Page 1

Red Hat Directory Server 8.0
Installation Guide
Page 2

Red Hat Directory Server 8.0
This manual provides a high-level overview of design and planning decisions you need to make
before installing Directory Server, and describes the different installation methods that you can
use.
Page 3

Red Hat Directory Server 8.0: Installation Guide
Copyright © 2008
Copyright © 2008 Red Hat, Inc.. This material may only be distributed subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the
Open Publication License, V1.0 or later with the restrictions noted below (the latest version of the OPL is presently
available at http://www.opencontent.org/openpub/).
Distribution of substantively modified versions of this document is prohibited without the explicit permission of the
copyright holder.
Distribution of the work or derivative of the work in any standard (paper) book form for commercial purposes is
prohibited unless prior permission is obtained from the copyright holder.
Red Hat and the Red Hat "Shadow Man" logo are registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc. in the United States and other
countries.
All other trademarks referenced herein are the property of their respective owners.
The GPG fingerprint of the security@redhat.com key is:
CA 20 86 86 2B D6 9D FC 65 F6 EC C4 21 91 80 CD DB 42 A6 0E
1801 Varsity Drive
Raleigh, NC 27606-2072
USA
Phone: +1 919 754 3700
Phone: 888 733 4281
Fax: +1 919 754 3701
PO Box 13588
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709
USA
Page 4

Red Hat Directory Server 8.0
Page 5

Preface .................................................................................................................... vii
1. Document Conventions ................................................................................ viii
2. We Need Feedback! ......................................................................................ix
1. Preparing for a Directory Server Installation ............................................................. 1
1. Directory Server Components ......................................................................... 1
2. Considerations before Setting up Directory Server ........................................... 1
2.1. Port Numbers ...................................................................................... 1
2.2. Directory Server User and Group ......................................................... 3
2.3. Directory Manager ............................................................................... 3
2.4. Directory Administrator ........................................................................ 3
2.5. Administration Server User .................................................................. 4
2.6. Directory Suffix ................................................................................... 4
2.7. Configuration Directory ........................................................................ 4
2.8. Administration Domain ......................................................................... 5
3. About the setup-ds-admin.pl Script .................................................................. 5
4. Overview of Setup .......................................................................................... 9
2. System Requirements ...........................................................................................15
1. Hardware Requirements ................................................................................15
2. Operating System Requirements ....................................................................16
2.1. Using dsktune ....................................................................................16
2.2. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5 ........................................................17
2.3. HP-UX 11i .........................................................................................20
2.4. Sun Solaris 9 .....................................................................................23
3. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux ............................29
1. Installing the JRE ..........................................................................................30
2. Installing the Directory Server Packages .........................................................31
3. Express Setup ..............................................................................................32
4. Typical Setup ................................................................................................35
5. Custom Setup ...............................................................................................39
4. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on HP-UX 11i .................................................45
1. Installing the JRE ..........................................................................................46
2. Installing the Directory Server Packages .........................................................46
3. Express Setup ..............................................................................................47
4. Typical Setup ................................................................................................50
5. Custom Setup ...............................................................................................54
5. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris ................................................61
1. Installing the JRE ..........................................................................................61
2. Installing the Directory Server Packages .........................................................63
2.1. Installing Individual Packages .............................................................63
2.2. Installing from an ISO Image ...............................................................64
3. Express Setup ..............................................................................................65
4. Typical Setup ................................................................................................68
5. Custom Setup ...............................................................................................73
6. Advanced Setup and Configuration ........................................................................79
1. Working with Administration Server Instances .................................................79
1.1. Configuring IP Authorization on the Administration Server .....................79
v
Page 6

Red Hat Directory Server 8.0
1.2. Configuring Proxy Servers for the Administration Server .......................80
2. Working with Directory Server Instances .........................................................80
2.1. Creating a New Directory Server Instance ............................................80
2.2. (Alternate) Installing Directory Server with setup-ds ..............................81
2.3. Registering an Existing Directory Server Instance with the Configuration
Directory Server .......................................................................................81
3. Silent Setup ..................................................................................................82
3.1. Silent Setup for Directory Server and Administration Server ..................82
3.2. Silent Directory Server Instance Creation .............................................83
3.3. Sending Parameters in the Command Line ..........................................85
3.4. Using the ConfigFile Parameter to Configure the Directory Server .........87
3.5. About .inf File Parameters ...................................................................88
4. Uninstalling Directory Server ..........................................................................95
4.1. Removing a Single Directory Server Instance .......................................95
4.2. Uninstalling Directory Server ...............................................................95
7. General Usage Information ....................................................................................99
1. Directory Server File Locations ......................................................................99
2. LDAP Tool Locations ...................................................................................101
3. Starting the Directory Server Console ...........................................................101
4. Getting the Administration Server Port Number .............................................102
5. Starting and Stopping Servers .....................................................................102
5.1. Starting and Stopping Directory Server ..............................................102
5.2. Starting and Stopping Administration Server ......................................103
6. Resetting the Directory Manager Password ..................................................103
7. Troubleshooting ..........................................................................................105
7.1. Running dsktune ..............................................................................105
7.2. Common Installation Problems ..........................................................106
8. Migrating from Previous Versions .........................................................................107
1. Migration Overview .....................................................................................107
2. About migrate-ds-admin.pl ...........................................................................108
3. Before Migration .........................................................................................111
3.1. Backing up the Directory Server Configuration ...................................112
3.2. Configuring the Directory Server Console ..........................................112
4. Migration Scenarios ....................................................................................113
4.1. Migrating a Server or Single Instance ................................................113
4.2. Migrating Replicated Servers ............................................................115
4.3. Migrating a Directory Server from One Machine to Another .................117
4.4. Migrating a Directory Server from One Platform to Another .................119
Glossary ................................................................................................................121
A. Revision History .................................................................................................139
Index .....................................................................................................................141
vi
Page 7

Preface
This installation guide describes the Red Hat Directory Server 8.0 installation process and the
migration process. This manual provides detailed step-by-step procedures for all supported
operating systems, along with explanations of the different setup options (express, typical,
custom, and silent), additional options for Directory Server instance creation, migrating previous
versions of Directory Server, and troubleshooting and basic usage.
IMPORTANT
Directory Server 8.0 provides a migration tool for upgrading or migrating from
earlier Directory Server versions. If you already have a Directory Server
deployment that is supported for migration, you must use the documented
migration procedure to migrate your data and configuration to version 8.0.
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions has for more information.
The Directory Server setup process requires information specific to the Directory Server
instance being configured, information about the host names, port numbers, passwords, and IP
addresses that will be used. The setup program attempts to determine reasonable default
values for these settings based on your system environment. Read through this manual before
beginning to configure the Directory Server to plan ahead what values to use.
TIP
If you are installing Directory Server for evaluation, use the express or typical
setup mode. These processes are very fast, and can help get your directory
service up and running quickly.
IMPORTANT
Red Hat Directory Server 8.0 introduces filesystem paths for configuration files,
scripts, commands, and database files used with Directory Server which comply
with Filesystem Hierarchy Standard (FHS). This file layout is very different than
previous releases of Directory Server, which installed all of the files and
directories in /opt/redhat-ds or /opt/netscape. If you encounter errors during
the installation process, look at Section 7, “Troubleshooting”. For more
information on how the file layout has changed, see Section 1, “Directory Server
File Locations”.
The latest Directory Server release is available for your platform and operating system through
Red Hat Network (RHN) at http://rhn.redhat.com/.
vii
Page 8

Preface
1. Document Conventions
Certain words in this manual are represented in different fonts, styles, and weights. This
highlighting indicates that the word is part of a specific category. The categories include the
following:
Courier font
Courier font represents commands, file names and paths, and prompts .
When shown as below, it indicates computer output:
Desktop about.html logs paulwesterberg.png
Mail backupfiles mail reports
bold Courier font
Bold Courier font represents text that you are to type, such as: service jonas start
If you have to run a command as root, the root prompt (#) precedes the command:
# gconftool-2
italic Courier font
Italic Courier font represents a variable, such as an installation directory:
install_dir/bin/
bold font
Bold font represents application programs and text found on a graphical interface.
When shown like this: OK , it indicates a button on a graphical application interface.
Additionally, the manual uses different strategies to draw your attention to pieces of information.
In order of how critical the information is to you, these items are marked as follows:
Note
viii
A note is typically information that you need to understand the behavior of the
system.
Page 9

We Need Feedback!
Tip
A tip is typically an alternative way of performing a task.
Important
Important information is necessary, but possibly unexpected, such as a
configuration change that will not persist after a reboot.
Caution
A caution indicates an act that would violate your support agreement, such as
recompiling the kernel.
Warning
A warning indicates potential data loss, as may happen when tuning hardware
for maximum performance.
2. We Need Feedback!
If you find a typographical error in this manual, or if you have thought of a way to make this
manual better, we would love to hear from you! Please submit a report in Bugzilla:
http://bugzilla.redhat.com/bugzilla/ against the product Red Hat Directory Server.
When submitting a bug report, be sure to mention the manual's identifier: RHDSIG 8.0
If you have a suggestion for improving the documentation, try to be as specific as possible when
describing it. If you have found an error, please include the section number and some of the
surrounding text so we can find it easily.
ix
Page 10

x
Page 11

Chapter 1.
Preparing for a Directory Server
Installation
Before you install Red Hat Directory Server 8.0, there are required settings and information that
you need to plan in advance. This chapter describes the kind of information that you should
provide, relevant directory service concepts Directory Server components, and the impact and
scope of integrating Directory Server into your computing infrastructure.
The information that is covered here and supplied during the Directory Server setup relates to
the design of your directory tree (the hierarchical arrangement of your directory, including all
major roots and branch points) and relates to your directory suffixes and databases. See the
Directory Server Administrator's Guide for more information on suffixes and databases.
1. Directory Server Components
Directory Server 8.0 is comprised of several components, which work in tandem:
• The Directory Server is the core LDAP server daemon. It is compliant with LDAP v3
standards. This component includes command-line server management and administration
programs and scripts for common operations like export and backing up databases.
• The Directory Server Console is the user interface that simplifies managing users, groups,
and other LDAP data for your enterprise. The Console is used for all aspects of server
management, including making backups; configuring security, replication, and databases;
adding entries; and monitoring servers and viewing statistics.
• The Administration Server is the management agent which administers Directory Servers. It
communicates with the Directory Server Console and performs operations on the Directory
Server instances. It also provides a simple HTML interface and on-line help pages. There
must be one Administration Server running on each machine which has a Directory Server
instance running on it.
2. Considerations before Setting up Directory Server
Depending on the type of setup that you perform, you will be asked to provide instance-specific
information for both the Administration Server and Directory Server during the installation
procedure, including port numbers, server names, and usernames and passwords for the
Directory Manager and administrator. If you will have multiple Directory Server instances, then it
is better to plan these configuration settings in advance so that the setup processes can run
without conflict.
2.1. Port Numbers
The Directory Server setup requires two TCP/IP port numbers: one for the Directory Server and
1
Page 12
Chapter 1. Preparing for a Directory Server Installation
one for the Administration Server. These port numbers must be unique.
The Directory Server instance (LDAP) has a default port number of 389. The Administration
Server port number has a default number of 9830. If the default port number for either server is
in use, then the setup program randomly generates a port number larger than 1024 to use as
the default. Alternatively, you can assign any port number between 1025 and 65535 for the
Directory Server and Administration Server ports; you are not required to use the defaults or the
randomly-generated ports.
NOTE
While the legal range of port numbers is 1 to 65535, the Internet Assigned
Numbers Authority (IANA) has already assigned ports 1 to 1024 to common
processes. Never assign a Directory Server port number below 1024 (except for
389/636 for the LDAP server) because this may conflict with other services.
For LDAPS (LDAP with TLS/SSL), the default port number is 636. The server can listen to both
the LDAP and LDAPS port at the same time. However, the setup program will not allow you to
configure TLS/SSL. To use LDAPS, assign the LDAP port number in the setup process, then
reconfigure the Directory Server to use LDAPS port and the other TLS/SSL parameters
afterward. For information on how to configure LDAPS, see the Directory Server Administrator's
Guide.
The Administration Server runs on a web server, so it uses HTTP or HTTPS. However, unlike
the Directory Server which can run on secure (LDAPS) and insecure (LDAP) ports at the same
time, the Administration Server cannot run over both HTTP and HTTPS simultaneously. The
setup program, setup-ds-admin.pl, does not allow you to configure the Administration Server
to use TLS/SSL. To use TLS/SSL (meaning HTTPS) with the Administration Server, first set up
the Administration Server to use HTTP, then reconfigure it to use HTTPS.
NOTE
When determining the port numbers you will use, verify that the specified port
numbers are not already in use by running a command like netstat.
If you are using ports below 1024, such as the default LDAP port (389), you must run the setup
program and start the servers as root. You do not, however, have to set the server user ID to
root. When it starts, the server binds and listens to its port as root, then immediately drops its
privileges and runs as the non-root server user ID. When the system restarts, the server is
started as root by the initscript. The setuid(2) man page1has detailed technical information.
1
http://grove.ufl.edu/cgi-bin/webman?SEARCH+man2+setuid.2.gz
2
Page 13

Directory Server User and Group
Section 2.2, “Directory Server User and Group” has more information about the server user ID.
2.2. Directory Server User and Group
The setup process sets a user ID (UID) and group ID (GID) as which the servers will run. The
default UID is a non-privileged (non-root) user, nobody on Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Solaris
and daemon on HP-UX. Red Hat strongly recommends using this default value. The same UID
can be used for both the Directory Server and the Administration Server, which simplifies
administration. If you choose a different UID for each server, those UIDs must both belong to
the group assigned to Directory Server.
For security reasons, Red Hat strongly discourages you from setting the Directory Server or
Administration Server user to root. If an attacker gains access to the server, he might be able
to execute arbitrary system commands as the root user. Using a non-privileged UID adds
another layer of security.
Listening to Restricted Ports as Unprivileged Users.
Even though port numbers less than 1024 are restricted, the LDAP server can listen to port 389
(and any port number less than 1024), as long as the server is started by the root user or by
init when the system starts up. The server first binds and listens to the restricted port as root,
then immediately drops privileges to the non-root server UID. setuid(2) man page2has detailed
technical information.
Section 2.1, “Port Numbers” has more information on port numbers in Directory Server.
2.3. Directory Manager
The Directory Server setup creates a special user called the Directory Manager. The Directory
Manager is a unique, powerful entry that is used to administer all user and configuration tasks.
The Directory Manager is a special entry that does not have to conform to a Directory Server
configured suffix; additionally, access controls. password policy, and database limits for size,
time, and lookthrough limits do not apply to the Directory Manager. There is no directory entry
for the Directory Manager user; it is used only for authentication. You cannot create an actual
Directory Server entry that uses the same DN as the Directory Manager DN.
The Directory Server setup process prompts for a distinguished name (DN) and a password for
the Directory Manager. The default value for the Directory Manager DN is cn=Directory
Manager. The Directory Manager password must contain at least 8 characters which must be
ASCII letters, digits, or symbols.
2.4. Directory Administrator
The Directory Server setup also creates an administrator user specifically for Directory Server
and Administration Server server management, called the Directory Administrator. The Directory
Administrator is the "super user" that manages all Directory Server and Administration Server
2
http://grove.ufl.edu/cgi-bin/webman?SEARCH+man2+setuid.2.gz
3
Page 14

Chapter 1. Preparing for a Directory Server Installation
instances through the Directory Server Console. Every Directory Server is configured to grant
this user administrative access.
There are important differences between the Directory Administrator and the Directory Manager:
• The administrator cannot create top level entries for a new suffix through an add operation.
either adding an entry in the Directory Server Console or using ldapadd, a tool provided with
OpenLDAP. Only the Directory Manager can add top-level entries by default. To allow other
users to add top-level entries, create entries with the appropriate access control statements in
an LDIF file, and perform an import or database initialization procedure using that LDIF file.
• Password policies do apply to the administrator, but you can set a user-specific password
policy for the administrator.
• Size, time, and lookthrough limits apply to the administrator, but you can set different
resource limits for this user.
The Directory Server setup process prompts for a username and a password for the Directory
Administrator. The default Directory Administrator username is admin. For security, the
Directory Administrator's password must not be the same as the Directory Manager's password.
2.5. Administration Server User
By default, the Administration Server runs as the same non-root user as the Directory Server.
Custom and silent setups provide the option to run the Administration Server as a different user
than the Directory Server.
The default Administration Server user is the same as the Directory Server user, which is
nobody. If the Administration Server is given a different UID, then that user must belong to the
group to which the Directory Server user is assigned.
2.6. Directory Suffix
The directory suffix is the first entry within the directory tree. At least one directory suffix must be
provided when the Directory Server is set up. The recommended directory suffix name matches
your organization's DNS domain name. For example, if the Directory Server hostname is
ldap.example.com, the directory suffix is dc=example,dc=com. The setup program constructs a
default suffix based on the DNS domain or from the fully-qualified host and domain name
provided during setup. This suffix naming convention is not required, but Red Hat strongly
recommends it.
2.7. Configuration Directory
The configuration directory is the main directory where configuration information — such as log
files, configuration files, and port numbers — is stored. These configuration data get stored in
the o=NetscapeRoot tree. A single Directory Server instance can be both the configuration
directory and the user directory.
4
Page 15

Administration Domain
If you install Directory Server for general directory services and there is more than one Directory
Server in your organization, you must determine which Directory Server instance will host the
configuration directory tree, o=NetscapeRoot. Make this decision before installing any
compatible Directory Server applications. The configuration directory is usually the first one you
set up.
Since the main configuration directory generally experiences low traffic, you can permit its
server instances to coexist on any machine with a heavier-loaded Directory Server instance.
However, for large sites that deploy a large number of Directory Server instances, dedicate a
low-end machine for the configuration directory to improve performance. Directory Server
instances write to the configuration directory, and for larger sites, this write activity can create
performance issues for other directory service activities. The configuration directory can be
replicated to increase availability and reliability.
If the configuration directory tree gets corrupted, you may have to re-register or re-configure all
Directory Server instances. To prevent that, always back up the configuration directory after
setting up a new instance; never change a hostname or port number while active in the
configuration directory; and do not modify the configuration directory tree; only the setup
program can directly modify a configuration.
2.8. Administration Domain
The administration domain allows servers to be grouped together logically when splitting
administrative tasks. That level of organization is beneficial, for example, when different
divisions within an organization want individual control of their servers while system
administrators require centralized control of all servers.
When setting up the administration domain, consider the following:
• Each administration domain must have an administration domain owner with complete access
to all the domain servers but no access to the servers in other administration domains. The
administration domain owner may grant individual users administrative access on a
server-by-server basis within the domain.
• All servers must share the same configuration directory. The Configuration Directory
Administrator has complete access to all installed Directory Servers, regardless of the
domain.
• Servers on two different domains can use different user directories for authentication and user
management.
3. About the setup-ds-admin.pl Script
The Directory Server and Administration Server instances are created and configured through a
script call setup-ds-admin.pl. Running this script launches an interactive setup program with a
series of dialog screens with a yes/no prompt or a simple text input prompt. Each prompt has a
5
Page 16
Chapter 1. Preparing for a Directory Server Installation
default answer in square brackets, such as the following:
Would you like to continue with setup? [yes]:
• Pressing Enter accepts the default answer and proceeds to the next dialog screen. Yes/No
prompts accept y for Yes and n for No.
• To go back to a previous dialog screen, type Control-B and press Enter. You can backtrack
all the way to the first screen.
• Two prompts ask for a password. After entering it the first time, confirm the password by
typing it in again. The password prompts do not echo the characters entered, so make sure to
type them correctly.
• When the setup-ds-admin.pl finishes, it generates a log file in the /tmp directory called
setupXXXXXX.log where XXXXXX is a series of random characters. This log file contains
all of the prompts and answers supplied to those prompts, except for passwords.
• Some options, such as s (silent) and f (file) allow you to supply values for the setup program
through a file. The .inf file (described in more detail in Section 3, “Silent Setup”) has three
sections for each of the major components of Directory Server: General (host server), slapd
(LDAP server), and admin (Administration Server). The parameters used in the .inf can be
passed directly in the command line. Command-line arguments with setup-ds-admin.pl
specify the .inf setup file section (General, slapd, or admin), parameter, and value in the
following form:
section.parameter=value
For example, to set the machine name, suffix, and Directory Server port of the new instance,
the command is as follows:
/usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl General.FullMachineName=ldap.example.com
“slapd.Suffix=dc=example, dc=com” slapd.ServerPort=389
NOTE
Passing arguments in the command line or specifying an .inf sets the defaults
used in the interactive prompt unless they are used with the s (silent) option.
Argument values containing spaces or other shell special characters must quoted to prevent
the shell from interpreting them. In the previous example, the suffix value has a space
character, so the entire parameter has to be quoted. If many of the parameters have to be
quoted or escaped, use an .inf file instead.
6
Page 17

About the setup-ds-admin.pl Script
• An .inf file can be used in conjunction with command line parameters. Parameters set in the
command line override those specified in an .inf file, which is useful for creating an .inf file
to use to set up many Directory Servers. Many of the parameters can be the same, such as
ConfigDirectoryLdapURL, ones specific to the host, such as FullMachineName have to be
unique. For example:
setup-ds-admin.pl -s -f common.inf
General.FullMachineName=ldap37.example.com
slapd.ServerIdentifier=ldap37
This command uses the common parameters specified in the common.inf file, but overrides
FullMachineName and ServerIdentifier with the command line arguments.
NOTE
The section names and parameter names used in the .inf files and on the
command line are case sensitive. Refer to Table 1.1, “setup-ds-admin Options”
to check the correct capitalization.
The .inf file has an additional option, ConfigFile which imports the contents of any LDIF
file into the Directory Server. This is an extremely useful tool for preconfiguring users,
replication, and other directory management entries. For more information on using the
ConfigFile parameter to configure the Directory Server, see Section 3.4, “Using the
ConfigFile Parameter to Configure the Directory Server”.
Option Alternate Options Description Example
--silent -s This sets that the
setup script will run in
silent mode, drawing
the configuration
information from a file
(set with the --file
parameter) or from
arguments passed in
the command line
rather than
interactively.
--file=name -f name This sets the path
and name of the file
/usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
-f /export/sample.inf
which contains the
configuration settings
for the new Directory
Server instance. This
7
Page 18
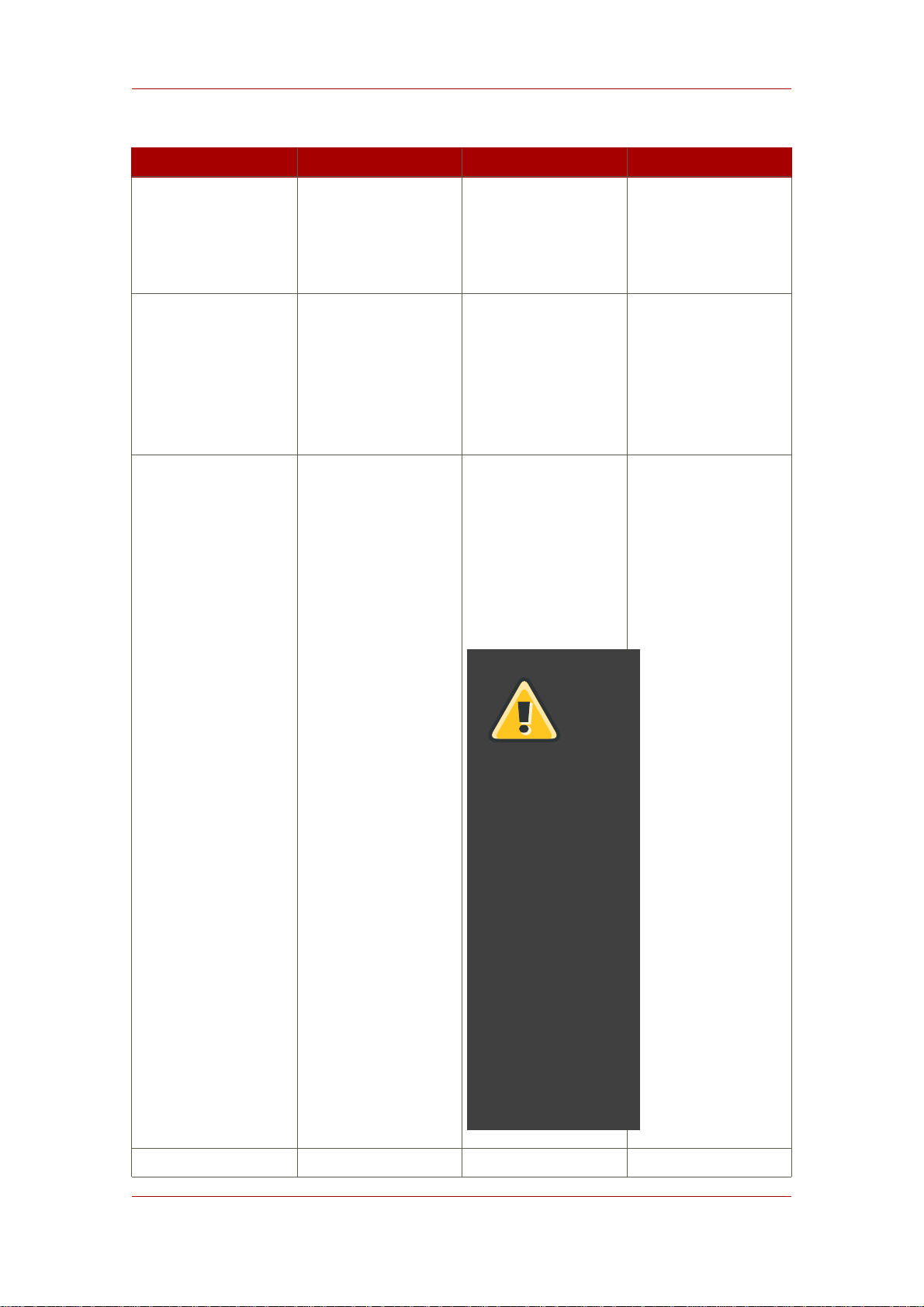
Chapter 1. Preparing for a Directory Server Installation
Option Alternate Options Description Example
can be used with the
--silent parameter;
if used alone, it sets
the default values for
the setup prompts.
--debug -d[dddd] This parameter turns
on debugging
information. For the
-d flag, increasing the
number of d's
increases the debug
level.
--keepcache -k This saves the
temporary installation
file, .inf that is
created when the
setup script is run.
This file can then be
reused for a silent
setup.
WARNING
The
cache
file
contains
the
cleartext
passwords
supplied
during
setup.
Use
appropriate
caution
and
protection
with
this
file.
--logfile name -l This parameter
8
Page 19

Overview of Setup
Option Alternate Options Description Example
specifies a log file to
which to write the
output. If this is not
set, then the setup
information is written
to a temporary file.
-l
/export/example2007.log
For no log file, set the
file name to
/dev/null:
-l /dev/null
Table 1.1. setup-ds-admin Options
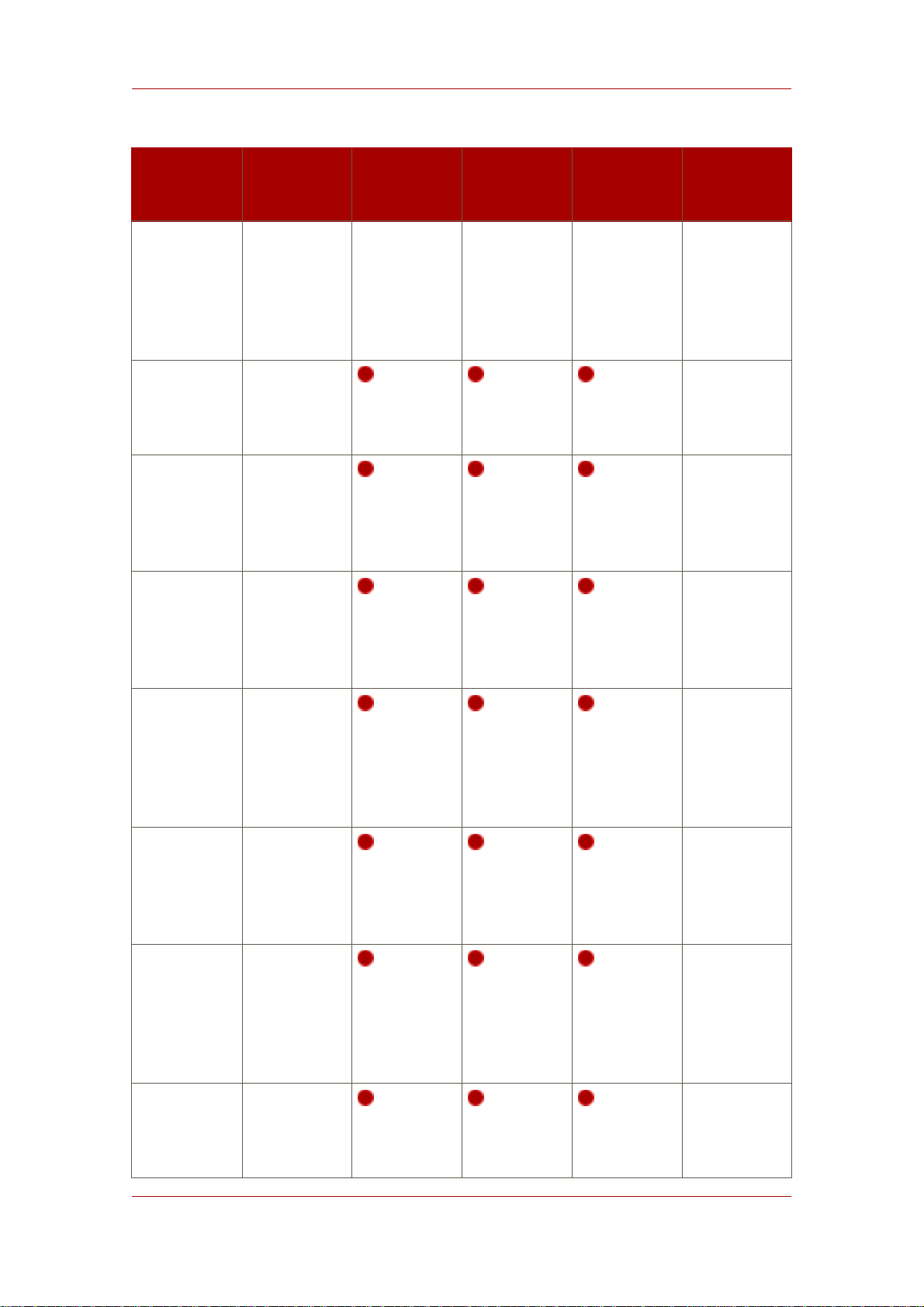
4. Overview of Setup
After the Directory Server packages are installed, there is a script, setup-ds-admin.pl, which
you run to configure the new Directory Server and Administration Server instance. This script
launches an interactive setup program. The setup program supplies default configuration values
which you can accept them or substitute with alternatives. There are three kinds of setup
modes, depending on what you select when you first launch the setup program:
• Express — The fastest setup mode. This requires minimal interaction and uses default values
for almost all settings. Because express installation does not offer the choice of selecting the
Directory Server server port number or the directory suffix, among other settings, Red Hat
recommends that you not use it for production deployments. Also, express setups can fail if
default configuration values are not available because there is no way to offer an alternative.
• Typical — The default and most common setup mode. This prompts you to supply more
detailed information about the directory service, like suffix and configuration directory
information, while still proceeding quickly through the setup process.
• Custom — The most detailed setup mode. This provides more control over Administration
Server settings and also allows data to be imported into the Directory Server at setup, so that
entries are already populated in the databases when the setup is complete.
The information requested with the setup process is described in Table 1.2, “Comparison of
Setup Types”.
There is a fourth setup option, silent setup, which uses a configuration file and command-line
options to supply the Directory Server settings automatically, so there is no user interaction
required. It is also possible to pass setup arguments with the script, as described in Section 3,
“About the setup-ds-admin.pl Script”. The possible .inf setup file parameters are listed and
described in Section 3.5, “About .inf File Parameters”.
9
Page 20
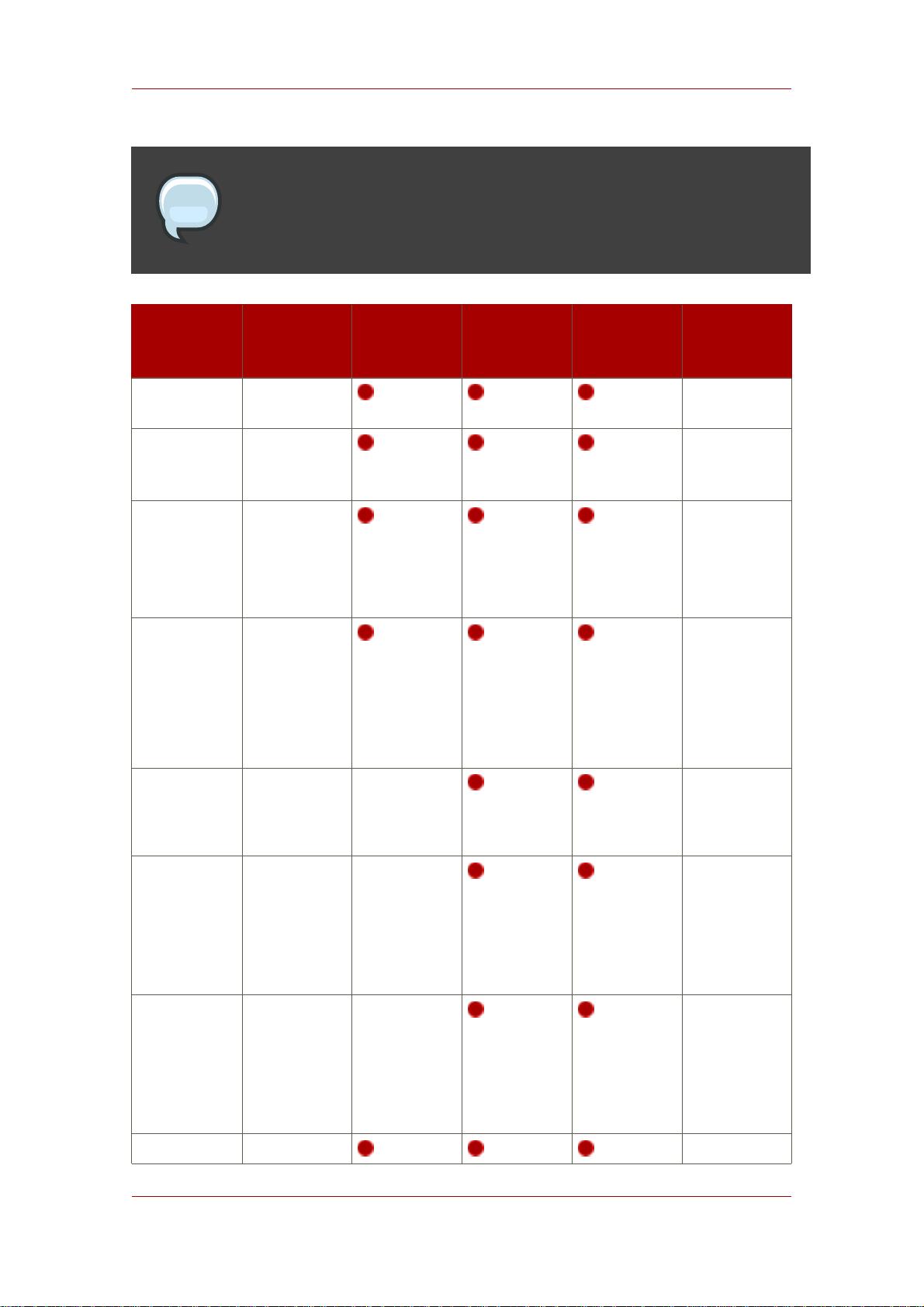
Chapter 1. Preparing for a Directory Server Installation
NOTE
It is possible to use y and n with the yes and no inputs described in Section 3.5,
“About .inf File Parameters”.
Setup
Screen
Continue with
setup
Accept
license
agreement
Accept
dsktune
output and
continue with
setup
Choose setup
type
Parameter
Input
Yes or no N/A
Yes or no N/A
Yes or no N/A
• 1 (express)
• 2 (typical)
• 3 (custom)
Express Typical Custom Silent Setup
File
Parameter
N/A
Set the
computer
name
Set the user
as which the
Directory
Server will
run
Set the group
as which the
Directory
Server will
run
Register the Yes or no N/A
10
ldap.example.com
nobody (Sun
and Red Hat
Enterprise
Linux) or
daemon
(HP-UX)
nobody (Sun
and Red Hat
Enterprise
Linux) or
daemon
(HP-UX)
[General]
FullMachineName=
ldap.example.com
[General]
SuiteSpotUserID=
nobody
[General]
SuiteSpotGroup=
nobody
Page 21
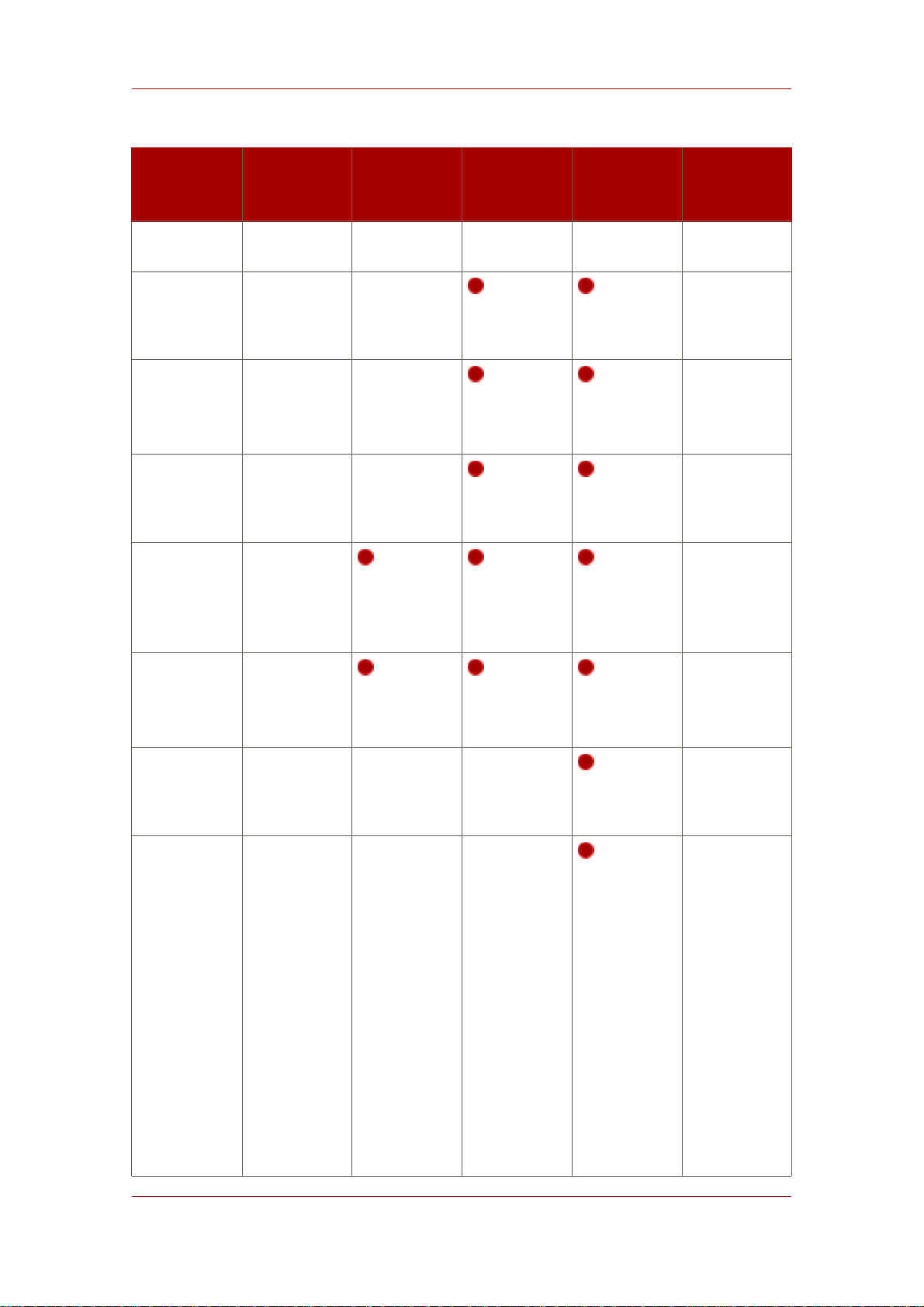
Overview of Setup
Setup
Screen
new Directory
Server with
an existing
Configuration
Directory
Server
Set the
Configuration
Directory
Server URL
Give the
Configuration
Directory
Server user
a
ID
Give the
Configuration
Directory
Server user
password
a
Parameter
Express Typical Custom Silent Setup
Input
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
a
admin
password
File
Parameter
[General]
ConfigDirectoryLdapURL=
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
[General]
ConfigDirectoryAdminID=
admin
[General]
ConfigDirectoryAdminPwd=
password
Give the
Configuration
Directory
Server
administration
domain
a
Give the path
to the CA
certificate (if
using
LDAPS)
a
Set the
Configuration
Directory
Server
Administrator
username
Set the
Configuration
Directory
Server
example.com
/tmp/cacert.asc
admin
password
[General]
AdminDomain=
example.com
[General]
CACertificate=/tmp/cacert.asc
b
[General]
ConfigDirectoryAdminID=
admin
b
[General]
ConfigDirectoryAdminPwd=
password
11
Page 22
Chapter 1. Preparing for a Directory Server Installation
Setup
Screen
Administrator
password
Set the
Directory
Server port
Set the
Directory
Server
identifier
Set the
Directory
Server suffix
Set the
Directory
Manager ID
Parameter
Input
389
ldap
dc=domain,
dc=component
cn=Directory
Manager
Express Typical Custom Silent Setup
File
Parameter
[slapd]
ServerPort=
389
[slapd]
ServerIdentifier=
ldap
[slapd]
Suffix=
dc=example,dc=com
[slapd]
RootDN=
cn=Directory
Manager
Set the
Directory
Manager
password
Install sample
entries
Populate the
Directory
Server with
entries
password
Yes or no
• Supply the
full path
and
filename to
an LDIF file
• Type
suggest,
which
imports
common
container
entries,
such as
[slapd]
RootDNPwd=
password
[slapd]
AddSampleEntries=
Yes
• Equivalent
to suggest
[slapd]
AddOrgEntries=
Yes
InstallLdifFile=
suggest
• Equivalent
to setting
the path
12
Page 23
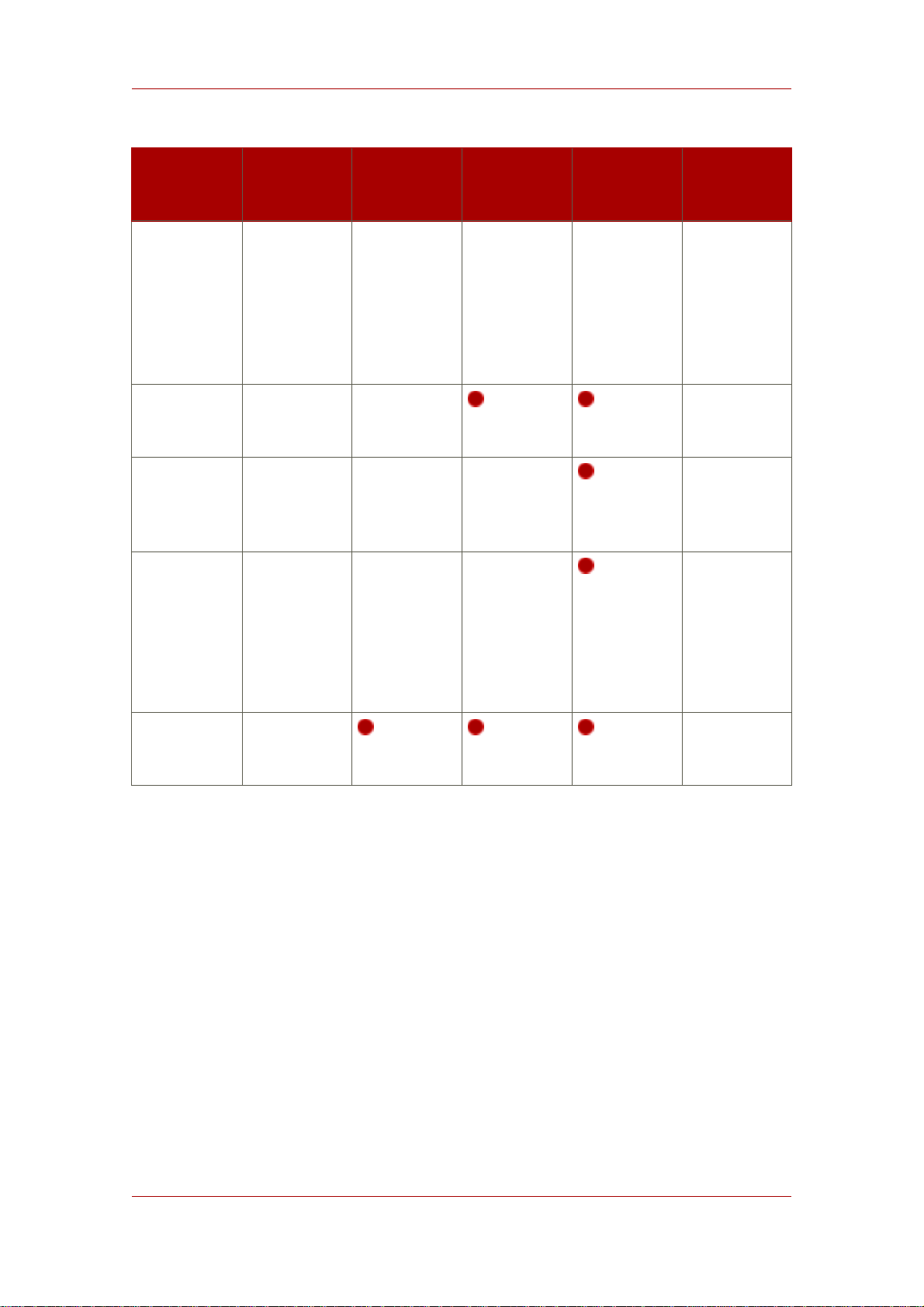
Overview of Setup
Setup
Screen
Set the
Administration
Server port
Set the
Administration
Server IP
address
Set user as
which the
Administration
Server runs
Parameter
Input
ou=People
• Type none,
which does
not import
any data
9830
blank (all
interfaces)
nobody (on
Red Hat
Enterprise
Linux and
Solaris) or
daemon (on
HP-UX)
Express Typical Custom Silent Setup
File
Parameter
[slapd]
AddOrgEntries=
Yes
InstallLdifFile=
/export/data.ldif
[admin]
Port= 9830
[admin]
ServerIpAddress=
111.11.11.11
[admin]
SysUser=
nobody
Are you ready
Yes or no N/A
to configure
your servers?
a
This option is only available if you choose to register the Directory Server instance with a Configuration Directory
Server.
b
This option is only available if you choose not to register the Directory Server instance with a Configuration Directory
Server. In that case, the Directory Server being set up is created and configured as a Configuration Directory Server.
Table 1.2. Comparison of Setup Types
13
Page 24

14
Page 25

Chapter 2.
System Requirements
Before configuring the default Red Hat Directory Server 8.0 instances, it is important to verify
that the host server has the required system settings and configuration:
• The system must have the required packages, patches, and kernel parameter settings.
• DNS must be properly configured on the target system.
• The host server must have a static IP address.
This chapter covers the software and hardware requirements, operating system patches and
settings, and system configurations that are necessary for Directory Server to perform well. It
also includes information on a Directory Server tool, dsktune, which is useful in identifying
required patches and system settings for Directory Server.
NOTE
The requirements outlined in this chapter apply to production systems. For
evaluating or prototyping Directory Server, you may choose not to meet all of
these requirements.
1. Hardware Requirements
Red Hat recommends minimum of 200 MB of disk space for a typical installation. Large test lab
environments can require 2 GB to support the complete deployment, including product binaries,
databases, and log files. Very large directories may require 4 GB and above.
Red Hat suggests 256 MB of RAM for average environments and 1 GB of RAM for large test lab
environments for increased performance.
Table 2.1, “Hardware Requirements” contains guidelines for Directory Server disk space and
memory requirements based upon on the number of entries that your organization requires. The
values shown here assume that the entries in the LDIF file are approximately 100 bytes each
and that only the recommended indices are configurable.
Number of Entries Disk Space/Required Memory
10,000 - 250,000 entries
Free disk space: 2 GB
Free memory: 256 MB
250,000 - 1,000,000 entries
Free disk space: 4 GB
Free memory: 512 MB
1,000,000 + entries
15
Page 26
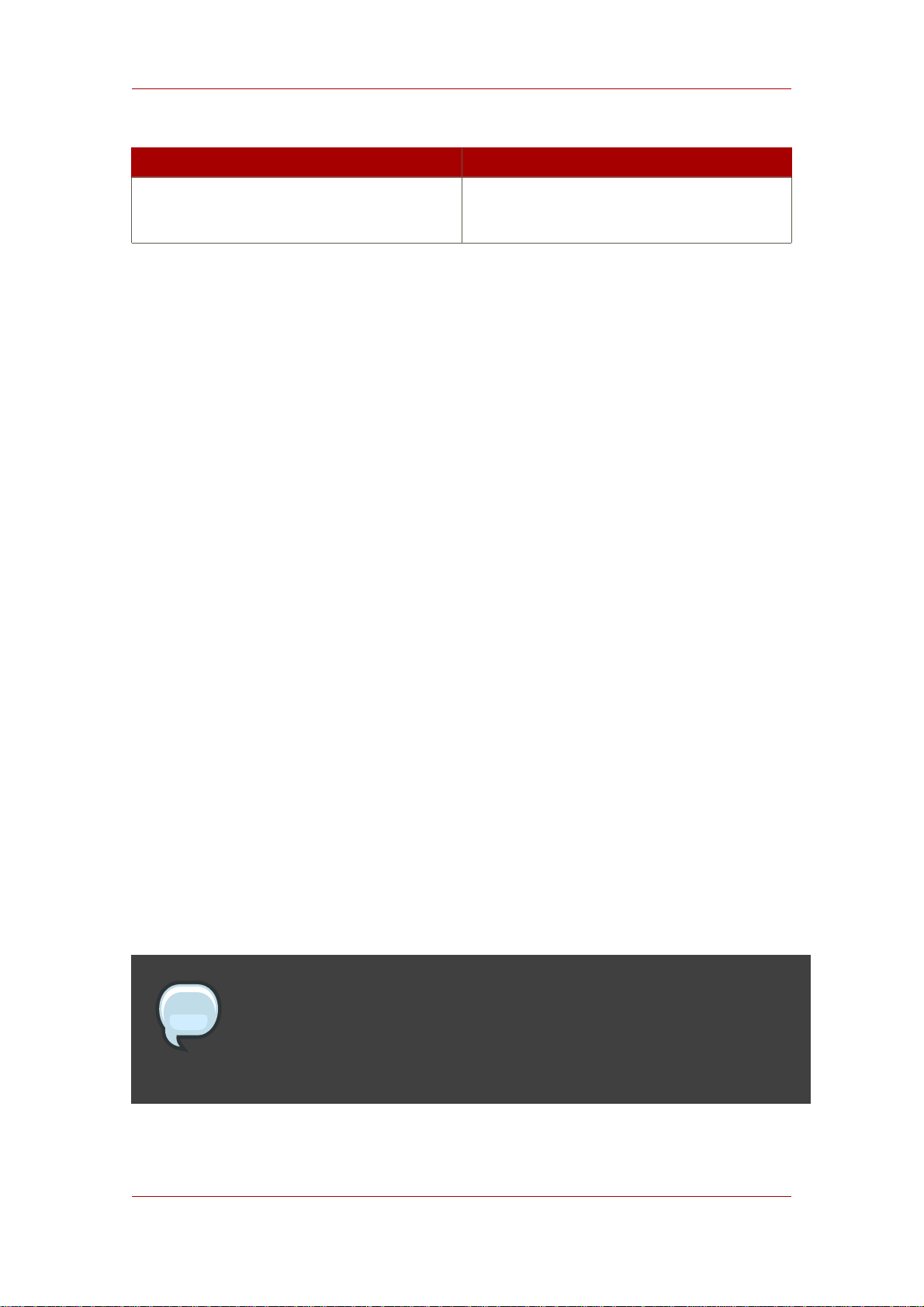
Chapter 2. System Requirements
Number of Entries Disk Space/Required Memory
Free disk space: 8 GB
Free memory: 1 GB
Table 2.1. Hardware Requirements
2. Operating System Requirements
Directory Server is supported on these operating systems: Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5
(x86 and x86_64), HP-UX 11i (IA 64), and Sun Solaris 9 (sparc 64-bit). The specific operating
system requirements and kernel settings, patches, and libraries are listed for each.
• Section 2.1, “Using dsktune”
• Section 2.2, “Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5”
• Section 2.3, “HP-UX 11i”
• Section 2.4, “Sun Solaris 9”
Along with meeting the required operating system patches and platforms, system settings, like
the number of file descriptors and TCP information, should be reconfigured to optimize the
Directory Server performance.
Directory Server includes a tool, dsktune, which simplifies configuring your system settings.
This section describes what settings to change on the machine on which Directory Server is
installed.
2.1. Using dsktune
After the packages for Directory Server are installed there is tool called dsktune which can scan
a system to check for required and installed patches, memory, system configuration, and other
settings required by Directory Server. The dsktune utility even returns information required for
tuning the host server's kernel parameters.
NOTE
The setup program also runs dsktune, reports the findings, and asks you if you
want to continue with the setup procedure every time a Directory Server instance
is configured.
Red Hat recommends running dsktune before beginning to set up the Directory Server
16
Page 27

Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5
instances so that you can properly configure your kernel settings and install any missing
patches. On Red Hat Enterprise Linux and Solaris, the dsktune utility is in the /usr/bin
directory; on HP-UX, it is in /opt/dirsrv/bin. To run it, simply use the appropriate command:
/usr/bin/dsktune
Red Hat Directory Server system tuning analysis version 10-AUGUST-2007.
NOTICE : System is i686-unknown-linux2.6.9-34.EL (1 processor).
WARNING: 1011MB of physical memory is available on the system.
1024MB is recommended for best performance on large production system.
NOTICE : The net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time is set to 7200000 milliseconds
(120 minutes). This may cause temporary server congestion from lost
client connections.
WARNING: There are only 1024 file descriptors (hard limit) available, which
limit the number of simultaneous connections.
WARNING: There are only 1024 file descriptors (soft limit) available, which
limit the number of simultaneous connections.
NOTE
dsktune is run every time the Directory Server configuration script,
setup-ds-admin, is run.
2.2. Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5
Directory Server is supported on two versions of Red Hat Enterprise Linux:
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 AS and ES on x86 and x86_64 platforms
• Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Server on x86 and x86_64 platforms
NOTE
Red Hat Directory Server is also supported running on a virtual guest on Red Hat
Enterprise Linux Virtualization Server 5.
Both Red Hat Enterprise Linux versions 4 and 5 on 32-bit and 64-bit platforms have the same
system requirements, as listed in Table 2.2, “Red Hat Enterprise Linux Operating System and
Hardware Requirements”. The patches required are listed in Section 2.2.1, “Red Hat Enterprise
17
Page 28
Chapter 2. System Requirements
Linux Patches”, and the recommended system configuration changes are described in
Section 2.2.2, “Red Hat Enterprise Linux System Configuration”.
Criteria Requirements
Operating System Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 or 5 with the latest
patches and upgrades
CPU Type Pentium 3 or higher; 500MHz or higher
Memory/RAM
256 MB minimum
Up to the system limit (on 32 bit systems,
typically 3 GB RAM or 4 GB RAM with
hugemem kernel) for large environments
Hard Disk
200 MB of disk space minimum for a typical
deployment
2 GB minimum for larger environments
4 GB minimum for very large environments
(more than a million entries)
Other To run the Directory Server using port
numbers less than 1024, such as the default
port 389, you must setup and start the
Directory Server as root, but it is not
necessary to run the Directory Server as
root.
Table 2.2. Red Hat Enterprise Linux Operating System and Hardware
Requirements
2.2.1. Red Hat Enterprise Linux Patches
The default kernel and glibc versions for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5 are the only required
versions for the Red Hat Directory Server host machine. If the machine has a single CPU, the
kernel must be presented in the form kernel-x.x.x.x. If the machine has multiple CPUs, the
kernel must be presented the form kernel-smp-x.x.x.x. To determine the components
running on the machine, run rpm -qa.
Run the dsktune utility to see if you need to install any other patches. dsktune helps verify
whether the appropriate patches are installed on the system and provides useful information for
tuning your kernel parameters for best performance. For information on dsktune, see
Section 2.1, “Using dsktune”.
Criteria Requirements
Operating System
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 AS and ES (x86
and x86_64)
18
Page 29

Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5
Criteria Requirements
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Server (x86 and
x86_64)
Required Filesystem ext3
Table 2.3. System Versions
2.2.2. Red Hat Enterprise Linux System Configuration
After verifying the system's kernel and glibc configuration and installing any required modules
and patches, fine-tune the Red Hat Enterprise Linux system to work with Directory Server. For
the best performance, configure the host server before configuring the Directory Server instance
by running the setup-ds-admin.pl script.
• Section 2.2.2.1, “Perl Prerequisites”
• Section 2.2.2.2, “File Descriptors”
• Section 2.2.2.3, “DNS Requirements”
2.2.2.1. Perl Prerequisites
For Red Hat Enterprise Linux systems, use the Perl version that is installed with the operating
system in /usr/bin/perl for both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Red Hat Directory Server.
2.2.2.2. File Descriptors
Editing the number of file descriptors on the Linux system can help Directory Server access files
more efficiently. Editing the maximum number of file descriptors the kernel can allocate can also
improve file access speeds.
1. First, check the current limit for file descriptors:
cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max
2. If the setting is lower than 64000, edit the /etc/sysctl.conf file, and reset the fs.file-max
parameter:
fs.file-max = 64000
3. Then increase the maximum number of open files on the system by editing the
19
Page 30

Chapter 2. System Requirements
/etc/security/limits.conf configuration file. Add the following entry:
* - nofile 8192
4. Edit the /etc/pam.d/system-auth, and add this entry:
session required /lib/security/$ISA/pam_limits.so
5. Reboot the Linux machine to apply the changes.
2.2.2.3. DNS Requirements
It is very important that DNS and reverse DNS be working correctly on the host machine,
especially if you are using TLS/SSL or Kerberos with Directory Server.
Configure the DNS resolver and the NIS domain name by the modifying the
/etc/resolv.conf, /etc/nsswitch.conf, and /etc/netconfig files, and set the DNS
resolver for name resolution.
Edit the /etc/defaultdomain file to include the NIS domain name. This ensures that the
fully-qualified host and domain names used for the Directory Server resolve to a valid IP
address and that that IP address resolves back to the correct hostname.
Reboot the Red Hat Enterprise Linux machine to apply these changes.
2.3. HP-UX 11i
Directory Server runs on HP-UX version 11i only; earlier HP-UX versions are not supported.
Directory Server runs on a 64-bit HP-UX 11i environment as a 64-bit process.
Table 2.4, “HP-UX 11i” lists the hardware requirements. Section 2.3.1, “HP-UX Patches” lists
the required patches, and the recommended system configurations are in Section 2.3.2, “HP-UX
System Configuration”.
Criteria Requirements
Operating System HP-UX 11i with the latest patches and
upgrades
CPU Type HP 9000 architecture with an Itanium CPU
Memory/RAM
256 MB minimum
1 GB RAM for large environments
Hard Disk
300 MB of disk space minimum for a typical
deployment
20
Page 31

Criteria Requirements
2 GB minimum for larger environments
4 GB minimum for very large environments
(more than a million entries)
You must use the largefile command to
configure database files larger than 2 GB.
Other To run the Directory Server using port
numbers less than 1024, such as the default
port 389, you must setup and start the
Directory Server as root, but it is not
necessary to run the Directory Server as
root.
Table 2.4. HP-UX 11i
HP-UX 11i
2.3.1. HP-UX Patches
The HP-UX 11i host must have the correct packages and dependencies installed to run
Directory Server. The patch list changes daily, so check the HP site regularly to ensure you
have the latest releases:
• http://www.software.hp.com/SUPPORT_PLUS/qpk.html
• http://welcome.hp.com/country/us/eng/support.htm
The first package to install is the PHSS_30966: ld(1) and linker tools cumulative patch.
The other required patches are listed in Table 2.5, “HP-UX 11i Patches”. Run the dsktune utility
to see if you need to install any other patches. dsktune helps verify whether the appropriate
patches are installed on the system and provides useful information for tuning your kernel
parameters for best performance. For information on dsktune, see Section 2.1, “Using
dsktune”.
Criteria Requirements
GOLDAPPS11i B.11.11.0406.5 Gold Applications Patches for
HP-UX 11i v1, June 2004
GOLDBASE11i B.11.11.0406.5 Gold Base Patches for HP-UX
11i v1, June 2004
GOLDQPK11i HP-UX 11i Quality Pack patch from June
2004 or later
Table 2.5. HP-UX 11i Patches
21
Page 32

Chapter 2. System Requirements
2.3.2. HP-UX System Configuration
Before setting up Directory Server, tune your HP-UX system so Directory Server can access the
respective kernel parameters. To tune HP-UX systems, enable large file support, set the
TIME_WAIT value, and modify kernel parameters.
• Section 2.3.2.1, “Perl Prerequisites”
• Table 2.6, “HP-UX 11i Kernel Parameters”
• Section 2.3.2.3, “TIME_WAIT Setting”
• Section 2.3.2.4, “Large File Support”
• Section 2.3.2.5, “DNS Requirements”
2.3.2.1. Perl Prerequisites
On HP-UX, Red Hat Directory Server uses the Perl version installed with the operating system
in /opt/perl_64/bin/perl. Contact Hewlett-Packard support if this Perl version is not
installed.
2.3.2.2. Kernel Parameters
The parameters to edit and the recommended values are listed in Table 2.6, “HP-UX 11i Kernel
Parameters”.
Parameter Setting
maxfiles 1024
nkthread 1328
max_thread_proc 512
maxuser 64
maxuprc 512
nproc 750
Table 2.6. HP-UX 11i Kernel Parameters
2.3.2.3. TIME_WAIT Setting
Normally, client applications that shut down correctly cause the socket to linger in a TIME_WAIT
state. Verify that the TIME_WAIT entry is set to a reasonable duration. For example:
ndd -set /dev/tcp tcp_time_wait_interval 60000
22
Page 33

This limits the socket TIME_WAIT state to 60 seconds.
2.3.2.4. Large File Support
To run Directory Server on HP-UX, you must enable large file support.
1. Unmount the filesystem using the umount command.
umount /export
2. Create the large filesystem.
fsadm -F vxfs -o largefiles /dev/vg01/rexport
Sun Solaris 9
3. Remount the filesystem.
/usr/sbin/mount -F vxfs -o largefiles /dev/vg01/export
2.3.2.5. DNS Requirements
It is very important that DNS and reverse DNS be working correctly on the host machine,
especially if you are using TLS/SSL or Kerberos with Directory Server.
Configure the DNS resolver and the NIS domain name by the modifying the
/etc/resolv.conf, /etc/nsswitch.conf, and /etc/netconfig files, and set the DNS
resolver for name resolution.
Edit the /etc/defaultdomain file to include the NIS domain name. This ensures that the
fully-qualified host and domain names used for the Directory Server resolve to a valid IP
address and that that IP address resolves back to the correct hostname.
Then, reboot the HP-UX machine to apply these changes.
2.4. Sun Solaris 9
Directory Server on Solaris 9 requires an UltraSPARC (SPARC v9) processor, which 64-bit
applications as well as high-performance and multi-processor systems. Earlier SPARC
processors are not supported. Use the isainfo command to verify that the system has support
for sparc9. Verify the system's kernel configuration, install the appropriate modules and
patches, and then fine-tune the system to work with Sun Solaris 9.
The system requirements are listed in Table 2.7, “Sun Solaris sparcv9”. The required patches
23
Page 34

Chapter 2. System Requirements
are listed in Section 2.4.1, “Solaris Patches”, and the recommended configuration changes are
described in Section 2.4.2, “Solaris System Configuration”.
Criteria Requirements
Operating System Solaris 9 with the latest patches and upgrades
CPU Type UltraSparc-IIi SPARC v9 300MHz or faster
(64-bit)
Memory/RAM
256 MB minimum
1 GB RAM for large environments
Hard Disk
200 MB of disk space minimum for a typical
deployment
2 GB minimum for larger environments
4 GB minimum for very large environments
(more than a million entries)
You must use the largefile command to
configure database files larger than 2 GB.
Other To run the Directory Server using port
numbers less than 1024, such as the default
port 389, you must setup and start the
Directory Server as root, but it is not
necessary to run the Directory Server as
root.
Table 2.7. Sun Solaris sparcv9
2.4.1. Solaris Patches
The patches required to run the Directory Server on Solaris 9 are listed in Table 2.8, “Sun
Solaris Patches”. Run the dsktune utility to see if you need to install any other patches.
dsktune helps verify whether the appropriate patches are installed on the system and provides
useful information for tuning your kernel parameters for best performance. For information on
dsktune, see Section 2.1, “Using dsktune”.
Patch ID Description
112998-03 SunOS 5.9: patch /usr/sbin/syslogd
112875-01 SunOS 5.9: patch
/usr/lib/netsvc/rwall/rpc.rwalld
113146-04 SunOS 5.9: Apache Security Patch
113068-05 SunOS 5.9: hpc3130 patch
112963-14 SunOS 5.9: linker patch
113273-08 SunOS 5.9: /usr/lib/ssh/sshd patch
24
Page 35

Sun Solaris 9
Patch ID Description
112233-12 SunOS 5.9: Kernel patch
112964-08 SunOS 5.9: /usr/bin/ksh patch
112808 CDE1.5: Tooltalk patch
113279-01 SunOS 5.9: klmmod patch
113278-07 SunOS 5.9: NFS Daemon patch
113023 SunOS 5.9: Broken preremove scripts from
S9 ALC packages
112601-09 SunOS 5.9: PGX32 Graphics
113923-02 X11 6.6.1: security font server patch
112817-18 SunOS 5.9: Sun Gigaswift Ethernet 1.0 driver
patch
113718-02 SunOS 5.9: usr/lib/utmp_udate patch
114135-01 SunOS 5.9: at utility patch
112834-04 SunOS 5.9: patch scsi
112907-03 SunOS 5.9: libgss patch
113319 SunOS 5.9: libnsl nispasswd
112785-43 SunOS 5.9: Xsun patch
112970-07 SunOS 5.9: patch libresolv
112951-09 SunOS 5.9: patchadd and patchrm patch
113277-24 SunOS 5.9: st, sd, and ssd patch
113579-06 SunOS 5.9: ypserv/ypxfrd patch
112908-14 SunOS 5.9: krb5 shared object patch
113073-14 SunOS 5.9: ufs and fsck patch
Table 2.8. Sun Solaris Patches
2.4.2. Solaris System Configuration
After installing any required patches or modules, tune the Solaris system to work with Directory
Server. There are three areas that may need modified for optimum Directory Server
performance: the TCP service, DNS/NIS service, and the file descriptors.
• Section 2.4.2.1, “Perl Prerequisites”
• Section 2.4.2.2, “TCP Tuning”
• Section 2.4.2.3, “DNS and NIS Requirements”
25
Page 36

Chapter 2. System Requirements
• Section 2.4.2.4, “File Descriptors”
2.4.2.1. Perl Prerequisites
On Solaris systems, Red Hat Directory Server is installed with a Perl package, RHATperlx, that
must be used. This package contains a 64-bit version of Perl 5.8. It is not possible to use the
Perl version installed in /usr/bin/perl on Solaris because it is 32 bit and will not work with
Directory Server's 64-bit components.
2.4.2.2. TCP Tuning
Edit the Solaris TCP configuration Directory Server can access local system ports better. If
tuned properly, this may enhance network connection speeds. The maximum achievable
throughput for a single TCP connection is determined by several factors, including the maximum
bandwidth on the slowest link on the path, bit errors that limit connections, and the total
round-trip time.
The configuration that must be edited is in the /dev/tcp directory. Reset the following
parameters:
• tcp_time_wait_interval determines the time (in milliseconds) that a TCP connection
remains in a kernel's table after being closed. If its value is above 30000 (or 30 seconds) and
the directory is being used in a LAN, MAN, or other network connection, reduce the value by
modifying the /etc/init.d/inetinit file:
ndd -set /dev/tcp tcp_time_wait_interval 30000
• The tcp_conn_req_max_q0 and tcp_conn_req_max_q parameters control the connection's
maximum backlog that gets accepted by the kernel. If a directory is used by a large number of
client hosts simultaneously, increase these values by at least 1024. Edit the
/etc/init.d/inetinit file:
ndd -set /dev/tcp tcp_conn_req_max_q0 1024
ndd -set /dev/tcp tcp_conn_req_max_q 1024
• The tcp_keepalive_interval setting determines the duration (in seconds) between the
keepalive packets sent for each open TCP connection. Edit this setting to remove client
connections that disconnect from the network.
• Check the tcp_rexmit_interval_initial parameter value for server maintenance testing
on a high speed LAN, MAN, or other network connection. For wide area networks, you do not
have to change the tcp_rexmit_interval_initial value.
• The tcp_smallest_anon_port setting determines the number of simultaneous server
26
Page 37

Sun Solaris 9
connections. If you increase the rlim_fd_max value to over 4096, you must decrease the
tcp_smallest_anon_port value in the /etc/init.d/inetinit file.
ndd -set /dev/tcp tcp_smallest_anon_port 8192
• Reboot the Solaris machine to apply these changes.
2.4.2.3. DNS and NIS Requirements
It is very important that DNS and reverse DNS be working correctly on the host machine,
especially if you are using TLS/SSL or Kerberos with Directory Server.
Configure the DNS resolver and the NIS domain name by the modifying the
/etc/resolv.conf, /etc/nsswitch.conf, and /etc/netconfig files, and set the DNS
resolver for name resolution.
Edit the /etc/defaultdomain file to include the NIS domain name. This ensures that the
fully-qualified host and domain names used for the Directory Server resolve to a valid IP
address and that that IP address resolves back to the correct hostname.
Then, reboot the Solaris machine to apply these changes.
2.4.2.4. File Descriptors
For a large deployment or to support a large number of concurrent connections, increase the
number of file descriptors available for the Directory Server. This requires accessing the
system-wide maximum file descriptor table. The governing parameter, rlim_fd_max, is in the
/etc/system file. By default, if this parameter is not present, the allowed maximum value is
1024. You can increase this to 4096 by adding the line, set rlim_fd_max=4096 to the
/etc/system file.
Reboot the Solaris machine to apply these changes.
To determine the soft limit for file descriptors, run the command ulimit -n. You can also use
the dsktune utility to determine the file descriptor hard and soft limits, as described in
Section 2.1, “Using dsktune”.
27
Page 38

28
Page 39

Chapter 3.
Setting up Red Hat Directory Server
on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Installing and configuring Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux has three
major steps:
1. Install the required version of the Java® Runtime Environment (JRE).
2. Install the Directory Server packages.
3. Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script. This is where all of the information about the new
Directory Server instance is supplied.
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
NOTE
Before beginning the installation process, make sure that your system meets the
requirements in Section 2.2, “Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4 and 5”.
NOTE
Red Hat Directory Server is also supported running on a virtual guest on Red Hat
Enterprise Linux Virtualization Server 5.
There are three interactive ways of setting up Directory Server: express, typical, and custom.
These setup types provide different levels of control over the configuration settings, such as port
numbers, directory suffixes, and users and groups for the Directory Server processes. Express
has the least amount of input, meaning it uses more default or randomly-generated settings,
while custom allows the most control over the configuration by having the user supply a lot of
configuration information. These setup types are described more in Table 1.2, “Comparison of
Setup Types”. For most deployments, the typical installation type is recommended.
29
Page 40

Chapter 3. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
NOTE
There is a fourth setup option called a silent installation. This provides two ways
of performing the setup without user interaction, either by passing arguments in
the command-line with the setup-ds-admin.pl script or to use a file with
settings already defined. This is extremely useful for doing large numbers of
Directory Server instances, since it does not require any user involvement after
the packages are installed. Silent installations are explained more in Section 3.1,
“Silent Setup for Directory Server and Administration Server”.
This chapter describes the complete procedure to install Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat
Enterprise Linux, including both the JRE and Directory Server packages, and the different setup
options.
1. Installing the JRE
Necessary Java JRE libraries are not bundled with Directory Server. They must be downloaded
and extracted separately before installing the Directory Server packages.
NOTE
Directory Server 8.0 requires JRE version 1.5.0.
Any Red Hat Enterprise Linux customer can download the required JRE packages from the
RHEL Extras or Supplemental channel in Red Hat Network, and then use native Red Hat tools
to install the package. For example, to install the JRE on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4, use the
up2date command:
up2date java-1.5.0-ibm
On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5, use the yum command:
yum install java-1.5.0-ibm
Using yum or up2date is the preferred and recommended way to install Java. However, it is also
possible to download the JRE from the Java site.
1. Download the Java libraries from http://www.java.com.
30
Page 41

Installing the Directory Server Packages
2. Log in as root, and install the JRE. For example:
rpm -Uvh java-1.5.0-ibm-1.5.0.5-1jpp.2.el4.i386.rpm
After installing the JRE, install the Directory Server packages, as described in Section 2,
“Installing the Directory Server Packages”.
2. Installing the Directory Server Packages
1. Install the Directory Server packages. There are two options for installing the packages:
using native Red Hat Enterprise Linux tools (yum or up2date) or downloading them from Red
Hat Network. The recommended way is to use the Red Hat Enterprise Linux tools. On Red
Hat Enterprise Linux 4, use up2date:
up2date redhat-ds
On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5, use yum:
yum install redhat-ds
NOTE
Both yum and up2date may install or require additional packages if dependencies
are missing or out-of-date.
Alternatively, download the latest packages from the Red Hat Directory Server 8.0 channel
on Red Hat Network, http://rhn.redhat.com.
It is also possible to install the Directory Server packages from media:
a. Download the packages from Red Hat Network, and burn them to CD or DVD.
b. Insert the media; the system should automatically recognize and mount the disc.
c. There is no autorun feature with the Directory Server packages, so open the directory on
the disc containing the Directory Server packages. For example:
cd /media/cdrecorder/RedHat/RPMS/
d. Install everything in the directory using rpm:
31
Page 42

Chapter 3. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
ls *.rpm | egrep -iv -e devel -e debuginfo | xargs rpm -ivh
2. After the Directory Server packages are installed, run the setup-ds-admin.pl script to set
up and configure the default Directory Server instance and the Administration Server.
/usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
3. Accept the licensing agreement.
4. On the next screen, review the dsktune output. If there are any issues that you should
address, exit the setup-ds-admin.pl program, and resolve them. Otherwise, accept the
output.
5. Select the setup type, and proceed with configuring the new Directory Server instance.
• Section 3, “Express Setup”
• Section 4, “Typical Setup”
• Section 5, “Custom Setup”
NOTE
Directory Server version 8.0 conforms to the Filesystem Hierarchy Standards.
This means that the directories and files are in different locations than previous
versions. For more information on FHS, see the http://www.pathname.com/fhs/
homepage. For a table showing the new file locations, see Section 1, “Directory
Server File Locations”.
3. Express Setup
Use express installation if you are installing Directory Server for an evaluation or trial. Because
express installation does not offer the choice of selecting the Directory Server server port
number or the directory suffix, among other settings, Red Hat recommends not using it for
production deployments.
32
NOTE
The setup program gets the host information from the /etc/resolv.conf file. If
Page 43

Express Setup
there are aliases in the /etc/hosts file, such as ldap.example.com, that do not
match the /etc/resolv.conf settings, the setup program cannot use the default
hostname option, and setup will fail.
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
1. After the Directory Server packages are installed as described in Section 2, “Installing the
Directory Server Packages”, then launch the setup-ds-admin.pl script.
# /usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
NOTE
Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script as root.
2. Select y to accept the Red Hat licensing terms.
3. The dsktune utility runs. Select y to continue with the setup.
dsktune checks the available disk space, processor type, physical memory, and other
system data and settings such as TCP/IP ports and file descriptor settings. If your system
does not meet these basic Red Hat Directory Server requirements, dsktune returns a
warning. dsktune warnings do not block the setup process; simply enter y to go to the next
step.
4. Next, choose the setup type. Enter 1 to perform an express setup.
5. The next step allows you to register your Directory Server with an existing Directory Server
instance, called the Configuration Directory Server. This registers the new instance so it can
be managed by the Console. If this is the first Directory Server instance set up on your
network, it is not possible to register it with another directory. Select n to set up this Directory
Server as a Configuration Directory Server and move to the next express install step, setting
up the administrator user.
33
Page 44

Chapter 3. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
NOTE
To register the Directory Server instance with an existing Configuration Directory
Server, select yes. This continues with the registration process rather than the
regular express setup process.
Registering a new instance with a Configuration Directory Server requires you to
supply information about the Configuration Directory Server:
• The Configuration Directory Server URL, such as
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
To use TLS/SSL, set the protocol as ldaps:// instead of ldap:// For
LDAPS, use the secure port (636) instead of the standard port (389), and
provide a CA certificate.
• The Configuration Directory Server administrator's user ID; by default, this is
admin.
• The administrator user's password.
• The Configuration Directory Server Admin domain, such as example.com.
• The CA certificate to authenticate to the Configuration Directory Server. This is
only required if the Directory Server instance will connect to the Configuration
Directory Server over LDAPS. This should be the full path and filename the CA
certificate in PEM/ASCII format.
This information is supplied in place of creating an admin user for the new
Directory Server in steps 6 and 7.
6. Set the administrator username. The default is admin.
7. Set the administrator password and confirm it.
8. Set the Directory Manager username. The default is cn=Directory Manager.
9. Set the Directory Manager password and confirm it.
10.The last screen asks if you are ready to set up your servers. Select yes.
Are you ready to set up your servers? [yes]:
Creating directory server . . .
Your new DS instance 'example' was successfully created.
Creating the configuration directory server . . .
Beginning Admin Server reconfiguration . . .
Creating Admin Server files and directories . . .
34
Page 45

Typical Setup
Updating adm.conf . . .
Updating admpw . . .
Registering admin server with the configuration directory server . . .
Updating adm.conf with information from configuration directory server . . .
Updating the configuration for the httpd engine . . .
Restarting admin server . . .
The admin server was successfully started.
Admin server was successfully reconfigured and started.
Exiting . . .
Log file is '/tmp/setup0C7tiV.log'
The setup-ds-admin.pl script applies all default options for the Directory Server configuration,
including the instance name (for example, ldap.example.com), domain (for example,
example.com), suffix (for example, dc=example, dc=com), and port numbers (389 for the
Directory Server instance and 9830 for the Administration Server).
When the setup-ds-admin.pl script is done, then the Directory Server is configured and
running. To log into the Directory Server Console to begin setting up your directory service, do
the following:
1. Get the Administration Server port number from the Listen parameter in the console.conf
configuration file.
grep \^Listen /etc/dirsrv/admin-serv/console.conf
Listen 0.0.0.0:9830
2. Using the Administration Server port number, launch the Console.
/usr/bin/redhat-idm-console -a http://localhost:9830
NOTE
If you do not pass the Administration Server port number with the
redhat-idm-console command, then you are prompted for it at the Console
login screen.
4. Typical Setup
The typical setup process is the most commonly-used setup process. It offers control over the
35
Page 46

Chapter 3. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
ports for the Directory and Administration Servers, the domain name, and directory suffix.
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
1. After the Directory Server packages are installed as described in Section 2, “Installing the
Directory Server Packages”, then launch the setup-ds-admin.pl script.
# /usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
NOTE
Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script as root.
2. Select y to accept the Red Hat licensing terms.
3. The dsktune utility runs. Select y to continue with the setup.
dsktune checks the available disk space, processor type, physical memory, and other
system data and settings such as TCP/IP ports and file descriptor settings. If your system
does not meet these basic Red Hat Directory Server requirements, dsktune returns a
warning. dsktune warnings do not block the setup process; simply enter y to go to the next
step.
4. Next, choose the setup type. Accept the default, option 2, to perform a typical setup.
5. Set the computer name of the machine on which the Directory Server is being configured.
This defaults to the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) for the host. For example:
Computer name [ldap.example.com]:
36
NOTE
The setup program gets the host information from the /etc/resolv.conf file. If
there are aliases in the /etc/hosts file, such as ldap.example.com, that do not
match the /etc/resolv.conf settings, you cannot use the default hostname
option.
Page 47

Typical Setup
The hostname is very important. It is used generate the Directory Server instance name, the
admin domain, and the base suffix, among others. If you are using SSL/TLS or Kerberos, the
computer name must be the exact name that clients use to connect to the system. If you will
use DNS, make sure the name resolves to a valid IP address and that IP address resolves
back to this name.
6. Set the user and group as which the Directory Server process will run. The default is
nobody:nobody. For example:
System User [nobody]:
System Group [nobody]:
7. The next step allows you to register your Directory Server with an existing Directory Server
instance, called the Configuration Directory Server. This registers the new instance so it can
be managed by the Console. If this is the first Directory Server instance set up on your
network, it is not possible to register it with another directory. Select n to set up this Directory
Server as a Configuration Directory Server and move to the next typical install step, setting
up the administrator user.
NOTE
To register the Directory Server instance with an existing Configuration Directory
Server, select yes. This continues with the registration process rather than the
regular typical setup process.
Registering a new instance with a Configuration Directory Server requires you to
supply information about the Configuration Directory Server:
• The Configuration Directory Server URL, such as
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
To use TLS/SSL, set the protocol as ldaps:// instead of ldap:// For
LDAPS, use the secure port (636) instead of the standard port (389), and
provide a CA certificate.
• The Configuration Directory Server administrator's user ID; by default, this is
admin.
• The administrator user's password.
• The Configuration Directory Server Admin domain, such as example.com.
• The CA certificate to authenticate to the Configuration Directory Server. This is
only required if the Directory Server instance will connect to the Configuration
Directory Server over LDAPS. This should be the full path and filename the CA
certificate in PEM/ASCII format.
37
Page 48

Chapter 3. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
This information is supplied in place of creating an admin user and domain for
the new Directory Server, steps 8, 9, and 10.
8. Set the administrator username. The default is admin.
9. Set the administrator password and confirm it.
10.Set the administration domain. This defaults to the host's domain. For example:
Administration Domain [example.com]:
11.Enter the Directory Server port number. The default is 389, but if that port is in use, the setup
program supplies a randomly generated one.
Directory server network port [30860]: 1025
12.Enter the Directory Server identifier; this defaults to the hostname.
Directory server identifier [example]:
13.Enter the directory suffix. This defaults to dc=domain name. For example:
Suffix [dc=redhat, dc=com]:
14.Set the Directory Manager username. The default is cn=Directory Manager.
15.Set the Directory Manager password and confirm it.
16.Enter the Administration Server port number. The default is 9830, but if that port is in use, the
setup program supplies a randomly generated one.
Administration port [9830]:
17.The last screen asks if you are ready to set up your servers. Select yes.
Are you ready to set up your servers? [yes]:
38
Page 49

Custom Setup
Creating directory server . . .
Your new DS instance 'example2' was successfully created.
Creating the configuration directory server . . .
Beginning Admin Server reconfiguration . . .
Creating Admin Server files and directories . . .
Updating adm.conf . . .
Updating admpw . . .
Registering admin server with the configuration directory server . . .
Updating adm.conf with information from configuration directory server . . .
Updating the configuration for the httpd engine . . .
Restarting admin server . . .
The admin server was successfully started.
Admin server was successfully reconfigured and started.
Exiting . . .
Log file is '/tmp/setupulSykp.log'
When the setup-ds-admin.pl script is done, then the Directory Server is configured and
running. To log into the Directory Server Console to begin setting up your directory service, do
the following:
1. Get the Administration Server port number from the Listen parameter in the console.conf
configuration file.
grep \^Listen /etc/dirsrv/admin-serv/console.conf
Listen 0.0.0.0:9830
2. Using the Administration Server port number, launch the Console.
/usr/bin/redhat-idm-console -a http://localhost:9830
NOTE
If you do not pass the Administration Server port number with the
redhat-idm-console command, then you are prompted for it at the Console
login screen.
5. Custom Setup
Custom setup provides two special configuration options that allow you to add information to the
39
Page 50

Chapter 3. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Directory Server databases during the setup period. One imports an LDIF file, which is useful if
you have existing information. The other imports sample data that is included with Directory
Server; this is useful for testing features of Directory Server and for evaluation.
NOTE
Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script as root.
The custom setup has the following steps:
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
1. After the Directory Server packages are installed as described in Section 2, “Installing the
Directory Server Packages”, then launch the setup-ds-admin.pl script.
# /usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
2. Select y to accept the Red Hat licensing terms.
3. The dsktune utility runs. Select y to continue with the setup.
dsktune checks the available disk space, processor type, physical memory, and other
system data and settings such as TCP/IP ports and file descriptor settings. If your system
does not meet these basic Red Hat Directory Server requirements, dsktune returns a
warning. dsktune warnings do not block the setup process; simply entree y to go to the next
step.
4. Next, choose the setup type. Accept the default, option 3, to perform a custom setup.
5. Set the computer name of the machine on which the Directory Server is being configured.
This defaults to the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) for the host. For example:
Computer name [ldap.example.com]:
40
Page 51

Custom Setup
NOTE
The setup program gets the host information from the /etc/resolv.conf file. If
there are aliases in the /etc/hosts file, such as ldap.example.com, that do not
match the /etc/resolv.conf settings, you cannot use the default hostname
option.
The hostname is very important. It is used generate the Directory Server instance name, the
admin domain, and the base suffix, among others. If you are using SSL/TLS or Kerberos, the
computer name must be the exact name that clients use to connect to the system. If you will
use DNS, make sure the name resolves to a valid IP address and that IP address resolves
back to this name.
6. Set the user and group as which the Directory Server process will run. The default is
nobody:nobody. For example:
System User [nobody]:
System Group [nobody]:
7. The next step allows you to register your Directory Server with an existing Directory Server
instance, called the Configuration Directory Server. This registers the new instance so it can
be managed by the Console. If this is the first Directory Server instance set up on your
network, it is not possible to register it with another directory. Select n to set up this Directory
Server as a Configuration Directory Server and move to the next custom install step, setting
up the administrator user.
NOTE
To register the Directory Server instance with an existing Configuration Directory
Server, select yes. This continues with the registration process rather than the
regular custom setup process.
Registering a new instance with a Configuration Directory Server requires you to
supply information about the Configuration Directory Server:
• The Configuration Directory Server URL, such as
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
To use TLS/SSL, set the protocol as ldaps:// instead of ldap:// For
LDAPS, use the secure port (636) instead of the standard port (389), and
provide a CA certificate.
41
Page 52

Chapter 3. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
• The Configuration Directory Server administrator's user ID; by default, this is
admin.
• The administrator user's password.
• The Configuration Directory Server Admin domain, such as example.com.
• The CA certificate to authenticate to the Configuration Directory Server. This is
only required if the Directory Server instance will connect to the Configuration
Directory Server over LDAPS. This should be the full path and filename the CA
certificate in PEM/ASCII format.
This information is supplied in place of creating an admin user and domain for
the new Directory Server steps 8, 9, and 10.
8. Set the administrator username. The default is admin.
9. Set the administrator password and confirm it.
10.Set the administration domain. This defaults to the host's domain. For example:
Administration Domain [redhat.com]:
11.Enter the Directory Server port number. The default is 389, but if that port is in use, the setup
program supplies a randomly generated one.
Directory server network port [389]: 1066
12.Enter the Directory Server identifier; this defaults to the hostname.
Directory server identifier [example]:
13.Enter the directory suffix. This defaults to dc=domain name. For example:
Suffix [dc=redhat, dc=com]:
14.Set the Directory Manager username. The default is cn=Directory Manager.
15.Set the Directory Manager password and confirm it.
42
Page 53

Custom Setup
16.Select whether you want to install sample entries with the Directory Server instance. This
means that an example LDIF, with preconfigured users, groups, roles, and other entries, is
imported into the Directory Server database. This option is helpful for evaluation or testing
Directory Server features.
This is not required.
17.Select whether to populate the Directory Server with data; this means whether to import an
LDIF file with existing data into the Directory Server database. If the answer is yes, then
supply a path to the LDIF file or select the suggested file. If the LDIF file requires custom
schema, perform a silent setup instead, and use the SchemaFile directive in the .inf to
specify additional schema files. See Section 3.5.1, “.inf File Directives” for information on
.inf directives.
The default option is none, which does not import any data.
18.Enter the Administration Server port number. The default is 9830, but if that port is in use, the
setup program supplies a randomly generated one.
Administration port [9830]:
19.Set an IP address for the new Administration Server to use. The Administration Server uses
a web server, and this parameter is set in the console.conf file for the server. Setting this
parameter restricts the Administration Server to that single IP. Leaving it blank, the default,
allows the Administration Server to acquire any IP address.
20.Set the user as which the Administration Server process will run. The default is nobody. For
example:
Run Administration Server as [nobody]:
21.The last screen asks if you are ready to set up your servers. Select yes.
Are you ready to set up your servers? [yes]:
Creating directory server . . .
Your new DS instance 'example3' was successfully created.
Creating the configuration directory server . . .
Beginning Admin Server reconfiguration . . .
Creating Admin Server files and directories . . .
Updating adm.conf . . .
Updating admpw . . .
Registering admin server with the configuration directory server . . .
Updating adm.conf with information from configuration directory server . . .
Updating the configuration for the httpd engine . . .
Restarting admin server . . .
The admin server was successfully started.
Admin server was successfully reconfigured and started.
43
Page 54

Chapter 3. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Exiting . . .
Log file is '/tmp/setupul88C1.log'
When the setup-ds-admin.pl script is done, then the Directory Server is configured and
running. To log into the Directory Server Console to begin setting up your directory service, do
the following:
1. Get the Administration Server port number from the Listen parameter in the console.conf
configuration file.
grep \^Listen /etc/dirsrv/admin-serv/console.conf
Listen 0.0.0.0:9830
2. Using the Administration Server port number, launch the Console.
/usr/bin/redhat-idm-console -a http://localhost:9830
NOTE
If you do not pass the Administration Server port number with the
redhat-idm-console command, then you are prompted for it at the Console
login screen.
44
Page 55

Chapter 4.
Setting up Red Hat Directory Server
on HP-UX 11i
Installing and configuring Red Hat Directory Server on HP-UX has three major steps:
1. Install the required version of the Java® Runtime Environment (JRE).
2. Install the Directory Server packages.
3. Run the setup program. The setup step is where all of the information about the new
Directory Server instance is supplied.
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
NOTE
Before beginning the installation process, make sure that your system meets the
requirements in Section 2.3, “HP-UX 11i”.
There are three interactive ways of setting up Directory Server: express, typical, and custom.
These setup types provide different levels of control over the configuration settings, such as port
numbers, directory suffixes, and users and groups for the Directory Server processes. Express
has the least amount of input, meaning it uses more default or randomly-generated settings,
while custom allows the most control over the configuration by having the user supply a lot of
configuration information. These setup types are described more in Table 1.2, “Comparison of
Setup Types”. For most deployments, the typical installation type is all that is required.
NOTE
There is a fourth setup option called a silent installation. This uses a file with
predefined settings to create a new Directory Server without any user interaction.
This is extremely useful for doing large numbers of Directory Server instances,
since it does not require any user involvement after the packages are installed.
Silent installations are explained more in Section 3.1, “Silent Setup for Directory
45
Page 56

Chapter 4. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on HP-UX 11i
Server and Administration Server”.
This chapter describes the complete process for installing Directory Server on HP-UX 11i,
including both the JRE and Directory Server packages, and the different setup options.
1. Installing the JRE
Necessary Java JRE libraries are not bundled with Directory Server. They must be downloaded
and extracted separately before installing the Directory Server packages.
NOTE
Directory Server 8.0 requires JRE version 1.5.0.
Download the JRE from http://www.hp.com/products1/unix/java/, and install it according to the
HP Java instructions.
After installing the JRE, install the Directory Server packages, as described in Section 2,
“Installing the Directory Server Packages”.
2. Installing the Directory Server Packages
The Directory Server packages for HP-UX 11i are included in an SD package which can be
downloaded from HP.
For complete instructions on installing the Red Hat Directory Server packages on HP-UX, see
the HP-specific release notes at
http://docs.hp.com/en/internet.html#Netscape%20Directory%20Server/Red%20Hat%20Directory%20Server.
After the Directory Server packages are installed, run the setup program to set up and
configure the default Directory Server instance and the Administration Server.
/opt/dirsrv/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
Accept the initial screens for licensing and dsktune output, then select the setup type, and
proceed with configuring the new Directory Server instance.
• Section 3, “Express Setup”
• Section 4, “Typical Setup”
• Section 5, “Custom Setup”
46
Page 57

Express Setup
NOTE
Directory Server version 8.0 conforms to the Filesystem Hierarchy Standards.
This means that the directories and files are in different locations than previous
versions. For more information on FHS, see the http://www.pathname.com/fhs/
homepage. For a table showing the new file locations, see Section 1, “Directory
Server File Locations”.
3. Express Setup
Use express installation if you are installing Directory Server for an evaluation or trial. Because
express installation does not offer the choice of selecting the Directory Server server port
number or the directory suffix, among other settings, Red Hat recommends not using it for
production deployments.
NOTE
The setup program gets the host information from the /etc/resolv.conf file. If
there are aliases in the /etc/hosts file, such as ldap.example.com, that do not
match the /etc/resolv.conf settings, the setup program cannot use the default
hostname option, and setup will fail.
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
1. After the Directory Server packages are installed as described in Section 2, “Installing the
Directory Server Packages”, then launch the setup-ds-admin.pl script.
# /opt/dirsrv/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
NOTE
Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script as root.
47
Page 58

Chapter 4. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on HP-UX 11i
2. Select y to accept the Red Hat licensing terms.
3. The dsktune utility runs. Select y to continue with the setup.
dsktune checks the available disk space, processor type, physical memory, and other
system data and settings such as TCP/IP ports and file descriptor settings. If your system
does not meet these basic Red Hat Directory Server requirements, dsktune returns a
warning. dsktune warnings do not block the setup process; simply enter y to go to the next
step.
4. Next, choose the setup type. Enter 1 to perform an express setup.
5. The next step allows you to register your Directory Server with an existing Directory Server
instance, called the Configuration Directory Server. This registers the new instance so it can
be managed by the Console. If this is the first Directory Server instance set up on your
network, it is not possible to register it with another directory. Select n to set up this Directory
Server as a Configuration Directory Server and move to the next express install step, setting
up the administrator user.
NOTE
To register the Directory Server instance with an existing Configuration Directory
Server, select yes. This continues with the registration process rather than the
regular express setup process.
Registering a new instance with a Configuration Directory Server requires you to
supply information about the Configuration Directory Server:
• The Configuration Directory Server URL, such as
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
To use TLS/SSL, set the protocol as ldaps:// instead of ldap:// For
LDAPS, use the secure port (636) instead of the standard port (389), and
provide a CA certificate.
• The Configuration Directory Server administrator's user ID; by default, this is
admin.
• The administrator user's password.
• The Configuration Directory Server Admin domain, such as example.com.
48
• The CA certificate to authenticate to the Configuration Directory Server. This is
only required if the Directory Server instance will connect to the Configuration
Directory Server over LDAPS. This should be the full path and filename the CA
certificate in PEM/ASCII format.
This information is supplied in place of creating an admin user for the new
Page 59

Express Setup
Directory Server in steps 6 and 7.
6. Set the administrator username. The default is admin.
7. Set the administrator password and confirm it.
8. Set the Directory Manager username. The default is cn=Directory Manager.
9. Set the Directory Manager password and confirm it.
10.The last screen asks if you are ready to set up your servers. Select yes.
Are you ready to set up your servers? [yes]:
Creating directory server . . .
Your new DS instance 'example' was successfully created.
Creating the configuration directory server . . .
Beginning Admin Server reconfiguration . . .
Creating Admin Server files and directories . . .
Updating adm.conf . . .
Updating admpw . . .
Registering admin server with the configuration directory server . . .
Updating adm.conf with information from configuration directory server . . .
Updating the configuration for the httpd engine . . .
Restarting admin server . . .
The admin server was successfully started.
Admin server was successfully reconfigured and started.
Exiting . . .
Log file is '/tmp/setup0C7tiV.log'
The setup-ds-admin.pl script applies all default options for the Directory Server configuration,
including the instance name (for example, ldap.example.com), domain (for example,
example.com), suffix (for example, dc=example, dc=com), and port numbers (389 for the
Directory Server instance and 9830 for the Administration Server).
When the setup-ds-admin.pl script is done, then the Directory Server is configured and
running. To log into the Directory Server Console to begin setting up your directory service, do
the following:
1. Get the Administration Server port number from the Listen parameter in the console.conf
configuration file.
grep \^Listen /etc/dirsrv/admin-serv/console.conf
Listen 0.0.0.0:9830
49
Page 60

Chapter 4. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on HP-UX 11i
2. Using the Administration Server port number, launch the Console.
/opt/dirsrv/bin/redhat-idm-console -a http://localhost:9830
NOTE
If you do not pass the Administration Server port number with the
redhat-idm-console command, then you are prompted for it at the Console
login screen.
4. Typical Setup
The typical setup process is the most commonly-used setup process. It offers control over the
ports for the Directory and Administration Servers, the domain name, and directory suffix.
NOTE
Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script as root.
The typical setup has the following steps:
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
1. After the Directory Server packages are installed as described in Section 2, “Installing the
Directory Server Packages”, then launch the setup-ds-admin.pl script.
# /opt/dirsrv/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
2. Select y to accept the Red Hat licensing terms.
50
Page 61

Typical Setup
3. The dsktune utility runs. Select y to continue with the setup.
dsktune checks the available disk space, processor type, physical memory, and other
system data and settings such as TCP/IP ports and file descriptor settings. If your system
does not meet these basic Red Hat Directory Server requirements, dsktune returns a
warning. dsktune warnings do not block the setup process; simply enter y to go to the next
step.
4. Next, choose the setup type. Accept the default, option 2, to perform a typical setup.
5. Set the computer name of the machine on which the Directory Server is being configured.
This defaults to the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) for the host. For example:
Computer name [ldap.example.com]:
NOTE
The setup program gets the host information from the /etc/resolv.conf file. If
there are aliases in the /etc/hosts file, such as ldap.example.com, that do not
match the /etc/resolv.conf settings, you cannot use the default hostname
option.
The hostname is very important. It is used generate the Directory Server instance name, the
admin domain, and the base suffix, among others. If you are using SSL/TLS or Kerberos, the
computer name must be the exact name that clients use to connect to the system. If you will
use DNS, make sure the name resolves to a valid IP address and that IP address resolves
back to this name.
6. Set the user and group as which the Directory Server process will run. The default is
daemon:daemon. For example:
System User [daemon]:
System Group [daemon]:
7. The next step allows you to register your Directory Server with an existing Directory Server
instance, called the Configuration Directory Server. This registers the new instance so it can
be managed by the Console. If this is the first Directory Server instance set up on your
network, it is not possible to register it with another directory. Select n to set up this Directory
Server as a Configuration Directory Server and move to the next typical install step, setting
up the administrator user.
51
Page 62

Chapter 4. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on HP-UX 11i
NOTE
To register the Directory Server instance with an existing Configuration Directory
Server, select yes. This continues with the registration process rather than the
regular typical setup process.
Registering a new instance with a Configuration Directory Server requires you to
supply information about the Configuration Directory Server:
• The Configuration Directory Server URL, such as
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
To use TLS/SSL, set the protocol as ldaps:// instead of ldap:// For
LDAPS, use the secure port (636) instead of the standard port (389), and
provide a CA certificate.
• The Configuration Directory Server administrator's user ID; by default, this is
admin.
• The administrator user's password.
• The Configuration Directory Server Admin domain, such as example.com.
• The CA certificate to authenticate to the Configuration Directory Server. This is
only required if the Directory Server instance will connect to the Configuration
Directory Server over LDAPS. This should be the full path and filename the CA
certificate in PEM/ASCII format.
This information is supplied in place of creating an admin user and domain for
the new Directory Server, steps 8, 9, and 10.
8. Set the administrator username. The default is admin.
9. Set the administrator password and confirm it.
10.Set the administration domain. This defaults to the host's domain. For example:
Administration Domain [example.com]:
11.Enter the Directory Server port number. The default is 389, but if that port is in use, the setup
program supplies a randomly generated one.
Directory server network port [30860]: 1025
52
Page 63

Typical Setup
12.Enter the Directory Server identifier; this defaults to the hostname.
Directory server identifier [example]:
13.Enter the directory suffix. This defaults to dc=domain name. For example:
Suffix [dc=redhat, dc=com]:
14.Set the Directory Manager username. The default is cn=Directory Manager.
15.Set the Directory Manager password and confirm it.
16.Enter the Administration Server port number. The default is 9830, but if that port is in use, the
setup program supplies a randomly generated one.
Administration port [9830]:
17.The last screen asks if you are ready to set up your servers. Select yes.
Are you ready to set up your servers? [yes]:
Creating directory server . . .
Your new DS instance 'example2' was successfully created.
Creating the configuration directory server . . .
Beginning Admin Server reconfiguration . . .
Creating Admin Server files and directories . . .
Updating adm.conf . . .
Updating admpw . . .
Registering admin server with the configuration directory server . . .
Updating adm.conf with information from configuration directory server . . .
Updating the configuration for the httpd engine . . .
Restarting admin server . . .
The admin server was successfully started.
Admin server was successfully reconfigured and started.
Exiting . . .
Log file is '/tmp/setupulSykp.log'
When the setup-ds-admin.pl script is done, then the Directory Server is configured and
running. To log into the Directory Server Console to begin setting up your directory service, do
the following:
1. Get the Administration Server port number from the Listen parameter in the console.conf
configuration file.
53
Page 64

Chapter 4. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on HP-UX 11i
grep \^Listen /etc/dirsrv/admin-serv/console.conf
Listen 0.0.0.0:9830
2. Using the Administration Server port number, launch the Console.
/opt/dirsrv/bin/redhat-idm-console -a http://localhost:9830
NOTE
If you do not pass the Administration Server port number with the
redhat-idm-console command, then you are prompted for it at the Console
login screen.
5. Custom Setup
Custom setup provides two special configuration options that allow you to add information to the
Directory Server databases during the setup period. One imports an LDIF file, which is useful if
you have existing information. The other imports sample data that is included with Directory
Server; this is useful for testing features of Directory Server and for evaluation.
NOTE
Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script as root.
The custom setup has the following steps:
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
1. After the Directory Server packages are installed as described in Section 2, “Installing the
Directory Server Packages”, then launch the setup-ds-admin.pl script.
54
Page 65

Custom Setup
# /opt/dirsrv/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
2. Select y to accept the Red Hat licensing terms.
3. The dsktune utility runs. Select y to continue with the setup.
dsktune checks the available disk space, processor type, physical memory, and other
system data and settings such as TCP/IP ports and file descriptor settings. If your system
does not meet these basic Red Hat Directory Server requirements, dsktune returns a
warning. dsktune warnings do not block the setup process; simply entree y to go to the next
step.
4. Next, choose the setup type. Accept the default, option 3, to perform a custom setup.
5. Set the computer name of the machine on which the Directory Server is being configured.
This defaults to the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) for the host. For example:
Computer name [ldap.example.com]:
NOTE
The setup program gets the host information from the /etc/resolv.conf file. If
there are aliases in the /etc/hosts file, such as ldap.example.com, that do not
match the /etc/resolv.conf settings, you cannot use the default hostname
option.
The hostname is very important. It is used generate the Directory Server instance name, the
admin domain, and the base suffix, among others. If you are using SSL/TLS or Kerberos, the
computer name must be the exact name that clients use to connect to the system. If you will
use DNS, make sure the name resolves to a valid IP address and that IP address resolves
back to this name.
6. Set the user and group as which the Directory Server process will run. The default is
daemon:daemon. For example:
System User [daemon]:
System Group [daemon]:
7. The next step allows you to register your Directory Server with an existing Directory Server
instance, called the Configuration Directory Server. This registers the new instance so it can
be managed by the Console. If this is the first Directory Server instance set up on your
55
Page 66

Chapter 4. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on HP-UX 11i
network, it is not possible to register it with another directory. Select n to set up this Directory
Server as a Configuration Directory Server and move to the next custom install step, setting
up the administrator user.
NOTE
To register the Directory Server instance with an existing Configuration Directory
Server, select yes. This continues with the registration process rather than the
regular custom setup process.
Registering a new instance with a Configuration Directory Server requires you to
supply information about the Configuration Directory Server:
• The Configuration Directory Server URL, such as
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
To use TLS/SSL, set the protocol as ldaps:// instead of ldap:// For
LDAPS, use the secure port (636) instead of the standard port (389), and
provide a CA certificate.
• The Configuration Directory Server administrator's user ID; by default, this is
admin.
• The administrator user's password.
• The Configuration Directory Server Admin domain, such as example.com.
• The CA certificate to authenticate to the Configuration Directory Server. This is
only required if the Directory Server instance will connect to the Configuration
Directory Server over LDAPS. This should be the full path and filename the CA
certificate in PEM/ASCII format.
This information is supplied in place of creating an admin user and domain for
the new Directory Server steps 8, 9, and 10.
8. Set the administrator username. The default is admin.
9. Set the administrator password and confirm it.
10.Set the administration domain. This defaults to the host's domain. For example:
Administration Domain [redhat.com]:
11.Enter the Directory Server port number. The default is 389, but if that port is in use, the setup
program supplies a randomly generated one.
56
Page 67

Directory server network port [389]: 1066
12.Enter the Directory Server identifier; this defaults to the hostname.
Directory server identifier [example]:
13.Enter the directory suffix. This defaults to dc=domain name. For example:
Suffix [dc=redhat, dc=com]:
14.Set the Directory Manager username. The default is cn=Directory Manager.
Custom Setup
15.Set the Directory Manager password and confirm it.
16.Select whether you want to install sample entries with the Directory Server instance. This
means that an example LDIF, with preconfigured users, groups, roles, and other entries, is
imported into the Directory Server database. This option is helpful for evaluation or testing
Directory Server features.
This is not required.
17.Select whether to populate the Directory Server with data; this means whether to import an
LDIF file with existing data into the Directory Server database. If the answer is yes, then
supply a path to the LDIF file or select the suggested file. If the LDIF file requires custom
schema, perform a silent setup instead, and use the SchemaFile directive in the .inf to
specify additional schema files. See Section 3.5.1, “.inf File Directives” for information on
.inf directives.
The default option is none, which does not import any data.
18.Enter the Administration Server port number. The default is 9830, but if that port is in use, the
setup program supplies a randomly generated one.
Administration port [9830]:
19.Set an IP address for the new Administration Server to use. The Administration Server uses
a web server, and this parameter is set in the console.conf file for the server. Setting this
parameter restricts the Administration Server to that single IP. Leaving it blank, the default,
allows the Administration Server to acquire any IP address.
20.Set the user as which the Administration Server process will run. The default is daemon. For
57
Page 68

Chapter 4. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on HP-UX 11i
example:
Run Administration Server as [daemon]:
21.The last screen asks if you are ready to set up your servers. Select yes.
Are you ready to set up your servers? [yes]:
Creating directory server . . .
Your new DS instance 'example3' was successfully created.
Creating the configuration directory server . . .
Beginning Admin Server reconfiguration . . .
Creating Admin Server files and directories . . .
Updating adm.conf . . .
Updating admpw . . .
Registering admin server with the configuration directory server . . .
Updating adm.conf with information from configuration directory server . . .
Updating the configuration for the httpd engine . . .
Restarting admin server . . .
The admin server was successfully started.
Admin server was successfully reconfigured and started.
Exiting . . .
Log file is '/tmp/setupul88C1.log'
When the setup-ds-admin.pl script is done, then the Directory Server is configured and
running. To log into the Directory Server Console to begin setting up your directory service, do
the following:
1. Get the Administration Server port number from the Listen parameter in the console.conf
configuration file.
grep \^Listen /etc/dirsrv/admin-serv/console.conf
Listen 0.0.0.0:9830
2. Using the Administration Server port number, launch the Console.
/opt/dirsrv/bin/redhat-idm-console -a http://localhost:9830
58
Page 69

Custom Setup
NOTE
If you do not pass the Administration Server port number with the
redhat-idm-console command, then you are prompted for it at the Console
login screen.
59
Page 70

60
Page 71

Chapter 5.
Setting up Red Hat Directory Server
on Sun Solaris
Installing and configuring Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris has three major steps:
1. Install the required version of the Java® Runtime Environment (JRE).
2. Install the Directory Server packages.
3. Run the setup program. The setup step is where all of the information about the new
Directory Server instance is supplied.
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
There are three interactive ways of setting up Directory Server: express, typical, and custom.
These setup types provide different levels of control over the configuration settings, such as port
numbers, directory suffixes, and users and groups for the Directory Server processes. Express
has the least amount of input, meaning it uses more default or randomly-generated settings,
while custom allows the most control over the configuration by having the user supply a lot of
configuration information. These setup types are described more in Table 1.2, “Comparison of
Setup Types”. For most deployments, the typical installation type is all that is required.
NOTE
There is a fourth setup option called a silent installation. This uses a file with
predefined settings to create a new Directory Server without any user interaction.
This is extremely useful for doing large numbers of Directory Server instances,
since it does not require any user involvement after the packages are installed.
Silent installations are explained more in Section 3.1, “Silent Setup for Directory
Server and Administration Server”.
This chapter describes the complete process to install Red Hat Directory Server on Solaris,
including both the JRE and Directory Server packages, and the different setup options.
1. Installing the JRE
61
Page 72

Chapter 5. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris
Necessary Java JRE libraries are not bundled with Directory Server. They must be downloaded
and extracted separately before installing the Directory Server packages.
NOTE
Directory Server 8.0 requires JRE version 1.5.0.
Install the latest version of the 64-bit Sun J2SE Java Runtime Environment 5.0 (Update 9),
available from the Sun download site, http://java.sun.com/javase/downloads/index.jsp.
IMPORTANT
Solaris requires installing the 32-bit version of the JRE as well as installing the
64-bit version. The 32-bit version is used for the applet and Java Web Start
support. Read http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/README.html,
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/ReleaseNotes.html, and
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.5.0/jre/install-solaris-64.html before installing the
Directory Server.
1. Under the section Java Runtime Environment (JRE) 5.0 Update 9, Sun only makes this
JRE available through a self-extracting file which is incompatible with Directory Server since
this format does not use the native Solaris packaging utility database.
2. It is possible to obtain the Sun 5.0 JRE in a compatible format. Click Download under the
JDK 5.0 Update 9 section, and, under Solaris SPARC Platform - J2SETM Development
Kit 5.0 Update 9, select Solaris SPARC 32-bit packages - tar.Z
(jdk-1_5_0_09-solaris-sparc.tar.Z) and Solaris SPARC 64-bit packages - tar.Z (use
32-bit version for applet and Java Web Start support)
(jdk-1_5_0_09-solaris-sparcv9.tar.Z).
3. After downloading these two files, uncompress them using the gunzip utility, and extract the
contents using the tar utility.
4. The contents of the 32-bit file, jdk-1_5_0_09-solaris-sparc.tar.Z, are COPYRIGHT,
LICENSE, README.html, SUNWj5cfg, SUNWj5dev, SUNWj5dmo, SUNWj5jmp, SUNWj5man, and
SUNWj5rt.
The contents of the 64-bit file, jdk-1_5_0_09-solaris-sparcv9.tar.Z, are SUNWj5dmx,
SUNWj5dvx, and SUNWj5rtx.
5. Since only the JRE is needed on Solaris 9 systems, use the pkgadd utility to add the 32-bit
package, SUNWj5rt, first, and then add the 64-bit package, SUNWj5rtx.
62
Page 73

Installing the Directory Server Packages
After installing the JRE, install the Directory Server packages, as described in Section 2,
“Installing the Directory Server Packages”.
2. Installing the Directory Server Packages
There are two ways to install the Directory Server packages. The packages can be downloaded
individually through Red Hat Network, or an ISO image can be downloaded and saved to a CD
or DVD.
• Section 2.1, “Installing Individual Packages”
• Section 2.2, “Installing from an ISO Image”
2.1. Installing Individual Packages
The Directory Server software is packaged in Solaris PKG format and incorporates the Solaris
pkgadd command. The latest Directory Server for Solaris packages are available through the
Red Hat Directory Server 8.0 Solaris channel.
To install the Directory Server on Solaris, do the following:
1. Create a temporary installation directory for the downloaded packages, then open that
directory.
mkdir /tmp/rhds80
cd /tmp/rhds80
2. Download the Directory Server packages from Red Hat Network. This can be done through a
web browser by logging into Red Hat Network and selecting the Red Hat Directory Server
8.0 channel or it can be done using a tool such as curl or wget with information available on
the Red Hat Network channel.
3. Install and update the Solaris packages using pkgadd.
for pkg in *.pkg ; do
pkgadd -d $pkg all
done
If another application such as Red Hat Certificate System is already installed on the server,
pkgadd detects the shared packages. Make sure that the pkgadd program replaces any
existing versions with the packages included with Directory Server.
4. When the pkgadd program completes, move all *.pkg files from the current directory to a
63
Page 74

Chapter 5. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris
backup directory.
5. Delete the temporary directory.
rm -rf /tmp/rhds80
6. After the Directory Server packages are installed, run the setup program to set up and
configure the default Directory Server instance and the Administration Server.
/usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
7. Accept the initial screens for licensing and dsktune output, then select the setup type, and
proceed with configuring the new Directory Server instance.
• Section 3, “Express Setup”
• Section 4, “Typical Setup”
• Section 5, “Custom Setup”
NOTE
Directory Server version 8.0 conforms to the Filesystem Hierarchy Standards.
This means that the directories and files are in different locations than previous
versions. For more information on FHS, see the http://www.pathname.com/fhs/
homepage. For a table showing the new file locations, see Section 1, “Directory
Server File Locations”.
2.2. Installing from an ISO Image
The Red Hat Network Red Hat Directory Server 8.0 Solaris channel also has an ISO image
which contains all of the required packages. Like installing the packages individually, the ISO
image uses Sun's pkgadd to manage the installation. To install the Directory Server on Solaris,
do the following:
1. Download the ISO image from Red Hat Network, and burn it to a CD or DVD.
2. Mount the CD on any writable drive:
mount -F hsfs -o ro `lofiadm -a
/directory/solaris9-rhdirserv-8.0-sparcv9-disc1.iso` /directory/tmp
cd /directory/tmp/RedHat/PKGS
64
Page 75

Express Setup
3. Translate the package to the Solaris filesystem format:
for i in `ls *.pkg`; do yes all | pkgtrans $i /directory/ ; done
4. Add the package:
yes yes | pkgadd -d /directory/ all
If another application such as Red Hat Certificate System is already installed on the server,
pkgadd detects the shared packages. Make sure that the pkgadd program replaces any
existing versions with the packages included with Directory Server.
5. After the Directory Server packages are installed, run the setup program to set up and
configure the default Directory Server instance and the Administration Server.
/usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
6. Accept the initial screens for licensing and dsktune output, then select the setup type, and
proceed with configuring the new Directory Server instance.
• Section 3, “Express Setup”
• Section 4, “Typical Setup”
• Section 5, “Custom Setup”
NOTE
Directory Server version 8.0 conforms to the Filesystem Hierarchy Standards.
This means that the directories and files are in different locations than previous
versions. For more information on FHS, see the http://www.pathname.com/fhs/
homepage. For a table showing the new file locations, see Section 1, “Directory
Server File Locations”.
3. Express Setup
Use express installation if you are installing Directory Server for an evaluation or trial. Because
express installation does not offer the choice of selecting the Directory Server server port
number or the directory suffix, among other settings, Red Hat recommends not using it for
production deployments.
65
Page 76

Chapter 5. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris
NOTE
The setup program gets the host information from the /etc/resolv.conf file. If
there are aliases in the /etc/hosts file, such as ldap.example.com, that do not
match the /etc/resolv.conf settings, the setup program cannot use the default
hostname option, and setup will fail.
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
1. After the Directory Server packages are installed as described in Section 2, “Installing the
Directory Server Packages”, then launch the setup-ds-admin.pl script.
# /usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
NOTE
Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script as root.
2. Select y to accept the Red Hat licensing terms.
3. The dsktune utility runs. Select y to continue with the setup.
dsktune checks the available disk space, processor type, physical memory, and other
system data and settings such as TCP/IP ports and file descriptor settings. If your system
does not meet these basic Red Hat Directory Server requirements, dsktune returns a
warning. dsktune warnings do not block the setup process; simply enter y to go to the next
step.
4. Next, choose the setup type. Enter 1 to perform an express setup.
5. The next step allows you to register your Directory Server with an existing Directory Server
instance, called the Configuration Directory Server. This registers the new instance so it can
be managed by the Console. If this is the first Directory Server instance set up on your
network, it is not possible to register it with another directory. Select n to set up this Directory
Server as a Configuration Directory Server and move to the next express install step, setting
66
Page 77

up the administrator user.
NOTE
To register the Directory Server instance with an existing Configuration Directory
Server, select yes. This continues with the registration process rather than the
regular express setup process.
Registering a new instance with a Configuration Directory Server requires you to
supply information about the Configuration Directory Server:
• The Configuration Directory Server URL, such as
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
To use TLS/SSL, set the protocol as ldaps:// instead of ldap:// For
LDAPS, use the secure port (636) instead of the standard port (389), and
provide a CA certificate.
Express Setup
• The Configuration Directory Server administrator's user ID; by default, this is
admin.
• The administrator user's password.
• The Configuration Directory Server Admin domain, such as example.com.
• The CA certificate to authenticate to the Configuration Directory Server. This is
only required if the Directory Server instance will connect to the Configuration
Directory Server over LDAPS. This should be the full path and filename the CA
certificate in PEM/ASCII format.
This information is supplied in place of creating an admin user for the new
Directory Server in steps 6 and 7.
6. Set the administrator username. The default is admin.
7. Set the administrator password and confirm it.
8. Set the Directory Manager username. The default is cn=Directory Manager.
9. Set the Directory Manager password and confirm it.
10.The last screen asks if you are ready to set up your servers. Select yes.
Are you ready to set up your servers? [yes]:
Creating directory server . . .
Your new DS instance 'example' was successfully created.
Creating the configuration directory server . . .
Beginning Admin Server reconfiguration . . .
67
Page 78

Chapter 5. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris
Creating Admin Server files and directories . . .
Updating adm.conf . . .
Updating admpw . . .
Registering admin server with the configuration directory server . . .
Updating adm.conf with information from configuration directory server . . .
Updating the configuration for the httpd engine . . .
Restarting admin server . . .
The admin server was successfully started.
Admin server was successfully reconfigured and started.
Exiting . . .
Log file is '/tmp/setup0C7tiV.log'
The setup-ds-admin.pl script applies all default options for the Directory Server configuration,
including the instance name (for example, ldap.example.com), domain (for example,
example.com), suffix (for example, dc=example, dc=com), and port numbers (389 for the
Directory Server instance and 9830 for the Administration Server).
When the setup-ds-admin.pl script is done, then the Directory Server is configured and
running. To log into the Directory Server Console to begin setting up your directory service, do
the following:
1. Get the Administration Server port number from the Listen parameter in the console.conf
configuration file.
grep \^Listen /etc/dirsrv/admin-serv/console.conf
Listen 0.0.0.0:9830
2. Using the Administration Server port number, launch the Console.
/usr/bin/redhat-idm-console -a http://localhost:9830
NOTE
If you do not pass the Administration Server port number with the
redhat-idm-console command, then you are prompted for it at the Console
login screen.
4. Typical Setup
68
Page 79

Typical Setup
The typical setup process is the most commonly-used setup process. It offers control over the
ports for the Directory and Administration Servers, the domain name, and directory suffix.
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
1. After the Directory Server packages are installed as described in Section 2, “Installing the
Directory Server Packages”, then launch the setup-ds-admin.pl script.
# /usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
NOTE
Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script as root.
2. Select y to accept the Red Hat licensing terms.
3. The dsktune utility runs. Select y to continue with the setup.
dsktune checks the available disk space, processor type, physical memory, and other
system data and settings such as TCP/IP ports and file descriptor settings. If your system
does not meet these basic Red Hat Directory Server requirements, dsktune returns a
warning. dsktune warnings do not block the setup process; simply enter y to go to the next
step.
4. Next, choose the setup type. Accept the default, option 2, to perform a typical setup.
5. Set the computer name of the machine on which the Directory Server is being configured.
This defaults to the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) for the host. For example:
Computer name [ldap.example.com]:
NOTE
The setup program gets the host information from the /etc/resolv.conf file. If
there are aliases in the /etc/hosts file, such as ldap.example.com, that do not
match the /etc/resolv.conf settings, you cannot use the default hostname
69
Page 80

Chapter 5. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris
option.
The hostname is very important. It is used generate the Directory Server instance name, the
admin domain, and the base suffix, among others. If you are using SSL/TLS or Kerberos, the
computer name must be the exact name that clients use to connect to the system. If you will
use DNS, make sure the name resolves to a valid IP address and that IP address resolves
back to this name.
6. Set the user and group as which the Directory Server process will run. The default is
nobody:nobody. For example:
System User [nobody]:
System Group [nobody]:
7. The next step allows you to register your Directory Server with an existing Directory Server
instance, called the Configuration Directory Server. This registers the new instance so it can
be managed by the Console. If this is the first Directory Server instance set up on your
network, it is not possible to register it with another directory. Select n to set up this Directory
Server as a Configuration Directory Server and move to the next typical install step, setting
up the administrator user.
NOTE
To register the Directory Server instance with an existing Configuration Directory
Server, select yes. This continues with the registration process rather than the
regular typical setup process.
Registering a new instance with a Configuration Directory Server requires you to
supply information about the Configuration Directory Server:
• The Configuration Directory Server URL, such as
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
To use TLS/SSL, set the protocol as ldaps:// instead of ldap:// For
LDAPS, use the secure port (636) instead of the standard port (389), and
provide a CA certificate.
70
• The Configuration Directory Server administrator's user ID; by default, this is
admin.
• The administrator user's password.
• The Configuration Directory Server Admin domain, such as example.com.
Page 81

• The CA certificate to authenticate to the Configuration Directory Server. This is
only required if the Directory Server instance will connect to the Configuration
Directory Server over LDAPS. This should be the full path and filename the CA
certificate in PEM/ASCII format.
This information is supplied in place of creating an admin user and domain for
the new Directory Server, steps 8, 9, and 10.
8. Set the administrator username. The default is admin.
9. Set the administrator password and confirm it.
10.Set the administration domain. This defaults to the host's domain. For example:
Typical Setup
Administration Domain [example.com]:
11.Enter the Directory Server port number. The default is 389, but if that port is in use, the setup
program supplies a randomly generated one.
Directory server network port [30860]: 1025
12.Enter the Directory Server identifier; this defaults to the hostname.
Directory server identifier [example]:
13.Enter the directory suffix. This defaults to dc=domain name. For example:
Suffix [dc=redhat, dc=com]:
14.Set the Directory Manager username. The default is cn=Directory Manager.
15.Set the Directory Manager password and confirm it.
16.Enter the Administration Server port number. The default is 9830, but if that port is in use, the
setup program supplies a randomly generated one.
Administration port [9830]:
71
Page 82

Chapter 5. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris
17.The last screen asks if you are ready to set up your servers. Select yes.
Are you ready to set up your servers? [yes]:
Creating directory server . . .
Your new DS instance 'example2' was successfully created.
Creating the configuration directory server . . .
Beginning Admin Server reconfiguration . . .
Creating Admin Server files and directories . . .
Updating adm.conf . . .
Updating admpw . . .
Registering admin server with the configuration directory server . . .
Updating adm.conf with information from configuration directory server . . .
Updating the configuration for the httpd engine . . .
Restarting admin server . . .
The admin server was successfully started.
Admin server was successfully reconfigured and started.
Exiting . . .
Log file is '/tmp/setupulSykp.log'
When the setup-ds-admin.pl script is done, then the Directory Server is configured and
running. To log into the Directory Server Console to begin setting up your directory service, do
the following:
1. Get the Administration Server port number from the Listen parameter in the console.conf
configuration file.
grep \^Listen /etc/dirsrv/admin-serv/console.conf
Listen 0.0.0.0:9830
2. Using the Administration Server port number, launch the Console.
/usr/bin/redhat-idm-console -a http://localhost:9830
NOTE
72
If you do not pass the Administration Server port number with the
redhat-idm-console command, then you are prompted for it at the Console
login screen.
Page 83

Custom Setup
5. Custom Setup
Custom setup provides two special configuration options that allow you to add information to the
Directory Server databases during the setup period. One imports an LDIF file, which is useful if
you have existing information. The other imports sample data that is included with Directory
Server; this is useful for testing features of Directory Server and for evaluation.
NOTE
Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script as root.
The custom setup has the following steps:
WARNING
If Directory Server is already installed on your machine, it is extremely important
that you perform a migration, not a fresh installation. Migration is described in
Chapter 8, Migrating from Previous Versions.
1. After the Directory Server packages are installed as described in Section 2, “Installing the
Directory Server Packages”, then launch the setup-ds-admin.pl script.
# /usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
2. Select y to accept the Red Hat licensing terms.
3. The dsktune utility runs. Select y to continue with the setup.
dsktune checks the available disk space, processor type, physical memory, and other
system data and settings such as TCP/IP ports and file descriptor settings. If your system
does not meet these basic Red Hat Directory Server requirements, dsktune returns a
warning. dsktune warnings do not block the setup process; simply entree y to go to the next
step.
4. Next, choose the setup type. Accept the default, option 3, to perform a custom setup.
5. Set the computer name of the machine on which the Directory Server is being configured.
This defaults to the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) for the host. For example:
Computer name [ldap.example.com]:
73
Page 84

Chapter 5. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris
NOTE
The setup program gets the host information from the /etc/resolv.conf file. If
there are aliases in the /etc/hosts file, such as ldap.example.com, that do not
match the /etc/resolv.conf settings, you cannot use the default hostname
option.
The hostname is very important. It is used generate the Directory Server instance name, the
admin domain, and the base suffix, among others. If you are using SSL/TLS or Kerberos, the
computer name must be the exact name that clients use to connect to the system. If you will
use DNS, make sure the name resolves to a valid IP address and that IP address resolves
back to this name.
6. Set the user and group as which the Directory Server process will run. The default is
nobody:nobody. For example:
System User [nobody]:
System Group [nobody]:
7. The next step allows you to register your Directory Server with an existing Directory Server
instance, called the Configuration Directory Server. This registers the new instance so it can
be managed by the Console. If this is the first Directory Server instance set up on your
network, it is not possible to register it with another directory. Select n to set up this Directory
Server as a Configuration Directory Server and move to the next custom install step, setting
up the administrator user.
NOTE
To register the Directory Server instance with an existing Configuration Directory
Server, select yes. This continues with the registration process rather than the
regular custom setup process.
Registering a new instance with a Configuration Directory Server requires you to
supply information about the Configuration Directory Server:
• The Configuration Directory Server URL, such as
ldap://ldap.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
74
To use TLS/SSL, set the protocol as ldaps:// instead of ldap:// For
LDAPS, use the secure port (636) instead of the standard port (389), and
provide a CA certificate.
Page 85

Custom Setup
• The Configuration Directory Server administrator's user ID; by default, this is
admin.
• The administrator user's password.
• The Configuration Directory Server Admin domain, such as example.com.
• The CA certificate to authenticate to the Configuration Directory Server. This is
only required if the Directory Server instance will connect to the Configuration
Directory Server over LDAPS. This should be the full path and filename the CA
certificate in PEM/ASCII format.
This information is supplied in place of creating an admin user and domain for
the new Directory Server steps 8, 9, and 10.
8. Set the administrator username. The default is admin.
9. Set the administrator password and confirm it.
10.Set the administration domain. This defaults to the host's domain. For example:
Administration Domain [redhat.com]:
11.Enter the Directory Server port number. The default is 389, but if that port is in use, the setup
program supplies a randomly generated one.
Directory server network port [389]: 1066
12.Enter the Directory Server identifier; this defaults to the hostname.
Directory server identifier [example]:
13.Enter the directory suffix. This defaults to dc=domain name. For example:
Suffix [dc=redhat, dc=com]:
14.Set the Directory Manager username. The default is cn=Directory Manager.
15.Set the Directory Manager password and confirm it.
75
Page 86

Chapter 5. Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris
16.Select whether you want to install sample entries with the Directory Server instance. This
means that an example LDIF, with preconfigured users, groups, roles, and other entries, is
imported into the Directory Server database. This option is helpful for evaluation or testing
Directory Server features.
This is not required.
17.Select whether to populate the Directory Server with data; this means whether to import an
LDIF file with existing data into the Directory Server database. If the answer is yes, then
supply a path to the LDIF file or select the suggested file. If the LDIF file requires custom
schema, perform a silent setup instead, and use the SchemaFile directive in the .inf to
specify additional schema files. See Section 3.5.1, “.inf File Directives” for information on
.inf directives.
The default option is none, which does not import any data.
18.Enter the Administration Server port number. The default is 9830, but if that port is in use, the
setup program supplies a randomly generated one.
Administration port [9830]:
19.Set an IP address for the new Administration Server to use. The Administration Server uses
a web server, and this parameter is set in the console.conf file for the server. Setting this
parameter restricts the Administration Server to that single IP. Leaving it blank, the default,
allows the Administration Server to acquire any IP address.
20.Set the user as which the Administration Server process will run. The default is nobody. For
example:
Run Administration Server as [nobody]:
21.The last screen asks if you are ready to set up your servers. Select yes.
Are you ready to set up your servers? [yes]:
Creating directory server . . .
Your new DS instance 'example3' was successfully created.
Creating the configuration directory server . . .
Beginning Admin Server reconfiguration . . .
Creating Admin Server files and directories . . .
Updating adm.conf . . .
Updating admpw . . .
Registering admin server with the configuration directory server . . .
Updating adm.conf with information from configuration directory server . . .
Updating the configuration for the httpd engine . . .
Restarting admin server . . .
The admin server was successfully started.
Admin server was successfully reconfigured and started.
76
Page 87

Custom Setup
Exiting . . .
Log file is '/tmp/setupul88C1.log'
When the setup-ds-admin.pl script is done, then the Directory Server is configured and
running. To log into the Directory Server Console to begin setting up your directory service, do
the following:
1. Get the Administration Server port number from the Listen parameter in the console.conf
configuration file.
grep \^Listen /etc/dirsrv/admin-serv/console.conf
Listen 0.0.0.0:9830
2. Using the Administration Server port number, launch the Console.
/usr/bin/redhat-idm-console -a http://localhost:9830
NOTE
If you do not pass the Administration Server port number with the
redhat-idm-console command, then you are prompted for it at the Console
login screen.
77
Page 88

78
Page 89

Chapter 6.
Advanced Setup and Configuration
After the default Directory Server and Administration Server have been configured, there are
tools available to manage, create, and remove server instances. These include Administration
Server conigurations to allow people to access the Directory Server files remotely, silent setup
tools for installing instances from file configuration, and instance setup and removal scripts.
1. Working with Administration Server Instances
There are two additional setup steps that can be done with the Administration Server. This first
allows the Administration Server to be accessed by remote clients, so that users can install and
launch the Directory Server Console and still access the remote Directory Server file, such as
help files.
NOTE
If you lock yourself out of the Console or Administration Server, you may have to
edit the Administration Server configuration directly via LDAP. See
http://directory.fedoraproject.org/wiki/Howto:AdminServerLDAPMgmt for
information on editing the Administration Server configuration.
1.1. Configuring IP Authorization on the Administration Server
The Directory Server Console can be launched from remote machines to access an instance of
Directory Server. The client running Directory Server Console needs access to the
Administration Server to access support files like the help content and documentation.
There are six steps to configure the Administration Server to accept the client IP address:
1. On the same machine on which the Administration Server is running launch the Console.
/usr/bin/redhat-idm-console
2. In the Administration Server Console, click the Configuration tab, then click the Network
tab.
3. In the Connection Restrictions Settings section, select IP Addresses to Allow from the
pull down menu.
4. Click Edit.
5. In the IP Addresses field, enter the following:
79
Page 90

Chapter 6. Advanced Setup and Configuration
*.*.*.*
This allows all IP addresses to access the Administration Server.
6. Restart the Administration Server.
CAUTION
Adding the client machine proxy IP address to the Administration Server creates
a potential security hole.
1.2. Configuring Proxy Servers for the Administration Server
If there are proxies for the HTTP connections on the client machine running the Directory Server
Console, the configuration must be changed in one of two ways:
• The proxy settings must be removed from the client machine. Removing proxies on the
machine running Directory Server Console allows the client to access the Administration
Server directly. To remove the proxy settings, edit the proxy configuration of the browser
which is used to launch the help files.
• Add the client machine proxy IP address to Administration Server's list of acceptable IP
addresses. This is described in Section 1.1, “Configuring IP Authorization on the
Administration Server”.
CAUTION
Adding the client machine proxy IP address to the Administration Server creates
a potential security hole.
2. Working with Directory Server Instances
2.1. Creating a New Directory Server Instance
Additional instances of the Directory Server can be created from the command line using the
setup-ds-admin.pl command. This offers the setup choices (express, typical, and custom)
that are described in Chapter 3, Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on Red Hat Enterprise
Linux, Chapter 4, Setting up Red Hat Directory Server on HP-UX 11i, and Chapter 5, Setting up
80
Page 91

(Alternate) Installing Directory Server with
Red Hat Directory Server on Sun Solaris.
It is also possible to provide Directory Server parameters on the command line, so that the
instance is created with pre-defined defaults. For example:
setup-ds-admin.pl slapd.ServerPort=1100 slapd.RootDNPwd=itsasecret
When the installer runs, the Directory Server port default is 1100, and the Directory Manager
password is itsasecret.
This script can also be run in silent mode, which means the setup program never opens; the
Directory Server instance values are taken from a specified file. For example:
setup-ds-admin.pl -s -f file.inf
-s runs the script in silent mode, and -f file.inf specifies the setup file to use. Silent
instance setup and .inf files are described in Section 3, “Silent Setup”.
NOTE
New Directory Server instances can be created through the Directory Server
Console; this is described in the Directory Server Administrator's Guide.
2.2. (Alternate) Installing Directory Server with setup-ds
There is also a command called setup-ds.pl. This command creates an instance of Directory
Server that is not managed by the Directory Server Console. It works exactly the same way as
setup-ds-admin.pl except that the questions about the Configuration Directory Server and
Administration Server are omitted. Using this command to create a Directory Server instance
means that the instance has to be managed through the command line or other tools, or it can
be registered with the Configuration Directory Server to manage it with the Console. See
Section 2.3, “Registering an Existing Directory Server Instance with the Configuration Directory
Server” for more information.
2.3. Registering an Existing Directory Server Instance with the
Configuration Directory Server
The Configuration Directory Server uses the o=NetscapeRoot database to store information
about the Directory Servers and Administration Servers in your network. This is used by the
Console and the Administration Servers. This database can belong to a separate Directory
Server instance, called the Configuration Directory Server. There is an option when an instance
is first set up to register it with a Configuration Directory Server. It is possible to register an
81
Page 92

Chapter 6. Advanced Setup and Configuration
existing Directory Server instance with a Configuration Directory Server using the
register-ds-admin script.
/usr/sbin/register-ds-admin.pl
IMPORTANT
Running register-ds-admin creates a default instance of the Administration
Server and Configuration Directory Server if they do not already exist, then
registers any existing Directory Servers with the Configuration Directory Server.
3. Silent Setup
Silent setup uses a file to predefine all the Directory Server configuration parameters that are
normally supplied interactively with the setup program. The silent functionality allows you to
script the setup of multiple instances of Directory Server.
3.1. Silent Setup for Directory Server and Administration Server
Silent setup is useful at sites where many server instances must be created, especially for
heavily replicated sites that will create a large number of consumer servers. Silent setup uses
the same scripts that are used to create instances of Directory Server and Administration
Server, with a special option signaling that the script is to be run silently. Silent mode requires
referencing a setup parameter file (-s -f setup.inf) or setting Directory Server parameters
on the command line.
To run a silent setup of both the Directory Server and Administration Server, do the following:
1. Install the Directory Server packages.
2. Make the setup .inf file. It must specify the following directives:
[General]
FullMachineName= dir.example.com
SuiteSpotUserID= nobody
SuiteSpotGroup= nobody
AdminDomain= example.com
ConfigDirectoryAdminID= admin
ConfigDirectoryAdminPwd= admin
ConfigDirectoryLdapURL= ldap://dir.example.com:389/o=NetscapeRoot
[slapd]
SlapdConfigForMC= Yes
UseExistingMC= No
ServerPort= 389
ServerIdentifier= dir
Suffix= dc=example,dc=com
82
Page 93

RootDN= cn=Directory Manager
RootDNPwd= password123
[admin]
Port= 9830
ServerIpAddress= 111.11.11.11
ServerAdminID= admin
ServerAdminPwd= admin
NOTE
There are three sections of directives in the .inf file to create the default
Directory and Administration Servers: [General], [slapd], and [admin].
Creating an additional instance, or installing a single instance of Directory Server
using setup-ds.pl, only requires two sections, [General] and [slapd].
setup-ds
This parameters correspond to the information supplied during a typical setup. The .inf file
directives are described more in Section 3.5.1, “.inf File Directives”.
3. Run the setup-ds-admin script with the -s and -f options.
/usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl -s -f /export/ds-inf/setup.inf
Running setup-ds-admin installs both the Directory Server instance and the Administration
Server instance. This means that the setup file must specify parameters for both the
Directory Server and the Administration Server. -s runs the script in silent mode, and -f
/export/ds-inf/setup.inf specifies the setup file to use.
After the script runs, the new Directory Server and Administration Server instances are
configured and running, as with a standard setup.
3.2. Silent Directory Server Instance Creation
Like setting up both the Directory Server and Administration Server, silent setup for a single
instance is useful for configuring multiple instances quickly. Silent setup uses the same scripts
that are used to create a new instances of Directory Server, with a special option signaling that
the script is to be run silently and referencing the setup file to use.
To run a silent setup of a Directory Server instance, do the following:
83
Page 94

Chapter 6. Advanced Setup and Configuration
NOTE
When creating a single instance of Directory Server, the Directory Server
packages must already be installed, and the Administration Server must already
be configured and running.
1. Make the setup .inf file. It must specify the following directives:
[General]
FullMachineName= dir.example.com
SuiteSpotUserID= nobody
SuiteSpotGroup= nobody
[slapd]
ServerPort= 389
ServerIdentifier= dir
Suffix= dc=example,dc=com
RootDN= cn=Directory Manager
RootDNPwd= password123
NOTE
There are two sections of directives in the instance creation: [General] and
[slapd]. Installing the Administration Server, which is done in a default setup
file, requires a third parameter as well, [admin], for the Administration Server.
This parameters correspond to the information supplied during a typical setup. The .inf file
directives are described more in Section 3.5.1, “.inf File Directives”.
2. Run the setup-ds-admin.pl script with the -s and -f options.
/usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl -s -f /export/ds-inf/setup-single.inf
Running setup-ds-admin.pl installs only a Directory Server instance, so the setup file must
specify parameters only for the Directory Server. -s runs the script in silent mode, and -f
/export/ds-inf/setup.inf specifies the setup file to use.
After the script runs, the new Directory Server instance is configured and running, as with a
standard setup.
84
Page 95

Sending Parameters in the Command Line
3.3. Sending Parameters in the Command Line
The setup utility, setup-ds-admin.pl, allows settings for all three configuration components —
General (host server), slapd (LDAP server), and admin (Administration Server) — to be
passed directly in the command line. Command-line arguments correspond to the parameters
and values set in the .inf file. The arguments used with setup-ds-admin.pl specify the .inf
setup file section (General, slapd, or admin), parameter, and value in the following form:
section.parameter=value
For example, to set the machine name, suffix, and Directory Server port of the new instance, the
command is as follows:
/usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl General.FullMachineName=ldap.example.com
“slapd.Suffix=dc=example, dc=com” slapd.ServerPort=389
NOTE
Passing arguments in the command line or specifying an .inf sets the defaults
used in the interactive prompt unless they are used with the s (silent) option.
Argument values containing spaces or other shell special characters must quoted to prevent the
shell from interpreting them. In the previous example, the suffix value has a space character, so
the entire parameter has to be quoted. If many of the parameters have to be quoted or escaped,
use an .inf file instead.
You can use an .inf file in conjunction with command line parameters. Parameters set in the
command line override those specified in an .inf file, which is useful for creating an .inf file to
use to set up many Directory Servers. Many of the parameters can be the same, such as
ConfigDirectoryLdapURL, ones specific to the host, such as FullMachineName have to be
unique. For example:
setup-ds-admin.pl -s -f common.inf
General.FullMachineName=ldap37.example.com
slapd.ServerIdentifier=ldap37
This command uses the common parameters specified in the common.inf file, but overrides
FullMachineName and ServerIdentifier with the command line arguments.
85
Page 96

Chapter 6. Advanced Setup and Configuration
NOTE
The section names and parameter names used in the .inf files and on the
command line are case sensitive. Refer to Table 6.1, “setup-ds-admin Options”
to check the correct capitalization.
Option Alternate Options Description Example
--silent -s This sets that the
setup script will run in
silent mode, drawing
the configuration
information from a file
(set with the --file
parameter) rather
than interactively.
--file=name -f name This sets the path
and name of the file
which contains the
configuration settings
for the new Directory
Server instance. This
can be used with the
--silent parameter;
if used alone, it sets
the default values for
the setup prompts.
--debug -d[dddd] This parameter turns
on debugging
information. For the
-d flag, increasing the
number of d's
increases the debug
level.
--keepcache -k This saves the
temporary installation
file, .inf that is
created when the
setup script is run.
This file can then be
reused for a silent
setup.
/usr/sbin/setup-ds-admin.pl
-f /export/sample.inf
86
Page 97

Using the ConfigFile Parameter to Configure
Option Alternate Options Description Example
WARNING
The
cache
file
contains
the
cleartext
passwords
supplied
during
setup.
Use
appropriate
caution
and
protection
with
this
file.
--logfile name -l This parameter
specifies a log file to
which to write the
output. If this is not
set, then the setup
information is written
to a temporary file.
-l
/export/example2007.log
For no log file, set the
file name to
/dev/null:
-l /dev/null
Table 6.1. setup-ds-admin Options
3.4. Using the ConfigFile Parameter to Configure the Directory Server
The ConfigFile parameter in the .inf is an extremely useful tool to configure the directory
from the time it is set up. The ConfigFile parameter specified an LDIF file to import into the
directory. Since the ConfigFile parameter can be used multiple times, it is a good idea to have
multiple LDIF files so that the individual entries are easy to manage.
The ConfigFile parameter is set in the [slapd] section of the .inf.
87
Page 98

Chapter 6. Advanced Setup and Configuration
For example, to configure a new Directory Server instance as a supplier in replication,
ConfigFile can be used to create the replication manager, replica, and replication agreement
entries:
[slapd]
...
ConfigFile = repluser.ldif
ConfigFile = changelog.ldif
ConfigFile = replica.ldif
ConfigFile = replagreement.ldif
...
The LDIF file contains the entry information. For example, the replica.ldif contains the
information to configure the new Directory Server instance as a supplier:
dn: cn=replica,cn="dc=example,dc=com",cn=mapping tree,cn=config
changetype: add
objectclass: top
objectclass: nsds5replica
objectclass: extensibleObject
cn: replica
nsds5replicaroot: dc=example,dc=com
nsds5replicaid: 7
nsds5replicatype: 3
nsds5flags: 1
nsds5ReplicaPurgeDelay: 604800
nsds5ReplicaBindDN: cn=replication manager,cn=config
For more information on LDIF, see the Directory Server Administrator's Guide.
The ConfigFile parameter can be used to create special user entries like the replication
manager, to configure views or classes of service, to add new suffixes and databases, to create
instances of the Attribute Uniqueness plug-in, and to set many other configurations for Directory
Server.
3.5. About .inf File Parameters
With a silent setup, all of the configuration information that is normally supplied interactively with
the setup program must be included in the .inf file or passed in the command line with the
setup-ds-admin.pl command.
NOTE
Providing configuration parameters with the setup-ds-admin.pl command is
described in Section 3, “About the setup-ds-admin.pl Script”.
The .inf file has three sections:
88
Page 99

the Directory Server
• General — which supplies information about the server machine; these are global directives
that are common to all your Directory Servers.
• slapd — which supplies information about the specific Directory Server instance; this
information, like the port and server ID, must be unique.
• admin — which supplies information specific to the Administration Server instance; this is not
used when creating additional Directory Server server instances or setting up a single
Directory Server instance.
The format of the .inf file is as follows:
[General]
directive=value
directive=value
directive=value
...
[slapd]
directive=value
directive=value
directive=value
...
[admin]
directive=value
directive=value
directive=value
The .inf file directives are explained more in the following sections.
• Section 3.5.1, “.inf File Directives”
• Section 3.5.2, “Sample .inf Files”
3.5.1. .inf File Directives
Directive Description Required
FullMachineName Specifies the fully qualified
domain name of the machine
on which you are installing
the server. The default is the
local host name.
SuiteSpotUserID Specifies the user name as
which the Directory Server
instance runs. This parameter
does not apply to the user as
which the Administration
No
No
89
Page 100

Chapter 6. Advanced Setup and Configuration
Directive Description Required
Server runs. The default is
user nobody on Linux and
Solaris and daemon on
HP-UX. This should be
changed for most
deployments.
SuiteSpotGroup Specifies the group as which
the servers will run. The
default is group nobodyon
Linux and Solaris and daemon
on HP-UX. This should be
changed for most
deployments.
ConfigDirectoryLdapURL Specifies the LDAP URL that
is used to connect to your
configuration directory. LDAP
URLs are described in the
Directory Server
Administrator's Guide.
AdminDomain Specifies the administration
domain under which this
Directory Server instance is
registered. See Section 2.8,
“Administration Domain” for
more information about
administration domains.
No
Yes
No
ConfigDirectoryAdminID Specifies the user ID of the
user that has administration
privileges to the configuration
directory. This is usually
admin.
ConfigDirectoryAdminPwd Specifies the password for
the admin user.
No
Yes
Table 6.2. [General] Directives
Directive Description Required Example
ServerPort Specifies the port the
server will use for
LDAP connections.
For information on
selecting server port
90
No 389
 Loading...
Loading...