Page 1

HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect
Switch Web-based Interface
Reference Guide
February 2003 (First Edition)
Part Number 322859-001
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:19 AM
Page 2

© 2003 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Microsoft®, Windows®, and Windows NT® are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
Netscape Navigator is a U.S. trademark of Netscape Communications Corporation.
Hewlett-Packard Company shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein. The
information in this document is provided “as is” without warranty of any kind and is subject to change without
notice. The warranties for HP products are set forth in the express limited warranty statements accompanying such
products. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from HP required for possession, use or copying. Consistent with
FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical
Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
February 2003 (First Edition)
Part Number 322859-001
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:19 AM
Page 3

Contents
About This Guide
Technician Notes...........................................................................................................................................v
Where to Go for Additional Help.................................................................................................................vi
Telephone Numbers...............................................................................................................................vi
Chapter 1
Overview
Introduction ............................................................................................................................................... 1-1
Additional Information.............................................................................................................................. 1-1
Accessing the Switch Modules.................................................................................................................. 1-2
Connecting using the Web-based Interface............................................................................................... 1-6
Configuring the Switch Modules............................................................................................................... 1-8
Chapter 2
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Overview ................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
Saving Changes ......................................................................................................................................... 2-1
Managing User Accounts .......................................................................................................................... 2-2
Configuring the Remote Management IP Interface Settings..................................................................... 2-4
Setting the Remote Management IP Interface Settings ...................................................................... 2-5
Displaying Basic Switch Module Information .......................................................................................... 2-6
Configuring Advanced Switch Module Features ...................................................................................... 2-9
Configuring Port Settings........................................................................................................................ 2-11
Configuring Port Mirroring ..................................................................................................................... 2-13
Configuring Port Trunking ...................................................................................................................... 2-14
Considerations when Creating a Port Trunking Group..................................................................... 2-15
Configuring IGMP Snooping .................................................................................................................. 2-16
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol Settings......................................................................................... 2-18
Setting Spanning Tree Parameters on the Switch Module Level...................................................... 2-19
Setting Spanning Tree Parameters on the Port Level ....................................................................... 2-20
Configuring Static (Destination Address) Filtering Table ...................................................................... 2-22
Adding Unicast Filter Actions .......................................................................................................... 2-23
Adding Multicast Filtering................................................................................................................ 2-23
Configuring VLANs................................................................................................................................ 2-24
Default VLAN .................................................................................................................................. 2-25
Setting the Port VLAN ID for a Port ................................................................................................ 2-26
Enabling Ingress Filtering on a Per Port Basis ................................................................................. 2-27
Configuring Bandwidth........................................................................................................................... 2-29
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide iii
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:19 AM
Page 4

Contents
Configuring the Restart Ingress Bandwidth Settings ........................................................................2-30
Displaying the Current Ingress Bandwidth Table .............................................................................2-30
Configuring the Restart Egress Bandwidth Settings .........................................................................2-31
Displaying the Current Egress Bandwidth Table ..............................................................................2-31
Configuring the Thresholds of Broadcast, Multicast, and DA-Unknown Storm Prevention or
Monitoring.........................................................................................................................................2-32
Configuring Class of Service, Default Port Priority, and Traffic Class...................................................2-32
Setting Port Priority........................................................................................................................... 2-33
Setting Traffic Class..........................................................................................................................2-34
Setting Class of Service..................................................................................................................... 2-35
Configuring Port Security ........................................................................................................................ 2-36
Configuring Priority MAC Addresses .....................................................................................................2-37
Configuring Switch Module Date and Time............................................................................................2-38
Setting the Current Time or Enabling SNTP..................................................................................... 2-38
Setting the Time Zone and Daylight Saving Time............................................................................2-40
Configuring the Security IP .....................................................................................................................2-42
Configuring SNMP Manager ...................................................................................................................2-43
Configuring Trap Manager ......................................................................................................................2-44
Monitoring Switch Module Functions .....................................................................................................2-45
Monitoring the Switch Module using the Active Switch Graphic ....................................................2-45
Monitoring Port Utilization ............................................................................................................... 2-46
Monitoring Port Packet Analysis.......................................................................................................2-47
Monitoring Port Error Packets...........................................................................................................2-51
Monitoring Packet Size .....................................................................................................................2-56
Monitoring Trunk Utilization............................................................................................................2-58
Monitoring MAC Address Forwarding Table...................................................................................2-60
Monitoring IGMP Snooping Table ...................................................................................................2-61
Monitoring Dynamic Group Registration .........................................................................................2-62
Monitoring VLAN Status..................................................................................................................2-62
Using System Utilities .............................................................................................................................2-63
Upgrading Firmware .........................................................................................................................2-63
Downloading a Configuration File from a TFTP Server................................................................... 2-64
Uploading a Configuration File to TFTP Server...............................................................................2-65
Uploading Switch History Log..........................................................................................................2-66
Displaying Switch Module History...................................................................................................2-67
Performing a Ping Test......................................................................................................................2-68
Resetting the Switch Module Configuration to Factory Defaults............................................................2-69
Rebooting the Switch Module .................................................................................................................2-70
Setting the Web Connection Timeout......................................................................................................2-70
Logging Out.............................................................................................................................................2-70
Index
iv HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:19 AM
Page 5

This reference guide can be used when configuring the interconnect switch using the
Web-based interface
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury from electric shock and hazardous
energy levels, only authorized service technicians should attempt to repair this
equipment. Improper repairs can create conditions that are hazardous.
Technician Notes
WARNING: Only authorized technicians trained by HP should attempt to repair this
equipment. All troubleshooting and repair procedures are detailed to allow only
subassembly/module-level repair. Because of the complexity of the individual boards
and subassemblies, no one should attempt to make repairs at the component level or
to make modifications to any printed wiring board. Improper repairs can create a safety
hazard.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury from electric shock and hazardous
energy levels, do not exceed the level of repairs specified in these procedures.
Because of the complexity of the individual boards and subassemblies, do not attempt
to make repairs at the component level or to make modifications to any printed wiring
board. Improper repairs can create conditions that are hazardous.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to the equipment:
• Disconnect power from the system by unplugging all power cords from the power
supplies.
• Do not disable the power cord grounding plug. The grounding plug is an important
safety feature.
About This Guide
• Plug the power cord into a grounded (earthed) electrical outlet that is easily
accessible at all times.
CAUTION: To properly ventilate the system, you must provide at least 7.6 cm (3.0 in.) of
clearance at the front and back of the server.
CAUTION: The computer is designed to be electrically grounded (earthed). To ensure proper
operation, plug the AC power cord into a properly grounded AC outlet only.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide v
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:19 AM
Page 6

About This Guide
NOTE: Any indications of component replacement or printed wiring board modifications may void any
warranty.
Where to Go for Additional Help
In addition to this guide, the following information sources are available:
• HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch User Guide
• HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Command Line Interface Reference
Guide
• HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Menu-driven Interface Reference
Guide
• Service Quick Reference Guide
• Service training guides
• Service advisories and bulletins
• QuickFind information services
• Insight Manager software
Telephone Numbers
For the name of your nearest HP authorized reseller:
• In the United States, call 1-800-345-1518.
• In Canada, call 1-800-263-5868.
For HP technical support:
• In the United States and Canada, call 1-800-652-6672.
• Outside the United States and Canada, refer to
www.hp.com
vi HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:19 AM
Page 7

Introduction
The ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch provides two console management
interfaces and a Web-based management interface. The command line interface (CLI) and
menu-driven interface allow you to set up and control the switch modules using either the
serial or Ethernet ports on the switch. The embedded Web-based (HTML) interface allows
users to manage each switch module from anywhere on the network through a standard
browser, such as Netscape Navigator or Microsoft® Internet Explorer. The Web browser acts
as a universal access tool and can communicate directly with the switch modules using the
HTTP protocol.
NOTE: Your browser window may differ compared with the screen shots in this guide.
The Web-based management interface and the console management interfaces are different
ways to access and configure the same internal switching software. All settings encountered
in Web-based management are the same as those found in the console management program.
1
Overview
This guide describes how to use the Web-based interface to access the switch modules,
change their settings, and monitor their operation.
Additional Information
Additional information about installing and configuring the interconnect switch is available in
the following guides, which are located on the ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect
Switch Management System Utilities and User Documentation CD.
•
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch User Guide
•
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Command Line Interface Reference
Guide
•
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Menu-driven Interface Reference
Guide
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 1-1
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:21 AM
Page 8

Overview
Accessing the Switch Modules
Before you can connect to a switch module using the Web-based interface, you must set up
the IP address. By default, if there is a DHCP server on the network, a switch module obtains
the IP address automatically. You can locate the IP address by accessing the switch module
through the Integrated Administrator. The IP address displays on the switch module logon
screen.
If there is no DHCP server on the network, access each switch module through the Integrated
Administrator and configure the IP address.
NOTE: The Integrated Administrator must be configured before you can use it to access and configure
the interconnect switch. For information on how to configure the Integrated Administrator, refer to the
“Configuring the Integrated Administrator” section in the HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect
Switch User Guide.
Access the switch modules from the Integrated Administrator command line interface, using
one of the following methods:
• • If you have already logged into the Integrated Administrator as the “Administrator,” you
can connect to either switch module console by typing one of the following commands:
connect switch a to access Switch A
or
connect switch b to access Switch B
If you have not logged on to the Integrated Administrator, you can type one of two
special logon accounts to access the switch module consoles directly, depending on
whether you want to access Switch A or Switch B. At the login prompt type in both the
user name and password as either:
switcha
or
switchb
The logon screen for Switch A or Switch B will now be displayed.
1-2 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:21 AM
Page 9

Overview
The interconnect switch logon screen displays the name of the switch module (Switch A or
Switch B), the MAC address, and the IP address for the switch module.
If the IP address displays, use this address to access the switch module through your
Web-based browser. Refer to the “Connecting using the Web-based Interface” section later in
this chapter.
If the IP address does not display on the logon screen
1. Leave the Username field blank and press the Tab key.
2. Leave the Password field blank and press the Enter key. The main menu for the switch
module is displayed.
IMPORTANT: The interconnect switch does not have any initial user names or passwords set. HP
recommends that after logging on, you create at least one Root-level user as the switch
administrator. (Refer to Table 2-1 in Chapter 2 for an explanation of user privileges.) If you forget
your password after it has been set up, call HP Customer Support for assistance.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 1-3
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:21 AM
Page 10
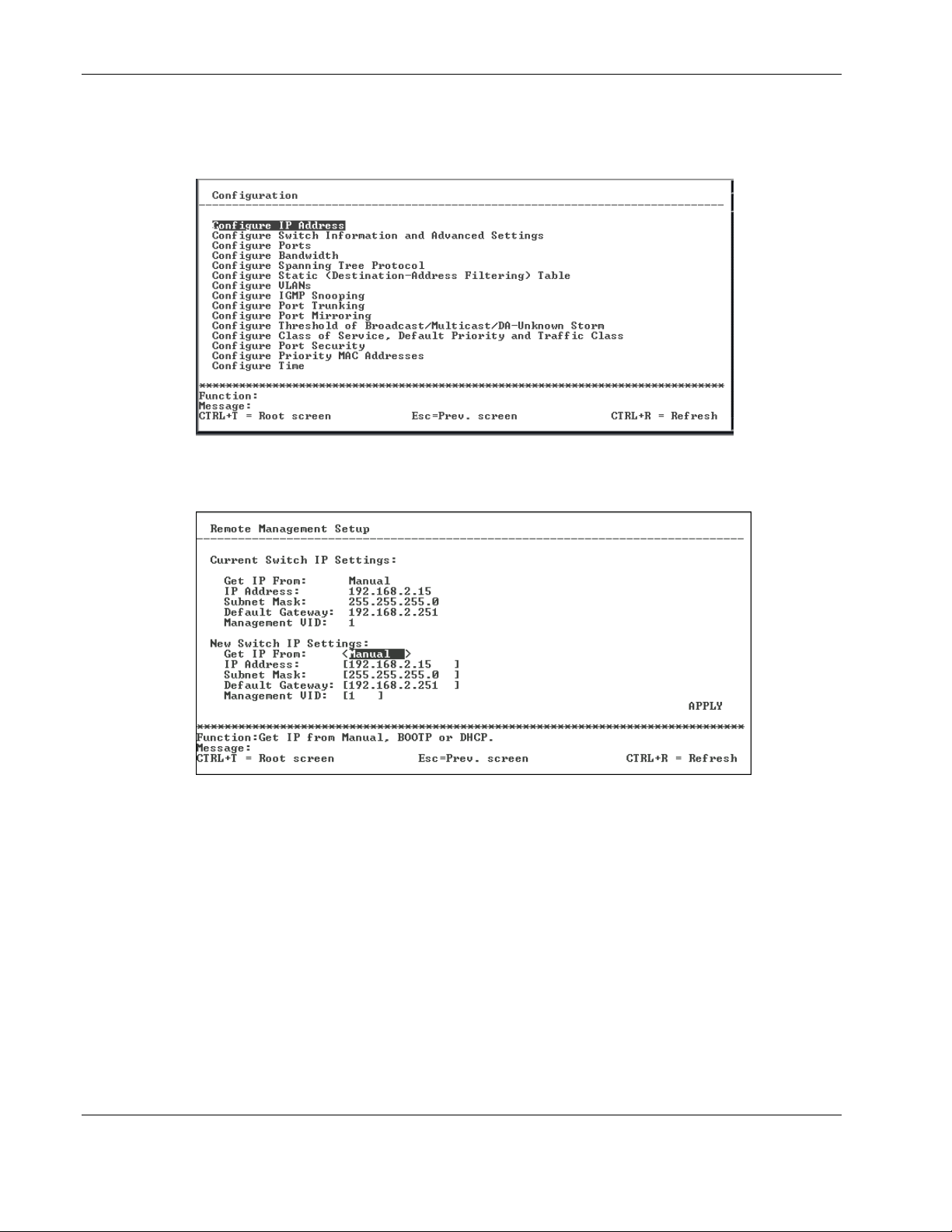
Overview
3. Highlight Configuration on the main menu.
4. Press the Enter key. The Configuration menu is displayed.
5. Highlight Configure IP Address from the Configuration menu.
6. Press the Enter key. The Remote Management Setup screen is displayed.
The Remote Management Setup screen lets you specify how the switch module will be
assigned an IP address. The fields listed under the Current Switch IP Settings heading
are those that are currently being used by the switch module.
1-4 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:21 AM
Page 11

Overview
7. Toggle the Get IP From field to select from Manual, BOOTP, or DHCP. This action
selects how the switch module will be assigned an IP address.
— BOOTP—The switch module sends out a BOOTP broadcast request. The BOOTP
protocol allows IP addresses, network masks, and default gateways to be assigned by
a central BOOTP server. If this option is set, the switch module first looks for a
BOOTP server to provide it with this information.
— DHCP—The switch module sends out a DHCP broadcast request. The DHCP
protocol allows IP addresses, network masks, and default gateways to be assigned by
a DHCP server. If this option is set, the switch module first looks for a DHCP server
to provide it with this information.
— Manual—This option allows the entry of an IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway for the switch module. The data in these fields should be of the form
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where each xxx is a number between 0 and 255. This address should
be a unique address on the network assigned for use by the Network Administrator.
The fields that require entries under this option include:
— Subnet Mask—A Bitmask that determines the extent of the subnet that the
switch module is on. The value should be 255.0.0.0 for a Class A network,
255.255.0.0 for a Class B network, and 255.255.255.0 for a Class C network, but
custom subnet masks are allowed.
— Default Gateway—An IP address that determines where packets with a
destination address outside the current subnet should be sent. This is usually the
address of a router or a host acting as an IP gateway. If your network is not part
of an intranet, or you do not want the switch module to be accessible outside your
local network, you can leave this field blank.
If you select Manual, type the appropriate data into the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and
Default Gateway fields.
8. Type the VLAN ID (VID) of a VLAN that will have access to the Telnet manager in the
Management VID field. This ID will be the VID of the VLAN on which a management
station is located. Management of the switch module using Telnet or SNMP will be
isolated to this VLAN.
9. Highlight APPLY and press the Enter key to make the change effective.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the main menu.
10. Press the ESC key until you return to the main menu.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 1-5
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:21 AM
Page 12

Overview
11. Highlight Save Changes on the main menu.
12. Press the Enter key. The following screen is displayed to verify that your new settings
have been saved to NVRAM.
After the configuration settings have been saved to NVRAM, they become the default
settings for the switch module. These settings are then used every time the GbE Interconnect
Switch is rebooted.
Connecting using the Web-based Interface
Once the IP address has been set on the switch module, you can use the Web-based interface
to connect to the switch module.
1-6 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:21 AM
Page 13
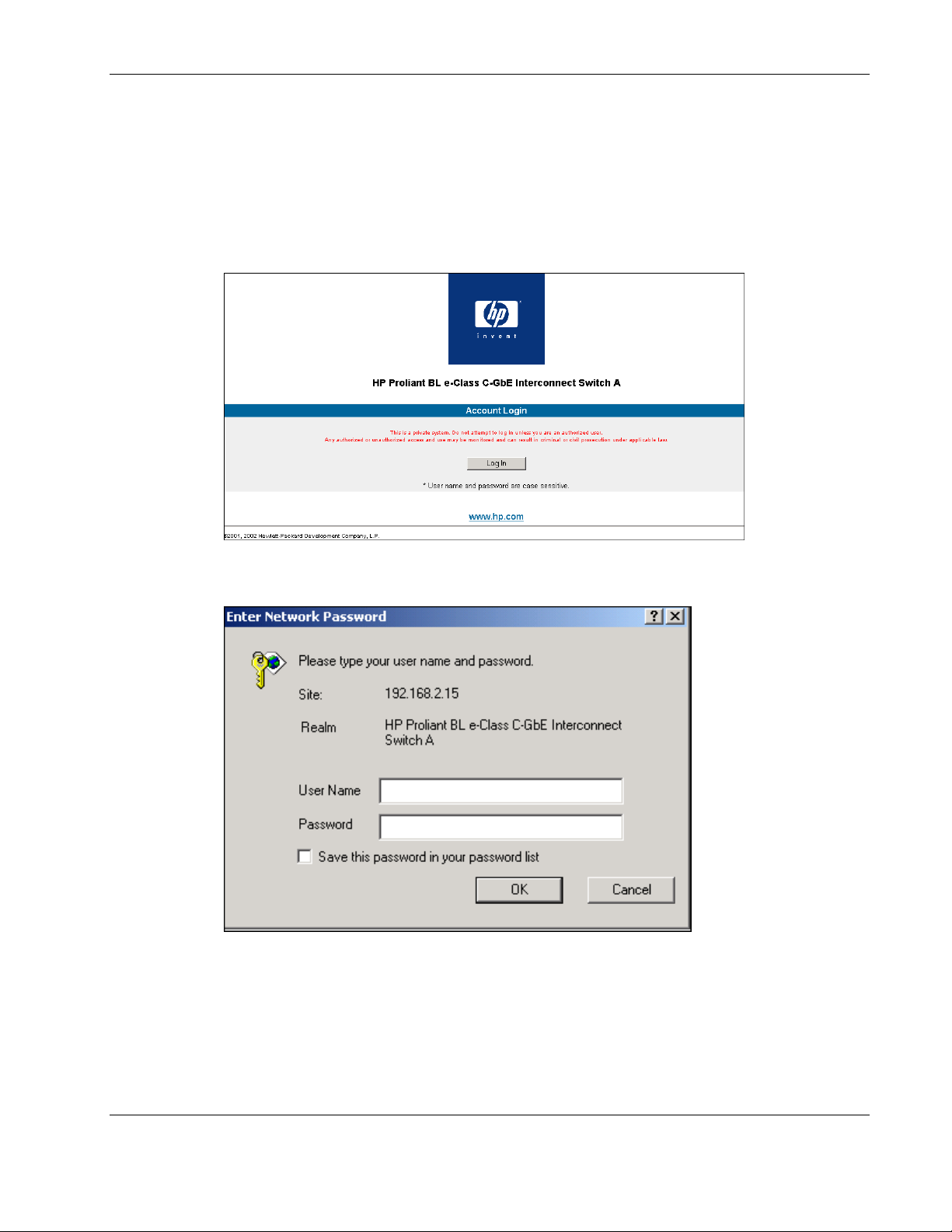
Overview
To connect to a switch module using the Web-based interface:
1. Start a Web browser, for example, Microsoft Internet Explorer version 5.5 or higher or
Netscape Navigator version 6.1 or higher.
2. Type the IP address you have defined for the switch module in the browser address bar.
The URL in the address bar should read something like:
http://10.24.22.8.
3. Press the Enter key. The Account Login screen is displayed.
4. Press Log in. The Enter Network Password dialog box for the switch module is
displayed.
IMPORTANT: The switch module does not have any initial user names or passwords set. HP
recommends that after logging on, you create at least one Root-level user as the switch administrator.
(Refer to Table 2-1 in Chapter 2, for an explanation of user privileges.) If you forget your password after
it has been set up, call HP Customer Support for assistance.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 1-7
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:21 AM
Page 14

Overview
5. Click OK at the Enter Network Password dialog box. No initial user name or password
is set for the first user. The main page in the Web-based management module is
displayed.
The main page displays the main menu, an active graphic of the switch module, and the
TCP/IP Parameters Setup window.
The active graphic of the switch module allows you to monitor the switch module status.
Graphical LEDs display current link speed and activity. Graphical RJ-45 connectors
allow you to display statistics for individual ports. In addition the current time displays,
once it is configured on the switch module.
Refer to the section “Configuring the Switch Module Date and Time” for information on
how to set the date and time. Refer to the section, “Monitoring the Switch Module Using
the Active Switch Graphic,” for detailed information about the active graphic.
The TCP/IP Parameters Setup window is used to determine whether the interconnect
switch should get its IP address settings from the user (Manual), a BOOTP server, or a
DHCP server. Refer to the section “Configuring the Remote Management IP Interface
Settings.”
6. Click the small square hyperlink to the left of the folder icons to display a list of
additional menus used to configure, manage, monitor, and maintain the switch module.
Configuring the Switch Modules
In addition to setting the IP address for each switch module, you will also want to
• • Set up users, passwords, and access privileges
Change default SNMP community strings for read/write and read-only
For information on how to configure these and other interconnect switch features, refer to
Chapter 2.
1-8 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:21 AM
Page 15

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based
Interface
Overview
This chapter describes how to configure the switch modules from the Web-based interface
Saving Changes
The switch module has two types of memory: dynamic RAM and non-volatile RAM
(NVRAM). Restarting the switch module erases all configuration settings in RAM and
reloads the stored settings from NVRAM. Thus, it is necessary to save all configuration
setting changes to NVRAM before rebooting the switch module.
After the configuration settings have been saved to NVRAM, they become the current
runtime settings for the switch module. These settings are then used every time the switch
module is rebooted.
2
Configuration changes on a screen are made effective by clicking Apply. The settings are
then immediately applied to the switching software in RAM.
To make your configuration changes permanent, save them to NVRAM using the Save
Changes option on the Maintenance menu before rebooting the system.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-1
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 16

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
To retain any configuration changes permanently:
1. Open the Maintenance folder on the main menu.
2. Click Save Changes. The Save Configuration window is displayed.
3. Click Save Configuration to save all the changes made in the current session to the
switch module’s NVRAM memory. A message box is displayed telling you that the save
is complete.
4. Click OK. After the switch module configuration settings have been saved to NVRAM,
they become the default settings for the switch module. These settings are used every
time the switch module is rebooted.
IMPORTANT: After saving your final configuration, HP highly recommends that you save the switch
module configuration image to TFTP server storage. Refer to the section, “Uploading a Configuration
File to TFTP Server,” in this chapter.
Managing User Accounts
After logging on to the switch module for the first time, you must set up at least one user
account with Root privileges. You can set up a maximum of eight users on a switch module.
You can set up a maximum of eight users on a switch module.
The following table summarizes the user access rights.
Table 2-1: User Access Rights
Privilege Root User+ User
Configuration Yes Read-only Read-only
Network Monitoring Yes Read-only Read-only
Community Strings and Trap Stations Yes Read-only Read-only
Update Firmware and Configuration Files Yes No No
System Utilities Yes Ping-only Ping-only
Factory Reset Yes No No
Reboot Switch Yes Yes No
Add/Update/Delete User Accounts Yes No No
View User Accounts Yes No No
2-2 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 17

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
To create a new user account:
1. Click the small square to the left of the Management folder on the main menu. The
Management menus are displayed.
2. Click User Accounts. The following window is displayed.
The User Account Management window displays all current users for the switch
module their current access level. The User Account Modify Table allows you to enter
user account information.
The following information is displayed on the User Account Management window:
— User Name—Displays all current users for the switch module.
— Access Right—Displays the current access level assigned to each corresponding
user. The available options are User, User+, or Root. A Root user has full read/write
access, while a User has read only access. A User+ has the same privileges as a
User, but with the added ability to restart the switch module.
— Add—Click this to add a new user.
— Modify—Click this modify the existing user’s account information.
3. Click Add on the User Account Management window.
4. On the User Account Modify Table, type the user name in the User Name field.
5. Type the user’s password in the New Password field.
6. Type the new password a second time in the Confirm Password field.
7. Click the drop-down arrow in the Access Right field to select the access level. The three
access levels are User, User+, and Root. A Root user has full read/write access, while a
User has read-only access. A User+ has the same privileges as a User, but with the
added ability to restart the switch module.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-3
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 18

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
8. Click Apply.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into the nonvolatile RAM (NVRAM) using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the
section, “Saving Changes” for more information.
Configuring the Remote Management IP Interface Settings
Each switch module must be assigned its own IP address, which is used for communication
with an SNMP network manager or other TCP/IP application (for example Web or TFTP).
The factory default is set for the switch module to automatically obtain the IP address using
DHCP service from a DHCP server on the attached network. You can also manually change
the default switch IP address to meet the specification of your networking address scheme. If
you select the manual mode and do not assign the IP address, the system assigns a default IP
address for Switch A as 10.90.90.90 and for Switch B as 10.90.90.91. The system also
assigns a default subnet mask of 255.0.0.0.
The switch module IP interface is also assigned a unique MAC address by the factory. This
MAC address cannot be changed and can be found on the initial boot console screen and
Logon screen, or by accessing basic switch information. Refer to the “Displaying Basic
Switch Module Information” section later in this chapter.
In addition, you can
•
Set an IP address for a default gateway. This becomes necessary when the network
management station is located on a different IP network from the switch module, making
it necessary for management packets to go through a router to reach the network
manager, and vice-versa.
•
Set a list of up to eight secure IP addresses of network management stations that are
allowed to manage the interconnect switch. Only those network management stations can
access the switch management inerfaces once set.
•
Set a management VLAN ID (VID) for the IP interface so that the interconnect switch
can be accessed from the designated management VLAN.
•
Change the default SNMP community strings in the switch module and set the access
rights of these community strings.
2-4 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 19

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Setting the Remote Management IP Interface Settings
To access and manage the interconnect switch from an SNMP-based Network Management
System, or by using the Telnet protocol or the Web, you must first configure the remote
management IP interface parameters.
The IP address can be assigned by one of the following methods:
•
Manual—This option allows you to manually configure an IP address, subnet mask, and
default gateway for the switch module.
•
BOOTP—This option configures the switch to send out a BOOTP broadcast request for
IP information. The BOOTP protocol allows IP addresses, network masks, and default
gateways to be assigned by a central BOOTP server attached to the same network to
which the interconnect switch is connected.
•
DHCP—This option configures the switch to send out a DHCP broadcast request. The
DHCP protocol allows IP addresses, network masks, and default gateways to be assigned
by a DHCP server attached to the same network to which the interconnect switch is
connected. DHCP protocol is the factory default mode.
To configure the remote management IP interface settings:
1. Select IP Address from the Configuration menu. The following screen is displayed.
The TCP/IP Parameters Setup window is used to determine whether the switch module
should get its IP address settings from the user (Manual), a BOOTP server, or a DHCP
server.
The window displays the following information:
— MAC Address—The Ethernet address for the device, also known as the physical
address
— Get IP From—The choices for how the switch module receives its IP address
settings: Manual, BOOTP, and DHCP
— IP Address—The host address for the device on the TCP/IP network
— Subnet Mask—The address mask that controls subnetting on your TCP/IP network
— Default Gateway—The IP address of the device, usually a router, that handles
connections to other subnets or other TCP/IP networks
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-5
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 20

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
— VID—The VLAN ID (VID) number for the switch management port
2. Select Manual, BOOTP, or DHCP in the Get IP From field:
— If you select Manual, type the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway of
the switch module.
— If you select BOOTP, you do not need to configure any IP parameters because a
BOOTP server automatically assigns IP configuration parameters to the GbE
Interconnect Switch.
— If you select DHCP, you do not need to configure any IP parameters because a
DHCP server automatically assigns IP configuration parameters to the GbE
Interconnect Switch.
3. Type the VLAN ID for the switch management port in the VID field.
4. Click Apply to activate the new settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
Displaying Basic Switch Module Information
You can quickly and easily obtain basic information about the switch module including: the
type of switch and the MAC address (assigned by the factory and unchangeable) for that
switch module. In addition, the boot PROM and firmware version numbers are displayed.
This information is helpful in monitoring PROM and firmware updates.
2-6 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 21
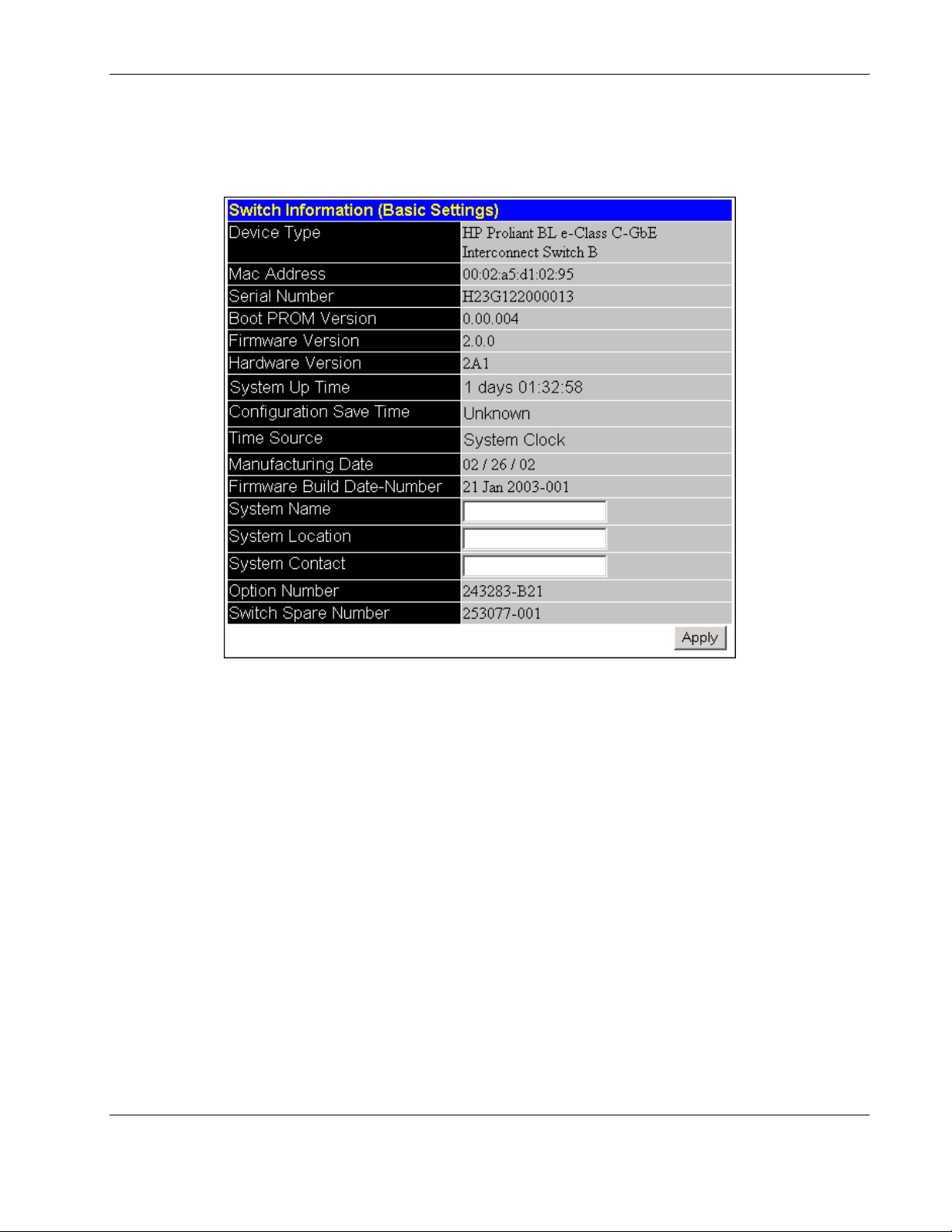
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
To display and configure basic switch module information:
1. Select Switch Information from the Configuration menu. The following screen is
displayed.
The Switch Information (Basic Settings) window displays the following information:
— Device Type—Displays the name of the switch module.
— MAC Address—Identifies the Ethernet address for the switch module.
— Serial Number—Identifies the switch module serial number.
— Boot PROM Version— Identifies the version number of Boot PROM code installed
on the interconnect switch.
— Firmware Version—Identifies the version number of the firmware installed on the
switch module. This information can be updated by using the Update Firmware
window in the Reset and Update section.
— Hardware Version—Identifies the version number of the interconnect switch
hardware build.
— System Up Time— Identifies the time the switch booted up, if the current time has
been set on the switch module. If the current time has never been set up on the
interconnect switch, this field identifies the time since the switch module was
booted up.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-7
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 22

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
— Configuration Save Time—Displays the time the current settings were saved to the
configuration file. If the current time has never been set up on the interconnect
switch, “Unknown” will be displayed.
— Time Source—Displays how the switch module obtains the current time: Primary
SNTP Server, Secondary SNTP Server, or System Clock.
— Manufacturing Date—Displays the manufacture date of the switch module.
— Firmware Build Date-Number—Displays the firmware build date and build
number.
— System Name—Displays a user-configured name for the switch module.
— System Location—Displays a user-configured description for the physical location
of the switch module.
— System Contact—Displays the user-configured name of the person to contact if
there are any problems or questions with the system. You may also want to include a
phone number or extension.
— Option Number—Displays the option number for the switch module and
Interconnect Module combination.
— Switch Spare Number—Displays the spare part number for the switch module.
— Module Spare Number—This field is not applicable.
2. To complete the switch module information, type the system name in the System Name
field.
3. Type the physical location of the switch module in the System Location field.
4. Type the name of the contact person responsible for the switch module (and telephone
number or other contact information) in the System Contact field.
5. Click Apply.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, they must be entered into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
2-8 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 23
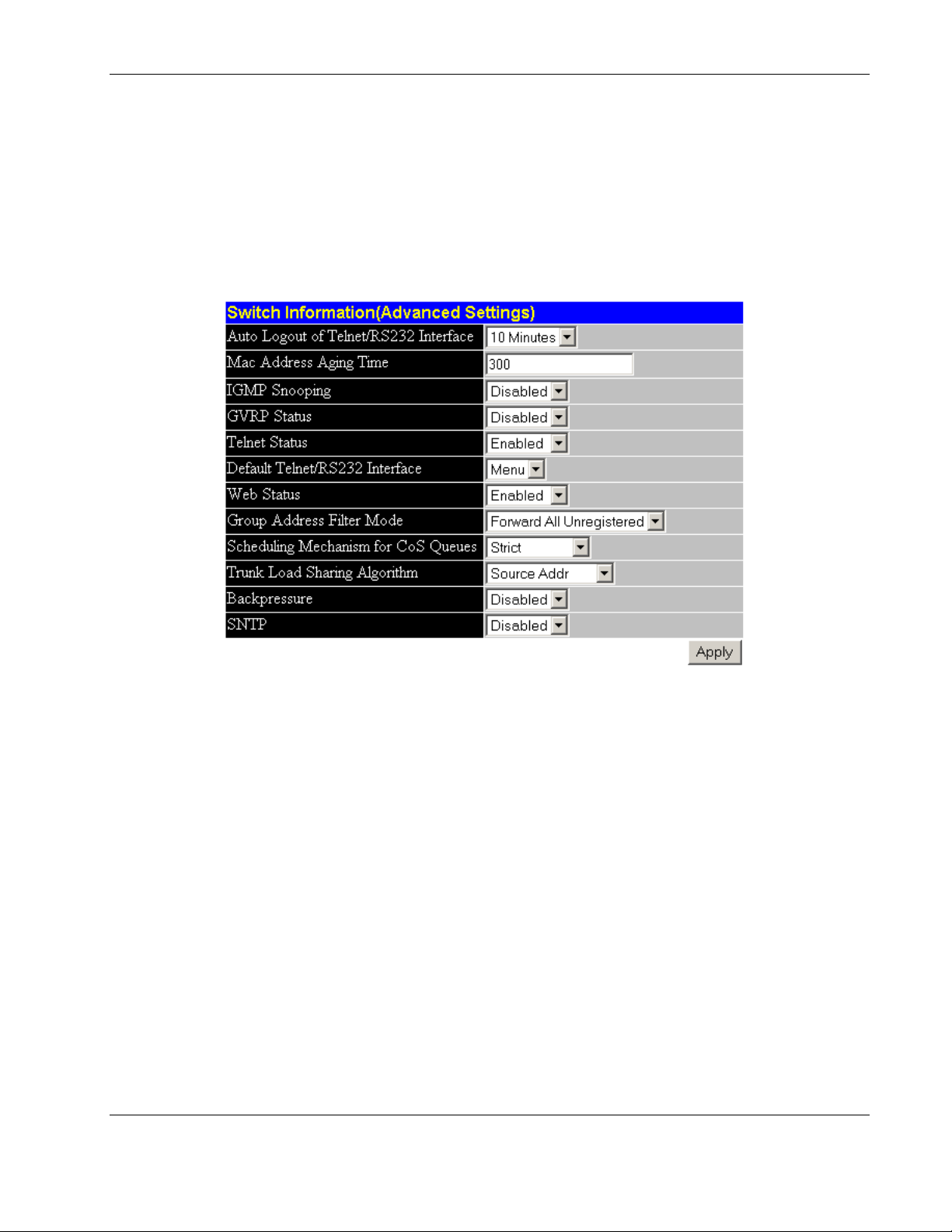
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Configuring Advanced Switch Module Features
You can configure advanced switch features including global settings for IGMP snooping,
GVRP, Telnet status, Web status, SNTP, and others.
To configure advanced switch module features:
1. Select Advanced Settings from the Configuration menu. The following screen is
displayed.
You can change the following parameters:
— Auto Logout of Telnet/RS232 Interface—Select the time that the RS-232 console
and Telnet management interface can be idle before the switch module automatically
logs-out the user: 2 minutes, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15 minutes, and Never. Never
indicates never timing out. The default is 10 minutes.
— MAC Address Aging Time—Select the length of time a learned MAC address
remains in the forwarding table without being seen as a source (that is, how long a
learned MAC address is allowed to remain idle before deleting from the address
table). The aging time can be set to any value between 1 and 1,000,000 seconds.
The switch module enters into its forwarding table the mapping between the MAC
address of the device and the Ethernet port to which the device is attached. This
information is used to forward packets. This reduces the traffic congestion on the
network, because packets are forwarded to the destination port only, instead of being
forwarded to all ports.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-9
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 24

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The MAC address aging timer prunes the forwarding table addresses entries that are
no longer used. Dynamic forwarding table entries, which are made up of MAC
addresses and their associated port numbers, are deleted from the table if they are not
seen within the aging timeout. The aging time can be from 10 to 1,000,000 seconds
with a default value of 300 seconds. A very long aging time can result in dynamic
forwarding table entries that are out-of-date or no longer are used.
If the aging time is too short, however, many entries may be aged out too soon. This
will result in a high percentage of received packets whose destination addresses
cannot be found in the forwarding table. In this case the switch module will broadcast
the packet to all ports, negating many of the benefits of having a switch.
Static forwarding entries are not affected by the aging time.
— IGMP Snooping—Select to enable or disable Internet Group Management Protocol
(IGMP) Snooping. IGMP Snooping enables the switch module to register IGMP
packets being forwarded through the switch module in order to obtain multicast
membership information from them, such as which ports are attached to which
multicast group members. For additional information, refer to the “Configuring
IGMP Snooping” section later in this chapter.
— GVRP Status—Select to enable or disable GARP VLAN Registration Protocol
(GVRP) on the switch module. GVRP allows dynamic propagation of VLAN
registration information across the GVRP-enabled switches on the same network. For
additional information, refer to the “Setting the Port VLAN ID for a Port” section
later in this chapter.
— Telnet Status—Select to enable or disable access to the switch module over the
network using the Telnet protocol.
— Default Telnet/RS232 Interface— Set either the CLI or menu-driven interface as
the default Telnet/RS232 interface.
— Web Status—Select to enable or disable management of the switch module over the
Web.
— Group Address Filter Mode—Select one of the forwarding or filtering options to
set the IGMP group address filter mode for forwarding multicast packets.
— Scheduling Mechanism for CoS Queues—Select one of the Class of Service queue
scheduling options. If you select Strict, then when the highest priority queue is full,
those packets will be the first to be forwarded. If you select RoundRobin, the
forwarding is based on the settings made on the Class of Service Configuration
screen. For more information, refer to the “Configuring the Class of Service, Default
Port Priority, and Traffic Class” section later in this chapter.
— Trunk Load Sharing Algorithm—Select one of the port trunk load sharing options,
Source Addr, Destination Addr, or Both, to determine if load balancing decisions
will be made based on the source MAC address, destination MAC address, or both
addresses.
2-10 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 25

— Backpressure— Select Enabled or Disabled to initiate or terminate backpressure
flow control in and out of the switch module. When backpressure is enabled and
there is incoming traffic congestion on a 10/100 port, the receiving port sends a
request to the transmitting port. The transmitting port acknowledges the request and
stops sending packets for a random amount of time, before it starts sending again.
— SNTP—Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) allows the system to get the
accurate time through the network. When SNTP is enabled, the interconnect switch
sends a request to a primary SNTP server in each period of a specified polling
interval asking for the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). If the primary SNTP server is
not available, the request is sent to a secondary SNTP server. For additional
information, refer to the “Configuring Switch Module Date and Time” section later in
this chapter.
2. After making your choices in Advanced Settings, click Apply.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, they must be entered into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
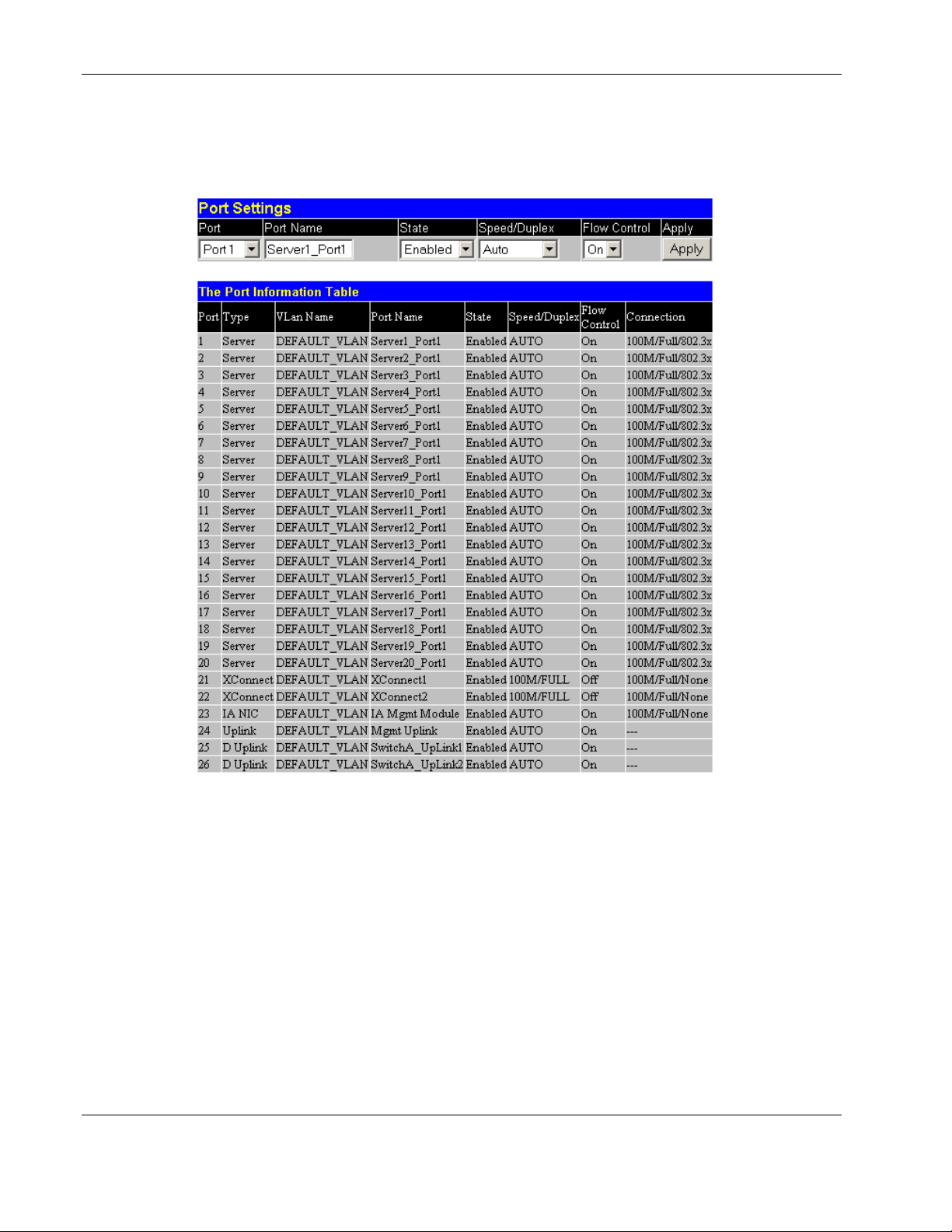
Configuring Port Settings
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
This section describes how to configure the following port settings: port name, state,
speed/duplex, and flow control. Refer to the “Configuring Port Security” section later in this
chapter for information on how to set the port security parameters.
The speed-duplex parameter for each port can be set to 1000M/Full, 100M/Full, 100M/Half,
10M/Full, 10M/Half, or Auto. The Auto setting allows the port to automatically determine
the fastest settings that the device the port is connected to can handle.
IMPORTANT: In the forced 100M/Full, 100M/Half, 10M/Full, and 10M/Half modes, auto MDI-X is
disabled and a cross-over cable must be used.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-11
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 26
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
To configure port settings:
1. Select Port Configuration from the Configuration menu. The following screen is
displayed.
2. Select the port you want to configure in the Port field. The port name displays in the
Port Name field.
3. Select Enabled or Disabled in the State field. If you selec1t Disabled, devices
connected to that port cannot use the switch module, and the switch module purges their
addresses from its address table after the MAC address aging time elapses.
4. Configure the Speed/Duplex setting for the port:
— Select Auto to allow the port to select the best transmission speed, duplex mode, and
flow control settings based on the capabilities of the device at the other end. The
other selections allow you to force the port to operate in the specified manner.
— Select 100M/FULL for port operation at 100 Mb/s and full duplex.
— Select 100M/HALF for port operation at 100 Mb/s and half duplex.
— Select 10M/FULL for port operation at 10 Mb/s and full duplex.
2-12 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 27

— Select 10M/HALF for port operation at 10 Mb/s and half duplex.
5. Configure the Flow Control setting for the port:
— Select On for flow control.
— Select Off for no flow control.
6. Click Apply.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into the
NVRAM using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
Configuring Port Mirroring
The switch module allows you to copy frames transmitted and received on a port (source) and
redirect the copies to another port (target). You can attach a monitoring device to the
mirrored (target) port, such as a sniffer or an RMON probe, to view details about the packets
passing through the source port. This setting is useful for network monitoring and
troubleshooting purposes.
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The following configuration rules apply to any port mirroring configuration:
•
A target mirror port cannot be configured as a trunk member.
•
VLAN configuration settings for any ports configured for mirroring cannot be changed.
•
The source and target ports should be members of the same VLAN.
The direction of traffic on the source port can be one of the following:
•
Ingress traffic (received packets) on the source port
•
Egress traffic (transmitted packets) on the source port
•
Ingress and egress traffic on the source port
IMPORTANT: You cannot mirror a fast port onto a slower port. For example, if you try to mirror the
traffic from a 1000-Mb/s port onto a 100-Mb/s port, you can cause throughput problems. The port from
which you are copying frames must support an equal or lower speed than the port to which you are
sending the copies. Also, the target port cannot be a member of a trunk group.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-13
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 28

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
To configure port mirroring:
1. Select Port Mirroring from the Configuration menu. The following screen is displayed
2. Select the Source Port from which you want to copy frames.
3. Select the Source Direction, either Ingress, Egress, or Either.
4. Select the Target Port that receives the copies from the source port. This is the port
where you would connect a monitoring/troubleshooting device, such as a sniffer or an
RMON probe.
5. Select Enabled in the Status field.
6. Click Apply.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into the
NVRAM using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
Configuring Port Trunking
This section describes how to configure port trunking. For information on how to set the
trunk load sharing algorithm parameter, refer to the “Configuring Advanced Switch Module
Features” section earlier in this chapter.
Port trunking allows several ports to be grouped together to act as a single link. This provides
a bandwidth that is a multiple of a single link bandwidth. Port trunking is most commonly
used to link a bandwidth-intensive network device or devices, such as a server, to the
backbone of a network.
The switch module allows the creation of up to six port trunk groups, each group consisting
of up to eight links (ports). HP recommends that the trunk ports be members of the same
VLAN. Only similar type ports can be members of port trunks. A combination of Fast
Ethernet (FE) and Gigabit (GE) ports cannot be members of the same port trunk.
2-14 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 29

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The configuration of the lowest numbered port in the group becomes the configuration for all
of the ports in the trunk group. This port is called the master port of the trunk group, and all
configuration options, including the VLAN configuration, which can be applied to the master
port, are applied to the entire port trunking group.
Load balancing is automatically applied to the ports in the trunked group, based on the setting
of the trunk load-sharing algorithm, and a link failure within the group causes the network
traffic to be directed to the remaining links in the group.
Spanning Tree Protocol treats a port trunking group as a single link on the switch module
level. STP uses the port parameters of the master port in the calculation of port cost and in
determining the state of the port trunking group. If two redundant port trunking groups are
configured on the switch module, STP blocks one entire group, similar to STP blocking a link
in case of two redundant links.
Considerations when Creating a Port Trunking Group
When creating a port trunking group, consider the following rules that determine how the port
trunk reacts in network topology:
•
The first port of the port trunk is implicitly configured to be the master logical port. This
is the reference port used in configuration commands. It can be thought of as the logical
port representing the entire port group.
•
When using a port trunk, always reference the master logical port of the group when
configuring or viewing VLANs.
•
VLANs configured to use other ports in the port trunk will have those ports deleted from
the VLAN when the port trunk becomes enabled.
•
The Spanning Tree algorithm views port trunk as a single Spanning Tree port. The
Spanning Tree port is represented by the master logical port.
•
If the VLAN settings of the master logical port are changed, the VLAN settings of all
members of that port trunk are changed similarly.
•
If the IGMP snooping configuration for any port trunk member is changed, the IGMP
snooping settings for all port trunk members are changed.
•
The port trunk takes precedence over any other setting. That is, the settings of trunked
ports are the same as the master port settings.
•
When any trunked port becomes a non-trunked port, all of the port configurations are
reset to default settings.
Refer to Appendix G in the HP ProLiant e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch User Guide for
additional information on port trunking.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-15
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 30

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
To configure port trunking:
1. Select Port Trunking from the Configuration menu. The following screen is displayed.
2. Type a user-assigned name in the Name field.
3. In the Member Ports area, check the ports that will compose the port trunk.
4. Change the State field to Enabled.
5. Click Apply.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
Configuring IGMP Snooping
This section describes how to configure IGMP snooping on a VLAN ID. For information on
how to set IGMP globally on the switch module and how to set the IGMP filter mode for
processing multicast packets, refer to the “Setting Advanced Switch Module Features”
section earlier in this chapter.
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping, when enabled and configured
properly, manages multicast traffic through a switch module. IP multicast traffic is forwarded
based on multicast group membership information registered by the switch module. The
switch module can use IGMP snooping to configure ports dynamically, so that IP multicast
traffic is forwarded only to those ports associated with IP multicast hosts, based on
membership information.
IGMP snooping allows the switch module to recognize IGMP queries and reports sent
between network stations or devices and an IGMP host that belongs to a specific multicast
group. When enabled for IGMP snooping, the switch module can open or close a port to a
specific device based on IGMP messages passing through the module. This feature further
limits unnecessary broadcasts. The switch module can be configured to make queries using
either IGMP version 1 or version 2.
When IGMP snooping is enabled globally on the switch module, you can enable or disable
individual VLANs for IGMP snooping.
2-16 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 31

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
When IGMP snooping is enabled, any port receiving IGMP response packets will forward
them to the CPU, and the CPU sets this port as a member of the corresponding multicast
address.
The switch module supports three multicast group address filtering modes for making
forwarding decisions regarding multicast packets.
•
Forward all group addresses—All multicast packets destined for all group MAC
addresses are forwarded according to the VLAN rules.
•
Forward all unregistered group addresses—All multicast packets with group MAC
address registration entries existing in the multicast table (both static multicast and group
multicast created by IGMP snooping) are forwarded to member ports. If the group MAC
address does not exist in the multicast table, packets are forwarded according to the
VLAN rules.
•
Filter all unregistered group addresses—All multicast packets with group MAC
addresses are forwarded only if such forwarding is explicitly permitted by a group
address entry in the multicast table. If the group MAC address exists in the multicast
table, then the packets are forwarded using the port member list for that entry. If the
group MAC address does not exist in the multicast table, the packets are dropped.
To configure IGMP snooping:
1. Select IGMP Snooping from the Configuration menu. The following screen is
displayed.
2. Select a VID number in the VLAN ID field.
3. Select Enabled in the State field.
4. In the Querier State field, select the IGMP version that will be used by the IGMP
interface when making queries. Select from Non-Querier, V1-Querier, and
V2-Querier.
5. In the Robustness Variable field, type a value between 1 and 255. Larger values are
specified for subnets that are expected to lose larger numbers of packets. The default is 2.
The robustness variable is a tuning variable that allows you to configure the acceptable
number of packets that may be lost.
6. In the Query Interval field, type a value between 1 and 65,500 seconds to specify the
length of time between sending IGMP queries. The default is 125 seconds.
7. In the Max Response field, type the maximum amount of time allowed before sending an
IGMP response report. The range is 1 to 25 seconds.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-17
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 32

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
8. Click Apply.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
Configuring Spanning Tree Protocol Settings
IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) allows for the blocking of links between
switches to avoid loops within the network. When multiple links between the switches are
detected, a primary link is established. Duplicated links are blocked from use and become
standby links. The protocol allows for the duplicate links to be used in the event of a failure
of the primary link. Once STP is configured and enabled, primary links are established and
duplicated links are blocked and put into standby automatically. The reactivation of the
blocked links (at the time of a primary link failure) is also accomplished automatically,
without operator intervention.
STP communicates between switches on the network using Bridge Protocol Data Units
(BPDUs). Each BPDU contains the following information:
•
The unique identifier of the switch that the transmitting switch currently believes is the
root switch
•
The path cost to the root from the transmitting port
•
The port identifier of the transmitting port
The switch sends BPDUs to communicate and construct the spanning-tree topology. All
switches connected to the LAN on which the packet is transmitted will receive the BPDU.
BPDUs are not directly forwarded by the switch, but the receiving switch uses the
information in the frame to calculate a BPDU, and if the topology changes, initiates a BPDU
transmission.
The communication between switches via BPDUs results in the following:
•
One switch is elected as the root switch.
•
The shortest distance to the root switch is calculated for each switch.
•
A designated switch is selected. This is the switch closest to the root switch through
which packets will be forwarded to the root.
•
A port for each switch is selected. This is the port providing the best path from the switch
to the root switch.
•
Ports included in the STP are selected.
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) can be enabled or disabled at the switch level. Only one
spanning tree domain per switch module is supported. You can configure ports to participate
in that spanning tree domain, by enabling or disabling the STP function on a per port basis.
Ports can also be configured in STP bypass mode (fast forward mode) that allows the port to
skip the initial STP states (listening and learning) before enabling it in the forwarding state.
2-18 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 33
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
IMPORTANT: The interconnect switch supports mono-Spanning Tree Protocol. Multiple Spanning Tree
domains are not supported.
NOTE: Refer to Appendix D in the HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch User Guide for
more information on Spanning Tree Protocol.
Setting Spanning Tree Parameters on the Switch Module Level
IMPORTANT: The factory default settings should cover the majority of installations. HP recommends
that you keep the default settings as set at the factory unless it is absolutely necessary to change them.
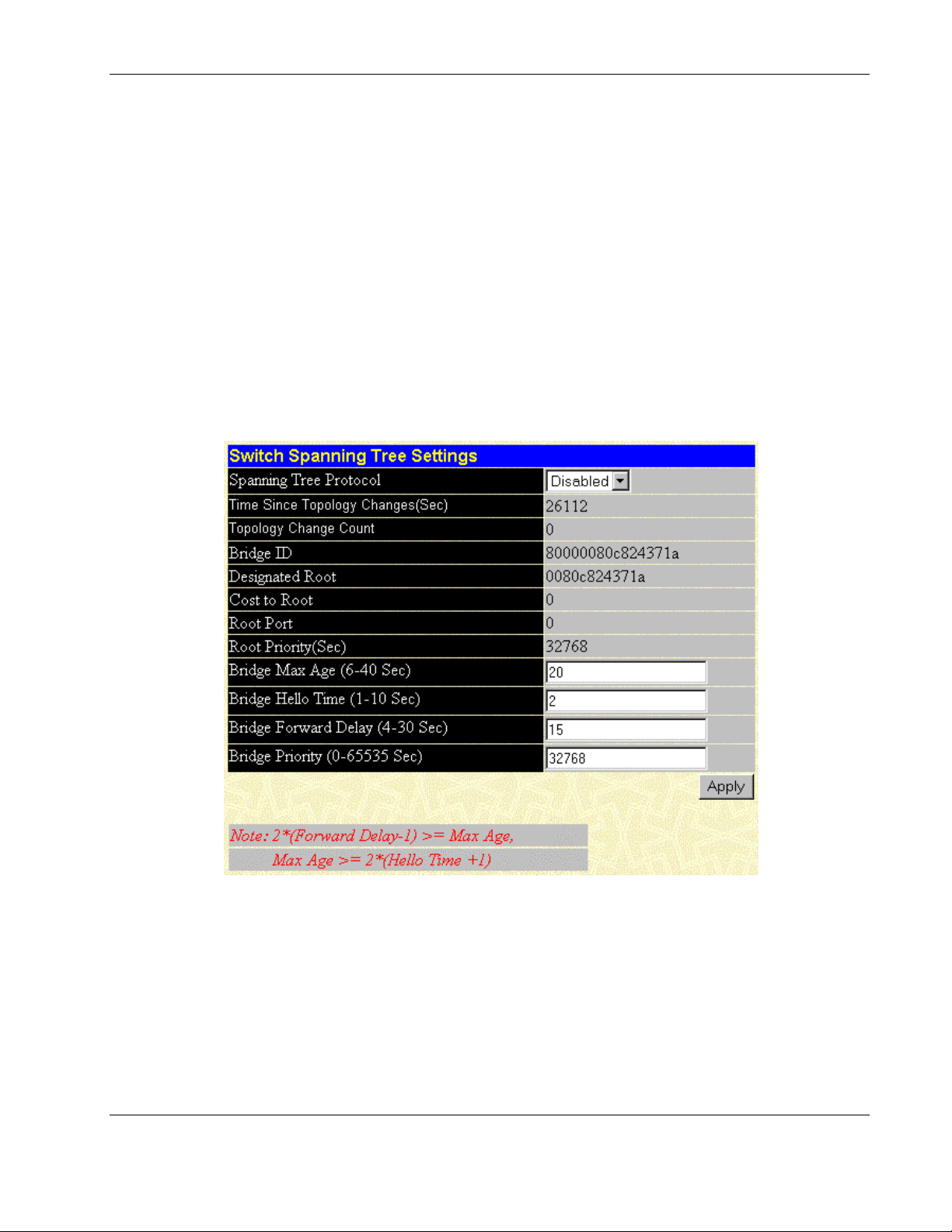
To set STP parameters on the switch level:
1. Select STP Switch Settings from the Spanning Tree menu. The following screen is
displayed.
The Switch Spanning Tree Settings screen allows you to configure STP parameters and
displays STP status information, including:
— Spanning Tree Protocol—Select to enable or disable the STP setting.
— Time Since Topology Changes (Sec)—Displays the number of seconds since the
last change in topology occurred that caused the spanning tree algorithm to be
recalculated.
— Topology Change Count—Displays the number of times there has been a change in
topology since the last reboot of the current bridge.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-19
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 34

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
— Bridge ID—Displays the ID of the bridge (switch) used only for spanning tree
functions. The ID is made up of the bridge priority and bridge MAC address.
— Designated Root—Displays the current elected root bridge. The root bridge has a
bridge ID lower than the other bridges.
— Cost to Root—Displays the summation of all path costs between the current bridge
and the root bridge via the root port.
— Root Port—Displays the port on the current bridge that has the best path to reach the
designated root bridge.
— Root Priority (Sec)—Displays the priority of the current designated root bridge.
— Bridge Max Age (6–40 Sec)—Type the maximum age. The range is 6 to 40 seconds.
When the maximum age is reached, if a Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU) has still
not been received from the Root Bridge, your switch module will start sending its
own BPDU to all other switches for permission to become the Root Bridge. If your
switch module has the lowest bridge identifier, it will become the Root Bridge.
— Bridge Hello Time (1–10 Sec)—Type the hello time. The range is 1 to 10 seconds.
This time is the interval between two transmissions of BPDU packets sent by the
Root Bridge to tell all other switches that it is indeed the Root Bridge. If you set a
hello time for your switch module and it is not the Root Bridge, the default hello time
will be used until your switch module becomes the Root Bridge.
— Bridge Forward Delay (4–30 Sec)—Type the forward delay time. The range is 4 to
30 seconds. This interval is the time any port on the switch module spends in the
listening state while moving from the blocking state to the forwarding state.
— Bridge Priority (0–65535 Sec)—Type the bridge priority. A priority for the switch
module can be set from 0 to 65,535. Zero indicates the highest priority. The priority
number is used in the voting process between switches on the network to determine
which switch will be the root switch. A low number indicates a high priority, and a
higher probability that this switch module will be elected as the root switch.
2. Click Apply after making changes to the settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM using
the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving Changes,” earlier in
this chapter.
Setting Spanning Tree Parameters on the Port Level
Once STP is enabled on the switch module, you can configure ports to participate in the
spanning tree domain, by enabling or disabling the STP function on a per port basis. Ports can
also be configured in STP bypass mode (fast forward mode) that allows the port to skip the
initial STP states (listening and learning) before enabling it in the forwarding state.
2-20 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 35

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
To enable STP on the port level:
1. Select STP Port Settings from the Spanning Tree menu. The following screen is
displayed.
2. Select the first port to be configured in the From field.
3. Select the last port to be configured in the To field.
4. In the State field, select the STP state for the port, either Enabled or Disabled.
5. In the Cost (1–65535) field, type a port cost between 1 and 65,535. The lower the cost,
the greater the probability that the port will be chosen as the designated port to forward
packets.
6. In the Priority (0–255) field, type a port priority from 0 to 255. The lower the priority,
the greater the probability that the port will be chosen as the root port.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-21
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 36

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
7. In the ByPass field, select Yes or No. The bypass sets the forward delay timer to zero,
thus bypassing the waiting time before the listening state. (This procedure is also known
as fast forward.)
8. Click Apply after making changes to the settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM using
the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving Changes,” earlier in
this chapter.
Configuring Static (Destination Address) Filtering Table
The interconnect switch uses a filtering database to segment the network and control
communications between segments. It can also filter packets off the network for intrusion
control. Static filtering entries can be made by MAC address.
Each port on the switch module is a unique collision domain and the interconnect switch
filters (discards) packets whose destination lies on the same port as where it originated. This
keeps local packets from disrupting communications on other parts of the network.
For intrusion control, whenever an interconnect switch encounters a packet originating from
or destined to a MAC address entered into the filter table, the interconnect switch will discard
the packet.
Some filtering is done automatically by the switch module, including:
•
Dynamic filtering, which is automatic learning and aging of MAC addresses and their
location on the network. Filtering occurs to keep local traffic confined to its segment.
•
Filtering done by the Spanning Tree Protocol that can filter packets based on topology,
making sure that the signal loops do not occur.
•
Filtering done for VLAN integrity. Packets from a member of a VLAN destined for a
device on another VLAN will be filtered.
Some filtering requires the manual entry of information into a filtering table. This includes
MAC address filtering, which is the manual entry of specific MAC addresses to be filtered
from the network. Packets sent from one manually entered MAC address can be filtered from
the network. The entry may be specified as source, destination, or both.
2-22 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 37

Adding Unicast Filter Actions
To add unicast filter actions:
1. Select Unicast Filtering from the Static Filtering Table menu. The following screen is
displayed.
2. In the VID field, type the VID number of the VLAN to which the MAC address belongs.
3. In the MAC Address field, type the MAC address from which packets will be statically
filtered.
4. In the Type field, select the filter type, either Permanent or DeleteOnReset.
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
5. In the Allow-to-Go-Port field, select the port on which the MAC address resides.
6. Click Apply after making changes to the settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM using
the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving Changes,” earlier in
this chapter.
Adding Multicast Filtering
To add multicast filter actions:
1. Select Multicast Filtering from the Static Filtering Table menu. The following screen
is displayed.
2. In the MAC Address field, type the MAC address of the static source of multicast
packets.
3. In the VID field, type the VID number of the VLAN to which the MAC address belongs.
4. In the Type field, select the filter type, either Permanent or DeleteOnReset.
5. In the Port Map field, select the ports that will be members of the static multicast group
and ports that have no restrictions from joining dynamically.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-23
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 38

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
6. Click Apply after making changes to the settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM using
the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving Changes,” earlier in
this chapter.
Configuring VLANs
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network topology configured according to a
logical scheme rather than the physical layout. VLANs can be used to combine any collection
of physical LAN segments into an autonomous user group that appears as a single LAN.
VLANs also logically segment the network into different broadcast domains so that logical
packets are forwarded only between ports within that VLAN. Typically, a VLAN
corresponds to a particular subnet, although not necessarily. VLANs can enhance
performance by conserving bandwidth, and improve security by limiting traffic to specific
domains.
The switch module supports only port-based IEEE 802.1Q tag-capable VLANs.
VLAN membership for each port can be set as follows:
• • Egress Port—This is a port on the interconnect switch that belongs to at least one
VLAN. By default all ports are egress members of DEFAULT_VLAN.
— Untagged Member—Ports that are untagged members of a VLAN participate in the
VLAN, but no tag is associated to the packet when leaving that port. Untagged
member ports can only be a member of one VLAN at a time.
— Tagged Member—Ports with tagging enabled will insert the IEEE 802.1Q tag with
the VID number into all packets that flow out of it. Tagged member ports can be
members of multiple VLANs at a time, as packets are tagged with the VLAN ID
from which they originated. Tagged member ports link IEEE 802.1Q trunks that
work as inter-switch connections to forward packets belonging to multiple VLANs,
to which those tagged member ports belong. If a packet has been tagged, the port
does not alter the packet, thus keeping the VLAN information intact. The VLAN
information in the tag can then be used by other 802.1Q compliant devices on the
network to make packet-forwarding decisions.
Forbidden Non-member—These ports are not a member of the VLAN and are also
forbidden from joining a VLAN dynamically when GVRP is enabled.
If ingress filtering is enabled for a port, the interconnect switch examines the VLAN
information in the packet header (if present) and decides whether or not to forward the
packet. The VID should match the PVID of that port, otherwise, that incoming packet is
discarded.
Packets cannot cross VLANs. If a member of one VLAN wants to connect to another VLAN,
it must do so through a router.
2-24 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 39

Default VLAN
The switch module reserves one VLAN, VID 1, also called DEFAULT_VLAN. The factory
default setting assigns all ports on the switch module to the default VLAN. As new VLANs
are configured, their respective member ports are removed from the default VLAN.
Characteristics of DEFAULT_VLAN include:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
DEFAULT_VLAN is an IEEE 802.1Q Static VLAN with VID equal to 1.
DEFAULT_VLAN cannot be deleted.
The VID cannot be changed. The VID that is equal to 1 is reserved for
DEFAULT_VLAN.
The VLAN name can be changed to any other valid VLAN name.
You cannot delete a port from DEFAULT_VLAN, unless it is a member of another
802.1Q VLAN.
You cannot forbid a port from DEFAULT_VLAN, unless it is a member of another
802.1Q VLAN.
If a port is deleted from the only 802.1Q VLAN of which it is a member, then it will
automatically become a member of DEFAULT_VLAN as an untagged, egress port.
•
If a port is assigned to a user-created 802.1Q VLAN, and is not a tagged egress port
member of DEFAULT_VLAN (in other words, it is an untagged egress port), then it will
be deleted automatically from DEFAULT_VLAN.
•
A tagged egress port of DEFAULT_VLAN will not be deleted from DEFAULT_VLAN,
when it is assigned to another user-created 802.1Q VLAN.
To configure a VLAN:
1. Select Static VLAN Entry from the VLAN menu. The following screen is displayed
The 802.1Q Static VLANs window allows you to create or delete entries to the 802.1Q
Static VLAN table. To add an entry to this table, click Add and then fill in the
appropriate information in the following window. To modify an entry, click Modify
beside the appropriate VID. To delete an entry, click the icon in the Delete column.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-25
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 40

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
2. Type the VLAN ID number of the VLAN you want to add in the VID field. The range is
1 to 4094. This field is grayed out in the Modify mode.
3. Type the name of the VLAN that is being created in the VLAN Name field.
4. In the Tag field, click the check box to designate the port as tagging. Leave the box
unchecked for untagging.
5. In the None field, select the radio button to specify that the port is not a static member of
the VLAN, and has no restrictions for joining the VLAN dynamically through GVRP.
6. In the Egress field, select the radio button to specify that the port is a static member of
the VLAN. Egress member ports transmit traffic for the VLAN.
7. In the Forbidden field, select the radio button to specify the port is not a member of the
VLAN, and is forbidden from dynamically becoming a member of the VLAN.
8. Click Apply to let the changes take effect.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
Setting the Port VLAN ID for a Port
Port VLAN ID (PVID) is a classification mechanism that associates a port with a specific
VLAN and is used to make forwarding decisions for untagged packets received by the port.
For example, if Port 2 is assigned a PVID of 3, then all untagged packets received on Port 2
will be assigned to VLAN 3. This number is generally the same as the VID number assigned
to the port.
Characteristics of a PVID include:
•
By default, the PVID of all ports is the same as the VID of DEFAULT_VLAN, which is
equal to 1.
•
When a user creates an untagged 802.1Q VLAN and assigns a port, the PVID will be
changed to the VID of that 802.1Q VLAN.
•
For a tagged port, the PVID will be the same as the VID of the IEEE 802.1Q VLAN to
which this port was first assigned.
2-26 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 41

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
• If the first IEEE 802.1Q VLAN to which the tagged port is assigned is deleted, the PVID
will change to that of the second IEEE 802.1Q VLAN to which the port was assigned.
•
The PVID of a port can only be set to a VID of a VLAN for which the port is already a
member.
GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) is a Generic Attribute Registration Protocol
(GARP) application that provides 802.1Q-compliant VLAN pruning and dynamic VLAN
creation on 802.1Q tagged ports.
GVRP updates dynamic VLAN registration entries and communicates the new VLAN
registration information across the network. This feature allows stations to physically move to
other switch module ports and keep their original VLAN settings, without having to
reconfigure the VLAN settings on the switch module.
With GVRP, the switch module can
•
Exchange VLAN configuration information with other GVRP switches.
•
Prune unnecessary broadcast and unknown unicast traffic.
•
Dynamically create and manage VLANs on switches connected through 802.1Q tagged
ports.
The switch module provides options to enable or disable GVRP capability. If an 802.1Q
tagged VLAN is enabled, but the GVRP is disabled, the only VLAN feature is static VLAN
registration entries. HP recommends backing up static VLAN register entries to the
configuration file.
Enabling Ingress Filtering on a Per Port Basis
If ingress filtering is enabled for a port, the interconnect switch will examine the VLAN
information in the packet header (if present) and decide whether or not to forward the packet.
The VID should match the PVID of that port, otherwise, that incoming packet is discarded.
If the packet is tagged with VLAN information, the ingress port will first determine if the
ingress port itself is a member of the tagged VLAN.
•
If the ingress port is not a member of the tagged VLAN, the packet is dropped.
•
If the ingress port is a member of the 802.1Q VLAN, the interconnect switch then
determines if the destination port is a member of the 802.1Q VLAN, the packet is
forwarded and the destination port transmits it to its attached network segment.
If the packet is not tagged with VLAN information, the ingress port tags the packet with its
own PVID as a VID (if the port is a tagging port). The interconnect switch then determines if
the destination port is a member of the same VLAN (has the same VID) as the ingress port.
•
If the destination port is not a member of the same VLAN, the packet is dropped.
•
If the destination port is a member of the same VLAN, the packet is forwarded and the
destination port transmits it on its attached network segment.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-27
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 42

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Ingress filtering is used to conserve bandwidth within the interconnect switch by dropping
packets that are not on the same VLAN as the ingress port at the point of reception. This
eliminates the subsequent processing of packets that will just be dropped by the destination
port.
To set the port VLAN ID (PVID) and enable GVRP for a port:
1. Select Port VLAN ID (PVID) from the VLANs menu. The following screen is
displayed.
The 802.1Q Port Settings window allows you to assign a Port VLAN ID (PVID)
number, enable or disable the ingress filtering check, and enable or disable GVRP for
individual ports. Ingress filtering means that a receiving port will check to see if the port
is a member of the VLAN ID in the packet before forwarding the packet.
2. In the From and To fields, select the range of ports to be included in the settings.
2-28 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 43

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
3. In the PVID field, type the PVID. This tuning variable allows for subnetworks that are
expected to lose a large number of packets. The PVID is used by the port to tag outgoing,
untagged packets and to make filtering decisions about incoming packets. If the port is
specified as tagging, and an untagged packet is forwarded to the port for transmission, the
port will add an 802.1Q tag using the PVID to write the VID in the tag. When the packet
arrives at its destination, the receiving device uses the PVID to make VLAN forwarding
decisions. If the port receives a packet, and ingress filtering is enabled, the port compares
the VID of the incoming packet to its PVID. If the two are unequal, the port drops the
packet. If the two are equal, the port receives the packet.
4. In the Ingress Filter field, select Off or On to specify that the port checks the VID of
incoming packets against its VID or PVID. If the two are equal, the port receives the
packet. It the two are unequal, the port drops the packet. This setting is used to limit
traffic to a single VLAN.
5. In the GVRP field, select Off or On to enable or disable GARP VLAN Registration
Protocol.
6. Click Apply after making changes to the settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM using
the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving Changes,” earlier in
this chapter.
Configuring Bandwidth
The GbE Interconnect Switch allows you to set a bandwidth limitation that restricts the
ingress (receiving) and egress (transmitting) packet rate for each port. If the packet rate
exceeds the allowed bandwidth rate, the excess packets will be dropped.
Bandwidth is configured in 1 to 127 units. Each unit is 117,481 bytes per second (around 0.94
Mb/s) for ports 1-26 and 939,850 bytes (about 7.52 Mb/s) for optional ports.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-29
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 44

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Configuring the Restart Ingress Bandwidth Settings
To configure the restart ingress bandwidth settings for a port:
1. Select Restart Ingress Bandwidth from the Port Bandwidth menu. The following
screen is displayed.
2. Select the desired port in the Port Num field.
3. Type a number between 1 and 127 in the Ingress Bandwidth (1–127 Units) field.
4. Click Apply.
5. Select Restart System from the Maintenance menu.
6. Select Yes to save the settings.
7. Click Restart. The system reboots and saves your settings.
NOTE: To delete an entry, click the icon in the Delete column on the Ingress Bandwidth
Setup Table.
Displaying the Current Ingress Bandwidth Table
To display the current ingress bandwidth table, select Current Ingress Bandwidth from the
Port Bandwidth menu. The following screen is displayed.
Current Ingress Bandwidth Table is a read-only screen displaying current ingress
bandwidth information.
2-30 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 45

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Configuring the Restart Egress Bandwidth Settings
To configure egress bandwidth for a specific port:
1. Select Restart Egress Bandwidth from the Port Bandwidth menu. The following
screen is displayed.
2. Select the desired port in the Port Num field.
3. Type a number between 1 and 127 in the Egress Bandwidth (1–127 Units) field.
4. Click Apply to save the change or addition.
5. Select Restart System from the Maintenance menu.
6. Select Yes to save the settings.
7. Click Restart. The system reboots and saves your settings.
NOTE: To delete an entry, click the icon in the Delete column on the Egress Bandwidth
Setup Table.
Displaying the Current Egress Bandwidth Table
To display the current egress bandwidth table, select Current Egress Bandwidth from the
Port Bandwidth menu. The following screen is displayed.
Current Egress Bandwidth Table is a read-only screen displaying current egress bandwidth
information.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-31
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 46

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Configuring the Thresholds of Broadcast, Multicast, and DA-Unknown Storm Prevention or Monitoring
The switch module allows you to set the threshold (in packets per second) for three types of
storms: broadcast, multicast, and one where the packet destination address (DA) is unknown.
The higher the threshold, the more packets the switch module can accept per second. If the
threshold is exceeded, any additional packets received are dropped. Entering a low value
means packets have a greater chance to exceed the threshold and be dropped from the switch
module.
To configure the thresholds of broadcast, multicast, and unknown storm prevention or
monitoring:
1. Select Threshold of Broadcast from the Configuration menu. The following screen is
displayed.
2. Select Enabled for the appropriate option.
3. Type a threshold value in the Threshold(Pkts/sec) field.
4. Click Apply to save the changes.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
Configuring Class of Service, Default Port Priority, and Traffic Class
This section describes how to configure class of service, default port priority, and traffic
class. For information on how to set the class of service queue options, refer to the
“Configuring Advanced Switch Module Features” section earlier in this chapter.
Class of Service (CoS) for packet prioritization allows you to set priority levels on the switch
module for forwarding packets based on the priority setting information in the packets. The
switch module supports four classes (0-3) of traffic (buffers or queues) for implementing
priority and allows eight priority levels (0-7) to be mapped to the four classes. Traffic from a
specific server port can be given priority over packets from other devices according to the
range of priority levels.
2-32 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 47

Setting Port Priority
To set the port priority:
1. Select Port Priority from the Configuration menu. The following screen is displayed.
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
2. Select the appropriate port in the From and To fields.
3. Type the priority in the Priority (0–7) field.
4. Click Apply to save the changes.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-33
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 48

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Setting Traffic Class
To set the traffic class:
1. Select Class of Traffic from the Configuration menu. The following screen is displayed.
The Configure Class of Traffic window allows you to configure traffic class priority by
specifying the class value, from 0 to 3, of the eight levels of priority of the switch
module.
2. Select the class value for each priority.
3. Click Apply to save the changes.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
2-34 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 49

Setting Class of Service
To set the class of service:
1. Select Class of Service from the Configuration menu. The following screen is
displayed..
The Class of Service Configuration window allows you to set the maximum number of
packets and the maximum allowable time a packet stays in the Class of Service (CoS)
queue.
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
2. In the Max. Packets field, type a value between 0 and 255. The Class of Service
scheduling algorithm starts from the highest CoS for a given port, sends the maximum
number of packets, then moves on to the next lower CoS. Entering zero instructs the
switch module to continue processing packets until there are no more packets in the CoS
transaction queue.
3. In the Max. Latency field, type the maximum allowable time a packet stays in the CoS
queue. The packets in this queue are not delayed more than the maximum allowable
latency entered in this field. The timer is disabled when this field is set to zero. Each unit
of this timer is equal to 16 microseconds.
4. Click Apply after making changes to the settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM using
the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving Changes,” earlier in
this chapter.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-35
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 50

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Configuring Port Security
To configure port security for a port or range of ports:
1. Select Port Security from the Configuration menu. The following screen is displayed.
2. Select the range of ports in the From and To fields.
3. Select Enabled in the Admin State field.
4. Type the maximum number of addresses in the Max. Address field.
5. Select the Mode that you want, either DeleteOnTimeout or DeleteOnReset.
6. Click Apply to apply your settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
2-36 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 51

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Configuring Priority MAC Addresses
To set the priority level for a MAC address:
1. Select Priority MAC Address from the Configuration menu. The following screens are
displayed.
2. Type the VLAN ID in the VLAN ID field.
3. Type the MAC address for which priority on the switch module is to be established in the
MAC Address field.
4. Type the priority level for the MAC address in the Priority Level field. The range is
from 0 to 7, with 0 being the highest priority.
5. In the Look at field, select the state under which the priority will be active. The
options are:
— Dst. Addr—Packets with the selected MAC address as their destination will be given
the selected priority.
— Src. Addr—Packets with the selected MAC address as their source will be given the
selected priority.
— Either—All packets with the selected MAC address will be given the selected
priority.
6. Click Apply to apply the changes.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-37
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 52

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Configuring Switch Module Date and Time
The switch module can maintain the current date and time. This information displays on the
management interfaces and is used to record the date and time of interconnect switch events
in the history log.
When a new switch module is first booted up, the firmware clock starts at zero (0) and counts
the seconds since bootup. In order for the clock to display the real date and time, you must
either
•
Manually set the date and time on the interconnect switch, or
•
Enable Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) on the switch module, and then set the
SNTP parameters.
SNTP allows the switch to synchronize its real time to the network time. When SNTP is
enabled, the switch module sends a request to a primary SNTP server in each period of a
specified polling interval asking for the Greenwich Mean Time (GMT). If the primary SNTP
server is not available, the request is sent to a secondary SNTP server.
When SNTP is enabled, the following events cause the switch module to request the date and
time through SNTP:
•
The polling interval time expires.
•
Changes are made to the configuration settings for Daylight Saving Time, time zone,
SNTP Server 1 or Server 2, or polling interval .
•
SNTP state is changed from disabled to enabled
IMPORTANT: If the system clock is set and power is lost to the interconnect switch, manual time
settings are reset to factory defaults when the interconnect switch is powered on. If this occurs,
manually reset the date and time. If SNTP is configured, losing power has no effect, so no manual
resetting of time is required.
Setting the Current Time or Enabling SNTP
To set the current time or enable SNTP:
1. Select Time Settings from the Configuration menu.
2-38 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 53

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
2. Select Current Time Settings. The following screen is displayed.
The Current Time screen allows you to set the current time and date, enable SNMP, and
set the SNMP parameters. The screen is divided into the following three sections:
— Current Time: Status displays the following:
— System Boot Time—The date and time when the last boot occurred
— Time Source—The method in which the switch module gets the current time
information: System Clock, Primary SNTP Server, or Secondary SNTP Server
— Current Time: SNTP Settings allows you to configure SNTP service:
— SNTP State—Select Disabled or Enabled. The default is disabled.
— SNTP Primary Server—Type the IP address for the primary SNTP server.
— SNTP Secondary Server— Type the IP address for the secondary SNTP server,
or leave as 0.0.0.0 to disable.
— SNTP Poll Interval in Seconds—Type the polling interval (in seconds) for
requesting the time from the server. A number from 30 to 99999 is allowed. The
default is 720.
— Current Time: Set Current Time allows you to manually set the current date and
time. This screen is grayed out if SNTP state is enabled. To manually set the date and
time, enter the following:
— Year—Select the current year.
— Month—Select the current month.
— Day—Select of the current day of the month.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-39
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 54
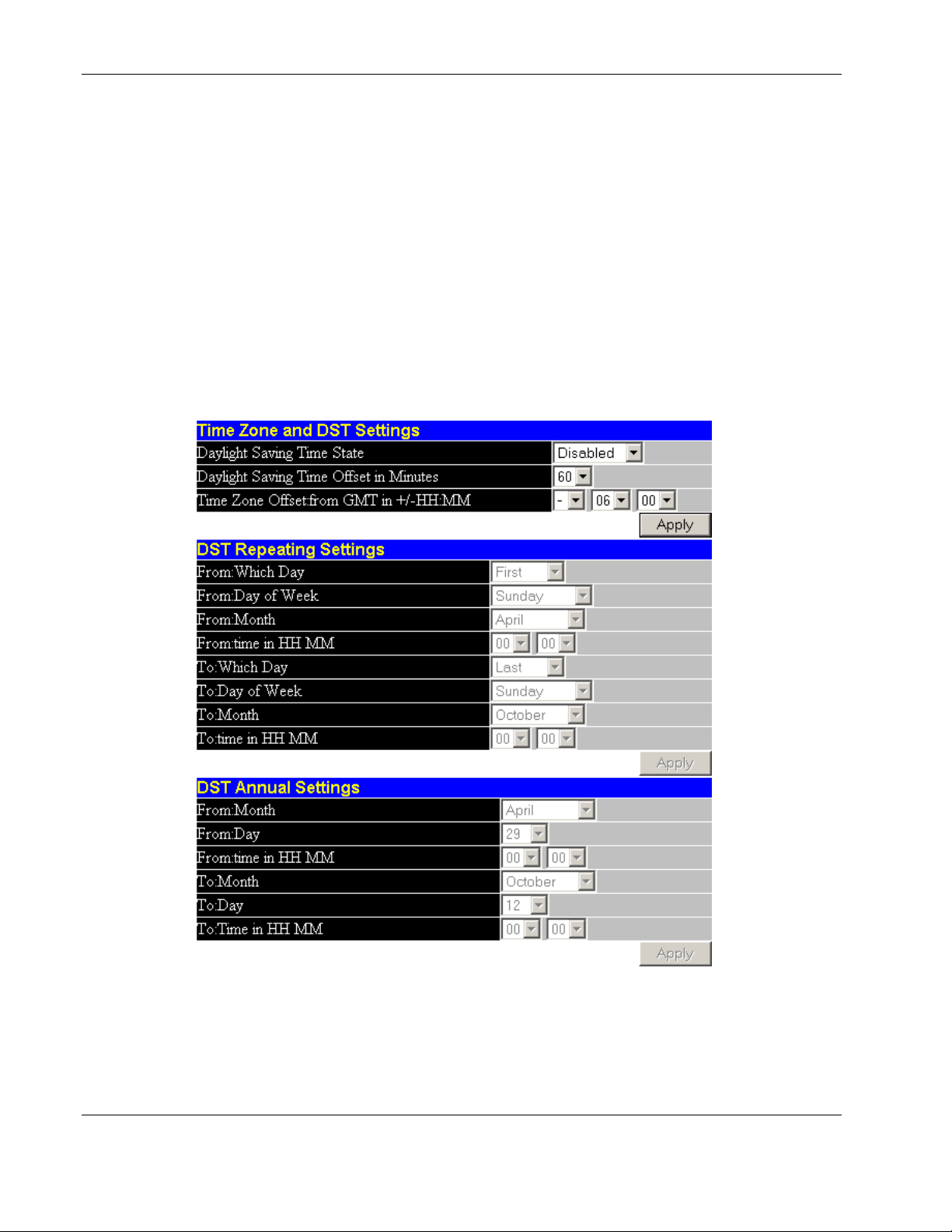
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
— Time in HH MM—Select the current time in hh mm format. Leading zeros (0)
are not required.
3. Click Apply after making changes to the settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM using
the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving Changes,” earlier in
this chapter.
Setting the Time Zone and Daylight Saving Time
To set the time zone and daylight saving time (DST):
1. Select Time Settings from the Configuration menu.
2. Select Time Zone and DST. The following screen is displayed:
2-40 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 55

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The Time Zone and DST screen allows you to set the time zone and daylight saving
time information. The screen is divided into the following three sections:
— Time Zone and DST Settings allows you to configure the following:
— Daylight Saving Time State—Select Disabled, Repeating, or Annual to set if
and how daylight saving time will be determined. Repeating allows you to set
specific days of the week and month, for example the first Sunday in April
through the fourth Sunday in October. Annual allow you to set specific dates for
the year, for example April 3 through October 27.
— Daylight Saving Time Offset in Minutes— Select the number of minutes that
the daylight saving time is offset from the current time. Valid values are 00 to 60.
— Time Zone Offset: from GMT in +/- HH:MM—Select the number of hours
before or after Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) that your time zone represents.
— DST Repeating Settings allows you to configure when the daylight saving time
offset will take effect and when its effect will be cancelled. These values only take
effect if the DST status is set to Repeating.
To set when the repeating offset will take effect, complete the following:
— From: Which Day—Select from First, Second, Third, and Fourth.
— From: Day of Week—Select the day of the week.
— From: Month—Select the month.
— From: Time in HH MM—Select the time in hh mm format.
To set when the offset will be cancelled, complete the following:
— To: Which Day—Select from First, Second, Third, and Fourth.
— To: Day of Week—Select the day of the week.
— To: Month—Select the month.
— To: Time in HH MM—Select the time in hh mm format.
— DST Annual Settings allows you to configure when the daylight saving time offset
will take effect and when its effect will be cancelled. These values only take effect if
the DST status is set to Annual.
Complete the following fields for when the annual offset will take effect:
— From: Month—Select the month.
— From: Day—Select the day of the month.
— From: Time in HH MM—Select the time in hh mm format.
Complete the following fields for when the offset will be cancelled:
— To: Month—Select the month.
— To: Day—Select the day of the month.
— To: Time in HH MM—Select the time in hh mm format.
3. Click Apply after making changes to the settings.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-41
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 56

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM using
the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving Changes,” earlier in
this chapter.
Configuring the Security IP
You can enter a list of IP addresses that are allowed to access the switch by means of SNMP,
Telnet, and the Web.
To specify which IP addresses are allowed to access the switch module:
1. Select Security IP from the Management menu. The following screen is displayed.
2. Type the appropriate IP addresses.
3. Click Apply.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
2-42 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 57

Configuring SNMP Manager
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Open Systems Interconnection (OSI)
Layer 7 (the application layer) protocol for remotely monitoring and configuring network
devices. SNMP enables network management stations to read and modify the settings of
gateways, routers, switches, and other network devices. SNMP can be used to perform many
of the same functions as a directly connected console, or can be used within an integrated
network management software package such as Insight Manager 7.
SNMP performs the following functions:
•
Sends and receives SNMP packets through the IP protocol
•
Collects information about the status and current configuration of network devices
•
Modifies the configuration of network devices
The switch module has software, called an agent, that processes SNMP requests. The user
program that makes the requests and collects the responses runs on the management station (a
designated computer on the network). The SNMP agent and the user program both use the
UDP/IP protocol to exchange packets.
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The authentication protocol ensures that both the switch SNMP agent and the remote user
SNMP application program discard packets from unauthorized users. SNMP (version 1)
implements a form of security by requiring that each request include a “community string.” A
community string is an arbitrary string of characters used as a “password” to control access to
the switch module.
To configure SNMP Manager parameters:
1. Select SNMP Manager from the Management menu. The following screen is displayed.
2. In the Community String field, type a user-defined SNMP community string.
3. In the Access Right field, select the access right of Read-Only or Read-Write.
4. In the Status field, set the status of the current community string to Valid or Invalid.
5. Click Apply after making changes to the settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-43
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 58

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Configuring Trap Manager
Traps are messages that alert you of events that occur on the switch module. The events can
be as serious as a reboot (someone accidentally reset the interconnect switch), or less serious
like a configuration file update. The switch module generates traps and sends them to the
network manager (trap recipient).
Trap recipients are special users of the network who are given certain rights and access in
overseeing the maintenance of the network. Trap recipients will receive traps sent from the
switch module, and they may take certain actions to avoid future failure or breakdown of the
network.
You can specify which network managers, may receive traps from the interconnect switch by
entering a list of the IP addresses of authorized network managers. Up to four trap-recipient
IP addresses and four corresponding SNMP community strings can be entered.
To configure the Trap Manager:
1. Select Trap Manager from the Management menu. The following screen is displayed.
The SNMP Trap Manager Configuration window allows you to set the trap receiving
station, which runs a network management application to receive and store traps.
2. In the Trap Receiving Station field, type the IP address of the trap receiving station.
3. In the Community String field, type a user-defined SNMP community string.
4. In the Status field, set the trap receiving station status to Valid or Invalid.
5. Click Apply after making changes to the settings.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM using
the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving Changes,” earlier in
this chapter.
2-44 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 59

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Monitoring Switch Module Functions
The Web-based monitoring screens allow you to monitor the following switch module
functions:
•
Port Utilization
•
Packets—Received (RX), UMB-cast (RX), Transmitted (TX)
•
Errors—Received (RX) and Transmitted (TX)
•
Size—Packet Size
•
Trunk Utilization
•
MAC Address Table
•
IGMP Snooping Table
•
Dynamic Group Registration
•
VLAN Status Table
Monitoring the Switch Module using the Active Switch Graphic
At the top of the main page, an active graphic of the switch module displays.
You can monitor the switch module status using the following:
•
Graphical LEDs display current link speed and activity.
•
RJ-45 connectors labeled 1 through 20 represent NIC 1 (on Switch A) or NIC 2 (on
Switch B) of server bays 1 through 20.
•
RJ-45 connectors labeled 21 and 22 on Switch A and Switch B represent cross-connect
ports.
•
RJ-45 connector labeled 23 on Switch A represents the port connected to the Integrated
Administrator.
•
RJ-45 connector labeled Mgmt represents the Integrated Administrator Management
connector (Switch A port 24 – 10/100 Ethernet).
•
RJ-45 connectors labeled UpLink1 and UpLink2 represent Gigabit Ethernet Port 25 and
Port 26 of the switch module.
IMPORTANT:
• RJ-45 connectors that are grayed out on the graphic of the current switch module belong to the
other switch module.
• Pointing on an RJ-45 connector that belongs to this switch module displays the port number.
• Selecting an RJ-45 connector that belongs to this switch module displays the port statistics.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-45
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 60

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Monitoring Port Utilization
When you select Port Utilization from the Monitoring menu, the following screen is
displayed.
The Port Utilization window shows the percentage of the total available bandwidth being
used on a specified port. The following information is displayed:
•
Utilization—Displays the percentage of the total bandwidth being used on the
specified port.
•
Time Interval—Select the frequency at which the information on the screen is refreshed.
The default is two seconds.
•
Record Number—Select the number of polling attempts. The default is 200.
•
Show/Hide—Select to show or hide the line graph for utilization.
•
Apply—Select to apply any changes made to the Time Interval, Record Number, and
Show/Hide fields.
•
Clear—Select to reset the counters.
2-46 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 61

Monitoring Port Packet Analysis
The Web manager allows various packet statistics to be viewed as either a line graph or a
table. You can select the type of graphic to display by clicking View Table or View Line
Chart.
Monitoring Received (RX) Packets
To monitor received packets, select Received (RX) Packets from the Packets menu. The
following screens are displayed.
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-47
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 62

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The Rx Packets Analysis window displays the number of bytes and packets received on
the port. The following information is displayed:
•
Time Interval—Select the frequency at which the information on the screen is refreshed.
The setting is between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default value is
one second.
•
Record Number—Select the number of times that the switch module will be polled. The
setting can be between 20 and 200. The default value is 20.
•
Bytes—Counts the number of bytes received on the port.
•
Packets—Counts the number of packets received on the port.
•
Unicast—Counts the total number of packets that were received by a unicast address.
•
Multicast—Counts the total number of packets that were received by a multicast address.
•
Broadcast—Counts the total number of packets that were received by a broadcast
address.
•
Show/Hide—Select to display or hide bytes and packets information.
•
Apply—Select to apply any changes made to the Time Interval, Record Number, and
Show/Hide fields.
•
Clear—Select to reset the counters.
2-48 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 63

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Monitoring Unicast, Multicast, and Broadcast (RX) Packets
To monitor unicast, multicast, and broadcast (UMB) packets, select UMB-cast (RX) Packets
from the Packets menu. The following screens are displayed.
The UMB-cast (RX) Packets window displays the number of good bytes and packets that
were received by a unicast, multicast, or broadcast address. The following information is
displayed:
• Time Interval—Select the frequency at which the information on the screen is refreshed.
The setting can be between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-49
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 64

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
• Record Number—Select the number of times the switch module will be polled. The
setting can be between 20 and 200.
•
Bytes—Counts the number of bytes received on the port.
•
Packets—Counts the number of packets received on the port.
•
Unicast—Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a unicast
address.
•
Multicast—Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a multicast
address.
•
Broadcast—Counts the total number of good packets that were received by a broadcast
address.
•
Show/Hide—Select to display or hide unicast, multicast, or broadcast packets.
•
Apply—Select to apply any changes made to the Time Interval, Record Number, and
Show/Hide fields.
•
Clear—Select to reset the counters.
Monitoring Transmitted (TX) Packets
To monitor transmitted packets, select Transmitted (TX) Packets from the Packets menu.
The following screens are displayed.
2-50 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 65
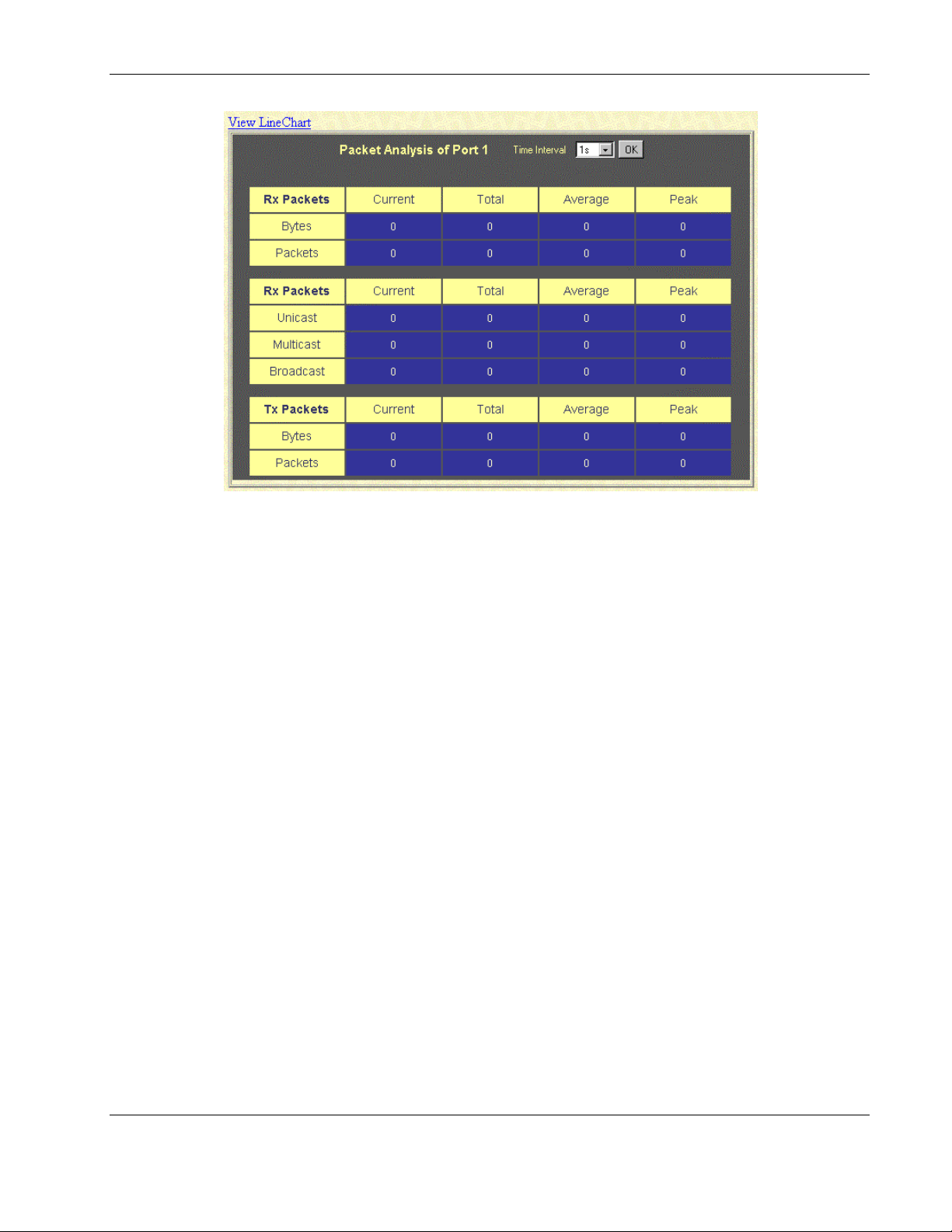
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The Tx Packets Analysis window displays the number of bytes and packets successfully sent
from the port. The following information is displayed:
•
Time Interval—Select the frequency at which the information on the screen is refreshed.
The setting can be between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default value is
one second.
•
Record Number—Select the number of times the switch module will be polled. The
setting can be between 20 and 200. The default value is 20.
•
Bytes—Counts the number of bytes successfully sent from the port.
•
Packets—Counts the number of packets successfully sent from the port.
•
Show/Hide—Select to display or hide bytes and packets information.
•
Apply—Select to apply any changes made to the Time Interval, Record Number, and
Show/Hide fields.
•
Clear—Select to reset the counters.
Monitoring Port Error Packets
The Web manager allows port error statistics compiled by the management agent of the
switch module to be viewed as either a line graph or a table. You can select the type of
graphic to display by clicking View Table or View Line Chart.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-51
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 66

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Monitoring Received (RX) Errors
To monitor received errors, select Received (RX) Errors from the Errors menu. The
following screens are displayed.
2-52 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 67

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The Rx Error Analysis window displays the number of errors received. The following
information is displayed:
•
Time Interval—Select the frequency at which the information on the screen is refreshed.
The setting can be between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default value is
one second.
•
Record Number—Select the number of times the switch module will be polled. The
setting can be between 20 and 200. The default value is 20.
•
CRCError—Counts packets with Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) errors.
•
UnderSize—Displays the number of frames detected that are less than the minimum
permitted frame size of 64 bytes and have a good CRC. Undersized frames usually
indicate collision fragments, a normal network occurrence.
•
OverSize—Counts packets received that were longer than 1518 bytes, or if a VLAN
frame, 1522 bytes, and less than the MAX_PKT_LEN. Internally, MAX_PKT_LEN is
equal to 1522.
•
Fragment—Displays the number of packets less than 64 bytes with either bad framing or
an invalid CRC. These packets are normally the result of collisions.
•
Jabber—Displays the number of frames with lengths more than the MAX_PKT_LEN
bytes. Internally, MAX_PKT_LEN is equal to 1522.
•
Drop—Displays the number of frames that were dropped by this port since the last
switch module reboot.
•
Show/Hide—Select to display or hide CrcError, UnderSize, OverSize, Fragment, Jabber,
and Drop errors.
•
Apply—Select to apply any changes made to the Time Interval, Record Number, and
Show/Hide fields.
•
Clear—Select to reset the counters.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-53
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 68
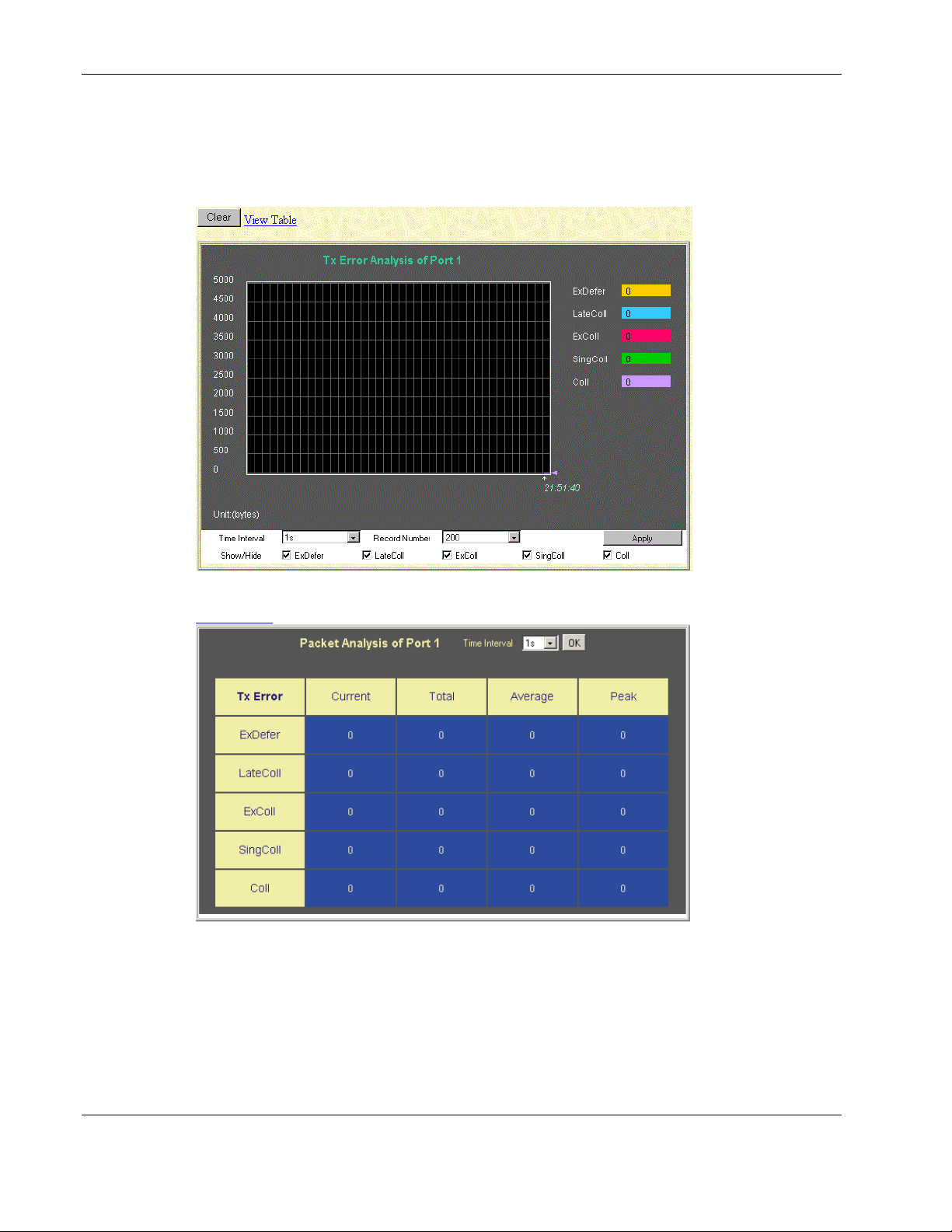
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Monitoring Transmitted (TX) Errors
To monitor transmitted errors, select Transmitted (TX) Errors from the Errors menu. The
following screens are displayed.
2-54 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 69

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The Tx Error Analysis window displays the number of errors that occurred during
transmission. The following information is displayed:
•
Time Interval—Select the frequency at which the information on the screen is refreshed.
The setting can be between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default value
is one second.
•
Record Number—Select the number of times the switch module will be polled. This
setting can be between 20 and 200. The default value is 20.
•
ExDefer—Counts the number of frames for which the first transmission attempt on a
particular interface was delayed because the medium was busy.
•
LateColl—Counts the number of times that a collision is detected later than 512 bittimes into the transmission of a packet.
•
ExColl—Counts the number of frames that experienced 16 collisions during transmission
and were aborted.
•
SingColl—Counts the number frames that experienced exactly one collision during
transmission.
•
Coll—Counts the number of collisions that occurred during the transmission of a frame.
•
Show/Hide—Select to display or hide ExDefer, LateColl, CRCError, SingColl, and Coll
errors.
•
Apply—Select to apply any changes made to the Time Interval, Record Number, and
Show/Hide fields.
•
Clear—Select to reset the counters.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-55
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 70

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Monitoring Packet Size
To monitor packet size, select Packet Size from the Size menu. The following screens are
displayed.
2-56 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 71

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The Rx Size Analysis window displays the number of packets received that were within a
certain range of bytes in length. The following information is displayed:
•
Time Interval—Select the frequency at which the information on the screen is refreshed.
The setting can be between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default value
is one second.
•
Record Number—Select the number of times the switch module will be polled. The
setting can be between 20 and 200. The default value is 20.
•
64—Displays the total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
64 bytes in length (excluding framing bits but including FCS bytes).
•
65–127—Displays the total number of packets (including bad packets) received that were
between 65 and 127 bytes in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including
FCS bytes).
•
128–255—Displays the total number of packets (including bad packets) received that
were between 128 and 255 bytes in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including
FCS bytes).
•
256–511—Displays the total number of packets (including bad packets) received that
were between 256 and 511 bytes in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but including
FCS bytes).
•
512–1023—Displays the total number of packets (including bad packets) received that
were between 512 and 1023 bytes in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS bytes).
•
1024–1518—Displays the total number of packets (including bad packets) received that
were between 1024 and 1518 bytes in length inclusive (excluding framing bits but
including FCS bytes).
•
Show/Hide—Select to display or hide received packets of the following lengths: 64, 65–
127, 128–255, 256–511, 512–1023, and 1024–1518.
•
Apply—Select to apply any changes made to the Time Interval, Record Number, and
Show/Hide fields.
•
Clear—Select to reset the counters.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-57
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 72

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Monitoring Trunk Utilization
To monitor trunk utilization, select Trunk Utilization from the Monitoring menu. The
following screens are displayed.
The Trunk Utilization window displays the port trunking groups and allows you to view
graphs of three items for an individual port trunking group: the percentage of total available
bandwidth being used by the group, the percentage of packets transmitted, and the percentage
of packets being received per second.
2-58 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 73

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The following information is displayed:
•
ID—Identifies the group ID for the port trunking group.
•
Group Name—Identifies the group name for the port trunking group.
•
Member Ports—Identifies ports that are members of the trunking group.
•
State—Identifies if the port trunking group is enabled or disabled.
•
Trunk Utilization View—Click View to view a line graph for the trunk utilization
•
Rx_Util—Displays the percentage of packets received.
•
Tx_Util—Displays the percentage of packets received.
•
R&Tx_Util—Displays the percentage of total available bandwidth being used by the
trunking group.
•
Time Interval—Select the frequency at which the information on the screen is refreshed.
The setting can be between 1s and 60s, where “s” stands for seconds. The default value
is one second.
•
Record Number—Select the number of times the switch module will be polled. The
setting can be between 20 and 200. The default value is 20.
•
Show/Hide—Select to display or hide Rx_Util, Tx_Util, R&Tx_Util information.
•
Apply—Select to apply any changes made to the Time Interval, Record Number, and
Show/Hide fields.
•
Clear—Select to reset the counters.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-59
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 74

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Monitoring MAC Address Forwarding Table
To monitor the MAC Address Forwarding Table, select MAC Address Table from the
Monitoring menu. The following screens are displayed.
The MAC Address Table displays the following information:
•
Search by VLAN ID—Type the VLAN ID you want to search for.
•
Search by MAC Address—Type the MAC address you want to search for.
•
Search by Port—Select the port number for which you want to search.
•
Jump—Click this to move to a sector of the database corresponding to a user defined
port, VLAN, or MAC address.
•
Find—Click this to find the data entry.
2-60 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 75

• Clear All—Click this to clear all forwarding table entries.
•
Clear By Port—Click this to clear the forwarding table entries that have the entered port
number.
•
VID—Identifies the VLAN ID of the VLAN that the port is a member of.
•
MAC Address—Identifies the MAC address entered into the address table.
•
Port—Identifies the port that the MAC address corresponds to.
•
Learned—Identifies the method that the switch module used to discover the MAC
address.
•
Next—Click this to view the next page of the address table.
Monitoring IGMP Snooping Table
To monitor IGMP snooping, select IGMP Snooping from the Monitoring menu. The
following screen is displayed.
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The IGMP Snooping Table is organized by VLAN ID (VID) and displays the following
information:
•
VID—Type the VLAN ID of the VLAN for which the IGMP Snooping table is to be
displayed.
•
Search—Click to search the IGMP Snooping Table for the current VID.
•
Multicast Group—Displays the IP address of a multicast group discovered by IGMP
Snooping.
•
MAC Address—Displays the corresponding MAC address discovered by IGMP
Snooping.
•
Port Map—Displays the ports that have forwarded multicast packets.
•
Reports—Displays the number of IGMP reports for the listed source.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-61
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 76

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Monitoring Dynamic Group Registration
When you select Dynamic Group Registration from the Monitoring menu, the following
screen is displayed.
The Dynamic Group Registration Table displays filtering information for VLANs that have
been discovered dynamically or have been configured into the bridge by local or network
management. The table specifies the set of ports that are allowed to be forwarded, based on
the frames received on a VLAN for this forwarding database (FDB) and the specific group
destination address for the VLAN.
Monitoring VLAN Status
When you select VLAN Status from the Monitoring menu, the following screen is
displayed.
The VLAN Status window displays information on which VLAN ports are in egress and
which are untagged.
The following information is displayed:
•
VLAN Index—Type the VLAN ID of the VLAN for which the information is to be
displayed.
•
Search—Click to search the VLAN ID.
•
IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID—Displays the VLAN for which the VLAN table is displayed.
•
Status—Displays the current status of the VID.
•
Creation time since switch power up—Displays the hours, minutes, and seconds since
the switch module was last rebooted.
2-62 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 77

• Current Egress Ports—Displays the current egress ports on the VLAN.
•
Current Untagged Ports—Displays the current untagged ports on the VLAN.
•
Prev—Click to display the previous VLAN.
•
Next—Click to display the next VLAN.
Using System Utilities
TFTP services allow the switch module firmware to be upgraded by downloading a new
firmware file from a TFTP server to the switch module. A configuration file can also be
loaded into the switch module, and switch module settings can be saved to a TFTP server. In
addition, the history log of the switch module can be uploaded from the switch module to a
TFTP server.
Please note that TFTP server software must be running on the management station for the
TFTP services to function. TFTP software is available in the interconnect switch utilities
package.
The TFTP screens share the following common fields:
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
•
TFTP Server IP Address—Identifies the IP address of the TFTP server. This server is
common for all TFTP services. The default TFTP server is 0.0.0.0.
•
TFTP Server Port Address— Identifies the port number on which the TFTP server is
listening. The default is 69. The valid values are 69 and 1024-65535.
•
File Name—Identifies the relative path based on the TFTP servers base path. The history
log path and firmware file path are unique. The path for the download and upload
configuration options is the same.
Upgrading Firmware
IMPORTANT: The TFTP server must be running TFTP server software to perform the file transfer.
TFTP server software is included as part of the utilities package.
To upgrade the switch module firmware:
1. Select Upgrade Firmware from the TFTP Services menu. The following screen is
displayed.
The Upgrade Firmware from TFTP Server window allows you to update the path of a
new firmware file on the TFTP server.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-63
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 78

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
2. Type the IP address of the TFTP Server in the TFTP Server IP Address field.
3. Type the TFTP server port number in the TFTP Server Port Number field.
4. Type the file name of the firmware file for the switch module in the File Name field.
5. Click Apply to save the TFTP server IP address, TFTP server port number, and file name
into the switch module RAM.
6. Click Start to initiate the file transfer. The system automatically reboots after the file
transfer is completed.
NOTE: A downloadable smart component, which further simplifies upgrading the switch module
firmware, is available at the following website:
www.compaq.com/support/servers
Downloading a Configuration File from a TFTP Server
IMPORTANT: Configuration files used in the earlier version of the switch module (firmware version 1.0)
are not supported by the present version (firmware version 2.0). The switch module Information window
displays the firmware version.
A configuration file can be downloaded from a TFTP server to the switch module. This file is
then used by the switch module to configure itself. Beginning in firmware version 2.0.0,
switch firmware configuration files are specified in XML format.
Downloaded XML configuration files do not need to specify every possible parameter. Only
the configuration parameters specified will be modified; others will remain unchanged.
To download a configuration file from a TFTP server:
1. Select Download Configuration from the TFTP Services menu. The following screen is
displayed.
2. Type the IP address of the TFTP Server in the TFTP Server IP Address field.
3. Type the TFTP server port number in the TFTP Server Port Number field.
4. Type the file name of the configuration file for the switch module in the File Name field.
5. Click Apply to save the TFTP server IP address, TFTP server port number, and file name
into the switch module RAM.
6. Click Start to initiate the file transfer.
2-64 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 79

Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
NOTE: For additional information, refer to Appendix H, XML Configuration, in the HP ProLiant e-class
C-GbE Interconnect Switch User Guide.
Uploading a Configuration File to TFTP Server
After saving the switch module configuration to NVRAM, HP highly recommends that you
upload the configuration image to TFTP server storage.
The management agent of the switch module can upload the current switch configuration
settings to a TFTP server.
To upload a configuration file to the TFTP server:
1. Select Upload Configuration from the TFTP Services menu. The following screen is
displayed.
2. Type the IP address of the TFTP server in the TFTP Server IP Address field.
3. Type the TFTP server port number in the TFTP Server Port Number field.
4. Type the complete path and file name of the firmware file for the switch module in the
File Name field.
5. Click Apply to save the TFTP server IP address, TFTP server port number, and file name
into the switch module RAM.
6. Click Start to initiate the file transfer.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter. If you do not save configurations to NVRAM, the configurations
you are uploading to a TFTP server will not be saved correctly.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-65
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 80
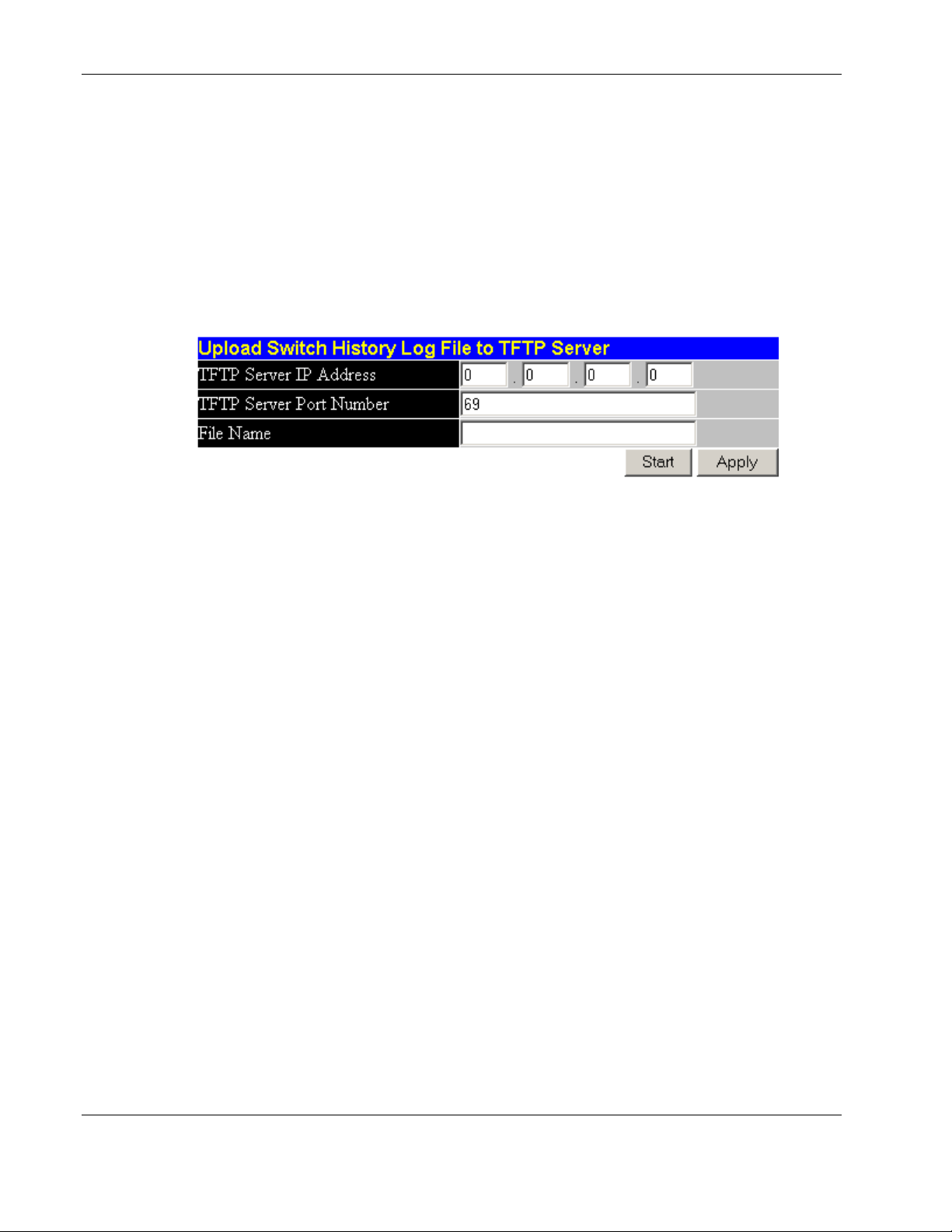
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Uploading Switch History Log
The switch module management agent can upload its history log file to a TFTP server.
IMPORTANT: An empty history file on the TFTP server must exist on the server before the switch
module can upload its history file.
To upload the switch history log:
1. Select Upload Switch History Log from the TFTP Services Maintenance menu. The
following screen is displayed.
2. Type the IP address of the TFTP Server in the TFTP Server IP Address field.
3. Type the TFTP server port number in the TFTP Server Port Number field.
4. Type the complete path and file name of the firmware file for the switch module in the
File Name field.
5. Click Apply to save the TFTP server IP address, TFTP server port number, and file name
into the switch module RAM.
6. Click Start to initiate the file transfer.
2-66 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 81

Displaying Switch Module History
The switch module can record event information to its own logs, to designated SNMP trap
receiving stations, and to the PC connected to the console manager.
To display switch module history, select Switch History from the Maintenance menu. The
following screen is displayed.
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
The following information is displayed:
•
Sequence—Displays a counter incremented whenever an entry to the switch module
history log is made. The table displays the last entry (highest sequence number) first.
•
Time—Displays the time of the event.
•
Log Text—Displays text describing the event that triggered the history log entry.
•
Clear—Clears the log.
•
Next—Click Next to display all of the Switch Trap Logs.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-67
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 82
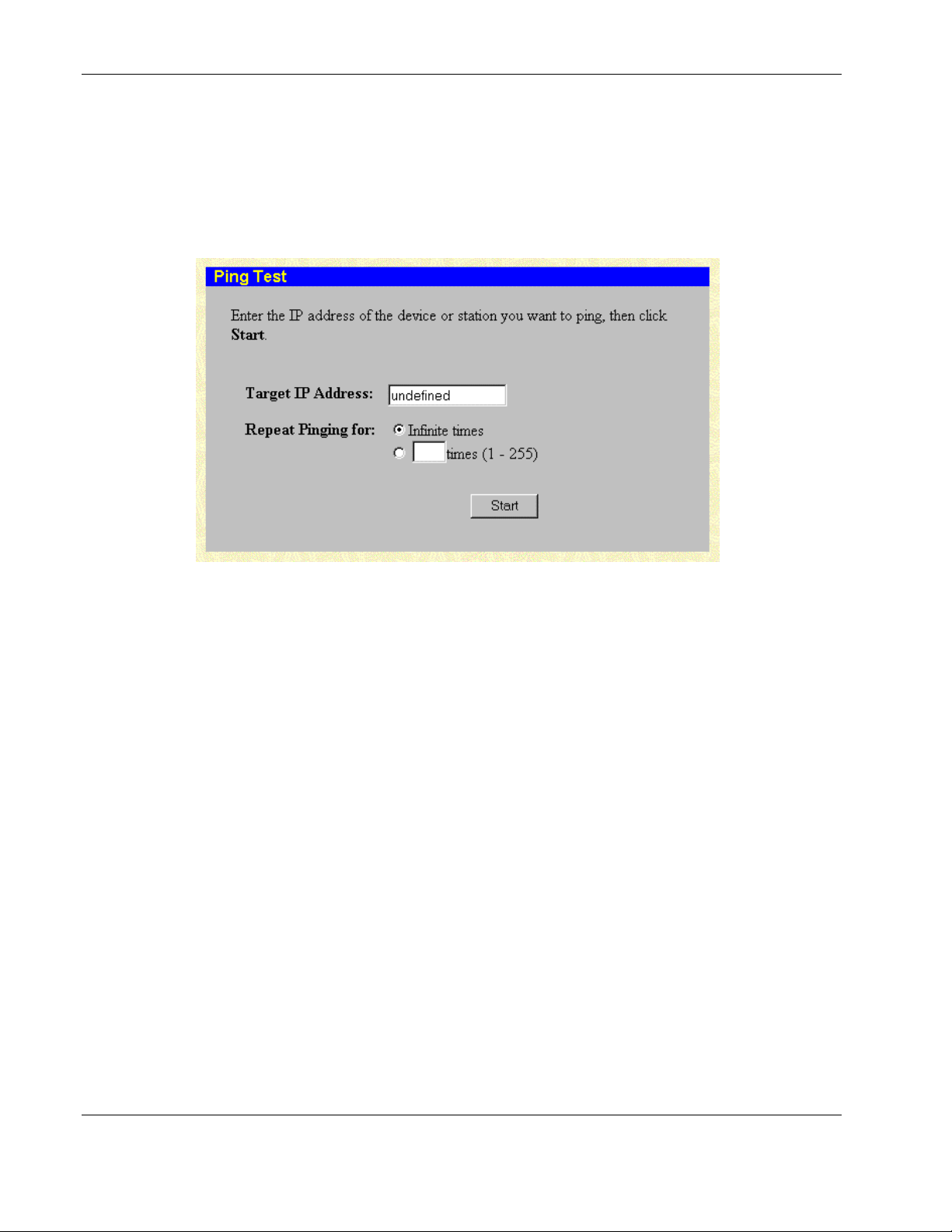
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Performing a Ping Test
The switch module can test the connection to another network device by pinging it.
To initiate the Ping program:
1. Select Ping Test from the Maintenance menu. The following screen is displayed.
2. Type the IP address of the network device to be pinged in the Target IP Address field.
3. Select the number of test packets to be sent (three is usually enough) in the Repeat
Pinging for field.
4. Click Start to initiate the Ping program.
2-68 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 83
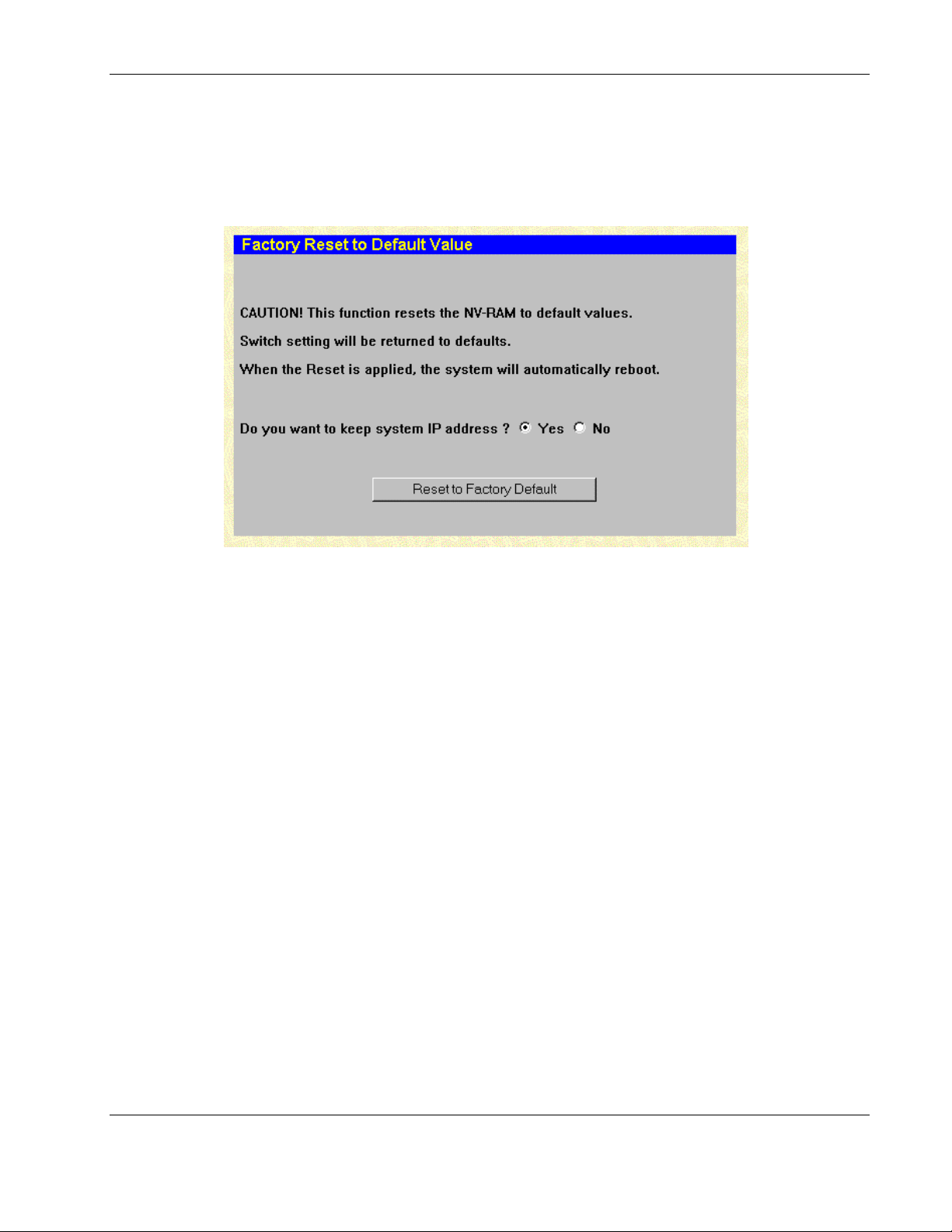
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Resetting the Switch Module Configuration to Factory Defaults
To reset the switch module configuration to the factory defaults:
1. Select Factory Reset from the Maintenance menu. The following screen is displayed.
2. Select Yes or No to keep the system IP address. If you want your IP address to default
from DHCP or BOOTP, select No.
3. Click Reset to Factory Default to reset the switch module.
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide 2-69
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 84
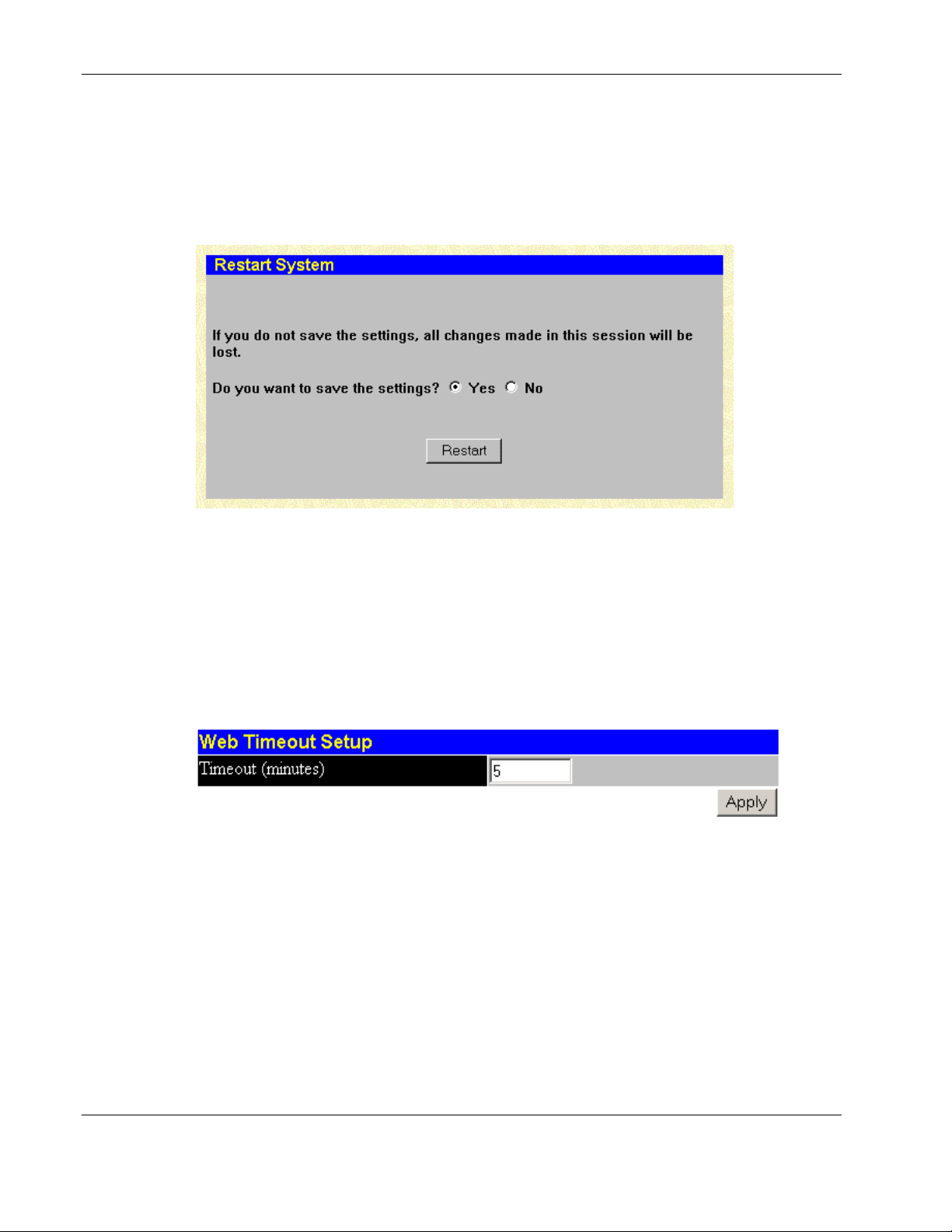
Configuring the Switch Modules using the Web-based Interface
Rebooting the Switch Module
You can perform a reboot of the switch module, which resets the system. To restart the
system:
1. Select Restart System from the Maintenance menu. The following screen is displayed.
2. Select Yes or No to save the settings.
3. Click Restart.
Setting the Web Connection Timeout
To set the Web connection timeout interval:
1. Select Connection Timeout from the Maintenance menu. The following screen is
displayed.
2. Type the desired age-out time in the Timeout (minutes) field.
3. Click Apply.
IMPORTANT: To save the configuration settings permanently, you must enter them into NVRAM
using the Save Changes option on the Maintenance menu. Refer to the section, “Saving
Changes,” earlier in this chapter.
Logging Out
To exit the setup pages, select Logout on the Maintenance menu. The Account Login
screen is displayed.
2-70 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
HP CONFIDENTIAL Codename: DeLorean Part Number: 322859-001 Last Saved On: 2/5/03 9:29 AM
Page 85

A E
active switch graphic 2-45 egress bandwidth settings 2-31
administrator 1-7 error packets, monitoring 2-51
advanced settings 2-9
auto-logout 2-9
F
Index
B
backpressure 2-11
bandwidth, configuring 2-29, 2-30
basic settings 2-6
Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP)
IP address assignment 1-5, 2-5
broadcast storm
configuring threshold 2-23, 2-32
browsers 1-1
C
Class of Service (CoS) 2-32
class of traffic 2-34
community names, SNMP 2-43
component-level repairs v
configuration 1-1
connecting procedures 1-2
connection timeout 2-70
current egress bandwidth settings 2-31
current ingress bandwidth settings 2-30
D
date, configuring 2-38
DA-unknown storm, configuring threshold 2-23,
2-32
daylight saving time, configuring 2-40
default settings
port priority 2-33
resetting factory defaults 2-69
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
IP address assignment 1-5, 2-5
Dynamic Group Registration Table 2-62
factory default reset 2-69
firmware upgrades 2-63
G
grounding v
grounding plug v
group address filter mode 2-10
GVRP (GARP VLAN Registration Protocol)
settings 2-10, 2-27, 2-28
H
help resources vi
history, switch 2-66
HP authorized reseller vi
HTTP protocol 1-1
I
IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol)
snooping
advanced settings 2-10
monitoring 2-61
overview 2-16
ingress bandwidth settings 2-30
ingress filtering 2-27
ingress filtering of ports 2-28
introduction 1-1
IP addresses 1-2, 1-6, 2-4, 2-5
L
logout procedures 2-70
M
MAC address aging time 2-9
HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide Index-1
Page 86

Index
MAC addresses
monitoring 2-60
manual assignment of IP addresses 1-5, 2-5
Microsoft Internet Explorer 1-1
mirroring of ports 2-13
monitoring functions 2-45
multicast filtering 2-16
multicast filtering, configuring 2-23
multicast storm, configuring threshold 2-23
N
Netscape Navigator 1-1
new user setup 2-2
NVRAM (non-volatile RAM) 2-1
P
packets, data
error monitoring 2-51
monitoring 2-47
prioritization service 2-32, 2-35
size monitoring 2-56
ping test 2-68
port trunking, configuring 2-14
ports
assigning VLANs to 2-26
configuring settings 2-21
default priority 2-33
GVRP settings 2-10, 2-27
mirroring of 2-13
monitoring utilization 2-46
security for 2-36
priority, port 2-33
privileges, user 2-2
protocols, network
BOOTP 1-5, 2-5
DHCP 1-5, 2-5
GVRP 2-10, 2-27
HTTP 1-1
SNMP 2-43
SNTP 2-11, 2-38
PVID (port VLAN ID) 2-26
R
rebooting switch 2-70
received (RX) packets 2-47, 2-52
remote management IP interface settings 2-4
restart egress bandwidth settings 2-31
restart ingress bandwidth settings 2-30
scheduling mechanism for CoS queues 2-10
security
configuring port 2-36
security IP management 2-42
size of packets, monitoring 2-56
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
configuring 2-43
SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol) 2-11, 2-38
spanning tree protocol (STP)
port level 2-20
switch module level 2-19
spanning tree protocol (STP) 2-18
T
technician notes v
telephone numbers vi
Telnet 2-10
TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol) server 2-63
time, configuring 2-38
timeout, connection 2-70
traffic classes, configuring 2-34
transmitted (TX) packets 2-50, 2-54
trap manager, configuring 2-44
trunk load sharing algorithm 2-10
trunking feature
configuring 2-14
monitoring utilization 2-58
U
UMB-cast (RX) packets 2-49
unicast filtering, configuring 2-22
upgrading firmware 2-63
users
privilege levels 2-2
setting up new 2-2
V
ventilation clearances v
VLANs (virtual local area networks)
monitoring 2-62
VLANs (virtual local area networks) 2-24
W
warranty vi
Web browsers 1-1
Web status 2-10
Web-based management 1-1
S
saving changes 2-1
Index-2 HP ProLiant BL e-Class C-GbE Interconnect Switch Web-based Interface Reference Guide
 Loading...
Loading...