HP STORAGEWORKS EVA DYNAMIC CAPACITY MANAGEMENT, STORAGEWORKS BUSINESS COPY EVA User Manual

HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions
Manager
user guide
Part number: T3680-96167
Third edition: February 2008

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2004-2008 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and
12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are
licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor’s standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth
in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting
an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows XP, and Windows NT are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Java is a US trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Oracle is a registered US trademark of Oracle Corporation, Redwood City, California.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
01.15.2008

Contents
Aboutthisguide ......................... 17
Intendedaudience..................................... 17
Prerequisites ....................................... 17
Relateddocumentation................................... 17
Documentconventionsandsymbols ............................. 18
HPtechnicalsupport.................................... 19
Subscriptionservice .................................... 19
HPwebsites ....................................... 19
Documentationfeedback .................................. 19
Productfeedback ..................................... 19
1ReplicationSolutionsManager .................. 21
Findingreplicationdocuments................................ 21
LoggingintotheGUI ................................... 21
What’snew........................................ 22
Newsupport ..................................... 22
NewGUIfeatures................................... 22
Newjobfeatures ................................... 22
Newjobtemplates................................... 22
Newjobcommands .................................. 22
NewCLUIfeatures................................... 22
ReleaseHistory .................................... 22
Overview......................................... 23
Capabilities...................................... 23
Localreplication.................................... 24
Remotereplication................................... 24
Serversoftware .................................... 25
Hostagentsoftware .................................. 25
CLUIsoftware..................................... 26
Jobs,templates,andcommands............................. 26
Simulationmode.................................... 27
Replicationkitsanddownloads ............................. 28
GUI........................................... 28
GUIwindowoverview ................................. 28
Configurationwindow ................................. 29
Contentpane..................................... 30
CLUIwindow(intheGUI)................................ 30
Keyboardandright-clickshortcuts ............................ 31
Menubar ...................................... 32
Navigationpane ................................... 33
Onlinehelpanduserguide............................... 33
Statusbar ...................................... 33
Toolbar ....................................... 33
Tooltips ....................................... 33
Viewhistory ..................................... 34
Configuration....................................... 34
Accessing the configurationwindow ........................... 34
CLUI ports configuration ................................ 35
RSM database configuration .............................. 35
RSMdatabasecleanup................................. 35
Jobs e-mail server configuration ............................. 35
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
3

Jobs run history configuration .............................. 36
Licenses configuration(applications) ........................... 36
Logs configuration................................... 36
Oracle security credentials configuration ......................... 36
Security credentials con fi guration ............................ 37
Securitycredentialsvs.tasks............................... 37
Simulationmode.................................... 39
Singlesign-on(SSO)withHPCommandViewEVA..................... 39
Storage management server configuration......................... 39
User preferences configuration.............................. 40
RSMdatabase ...................................... 40
AbouttheRSMdatabase................................ 40
Aboutexports..................................... 40
Aboutimports..................................... 40
ExportinganRSMdatabase............................... 41
ImportinganRSMdatabase............................... 41
ImportingaremoteRSMdatabase............................ 42
Completingimports .................................. 42
Troubleshooting...................................... 43
Troubleshooting-General................................ 43
Allstorageresourcesinunknownstate ........................ 43
Browserwindowisblank.............................. 43
Database filenameextensionismissing........................ 44
Documentsarenotvisiblewhenselected ....................... 44
Enablingfailsafemodewithamanagedsetfails.................... 44
Illegalcharacters ................................. 44
InvalidDRgrouppair-sourceandsource....................... 45
InvalidDRgroupsettings-failsafewithsynchronous................... 46
Jobinstancefailswithgeterrorlockmessage ..................... 46
Jobinteractswithwrongarray............................ 46
Jobwithhostvolumeremountfailsafteranuncleanunmount............... 46
Logicalvolumesandvolumegroupsinjobcommands.................. 47
Low-levelrefreshreturnsanerror........................... 47
MaximumDRGrouplogsizeerror.......................... 48
Monitorjobwindowhasnodetails.......................... 48
Pop-upwindowsarenotvisible ........................... 48
Resourceisnotselectable.............................. 49
Scheduledjobeventsdonotrun........................... 49
Scheduledjobeventruntimesarewrong(AM/PM)................... 49
Secondsnapcloneofthesamestoragevolumeorhostvolumefails ............ 50
Slowlogintimes.................................. 50
UnabletoresumeaDRgroup............................ 51
Troubleshooting-HP-UX ................................ 51
Hostagentdiscoveryhangsandtimesout-HP-UX ................... 51
JobwithCreateHostVolumecommandfails-HP-UX................... 51
JobwithMountEntireVolumeGroupcommandfails-HP-UX................ 52
HostvolumewithPVLinksmultipathing ........................ 52
Troubleshooting-Linux ................................. 52
Jobthatcreatesahostvolumerunsslowly-Linux.................... 52
Jobwithvolumegroupremountfails-Linux ...................... 53
Troubleshooting-Windows ............................... 53
Explorerdoesnotshowahostvolumeafterajobisrun-Windows ............ 53
Troubleshooting-Tru64UNIX .............................. 54
JobwithAdvFSreplicationfails-Tru64UNIX ..................... 54
2Replicationresources ...................... 55
Workingwithresources................................... 55
Bestpracticesforautomaticrefresh............................ 55
Copyingproperties .................................. 55
4

Copyingproperties-tips ................................ 56
Filteringdisplayedresources............................... 56
Globalrefreshmonitor ................................. 57
Organizingdisplayedresources ............................. 57
Refreshingdisplaypanes ................................ 58
Refreshingresources(automatic)............................. 58
Refreshingresources(global) .............................. 59
Refreshingindividualresources.............................. 59
Selectionofmultipleresources.............................. 60
Simulationmode.................................... 60
Resourceconcepts..................................... 60
Aboutreplicationresources ............................... 60
Resourcestates .................................... 61
ResourcenamesandUNCformats............................ 62
Simulationmode.................................... 63
Licenses ....................................... 64
Licensedisplays.................................. 64
Licensestates ................................... 65
Oracle-integrationlicensesoverview ......................... 65
Oracle-integrationlicensepolicies .......................... 65
Replicationlicensesoverview ............................ 66
Replicationlicensepolicies ............................. 66
Dynamiccapacitymanagementlicensepolicy..................... 67
SecurityCredentials .................................. 67
Securitycredentialsfortheserver........................... 67
Securitycredentialsforenabledhosts......................... 67
SecuritycredentialsforOracledatabases ....................... 68
Securitycredentialsvs.tasks............................. 69
Topologyviews ...................................... 70
Abouttopologyviews ................................. 70
Displayingthetopologytab............................... 72
DRgroupstopologyview................................ 72
Hostvolumestopologyview............................... 74
Virtualdiskstopologyview ............................... 76
Filtersfortopologyviews ................................ 78
Tips(topologyviews).................................. 79
3DRGroups........................... 81
WorkingwithDRgroups .................................. 81
AboutDRgroupresources ............................... 81
DRgroupactionssummary ............................... 81
DRgroupactionscrossreference............................. 82
DRgrouppropertiessummary.............................. 84
DRgroupviews .................................... 84
AddingDRgroupstoamanagedset........................... 85
AddingvirtualdiskstoaDRgrouppair.......................... 85
CreatingaDRgrouppair................................ 86
DeletingaDRgrouppair................................ 86
EditingDRgroupproperties............................... 87
EnablingfailsafemodeforaDRgrouppair ........................ 87
Disablingfailsafemode................................. 88
FailingoveraDRgrouppair .............................. 88
Forcingafullcopy................................... 89
Launchingthedevicemanager.............................. 89
Listingindividualresourceevents............................. 89
Low-levelrefreshingDRgroups.............................. 90
RemovingDRgroupsfromamanagedset......................... 90
RemovingvirtualdisksfromaDRgrouppair........................ 90
ResumingaDRgrouppair ............................... 91
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
5

RevertingaDRgrouppairtohome............................ 91
SuspendingaDRgrouppair .............................. 92
UsingDRgroups ................................... 92
ViewingDRgroups .................................. 94
ViewingDRgroupproperties .............................. 95
DRgroupconcepts..................................... 95
DRgrouppairs(sourceanddestination).......................... 95
Autosuspend..................................... 97
Cascadedreplication ................................. 97
Copystate ...................................... 98
Destinationaccessmode ................................ 98
DRgroupstatesandicons ............................... 98
Failover ....................................... 98
Failsafemodeandstates ................................ 99
Fullcopymode .................................... 99
Home ........................................ 100
I/Othrottling ..................................... 100
Jobcommandprocessing................................ 101
Logs......................................... 101
Logoverviewandstates .............................. 101
Loganddiskgroupplanning ............................ 102
Logsize ..................................... 102
Logging ..................................... 103
Logmerging ................................... 103
Logdiskandstates................................... 104
Low-levelrefresh.................................... 104
ManagedsetsofDRgroups............................... 104
Normalization..................................... 105
Operationalstate-blocked ............................... 105
Remotereplicationguidelines .............................. 106
Suspendonfailover .................................. 107
Suspensionstate.................................... 107
Writemode(async/syncreplication) ........................... 108
Writemodetransitions ................................. 109
4Enabledhosts.......................... 111
Workingwithenabledhosts................................. 111
Aboutenabledhostresources .............................. 111
EnabledHostsactionssummary ............................. 111
Enabledhostsactionscrossreference........................... 111
Enabledhostspropertiessummary ............................ 112
Enabledhostsviews .................................. 112
Addingenabledhosts ................................. 113
Addingenabledhoststoamanagedset ......................... 113
Deletingenabledhosts................................. 114
Executing a host script, command or batch file....................... 114
Low-levelrefreshingenabledhosts ............................ 115
Removingenabledhostsfromamanagedset ....................... 115
Settingsecuritycredentialsforenabledhosts........................ 116
Viewingenabledhosts ................................. 116
Viewingenabledhostproperties............................. 116
Enabledhostconcepts ................................... 117
Enabledandstandardhosts............................... 117
Hostnamesandports ................................. 117
Low-levelrefreshofenabledhosts ............................ 117
Securitycredentialsforenabledhosts........................... 117
5Hostvolumes.......................... 119
Workingwithhostvolumes ................................. 119
6

Abouthostvolumeresources .............................. 119
Hostvolumeactionssummary.............................. 119
Hostvolumeactionscrossreference ........................... 120
Hostvolumepropertiessummary............................. 124
Hostvolumeviews................................... 124
Addinghostvolumestoamanagedset.......................... 126
Cancelling(removing)replicasfromroundrobinrotation................... 126
CreatingaDRgrouppair(fromhostvolume)........................ 126
Creatingamanagedsetforahostdiskdevicecontainer .................. 127
Creatingamanagedsetofcontainersforhostvolumes ................... 127
Creatingamanagedsetofcontainersforhostvolumegroups ................ 128
Creatinghostvolumes ................................. 128
Creatinglocalreplicas................................. 129
Creatinground-robinreplicas .............................. 129
Deletingreplicas.................................... 129
Deletinghostvolumes,hostvolumegroups,andhostdiskdevices............... 130
Editingreplicaproperties................................ 130
Flushing the filesystemcacheofhostvolumesandhostvolumegroups............. 130
Mountinghostvolumes(assigningadriveletter) ...................... 131
Removinghostvolumesfromamanagedset........................ 131
Restoringhostvolumes(InstantRestore) .......................... 131
Unmountinghostvolumes(removingadriveletter) ..................... 132
Usingsnapclones ................................... 132
Usingsnapshots.................................... 133
Usinglogicalvolumesandvolumegroups......................... 133
Usingrawdisks.................................... 133
Viewinghostvolumeresources.............................. 134
Viewinghostvolumeresourceproperties ......................... 134
Extendinghostvolumecapacity ............................. 135
Shrinkinghostvolumecapacity ............................. 135
Settingadynamiccapacitypolicy ............................ 136
Editingadynamiccapacitypolicy ............................ 136
Removingadynamiccapacitypolicy........................... 136
Hostvolumeconcepts ................................... 137
Hostvolumesoverview................................. 137
HostvolumesFAQ................................... 138
DiskDevices ..................................... 139
Filesystemtypes.................................... 139
InstantRestore..................................... 139
Logicalvolumesandvolumegroups ........................... 139
LUN......................................... 140
Mirrorclones-fractured................................. 140
Mirrorclones-synchronized ............................... 141
MirrorcloneFAQ.................................... 142
Mirrorcloneguidelines ................................. 142
Mirrorclonestates ................................... 143
Mountingalllogicalvolumesinareplicatedvolumegroup.................. 144
Mountpoints(driveletters)anddevicenames ....................... 144
Partitionsandslices .................................. 145
Rawdisks ...................................... 148
Localreplicationwizard ................................ 148
ReplicaRepository................................... 148
Roundrobinreplicas(wizard) .............................. 149
Snapclones(hostvolume)................................ 149
Snapshots(hostvolume) ................................ 149
SnapshotFAQ..................................... 149
Snapshottypes(allocationpolicy) ............................ 150
Types(components) .................................. 151
Dynamiccapacitymanagement ............................. 151
DC-Managementoperation............................. 151
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
7

Methods for resizing a host volume filesystemandvirtualdisk .............. 152
DC-Managementsupport.............................. 153
Selectingtheproperdynamiccapacitypolicythresholds................. 155
UsingDC-Managementwithreplication........................ 156
DC-ManagementFAQ ............................... 156
DC-Managementbestpractices ........................... 157
DC-Managementexamples ............................. 157
6Jobs.............................. 159
Workingwithjobs..................................... 159
Aboutjobs ...................................... 159
Jobactionssummary.................................. 159
JobPlanning-Tru64UNIX ............................... 160
SuspendingI/ObeforereplicatingAdvFSvolumes-Tru64UNIX ............. 160
Jobactionscrossreference ............................... 161
Jobpropertiessummary ................................ 162
Jobviews....................................... 162
Abortingjobinstances ................................. 163
Continuingjobinstances ................................ 164
Copyingjobs..................................... 164
Creatingjobs..................................... 165
Deletingjobs ..................................... 165
Deletingjobinstances ................................. 165
Developingjobs.................................... 166
Editingjobs...................................... 166
Jobeditingtipsandshortcuts .............................. 167
Editingindividualcommands(tasks) ........................... 168
Generatingjobtemplates................................ 169
Importinglegacyjobs ................................. 169
Importingoverview................................. 169
Preparingtoimport ................................ 170
LegacyBC2.xjobcommandequivalence....................... 170
Logicalvolumesandvolumegroupsinjobcommands.................... 173
Monitoringandmanagingjobinstances ......................... 174
Pausingjobinstances.................................. 174
Resourceisnotselectable................................ 175
Scheduledjobeventsdonotrun............................. 175
Runningjobs ..................................... 176
Selectingvaluesforarguments.............................. 176
Schedulingjobevents ................................. 177
Creatingscheduledjobevents............................ 177
Editingscheduledjobevents............................. 177
Enablinganddisablingscheduledjobevents ..................... 177
Choosingaruninterval............................... 178
Removingscheduledjobevents ........................... 179
Viewingscheduledjobevents............................ 179
Validatingjobs .................................... 179
Viewingjobstatus................................... 180
Viewingjobsandjobinstances ............................. 180
Viewingjobproperties................................. 181
Jobconcepts ....................................... 181
Joblanguageoverview................................. 181
Jobs,templates,andcommands............................. 182
Jobinstances ..................................... 183
Abortedjobinstances ................................. 183
Arguments ...................................... 184
Argumentlists..................................... 184
Assignments(variables)................................. 184
Branches....................................... 185
Commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
8

Commandresultvalues................................. 186
Comments ...................................... 190
E-mailfromjobs.................................... 191
Exits......................................... 191
Implicitjobs...................................... 191
Implicitjobstartup................................... 191
Importedjobs..................................... 191
Jobcommandslist................................... 192
Jobtemplateslist ................................... 199
Labels ........................................ 200
Pauseandcontinue .................................. 200
ResourcenamesandUNCformats............................ 200
Simultaneousjobinstances ............................... 202
Statusandstates.................................... 203
Transactions ..................................... 204
Validation ...................................... 204
Wait/nowaitargument................................. 205
Jobtemplates....................................... 206
Emptytemplate .................................... 206
Fracturehostvolumes,mounttoahost(template)...................... 207
Instant restore storage volumes to other storage volumes (template) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Mountexistingstoragevolumes(template)......................... 210
Performcascadedreplication(template).......................... 212
Performplannedfailover(template)............................ 216
Performunplannedfailover(template)........................... 218
Replicate (via snapclone) a host volume multipletimes,mounttoahost(template)........ 219
Replicatehostdiskdevices,mounttoahost(template).................... 222
Replicatehostvolumegroup,mountcomponentstoahost(template) ............. 223
Replicatehostvolumegroup,mountentiregrouptoahost(template) ............. 226
Replicatehostvolumes(template)............................. 228
Replicatehostvolumes,mounttoahost(template) ..................... 229
Replicatehostvolumes,mounttoahost,thentoadifferenthost(template) ........... 232
Replicatehostvolumesviapreallocatedreplication,mounttoahost(template) ......... 234
Replicatehostvolume,mountcomponentstoahost(template) ................ 236
Replicaterawstoragevolumesmount(raw)toahost(template)................ 238
Replicatestoragevolumes(template) ........................... 239
Replicatestoragevolumesviapreallocatedreplication(template)............... 241
ReplicateOracletablespaces(template).......................... 243
ReplicateOracletablespaces,mounttoahost(template) .................. 244
Replicate Oracle tablespaces via preallocatted replication, mount to a host (template) . . . . . . 246
RestoreOracletablespaces(template) .......................... 249
SetupContinuousAccess(remotereplicationtemplate) ................... 250
ThrottlereplicationI/O(remotereplicationtemplate) .................... 252
Unmountanddeleteexistinghostvolumes(template) .................... 253
Unmountexistinghostvolumes(template) ......................... 254
Jobcommands ...................................... 255
//(comment)..................................... 255
AddAllOracleTablespacesToRepository .......................... 255
AddDrGroupMember ................................. 256
AddOracleArchiveLogFilesToRepository.......................... 257
AddOracleTablespacesToRepository ........................... 257
AddReplicaToReplicaRepository ............................. 258
AddReplicasToReplicaRepository............................. 258
CombineLists ..................................... 259
ConvertStorageVolumeIntoContainer ........................... 259
ConvertStorageVolumesInManagedSetIntoContainers .................... 260
ConvertStorageVolumesIntoContainers .......................... 260
ConvertStorageVolumesIntoContainersUsingRepository.................... 261
CreateContainer.................................... 261
CreateContainerForHostDiskDevice............................ 262
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
9

CreateContainersForHostVolume............................. 263
CreateContainersForHostVolumeGroup .......................... 263
CreateDiskDevice ................................... 264
CreateDrGroup .................................... 265
CreateDrGroupFromHostVolume............................. 266
CreateHostVolume................................... 268
CreateHostVolumeDiscrete ............................... 269
CreateHostVolumeFromDiskDevices............................ 270
CreateHostVolumeGroup ................................ 271
CreateHostVolumesUsingRepository ........................... 272
CreateOracleRepository ................................ 273
CreateRestoredHostVolumesUsingRepository........................ 273
CreateReplicaRepository ................................ 274
CreateStorageVolume ................................. 275
DeleteContainer.................................... 276
DeleteDrGroup .................................... 276
DeleteDrGroupMember................................. 277
DeleteHostVolume................................... 277
DeleteHostVolumeGroup ................................ 278
DeleteHostVolumesUsingRepository............................ 279
DeleteOracleRepository................................. 280
DeleteReplicaRepository ................................ 280
DeleteStorageVolume.................................. 280
DeleteStorageVolumes ................................. 281
DeleteStorageVolumesInManagedSet........................... 281
DeleteStorageVolumesUsingRepository .......................... 282
DetachMirrorclones .................................. 282
DiscoverDiskDevice .................................. 283
DiscoverDiskDevices .................................. 283
DiscoverDiskDevicesForDrGroup............................. 284
DiscoveryRefresh(obsolete) ............................... 285
Exit ......................................... 285
Export........................................ 286
FailoverDrGroup.................................... 286
FailoverDrGroups ................................... 287
FlushCache...................................... 287
ForceFullCopyDrGroup................................. 288
FractureHostDiskDeviceMirrorclone............................ 289
FractureHostVolumeGroupMirrorclones .......................... 289
FractureHostVolumeMirrorclones............................. 290
FractureMirrorclones .................................. 291
Import........................................ 291
InstantRestoreFromMirror ................................ 292
InstantRestoreFromSnapshot............................... 293
Launch........................................ 293
LaunchJob ...................................... 294
Log ......................................... 295
MirrorcloneHostDiskDeviceToContainer .......................... 295
MirrorcloneHostDiskDeviceToContainerInManagedSet.................... 296
MirrorcloneHostVolumeGroupToContainers ........................ 297
MirrorcloneHostVolumeGroupToContainersInManagedSet .................. 298
MirrorcloneHostVolumeToContainers ........................... 299
MirrorcloneHostVolumeToContainersInManagedSet..................... 300
MirrorcloneStorageVolumeToContainer .......................... 301
MountEntireVolumeGroup................................ 302
MountHostVolume................................... 303
MountHostVolumesUsingRepository............................ 304
MountVolumeGroupComponent ............................. 304
Pause ........................................ 305
PresentStorageVolume ................................. 306
10

PresentStorageVolumes................................. 306
RemoveDiskDevice................................... 307
ResyncMirrorclone................................... 308
ResyncMirrorclones .................................. 308
RetainLatestRoundRobinReplicasForHostDiskDevice ..................... 309
RetainLatestRoundRobinReplicasForHostVolume....................... 309
RetainLatestRoundRobinReplicasForHostVolumeGroup.................... 310
SendEmail ...................................... 311
SetDiskGroupForSnapclone............................... 311
SetDrGroupAutoSuspend................................ 312
SetDrGroupComments ................................. 312
SetDrGroupDestinationAccess.............................. 313
SetDrGroupFailsafe .................................. 313
SetDrGroupHome ................................... 314
SetDrGroupIoMode .................................. 314
SetDrGroupMaxLogSize ................................ 315
SetDrGroupName................................... 315
SetDrGroupSuspend.................................. 316
SetHostDiskDeviceWriteCacheMode ........................... 317
SetHostVolumeGroupWriteCacheMode.......................... 318
SetHostVolumeWriteCacheMode............................. 319
SetHostVolumesWriteCacheMode ............................ 320
SetListVariable..................................... 321
SetMountPointsPrefixInRepository............................. 321
SetNotificationPolicy.................................. 322
SetOracleModeUsingRepository............................. 323
SetStorageVolumeName ................................ 324
SetStorageVolumeWriteCacheMode ........................... 324
SetStorageVolumesWriteCacheMode ........................... 325
SetVariable...................................... 325
SetWriteCacheModesUsingRepository .......................... 326
SnapcloneDiskDevice.................................. 326
SnapcloneHostDiskDeviceToContainerInManagedSet .................... 327
SnapcloneHostVolume ................................. 328
SnapcloneHostVolumeGroup .............................. 329
SnapcloneHostVolumeGroupToContainersInManagedSet .................. 330
SnapcloneHostVolumeToContainers............................ 331
SnapcloneHostVolumeToContainersInManagedSet ..................... 332
SnapcloneOracleToContainersUsingRepository....................... 333
SnapcloneOracleUsingRepository ............................ 334
SnapcloneStorageVolume................................ 335
SnapcloneStorageVolumeToContainer........................... 336
SnapcloneStorageVolumesToContainers.......................... 336
SnapshotDiskDevice .................................. 337
SnapshotHostDiskDeviceToContainerInManagedSet..................... 338
SnapshotHostVolume.................................. 339
SnapshotHostVolumeGroup............................... 340
SnapshotHostVolumeGroupToContainersInManagedSet ................... 341
SnapshotHostVolumeToContainers ............................ 342
SnapshotHostVolumeToContainersInManagedSet...................... 343
SnapshotOracleToContainersUsingRepository ....................... 344
SnapshotOracleUsingRepository............................. 345
SnapshotStorageVolume ................................ 346
SnapshotStorageVolumeToContainer ........................... 347
SnapshotStorageVolumesToContainers .......................... 347
SwitchOracleArchiveLogFilesUsingRepository........................ 348
TestJobState...................................... 348
UnmountEntireVolumeGroup............................... 349
UnmountHostVolume.................................. 350
UnmountHostVolumes ................................. 350
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
11

UnmountHostVolumesUsingRepository........................... 351
UnpresentStorageVolume ................................ 352
UnpresentStorageVolumes................................ 352
ValidateHost ..................................... 353
ValidateHostVolume .................................. 353
ValidateHostVolumeDoesNotExist ............................ 354
ValidateHostVolumeGroup ............................... 355
ValidateHostVolumeMirrorclones............................. 355
ValidateOracleDatabase ................................ 356
ValidateOracleTablespaces ............................... 357
ValidateSnapcloneHostVolume.............................. 357
ValidateSnapcloneHostVolumeGroup........................... 358
ValidateSnapcloneStorageVolume ............................ 359
ValidateSnapshotHostVolume .............................. 359
ValidateSnapshotHostVolumeGroup ........................... 360
ValidateSnapshotStorageVolume............................. 361
ValidateStorageSystem ................................. 361
ValidateStorageVolume................................. 362
ValidateStorageVolumes ................................ 362
Wait......................................... 363
WaitDrGroupNormalization............................... 363
WaitDrGroupSynchronizationTransition .......................... 364
WaitForHostDiskDeviceWriteCacheFlush ......................... 364
WaitForHostVolumeGroupWriteCacheFlush ........................ 365
WaitForHostVolumeWriteCacheFlush ........................... 365
WaitForHostVolumesWriteCacheFlush........................... 366
WaitForJob...................................... 367
WaitForStorageVolumeDiscovery............................. 368
WaitForStorageVolumesDiscovery ............................ 368
WaitForStorageVolumeWriteCacheFlush.......................... 369
WaitForStorageVolumesWriteCacheFlush ......................... 369
WaitForWriteCacheFlushUsingRepository ......................... 370
WaitHostDiskDeviceNormalization............................ 370
WaitHostVolumeNormalization ............................. 371
WaitStorageVolumeNormalization ............................ 371
WaitStorageVolumesNormalization............................ 372
WaitUntil....................................... 372
WaitVolumeGroupNormalization............................. 373
7Managedsets ......................... 375
Workingwithmanagedsets................................. 375
Aboutmanagedsets.................................. 375
Managedsetactionssummary ............................. 375
Managedsetactionscrossreference ........................... 375
Managedsetpropertiessummary ............................ 376
Managedsetviews .................................. 376
Addingresourcestoamanagedset ........................... 377
Creatingmanagedsets................................. 377
Deletingmanagedsets................................. 378
Renamingmanagedsets ................................ 378
Removingresourcesfrommanagedsets.......................... 378
Viewingmanagedsets................................. 379
Viewingmanagedsetproperties............................. 379
Managedsetsconcepts................................... 379
Managedsetsoverview................................. 379
ManagedsetsofDRgroups............................... 380
Managedsetsofvirtualdisks(orcontainers)........................ 380
8Oracle............................. 383
12

WorkingwithOracleresources ............................... 383
AboutOracleresources................................. 383
Replicating(backingup)Oracleresources......................... 383
ReplicatingOracleresourcesusingtheGUI ...................... 383
ReplicatingOracleresourcesusingjobs........................ 384
ReplicatingOracledatabasesusingpreallocatedsnapclones............... 385
ReplicatingOracledatabasesusingsnapclones .................... 385
ReplicatingOracledatabasesusingsnapshots..................... 385
ReplicatingOracletablespacesusingpreallocatedsnapclones.............. 386
ReplicatingOracletablespacesusingsnapclones.................... 386
ReplicatingOracletablespacesusingsnapshots .................... 387
Restoring(recovering)Oracleresources.......................... 387
RestoringOracleresourcesusingtheGUI ....................... 387
RestoringOracleresourcesusingjobs......................... 387
Oracleactionssummary ................................ 388
Oracleactionscrossreference.............................. 389
Oraclepropertiessummary............................... 390
Oracleviews ..................................... 391
CheckingOracle-integrationlicenses............................ 392
CreatingrepositoriesofOracleresources ......................... 392
DeletingrepositoriesofOracleresources ......................... 392
SettingsecuritycredentialsforOracledatabases...................... 393
ViewingOracleresources................................ 393
ViewingOracleresourceproperties............................ 393
Oracleresourceconcepts.................................. 394
Oraclereplication(backup)andrestore(recovery)overview ................. 394
Oracle-integrationlicensesoverview ........................... 395
Oracle-integrationlicensepolicies ............................ 395
Oracleresourceguidelines ............................... 395
Oraclearchivedredologs ............................... 396
Oracle control files................................... 396
Oracledatabases ................................... 396
Oracle datafiles.................................... 396
Licensedisplays.................................... 396
Licensestates ..................................... 397
MountpointsforOraclerestores............................. 397
Oracleonlineredologs ................................ 397
Oracleresourcesmode................................. 398
RepositoriesforOracleresources............................. 398
SecuritycredentialsforOracledatabases ......................... 398
Oracletablespaces .................................. 399
9Storagesystems......................... 401
Workingwithstoragesystems................................ 401
Aboutstoragesystemresources ............................. 401
Storagesystemactionssummary............................. 401
Storagesystemactionscrossreference .......................... 401
Storagesystempropertiessummary............................ 402
Storagesystemviews.................................. 402
Addingstoragesystemstoamanagedset......................... 403
Checkingandprintingstoragesystemlicenses....................... 403
Launchingthedevicemanager.............................. 403
Listingindividualresourceevents............................. 404
Removingstoragesystemsfromamanagedset....................... 404
Viewingstoragesystems ................................ 404
Viewingstoragesystemproperties ............................ 405
Storagesystemconcepts .................................. 405
Replicationlicensesoverview .............................. 405
Replicationlicensepolicies ............................... 405
Controllersoftwarefeatures............................... 406
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
13

Controllersoftwarefeatures-localreplication ....................... 406
Controllersoftwarefeatures-remotereplication ...................... 407
Diskgroups...................................... 408
Storagesystemtypes.................................. 408
10Virtualdisks.......................... 409
Workingwithvirtualdisks.................................. 409
Aboutvirtualdiskresources............................... 409
Virtualdiskactionssummary .............................. 409
Virtualdiskactionscrossreference............................ 410
Virtualdiskpropertiessummary ............................. 411
Virtualdiskviews ................................... 412
Addingvirtualdiskstoamanagedset .......................... 412
Creatingcontainersforvirtualdisks ........................... 413
CreatingaDRgrouppair................................ 413
Creatingmirrorclones ................................. 414
Creatingsnapclones(preallocated)............................ 414
Creatingsnapclones(standard) ............................. 414
Creatingsnapshots(preallocated) ............................ 415
Creatingsnapshots(standard).............................. 415
Creatingvirtualdisks.................................. 416
Deletingvirtualdisks.................................. 416
Detachingmirrorclones................................. 417
Editingvirtualdiskproperties .............................. 417
Fracturingmirrorclones................................. 417
Launchingthedevicemanager.............................. 418
Listingindividualresourceevents............................. 418
Restoringvirtualdisks(InstantRestore)........................... 419
Low-levelrefreshingvirtualdisks ............................. 419
Presentingvirtualdisks ................................. 419
Removingvirtualdisksfromamanagedset ........................ 420
RemovingvirtualdisksfromaDRgrouppair........................ 420
Restoringvirtualdisks(InstantRestore)........................... 421
Resynchronizingmirrorclones .............................. 421
Unpresentingvirtualdisks................................ 422
Viewingvirtualdisks.................................. 422
Viewingvirtualdiskproperties.............................. 423
Virtualdiskconcepts.................................... 423
Virtualdisksoverview ................................. 423
Controllersoftwarefeatures............................... 423
Controllersoftwarefeatures-localreplication ....................... 423
Controllersoftwarefeatures-remotereplication ...................... 424
Cachepolicies .................................... 425
Containers ...................................... 426
Containerguidelines.................................. 427
Diskgroups...................................... 427
CrossVraidreplication................................. 428
CrossVraidFAQ.................................... 428
Diskgroups...................................... 428
CrossVraidguidelines ................................. 429
Instantrestoreoverview(virtualdisks)........................... 430
Instantrestorefrommirrorclones ............................. 430
Instantrestorefromsnapclones.............................. 431
Instantrestorefromsnapshots .............................. 431
Instantrestore..................................... 431
Normalization..................................... 432
Low-levelrefreshofvirtualdisks ............................. 432
LUN......................................... 432
Preferredcontroller................................... 432
Presentation(tohost).................................. 433
14

Remotereplicationguidelines .............................. 433
Redundancylevel(Vraid) ................................ 434
Snapclones...................................... 434
SnapcloneFAQ.................................... 435
Snapcloneguidelines.................................. 435
Snapshots ...................................... 436
SnapshotFAQ..................................... 436
Snapshotguidelines .................................. 437
Snapshotspervirtualdisk................................ 437
Snapshottypes(allocationpolicy) ............................ 438
Tru64UNIXhostvolumes................................ 439
Types ........................................ 439
Virtualdiskguidelines ................................. 439
11Events ............................ 441
Workingwithevents .................................... 441
Aboutevents ..................................... 441
Eventactionssummary................................. 441
Eventactionscrossreference .............................. 441
Refreshingdisplaypanes ................................ 442
Organizingdisplayedevents .............................. 442
Viewingevents .................................... 443
Viewingthetracelog.................................. 444
Filteringdisplayedevents................................ 444
Eventconcepts ...................................... 444
Eventsoverview.................................... 444
Eventslog ...................................... 445
Eventlogviews .................................... 446
Eventseverity ..................................... 446
Tracelog....................................... 446
12CLUI............................. 447
AccessingtheCLUIviaGUI................................. 447
CLUIdocumentation .................................... 447
CopyingCLUIcommandresponses.............................. 447
LegacyHPEVMCLcommandscrossreference ......................... 448
ReusingCLUIcommands .................................. 449
UsingCLUIhelp...................................... 449
13Glossary ........................... 453
Glossary......................................... 453
Index .............................. 455
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
15

Tables
1
..Documentconventions ............................. 18
16

About this guide
This guide describes how to use HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager (the replication
manager).
For the latest information about this product, see HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager release
notes. The location of this and other documents and web sites mentioned in this guide is provided in
“Related documentation” on page 17.
Intended aud
This g uide is intended for operators and administrators of storage area networks (SANs) that include
supported HP storage arrays. Readers should be familiar with:
• Local area networks
• Storage are
• Operating systems, including Windows
• Oracle administration, if using the replication manager to replicate Oracle databases
ience
anetworks
Prerequisites
Use of this product requires:
• HP storage array and controller software
• Array management sof tware
• Local and/or remote replication licenses
• Replication manager server and host agent software
• Application integration license (optional)
For supported storage arrays, management server hardware and software, and replication environments,
including restrictions, see HP StorageWorks EVA software compatibility reference on the HP StorageWorks
Continuous Access EVA or HP StorageWorks Business Copy EVA web site.
Related documentation
To find the following documents, browse to the Manuals page of the HP Business Support Center web site:
ttp://www.hp.com/support/manuals. In the Storage section, click Storage software and then select
h
the prod
uct.
Replication Solutions Manager
• HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager online help
• HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager user guide
• HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager job command reference
• HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Ma nager command line user interface reference
• HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager administrator guide
• HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager installation guide
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
17

Other
• HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager release notes
• HP StorageWorks Enterprise Virtual Array compatibility reference
• HP StorageWorks Enterprise Virtual Array license key installation instructions
• HP StorageWorks Business Copy EVA administrator guide
• HP StorageWorks Continuous Access EVA administrator guide
Document con
Table 1 Document conventions
Convention
Blue text: Table 1
Blue, underlined text: http://www.hp.com
Bold text
Italic text Text emphasis
Monospace text
Monospace, italic text
Monospace, bold text
ventions and symbols
Element
Cross-reference links and e-mail addresses
Web site addresses
• Keys that ar
• Text typed
• GUI elemen
• File and directory names
• System output
• Code
• Commands, their arguments, and argument values
• Code variables
• Command variables
Emphasized monospace text
as menu an
boxes
epressed
into a GUI element, such as a box
ts that are clicked or selected, such
d list items, buttons, tabs, and check
CAUTION:
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
IMPORTANT:
Provides clarifying information or specific instructions.
NOTE:
Provides additional information.
TIP:
Provides helpful hints and shortcuts.
18
About this guide

HP technical support
Telephone numbers for worldwide technical support are listed on the HP support web site:
h
ttp://www.hp.com/support/.
Collect the f
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Product mod
• Error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed q
For continuous quality improvement, calls may b e recorded or monitored.
ollowing information before calling:
el names and numbers
uestions
Subscription service
HP recommends that you register your product at the Subscriber’s Choice for Business web site:
h
ttp://www.hp.com/go/e-updates.
After registering, you will receive e-mail notification of product enhancements, new driver versions,
firmware updates, and other product resources.
HP web si
For additional information, see the following HP web sites:
•h
•http://
•http://www.hp.com/service_locator
•http://www.docs.hp.com
tes
ttp://www.hp.com
www.hp.com/go /storage
Documentation feedback
HP welcomes your feedback.
To make comments and suggestions about product documentation, please send a message to
storagedocsfeedback@hp.com. All submissions become the property of H P.
Produc
t feedback
To make comments and suggestions about HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager, please send
a message to EVAReplication@hp.com.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
19

20
About this guide

1 Replication Solutions Mana ger
Finding replication documents
Replication software kits.Ifyouhaveareplication kit, the Documentation CD includes PDF fi les of several
(but not all) print-based documents and a stand-alone copy of the replication manager online help and
user guide. No printed documents are in the kit, other than a kit contents booklet.
To view the replication manager online help directly from the Documentation CD:
1. Insert the Documentation CD into a CD drive.
2. Navigate to the folder hpRsmHelpUserGuide.
3. In the folder, double-click the file help_start.htm.Theonline help and user guide opens in
abrowserwindow.
Replication manager GUI. The replication manager GUI includes the online help and user guide and PDF
files of several (but not all) print-based documents.
1. Start or browse to the replication manager GUI.
2. To view the online help and user guide, select Help > Topics.
3. To view a PDF document, select Help > document name.
HP web site. Replication documents are available on the HP StorageWorks web site.
1.
Browse to the HP web site. See “ Helpful web sites”onpage19.
2. Navigate to the HP Business Copy EVA and/or HP Continuous Access EVA pages.
• For print-based documents, select Technical documentation.
• For a stand-alone copy of the replication manager online help and user guide, select
Software & d rivers.
Logging in to the GUI
To log in
1. Do one o
2. Enter
Notes
• Replication manager service. The replication manager server software runs continuously as a
• Browsing. You can enter a server name, fully-qualified server name, or I P address. Specific
the replication manager GUI:
f the following,
•Browseto<server name>:4096.Seenotes.
• On a management server desktop, select Start > Programs > HP Replication Solutions
Manage
• Open the replication manager through another HP application. See notes.
An account login window opens.
The replication manager GUI appears.
service on a m anag em ent server. This enables the server to run jobs, process CLUI commands,
interact with enabled hosts (host agents), and access storage resources whether or not the GUI is
active.
browsers and JREs are required. See HP StorageWorks EVA software compatibility reference for
support details.
r, or double-click the replication manager icon.
auseraccountnameandpasswordandthenclickOK.Seenotes.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
21

• Desktop The replication manager appears in a management server’s start menu and as
adesktopicon.
• Other applicat
Manager Administrator guide.
• User accounts. A default account may exist (user name: admin,password: nimda). For more
about securit
What’s new
New support
ions. For other access m ethods, see the HP StorageW orks Replication Solutions
y, see the HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager Administrator guide.
Version 4.0 i
StorageWork
• Dynamic capacity management. Dynamic capacity management (DC-Management) is
supported on HP-UX host agents. For more information on the con figuration required for using
DC-Management, see DC-Management support.
• Storage sy
• HP Command View EVA. Support is added for HP Command View EVA version 7.0.1 and
version 8.0.
• Create con
disk devi
ncludes the following new or updated support compared to version 3.1. See the HP
s Enterprise Virtual Array compatibility reference for support details.
stems. Support is added for the EVA4400.
tainer for h os t disk d evice. You can now create a storage container for a specified host
ce. The storage container is added to a managed set. For more information, see ???.
New GUI features
Version 4.0 includes the following new or updated GUI features compared to version 3.1.
• The RSM — Host Volumes page, Dynamic Capacity Volumes tab, now displays Used Capacity in
both gigabytes (GB) a nd percent (%).
Version 4.0 includes other new GUI features compared to version 3.0. See ???.
New job f
eatures
Version 4.0 includes no new or updated job features compared to version 3.1.
New job templates
Version 4.0 includes no new job templates compared to version 3.1.
New job commands
Version 4.0 includes no new or updated job commands compared to version 3.1.
New CLUI features
Version 4.0 includes no new or updated CLUI features compared to version 3.1.
Relea
se History
rageWorks Replications Solutions Manager releases:
HP Sto
22
Replication Solutions Manager
Release
February 2008
Kit and Web update
November 2007
Kit and Web update
June 2007
Kit and Web update
June 2006
Kit and Web update
February 2006
Kit and Web update
August 2005
Kit and Web update
May 2005
Kit and Web update
December 2004
Kit and Web update
Version
4.0
3.1
3.0
2.1
2.0
1.2
1.1 HP-UX
1.0
Host agents Arrays
HP-UX
HP OpenVMS
HP Tru64 UNIX
IBM AIX
Linux
Sun Solaris
Microsoft Windows
HP-UX
HP OpenVMS
HP Tru64 UNIX
IBM AIX
Linux
Sun Solaris
Microsoft Windows
HP-UX
HP OpenVMS
HP Tru64 UNIX
IBM AIX
Linux
Sun Solaris
Microsoft Windows
HP-UX
HP OpenVMS
HP Tru64 UNIX
IBM AIX
Linux
Sun Solaris
Microsoft Windows
HP-UX
HP OpenVMS
IBM AIX
Linux
Sun Solaris
Microsoft Window
HP-UX
IBM AIX
Linux
Sun Solaris
Microsoft Windows
IBM AIX
Linux
Sun Solaris
Microsoft Windows
HP-UX
Linux
Sun Solaris
Microsoft Windows
s
HP EVA
HP EVA
HP EVA
HP EVA
HP EVA
HP EVA
HP EVA
HP EVA
Overview
Capabilities
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager is a centralized tool that simplifies and automates local
and remote replication features of HP arrays. The replication manager allows you to perform tasks by
using its graphical user interface (GUI), jobs, and a command line user interface (CLUI).
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
23

General replication management
• Automatically discover resources such as arrays, virtual disks, and hosts. See
automatic refresh of resources.
• View resource properties in g raphical trees and tabular lists. For example, see virtual disk views
• Create and manage copies of data (replicas) in real time.
• Create, run, monitor, and manage jobs that automate replication tasks. See
jobs, templates and commands.
• Present storage volumes to hosts.
• Dynamically mount storage volumes containing file systems on enabled hosts *.
• Dynamically extend or shrink a host volume on enabled hosts*.
• Interact with host applications on enabled hosts *.
• Interact with Oracle ap plications on enabled hosts *.
• Create and manage collections of resources (managed sets). See m anaged sets.
• View replication event logs.
• Run the replication manager in a resource simulation mode. See simulation mode.
* Requires an HP Replication Solutions Manager host agent.
Local replication
• Create loc
• Create local copies by specifying source arrays and virtual disk names.
• Create local copies by specifying source enabled hosts and volume names *.
• Create lo
• Create local copies by specifying O racle resources on enabled hosts *.
* Requires an HP Replication Solutions Manager host agent.
al copies using snapclone and snapshot technology. See snapclones and snapshots.
cal copies by specifying source enabled hosts and logical volume names *.
Remote replication
• Create, configure, and manage DR groups (remote copies). See DR group pairs.
• Reverse (fail over) remote replication direction. See DR group failover.
• Manage remote replication. See using DR groups.
Local replication
Local re
copies
snapclones and snapshots.
• Business Copy EVA is the HP brand name for the set of features, replication licenses, and
• Local replication features are part of (installed with) the controller software on
• To use
plication is a licensed feature of HP StorageWorks arrays that allows you to quickly create local
of your data using the array’s replication engine. These copies are known as mirrorclones,
faces for local replication on EVA arrays.
inter
each storage array and can vary with the controller software version. See
controller software features - local replication.
the local replication features on a given array, the replication manager verifies that a
d HP Business Copy EVA replication license-to-use (LTU) exists for the array. For information
vali
on acquiring and installing local replication licenses, see the HP StorageWorks Business Copy
EVA administrator guide.
Remote replication
Remote replication is a licensed feature of HP StorageWorks arrays that allows you to create remote,
disaster-tolerant copies of your data using the array’s replication engine. Remote copies are created
and managed through the use of DR group pairs.
24
Replication Solutions Manager

• Continuous Access EVA is the HP brand name for the set of features, replication licenses, and
interfaces for remote replication on EVA arrays.
• Remote replication features are part of (installed with) the controller software
on each storage array and can vary with the controller software version. See
controller software features - remote replication.
• To use the remote replication features on a given pair of arrays, the replication manag er verifies
that a valid HP Continuous Access EVA replication license-to-use (LTU) exists for each array. For
information on acquiring and installing remote replication licenses, see the HP StorageWorks
Continuous Access EVA administrator guide.
Server software
The replicat
database, a
GUI and job engine
The GUI allows you to:
• View all available resources in tabular lists, graphical tree views, and topology views. See
about replication resources.
• Perform actions on resources.
• Create jobs using the integrated job editor and job templates.
• Validate job task logic and syntax before running a job.
• Monitor job progress and view detaile d job activity logs.
• Configure the replication manager.
• View replication manager events and logs.
ion manager server software includes a graphical user interface (GUI) and job engine, a
nd a command line user interface (CLUI).
For a visual overview, see GUI window.
Replica
tion manager database
The serve
replication manager events. See about the RSM database.
The database can be exported and imported allowing you to:
• Backup a
• Copy the database to other instances of the replication manager. This is especially useful in
r software includes an internal database of available resources, jobs, job instances, and
nd restore the database.
remote replication environments with multiple management server.
CLUI server
The server software also includes a CLUI server application which supports several types of command line
style CLUI clients. See CLUI overview.
Host agent software
A replication manager host agent is OS-specific software that enables interactions between a host and
lication ma nag er server. A host that has a replication manager host agent installed is called an
the rep
enabled host. See enabled and standard hosts.
A host agent allows you to:
• Perfo
• Mount virtual disks on the host without rebooting the host (dynamic mount).
• Dynamically extend or shrink a host volume.
• Suspe
• Launch (run) applications on the host.
rm replication by specifying the host and host volume name.
nd and resume application I/O on the host.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
25

• Interact with database, backup, and other applications.
• View host properties, such as: operating systems, file systems, logical volume managers, cluster
software, multipathing software and Fibre Channel HBAs.
CLUI remote client
Host agents also include a CLUI remote client that you can use to run replication manager CLUI
commands from the host’s command line.
CLUI software
The replication manager includes a CLUI server and client in the server software and a CLUI remote
client in the host agent software.
TheCLUIsoftwareallowsyouto:
• Issue CLUI commands and run scripts from CLUI clients
• Run jobs and manage job instances from CLUI clients.
• Use job return codes for conditional interactions between jobs and scripts.
See also accessing the CLUI via GUI and CLUI documentation.
Jobs,templates,andcommands
You can create, save, run, schedule, and manage jobs that automate replication tasks.
Job editor
Use the replication manager’s specialized job editor to create and edit jobs.
26
Replication Solutions Manager

Job templa
tes
Job templ
virtual disks. See job templates list.
Job commands
You can also create custom jobs from the set of specialized job commands. See job commands list.
Simulati
on mode
For more information, see the HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager Simulation guide.The
guide is available from the help menu of the replication manager GUI and from the H P Storage web site.
See “Helpful web sites” on page 19.
CAUTION
HP stron
machine
lose co
replication manager database and have not backed it up, you will lose all jobs.
Overview
Simulation mode allows you to use all of the functions of the replication manager without having to use
any of your production data or resources. These functions include creating snapshots and snapclones,
creating DR groups and adding virtual disks to them, and performing failovers.
ates allow you to quickly create typical jobs, for example, making local or remote copies of
:
gly recommends that you do not run simulation mode on a production machine (that is, on the same
as Command View EVA). If you disconnect the replication manager from Command View EVA, you
ntrol of the storage resources that were being managed by the replication manager. If you purge the
Features and benefits:
• No SAN infrastructure, storage arrays, hosts, or management servers are required.
• Requires only replication manager server software running on a business class Windows desktop
or laptop computer.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
27

• True simulation – not a set of predefined scenarios. Simulates GUI actions, jobs, and CLUI
commands.
• Allows you to create your own:
• Simulated storage arrays. Select features such as array capacity, controller software versions
and number of virtual disks.
• Simulated hosts. Include hosts and select the storage arrays they are connect to.
• Simulated Oracle databases. Simulate Oracle databases, tablespaces, datafiles, archived
redo logs, control files, and repositories.
Replication kits and downloads
Replication software kits
HP StorageWorks replication kits for Business Copy EVA and Continuous Access EVA include:
• Overview Document (printed)
• Replication Solutions Manager - Server CD
• Replication Solutions Manager - Host Agents CD
• Documentation CD, including a stand-alone version of the online help and user guide.
Replication software downloads
HP StorageWorks replication downloads for Business Copy EVA and Continuous Access EVA include:
• Replication Solutions Manager - Server zip download
• Replicat
• Documentation zip download
• Stand-alone version of the online help and user guide.
ion Solutions Manager - Host Agents zip downloads (multiple, by OS)
See “Helpful web sites” on page 19.
GUI
GUI wind
The GUI window provides a menu bar, toolbar, navigation pane, content pane, event pane, and status
bar. Click the links below for m ore information.
1. Menu bar
2. Toolbar
ow overview
3. Navigation pane
4. Event pane
5. Status bar
6. Content pane (jobs example)
28
Replication Solutions Manager

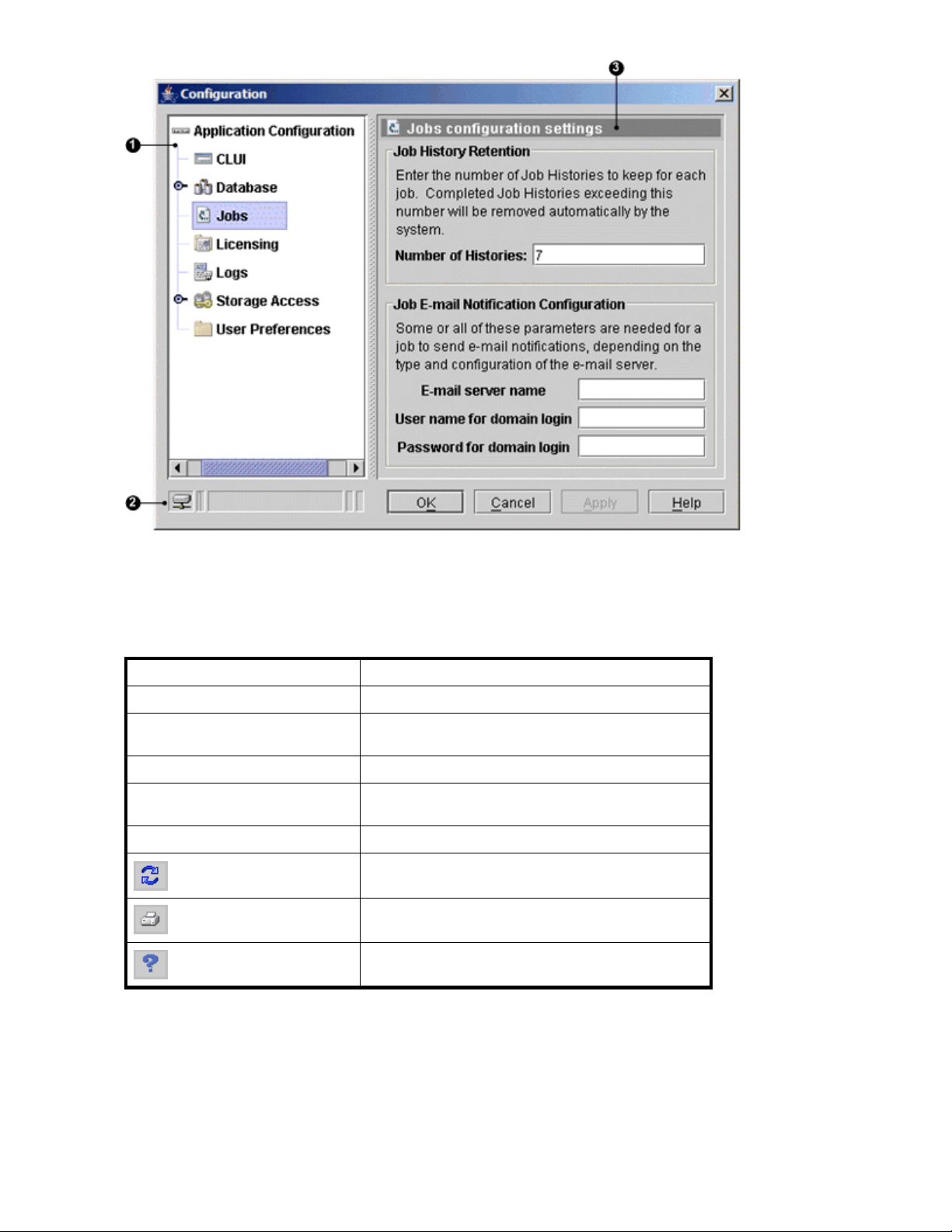
Configuration window
The configuration window provides access to the replication manager configuration settings. See also
accessing the configuration window.
1. Navig
ation pane
2. Status bar 3. Settings p ane (jobs example)
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
29
Content pane
Information about available replication resources is displayed in the content pane. See
replication resources.
The following features are available in the pane.
Item
Actions > Print
Actions > Refresh Refreshes the content pane, using data from the
Actions > Help Displays context-sensitive help
Filter
View
CLUI window (in the GUI)
The CLUI window (in the GUI) includes a command line, command history and response pane. See also
accessing the CLUI via GUI.
Description
Prints the content pane.
database.
Select and filter information displayed in list tabs. See
filtering
Select the information displayed in tree tabs.
Refreshes the content pane, using data from the
database.
Prints the content pane.
Displays context-sensitive help.
30
Replication Solutions Manager

1. Command line
2. Response pane
Keyboard and right-click shortcuts
Right-click actions
3. Command history
ick a resource to open its Actions menu.
Right-cl
General shortcuts
Action
Copy selection Ctrl+C
Cut selection Ctrl+X
Extend selection left or right Shift+Left arrow or Shift+Right arrow
Extend selection left or right Ctrl+Shift+Left or Ctrl+Shift+Right
Extend selection to start or end
Move to start or end of text
Paste from clipboard
Select all Ctrl+A
Print
Refresh
Help
Button
shortcuts
Key combination
Shift+Home or Shift+End
Home or E
Ctrl+V
ALT+P
ALT+R
ALT+H
nd
Action
Navigate forward
Navigate backward
Key combination
Tab
Tab
Shift+
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
31

List view shortcuts
shortcuts
Action
Extend selecti
Extend selection down
Move to next cell Tab or right arrow
Move to previous cell
Move to first cell in row
Move to last cell in row End
Move to first row in table
Move to last row in table Ctrl+End
Select all c ells Ctrl+A
Edit cell wit
on up
hout overriding content
Action
Move bet wee
Select first item
Select next item Right arrow
nitemsinthemenu
Key combination
Shift+Up arrow
Shift+Down arrow
Shift+tab or le
Home
Ctrl+Home
F2
ft arrow
Key combination
Arrow keys
F10
Select pre
Select default or selected item
vious item
Tree view shortcuts
Action
Navigate out forward
Navigate out backward
Move up/do
Move to first entry
Move to last visible entry End or Pg Dn
Menu bar
The menu b
• File. Export and import an RSM database. See exporting a n RSM database,
importing an RSM database and importing a remote RSM database.
• View. Display a session’s view history and select a previously displayed view.
• Tools.Configure the replication manager, issue CLUI commands, and run the replication manager
in simulation mode. See accessing the configuration window, accessing the CLUI via GUI,
and simulation m o d e.
• Help. Display the replication manager version, access the online help and user guide and other
documentation. See online help and user guide.
Left arrow
Enter
ation
wn one entry
Key combin
Tab
Shift+Tab
Up, Down
Home or PgUp
ar provides access to features, tools, the online help and user guide, and other documentation.
32
Replication Solutions Manager

Navigation pane
The navigation pane alphabetically lists the data replication resources you can manage, organizing them
by group in the hierarchical tree. Icons identify the state of the resources. (States other than normal are
displayed in the navigation pane. In the tree, the resource group displays the most critical state of
all its resources.)
• To view a resou
• To display online help for the resource, right-click its group and select Help.
Behaviors
• To expand or collapse an item in the tree, click the expand icon.
• To size the navigation pane, place your cursor over the sizing bar until your cursor changes to a
double-headed arrow; then, click and drag the pane larger or s maller as needed.
rce in the content pane, click its group, or right-click its g roup and select View.
Online help
The replica
includes t
• Main help (user guide). The main help (user guide) is accessed from the Help button on the
toolbar. Information is organized and easily accessed with the use of Contents, Index, and
Search tabs.
• Context-
accessed by clicking a question mark icon or help button in the window.
The online help and user guide system includes the following features:
• Contents tab. Displays the help and user guide contents. The contents are organized into books
and topi
• Index tab.Displaysanindexoftopics.
• Search tab. Displays a list of topics containing the words that you searched for.
Status bar
The Status bar, located at the bottom of the page, d isplays an icon indicating the status of the server
connection as well as a graphical indication of server communication activity.
Toolba
r
Item
and user guide
tion manager online help and user guide is a cross-platform, browser-based application that
he following types of help:
sensitive help. Context-sensitive help is specific to the window that you are viewing and is
c pages.
Description
Tooltips
View history - back. Changes the content pane to show
one view back in the view history.
View history - forward. Changes the content pane to
showoneviewforwardintheviewhistory.
View home. Changes the content pane to the home
view (replication)
Global refresh.Performsaglobalresource
discovery and refresh of the database. See
refreshing resources (global).
Placing the cursor over an item momentarily displays a tooltip.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
33

View history
The View History shows a list recently displayed resource views. See about replication resources.
• The view that is currently displayed in the content pane is indicated with a checkmark. Selecting
(checking) another view changes the contents pane to that view.
• When a new session begins, the history list includes the top level Replication view a nd last view
from the previous session.
• History list navigation:
< tooltip
Navigation
Back
Forward
Up
• For leg ibility, only the most recent views are shown in the list. However, older views are tracked
and can be displayed from a Back or Forward selection.
Remarks
Displays one view before to the current view (if any).
Displaysoneviewafterthecurrentview(ifany).
s the top level resource view (Replication)
Display
Configuration
Accessing the configuration window
Open the configuration window. See configuration window.
Considerations
IMPORTANT:
Changing the configuration, especially storage access, should be carefully planned to avoid impacting
running jobs and scheduled jobs.
Procedure
1. On the toolbar, select Tools > Configure.TheConfiguration window opens.
34
Replication Solutions Manager

2. In the Configuration navigation pane, select the item to configure.
CLUI por ts confi
You can con figur
• Default:
Unsecure port: enabled, port 9000, 10 simultaneous sessions
Secure SSL port
• HP recommends not changing a default port number unless it conflicts with other applications
on the management server.
• To allow unlim
For the procedure, see accessing the configuration window.
guration
e the ports that are used by CLUI clients to access the CLUI server.
: enabled, port 9001, 10 simultaneous sessions
ited simultaneous sessions, enter zero (0) in the Maximum Sessions box.
RSM database configuration
You can configure the port that the replication manager server uses to access its internal database. You
can also review the database size and compact it.
Database por
Database size and compaction
t
• Default:port1315.
• HP recommen
management server.
• The size of the replication manager database is displayed in the configuration window.
• You can compact the database to remove unused space. Compaction does not take effect until
the replication manager server (service) is restarted.
ds not changing the default unless the port conflicts with other applications on the
For the procedure, see accessing the configuration window.
RSM datab
ase cleanup
You can remove records of unavailable storage resources from the database by using the cleanup feature.
• Over time
replication manager can no longer communicate with.
• HP recommends exporting a copy of the database (as backup) before performing a cleanup.
See expo
For the p
, the database can accumulate records of resources on storage systems that the
rting an RSM database.
rocedure, see accessing the configuration window.
Jobs e-mail server configuration
You can c onfigure the replication manager to use an e-mail server to send messages from jobs.
• Default: No e-mail server is specified.
• To configure an e-mail server, you must know its network name and a user name and password to
access the e-mail application.
• See also Send Email and SetNotificationPolicy job commands.
For the procedure, see accessing the configuration window.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
35

Jobs run history
configuration
You can configur
and retained in the database.
• Default:7runhistoriesperjob
• The minimum is 1
such as readability in the GUI and RSM database size and performance.
• When the limit is exceeded, a job’s oldest run history is no longer d isplayed and the (job
instance) record is deleted from the database.
For the proced
e the number of run histories (job instances) per job that are displayed in the GUI
run history per job. The maximum is limited only by practical considerations
ure, see accessing the configuration window.
Licenses configuration (applications)
You can review and add HP application-integration licenses to the replication manager configuration.
• Review details of installed H P application-integration licenses.
• Retrieve an HP application-integration license key file from a web site.
• AddaretrievedlicensekeytotheRSMdatabase.
For the general configuration procedure, see accessing the configuration window.
Logs configuration
See event log and trace log below.
Event log configuration
You can con figure when the replication manager event log is rolled. When the log is rolled, the current
eventlogissavedasanhistoricallogandnewcurrentlogisstarted.
• Default: roll over on size. The current event log is rolled when its size exceeds 1 0 MB.
• Instead of size, you can configure the event log to roll on a regular interval. Interval choices
include every hour, day, week or month.
• You can delete historical event logs by using the configuration window.
• Properties. See event log.
For the procedure, see accessing the con figuration window.Seealsoviewing events.
Trace log configuration
You can enable and disable the replication manager trace log.
• Default
events are discarded.
• You can disable the trace log by using the configuration window.
• Proper
For the
: enabled. The log file has a maximum size of 60 MB. As the log gets full, the oldest
ties. See trace log.
procedure, see accessing the configuration window.Seealsoviewing the trace log.
Oracle security credentials configuration
To interact with Oracle applications, an Oracle database administrator must configure a replication
manager account with appropriate security privileges on each enabled host that is running Oracle.
• For further information on security credentials for configurations that include Oracle databases,
see the HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager installation g uide and the HP
StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager administrator guide.
36
Replication Solutions Manager

• Once replication manager accounts and security privileges have been configured by an Oracle
administrator, you can add or update the credentials that are stored in the RSM database. See
security credentials for O racle database and setting security credentials for Oracle databases.
• See also Oracle-integration licenses overview.
Security credentials configuration
To logon and use the replication manager, special security groups must be configured on the management
server and eac
• You cannot establish or maintain security credentials by using the replication manager
configuration window.
• For further information on the creation and administration of security groups, see the HP
StorageWork
Replication Solutions Manager a dministrator guide.
Management server security groups
The following Windows OS-based security groups are required or supported on the management server.
IMPORTANT:
Groupnamesarecasesensitive. Theuseofallfunctionsandfeaturesinthereplicationmanager,except
viewing data, require membership in the administrator group.
• HP Storage Admins. To access the replication m anager ser ver, this security group is required on
the management server and must have at least one member (user account). Members have full
replication manager execute and read/write privileges.
• HP Storage Users. Members have only view/read replication manager privileges. This group is
required only when a group with extremely limited use of the replication manager is required.
henabledhost.
s Replication Solutions Manager installation guide and the HP StorageWorks
Enabled hosts security g roups
One of the following OS-based security groups is required on each enabled host, as appropriate.
IMPORTANT:
Groupnamesarecasesensitive.
• HP Host Agent Admins. To interact with the replication manager server, e ach Windows enabled
host must have this security group and at least one member (user account).
• hphaadm. To interact with the replication manager server, each Linux, UNIX, and OpenVMS
enabled host must have this security group and at least one member (user account).
Securi
ty credentials vs. tasks
Replication manager tasks can only be performed by members of the HP Storage Admins group or HP
Storage Users security groups on the management server. See security credentials configuration.
Most tasks require mem bership in the HP Storage Admins group. The following table s hows the
ionship between security credentials and tasks that are allowed.
relat
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
37

Item or
resource
Task Credential Remarks
Admin
allowed
User
allowed
Replication
manager
DR groups
Enabled hosts Add, change, delete and
Host volumes Add, change, delete and
Configure
Enable an d dis
simulation m
Export and import RSM
database
Manage and view event logs
Add, change, delete and
view
Fail over
and force
view
Runhostscriptandset
security credentials
view
Replicate
able
ode
,suspend,resume
full copy
yes no
yes no
yes no
yes
yes
yes no
yes
yes no
yes
yes no
partial Users can only
partial Users can only
partial Users can only
partial Users can only
Users can only
view.
view.
view.
view.
view.
Jobs Add, edit, delete, monitor
Managed sets Add, change, delete and
acle
Or
tegration
in
Storage systems
and view
dule, run, pause,
Sche
inue, and abort
cont
view
d, change, delete and
Ad
ew Oracle resources
vi
Back up and restore Oracle
databases
Add, change, delete and
view resources
Manage replication licenses
yes
yes no
yes
yes
yes no
yes no
yes
partial Users can only
partial Users can only
pa
partial Users can only
rtial
view.
view.
ers can only
Us
ew.
vi
view.
38
Replication Solutions Manager

Item or
resource
Task Credential Remarks
Virtual disks Add, change, delete and
Simulation mode
For more info
guide is ava
See “Helpfu
CAUTION:
HP strongly recommends that you do not run simulation mode on a production machine (that is, on the same
machine as Command View EVA). If you disconnect the replication manager from Command View EVA, you
lose control of the storage resources that were being managed by the replication manager. If you purge the
replication manager database and have not backed it up, you will lose all jobs.
Overview
Simulation mode allows you to use all of the functions of the replication manager without having to use
any of your production data or resources. These functions include creating snapshots and snapclones,
creating DR groups and adding virtual disks to them, and performing failovers.
Features and benefits:
• No SAN infrastructure, storage arrays, hosts, or management servers are required.
• Requires only replication manager server software running on a business class Windows desktop
or laptop computer.
• True simulation – not a set of predefined scenarios. Simulates GUI actions, jobs, and CLUI
commands.
• Allows you to create your own:
• Simulated storage arrays. Select features such as array capacity, software controller versions
and number of virtual disks.
• Simulated hosts. Include hosts and select the storage arrays they are connect to.
• Simulated Oracle databases. Simulate Oracle databases, tablespaces, datafiles, archived
redo logs, control files, and repositories.
yes
view resources
Replicate, present and
unpresent
rmation, see the HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager Simulation guide.The
ilable from the help menu of the replication manager GUI and from the HP Storage web site.
lwebsites” on page 19.
yes no
partial Users can only
view.
Single sign-on (SSO) with HP Command View EVA
Administrators can establish a single sign-on (SSO) trust relationship in HP Command View EVA that
allows the replication manager to connect without sending the Storage Agent user name and password.
The on/off status of SSO is displayed in the replication manager GUI but cannot be con fi gured from there.
To configure SSO, access HP Command View EVA and select Se rver Options > System Insight
Manager/Replication Solutions Manager trust relationships.
Storage management server configuration
Administrators can review and change settings for the management server.
• Manage. Enable and disable management of storage systems via the lo cal instance of HP
Command View EVA.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
39

• Refresh Period. Set the interval for automatic discovery and refresh of resources. See
refreshing resources (automatic).
IMPORTANT:
Best practices apply. See best practices for automatic refresh.
• Storage Agent Login Password. Save the user na me and password for the local instance of HP
Command View EVA in the replication manager database.
For the procedure, see accessing the configuration window.
User preferences configuration
You can configure various display aspects of lists and trees so that changes are remembered.
• Default:userpreferencesaredisabled.
• Configurable display aspects include: column order, relative column width, sort column, and
tree expansion state.
For the procedure, see accessing the configuration window.Seealsoorganizing displayed resources.
RSM database
About the RSM database
The RSM database contains information on available resources, jobs, job instances, replication manager
events, and DC-Management settings. The database is updated through several methods, including
real-time updates, automatic refreshes, and manual global refreshes. See refreshing resources (automatic)
and refreshing resources (global).
The active RSM database cannot be accessed by administrators or users. Administrators, however, can
export and import copies of the database. See exporting an RSM database, impor ting an RSM database
and importing a remote RSM database.
About exports
Theexportfeaturecreatesacopy(XMLfile) of the active RSM database.
• Exported copies can only be created in an existing folder on the storage management server.
• You can assign a file name or let the replication manager automatically assign a name.
• Automatically assigned file names have the format: CADATA_timestamp.export.xml
where timestamp is the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second the file was created. For
example, the file CADATA_20050211135232.export.xml was created on February 11,
2005, at 13:52:32 hours.
• Stored security credentials for resources and scheduled job events are not included in the
exported copies.
• All scheduled job events are exported with a status of a run status of disabled. See
Enabling and disabling scheduled job events.
• See also exporting an RSM database.
About imports
The import feature merges the content of a previously exported RSM database or a remote RSM database
with the content of the currently active database.
• Importingprocessingisasfollows:
40
Replication Solutions Manager

When a storage or host resource exists in both the imported and active RSM database, the active
database record is overwritten with the imported record.
When a storage or host resource exists only in the impor ted RSM database, a record is added to the
active da tabase.
When a job or managed set exists in both the imported and active RSM database, the active database
record is not overwritten. Instead, a new record is added and the job or managed set name is modified
with the characters _# to make it unique.
• After an import has been run, additional procedures are required to make the imported resources
available. See completing imports.
• See also importing an RSM database and importing a remote RSM database.
Exporting an RSM database
This feature allows administrators to create a copy of the active RSM database. The copy is created on
the same management server as the active database. See RSM database.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See the Export jobcommandandCLUISetServer
command.
• After creating a copy, HP recommends that administrators move or back up the copy to a
physically separate server or storage device.
• The security credentials for enabled hosts are not included in an exported database.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. Select Fil
2. Enter an existing directory (full path) where you want the copy to be created. For example:
C:\colorado
3. Do one of t
• If you want to name the file yourself, enter a name, for example
• If you want the replication manager to assign a file name, leave the file name box empty.
4. Accept or deselect the option to overwrite the file you entered in the step above.
5. Click O
the Monitor job window. See implicit job startup.
6. The replication manager creates and XML copy of the RSM database in the loc a tion that you
specified. See about exports.
e > Export RSM Database. The Export RSM Database window opens.
he following:
RSMdb_on_server2_Mar_15_2007.Donotincludeafile extension. The
replicat
See About exports for the file name format.
ion manager automatically adds the extension .xml.
K. An implicit job is started. The results and number of processed resources appear in
Importing an RSM database
This feature allows administrators to import a previously exported copy of the RSM database. See
RSM database.SeealsoImporting a remote RSM database.
Considerations
• You c
command.
• The database copy to be imported must be on the same ma n agement server as the active
database. Impor ting an RSM database by specifying a network share drive is not supported.
an use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See the Import job command and CLUI Set Server
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
41

• You must know the exact database copy file name and location (drive letter, full pa th name). You
cannot search for exported files from the replication manager.
• Security
IMPORTANT:
The security credentials for enabled hosts are not included in an exported database.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. Select File > Import RSM Database. The Import RSM Database window opens.
2. Enter the drive letter, full path and file name of the RSM database copy to
import, for example C:\colorado\RSMdb_on_server2_Mar_15_2007.xml or
C:\colorado\CADATA_20050211135232.export.xml
3. Click OK. An implicit job is started. The results and number of processed resources appear in
the Monitor job window. See implicit job startup.
4. After importing, perform required follow up procedures to ensure that all required resources are
available. See c ompleting an impor t.
Importing a remote RSM database
This feature allows administrators to import an RSM database from another management server. See
RSM database.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI or the CLUI. See CLUI Set Server command.
• After importing, HP recommends that administrators examine the active database for duplicate
jobs and managed sets and m ake corrections, as necessary.
• Security
IMPORTANT:
The security credentials for enabled hosts are not included in an exported database.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. Select F
2. Enter the network n ame o r IP address of the remote management server.
3. Enter the user name and password to access the remote instance of the replication manager.
4. Click OK. An implicit job is started. The results and number of processed resources appear in
the Monitor job window. See implicit job startup.
5. After i
available. See c ompleting an impor t.
ile > Import RSM Database from Remote RSM. The Import RSM Database window opens.
mporting, perform required follow up procedures to ensure that all required resources are
Completing imports
After an import is run, perform the following procedures, as appropriate:
42
Replication Solutions Manager

IMPORTANT:
These procedures help ensure that resources, jobs, and managed sets a re available after importing an RSM
database.
• Re-enter the password to access the local instance of HP Command View EVA. See
storage management server configuration.
• Re-enter the security credentials that are required to access enabled hosts. See
setting security credentials for enabled hosts.
• Re-enter the security credentials required to access Oracle databases, if any. See
setting security credentials for Oracle databases.
• Re-enter the security credentials for imported scheduled job events, if any. See
editing scheduled job events and security credentials for the server.
• Re-enable scheduled job events to run automatically. See
Enabling and disabling scheduled job events.
• Re-configure the replication manager to use an e-ma il server for jobs notification, if any. See
jobs email server configuration.
• HP recommends that administrators examine the active database for duplicate jobs and managed
sets and make corrections, as necessary. See about imports .
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting - G eneral
All storage resources in unknown state
Problem
The status of all storage systems, DR groups, and virtual disks have changed to an unknown state.
Explanation / resolution
The RSM administrator should check if the replication ma nager database was recently imported
from another management server. See resources database. If so, the problem is probably that the
management server passwords are different. Passwords for the active and standby management servers
must match for the database import to succeed.
To change the password for a management server:
1. From the toolbar, select Tools > Configure > Storage Access > Management Server.
2. Select the management server for which you want to change the password. The server shows a
state of authorization_failure or bad_connection.
3. Click Properties.
4. In the Storage Agent Login area, Agent Password box, enter the correct password.
5. Click OK.
Browser window is blank
Problem
The replication manager GUI is blank (gray) in the browser window.
Explanation / resolution
This can b e caused by browsing away from, and back to, the replication manager.
To display the GUI:
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
43

1. While viewing the blank browser window, press and hold the CTRL key then click the browser
refresh button. The replication manager logon window opens.
2. Log on to the replication manager.
3. The replication manager GUI appears.
Database file name extension is missing
Problem
When viewing an exported copy of the replication manager database on the management server (that is
a Windows computer), the file nam e may appear to be missing the .XML extension.
Explanation / resolution
When a copy is created, the file name is automatically assigned in the following format:
CADATA_times
tamp.export.xml
When viewing
CADATA_timestamp.export
This can occur when the Window is set to hide known file name extensions.
To resolve this issue:
1. In the window
2. Select the View tab.
3. Under Files and Folders, clear the item Hide extensions for known file types.
4. Click OK.Fi
filesonaWindowscomputer,thefile name may appear as:
, select Tools > Folder Options. The Folder Options window opens.
le name extensions are displayed in the window.
Documents are not visible when selected
Problem
Documents are not visible when selected from the Help menu.
Explanation / resolution
This can happen when the document’s File Download window opens behind the replication manager
window. This only occurs when running the replication manager in an application mode on the
management server desktop.
To make the document’s File Download window visible, select it from the Taskbar or minimize the
replication manager window.
Enabling f
ailsafe mode with a managed set fails
Problem
Attempting to enable failsafe mode for a managed set of DR groups fails. The replication manager
logs the me
Not available:: ERROR: failsafe() not available in current state
Explanation / resolution
This can oc
whose rem
invalid D
See also I
Illegal characters
In some cases the following characters are not valid in entries.
44
Replication Solutions Manager
ssage:
cur when the managed set in a GUI action or CLUI command contains one or more DR groups
ote replication I/O mode is set to asynchronous. Enabling the failsafe mode would result in an
Rgroupconfiguration, so the action is failed.
nvalid DR group pair configuration.

Description
Resource
names
&
*
:
, comma no no
>
<
%
+
?
"
\
/ slash, forward (virgule, solidus)
|
Spaces at the end of a virtual disk name
Two or more consecutive spaces
ampersand
asterisk
colon
greater than symbol
less than symbol
per cent sign
plus sign
question mark
quotes (double)
slash, backward (virgule,
solidus)
vertical bar
Other
no no no
no no
no no
no no
no no no
no no no
no no no
no no no
no no no
no no
no no no
no no
~no~
ok
Valid inCharacter
Virtual disk
names
no
Comments
ok
ok
ok
ok
ok
ok
ok
InvalidDRgrouppair-sourceandsource
Problem
Both groups in a suspended DR group pair are identified as the source group.
Explanation / resolution
If a D R group pair is suspended while the intersite links are unavailable, when the intersite links become
available again both DR groups are identified as the source. The source-source identifi cation continues
until remote replication is resumed.
Thiscanhappenwhen:
• The DR g roup pair is suspended while the intersite links were unavailable. See suspension state.
• The DR g roup pair is failed over with the suspend-on-failover action while the intersite links
were unavailable. See suspend on failover.
• Auto suspend mode is enabled while the intersite links are unavailable. See auto suspend.
To resolve this issue
1. Use HP Command View EVA to resume the suspended DR group pair.
2. After resuming the DR group pair, perform a manual refresh of the DR groups. See
low-level refreshing DR groups. The source and destination DR groups are correctly identified.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
45

NOTE:
While the incorrect source-source identification exists:
•
The GUI Actions menu correctly shows only actions that are appropriate for the true role of the DR group
(source actions for the true source and destination actions for the true destination).
•
In the CLUI, issuing a Show DR_group command on the "new source group" shows it correctly it as a
destination and only destination operations can be executed.
Invalid DR group settings - failsafe with synchronous
Problem
When attempting to use C LUI commands to disable the failsafe mode, the replication manager l ogs
the message:
Failed to set failsafe for DR Group, group is currently :failsafe is
already enabled.
Explanation / resolution
You can use GUI actions or CLUI commands to create a DR group pair with the following invalid
configuration: failsafe mode enabled with synchronous remote replication I/O mode. Attempting to
disable the failsafe mode in this invalid configurationresultsinanerror.
To resolve this issue, use the GUI or CLUI commands to set a valid confi guration. To retain an
asynchronous I/O mode and disable the failsafe mode:
1. Change the remote replication I/O mode to synchronous.
2. Change the failsafe m ode to disabled.
3. Change the remote replication I/O mode back to asynchronous.
Job instance fails with get error lock message
Problem
A job instance fails with a message like: get error lock failed.
Explanation / resolution
Too many job instances that interact with a specific enabled host may be running simultaneously. See
simultaneous job instances.
To resolve the problem, reduce the number of running job instances that involve the enabled host.
Job interacts with wrong array
Problem
When a job is run, storage commands are attempted on the wrong array. Typically, the job does
not validate properly or fails.
Explanation / resolution
If two storage arrays in a replication manager configuration have the same name, a job can attempt to
interact with the wrong array. Ensure that all arrays have unique names.
Job with host volume remount fails after an unclean unmount
Problem
A job with host volume remount fails and the replication manager logs the error message:
46
Replication Solutions Manager

The filename, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrect for the
operating system associated with this mount point.
Explanation / resolution
If a host volume is uncleanly unmounted, such as during an unplanned failover, the host OS or file system
may retain information about the host volume. When the replication manager attempts to remount that
same volume, the host treats the request as a duplication and the remount fails. To resolve this issue:
1. Ensure that the host volume is cleanly unmounted.
2. If necessary, clean up resources that were involved in the failed job.
3. After the host volume is cleanly unmounted, you can aga in use the replication manager to
mount it.
Logical volumes and volume groups in job commands
Some command arguments require the selection or entry of a logical volume (a com ponent of a volume
group). Because the replication manager considers logical volumes and volume groups to be host
volumes, you must select the resource from a host volumes list. There is not a separate list of logical
volumes or v
olume groups.
See also, host volumes and logical volumes and volume groups.
Low-level refresh returns an error
Problem
When you perform a low-level refresh on a virtual disk or DR group, the replication manager may
log the message:
Unable to complete the requested action because of an unexpected error.
Explanation / resolution
This ca n o ccur when the replication manager is unable to discover a virtual disk or DR group. Use HP
Command View EVA to verify that the virtual disk or DR group exists, and then retry the low-level refresh.
The following table lists the CLUI commands and GUI actions that perform a low-level refresh.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
47

CLUI command and switch
GUI action
See also Tru64 UNIX host volumes.
Set DR_Group refresh Managed Sets > Actions > Low-Level Refresh
Set Vdisk refresh Virtual Disks > Actions > Low-Level Refresh
Show Container refresh
Show DR_Group r
Show Snapclone refresh
Show Snapshot refresh
Show Vdisk refr
efresh
esh
Maximum DR Group log size error
Problem
If you enter an invalid size, the replication manager logs an error and does not set the maximum log
size for the DR group.
Explanation / resolution
Invalid sizes are ignored.
To resolve this issue, do one of the following:
• Accept or enter zero (0) to apply the controller software default size algorithm.
• Enter a valid size. See maximum log disk size.
DRGroups>Actions>Low-LevelRefresh
(for virtual di
sk and DR group managed sets)
Monitor job window has no details
Problem
The Monitor Job window indicates that job details are currently unavailable for display. Even after waiting
several minutes, the details are not displayed. This happens frequently, regardless of the job being run.
Explanation / resolution
If this happens frequently, there may be a port conflict between the replication manager server software
and other ap
Contact th
plications on the management server.
e replication manager administrator to have the issue resolved. Default ports are listed in the
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager administrator guide.
Pop-up windows are not visible
Problem
After navigating from an open replication manager pop-up window to the replication manager main
window, or to another application window, clicking a taskbar button does not redisplay the pop-up
window.
Explanation / resolution
Replication manager pop-up windows can become hidden under the main replication manager window,
or und er other application windows. Clicking the taskbar button for the replication manager displays the
main window, but not the hidden pop-up window.
To resolve this issue on a Windows computer:
1. Press and hold the Alt key.
2. Press and release the Tab key once. A menu of available windows opens.
48
Replication Solutions Manager

3. Press and release the Tab key until the po p-up window is selected.
4. Release the Alt key. The selected pop-up window is displayed.
Resource is not selectable
When a command’s argument is not selectable (does not appear in a selection list), you must manually
enter the resou
Such circumstances typically occur when one command in a job refers to a resource that is created
by another command in the same job.
Example - Mounting a replica
When a job creates a replica of a di sk, the replica will not exist until the job is run. Thus, when editin g a
command that refers to the replica, the replica’s UNC name does not appear in a selection list. In this
case, you can manually enter the name (as specified by the command that creates it), or reference the
resource by using a variable.
Example - Working with a new DR group
When a job cre
Thus, when ed
selection l
enter the name (as specified by the comma nd that creates it).
rce name or a enter variable that represents the resource.
ates a new DR group, a new destination storage volume will not exist until the job is run.
iting the commands that refer to the new disks, the disk’s UNC name does not appear in a
ist. Because in this case the new disk cannot be referenced by a variable, you must manually
Scheduled job events do not run
Problem
Scheduled job events do not run. In the events pane, the following message appears:
Internal e
See events pane.
Explanation / resolution
The security credentials (user na m e and password) that were saved with scheduled job events may not be
correct. See security credentials for the server.
1. Open a scheduled job event. See editing scheduled job events.
2. Enter the correct security credentials (to log on to the replication manager server) and click OK.
3. Repeat for each scheduled job event that has incorrect security credentials.
In some cases, subject to your security policies, consider changing the security credentials of the
replication manager server (one change) to match those saved with the job events (potentially many
changes).
rror occurred starting job <job name>.
Scheduled job event run times are wrong (AM/PM)
Problem
Symptoms that can indicate this problem:
• When using the Schedule a Job wizard, a time of day entered as PM appears as AM on the
final page.
• A scheduled job runs at an unexpected time.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
49

Explanation / resolution
This can occur due to a non-English setting on a Windows-based storage management server. A
non-English setting changes the time entered in the Schedule a Job wizard to an AM time. For example, a
time entered in the wizard as 2:00 PM is saved as 2:00 AM.
To correct this problem, perform the following procedure. You must be a member of the server’s
Administrators group.
CAUTION:
Performing this procedure requires a reboot.
1. Coordinate reboot activities to avoid disruption of services to others. Ensure that no replication
manager jobs are running or are scheduled to run during the reboot.
2. On the Window-based storage management server, select Start > Control Panel > Regional and
Language Options > Advanced tab.
3. On the Advanced tab, under Standards and formats, select Englis h (United States).
4. Click OK and follow the Windows on-screen instructions.
5. When prompted, reboot the computer. Click Yes to complete the change to Windows.
6. In the replication manager, edit any scheduled job events that had incorrect run times. See
Editing scheduled job events.
7. If you have previously exported the replication manager da tabase (that included incorrect times),
HP recommends that you perform a new export.
Second snapclone of the same storage volume or host volume fails
Problem
Thesecondsnapcloneofthesamestoragevolumeorhostvolumefailsandthereplicationmanager
logs a message like:
Copy type CLONE not available or no resource bundle
Explanation / resolution
You can make multiple snapclones of a source volume. However, only one snapclone can b e in the
normalization (unsharing) phase at one time. If the second snapclone action is started too soon, the
action can fail.
This issue can occur when:
• You run and then quickly rerun the same job.
• The replication ma nag er database was not refreshed after the first snapclone was completed.
When the second snapclone is requested, the replication manager encounters the out-of-date
normalization status in the database and fails the requested snapclone action.
To resolve this issue:
• Allow sufficient time after between snapclones to allow the unsharing process to complete.
• Allow sufficient time between snapclones to allow the replication manager database to be
refreshed.
Slow login times
Problem
After entering a user name and password to log in to the replication manager ser ver, there is no response
for 30 seconds or more.
Explanation / resolution
50
Replication Solutions Manager

In some cases, a slow login response can occur. This does not indicate that the server application
has stopped.
Unable to resume a DR group
Problem
When attemptin
g to resume a DR group, the replication manager logs the message:
Unable to resum
Explanation /
You cannot use the replication manager to resume remote replication if the status of a DR group pair is
failed.
In some cases, the replication manager may temporarily report the status as failed, even thoug h the
actual status is normal (as reported by HP Command View EVA). This can happen because the status of
aDRgrouppair
manually per
To resolve this issue and resume the DR group as quickly as possible:
1. In the replication manager DR Groups List tab or Tree tab, check the operational status of
the DR group.
2. If the status is failed (red), use HP Command View EVA to check the status of the DR group
(see HP Comm
3. In HP Command View EVA, if the status is normal, issue a resume command to resume the
DR group.
4. After the DR group is resumed, manually refresh it. See low-level refreshing DR groups.
5. You can again use the replication manager to resume/suspend the DR group.
e DR group <G roupName> because of current state of group for job <JobName>
resolution
is updated in the replication m a nager only when an automatic refresh o ccurs or you
form a refresh.
and View EVA online help).
Troubleshooting - HP-UX
Host age
nt discovery hangs and times out - HP-UX
Problem
IfadeviceonanHP-UXenabledhostisinafailedstate,thediscoveryofhostvolumesonthathost
can hang
Explana
This issue is caused by HP-UX and can happen on versions 11.23 and 11.11.
To resolve this issue:
1. On the en
2. Allow sufficient time for a discovery of enabled hosts to occur. See automatic refresh of resources.
3. Verify that the discovery was completed.
and cause the discovery to time out.
tion / resolution
abled host, remove or correct the failed devices.
Job with CreateHostVolume command fails - HP-UX
Problem
A job that replicates a storage volume fails at a C reateHostVolume command when attempting to create
a host volume on an HP-UX enabled host. The replication manager logs a message such as:
Unknown exception on host: Volume group /dev/h32xg02_RV0 failed to create:
Volume Group /dev/h32xg02_RV0 is still active.
Explanation / resolution
The HP-UX kernel recognizes device drivers and peripheral devices by major and minor numbers. The
driver uses minor numbers to locate specific devices. HP-UX sometimes does not release device minor
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
51

numbers after a volume group is removed. When the CreateHostVolume command is run, the volume
group appears to still be active and the command fails.
To resolve this issue, you must reboot the enabled host:
IMPORTANT:
Before proceeding, coordinate the reboot activities to avoid disruption of host services to others.
1. Ensure that no replication manager jobs involving the host are running or scheduled to run
during the reboot.
2. On the enabled host, close applications, as appropriate.
3. Reboot the host. This clears the device minor numb ers for the host memory.
4. Restart applications on the host, as appropriate.
5. If necessary, clean up resources that were involved in the failed job.
6. Rerun the job.
Job with MountEntireVolumeGroup command fails - HP-UX
Problem
A job that replicates and mounts an HP-UX volume group fails at a MountEntireVolumeGroup command
when attempting to mount the volume group on an enabled host. The replication manager logs a
message such as:
Host Volume has unknown or incompatible ...
Explanation / resolution
This can occur when a job is rerun.
IfthereplicationmanagerdiscoversanHP-UXvolumegroupatthesametimethatajobcommandis
attempting to remove the volume group, an error allows the underlying storage to be unpresented from
the host, even though the volume group is still active.
When the job is run again, the volume group cannot be replicated and the job fails at the mount step
because there is no underlying storage available.
To resolve this issue:
1. In the replication manager or HP Command View EVA, correct the presentation of the underlying
storage for the volume group.
2. If necessary, clean up resources that were involved in the failed job.
3. Rerun the job.
Host volume with PVLinks multipathing
Problem
If the source host volume uses HP-UX PVLinks for multiple paths, a replica will have only one path defined.
Explanation / resolution
When replicating a host volume with PVLinks multipathing, replication manager jobs define only one
path in the replica. If necessary, you can use PVLinks to add paths to the replica after the job is finished.
See CreateHostVolume and CreateHostVolumeGroup job commands.
Troubleshooting - Linux
Jobthatcreatesahostvolumerunsslowly-Linux
Problem
52
Replication Solutions Manager

A job that creates a Linux host volume runs slowly or appears to hang.
Explanation / resolution
First, check the job to see if it contains one of the following commands:
CreateHostVolume CreateHostVolumeDiscrete CreateHostVolumeGroup
If so, one of the following conditions may apply.
Host QLogic HBA driver LUN setting is exceeded
The d efault support for QLogic HBA drivers is 32 LUNs (virtual disks). If there are more than 32 LUNs
(which is typical with EVA storage systems) the create host volume style commands can execute for an
extended period of time because the LUN is not found on the host.
To resolve this problem:
1. On the enabled host, open the probe-luns fi le in a text editor. It is located at:
/opt/hp/hp_fibreutils/probe-luns
2. In the file, modify the LUNEND variable to allow for the number of LUNs in your situation.
Save the file.
3. If necessary, clean up resources that were involved in the failed job.
4. Rerun the job.
Host QLogic HBA driver is frozen
If the QLogic HBA driver is frozen, none of the LUNs may be visible to the host.
To resolve this issue:
1. On the enabled host, reload the QLogic HBA driver or reboot the host.
2. If necessary, cleanup resources that were involved in the failed job.
3. Rerun the job.
Job with volume group remount fails - Linux
Problem
A job creates a replica of a Linux volume group and mounts it on a host. In subsequent steps the job
unmounts the replica and then attempts to remount it on another host. During the remount step the job fails.
Explanation / resolution
You cannot remount the replica of a Linux volume g roup because the context of the volume group is
lost after the first mount.
IMPORTAN
The job te
mountandremountareplica. DonotusethetemplatewithLinuxvolumegroups.
To resolve this issue:
1. If necessary, cleanup resources that were involved in the failed job.
2. Edit the job and remove the remount steps.
3. Create another job to mount the replica on a different enabled host.
T:
mplate named
Replicate host volume(s), mount to a host, then to a different host,
Troubleshooting - Windows
Explorer does not show a host volume after a job is run - Windows
contains steps to
Problem
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
53

A job is run that mounts, unmounts, and remounts a host volume (for example, drive F) on a Windows
enabled host.
After the job completes successfully, Windows Explorer on the host does not show the disk (drive letter
F). The disk does appear in the host Disk Management window, but Open and Explore operations
on the disk fail.
Explanation / resolution
The dynamic remounting (mount without a reboot) step in the job causes the host OS to loose track of
some drive information.
To resolve this issue:
1. Ensure that no replication manager jobs involving the host are running or scheduled to run
during the reboot.
2. On the enabled host, close applications, as appropriate.
3. Reboot the host. This clears the drive information issue.
4. Restart applications on the host, as appropriate.
5. Consider rewriting the job to eliminate the remount issue.
Troubleshooting - Tru64 UNIX
Job with AdvFS replication fails - Tru64 UNIX
Problem
Job that replicates Tru64 UNIX AdvFS host volumes fails on job commands like:
CreateHostVolumeFromDiskDevices
CreateHostVolumeGroup.
Messages in the replication manager event log indicate that the host volume could not be found in
the volume group.
In the host directory /var/adm/messages, a message like the following can appear:
Jun 5 18:50:44 rita vmunix: Found bad xor in sbm_total_free_space!
Corrupted SBM metadata file!
Jun 5 18:50:44 rita vmunix: An AdvFS domain panic has occurred due to
either a metadata write error or an internal inconsistency. This domain is
being rendered Jun 5 18:50:44 rita vmunix: Please refer to guidelines in
AdvFS Guide to File System Administration regarding what steps to take to
recover this domain.
Explanation / resolution
When a job is run, heavy I/O in any of the mounted fi lesets in the domain can lead to domain panic,
causing the job to fail.
Resolve any issues on the host, modif y the job to use freezefs and thawfs utilities, and rerun the job. For
the necessary steps in the job, see Suspending I/O before replicating AdvFS volumes - Tru64 UNIX.
54
Replication Solutions Manager

2 Replication resources
Working with resources
Best practices for automatic refresh
The refresh of storage systems information during an automatic refresh can take a significant
amount of time and plac e heavy dema n ds on the management server and storage systems. See
refreshing resources (automatic).
Depending on the circumstances, administrators may want to adjust the replication managers’s automatic
refresh interval. See configuration, setting the refresh period.
Typical cir
• If other applications are using the same storage arrays, or are installed on the same management
• If the stor
• If you are configuring an environment or performing testing, the default discovery and database
• If you ar
cumstances include:
server, a short discovery and database refresh interval may slow the performance of the storage
arrays or management server. In this case, consider a longer period.
age configuration is large, or there are delays in the environment, discovery and
database r
consider a longer interval.
refresh inter val may be too long for changes to be reflected quickly. In this case, consider
temporarily setting the interval to a few minutes.
shorter than required. In this case, consider setting the interval to several hours.
efresh can take a long time and may slow the replication manager. In this case,
e only monitoring storage, the default discovery and database refresh interval may be
Copying properties
Select a resource’s properties and copy them to another window or application.
Consid
Procedure
erations
• You can copy a single property, multiple ad jacent properties, or all properties in a window or
w section. See copying properties tips.
windo
• The entire property is copied. Except for comments, you cannot copy individual words or
characters in a property.
• The co
1. Open the window from which to copy properties.
2. Select the properties and press Ctrl+C. The p roperties are copied to the clipboard (Windows) or
3. Open the window or application in which to paste the properties, navigate to the appropriate
py-properties feature is not available in Configuration windows or the Licensing tab in the
Storage Systems Properties window.
See viewing properties for: DR groups, enabled hosts, host volumes, jobs, managed sets, Oracle,
storage systems and virtual disks.SeealsoEditing DR group properties.
similar memory area (other OSs).
location and press Ctrl+V. The properties are pasted.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
55

Copying properties - tips
Each procedure
below is co mpleted by pressing Ctrl+C to copy the selection.
Selecting adjacent property cells
In a properties window, do one of the following:
1. Click the first property cell to copy then press and hold the mouse button.
2. Drag the selection to the adjacent property cells. On the last property cell to copy, release the
mouse button.
or
1. Select th e first property cell to copy.
2. Press and hold the Shift key then select the last property cell to copy.
Selecting all property cells
1. Click any cell in a property window or section of a window.
2. Press Ctrl+A
.
Selecting a comment
In a comment cell, do one of the following:
1. To select the entire comment, click anywhere in the comment cell.
2. Press Ctrl+A.
or
1. To select part of a comment, click before the first character to copy then press and hold the
mouse button.
2. Drag the selection past the last character to copy and release the m ouse button.
Nonadjacent cells
The replication manager does not support selection of nonadjacent cells.
Filtering displayed resources
You can fi lter (select) the resources to display in content pane the list tabs.
Procedure
1. Filter
1. On the content pane, click the filter p roper t y box. A list of filters appears.
2. Select a resource filter. The selected filter type is displayed.
3. Click the filter value box. A list of values for the filter appears.
4. Select a value. Selecting <Choose Value> is the same as selecting no filter.
5. The filter is applied a nd only the selected resources appear.
type
2. Filter
value
56
Replication resources

Global refresh m onitor
The Global Refre
percent of the r
sh Monitor window opens when you start a global refresh. Progress bars indicate the
esources that have been refreshed.
1. Refresh button.
(restarts the refresh)
2. Progress bar for enabled hosts
and host volum
es refresh.
3. Progress bar for HP licences
refresh.
4. Progress bar for Oracle
resources ref
resh.
5. Progress bar for storage systems
refresh.
(includes DR groups and virtual
disks)
Organizing displayed resources
On the content pane, you can change the size and position of the columns in list and tree views. You can
sort displayed resources in list views.
1. Sort indicator 2. Column edge
Procedures
Resizing columns
1. Move the cursor over a column edge in the heading.
2. When a selection arrow appears, click and drag the column edge as required.
Moving columns
1. Click the heading of the column to move.
2. Hold
and drag the column to the desired location.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
57

Sorting a list v iew
1. Click the heading of the column on which to sort the list.
2. The list is sorted and a sort indicator appears.
3. To reverse the sort order, click the column heading again.
Refreshing display panes
Update the information that is displayed in the content and event panes.
Considerations
• Do not use browser refresh button.
IMPORTANT:
Do not use your browser’s refresh button to update the panes. Using the browser refresh may end the
replication manager session. To restart the session you must login again to the replication manager
server. See troubleshooting.
• The content pane is not updated automatically. Following a resource change that is initiated with
the replication manager (GUI, jobs or CLUI) you should refresh the content pan e.
• Whenever you select a different type of resource, the content pane is refreshed. For example, if
you are viewing DR Groups in the content pane and then select Host Volumes, the content pane is
refreshed and displays the current host volume resources.
• See also refreshing resources (automatic) and refreshing resources (global).
Procedure
1. On the content or event pane, click the refresh icon.
1. Refresh icon for content or event pane
2. The display is refreshed.
Refreshing resources (automatic)
The replication manager automatically discovers resources and refreshes its database at the intervals
noted below.
Automatic discovery type
Known storage systems, their DR groups and virtual disks
New storage systems, their DR groups and virtual disks
Known enabled hosts and their host volumes Every 2 hours Not changeable
New host volumes on known enabled hosts
Oracle resources on known enabled hosts Every 2 hours Not changeable
HP replication and application-integration licenses Every 6 hours Not changeable
Refresh interval
Every 30 minutes
Every minute
Every 10 minutes
Remarks
Changeable
Not changeable
Not changeable
58
Replication resources

IMPORTANT:
New enabled hosts are not automatically discovered or added to the database. To be visible to the
replication manager, an administrator must manually add them after installing replication manager
host agents.
• You can change the automatic storage refresh interval. See configuring the replication mana ger .
• When new resources are found, it may take some time to gather the new information and add it
to the RSM database.
Refreshing resources (global)
Update replication manager database entries by m anually performing a global discovery and refresh of
resources.
Considerations
• Manual refresh
IMPORTANT:
HP recommends that you manually refresh storage resources after using another interface that
changes the properties of storage systems, DR groups, or virtual disks. Refreshing resources,
especially storage resources, can take a significant amount of time and place heavy demands on
the management server and storage systems.
• Information in the content pane is not automatically updated after a refresh.
Procedure
1. On the toolbar, click the refresh icon.
1. Globalrefreshiconontoolbar
2. The Global Refresh Monitor window appears. See glob al refresh monitor.
3. You can do one of the following:
•ClickClose to close the window and continue working.
• View the refresh progress bars.
•ClickRefresh to restart the refresh.
4. Update the content pane. See refreshing display panes.
shing individual resources
Refre
e replication manager database entries by manually performing a discovery and refresh of
Updat
individual resources.
Considerations
• Individual resource refresh is only available for DR groups, enabled hosts, and virtual disks.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
59

• You can use the GUI or CLUI.
Procedures
• DR groups.Seelow-level refreshing DR groups.
• Enabled hosts
• Virtual disks.Seelow-level refreshing virtual disks.
.Seelow-level refreshing enabled hosts.
Selection of mu ltiple resources
When performing an action from the GUI, HP recommends selecting only a few resources at one time.
Selecting a large number of resources at once can cause slow response times.
For example, when deleting several virtual disks, it may appear to take a few seconds in the GUI.
However, deleting 50 virtual disks may take several minutes. The slower response can be m isinterpreted
as a problem.
Simulation mode
For more inf
guide is ava
See “Helpf
CAUTION:
HP strongly recommends that you do not run simulation mode on a production machine (that is, on the same
machine as Command View EVA). If you disconnect the replication manager from Command View EVA, you
lose control of the storage resources that were being managed by the replication manager. If you purge the
replication manager database and have not backed it up, you will lose all jobs.
ormation, see the HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager Simulation guide.The
ilable from the help menu of the replication manager GUI and from the HP Storage web site.
ul web sites” on page 19.
Overview
Simulation m o de allows you to use all of the functions of the replication manager without having to use
any of your production data or resources. These functions include creating snapshots and snapclones,
creating DR groups and adding virtual disks to them, and performing failovers.
Features and benefits:
• No SAN infrastructure, storage arrays, hosts, or management servers are required.
• Requires only replication manager server software running on a business class Windows desktop
or laptop computer.
• True simulation – not a set of predefined scenarios. Simulates GUI actions, jobs, and CLUI
commands.
• Allows you to create your own:
• Simulated storage arrays. Select features such as array capacity, software controller versions
and number of virtual disks.
• Simulated hosts. Include hosts and select the storage arrays they are connect to.
• Simulated Oracle databases. Simulate Oracle databases, tablespaces, datafiles, archived
redo logs, control files, and repositories.
Resource concepts
About replication resources
Resource types are displayed on the left, in the navigation pane. Individual resources are displayed on
the right, in the content pane.
60
Replication resources

1. Resource types
Resource types
The following resources types are supported. For more information on each type, click the link.
2. Individual resources
DR groups
Enabled hosts About enabled hosts
Host volumes About host volumes
Jobs About jobs
Managed sets About managed sets
Oracle About Oracle resources
Storage systems
Virtual disks About virtual disks
Resource states
The state
Icon
Description
Normal/Good. Resource is operating normally.
Warning. Resource is o perating normally but is in a temporary abnormal
state; the operator should monitor the resource. Also, indicates any
condition that needs attention.
About About DR groups groups
About storage systems
s of resources are indicated as follows.
Severe.
act imme
Unknown. Resource cannot be reached or its state cannot be determined.
Resource has experienced a catastrophic failure; the operator must
diately to prevent further failures or data loss.
Event states are similar and are d isplayed in the event pane. A DR group’s operational state uses
special icons to represent a combination of DR group states and modes.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
61

Resource names a
Resources in a SAN are identified in several ways, including UNC format. UNC (Universal or Uniform
Naming Convention) identifies a resource in terms of its hierarchical location in a network.
See the following for name and UNC formats: DR groups, enabled hosts, host volumes, Oracle,
storage systems,andvirtual disks (storage volumes)
nd UNC formats
Resource names in job commands
When you initially enter a command in a job, the comm and’s resource arguments are displayed
as %variable% names, for example:
CreateDiskDevice (%storvol_unc_name%, %host_name%,0,READ_WRITE)
When selecting a specific resource from an Editing Task menu, the resource names are presented in a
UNC format, or other format, as appropriate for the resource. If you enter a resource name from the
keyboard, you must use the appropriate format.
IMPORTANT:
UNC names in
After selection or entry of arguments, the comma nd is displayed with resource names in quotes, for
example:
CreateDiskDevice ( "\\ArrayA2\Cats", "HostA6", 12, READ_WRITE )
job commands are case sensitive.
Name formats and examples for resource types follow.
DR groups
Name format (UNC)
\\array name\path\DR group name
Enabled hosts
The job editor and command validation accept these formats.
Name format (other)
Computer network name
Fully qualified network name
IP address
Host volumes
Applies to standard host volumes, volume groups, logical volumes, and host volume components such as
partitions and slices.
Example
\\ArrayA2\DrGrpPets
Identifies the DR group named DrGrpPets on th e
storage array named ArrayA2.
Example
HostA6
HostA6.SiteA.corp
88.15.42.101
Each example identifies an enabled host using
an accepted format.
62
Replication resources

Name format (UNC) OS specificExample
Oracle
\\host name\path\host volume name
Name format (U
\\enabled host\database name \\HostA2\Cats_db
\\enabled h ost\repository name \\HostA2\Catalog 2005121 8.024153
NC)
AIX
HP-UX
Linux
OpenVMS
Solaris
Windows
For each OS, identifies the path and file named
Cats on the enabled host named HostA2
\\HostA2\/home/cats
\\HostA2\/users/cats
\\HostA2\/var/cats
\\HostA2\[pets.cats]
\\HostA2\/usr/cats
\\HostA2\E:\pets\cats
Example
IdentifiestheOracledatabasenamedCats_db
on the enabled host named HostA2.
Identifies the repository named Catalog
20051218.024153 on the enabled host named
HostA2.
Storage sys
tems
Name format (other)
storage nam
e
Virtual disks (storage volumes)
Applies to standard storage volumes (virtual d isks), snapclones (standard virtual disks), snapshot virtual
disks, and storage containers.
Name format (UNC)
\\array name\path\storage volume name \\ArrayA2\Cats
Simulation mode
For more i
guide is
See “Hel
nformation, see the HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager Simulation guide.The
available from the help menu of the replication manager GUI and from the HP Storage web site.
pful web sites” on page 19.
Example
ArrayA2
Identifies t
he storage array named ArrayA2.
Example
Identifies the storage volume named Cats on the
storage array named ArrayA2.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
63

Overview
CAUTION:
HP strongly recommends that you do not run simulation mode on a production machine (that is, on the
same machine as Command View EVA).
If you disconnect the replication manager from Command View EVA, you lose control of the storage resources
that were being managed by the replication manager. If you purge the replication manager database
and have not backed it up, you will lose all jobs.
Simulation m o de allows you to use all of the functions of the replication manager without having to use
any of your production data or resources. These functions include creating snapshots and snapclones,
creating DR groups and adding virtual disks to them, and performing failovers.
Features and benefits:
• No SAN infrastructure, storage arrays, hosts, or management servers are required.
• Requires only replication manager server software running on a business class Windows desktop
or laptop computer.
• True simulation – not a set of predefined scenarios. Simulates GUI actions, jobs, and CLUI
commands.
• Allows you to create your own:
• Simulated storage arrays. Select features such as array capacity, software controller versions
and number of virtual disks.
• Simulated hosts. Include hosts and select the storage arrays they are connect to.
• Simulated Oracle databases. Simulate Oracle databases, tablespaces, datafiles, archived
redo logs, control files, and repositories.
Licenses
License displays
License information is displayed in the GUI. See the following table.
If the licenses summary indicates an issue, you c an use the License Events pane to identify the affected
storage array. Then, you can review the affected array’s license information in the Storage Properties
window.
64
Replication resources

License display Remarks
License summary. A license status summary appears
on the right side of the status bar at the bottom of the
replication manager window.
• The status includes replication licenses and
Oracle-integration licenses.
• Status messages indicate if all discovered licenses
arevalidorifthereisanissue.
License events.. Events that involve license status
appear on the License Events tab of the events content
pane.
Licenses for
individual
Properties
Licenses for Oracle resources. The license status
an individual tablespace appears on the Oracle
Tablespaces properties window.
License details appear in the Configuration window.
License states
General
• Expiring. All discovered licenses are currently valid. However, one or more expires within 60
days.
• Over capa city. One or more resources has exceeded a license’s capacity.
an array. The status of licenses for an
array appears on the array’s Storage
window.
• License events include replication licenses and
Oracle-integration licenses.
• See events overview and viewing events.
• Properties include the status of replication licenses
and Oracle-integration licenses.
• See Storage Properties window - Licensing tab
and viewing storage properties.
• See viewing Oracle resource properties.
• See licenses configuration - applications.
-integration
Oracle
• Not licensed. N one of the arrays on which the resource is stored are licensed.
• Partia
lly licensed. One or more arrays on which the resource is stored are licensed, but not a ll.
• Fully licensed. All arrays on which the resource is stored are licensed.
Oracle-integration licenses overview
To use the replication manager’s Oracle-integration features with a given array, the replication manager
verifies that appropriate HP Oracle-integration licenses exist for that array.
• For information on acquiring and installing Oracle-integration licenses, see the HP StorageWorks
Replication Solutions Manager a dministrator guide.
• Oracle-integration licenses are verified during automatic and global refreshes. See
refreshing resources (automatic) and refreshing resources (global)
• Oracle-integration license status is displayed in the GUI. See license status.
Oracle-integration license policies
HP license policies determine how the replication man ager interacts with resources that require HP
cle-integration licenses.
Ora
following summarizes the policies.
The
• Verification.Licenseverification includes factors such as:
•Typeoflicense
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
65

• Expiration date (if any)
• Capacity range (amount of storage)
• Multi-array resources. If an Oracle resource such as a database or tablespace is comprised of
virtual d isks on two or more arrays, each array must have an HP Oracle-integration license.
• GUI actions. Some GUI actions may be disabled if an applicable HP license is not verified.
Disabled actions appear in gray and cannot be selected. A tooltip indicates why the action
cannot be performed. See tooltips.
For example, if you select an Oracle database and the Replicate Database (Snapclone) action is disabled,
itcanbebecausethestoragesystemthatcontainsthedatabasedoesnothaveanappropriatelicense.
• Job commands. Some job commands m ay not be executed if an applicable HP license is not
verified when a job is run. An event in the job log indicates the command d id not execute due
to a licensing issue.
For example, if a CreateHostVolumesUsingRepository command in a job did not execute when the
job was run, it may be because a storage system on which the database is located did not have an
HP Oracle-integration license.
IMPORTANT:
HP recommends that you include validation commands in jobs and perform validation tests to prevent or
minimize the effect of license-related issues at run time.
Replication l icenses overview
To use loc al and remote replication features on a given array, the replication manager verifies that
appropriate HP replication licenses exist for that array.
• For information on acquiring and installing local replication licenses, see the HP StorageWorks
Business Copy EVA administrator guide.
• For information on acquiring and installing remote replication licenses, see the HP StorageWorks
Continuous Access EVA administrator guide.
• Replication licenses are verified during automatic and global refreshes. See
refreshing resources (automatic) and refreshing resources (global).
• Replication license status is displayed in the GUI. See license status.
Replication license policies
HP license policies determine how the replication manager interacts with resources that require HP
replication licenses.
The following summarizes the policies.
• Verification.Licenseverification includes factors such as:
•Typeoflicense
• Expiration date (if any)
• Capacity range (amount of storage)
• Multi-array volumes. If a volume is comprised of virtual disks o n two or more arrays, each array
must have an HP replication license in order in order to be considered fully licensed.
• GUI actions. Some GUI actions may be disabled if an applicable HP license is not verified.
Disabled actions appear in gray and cannot be selected. A tooltip indicates why the action
cannot be performed. See tooltips.
For example, if you select a virtual disk and the New Snapclone action is disabled, it can be because the
storage system that contains the disk does not have a local replication license.
• Job commands. Some job commands m ay not be executed if an applicable HP license is not
verified when a job is run. An event in the job log indicates the command d id not execute due
to a licensing issue.
66
Replication resources

For example, if a SnapcloneStorageVo lume command in a job did not execute when the job was run, it
may be bec ause the storage system that contains the disk did not have a local replication license.
IMPORTANT:
HP recommends that you include validation commands in jobs and perform validation tests to prevent or
minimize the effect of license-related issues at run time.
• CLUI commands. CLUI commands that run jobs or create implicit jobs behave like job commands.
An event in the job log indicates that the command did not execute due to a licensing issue.
Dynamic capacity management license policy
The DC-Management feature requires an array-based DC-Management license in RSM.
DC-Management license
RSM 3.1 ships with an instant-on license for the DC-Management feature. The instant-on license is valid
for 60 days from the time of install, after which you may request an extension to the license. This license
enables the DC-Management feature for all arrays during the validity period.
When the instant-on license expires, the DC-Management feature is disabled unless a permanent license
is installed. Permanent licenses are installed on a per-array basis.
The DC-Management license can be viewed, retrieved, and added by selecting Tools > Configure >
Licensing.
Security Credentials
Security credentials for the server
To establish and manage replication manager server security credentials, administrators must use the
OS on the m anag em ent server See security groups configuration and the HP StorageWorks Replication
Solutions Manager installation guide and HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager administrator
guide.
Server security credentials (user name and password) must be provided for the following cases:
• GUI logon. To access the GUI, you must enter replication manager security credentials in the
logon window.
• Creating a scheduled job event. To schedule a job event, you must enter replication manager
security credentials in the Schedule Job window.
• CLUI logon. To access the CLUI via any method other than the GUI, you must enter include
replication manager security credentials in the CLUI logon commands.
Passw or d change considerations
Administrators should carefully plan and coordinate sever security credential changes with replication
manager operations. For example, if the security policy in your environment is to reset passwords every
six m onths, consider that such changes can result in the following:
• Logging on to the GUI is prevented
• Scheduled job events are p revented from running.
• Logging on to the CLUI is prevented.
Security credentials for enabled hosts
To establish and manage replication man ager host agent security credentials, administrators must use
the OS on each enabled host. See security groups configuration and the HP StorageWorks Replication
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
67

Solutions Manager installation guide and HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager ad ministrator
guide.
For an enabled host to interact with the server, a valid host agent security credential must be
present in the replication manager database. See setting security credentials for enabled hosts and
adding a new enabled host.
IMPORTANT:
If a valid security credential is not entered or if the credential expires or is changed, the replication manager
(GUI, jobs, and CLUI) will not be able to interact with the enabled host.
Hostagentsecuritycredentials(usernameandpassword)mustbeprovidedforthefollowingcases:
• New enabled host. To add a new enabled host to the replication manager database, an
administrator must enter a valid security credential.
• Changed credentials. To update the security credential that is saved in the database, an
administrator must enter a new security credential.
• Imported RSM database. After importing an RSM database that includes enabled hosts, an
administrator must re-enter the security credentials.
Password change considerations
Administrators should carefully plan and coordinate host agent security credential changes with
replication manager operations. For example, if the security policy in your environment is to reset
passwords every six months, consider that such changes can result in enabled hosts n ot interacting with
the replication m anager server. This can lead to the following:
• Jobs that interact with impacted enabled host do not validate or fail while running.
• CLUI commands that interact with impacted enabled host fail.
• Enabled host and host volume information is not updated in the server.
• Oracle d atabase information is not updated in the replication manager server.
Security credentials for Oracle databases
For the replication manager to interact with an Oracle application, an account for the replication manager
must be established by an Oracle database administrator. See the HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions
Manager installation guide and HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions Manager administrator guide.
For the replication manager to interact with an Oracle database, a valid security
credential for the database must be present in the replication manager database. See
setting security credentials for Oracle databases.
IMPORTANT:
If a valid security credential is not entered or if the credential expires or is changed, the replication manager
(GUI and jobs) will not be able to interact with the Oracle database.
Oracle database security credentials (user name and password) must be provided for the following cases:
• New Oracle database. To add a new Oracle database to the replication manager database, an
strator must enter a valid security credential.
admini
• Changed credentials. To update the security credential that is saved in the database, an
administrator must enter a new security credential in the Set Credentials window.
• Impor
ted RSM datab ase. After impor ting a n RSM database that includes Oracle resources, an
administrator must re-enter the security credentials.
68
Replication resources

Passw or d change considerations
Administrators should carefully plan and coordinate Oracle database security credential changes with
replication manager operations. For example, if the security policy in your environment is to reset
passwords every six months, consider that such changes can result in the replication manager server not
interacting with an Oracle database. This can lead to the following:
• Jobs that interact with impacted databases do not validate or fail while running.
• Oracle database information is not updated in the replication manager server.
Security cre
Replication
Storage Use
Most tasks r
relationship between security credentials and tasks that are allowed.
Item or
resource
Replication
manager
DR groups
dentials vs. tasks
manager tasks can only be performed by members of the HP Storage Admins group or HP
rs security groups on the management server. See security credentials configuration.
equire membership in the HP Storage Admins group. The following table shows the
Task Credential Remarks
Configure
Enable and disable
simulation mode
Export a
databas
Manage and view event logs
Add, change, delete and
view
Failover,suspend,resume
and force full copy
nd import RSM
e
Admin
allowed
yes no
yes no
yes no
yes
yes
yes no
User
allowed
Users can only
view.
partial Users can only
view.
partial Users can only
view.
Enabled hosts Add, change, delete and
tvolumes
Hos
Jobs Add, edit, delete, monitor
view
Run host script and set
security credentials
, change, delete and
Add
ew
vi
Replicate
and view
Schedule, run, pause,
continue, and abort
yes
yes no
yes
yes no
yes
es
y
partial Users can only
par
partial Users can only
n
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
tial
o
view.
rs can only
Use
ew.
vi
view.
69

Item or
Task Credential Remarks
resource
Managed sets Add, change, delete and
view
yes
partial Users can only
view.
Oracle
integration
Storage systems
Virtual disks Add, change, delete and
Topology views
About to
pology views
The top
replication tasks.
ology tab provides an interactive graphical environment in which to view resources and perform
Add, change, delete and
view Oracle resources
Back up and res
databases
Add, change, delete and
view resources
Manage replication licenses
view resources
Replicate, present and
unpresent
tore Oracle
yes
yes no
yes no
yes
yes
yes no
partial Users can only
partial Users can only
partial Users can only
view.
view.
view.
Key features include:
• Select from predefined resource views.
• Perform actions on resources
• View resource properties and labels
• Change the layout
• Filter the view using managed sets.
Sample topology view of two
storage systems and their virtual
disks.
ccess the topology tab, see displaying the topology tab.
To a
IMPORTANT:
Do not use browser buttons to refresh the topology view or to navigate. Using browser buttons will end
the session. See troubleshooting browser window is blank.Theviewisautomaticallyrefreshedfromthe
replication manager
database
every 15 seconds. See also automatic refresh of resources.
70
Replication resources

Views
The View menu allows you to select the resources to display. Each of the predefined views shows the
logical relationships among resources. See DR groups topology view, host volumes topology view, and
virtual disks topology view.
Menu of actions
You can right-click a resource to display a menu of
actions or to navigate (jump) from the topology tab to
the appropriate content pane.
Properties
You can mouse over a resource to display its key
properties.
Labels
To show or hide all resource labels, use the Toggle Labels action.
Layout control
You can change the layout by using the following:
• Drag-and-drop.Movearesourcetoanewlocation.Seepinned view tips.
• Zoom buttons
• Layout button
• Pin/unpin button
See pinned view tips and layout tips.
• Clear all pins action. Unpin (unlock) the locations of all resources in a ll views. See
clear all pins tips.
. Change the size and extent of the view.
.Redrawtheview.Layoutbehaviorvaries.Seelayout tips and pinned view tips.
. Pin (lock) or unpin (unlock) the locations of resources in the view.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
71

Filters
By default all appropriate objects for a view are displayed. You can use the Filter menu to select and
apply a custom filter to the view. See filters for views.
Displaying the topology tab
1. In the GUI navi
The Replication content pane is displayed.
2. In the Replication content pane, select the Topology tab. The Topology tab and its current
view appear.
IMPORTANT:
Do not use browser buttons to refresh the topology view or to navigate. Using browser buttons will end
the session. See troubleshooting browser window is blank.Theviewisautomaticallyrefreshedfromthe
replication manager
gation pane, select Replication.
database
DR groups topology view
Description
The DR groups topology view shows logical relationships among storage systems, DR groups, and virtual
disks within DR groups. The default layout is organized in centric circles. Storage systems, DR groups,
and virtual disks appear in the inner, middle and outer circles, respectively
every 15 seconds. See also automatic refresh of resources.
Features
Sample default layout
Thefollowingfeaturesareavailableinthetab:
Typical resources in a view
1. Storage system
2. DR group (source)
3. Virtual disks in DR group
4. Remote replication link
(points from source to destination)
5. DR group (destination)
6. Virtual disks in DRgroup
7. St o ra g e sys t em
72
Replication resources

Item
Actions > Toggle Labels Displays or hides resource labels in all views.
Description
Actions > Clear all pins
Filter
View
Double-click
Mouse over a resource
Right-click a resource
Drag-and-dro
aresource
paresource
Unpins (unlock
clear all pins t
Filters the resources that are displayed. See filters for views
Selects the resource type (and related resources) to view.
Opensthecontentpanefortheresource(andclosesthetopologytab
Displays a short list of the resource’s properties.
Opens an actions menu for the resource.
Moves a resour
pinned view ti
Pin toggle. Pins and unpins (locks/unlocks) all resource locations in a view.
See pinned view tips.
Zooms the view in and out.
Redraws the view. Layout behavior varies. See layout tips and
pinned view tips.
Prints the view.
Displays context-sensitive help.
s ) the locations of all resources in all views. See
ips
ce to a new location in an unpinned view. See
ps.
Icons
IMPORTANT:
Do not use browser buttons to refresh the topology view or to navigate. Using browser buttons will end
the session. See troubleshooting browser window is blank.Theviewisautomaticallyrefreshedfromthe
replication manager
database
every 15 seconds. See also automatic refresh of resources.
The following icons may appear in the view:
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
73

Icon
Description
Storagesystemisnormal
Storagesystemisinitializingorinanunknownstate
More help
• Overview.
• Tips.Seetopologyviewtips.
• Filters.Seefilters for views.
Storage system
Storage system is failed or there is a bad connection to the storage manager
DR group is nor
DR group is disabled, degraded, unknown, copying, constructing or d eleting
DR group is failed
Remote repli
Remote replication is not in a steady state
Virtual dis
Virtualdiskisinanunknownstate
Virtual disk degraded, disabled, deleting, copying, or constructing
Virtual disk is failed
is disabled, degraded, or unmanaged
mal
cation is in a steady state
kisnormal
See about topology views.
Host volumes topology view
Descript
ion
The host volumes topology view shows logical relationships among enabled hosts, their host volumes,
and the underlying virtual disks in the host volumes. The default layout is organized in centric circles.
Enabled hosts, host volumes, and virtual disks appear in the inner, middle an d outer circles, respectively.
74
Replication resources

Features
Sample default layout
For more information, see about host volumes.
Thefollowingfeaturesareavailableinthepane:
Typical resources in a view
1. Enabled host
2. Host volume
3. Virtual disk
Item
Actions > Toggle Labels Displays or hides resource labels in all views.
Actions > Clear all pins
Filter
View
Double-click a resource
Mouse over a resource
Right-click a resource
Drag-and-drop a resource Moves a resource to a new location in a n unpinned view. See
Description
Unpins (unlocks ) the locations of all resources in all views. See
clear all pins tips
Filters th
Selects the resource type (and related resources) to view.
Opensthecontentpanefortheresource(andclosesthetopologytab
Displays a short list of the resource’s properties.
Opens an actions menu for the resource.
pinned view tips.
Pin toggl
See pinne
Zooms the view in and out.
Redraws the view. Layout behavior varies. See layout tips and
pinned view tips.
Prints the view.
e resources that are displayed. See filters for views
e. Pins and unpins (locks/unlocks) all resource locations in a view.
dviewtips.
Displays context-sensitive help.
IMPORTANT:
Do not use browser buttons to refresh the topology view or to navigate. Using browser buttons will end
the session. See troubleshooting browser window is blank.Theviewisautomaticallyrefreshedfromthe
replication manager
database
every 15 seconds. See also automatic refresh of resources.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
75

Icons
The following icons may appear in the view:
Icon
Description
Enabled host is normal
Enabled host is in an unknown state
Host volume
Virtual disk
Virtualdiskisinanunknownstate
Virtual disk degraded, disabled, deleting, copying, or constructing
Virtual disk is failed
Snapshot of a virtual disk
is normal
More help
• Overview.Seeabout topology views.
• Tips.Seetopologyviewtips.
• Filters.S
ee filters for views.
Virtual disks topology view
Description
The virtual disks topology view shows logical relationships between storage systems and virtual disks.
The default layout is organized into centric circles. Storage systems and virtual disks app ear in the
inner an
d outer circles, respectively.
Sample default layout
Typical resources in a view
Featu
res
The following features are available in the pane:
76
Replication resources
1. Storage system
2. Container
3. Virtual disk, original
4. Virtual disk, snapshot
5. Virtual disk, mirrorclone

Item
Actions > Toggle Labels Displays or hides resource labels in all views.
Description
Actions > Clear all pins
Filter
View
Double-click
Mouse over a resource
Right-click a resource
Drag-and-dro
aresource
paresource
Unpins (unlock
clear all pins t
Filters the resources that are displayed. See filters for views
Selects the resource type (and related resources) to view.
Opensthecontentpanefortheresource(andclosesthetopologytab
Displays a short list of the resource’s properties.
Opens an actions menu for the resource.
Moves a resour
pinned view ti
Pin toggle. Pins and unpins (locks/unlocks) all resource locations in a view.
See pinned view tips.
Zooms the view in and out.
Redraws the view. Layout behavior varies. See layout tips and
pinned view tips.
Prints the view.
Displays context-sensitive help.
s ) the locations of all resources in all views. See
ips
ce to a new location in an unpinned view. See
ps.
Icons
IMPORTANT:
Do not use browser buttons to refresh the topology view or to navigate. Using browser buttons will end
the session. See troubleshooting browser window is blank.Theviewisautomaticallyrefreshedfromthe
replication manager
database
every 15 seconds. See also automatic refresh of resources.
The following icons may appear in the view:
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
77

Icon
Description
Storagesystemisnormal
Storagesystemisinitializingorinanunknownstate
Storage system
Storage system is failed or there is a bad connection to the storage manage
Virtual disk i
Virtualdiskisinanunknownstate
Virtual disk degraded, disabled, deleting, copying, or constructing
Virtual disk is failed
Snapshot of a virtual disk
Container for a virtual disk
is disabled, degraded, or unmanaged
snormal
More help
• Overview.Seeabout topology views.
• Tips.Seeto
pology view tips.
• Filters.Seefilters for views.
Filters for topology views
There can be many resources in a default view. To simplify a view, you can create a managed set
then select it as a filter for the view.
In the following example, a filter is applied to a complex view. The example filter is a managed set of
virtual disks that includes three disks.
Sample view without a filter Sample view with a filter
Applicable filters
The following table identifies the types of managed sets that are applicable to ea ch view. If you select a
filer that is not applicable to a view, the view is not filtered.
78
Replication resources

View
DR groups view
storage systems > DR groups > virtual disk
Host volumes view
enabled hosts > host volumes > virtual disks
Virtual disks view
storage systems > virtual disks
More help
• General information.Seeabout managed sets.
• Procedures.Seecreating managed sets and adding resources to a managed set.
Tips (topology views)
General
IMPORTANT:
Do not use browser buttons to refresh the topology view or to navigate. Using browser buttons will end
the session. See troubleshooting browser window is blank.Theviewisautomaticallyrefreshedfromthe
replication manager
database
Applicable managed set filter
DR
groups
yes - - yes yes
-yesyes- -
yes - - yes yes
Enabled
hosts
Host
volumes
Storage
systems
every 15 seconds. See also automatic refresh of resources.
Virtual
disks
Pinned view
• When a view is pinned (locked) you cannot move (drag-and-drop) resources in the layout. To
• Each view can be independently pinned or unpinned.
Layout
• An unpinned view is redrawn in its default layout and is sized to fit the current image area.
IMPORTANT:
The locations of all moved resources in the view are discarded. If you have moved many resources, HP
recommends that you pin the view.
• A pinned view is not redrawn unless it has been previously zoomed. When redrawn, the layout is
• In some cases, resources can extend beyond the scrollable image area. This is indicated by
move resources, unpin the view, move the resources, then re-pin the view.
the original size but retains the locations of m oved resources.
resource connection lines that extend off the tab.
To access these resources, you can zoom out until the resources appear in the view.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
79

Clear all pins action
• The Clear all pins action unpins all views and resets all views to their defaults. The displayed view
is immediately redrawn to fitthetab.
IMPORTANT:
You cannot undo a Clear all pins action.
Toggle labels action
• The Toggle labels action displays or hides all labels in all views.
• You cannot move a label independently of the object. If necessary to improve legibility, move
the object.
Filters
• You can have multiple m a nag ed sets that are used as filters. However, only one managed set can
be applied as a filter at one time.
• If you create an empty (but applicable) managed set and apply it to a view, no objects are
displayed.
• If you create a managed set only for the purpose of filtering a view, H P recommends that you
assign a filter-related name. For example, you might assign a na me like: disk filter - sales
department
This can help to quickly identify the type of filter. It can also help reduce the chance of subsequently
applying an action to the managed set (in the managed set content pane) that might be undesirable,
for example attempting to create snapshots of all the virtual disks in the man age d set.
80
Replication resources

3DRGroups
Working with DR groups
About DR group resources
The DR Groups content pane displays storage resources for remote replication. See GUI window
content pane.
The propertie
controller s
s of DR groups, and the remote replication actions that you can perform, depend on the
oftware version of the storage systems. See controller software features - remote replication.
For overview
replicatio
for remote r
s of remote replication and licensing, see remote replication overview and
n licenses overview. DR group resources are available only if a storage system is licensed
eplication.
Views
• Tabular list view. See DR groups list view.
• Graphical tree views. See: DR Grp Source/Destination tree view and
System/DR G rp/Virtual Disk tree view
Actions
• Actions in the GUI. See DR groups actions summary.
• You can al
actions
so interact with DR groups from a job and the CLUI. See DR groups
cross reference.
Properties
• Properties displayed in the GUI. See DR groups properties summary.
• You can also display properties from the CLUI. See the CLUI command Show DR group.
DR group actions summary
The following DR group actions are available on the content pane. Some actions have equivalent job
commands or CLUI commands. See DR groups actions cross reference.
Some actions are permitted only on a source DR group; other actions are permitted only on a destination
DR grou
• View Properties. View the properties of a DR group. Procedure.
• Edit Properties. Edit the properties of a DR group. Procedure.
• New.C
• Delete. Delete a DR group pair. Procedure.
• Add to Managed Set. AddaDRgrouptoamanagedset. Procedure.
• Remo
• Add Members.AddvirtualdiskstoaDRgrouppair.SeeProcedure.
• Remove Members. Remove virtual disks from a DR group pair. Procedure.
• Susp
• Resume. Resume remote replication in a DR group pair. Procedure.
• Failover. Reverse direction the remote replication in a DR group pair. Procedure.
p. See using DR group actions.
reate a DR group pair. Procedure.
ve from Managed Set. Remove a D R group from a managed set. Procedure.
end. Stop remote replication in a DR group pair. Procedure.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
81

• Enable Failsafe. Enable remote replication failsafe mode for a DR group pair. See DR g roups
failsafe mode. Procedure.
• Disable Failsafe. Disable remote replication failsafe mode for a DR group pair. See DR groups
failsafe mode. Procedure.
• Revert to Home Roles. Revert the DR g roup pair to its home configuration. See DR groups
home configuration. Procedure.
• Force Full Copy. Force data in a source DR group to be copied to its destination DR group, rather
than logging the data. See DR groups full copy mode. Procedure.
• Low-Level Refresh. Update the properties of a DR group. Procedure.
• List Events.Displayalistofeventsfortheresource.Procedure.
• Launch t he Device Manager. Access HP Command View EVA from the replication manager.
Procedure.
DR group ac
tions cross reference
You can work with DR groups using GUI actions, jobs and CLUI commands. This table provides a cross
reference for performing typical tasks.
Create DR group
GUI action
DR Groups
Virtual D
-
-
-
Job template or command CLUI command
> New (New DR Group Wizard) or
isk > Create DR Group (Replicate Wizard)
CreateDr
Setup HP Continuous Access (template)
Perform Cascaded Replication (template)
CreateD
Group
rGroupFromHostVolume
Add DR_G r
-
-
-
oup
82 DR Groups

Configure DR group
GUI action
DR Groups > Add Members AddDrGroupMember
DR Groups > Remove Members
DR Groups > Failover
(with or without suspend)
-
-
DR Groups > Force Full Copy ForceFullCopyDrGroup
DR Groups > Edit SetDrGroupAutoSuspend
DR Groups > Edit
DR Groups > Edit
DR Groups > Enable Failsafe
DR Groups > Disable Failsafe
DR Groups > Edit
DR Groups > Revert to Home Roles
DR Groups > Edit
DR Groups > Edit SetDrGroupIoMode
DR Groups > Edit
DR Groups > E
DR Groups > Suspend
DR Groups > Resume
DR Groups > Edit
dit
Job template or command CLUI command
-
FailoverDrGroup
(with or without suspend)
Perform plann ed failover (template)
Perform unpla
SetDrGroupComments Set DR_Group
SetDrGroupDestinationAccess
SetDrGroupFailsafe
SetDrGroupHome Set DR_Group
SetDrGroupMaxLogSize
SetDrGroupName
SetDrGroupSuspend
nned failover
Set DR_Group
Set DR_Group
Set DR_Group
(with or without suspend)
-
-
Set DR_Group
Set DR_Group
Set DR_Group
Set DR_Group
Set DR_Group
Set DR_Group
Set DR_Grou
Set DR_Group
p
Delete DR group
GUI action
DR Groups > Delete DeleteDrGroup Delete DR_Group
Edit DR group
GUI actio
DR Groups > Edit
n
Manage sets of DR groups
GUI act
DR Groups > Add to Managed Set
DR Groups > Remove from Managed Set
ion
Job templa
Job temp
-
Job tem
-
-
late or comm and
plate or command
te or com m and
CLUI comma
CLUI com
Set DR_Group
CLUI co
Set Managed_Set
Set Managed_Set
nd
mand
mmand
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
83

Other DR group tasks
GUI action
DR groups > Low-Level Refresh
-
-
-
View DR groups
GUI action
DR groups > Lo
DR groups > View Properties
DR group pro
For help on p
• DR group and the DR group pair. See General tab.
• DR group’s log disk. See Log tab.
• Virtual di
• Managed sets in which the DR group is a member. See Membership tab.
See also viewing DR group properties.
Job template or command CLUI command
-
DiscoverDiskDevicesForDrGroup
Throttle replication I/O (template)
WaitDrGroupNormalization
Job template or command CLUI command
w-Level Refresh
-
-
perties summary
roperties, see the following tabs in the D R group properties window.
sks in a DR group. See Members tab.
Set DR_Group
-
-
-
Set DR_Group
Show DR_Group
DR group views
See the following examples: List view, Grp Source/Destination tree view,and
System/DR Grp/Virtual Disk tree view.
List view
84
DR Groups

DR Grp Source/Destination tree view
System/DR Grp/Virtual Disk tree view
Adding DR groups to a managed set
AddDRgroupstoamanagedset.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidelines apply. See manage d sets of DR groups.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the
2. On the List tab, select the DR groups to add to a managed set.
3. Select Actions > Add to Managed Set. The Create New Managed Set window opens.
4. Selec
5. Click OK.
navigation pane, select DR Groups.
t a managed set, or select Create New Managed Set andenteraname.
Adding virtual disks to a DR group pair
Add source and destination virtual disks to a DR group pair (source and destination).
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
85

When you add virtual disks to a source DR group, the remote copies (virtual disks) are automatically
added to the destination DR group.
Considerations
• You can use the G
• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
• To add virtual disks to a D R group pair, you must specify the source DR group. See DR group pair.
• You ca nnot dir
UI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
ectly ad d virtual disks to a destination DR group.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select the source group of the DR group pair in which to add virtual disks.
3. Select Actions > Add Members. The Add Members wizard opens.
4. Follow the instructions in the wizard.
Creating a DR group pair
Create a DR
group pa ir (source and destination). See DR group pair.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
Procedures
The follo
wing procedure uses the GUI. See also virtual disks creating a DR group pair.
DR group procedure
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select Actions > New.TheNewDRGroupwizardopens.
3. Follow the instructions in the wizard.
Deleting a DR group pair
a DR group pair (source and destination). See DR group pair.
Delete
When you delete a DR group, you delete the DR group pair (source and destination). Virtual disks that are
members of the source DR group are retained. You can discard or retain the remote copies (virtual disks).
Considerations
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
• If you choose to discard the remote copies when the remote link is not operational, the remote
virtual disks are not deleted. You will need to manually delete them.
• You cannot delete a DR group pair if any destination virtual disk is presented to a host.
CAUTION:
Ifyoudiscardaremotecopy,thedestinationvirtualdiskanditsdataaredeleted.
86 DR Groups

Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select the source or destination DR group in the DR group pair to delete.
3. Select Actions > Delete. The Discard Remote Copies window opens.
4. Select the remote copy you want to discard, and then click OK.
5. Click Finish.
Editing DR group properties
Edit (set) the properties of a DR group.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
• DR groups exist in pairs. Editing one partner’s property can affect the properties in the other
partner. For example, if you enable failsafe mode on a source DR group, its destination DR
group is failsafe-enabled, too.
Procedure
This proce
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select the DR group to edit.
3. Select Ac
4. Edit the properties.
5. Click Finish.
dure uses the GUI.
tions > Edit Properties. The Editing DR Group window opens.
Enabling failsafe mode for a DR group pair
EnablethefailsafemodeofaDRgrouppair. SeeDRgroupsfailsafe mode and states.
Conside
Procedure
rations
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidel
• To set the failsafe mode on a DR group pair, you must specify the source DR group. See
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select the source group in the DR group pair to failsafe-enable.
3. Select Actions > Enable Failsafe.
ines apply. See virtual disks remote replication guidelines.
DR group pair.
IMPORTANT:
The failsafe mode setting for a DR group pair can impact host I/O and data consistency between the
source and destination DR groups. Ensure that you understand the potential impacts of changing
the mod
e.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
87

4. Click OK.
Disabling failsafe mode
DisablethefailsafemodeofaDRgrouppair. SeeDRgroupsfailsafe mode and states.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
• To set the failsafe mode on a DR group pair, you must specify the source DR group. See
DR group pair.
• You cannot disable failsafe mode if the status of the DR group pair is failsafe locked. See DR
groups failsafe mode and states.
IMPORTANT:
The failsafe mode setting for a DR group p air can impact host I/O and data consistency between the
source and destination DR groups. Ensure that you understand the potential impacts of changing
the mode.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select the source group in the DR group pair to failsafe-disable.
3. Select Actions > Disable Failsafe.
4. Click OK.
Failing over a DR group pair
Fail over a DR group pair. See DR groups failover.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
• HP recommends not failing over a DR group pair more often than every 15 minutes.
• To fail over a DR group pair, you must specify the destination DR group. See DR group pair.
• You cannot fail over a DR group pair if remote replication is suspended or if a remote copy (virtual
disk)isinanunknownstate. SeeDRgroupssuspension state and virtual disks resource states.
• If supported by controller software, an option is available to suspend remote replication after the
failover. See controller software features - remote replication and DR groups suspend on failover.
IMPORTANT:
Failing over a DR group pair impacts host I/O. Ensure that you understand the potential impacts of
performing a failover.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In th
88 DR Groups
e navigation p ane, select DR Groups.

2. On the List tab, select the destination group in the DR group pair to failover.
3. Select Actions > Failover.TheConfirm Failover window appears.
4. If supported by controller software, an option to suspend remote replication is enabled. Select
Suspend on failover to suspend remote replication immediately after the failover is executed.
IMPORTANT:
Do not perform this action when the links are down
socancreateaninvalidsource-sourceconfiguration. See invalid DR group pair - source and source.
5. Click OK.
Forcing a full copy
Force a full copy in a DR group pair. See DR groups full copy.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
• To force a full copy in a DR group pair, you must specify the source DR group. See DR group pair.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
, especially during an unplanned failover. Doing
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select the source group in the DR group pair to force a full copy.
3. Select Ac tions > Force Full Copy.
4. Click OK.
Launching the device manager
AccessHPCommandViewEVAfromthereplicationmanager. Eachtimeyouusethisactioninthesame
replication manager session, a new window for HP Command View EVA is opened.
Considerations
• You can only use the GUI to launch the device manager. The action is not available unless an
individual resource is selected (highlighted) in the replication manager content pane.
• You must know the security credentials (user name and password) to log on to HP Command
View EVA.
Procedure
1. In the navigation pane, select DR G roups, Storage Systems or Virtual Disks.
2. On a List or Tree tab select any storage resource.
3. Select Actions>LaunchtheDeviceManager. A new browser window opens.
4. Respond to the security alert message and then log on to HP Command View EVA.
Listing individual resource events
Display the events for an individual resource.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
89

Considerations
• You can only use the GU I.
• Applies to only to individual D R groups, storage systems, and virtual disks.
Procedure
1. In the navigation pane, select resource type.
2. On the List tab, select the specific resource whose events are to be displayed.
3. Select Actio
ns > List events.Aneventswindowfortheresourceopens.
Low-level refreshing D R groups
Perform a low-level refresh of the virtual disks and log disk in a DR group. See virtual disks
low-level refresh.
Considerations
• You ca n use t
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select the DR group whose virtual disks and log disk properties are to be updated.
3. Select Actions > Low-Level Refresh.TheConfirmation Action window appears.
4. To continue, click OK. The properties of the virtual disks and log d isk in the DR group are
updated.
he GUI or CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
Removin
g DR groups from a managed set
Remove D
R groups from a managed set.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the n
2. On the L
3. Select Actions > Remove From Managed Set. The Select Managed Sets window opens.
4. Select the managed set from which to remove the D R groups.
5. Click OK.
avigation pane, select DR Groups.
isttab,selecttheDRgroupstoremovefromamanagedset.
Removing virtual disks from a DR group pair
Remove virtual disks from a DR group pair.
When you remove virtual disks from a source D R g roup, the source disks are retained. You can discard
or retain the remote copies (virtual disks).
Considerations
• You c
an use the GUI, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
90 DR Groups

• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
• To remove virtual disks from a DR group pair, you must specify the source DR group. See
DR group pair.
• You cannot directly remove virtual disks from a destination DR group.
• If you choose to discard the remote copies when the remote link is not operational, the remote
virtual disks are not deleted. You will need to manually delete them.
• You cannot remove virtual disks from a DR group pair if remote replication is suspended. See
DR groups suspension state.
CAUTION:
Ifyoudiscardaremotecopy,thedestinationvirtualdiskanditsdataaredeleted.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. OntheListtab,selectthesourcegroupintheDRgrouppairfromwhichtoremovevirtualdisks.
3. Select Actions > Remove members. The Remove Member Wizard opens.
4. Follow the instructions in the wizard.
Resuming a DR group pair
Resume (allow) remote replication in a suspended DR group pair. Se e DR groups suspension state.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
• To resume remote replication in a DR group pair, you must specify the source DR group. See
DR group pair.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select the source group of the DR group pair in which to resume remote
replication.
3. Select Actions > Resume.
4. Click OK.
Reverting a DR group pair to home
Revert a DR group pair to its home con fig uration. See DR groups home.
Considerations
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
• To revert a DR group pair to its home configuration, you must specify the destination D R group.
See DR group pair.
• You cannot revert to home if the DR group pair is suspended. See DR groups suspension state.
• If the DR group pair is already in its home configuration, reverting to home has no impact.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
91

• If the DR group pair is not already in its home configuration, reverting to home causes a failover.
See DR groups failover.
IMPORTANT:
Failing over a DR group pair impacts host I/O. Ensure that you understand the potential impacts of
performing a failover.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select the destination group in the DR group pair to revert to hom e configuration.
3. Select Actions > Revert to Home.
4. Click OK.
Suspending a DR group pair
Suspend remote replication in a DR group pair. See DR groups suspension state.
Considerations
IMPORTANT:
Do not suspend remote replication when the links are down
so can create an invalid source-source configuration. See invalid DR group pair - source and source.
, especially during an unplanned failover. Doing
• You can use the GUI, jobs, or the CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Guidelines apply. See remote replication guidelines.
• To suspend remote replication in a DR group pair, you must specify the source DR group. See
DR group pair.
• You cannot suspend a DR group pair if it is failsafe-enabled. See DR groups failsafe mode.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the na
2. On the Li
replication.
3. Select Actions > Suspend.Aconfirmation window appears.
IMPORTANT:
Read the confirmation notice before performing the next step.
4. Click OK.
Using DR groups
When using a DR group pair, some actions and properties require that you specify either the source or
destination. See the following tables: controlling, creating and deleting, adding and deleting virtual disks,
and editing (setting) properties.
vigation pane, select DR Groups.
st tab, select the source group of the DR group pair in which to suspend remote
92 DR Groups

Controlling
Task
Fail over aDRgroup
pair (do not suspend).
Fail over and suspend a
DR group pair.
Force a full copy in a DR
group pair.
Resume remote
replication in a D R
group pair.
Revert aDRgrouppairto
its home configuration.
pend remote
Sus
lication in a DR
rep
up pair.
gro
DR
group
to
specify
Destina-
tion
Destina-
tion
Source
Source
Destina-
tion
ce
Sour
Result on source
DR group
The source becomes
destination.
The source becomes
the destination, then
remote replication is
suspended.
When applie
after resum
source beg
copy all da
virtual di
destinat
are used.
Remote replication
from the source
is allowed. If
applicable, begins
log merging or
full copy from the
source.
If the DR group
pair is not in its
home configuration
afailoveroccurs.
Otherwise, there
is no change in
operation.
ote replication
Rem
mthesourceis
fro
allowed. Host
not
ites to the source
wr
ntinue but are
co
gged.
lo
d
ing, the
ins to
ta on its
sks to the
ion. No logs
Result on
destination DR
group
The destination
becomes source.
The destination
becomes the
source, then remote
replication is
suspended.
The destina
begins to re
the data from the
source virtual disks.
No logs are used.
Remote replication
to the destination
is allowed. If
applicable, begins
log merging or
full copy to the
destination.
If the DR group
pair is not in its
home configuration
afailoveroccurs.
Otherwise, there
is no change in
operation.
Rem
he destination is
to t
allowed.
not
tion
ceive
ote replication
Remarks
Procedure.Seealso
DR group failover
Procedure.See
also DR group
suspend on failover.
Procedure.
also DR grou
full copy mode.
Procedure.See
also DR group
suspension state.
Procedure.Seealso
DR group home.
cedure.See
Pro
oDRgroup
als
pension state.
sus
See
p
Creating and deleting
Task
Create a DR group pair. Source Creates a source DR
Delete aDRgroupor
pair.
DR
group
Result on source
DR group
to
specify
group that includes
the specified virtual
disks.
Either Deletes the source
DR group. Its virtual
disks are retained.
Result on
Remarks
destination DR
group
Creates the
destination DR group
and remote copies
(virtual disks).
Deletes the
destination DR
group. Its virtual
disks are retained or
discarded (deleted)
as requested.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
Procedure.
Procedure.
93

Adding and deleting virtual disks
Editing (s
Task
Add virtual disks to a DR
group pair.
Remote virtual disks from
a DR group pair.
etting) properties
Task
Edit (general) a DR
group.
Auto suspend on links
down mode for a DR
group pair.
DR
group
to
specify
Source
Source
DR
group
to
specify
Either
Source
Result on source
DR group
Adds a source virtual
disk to the source DR
group.
Deletes a source
virtual disk from the
source DR group.
Result on source
DR group
Properties are
changed.
Auto suspend
on links down is
disabled or enabled.
Result on
destination DR
group
Adds a
corresponding
remote copy to
the corresponding
destination DR
group.
Prompts you to
keep or discard
the corresponding
remote copy.
Result on
destinat
ion DR
group
Properties are
changed.
Auto suspend
on lin ks down is
disabled or enabled.
Remarks
Procedure.
Procedure
Remarks
Procedure.
Procedure.Seealso
DR groupauto suspend
on links down mode.
Comment for a DR
group.
Destination access mode
Failsafe mode for a DR
group pair.
Home
ode
I/O m
Maximum log disk size
Name
Viewing DR groups
Display DR group list and tree views. See DR groups views.
Either
Destina-
tion
Source
Either Sets home true or
Source
Source
Either
Comment for the DR
group is edited.
Destination access
mode is changed.
Failsafe mode is
disabled or enabled.
false in coordination
with other group.
Remote replication
I/O mode is
changed.
Maximum log disk
size is changed.
Name of the DR
group is changed.
Comment for the DR
group is edited.
Destination access
mode is changed.
Failsafe mode is
disabled or enabled.
Sets home true or
false in c oordination
with other group.
Remote replication
I/O mode is
changed.
Maximum log disk
size is changed.
Name of the DR
group is changed
Procedure.
Procedure
Disabling - Procedure.
Enabling - Procedure.
See also DR group
failsafe mode.
Procedure.Seealso
DR group home.
Procedure .Seealso
DR group I/O mode.
Procedure.See
also DR group
maximum log disk size.
Procedure
Considerations
ou can use the GUI or CLUI to display lists. See DR groups actions cross reference.
• Y
94
DR Groups

• Tree views are available only in the GUI.
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups. The content pane displays DR groups.
2. Click the List tab. A tabular list of DR groups is displayed.
3. Click the Tree tab. A graphical tree of DR groups is displayed. Click View to select another
tree view.
Viewing DR group properties
View the properties of a specificDRgroup. SeeDRgroupsproperties summary.
Considerations
• You c an use t
Procedure
This procedure uses the GUI.
1. In the navigation pane, select DR Groups.
2. On the List tab, select the DR group to view.
3. Select Actions > View Properties. The DR Group Properties window opens.
4. Click the properties tabs.
he GUI or CLUI. See DR groups actions cross reference.
DR group concepts
DR group pairs (source and destination)
DR groups operate in a paired relationship, with one DR group being a source and the other a
destination.Thetermssource and destination are sometimes referred to as a DR mode or DR role. The
terms source and destination are also applied to virtual disks, with a destination virtual disk also being
known as a remote copy. Various actions, such as a planned or unplanned failover, allow you to
reverse the relationship so that the source DR group becomes the destination and destination becomes
thesource. SeeDRgroupsfailover.
IMPORTANT:
The role of a DR group in remote replication is of critical importance and can be reversed at any time.
For example, a DR group can be a source at 8:00 and then, after a user-initiated failover, be a destination at
8:05. When reviewing a DR group’s role, ensure that you are looking at current properties.
In a typical environment, hosts perform I/O with the virtual disks in the source D R group at one site and
the data is remotely replicated to the destination D R group at another site. The virtual disks in a source
DR group remotely replicate to the same destination, fail over together, share a DR group log, and
preserve write-order within the group.
1. A source virtual disk
(1 of 3 in the source DR group)
2. A destination virtual disk
(remote copy)
(1 of 3 in the destination DR group)
3. The source DR group log disk
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
95

Site 1 < remote link > Site 2
A DR group log is a designated virtual disk in a source D R group that is used under certain circumstances
to temporarily store host writes to source virtual disks. Logging can be started automatically when remote
replication to the destination DR group cannot be performed, for example when a remote link is down.
Logging can also be started on demand by performing a suspend action from the GUI, jobs, or a CLUI
command. When remote replication is re-established, the contents of the source DR group log are written
to the destination virtual disks. See DR groups logs.
Home group and home configuration
When designated as a home group, the group is considered be the preferred source in the remote
replication relationship. By default, the property for the source and destination DR group is set true and
false,respectively. Thisiscalledthehome configuration.SeeDRgroupshome.
DR group names
When a DR group pair is created, the same DR group name is assigned to the source and destination
DR group.
IMPORTANT:
After creation, HP recommends that you edit partner DR groups and change the names.
96 DR Groups

After creation, you can change the names to something logical for your environment. For example,
rename them based on their physical locations, Boston and London, or their home roles SiteA_Srce and
SiteB_Dest. Certain characters are illegal in the names. See illegal characters.
Auto suspend
Auto suspend s
pecifies whether remote replication in a D R group pair is automatically suspended after a
remote link goes down. Values are:
• Enabled. Remote replication in the DR group pair is automatically suspended after a remote
link goes down
.
• Disabled. Remote replication in the DR group pair is not automatically suspended after a remote
link goes down.
Usage guidel
ines:
• Remote replication is not automatically restarted after the link becomes operational again.
IMPORTANT:
A resume command must be issued to resume remote replication.
• Improper use of auto suspend can create and invalid source-source configuration. See
invalid DR group pair - source and source.
IMPORTANT:
Do not set auto suspend when the links are down
, especially during an unplanned failover.
• If not specified when creating a DR group pair, the value is set to disabled.
• You cannot change this property when failsafe mode is enabled. See DR groups failsafe mode.
See also DR groups suspension state.
Controller software versions
Implementation of this feature is controller software depend ent. See
controlle
r software features - remote replication.
Cascaded replication
Cascaded replication refers to a replication event, and a configuration, that involves three sites (storage
systems). See the diagram blow.
The source volume (a) at site 1 is in a remote replication relationship with its copy (b) at site 2. Whenever
a point-in-time snapclone copy is needed (c) , it is created at site 2. The snapclone copy is then remotely
replicated (cascaded) to another remote copy (d) at site 3.
Site 1 Site 2 Site 3
source (a)
The result is that a point-in-time replica of the source exists at two different sites.
>>>
remote copy (b)
\/
snapclone
\/
snapclone (c)
>>>
remote copy (d)
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
97

Copy state
Copy state identifies the state of remote replication between a source and destination virtual disk.
Values are:
• Normal.Remote
involving the virtual disk.
• Full Copy. The DR Group log threshold has been reached and the virtual disk is involved in
a full copy. See DR groups full copy mode.
replication involving the virtual disk is normal. There is no logging or merging
Destination access mode
Destination access mode specifies the type of host I/O that is allowed when a virtual disk is in a
destination (remote copy) role. Values are:
• None. Thevirtualdiskcannotbepresentedtoanyhosts.
• No Read. The virtual disk can be presented to hosts, but no reads (or writes) are allowed.
• Read Only. The virtual d isk can be presented to hosts for read only.
The no read mode allows SCSI inquiry but prohibits host reads. This mode is typically used to support
host clusters.
Controller software versions
Implementation of this feature is controller software dependent. See
controller
software features - remote replication.
DR group states and icons
Icons in the DR group content pane indicate the key states of each DR group. You can mouse over an
icon to display a detailed state message.
1. Operational state
2. Failsafe state
Failover
To fail over means to reverse the direction of remote replication in a DR group pair. A failover event
is an event in which the remote replication direction was reversed.
When a failover event occurs, the roles of source and destination in a DR group pair are reversed.
For example, in a planned failover, if DRgroupA was originally the source and DRgroupB was the
destination, those roles are reversed when DRgroupB is failed over.
In the case of an unplanned failover (disaster), there may not be a literal reversal of remote replication
because SiteA may not be operational. Instead, when DRgroupB is failed over, S iteB may become an
independent site, or a source that remotely replicates to third site.
Performing a planned or unplanned failover involves technical preparation and significant operational
planning. Host I/O is impacted by a failover. The following guidelines capture just a few of the
technical considerations.
3. Suspension state
4. Log state
98 DR Groups

• To fail over a DR group pair, you must specify the destination DR group. See DR group pair.
• You cannot fail over a DR group pair if remote replication is suspended or if a remote copy (virtual
disk)isinanunknownstate. SeeDRgroupssuspension state and virtual disks resource states.
• If only one component in a DR group pair fails, repairing that single component may be
preferable to performing a failover.
IMPORTANT:
Failing over a DR group pair impacts host I/O. Ensure that you understand the potential imp acts of
performing a failover.
See also DR groups suspend on failover and remote replication guidelines.
Failsafe mode and states
Failsafe mode specifies how host-writes, logging, and remote replication occur when a component in
the DR pair fails. Values are:
• Enabled
• Disabled. Host writes and remote replication continue normally while all components in the DR
group pair are functioning normally.
Failsafe mode enabled
When failsafe mode is enabled, there are two operational states.
• Host writes and remote replication c ontinue normally while all components in the DR group pair
function normally. This is the failsafe unlocked state.
• Host writes and remote replication stop (are locked) when any virtual disk in the DR group pair
fails or becomes unavailable. This is the failsafe locked state.
Failsafe mode disabled
When failsafe mode is disabled:
• All host writes and remote replication continue normally as long as all components in the remote
relationship are functioning normally.
• If any remote copy (virtual disk) in the DR group pair fails or becomes unavailable, all host
writes to the source DR group continue, but all remote replication to the destination D R group
automatically stops. Host writes are stored in the source DR group log until remote replication is
re-established.
• If a source virtual disk fails, host writes to the failed disk automatically stop. Remote replication
to the remote copy automatically stop, too. Host writes and remote replication to other virtual
disks in the source and destination DR groups continue normally.
See also remote replication guidelines.
Full copy mode
Full copy mode is when data in a DR group pair is copied directly from the source group virtual disk to the
destination group, without using any data in the log disk. Typically, this is an automatic event that happens
when remote replication is resumed and the DR group log disk is full. See default maximum log size.
Force full copy
Inaforcedfullcopy:
• All virtual disks in the source DR group are copied; you cannot copy individual disks.
• All host write-transactions in the DR group log are deleted.
HP StorageWorks Replication Solutions M anager
99

Even when supported by the controller soft ware, the force full copy feature is not available if conditions in
the DR group pair are not appropriate.
Controller software versions
Implementation of this feature is controller software dependent. See
controller sof
tware features - remote replication.
Home
When designated as home, the DR group is the preferred source in the DR group pa ir. Values are:
• True/Yes. The DR group is the preferred source.
• False/No. The DR group is the preferred destination.
Home group is a property that is maintained only by the replication manager.
Home configuration
When the replication manager creates a DR group pair, the h om e property for the source and destination
groups is set to true and false, respectively. This is called the home configuration.Whenfailedover
from the home configuration, the home property remains u nchanged.
Reverting to home
Reverting to home is an event that causes a failed over DR group pair to return to their original roles in
the home configuration.
Setting the home property
• You can cha
DR groups a
• During discovery, the replication manager automatically adds the home group property to source
and destination DR group pairs that do not have it. See resources discovery.
nge the home property using a GUI action, job command, and CLUI command. See
ctions cross reference.
Use of home
The home concept is useful because the preferred source is flagged by the home property, even if it is
currently operating as the destination. This helps you to revert to home configuration easily.
Consider using home group to designate a business center for your replication activities. For example, if
your headquarters is in Chicago, you can set your Chicago DR group as home. If your headquarters
moves or becomes inoperable, you can then change home to some other location.
I/O throttling
I/O throttling refers to suspending some DR groups during a log merge or full copy event. By suspending
non-critical DR groups, the critical DR groups complete the merge or full copy sooner.
Throttling of I/O after logging
When logging, and not in the failsafe mode, remote replication automatically resumes when the links
are restored. If there are several DR groups with large logs, they can compete for remote replication
bandwidth, thus slowing the overall merge or full copy between the two sites.
By suspending the merge or full copy of the non-critical DR groups, the critical data is available sooner
at the destination. After the critical DR groups finish merging or copying, the remote replication of the
non-critical DR groups can be resumed.
100 DR Groups
 Loading...
Loading...