Page 1

HP BIOS Serial Console
User Guide
July 2004 (First Edition)
Part Number 372432-001
Page 2

© Copyright 2004 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Microsoft and Windows are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Intel is a trademark or registered trademark of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and
other countries.
Linux is a U.S. registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent
with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and
Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard
commercial license.
Hewlett-Packard Company shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained
herein. The information in this document is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind and is subject to
change without notice. The warranties for HP products are set forth in the express limited warranty
statements accompanying such products. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional
warranty.
HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
July 2004 (First Edition)
Part Number 372432-001
Audience Assumptions
This document is for the person who installs, administers, and troubleshoots servers and storage
systems. HP assumes you are qualified in the servicing of computer equipment and trained in
recognizing hazards in products with hazardous energy levels.
Page 3
3
Contents
Console Redirection Overview 5
Purpose.................................................................................................................................................5
Introduction.......................................................................................................................................... 5
BIOS Serial Console Overview................................................................................................ 6
EMS Support Overview............................................................................................................6
Initialization .........................................................................................................................................6
Connectivity.........................................................................................................................................6
Console Redirection Features ..............................................................................................................6
HP BIOS Serial Console/EMS Support Settings and Configuration 9
RBSU and BIOS Serial Console Configuration................................................................................... 9
Virtual Serial Port...................................................................................................................10
Terminal Emulation Support ..................................................................................................11
Baud Rate ...............................................................................................................................14
Port Settings............................................................................................................................14
Keystroke Emulation..........................................................................................................................15
Escape Sequences ..............................................................................................................................15
Character Translations in VT100 Mode.............................................................................................17
Operating System Support .................................................................................................................17
Emergency Management Services..................................................................................................... 18
Linux Red Hat 7 Serial Console Settings...........................................................................................19
Linux Red Hat 7 ATA Driver Settings ...................................................................................20
Linux Red Hat 7 NIC Driver Settings ....................................................................................20
Linux Red Hat 7 Services Configuration................................................................................20
Terminal Emulation Programs 20
Microsoft HyperTerminal Setup ........................................................................................................21
Acronyms and Abbreviations 29
Index 33
Page 4

Page 5

5
Console Redirection Overview
In This Section
Purpose ...........................................................................................................................................5
Introduction ....................................................................................................................................5
Initialization....................................................................................................................................6
Connectivity ...................................................................................................................................6
Console Redirection Features.........................................................................................................6
Purpose
The purpose of console redirection is to provide the capability to remotely
manage a server in a headless environment. Through BIOS Serial Console
redirection, you can see POST messages, navigate option ROM (such as ORCA)
setup menus, and use RBSU through a serial connection to the server COM port.
The local keyboard and monitor are no longer required to set up or configure the
system. The remote server setup and configuration can also be performed
remotely through the terminal server, iLO Management Processor, or RILOE
board. Some OSs support console redirection as well.
Introduction
Two separate technologies enable console redirection. The first, BIOS Serial
Console, is the focus of this document and can be enabled in the ROM. The other
is console redirection through the OS, such as EMS support, and requires OS
support and ROM support.
IMPORTANT: For documentation purposes, the local server refers to
the one that you are remotely configuring. Though this local server does
not require a keyboard and monitor, you will need a keyboard and
monitor on the system you are using to enter BIOS Serial Console
commands.
NOTE: This document is designed to provide information for BIOS
Serial Console on any compatible server. It is generic in nature and
therefore may contain options that are not valid on all servers.
Page 6

6 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
BIOS Serial Console Overview
BIOS Serial Console can be enabled in RBSU. By default, BIOS Serial Console
is disabled.
EMS Support Overview
EMS support is a Microsoft® feature for the Windows® Server 2003 OS, which
is enabled by default in the OS, but which also must be enabled in the system
ROM. By default, EMS support is disabled for ML and DL servers, and is
enabled for BL servers.
Refer to "Operating System Support (on page 17
using supported OSs.
Initialization
BIOS Serial Console initialization occurs during power-up or system reset,
before the first message is displayed on the screen.
Connectivity
A null modem cable should be connected to one of the serial ports on the server
for console redirection. Be sure to connect the cable to the serial port that
corresponds to the correct COM port on which BIOS Serial Console is enabled.
The default COM port is COM 1 for systems with BIOS Serial Console enabled
by default. This setup can be configured in RBSU.
Refer to "RBSU and BIOS Serial Console Configuration (on page 9
port settings.
Console Redirection Features
)" for more information about
)" for COM
The following console redirection features are discussed in further detail in "HP
BIOS Serial Console/EMS Support Settings and Configuration (on page 9
)":
Page 7

Console Redirection Overview 7
• RBSU and BIOS Serial Console Configuration (on page 9)
− Terminal Emulation Support (on page 11)
− Baud Rate (on page 14
)
− Port Settings (on page 14)
• Keystroke Emulation (on page 15)
− Escape Sequences (on page 15)
− Character Translation in VT100 Mode ("Keystroke Emulation" on page
15
)
• Operating System Support (on page 17
)
− Emergency Management Services (on page 18)
− Linux Red Hat ("Linux Red Hat 7 Serial Console Settings" on page 19)
• Terminal Emulation Programs (on page 20)
− Microsoft® HyperTerminal ("Microsoft HyperTerminal Setup" on page
)
21
Page 8

Page 9

9
HP BIOS Serial Console/EMS Support Settings and Configuration
In This Section
RBSU and BIOS Serial Console Configuration .............................................................................9
Keystroke Emulation ....................................................................................................................15
Escape Sequences.........................................................................................................................15
Character Translations in VT100 Mode .......................................................................................17
Operating System Support............................................................................................................17
Emergency Management Services................................................................................................18
Linux Red Hat 7 Serial Console Settings .....................................................................................19
RBSU and BIOS Serial Console Configuration
BIOS Serial Console supports console redirection of POST error messages and
configuration utilities and is disabled in the ROM by default. EMS support is
enabled in the OS by default, but also requires system ROM support. This section
takes you through RBSU configuration, basic OS initialization, and terminal
emulation for console redirection.
NOTE: On some newer servers, the BIOS Serial Console default will
be AUTO instead of disabled. During the boot process, the server will
check for the presence of a VT100 compatible client running at 9600
Baud connected to the server and automatically will enable the BIOS
Serial Console for that boot if one is found. This eliminates the need to
run RBSU with a local keyboard and monitor attached to enable the
BIOS Serial Console feature.
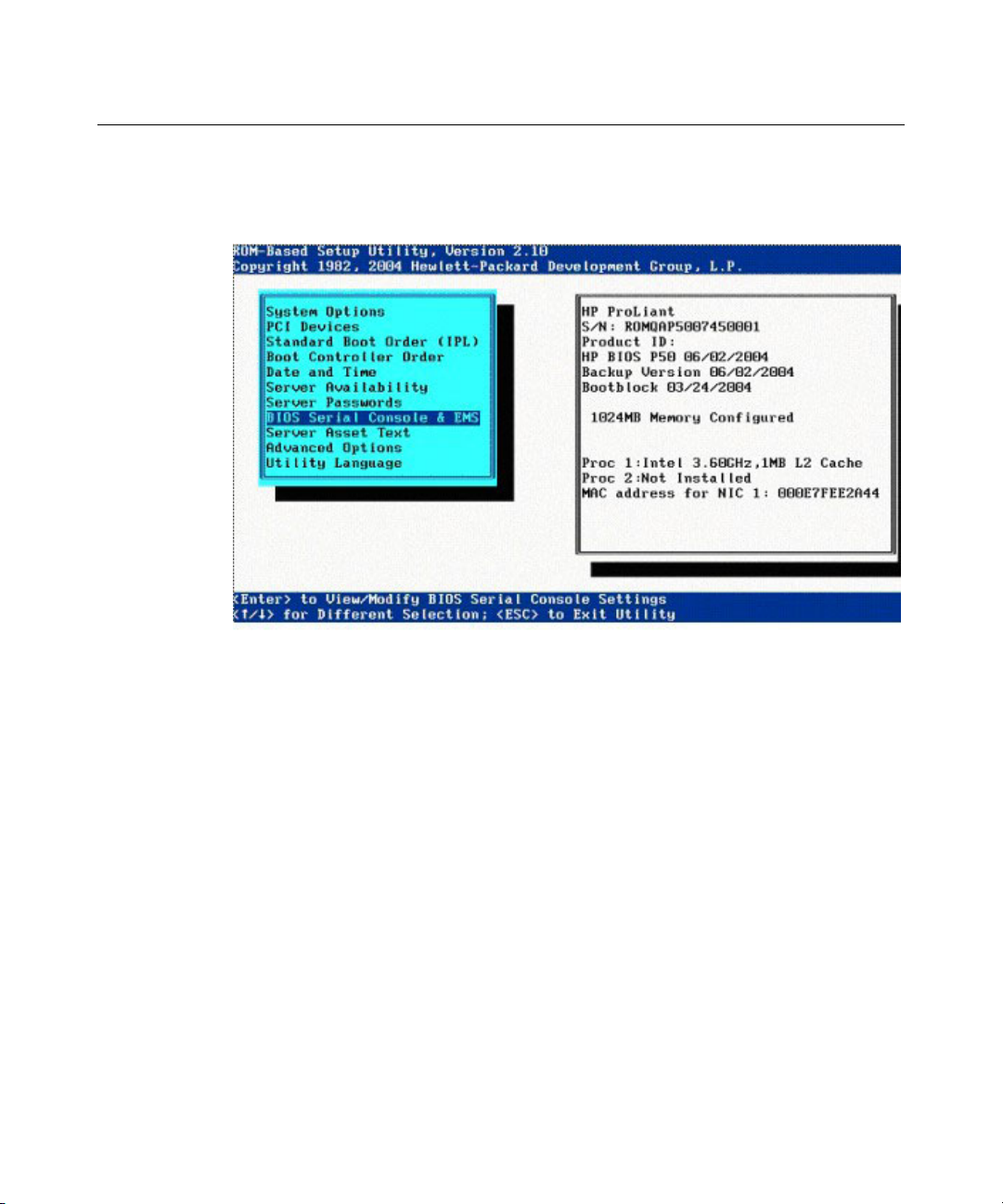
RBSU displays and modifies the system configuration settings of a server. The
figures in this section show settings for BIOS Serial Console options on the
RBSU menu. Except for the following figure, these screens are shown with
ANSI emulation.
Press the Enter key while BIOS Serial Console is selected on the RBSU main
menu to display the options.
Page 10
10 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
IMPORTANT: Settings take effect on the next RBSU-prompted reboot,
but you must disconnect and then reconnect for new settings to take
effect on both local and remote machines.
Virtual Serial Port
When enabled, Virtual Serial Port provides remote access through the iLO
management controller to BIOS Serial Console.
Page 11

HP BIOS Serial Console/EMS Support Settings and Configuration 11
For detailed information about iLO configurations, refer to the HP Integrated
Lights-Out User Guide on the Documentation CD or to the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/lights-out
).
Terminal Emulation Support
BIOS Serial Console supports ANSI and VT100 terminal emulation. Although
the screens displayed in this guide show the ANSI console for clarity, VT100 is
supported by all terminal emulation programs. It should be chosen if the terminal
emulation program is running in VT100 mode. BIOS Serial Console will support
a CLI for RBSU and other embedded ROM utilities on select new servers for
faster, more compatible display with VT100 and compatible terminals. On these
newer servers, BIOS Serial Console support will default to Enabled/VT100/9600
Baud for maximum compatibility with VT100 users. ANSI emulation and the
menu-based RBSU interface may not be supported when BIOS Serial Console is
enabled or in use due to limited compatibility with VT100. The menu-based
RBSU interface will continue to be supported automatically in modes in which
BIOS Serial Console is disabled or not in use. Refer to the HP ROM-Based Setup
Utility User Guide, available on the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/servers/smartstart
), for more information on CLI.
Page 12

12 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
Press the Enter key while Terminal Emulation Mode is selected to display the
emulation mode options. Select the option that matches the terminal emulation
program being used.
BIOS Serial Console is designed to support most terminal emulation programs.
No special version of a terminal emulation program is required, although the
emulation modes supported may vary by vendors. To avoid compatibility
problems, only the core set of VT100 and ANSI terminal emulation is used in
BIOS Serial Console. Although this limits some capabilities, this protocol
guarantees the maximum compatibility across different platforms and vendors.
NOTE: On some newer servers, emulation will be limited to VT100
compatibility.
Default settings for terminal emulation and baud rate can be changed through the
ProLiant BL e-Class Integrated Administrator for the current session only. Refer
to the HP ProLiant BL e-Class Integrated Administrator User Guide for more
information.
Page 13

HP BIOS Serial Console/EMS Support Settings and Configuration 13
Some new servers, which use CLI and are configured using BIOS Serial
Console, will display a command prompt screen.
Page 14

14 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
Baud Rate
Press the Enter key while BIOS Serial Console Baud Rate is selected to display
the baud rate. The default setting is 9600 when BIOS Serial Console is enabled
by default. This setting can be configured in RBSU.
Port Settings
Press the Enter key while BIOS Serial Console Port is selected to display the
port settings. When BIOS Serial Console is enabled by default, the default port
setting is COM1. BIOS Serial Console is disabled by default. To enable port
settings, select the COM port used for serial console redirection.
Page 15

HP BIOS Serial Console/EMS Support Settings and Configuration 15
IMPORTANT: Enabling port settings enables console redirection only
at POST commands and configuration utilities. For information on
console redirection of the OS, refer to "Operating System Support (on
page 17
)."
NOTE: Systems with iLO require version 1.05 iLO firmware or greater
to run BIOS Serial Console.
Keystroke Emulation
Because not all terminal emulation programs support function keys or special
characters, certain keystroke sequences are required for some commands.
Escape Sequences
BIOS Serial Console enables you to manually input unsupported keystrokes by
entering escape sequences. Each character must be entered within 2 seconds of
pressing and holding down the Esc key to emulate the escape sequence.
Page 16

16 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
NOTE: You must use escape sequences if the emulation program does
not support function keys, but they also work if the emulation program
does support function keys. Refer to the terminal emulation guide to be
sure that you may use function keys.
Function Keys
Keyboard Entry Defined As
<ESC>1 F1
<ESC>2 F2
<ESC>3 F3
<ESC>4 F4
<ESC>5 F5
<ESC>6 F6
<ESC>7 F7
<ESC>8 F8
<ESC>9 F9
<ESC>0 F10
<ESC>! F11
<ESC>@ F12
Control Keys
Keyboard Entry Defined As
<ESC>h Home
<ESC>k End
<ESC>+ Insert
<ESC>- Delete
<ESC>? Page Up
<ESC>/ Page Down
Reset Key
Page 17

HP BIOS Serial Console/EMS Support Settings and Configuration 17
Keyboard Entry Defined As
<ESC>R<ESC>r<ESC>R System Reset
Character Translations in VT100 Mode
The VT100 protocol does not support special characters such as line draw
characters. These characters are translated so that they can be displayed on the
VT100 screen. Character translation is used for improved VT100 screen display
and has no effect on functionality of BIOS Serial Console.
Currently, the special characters in the table are translated into VT100 characters
using VT100 protocol.
Special Character Translated Into
Line draw character upper left corner +
Line draw character lower left corner +
Line draw character upper right corner +
Line draw character lower right corner +
Line draw character horizontal line -
Line draw character vertical line |
Operating System Support
Some OSs offer console redirection within the OS. Microsoft® Windows®
Server 2003 and Linux can be configured for console redirection.
Page 18

18 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
When Enable Local is selected, the OS redirects through the local serial port.
When Enable Remote is selected, the OS redirects through iLO or RILOE II.
Data becomes available through the browser configured for iLO instead of
through the serial port. Enabling remotely requires iLO 1.10 firmware or later.
NOTE: Currently, Microsoft® Windows® Server 2003, Linux, and
FreeBSD are the only OSs with console redirection support. Linux and
FreeBSD allow for generic Serial Console sessions, and Windows®
Server 2003 includes EMS.
NOTE: The Japanese character set (multi-byte character set) does not
display on BIOS Serial Console screens. Do not select Japanese as the
language display.
Emergency Management Services
EMS support provides input/output support for all Microsoft® Windows® kernel
components: the loader, setup, recovery console, OS kernel, blue screens, and the
Special Administration Console. The Special Administration Console is a text
mode management console available after Windows® Server 2003 OS has
initialized. For more information on EMS support, go to the Microsoft® website
(http://www.microsoft.com/hwdev/headless
).
Page 19

HP BIOS Serial Console/EMS Support Settings and Configuration 19
Microsoft® enables EMS support in the OS, but EMS support also requires
ROM support. EMS support, when enabled, assumes the serial port for
redirection and may cause interference with other devices attached to the serial
port. To avoid interference, EMS is disabled in the system ROM by default on
ML and DL servers. To enable this feature, Enable Local or Enable Remote must
be selected under the BIOS Serial Console/EMS Support menu in RBSU before
installing Windows® Server 2003. If you install Windows® Server 2003 with
EMS disabled, and later decide to enable it, perform the following steps to update
the boot.ini file:
1. Enable EMS in RBSU.
2. Run bootcfg/ems on/id 1.
3. Reboot.
Linux Red Hat 7 Serial Console Settings
If you are using an HP ProLiant BL e-Class server, each server blade maintains a
connection to COM 1, so they are primarily used remotely through the Integrated
Administrator. To enable BIOS Serial Console for Linux Red Hat 7 OS:
1. Remove the line:
message=/boot/message from /etc/lilo.conf
2. Add the following line to the Linux image specification in /ect/lilo.conf:
Append="console=tty0 console=ttyS0, 115200"
3. Run /sbin/lilo to make the changes take effect.
4. Add the following line to the end of /etc/inittab to enable agetty on COM1
(ttyS0):
7:12345:respawn:/sbin/agetty 115200 ttyS0 vt100
5. Set SAFE=yes in the file /etc/sysconfig/kudzu, so it does not probe the
serial port during initialization.
6. Add the following line to /etc/securetty to allow root to log in on the ttyS0:
ttyS0
7. Reboot the server blade with these new settings.
Page 20

20 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
Linux Red Hat 7 ATA Driver Settings
By default, Linux Red Hat 7.1 OS uses only the ATA driver in PIO mode for the
server blades ATA controller. Use the following change to set the driver to use
DMA and higher speeds (66 MHz/100 MHz):
1. Add ide0=ata66 to the LILO append line described in step 2 in Linux
Red Hat 7 Serial Console Settings (on page 19
Append="console=tty0 console=ttyS0, 115200
ide0=ata66"
2. Run /sbin/lilo to make the changes take effect.
Linux Red Hat 7 NIC Driver Settings
By default, Linux Red Hat 7.1 OS uses the eepro100 driver. HP has tested the
Intel® e100 driver and recommends changing to this driver. To change the
default driver, change the lines eepro100 in /etc/modules.conf to e100.
For example, networking lines in modules.conf are:
alias eth0 e100
alias eth1 e100
):
This change takes effect at the next reboot.
Linux Red Hat 7 Services Configuration
Change the runlevel configuration of the following services (if installed) since
they are not needed on HP ProLiant BL e-Class server blades:
Chkconfig --level 0123456 apmd off
Chkconfig --level 0123456 gpm off
Terminal Emulation Programs
Console redirection is supported using many terminal emulation programs. Any
terminal emulation program can be used with BIOS Serial Console and with OS
console redirection.
Page 21

Terminal Emulation Programs 21
Microsoft HyperTerminal Setup
Because Microsoft® HyperTerminal is a widely used terminal emulation
program, examples of HyperTerminal 6.3 setup screens follow to aid in the
initialization process. Be sure that the remote terminal screen settings match the
screens in this section. If using an emulation program other than HyperTerminal,
refer to the software reference material for settings information.
NOTE: For information on additional settings through Microsoft®
Windows Server 2003, go to the Microsoft® website
(http://www.microsoft.com/hwdev/headless
NOTE: Microsoft® HyperTerminal settings must match BIOS Serial
Console settings. Access the OS terminal settings or RBSU to change
the default settings.
1. To access the font screen, select the View menu from the HyperTerminal
main screen, and then click Font. Select Terminal.
).
2. Access connection settings from the HyperTerminal main screen by selecting
the File menu, and then clicking Properties.
Page 22

22 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
3. On the Connect To tab, click Configure to display the Port Settings tab.
NOTE: If using a notebook computer, the Connect using field should be
set to COM1 or COM2, depending on your configuration. COM1 is the
HP default setting.
Page 23

Terminal Emulation Programs 23
4. Select Port Settings. Then click OK to return to the Properties screen.
5. On the Properties screen, click the Settings tab.
Page 24

24 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
6. If using ANSI emulation, click Terminal Setup and select ANSI (if using
VT100 emulation, refer to step 9). ANSI is the default setting.
IMPORTANT: Both the remote and local machines must be set to the
same emulation.
Page 25

Terminal Emulation Programs 25
7. Select Terminal Settings.
8. Click OK to return to the Settings tab, and click OK again to complete the
HyperTerminal setup process.
Page 26

26 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
9. If using VT100 emulation, click Terminal Setup and select VT100.
IMPORTANT: If using VT100 emulation, the setting must be changed
from the default ANSI setting in RBSU.
Page 27

Terminal Emulation Programs 27
10. Select Terminal Settings. Click OK to return to the Settings tab.
11. On the Settings tab, click ASCII Setup.
Page 28

28 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
12. Deselect Wrap lines that exceed terminal width. Click OK to return to the
Settings tab. Then click OK to complete the HyperTerminal setup process.
Page 29

29
Acronyms and Abbreviations
ASR
Automatic Server Recovery
CLI
Command Line Interface
ConRep
Configuration Replication Utility
ECC
error checking and correcting
EMS
Emergency Management Services
IDE
integrated device electronics
iLO
Integrated Lights-Out
IMD
Integrated Management Display
Page 30

30 HP BIOS Serial Console User Guide
IPL
initial program load
IRQ
interrupt request
MPS
multi-processor specification
NIC
network interface controller
NMI
non-maskable interrupt
ORCA
Option ROM Configuration for Arrays
PCI
peripheral component interface
POST
Power-On Self-Test
PXE
preboot eXecution environment
RBSU
ROM-Based Setup Utility
Page 31

Acronyms and Abbreviations 31
RILOE
Remote Insight Lights-Out Edition
RILOE II
Remote Insight Lights-Out Edition II
Page 32

Page 33

33
Index
A
ASR (Automatic Server Recovery) 29
ATA driver settings 20
B
baud rate 14
BIOS Serial Console 5, 6
C
COM port 6
commands 15
connectivity 6
console redirection, features 6
control keys 15
E
Emergency Management Services 18
EMS Console 6
escape sequences 15
N
NIC (network interface controller) 30
O
operating systems 17
P
port settings 14
R
RBSU (ROM-Based Setup Utility) 9
RBSU configuration 9
reset keys 15
T
terminal emulation support 11, 20
V
Virtual Serial port 10
VT100 17
F
function keys 15
K
keystroke emulation 15
L
Linux Red Hat 7 19, 20
M
Microsoft HyperTerminal 21
 Loading...
Loading...