Page 1

HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide
This guide provides information about accessing and using the graphical user interface (GUI) and the command
line interface (CLI) of the HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform (SVSP) Data Path Module
(DPM).
Part Number: 5697–0772
Fourth edition: November 2010
Page 2

Legal and notice information
© Copyright 2008-2010 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211
and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items
are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set
forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as
constituting an additional warranty. HP shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Java is a U.S. trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Page 3

Contents
1 Data Path Module management interface options ................................... 9
2 Using the command line interface ...................................................... 11
CLI overview ............................................................................................................................ 11
Command quick reference by object ..................................................................................... 11
Command syntax and command completion .......................................................................... 12
Online help ....................................................................................................................... 13
Accessing the CLI ..................................................................................................................... 13
Users and groups ............................................................................................................... 15
3 CLI commands ................................................................................. 17
Activate command .................................................................................................................... 17
Add license command ............................................................................................................... 17
Add syslog command ................................................................................................................ 17
Clear command ....................................................................................................................... 18
Create debug command ............................................................................................................ 18
Create snmp command ............................................................................................................. 19
Create user command ............................................................................................................... 19
Delete config command ............................................................................................................. 20
Delete license command ............................................................................................................ 20
Delete snmp command .............................................................................................................. 21
Delete syslog command ............................................................................................................. 21
Delete user command ................................................................................................................ 22
Disable eth command ............................................................................................................... 22
Disable ftp command ................................................................................................................ 23
Disable http command .............................................................................................................. 23
Disable insecure command (oboslete) .......................................................................................... 23
Disable ntp command ............................................................................................................... 24
Disable port command .............................................................................................................. 24
Disable secure command (obsolete) ............................................................................................ 25
Disable snmp command ............................................................................................................ 25
Disable ssh command ............................................................................................................... 26
Disable syslog command ........................................................................................................... 26
Disable telnet command ............................................................................................................ 26
Disable user command .............................................................................................................. 26
Enable bootset command .......................................................................................................... 27
Enable eth command ................................................................................................................ 27
Enable ftp command ................................................................................................................. 28
Enable http command ............................................................................................................... 28
Enable insecure command (obsolete) ........................................................................................... 28
Enable ntp command ................................................................................................................ 29
Enable port command ............................................................................................................... 29
Enable secure command (obsolete) ............................................................................................. 30
Enable snmp command ............................................................................................................. 30
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 3
Page 4

Enable ssh command ................................................................................................................ 31
Enable syslog command ............................................................................................................ 31
Enable telnet command ............................................................................................................. 31
Enable user command ............................................................................................................... 32
Exit command .......................................................................................................................... 32
Help command ........................................................................................................................ 32
Help commands ....................................................................................................................... 33
Install image command ............................................................................................................. 34
Load config command ............................................................................................................... 34
Load debug command .............................................................................................................. 34
Load factory command .............................................................................................................. 35
Modify chassis command .......................................................................................................... 35
Modify date command .............................................................................................................. 36
Modify eth command ................................................................................................................ 36
Modify factory command ........................................................................................................... 37
Modify ntp command ................................................................................................................ 38
Modify port command .............................................................................................................. 38
Modify ports command ............................................................................................................. 39
Modify san command ............................................................................................................... 40
Modify snmp command ............................................................................................................. 40
Modify therm command ............................................................................................................ 41
Modify timezone command ........................................................................................................ 41
Modify user command .............................................................................................................. 42
Quit command ......................................................................................................................... 42
Reboot command ..................................................................................................................... 43
Remove image command ........................................................................................................... 43
Rescan command ..................................................................................................................... 43
Reset debug command .............................................................................................................. 43
Reset port command ................................................................................................................. 44
Restart ntp command ................................................................................................................. 45
Restart snmp command .............................................................................................................. 45
Restart ssh command ................................................................................................................. 45
Save config command ............................................................................................................... 46
Save debug command .............................................................................................................. 46
Set debug command ................................................................................................................. 46
Set eth command ...................................................................................................................... 47
Show bootset command ............................................................................................................ 48
Show bootsets command ........................................................................................................... 49
Show chassis command ............................................................................................................. 49
Show configs command ............................................................................................................. 50
Show copyright command ......................................................................................................... 50
Show date command ................................................................................................................ 51
Show debug command ............................................................................................................. 51
Show eth command .................................................................................................................. 54
Show eths command ................................................................................................................. 55
Show events command .............................................................................................................. 55
Show factory command ............................................................................................................. 55
Show fan command .................................................................................................................. 55
Show fans command ................................................................................................................. 56
Show ftp command ................................................................................................................... 56
Show group command .............................................................................................................. 57
Show groups command ............................................................................................................. 57
Show http command ................................................................................................................. 57
Show ID command ................................................................................................................... 57
Show image command .............................................................................................................. 58
4
Page 5

Show images command ............................................................................................................ 58
Show license command ............................................................................................................. 58
Show log command .................................................................................................................. 59
Show ntp command .................................................................................................................. 59
Show port command ................................................................................................................. 59
Show ports command ............................................................................................................... 60
Show ps command ................................................................................................................... 61
Show pss command .................................................................................................................. 61
Show rport command ................................................................................................................ 62
Show security command ............................................................................................................ 62
Show snmp command ............................................................................................................... 62
Show ssh command .................................................................................................................. 63
Show status command ............................................................................................................... 63
Show syslog command .............................................................................................................. 63
Show telnet command ............................................................................................................... 64
Show therm command ............................................................................................................... 64
Show therms command ............................................................................................................. 64
Show timezone command .......................................................................................................... 65
Show user command ................................................................................................................. 65
Show users command ............................................................................................................... 65
Show version command ............................................................................................................. 66
Show version_number command ................................................................................................. 66
Show voltage command ............................................................................................................ 66
Show voltages command ........................................................................................................... 66
Shutdown command ................................................................................................................. 67
Version command ..................................................................................................................... 67
Watch debug command ............................................................................................................ 67
Watch log command ................................................................................................................ 68
4 Using the Data Path Module management GUI .................................... 69
Installing Java WebStart ............................................................................................................ 69
Downloading the DPM Management GUI .................................................................................... 71
Logging into the DPM Management GUI ...................................................................................... 72
Navigating the DPM Management GUI ....................................................................................... 72
System function .................................................................................................................. 73
Chassis panel (system) .................................................................................................. 75
Global panel (system) ................................................................................................... 75
Ethernet panel (system) ................................................................................................. 75
SNMP panel (system) ................................................................................................... 76
Network Protocols panel (system) ................................................................................... 77
Time Base panel (system) .............................................................................................. 78
Software panel (system) ................................................................................................ 79
Sensors panel (system) .................................................................................................. 79
Diagnostics function ............................................................................................................ 80
Telnet function .................................................................................................................... 81
Log function ....................................................................................................................... 82
5 Support and other resources .............................................................. 83
Contacting HP .......................................................................................................................... 83
Before you contact HP ......................................................................................................... 83
HP contact information ........................................................................................................ 83
Subscription service .................................................................................................................. 83
Related documentation .............................................................................................................. 84
Document conventions and symbols ............................................................................................. 85
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 5
Page 6

Product warranties .................................................................................................................... 86
HP websites ............................................................................................................................. 86
Documentation feedback ........................................................................................................... 86
Glossary ............................................................................................ 87
6
Page 7

Figures
PuTTYtel Configuration screen ................................................................................... 141
PuTTYtel session login screen .................................................................................... 142
PuTTYtel console menu options .................................................................................. 153
HP Storage Services Platform screen .......................................................................... 714
DPM Management GUI Login screen ......................................................................... 725
DPM Management GUI screen ................................................................................. 736
System port information screen .................................................................................. 747
System Global panel ............................................................................................... 758
System Ethernet panel .............................................................................................. 769
System SNMP panel ................................................................................................ 7710
System Networks Protocols panel .............................................................................. 7711
System Time Base panel ........................................................................................... 7812
System Software panel ............................................................................................. 7913
System Sensors panel .............................................................................................. 8014
Diagnostic screen displaying port utilization ............................................................... 8115
Telnet screen initiated from the DPM Management GUI ................................................ 8116
Diagnostic screen log panel ..................................................................................... 8217
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 7
Page 8

Tables
Commands by object type ....................................................................................... 111
Built-in users and groups .......................................................................................... 162
DPM Management GUI functions .............................................................................. 733
Document conventions ............................................................................................. 854
8
Page 9

1 Data Path Module management interface options
There are two ways to interface with the Data Path Module (DPM):
• Over a serial connection using the DPM management command line interface (CLI)
• Over an IP connection using the DPM management graphical user interface (GUI)
Most activity with the DPM GUI occurs during initial configuration and debugging (when requested
by HP Support). Therefore, under normal operation, the DPM GUI is seldom used. Of the two interface
methods, using the serial connection is the preferred method because it more secure than using the
Internet.
This document describes the two interface methods beginning with the CLI.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 9
Page 10

Data Path Module management interface options10
Page 11
2 Using the command line interface
This chapter describes the use of the HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data
Path Module (DPM) command line interface (CLI). You can configure and manage the DPM with these
common command sets that provide the same functions as the DPM GUI.
CLI overview
The DPM provides a command line user interface through serial, telnet, and ssh connections with
serial being the preferred default. All configuration, maintenance, and monitoring of the DPM is
performed through the CLI.
Command quick reference by object
Table 1 shows which commands are available for the major object types.
Table 1 Commands by object type
PageCommandObject type
22Disable eth command
eths
ports
users 22Delete user command
27Enable eth command
36Modify eth command
47Set eth command
54Show eth command
55Show eths command
24Disable port command
29Enable port command
38Modify port command
39Modify ports command
44Reset port command
59Show port command
60Show ports command
19Create user command
26Disable user command
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 11
Page 12

PageCommandObject type
32Enable user command
65Show user command
65Show users command
19Create snmp command
25Disable snmp command
snmp
date/timezone 41Modify timezone command
fans
groups
therms
ps
30Enable snmp command
40Modify snmp command
62Show snmp command
36Modify date command
51Show date command
55Show fan command
56Show fans command
57Show group command
57Show groups command
64Show therm command
64Show therms command
61Show ps command
61Show pss command
voltages
Command syntax and command completion
The CLI command syntax is as follows:
command
keyword [value]
keyword [value1] [value2]
The command is followed by one or more keywords. Consider the following rules and conventions:
• Commands and keywords are case sensitive.
• Required keyword values appear in standard font: [value]. Optional keyword values are shown
in italics: [value].
Using the command line interface12
66Show voltage command
66Show voltages command
Page 13

This CLI provides command completion to minimize the typing needed to run commands. This feature
enables you to press the completion key (the Tab key) to complete a partially typed command line.
If the command line fragment is unambiguous, it is completed with the remainder of the command
line.
If there is more than one possible match for a command line fragment, continue pressing the Tab key
to see each of the possible matches. You then type enough of the command line to distinguish it from
the other possible matches.
In addition, you can get a list of legal fields at any point in the command line. For example, if you
type set debug p, and then press the Tab key, a list of valid debug options beginning with the
letter p is returned.
The completion feature in the CLI also validates previously typed input. If there is an error in the
command line prior to the point where you have requested completion, an error is printed and the
cursor is set to the point where the command line breaks the defined syntax rules.
Online help
The CLI for the DPM includes online help. Type part of a command, and press Enter, to view the help
information, such as a list of arguments or the proper syntax.
Help commands
For information about getting a list of commands, see “Help commands” on page 33. For information
about getting help with a particular command, see “Help command” on page 32.
Example 1.
Typing modify and pressing Enter returns these results:
required arg not present
one of [eth, ntp, snmp, factory, chassis, therm, port, ports, date, timezone,
user, san '?'] required
Example 2.
Typing show use and pressing Enter returns these results:
admin@k-> show use
show user <user name>
show users
“use” is ambiguous, must differentiate between: [user, users]
Please refer to command syntax for detail.
Accessing the CLI
The DPM management (MGMT) port is configured when the HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization
Service Platform solution is installed on site. The following procedure describes how to use the serial
port with PuTTYtel to access the DPM CLI on the VSM server. The PuTTYtel terminal emulator is provided
on the open source CD in your media kit.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 13
Page 14

1. With a serial cable between the VSM server and the DPM, open a PuTTYtel session.
Figure 1 PuTTYtel Configuration screen
.
2. Ensure a speed of 9600 is used with a Serial connection type, and click Open. A login screen
appears.
Figure 2 PuTTYtel session login screen
.
Using the command line interface14
Page 15

3. Log in to the DPM with the default login and password.
NOTE:
HP recommends that you change the default password. If you have not already done so,
run the “Modify user command” on page 42 to change the password.
login: admin
password: password
The following menu options are displayed (see Figure 3).
Figure 3 PuTTYtel console menu options
.
4. Enter commands from the command line to begin managing the DPM with the CLI commands.
Users and groups
The DPM provides two built-in users and two built-in groups: admin is a member of the Administrator
group, and kmonitor is a member of the Monitor group.
Table 2 shows the default password for both accounts. See “Modify user command” on page 42 for
information about changing the password.
NOTE:
The default passwords may have been changed prior to your installation of the DPM. See the records
of the installation for details.
Users in the Monitor group are limited to commands that only view system configuration and status;
Monitor users cannot change the system configuration. See the show commands, such as “Show user
command” on page 65, “Show port command” on page 59, and so on, for more information.
Users in the Administrator group can create and delete users, and they can also modify users, eths,
ports, and perform all of the other commands listed in this document. See “Create user
command” on page 19, “Delete user command” on page 22, “Modify user command” on page 42,
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 15
Page 16

“Modify eth command” on page 36, “Modify port command” on page 38, and “Modify ports
command” on page 39 for more information.
Table 2 summarizes the features of the built-in groups.
Table 2 Built-in users and groups
Built-in groupsBuilt-in users
Default password
View system configuration and status
Create/delete users and
modify
eths/ports/users/...
yesyespasswordadminadmin
noyeskahunaMonitorkmonitor
Using the command line interface16
Page 17

3 CLI commands
Activate command
Makes sure that the DPM is active (init 3 is up, and all SOAP modules are loaded).
Syntax
activate
Add license command
Adds a new license.
Syntax
add license [key]
Keyword values
[key]
License key to be added.
Notes
Only users belonging to the Administrator group can add or delete licenses.
See also
“Delete license command” on page 20
“Show license command” on page 58
Add syslog command
Adds a remote logging server.
Syntax
add syslog server [host]
port [port number]
socket [socket-protocol]
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 17
Page 18

Keyword values
[host]
Host name of the remote logging server.
[port-number]
IP port number to which the host connects.
[socket-protocol]
Socket protocol (either TCP or UDP, with default being TCP).
Notes
Only users belonging to the Administrator group can add or delete syslog servers.
See also
“Add syslog command” on page 21
“Disable syslog command” on page 26
“Enable syslog command” on page 31
“Show syslog command” on page 63
Clear command
Clears the screen of text.
Syntax
clear
Create debug command
Creates a save state file; erasing any old save state files.
Syntax
create debug dump
See also
“Load debug command” on page 34
“Reset debug command” on page 43
“Save debug command” on page 46
“Set debug command” on page 46
“Show debug command” on page 51
“Watch debug command” on page 67
CLI commands18
Page 19

Create snmp command
Creates an SNMP receiver.
Syntax
create snmp receiver [name]
Keyword values
[name]
Name of the SNMP trap receiver.
See also
“Delete snmp command” on page 21
“Disable snmp command” on page 25
“Enable snmp command” on page 30
“Modify snmp command” on page 40
“Show snmp command” on page 62
Create user command
Creates a new user in the specified group, or views user settings. The groups defined for the DPM
are Administrator and Monitor. When new users are added, they get the same permissions as the
existing admin or kmonitor users, depending on the group specified in the command. When you issue
this command, you must enter a password for the newly created user that is at least eight characters
in length.
Syntax
create user [user name] group [group name]
Keyword values
[user name]
Name of the new user
[group name]
Name of the group to which the user will belong: Administrator or Monitor.
Notes
Only users belonging to the Administrator group can add, delete, and disable/enable users, and the
current user cannot be disabled or deleted.
See also
“Delete user command” on page 22
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 19
Page 20

“Disable user command” on page 26
“Enable user command” on page 32
“Show user command” on page 65
“Show users command” on page 65
Delete config command
Removes a configuration that was saved by the save config command.
Syntax
delete config [configuration file]
Keyword values
[configuration file]
Configuration file name.
See also
“Load config command” on page 34
“Save config command” on page 46
“Show configs command” on page 50
Delete license command
Removes a license.
Syntax
delete license [key]
Keyword values
[key]
License key to be deleted.
Notes
Only users belonging to the Administrator group can add or delete licenses.
See also
“Add license command” on page 17
“Show license command” on page 58
CLI commands20
Page 21

Delete snmp command
Removes an SNMP receiver.
Syntax
delete snmp receiver [name]
Keyword values
[name]
Name of SNMP trap receiver.
See also
“Create snmp command” on page 19
“Disable snmp command” on page 25
“Enable snmp command” on page 30
“Modify snmp command” on page 40
“Show snmp command” on page 62
Delete syslog command
Removes a remote logging server.
Syntax
delete syslog server [host]
Keyword values
[host]
Host name of the remote logging server.
Notes
Only users belonging to the Administrator group can add or delete syslog servers.
See also
“Add syslog command” on page 17
“Disable syslog command” on page 26
“Enable syslog command” on page 31
“Show syslog command” on page 63
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 21
Page 22

Delete user command
Removes the specified user from the list of administrators who can access the DPM.
Syntax
delete user [user name]
Keyword values
[user name]
Name of the user that you are removing from the system.
Notes
Only users belonging to the Administrator group can add, delete, and disable/enable users, and the
current user cannot be disabled or deleted.
See also
“Create user command” on page 19
“Disable user command” on page 26
“Enable user command” on page 32
“Show user command” on page 65
“Show users command” on page 65
Disable eth command
The DPM includes four Ethernet interfaces: MGMT, GE1, GE2, and GE3. This command disables the
specified Ethernet interface so that it cannot send or receive network traffic.
This command is used for tightened security purposes. Once you disable the MGMT Ethernet interface
using this command, you can access the CLI and administer the DPM only from the serial console.
Syntax
disable eth [interface name]
Keyword values
[interface name]
Name of the Ethernet interface that you are disabling: MGMT, GE1, GE2, or GE3.
IPv4 or IPv6
Notes
If you are connected through the management port, disabling the MGMT Ethernet terminates any
active network GUI and CLI sessions, requiring a re-login through the serial console. If you are using
the CLI on the serial console, the connection is not be disrupted.
CLI commands22
Page 23

See also
“Enable eth command” on page 27
“Modify eth command” on page 36
“Set eth command” on page 47
“Show eth command” on page 54
“Show eths command” on page 55
Disable ftp command
Disables use of the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) program to copy files onto the DPM.
Syntax
disable ftp
See also
“Enable ftp command” on page 28
“Show ftp command” on page 56
Disable http command
Disables use of the http protocol and DPM network management interfaces. Disables the use of the
DPM GUI and other remote management tools.
Syntax
disable http
See also
“Enable http command” on page 28
“Show http command” on page 57
Disable insecure command (oboslete)
NOTE:
This command is obsolete and has been removed from the current version of the CLI.
Disables permissions on plain-text transmissions.
Syntax
disable insecure [permission]
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 23
Page 24

Keyword values
[permission]
Either read, write, or all.
See also
“Enable insecure command” on page 28
“Show security command” on page 62
Disable ntp command
Disables use of the ntp protocol on the DPM.
Syntax
disable ntp
See also
“Enable ntp command” on page 29
“Modify ntp command” on page 38
“Restart ntp command” on page 45
“Show ntp command” on page 59
Disable port command
Disables the specified Fibre Channel port number so that it cannot send and receive Fibre Channel
traffic.
Syntax
disable port
[port number]
*
Keyword values
[port number]
Port number is an integer 0–15 to indicate the DPM Fibre Channel port to be disabled.
* indicates all Fibre Channel ports.
See also
“Enable port command” on page 29
“Modify port command” on page 38
“Modify ports command” on page 39
CLI commands24
Page 25

“Show port command” on page 59
“Show ports command” on page 60
Disable secure command (obsolete)
NOTE:
This command is obsolete and has been removed from the current version of the CLI.
Disables permissions on SSL-encrypted transmissions.
Syntax
disable secure [permission]
Keyword values
[permission]
Either read, write, or all.
See also
“Enable secure command” on page 30
“Show security command” on page 62
Disable snmp command
Disables the specified Simple Network Management Protocol component. By default, the system runs
SNMP version 2. Disabling v3 means that SNMP v3 is turned off, but does not affect SNMP v2.
Syntax
disable snmp [component]
Keyword values
[component]
Either v2, v3, or daemon. Disabling the daemon disables SNMP.
See also
“Create snmp command” on page 19
“Delete snmp command” on page 21
“Enable snmp command” on page 30
“Modify snmp command” on page 40
“Show snmp command” on page 62
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 25
Page 26

Disable ssh command
Disables use of the secure shell (ssh) application to connect to the DPM CLI.
Syntax
disable ssh
See also
“Enable ssh command” on page 31
Disable syslog command
Stops logging to the specified remote logging server. Returns to the local logging mode.
Syntax
disable syslog [host]
Keyword values
[host]
Host name of the remote logging server.
See also
“Add syslog command” on page 17
“Add syslog command” on page 21
“Enable syslog command” on page 31
“Show syslog command” on page 63
Disable telnet command
Disables use of the telnet application to connect to the DPM CLI.
Syntax
disable telnet
See also
“Enable telnet command” on page 31
Disable user command
Temporarily disables the user account without deleting it. The account can later be enabled using the
Enable user command.
CLI commands26
Page 27

Syntax
disable user [user name]
Keyword values
[user name]
Name of the user account that you are disabling.
See also
“Create user command” on page 19
“Delete user command” on page 22
“Enable user command” on page 32
“Modify user command” on page 42
“Show user command” on page 65
“Show users command” on page 65
Enable bootset command
Set the active bootset.
Syntax
enable bootset [number]
Keyword values
[number]
The number 1 or 2.
Notes
Since there are only two bootsets, enabling one bootset effectively disables the other. Therefore, there
is no “disable bootset” command.
See also
“Show bootset command” on page 48
“Show bootsets command” on page 49
Enable eth command
The DPM includes four Ethernet interfaces: MGMT, GE1, GE2, and GE3. This command enables the
specific Ethernet interface so that it can send or receive network traffic.
Syntax
enable eth [interface name]
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 27
Page 28

Keyword values
[interface name]
Name of the Ethernet interface that you are enabling: MGMT, GE1, GE2, or GE3.
See also
“Disable eth command” on page 22
“Modify eth command” on page 36
“Set eth command” on page 47
“Show eth command” on page 54
“Show eths command” on page 55
Enable ftp command
Enables use of the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) program to copy files onto the DPM.
Syntax
enable ftp
See also
“Disable ftp command” on page 23
“Show ftp command” on page 56
Enable http command
Enables the use of the http protocol and DPM network management interfaces. Enables the use of the
DPM GUI and other remote management tools.
Syntax
enable http
See also
“Disable http command” on page 23
“Show http command” on page 57
Enable insecure command (obsolete)
NOTE:
This command is obsolete and has been removed from the current version of the CLI.
Enables permissions on plain-text transmissions.
CLI commands28
Page 29

Syntax
enable insecure [permission]
Keyword values
[permission]
Either read, write, or all.
See also
“Disable insecure command” on page 23
“Show security command” on page 62
Enable ntp command
Enables use of the ntp protocol on the DPM.
Syntax
enable ntp
See also
“Disable ntp command” on page 24
“Modify ntp command” on page 38
“Restart ntp command” on page 45
“Show ntp command” on page 59
Enable port command
Enables the specified Fibre Channel port number so that it can send and receive Fibre Channel traffic.
Syntax
enable port
[port number]
*
Keyword values
port number
Port number is an integer 0–15 to indicate the DPM Fibre Channel port to be enabled.
* indicates all Fibre Channel ports.
See also
“Disable port command” on page 24
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 29
Page 30
“Modify ports command” on page 39
“Modify ports command” on page 39
“Show port command” on page 59
“Show ports command” on page 60
Enable secure command (obsolete)
NOTE:
This command is obsolete and has been removed from the current version of the CLI.
Enables permissions on SSL-encrypted transmissions.
Syntax
enable secure [permission]
Keyword values
[permission]
Either read, write, or all.
See also
“Disable secure command” on page 25
“Show security command” on page 62
Enable snmp command
Enables the specified Simple Network Management Protocol component. By default, the system runs
SNMP version 2. Enabling SNMP v3 means that SNMP v3 is turned on but does not affect SNMP
v2.
Syntax
enable snmp [component]
Keyword values
[component]
The states of v2, v3, or daemon. Enabling the daemon enables SNMP.
See also
“Create snmp command” on page 19
“Delete snmp command” on page 21
“Disable snmp command” on page 25
CLI commands30
Page 31

“Modify snmp command” on page 40
“Show snmp command” on page 62
Enable ssh command
Enables use of the secure shell (ssh) application to connect to the DPM CLI.
Syntax
enable ssh
See also
“Disable ssh command” on page 26
“Show ssh command” on page 63
Enable syslog command
Begins logging to the specified remote logging server. The remote server must have been added with
the add syslog command.
Syntax
enable syslog [host]
Keyword values
[host]
Host name of the remote logging server.
See also
“Add syslog command” on page 17
“Add syslog command” on page 21
“Disable syslog command” on page 26
“Show syslog command” on page 63
Enable telnet command
Enables use of the telnet application to connect to the DPM CLI.
Syntax
See also
enable telnet
“Disable telnet command” on page 26
“Show telnet command” on page 64
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 31
Page 32

Enable user command
Enables the user account that was previously disabled using the Disable user command.
Syntax
enable user [user name]
Keyword values
[user name]
Name of the user account that you are enabling.
Notes
Only users belonging to the Administrator group can add, delete, disable and enable users. The
current user cannot be disabled or deleted.
See also
“Create user command” on page 19
“Delete user command” on page 22
“Disable user command” on page 26
“Modify user command” on page 42
“Show user command” on page 65
“Show users command” on page 65
Exit command
Quits this command line interface session, terminates the session, and logs the user out.
Syntax
exit
See also
“Quit command” on page 42
Help command
Provides information about using the specified commands. Help [object] displays the syntax for
all commands that can be performed on the object. [partial command name]? displays the help
for all commands starting with the text. [command]? returns all allowed uses of the command.
Syntax
[partial command name]?
CLI commands32
Page 33

[command]?
help [object]
Keyword values
[partial command name]
Part of a help command (enough of the command to uniquely identify it).
[command]
Entire command name.
[object]
Object of the command (for example, in the show snmp command, snmp is the object).
Examples
create? returns this help information:
create snmp receiver <name>
create debug dump
create user <user name> group <group name>
re? returns this help information:
remove -- Remove an object.
rescan -- Rescan for new devices.
reset -- Reset to a known state.
restart -- Restart a process.
reboot -- Reboot system.
help timezone returns this help information:
show timezone
modify timezone <zone>
<zone> one of: ['Africa/', 'America/', ...]
See also
“Help commands” on page 33
Help commands
Provides a list of all commands and command syntax.
Syntax
See also
help commands
“Help command” on page 32
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 33
Page 34

Install image command
Installs an image onto a bootset.
Syntax
install image [image-name]
Keyword values
[image-name]
Image to be installed.
See also
“Show image command” on page 58
“Remove image command” on page 43
Load config command
Load a configuration generated by a save config command.
Syntax
load config [configuration]
Keyword values
[configuration]
Configuration to be loaded.
See also
“Delete config command” on page 20
“Save config command” on page 46
“Show configs command” on page 50
Load debug command
Loads the debug state saved by the last save debug command.
Syntax
load debug
See also
“Create debug command” on page 18
“Reset debug command” on page 43
CLI commands34
Page 35

“Save debug command” on page 46
“Show debug command” on page 51
“Watch debug command” on page 67
Load factory command
Restore the factory defaults (original values for rank and WWNN).
Syntax
load factory defaults
See also
“Modify factory command” on page 37
“Show factory command” on page 55
Modify chassis command
Allows the user to set values for the DPM's name, location, WWNN, maxframesize, and rank values.
Syntax
modify chassis location [location]
modify chassis maxframesize [maxframesize]
modify chassis name [new-name]
modify chassis rank [new-rank]
modify chassis wwnn [new-wwnn]
Keyword values
[location]
An arbitrary location code provided by the administrator.
[maxframesize]
Maximum size of a Fibre Channel frame that can be sent or received by this DPM. Typically 2 k,
should be set to the smallest frame size of any connected device.
[new-name]
Host name for this DPM.
[new-rank]
Controller rank for this DPM, such as “Primary” or “Secondary.”
[new-wwnn]
The Fibre Channel world wide node name for this DPM.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 35
Page 36

Examples
modify chassis location “Second floor lab, Main Street office”
modify chassis maxframesize 1024
See also
“Show chassis command” on page 49
Modify date command
Sets the system date and time.
Syntax
modify date [MM/DD/YYYY hh:mm:ss]
Keyword values
[MM/DD/YYYY hh:mm:ss]
MM/DD/YYYY is the month, day, and year for the system time (year must be 4–digits long). hh:mm:ss
is the hours, minutes, and seconds for the system time.
Notes
Once the time zone is set, the system automatically switches between Standard Time and Daylight
Saving Time.
See also
“Modify timezone command” on page 41
“Show date command” on page 51
Modify eth command
Configures the Ethernet properties—IP address, gateway, and subnet—for the specified Ethernet
interface.
Syntax
modify eth [interface name] [family]
address [IP address] | gateway [gateway address] | netmask [subnet
mask]
Keyword values
At least one of the optional keywords is required:
[interface name]
Ethernet interface that you are modifying: MGMT, GE1, GE2, or GE3.
[family]
CLI commands36
Page 37

Notes
See also
IPv4, IPv6
address [IP address]
IP address of the interface.
gateway [gateway address]
IP address of the network gateway.
netmask [subnet mask]
Mask bits for subnet routing.
If you are connected through the management port, modifying the MGMT Ethernet terminates any
active network GUI and CLI sessions, requiring a re-login through the serial or MGMT port. If you are
using the CLI on the serial console, the connection is not disrupted.
“Disable eth command” on page 22
“Enable eth command” on page 27
“Set eth command” on page 47
“Show eth command” on page 54
“Show eths command” on page 55
Modify factory command
Restore the factory rank or the factory WWNN value.
Syntax
modify factory rank [rank-value]
modify factory wwnn [wwnn-value]
Keyword values
At least one of the optional keywords is required:
[rank-value]
New rank value (Primary or Secondary).
[wwnn-value]
New WWNN to set.
See also
“Load factory command” on page 35
“Show factory command” on page 55
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 37
Page 38

Modify ntp command
Change the NTP server.
Syntax
modify ntp server [server-name]
Keyword values
[server-name]
New server to be used to get the time.
See also
“Disable ntp command” on page 24
“Enable ntp command” on page 29
“Restart ntp command” on page 45
“Show ntp command” on page 59
Modify port command
Changes the specified options—type, capability, speed—for the specified Fibre Channel port number.
Syntax
modify port [port number]
capability [port capability]
speed [port speed]
type [port type]
Keyword values
At least one of the optional keywords is required:
[port number]
An integer 0–15 to indicate the DPM Fibre Channel port.
capability [port capability]
FCP_TARGET: to enable the port to be used as a front-end (looks like a storage array port to
servers).
FCP_INITIATOR: to initiate back-end traffic to the supported storage arrays (is not available
to servers).
both: traffic can go both ways.
speed [port speed]
1G, 2G, 4G, NEGOTIATE
CLI commands38
Page 39

Notes
See also
type [port name]
UNKNOWN, AUTO, FABRIC, LOOP
FABRIC: the port functions only in conjunction with a single-attached device that is capable
of fabric mode operation. The default is fabric mode, with the fabric yielding better throughput,
and links recover more quickly.
NOTE:
Only the FABRIC port name is supported with the HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services
Platform.
You must restart the system for port capability or port speed changes to take effect.
maxframesize is not a keyword for this command because all ports must share the same frame
size. See the Modify ports command.
“Disable port command” on page 24
“Enable port command” on page 29
“Modify ports command” on page 39
“Reset port command” on page 44
“Show port command” on page 59
“Show ports command” on page 60
Modify ports command
Changes the specified keywords—type, capability, speed—for all DPM ports.
Syntax
modify ports
type [port type]
capability [port capability]
speed [port speed]
maxframesize [size (in bytes)]
Keywords and values
At least one of the optional keywords is required:
type [port type]
FABRIC: the port functions only in conjunction with a single-attached device that is capable
of fabric mode operation. This is the default and the only supported mode.
capability [port capability]
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 39
Page 40

Notes
See also
FCP_TARGET: to enable the port to be used as a front-end (looks like a storage array port).
FCP_INITIATOR: to initiate back-end traffic to disks (cannot receive storage).
both: traffic can go both ways.
speed [port speed]
1G, 2G, 4G, NEGOTIATE
maxframesize [size (in bytes)]
Smallest maximum frame size of any device on the SAN, usually 2048. Some systems require 1024,
or even smaller.
This number specifies the maximum frame size that the DPM can negotiate to exchange with other
Fibre Channel devices. This number must be the same throughout the SAN.
You must restart the DPM for port capability or port speed changes to take effect.
“Disable port command” on page 24
“Enable port command” on page 29
“Modify port command” on page 38
“Reset port command” on page 44
“Show port command” on page 59
“Show ports command” on page 60
Modify san command
Runs SANAPI. Ctrl-C returns control to the CLI.
Syntax
modify san
Modify snmp command
Changes the SNMP community name.
Syntax
modify snmp community [name]
Keyword values
[name]
The SNMP community string is similar to a user ID or password that allows access to a router's or
other device's statistics. The default is “public,” but any string can be used. It is standard practice for
CLI commands40
Page 41

network managers to change the community string so that outsiders cannot see information about the
internal network.
See also
“Create snmp command” on page 19
“Delete snmp command” on page 21
“Disable snmp command” on page 25
“Enable snmp command” on page 30
“Restart snmp command” on page 45
“Show snmp command” on page 62
Modify therm command
Sets the maximum or minimum temperature thresholds allowed for the thermometer specified.
Syntax
modify therm [number] maximum [max-temp] minimum [min-temp]
Keyword values
[number]
Thermometer number (in the range 0–6)
[max-temp]
Maximum temperature threshold (in Centigrade)
[min-temp]
Minimum temperature threshold (in Centigrade)
See also
“Show therm command” on page 64
“Show therms command” on page 64
Modify timezone command
Starts a Time Zone Configuration utility that enables you to select your geographical area and time
zone, and modify your local time, if needed.
Syntax
modify timezone [zone]
Keyword values
[zone]
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 41
Page 42

Your time zone, for example, “EST,” “GMT,” “Japan,” and so on. Type modify timezone for a
full list of possible values.
Notes
Once the time zone is set, the system automatically switches between Standard Time and Daylight
Saving Time.
See also
“Show timezone command” on page 65
Modify user command
Adds the specified user to the specified group and/or changes the password defined for the specified
user.
The groups defined for the DPM are Administrator and Monitor. When new users are added, they
get the same permissions as the existing admin or kmonitor users.
Syntax
modify user [user name]
group [group name]
password
Keyword values
[user name]
User name that you want to add to the specified group.
group [group name]
Name of the group to which you are adding the specified user: Administrator or monitor.
password
Include this keyword if you want to change the password.
See also
“Create user command” on page 19
“Delete user command” on page 22
“Disable user command” on page 26
“Enable user command” on page 32
“Show user command” on page 65
“Show users command” on page 65
Quit command
Exits this command line interface session, terminates the session, and logs the user out.
CLI commands42
Page 43

Syntax
quit
See also
“Exit command” on page 32
Reboot command
Restarts the Data Path Module.
Syntax
reboot
Remove image command
Removes an image.
Syntax
remove image [image-name]
Keyword values
[image-name]
Name of image
See also
“Install image command” on page 34
“Show image command” on page 58
“Show images command” on page 58
Rescan command
Rescan for new devices.
Syntax
rescan
Reset debug command
Syntax
Resets the kernel module debug levels to their previously installed values.
reset debug
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 43
Page 44

reset debug level [module]
Keyword values
[module]
Kernel module that will specifically have its debug level reset. If no value is specified (reset debug),
then all debug levels for all modules are reset.
See also
“Create debug command” on page 18
“Load debug command” on page 34
“Save debug command” on page 46
“Set debug command” on page 46
“Show debug command” on page 51
Reset port command
Shuts down the port and then restarts it, leaving the properties of the port unchanged. Use this command
to clear a port that is in an unknown state and trigger the discovery process.
CAUTION:
Running this command disrupts any traffic on this port, and should never be performed on a port that
is moving data. Doing so could cause read/write failure and error conditions in software if traffic
has occurred.
Syntax
reset port
[port number]
*
Keyword values
[port number]
Port number is an integer 0–15 for the DPM to indicate the Fibre Channel port.
* indicates all Fibre Channel ports.
See also
“Modify ports command” on page 39
“Show port command” on page 59
“Show ports command” on page 60
CLI commands44
Page 45

Restart ntp command
Stops and then restarts the ntp service.
Syntax
restart ntp
See also
“Disable ntp command” on page 24
“Enable ntp command” on page 29
“Modify ntp command” on page 38
“Show ntp command” on page 59
Restart snmp command
Stops and then restarts the Simple Network Management Protocol.
Syntax
restart snmp
See also
“Create snmp command” on page 19
“Delete snmp command” on page 21
“Disable snmp command” on page 25
“Enable snmp command” on page 30
“Modify snmp command” on page 40
“Show snmp command” on page 62
Restart ssh command
Stops and then restarts the ssh service.
Syntax
restart ssh
See also
“Disable ssh command” on page 26
“Enable ssh command” on page 31
“Show ssh command” on page 63
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 45
Page 46

Save config command
Saves a configuration file.
Syntax
save config [name]
Keyword values
[name]
Name of configuration file.
See also
“Delete config command” on page 20
“Load config command” on page 34
“Show configs command” on page 50
Save debug command
Save the current debug state for all the kernel modules. These values can be restored later using the
load debug command.
Syntax
save debug
See also
“Create debug command” on page 18
“Load debug command” on page 34
“Reset debug command” on page 43
“Set debug command” on page 46
“Show debug command” on page 51
“Watch debug command” on page 67
Set debug command
Sets debug values for kernel modules. Used by HP support engineers in debugging a problem. See
examples below for more information.
Syntax
set debug [module-name] level [level value]
set debug [module-name] type [type-list] level [level value]
CLI commands46
Page 47

Keyword values
[module name]
Kernel module where the debug values will be set.
[level value]
New level to be set.
[type-list]
Comma-separated list of types to be set.
Examples
show debug modules fcpt returns:
fctp=err (newcmd,iocomp,tmf,abts,puntrsp,quefull,rsp,dump)
set debug fcpt level warning sets the fctp module level value to warning.
show debug modules fcpt would now show:
fctp=warning (newcmd,iocomp,tmf,abts,puntrsp,quefull,rsp,dump)
set debug fcpt type tmf,dump level crit sets the types tmf and dump in fcpt to have
debug levels of crit.
show debug modules fcpt would now show:
fctp=warning/tmf,dump=crit (newcmd,iocomp,abts,puntrsp,quefull,rsp)
set debug fcpt level info sets the fsct module level value to info.
show debug modules fcpt would now show:
fctp=info/tmf,dump=crit (newcmd,iocomp,abts,puntrsp,quefull,rsp)
reset debug level fcpt resets the fcpt debug levels to the original values.
show debug modules fcpt would now show:
fctp=err (newcmd,iocomp,abts,puntrsp,quefull,rsp,dump)
See also
“Create debug command” on page 18
“Load debug command” on page 34
“Reset debug command” on page 43
“Save debug command” on page 46
“Show debug command” on page 51
“Watch debug command” on page 67
Set eth command
Changes the Ethernet family address resolution method, duplex, and link speed for the specified
Ethernet interface.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 47
Page 48

Syntax
set eth [interface name] link [auto | duplex <duplex value> | speed <link
speed>]
or
set eth [interface name] [family] [method]
Keywords and values
Description of keywords:
[interface name]
Ethernet interface that you are changing: MGMT, GE1, GE2, or GE3.
link [auto]
Auto negotiate duplex and link speed
link [duplex <duplex value>]
Full or half
link [speed <link speed>]
10, 100, or 1000.
family
IPv4, IPv6
method
Address resolution method—auto or manual
See also
“Disable eth command” on page 22
“Enable eth command” on page 27
“Modify eth command” on page 36
“Show eth command” on page 54
“Show eths command” on page 55
Show bootset command
Displays the platform, version, status, checksum, and active status of the bootset specified.
Syntax
show bootset [number]
Keyword values
[number]
Number of the bootset (1 or 2).
CLI commands48
Page 49

See also
“Enable bootset command” on page 27
“Show bootsets command” on page 49
Show bootsets command
Displays the platform, version, status, checksum, and active status of all the bootsets.
Syntax
show bootsets
See also
“Enable bootset command” on page 27
“Show bootset command” on page 48
Show chassis command
Returns the name, location, part number, MAC base address, serial number, original manufacture
date, Fibre Channel World Wide Node Name, Fibre Channel maximum frame size, or rank for the
DPM.
Syntax
show chassis
[location]
[MAC_base_address]
[maxframesize]
[name]
[orig_mfg_date]
[part_num]
[rank]
[serial_num]
[wwnn]
Keyword values
At least one of the following keyword values is required:
[location]
An arbitrary location code provided by the administrator.
[MAC_base_address]
Indicates the base address for the Ethernet MAC on the Data Path Module.
[maxframesize]
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 49
Page 50

Examples
Maximum size of a Fibre Channel frame that can be sent or received by this DPM. Typically 2 k,
should be set to the smallest frame size of any connected device.
[name]
Host name for this DPM.
[orig_mfg_date]
Indicates the original manufacturing date for this DPM.
[part_num]
Indicates the part number of the DPM. Use it to determine the original equipment manufacturer or
manufacturing information about the switch.
[rank]
Controller rank for this DPM, such as “Primary” or “Secondary.”
[serial_num]
Indicates the serial number for this DPM.
[wwnn]
The Fibre Channel world wide node name for this DPM.
show chassis part_num
show chassis MAC_base_address orig_mfg_date
show chassis orig_mfg_date serial_num
See also
“Modify chassis command” on page 35
Show configs command
Displays the name, date, and config zip file name of all configs.
Syntax
show configs
See also
“Delete config command” on page 20
“Load config command” on page 34
“Save config command” on page 46
Show copyright command
Displays the copyright.
CLI commands50
Page 51

Syntax
show copyright
Show date command
Returns the current date, time, and the time zone.
Syntax
show date
See also
“Modify date command” on page 36
Show debug command
Returns information that may be helpful to HP support engineers in debugging a problem. There are
currently three different forms of the show debug command. The first form allows you to look at
various types of diagnostic data. The second form (show debug modules) allows you to look at
the current debug settings for kernel modules. The third form (show debug sac) allows you to look
at sac data from the sac fifo.
Syntax
show debug
[agentstate]
[dump]
[fcptstate]
[fcsdb]
.
.
.
[wwpn]
show debug modules [optional-module-name]
show debug sac [sac-command]
Keyword values
At least one of the following keyword values is required:
[agentstate]
Shows diagnostic information related to the fabric agent (the software component that interfaces with
the VSM).
[dump]
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 51
Page 52

Shows cumulative system debug information.
[fcptstate]
Provides the state of the SCSI target driver.
[fcsdb]
Shows information about the Fibre Channel ports and SCSI LUNs visible to the DPM.
[fcsexch]
Provides per port Fibre Channel Services (FCS) exchange allocation diagnostic. Used by support
personnel.
[fcsluns]
FCS LUN discover. Local port database of remote ports with LUNs per remote port.
[fcsstate]
Provides a summary table showing how many targets, LUNs, and initiators are discovered by each
port. Each port discovers itself.
[fpsdiag]
Shows firmware debugging information.
[fpskdstats]
Shows fastpath activity per virtual disk exposure on the DPM.
[fpspsc]
Provides a list of the physical disks in use by the firmware/fastpath.
[fpsstats]
Shows the firmware/fastpath statistics.
[hwstate]
Provides the state of the HBA hardware driver.
[interrupts]
Shows interrupt load.
[kdisks]
Shows the virtual disks created by the application, remote initiator WWN, port WWN, LUN identifier,
current state, type, and handle.
[kdstats]
Shows virtual disk I/O statistics, such as number of forwarded commands and the number of reads
handled by the DPM software.
[kmodules]
Provides a list of loaded kernel modules, the same as “modules.”
[levels]
Provides the definitions of the debug levels settable by the set debug command.
[meminfo]
Shows memory usage.
CLI commands52
Page 53
[modules]
Provides a list of the loaded kernel modules.
[ppeinfo]
Shows firmware status.
[pscs]
Provides a list of the physical storage containers (PSCs) registered by the application.
[pscstats]
Provides statistics for each PSC registered by the application, such as total reads and writes issued
on the PSC by the DPM software.
[scsi]
Provides information about all SCSI devices (Fibre Channel LUNs) visible to the DPM.
[shimstate]
Shows diagnostic information related to the storage application software component.
[top]
Shows CPU activity by task.
[wwn]
Shows the list of World Wide Names for the DPM ports.
NOTE:
Port 0 in the list corresponds with the physical port labeled Port 1.
[wwnmap]
Provides local port display of World Wide Name and port capabilities.
[wwpn]
Provides a list of World Wide Port Names discovered on each of the DPM ports.
NOTE:
Port 0 in the list corresponds with the physical port labeled Port 1.
modules [optional-module-name]
Without this entry, all of the module names are displayed. Each module name will also have its debug
level displayed, along with the debug level for any types that are different. The rest of the available
type data will be included within parentheses on the display line. See “Set debug command” on page
46 for information on setting debug levels.
sac [sac-command]
Command that is sent to the sac in order to extract sac data. Show debug sac will return a list of
available sac commands. Show debug sac status returns the status of the sac.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 53
Page 54

Notes
Examples
See also
As this command returns a large amount of information to the screen, turn on logging in your terminal
program so that you can capture all the information in a file to send to HP.
show debug modules cssdev will return a line that looks like:
cssdev=err (ucmd) which indicates that the kernel module cssdev has a debug level set
to err. There is one extra type ucmd that can have different debug level set in cssdev. Show
debug sac initiators will display initiator information from the sac.
“Create debug command” on page 18
“Load debug command” on page 34
“Reset debug command” on page 43
“Save debug command” on page 46
“Set debug command” on page 46
“Watch debug command” on page 67
Show eth command
Returns the configuration—IP address, subnet mask, and gateway—for the specified Ethernet interface.
Syntax
show eth [interface]
Keyword values
[interface]
Ethernet interface that you are showing: MGMT, GE1, GE2, or GE3
family
IPv4, IPv6
See also
“Disable eth command” on page 22
“Enable eth command” on page 27
“Modify eth command” on page 36
“Set eth command” on page 47
“Show eths command” on page 55
CLI commands54
Page 55

Show eths command
Returns the configuration—IP address, subnet mask, MAC base address, and gateway—for the four
Ethernet interfaces: MGMT, GE1, GE2, or GE3.
Syntax
show eths
See also
“Disable eth command” on page 22
“Enable eth command” on page 27
“Modify eth command” on page 36
“Set eth command” on page 47
“Show eth command” on page 54
Show events command
Reads the SOAP event log and displays the number of entries requested.
Syntax
show events [number]
Keyword values
[number]
Number of events to display.
Show factory command
Display the factory setting for either the rank or WWNN values.
Syntax
show factory rank
show factory wwnn
See also
“Load factory command” on page 35
“Modify factory command” on page 37
Show fan command
Displays the fan location, the status (either OK or Error), and the RPM of the specified fan.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 55
Page 56

Syntax
show fan
[fan number]
*
Keyword values
[fan number]
An integer between 1 through 10, inclusive.
* indicates all fans.
Notes
If the fan is a power supply fan, the RPM is not available. The RPM displays as 0 if the fan is not
operational; as 1 if the fan is operational.
See also
“Show fans command” on page 56
Show fans command
Displays the fan location, the status (either OK or Error), and the RPM for all fans in the DPM.
Syntax
show fans
Notes
If the fan is a power supply fan (Fan 1 and Fan 3), the RPM is not available. The RPM displays as 0
if the fan is not operational; as 1 if the fan is operational.
See also
“Show fan command” on page 55
Show ftp command
Indicates whether or not FTP is enabled or disabled.
Syntax
show ftp
See also
“Disable ftp command” on page 23
“Enable ftp command” on page 28
CLI commands56
Page 57

Show group command
Returns the list of user names that belong to the specified group name. The groups defined for the
DPM are Administrator and Monitor.
Syntax
show group [group name]
Keyword values
[group name]
Name of the group to which users belong: Administrator or Monitor.
Show groups command
Returns a list of the users assigned to each group that is defined for this DPM. The groups defined for
the DPM are Administrator and Monitor.
Syntax
show groups
See also
“Show users command” on page 65
Show http command
Indicates whether or not the http protocol is enabled or disabled.
Syntax
show http
See also
“Disable http command” on page 23
“Enable http command” on page 28
Show ID command
Returns the user account that was authenticated for the current session.
Syntax
show id
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 57
Page 58

Show image command
Displays the name, version, description, filename, and md5sum of the image specified.
Syntax
show image [image]
Keyword values
[image]
Name of image.
See also
“Install image command” on page 34
“Remove image command” on page 43
“Show images command” on page 58
Show images command
Displays the name, version, description, filename, and md5sum for all images.
Syntax
show images
See also
“Install image command” on page 34
“Remove image command” on page 43
“Show image command” on page 58
Show license command
Displays the license key and a description of all licenses. Lines marked with an asterisk are disabled.
Syntax
show license
See also
“Add license command” on page 17
“Delete license command” on page 20
CLI commands58
Page 59

Show log command
Displays the contents of a log file.
Syntax
show log [logfile]
Keyword values
[logfile]
Name of log file to be displayed.
See also
“Watch log command” on page 68
Show ntp command
Displays the status of NTP for all regular and broadcast messages. Also shows the NTP server name
and state of the NTP service.
Syntax
show ntp
See also
“Disable ntp command” on page 24
“Enable ntp command” on page 29
“Modify ntp command” on page 38
“Restart ntp command” on page 45
Show port command
Returns diagnostic and status information for ports 0–15 on the DPM. See the sample output in the
Examples section below for more information.
Syntax
show port
[port number]
*
Keyword values
[port number]
An integer 0–15 to indicate the DPM Fibre Channel port.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 59
Page 60

Examples
See also
* indicates all Fibre Channel ports on the DPM.
Here is a sample output for port 1 on a system after running show port 1.
Port1:
WWPN: 5000-XXXX-XXXX-XX21
State: LINK-ESTABLISHED
Capability: ['FCP_INITIATOR']
Type - Configured: FABRIC Actual: FABRIC
Speed - Configured: NEGOTIATE Actual: 4G
Class - Configured: ['THREE']
Max Frame Size (in bytes): 2048
License: YES
“Disable port command” on page 24
“Enable port command” on page 29
“Modify port command” on page 38
“Modify ports command” on page 39
“Reset port command” on page 44
“Show ports command” on page 60
Show ports command
Returns diagnostic and status information for all ports on the DPM. See the sample output in the
Examples section below for more information.
Syntax
show ports
Keywords
ports
Indicates all Fibre Channel ports on the DPM.
Examples
Here is a sample output after running show ports.
Num State Cap. Type(conf/act) Speed Mtu
0 ESTABLISHED TARG FABRIC/FABRIC NEG/4G 2048
1 ESTABLISHED INIT FABRIC/FABRIC NEG/4G 2048
2 ESTABLISHED TARG FABRIC/FABRIC NEG/4G 2048
3 ESTABLISHED INIT FABRIC/FABRIC NEG/4G 2048
4 NO-SIGNAL TARG FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
5 NO-SIGNAL INIT FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
6 NO-SIGNAL TARG FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
7 NO-SIGNAL INIT FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
8 NO-SIGNAL TARG FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
9 NO-SIGNAL INIT FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
CLI commands60
Page 61

10 NO-SIGNAL TARG FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
11 NO-SIGNAL INIT FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
12 NO-SIGNAL TARG FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
13 NO-SIGNAL INIT FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
14 NO-SIGNAL TARG FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
15 NO-SIGNAL INIT FABRIC/UNSET NEG/UND 2048
See also
“Disable port command” on page 24
“Enable port command” on page 29
“Modify port command” on page 38
“Modify ports command” on page 39
“Reset port command” on page 44
“Show port command” on page 59
Show ps command
Returns the status (Error or OK) and voltage information for the specified power supply. The DPM
arrives with two power supplies already installed.
Syntax
show ps
[power supply number]
*
Keyword values
[power supply number]
1 or 2.
* indicates both power supplies.
Notes
When looking at the fan side of the DPM, power supply 1 is on the right side, and power supply 2
is on the left side.
See also
“Show pss command” on page 61
Show pss command
Returns the status (Error or OK) and voltage information for each of the two power supplies on the
DPM.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 61
Page 62

Syntax
show pss
Notes
When looking at the fan side of the DPM, power supply 1 is on the right side, and power supply 2
is on the left side.
See also
“Show ps command” on page 61
Show rport command
Displays information for all ports matching the partial value of the WWPN specified.
Syntax
show rport [partial-name]
Keyword values
[partial-name]
String of digits from the WWPN to match on.
Show security command
Displays permissions (read or write) for plain-text transmissions and SSL-encrypted transmissions.
Syntax
show security
See also
“Disable secure command” on page 25
“Enable secure command” on page 30
“Disable insecure command” on page 23
“Enable insecure command” on page 28
Show snmp command
Reports the status of the Simple Network Management Protocol and its components.
Syntax
show snmp
CLI commands62
Page 63

See also
“Create snmp command” on page 19
“Disable snmp command” on page 25
“Enable snmp command” on page 30
“Modify snmp command” on page 40
Show ssh command
Indicates whether or not ssh is enabled or disabled.
Syntax
show ssh
See also
“Disable ssh command” on page 26
“Enable ssh command” on page 31
“Restart ssh command” on page 45
Show status command
Returns the current status of all power supplies, fans, thermometers, and voltages for the DPM, and
reports errors where detected.
Syntax
show status
Show syslog command
Returns the port number, socket protocol, name, and IP address of each remote logging server. Lines
marked with an asterisk are disabled.
Syntax
show syslog
See also
“Add syslog command” on page 17
“Add syslog command” on page 21
“Disable syslog command” on page 26
“Enable syslog command” on page 31
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 63
Page 64

Show telnet command
Enables use of the telnet application to connect to the DPM CLI.
Syntax
show telnet
See also
“Disable telnet command” on page 26
“Enable telnet command” on page 31
Show therm command
Returns the status, current temperature in Celsius and Fahrenheit, and the minimum and maximum
thresholds for the specified thermometer. The DPM has six thermometers.
Syntax
show therm
[therm number]
*
Keyword values
therm number
An integer between 1 and 6, inclusive.
* indicates all thermometers in the DPM.
See also
“Show therms command” on page 64
Show therms command
Returns the status, current temperature in Celsius and Fahrenheit, and the minimum and maximum
thresholds for each of the six thermometers in the DPM.
Syntax
show therms
See also
“Show therm command” on page 64
CLI commands64
Page 65

Show timezone command
Shows the time zone configuration settings for this DPM. Use the “Modify timezone command” on page
41 to change the settings.
Syntax
show timezone
Notes
Once the time zone is set, the system automatically switches between Standard Time and Daylight
Saving Time.
See also
“Modify timezone command” on page 41
Show user command
Returns the name of the group to which the specified user belongs and whether the user is enabled.
Syntax
show user [user name]
Keyword values
user name
Name of the user for which you need the group name and whether enabled.
See also
“Disable user command” on page 26
“Enable user command” on page 32
“Modify user command” on page 42
“Show users command” on page 65
Show users command
Returns a list of the users assigned to each group and whether the users are enabled. The groups
defined for the DPM are Administrator and Monitor, and the users are admin and kmonitor.
Syntax
show users
See also
“Disable user command” on page 26
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 65
Page 66

“Enable user command” on page 32
“Modify user command” on page 42
“Show groups command” on page 57
“Show user command” on page 65
Show version command
Shows the firmware version number.
Syntax
show version
Show version_number command
Shows the firmware version number.
Syntax
show version_number
Show voltage command
Returns the nominal and actual voltages for the DPM. The nominal voltage is the expected voltage
when everything is operating correctly. The actual voltage is the current voltage.
Syntax
show voltage
[voltage number]
*
Keyword values
voltage number
An integer between 1 and 15 inclusive, that is the location in the DPM circuitry where the voltage is
measured. Used by support personnel as a diagnostic tool.
* indicates all voltages in the DPM.
See also
“Show voltages command” on page 66
Show voltages command
Returns the nominal and actual voltages for the DPM. The nominal voltage is the expected voltage
when everything is operating correctly. The actual voltage is the current voltage.
CLI commands66
Page 67

Syntax
show voltages
See also
“Show voltage command” on page 66
Shutdown command
Powers off the DPM.
Syntax
shutdown
Version command
Returns the DPM version.
Syntax
version
Watch debug command
Monitors activity of processes. Ctrl-C returns control to the CLI.
Syntax
watch debug [process]
Keyword values
[process]
Process to monitor. (For a full list, enter watch debug.)
See also
“Create debug command” on page 18
“Load debug command” on page 34
“Reset debug command” on page 43
“Save debug command” on page 46
“Set debug command” on page 46
“Show debug command” on page 51
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 67
Page 68

Watch log command
Monitors log activity. Ctrl-C returns control to the CLI.
Syntax
watch log [log-name]
Keyword values
[process]
Log to monitor. (For a full list, enter watch log.)
See also
“Show log command” on page 59
CLI commands68
Page 69
4 Using the Data Path Module management GUI
The DPM Management GUI is supported on Microsoft Windows platforms running Internet Explorer
version 5 or greater. To run the DPM Management GUI, install Java WebStart on your management
station. Java WebStart is an application that allows you to download and run a full-featured Java
application, such as the DPM Management GUI, directly from a web page.
The DPM simplifies the task of configuring the management station by automatically detecting whether
Java WebStart needs to be installed when the management station first accesses the DPM. If Java
WebStart is not present on the management station, the DPM can provide a copy of the application
that you can download and install. See “To install Java WebStart” on page 69 and “To download
the DPM Management GUI from a Web browser” on page 71 for more information.
Once you have installed the WebStart application, the web console enables you to access the DPM
Management GUI remotely using your standard web browser. For web browsers already running
Sun's Java WebStart application, skip the next two sections and see “To log into the DPM Management
GUI” on page 72.
NOTE:
Sun Microsystems provides versions of Java WebStart for Windows and other platforms through its
Java website. You may be able to use the DPM Management GUI from non-Windows management
stations using a version of Java WebStart provided by Sun; however, HP only supports the use of the
DPM Management GUI on Windows platforms running Internet Explorer version 5 or greater in
conjunction with the version of the Java WebStart application provided with your Data Path Module.
Installing Java WebStart
For web browsers on Windows platforms that are already running Sun's Java WebStart application,
see the next section “To download the DPM Management GUI from a Web browser”. For web
browsers on Windows platforms that do not yet have Sun's Java WebStart application installed,
follow this procedure:
1. From a web browser, enter the management port (labeled MGMT) IP address as the URL and
press Enter.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 69
Page 70

2. In the screen that displays, click the version for Windows, local copy to install and run the Sun
Java WebStart application on your machine.
3. On the Security Warning window, click Run.
NOTE:
You may need to manually download and install Java 1.5 or later before installing the VSM
client interface.
4. The License Agreement dialog box is displayed. In the License Agreement dialog box, click Accept
to begin software installation.
5. Click Start.
6. Click Yes if you want a desktop shortcut.
7. The Installation Completed dialog box is displayed. Click Finish to complete the installation.
NOTE:
If the WebStart application does not start, then manually install Java 1.5 or later onto the server or
workstation. To obtain Java, go to http://www.java.com/en/download/index.jsp.
Using the Data Path Module management GUI70
Page 71

Downloading the DPM Management GUI
NOTE:
At least 100 MB of free disk space must be available on the hard drive of your host system for the
DPM Management GUI and WebStart software. Install WebStart from the browser used to access the
DPM Management GUI. For example, you cannot install WebStart using Netscape and run the DPM
Management GUI from Internet Explorer.
1. In your web browser, type the IP address of the DPM management port, labeled MGMT (for
example, http://10.0.0.1). The following screen is displayed.
NOTE:
The version number of the DPM Management GUI is listed in the following screen.
Figure 4 HP Storage Services Platform screen
.
2. Click Web Console to start loading the DPM Management GUI application. WebStart downloads
the DPM Management GUI from the web server and installs it on your host system.
3. Click Run when WebStart prompts Do you want to install this application?
The DPM Management GUI application starts up automatically after WebStart downloads the
jar file.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 71
Page 72
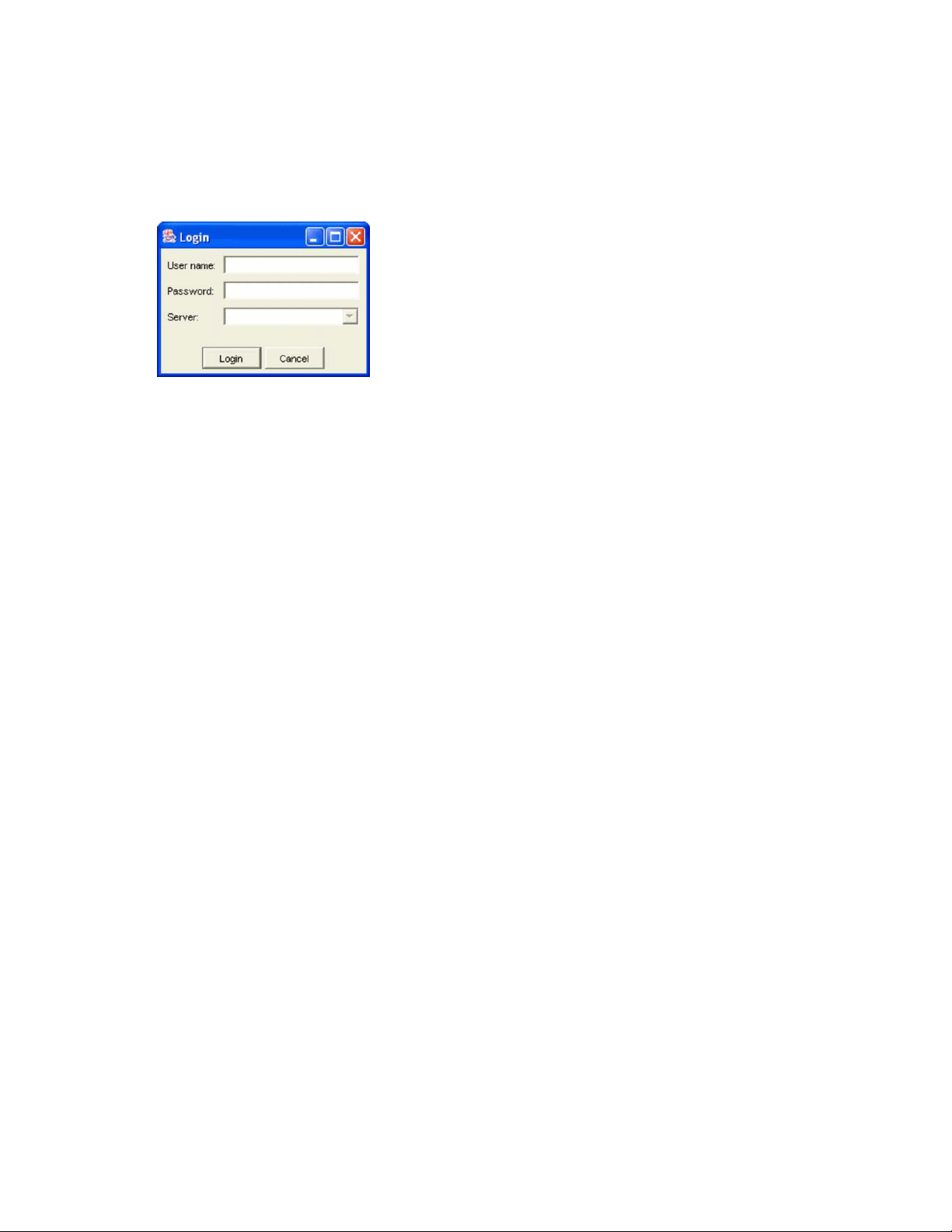
Logging into the DPM Management GUI
1. From a web browser, log in with the username and password, using the same web browser from
which the WebStart application was installed.
User name: admin
Password: password
Figure 5 DPM Management GUI Login screen
.
2. Click Login.
3. HP recommends that you change the password if you did not already do so during setup:
• If you are using the DPM Management GUI, change the password on the telnet screen. See
“Telnet” on page 81 for more information.
• If you are using the CLI, run the Modify User command to change the password.
Navigating the DPM Management GUI
Navigation begins for the DPM Management GUI with the Chassis panel on the System icon. The
Chassis panel provides property information for the Data Path Module.
Using the Data Path Module management GUI72
Page 73
Figure 6 DPM Management GUI screen
.
Using the DPM Management GUI, you can access these functions.
Table 3 DPM Management GUI functions
For more information, see:FunctionGUI area
System
System function
System allows you to manage and configure port settings on the Data Path Module.
To manage external port behavior:
1. Click System on the left pane window.
2. Navigate within the lower window to the Ports folder.
Overall system functionality, DPM status, port management, system configuration
“System” on page 73
“Diagnostics” on page 80Diagnostics for ports and virtual disksDiagnostics
“Telnet” on page 81Telnet windowTelnet
“Log” on page 82List of system eventsLog
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 73
Page 74
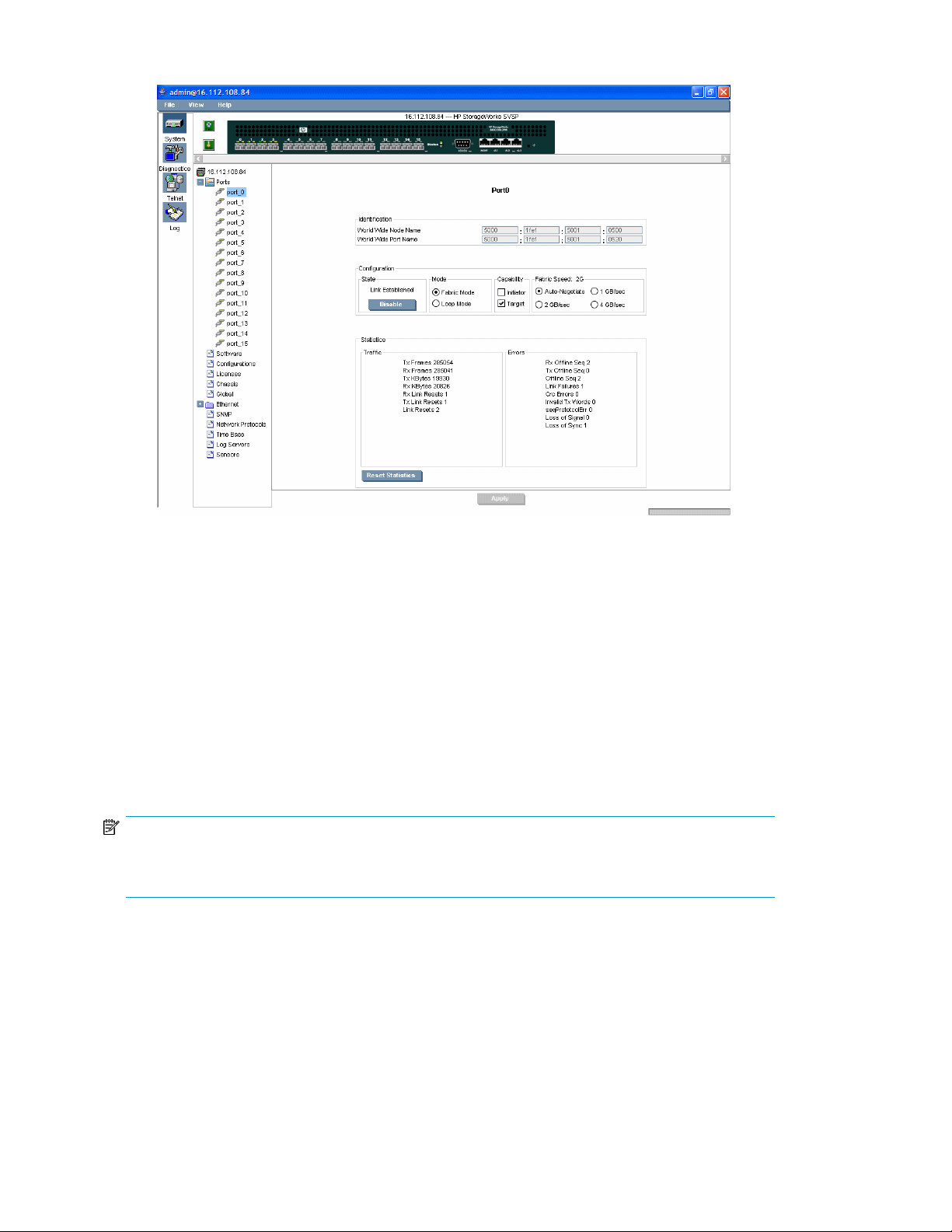
3. Click the specific port to manage. The port information screen is displayed (see Figure 7).
Figure 7 System port information screen
.
The following information is displayed for each selected port:
• World Wide Node Name
• World Wide Port Name
• State of link (enabled/disabled)
• Mode (fabric or loop): Only fabric is supported with SVSP.
• Capability (initiator or target): Even ports are targets, odd ports are initiators
• Fabric speed
• Statistics (Traffic and Errors)
In addition, the following settings can be changed on the System screen:
NOTE:
For all the Initiator, Target, and Fabric Speed settings, click Apply before the settings are saved. The
Initiator, Target, and Max Frame Size settings take effect only after rebooting the Data Path Module.
Capability; Initiator: Select this box to enable initiator (storage to back-end) operations through odd
ports. All DPM ports that are in back-end zones should be set to Initiator-only mode.
Capability; Target: Select this box to enable target (to front-end servers) operations through even ports.
All DPM ports that are in front-end zones should be set to Target-only mode.
Fabric Speed: Changing this box enables you to force the speed operation of the DPM port.
Enabling and disabling ports:
Using the Data Path Module management GUI74
Page 75
NOTE:
Enabling and disabling ports takes effect immediately after clicking the Enable/Disable buttons.
Disable: Click Disable to disable a port.
Enable: Click Enable to enable a port.
Chassis panel (system)
The Chassis panel displays information about the DPM, such serial number and hardware versions.
You can also set the description of the DPM and add a location comment. The DPM can also be
rebooted from the Chassis panel.
Global panel (system)
The Global panel allows the maximum frame size (MTU) of the unit to be set. The max frame size
should be set to the lowest MTU of all devices in the fabric.
Figure 8 System Global panel
.
You can also specify the Rank of the DPM, which will effect the WWPN numbering of the DPM ports
during initial configuration. See also the “Modify factory command” on page 37. Rank can be set to
Primary or Secondary.
Ethernet panel (system)
The Ethernet panel for the System function shows Ethernet configuration information for the Data Path
Module. To view, click the top-level icon in the tree hierarchy on the left side, and then click Ethernet.
Figure 9 shows the Ethernet panel.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 75
Page 76
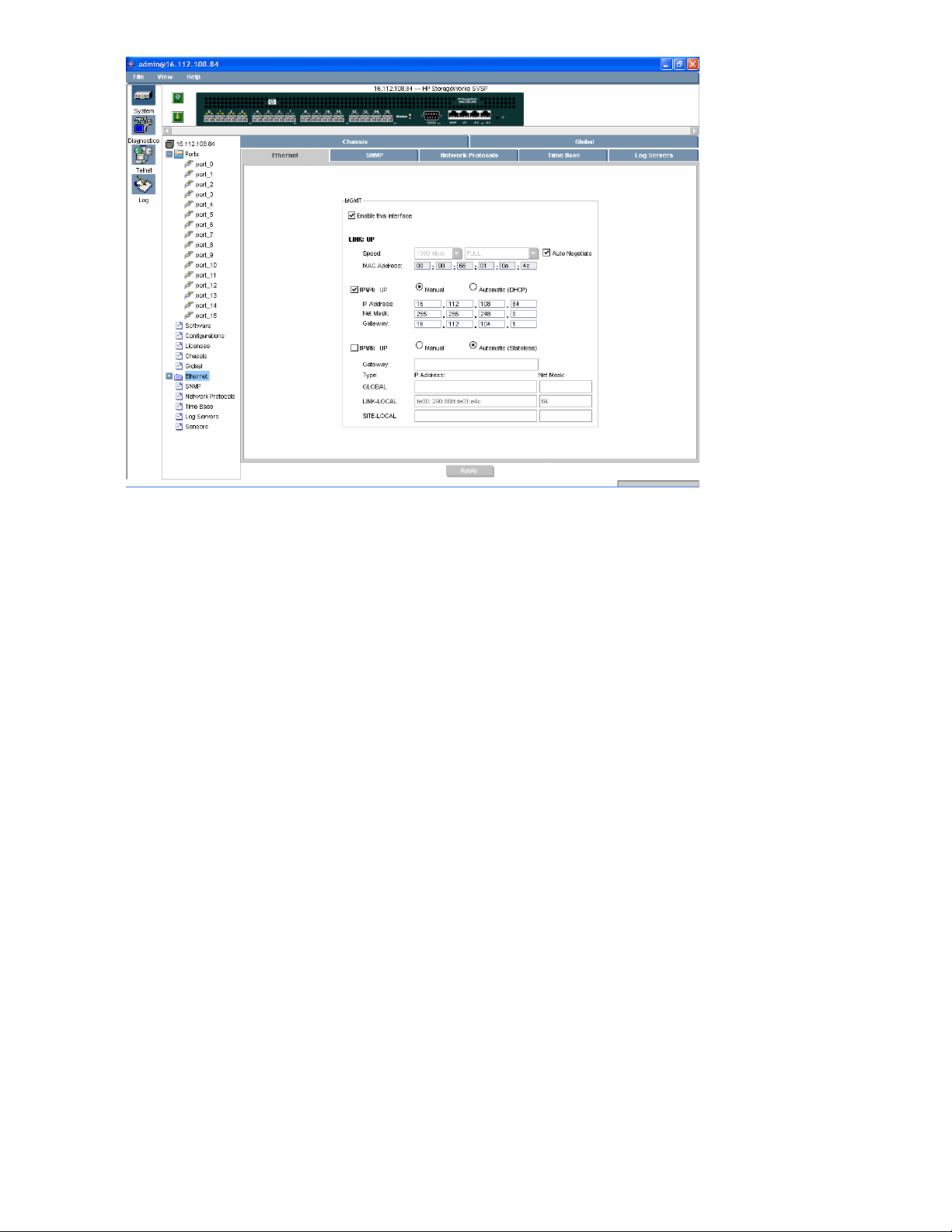
Figure 9 System Ethernet panel
.
An amber LED indicates that the corresponding component is missing, has failed, or will likely fail
soon. Even if your DPMs appear to be performing normally, replace the part if the corresponding LED
has turned amber.
SNMP panel (system)
Figure 10 shows the SNMP panel. This panel allows SNMP v2 or v3 to be enabled or disabled. A
trap receiver can also be specified that will receive SNMP trap events from the DPM, if not enabled
during the initial installation.
Using the Data Path Module management GUI76
Page 77
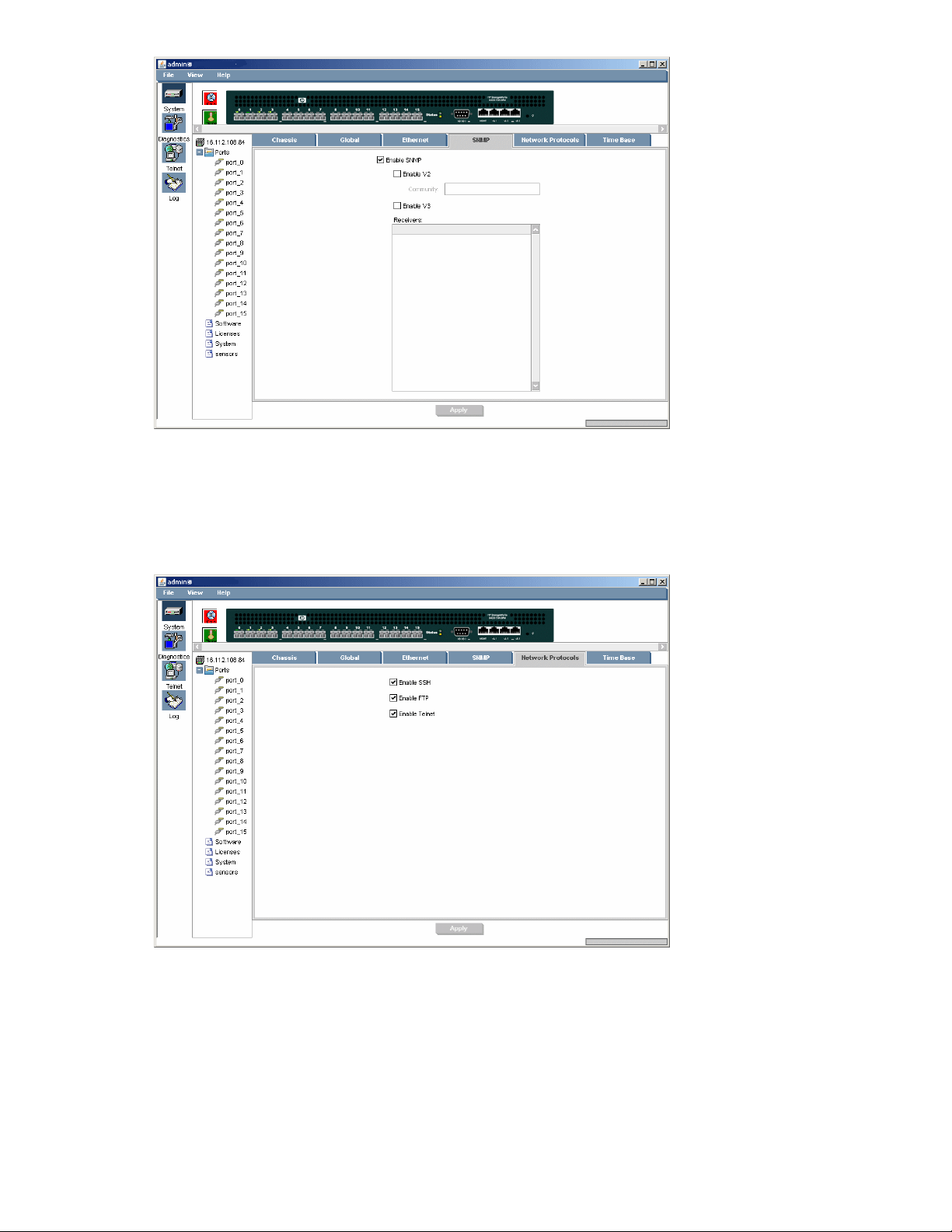
Figure 10 System SNMP panel
.
Network Protocols panel (system)
The Network Protocols panel allows the configuration of networking options on the Data Path Module.
Figure 11 shows the Network Protocols panel.
Figure 11 System Networks Protocols panel
.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 77
Page 78

NOTE:
If maximum network security is required, all the settings on this panel should be turned off in normal
operation, and enabled only when needed.
Enable SSH: Enables Secure Shell (SSH) support in the DPM. SSH is a remote login facility (similar to
telnet) with security features, including strong encryption and authentication. Use SSH as a alternative
to telnet for administrative logins to the DPM. To be useful, the client machines used for administrative
access must be running as SSH client application.
Enable FTP: Enables File Transfer Protocol (FTP) support in the DPM. FTP is used to transfer software
updates and patches to the DPM, and to transfer configuration information, logs, and diagnostic
information from the DPM. When enabled, the DPM runs an FTP server that can be accessed through
TCP/IP. Only enable when needed, then disable afterwards.
Enable Telnet: Enables telnet remote login support. Telnet is a low-security remote login facility, used
to access the administrative login.
Time Base panel (system)
The Time Base panel allows the time on the DPM to be set to manual or Network Time Protocol (NTP).
Setting to NTP requires a server on the network running the NTP service. The DPM can be configured
to passively listen for NTP broadcast messages or with the IP address of the NTP server to send NTP
requests directly. If NTP broadcast is used, the NTP server must also be configured correctly to send
NTP broadcast messages.
Figure 12 System Time Base panel
.
Using the Data Path Module management GUI78
Page 79
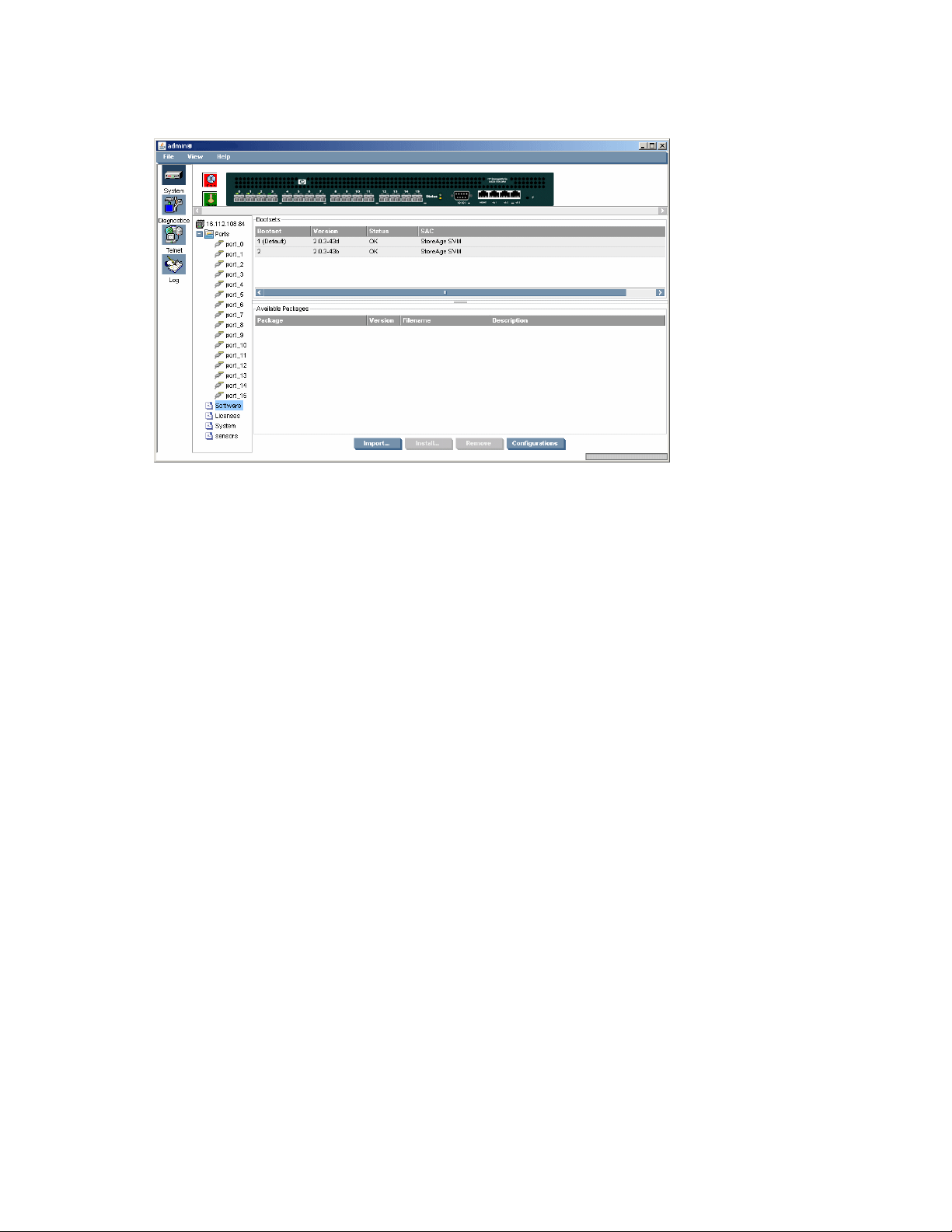
Software panel (system)
The Software panel shows the current and backup bootset information.
Figure 13 System Software panel
.
Sensors panel (system)
The Sensors panel for the System function shows diagnostic information for temperatures, fans, power
supplies, and voltages for the power supplies on the Data Path Module. To view the Sensors panel,
click Sensors in the tree hierarchy on the left. Figure 14 shows the System Sensors panel.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 79
Page 80

Figure 14 System Sensors panel
.
Diagnostics function
The Diagnostics screen provides statistics for various aspects of the system.
To use the Diagnostics panel:
1. Select an object type:
• Ports
• Software
• Licenses
• System
• Sensors
2. Select a value for the object, such as port number if the object is a port.
Using the Data Path Module management GUI80
Page 81

3. Select a variable to graph.
For example: utilization, errors, and transmit frames are among the variables that you can graph
for a port on the Diagnostics screen.
Figure 15 shows utilization for ports 4 and 8.
Figure 15 Diagnostic screen displaying port utilization
.
Telnet function
The telnet panel enables you to initiate a telnet session from the DPM Management GUI.
To begin a telnet session from the DPM Management GUI:
1. Click Telnet in the left-most pane.
2. Enter the correct administrative login and default password (admin is the username, and
password is the password).
The following telnet screen is displayed (see Figure 16):
Figure 16 Telnet screen initiated from the DPM Management GUI
.
The options in the lower window are:
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 81
Page 82

Reconnect Telnet: Re-establishes a telnet session.
Disconnect Telnet: Disconnects a telnet session.
Log function
Click Log in the left-most pane. The Log panel shows a list of system events (see Figure 17).
Figure 17 Diagnostic screen log panel
.
Events are reported for the following channels on the Log screen:
• System
• Port
• Chassis
• Hardware
• Storage application
Each event is assigned one of the following severity levels, in order of severity:
• Emergency
• Alert
• Critical
• Error
• Warning
• Notice
• Information
• Debug
Using the Data Path Module management GUI82
Page 83

5 Support and other resources
Contacting HP
Before you contact HP
Be sure to have the following information available before you contact HP:
http://www.hp.com/support
Before contacting HP, collect the following information:
• Product model names and numbers
• Technical support registration number (if applicable)
• Product serial numbers
• Error messages
• Operating system type and revision level
• Detailed questions
HP contact information
For the name of the nearest HP authorized reseller:
• See the Contact HP worldwide (in English) webpage http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/en/
wwcontact.html.
For HP technical support:
• In the United States, for contact options see the Contact HP United States webpage (http://wel-
come.hp.com/country/us/en/contact_us.html)). To contact HP by phone:
• Call 1–800–HP–INVENT (1–800–474–6836). This service is available 24 hours a day, 7
days a week. For continuous quality improvement, calls may be recorded or monitored.
• If you purchase a Care Pack (service upgrade), call 1–800–633–3600. For more information
about Care Packs, refer to the HP website (http://www.hp.com/hps).
• In other locations, see the Contact HP worldwide (in English) webpage (http://welcome.hp.com/
country/us/en/wwcontact.html).
Subscription service
HP recommends that you register your product at the Subscriber's Choice for Business website:
http://www.hp.com/go/wwalerts
After registering, you will receive e-mail notification of product enhancements, new driver versions,
firmware updates, and other product resources.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 83
Page 84

Related documentation
The following documents provide related information:
• HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Manager User Guide
• HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Manager Command Line Interface User
Guide
• HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Administrator Guide
• HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Release Notes
You can find the documents on the Manuals page of the HP Business Support Center website:
http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
In the storage section, click Storage Software > Storage Virtualization Software and then select your
product.
Support and other resources84
Page 85

Document conventions and symbols
Table 4 Document conventions
ElementConvention
Cross-reference links and e-mail addressesBlue text: Table 4
website addressesBlue, underlined text: http://www.hp.com
• Keys that are pressed
Bold text
Monospace text
• Text typed into a GUI element, such as a box
• GUI elements that are clicked or selected, such as menu
and list items, buttons, tabs, and check boxes
Text emphasisItalic text
• File and directory names
• System output
• Code
• Commands, their arguments, and argument values
Monospace, italic text
Monospace, bold text
• Code variables
• Command variables
Emphasized monospace text
WARNING!
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in bodily harm or death.
CAUTION:
Indicates that failure to follow directions could result in damage to equipment or data.
IMPORTANT:
Provides clarifying information or specific instructions.
NOTE:
Provides additional information.
TIP:
Provides helpful hints and shortcuts.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 85
Page 86

Product warranties
For information about HP StorageWorks product warranties, see the warranty information website:
http://www.hp.com/go/storagewarranty
HP websites
For additional information on HP storage products, see the following HP websites:
• http://www.hp.com
• http://www.hp.com/go/storage
• http://www.hp.com/go/svsp
• http://www.hp.com/support/manuals
• http://www.hp.com/support/downloads
Documentation feedback
HP welcomes your feedback.
To make comments and suggestions about product documentation, please send a message to
storagedocs.feedback@hp.com. All submissions become the property of HP.
Support and other resources86
Page 87

Glossary
This glossary defines acronyms and terms used with the SVSP solution.
access path A specific series of physical connections through which a device is recognized
active boot set The boot set used to supply system software in a running system. Applies to the
active path A path that is currently available for use.
active/active RAID A storage device that presents virtual disks on multiple ports, and the virtual disks
by another device.
DPM.
See also boot set.
See also passive path, and in use path.
are simultaneously active on all ports.
active/passive
RAID
active/standby
RAID
ALUA A SCSI term for asymmetrical logical unit access.
asynchronous
mirroring
auxiliary virtual
disk
back-end LU In VSM, a logical unit (LUN) of storage presented by a storage system (for
A storage device that presents virtual disks on multiple ports of multiple storage
controllers, and at any point in time a virtual disk is only active on the ports of
one controller and passive on the ports of the other controllers. Applies to the
HP EVA.
One storage device per path is in use and the others are in backup/standby
mode. See the product release notes.
A mode of data mirroring in which the updates on the mirror site are always
lagging behind the source site.
In VSM, either of the following:
A backup virtual disk created by a migration task that initially resides on the
•
destination storage pool and switches to the source storage pool when the
task is complete. After task completion, the auxiliary virtual disk contains the
data that the original virtual disk created when the migration group was
created.
• A virtual disk created by mirroring for the VSM agent on a VSM server to
keep track of the state of the sync mirror group that mirrors the setup virtual
disk and its tasks.
example, an EVA).
back-side path A path between the Data Path Module and the physical storage (for example,
an HP EVA).
boot set Either of two selectable locations provided by the Data Path Module for storing
a system software image.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 87
Page 88

Business Copy
SVSP
An HP StorageWorks product that works with SAN storage systems to provide
local replication capabilities within the SVSP domain, providing local point-in-time
(PiT) copies of data, using snapshots of data, based on changes to virtual disks.
CLI Command line interface. The Data Path Module provides a CLI through the local
administrative console (serial port console), telnet, or SSH.
Continuous Access
SVSP
An HP StorageWorks product that works with SAN storage systems to provide
asynchronous data replication (remote mirroring) between SVSP domains to
support disaster tolerance requirements. Data replication can be bidirectional,
meaning that an SVSP domain can be both a source and a destination.
crash consistent The state of the media behind a logical unit after a server crash. Pending writes
are lost.
cross-connected A property of a high-availability configuration in which both Data Path Modules
connect to a dual fabric SAN, allowing either Data Path Module to access both
controllers of a dual-controller storage array.
Data Path Module A SAN-based device, separate from the core Fibre Channel switching
infrastructure, that provides storage virtualization services across heterogeneous
hosts, storage, and SAN fabrics. The device runs a VSM fabric agent,
communicates with a VSM server, is able to process virtual disk information,
present virtual disks to servers as LUNs, and handle their I/Os by routing them
to storage systems managed by the VSM server.
default boot set The boot set that becomes the active boot set when the system is started, unless
the user selects a different boot set. Applies to the DPM.
DPM See Data Path Module.
DPM group An entity that contains one primary and one secondary Data Path Module. Data
Path Modules can only present virtual disks to hosts after they have been added
to DPM groups.
entity A virtual object defined as part of VSM’s virtualized configuration of a SAN.
EVA HP StorageWorks Enterprise Virtual Array. A high-performance, high-capacity,
and high-availability storage solution for the high-end enterprise class marketplace.
Each EVA storage system consists of a pair of HSV virtualizing storage controllers
and the disk drives they manage.
fabric A network of one or more Fibre Channel switches that transmit data between
any two N_ports attached to the member switches.
fabric agent In VSM, a virtualization agent that runs on a DPM. The fabric agent receives
virtual disk information from a VSM server, sets the mapping tables of the DPM,
and enables the DPM to route I/O data from hosts to storage systems.
FC Fibre Channel. A serial data transfer architecture developed by a consortium of
computer and mass storage system manufacturers that requires very high
bandwidth. Fibre Channel provides high reliability transport protocols.
See also http://www.fibrechannel.org/ and http://www.t11.org/.
front-side path A path between the host (host bus adapter) and the Data Path Module.
Glossary88
Page 89

Group In VSM, a virtual container that defines one or more elements for a data moving
task.
See also VDG.
HBA See host bus adapter.
host In VSM, every server that uses VSM virtual disks. Servers that run as VSM servers
are also considered hosts.
host bus adapter A device that provides input/output (I/O) processing and physical connectivity
between a server and a storage system. In order to minimize the impact on host
processor performance, the host bus adapter performs many low-level interface
functions automatically or with minimal processor involvement.
host group A group of hosts that facilitates granting permission for multiple hosts to access
the same storage elements.
I/O Input/Output. Data transferred from one device to another.
in use path A path that is currently being used for I/O traffic.
See also active path.
inactive boot set The boot set that is not in use in a running system. Applies to the DPM.
initiator See initiator device.
initiator device A device, such as an HBA installed into a server, that contains one or more
initiator ports.
initiator port A Fibre Channel port capable of issuing new SCSI commands over Fibre Channel
(FCP) commands.
interswitch link
(ISL)
invalid boot set A boot set that is empty or otherwise does not contain a usable system image.
iSCSI Internet Small Computer System Interface. An IP-based standard for transferring
kdisk A path from a virtual disk presentation on the DPM front side to a server. For
LBA Logical Block Addressing. The addressing mode used for reading from or writing
A connection between two Fibre Channel switches that creates a single switch
fabric. Multiple physical connections between the same two Fibre Channel
switches create multiple ISLs. Each independent ISL is treated as a single path
between the two switches.
data by carrying SCSI commands over IP networks (by encapsulating SCSI data
in TCP packets).
example, there is one kdisk per virtual disk for each unique server initiator
port–to–DPM target port combination.
to a specific sector on a back-end LU. Early PC hard drives specified the sector
in terms of its cylinder number, its head number, and its sector number. LBA
addressing uses just one number. In LBA addressing, the first sector on the
back-end LU is sector zero and all sectors on the back-end LU are simply
incremented from there. Also known as the Logical Block Number (LBN).
LUN Logical Unit Number. A unit of storage that a storage system presents to the SAN
and shows up as a back-end LU when presented to servers. Every storage system
can usually expose multiple logical units, each having a unique number (Logical
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 89
Page 90

Unit Number), which allows servers to access that particular logical unit. LUNs
that a storage system exposes to the SVSP domain are identified by VSM as
back-end LUs.
migration A VSM service that migrates virtual disks from one storage pool to another while
the host application remains online.
mirror A VSM service that mirrors virtual disks synchronously and asynchronously.
See also asynchronous mirroring and synchronous mirroring.
mirroring The creation and continuous updating of one or more redundant copies of data,
usually for the sake of fault or disaster recovery.
OpenVMS Unit ID Abbreviated as OUID. A storage element identifier that is necessary for hosts
running OpenVMS to interact with the storage elements presented to them. This
identifier is relevant to virtual disks, snapshots, and synchronous mirror groups.
passive path A path that must have some operation (for example, a SCSI start unit command
that is issued by the server) performed on it to make it active.
See also active/active RAID, active/passive RAID, and secondary path.
patch file Incremental update to an existing system image.
persistent
reservation
A mechanism for the resolution of dynamic SCSI contention in systems with
multiple initiator ports accessing a logical unit, whereby a single initiator port
or a set of initiator ports can reserve the logical unit indefinitely. While reserved,
the storage device server rejects all commands for that logical unit from any other
initiator ports.
personality The way in which a DPM exposes LUNs to the hosts that use them. Exposing a
LUN with the correct personality (such as HP EVA VS-ALUA or HP EVA MS-DPM)
for the hosts enables features such as failover and failback between DPMs in
conjunction with the appropriate multipath software running on the host. See the
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Manager User Guide
for a list of personalities used with SVSP.
physical disk A disk device that can be discovered and managed by VSM.
PiT Point-in-Time. A VSM term denoting an entity created by a snapshot that represents
the freezing of a virtual disk’s data at a particular time and the redirection of
any further modifications to the virtual disk’s data to a new virtual disk, called a
temporary virtual disk.
POST Power-on Self Test. The diagnostic sequence executed by devices during system
startup.
primary path For an active/active or active/passive device, a path belonging to the set of
paths that are active by default, as viewed by the server.
See also active/passive RAID, active path, and secondary path.
PSC Physical storage container. A path from a DPM to a back-end LU. There are eight
PSCs between any two DPM initiator ports and a back-end LU presented to the
domain by an eight-port storage array (for example, an HP EVA8100).
quad A Data Path Module purpose-built ASIC that is capable of directing the data to
and from the hosts. The DPM has four quads, with all capable of communicating
across all ports, although it is desirable to keep traffic within a quad if possible.
Glossary90
Page 91

Each quad contains two front or host-facing ports, and two back or storage ports.
Each of these ports is capable of a 4 Gbit/s Fibre Channel rate. Therefore, using
additional quads may be necessary as a multiple of that 8 Gbit/s or 6.4 MB/s
rate.
RPO Recovery Point Objective. The point in time to which you must recover data as
defined by your organization. This is generally a definition of what an
organization determines is an acceptable loss in a distressed situation.
RTO Recovery Time Objective. The duration of time and a service level within which
a business process must be restored after a disaster to avoid unacceptable
consequences associated with a break in business continuity.
SAN Storage Area Network. A network specifically dedicated to the task of transporting
data between storage systems and servers. SANs are traditionally connected
over FC networks but have also been built using iSCSI technology.
secondary path For an active/passive device, the set of paths that are passive by default.
See also active/passive RAID, passive path, and primary path.
setup virtual disk A virtual disk that contains the virtualized VSM configuration for the SVSP domain,
including, for example, information about storage pools and virtual disks defined
on the domain.
SFP Small form-factor pluggable. The 2 Gbps or faster form factor of the removable
optical transceiver used by the Data Path Module, HBAs, and most Fibre Channel
switches. It uses the LC-type connector.
snapclone A VSM service that creates physical copies of VSM virtual disks without using
host resources.
snapshot Either of the following:
• A VSM service that creates multiple low-capacity, read-write snapshots of
virtual disks and makes the snapshots available to any number of hosts, for
purposes such as data recovery, backup and testing, while the original virtual
disk stays online and continues to be updated.
• A read-write entity that makes PiT data available to any host as a logical
drive.
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol. The protocol used by the Data Path
Module to report exception conditions to third-party network management
applications.
SSH Secure Shell. A protocol and application for communicating with a remote
computer system. SSH is a more secure alternative to using telnet to communicate
with the Data Path Module.
storage pool In VSM, a set of back-end LUs or stripe sets from which you can create virtual
disks and allocate them to hosts. SVSP storage pools enable you to classify
storage elements into classes of service and provide different classes of service
to different hosts.
stripe set In VSM, a set of back-end LUs across which VSM stripes data, optionally used
to build storage pools.
SVSP domain Consists of all SVSP components and the storage they manage.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 91
Page 92

synchronous
mirroring
A mode of data mirroring in which the updates on the mirror site are synchronized
between destinations.
system software
image
A software component, capable of being updated, that contains the operating
environment for the Data Path Module, including the SVSP VSM agent for the
Data Path Module.
target Receives commands from the initiator, and after execution, returns
acknowledgement to the initiator.
See also initiator.
target device A device that contains one or more target ports.
target port A Fibre Channel port capable of presenting one or more SCSI LUNs to servers.
A target is also known as the destination of a server's I/O request.
task In VSM, a process that carries out a data moving task on a group.
temporary virtual
disk
A virtual disk created when a PiT is created on another virtual disk. The temporary
virtual disk holds any modifications redirected from the original virtual disk after
the PiT is created.
thick provisioned A quality of virtual disks wherein the virtual disk’s allocated capacity is always
equal to its total capacity.
See also virtual disk.
thin provisioned A quality of virtual disks wherein the virtual disk’s allocated capacity is set to a
small initial value that can expand up to the virtual disk’s total capacity according
to actual usage.
transaction
consistent
The state of the media behind a logical unit, such that all pending writes have
been completed, and all caches are empty.
transceiver A device that provides an interface between the Data Path Module hardware
and the external network cable. The Data Path Module uses 4–Gbps optical
small form-factor pluggable transceivers.
trunk A group of interswitch links (ISLs) configured to work together to connect two
Fibre Channel switches with a higher bandwidth than a single ISL. Each trunk is
treated as a single path for the switch to route I/O destined for a device on the
other switch.
UDH User defined hosts are all servers other than the VSM servers that are attached
to the SVSP domain.
valid boot set A DPM boot set that contains a usable system image.
VDG Virtual Disk Group. A single entity that encapsulates multiple virtual disks or
snapshots to enable synchronized operations on the members.
virtual disk In VSM, a unit of storage allocated to one or more hosts from a storage pool. A
virtual disk can range in size from 1 GB to 2 TB. DPMs present allocated virtual
disks to hosts as logical drives.
VMA Virtualization Management Appliance.
Glossary92
Page 93

Volume Shadow
Copy Service
VSM Virtualization Services Manager. Short for the HP StorageWorks SAN
A backup infrastructure for the Microsoft Windows Server 2003/2008 operating
systems, as well as a mechanism for creating consistent point-in-time copies of
data known as shadow copies.
Virtualization Services Platform Manager application.
VSM API virtual
disk
VSM client The management interface for VSM servers. The VSM client runs on any PC
VSM GUI Graphical user interface used to manage the HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization
VSM server VSM software that runs on a dedicated appliance connected to a SAN fabric
VSS See Volume Shadow Copy Service.
VSS freeze A period of time during the shadow copy creation process when all services
VSS thaw The completion of a VSS shadow copy freeze.
WWNN World Wide Node Name. The globally unique identifier for a system containing
A virtual disk that enables a host to direct VSM CLI commands to a VSM server
through a DPM. May also be seen as SANAPI on the VSM GUI Maintenance
screen.
connected to a VSM server workstation through an IP connection.
Services Platform environment.
and manages and controls all storage systems on the SAN. A VSM server
virtualizes the storage space on the storage systems, creates storage pools and
virtual disks, and provides agents with virtual disk information. The VSM server
also moves data in snapclone, migration, and asynchronous mirroring operations.
(writers) have flushed their writes to the virtual disks and are not initiating
additional writes.
Fibre Channel ports.
A WWN is a 64–bit value, typically represented as a string of 16 hexadecimal
digits.
WWPN World Wide Port Name. The globally unique identifier for an individual Fibre
Channel port.
A WWPN is a 64–bit value, typically represented as a string of 16 hexadecimal
digits.
zone A collection of devices or user ports that are permitted to communicate with each
other through a fabric. Any two devices or user ports that are not members of
at least one common zone are not permitted to communicate with each other.
HP StorageWorks SAN Virtualization Services Platform Data Path Module User Guide 93
Page 94

Glossary94
 Loading...
Loading...