HP ProLiant BL460c G6 User Manual

HP ProLiant BL460c G6 Server Blade
Part Number: 501274-002
User Guide
Abstract
This document is for the person who installs, administers, and troubleshoots servers and storage systems. HP assumes you are qualified in the
servicing of computer equipment and trained in recognizing hazards in products with hazardous energy levels.
March 2011
Edition: 2

© Copyright 2009, 2011 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP shall
not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein.
Microsoft, Windows, and Windows Server are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
AMD Athlon is a trademark of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Intel and Pentium are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
Java is a US trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.

Contents
Component identification ............................................................................................................... 6
Front panel components ............................................................................................................................. 6
Front panel LEDs ....................................................................................................................................... 7
SAS and SATA hard drive LEDs ................................................................................................................... 8
SAS and SATA hard drive LED combinations ................................................................................................ 8
System board components .......................................................................................................................... 9
Mezzanine connector definitions ..................................................................................................... 10
DIMM slot locations ....................................................................................................................... 10
System maintenance switch ............................................................................................................. 10
HP c-Class Blade SUV Cable..................................................................................................................... 11
Operations ................................................................................................................................. 12
Power up the server blade ........................................................................................................................ 12
Power down the server blade .................................................................................................................... 12
Remove the server blade .......................................................................................................................... 13
Remove the access panel.......................................................................................................................... 14
Install the access panel............................................................................................................................. 14
Remove the DIMM baffle .......................................................................................................................... 14
Setup ......................................................................................................................................... 15
Overview ............................................................................................................................................... 15
Installing an HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosure ........................................................................................... 15
Installing server blade options ................................................................................................................... 15
Installing interconnect modules .................................................................................................................. 15
Interconnect bay numbering and device mapping .............................................................................. 16
Connecting to the network ........................................................................................................................ 18
Installing a server blade ........................................................................................................................... 18
Hardware options installation ....................................................................................................... 21
Introduction ............................................................................................................................................ 21
Hard drive option .................................................................................................................................... 21
Processor option ...................................................................................................................................... 22
Memory options ...................................................................................................................................... 27
Memory subsystem architecture ....................................................................................................... 28
Single-, dual-, and quad-rank DIMMs ............................................................................................... 28
DIMM identification ....................................................................................................................... 28
Memory configurations ................................................................................................................... 29
General DIMM slot population guidelines ......................................................................................... 31
Installing a DIMM .......................................................................................................................... 33
Mezzanine card option ............................................................................................................................ 34
Cache module and battery pack option ...................................................................................................... 35
HP Trusted Platform Module option ............................................................................................................ 39
Installing the Trusted Platform Module board ..................................................................................... 40
Retaining the recovery key/password .............................................................................................. 43
Enabling the Trusted Platform Module ............................................................................................... 43
Cabling ..................................................................................................................................... 45
BBWC battery pack cabling ..................................................................................................................... 45
Contents 3

Using the HP c-Class Blade SUV Cable ...................................................................................................... 45
Connecting locally to a server blade with video and USB devices .................................................................. 45
Accessing a server blade with local KVM ......................................................................................... 46
Accessing local media devices ........................................................................................................ 46
Software and configuration utilities ............................................................................................... 48
Server blade deployment tools .................................................................................................................. 48
Software drivers and additional components ..................................................................................... 48
HP BladeSystem c-Class Advanced management ............................................................................... 48
Network-based PXE deployment ...................................................................................................... 49
Deployment methods ...................................................................................................................... 51
Configuration tools .................................................................................................................................. 54
SmartStart software ........................................................................................................................ 54
HP ROM-Based Setup Utility ............................................................................................................ 55
Array Configuration Utility .............................................................................................................. 57
Option ROM Configuration for Arrays ............................................................................................. 58
Re-entering the server serial number and product ID ........................................................................... 58
Management tools ................................................................................................................................... 59
Automatic Server Recovery ............................................................................................................. 59
ROMPaq utility .............................................................................................................................. 59
Integrated Lights-Out 2 technology ................................................................................................... 59
Erase Utility .................................................................................................................................. 60
Redundant ROM support ................................................................................................................ 60
USB support and functionality ......................................................................................................... 60
Diagnostic tools ...................................................................................................................................... 61
HP Insight Diagnostics .................................................................................................................... 61
HP Insight Diagnostics survey functionality ........................................................................................ 61
Integrated Management Log ........................................................................................................... 61
Remote support and analysis tools ............................................................................................................. 62
HP Insight Remote Support software ................................................................................................. 62
Keeping the system current ....................................................................................................................... 62
Drivers ......................................................................................................................................... 62
ProLiant Support Packs ................................................................................................................... 63
Operating System Version Support .................................................................................................. 63
HP Smart Update Manager ............................................................................................................. 63
Change control and proactive notification ........................................................................................ 63
Care Pack .................................................................................................................................... 64
Troubleshooting .......................................................................................................................... 65
Troubleshooting resources ........................................................................................................................ 65
Pre-diagnostic steps ................................................................................................................................. 65
Important safety information ............................................................................................................ 65
Symptom information ..................................................................................................................... 67
Prepare the server for diagnosis ...................................................................................................... 67
Loose connections ................................................................................................................................... 69
Service notifications ................................................................................................................................. 69
Server health LEDs ................................................................................................................................... 69
Troubleshooting flowcharts ....................................................................................................................... 69
Start diagnosis flowchart ................................................................................................................ 70
General diagnosis flowchart ........................................................................................................... 71
Server blade power-on problems flowchart ....................................................................................... 73
POST problems flowchart ............................................................................................................... 75
OS boot problems flowchart ........................................................................................................... 77
Server fault indications flowchart ..................................................................................................... 79
Contents 4

POST error messages and beep codes ....................................................................................................... 81
Battery replacement .................................................................................................................... 83
Regulatory compliance notices ..................................................................................................... 85
Regulatory compliance identification numbers ............................................................................................. 85
Federal Communications Commission notice ............................................................................................... 85
FCC rating label ............................................................................................................................ 85
Class A equipment......................................................................................................................... 85
Class B equipment ......................................................................................................................... 85
Declaration of conformity for products marked with the FCC logo, United States only ....................................... 86
Modifications .......................................................................................................................................... 86
Cables ................................................................................................................................................... 86
Canadian notice (Avis Canadien) .............................................................................................................. 86
European Union regulatory notice ............................................................................................................. 87
Disposal of waste equipment by users in private households in the European Union ......................................... 87
Japanese notice ...................................................................................................................................... 88
BSMI notice ............................................................................................................................................ 88
Korean notice ......................................................................................................................................... 88
Chinese notice ........................................................................................................................................ 89
Laser compliance .................................................................................................................................... 89
Battery replacement notice ........................................................................................................................ 89
Taiwan battery recycling notice ................................................................................................................. 90
Acoustics statement for Germany (Geräuschemission) .................................................................................. 90
Electrostatic discharge ................................................................................................................. 91
Preventing electrostatic discharge .............................................................................................................. 91
Grounding methods to prevent electrostatic discharge .................................................................................. 91
Specifications ............................................................................................................................. 92
Environmental specifications ..................................................................................................................... 92
Server blade specifications ....................................................................................................................... 92
Technical support ........................................................................................................................ 93
Before you contact HP .............................................................................................................................. 93
HP contact information ............................................................................................................................. 93
Customer Self Repair ............................................................................................................................... 93
Acronyms and abbreviations ...................................................................................................... 101
Index ....................................................................................................................................... 104
Contents 5
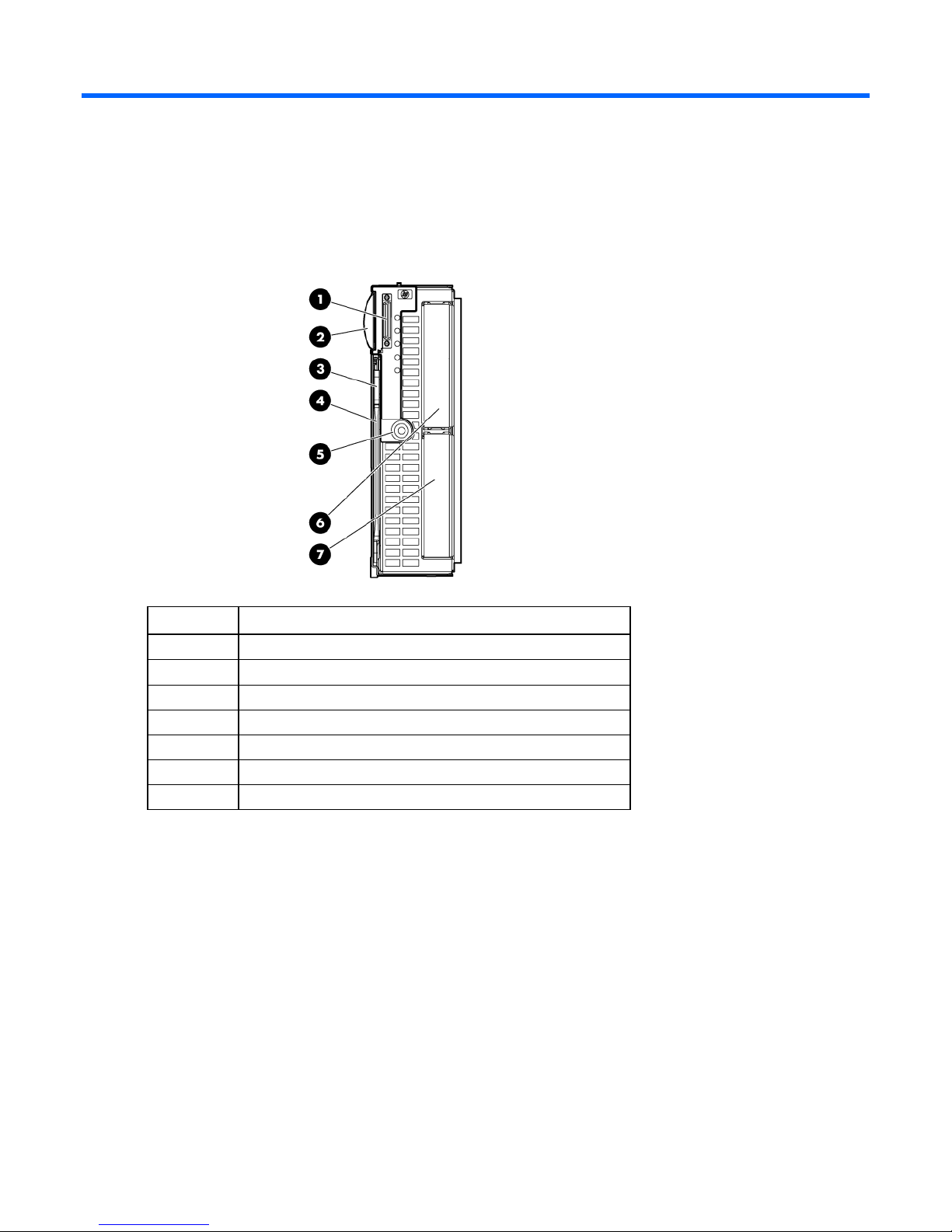
Component identification
Front panel components
Item Description
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
*The SUV connector and the HP c-Class Blade SUV Cable are for some server blade configuration and diagnostic
procedures.
SUV connector*
Serial label pull tab
Release button
Server blade release lever
Power On/Standby button
Hard drive bay 1
Hard drive bay 2
Component identification 6
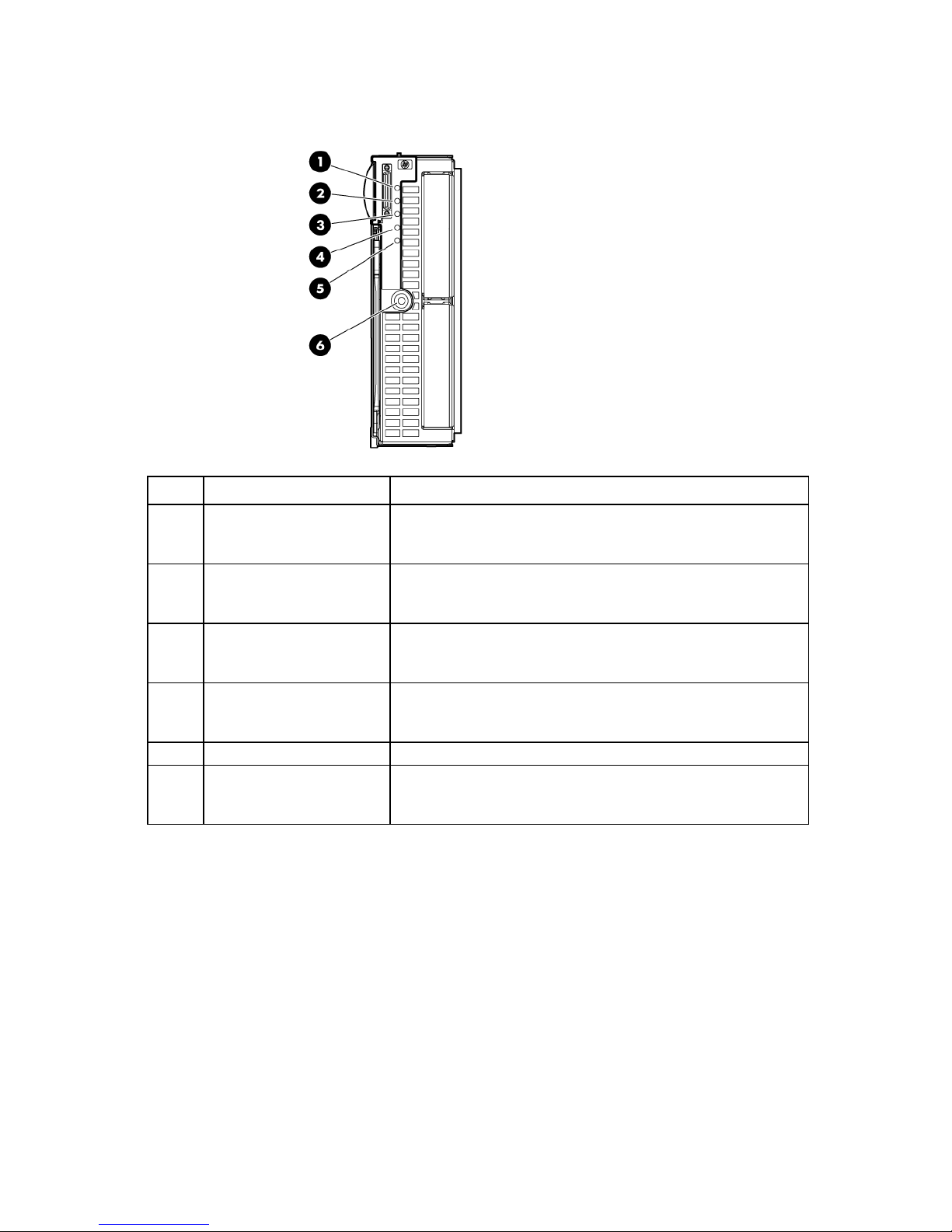
Front panel LEDs
Item Description Status
1
2
3
4
5
6
*Actual NIC numbers depend on several factors, including the operating system installed on the server blade.
UID LED Blue = Identified
Blue flashing = Active remote management
Off = No active remote management
Health LED Green = Normal
Amber flashing = Degraded condition
Red flashing = Critical condition
Flex-10 NIC 1 LED* Green = Network linked
Green flashing = Network activity
Off = No link or activity
Flex-10 NIC 2 LED* Green = Network linked
Green flashing = Network activity
Off = No link or activity
Reserved —
System power LED Green = On
Amber = Standby (auxiliary power available)
Off = Off
Component identification 7

SAS and SATA hard drive LEDs
Off
Do not remove the drive. Removing a drive may terminate the
Item Description
1
2
Fault/UID LED (amber/blue)
Online LED (green)
SAS and SATA hard drive LED combinations
Online/activity
LED (green)
On, off, or flashing
On, off, or flashing
On
On
Flashing regularly
(1 Hz)
Flashing regularly
(1 Hz)
Flashing irregularly
Flashing irregularly
Fault/UID LED
Interpretation
(amber/blue)
Alternating amber
and blue
Steadily blue The drive is operating normally, and it has been selected by a
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Off The drive is online, but it is not active currently.
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Off The drive is active, and it is operating normally.
The drive has failed, or a predictive failure alert has been received
for this drive; it also has been selected by a management
application.
management application.
A predictive failure alert has been received for this drive.
Replace the drive as soon as possible.
Do not remove the drive. Removing a drive may terminate the
current operation and cause data loss.
The drive is part of an array that is undergoing capacity expansion
or stripe migration, but a predictive failure alert has been received
for this drive. To minimize the risk of data loss, do not replace the
drive until the expansion or migration is complete.
current operation and cause data loss.
The drive is rebuilding, erasing, or it is part of an array that is
undergoing capacity expansion or stripe migration.
The drive is active, but a predictive failure alert has been received
for this drive. Replace the drive as soon as possible.
Component identification 8
Steadily amber
A critical fault condition has been identified for this drive, and the
Hard drive backplane connector
Online/activity
LED (green)
Fault/UID LED
(amber/blue)
Interpretation
Off
controller has placed it offline. Replace the drive as soon as
possible.
Off
Amber, flashing
regularly (1 Hz)
Off
Off The drive is offline, a spare, or not configured as part of an array.
A predictive failure alert has been received for this drive. Replace
the drive as soon as possible.
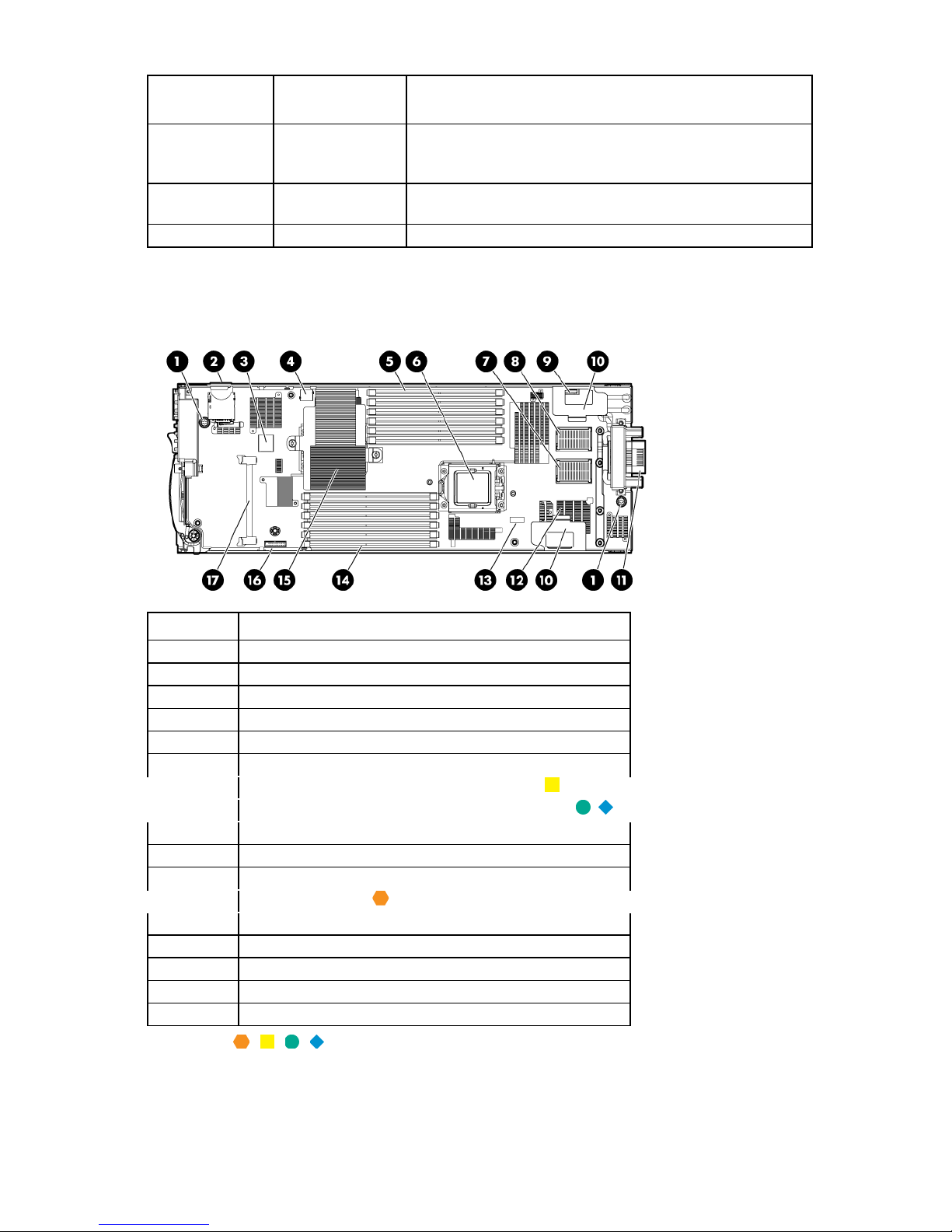
System board components
Item Description
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
The symbols correspond to the symbols located on the interconnect bays. For more information, see the
HP ProLiant BL460c G6 Server Blade Installation Instructions that ship with the server blade.
System board thumbscrews (2)
SD card slot
Internal USB connector
Processor 2 DIMM slots (6)
Processor socket 2
Mezzanine connector 1 (Type I mezzanine only)
Mezzanine connector 2 (Type I or Type II mezzanine)
System battery
Battery tray
Enclosure connector
Embedded NICs (2)
System maintenance switch
Processor 1 DIMM slots (6)
Processor socket 1 (populated)
TPM connector
Cache module connector
Component identification 9
Mezzanine connector definitions
A PCIe x8 mezzanine connector supports x16 cards at up to x8 speeds.
Item PCIe
Mezzanine connector 1
Mezzanine connector 2
x8, Type I mezzanine card only
x8, Type 1 or II mezzanine card
DIMM slot locations
DIMM slots are numbered sequentially (1 through 6) for each processor. The supported AMP modes use the
letter assignments for population guidelines.
System maintenance switch
Position Function Default
1*
2
3
4
5*
6*
7
8
*To access redundant ROM, set S1, S5, and S6 to ON.
iLO 2 security override Off
Configuration lock Off
Reserved Off
Reserved Off
Password disabled Off
Reset configuration Off
Reserved Off
Reserved Off
Component identification 10
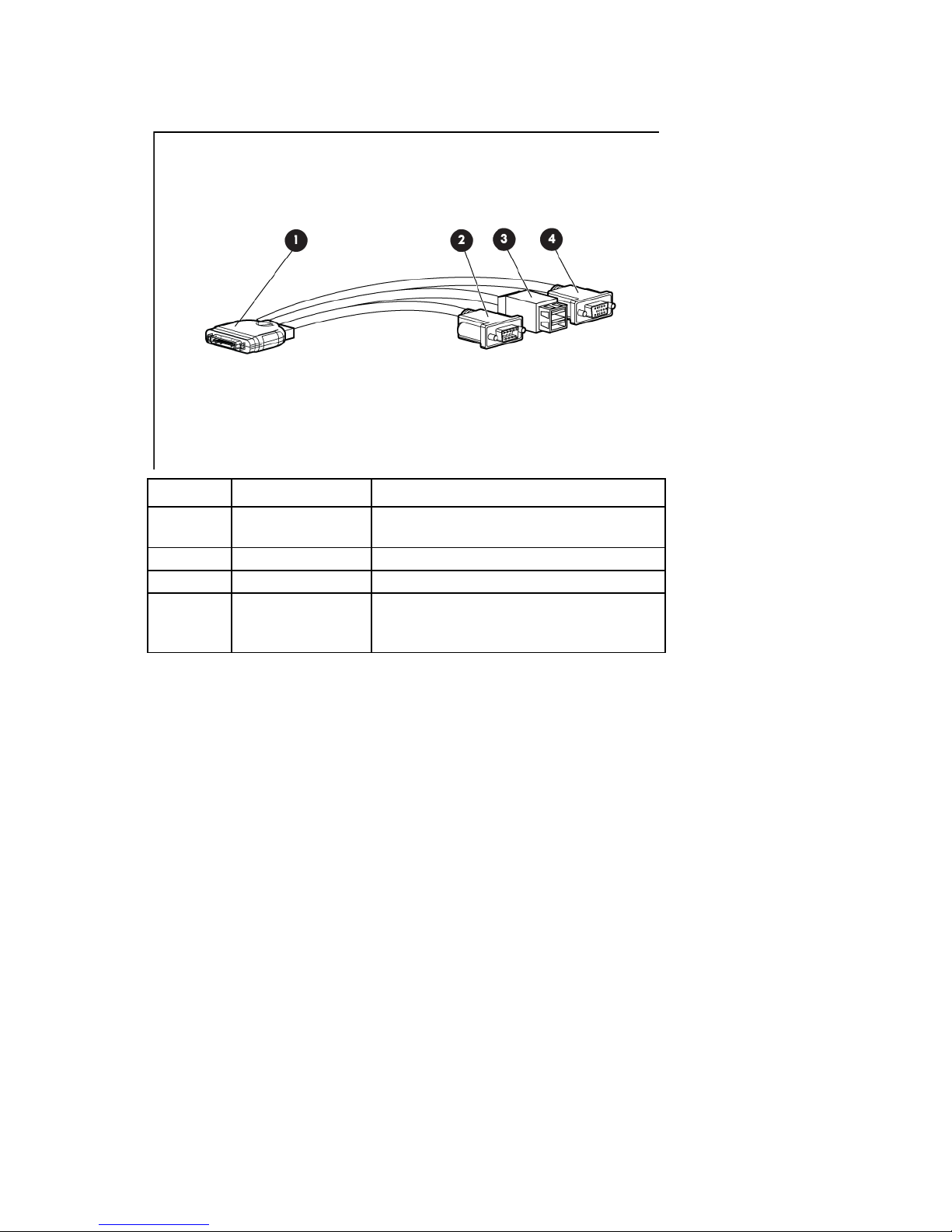
HP c-Class Blade SUV Cable
Item Connector Description
1
2
3
4
Server blade For connecting to the SUV connector on the
server blade front panel
Video For connecting a video monitor
USB For connecting up to two USB devices
Serial For trained personnel to connect a null modem
serial cable and perform advanced diagnostic
procedures
Component identification 11

Operations
Power up the server blade
The Onboard Administrator initiates an automatic power-up sequence when the server blade is installed. If
the default setting is changed, use one of the following methods to power up the server blade:
• Use a virtual power button selection through iLO 2.
• Press and release the Power On/Standby button.
When the server blade goes from the standby mode to the full power mode, the system power LED changes
from amber to green.
For more information about the Onboard Administrator, see the enclosure setup and installation guide on the
HP website (http://www.hp.com/support).
For more information about iLO 2, see "Integrated Lights-Out 2 technology (on page 59)."
Power down the server blade
Before powering down the server blade for any upgrade or maintenance procedures, perform a backup of
critical server data and programs.
Depending on the Onboard Administrator configuration, use one of the following methods to power down
the server blade:
• Use a virtual power button selection through iLO 2.
This method initiates a controlled remote shutdown of applications and the OS before the server blade
enters standby mode.
• Press and release the Power On/Standby button.
This method initiates a controlled shutdown of applications and the OS before the server blade enters
standby mode.
• Press and hold the Power On/Standby button for more than 4 seconds to force the server blade to enter
standby mode.
This method forces the server blade to enter standby mode without properly exiting applications and the
OS. It provides an emergency shutdown method if an application stops responding.
• Execute one of the following commands using the Onboard Administrator CLI:
poweroff server [bay number]
or
poweroff server [bay number] force
The first command initiates a controlled shutdown of applications and the OS before the server blade
enters standby mode. The second form of the command forces the server blade to enter standby mode
without exiting applications and the OS. This emergency method forces a shutdown if an application
stops responding.
• Use the Onboard Administrator GUI to initiate a shutdown:
Operations 12
a. Select the Enclosure Information tab, and then select the Overall checkbox in the Device Bays item.
b. Initiate a shutdown from the Virtual Power menu:
— Select Momentary Press to initiate a controlled shutdown of applications and the OS.
— Select Press and Hold to initiate an emergency shutdown of applications and the OS.
IMPORTANT: When the server blade is in standby mode, auxiliary power is still being provided.
To remove all power from the server blade, remove the server blade from the enclosure.
After initiating a virtual power down command, be sure that the server blade is in standby mode by
observing that the system power LED is amber.
Remove the server blade
CAUTION: Do not use the server blade release lever to lift or carry the server blade. Always
support the weight of the server blade by handling the chassis directly. Improper use can damage
To remove the component:
1. Identify the proper server blade.
2. Power down the server blade (on page 12).
3. Remove the server blade.
the release lever and the server blade.
4. Place the server blade on a flat, level work surface.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury from hot surfaces, allow the drives and the
internal system components to cool before touching them.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to electrical components, properly ground the server blade
before beginning any installation procedure. Improper grounding can cause ESD.
Operations 13
Remove the access panel
To remove the component:
1. Power down the server blade (on page 12).
2. Remove the server blade (on page 13).
3. Lift the access panel latch and slide the access panel to the rear.
4. Remove the access panel.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury from hot surfaces, allow the drives and the
internal system components to cool before touching them.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to electrical components, properly ground the server blade
before beginning any installation procedure. Improper grounding can cause ESD.
Install the access panel
1. Place the access panel on top of the server blade with the hood latch open. Allow the panel to extend
past the rear of the server blade approximately 0.8 cm (0.2 in).
2. Engage the anchoring pin with the corresponding hole in the latch.
3. Push down on the hood latch. The access panel slides to a closed position.
Remove the DIMM baffle
To remove the component:
1. Power down the server blade (on page 12).
2. Remove the server blade (on page 13).
3. Remove the access panel (on page 14).
4. Remove the DIMM baffle.
Operations 14

Setup
Overview
Installation of a server blade requires the following steps:
1. Install and configure an HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosure.
2. Install any server blade options.
3. Install interconnect modules in the enclosure.
4. Connect the interconnect modules to the network.
5. Install a server blade.
6. Complete the server blade configuration.
For definitions of the acronyms used in this document, refer to "Acronyms and abbreviations" in the server
blade user guide.
Installing an HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosure
Before performing any server blade-specific procedures, install an HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosure.
The most current documentation for server blades and other HP BladeSystem components is available at the
HP website (http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/documentation).
Documentation is also available in the following locations:
• Documentation CD that ships with the enclosure
• HP Business Support Center website (http://www.hp.com/support)
Installing server blade options
Before installing and initializing the server blade, install any server blade options, such as an additional
processor, hard drive, or mezzanine card.
Installing interconnect modules
For specific steps to install interconnect modules, see the documentation that ships with the interconnect
module.
Setup 15
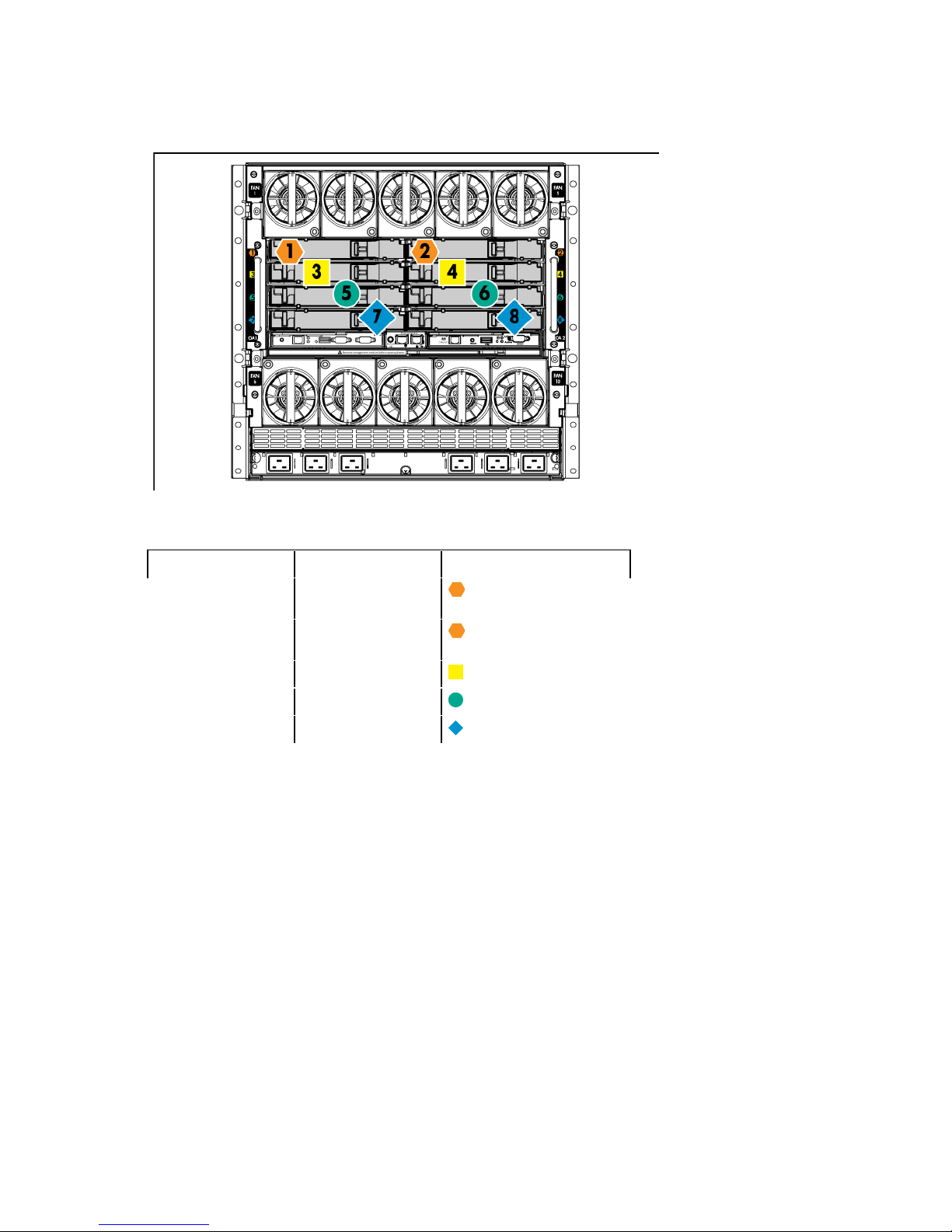
Interconnect bay numbering and device mapping
• HP BladeSystem c7000 Enclosure
To support network connections for specific signals, install an interconnect module in the bay corresponding
to the embedded NIC or mezzanine signals.
Server blade signal Interconnect bay Interconnect bay labels
Flex-10 NIC 1
(embedded)
Flex-10 NIC 2
(embedded)
Mezzanine 1
Mezzanine 2
1
2
3 and 4
5 and 6
7 and 8
For detailed port mapping information, see the HP BladeSystem enclosure installation poster or the
HP BladeSystem enclosure setup and installation guide on the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/documentation).
Setup 16
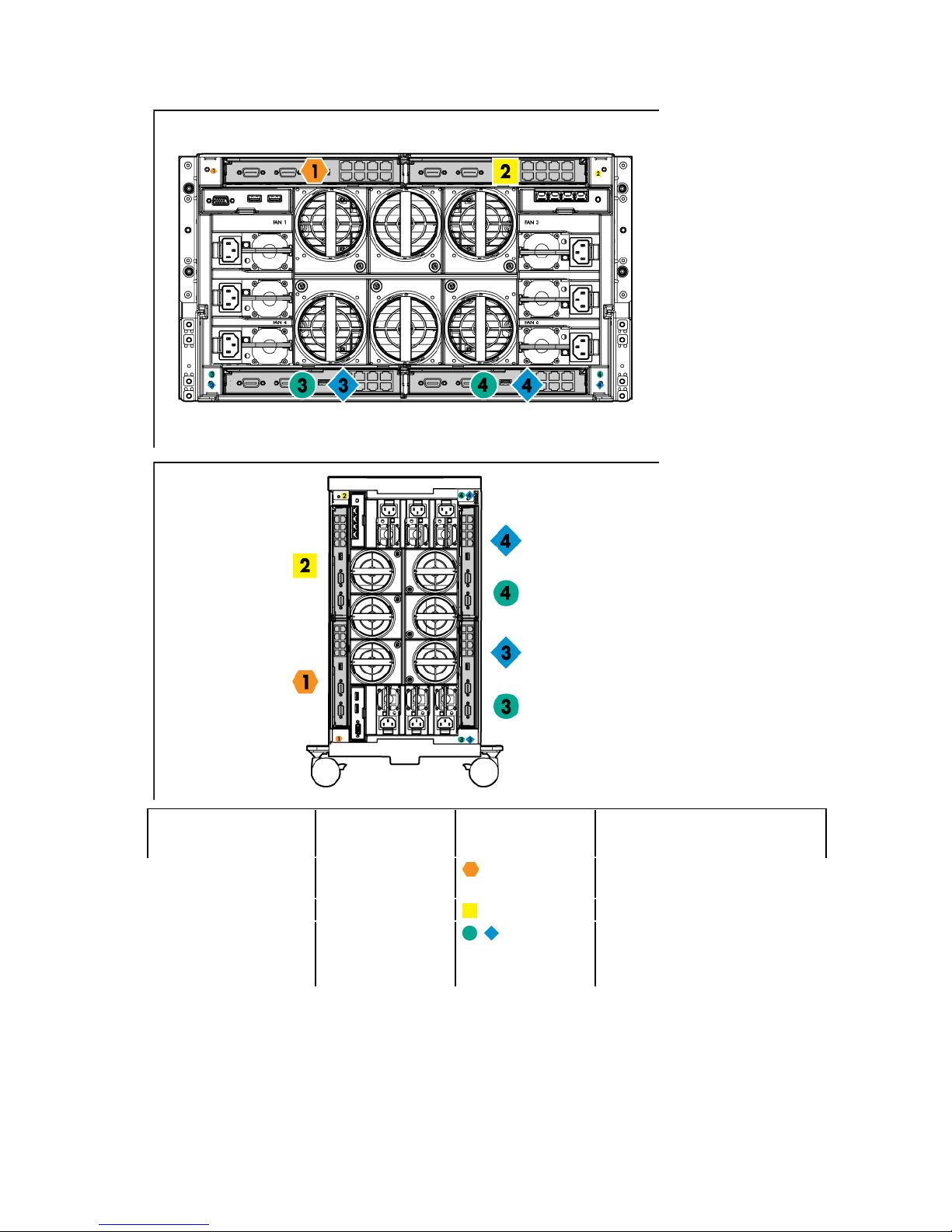
• HP BladeSystem c3000 Enclosure and Tower Enclosure
•
•
•
Server blade signal Interconnect bay
Flex-10 NIC 1, 2
(embedded)
Mezzanine 1
Mezzanine 2
For detailed port mapping information, see the HP BladeSystem enclosure installation poster or the
HP BladeSystem enclosure setup and installation guide on the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/documentation).
number
1
2
3,4
Interconnect bay
label
Notes
—
Four port cards connect to bay 2
Four port cards
Ports 1 and 3 connect to bay 3
Ports 2 and 4 connect to bay 4
Setup 17
Connecting to the network
To connect the HP BladeSystem to a network, each enclosure must be configured with network interconnect
devices to manage signals between the server blades and the external network.
Two types of interconnect modules are available for HP BladeSystem c-Class enclosures: Pass-Thru modules
and switch modules. For more information about interconnect module options, see the HP website
(http://www.hp.com/go/bladesystem/interconnects).
IMPORTANT: To connect to a network with a Pass-Thru module, always connect the Pass-Thru
module to a network device that supports Gigabit speed.
Installing a server blade
CAUTION: To prevent improper cooling and thermal damage, do not operate the server blade
or the enclosure unless all hard drive and device bays are populated with either a component or
1. Remove the device bay blank.
a blank.
Setup 18
2. Remove the enclosure connector cover.
3. Prepare the server blade for installation.
Setup 19
4. Install the server blade.
Setup 20
Hardware options installation
Introduction
If more than one option is being installed, read the installation instructions for all the hardware options and
identify similar steps to streamline the installation process.
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury from hot surfaces, allow the drives and the
Hard drive option
internal system components to cool before touching them.
CAUTION: To prevent damage to electrical components, properly ground the server before
beginning any installation procedure. Improper grounding can cause electrostatic discharge.
The server blade supports up to two SAS or SATA drives.
CAUTION: To prevent improper cooling and thermal damage, do not operate the server blade
or the enclosure unless all hard drive and device bays are populated with either a component or
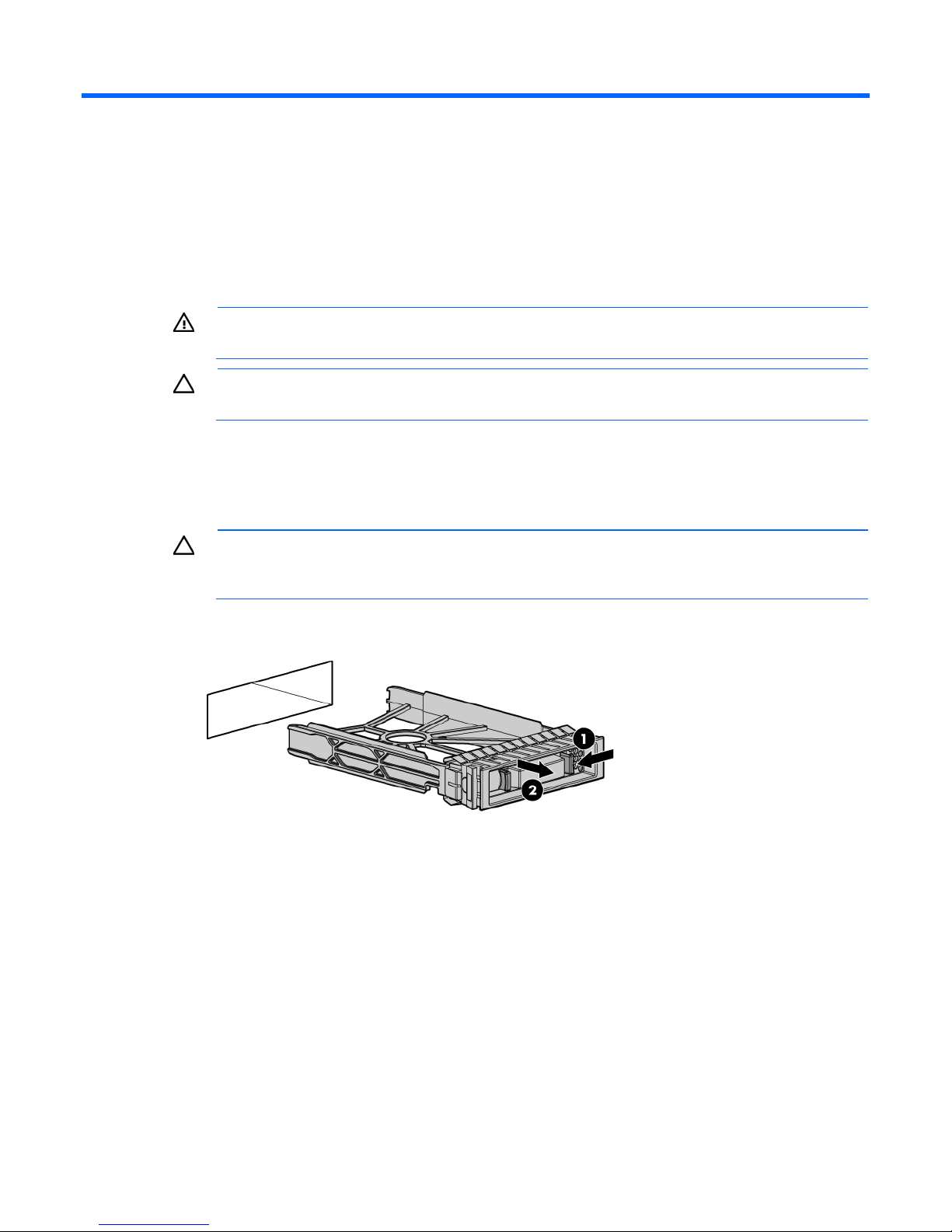
1. Remove the SAS hard drive blank.
a blank.
Hardware options installation 21
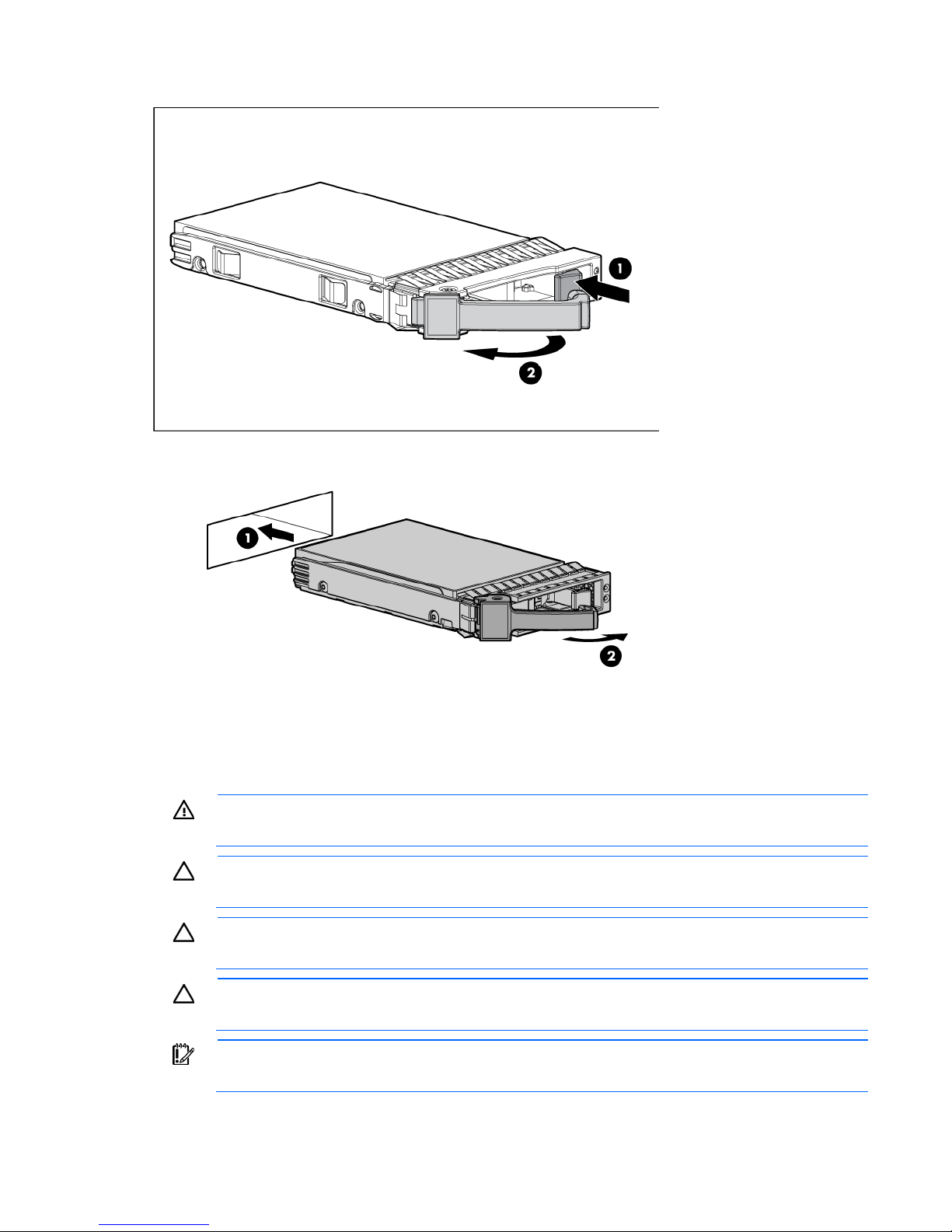
2. Prepare the hard drive.
3. Install the hard drive.
4. Determine the status of the hard drive from the hot-plug SAS hard drive LED combinations ("SAS and
SATA hard drive LED combinations" on page 8).
Processor option
WARNING: To reduce the risk of personal injury from hot surfaces, allow the drives and the
internal system components to cool before touching them.
CAUTION: To prevent possible server blade malfunction and damage to the equipment,
multiprocessor configurations must contain processors with the same part number.
CAUTION: To prevent possible server blade overheating, always populate processor socket 2
with a processor and a heatsink or a processor socket cover and a heatsink blank.
CAUTION: The heatsink thermal interface media is not reusable and must be replaced if the
heatsink is removed from the processor after it has been installed.
IMPORTANT: When installing the heatsink, align the guide pins on the processor retention
bracket with the alignment holes in the heatsink.
Hardware options installation 22
IMPORTANT:
Processor socket 1 must always be populated. If processor socket 1 is empty, the
server blade does not power up.
To install the component:
1. Update the system ROM using any standard ROM flash mechanism.
2. Power down the server blade (on page 12).
3. Remove the server blade (on page 13).
4. Remove the access panel (on page 14).
5. Remove all DIMM baffles ("Remove the DIMM baffle" on page 14).
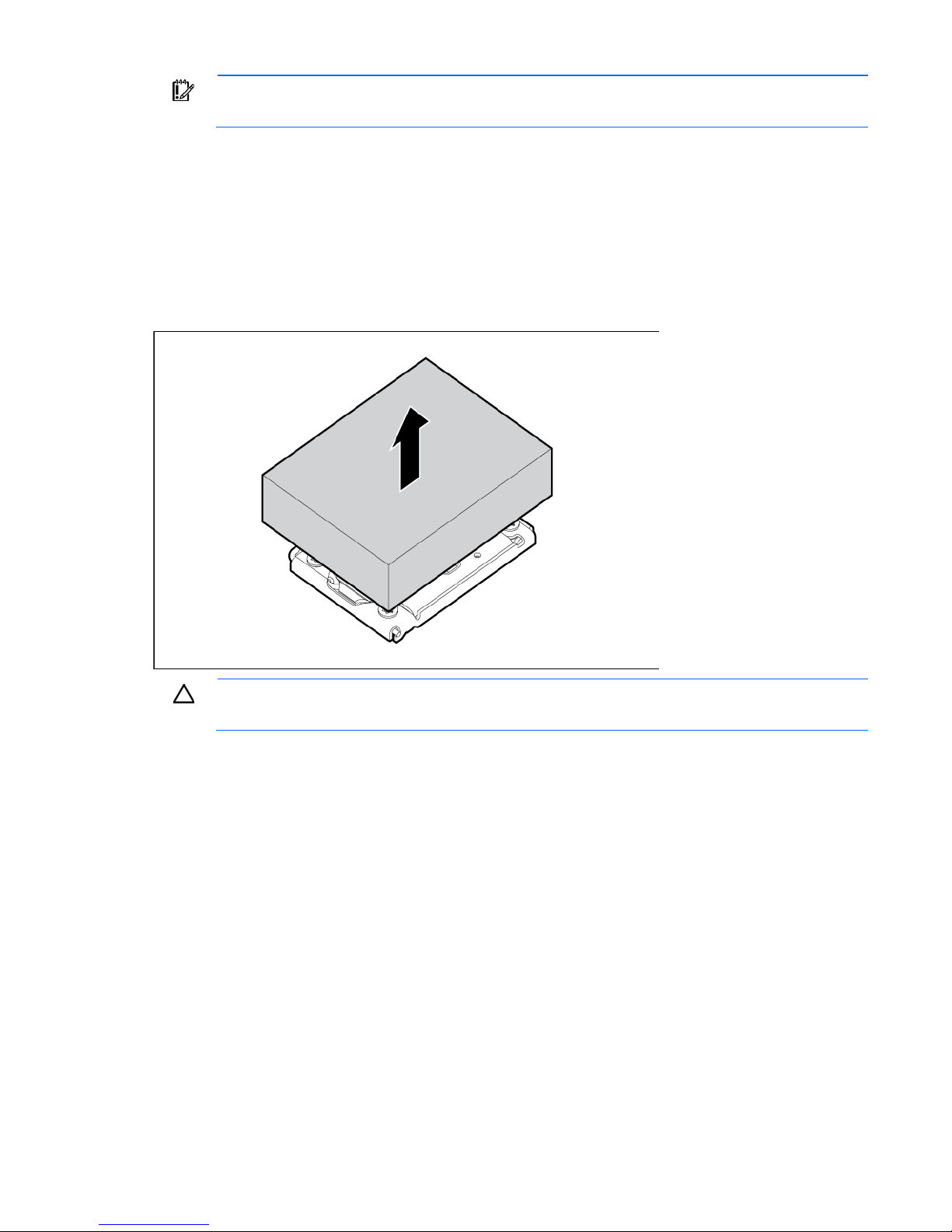
6. Remove the heatsink blank. Retain the heatsink blank for future use.
CAUTION: Failure to completely open the processor locking lever prevents the processor from
seating during installation, leading to hardware damage.
Hardware options installation 23
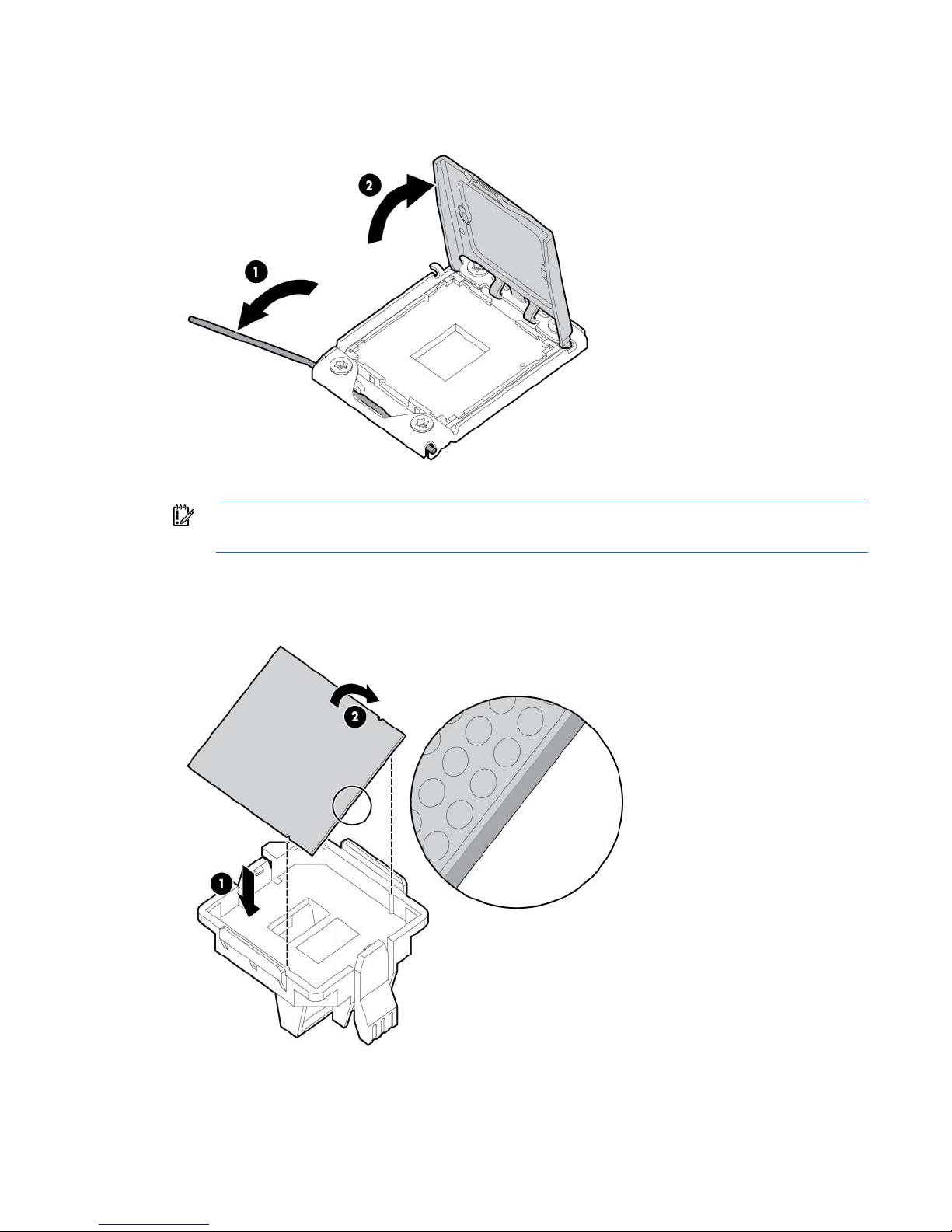
7. Open the processor locking lever and the processor socket retaining bracket. Do not remove the
processor socket cover.
IMPORTANT: Be sure the processor remains inside the processor installation tool.
8. If the processor has separated from the installation tool, carefully re-insert the processor in the tool.
Handle the processor by the edges only, and do not touch the bottom of the processor, especially the
contact area.
Hardware options installation 24

9. Align the processor installation tool with the socket, and then install the processor. THE PINS ON THE
SYSTEM BOARD ARE VERY FRAGILE AND EASILY DAMAGED.
CAUTION: THE PINS ON THE SYSTEM BOARD ARE VERY FRAGILE AND EASILY DAMAGED. To
avoid damage to the system board:
• Never install or remove a processor without using the processor installation tool.
• Do not touch the processor socket contacts.
• Do not tilt or slide the processor when lowering the processor into the socket.
Hardware options installation 25
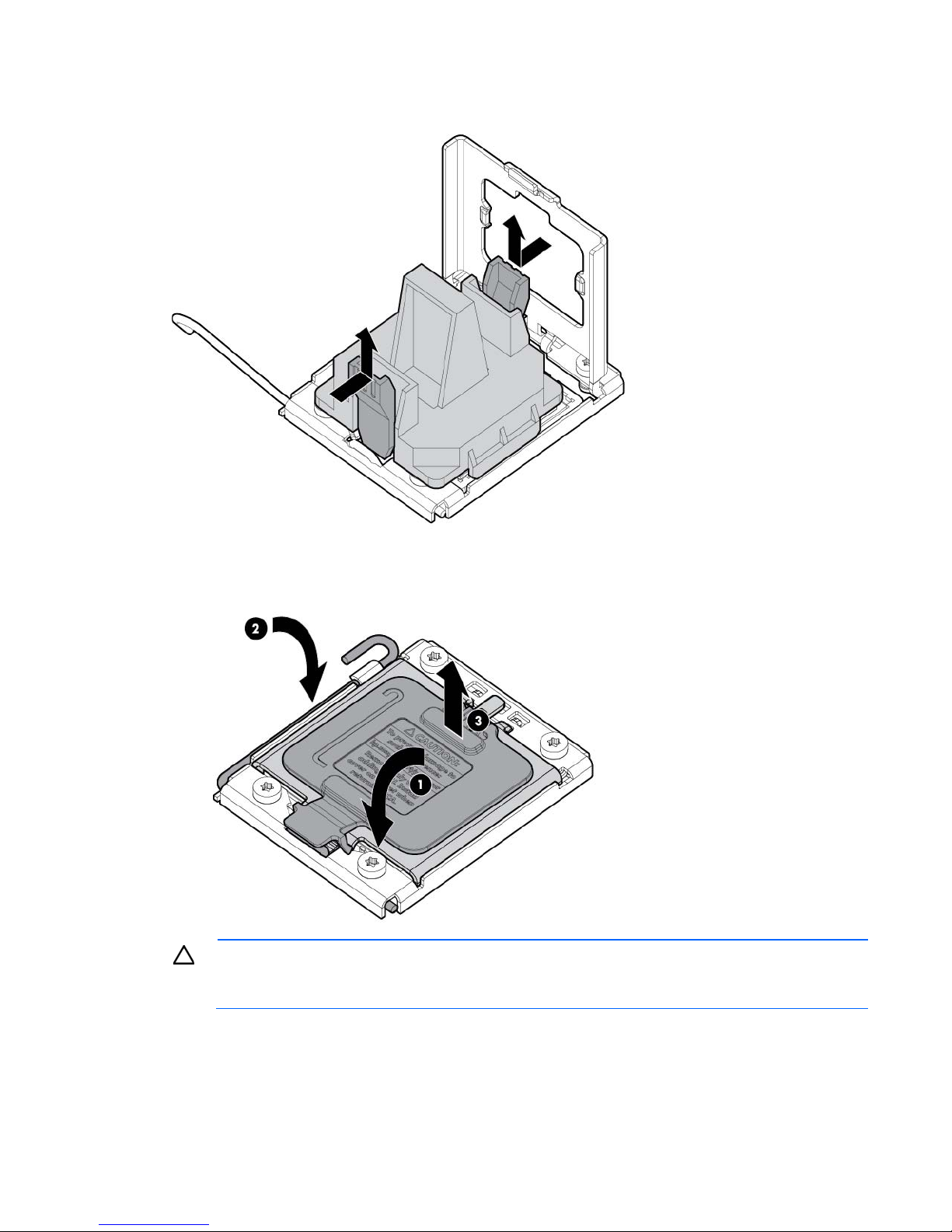
10. Press the tabs on the processor installation tool to separate it from the processor, and then remove the
retaining bracket before closing the processor
locking lever. The lever should close without resistance. Forcing the lever closed can damage the
tool.
11. Close the processor socket retaining bracket and the processor locking lever. The processor socket
cover is automatically ejected. Remove the cover.
CAUTION: Be sure to close the processor socket
processor and socket, requiring system board replacement.
Hardware options installation 26
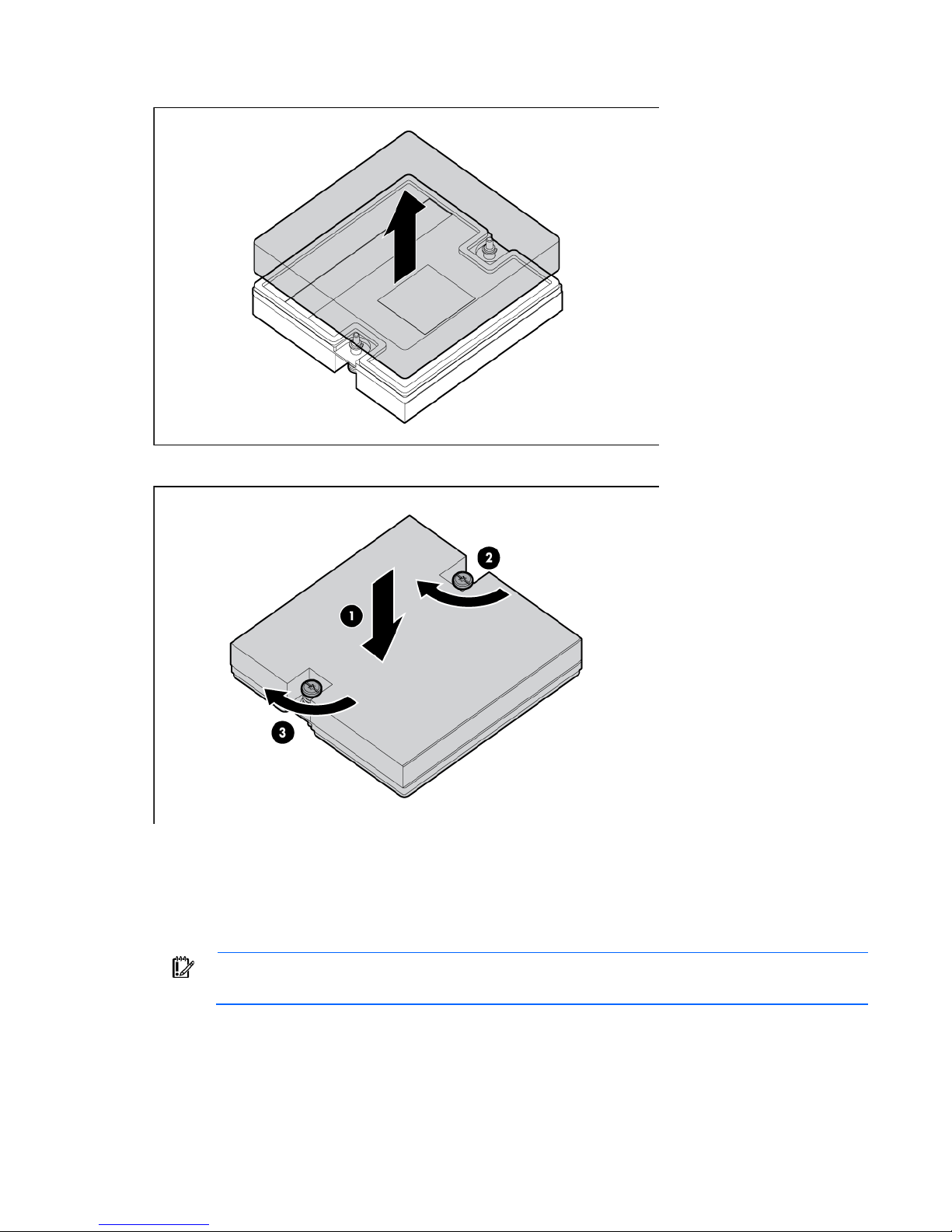
12. Remove the thermal interface protective cover from the heatsink.
13. Align and install the heatsink. Alternate tightening the screws until the heatsink is seated properly.
14. Install all DIMM baffles.
15. Install the access panel (on page 14).
Memory options
IMPORTANT: This server blade does not support mixing RDIMMs and UDIMMs. Attempting to
mix these two types causes the server to halt during BIOS initialization.
The memory subsystem in this server blade can support RDIMMs or UDIMMs. Both types are referred to as
DIMMs when the information applies to both types. When specified as RDIMM or UDIMM, the information
applies to that type only. All memory installed in the server blade must be the same type.
The server blade supports the following DIMM speeds:
Hardware options installation 27
• Single- and dual-rank PC3-10600 (DDR-1333) DIMMs operating at 1333 and 1066 MHz
F C 5
• Quad-rank PC3-8500 (DDR-1067) DIMMs operating at 1066 MHz
Depending on the processor model, the number of DIMMs installed, and whether UDIMMs or RDIMMs are
installed, the memory clock speed may be reduced to 1066 or 800 MHz. For more information on the effect
of DIMM slot population, see "General DIMM slot population guidelines (on page 31)."
Memory subsystem architecture
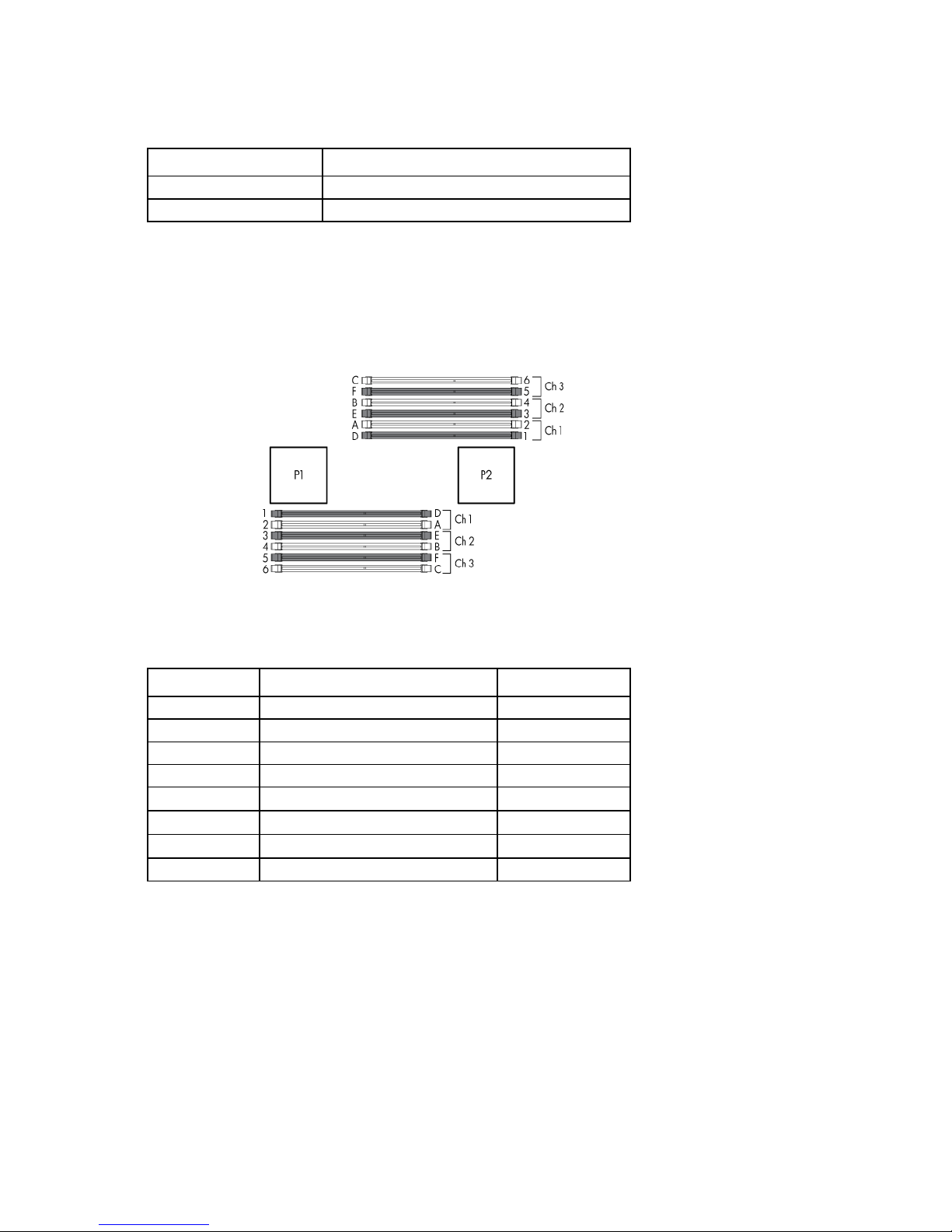
The memory subsystem in this server blade is divided into channels. Each processor supports three channels,
and each channel supports two DIMM slots, as shown in the following table.
Channel Slot Slot number
1
2
3
This multi-channel architecture provides enhanced performance in Advanced ECC mode. This architecture
also enables the Mirrored Memory and Lockstep memory modes. This server blade supports both Registered
PC3 DIMMs (RDIMMs) and Unbuffered DIMMs (UDIMMs).
D
A
E
B
1
2
3
4
6
DIMM slots in this server are identified by number and by letter. Letters identify the slots to populate for
specific AMP modes. Slot numbers are reported by ROM messages during boot and for error reporting.
Single-, dual-, and quad-rank DIMMs
To understand and configure memory protection modes properly, an understanding of single-, dual-, and
quad-rank DIMMs is helpful. Some DIMM configuration requirements are based on these classifications.
A single-rank DIMM has one set of memory chips that is accessed while writing to or reading from the
memory. A dual-rank DIMM is similar to having two single-rank DIMMs on the same module, with only one
rank accessible at a time. A quad-rank DIMM is, effectively, two dual-rank DIMMs on the same module. Only
one rank is accessible at a time. The server blade memory control subsystem selects the proper rank within
the DIMM when writing to or reading from the DIMM.
Dual- and quad-rank DIMMs provide the greatest capacity with the existing memory technology. For
example, if current DRAM technology supports 2-GB single-rank DIMMs, a dual-rank DIMM would be 4-GB,
and a quad-rank DIMM would be 8-GB.
DIMM identification
IMPORTANT: This server blade does not support mixing RDIMMs and UDIMMs. Attempting to
mix these two types causes the server to halt during BIOS initialization.
Hardware options installation 28
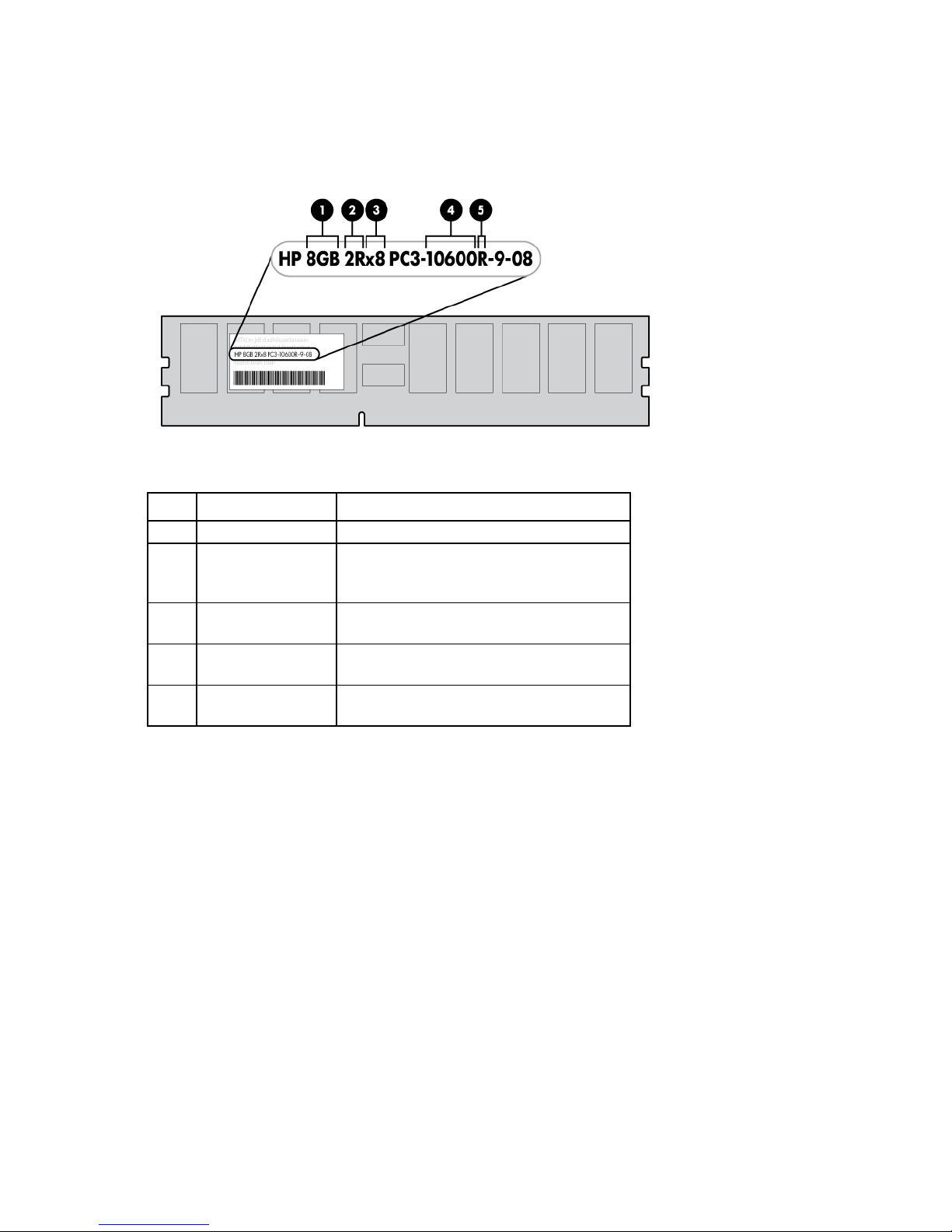
The memory subsystem may be populated with either RDIMMs or UDIMMs, but mixing the two types is not
supported. To determine DIMM characteristics, use the label attached to the DIMM and the following
illustration and table.
Item Description Definition
1
2
3
4
5
For the latest supported memory information, see the QuickSpecs on the HP website (http://www.hp.com).
Size —
Rank 1R = Single-rank
2R = Dual-rank
4R = Quad-rank
Data width x4 = 4-bit
x8 = 8-bit
Memory speed 10600 = 1333-MHz
8500 = 1066-MHz
DIMM type R = RDIMM (registered)
E = UDIMM (unbuffered with ECC)
Memory configurations
To optimize server blade availability, the server blade supports the following AMP modes:
• Advanced ECC—provides the greatest memory capacity for a given DIMM size, while providing up to
4-bit error correction. This mode is the default option for this server blade.
• Mirrored Memory—provides maximum protection against failed DIMMs. Uncorrectable errors in one
channel are corrected by the mirror channel.
• Lockstep—provides enhanced protection while making all installed memory available to the operating
system. The server blade can continue to function if a single- or multi-bit memory failure within a single
DRAM device occurs.
Advanced Memory Protection options are configured in RBSU. If the requested AMP mode is not supported
by the installed DIMM configuration, the server blade boots in Advanced ECC mode. For more information,
see "HP ROM-Based Setup Utility (on page 55)."
Hardware options installation 29

For the latest memory configuration information, see the QuickSpecs on the HP website
(http://www.hp.com).
RDIMM maximum memory configurations
The following table lists the maximum memory configuration possible with 8-GB RDIMMs.
Rank Single-processor Dual-processor
Single-rank
Dual-rank
Quad-rank
48 GB 96 GB
48 GB 96 GB
32 GB 64 GB
UDIMM maximum memory configurations
The server blade supports a maximum of 12 GB with one processor and 24 GB with two processors using
2-GB single- or dual-rank UDIMMs.
Advanced ECC memory configuration
Advanced ECC memory is the default memory protection mode for this server blade. Standard ECC can
correct single-bit memory errors and detect multi-bit memory errors. When multi-bit errors are detected using
Standard ECC, the error is signaled to the server blade and causes the server blade to halt.
Advanced ECC protects the server blade against some multi-bit memory errors. Advanced ECC can correct
both single-bit memory errors and 4-bit memory errors if all failed bits are on the same DRAM device on the
DIMM.
Advanced ECC provides additional protection over Standard ECC because it is possible to correct certain
memory errors that would otherwise be uncorrected and result in a server blade failure. The server blade
provides notification that correctable error events have exceeded a pre-defined threshold rate.
Mirrored memory configuration
Mirroring provides protection against uncorrected memory errors that would otherwise result in server blade
downtime. Mirroring is performed at the channel level. Channels 1 and 2 are used; channel 3 is not
populated.
Data is written to both memory channels. Data is read from one of the two memory channels. If an
uncorrectable error is detected in the active memory channel, data is retrieved from the mirror channel. This
channel becomes the new active channel, and the system disables the channel with the failed DIMM.
Lockstep memory configuration
Lockstep mode provides protection against multi-bit memory errors that occur on the same DRAM device.
Lockstep mode can correct any single DRAM device failure on x4 and x8 DIMM types. The DIMMs in each
channel must have identical HP part numbers.
Lockstep mode uses channel 1 and channel 2. Channel 3 is not populated. Because channel 3 cannot be
populated when using Lockstep mode, the maximum memory capacity is lower than Advanced ECC mode.
Memory performance with Advanced ECC is also slightly higher.
Hardware options installation 30
 Loading...
Loading...