HP PROLIANT DL560 User Manual

ProLiant DL560 server technologies
technology brief
Abstract.............................................................................................................................................. 3
Introduction......................................................................................................................................... 3
System architecture .............................................................................................................................. 3
Processor subsystem ......................................................................................................................... 5
400-MHz front side bus ................................................................................................................ 6
NetBurst Microarchitecture ............................................................................................................ 6
Hyper-Threading technology .......................................................................................................... 7
Multilevel cache system ................................................................................................................. 8
Memory subsystem........................................................................................................................... 9
Advanced memory protection ......................................................................................................10
2-way interleaved memory .......................................................................................................... 10
I/O subsystem ............................................................................................................................... 10
Storage subsystem.......................................................................................................................... 11
Power and cooling ......................................................................................................................... 11
Racking technology............................................................................................................................ 12
Hardware reusability.......................................................................................................................... 13
Deployment, management, and troubleshooting technologies.................................................................. 13
Deployment technologies ................................................................................................................ 13
SmartStart ................................................................................................................................. 13
SmartStart Scripting Toolkit.......................................................................................................... 14
Rapid Deployment Pack .............................................................................................................. 14
Management technologies .............................................................................................................. 14
Sensors and indicators................................................................................................................ 15
Insight Manager 7...................................................................................................................... 15
Lights-out technology................................................................................................................... 15
ActiveUpdate............................................................................................................................. 16
Troubleshooting technologies........................................................................................................... 16
Survey Utility.............................................................................................................................. 16
Performance Management Pack ................................................................................................... 17

Consolidation technologies ................................................................................................................. 17
Resource Partitioning Manager ........................................................................................................ 17
VMware GSX and ESX Server ......................................................................................................... 18
Conclusion........................................................................................................................................ 18
For more information.......................................................................................................................... 19
Call to action .................................................................................................................................... 19

Abstract
)
The HP ProLiant DL560 server is a groundbreaking, ultra-dense 4-way server designed for
environments that require a high concentration of servers in a single rack. This server delivers
enterprise class performance in a compact 2U form factor that uses 50 percent less rack space than
most other enterprise servers on the market. This paper describes the system architecture and the
many technologies HP implemented and supports in the ProLiant DL560 server to make it an excellent
platform for server consolidation.
Introduction
With continuous demands for increased computing power, a growing number of Information
Technology (IT) centers are searching for cost-effective ways to deploy more servers within their
existing space and to stem rising power and air conditioning costs. The ProLiant DL560 server is a
groundbreaking, ultra-dense 4-way server designed for environments that require high levels of
computing power while maintaining maximum cooling and power efficiency. The ProLiant DL560
server (Figure 1) delivers enterprise class performance in a compact 2U form factor that uses 50
percent less rack space than most other enterprise servers on the market. ProLiant management
technology such as remote administration from a standard web browser and Insight Manager event
and configuration management significantly reduce total cost of ownership.
This technology brief describes the system architecture and discusses the many technologies that make
the ProLiant DL560 an excellent platform for server consolidation.
Figure 1. ProLiant DL560 server, front view
2U (3.5”
System architecture
The system architecture is the key to the high level of performance and efficiency of the ProLiant
DL560 server. This server shares the same chipset and basic architecture as the ProLiant DL380 G3
server; but it features the much more powerful Intel® Xeon MP processor. The system is based on the
industry-standard ServerWorks Grand Champion LE (GC-LE) chipset. HP is the first vendor to use this
chipset to develop a 4-processor server, and ServerWorks fully supports HP’s 4-way implementation
of the chipset.
Intel designed the GC-LE chipset (Figure 2) primarily as a highly scalable system I/O solution for the
volume 2-way server market.
4-way ProLiant DL560 server because it supports the desired system features economically. The GC-LE
chipset provides the combination of performance, scalability, and power efficiency customers need,
and it costs significantly less than the ServerWorks Grand Champion HE chipset.
1
After evaluating chipset options, HP chose the GC-LE chipset for the
1
ServerWorks Product Brief, www.serverworks.com/products/GCLE.html.
3
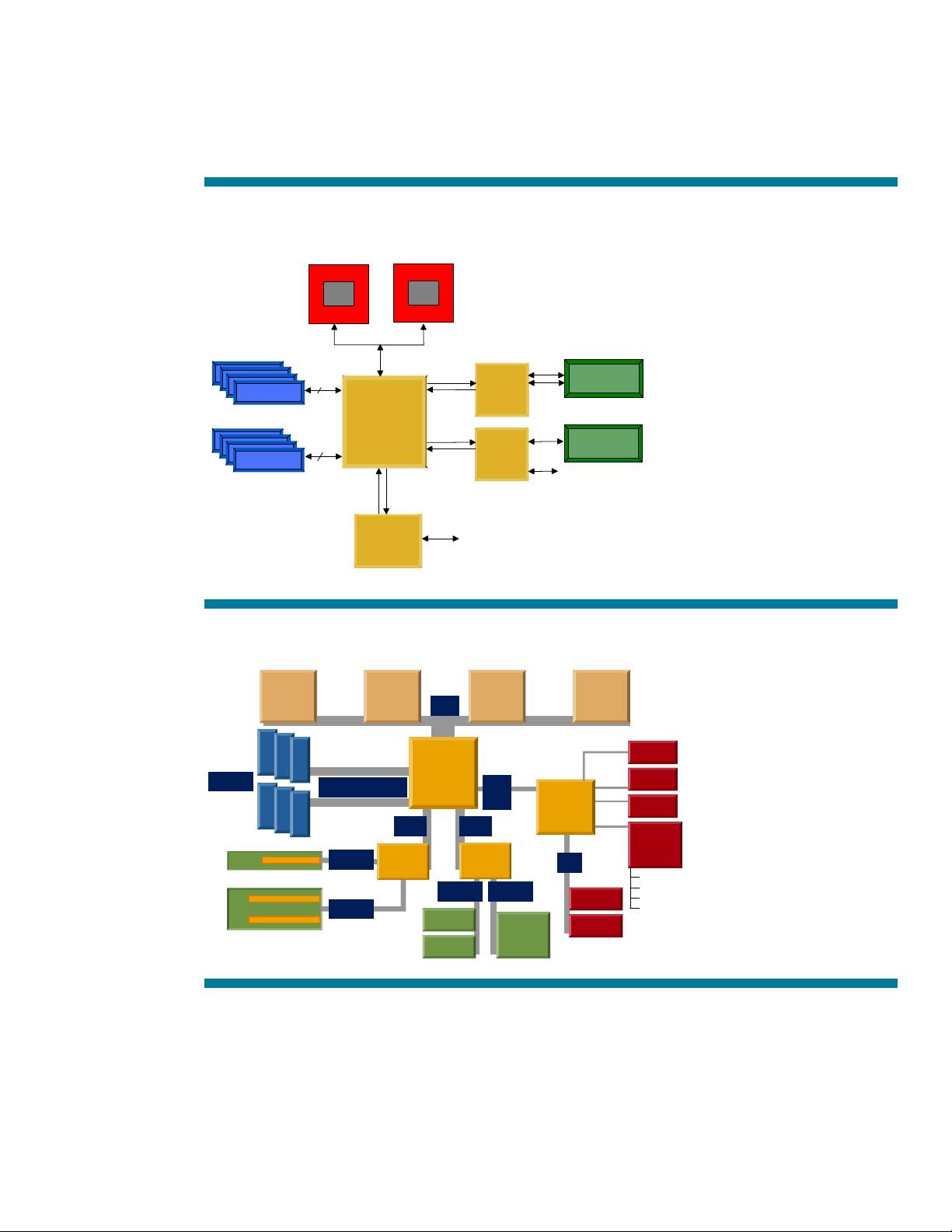
For hyper-dense servers, form factor dictates the memory footprint and I/O slot count. The GC-LE
chipset offers an integrated memory controller that reduces board space and cost while offering
excellent performance for memory capacities up to 12 gigabytes (GB). In the ProLiant DL560 server,
use of direct-attach memory (Figure 3) eliminates the need for and cost of memory buffers like those
used in the ProLiant DL580 Generation 2 server (Figure 4).
Figure 2. ServerWorks Grand Champion LE chipset architecture
Pentium 4 Xeon Processors
PCI-X
DDR 200
DDR 200
8B
8B
GC LE
CMIC-
CIOB-X
L
IMBus
E
CIOB-X
BMC5701
BMC5701
CSB5
Legacy I/O
32-bit PCI
Figure 3. Block diagram of the ProLiant DL560 system architecture
Xeon with
2MB L3
cache
Dual interleaved
133MHz
100MHz
CIOB-X2
Xeon with
FSB
CMIC-LE
IMB 2 IMB 1
CIOB-X2
100MHz 100MHz
NC7781
NC7781
2MB L3
cache
Thin
IMB
CSB5
Smart
Array
5i Plus
200MHz
PCI-XPCI-X
PCI-XPCI-X
Xeon with
2MB L3
cache
PC2100
PC2100
PC2100
PC2100
PC2100
PC2100
Xeon with
2MB L3
PCI
Rage XL
cache
iLO
USB (2)
IDE
ROM
PC87413
Super I/O
Keyboard
Mouse
Serial
Diskette
4
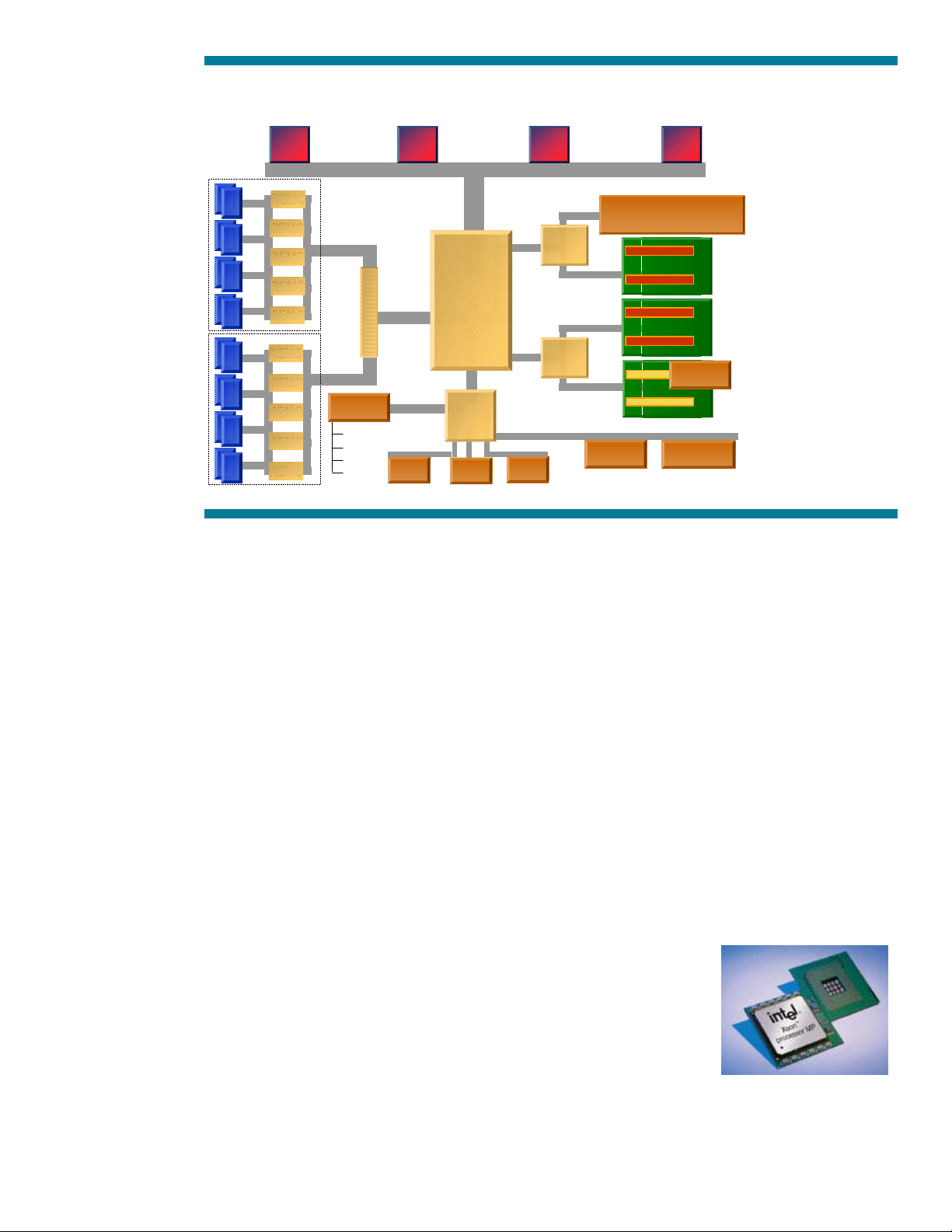
Figure 4. Block diagram of the ProLiant DL580 G2 system architecture
Xeon Xeon Xeon Xeon
Frontside Bus
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
CMIC
IMB
CIOB-X
Embedded Smart Array
5i Plus Controller
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
REMC
SuperI/O
Keyboard
Mouse
Serial
Diskette
Quick Switches
LPC
X-Bus
ROM
CSB5
USB
IMB
Thin IMB
IDE
CIOB-X
PCI Compatibility Bus
iLO
NC7770NC7770
RagePro XL
The ProLiant DL560 server has a tool-free and virtually cable-free internal design. Essential features of
the server architecture include:
• Up to four Intel Xeon MP processors
• 400-MHz front side bus
• Intel Hyper-Thread technology for optimized performance
• DDR SDRAM memory with Advanced Memory Protection technology
• PCI-X architecture
• Wide Ulltra320 SCSI technology
• Gigabit networking technology
• Embedded technologies
• Hot-plug technology
• Flexibility of high line or low line AC power
• Support for today’s leading industry-standard operating systems
Processor subsystem
Models of the ProLiant DL560 server ship standard with one or two Intel
Xeon processors MP (right). For first generation DL560 servers,
customers may choose from available processor speeds of 1.50, 1.90,
2.00, 2.5, or 2.8 gigahertz (GHz). The 400-MHz system bus, which is
quad-pumped and runs off a 100-MHz system bus clock, provides data
transfer rates of up to 3.2 gigabytes per second (GB/s).
The Intel Xeon Processor MP is manufactured using a 130-nanometer
(0.13-micron) process to allow higher frequencies and better
performance. The term 0.13 micron refers to the circuit (feature) size.
By reducing the feature size, processor manufacturers can pack more
Intel Xeon MP processor
5
transistors into the circuit. Feature size is a major limiting factor in processing speed: As the feature
size decreases, the processing speed increases and the power requirements decrease. The
0.13-micron Xeon processor has a smaller feature size and faster circuitry than 0.18-micron Intel
processors.
HP manufactures the DL560 microprocessor/heatsink assembly as a single piece. It includes an
alignment mechanism to prevent damage to the processor during installation and pin protection to
prevent damage when the processor is placed on a flat surface.
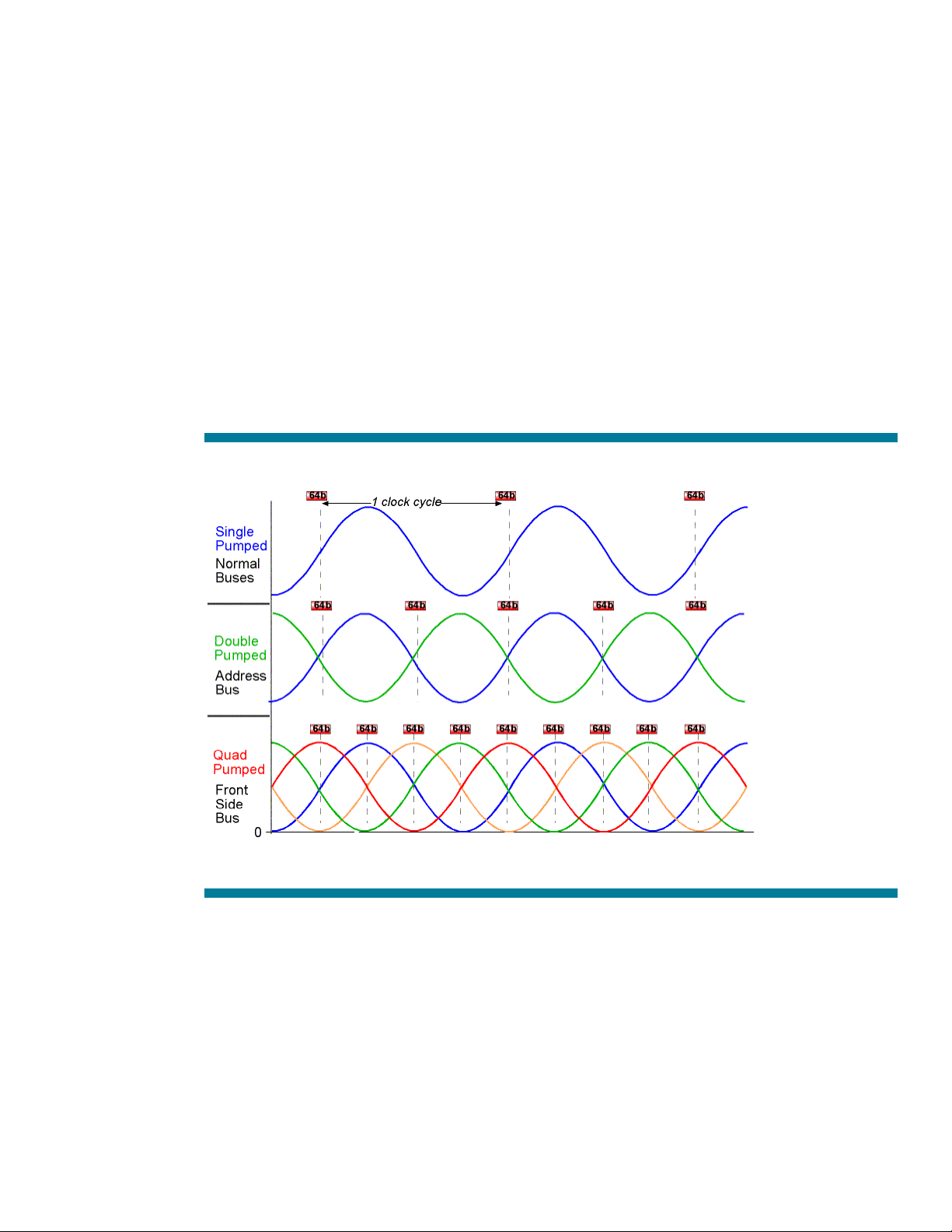
400-MHz front side bus
All data transfers go to and from the processor over the front side bus (FSB). The Intel Xeon processor
MP has a 64-bit, quad-pumped bus running at 100 MHz. A normal (single-pumped) bus sends, or
latches, data out once per clock cycle on the rising or falling edge of the bus clock signal. A quadpumped bus latches data at four times the rate of a normal bus (Figure 5). This faster rate is achieved
by means of four overlapping clock strobes, each operating 90 degrees out of phase with the next.
Data is transmitted on the rising edge of each of the four strobes, four times per clock cycle. This
makes it possible to transfer 3.2 GB/s of data on a 100-MHz FSB, which is triple the data rate of the
Pentium III FSB (1.06 GB/s with a 133-MHz FSB).
Figure 5. Comparison of clock signals for a quad-pumped and a single pumped 100-MHz front side bus
Note: Only the data is quad pumped on these buses. The address bus for the processor is double pumped.
NetBurst Microarchitecture
The Intel Xeon processor MP features Intel NetBurst microarchitecture. The NetBurst microarchitecture
supports MP speeds of up to 2.80 GHz and doubles the pipeline depth in the processor to enable
400-MHz core frequency. NetBurst microarchitecture also adds a Rapid Execution Engine and
Advanced Dynamic Execution. The Rapid Execution Engine allows the two integer Arithmetic Logic
Units (ALUs) in the processor to run at twice the core frequency, which increases performance by
allowing many integer instructions to execute in one half of the internal core clock period. Advanced
Dynamic Execution improves speculative execution and branch prediction internal to the processor.
6
 Loading...
Loading...