
HP Prime Graphing Calculator
User Guide

Edition1
Part Number NW280-2001
Legal Notices
This manual and any examples contained herein are provided "as is" and are subject to
change without notice. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty of any kind with regard
to this manual, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability, noninfringement and fitness for a particular purpose.
Portions of this software are copyright 2013 The FreeType Project (www.freetype.org). All rights
reserved.
• HP is distributing FreeType under the FreeType License.
• HP is distributing google-droid-fonts under the Apache Software License v2.0.
• HP is distributing HIDAPI under the BSD license only.
• HP is distributing Qt under the LGPLv2.1 license. HP is providing a full copy of the Qt
source.
• HP is distributing QuaZIP under LGPLv2 and the zlib/libpng licenses. HP is providing a full
copy of the QuaZIP source.
Hewlett-Packard Company shall not be liable for any errors or for incidental or consequential
damages in connection with the furnishing, performance, or use of this manual or the examples contained herein.
Product Regulatory & Environment Information
Product Regulatory and Environment Information is provided on the CD shipped with this
product.

Copyright © 2013 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
Reproduction, adaptation, or translation of this manual is prohibited without prior written permission of Hewlett-Packard Company, except as allowed under the copyright laws.
Printing History
Edition 1 July 2013


Contents
Preface
Manual conventions ................................................................ 9
Notice ................................................................................. 10
1 Getting started
Before starting ...................................................................... 11
On/off, cancel operations...................................................... 12
The display .......................................................................... 13
Sections of the display ...................................................... 14
Navigation........................................................................... 16
Touch gestures ................................................................. 17
The keyboard ....................................................................... 18
Context-sensitive menu ...................................................... 19
Entry and edit keys................................................................ 20
Shift keys......................................................................... 22
Adding text...................................................................... 23
Math keys ....................................................................... 24
Menus ................................................................................. 28
Toolbox menus................................................................. 29
Input forms ........................................................................... 29
System-wide settings .............................................................. 30
Home settings .................................................................. 30
Specifying a Home setting ................................................. 35
Mathematical calculations ...................................................... 36
Choosing an entry type ..................................................... 36
Entering expressions ......................................................... 37
Reusing previous expressions and results ............................. 40
Storing a value in a variable.............................................. 42
Complex numbers ................................................................. 44
Sharing data ........................................................................ 44
Online Help ......................................................................... 46
2 Reverse Polish Notation (RPN)
History in RPN mode ............................................................. 48
Sample calculations............................................................... 49
Manipulating the stack........................................................... 51
3 Computer algebra system (CAS)
CAS view............................................................................. 53
CAS calculations................................................................... 54
Settings................................................................................ 55
Contents 1

4 Exam Mode
Modifying the default configuration.....................................62
Creating a new configuration ............................................. 63
Activating Exam Mode ........................................................... 64
Cancelling exam mode......................................................66
Modifying configurations........................................................66
To change a configuration ................................................. 66
To return to the default configuration ...................................67
Deleting configurations ......................................................67
5 An introduction to HP apps
Application Library ................................................................ 71
App views ............................................................................ 73
Symbolic view ..................................................................73
Symbolic Setup view ......................................................... 74
Plot view.......................................................................... 75
Plot Setup view .................................................................76
Numeric view................................................................... 77
Numeric Setup view ..........................................................78
Quick example......................................................................79
Common operations in Symbolic view...................................... 81
Symbolic view: Summary of menu buttons............................ 86
Common operations in Symbolic Setup view.............................87
Common operations in Plot view ............................................88
Zoom ..............................................................................88
Trace...............................................................................94
Plot view: Summary of menu buttons....................................96
Common operations in Plot Setup view.....................................96
Configure Plot view ...........................................................96
Common operations in Numeric view .................................... 100
Zoom ............................................................................100
Evaluating......................................................................102
Custom tables.................................................................103
Numeric view: Summary of menu buttons...........................104
Common operations in Numeric Setup view............................105
Combining Plot and Numeric Views....................................... 106
Adding a note to an app...................................................... 106
Creating an app.................................................................. 107
App functions and variables .................................................109
2 Contents

6 Function app
Getting started with the Function app .................................... 111
Analyzing functions............................................................. 118
The Function Variables......................................................... 122
Summary of FCN operations ................................................ 124
7 Advanced Graphing app
Getting started with the Advanced Graphing app ................... 126
Plot Gallery ........................................................................ 134
Exploring a plot from the Plot Gallery................................ 134
8Geometry
Getting started with the Geometry app .................................. 135
Plot view in detail................................................................ 141
Plot Setup view............................................................... 146
Symbolic view in detail........................................................ 148
Symbolic Setup view....................................................... 150
Numeric view in detail ........................................................ 150
Geometric objects ............................................................... 153
Geometric transformations ................................................... 161
Geometry functions and commands....................................... 165
Symbolic view: Cmds menu ............................................. 165
Numeric view: Cmds menu.............................................. 182
Other Geometry functions................................................ 189
9 Spreadsheet
Getting started with the Spreadsheet app............................... 195
Basic operations ................................................................. 199
Navigation, selection and gestures ................................... 199
Cell references ............................................................... 200
Cell naming................................................................... 200
Entering content ............................................................. 201
Copy and paste ............................................................. 204
External references .............................................................. 204
Referencing variables...................................................... 205
Using the CAS in spreadsheet calculations ............................. 206
Buttons and keys ................................................................. 207
Formatting options .............................................................. 208
Spreadsheet functions.......................................................... 210
10 Statistics 1Var app
Getting started with the Statistics 1Var app ............................ 211
Entering and editing statistical data....................................... 215
Computed statistics.............................................................. 218
Plotting .............................................................................. 219
Contents 3

Plot types ....................................................................... 219
Setting up the plot (Plot Setup view)...................................221
Exploring the graph ........................................................221
11 Statistics 2Var app
Getting started with the Statistics 2Var app.............................223
Entering and editing statistical data ....................................... 228
Numeric view menu items ................................................229
Defining a regression model ................................................. 231
Computed statistics ..............................................................233
Plotting statistical data..........................................................234
Plot view: menu items ...................................................... 236
Plot setup ....................................................................... 236
Predicting values.............................................................237
Troubleshooting a plot .....................................................238
12 Inference app
Getting started with the Inference app....................................239
Importing statistics ...............................................................243
Hypothesis tests................................................................... 245
One-Sample Z-Test .......................................................... 246
Two-Sample Z-Test .......................................................... 247
One-Proportion Z-Test ...................................................... 248
Two-Proportion Z-Test ...................................................... 249
One-Sample T-Test ..........................................................250
Two-Sample T-Test........................................................... 251
Confidence intervals ............................................................ 253
One-Sample Z-Interval .....................................................253
Two-Sample Z-Interval...................................................... 253
One-Proportion Z-Interval .................................................254
Two-Proportion Z-Interval.................................................. 255
One-Sample T-Interval...................................................... 256
Two-Sample T-Interval ......................................................256
13 Solve app
Getting started with the Solve app .........................................259
One equation.................................................................260
Several equations ...........................................................263
Limitations...................................................................... 264
Solution information............................................................. 265
14 Linear Solver app
Getting started with the Linear Solver app...............................267
Menu items.........................................................................269
4 Contents

15 Parametric app
Getting started with the Parametric app ................................. 271
16 Polar app
Getting started with the Polar app ......................................... 277
17 Sequence app
Getting started with the Sequence app .................................. 281
Another example: Explicitly-defined sequences ....................... 285
18 Finance app
Getting Started with the Finance app..................................... 287
Time value of money (TVM) .................................................. 290
TVM calculations: Another example....................................... 291
Calculating amortizations..................................................... 293
19 Triangle Solver app
Getting started with the Triangle Solver app ........................... 295
Choosing triangle types ....................................................... 297
Special cases ..................................................................... 298
20 The Explorer apps
Linear Explorer app............................................................. 299
Quadratic Explorer app....................................................... 302
Trig Explorer app................................................................ 304
21 Functions and commands
Keyboard functions ............................................................. 309
Math menu......................................................................... 313
Numbers ....................................................................... 313
Arithmetic...................................................................... 314
Trigonometry.................................................................. 316
Hyperbolic .................................................................... 317
Probability..................................................................... 317
List................................................................................ 322
Matrix........................................................................... 323
Special ......................................................................... 323
CAS menu.......................................................................... 324
Algebra ........................................................................ 324
Calculus ........................................................................ 326
Solve ............................................................................ 330
Rewrite.......................................................................... 332
Integer .......................................................................... 337
Polynomial..................................................................... 339
Plot............................................................................... 346
Contents 5

App menu ..........................................................................347
Function app functions..................................................... 348
Solve app functions......................................................... 349
Spreadsheet app functions ...............................................349
Statistics 1Var app functions............................................. 363
Statistics 2Var app functions............................................. 365
Inference app functions....................................................366
Finance app functions .....................................................372
Linear Solver app functions .............................................. 374
Triangle Solver app functions ...........................................374
Linear Explorer functions .................................................. 376
Quadratic Explorer functions ............................................377
Common app functions....................................................377
Ctlg menu...........................................................................378
Creating your own functions ................................................. 421
22 Variables
Qualifying variables ............................................................ 427
Home variables................................................................... 428
App variables ..................................................................... 429
Function app variables ....................................................429
Geometry app variables ..................................................430
Spreadsheet app variables............................................... 431
Solve app variables ........................................................431
Advanced Graphing app variables ...................................432
Statistics 1Var app variables ............................................433
Statistics 2Var app variables ............................................435
Inference app variables ................................................... 437
Parametric app variables .................................................439
Polar app variables.........................................................440
Finance app variables .....................................................440
Linear Solver app variables..............................................441
Triangle Solver app variables ...........................................441
Linear Explorer app variables........................................... 441
Quadratic Explorer app variables..................................... 441
Trig Explorer app variables ..............................................442
Sequence app variables ..................................................442
23 Units and constants
Units .................................................................................. 443
Unit calculations ..................................................................444
Unit tools............................................................................446
Physical constants................................................................ 447
List of constants...............................................................449
6 Contents

24 Lists
Create a list in the List Catalog ............................................. 451
The List Editor................................................................. 453
Deleting lists ....................................................................... 455
Lists in Home view............................................................... 455
List functions ....................................................................... 457
Finding statistical values for lists............................................ 461
25 Matrices
Creating and storing matrices............................................... 464
Working with matrices......................................................... 465
Matrix arithmetic................................................................. 469
Solving systems of linear equations ....................................... 472
Matrix functions and commands............................................ 474
Matrix functions .................................................................. 475
Examples....................................................................... 486
26 Notes and Info
The Note Catalog ............................................................... 489
The Note Editor .................................................................. 490
27 Programming in HP PPL
The Program Catalog .......................................................... 498
Creating a new program ..................................................... 501
The Program Editor ......................................................... 502
The HP Prime programming language ................................... 511
The User Keyboard: Customizing key presses .................... 516
App programs ............................................................... 520
Program commands ............................................................ 527
Commands under the Tmplt menu..................................... 528
Block ............................................................................ 528
Branch .......................................................................... 528
Loop ............................................................................. 529
Variable........................................................................ 533
Function ........................................................................ 533
Commands under the Cmds menu .................................... 534
Strings .......................................................................... 534
Drawing........................................................................ 536
Matrix........................................................................... 544
App Functions ................................................................ 546
Integer .......................................................................... 547
I/O .............................................................................. 549
More ............................................................................ 554
Variables and Programs .................................................. 556
Contents 7

28 Basic integer arithmetic
The default base.................................................................. 582
Changing the default base ............................................... 583
Examples of integer arithmetic...............................................584
Integer manipulation ............................................................ 585
Base functions .....................................................................586
A Glossary
B Troubleshooting
Calculator not responding .................................................... 591
To reset ......................................................................... 591
If the calculator does not turn on .......................................591
Operating limits ..................................................................592
Status messages .................................................................. 592
C Product regulatory information
Federal Communications Commission notice...........................595
European Union Regulatory Notice........................................597
Index ...................................................................................601
8 Contents

Preface
Manual conventions
The following conventions are used in this manual to
represent the keys that you press and the menu options
that you choose to perform operations.
• A key that initiates an unshifted function is
represented by an image of that key:
e,B,H, etc.
• A key combination that initiates a shifted unction (or
inserts a character) is represented by the appropriate
shift key (
function or character:
Sh initiates the natural exponential function
and
The name of the shifted function may also be given in
parentheses after the key combination:
SJ(Clear), SY (Setup)
• A key pressed to insert a digit is represented by that
digit:
S or A) followed by the key for that
Az inserts the pound character (#)
5, 7, 8, etc.
• All fixed on-screen text—such as screen and field
names—appear in bold:
CAS Settings,
• A menu item selected by touching the screen is
represented by an image of that item:
, , .
Note that you must use your finger to select a menu
item. Using a stylus or something similar will not
select whatever is touched.
Preface 9
XSTEP, Decimal Mark, etc.

• Items you can select from a list, and characters on the
entry line, are set in a non-proportional font, as
follows:
Function, Polar, Parametric, Ans, etc.
Notice
• Cursor keys are represented by
You use these keys to move from field to field on a
screen, or from one option to another in a list of
options.
• Error messages are enclosed in quotation marks:
“Syntax Error”
This manual and any examples contained herein are
provided as-is and are subject to change without notice.
Except to the extent prohibited by law, Hewlett-Packard
Company makes no express or implied warranty of any
kind with regard to this manual and specifically disclaims
the implied warranties and conditions of merchantability
and fitness for a particular purpose and Hewlett-Packard
Company shall not be liable for any errors or for
incidental or consequential damage in connection with
the furnishing, performance or use of this manual and the
examples herein.
1994–1995, 1999–2000, 2003–2006, 2010–2013
Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P.
=, \, >, and <.
The programs that control your HP Prime are copyrighted
and all rights are reserved. Reproduction, adaptation, or
translation of those programs without prior written
permission from Hewlett-Packard Company is also
prohibited.
For hardware warranty information, please refer to the
HP Prime Quick Start Guide.
Product Regulatory and Environment Information is
provided on the CD shipped with this product.
10 Preface

Getting started
The HP Prime Graphing Calculator is an easy-to-use yet
powerful graphing calculator designed for secondary
mathematics education and beyond. It offers hundreds of
functions and commands, and includes a computer
algebra system (CAS) for symbolic calculations.
In addition to an extensive library of functions and
commands, the calculator comes with a set of HP apps.
An HP app is a special application designed to help you
explore a particular branch of mathematics or to solve a
problem of a particular type. For example, there is a HP
app that will help you explore geometry and another to
help you explore parametric equations. There are also
apps to help you solve systems of linear equations and to
solve time-value-of-money problems.
The HP Prime also has its own programming language
you can use to explore and solve mathematical problems.
1
Functions, commands, apps and programming are
covered in detail later in this guide. In this chapter, the
general features of the calculator are explained, along
with common interactions and basic mathematical
operations.
Before starting
Charge the battery fully before using the calculator for the
first time. To charge the battery, either:
• Connect the calculator to a computer using the USB
cable that came in the package with your HP Prime.
(The PC needs to be on for charging to occur.)
• Connect the calculator to a wall outlet using the HPprovided wall adapter.
Getting started 11

When the calculator is on, a battery symbol appears in
the title bar of the screen. Its appearance will indicate how
much power the battery has. A flat battery will take
approximately 4 hours to become fully charged.
Battery Warning • To reduce the risk of fire or burns, do not
disassemble, crush or puncture the battery; do not
short the external contacts; and do not dispose of the
battery in fire or water.
• To reduce potential safety risks, only use the battery
provided with the calculator, a replacement battery
provided by HP, or a compatible battery
recommended by HP.
• Keep the battery away from children.
• If you encounter problems when charging the
calculator, stop charging and contact HP
immediately.
Adapter Warning • To reduce the risk of electric shock or damage to
equipment, only plug the AC adapter into an AC
outlet that is easily accessible at all times.
• To reduce potential safety risks, only use the AC
adapter provided with the calculator, a replacement
AC adapter provided by HP, or an AC adapter
purchased as an accessory from HP.
On/off, cancel operations
To turn on Press
To cancel When the calculator is on, pressing the J key cancels
the current operation. For example, it will clear whatever
you have entered on the entry line. It will also close a
menu and a screen.
To turn off Press
To save power, the calculator turns itself off after several
minutes of inactivity. All stored and displayed information
is saved.
12 Getting started
to turn on the calculator.
O
SO
(Off) turn the calculator off.

The Home View Home view is the starting point for many calculations.
Most mathematical functions are available in the Home
view. Some additional functions are available in the
computer algebra system (CAS). A history of your
previous calculations is retained and you can re-use a
previous calculation or its result.
To display Home view, press
H
.
The CAS View CAS view enables you to perform symbolic calculations. It
is largely identical to Home view—it even has its own
history of past calculations—but the CAS view offers some
additional functions.
To display CAS view, press
K
.
Protective cover The calculator is provided with a slide cover to protect the
display and keyboard. Remove the cover by grasping
both sides of it and pulling down.
You can reverse the slide cover and slide it onto the back
of the calculator. This will ensure that you do not misplace
the cover while you are using the calculator.
To prolong the life of the calculator, always place the
cover over the display and keyboard when you are not
using the calculator.
The display
To adjust the
brightness
To clear the display • Press J or O to clear the entry line.
Getting started 13
To adjust the brightness of the display, press and hold
O, then press the
decrease the brightness. The brightness will change with
each press of the
• Press
SJ (Clear) to clear the entry line and the
history.
or w key to increase or
+
+
or
w
key.

Sections of the display
Title bar
History
Menu buttons
Entry line
π
SS
Home view has four sections (shown above). The title bar
shows either the screen name or the name of the app you
are currently using—Function in the example above. It
also shows the time, a battery power indicator, and a
number of symbols that indicate various calculator
settings. These are explained below. The
a record of your past calculations. The
displays the object you are currently entering or
modifying. The
relevant to the current display. These options are selected
by tapping the corresponding menu button. You close a
menu, without making a selection from it, by pressing
J.
Annunciators. Annunciators are symbols or characters
that appear in the title bar. They indicate current settings,
and also provide time and battery power information.
history displays
entry line
menu buttons are options that are
Annunciator Meaning
[Lime green] The angle mode setting is currently
degrees.
[Lime green] The angle mode setting is currently
radians.
[Cyan] The Shift key is active. The function
shown in blue on a key will be
activated when a key is pressed.
Press
14 Getting started
S to cancel shift mode.

Annunciator Meaning (Continued)
A
UU
CAS
[White] You are working in CAS view, not
Home view.
...Z
[orange] In Home view
The Alpha key is active. The character shown in orange on a key will
be entered in uppercase when a
key is pressed. See “Adding text”
on page 23 for more information.
In CAS view
The Alpha–Shift key combination is
active. The character shown in
orange on a key will be entered in
uppercase when a key is pressed.
See “Adding text” on page 23 for
more information.
[orange] In Home view
a...z
The Alpha–Shift key combination is
active. The character shown in
orange on a key will be entered in
lowercase when a key is pressed.
See “Adding text” on page 23 for
more information.
In CAS view
The Alpha key is active. The character shown in orange on a key will
be entered in lowercase when a key
is pressed. See “Adding text” on
page 23 for more information.
[Yellow] The user keyboard is active. All the
following key presses will enter the
customized objects associated with
the key. See “The User Keyboard:
Customizing key presses” on page
516 for more information.
Getting started 15

Annunciator Meaning (Continued)
1U1U
[Yellow] The user keyboard is active. The
next key press will enter the customized object associated with the key.
See “The User Keyboard: Customizing key presses” on page 516 for
more information.
[Time] Current time. The default is 24-hour
format, but you can choose
AM–PM
format. See “Home settings” on
page 30 for more information.
Navigation
[Green with
gray border]
Battery-charge indicator.
The HP Prime offers two modes of navigation: touch and
keys. In many cases, you can tap on an icon, field, menu,
or object to select (or deselect) it. For example, you can
open the Function app by tapping once on its icon in the
Application Library. However, to open the Application
Library, you will need to press a key:
I.
Instead of tapping an icon in the Application Library, you
can also press the cursor keys—
=,\,<,>—until the
app you want to open is highlighted, and then press
E. In the Application Library, you can also type the
first one or two letters of an app’s name to highlight the
app. Then either tap the app’s icon or press
open it.
Sometimes a touch or key–touch combination is available.
For example, you can deselect a toggle option either by
tapping twice on it, or by using the arrow keys to move to
the field and then tapping a touch button along the bottom
of the screen (in this case ).
E to
Note that you must use your finger or a capacitive stylus
to select an item by touch.
16 Getting started

Touch gestures
In addition to selection by tapping, there are other touchrelated operations available to you:
To quickly move from page to page, flick:
Place a finger on the screen and quickly swipe it in the
desired direction (up or down).
To pan, drag your finger horizontally or vertically across
the screen.
To quickly zoom in, make an open pinch:
Place the thumb and a finger close together on the
screen and move them apart. Only lift them from the
screen when you reach the desired magnification.
To quickly zoom out, make an closed pinch:
Place the thumb and a finger some distance apart on
the screen and move them toward each other. Only lift
them from the screen when you reach the desired
magnification.
Note that pinching to zoom only works in applications
that feature zooming (such as where graphs are plotted).
In other applications, pinching will do nothing, or do
something other than zooming. For example, in the
Spreadsheet app, pinching will change the width of a
column or the height of a row.
Getting started 17

The keyboard
The numbers in the legend below refer to the parts of the
keyboard described in the illustration on the next page.
Number Feature
1 LCD and touch-screen: 320 × 240 pixels
2 Context-sensitive touch-button menu
3HP Apps keys
4 Home view and preference settings
5 Common math and science functions
6Alpha and Shift keys
7On, Cancel and Off key
8 List, matrix, program, and note catalogs
9Last Answer key (Ans)
10 E n t e r key
11 Backspace and Delete key
12 Menu (and Paste) key
13 CAS (and CAS preferences) key
14 View (and Copy) key
15 Es ca pe (a nd Cl ea r) key
16 He l p k e y
17 Rocker wheel (for cursor movement)
18 Getting started

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
13
14
12
15
16
10
17
Context-sensitive menu
A context-sensitive menu occupies the bottom line of the
screen.
The options available depend on the context, that is, the
view you are in. Note that the menu items are activated by
touch.
Getting started 19

There are two types of buttons on the context-sensitive
menu:
• menu button: tap to display a pop-up menu. These
buttons have square corners along their top (such as
• command button: tap to initiate a command. These
buttons have rounded corners (such as in the
illustration above).
Entry and edit keys
The primary entry and edit keys are:
Keys Purpose
N to r Enter numbers
or J Cancels the current operation or
O
in the illustration above).
clears the entry line.
E
Q
Enters an input or executes an
operation. In calculations,
acts like “=”. When or
is present as a menu key,
E
For entering a negative number. For
example, to enter –25, press
acts the same as pressing
or .
E
Q25. Note: this is not the same
operation that is performed by the
subtraction key (
w).
F Math template: Displays a palette
of pre-formatted templates representing common arithmetic expressions.
d
20 Getting started
Enters the independent variable
(that is, either X, T, or N, depend-
ing on the app that is currently
active).

Keys Purpose (Continued)
Sv Relations palette: Displays a palette
of comparison operators and Boolean operators.
Sr Special symbols palette: Displays a
palette of common math and Greek
characters.
Sc Automatically inserts the degree,
minute, or second symbol according to the context.
C Backspace. Deletes the character to
the left of the cursor. It will also
return the highlighted field to its
default value, if it has one.
C
S
SJ
(Clear) Clears all data on the screen
<>=\
Delete. Deletes the character to the
right of the cursor.
(including the history). On a settings screen—for example Plot
Setup—returns all settings to their
default values.
Cursor keys: Moves the cursor
around the display. Press
move to the end of a menu or
screen, or
start. (These keys represent the
directions of the rocker wheel.)
S=
to move to the
S\
to
Getting started 21

Keys Purpose (Continued)
Shift keys
Sa
There are two shift keys that you use to access the
operations and characters printed on the bottom of the
S
and A.
keys:
Key Purpose
S
Displays all the available
characters. To enter a character, use
the cursor keys to highlight it, and
then tap . To select multiple
characters, select one, tap ,
and continue likewise before
pressing . There are many
pages of characters. You can jump
to a particular Unicode block by
tapping and selecting the
block. You can also flick from page
to page.
Press S to access the operations
printed in blue on a key. For
instance, to access the settings for
Home view, press
SH.
A Press the A key to access the
characters printed in orange on a
key. For instance, to type Z in Home
view, press
y. For a lowercase letter, press
AS and then the letter. In CAS
view,
A
lowercase letter, and
another letter gives an uppercase
letter.
22 Getting started
and then press
A
and another key gives a
AS and

Adding text
The text you can enter directly is shown by the orange
characters on the keys. These characters can only be
entered in conjunction with the
A and S keys. Both
uppercase and lowercase characters can be entered, and
the method is exactly the opposite in CAS view than in
Home view.
Keys Effect in Home view Effect in CAS view
A
AA
S
AS
AS
A
S
SA
A
AA
AA
Makes the next character uppercase
Lock mode: makes all
characters uppercase
until the mode is reset
With uppercase locked,
makes the next character
lowercase
Makes the next character lowercase
Lock mode: makes all
characters lowercase until
the mode is reset
With lowercase locked,
makes the next character
uppercase
With lowercase locked,
makes all characters
uppercase until the mode
is reset
Reset uppercase lock
mode
Reset lowercase lock
mode
Makes the next character lowercase
Lock mode: makes all
characters lowercase until
the mode is reset
With lowercase locked,
makes the next character
uppercase
Makes the next character uppercase
Lock mode: makes all
characters uppercase
until the mode is reset
With uppercase locked,
makes the next character
lowercase
With uppercase locked,
makes all characters lowercase until the mode is
reset
Reset lowercase lock
mode
Reset uppercase lock
mode
You can also enter text (and other characters) by
displaying the characters palette:
Getting started 23
Sa
.

Math keys
The most common math functions have their own keys on
the keyboard (or a key in combination with the
Example 1: To calculate SIN(10), press e10 an d
press
E
angle measure setting is radians).
Example 2: To find the square root of 256, press
Sj 256 and press
is 16. Notice that the
represented in blue on the next key pressed (in this case √
on the
The mathematical functions not represented on the keyboard
are on the
“Functions and commands”, starting on page 307).
Note that the order in which you enter operands and
operators is determined by the entry mode. By default, the
entry mode is textbook, which means that you enter
operands and operators just as you would if you were
writing the expression on paper. If your preferred entry
mode is Reverse Polish Notation, the order of entry is
different. (See chapter 2, “Reverse Polish Notation (RPN)”,
starting on page 47.)
. The answer displayed is –0.544… (if your
E
. The answer displayed
S key initiates the operator
j key).
Math, CAS, and Catlg menus (see chapter 21,
S key).
Math
template
24 Getting started
The math template key (F)
helps you insert the framework
for common calculations (and for
vectors, matrices, and
hexagesimal numbers). It
displays a palette of pre-formatted outlines to which you
add the constants, variables, and so on. Just tap on the
template you want (or use the arrow keys to highlight it
and press
to complete the calculation.
E). Then enter the components needed
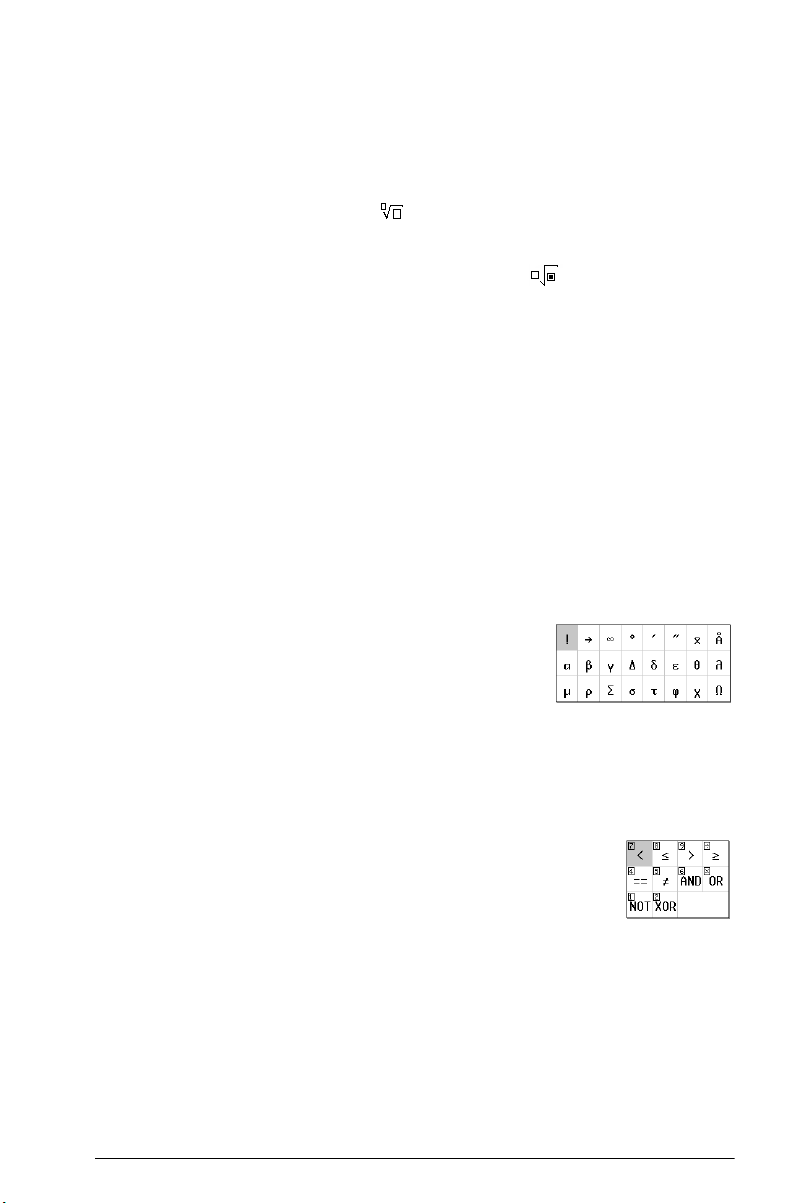
Example: Suppose you want to find the cube root of
945:
Math
shortcuts
1. In Home view, press
2. Select .
The skeleton or framework for your calculation now
appears on the entry line:
3. Each box on the template needs to be completed:
3
>945
4. Press
The template palette can save you a lot of time, especially
with calculus calculations.
You can display the palette at any stage in defining an
expression. In other words, you don’t need to start out with
a template. Rather, you can embed one or more templates
at any point in the definition of an expression.
As well as the math template,
there are other similar screens
that offer a palette of special
characters. For example,
pressing
special symbols palette, shown at the right. Select a
character by tapping it (or scrolling to it and pressing
E to display the result: 9.813…
Sr displays the
F.
E).
A similar palette—the relations
palette—is displayed if you press
Sv. The palette displays operators
useful in math and programming. Again,
just tap the character you want.
Other math shortcut keys include
inserts an X, T, , or N depending on what app you are
using. (This is explained further in the chapters describing
the apps.)
d. Pressing this key
Similarly, pressing
second character. It enters ° if no degree symbol is part of
your expression; enters ′ if the previous entry is a value in
Getting started 25
Sc enters a degree, minute, or
degrees; and enters ″ if the previous entry is a value in
5
219602
98209
------------------
2
23184
98209
---------------
+
11
8
------
5
minutes. Thus entering:
Sc40Sc20Sc
36
yields 36°40′ 20″. See “Hexagesimal numbers” on page
26 for more information.
Fractions The fraction key (c) cycles through thee varieties of
fractional display. If the current answer is the decimal
fraction 5.25, pressing
common fraction 21/4. If you press c again, the
answer is converted to a mixed number (5 + 1/4). If
pressed again, the display returns to the decimal fraction
(5.25).
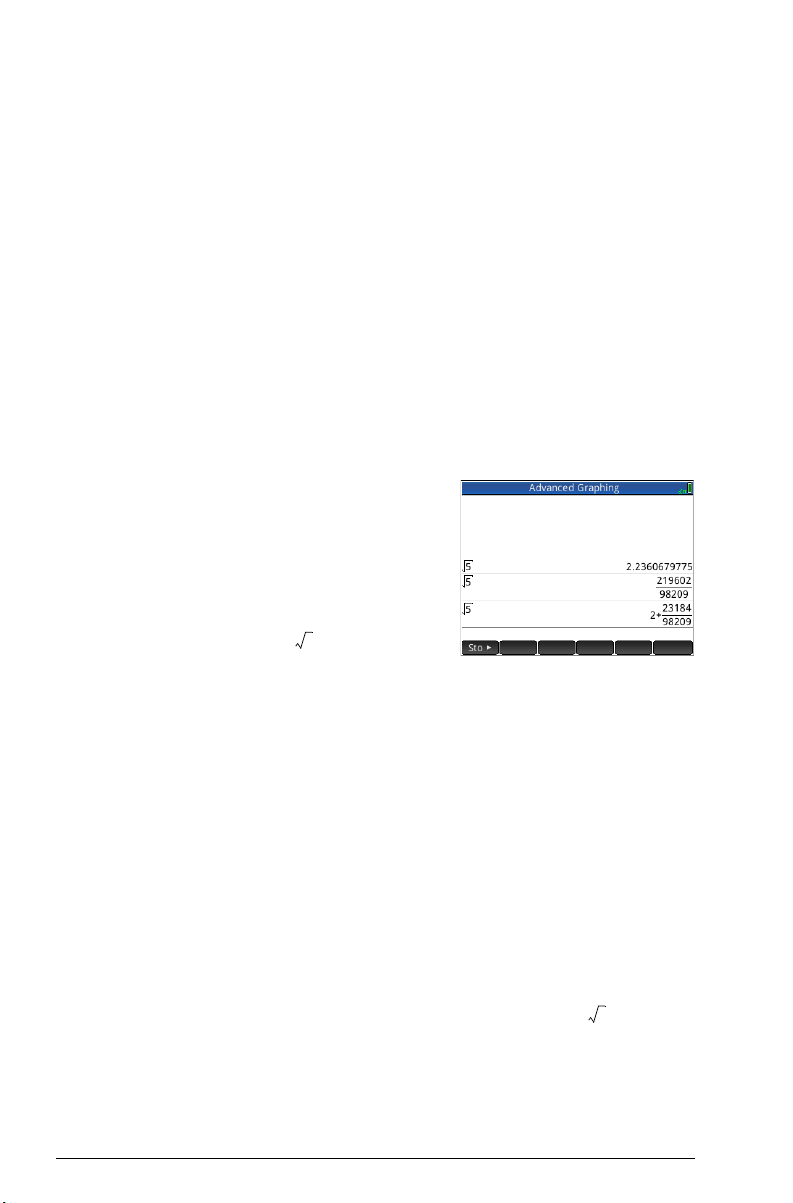
The HP Prime will
approximate fraction and
mixed number
representations in cases
where it cannot find
exact ones. For example,
enter to see the
decimal approximation:
2.236…. Press
c once to see and again to see
. Pressing
original decimal representation.
c converts the answer to the
c a third time will cycle back to the
Hexagesimal
numbers
Any decimal result can de displayed in hexagesimal
format; that is, in units subdivided into groups of 60. This
includes degrees, minutes, and seconds as well as hours,
minutes, and seconds. For example, enter to see the
decimal result: 1.375. Now press
1°22′ 30. Press
S c again to return to the decimal
S c to see
representation.
HP Prime will produce the best approximation in cases
where an exact result is not possible. Enter to see the
decimal approximation: 2.236… Press
S c to see
2°14′ 9.84472 .
26 Getting started

Note that the degree and minute entries must be integers,
510
4
3.21 107–
410
13–
610
23
310
5–
----------------------------------------------------
and the minute and second entries must be positive.
Decimals are not allowed, except in the seconds.
Note too that the HP
Prime treats a value in
hexgesimal format as a
single entity. Hence any
operation performed on
a hexagesimal value is
performed on the entire
value. For example, if
2
you enter 10°25′ 26″
, the whole value is squared, not just
the seconds component. The result in this case is
108°39′ 26.8544″ .
EEX key
(powers of
10)
Numbers like and are expressed in
scientific notation, that is, in terms of powers of ten. This is
simpler to work with than 50 000 or 0.000000 321. To
enter numbers like these, use the
easier than using
Example: Suppose you want to calculate
s10k
B functionality. This is
.
First select Scientific as the number format.
1. Op e n t h e Home Settings window.
SH
2. Select Scientific
from the
Format
3. Return home:
Number
menu.
H
4. Enter 4BQ13
s6B23n
BQ5
3
Getting started 27

Menus
5. Press E
The result is
8.0000E15. This is
equivalent to
15
8 × 10
A menu offers you a
choice of items. As in the
case shown at the right,
some menus have submenus and sub-submenus.
.
To select from a
menu
Shortcuts • Press
There are two techniques for selecting an item from a
menu:
• direct tapping and
• using the arrow keys to highlight the item you want
and then either tapping or pressing
Note that the menu of buttons along the bottom of the
screen can only be activated by tapping.
immediately display the last item in the menu.
• Press \ when you are at the bottom of the menu to
immediately display the first item in the menu.
• Press
menu.
• Press S= to jump straight to the top of the menu.
• Enter the first few characters of the item’s name to
jump straight to that item.
• Enter the number of the item shown in the menu to
jump straight to that item.
when you are at the top of the menu to
=
S
to jump straight to the bottom of the
\
E
.
28 Getting started

To close a menu A menu will close automatically when you select an item
from it. If you want to close a menu without selecting
anything from it, press
O
or J.
Toolbox menus
The Toolbox menus (D) are a collection of menus
offering functions and commands useful in mathematics
and programming. The
offer over 400 functions and commands. The items on
these menus are described in detail in chapter 21,
“Functions and commands”, starting on page 307.
Math, CAS, and Catlg menus
Input forms
An input form is a screen that provides one or more fields
for you to enter data or select an option. It is another name
for a dialog box.
• If a field allows you to enter data of your choice, you
can select it, add your data, and tap . (There
is no need to tap first.)
• If a field allows you to choose an item from a menu,
you can tap on it (the field or the label for the field),
tap on it again to display the options, and tap on the
item you want. (You can also choose an item from an
open list by pressing the cursor keys and pressing
E when the option you want is highlighted.)
• If a field is a toggle field—one that is either selected
or not selected—tap on it to select the field and tap
on it again to select the alternate option.
(Alternatively, select the field and tap .)
The illustration at the right
shows an input form with
all three types of field:
Calculator Name is a
free-form data-entry field,
Font Size provides a
menu of options, and
Textbook Display is a
toggle field.
Getting started 29

Reset input
form fields
To reset a field to its default value, highlight the field and
press C. To reset all fields to their default values, press
SJ (Clear).
System-wide settings
System-wide settings are values that determine the
appearance of windows, the format of numbers, the scale
of plots, the units used by default in calculations, and
much more.
There are two system-wide settings: Home settings and
CAS settings. Home settings control Home view and the
apps. CAS settings control how calculations are done in
the computer algebra system. CAS settings are discussed
in chapter 3.
Although Home settings control the apps, you can
override certain Home settings once inside an app. For
example, you can set the angle measure to radians in the
Home settings but choose degrees as the angle measure
once inside the Polar app. Degrees then remains the angle
measure until you open another app that has a different
angle measure.
Home settings
You use the Home
Settings input form to
specify the settings for
Home view (and the
default settings for the
apps). Press
(Settings) to open the
Home Settings input
form. There are four pages of settings.
30 Getting started
SH

Page 1
Setting Options
Angle Measure Degrees: 360 degrees in a circle.
Radians: 2 radians in a circle.
The angle mode you set is the angle
setting used in both Home view and
the current app. This is to ensure
that trigonometric calculations done
in the current app and Home view
give the same result.
Number
Format
The number format you set is the format used in all Home view calculations.
Standard: Full-precision display.
Fixed: Displays results rounded to
a number of decimal places. If you
choose this option, a new field
appears for you to enter the number
of decimal places. For example,
123.456789 becomes 123.46 in
Fixed 2 format.
Scientific: Displays results with an
one-digit exponent to the left of the
decimal point, and the specified
number of decimal places. For
example, 123.456789 becomes
1.23E2 in Scientific 2
format.
Engineering: Displays results with
an exponent that is a multiple of 3,
and the specified number of
significant digits beyond the first
one. Example: 123.456E7
becomes 1.23E9 in Engineer-
ing 2 format.
Getting started 31

Setting Options (Continued)
Entry Textbook: An expression is
entered in much the same way as if
you were writing it on paper (with
some arguments above or below
others). In other words, your entry
could be two-dimensional.
Algebraic: An expression is
entered on a single line. Your entry
is always one-dimensional.
RPN: Reverse Polish Notation. The
arguments of the expression are
entered first followed by the
operator. The entry of an operator
automatically evaluates what has
already been entered.
Integers Sets the default base for integer
arithmetic: binary, octal, decimal,
or hex. You can also set the number
of bits per integer and whether integers are to be signed.
Complex Choose one of two formats for
displaying complex numbers:
(a,b) or a+b*i.
To the right of this field is an
unnamed checkbox. Check it if you
want to allow complex output from
real input.
Language Choose the language you want for
menus, input forms, and the online
help.
32 Getting started

Page 2
45
62
Setting Options (Continued)
Decimal Mark Dot or Comma. Displays a number
as 12456.98 (dot mode) or as
12456,98 (comma mode). Dot
mode uses commas to separate
elements in lists and matrices, and
to separate function arguments.
Comma mode uses semicolons as
separators in these contexts.
Setting Options
Font Size Choose between small, medium,
and large font for general display.
Calculator
Enter a name for the calculator.
Name
Textbook
Display
If selected, expressions and results
are displayed in textbook format
(that is, much as you would see in
textbooks). If not selected, expressions and results are displayed in
algebraic format (that is, in onedimensional format). For example,
is displayed as
[[4,5],[6,2]]
in algebraic format.
Menu Display This setting determines whether the
commands on the
Math and CAS
menus are presented descriptively
or in common mathematical
shorthand. The default is to provide
the descriptive names for the
functions. If you prefer the functions
to be presented in mathematical
shorthand, deselect this option.
Getting started 33

Setting Options (Continued)
Time Set the time and choose a format:
24-hour or
AM–PM format. The
checkbox at the far right lets you
choose whether to show or hide the
time on the title bar of screens.
Date Set the date and choose a format:
YYYY/MM/DD, DD/MM/YYYY, or
MM/DD/YYYY.
Color Theme
Light: black text on a light back-
ground
Dark: white text on a dark back-
ground
At the far right is a option for you to
choose a color for the shading
(such as the color of the highlight).
Page 3 Pag e 3 of the Home Settings input form is for setting
Exam mode. This mode enables certain functions of the
calculator to be disabled for a set period, with the
disabling controlled by a password. This feature will
primarily be of interest to those who supervise
examinations and who need to ensure that the calculator
is used appropriately by students sitting an examination.
It is described in detail in chapter 4, “Exam Mode”,
starting on page 61.
Page 4 Pag e 4 of the Home Settings input form is for
configuring your HP Prime to work with the HP Prime
Wireless Kit. Visit www.hp.com/support for further
information.
34 Getting started

Specifying a Home setting
This example demonstrates how to change the number
format from the default setting—Standard—to Scientific
with two decimal places.
1. Press SH
(Settings) to open the
Home Settings
input form.
The Angle
Measure
highlighted.
2. Tap on
3. Tap on Number
4. Tap on Scientific.
Number
Format
the field. (You could also have pressed
it.)
Format
menu of number
format options
appears.
The option is chosen
and the menu closes. (You can also choose an item
by pressing the cursor keys and pressing
when the option you want is highlighted.)
(either the field label or the field). This selects
again. A
field is
\ to select
E
5. Notice that a number
appears to the right
of the Number
Format field. This is
the number of
decimal places
currently set. To
change the number
to 2, tap on it twice, and then tap on 2 in the menu
that appears.
6. Press
Getting started 35
to return to Home view.
H

Mathematical calculations
The most commonly used math operations are available
from the keyboard (see “Math keys” on page 24). Access
to the rest of the math functions is via various menus (see
“Menus” on page 28).
Note that the HP Prime represents all numbers smaller
than 1 × 10
9.99999999999 × 10
this number.
–499
as zero. The largest number displayed is
499
. A greater result is displayed as
Where to
start
The home base for the calculator is the Home view (H).
You can do all your non-symbolic calculations here. You
can also do calculations in CAS view, which uses the
computer algebra system (see chapter 3, “Computer
algebra system (CAS)”, starting on page 53). In fact, you
can use functions from the
menus) in an expression you are entering in Home view,
and use functions from the
Toolbox menus) in an expression you are entering in CAS
view.
Choosing an entry type
The first choice you need to make is the style of entry. The
three types are:
• Textbook
An expression is
entered in much the
same way as if you
were writing it on paper (with some arguments above
or below others). In other words, your entry could be
two-dimensional, as in the example above.
CAS menu (one of the Toolbox
Math menu (another of the
• Algebraic
An expression is
entered on a single
line. Your entry is
always one-dimensional.
36 Getting started

• RPN (Reverse Polish Notation). [Not available in CAS
view.]
The arguments of the expression are entered first
followed by the operator. The entry of an operator
automatically evaluates what has already been
entered. Thus you will need to enter a two-operator
expression (as in the example above) in two steps, one
for each operator:
Step 1: 5
calculated and displayed in history.
Step 2:
applied to the previous result.
More information about RPN mode can be found in
chapter 2, “Reverse Polish Notation (RPN)”, starting
on page 47.
Note that on page 2 of the Home Settings screen, you
can specify whether you want to display your calculations
in Textbook format or not. This refers to the appearance of
your calculations in the history section of both Home view
and CAS view. This is a different setting from the Entry
setting discussed above.
Entering expressions
The examples that follow assume that the entry mode is
Textbook.
• An expression can contain numbers, functions, and
variables.
• To enter a function, press the appropriate key, or
open a Toolbox menu and select the function. You
can also enter a function by using the alpha keys to
spell out its name.
• When you have finished entering the expression,
press
h – the natural logarithm of 5 is
Szn – is entered as a divisor and
E to evaluate it.
Getting started 37

If you make a mistake while entering an expression, you
23214 8–
3–
----------------------------
45ln
can:
• delete the character to the left of the cursor by
pressing
• delete the character to the right of the cursor by
pressing
• clear the entire entry line by pressing O or J.
Example Calculate
23jw14 S
R
j
8>>nQ3
>h45E
This example illustrates a
number of important
points to be aware of:
• the importance of
delimiters (such as parentheses)
• how to enter negative numbers
• the use of implied versus explicit multiplication.
C
S
C
Parentheses As the example above shows, parentheses are
automatically added to enclose the arguments of
functions, as in LN(). However, you will need to manually
add parentheses—by pressing
of objects you want operated on as a single unit.
Parentheses provide a way of avoiding arithmetic
ambiguity. In the example above we wanted the entire
numerator divided by –3, thus the entire numerator was
enclosed in parentheses. Without the parentheses, only
14√8 would have been divided by –3.
38 Getting started
—to enclose a group
R

The following examples show the use of parentheses, and
45 +sin
45sin +
85 9
85 9
the use of the cursor keys to move outside a group of
objects enclosed within parentheses.
Entering ... Calculates …
e45+Sz
Algebraic
precedence
45
e
>+Sz
Sj
85>s9
Sj85s
9
The HP Prime calculates according to the following order
of precedence. Functions at the same level of precedence
are evaluated in order from left to right.
1. Expressions within parentheses. Nested parentheses
are evaluated from inner to outer.
2. !, √, reciprocal, square
th
root
3. n
4. Power, 10
n
5. Negation, multiplication, division, and modulo
6. Addition and subtraction
7. Relational operators (<, >, ≤, ≥, ==, ≠, =)
8. AND and NOT
9. OR an d XOR
10.Left argument of | (where)
11. Assign to variable (:=)
Negative
numbers
It is best to pres s Q to sta rt a negative nu mber or t o inser t
a negative sign. Pressing
w instead will, in some
situations, be interpreted as an operation to subtract the
next number you enter from the last result. (This is
explained in “To reuse the last result” on page 41.)
To raise a negative number to a power, enclose it in
2
parentheses. For example, (–5)
Getting started 39
= 25, whereas –52 = –25.

Explicit and
implied
multiplication
Implied multiplication takes place when two operands
appear with no operator between them. If you enter AB,
for example, the result is A*B. Notice in the example on
page 38 that we entered 14
multiplication operator after 14. For the sake of clarity, the
calculator adds the operator to the expression in history,
but it is not strictly necessary when you are entering the
expression. You can, though, enter the operator if you
wish (as was done in the examples on page 39). The
result will be the same.
Sk8 without the
Large results If the result is too long or too tall to be seen in its
entirety—for example, a many-rowed matrix—highlight it
and then press . The result is displayed in fullscreen view. You can now press
= and \ (as well as
>and <) to bring hidden parts of the result into view.
Tap to return to the previous view.
Reusing previous expressions and results
Being able to retrieve and reuse an expression provides a
quick way of repeating a calculation that requires only a
few minor changes to its parameters. You can retrieve and
reuse any expression that is in history. You can also
retrieve and reuse any result that is in history.
To retrieve an expression and place it on the entry line for
editing, either:
• tap twice on it, or
• use the cursor keys to highlight the expression and
then either tap on it or tap .
To retrieve a result and place it on the entry line, use the
cursor keys to highlight it and then tap .
If the expression or result you want is not showing, press
= repeatedly to step through the entries and reveal those
that are not showing. You can also swipe the screen to
quickly scroll through history.
40 Getting started

Tip
Pressing S= takes you straight to the very first entry
in history, and pressing
most recent entry.
S\ takes you straight to the
Using the clipboard Your last four expressions are always copied to the
clipboard and can easily be retrieved by pressing
SZ. This opens the clipboard from where you can
quickly choose the one you want.
Note that expressions and not results are available from
the clipboard. Note too that the last four expressions
remain on the clipboard even if you have cleared history.
To reuse the last
result
Tip
Press S+ (Ans) to
retrieve your last answer
for use in another
calculation. Ans
appears on the entry
line. This is a shorthand for your last answer and it can be
part of a new expression. You could now enter other
components of a calculation—such as operators, number,
variables, etc.—and create a new calculation.
You don’t need to first select Ans before it can be part of
a new calculation. If you press a binary operator key to
begin a new calculation, Ans is automatically added to
the entry line as the first component of the new
calculation. For example, to multiply the last answer by
13, you could enter
first two keystrokes are unnecessary. All you need to enter
is s13E.
The variable Ans is always stored with full precision
whereas the results in history will only have the precision
determined by the current Number Format setting (see
page 31). In other words, when you retrieve the number
assigned to Ans, you get the result to its full precision; but
when you retrieve a number from history, you get exactly
what was displayed.
S+ s13E. But the
Getting started 41

You can repeat the previous calculation simply by pressing
2
32
E. This can be useful if the previous calculation
involved Ans. For example, suppose you want to calculate
the nth root of 2 when n is 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, and so on.
1. Calculate the square root of 2.
Sj2E
2. Now enter √Ans.
SjS+E
This calculates the fourth root of 2.
3. Press E
repeatedly. Each time
you press, the root is
twice the previous
root. The last answer
shown in the
illustration at the right
is .
To reuse an
expression or result
from the CAS
When your are working in Home view, you can retrieve
an expression or result from the CAS by tapping Z and
selecting Get from CAS. The CAS opens. Press = or
until the item you want to retrieve is highlighted and
\
press E. The highlighted item is copied to the cursor
point in Home view.
Storing a value in a variable
You can store a value in a variable (that is, assign a value
to a variable). Then when you want to use that value in a
calculation, you can refer to it by the variable’s name. You
can create your own variables, or you can take advantage
of the built-in variables in Home view (named A to Z and
) and in the CAS (named a to z, and a few others). CAS
variables can be used in calculations in Home view, and
Home variables can be used in calculations in the CAS.
There are also built-in app variables and geometry
variables. These can also be used in calculations.
42 Getting started

Example: To assign
2
to to the variable A:
Szj AaE
Your st ored va l ue
appears as shown at the
right. If you then wanted
to multiply your stored
value by 5, you could
Aas5E.
enter:
You can also create your own variables in Home view. For
example, suppose you wanted to create a variable called
2
ME and assign
to it. You would enter:
Szj AQAcE
A message appears asking if you want to create a
variable called ME. Tap or press
confirm your intention. You can now use that variable in
subsequent calculations: ME*3 will yield 29.6088132033,
for example.
You can also create variables in CAS view in the same
way. However, the built-in CAS variables must be entered
in lowercase. However, the variables you create yourself
can be uppercase or lowercase.
E to
See chapter 22, “Variables”, starting on page 423 for
more information.
As well as built-in Home and CAS variables, and the
variables you create yourself, each app has variables that
you can access and use in calculations. See “App
functions and variables” on page 109 for more
information.
Getting started 43

Complex numbers
1–
You can perform arithmetic operations using complex
numbers. Complex numbers can be entered in the
following forms, where x is the real part, y is the
imaginary part, and i is the imaginary constant, :
• (x, y)
• x + yi (except in RPN mode)
• x – yi (except in RPN mode)
• x + iy (except in RPN mode), or
• x – iy (except in RPN mode)
To enter i:
Sharing data
• press
• press
There are 10 built-in variables available for storing
complex numbers. These are labeled Z0 to Z9. You can
also assign a complex number to a variable you create
yourself.
To store a complex
number in a variable,
enter the complex
number, press ,
enter the variable that
you want to assign the complex number to, and then press
E
ASg
or
Sy.
. For example, to store 2+3i in variable Z6:
R2o3>Ay6E
As well as giving you access to many types of
mathematical calculations, the HP Prime enables you to
create various objects that can be saved and used over
and over again. For example, you can create apps, lists,
matrices, programs, and notes. You can also send these
objects to other HP Primes. Whenever you encounter a
44 Getting started

screen with as a menu item, you can select an item
Micro-A: sender Micro-B: receiver
on that screen to send it to another HP Prime.
You use one of the
supplied USB cables to
send objects from one
HP Prime to another.
This is the micro-A–micro B USB cable. Note that the
connectors on the ends of the USB cable are slightly
different. The micro-A connector has a rectangular end
and the micro-B connector has a trapezoidal end. To
share objects with another HP Prime, the micro-A
connector must be inserted into the USB port on the
sending calculator, with the micro-B connector inserted
into the USB port on the receiving calculator.
General procedure The general procedure for sharing objects is as follows:
1. Navigate to the screen that lists the object you want
to send.
This will be the Application Library for apps, the List
Catalog for lists, the Matrix Catalog for matrices, the
Program Catalog for programs, and the Notes
Catalog for notes.
Getting started 45
2. Connect the USB cable between the two calculators.
The micro-A connector—with the rectangular
end—must be inserted into the USB port on the
sending calculator.
3. On the sending calculator, highlight the object you
want to send and tap .
In the illustration at
the right, a program
named
TriangleCalcs
has been selected in
the Program Catalog
and will be sent to the
connected calculator
when is
tapped.

Online Help
Press W to open the online help. The help initially
provided is context-sensitive, that is, it is always about the
current view and its menu items.
For example, to get help on the Function app, press
select Function, and press
From within the help system, tapping displays a
hierarchical directory of all the help topics. You can
navigate through the directory to other help topics, or use
the search facility to quickly find a topic. You can find help
on any key, view, or command.
W.
I,
46 Getting started

Reverse Polish Notation (RPN)
The HP Prime provides you with three ways of entering objects in
Home view:
• Textbook
An expression is entered in much the same way was if you
were writing it on paper (with some arguments above or
below others). In other words, your entry could be twodimensional, as in the following example:
• Algebraic
An expression is entered on a single line. Your entry is always
one-dimensional. The same calculation as above would
appear like this is algebraic entry mode:
• RPN (Reverse Polish Notation).
The arguments of the expression are entered first followed by
the operator. The entry of an operator automatically
evaluates what has already been entered. Thus you will need
to enter a two-operator expression (as in the example above)
in two steps, one for each operator:
2
Step 1: 5
displayed in history.
Step 2: Szn – is entered as a divisor and
applied to the previous result.
You choose your preferred entry method from page 1 of the
Home Settings screen (SH). See “System-wide settings”,
starting on page 30 for instructions on how to choose settings.
RPN is available in Home view, but not in CAS view.
Reverse Polish Notation (RPN) 47
h – the natural logarithm of 5 is calculated and

The same entry-line editing tools are available in RPN mode as
in algebraic and textbook mode:
• Press
• Press
• Press
• Press SJ to clear the entire entry line.
C to delete the character to the left of the cursor.
SC to delete the character to the right of the
cursor.
J to clear the entire entry line.
History in RPN mode
The results of your calculations are kept in history. This history is
displayed above the entry line (and by scrolling up to
calculations that are no longer immediately visible). The
calculator offers three histories: one for the CAS view and two for
Home view. CAS history is discussed in chapter 3. The two
histories in Home view are:
• non-RPN: visible if you have chosen algebraic or textbook
as your preferred entry technique
• RPN: visible only if you have chosen RPN as your preferred
entry technique. The RPN history is also called the stack. As
shown in the illustration below, each entry in the stack is
given a number. This is the stack level number.
As more calculations are added, an entry’s stack level number
increases.
If you switch from RPN to algebraic or textbook entry, your
history is not lost. It is just not visible. If you switch back to RPN,
your RPN history is redisplayed. Likewise, if you switch to RPN,
your non-RPN history is not lost.
When you are not in RPN mode, your history is ordered
chronologically: oldest calculations at the top, most recent at the
48 Reverse Polish Notation (RPN)

bottom. In RPN mode, your history is ordered chronologically by
default, but you can change the order of the items in history. (This
is explained in “Manipulating the stack” on page 51.)
Re-using
results
There are two ways to re-use a result in history. Method 1
deselects the copied result after copying; method 2 keeps the
copied item selected.
Method 1
1. Select the result to be copied. You can do this by pressing
= or \ until the result is highlighted, or by tapping on it.
2. Press
Method 2
1. Select the result to be copied. You can do this by pressing
E. The result is copied to the entry line and is
deselected.
= or \ until the result is highlighted, or by tapping on it.
2. Tap and select ECHO. The result is copied to the
entry line and remains selected.
Note that while you can copy an item from the CAS history to
use in a Home calculation (and copy an item from the Home
history to use in a CAS calculation), you cannot copy items from
or to the RPN history. You can, however, use CAS commands
and functions when working in RPN mode.
Sample calculations
The general philosophy behind RPN is that arguments are
placed before operators. The arguments can be on the entry line
(each separated by a space) or they can be in history. For
example, to multiply by 3, you could enter:
SzX 3
on the entry line and then enter the operator (
entry line would look like this before entering the operator:
s). Thus your
Reverse Polish Notation (RPN) 49

However, you could also have entered the arguments separately
and then, with a blank entry line, entered the operator (
Your history would look like this before entering the operator:
If there are no entries in history and you enter an operator or
function, an error message appears. An error message will also
app ear if t here is an en try on a s tack l eve l that a n operator ne eds
but it is not an appropriate argument for that operator. For
example, pressing
an error message.
An operator or function will work only on the minimum number of
arguments necessary to produce a result. Thus if you enter on the
entry line 2 4 6 8 and press
Multiplication needs only two arguments, so the two arguments last
entered are the ones that get multiplied. The entries 2 and 4 are not
ignored: 2 is placed on stack level 3 and 4 on stack level 2.
Where a function can accept a variable number of arguments,
you need to specify how many arguments you want it to include
in its operation. You do this by specifying the number in
parentheses straight after the function name. You then press
f when there is a string on level 1 displays
s, stack level 1 shows 48.
s).
E to evaluate the function. For example, suppose your
stack looks like this:
Suppose further that you want to determine the minimum of just
the numbers on stack levels 1, 2, and 3. You choose the MIN
function from the MATH menu and complete the entry as
MIN(3). When you press
three items on the stack is displayed.
50 Reverse Polish Notation (RPN)
E, the minimum of just the last

Manipulating the stack
A number of stack-manipulation options are available. Most
appear as menu items across the bottom the screen. To see these
items, you must first select an item in history:
PICK Copies the selected item to stack level 1. The item below the one
that is copied is then highlighted. Thus if you tapped four
times, four consecutive items will be moved to the bottom four
stack levels (levels 1–4).
ROLL There are two roll commads:
• Tap to move the selected item to stack level 1. This is
similar to PICK, but PICK duplicates the item, with the
duplicate being placed on stack level1. However,
doesn’t duplicate an item. It simply moves it.
• Tap to move the item on stack level 1 to the currently
highlighted level
ROLL
Swap You can swap the position of the objects on stack level 1 with
those on stack level 2. Just press
remains unchanged. Note that the entry line must not be active
at the time, otherwise a comma will be entered.
o. The level of other objects
Stack Tapping displays further stack-manipulation tools.
DROPN Deletes all items in the stack from the highlighted item down to
and including the item on stack level 1. Items above the
highlighted item drop down to fill the levels of the deleted items.
If you just want to delete a single item from the stack, see “Delete
an item” below.
Reverse Polish Notation (RPN) 51

DUPN Duplicates all items between (and including) the highlighted item
and the item on stack level 1. If, for example, you have selected
the item on stack level 3, selecting DUPN duplicates it and the
two items below it, places them on stack levels 1 to 3, and moves
the items that were duplicated up to stack levels 4 to 6.
Echo Places a copy of the selected result on the entry line and leaves
the source result highlighted.
LIST Creates a list of results, with the highlighted result the first element
in the list and the item on stack level 1 the last.
Before After
Show an
item
Delete an
item
Delete all
To show a result in full-screen textbook format, tap .
Tap to return to the history.
To delete an item from the stack:
1. Select it. You can do this by pressing
is highlighted, or by tapping on it.
2. Press
To delete all items, thereby clearing the history, press SJ.
C.
= or \ until the item
items
52 Reverse Polish Notation (RPN)

Computer algebra system (CAS)
1
3
---
2
7
---
+
13
21
------
A computer algebra system (CAS) enables you to perform
symbolic calculations. By default, CAS works in exact mode,
giving you infinite precision. On the other hand, non-CAS
calculations, such as those performed in HOME view or by an
app, are numerical calculations and are often approximations
limited by the precision of the calculator (to 12 significant
digits in the case of the HP Prime). For example, yields
the approximate answer .619047619047 in Home view (with
Standard numerical format), but yields the exact answer in
the CAS.
The CAS offers many hundreds of functions, covering algebra,
calculus, equation solving, polynomials, and more. You select
a function from the
discussed in chapter 21, “Functions and commands”,
beginning on page 307. Consult that chapter for a
description of all the CAS functions and commands.
CAS view
CAS calculations are done
in CAS view. CAS view is
almost identical to Home
view. A history of
calculations is built and you
can select and copy previous
calculations just as you can
in Home view, as well as
store objects in variables.
To open CAS view, press
of the title bar to indicate that you are in CAS view rather than
Home view.
CAS menu, one of the Toolbox menus
K. CAS appears in red at the left
3
Computer algebra system (CAS) 53

The menu buttons in CAS view are:
• : assigns an object to a variable
• : applies common simplification rules to reduce an
expression to its simplest form. For example,
simplify(e
• : copies a selected entry in history to the entry line
• : displays the selected entry in full-screen mode,
with horizontal and vertical scrolling enabled. The entry
is also presented in textbook format.
CAS calculations
With one exception, you perform calculations in CAS view
just as you do in Home view. (The exception is that there is no
RPN entry mode in CAS view, just algebraic and textbook
modes). All the operator and function keys work in the same
way in CAS view as Home view (although all the alpha
characters are lowercase rather than uppercase). But the
primary difference is that the default display of answers is
symbolic rather than numeric.
You can also use the template key (
framework for common calculations (and for vectors and
matrices). This is explained in detail in “Math template” on
page 24.
The most commonly used
CAS functions are available
from the CAS menu, one of
the Toolbox menus. To
display the menu, press
D. (If the CAS menu is not
open by default, tap
commands are available from the Catlg menu (another of the
Toolbox menus).
To choose a function, select a category and then a command.
a + LN(b*ec)
.) Other CAS
) yields b *EXP(a)* EXP(c).
F) to help you insert the
54 Computer algebra system (CAS)

Example 1 To find the roots of 2x
1. With the CAS menu open, select Polynomial and then
Find Roots.
The function proot()
appears on the entry
line.
2. Between the
parentheses, enter:
2
Asj+3
Asw2
3. Press E.
2
+ 3x – 2:
Example 2 To find the area under the graph of 5x
x = 3:
1. With the CAS menu open, select Calculus and then
Integrate.
The function int()
appears on the entry
line.
2. Between the
parentheses, enter:
5
Asjw6
oAso1o
3
3. Press
E.
Settings
Various settings allow you to
configure how the CAS
works. To display the
settings, press
modes are spread across
two pages.
SK. The
2
– 6 between x =1 and
Computer algebra system (CAS) 55

Page 1
26
5
-----------
Setting Purpose
Angle Measure Select the units for angle measure-
ments: Radians or Degrees.
Number Format
(first drop-down
list)
Select the number format for displayed solutions:
Standard or Scientific or
Engineering
Number Format
(second dropdown list)
Integers (dropdown list)
Select the number of digits to display in approximate mode (mantissa + exponent).
Select the integer base:
Decimal (base 10)
Hex (base 16)
Octal (base 8)
Integers (check
box)
If checked, any real number equivalent to an integer in a non-CAS
environment will be converted to
an integer in the CAS. (Real numbers not equivalent to integers are
treated as real numbers in CAS
whether or not this option is
selected.)
Simplify Select the level of automatic sim-
plification:
None: do not simplify automatically (use for manual simplification)
Minimum: do basic simplifications
Maximum: always try to simplify
Exact If checked, the calculator is in
exact mode and solutions will be
symbolic. If not checked, the calculator is in approximate mode and
solutions will be approximate. For
example, 26
n5 yields in
exact mode and 5.2 in approximate mode.
56 Computer algebra system (CAS)

Setting Purpose (Cont.)
Complex Select this to allow complex results
in variables.
Use √
If checked, second order polynomials are factorized in complex
mode or in real mode if the discriminant is positive.
Use i If checked, the calculator is in
complex mode and complex solutions will be displayed when they
exist. If not checked, the calculator
is in real mode and only real solutions will be displayed. For example, factors(x
4
–1) yields
(x–1),(x+1),(x+i),(x–i) in complex
mode and
(x–1),(x+1) ,( x
2
+1) in real mode.
Principal If checked, the principal solutions
to trigonometric functions will be
displayed. If not checked, the general solutions to trigonometric functions will be displayed.
Increasing If checked, polynomials will be
displayed with increasing powers
(for example, –4+x+3x
2+x3
). If not
checked, polynomials will be displayed with decreasing powers
(for example, x
3
+3x2+x–4).
Page 2
Setting Purpose
Recursive
Evaluation
Computer algebra system (CAS) 57
Specify the maximum number of
embedded variables allowed in
an interactive evaluation. See also
Recursive Replacement
below.

Setting Purpose (Cont.)
Setting the form
of menu items
Recursive
Replacement
Specify the maximum number of
embedded variables allowed in a
single evaluation in a program.
See also Recursive Evalua-
tion above.
Recursive
Function
Specify the maximum number of
embedded function calls allowed.
Epsilon Any number smaller than the
value specified for epsilon will be
shown as zero.
Probability Specify the maximum probability
of an answer being wrong for
non-deterministic algorithms. Set
this to zero for deterministic algorithms.
Newton Specify the maximum number of
iterations when using the Newtonian method to find the roots of a
quadratic.
One setting that affects the CAS is made outside the CAS
Settings screen. This setting determines whether the
commands on the CAS menu are presented descriptively or by
their command name. Here are some examples of identical
functions that are presented differently depending on what
presentation mode you select:
Descriptive name Command name
Factor List ifactors
Complex Zeros cZeros
Groebner Basis gbasis
Factor by Degree factor_xn
Find Roots proot
The default menu presentation mode is to provide the
descriptive names for the CAS functions. If you prefer the
58 Computer algebra system (CAS)

functions to be presented by their command name, deselect
the Menu Display option on the second page of the Home
Settings screen (see “Home settings” on page 30).
To use an
expression or
result from
Home view
To use a Home
variable in CAS
When your are working in CAS, you can retrieve an expression or result from Home view by tapping
Get from Home. Home view opens. Press
the item you want to retrieve is highlighted and press
The highlighted item is copied to the cursor point in CAS.
You can access Home variables from within the CAS. Home
variables are assigned uppercase letters; CAS variables are
assigned lowercase letters. Thus SIN(x) and SIN(X) will yield
different results.
To use a Home variable in the CAS, simply include its name
in a calculation. For example, suppose in Home view you
have assigned variable Q to 100. Suppose too that you have
assigned variable q to 1000 in the CAS. If you are in the CAS
and enter 5*q, the result is 5000. If you had entered 5*Q
instead, the result would have been 500.
In a similar way, CAS variables can be used in calculations
in Home view. Thus you can enter 5*q in Home view and get
5000, even though q is a CAS variable.
Z and selecting
or
\
until
=
E.
Computer algebra system (CAS) 59

60 Computer algebra system (CAS)

Exam Mode
4
The HP Prime can be precisely configured for an
examination, with any number of features or functions
disabled for a set period of time. Configuring a HP Prime
for an examination is called exam mode configuration.
You can create and save multiple exam mode
configurations, each with its own subset of functionality
disabled. You can set each configuration for its own time
period, with or without a password. An exam mode
configuration can be activated from an HP Prime, sent
from one HP Prime to another via USB cable, or sent to
one or more HP Primes via the Connectivity Kit.
Exam mode
configuration will
primarily be of interest to
teachers, proctors, and
invigilators who want to
ensure that the calculator
is used appropriately by
students sitting for an
examination. In the illustration to the right, user-customized
apps, the help system and the computer algebra system
have been selected for disabling.
As part of an exam mode configuration, you can choose
to activate 3 lights on the calculator that will flash
periodically during exam mode. The lights are on the top
edge of the calculator. The lights will help the supervisor
of the examination detect if any particular calculator has
dropped out of exam mode. The flashing of lights on all
calculators placed in exam mode will be synchronized so
that all will flash the same pattern at the same time.
Exam Mode 61

Modifying the default configuration
A configuration named Default Exam appears when
you first access the
has no functions disabled. If only one configuration is
needed, you can simply modify the default exam
configuration. If you envisage the need for a number of
configurations—different ones for different examinations,
for example—modify the default configuration so that it
matches the settings you will most often need, and then
create other configurations for the settings you will need
less often. There are two ways to access the screen for
configuring and activating exam mode:
Exam Mode screen. This configuration
• press
• choose the third page of the Home Settings screen.
The procedure below illustrates the second method.
1. P r e s s
2. Tap .
3. Tap .
4. Tap . The
5. Select those features
O + A + c
SH. The Home Settings screen appears.
The
Exam Mode
screen appears. You
use this screen to
activate a particular
configuration (just
before an
examination begins,
for example).
Exam Mode
Configuration
screen appears.
you want disabled,
and make sure that
those features you
don’t want disabled are not selected.
62 Exam Mode

An expand box at the left of a feature indicates that it
is a category with sub-items that you can individually
disable. (Notice that there is an expand box beside
System Apps in the example shown above.) Tap on
the expand box to see the sub-items. You can then
select the sub-items individually. If you want to disable
all the sub-item, just select the category.
You can select (or deselect) an option either by
tapping on the check box beside it, or by using the
cursor keys to scroll to it and tapping .
6. When you have finished selecting the features to be
disabled, tap
If you want to activate exam mode now, continue with
“Activating Exam Mode” below.
Creating a new configuration
You can modify the default exam configuration when new
circumstances require a different set of disabled functions.
Alternatively, you can retain the default configuration and
create a new configuration. When you create a new
configuration, you choose an existing configuration on
which to base it.
.
1. P r e s s
2. Tap .
3. Tap .
4. Choose a base
Exam Mode 63
SH. The Home Settings screen
appears.
Exam Mode
The
screen appears.
configuration from
the Configuration
list. If you have not
created any exam
mode configurations
before, the only base configuration will be Default
Exam.

5. Tap
name for the new configuration.
See “Adding text” on page 23 if you need help with
entering alphabetic characters.
6. Tap
7. Tap . The Exam Mode Configuration
screen appears.
8. Select those features you want disabled, and make
sure that those features you don’t want disabled are
not selected.
9. When you have finished selecting the features to be
disabled, tap
Note that you can create exam mode configurations
using the Connectivity Kit in much the same way you
create them on an HP Prime. You can then activate
them on multiple HP Primes, either via USB or by
broadcasting them to a class using the wireless
modules. For more information, install and launch the
HP Connectivity Kit that came on your product CD.
From the Connectivity Kit menu, click
HP Connectivity Kit User Guide.
If you want to activate exam mode now, continue with
“Activating Exam Mode” below.
, select Copy from the menu and enter a
twice.
.
Help and select
Activating Exam Mode
When you activate exam mode you prevent users of the
calculator from accessing those features you have
disabled. The features become accessible again at the
end of the specified time-out period or on entry of the
exam-mode password, whichever occurs sooner.
64 Exam Mode

To activate exam mode:
1. I f th e
Exam Mode
screen is not
showing, press
SH, tap
and
tap .
2. If a configuration
other than Default
Exam is required, choose it from the
list.
3. Select a time-out period from the
Note that 8 hours is the maximum period. If you are
preparing to supervise a student examination, make
sure that the time-out period chosen is greater than
the duration of the examination.
4. Enter a password of between 1 and 10 characters.
The password must be entered if you—or another
user—wants to cancel exam mode before the time-out
period has elapsed.
5. If you want to erase the memory of the calculator,
Erase memory. This will erase all user entries
select
and return the calculator to its factory default settings.
6. If you want the exam mode indicator to flash
periodically while the calculator is in exam mode,
Blink LED.
select
7. Using the supplied USB cable, connect a student’s
calculator.
Insert the micro-A connector—the one with the
rectangular end—into the USB port on the sending
calculator, and the other connector into the USB port
on the receiving calculator.
8. To activate the configuration on an attached
calculator, tap
Exam Mode screen
The
.
closes. The connected calculator is now in exam
Configuration
Timeout list.
Exam Mode 65

mode, with the specified disabled features not
accessible to the user of that calculator.
9. Repeat from step 7 for each calculator that needs to
have its functionality limited.
Cancelling exam mode
If you want to cancel exam mode before the set time
period has elapsed, you will need to enter the password
for the current exam mode activation.
1. I f th e
Exam Mode screen is not showing, press
SH, tap and tap .
2. Enter the password for the current exam mode
activation and tap
You can also cancel exam mode using the Connectivity
Kit. See the HP Connectivity Kit User Guide for more
details.
Modifying configurations
Exam mode configurations can be changed. You can also
delete a configuration and restore the default
configuration.
To change a configuration
1. I f th e Exam Mode screen is not showing, press
SH, tap and tap .
2. Select the configuration you want to change from the
Configuration list.
3. Tap .
4. Make whatever changes are necessary and then tap
.
twice
.
66 Exam Mode

To return to the default configuration
1. P r e s s SH. The Home Settings screen
appears.
2. Tap .
3. Tap .
Exam Mode screen appears.
The
4. Choose Default Exam from the
list.
5. Tap
configuration to its default settings.
, select Reset from the menu and tap
to confirm your intention to return the
Deleting configurations
You cannot delete the default exam configuration (even if
you have modified it). You can only delete those that you
have created. To delete a configuration:
Configuration
1. I f th e
Exam Mode screen is not showing, press
SH, tap and tap .
2. Select the configuration you want to delete from the
Configuration list.
3. Tap
4. When asked to confirm the deletion, tap
press
Exam Mode 67
and choose Delete.
E.
or

68 Exam Mode

An introduction to HP apps
x2y2+64=
y 2x23x 5++=
Much of the functionality of the HP Prime is provided in packages
called HP apps. The HP Prime comes with 18 HP apps: 10
dedicated to mathematical topics or tasks, three specialized
Solvers, three function Explorers, a spreadsheet, and an app for
recording data streamed to the calculator from an external
sensing device. You launch an app by first pressing
displays the Application Library screen) and tapping on the
icon for the app you want.
What each app enables you to do is outlined in the following,
where the apps are listed in alphabetical order.
App name Use this app to:
5
I (which
Advanced
Graphing
DataStreamer Collect real-world data from scientific
Finance Solve time-value-of-money (TVM) problems
Function Explore real-valued, rectangular functions
Geometry Explore geometric constructions and
Inference Explore confidence intervals and
Linear Explorer Explore the properties of linear equations
An introduction to HP apps 69
Explore the graphs of symbolic open
sentences in x and y. Example:
sensors and export it to a statistics app for
analysis.
and amortization problems.
of y in terms of x. Example:
perform geometric calculations.
hypothesis tests based on the Normal and
Student’s t-distributions.
and test your knowledge.

App name Use this app to: (Cont.)
r 24cos=
U
n 1–Un 2–U1
0=
U21=
UnU
n 2–
U
n 1–
+=
x 1+ x2x–2–=
Linear Solver Find solutions to sets of two or three linear
equations.
Parametric Explore parametric functions of x and y in
terms of t. Example: x = cos (t) and
y = sin(t).
Polar Explore polar functions of r in terms of an
angle . Example:
Quadratic
Explorer
Explore the properties of quadratic
equations and test your knowledge.
Sequence Explore sequence functions, where U is
defined in terms of n, or in terms of
previous terms in the same or another
sequence, such as and .
Example: , and
Solve Explore equations in one or more real-
valued variables, and systems of equations.
Example:
Spreadsheet To solve problems or represent data best
suited to a spreadsheet.
Statistics 1Var Calculate one-variable statistical data (x)
Statistics 2Var Calculate two-variable statistical data
(x and y)
Triangle Solver Find the unknown values for the lengths
and angles of triangles.
Trig Explorer Explore the properties of sinusoidal
equations and test your knowledge.
As you use an app to explore a lesson or solve a problem, you
add data and definitions in one or more of the app’s views. All
this information is automatically saved in the app. You can come
back to the app at any time and all the information is still there.
You can also save a version of the app with a name you give it
and then use the original app for another problem or purpose.
See “Creating an app” on page 107 for more information about
customizing and saving apps.
70 An introduction to HP apps

With one exception, all the apps mentioned above are described
in detail in this user guide. The exception is the DataStreamer
app. A brief introduction to this app is given in the HP Prime
Quick Start Guide. Full details can be found in the HP
StreamSmart 410 User Guide.
Application Library
Apps are stored in the Application Library, displayed by pressing
I.
To open an
app
To reset an
app
1. Open the Application
Library.
2. Find the app’s icon and tap
on it.
You can also use the cursor
keys to scroll to the app
and, when it is highlighted,
either tap or press
E.
You can leave an app at any time and all the data and settings
in it are retained. When you return to the app, you can continue
as you left off.
However, if you don’t want to use the previous data and settings,
you can return the app to its default state, that is, the state it was
in when you opened it for the first time. To do this:
1. Open the Application Library.
2. Use the cursor keys to highlight the app.
3. Tap .
4. Tap to confirm your intention.
You can also reset an app from within the app. From the main
view of the app—which is usually, but not always, the Symbolic
view—press
SJ and tap to confirm your intention.
To sort apps By default, the built-in apps in the Application Library are sorted
chronologically, with the most recently used app shown first.
(Customized apps always appear after the built-in apps.)
An introduction to HP apps 71

You can change the sort order of the built-in apps to:
• Alphabetically
The app icons are sorted alphabetically by name, and in
ascending order: A to Z.
• Fixed
Apps are displayed in their default order: Function,
Advanced Graphing, Geometry … Polar, and Sequence.
Customized apps are placed at the end, after all the built-in
apps. They appear in chronological order: oldest to most
recent.
To change the sort order:
1. Open the Application Library.
2. Tap .
3. From the Sort Apps list, choose the option you want.
To delete an
app
Other
options
The apps that come with the HP Prime are built-in and cannot be
deleted, but you can delete an app you have created. To delete
an app:
1. Open the Application Library.
2. Use the cursor keys to highlight the app.
3. Tap .
4. Tap to confirm your intention.
The other options available in the Application Library are:
•
Enables you to save a copy of an app under a new name.
See “Creating an app” on page 107.
•
Enables you to send an app to another HP Prime. See
“Sharing data” on page 44.
72 An introduction to HP apps

App views
Most apps have three major views: Symbolic, Plot, and Numeric.
These views are based on the symbolic, graphic, and numeric
representations of mathematical objects. They are accessed
through the
keyboard. Typically these views enable you to define a
mathematical object—such as an expression or an open
sentence—plot it, and see the values generated by it.
Each of these views has an accompanying setup view, a view that
enables you to configure the appearance of the data in the
accompanying major view. These views are called Symbolic
Setup, Plot Setup, and Numeric Setup. They are accessed by
pressing
Not all apps have all the six views outlined above. The scope and
complexity of each app determines its particular set of views. For
example, the Spreadsheet app has no Plot view or Plot Setup view,
and the Quadratic Explorer has only a Plot view. What views are
available in each app is outlined in the next six sections.
Note that the DataStreamer app is not covered in this chapter. See
HP StreamSmart 410 User Guide for information about this app.
Symbolic view
The table below outlines what is done in the Symbolic view of
each app.
Y, P, and M keys near the top left of the
JY, JP, and JM.
App Use the Symbolic view to:
Advanced
Graphing
Finance Not used
Function Specify up to 10 real-valued, rectangular
Geometry View the symbolic definition of geometric
Inference Choose to conduct a hypothesis test or test
Linear Explorer Not used
An introduction to HP apps 73
Specify up to 10 open sentences.
functions of y in terms of x.
constructions.
a confidence level, and select a type of
test.

App Use the Symbolic view to: (Cont.)
Linear Solver Not used
Parametric Specify up to 10 parametric functions of x
and y in terms of t.
Polar Specify up to 10 polar functions of r in
terms of an angle .
Quadratics
Explorer
Sequence Specify up to 10 sequence functions.
Solve Specify up to 10 equations.
Spreadsheet Not used
Statistics 1Var Specify up to 5 univariate analyses.
Statistics 2Var Specify up to 5 multivariate analyses.
Triangle Solver Not used
Trig Explorer Not used
Symbolic Setup view
The Symbolic Setup view is the
same for each app. It enables
you to override the system-wide
settings for angle measure,
number format, and complexnumber entry. The override
applies only to the current app.
To change the settings for all
apps, see “System-wide settings” on page 30.
Not used
74 An introduction to HP apps

Plot view
The table below outlines what is done in the Plot view of each
app.
App Use the Plot view to:
Advanced
Graphing
Finance Display an amortization graph.
Function Plot and explore the functions selected in
Geometry Create and manipulate geometric
Inference View a plot of the test results.
Linear Explorer Explore linear equations and test your
Linear Solver Not used
Parametric Plot and explore the functions selected in
Polar Plot and explore the functions selected in
Quadratics
Explorer
Sequence Plot and explore the sequences selected in
Solve Plot and explore a single function selected
Spreadsheet Not used
Statistics 1Var Plot and explore the analyses selected in
Statistics 2Var Plot and explore the analyses selected in
Triangle Solver Not used
Trig Explorer Explore sinusoidal equations and test your
Plot and explore the open sentences
selected in Symbolic view.
Symbolic view.
constructions.
knowledge of them.
Symbolic view.
Symbolic view.
Explore quadratic equations and test your
knowledge of them.
Symbolic view.
in Symbolic view.
Symbolic view.
Symbolic view.
knowledge of them.
An introduction to HP apps 75

Plot Setup view
The table below outlines what is done in the Plot Setup view of
each app.
App Use the Plot Setup view to:
Advanced
Graphing
Finance Not used
Function Modify the appearance of plots and the
Geometry Modify the appearance of the drawing
Inference Not used
Linear Explorer Not used
Linear Solver Not used
Parametric Modify the appearance of plots and the
Polar Modify the appearance of plots and the
Quadratics
Explorer
Sequence Modify the appearance of plots and the
Solve Modify the appearance of plots and the
Modify the appearance of plots and the
plot environment.
plot environment.
environment.
plot environment.
plot environment.
Not used
plot environment.
plot environment.
Spreadsheet Not used
Statistics 1Var Modify the appearance of plots and the
plot environment.
Statistics 2Var Modify the appearance of plots and the
plot environment.
Triangle Solver Not used
Trig Explorer Not used
76 An introduction to HP apps

Numeric view
The table below outlines what is done in the Numeric view of
each app.
App Use the Numeric view to:
Advanced
Graphing
Finance Enter values for time-value-of-money
Function View a table of numbers generated by the
Geometry Perform calculations on the geometric
Inference Specify the statistics needed to perform the
Linear Explorer Not used
Linear Solver Specify the coefficients of the linear
Parametric View a table of numbers generated by the
Polar View a table of numbers generated by the
Quadratics
Explorer
Sequence View a table of numbers generated by the
View a table of numbers generated by the
open sentences selected in Symbolic view.
calculations.
functions selected in Symbolic view.
objects drawn in Plot view.
test selected in Symbolic view.
equations to be solved.
functions selected in Symbolic view.
functions selected in Symbolic view.
Not used
sequences selected in Symbolic view.
Solve Enter the known values and solve for the
unknown value.
Spreadsheet Enter numbers, text, formulas, etc. The
Numeric view is the primary view for this
app.
Statistics 1Var Enter data for analysis.
Statistics 2Var Enter data for analysis.
An introduction to HP apps 77

App Use the Numeric view to: (Cont.)
Triangle Solver Enter known data about a triangle and
Trig Explorer Not used
Numeric Setup view
The table below outlines what is done in the Numeric Setup view
of each app.
App Use the Numeric Setup view to:
solve for the unknown data.
Advanced
Graphing
Finance Not used.
Function Specify the numbers to be calculated
Geometry Not used
Inference Not used
Linear Explorer Not used
Linear Solver Not used
Parametric Specify the numbers to be calculated
Polar Specify the numbers to be calculated
Quadratics
Explorer
Sequence Specify the numbers to be calculated
Specify the numbers to be calculated
according to the open sentences specified
in Symbolic view, and set the zoom factor.
according to the functions specified in
Symbolic view, and set the zoom factor.
according to the functions specified in
Symbolic view, and set the zoom factor.
according to the functions specified in
Symbolic view, and set the zoom factor.
Not used.
according to the sequences specified in
Symbolic view, and set the zoom factor.
Solve Not used
78 An introduction to HP apps

App Use the Numeric Setup view to: (Cont.)
r 42
2
coscos=
r 42
2
coscos=
Spreadsheet Not used
Statistics 1Var Not used
Statistics 2Var Not used
Triangle Solver Not used
Trig Explorer Not used
Quick example
The following example uses all six app views and should give you
an idea of the typical workflow involved in working with an app.
The Polar app is used as the sample app.
Open the app
1. Open the Application Library by pressing I.
2. Tap once on the icon of the Polar app.
The Polar app opens in Symbolic View.
Symbolic view
The Symbolic view of the Polar app is where you define or specify
the polar equation you want to plot and explore. In this example
we will plot and explore the equation
3. Define the equation by entering:
4
Szf
n
>
(If you are using algebraic
entry mode, you would
enter 4
This equation will draw symmetrical petals provided that the
angle measure is set to radians. The angle measure for this
app is set in the Symbolic Setup view.
2>>
f
jE
Szf
2>
n
>
jE
f
.)
An introduction to HP apps 79

Symbolic Setup view
4. Press SY.
5. Select Radians from the
Plot view
6. Press P.
Plot Setup View
7. Press SP.
8. Set the second RNG field to
Angle Measure menu.
A graph of the equation is
plotted. However, as the
illustration at the right
shows, only a part of the
petals is visible. To see the
rest you will need to change
the plot setup parameters.
4 by entering:
>4Sz
(
9. Press
80 An introduction to HP apps
P to return to Plot
view and see the complete
plot.

Numeric View
The values generated by the
equation can be seen in
Numeric view.
10. P re ss
Suppose you want to see just
whole numbers for ; in other
words, you want the increment
between consecutive values in
the column to be 1. You set this up in the Numeric Setup view.
Numeric Setup View
11 . P r e s s SM.
12. Change the NUMSTEP field
13 . P r e s s
M.
to 1.
M to return to
Numeric view.
You will see that the
column now contains
consecutive integers starting from zero, and the
corresponding values calculated by the equation specified in
Symbolic view are listed in the R1 column.
Common operations in Symbolic view
[Scope: Advanced Graphing, Function, Parametric, Polar,
Sequence, Solve. See dedicated app chapters for information
about the other apps.]
Symbolic view is typically used to define a function or open
sentence that you want to explore (by plotting and/or
evaluating). In this section, the term definition will be used to
cover both functions and open sentences.
Press
Y to open Symbolic view.
An introduction to HP apps 81

Add a definition
With the exception of the Parametric app, there are 10 fields for
entering definitions. In the Parametric app there are 20 fields, two
for each paired definition.
1. Highlight an empty field you want to use, either by tapping
on it or scrolling to it.
2. Enter your definition.
If you need help, see “Definitional building blocks” on
page 82.
3. Tap or press
Your new definition is added to the list of definitions.
Note that variables used in definitions must be in uppercase.
A variable entered in lowercase will cause an error message
to appear.
Modify a definition
1. Highlight the definition you want to modify, either by tapping
on it or scrolling to it.
2. Tap .
The definition is copied to the entry line.
3. Modify the definition.
4. Tap or press
Definitional building blocks
E when you have finished.
E when you have finished.
The components that make up a symbolic definition can come
from a number of sources.
• From the keyboard
You can enter components directly from the keyboard. To
enter 2X
2
– 3, just press 2AXjw3.
• From user variables
If, for example, you have created a variable called COST,
you could incorporate that into a definition either by typing
it or choosing it from the User menu (one of the sub-menus
of the Variables menu). Thus you could have a definition that
reads F1(X)=X
2
+COST.
To select a user variable, press a, tap , select
User Variables, and then select the variable of interest.
82 An introduction to HP apps

• From Home variables
Some Home variables can be incorporated into a symbolic
definition. To access a Home variable, press
a, tap
, select a category of variable, and select the
variable of interest. Thus you could have a definition that
reads F1(X)=X
2
+Q. (Q is on the Real sub-menu of the
Home menu.)
Home variables are discussed in detail in chapter 28,
“Troubleshooting”, beginning on page 507.
• From app variables
All settings, definitions, and results, for all apps, are stored
as variables. Many of these variables can be incorporated
into a symbolic definition. To access app variables, press
a, tap , select the app, select the category of
variable, and then select the variable of interest. You could,
for instance, have a definition that reads
F2(X)=X
the Function app is substituted for Root when this definition
is evaluated.
App variables are discussed in detail in chapter 28,
“Troubleshooting”, beginning on page 507.
• From math functions
Some of the functions on the Math menu can be incorporated
into a definition. The Math menu is one of the Toolbox menus
(
D). The following definition combines a math function
(Size) with a Home variable (L1): F4(X)=X
is equivalent to x
list named L1. (Size is an option on the List menu, which is a
sub-menu of the Math menu.)
• From CAS functions
Some of the functions on the CAS menu can be incorporated
into a definition. The CAS menu is one of the Toolbox menus
(
D). The following definition incorporates the CAS
function irem: F5(X)=X
entered by choosing Remainder, an option on the
Division menu, which is a sub-menu of the Integer menu.
Note that any CAS command or function selected to operate
outside the CAS is given the CAS. prefix.)
2
+X–Root. The value of the last root calculated in
2
2
– n where n is the number of elements in the
2
+CAS.irem(45,7). (irem is
–SIZE(L1). It
An introduction to HP apps 83

• From app functions
Some of the functions on the App menu can be
incorporated into a definition. The App menu is one of the
Toolbox menus (
the app function PredY:
F9(X)=X
2
+Statistics_2Var.PredY(6).
• From the Catlg menu
Some of the functions on the Catlg menu can be
incorporated into a definition. The Catlg menu is one of the
Toolbox menus (
a command from that menu and an app variable:
F6(X)=X
2
+INT(Root). The integer value of the last root
calculated in the Function app is substituted for INT(Root)
when this definition is evaluated.
• From other definitions
You could, for example, define F3(X)as F1(X)*F2(X).
Evaluate a dependent definition
If you have a dependent definition—that is, one defined in terms
of another definition—you can combine all the definitions into
one by evaluating the dependent definition.
1. Select the dependent expression.
2. Tap .
Consider the example at the
right. Notice that F3(X)is
defined in terms of two other
functions. It is a dependent
definition and can be evaluated.
If you highlight F3(X)and tap
, F3(X)becomes
2
2*X
+X+ 2 *(X2–1).
D). The following definition incorporates
D). The following definition incorporates
Select or deselect a definition to explore
In the Advanced Graphing, Function, Parametric, Polar,
Sequence, and Solve apps you can enter up to 10 definitions.
However, only those definitions that are selected in Symbolic view
will be plotted in Plot view and evaluated in Numeric view.
84 An introduction to HP apps

You can tell if a definition is selected by the tick (or checkmark)
beside it. A checkmark is added by default as soon as you create
a definition. So if you don’t want to plot or evaluate a particular
definition, highlight it and tap . (Do likewise if you want to
re-select a deselected function.)
Choose a color for plots
Each function and open
sentence can be plotted in a
different color. If you want to
change the default color of a
plot:
1. T a p t h e c o l o r e d s q u a r e t o
the left of the function’s
definition.
You can also select the square by pressing
the definition is selected. Pressing
selection from the definition to the colored square and from
the colored square to the definition.
2. tap .
3. Select the desired color from the color-picker.
Delete a definition
To delete a single definition:
1. Tap once on it (or highlight it using the cursor keys).
2. Press
To delete all the definitions:
1. P r e s s
2. Tap or press
E while
E moves the
C.
SJ.
E to confirm your intention.
An introduction to HP apps 85

Symbolic view: Summary of menu buttons
Button Purpose
Copies the highlighted definition to the
entry line for editing. Tap when
done.
To add a new definition—even one that is
replacing an existing one—highlight the
field and just start entering your new
definition.
Selects (or deselects) a definition.
Enters the independent variable in the
[Function only]
[Advanced
Graphing only]
[Advanced
Graphing only]
[Parametric only]
Function app. You can also press
Enters an X in the Advanced Graphing
app. You can also press
d.
Enters an Y in the Advanced Graphing
app.
Enters the independent variable in the
Parametric app. You can also press
d.
d.
Enters the independent variable in the Polar
[Polar only]
app. You can also press
d.
Enters the independent variable in the
[Sequence only]
Sequence app. You can also press
d.
Enters the equals sign in the Solve app. A
[Solve only]
shortcut equivalent to pressing
S..
Displays the selected definition in fullscreen mode. See “Large results” on
page 40 for more information.
Evaluates dependent definitions. See
“Evaluate a dependent definition” on
page 84.
86 An introduction to HP apps

Common operations in Symbolic Setup view
[Scope: all apps]
The Symbolic Setup view is the
same for all apps. Its primary
purpose is to allow you to
override three of the system-wide
settings specified on the Home
Settings window.
Press
SY to open Symbolic
Setup view.
Override system-wide settings
1. Tap once on the setting you want to change.
You can tap on the field name or the field.
2. Tap again on the setting.
A menu of options appears.
3. Select the new setting.
Note that selecting the Fixed, Scientific, or
Engineering option on the Number Format menu
displays a second field for you to enter the required number
of significant digits.
You could also select a field, tap , and select the new
setting.
Restore default settings
To restore default settings is to return precedence to the settings
on the Home Settings screen.
To restore one field to its default setting:
1. Select the field.
2. Press
To restore all default settings, press SJ.
An introduction to HP apps 87
C.

Common operations in Plot view
Plot view functionality that is common to many apps is described
in detail in this section. Functionality that is available only in a
particular app is described in the chapter dedicated to that app.
Press
P to open Plot view.
Zoom
[Scope: Advanced Graphing, Function, Parametric, Polar,
Sequence, Solve, Statistics 1 Var, and Statistics 2Var. Also, to a
limited degree, Geometry.]
Zooming redraws the plot on a larger or smaller scale. It is a shortcut
for changing the range settings in Plot Setup view. The extent of most
zooms is determined by two zoom factors: a horizontal and a vertical
factor. By default, these factors are both 2. Zooming out multiplies the
scale by the factor, so that a greater scale distance appears on the
screen. Zooming in divides the scale by the factor, so that a shorter
scale distance appears on the screen.
Zoom factors To change the default zoom factors:
1. Open the Plot view of the app (P).
2. Tap to open the Plot view menu.
3. Tap to open the Zoom menu.
4. Scroll and select Set
Factors.
The Zoom Factors screen
appears.
5. Change one or both zoom
factors.
6. If you want the plot to be
centered around the current position of the cursor in Plot
view, select Recenter.
7. T a p o r p r es s
E.
Zoom
options
88 An introduction to HP apps
Zoom options are available from three sources:
• the keyboard
• the menu in Plot view
• the Views menu (
V).

Zoom keys There are two zoom keys: pressing + zooms in and pressing
w zooms out. The extent of the scaling is determined by the
ZOOM FACTOR settings (explained above).
Zoom menu In Plot view, tap and tap
an option. (If is not
displayed, tap .)
The zoom options are explained
in the following table. Examples
are provided on “Zoom
examples” on page 91.
Option Result
Center on
Cursor
Redraws the plot so that the cursor is in the
center of the screen. No scaling occurs.
Box Explained in “Box zoom” on page 90.
In Divides the horizontal and vertical scales
by X Zoom and Y Zoom (values set with
the Set Factors option explained on
page 88). For instance, if both zoom
factors are 4, then zooming in results in 1/
4 as many units depicted per pixel.
(Shortcut: press
+.)
Out Multiplies the horizontal and vertical scales
by the X Zoom and Y Zoom settings.
(Shortcut: press
w.)
X In Divides the horizontal scale only, using the
X Zoom setting.
X Out Multiplies the horizontal scale only, using
the X Zoom setting.
Y In Divides the vertical scale only, using the Y
Zoom setting.
Y Out Multiplies the vertical scale only, using the
Y Zoom setting.
An introduction to HP apps 89

Option Result (Cont.)
Square Changes the vertical scale to match the
horizontal scale. This is useful after you
have done a box zoom, X zoom or Y
zoom.
Autoscale Rescales the vertical axis so that the display
shows a representative piece of the plot
given the supplied x axis settings. (For
Sequence, Polar, parametric, and Statistics
apps, autoscaling rescales both axes.)
The autoscale process uses the first selected
function to determine the best scale to use.
Decimal Rescales both axes so each pixel is 0.1
units. This is equivalent to resetting the
Integer
Trig
default values for
Rescales the horizontal axis only, making
each pixel equal to 1 unit.
Rescales the horizontal axis so that
XRNG and YRNG.
1 pixel equals /24 radians or 7.5
degrees; rescales the vertical axis so that 1
pixel equals 0.1 units.
Undo Zoom
Returns the display to the previous zoom, or
if there has been only one zoom, displays
the graph with the original plot settings.
Box zoom A box zoom enables you to zoom in on an area of the screen that
you specify.
1. With the Plot view menu open, tap and select Box.
2. Tap one corner of the area you want to zoom in on and then
tap .
3. Tap the diagonally opposite corner of the area you want to
zoom in on and then tap .
The screen fills with the area you specified. To return to the
default view, tap and select Decimal.
You can also use the cursor keys to specify the area you want to
zoom in on.
90 An introduction to HP apps

Views menu The most commonly used zoom
3 xsin
options are also available on the
Views menu. These are:
• Autoscale
• Decimal
• Integer
• Trig.
These options—which can be applied whatever view you are
currently working in—are explained in the table immediately
above.
Testing a
zoom with
split-screen
viewing
Zoom
examples
A useful way of testing a zoom is
to divide the screen into two
halves, with each half showing
the plot, and then to apply a
zoom only to one side of the
screen. The illustration at the
right is a plot of y = 3sin x. To
split the screen into two halves:
1. O p en t h e Views menu.
Press
V
2. Select Split Screen:
Plot Detail.
The result is shown at the
right. Any zoom operation
you undertake will be
applied only to the copy of the plot in the right-hand half of
the screen. This will help you test and then choose an
appropriate zoom.
Note that you can replace the original plot on the left with the
zoomed plot on the right by tapping
To un-split the screen, press
The following examples show the effects of the zooming options
on a plot of using the default zoom factors (2 × 2). Splitscreen mode (described above) has been used to help you see the
effect of zooming.
P.
.
An introduction to HP apps 91

Note that there is an Unzoom option on the Zoom menu. Use
this to return a plot to its pre-zoom state. If the Zoom menu is not
shown, tap .
Zoom In
In
Shortcut: press
+
Zoom Out
Out
Shortcut: press w
X In
XIn
X Out
X Out
Y In
YIn
92 An introduction to HP apps

Y Out
Y Out
Square
Square
Notice that in this example, the
plot on left has had a YIn zoom
applied to it. The Square zoom
has returned the plot to its
default state where the X and Y
scales are equal.
Autoscale
Autoscale
Decimal
Decimal
Notice that in this example, the
plot on left has had a XIn zoom
applied to it. The Decimal
zoom has reset the default
values for the x-range and y-
range.
Integer
Integer
An introduction to HP apps 93

Trace
Trig
Trig
[Scope: Advanced Graphing, Function, Parametric, Polar,
Sequence, Solve, Statistics 1 Var, and Statistics 2Var.]
The tracing functionality enables
you to move a cursor (the trace
cursor) along the current graph.
You move the trace cursor by
pressing
move the trace cursor by tapping
on or near the current plot. The
trace cursor jumps to the point
on the plot that is closest point to where you tapped.
The current coordinates of the cursor are shown at the bottom of
the screen. (If menu buttons are hiding the coordinates, tap
Trace mode and coordinate display are automatically turned on
when a plot is drawn.
or >. You can also
<
to hide the buttons.)
To select a
plot
94 An introduction to HP apps
Except in the Advanced Graphing app, if there is more than one
plot displayed, press
you are interested in.
In the Advanced Graphing app, tap-and-hold on the plot you are
interested in. Either the plot is selected, or a menu of plots
appears for you select one.
or \ until the trace cursor is on the plot
=

To evaluate a
definition
One of the primary uses of the trace functionality is to evaluate a
plotted definition. Suppose in Symbolic view you have defined
F1(X) as (X – 1)
2
–3. Suppose further that you want to know
what the value of that function is when X is 25.
1. Open Plot view (
P).
2. If the menu at the bottom of the screen is not open, tap
.
3. If more than one definition is plotted, ensure that the trace
cursor is on the plot of the definition you want to evaluate.
You can press
press
= or \ to move the trace cursor from plot to plot.
4. If you pressed
to see the definition of a plot, and
to see the definition of a plot, the menu
at the bottom of the screen will be closed. Tap to reopen it.
5. Tap .
6. Enter 25 and tap .
7. T a p .
The value of F1(X) when X
is 25 as shown at the
bottom of the screen.
This is one of many ways the HP
Prime provides for you to
evaluate a function for a specific
independent variable. You can
also evaluate a function in
Numeric view (see page 102). Moreover, any expression you
define in Symbolic view can be evaluated in Home view. For
example, suppose F1(X)is defined as (x –1)
F1(4) in Home view and press
2
(4– 1)
–3 = 6.
E you get 6, since
2
– 3. If you enter
To turn
tracing on or
off
• To turn off tracing, tap .
• To turn on tracing, tap .
If these options are not displayed, tap .
When tracing is off, pressing the cursor keys no longer
constrains the cursor to a plot.
An introduction to HP apps 95

Plot view: Summary of menu buttons
Button Purpose
Displays a menu of zoom options. See
“Zoom options” on page 88.
/
[Function only]
A toggle button for turning off and turning
on trace functionality. See “Trace” on
page 94.
Displays an input form for you to specify a
value you want the cursor to jump to. The
value you enter is the value of the
independent variable.
Displays a menu of options for analyzing a
plot. See “Analyzing functions” on
page 118.
Displays the definition responsible for
generating the selected plot.
A toggle button that shows and hides the
other buttons across the bottom of the
screen.
Common operations in Plot Setup view
This section covers only operations common to the apps
mentioned. See the chapter dedicated to an app for the appspecific operations done in Plot Setup view.
Press
SP to open Plot Setup view.
Configure Plot view
[Scope: Advanced Graphing,
Function, Parametric, Polar,
Sequence, Statistics 1 Var,
Statistics 2Var]
The Plot Setup view is used to
configure the appearance of Plot
view and to set the method by
which graphs are plotted. The
96 An introduction to HP apps
 Loading...
Loading...