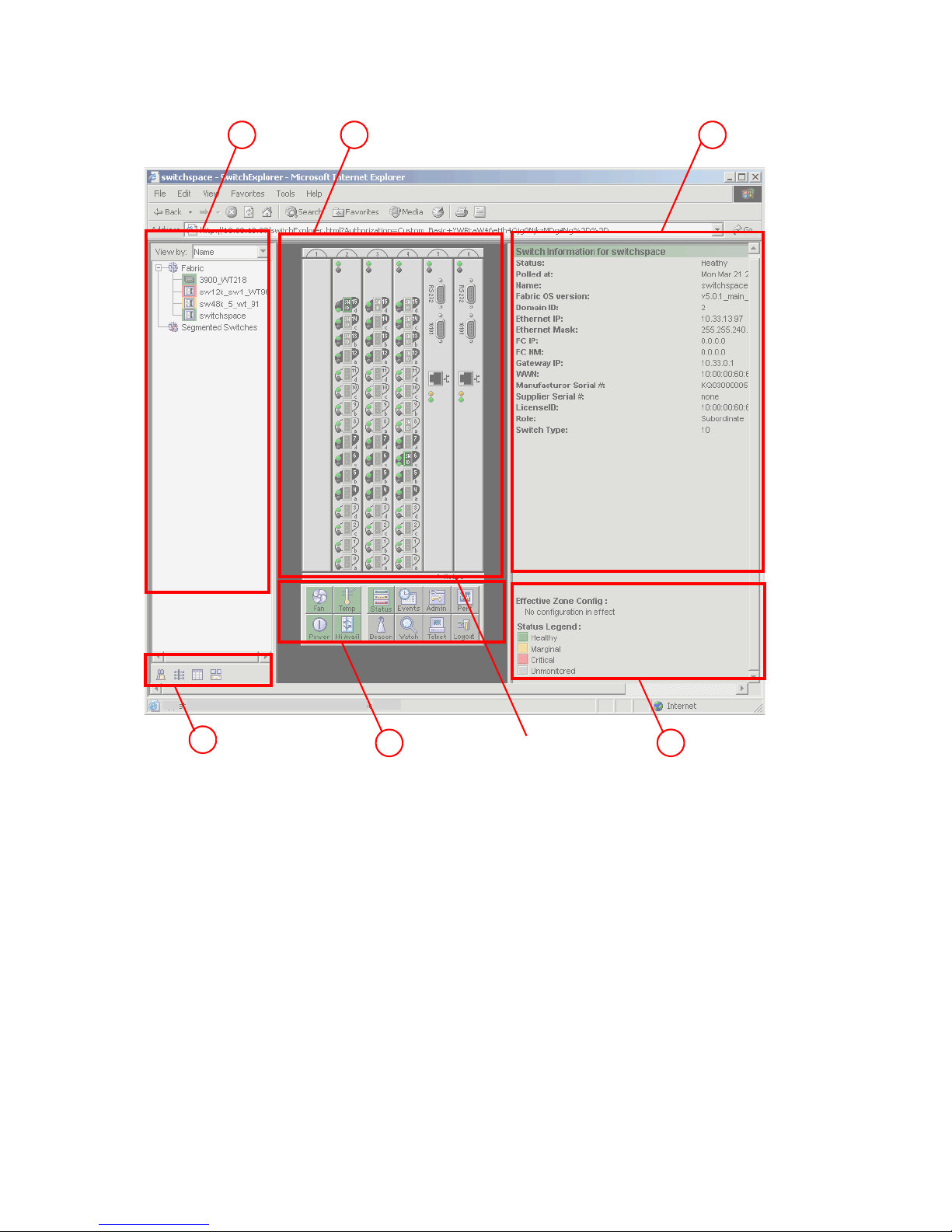
Core Switch 2/64
Figure 3 shows an example of the Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a Core Switch 2/64.
A C
E
B
Figure 3 Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a Core Switch 2/64
In this figure, the Core Switch 2/64 has two domains; however, only one domain is displayed. You can
view and manage only one domain at a time, even though both domains are enclosed in the same
chassis. To manage the other domain, you must log in to it separately.
The active control processor (CP) in the Core Switch 2/64 is labeled with a small arrow at the bottom of
the CP.
SAN Director 2/128
Figure 4 shows an example of the Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a SAN Director 2/128 (see
the legend in Table 5 on page 25). In this figure, the SAN Director 2/128 has two domains; only one
domain is displayed. You can view and manage only one domain at a time, even though both domains
are enclosed in the same chassis. To manage the other domain, you must log in to it separately.
26 Using Advanced Web Tools
D
Active CP Arrow
F
Page 27
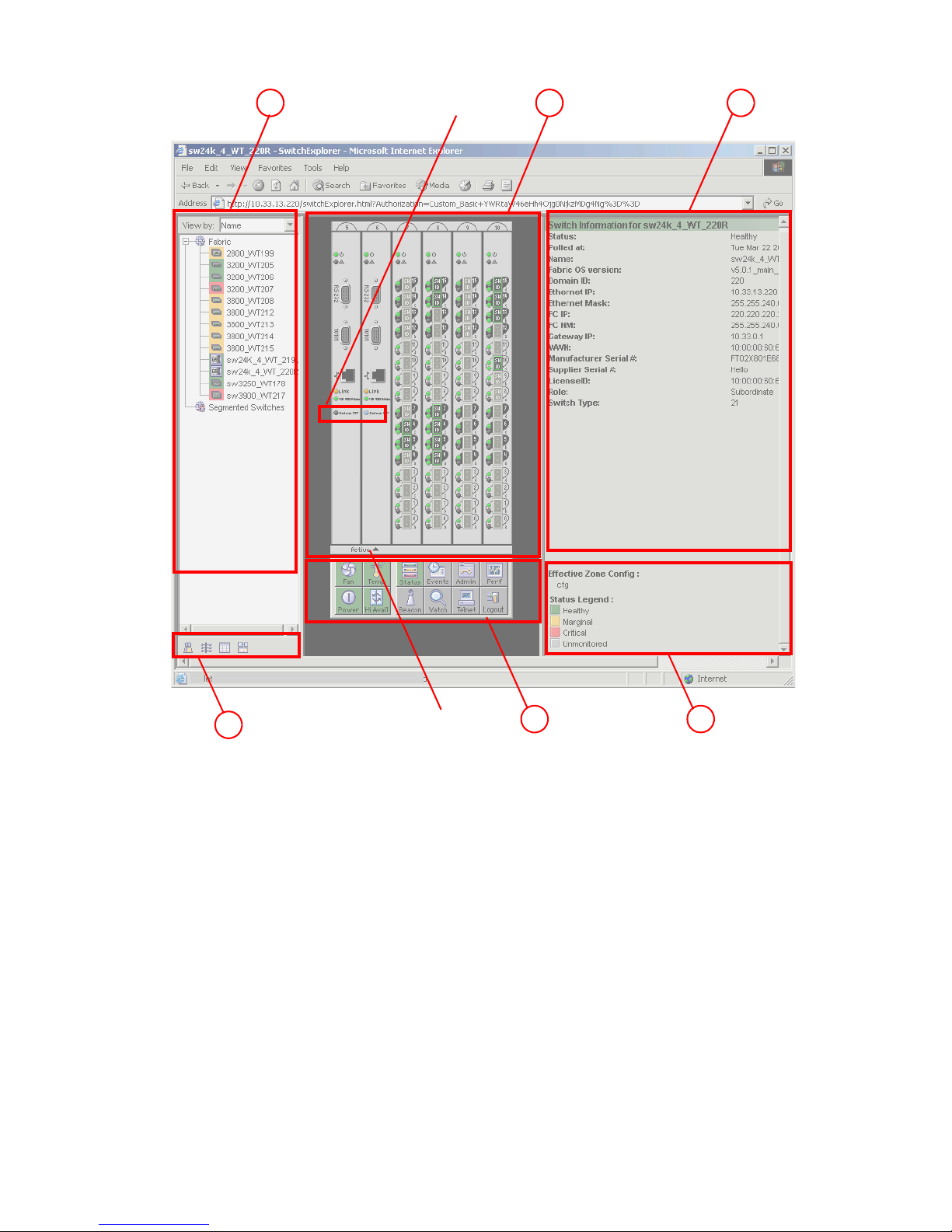
A C
Active CP LED Indicators
E
B
Figure 4 Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a SAN Director 2/128
The active CP in the SAN Director 2/128 is labeled with a small arrow at the bottom of the CP display.
The SAN Director 2/128 active CP is also indicated with the blue Active CP LED indicator, as shown in
the figure.
4/256 SAN Director
Although the 4/256 SAN Director has a single chassis, it can contain one domain or two domains.
Figure 5 shows an example of the Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a single-domain 4/256 SAN
Director (see the legend in Table 5 on page 25).
Active CP Arrow
D
F
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 27
Page 28
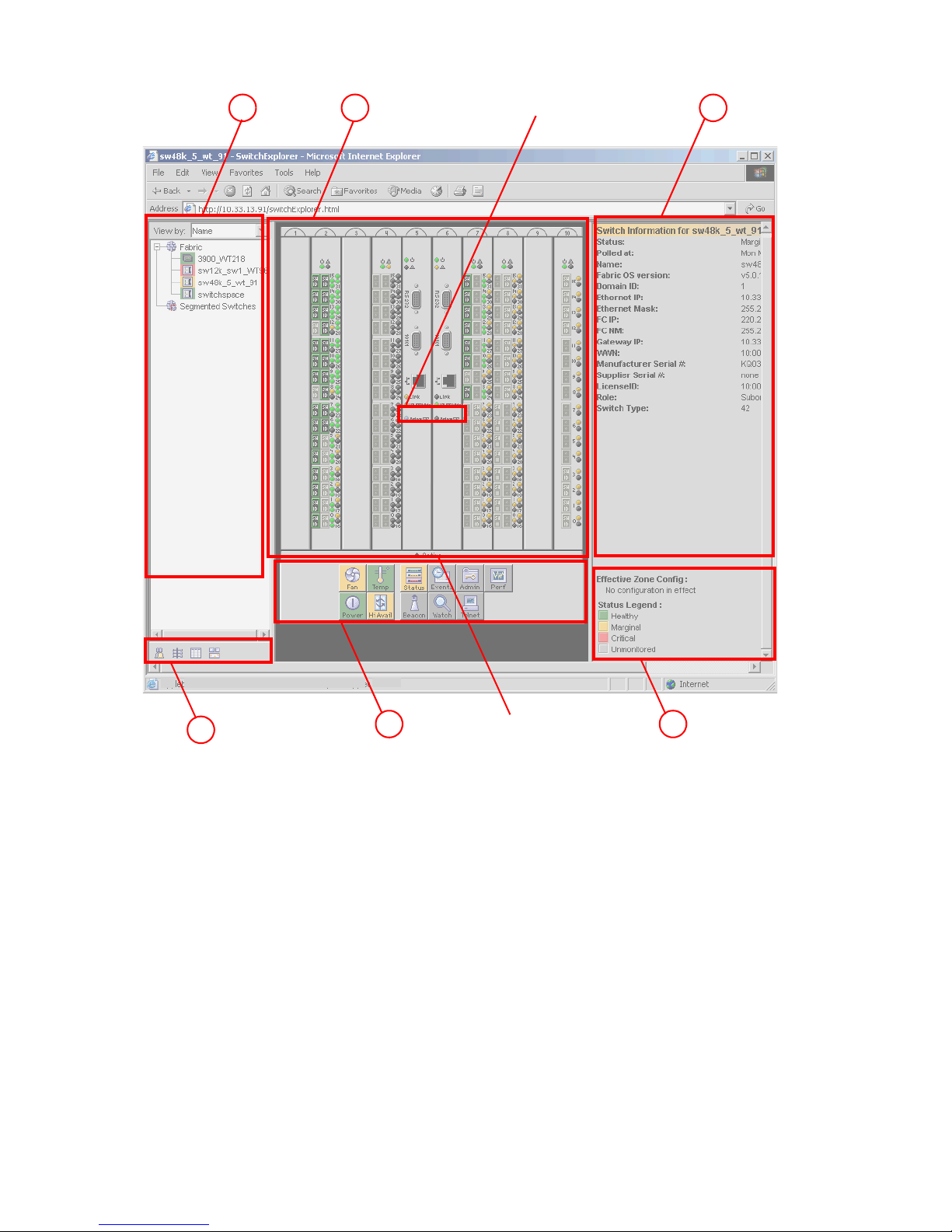
A C
Active CP LED Indicators
E
B
Figure 5 Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a 4/256 SAN Director
SAN Switch 2/8V
Figure 6 shows an example of the Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a SAN Switch 2/8V (see the
legend in Table 5 on page 25). This is the same format as the Switch Explorer used in Advanced Web
Tools for the 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32, and SAN
Switch 4/32.
D
Active CP Arrow
F
28 Using Advanced Web Tools
Page 29
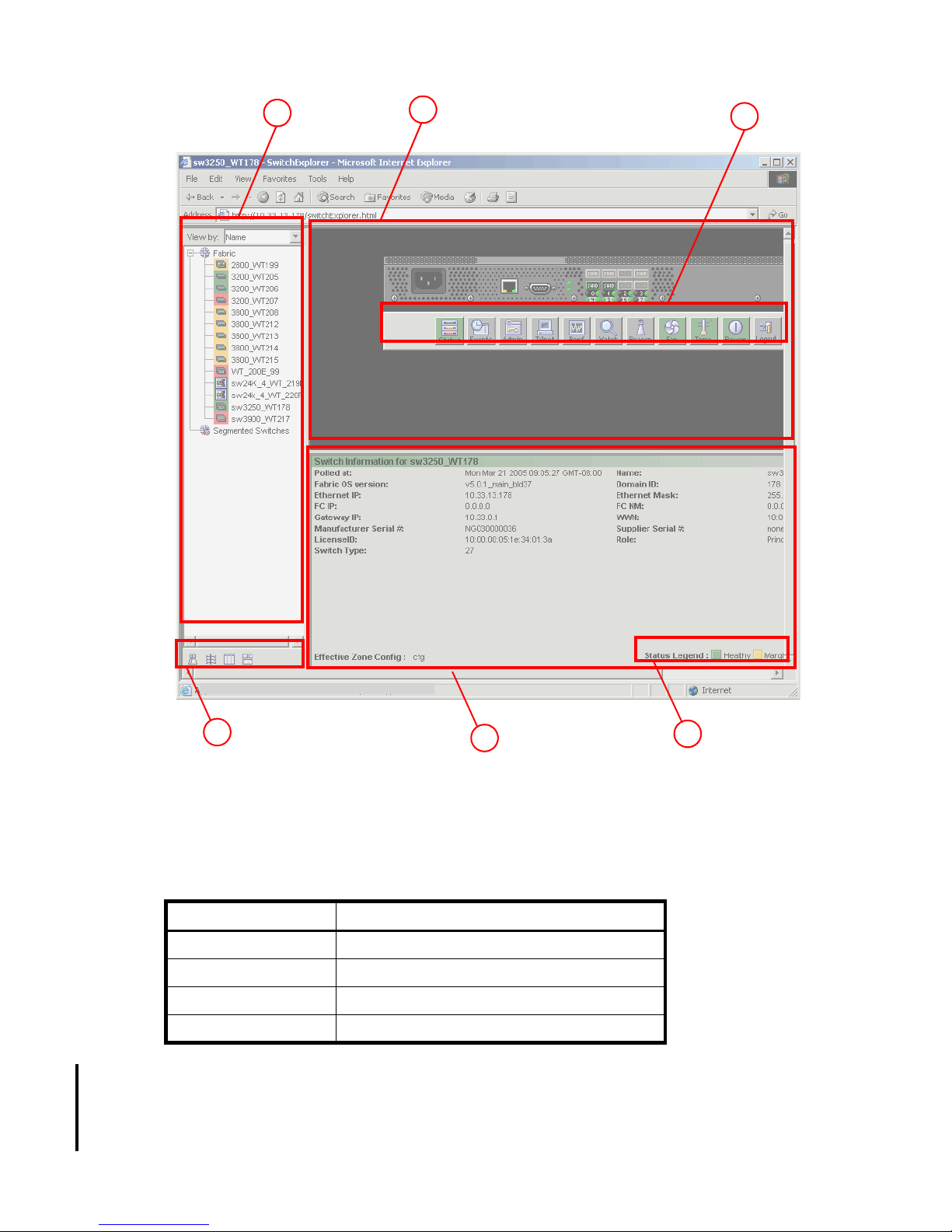
A
C
D
Figure 6 Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer for a SAN Switch 2/8V
Refresh rates
Different panels of Advanced Web Tools refresh at different rates. Table 6 lists the polling rates for the
various panels in Advanced Web Tools.
Table 6 Polling rate in the Switch Explorer window
Switch explorer area Polling rate
Name Server User-defined; 15 seconds minimum
Zoning Database 60 seconds
Fabric Watch 15 seconds
Performance Monitor 30 seconds
The refresh, or polling, rates listed in this section and throughout the book indicate the time between the
end of one polling and the start of the next, and not how often the screen is refreshed. That is, a refresh
rate of 15 seconds does not mean that a refresh occurs every 15 seconds. It means that a new refresh
starts 15 seconds after the previous refresh finished.
B
E
F
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 29
Page 30

Fabric Tree
The Fabric Tree is the left panel of the Switch Explorer. The Fabric Tree displays all switches in the fabric,
including switches that do not have an Advanced Web Tools license. Any switches segmented before
Advanced Web Tools is launched are not displayed.
Although all switches in the fabric are displayed, only switches that have an Advanced Web Tools license
installed can be managed through Advanced Web Tools. Other switches must be managed through the
Fabric OS command line interface (CLI) or another management application. For information on adding
an Advanced Web Tools license to a switch, see ”Installing an Advanced Web Tools license” on page 18.
Use the drop-down menu at the top of the panel to view switches in the Fabric Tree by switch name, IP
address, or WWN. The background color of the switch icon indicates the current status of the switch. You
can mouse-over a switch in the fabric tree to display the IP address and current status.
You can manually refresh the status of a switch within the fabric by right-clicking that switch in the Fabric
Tree and clicking Refresh.
Fabric toolbar
The Fabric Toolbar at the bottom of the Fabric Tree enables you to access fabric-wide administration tasks
quickly. The Fabric Toolbar icons provide access to:
• Fabric events
This information is collected from the launch switch. See ”Monitoring events” on
page 50 for more information.
• Topology module
This information is collected from the selected switch. See ”Displaying a fabric
topology report” on page 55 for more information.
• Name Server information
This information is collected from the selected switch. See ”Displaying the
Name Server entries” on page 55 for more information.
• Zone Administration module
This information is collected from the selected switch. This icon is displayed only
if an HP Advanced Zoning license is installed on the switch. If secure mode is
enabled, zoning can be administered only from the primary fabric
configuration server (FCS) switch. If the selected switch has a zoning license
installed but is not the primary switch, the Zone Admin icon is displayed but not
activated. See ”Managing zoning with Advanced Web Tools” on page 81 for
more information.
It is important to note that the information displayed is gathered from different areas; switches in the fabric
might be running different versions of Fabric OS, and different versions of Fabric OS support different
features, so the information displayed might not always be the same for switches running different
versions of Fabric OS.
30 Using Advanced Web Tools
Page 31

Switch View
The Switch View displays a graphical representation of the selected switch, including a real-time view of
switch and port status. This view is accessed by selecting a switch icon in the Fabric Tree.
NOTE: The Switch View display is updated approximately once every 15 seconds. However, the initial
display of the Switch Explorer might take from 30 to 60 seconds after the switch is booted.
The layout of information is different for the Switch View of different switch types. See Figure 3 on
page 26 through Figure 6 on page 29 for examples of different Switch Views.
Switch View button menu
The Switch View button menu is the launch point for the Switch Events screen, telnet interface, Fabric
Watch module, Switch Admin module, Performance Monitor module, and High Availability (HA) Admin
module. Some of these functions require a license key to activate. The Switch View button menu also
includes buttons that display the status of the switch fans, temperature monitors, switch information, power
supply, and beacon. If upfront login is enabled, the Switch View button menu also includes a Logout
button.
It is important to note that certain Fabric OS features are available only on particular switch types;
therefore, the icons for those features are displayed only for those switch types. For example, the HA
feature is available only on the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director;
therefore, the HA Admin button is displayed in the Switch View button menu only for those directors.
The following buttons have a color-coded background, which indicates status for that area:
• Status
• Fan
• Temp
• Power
• Hi Avail (HA)
The colors follow the status legend (see ”Status Legend”).
Switch Information View
The Switch Information View displays vital switch information such as name, status, Fabric OS version,
domain ID, IP address, WWN, and current zone configuration. The information in the Switch Information
View is polled every 15 seconds.
The Switch Information View is located beside the graphic representation of the switch for the Core Switch
2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director. For all other switch types (4/8 SAN Switch,
4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch 2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP
p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32), the Switch Information View is located beneath the graphic
representation of the switch.
For more information, see ”Displaying switch information” on page 105.
Status Legend
The Status Legend is included in the Switch Information View and defines the meaning of colors visible in
the background of the various icons in the Switch Explorer. Each color indicates a different operational
state:
• Green: healthy
• Yellow: marginal
• Red: critical
• Gray: unknown or unmonitored
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 31
Page 32

NOTE: For all status displays based on errors per time interval, any errors cause the status to show faulty
until the entire sample interval has passed.
Displaying switches in the fabric
If your fabric has more than one switch, you can launch Advanced Web Tools from one switch and then
access other switches.
Accessing the Switch Explorer for a particular switch
1. Launch Advanced Web Tools as described in ”Launching Advanced Web Tools” on page 20.
The Switch Explorer is displayed for the switch you logged in to. The Fabric Tree is expanded by
default when you first launch Advanced Web Tools.
2. If the Fabric Tree is not expanded, click the + in the Fabric Tree to view all the switches in the fabric.
3. Click a switch in the Fabric Tree.
A separate browser window opens and displays the selected switch. (If the launch switch is running a
Fabric OS version earlier than 5.0.1, the selected switch is displayed in the same browser window.)
The graphic of the selected switch is displayed in the ”Switch View” on page 31. Additional switch
information is displayed in the ”Switch Information View” on page 31.
Ending the Advanced Web Tools session
You can end your Advanced Web Tools session either by logging out or by closing the Switch Explorer
browser window.
A session times out if it has been inactive for longer than two hours. If the session times out, you must
restart Advanced Web Tools and log in again. See ”Session management” on page 22 for more
information about sessions.
Ending the Advanced Web Tools session
Click Logout in the Switch Explorer (the logout button is displayed only if upfront login is enabled) or click
the X in the upper-right corner of the Switch Explorer browser window to close the window.
Using Advanced Web Tools and secure mode
When secure mode is enabled on switches you manage through Advanced Web Tools, there are certain
requirements and scenarios you should be aware of. You should read through the requirements and
scenarios in this section if you plan to use Advanced Web Tools to manage any switches that have secure
mode enabled.
Advanced Web Tools access and HTTP_POLICY
When secure mode is enabled, access to the Advanced Web Tools interface is controlled by
HTTP_POLICY. If secure mode is enabled and HTTP_POLICY has been defined, your workstation IP
address must be included in this policy or you will not have access to Advanced Web Tools for any switch
in the fabric. If your workstation IP address is not included in this policy, the Interface Disabled page is
displayed when you attempt to access a switch. For instructions on including your workstation in
HTTP_POLICY, see the HP StorageWorks Secure Fabric OS administrator guide.
NOTE: If a secure mode change is made in the fabric—that is, secure mode is enabled, secure mode is
disabled, or there is a change to the primary FCS—you must exit and relaunch Advanced Web Tools. If
Advanced Web Tools is kept open after a secure mode change occurs, behavior is undefined.
32 Using Advanced Web Tools
Page 33

Opening modules in a secure fabric
When opening more than one module in a secure fabric, wait for each module to load completely before
opening another. For example, if you want to access both the Zone Admin and the Switch Admin
modules, open one of the modules and wait for it to load completely before opening the second module.
Abnormal behavior might occur if you attempt to open two modules simultaneously in a fabric with secure
mode enabled.
Certain Advanced Web Tools features are limited or disabled when secure mode is enabled on a fabric.
For more information about secure mode, see the HP StorageWorks Secure Fabric OS administrator
guide.
Primary-FCS-only functionality
The following Advanced Web Tools functionality is reserved for the primary FCS when secure mode is
enabled:
• Zoning administration is allowed only from the primary FCS switch when secure mode is enabled. For
all other switches in a secure fabric, the Zoning button is disabled.
• SNMP community strings can be modified only from the primary FCS switch when secure mode is
enabled. For non-FCS switches, you can view the SNMP community strings, but they are read-only,
and the SNMP access control lists on the SNMP tab are not displayed.
• User account administration is allowed only from the primary FCS switch when secure mode is
enabled. The changes are then propagated to all switches in the fabric.
Disabled functionality
Telnet access to a switch and the Telnet button in Advanced Web Tools are both disabled when secure
mode is enabled for a fabric. You must use sectelnet or SSH to access the Fabric OS CLI in a secure
fabric. These capabilities are not accessible from Advanced Web Tools. For more information on
sectelnet or SSH, see the HP StorageWorks Secure Fabric OS administrator guide.
The SNMP Access Control List is replaced with RSNMP_POLICY and WSNMP_POLICY when secure
mode is enabled for a fabric. The SNMP Access Control List is not displayed in Advanced Web Tools.
Recommendations for working with Advanced Web Tools
Listed below are recommendations when working with Advanced Web Tools:
• When using a mixed fabric—that is a fabric containing switches and directors running 4.x, 3.x, and
2.x firmware—use the most advanced switches or directors to control the fabric. For example, use the
5.x and 4.x switches or directors as the primary FCS, the location to perform zoning tasks, and the
time server (CLI). You should use the most recently released firmware on your switches.
• If switches are accessed simultaneously from different connections (for example, Advanced Web
Tools, CLI, and API), changes from one connection might not be updated to the other, and some
modifications might be lost. Make sure when connecting with simultaneous multiple connections that
you do not overwrite the work of another connection.
• Several tasks in Advanced Web Tools make fabric-level changes, for example, the tasks in the Zone
Admin module. When executing fabric-level configuration tasks, wait until you have received
confirmation that the changes are implemented before executing any subsequent tasks. For a large
fabric, this can be up to a few minutes.
• HP recommends a maximum of five simultaneous HTTP sessions to any one switch. An HTTP session is
considered a Fabric Manager or Advanced Web Tools connection to the switch.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 33
Page 34

34 Using Advanced Web Tools
Page 35

3 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Managing fabrics, switches, and ports using Advanced Web Tools, page 35
• Launching the telnet window, page 37
• Configuring IP and netmask information, page 37
• Configuring a syslog IP address, page 38
• Configuring a switch, page 39
• Rebooting a switch, page 40
• Changing system configuration parameters, page 40
• Configuring ports, page 44
• Activating Ports on Demand, page 47
• Maintaining licensed features, page 47
• Administering high availability, page 49
• Monitoring events, page 50
• Displaying a fabric topology report, page 55
• Displaying the Name Server entries, page 55
• Physically locating a switch using beaconing, page 57
• Displaying swapped port area IDs, page 57
Managing fabrics, switches, and ports using Advanced Web Tools
You can perform most of the management tasks described in this chapter through the Switch Admin
module. Information in the Switch Admin module is retrieved from the selected switch.
Click the Admin button in the Switch View to access the Switch Admin module. Figure 7 shows the Switch
Admin module.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 35
Page 36

Figure 7 Switch Admin Module
With the exception of switch time, information displayed in the Switch Admin module is not updated by
Advanced Web Tools. To update the information displayed in the Switch Admin module, see ”Refreshing
the switch Admin Module” on page 37.
CAUTION: Any changes you make in the Switch Admin module are in a buffered environment and are
not applied to the switch until you save the changes. (The exception to this is the License tab, where
changes are applied immediately and there is no Apply button, and the upload trace function in the Trace
tab.) If you close the Switch Admin module without saving your changes, your changes are lost. To save
the buffered changes you make in the Switch Admin module to the switch, click Apply before closing the
module or before switching to another tab.
Some of the management tasks for the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN
Director are performed through the Hi Avail module. This module and the associated tasks are described
in”Administering high availability” on page 49.
You can also use telnet commands to perform management tasks. See ”Launching the telnet window” on
page 37 for information on how to launch a telnet window through Advanced Web Tools.
The remainder of this section describes basic Switch Admin module procedures that are useful for many
switch-management operations.
Launching the switch Admin Module
Most of the management procedures in this chapter are performed from the Switch Admin module.
Accessing the Switch Admin module
1. Select a switch from the Fabric Tree.
The selected switch appears in the Switch View.
36 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 37

2. Click the Admin button on the Switch View.
The Switch Admin module is displayed (as shown in Figure 7 on page 36).
Refreshing the switch Admin Module
To refresh the fabric element information displayed at any time, click the Refresh button in any tabbed
page of the Switch Admin module.
When you click a different tab in the Switch Admin module, the information in the newly selected tab is
refreshed.
Launching the telnet window
When you launch a telnet window for the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, or 4/256 SAN
Director, the launch is on a logical-switch basis. This means that for each logical switch, you must launch
a separate telnet window. See the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command reference guide for
information about the telnet commands.
NOTE: Advanced Web Tools does not support telnet on the Mozilla browser. You must use an external
CLI if using Mozilla.
Telnet access to a switch and the Telnet button in Advanced Web Tools are both disabled when secure
mode is enabled for a fabric. You must use sectelnet or SSH to access the Fabric OS CLI in a secure
fabric. These capabilities are not accessible from Advanced Web Tools. For more information on
sectelnet or SSH, see the HP StorageWorks Secure Fabric OS administrator guide.
Accessing telnet through Advanced Web Tools
1. Select a switch from the Fabric Tree.
The selected switch appears in the Switch View.
2. Click the Telnet button on the Switch View.
The Telnet window opens.
3. To close the session when you are done, issue the exit command at the telnet prompt.
Configuring IP and netmask information
When you configure IP address and netmask information for the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director
2/128, or 4/256 SAN Director, the configuration is on a logical-switch basis. This means that for each
logical switch, you must configure IP and subnet mask information individually.
When changing the Ethernet IP/netmask, the Gateway IP, or the Fibre Channel net IP/netmask from
Advanced Web Tools, there is a normal loss of network connection to the switch. If the IP properties have
changed, you must close all current windows and restart Advanced Web Tools with the new IP address.
Configuring IP and netmask information
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described in ”Launching the switch Admin Module” on page 36.
2. Click the Network tab (see Figure 8).
3. Enter a new value in the appropriate field (for example, 10.77.77.77).
4. For the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director only:
a. Click Advanced.
b. Enter a valid IP addresses for the Ethernet IP addresses and subnet mask for CP0 and CP1.
c. Click OK to return to the Network tab.
5. Click Apply.
6. Exit and relaunch Advanced Web Tools to continue working.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 37
Page 38

Figure 8 Network tab
Configuring a syslog IP address
The syslog IP address represents the IP address of the server that is running the syslog process. The syslog
daemon reads and forwards system messages to the appropriate log files and/or users, depending on the
system configuration. When one or more IP addresses are configured, the switch forwards all error log
entries to the syslog on the specified servers. Up to six servers are supported. See the HP StorageWorks
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide for more information on configuring the syslog daemon.
When you configure a syslog IP address for the Core Switch 2/64 or for a SAN Director 2/128 or
4/256 SAN Director configured with two logical switches, it is on a logical-switch basis. This means that
for each logical switch, you must configure a syslog IP address individually.
Configuring the syslog IP address
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Network tab (see Figure 8).
3. Enter a valid IP address in the New IP field (for example, 10.77.77.77).
4. Click Add.
The configured IP is displayed in the Syslog IP window.
5. Click Apply.
Removing a syslog IP address
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Network tab.
3. Select a syslog IP from the table.
4. Click Remove.
5. Optional: Click Clear All to remove all of the syslog IP addresses.
6. Click Apply.
38 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 39

Configuring a switch
Use the Switch tab of the Switch Admin module to perform basic switch configuration. Figure 7 on
page 36 shows an example of the Switch tab.
Enabling and disabling a switch
You can identify if a switch is enabled or disabled in the Switch Admin module by looking at the bottom
right corner: the icon means that the switch is enabled, and the icon means that the switch is
disabled.
Use the following procedure to enable or disable a switch.
Enabling or disabling a switch
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Switch tab.
3. Select the Enable radio button in the Switch Status section to enable the switch, or select the Disable
radio button to disable the switch.
4. Click Apply.
Changing the switch name
Switches can be identified by IP address, domain ID, WWN, or customized switch names that are unique
and meaningful.
Switch names can be a maximum of 15 characters long for Fabric OS 5.0.1. They must begin with an
alpha character, but otherwise can consist of any combination of alphanumeric and underscore
characters.
Changing the switch name
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Switch tab.
3. Enter a new name in the Name field.
4. Click Apply.
NOTE: Beginning with Fabric OS 4.4.0, HP recommends that you customize the chassis name for each
switch. Some system messages identify a switch service by chassis name, so if you assign meaningful
chassis names in addition to meaningful switch names, logs will be more useful. You change the chassis
name using the CLI. See the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide for instructions on
changing the chassis name.
Changing the switch domain ID
Although domain IDs are assigned dynamically when a switch is enabled, you can request a specific ID
to resolve a domain ID conflict when you merge fabrics.
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Disable the switch, as described in “Enabling and disabling a switch.”
3. Click the Switch tab.
4. Enter a new domain ID in the Domain ID field.
The domain ID is an integer between 1 and 239.
5. Click Apply.
6. Enable the switch, as described in “Enabling and disabling a switch.”
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 39
Page 40

Viewing and printing a switch report
The switch report includes the following information:
• A list of switches in the fabric
• Switch configuration parameters
• A list of ISLs and ports
• Name Server information
• Zoning information
• SFP serial ID information
Viewing or printing a switch report
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Switch tab.
3. Click View Report.
A switch report is displayed in a new window.
4. View or print the report using your browser.
Rebooting a switch
When you reboot the switch, the reboot takes effect immediately.
Performing a fast boot
A fast boot reduces boot time significantly by bypassing power-on self test (POST).
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Firmware tab (see Figure 8 on page 38).
3. Select the Fastboot radio button.
4. Click Apply.
Performing a switch reboot
Use the following procedure to reboot the CP and execute the normal power-on booting sequence.
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Firmware tab (see Figure 8 on page 38).
3. Select the Reboot radio button.
4. Click Apply.
Changing system configuration parameters
When you change system configuration parameters for the Core Switch 2/64 or for a SAN Director
2/128 or 4/256 SAN Director configured with two logical switches, the change is made on a
logical-switch basis. This means that for each logical switch, you must change the system configuration
parameters individually.
You must disable the switch before you can configure fabric parameters.
You can change the following system configuration parameters:
• Switch fabric settings
• Virtual channel settings
• Arbitrated loop parameters
• System services
40 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 41

Configuring fabric parameters
You can configure the following fabric parameters using the Configure tab and Fabric subtab of the
Switch Admin module (as shown in Figure 9):
• BB Credit, which is the number of buffers available to attached devices for frame receipt. The default
BB Credit is 16. The range is 1 through 27.
• R_A_TOV, which is the resource allocation timeout value (in milliseconds). This variable works with the
E_D_TOV to determine switch actions when presented with an error condition. The default is 10000.
The possible range is 4000 through 120000.
• E_D_TOV, which is the error detect timeout value (in milliseconds). This timer is used to flag a potential
error condition when an expected response is not received within the set time. The valid range is
1000 through 5000.
• Datafield size, which is the largest possible datafield size (in bytes). The valid range is 256 through
2112.
• Switch PID Format, which selects a switch PID format from one of the following:
• Format 1 (0-base, 256 encoding)
• Format 2 (16-base, 256 encoding)
• Sequence Level Switching: Check this box to enable frames of the same sequence from a particular
group to be transmitted together. When this option is not selected, frames are transmitted interleaved
among multiple sequences. Under normal circumstances, sequence-level switching should be disabled
for better performance. However, some host adapters have issues when receiving interleaved frames
among multiple sequences.
• Disable Device Probing: Set this mode only if the switch N_Port discovery process (PLOGI, PRLI,
INQUIRY) causes an attached device to fail. When set, devices that do not register with the Name
Server are not present in the Name Server database.
• Per-Frame Routing Priority: Choose to select or deselect per-frame routing priority. When enabled, the
virtual channel ID is used in conjunction with a frame header to form the final virtual channel ID.
• Suppress Class F Traffic: Applies only if VC-encoded address mode is also set. When checked,
translative addressing (which allows private devices to communicate with public devices) is disabled.
• Insistent Domain ID Mode: Set this mode to make the current domain ID insistent across reboots,
power cycles, and failovers. This mode is required fabric wide to transmit FICON data.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 41
Page 42

Figure 9 Configure tab, Fabric subtab
Configuring fabric parameters
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Disable the switch as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on page 39.
3. Click the Configure tab.
4. Click the Fabric subtab.
5. Make the fabric parameter configuration changes.
6. Click Apply.
7. Enable the switch as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on page 39.
Enabling insistent domain ID mode (FICON only)
When insistent domain ID (ID_ID) mode is enabled, the current domain setting for the switch is insistent;
that is, the same ID is requested during switch reboots, power cycles, CP failovers, firmware downloads,
and fabric reconfigurations. If the fabric does not assign the insistent domain ID, the switch segments from
the fabric.
This parameter is for use with FICON only.
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Disable the switch as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on page 39.
3. Click the Configure tab.
4. Click the Fabric subtab.
5. Check the Insistent Domain ID Mode check box.
6. Click Apply.
7. Enable the switch as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on page 39.
42 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 43

Configuring virtual channel settings
You can configure the parameters for eight virtual channels to enable fine-tuning for a specific
application. You cannot modify the first two virtual channels, which are reserved for switch internal
functions.
CAUTION: The default virtual channel settings have already been optimized for switch performance.
Changing the default values can improve switch performance but can also degrade performance. Do not
change these settings without fully understanding the effects of the changes.
VC Priority specifies the class of frame traffic given priority for a virtual channel.
Configuring system services
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Disable the switch as described on page 39.
3. Click the Virtual Channel subtab.
4. Enter a value in the VC Priority field you want to change. Valid values for all fields are 2 or 3.
5. Click Apply.
6. Enable the switch as described on page 39.
Configuring arbitrated loop parameters
You can configure the following arbitrated loop parameters using the Configure tab and Arbitrated Loop
subtab of the Switch Admin module:
Send Fan Frames Check this box to specify that fabric address notification (FAN) frames are sent to
Always Send RSCN Following the completion of loop initialization, a remote state change notification
Do Not Allow
AL_PA 0x00
Configuring arbitrated loop parameters
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Disable the switch as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on page 39.
3. Select the Configure tab.
4. Select the Arbitrated Loop subtab.
5. Select or clear the boxes to enable or disable the corresponding arbitrated loop parameters.
6. Click Apply.
7. Enable the switch as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on page 39.
Configuring system services
You can configure the following system services:
rstatd Dynamically enables or disables a server that returns system operation information through
remote procedures calls (RPC).
rapid Allows or disallows the API to communicate with the switch.
rusersd Dynamically enables or disables a server that returns information about the user logged into the
system through remote procedure calls (RPC).
Disable RLS
Probing
Enables or disables FCP read link status (RLS) information probing for F_Ports and FL_Ports. It is
disabled by default.
public loop devices to notify them of their node ID and address.
(RSCN) is issued when FL_Ports detect the presence of new devices or the absence of
pre-existing devices. Check this box to issue an RSCN upon completion of loop
initialization, regardless of the presence or absence of new or pre-existing devices.
Check this box to disable 0x00 as an arbitrated loop physical address (AL_PA) value.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 43
Page 44

Configuring system services
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Disable the switch as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on page 39.
3. Click the Configure tab.
4. Click the System subtab.
5. Select the boxes next to the system services that you want to enable. Clear a box to disable a service.
NOTE: Selecting the Disable RLS Probing box disables RLS probing. Clearing this box enables RLS
probing.
6. Click Apply.
7. Enable the switch as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on page 39.
Configuring ports
Use the Ports tab of the Switch Admin module to perform the basic port configuration procedures
described in this section. Figure 10 shows an example of the Ports tab.
Figure 10 Ports tab
44 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 45

Configuring port type
The Current Type column in the Ports tab indicates the actual or current type of the port:
• If the port is offline, this value is the allowed types or U-Port, if no type constraint has been specified.
• If the port is online, this value is the type the port has actually negotiated to (normally L-Port for storage
ports, F-Port for HBA or host ports, and E-Port for ISLs).
The L-Port, F-Port, and E-Port columns indicate any constraints on what types the port can negotiate to
when it comes up.
Use the following procedure to configure the port type.
Configuring the port type
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Ports tab.
3. Perform the following, according to switch type:
• For Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, select the subtab that
corresponds to the correct slot for the logical switch.
• For 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, proceed directly to
the next step.
4. Select a port by clicking the port number.
5. Clear the following check boxes, depending on how you want to configure the port type:
• L-Port: The port can be used to connect a loop device.
• F-Port: The port can be used to connect a non-loop device.
• E-Port: The port can be used to connect to another switch.
By default, all of these boxes are selected, meaning that there is no constraint on port type. The port
negotiates to its preferred type when the switch comes up, depending on what type of device or switch
it is attached to.
Clearing a check box guarantees that the port does not attempt to function as a port of the cleared
type.
At least one type must remain selected. L-Port and F-Port cannot both be cleared.
6. Click Apply.
Configuring port speed
The Current Speed column in the Ports tab indicates the current speed of the port. Use the following
procedure to change the port speed.
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Ports tab.
3. Perform the following, according to switch type:
• For Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, select the subtab that
corresponds to the correct slot for the logical switch.
• For 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, proceed directly to
the next step.
4. Select a port speed from the Change Speed drop-down list corresponding to the port for which you
want to change the speed.
5. Click Apply.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 45
Page 46

Assigning a name to a port
Port names are optional. You can assign a name to a port to make port grouping easier. The Port Name
column in the Ports tab displays the port name, if one exists.
Naming a port
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Ports tab.
3. Perform the following, according to switch type:
• For Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, select the slot subtab that
corresponds to the correct slot for the logical switch.
• For 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, proceed directly to
the next step.
4. Double-click the Port Name field for the port you want to change.
5. Enter a name for the port. Port names can be from 0 through 32 alphanumeric characters. HP
recommends unique part names, although they are not required.
6. Click Apply.
Disabling a port over reboots
Use the following procedure to disable a port so that it remains disabled if the switch reboots.
Disabling a port so that it remains disabled over reboots
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Ports tab.
3. Perform the following, according to switch type:
• For Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, select the slot subtab that
corresponds to the correct slot for the logical switch.
• For 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, proceed directly to
the next step.
4. Select the Persistent Disable check box for the port you want to keep disabled over reboots.
5. Click Apply.
Enabling and disabling a port
All licensed ports are enabled by default. You can disable and reenable them as necessary.
If a port is not licensed you cannot enable it until you install the Ports on Demand license. (See Activating
Ports on Demand for more information.) The Licensed Port column indicates whether a port is licensed.
NOTE: If you disable a principal ISL port (an ISL port that is used to communicate with the principal
switch), the fabric reconfigures. If the port was connected to a device, that device is no longer accessible
from the fabric. For more information, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide.
Enabling or disabling a port
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Ports tab.
3. Perform the following, according to switch type:
• For Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, select the slot subtab that
corresponds to the correct slot for the logical switch.
• For 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, proceed directly to
the next step.
46 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 47

4. Select the box in the Enable Port column that corresponds to the port you want to enable, or
clear the box in the Enable Port column that corresponds to the port you want to disable.
5. Click Apply.
6. Review the log at the bottom of the tab for information regarding the switch configuration changes.
Activating Ports on Demand
The 4/8 SAN Switch and 4/16 SAN Switch can be purchased with 8, 12, or 16 licensed ports. The
SAN Switch 4/32 can be purchased with 16 or 32 licensed ports. As your needs increase, you can
activate unlicensed ports by purchasing and installing the HP StorageWorks 4- or 8-port upgrade license.
By default, ports 0 through 7 are enabled on the 4/8 SAN Switch and 4/16 SAN Switch, and ports 0
through 15 are enabled on the SAN Switch 4/32. By installing a Port Upgrade License, you can enable
an additional 4 ports on the 4/8 SAN Switch and an additional 8 ports on the SAN Switch 4/32. You
can install up to two Port Upgrade Licenses on each switch.
For each switch model, Table 7 shows the ports that are enabled by default and the ports that can be
enabled after you install the first and second Port Upgrade Licenses.
Table 7 Por ts enabled with Ports on Demand licenses
Enabled ports 4/8 and 4/16
SAN Switch
Ports enabled without Port Upgrade License (default) 0–7 0–15
Ports enabled when you install first Port Upgrade License 8–11 16–23
Ports enabled when you install second Port Upgrade License 12–15 24–31
Once you have installed the license keys, you must enable the ports. You can do so without disrupting
switch operation, as described in ”Enabling and disabling a port” on page 46. Alternatively, you can
disable and reenable the switch to activate all ports as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on
page 39.
To unlock a Ports on Demand license, you can either use the supplied license key or generate a license
key. If you need to generate a key, launch an Internet browser and go to the HP licensing web site at
http://webkey.external.hp.com/welcome.asp
to generate the key.
. Select Generate a license key and follow the instructions
SAN Switch
4/32
Enabling a Port Upgrade License
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Ports tab.
In the Ports tab, the Licensed Port column indicates whether the port is licensed or not.
3. Install the Port Upgrade License.
For instructions, see “Maintaining licensed features.”
4. Enable the ports, as described in ”Enabling and disabling a port” on page 46.
If you remove a Port Upgrade License, the licensed ports become disabled after the next platform reboot
or the next port deactivation.
Maintaining licensed features
Feature licenses might be supplied with switch software, or you can purchase licenses separately from
your switch vendor, who will provide you with keys to unlock the features. License keys are provided on a
per-chassis basis, so for products that support multiple logical switches (domains), a license key applies to
all domains within the chassis.
The licensed features currently installed on the switch are listed in the License tab of the Switch Admin
module, as shown in Figure 11. If the feature is listed, it is installed and immediately available. When you
enable some licenses, such as ISL Trunking, you might need to change the state of the port to enable the
feature on the link.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 47
Page 48

Figure 11 License tab
Activating a license on a switch
Before you can unlock a licensed feature, you must obtain a license key by visiting the HP licensing web
site at http://webkey.external.hp.com/welcome.asp
instructions to generate the key.
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the License tab.
3. Click Add.
The Add License dialog box opens.
4. Paste or enter a license key in the box.
5. Click Add License.
6. Click Refresh to display the new licenses in the License tab.
NOTE: Some licenses (for example, ISL Trunking) do not take effect until the switch is rebooted.
Removing a license from a switch
CAUTION: Removing the Advanced Web Tools license from a switch makes that switch unavailable from
Advanced Web Tools. If you remove the Advanced Web Tools license from a Core Switch 2/64, SAN
Director 2/128, or 4/256 SAN Director, both logical switches are then unavailable from Advanced
Web Tools.
. Select Generate a license key and follow the
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the License tab.
48 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 49

3. Click the license you want to remove.
4. Click Remove.
Administering high availability
The procedures in this section apply only to the Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256
SAN Director, because the HA module is available only on these switch types. See the HP StorageWorks
Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide for additional information about HA.
Launching the High Availability module
The background color of the Hi Avail button indicates the overall status of the switch. The High
Availability module displays information about the status of the HA feature on the Core Switch 2/64,
SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director and each CP. It also enables you to perform tasks such
as CP failover or to synchronize services on the CPs.
To launch the High Availability module
1. Select a Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, or 4/256 SAN Director from the Fabric Tree.
The selected director appears in the Switch View.
2. Click the Hi Avail button on the Switch View.
The HA Admin module is displayed, as shown in Figure 12.
Figure 12 High availability mode
Note that there is a background color with the HA Status for each CP. The HA Admin module is not
refreshed.
3. Click Refresh to update the information displayed in the HA Admin module.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 49
Page 50

Synchronizing services on the CP
A nondisruptive CP failover is possible only when all the services on it have been synchronized.
1. Launch the Hi Avail module as described in ”Launching the High Availability module” on page 49.
2. If the HA Status box displays Non-Disruptive Failover Ready, you are done.
If the HA Status box displays Disruptive Failover Ready, continue with step 3.
3. Click the Synchronize Services button.
The Warning dialog box opens.
4. Click Yes and wait for the CPs to complete a synchronization of services, so that a nondisruptive
failover is ready.
5. Click Refresh to update the HA Status box.
When the HA Status box displays Non-Disruptive Failover Ready, a failover can be initiated
without disrupting frame traffic on the fabric.
Initiating a CP failover
A nondisruptive failover might take about 30 seconds to complete. During the failover, the Advanced
Web Tools session and associated windows are invalidated. You must close all Advanced Web Tools
windows and relaunch Advanced Web Tools.
To initiate a CP failover
1. Launch the Hi Avail module as described in ”Launching the High Availability module” on page 49.
2. Verify that the HA Status box displays Non-Disruptive Failover Ready or Disruptive
Failover Ready. See Synchronizing services on the CP for more information.
3. Click Initiate Failover.
The Warning dialog box opens.
4. Click Yes to initiate a non-disruptive failover.
5. When prompted, close the Advanced Web Tools Switch Explorer window and all associated
windows, and relaunch Advanced Web Tools.
Monitoring events
Advanced Web Tools displays fabric-wide and switch-wide events. Event information includes sortable
fields for the following:
• Switch name
• Message number
• Time stamp
• Indication that the event is from a logical switch or a chassis
• Severity level
• Unique message identifier (in the form moduleID-messageType)
• Detailed error message for root cause analysis
There are four message severity levels: Critical, Error, Warning, and Info. Table 8 lists the event message
severity levels displayed in the Switch Events and Fabric Events windows, and explains what qualifies
event messages to be certain levels.
In both the Switch Events window and the Fabric Events window, you can click the Filter button to launch
the Filter Events dialog box. The Filter Events dialog box allows you to define which events should be
displayed in the Switch Events window or Fabric Events window. For more information on filtering events,
see ”Filtering fabric and switch events” on page 53.
50 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 51

Table 8 Event severity levels
Icon and level Description
Critical-level messages indicate that the software has detected serious problems that will
eventually cause a partial or complete failure of a subsystem if not corrected immediately. For
Critical (1)
Error (2)
Warning (3)
Info (4)
example, a power supply failure or rise in temperature must receive immediate attention.
Error-level messages represent an error condition that does not significantly affect overall
system functionality. For example, error-level messages might indicate timeouts on certain
operations, failures of certain operations after retries, invalid parameters, or failure to
perform a requested operation.
Warning-level messages highlight a current operating condition that should be checked or it
might lead to a failure in the future. For example, a power supply failure in a redundant
system relays a warning that the system is no longer operating in redundant mode and that
the failed power supply needs to be replaced or fixed.
Information-level messages report the current nonerror status of the system components, for
example, the online and offline status of a fabric port.
Displaying fabric events
Events are displayed for all switches in the fabric in the Fabric Events window (see Figure 13). Fabric
events are not polled. You must click Refresh from the Fabric Events window to poll fabric events. Switch
events are polled every 15 seconds.
Fabric Events can be collected only for switches that have the same security level (http or https) as the
launch switch. For switches that have a different level of security from the launch switch, a message is
displayed at the top of the window indicating how many switches have no events reported from the last
polling. For detailed information on the switch names and reasons for not polling (if available), click
Details.
To display fabric events
1. Click a fabric from the Fabric Tree.
2. Click the Fabric Events icon on the Fabric Toolbar.
The Fabric Events window is displayed (see Figure 13).
3. Optional: Click the column head to sort the events by a particular column.
Drag the column divider to resize a column.
You can also filter events, as described in ”Filtering fabric and switch events” on page 53.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 51
Page 52

Figure 13 Fabric Events window
Displaying switch events
The Switch Events window displays a running log of events for the selected switch (see Figure 14). Switch
events are polled and updated every 15 seconds, so there is no refresh-on-demand option for switch
events, as there is for the fabric events.
For two-switch configurations, all chassis-related events are displayed in the event list of each logical
switch for convenience.
Figure 14 Switch Events window
52 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 53

Displaying switch events
1. Click the switch from the Fabric Tree.
The Switch View opens.
2. Click the Events button on the Switch View.
The Switch Events window is displayed (see Figure 14 on page 52).
3. Optional: Click the column head to sort the events by a particular column.
Drag the column divider to resize a column.
You can also filter events, as described in Filtering fabric and switch events next.
Filtering fabric and switch events
You can filter the events in the Fabric Events window and Switch Events window by time, severity,
message ID, and service. You can apply either one type of filter at a time or multiple types of filters at the
same time. The Switch Events and Fabric Events windows both have a Filter button. Click the Filter button
to display the Event Filter dialog box (see Figure 15).
When a filter is applied, the Show All button is active in the events window and the type of filter applied
is identified at the top of the events window (see Figure 14 on page 52). To unapply a filter, click the
Show All button in the events window.
NOTE: For two-switch configurations, clicking the Events button for a given switch filters out switch
service events from the other switch. Chassis service is shown in both events lists.
Figure 15 Event Filter dialog box
Filtering events by time intervals
1. Launch the Fabric Events or Switch Events window as described in ”Displaying fabric events” on
page 51 and ”Displaying switch events” on page 52.
2. Click Filter.
The Event Filter dialog box opens.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 53
Page 54

3. To filter events within a certain time period:
a. Click From and enter the start time and date in the boxes.
b. Click To and enter the finish time and date in the boxes.
4. To filter all events beginning at a certain date and time, click From and enter the start time and date in
the boxes.
5. To filter events up until a certain date and time, click To and enter the finish time and date in the
boxes.
6. Click OK.
The filter is enabled and the enabled filter type is displayed in the events window.
Filtering events by event severity levels
1. Launch the Fabric or Switch Events window as described in ”Displaying fabric events” on page 51 or
”Fabric Events window” on page 52.
2. Click Filter.
The Event Filter dialog box opens.
3. Click Level.
The event severity level check boxes are enabled.
4. Click the event levels you want to display.
5. Click OK.
The filter is enabled and the enabled filter type is displayed in the events window.
Filtering events by message ID
1. Launch the Fabric Events or Switch Events window as described in ”Displaying fabric events” on
page 51 or ”Fabric Events window” on page 52.
2. Click Filter.
The Event Filter dialog box opens.
3. Click Message ID.
4. Enter the message IDs in the associated box.
You can enter multiple message IDs as long as you separate them by commas. You can enter either the
full message ID (moduleID-messageType) or a partial ID (moduleID only).
5. Click OK.
The filter is enabled and the enabled filter type is displayed in the events window.
Filtering events by service component
1. Launch the Fabric Events or Switch Events window as described in ”Displaying fabric events” on
page 51 or ”Fabric Events window” on page 52.
2. Click Filter.
The Event Filter dialog box opens.
3. Click Service.
The event service drop-down list is enabled.
4. Select either Switch or Chassis from the drop-down list to show only those messages from the logical
switch or from the chassis.
5. Click OK.
The filter is enabled and the enabled filter type is displayed in the events window.
54 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 55

Displaying a fabric topology report
A fabric topology report lists all of the domains in the fabric and the active paths for each domain. A
sample fabric topology report is shown in Figure 16.
Viewing a fabric topology report
1. Click the Fabric Topology icon on the Fabric Toolbar.
The Fabric Topology window opens.
2. Click the Print button to print a topology report.
A Print button is located at the top and bottom of the report. Both Print buttons have the same function.
Figure 16 Fabric topology report
Displaying the Name Server entries
Advanced Web Tools displays Name Server entries listed in the Simple Name Server database (see
Figure 17). This includes all Name Server entries for the fabric, not only those related to the local domain.
Each row in the table represents a different device.
NOTE: Name Server entries are not polled by default. Click Refresh in the Name Server window to poll
Name Server entries. You can also click the Auto Refresh check box and specify a time interval at which
the Name Server entries will be refreshed.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 55
Page 56

Figure 17 Name server window
Viewing a list of the switches in the Name Server
1. Click the Name Server icon on the Fabric Toolbar.
The Name Server Table is displayed.
2. Optional: Check the Auto Refresh check box on the Name Server window. Enter an auto-refresh
interval (in seconds); the minimum (and default) interval is 15 seconds.
The Name Server entries refresh at the rate you set.
Printing the Name Server entries
1. Click the Name Server icon on the Fabric Toolbar.
The Name Server Table is displayed.
2. Click Print.
The Page Setup dialog box opens.
3. Make changes, as appropriate.
4. Click OK in the Page Setup dialog box.
The Print dialog box opens.
5. Select a printer and click OK in the Print dialog box.
Displaying detailed Name Server information for a particular device
1. Click the Name Server icon on the Fabric Toolbar.
The Name Server Table opens.
2. Click a device in the Domain column.
3. Click Detail View.
The Name Server Information dialog box displays information specific to that device.
56 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 57

Displaying the zone members of a particular device
1. Click the Name Server icon on the Fabric Toolbar.
The Name Server Table opens.
2. Click a device in the Domain column.
3. Click Accessible Devices.
The Zone Accessible Devices window displays accessible zone member information specific to that
device.
Physically locating a switch using beaconing
Use the Beacon button to physically locate a switch in a fabric. The beaconing function helps to physically
locate a switch by sending a signal to the specified switch, resulting in an LED light pattern that cycles
through all ports for each switch (from left to right).
Enabling beaconing
1. Select a switch from the Fabric Tree.
The selected switch appears in the Switch View.
2. Click the Beacon button on the Switch View.
The LED lights on the actual switch (selected in the GUI) light up on the physical switch in a pattern
running back and forth across the switch itself. The beaconing is not shown in the GUI.
3. Look at the physical switches in your installation location to identify the switch.
Displaying swapped port area IDs
Use this procedure to view swapped ports on the switch. You cannot swap ports using Advanced Web
Tools; you can swap ports using the Fabric OS CLI only.
Determining whether a port area ID has been swapped with another switch port
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described in ”Launching the switch Admin Module” on page 36.
2. Click the Ports tab.
3. View the Port (Area ID) column in the Port Settings tab.
For ports that have been swapped, the port number is followed by the area ID, in parentheses.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 57
Page 58

58 Managing your fabrics, switches, and ports
Page 59

4 Maintaining configurations and firmware
This chapter contains the following information:
• Maintaining configurations, page 59
• Performing a firmware download, page 60
Maintaining configurations
It is important to maintain consistent configuration settings on all switches in the same fabric, because
inconsistent parameters (such as inconsistent PID formats) can cause fabric segmentation. As part of
standard configuration maintenance procedures, HP recommends that you back up configuration data for
every switch on a host computer server for emergency reference.
This section contains procedures for basic switch configuration maintenance. Use the Configure tab and
Upload/Download subtab of the Switch Admin module to perform these tasks (see Figure 18).
Figure 18 Configure tab, Upload/Download Subtab
Backing up a configuration file
Keep a backup copy of the configuration file in case the configuration is lost or unintentional changes are
made. You should keep individual backup files for all switches in the fabric. You should avoid copying
configurations from one switch to another.
When you back up a configuration file for the Core Switch 2/64 or for a SAN Director 2/128 or 4/256
SAN Director configured with two logical switches, the backup is performed on a logical-switch basis.
This means that you must back up a separate configuration file for each logical switch.
To back up a configuration file
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Configure tab.
3. Click the Upload/Download subtab (see Figure 18).
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 59
Page 60

4. Select the Config Upload to Host radio button.
5. Enter the user name, password, and host IP information.
6. Enter the configuration file with a fully qualified path.
7. Click Apply.
You can monitor the progress by looking at the Upload/Download Progress bar on the Configure tab.
Restoring a configuration
Restoring a configuration involves overwriting the configuration on the switch by downloading a
previously saved backup configuration file. Perform this procedure during a planned down time.
Make sure that the configuration file you are downloading is compatible with your switch model, because
configuration files from other model switches might cause your switch to fail.
Downloading a configuration to the switch
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Disable the switch, as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on page 39.
You can download configurations only to a disabled (offline) switch.
3. Click the Configure tab.
4. Click the Upload/Download subtab (see Figure 18 on page 59).
5. Select the Config Download to Switch radio button.
6. Enter the user name, password, and host IP information.
7. Enter the configuration file with a fully qualified path.
8. Click Apply.
You can monitor the progress by looking at the Upload/Download Progress bar on the Configure tab.
9. Enable the switch, as described in ”Enabling and disabling a switch” on page 39.
Performing a firmware download
During a firmware download, the switch reboots and the browser temporarily loses connection with the
switch. When the connection is restored, the version of the software running in the browser is different
from the new software version that has been installed and activated on the switch. You must close all of
the Advanced Web Tools windows and log in again to avoid a firmware version mismatch. Note that for
chassis-based switches, you might get pop-up messages that imply the loss of connection is temporary and
will soon be resolved. You still need to close all windows and log in again.
When you request a firmware download, the system first checks the file size that is to be downloaded. If
the compact flash does not have enough space, Advanced Web Tools displays a message and the
download does not occur. If this happens, contact your switch support supplier.
Downloading a new version of the firmware
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Firmware tab (see Figure 19).
3. Select the Firmware Download radio button.
4. Enter the host IP address, user name, password, and fully qualified path to the file name.
5. Click Apply.
The firmware download begins. You can monitor the firmware download status on the Firmware
Download progress bar.
About halfway through the download process, connection to the switch is lost and Advanced Web
Tools invalidates the current session. (Advanced Web Tools invalidates all windows if upfront login is
enabled, but invalidates only the Switch Admin session, if upfront login is not enabled.)
6. Close all Advanced Web Tools windows and log in again.
If the firmware download is in progress when you log in, you can continue to monitor its progress.
60 Maintaining configurations and firmware
Page 61

Figure 19 Firmware tab
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 61
Page 62

62 Maintaining configurations and firmware
Page 63

5 Configuring standard security features
This chapter contains the following information:
• Creating and maintaining user-defined accounts, page 63
• Configuring SNMP information, page 65
• Managing the RADIUS server, page 67
Creating and maintaining user-defined accounts
In addition to the five default accounts—root, factory, admin, switchAdmin, and user—Fabric OS
supports up to 15 user-defined accounts in each logical switch (domain). These accounts expand your
ability to track account access and audit administrative activities.
The User tab of the Switch Admin module (see Figure 20) displays account information and enables you
to create and manage user accounts, if you are logged in as an admin. If you are logged in as a
switchAdmin, you can change your own password but cannot view or modify other accounts. If you are
logged in as a user role, you cannot access the Switch Admin module.
NOTE: If you are operating in secure mode, you can perform these operations only on the primary FCS
switch.
Figure 20 User tab
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 63
Page 64

Displaying account information
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the User tab.
A list of the default and user-defined accounts is displayed. If you are logged in using the switchAdmin
role, only your account information is displayed.
Creating a user-defined account
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the User tab.
3. Click the Add button.
The Add User Account dialog box opens.
4. Enter the user name, which must begin with an alphabetic character. The name can be up to 40
characters long. It is case-sensitive and can contain alphabetic and numeric characters, the dot and
the underscore. It must be different from all other account names on the logical switch.
5. Select a role from the drop-down list: admin, switchAdmin, or user in nonsecure mode; admin,
switchAdmin, user, or nonfcsadmin in secure mode.
See ”Role-based access control” on page 22 for information about these roles.
6. Optional: Enter a description of the account.
7. Select the Enabled or Disabled radio button to enable or disable the account.
8. Enter the password for the account.
Passwords can contain 8 to 40 characters. They must begin with an alphabetic character. They can
include numeric characters, the dot, and the underscore. Passwords are case-sensitive; they are not
displayed when you enter them on the command line.
9. Reenter the password in the Confirm Password field for confirmation.
10.Click OK.
11.Click Apply to save your changes.
Deleting a user-defined account
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the User tab.
3. Select the account to remove.
4. Click the Remove button.
5. Click Apply to save your changes.
You cannot delete the default accounts. An account cannot delete itself. All active CLI sessions for the
deleted account are logged out.
Changing account parameters
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the User tab.
3. Select the account to modify.
You cannot modify the default root and factory accounts, even if you are logged in as root.
4. Click the Modify button.
The Modify User Account dialog box opens. You cannot change the user name of the account. To
change the user name, you must delete the account and create a new account.
5. Select a role from the drop-down list: admin, switchAdmin, or user in nonsecure mode; admin,
switchAdmin, user, or nonfcsadmin in secure mode.
You can change the role only on user-level accounts. You cannot change the role on the default
accounts. You cannot change the role of your own account.
6. Enter a new description.
You can change the description only on user-level accounts. You cannot change the description of the
default accounts. You cannot change the description of your own account.
64 Configuring standard security features
Page 65

7. Select the Enabled or Disabled radio button to enable or disable the account.
You can enable and disable user- and admin-level accounts except for your own account. You cannot
enable or disable your own account or the factory account. Only the root account can disable itself.
If you disable an account, all active CLI sessions for that account are logged out.
8. Click OK.
9. Click Apply to save your changes.
Changing an account password
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the User tab.
3. Select the account to modify.
If you are logged in as admin, you can change the password of your own account, peer admin
accounts, switchAdmin accounts, and user accounts. You cannot change the root or factory account
passwords.
If you are logged in as a switchAdmin, you can change the password only on your own account.
4. Click the Change Password button.
The Set User Account Password dialog box opens.
If you are changing the password of an admin account, you must also provide the current password.
You do not need to provide the current password if you are changing the password of a lower-level
user account.
5. Enter the current password of the account. This step is required only if you are changing the password
of your own or a peer admin account.
6. Enter the new password of the account.
The new password must have at least one character different from the old password.
7. Reenter the new password in the Confirm Password box.
8. Click OK.
9. Click Apply to save your changes.
Configuring SNMP information
This section describes how to manage the configuration of the SNMP agent in the switch. The
configuration includes SNMPv1 and SNMPv3 configuration, accessControl, and systemGroup
configuration parameters.
For more information, see the snmpConfig command in the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x command
reference guide.
Setting SNMP trap levels
When you set trap levels for the Core Switch 2/64 or for a SAN Director 2/128 or 4/256 SAN Director
configured with two logical switches, trap levels are set on a logical-switch basis. This means that for each
logical switch, you must set trap levels individually.
Setting trap levels
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the SNMP tab (see Figure 21).
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 65
Page 66

Figure 21 SNMP tab
3. Select a trap level for a recipient from the corresponding Trap Level drop-down list in the SNMPv1 and
SNMPv3 sections.
The level you select identifies the minimum event level that prompts a trap.
4. Click Apply.
Configuring SNMP information
When you configure SNMP information for the Core Switch 2/64 or for a SAN Director 2/128 or
4/256 SAN Director configured with two logical switches, it is on a logical-switch basis. This means that
for each logical switch, you must configure SNMP information individually.
Changing the systemGroup configuration parameters
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the SNMP tab (see Figure 21).
3. Enter a contact name, a description, and a location in the SNMP Information section.
4. Optional: Select the Enable Authentication Trap check box to allow authentication traps to be sent to
the reception IP address.
5. Click Apply.
Setting SNMPv1 configuration parameters
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the SNMP tab (see Figure 21).
3. Double-click a community string in the SNMPv1 section and enter a new community string.
4. Double-click a recipient IP address in the SNMPv1 section and enter a new IP address.
5. Click Apply.
66 Configuring standard security features
Page 67

Setting SNMPv3 configuration parameters
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Select the SNMP tab (see Figure 21 on page 66).
3. Select a user name from the User Name drop-down list in the SNMPv3 section.
4. Double-click a recipient IP address in the SNMPv3 section and enter a new IP address.
5. Select a trap level from the Trap Level drop-down list.
6. Click Apply.
Changing the accessControl configuration
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the SNMP tab (see Figure 21 on page 66).
3. Double-click an access host IP address in the Access Control List section and enter a new host IP
address.
4. Select a permission for the host from the Access Control List drop-down list.
Options are Read Only and Read Write.
5. Click Apply.
Managing the RADIUS server
Fabric OS supports RADIUS authentication, authorization, and accounting service (AAA). When
configured for RADIUS, the switch becomes a Network Access Server (NAS) that acts as a RADIUS client.
In this configuration, authentication records are stored in the RADIUS host server database. Login and
logout account name, assigned role, and time accounting records are also stored on the RADIUS server.
You should set up RADIUS service through a secure connection, such as SSH.
Use the AAA Service tab of the Switch Admin module to manage the RADIUS server (see Figure 22).
Figure 22 AAA Service tab
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 67
Page 68

Enabling and disabling RADIUS service
At least one RADIUS server must be configured before you can enable RADIUS service.
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the AAA Service tab.
3. To enable RADIUS service, select a RADIUS service from the Primary AAA Service drop-down list,
select None or Switch Database from the Secondary AAA Service drop-down list.
To disable RADIUS service, select Switch Database from the Primary AAA Service drop-down list and
select None from the Secondary AAA Service drop-down list.
4. Click Apply.
Configuring the RADIUS server
The configuration is chassis-based, so it applies to all logical switches (domains) on the switch and
replicates itself on a standby CP, if one is present. It is saved in a configuration upload, and so it can be
applied to other switches in a configuration download. You should configure at least two RADIUS servers
so that if one fails, the other assumes service.
You can configure the RADIUS server even if it is disabled. You can configure up to five RADIUS servers.
You must be logged in as admin or switchAdmin to configure the RADIUS server.
To configure the RADIUS server
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the AAA Service tab.
3. Click Add.
The RADIUS Configuration dialog box opens.
NOTE: You can configure up to five RADIUS servers. If five RADIUS servers are already configured, the
Add button is disabled.
4. Enter the RADIUS server name, which is a valid IP address or Dynamic Name Server (DNS) string.
Each RADIUS server must have a unique IP address or DNS name for the RADIUS server.
5. Optional: Enter the port number.
6. Optional: Enter the secret string.
7. Optional: Enter the timeout time in minutes.
8. Optional: Select an authentication protocol from CHAP or PAP.
The default value is CHAP; if you do not change it, CHAP becomes the authentication protocol.
9. Click OK to return to the AAA Service tab.
10.Click Apply.
Modifying the RADIUS server
Use the following procedure to change the parameters of a RADIUS server that is already configured.
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the AAA Service tab.
3. Click a RADIUS server from the RADIUS Configuration list.
4. Click Modify.
The RADIUS Configuration dialog box opens.
5. Enter new values for the port number, secret string, and timeout time (in minutes).
6. Select an authentication protocol from CHAP or PAP.
The default value is CHAP; if you do not change it, CHAP becomes the authentication protocol.
7. Click OK to return to the AAA Service tab.
8. Click Apply.
68 Configuring standard security features
Page 69

Modifying the RADIUS server order
The RADIUS servers are contacted in the order they are listed, starting from the top of the list and moving
to the bottom.
Modifying the order in which the RADIUS servers are contacted
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Select the AAA Service tab.
3. Click a RADIUS server from the RADIUS Configuration list.
4. Click the up and down arrows to rearrange the order of the RADIUS servers.
5. Click Apply.
Removing a RADIUS server
Use the following procedure to remove a RADIUS server.
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Select the AAA Service tab.
3. Select a RADIUS server from the RADIUS Configuration list.
4. Click Remove.
If there is no RADIUS server configured, the Remove button is disabled. You cannot remove the only
RADIUS server, if the RADIUS service is the primary AAA service.
The RADIUS server is not deleted until you apply the changes from the AAA Services tab.
5. Click Apply in the AAA Services tab.
A confirmation is displayed, warning you that you are about to remove the selected RADIUS server.
6. Click Yes in the confirmation.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 69
Page 70

70 Configuring standard security features
Page 71

6 Routing traffic
This chapter contains the following information:
• Introducing routing, page 71
• Displaying FSPF routing, page 72
• Configuring a static route, page 72
• Enabling and disabling dynamic load sharing, page 73
• Specifying frame order delivery, page 73
• Configuring link cost, page 74
Introducing routing
For Fabric OS 5.x, the supported routing policies are:
• Port -based
• Device-based (4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem and SAN Switch 4/32 only)
• Exchanged-based (4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, SAN Switch 4/32, and 4/256
SAN Director only)
For the 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, SAN Switch 4/32, and 4/256 SAN Director, the
exchange-based routing policy is the default.
Using port-based routing, you can assign a static route, in which the path chosen for traffic never
changes. In contrast, device-based and exchange-based routing policies always employ dynamic path
selection, in which the software chooses a path based on current traffic conditions. See the HP
StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide for more information.
To optimize port-based routing, the dynamic load sharing (DLS) feature can be enabled to balance the
load across the available output ports within a domain. Device-based and exchange-based routing
require the use of DLS; when these policies are in effect, you cannot disable the DLS feature.
To configure routing policies, you must use the CLI. After the routing policies are configured, you can use
Advanced Web Tools to display the routing paths, configure static routes, and configure routing
parameters, such as DLS, frame order delivery, and link cost.
The Routing tab of the Switch Admin module displays routing information. Figure 23 shows the Routing
tab when the port-based routing policy is enabled. When a device-based or exchange-based routing
policy is enabled, the interface is different: the Static Route information and the DLS radio buttons are not
displayed.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 71
Page 72

Figure 23 Routing tab for port-based routing policy
Displaying FSPF routing
The Routing tab of the Switch Admin module displays information about routing paths.
Viewing FSPF routing
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Routing tab.
3. Perform the following, according to switch type:
• For Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, or 4/256 SAN Director, click a slot number under
the FSPF Route category in the navigation tree.
• For 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, click the FSPF Route
category in the navigation tree.
Configuring a static route
A static route can be assigned only when the active routing policy is port-based. When device-based or
exchange-based routing is active, you cannot disable DLS and you cannot view and configure static
routes.
When you configure a static route for a Core Switch 2/64 or for a SAN Director 2/128 or 4/256 SAN
Director configured for two logical switches, the static route is configured on a logical-switch basis. This
means that for each logical switch, you must configure a static route individually.
To configure a static route
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Routing tab.
72 Routing traffic
Page 73

3. Perform the following, according to switch type:
• For Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, or 4/256 SAN Director, click a slot number under
the Static Route category in the navigation tree. Click Add.
• For 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, click the Static Route
category in the navigation tree. Click Add.
A new blank line appears in the window. Note that when device-based or exchange-based routing
policies are in effect, the Static Route category is not displayed in the navigation tree.
4. Enter the In Port number for the route.
5. Enter the Destination Domain.
The destination domain IDs match the outports in the cell.
6. Enter the Out Port number for the route.
7. Click OK to add the static route.
8. Click Apply.
Enabling and disabling dynamic load sharing
The device-based and exchange-based routing policies depend on the Fabric OS DLS for dynamic routing
path selection. When these policies are in force, DLS is always enabled and cannot be disabled.
When the port-based policy is in force, you can enable DLS to optimize routing. When DLS is enabled, it
shares traffic among multiple equivalent paths between switches. DLS recomputes load sharing either
when a switch boots up or each time an E_Port or Fx_Port goes online or offline. Enabling this feature
allows a path to be discovered by the FSPF path-selection protocol.
For more information regarding DLS, see the dlsset command in the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x
command reference guide.
When you enable or disable DLS for the Core Switch 2/64 or for a SAN Director 2/128 or 4/256 SAN
Director configured for two logical switches, the DLS is enabled or disabled on a logical-switch basis. This
means that for each logical switch, you must enable or disable DLS individually.
Configuring the DLS setting
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Select the Routing tab.
3. Click On in the Dynamic Load Sharing area to enable DLS or click Off to disable DLS.
Note that when device-based or exchange-based routing policies are in effect, the DLS radio buttons
are not displayed in the Routing tab.
4. Click Apply.
Specifying frame order delivery
In a stable fabric, frames are always delivered in order, even when the traffic between switches is shared
among multiple paths. However, when topology changes occur in the fabric (for example, if a link goes
down), traffic is rerouted around the failure, and some frames could be delivered out of order.
By default, frame delivery is out-of-order across topology changes. However, if the fabric contains
destination devices that do not support out-of-order delivery, you can force in-order frame delivery across
topology changes.
Enabling in-order delivery (IOD) guarantees that frames are either delivered in order or dropped. For
more information regarding IOD, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide.
When you enable or disable IOD for the Core Switch 2/64 or for a SAN Director 2/128 or 4/256 SAN
Director configured for two logical switches, IOD is enabled or disabled on a logical-switch basis. This
means that for each logical switch, you enable or disable IOD individually.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 73
Page 74

NOTE: Enabling IOD can cause a delay in the establishment of a new path when a topology change
occurs, and therefore should be used with care.
Configuring the IOD setting
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Routing tab.
3. Click On in the In-Order Delivery area to force in-order frame delivery across topology changes or
click Off to restore out-of-order frame delivery across topology changes.
4. Click Apply.
Configuring link cost
When you configure link cost for the Core Switch 2/64, or for a SAN Director 2/128, or 4/256 SAN
Director configured for two logical switches, link cost is configured on a logical-switch basis. This means
that for each logical switch, you configure link cost individually.
For information regarding link cost, see the linkCost command in the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x
command reference guide.
Configuring the link cost for a port
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Routing tab.
3. Perform the following, according to switch type:
• For Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, click the slot number of
the logical switch under Link Cost in the navigation tree.
• For 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, click Link Cost in the
navigation tree.
4. Double-click in the row in the Cost column that corresponds to the appropriate port.
5. Enter the link cost. For a 1 Gbit/sec ISL, the default cost is 1000.
For a 2 Gbit/sec or a 4 Gbit/sec ISL, the default cost is 500. Valid values for link cost are 1 through
9999. Setting the value to 0 sets the link cost to the default value for that port.
6. Click Apply.
74 Routing traffic
Page 75

7 Administering extended fabrics
This chapter contains the following information:
• About extended link buffer allocation, page 75
• Configuring for long distance, page 76
About extended link buffer allocation
As the distance between switches and the link speed increases, additional buffer-to-buffer credits are
required to maintain maximum performance. The number of credits reserved for a port depends on the
switch model and on the extended ISL mode for which it is configured.
The Extended Fabric tab of the Switch Admin module displays information about the port speed,
long-distance setting, and buffer credits, as shown in Figure 24. Use this tab to configure the
long-distance setting of a port. For detailed information on managing extended fabrics, see the HP
StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x administrator guide.
The Extended Fabric tab provides the following information:
• Port Number
• Buffer Limited: A buffer-limited port can come online with fewer buffer credits allocated than its
configuration specifies, allowing it to operate at a reduced bandwidth instead of being disabled for
lack of buffers.
Buffer-limited operation is supported for the L0 and LD extended ISL modes only and is persistent
across reboots, switch disabling and enabling, and port disabling and enabling.
• Port Speed, which is displayed as follows:
• 1G 1 Gbit/sec
• 2G 2 Gbit/sec
• 4G 4 Gbit/sec
• N1 Negotiated 1 Gbit/sec
• N2 Negotiated 2 Gbit/sec
• N4Negotiated 4 Gbit/sec
•Auto-Negotiation
• Buffer Needed/Allocated: The number of buffers needed and the number of buffers that are actually
allocated.
• Actual Distance: The actual distance, in kilometers, for the link.
• Desired Distance: Required for a port configured in LD mode (see Table 9), the desired distance, in
kilometers, for the link. This value is the upper limit for calculating buffer availability for the port. If the
measured distance is more than the specified desired distance, the port is allocated the number of
buffers required by the specified desired distance.
• Long Distance: Table 9 describes the long-distance settings and identifies which settings require an
Extended Fabrics license.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 75
Page 76

Figure 24 Extended Fabric tab
Table 9 Long-distance settings and license requirements
Value Description Extended fabric
license required?
L0 No long-distance setting is enabled. The maximum supported link
distance is 10 km, 5 km, or 2.5 km for ports at speeds of 1 Gbit/sec,
2 Gbit/sec, and 4 Gbit/sec, respectively.
LE Extended normal setting is enabled, 10 km (6 miles) or less. No
L0.5 Setting of 25 km (15.5 miles) or less is enabled. Yes
L1 Medium long-distance setting is enabled, 50 km (31 miles) or less. Yes
L2 Long-distance setting is enabled, 100 km (62 miles) or less. Yes
LD Dynamic setting is enabled. The LD-level link can operate at distances
up to 500 km at 1 Gbit/sec, 250 km at 2 Gbit/sec, or 125 km at 4
Gbit/sec, depending on the availability of frame buffers within the
port group.
Configuring for long distance
When you configure a long-distance ISL, ensure that the ports on both sides of the ISL have the same
configuration, to avoid fabric segmentation.
Configuring a port for long-distance connection
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Click the Extended Fabric tab.
No
Yes
76 Administering extended fabrics
Page 77

3. Perform the following, according to switch type:
• For Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, click the slot subtab that
corresponds to the correct slot for the logical switch.
• For 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, proceed directly to
the next step.
4. Select a port by clicking anywhere in the row for that port.
5. Select a distance from the Long Distance drop-down list that corresponds to the port.
Depending on the distance selected, this might require an optional license. For information about the
various distances, see Table 9.
If you select a long-distance setting of LD, you must also enter a value in the Desired Distance column
for that port number:
a. Double-click the Desired Distance box for the port, as shown in Figure 24 on page 76.
b. Enter a number in the field to indicate the distance in kilometers:
• For 1 Gbit/sec ports, enter a number between 10 and 500, inclusive.
• For 2 Gbit/sec ports, enter a number between 10 and 250, inclusive.
• For 4 Gbit/sec ports, enter a number between 10 and 125, inclusive.
This value is the upper limit for calculating buffer availability for other ports in the same port group.
If the actual distance is more than the desired distance, the port operates in buffer-limited mode.
c. Press Enter or click another port entry for the value to be accepted.
6. Optional: If the fabric contains HP StorageWorks 1 GB switches extended ISLs, select the On radio
button for Long Distance Compatibility. The switch must be disabled before you can select this option.
If you select this option, you must have an Extended Fabrics license, and both E_Ports in an ISL must be
configured with the same long-distance compatibility setting. The SAN Switch 4/32 cannot be part of
such a fabric.
7. Click Apply.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 77
Page 78

78 Administering extended fabrics
Page 79

8 Administering ISL trunking
This chapter contains the following information:
• Displaying trunk group information, page 79
• Disabling or reenabling trunking mode on a port, page 80
ISL trunking optimizes network performance by forming trunking groups that can distribute traffic across a
shared bandwidth.
A trunking license is required on each switch that participates in the trunk. (For details on obtaining and
installing licensed features, see ”Maintaining licensed features” on page 47.)
For additional information about ISL Trunking, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x administrator
guide.
Use the Trunking tab of the Switch Admin module to view and manage trunks through Advanced Web
Tools (see Figure 25).
Figure 25 Trunking tab
Displaying trunk group information
Use this procedure to display the following information about ISL Trunking groups:
• Trunk group number identifier
• Master port
• Member ports
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 79
Page 80

Viewing information on a trunk group
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Select the Trunking tab.
3. Optional: Click Refresh to refresh the information.
Disabling or reenabling trunking mode on a port
When the trunking license is activated, trunks are established on eligible ISLs and trunking capability is
enabled by default on all ports. Use the following procedure to disable trunking on a port or to reenable
trunking if it has been disabled.
1. Launch the Switch Admin module as described on page 36.
2. Select the Ports tab (see Figure 10 on page 44).
3. Perform the following, according to switch type:
• For Core Switch 2/64, SAN Director 2/128, and 4/256 SAN Director, click the slot subtab that
corresponds to the correct slot for the logical switch.
• For 4/8 SAN Switch, 4/16 SAN Switch, SAN Switch 2/8V, SAN Switch 2/16V, SAN Switch
2/32, 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem, and SAN Switch 4/32, proceed directly to
the next step.
4. To enable trunking mode on a port, select the check box in the Enable Trunking column that
corresponds to the port you want to trunk.
To disable trunking mode on a port, clear the box.
5. Click Apply.
80 Administering ISL trunking
Page 81

9 Administering zoning
This chapter briefly describes zoning and provides the procedures for managing zoning using Advanced
Web Tools. It contains the following sections:
• Introducing zoning, page 81
• Managing zoning with Advanced Web Tools, page 81
• Managing zone aliases, page 86
• Managing zones, page 87
• Managing QuickLoops, page 88
• Managing Fabric Assist zones, page 90
• Managing zone configurations, page 91
• Managing the zoning database, page 98
• Best practices for zoning, page 102
Introducing zoning
Zoning enables you to partition your SAN into logical groups of devices that can access each other. For
example, you can partition your SAN into two zones, winzone and unixzone, so that your Windows
servers and storage do not interact with your UNIX® servers and storage.
Zones can be configured dynamically. They can vary in size, depending on the number of
fabric-connected devices, and devices can belong to more than one zone. Because zone members can
access only other members of the same zone, a device not included in a zone is not available to members
of that zone.
When using a mixed fabric—that is, a fabric containing 5.x, 4.x, 3.x, and 2.x switches—you should use
the switch with the highest Fabric OS level to perform zoning tasks. See ”Entering a zone alias in the
Define Device Alias wizard” on page 102 for more recommendations about zoning.
When zone or Fabric Assist (FA) zone members are specified by fabric location (domain, area) only, or
by device name (node name or port WWN) only, then zone boundaries can be enforced at the hardware
level, and the zone is referred to as a hard zone.
When zone elements are specified by fabric location (domain, area) and other elements of the same zone
are specified by device name (node name or port WWN), zone enforcement depends on Name Server
lookups, and the zone is referred to as a soft zone.
For more specific information about zoning concepts, see the HP StorageWorks Fabric OS 5.x
administrator guide.
Managing zoning with Advanced Web Tools
You can monitor and manage zoning through the Advanced Web Tools Zone Admin module. Click the
Zone Administration icon in the Fabric Toolbar to access the Zone Admin module, shown in Figure 26.
The Zone Admin icon is displayed in the Fabric Toolbar only if an Advanced Zoning license is installed on
the switch.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 81
Page 82

Figure 26 Zone Admin Module
The information in the Zone Admin module is collected from the selected switch.
If secure mode is enabled, zoning can be administered only from the primary FCS switch. If the selected
switch has an Advanced Zoning license installed but is not the primary FCS switch, the Zone Admin icon
is displayed in the Fabric Toolbar but not activated. For specific information regarding secure fabrics, see
the HP StorageWorks Secure Fabric OS administrator guide.
You must be logged in as an admin or switchAdmin to launch the Zone Admin module. If you are logged
in as a switchAdmin, you can access the Zone Admin module in read-only mode only; most of the zoning
operations are disabled in read-only mode.
A snapshot is taken of all the zoning configurations at the time you launch the Zone Admin module; this
information is not updated by Advanced Web Tools. To update this information, see ”Refreshing the Zone
Admin module information” on page 84.
NOTE: Any changes you make in the Zone Admin module are held in a buffered environment and do
not update the zoning database until you save the changes. If you close the Zone Admin module without
saving your changes, your changes are lost. To save the buffered changes you make in the Zone Admin
module to the zoning database on the switch, see ”Saving local zoning changes” on page 84.
Saving means updating the zoning database on the switch with the local changes from the Advanced
Web Tools buffer. Refreshing means copying the current state of the zoning database on the switch to the
Advanced Web Tools buffer, overwriting its current contents.
82 Administering zoning
Page 83

In the Zone Admin module, all WWNs also display vendor names. In the Member Selection List panel
(see Figure 27), you can right-click port and device nodes to display which aliases the port or device is a
member of. In addition, you can right-click the device nodes and then select View Device Detail to display
detailed information about the selected device, as shown in Figure 27.
Figure 27 Device detail example
NOTE: In the Detail View window, the scroll bars in the Member of Zones and Member of Aliases
sections do not scroll unless you double-click them first.
The remainder of this section describes basic zoning procedures you can perform in the Zone Admin
module that are useful for all zoning operations.
Launching the Zone Admin module
This section describes how to launch the Zone Admin module, from which all zoning procedures are
performed.
1. Select a switch from the Fabric Tree.
The selected switch appears in the Switch View.
2. Click the Zone Administration icon in the Fabric Toolbar.
The Zone Admin module is displayed (see Figure 26 on page 82).
Refreshing the fabric information
This function refreshes the display of fabric elements (switches, ports, devices, and AL_PAs) only. It does
not affect any zoning element changes or update zone information in the Zone Admin module. To refresh
the zone information displayed in the Zone Admin module, see ”Refreshing the Zone Admin module
information” next.
This option allows you to refresh the fabric element information displayed at any time.
To refresh the fabric information
In the Zone Admin module, select View > Refresh Fabric.
This refreshes the status for the fabric, including switches, ports, and devices.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 83
Page 84

Refreshing the Zone Admin module information
The information displayed in the Zone Admin module is initially a snapshot of the contents of the fabric
zoning database at the time the module is launched. Any changes you make to this window are saved to
a local buffer; they are not applied to the fabric zoning database until you invoke one of the transactional
operations listed in the Actions menu.
Any local zoning changes are buffered by the Zone Admin module until explicitly saved to the fabric. If
the fabric zoning database is independently changed by another user or from another interface (for
example, the CLI) while Advanced Web Tools zoning changes are still pending, the refresh icon starts
to blink (after a 15 second polling delay). You can then choose to refresh the current Advanced Web
Tools zoning view to reflect the new, externally changed contents of the fabric zoning database, in which
case any pending local changes are lost, or you can ignore the blinking refresh icon and save your local
changes, overwriting the external changes that triggered the icon to blink.
Another reason to refresh zoning is to back out of current, unsaved work and start over.
You can refresh the zoning information at any time, either using the refresh icon (whether it is flashing or
not) or from the View menu.
The following procedure updates the information in the Zone Admin module with the information saved in
the zoning database on the switch.
CAUTION: When you refresh the buffered information in the Zone Admin module, any zoning
configuration changes you have made and not yet saved are erased from the buffer and replaced with
the currently enabled zone configuration information that is saved on the switch.
Refreshing the local Zone Admin buffer from the fabric zoning database
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select View > Refresh Zoning or click the zone refresh icon (located in the lower right corner of the
Zone Admin module).
This refreshes the information in the Zone Admin module with the information in the switch’s zoning
database. This action also refreshes the fabric information as described in ”Refreshing the fabric
information” on page 83. Any unsaved zoning changes are deleted.
Saving local zoning changes
All information displayed and all changes made in the Zone Admin module are buffered until you save
the changes. That means that any other user looking at the zone information for the switch does not see
the changes you have made until you save them.
Saving the changes propagates any changes you have made in the Zone Admin module (buffered
changes) to the zoning database on the switch. If another user has a zoning operation in progress at the
time that you attempt to save changes, a warning is displayed that indicates that another zoning
transaction is in progress on the fabric. You can select to abort the other transaction and override it with
yours.
If the zoning database size exceeds the maximum allowed, you cannot save the changes. The zoning
database summary displays the maximum zoning database size (see ”Displaying the zone configuration
summary” on page 96).
This action updates the entire contents of the Zone Admin module, not just the selected zone, alias, or
configuration. You can save your changes at any time during the zone administration session.
84 Administering zoning
Page 85

Saving Zone Admin module changes to the switch zoning database
1. Make your zoning changes in the Zone Admin module.
2. Select Actions > Save Config Only.
NOTE: If you made changes to a configuration, you must enable the configuration before the changes
become effective. To enable the configuration, see ”Enabling a zone configuration” on page 94.
Closing the Zone Admin module
It is very important to remember that any changes you make in the Zone Admin module are not saved. It
is recommended that you always close the Zone Admin module from the File menu, as described in the
procedure below.
CAUTION: If you click the X in the top right corner of the Zone Admin module, the Zone Admin session is
closed immediately, and any changes you made without saving are lost. To avoid potential loss of data,
use the following procedure to close the Zone Admin module. In this procedure, the Zone Admin session
displays a warning if you have unsaved changes when you are trying to close the Zone Admin module.
Safely closing the Zone Admin module
1. From the Zone Admin module, select File > Close.
If any changes exist in the buffer that have not been saved, a warning dialog box opens, asking you
to confirm that you want to close the Zone Admin session without saving the changes.
2. Click Yes to close without saving changes, or click No to go back to the Zone Admin module to save
the changes as described in ”Saving local zoning changes” on page 84.
Zoning views
You can choose how zoning elements are displayed in the Zone Admin module. The zoning view you
select determines how members are displayed in the Member Selection List panel (see Figure 26 on
page 82). The views filter the fabric and device information displayed in the Member Selection List for the
selected view, making it easier for you to create and modify zones, especially when creating hard zones.
Depending on the method you use to zone, certain tabs might or might not be available in the Zone
Admin window.
There are four views of defining members for zoning:
• Mixed zoning, which displays the port area number, device WWNs, or QuickLoop AL_PAs, and is
useful when creating a soft zone
• Port zoning, which displays port area numbers only, and is useful when creating a hard zone
• WWN zoning, which displays device WWNs only, and is useful when creating a hard zone
• AL_PA zoning, which displays QuickLoop AL_PAs only, and is useful when creating a soft zone
Selecting a zoning view
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. From the View menu, select one of the following:
• Mixed Zoning
•Port Zoning
• WWN Zoning
• AL_PA Zoning
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 85
Page 86

Managing zone aliases
An alias is a logical group of port area numbers, WWNs, or AL_PAs. Specifying groups of ports or
devices as an alias makes zone configuration easier, by enabling you to configure zones using an alias
rather than inputting a long string of individual members. You can specify members of an alias using the
following methods:
• A switch domain and port area number pair: for example, 2, 20
• Device node and device port WWNs
• QuickLoop AL_PAs
Creating and populating a zone alias
Use the following procedure to create a zone alias.
Creating an alias
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select a format to display zoning members in the Member Selection List as described in ”Zoning
views” on page 85.
3. Click the Alias tab.
4. Click Create.
The Create New Alias dialog box opens.
5. Enter a name for the new alias, and click OK in the Create New Alias dialog box.
The new alias is displayed in the Name list in the Alias tab.
6. Click + signs in the Member Selection List to view the nested elements.
The choices available in the Member Selection List depend on the selection made in the View menu.
7. Select elements in the Member Selection List that you want to include in your alias.
The Add Member button becomes active.
8. Click Add Member to add alias members.
Selected members move to the Alias Members window.
9. Optional: Repeat step 7 and step 8 to add more elements to your alias.
10.Optional: Click Add Other to include a WWN, port, or QuickLoop (AL_PA) that is not currently a part
of the fabric.
11.Optional: Click Add Other Host to include a WWN, port, or QuickLoop (AL_PA) that is not currently a
part of the fabric.
Adding and removing members of a zone alias
Use the following procedure to add or remove zone alias members.
Modifying the members of an alias
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Alias tab.
3. Select the alias you want to modify from the Name drop-down list.
4. Highlight an element in the Member Selection List that you want to add to your alias, or highlight an
element in the Alias Members list that you want to delete.
5. Click Add Member to add the selected alias member, or click Remove Member to remove the selected
alias member.
The alias is modified in the Zone Admin buffer.
86 Administering zoning
Page 87

Renaming a zone alias
Use the following procedure to change the name of a zone alias.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Alias tab.
3. Select the alias you want to rename from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click Rename.
The Rename an Alias dialog box opens.
5. Enter a new alias name and click OK.
The alias is renamed in the Zone Admin buffer.
Deleting a zone alias
You can remove a zone alias from the Zone Admin buffer. When a zone alias is deleted, it is no longer a
member of the zones of which it was once a member.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Alias tab.
3. Select the alias you want to delete from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click Delete.
The Confirm Deleting Alias dialog box opens.
5. Click Yes.
The selected alias is deleted from the Zone Admin buffer.
Managing zones
A zone is a region within the fabric in which specified switches and devices can communicate. A device
can communicate only with other devices connected to the fabric within its specified zone. You can
specify members of a zone using the following methods:
• Alias names
• Switch domain and port area number pair: for example, 2, 20.
• WWN (device)
• QuickLoop AL_PAs (device)
Creating and populating a zone
Use the following procedure to create a zone.
Creating a zone
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select a format to display zoning members in the Member Selection List as described in ”Zoning
views” on page 85.
3. Click the Zone tab.
4. Click Create.
The Create New Zone dialog box opens.
5. Enter a name for the new zone in the Create New Zone dialog box, and click OK.
The new zone is displayed in the Name list.
6. Click + signs in the Member Selection List to view the nested elements.
The choices available in the Member Selection List depend on the selection made in the View menu.
7. Select an element in the Member Selection List that you want to include in your zone.
The Add Member button becomes active.
8. Click Add Member to add the zone member.
The selected member is moved to the Zone Members window.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 87
Page 88

9. Optional: Repeat step 7 and step 8 to add more elements to your zone.
10.Optional: Click Add Other to include a WWN, port, or QuickLoop (AL_PA) that is not currently a part
of the fabric.
Adding and removing the members of a zone
Use the following procedure to add or remove zone members.
Modifying the members of a zone
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Zone tab.
3. Select the zone you want to modify from the Name drop-down list.
The zone members for the selected zone are listed in the Zone Members list.
4. Highlight an element in the Member Selection List that you want to include in your zone, or
highlight an element in the Zone Members list that you want to delete.
5. Click Add Member to add a zone member or click Remove Member to remove a zone member.
The zone is modified in the Zone Admin buffer.
Renaming a zone
Use the following procedure to change the name of a zone.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Zone tab.
3. Select the zone you want to rename from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click Rename.
The Rename a Zone dialog box opens.
5. Enter a new zone name and click OK.
The zone is renamed in the Zone Admin buffer.
Deleting a zone
Use the following procedure to delete a zone.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Zone tab.
3. Select the zone you want to delete from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click Delete.
The Confirm Deleting Zone dialog box opens.
5. Click Yes.
The selected zone is deleted from the Zone Admin buffer.
Managing QuickLoops
QuickLoop is an HP software product that allows multiple ports on a switch to create a logical loop.
Devices connected via QuickLoop appear to each other as if they are on the same arbitrated loop.
QuickLoop can be administered using Fabric OS 5.x; the following switches and directors running Fabric
OS 5.x, however, cannot be members of a QuickLoop:
• Core Switch 2/64
• SAN Director 2/128
• 4/256 SAN Director
• 4/8 SAN Switch
• 4/16 SAN Switch
• SAN Switch 2/8V
• SAN Switch 2/16V
88 Administering zoning
Page 89

• SAN Switch 2/32
• 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem
• SAN Switch 4/32
NOTE: You must have a QuickLoop license installed to create or modify a QuickLoop.
Creating a QuickLoop
Use the following procedure to create a QuickLoop.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select a format to display zoning members in the Member Selection List as described in ”Zoning
views” on page 85.
3. Click the QuickLoop tab.
4. Click Create.
The Create New QuickLoop dialog box opens.
5. Enter a name for the new QuickLoop.
6. Click OK.
7. Click an element in the Member Selection List that you want to include in your QuickLoop.
The Add Member button becomes active.
NOTE: There is a limit of two members per QuickLoop. Only switches capable of running QuickLoop are
displayed in the Member Selection List.
8. Click Add Member to add QuickLoop members.
Selected members are moved to the QuickLoop Members area.
9. Optional: Repeat step 7 and step 8 to add a second element to your QuickLoop.
Adding and removing members of a QuickLoop
Use the following procedure to add or remove members of a QuickLoop.
Modifying the members of a QuickLoop
1. Launch the Zone Administration module as described on page 83.
2. Click the QuickLoop tab.
3. Select the QuickLoop you want to modify from the Name drop-down list.
4. Highlight an element in the Member Selection List that you want to include in your QuickLoop, or
highlight an element in the QuickLoop Members that you want to delete.
NOTE: There is a limit of two members per QuickLoop. Only switches capable of running QuickLoop are
displayed in the Member Selection List.
5. Click Add Member to add a QuickLoop member or click Remove Member to remove a QuickLoop
member.
Renaming a QuickLoop
Use the following procedure to change the name of a QuickLoop.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the QuickLoop tab.
3. Select the QuickLoop you want to rename from the Name drop-down list.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 89
Page 90

4. Click Rename.
The Rename a QuickLoop dialog box opens.
5. Enter a new QuickLoop name and click OK.
The QuickLoop is renamed in the Zone Admin buffer.
Deleting a QuickLoop
Use the following procedure to delete a QuickLoop.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the QuickLoop tab.
3. Select the QuickLoop you want to delete from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click Delete.
The Confirm Deleting QuickLoop dialog box opens.
5. Click Yes.
The selected QuickLoop is deleted from the Zone Admin buffer.
Managing Fabric Assist zones
FA is an extension to QuickLoop. An FA zone allows private hosts to communicate with public or private
targets across the fabric.
FA zones can be administered using Fabric OS 5.x; however, the following switches and directors
running Fabric OS 5.x cannot be members of an FA zone:
• Core Switch 2/64
• SAN Director 2/128
• 4/256 SAN Director
• 4/8 SAN Switch
• 4/16 SAN Switch
• SAN Switch 2/8V
• SAN Switch 2/16V
• SAN Switch 2/32
• 4Gb SAN Switch for HP p-Class BladeSystem
• SAN Switch 4/32
NOTE: You must have a QuickLoop license installed to create or modify an FA zone.
Creating a Fabric Assist zone
Use the following procedure to create an FA zone. For this example, the Mixed Zone level is used.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select View > Mixed Zoning (you can select any view except the AL_PA view).
The Mixed View tab is displayed.
3. Click the Fabric Assist tab.
4. Click Create.
The Create New FA dialog box opens.
5. Enter a name for the new FA zone and click OK.
A fabric host is required.
6. Click + signs in the Member Selection List to view the nested elements.
The choices available in the Member Selection List depend on the selection made in the View menu.
90 Administering zoning
Page 91

7. Select an element in the Member Selection List that you want to include in your zone.
The Add Member button becomes active.
8. Click Add Member to add the zone member.
The selected member is moved to the Zone Members window.
9. Optional: Repeat step 7 and step 8 to add more elements to your FA zone.
10.Optional: Click Add Other to include a WWN, port, or QuickLoop (AL_PA) that is not currently a part
of the fabric.
11.Optional: Click Add Other Host to include a WWN, port, or QuickLoop (AL_PA) that is not currently a
part of the fabric.
The new members appear in the Fabric Assist Members area. The newly created FA zone also is
displayed in the Config tab.
Adding and removing Fabric Assist zone members
Use the following procedure to add and remove FA zone members.
Modifying the members of a Fabric Assist zone
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Fabric Assist tab.
3. Select the FA zone you want to modify from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click an element in the Member Selection List that you want to include in your FA zone, or click an
element in the FA Zone Members that you want to delete.
5. Click Add Member to add an FA zone member, or click Remove Member to remove an FA zone
member.
Renaming a Fabric Assist zone
Use the following procedure to change the name of an FA zone.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Fabric Assist tab.
3. Select the FA Zone you want to rename from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click Rename.
The Rename a Fabric Assist Zone dialog box opens.
5. Enter a new FA zone name and click OK.
The FA zone is renamed in the Zone Admin buffer.
Deleting a Fabric Assist zone
Use the following procedure to delete an FA zone.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Fabric Assist Zone tab.
3. Select the FA zone you want to delete from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click Delete.
The Confirm Deleting Fabric Assist Zone dialog box opens.
5. Click Yes.
The selected FA zone is deleted from the Zone Admin buffer.
Managing zone configurations
A zone configuration is a group of zones; zoning is enabled on a fabric by enabling a specific
configuration. You can specify members of a configuration using the following methods:
• Zone names
• QuickLoop names
• FA zone names
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 91
Page 92

Figure 28 shows a sample zoning database and the relationship between the zone aliases, zones, and
zoning configuration. The database contains one zoning configuration, myconfig, which contains two
zones: Zone A and Zone B. The database also contains four aliases, which are members of Zone A and
Zone B. Zone A and Zone B also have additional members other than the aliases.
Zone C onfiguration: myc onfig
Zone A
Alia s 1
WWN 1; WWN 2; WWN 3
Other E lements
<domain, portare a >; <A L _ P A>
Alia s 3
WWN 5; <AL_PA>
Other E lements
WWN 4; <domain, portarea>
Zone B
WWW 9
Figure 28 Sample zoning database
Alias 2
Alias 4
WWW 5; WWN 6; WWN7
Creating a zone configuration
Use the following procedure to create a zone configuration. After creating a zone configuration, you must
explicitly enable it for it to take effect.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select a format to display zoning members in the Member Selection List as described in ”Zoning
views” on page 85.
3. Click the Config tab.
4. Click Create.
The Create New Config dialog box appears.
5. Enter a name for the new configuration and click OK.
The new configuration is displayed in the Name list.
6. Click + signs in the Member Selection List to view the nested elements.
The choices available in the list depend on the selection made in the View menu.
7. Highlight an element in the Member Selection List that you want to include in your configuration.
The Add Member button becomes active.
8. Click Add Member to add configuration members.
Selected members are moved to the Config Members Window.
9. Repeat step 7 and step 8 to add more elements to your configuration.
92 Administering zoning
Page 93

10.Select Actions > Save Config Only to save the configuration changes.
To enable the configuration, see ”Enabling a zone configuration” on page 94.
NOTE: Changes made to the currently enabled configuration do not appear until you reenable the
configuration.
Adding or removing zone configuration members
Use the following procedure to add or remove members of a zone configuration.
NOTE: You can make changes to a configuration that is currently enabled; changes do not appear,
however, until you reenable the configuration.
Modifying the members of a zone configuration
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Config tab.
3. Select the configuration you want to modify from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click an element in the Member Selection List that you want to include in your configuration or click an
element in the Config Members that you want to delete.
5. Click Add Member to add a configuration member, or click Remove Member to remove a
configuration member.
6. Select Actions > Save Config Only to save the configuration changes.
To enable the configuration, see ”Enabling a zone configuration” on page 94.
Renaming a zone configuration
Use the following procedure to change the name of a zone configuration.
NOTE: You cannot rename the currently enabled configuration.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Config tab.
3. Click the configuration you want to rename from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click Rename.
The Rename a Config dialog box opens.
5. Enter a new configuration name and click OK.
The configuration is renamed in the configuration database.
6. Select Actions > Save Config Only to save the configuration changes.
To enable the configuration, see ”Enabling a zone configuration” on page 94.
Deleting a zone configuration
Use the following procedure to delete a zone configuration.
NOTE: You cannot delete a currently enabled configuration.
Deleting a disabled configuration
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Config tab.
3. Select the configuration you want to delete from the Name drop-down list.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 93
Page 94

4. Click Delete.
The Confirm Deleting Config dialog box opens.
5. Click Yes.
The selected configuration is deleted from the configuration database.
Enabling a zone configuration
Several zone configurations can reside on a switch at once, and you can quickly alternate between them.
For example, you might want to have one configuration enabled during business hours and another
enabled overnight. Only one zone configuration can be enabled at a time, however.
When you enable a zone configuration from Advanced Web Tools, keep in mind that the entire zoning
database is saved, and then the selected zone configuration is enabled.
If the zoning database size exceeds the maximum allowed, you cannot enable the zone configuration.
The zoning database summary displays the maximum zoning database size (see ”Displaying the zone
configuration summary” on page 96).
To enable a zone configuration
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select Actions > Enable Config.
The Enable Config dialog box opens.
3. Select the configuration to be enabled from the menu.
A warning is displayed.
4. Click OK to save and enable the selected configuration.
Disabling a zone configuration
When you disable the active configuration, the Advanced Zoning feature is disabled on the fabric, and
all devices within the fabric can communicate with all other devices. This does not mean that the zoning
database is deleted, however, it does mean that there is no configuration active on the fabric.
When you disable a zone configuration from Advanced Web Tools, keep in mind that the entire zoning
database is saved, and then the selected zone configuration is disabled.
To disable a zone configuration
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select Actions > Disable Zoning.
The Disable Config warning is displayed.
3. Click Yes to save and disable the current configuration.
Displaying the enabled zone configuration
The enabled zone configuration screen displays the actual content of the single zone configuration that is
currently enabled on the fabric, and whether it matches the configuration that was enabled when the
current zone admin session was launched or last refreshed (see Figure 29). The zones, QuickLoops, and
FA zones are displayed, and their contents (ports, WWNs, AL_PAs) are displayed next to them. Aliases
are not displayed in the enabled zone configuration. If there is no active zone configuration enabled on
the switch, a message is displayed to that effect.
The enabled configuration is listed in the top right corner of the Zone Admin module.
94 Administering zoning
Page 95

Figure 29 Effective Configuration window
Viewing the enabled zone configuration name without launching the Zone Admin module
Select a switch from the Fabric Tree.
The selected switch appears in the Switch View. The current zone configuration name (if one is enabled)
is displayed in the lower portion of the Switch Information View. If no zone configuration is enabled, the
field displays none.
Viewing detailed information about the enabled zone configuration
1. Launch the Zone Admin module, as described on page 83.
The zone configuration in effect at the time you launched the Zone Admin module is identified in the
top right corner. This information is updated every 15 seconds. It is also updated if you manually
refresh the Zone Admin module contents by clicking the refresh icon at the bottom right corner of the
Zone Admin module, or when you enable a configuration through the Zone Admin module.
CAUTION: Clicking the refresh icon overwrites all local unsaved zoning changes. If anyone has made
any changes to the zones outside of your Zone Admin session, those changes are applied.
2. Use one of the following methods to identify the most recently effective zone configuration without
saving or applying any changes you have made in the Zone Admin module:
• Select File > View Effective Configuration in the Zone Admin module.
• Click the enabled configuration button in the Zone Admin module.
Both of these actions display the Effective Configuration window. If no zone is enabled, a message is
displayed, indicating that there is no active zoning configuration on the switch.
3. Optional: Click Print to print the enabled zone configuration details.
The print dialog box opens.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 95
Page 96

Displaying the zone configuration summary
The zone configuration summary hierarchically lists all defined zoning elements known to the current Zone
Admin session, whether any of the listed configurations has been enabled, and whether any of the lower
level elements has been added as members of the higher level (aliases, zones, QuickLoops, FA zones)
structures. The zone configuration summary displays the entire contents of the fabric zoning database as it
was at the time the Zone Admin session was launched, or the most recently saved or refreshed
information, and any unsaved changes you make since the time the Zone Admin session is launched. It
provides the name of the zone configuration that was enabled at the time you launched the Zone Admin
session; however, keep in mind that the enabled configuration might have changed since then and that
this screen does not reflect those changes.
Viewing a zone configuration summary report
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select File > Print Summary.
The Zone Configuration summary window is displayed, as shown in Figure 30.
It is important to note that the summary displays the information based on the changes just made. If
current Zone Admin session changes have not yet been saved to the fabric, the information displayed
here is different from what is seen from the switch.
3. Optional: Click Print to print the zone configuration summary.
The print dialog box opens.
Figure 30 Zone Configuration summary
Creating a configuration analysis report
The configuration analysis report lists the following:
• SAN components (ports, WWNs, and AL_PAs) that are not included in the configuration
• SAN components (ports, WWNs, and AL_PAs) that are contained in the configuration but not in the
fabric
To create a configuration analysis report
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select the Config tab.
96 Administering zoning
Page 97

3. From the Name drop-down list, select a configuration to be analyzed.
4. Click Analyze Config.
A dialog box opens, asking whether you want to refresh the fabric before running the analysis.
5. Click Yes or No.
The configuration analysis window opens.
Displaying Initiator/Target Accessibility Matrix
The Initiator/Target Accessibility Matrix shows a list of initiators and a list of targets and indicates which
initiator can access which target, as shown in Figure 31.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Click the Config tab.
3. Select a configuration to be analyzed for device accessibility from the Name drop-down list.
4. Click Device Accessibility.
The Initiator/Target Accessibility Matrix for Config- Device Selection dialog box opens.
5. Select devices you want displayed in the accessibility matrix; select the radio button to select all
devices in the fabric or to select a subset of the devices.
If you select a subset, you must click the devices from the Select Devices list and click Add to move
them to the Evaluate for Accessibility list.
6. Click OK.
The Initiator/Target Accessibility Matrix opens. You can mouse over a target to display the symbolic
name of the device. You can also right-click the device nodes and click View Device Detail to display
detailed information about the selected device.
Figure 31 Initiator/Target Accessibility Matrix
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 97
Page 98

Managing the zoning database
This section contains the following procedures for managing the zoning database:
• Adding a WWN to multiple aliases, zones, and Fabric Assist zones, page 98
• Removing a WWN from multiple aliases, zones, and Fabric Assist zones, page 98
• Replacing a WWN in multiple aliases, Fabric Assist zones, and zones, page 98
• Searching for a zone member, page 99
• Clearing the zoning database, page 99
• Adding unzoned online devices to a zone or alias, page 100
• Removing offline devices from the zoning database, page 101
• Replacing offline devices, page 101
• Defining device aliases, page 101
Adding a WWN to multiple aliases, zones, and Fabric Assist zones
This procedure enables you to configure a WWN as a member in a zone configuration prior to adding
that device to the fabric. Specifically, it is useful if you want to add a WWN to all or most zoning entities.
The added WWN does not need to currently exist in the fabric.
Adding a WWN to the Zone Admin buffer
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select Edit > Add WWN.
The Add WWN dialog box opens.
3. Enter a WWN value in the WWN box.
4. Click OK.
The Add WWN dialog box shows all the zoning elements that will include the new WWN, including
aliases, zones, and FA zones. All of the elements are selected by default.
5. Click items in the list to select or unselect, and click Add to add the new WWN to all the selected
zoning elements.
The WWN is added to the Zone Admin buffer and can be used as a member.
Removing a WWN from multiple aliases, zones, and Fabric Assist zones
This procedure is useful if you want to remove a WWN from all or most zoning entities.
Deleting a WWN from the Zone Admin buffer
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select Edit > Delete WWN.
The Delete WWN dialog box opens.
3. Enter a WWN value in the WWN box.
4. Click OK.
The Delete WWN dialog box shows all the zoning elements that include the WWN.
5. Click elements in the list to select or unselect, and then click Delete to delete the WWN from all the
selected zoning elements.
The WWN is deleted from the selected items in the Zone Admin buffer.
Replacing a WWN in multiple aliases, Fabric Assist zones, and zones
This procedure enables you to replace a WWN throughout the Zone Admin buffer. This is helpful when
exchanging devices in your fabric and helps you to maintain your current configuration.
98 Administering zoning
Page 99

Replacing a WWN in the Zone Admin buffer
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select Edit > Replace WWN.
The Replace WWN dialog box opens.
3. Enter the WWN to be replaced in the Replace box.
4. Enter the new WWN in the By box.
5. Click OK.
The Replace WWN dialog box opens. It lists all the zoning elements that include the WWN.
6. Click elements in the list to select or unselect, and the click Replace to replace the WWN in all the
selected zoning elements.
The former WWN is replaced in the Zone Admin buffer by the new WWN, including within any alias
or zone in which the old WWN was a member.
Searching for a zone member
You can search zone member selection lists for specified strings of text. If you know some identifying
information about a possible member of a zoning entity, you can select the tab and view for that entity
and then search through its member selection list using the Search for Zone Member option. If the target
entity is an alias, zone, QuickLoop, or FA zone, the search domain includes elements like switch names
and domain numbers, port names and domain, port addresses, device WWNs and manufacturer names,
and also any aliases that might already have been defined. If the target entity is a configuration, zones,
FA zones, and QuickLoops are also included, along with the elements they contain.
The search starts from the top of the list, and when the target element is found, it is also selected in the
Member Selection List so it can be added or its parent or children can be found. By default, the Member
Selection List is searched from beginning to end one time. If you select the wraparound option, the search
continues to loop from the beginning to the end of the Member Selection List.
To search for a zone member
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select Edit > Search Member.
3. Enter the zone member name in the Member Name field.
Optional: Narrow the search by selecting one or more of the check boxes, such as Match Case.
4. Click Next to begin the zone member search.
Clearing the zoning database
Use the following procedure to disable the active zoning configuration, if one exists, and delete the entire
zoning database.
CAUTION: This action not only disables zoning on the fabric, but also deletes the entire zoning
database. This results in all devices being able to communicate with each other.
Disabling any active configuration and deleting the entire zoning database
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select Actions > Clear All.
The Disable Config warning is displayed.
3. Click Yes to do all of the following:
• Disable the current configuration.
• Clear the entire contents of the current Zone Admin buffer.
• Delete the entire persistent contents of the fabric zoning database.
This action is not recoverable.
Fabric OS 5.x Advanced Web Tools administrator guide 99
Page 100

Using zoning wizards
The Zone Admin module contains the following wizards to help you perform the zoning tasks:
• Add Un-zoned Devices
• Remove Offline Devices
• Replace Offline Devices
• Define Device Alias
The wizards are accessed through the Tools menu in the Zone Admin module. The following sections
describe the zoning tasks and the procedure for accessing the wizards for each task. The wizards are
self-explanatory, so the specific steps are not documented here.
NOTE: The left side of each wizard window lists the steps you need to take to complete the task. The
current step is in blue, as shown in Figure 32. Some of the wizards allow you to loop and repeat the task
multiple times; as a result, each step is listed in this panel, so that you not only see the steps that you still
need to perform, but also the steps that you have already performed. The step numbers may not match the
overall numbering in this panel.
Figure 32 Add Un-zoned Devices wizard
Adding unzoned online devices to a zone or alias
When zoning is enabled, devices that are not included in a zone configuration are inaccessible to other
devices in the fabric. Use the following procedure to identify online devices that are not zoned in any
zone configuration and add them to a zone or alias.
1. Launch the Zone Admin module as described on page 83.
2. Select Tools > Add Un-zoned Devices.
The Add Un-zoned Devices wizard starts.
3. Follow the steps outlined in the wizard.
The wizard displays unzoned devices and prompts you to select them and add them to an alias or a
zone.
100 Administering zoning
 Loading...
Loading...