Page 1

HP Notebook PC
Reference Guide
Page 2

Please check out our eBay auctions for more great
deals on Factory Service Manuals:
Page 3

Notice
This manual and any examples contained herein are provided “as is” and are subject to
change without notice. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no warranty of any kind with
regard to this manual, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Hewlett-Packard Co. shall not be
liable for any errors or for incidental or consequential damages in connection with the
furnishing, performance, or use of this manual or the examples herein.
Consumer transactions in Australia and the United Kingdom: The above disclaimers and
limitations shall not apply to Consumer transactions in Australia and the United Kingdom
and shall not affect the statutory rights of Consumers.
© Copyright Hewlett-Packard Company 2002. All rights reserved. Reproduction,
adaptation, or translation of this manual is prohibited without prior written permission of
Hewlett-Packard Company, except as allowed under the copyright laws.
The programs that control this product are copyrighted and all rights are reserved.
Reproduction, adaptation, or translation of those programs without prior written
permission of Hewlett-Packard Co. is also prohibited.
Portions of the programs that control this product may also be copyrighted by Microsoft
Corporation, Phoenix Technologies, Ltd., ATI Technologies Inc., S3 Graphics
Incorporated, Intel Corporation, and Adobe Systems Incorporated. See the individual
programs for additional copyright notices.
This product incorporates copyright protection technology that is protected by method
claims of certain U.S. patents and other intellectual property rights owned by
Macrovision Corporation and other rights owners. Use of this copyright protection
technology must be authorized by Macrovision Corporation and is intended for home and
other limited viewing uses only unless otherwise authorized by Macrovision Corporation.
Reverse engineering or disassembly is prohibited.
Microsoft®, MS-DOS®, and Windows® are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation. Pentium® and the Intel Inside logo are U.S. registered trademarks and
Celeron™ and SpeedStep™ are U.S. trademarks of Intel Corporation. Adobe® and
Acrobat® are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated.
Hewlett-Packard Company
HP Notebook Customer Care
1000 NE Circle Blvd., MS 425E
Corvallis, OR 97330
2 Reference Guide
Page 4
Important Safety Information
CAUTION
To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunications line
cord to connect a modem to the telephone wall jack. In Australia, the computer
must be connected to the Telecommunication Network through a line cord that
meets the requirements of ACA Technical Standard TS008.
When using your computer with a telephone connection, always follow basic safety
precautions to reduce the risk of fire, electric shock, and injury to persons:
• Do not use this product with a telephone connection near water (for example, near a
bathtub, sink, swimming pool, or in a wet basement).
• Avoid using a telephone connection (other than a cordless type) during an electrical
storm. There may be a remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• Do not use a telephone connection to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
• Use only the power cord and batteries indicated in this manual. Do not dispose of
batteries in a fire. They may explode. Check with local codes for possible special
disposal instructions.
HP Software Product License Agreement
Your HP product contains software programs. CAREFULLY READ THIS LICENSE
AGREEMENT BEFORE PROCEEDING TO OPERATE THIS EQUIPMENT. RIGHTS
IN THE SOFTWARE ARE OFFEREDONLY ON THE CONDITION THAT THE
CUSTOMER AGREES TO ALL TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THE LICENSE
AGREEMENT. PROCEEDING TO OPERATE THE EQUIPMENT INDICATES
YOUR ACCEPTANCE OF THESE TERMS AND CONDITIONS. IF YOU DO NOT
AGREE WITH THE TERMS OF THE LICENSE AGREEMENT, YOU MUST NOW
EITHER REMOVE THE SOFTWARE FROM YOUR HARD DISK DRIVE AND
DESTROY THE MASTER DISKETTES, OR RETURN THE COMPLETE HP
PRODUCT AND SOFTWARE FOR A FULL REFUND. PROCEEDING WITH
CONFIGURATION SIGNIFIES YOUR ACCEPTANCE OF THE LICENSE TERMS.
UNLESS OTHERWISE STATED BELOW, THIS HP SOFTWARE LICENSE
AGREEMENT SHALL GOVERN THE USE OF ALL SOFTWARE THAT IS
PROVIDED TO YOU AS PART OF THE HP PRODUCT AND SHALL SUPERSEDE
ANY OTHER SOFTWARE WARRANTY STATEMENT THAT MAY BE INCLUDED
IN THIS HP PRODUCT OR MAY BE FOUND ONLINE.
Operating system and software applications by Microsoft are licensed to you under the
Microsoft License Agreement contained in the Microsoft documentation or displayed on
your screen when Microsoft Software Products are launched.
Reference Guide 3
Page 5

For a PC supplied with a Microsoft operating system: When you start the PC and accept
the Microsoft End-user License Agreement (“EULA”), your license rights are valid only
if a Certificate of Authenticity (“COA”) label corresponding to your Microsoft operating
system is provided with your PC. The COA label can usually be found on the bottom of
the computer. If the COA label does not correspond to your Microsoft operating system
or is missing, contact your HP reseller for details.
Other non-HP Software and Operating Systems are covered by the appropriate vendor
license. The following License Terms govern the use of the HP software:
USE. Customer may use the software on any one HP product. Customer may not network
the software or otherwise use it on more than one HP product. Customer may not reverse
assemble or decompile the software unless authorized by law.
COPIES AND ADAPTATIONS. Customer may make copies or adaptations of the
software a) for archival purposes or (b) when copying or adaptation is an essential step in
the use of the software with an HP product so long as the copies and adaptations are used
in no other manner.
OWNERSHIP. Customer agrees that he/she does not have any title or ownership of the
software, other than ownership of the physical media. Customer acknowledges and
agrees that the software is copyrighted and protected under the copyright laws. Customer
acknowledges and agrees that the software may have been developed by a third party
software supplier named in the copyright notices included with the software, who shall be
authorized to hold the Customer responsible for any copyright infringement or violation
of this Agreement.
PRODUCT RECOVERY CD-ROM or DVD. If your HP product was shipped with a
product recovery CD-ROM or DVD: (i) The product recovery CD-ROM or DVD and/or
support utility software may only be used for restoring the hard disk of the HP product
with which the product recovery CD-ROM or DVD was originally provided. (ii) The use
of any operating system software by Microsoft contained in any such product recovery
CD-ROM or DVD shall be governed by the Microsoft License Agreement.
TRANSFER OF RIGHTS IN SOFTWARE. Customer may transfer rights in the software
to a third party only as part of the transfer of all rights and only if Customer obtains the
prior agreement of the third party to be bound by the terms of this License Agreement.
Upon such a transfer, Customer agrees that his/her rights in the software are terminated
and that he/she will either destroy his/her copies and adaptations or deliver them to the
third party.
SUBLICENSING AND DISTRIBUTION. Customer may not lease, sublicense the
software or distribute copies or adaptations of the software to the public in physical
media or by telecommunication without the prior written consent of Hewlett-Packard.
TERMINATION. Hewlett-Packard may terminate this software license for failure to
comply with any of these terms provided Hewlett-Packard has requested Customer to
cure the failure and Customer has failed to do so within thirty (30) days of such notice.
UPDATES AND UPGRADES. Customer agrees that the software does not include
updates and upgrades which may be available from Hewlett-Packard under a separate
support agreement.
4 Reference Guide
Page 6

EXPORT CLAUSE. Customer agrees not to export or re-export the software or any copy
or adaptation in violation of the U.S. Export Administration regulations or other
applicable regulation.
U.S. GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS. Use, duplication, or disclosure is subject
to HP standard commercial license terms and for non-DOD Departments and Agencies of
the U.S. Government, the restrictions set forth in FAR 52.227-19(c)(1-2) (June 1987)
Hewlett-Packard Company, 3000 Hanover Street, Palo Alto, CA 94304 U.S.A. Copyright
(c) 2000 Hewlett-Packard Company. All Rights Reserved. Customer further agrees that
Software is delivered and licensed as “Commercial computer software” as defined in
DFARS 252-227-7014 (June 1995) or as a “commercial item” as defined in FAR
2.101(a), or as “Restricted computer software” as defined in FAR 52.227-19 (or any
equivalent agency regulation or contract clause), whichever is applicable. The Customer
agrees that it has only those rights provided for such Software by the applicable FAR or
DFARS clause or the HP standard software agreement for the product involved.
Support Policy for Microsoft Operating Systems Service Pack. HP will provide end user
support for HP PCs that use Microsoft Operating Systems, including its latest service
packs. This support will be available 30 days after the service pack being released by
Microsoft.
Edition History
Edition 1 (KD).......................................... May 2002
This manual is printed on recycled paper.
Reference Guide 5
Page 7

Page 8

Contents
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook ..................................................................... 11
Taking Inventory......................................................................................................... 12
What’s in the box? ................................................................................................ 12
To buy accessories................................................................................................ 12
To find more information...................................................................................... 13
Identifying Parts of the Computer............................................................................... 14
Front View ............................................................................................................ 14
Back View............................................................................................................. 15
Bottom View......................................................................................................... 16
Status Lights.......................................................................................................... 17
Setting Up Your Computer......................................................................................... 19
Step 1: Install the battery ...................................................................................... 19
Step 2: Connect AC power.................................................................................... 21
Step 3: Connect a phone line................................................................................. 22
Step 4: Turn on the computer................................................................................ 23
Step 5: Set up Windows........................................................................................ 24
Step 6: Register your notebook............................................................................. 24
To connect to the Internet ..................................................................................... 25
What to do next..................................................................................................... 25
Basic Operation .............................................................................................................. 27
Operating Your Computer.......................................................................................... 28
To turn the computer on and off ........................................................................... 28
To reset the computer............................................................................................ 29
To change the boot device..................................................................................... 30
To use the touch pad ............................................................................................. 31
To use the Fn hot keys .......................................................................................... 33
To use the One-Touch buttons.............................................................................. 34
To use the Windows and Applications keys ......................................................... 35
To use the embedded keypad................................................................................ 36
To use the ALT GR key........................................................................................ 36
To adjust the display ............................................................................................. 37
To adjust the volume.............................................................................................38
To change computer settings for a presentation.................................................... 39
Using CDs or DVDs................................................................................................... 40
To insert or remove a CD or DVD........................................................................40
To play DVD movies............................................................................................ 41
To create or copy CDs .......................................................................................... 41
Securing Your Computer............................................................................................ 42
To set up password protection............................................................................... 42
To lock your computer.......................................................................................... 43
To attach a security cable...................................................................................... 43
Reference Guide 7
Page 9

To protect against viruses ..................................................................................... 44
Working in Comfort with a Notebook PC.................................................................. 45
Taking Care of Your Computer.................................................................................. 47
To protect your hard disk drive............................................................................. 47
To maintain your computer................................................................................... 47
To safeguard your data.......................................................................................... 48
To extend the life of the display............................................................................ 48
To clean your computer ........................................................................................ 49
Batteries and Power Management................................................................................ 51
Managing Power Consumption .................................................................................. 52
How the computer manages power automatically ................................................ 52
To manage power manually.................................................................................. 54
Using Battery Power................................................................................................... 55
To check battery status.......................................................................................... 55
To respond to a low-battery warning .................................................................... 56
To recharge the battery ......................................................................................... 56
To get the most from your batteries...................................................................... 56
Modem and Network Connections................................................................................ 59
Using the Modem........................................................................................................ 60
To connect the modem.......................................................................................... 61
To connect to the Internet ..................................................................................... 62
To disconnect from the Internet............................................................................ 63
To dial in to a network.......................................................................................... 63
To change your modem settings ........................................................................... 64
To send and receive e-mail ................................................................................... 65
To send and receive faxes (Windows XP)............................................................ 66
To send and receive faxes (Windows 2000) ......................................................... 67
Connecting to a LAN.................................................................................................. 68
To connect to a LAN............................................................................................. 68
Making Wireless Connections.................................................................................... 69
To prepare for connections (Windows XP)........................................................... 69
To prepare for connections (Windows 2000)........................................................ 71
To turn wireless communication on and off.......................................................... 73
Add-On Devices.............................................................................................................. 75
Connecting PC Cards.................................................................................................. 76
To insert or remove a PC Card.............................................................................. 76
Connecting External Devices...................................................................................... 78
To identify connectors for external devices.......................................................... 78
To connect a printer or other parallel device......................................................... 80
To connect an external keyboard or mouse........................................................... 80
To connect a USB device...................................................................................... 80
To connect an audio device................................................................................... 81
8 Reference Guide
Page 10

To use an external monitor.................................................................................... 82
To use a TV set as a monitor................................................................................. 84
To connect an IEEE 1394 device.......................................................................... 85
To connect a serial device..................................................................................... 85
To connect an infrared device............................................................................... 85
To use a port replicator ......................................................................................... 86
Installing Additional RAM......................................................................................... 89
To install a RAM expansion module .................................................................... 89
To remove a RAM expansion module .................................................................. 90
Replacing the Hard Disk Drive................................................................................... 92
To replace the hard disk drive............................................................................... 92
To replace the hard disk drive holder.................................................................... 93
To prepare a new hard disk drive.......................................................................... 94
Troubleshooting and Maintenance ............................................................................... 95
Troubleshooting Your Computer................................................................................ 96
Audio Problems..................................................................................................... 96
CD-ROM and DVD Problems.............................................................................. 97
Display Problems.................................................................................................. 99
Hard Disk Drive Problems.................................................................................. 100
Heat Problems..................................................................................................... 101
Infrared Problems................................................................................................ 101
Keyboard and Pointing Device Problems ........................................................... 102
LAN Problems .................................................................................................... 103
Memory Problems...............................................................................................104
Modem Problems................................................................................................ 105
PC Card (PCMCIA) Problems............................................................................ 107
Performance Problems........................................................................................ 108
Port Replicator Problems .................................................................................... 109
Power and Battery Problems............................................................................... 110
Printing Problems................................................................................................ 111
Serial, Parallel, and USB Problems..................................................................... 112
Startup Problems................................................................................................. 114
Wireless Problems............................................................................................... 115
Testing the Hardware................................................................................................ 116
To run the e-Diagtools diagnostic test ................................................................ 116
Configuring the Computer........................................................................................ 118
To run the BIOS Setup utility ............................................................................. 118
To set up TopTools............................................................................................. 121
Reinstalling and Updating Software......................................................................... 122
To recover the factory installation of your hard disk.......................................... 122
To create a boot disk (Windows 2000) ............................................................... 123
To replace a damaged Recovery CD or DVD..................................................... 123
To update the BIOS............................................................................................. 124
To update Windows drivers................................................................................ 125
Reference Guide 9
Page 11

HP Support and Service............................................................................................... 127
Getting Assistance for Your Computer..................................................................... 128
To get help from the Web ................................................................................... 128
To contact HP for support or service .................................................................. 128
To receive repair service..................................................................................... 131
To prepare your computer for shipment.............................................................. 132
Hewlett-Packard Limited Warranty Statement......................................................... 133
Reference Information................................................................................................. 135
Hardware Specifications........................................................................................... 136
Modem Reference Information................................................................................. 139
Modem Reference (Conexant)............................................................................ 139
Safety Information.................................................................................................... 146
Power Cords........................................................................................................ 146
Ergonomics ......................................................................................................... 147
Battery Safety...................................................................................................... 147
Laser Safety......................................................................................................... 148
LED Safety.......................................................................................................... 148
Mercury Safety.................................................................................................... 149
Exposure to Radio Frequency Radiation............................................................. 149
Regulatory Information............................................................................................. 150
U.S.A................................................................................................................... 150
Canada................................................................................................................. 151
European Union .................................................................................................. 152
Japan ................................................................................................................... 154
Russia.................................................................................................................. 155
International........................................................................................................ 155
Index ..............................................................................................................................157
10 Reference Guide
Page 12

Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Reference Guide 11
Page 13
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Taking Inventory
Taking Inventory
Congratulations! Your notebook computer sets a new standard in personal computing.
Although compact and easy to carry, your computer is made with the quality and
attention to detail that are the hallmark of Hewlett-Packard.
This manual shows how to set up and operate your computer, as well as what to do if you
run into trouble.
What’s in the box?
• HP notebook PC.
• Battery (installed).
• AC adapter and power cord.
• Quick Start sheet.
• Startup Guide.
• Recovery CD or DVD, for restoring Windows and all software included with your
computer.
• Microsoft Windows manual.
In addition, your HP notebook includes preinstalled software. (The exact software
installed depends on your particular notebook model.)
To buy accessories
You can buy accessories for your computer online. For the latest accessories and options,
visit the HP Notebook Web site (www.hp.com/notebooks).
HP currently offers accessories, such as the following:
• AC adapter.
• Replacement hard disk drive module.
• RAM modules for expanding memory.
12 Reference Guide
Page 14
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Taking Inventory
• Battery.
• Port replicator.
To find more information
The following table lists other sources of information about your computer and related
products.
Source Description and Location
Startup Guide
Online
Reference
Guide
Online HP Notes For late-breaking information available after the manuals were completed, see the
Microsoft Windows
manual
HP Notebook Web
Site
HP Business
Support Web Site
Corporate
Evaluator’s Guide
This printed manual introduces your computer. It also contains setup instructions,
basic operation guidelines, troubleshooting information, and warranty information.
The full
complete source for operating and maintaining the computer. Look in the online HP
Library, or on the
Library is in the Help and Support Center.
HP Notes in the online HP Library, or on the
This is shipped with your computer and contains information about using the version
of Microsoft Windows shipped with your computer.
www.hp.com/notebooks
www.europe.hp.com/notebooks (European mirror).
To select another language, see www.hp.com.
www.hp.com/go/bizsupport
This provides information about installing alternate operating systems, as well as
how to configure your notebook computer in a corporate, networked environment.
Located at the HP Business Support Web site.
Reference Guide
Recovery CD
is shipped on the computer’s hard drive, and provides a
or
DVD
in \hp\Library. For Windows XP, the HP
Recovery CD
or
DVD
in \hp\Library.
Reference Guide 13
Page 15
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Identifying Parts of the Computer
Identifying Parts of the Computer
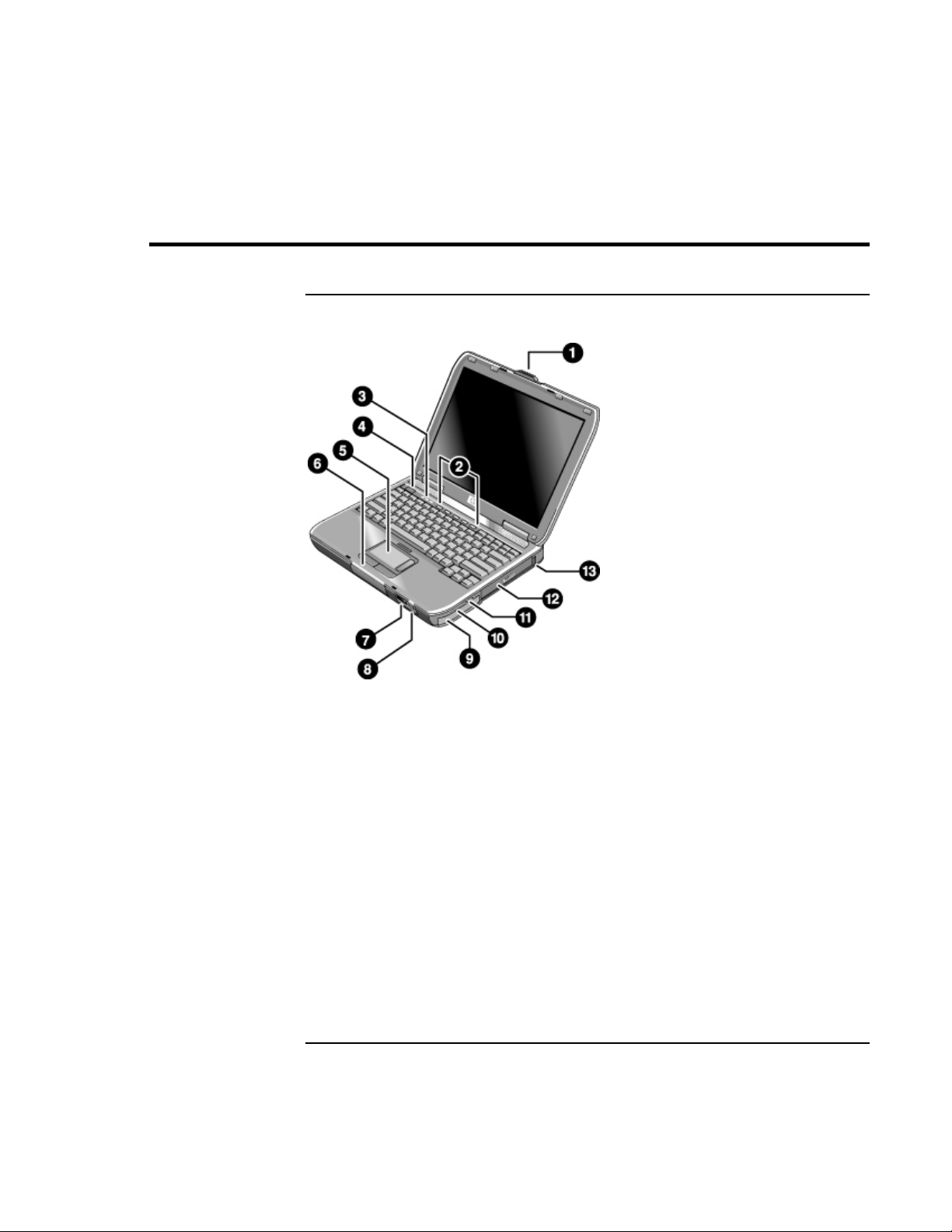
Front View
1. Computer open/close latch.
2. One-Touch buttons.
3. Keyboard status lights.
4. Power button. Turns the computer on and off.
5. Touch pad, scroll pad, click buttons, plus on-off
button.
6. Main status lights (left to right): power mode,
battery, hard disk activity.
7. Infrared port.
14 Reference Guide
8. Wireless on-off button and indicator light (on
certain models).
9. Battery.
10. Audio mute button, audio mute light, and volume
control.
11. Audio jacks (left to right): audio out (headphones),
external microphone.
12. CD-ROM, DVD, or other drive.
13. Universal serial bus port (USB).
Page 16
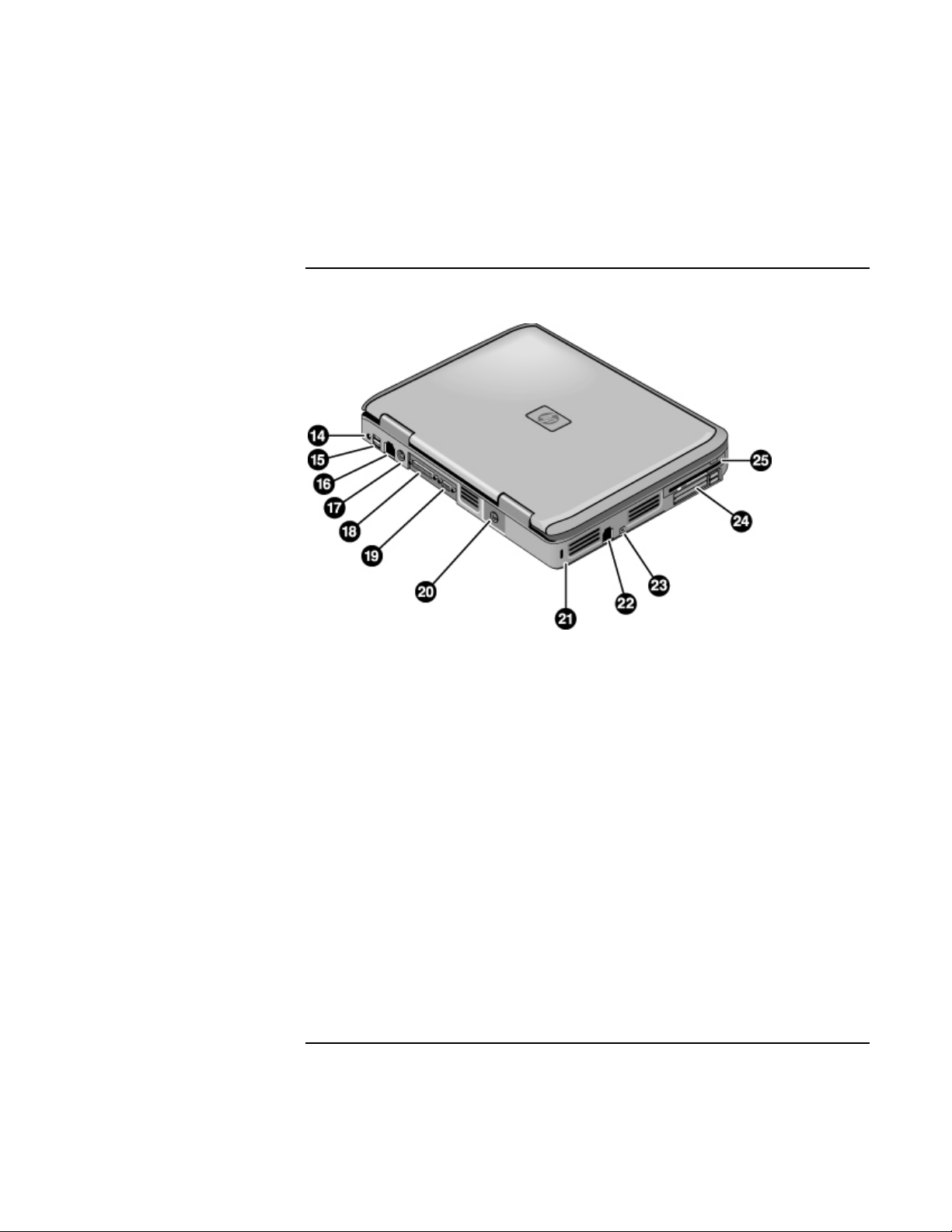
Back View
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Identifying Parts of the Computer
14. AC adapter jack.
15. Two USB ports.
16. LAN port.
17. PS/2 keyboard or PS/2 mouse port (supports Y
adapter).
18. Parallel port (LPT1). Use this port for a parallel
printer or other parallel device.
19. External monitor port.
20. S-video port.
21. Kensington lock slot (security connector).
22. Modem port.
23. IEEE 1394 port (on certain models).
24. PC Card and CardBus slot and buttons.
25. Floppy disk drive (on certain models).
Reference Guide 15
Page 17
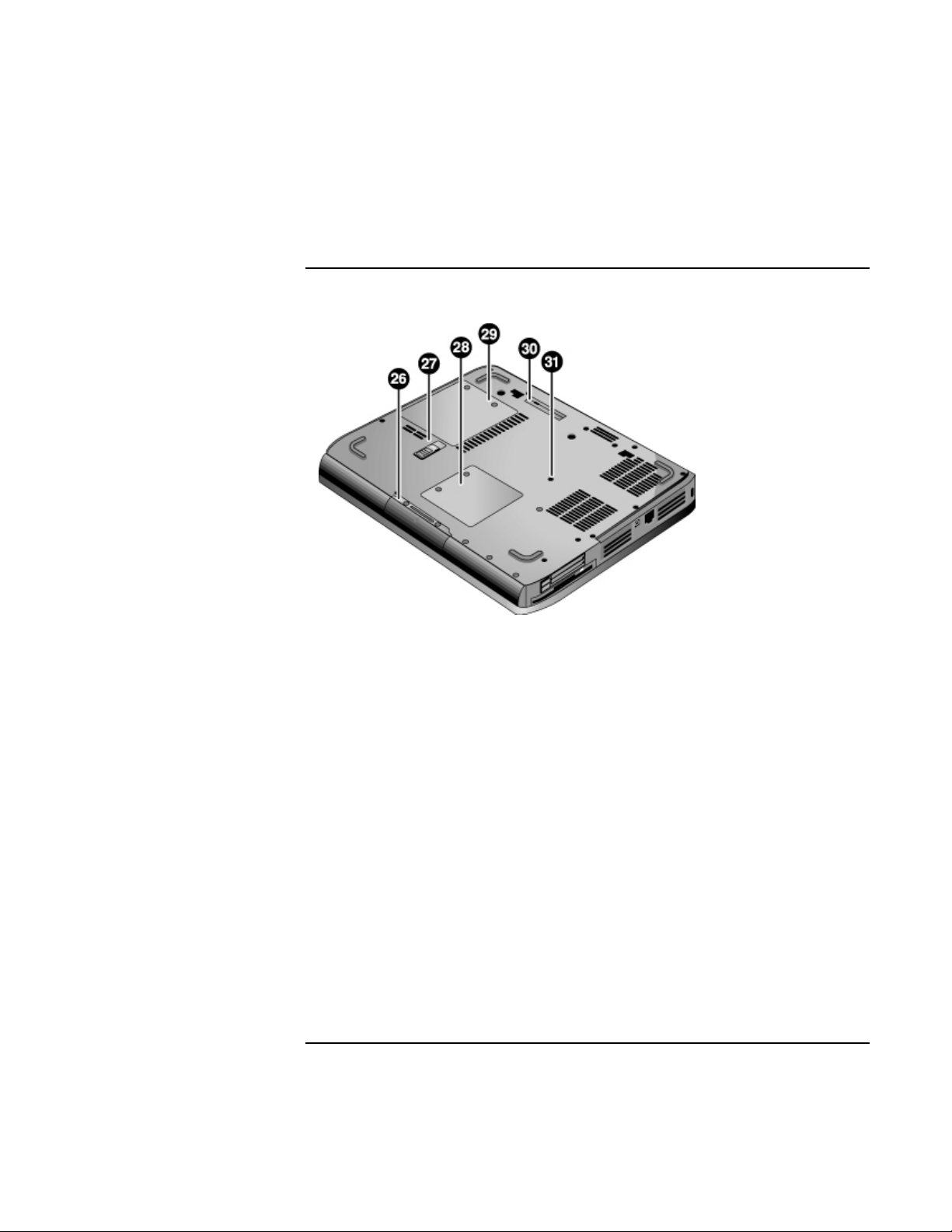
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Identifying Parts of the Computer
Bottom View
26. Hard disk drive.
27. Battery latch.
28. Mini-PCI cover (no user parts inside).
16 Reference Guide
29. RAM cover.
30. Docking port.
31. Reset button.
Page 18
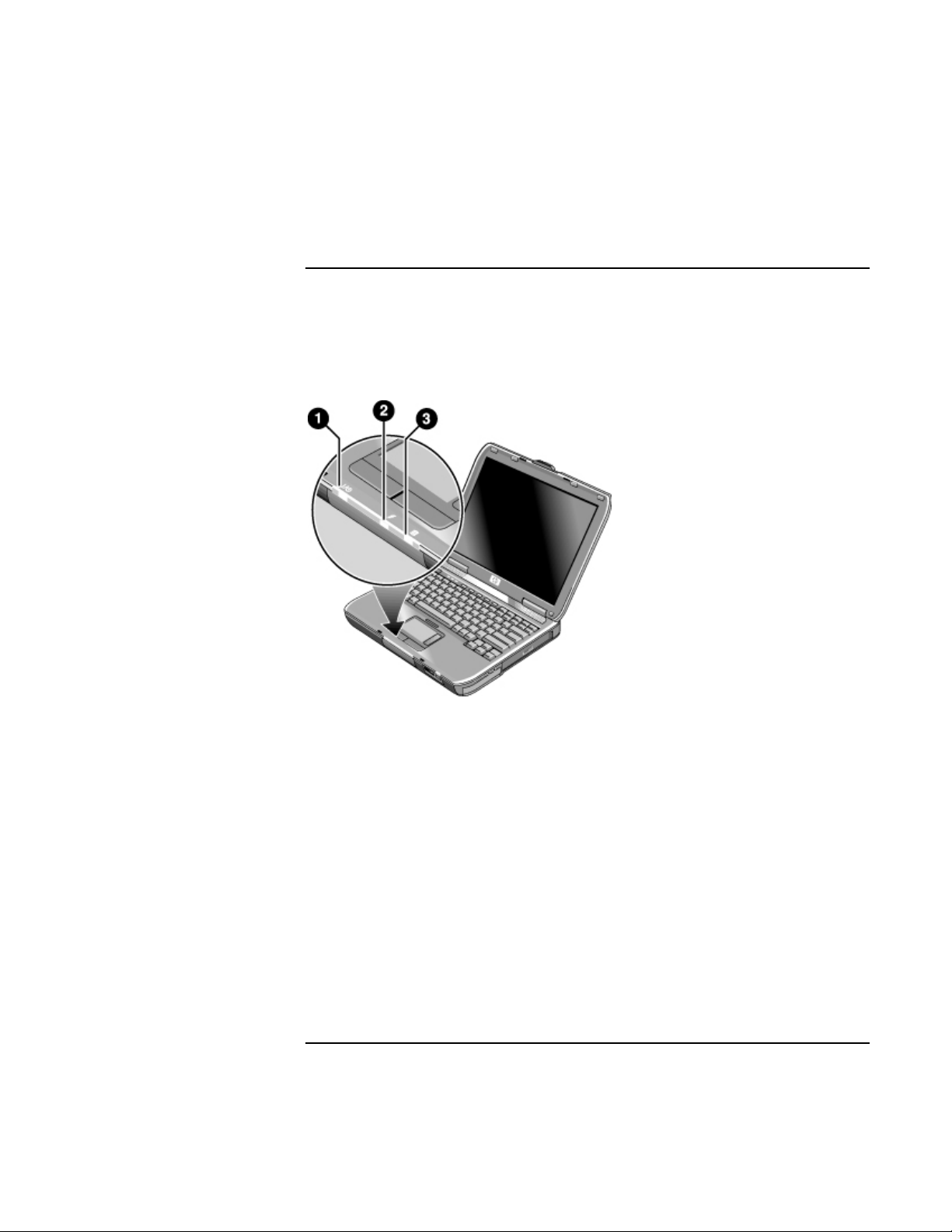
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Identifying Parts of the Computer
Status Lights
The computer includes a number of status lights that report power and battery status,
drive activity, and keyboard functions such as Caps Lock and Num Lock.
The following diagram shows the main status lights on the front of the computer.
1. Power mode.
• On: the computer is on (even if the display is off).
• Blinking: the computer is in Standby mode.
• Off: the computer is off or in Hibernate mode.
2. Hard disk drive activity.
• On: computer is accessing the hard disk drive.
3. Battery status.
• Green: the AC adapter is connected and the battery is fully charged.
• Amber: the AC adapter is connected and the battery is charging.
Reference Guide 17
Page 19
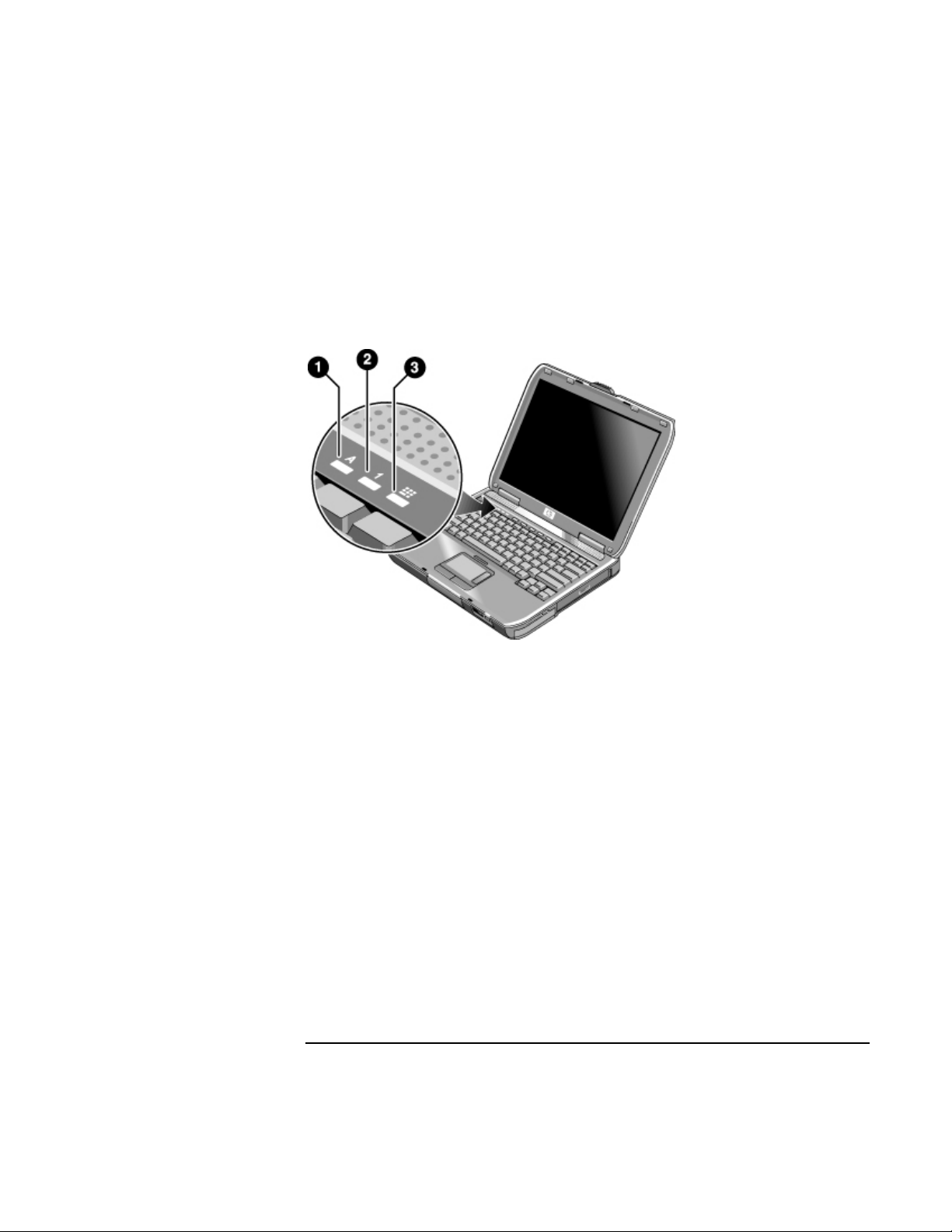
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Identifying Parts of the Computer
• Blinking: the AC adapter is connected and the battery is missing or has a fault.
• Off: the AC adapter is not connected.
The keyboard status lights, located above the keyboard, indicate the states of the
keyboard locks.
1. Caps Lock. Caps Lock is active.
2. Num Lock. Num Lock is active. (The Keypad Lock must also be on to use the
embedded keypad.)
3. Keypad Lock. The embedded keypad is active (Fn+F8). Num Lock must also be on
for the numeric keys—otherwise, cursor control is active (as marked on an external
keyboard).
18 Reference Guide
Page 20
Setting Up Your Computer
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Setting Up Your Computer
WARNING
WARNING
Improper use of keyboards and other input devices has been associated with
ergonomic injury. For information about reducing your risk, see Working in
Comfort in the online HP Library, or visit our ergonomics Web site,
www.hp.com/ergo. For a summary about working with a notebook computer, see
“Working in Comfort with a Notebook PC” on page 45.
If you are using your notebook computer as your primary computer, or using it for
extended periods, you should use it with a full-size keyboard, monitor, and mouse.
HP docking accessories offer quick, easy connections to these devices. This can
reduce the risk of ergonomic injury. See Working in Comfort in the online HP
Library.
When you set up your computer for the first time, you’ll install and charge the battery,
connect the AC adapter, turn on the computer, and run the Windows setup program.
Step 1: Install the battery
Do not mutilate or puncture batteries. Do not dispose of batteries in fire, or they
can burst or explode, releasing hazardous chemicals. Rechargeable batteries must
be recycled or disposed of properly.
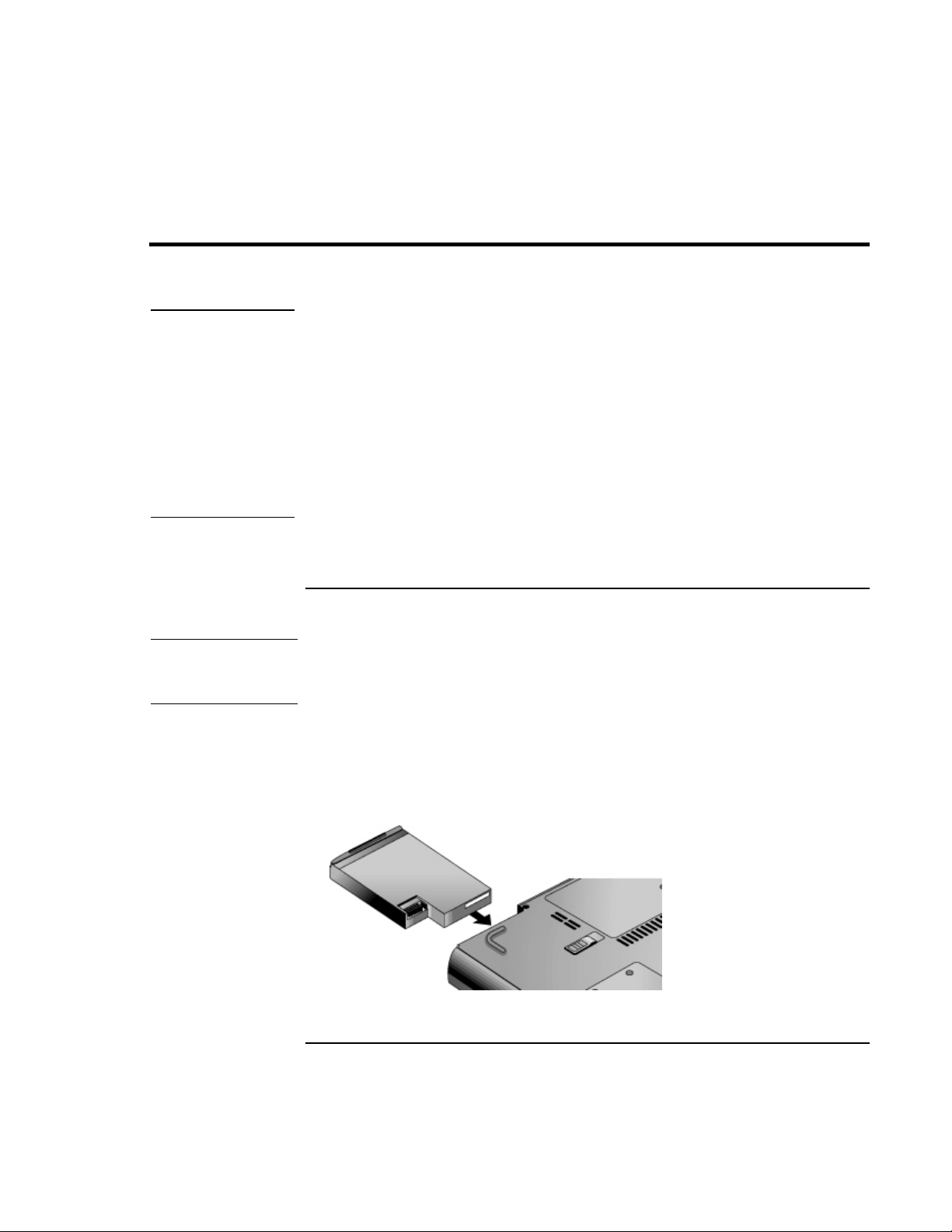
Your computer is shipped with the battery installed. If the battery has been removed, you
should install it:
1. Turn the computer upside down.
2. Insert the connector end of the battery into the battery compartment and slide it in
until it latches.
Reference Guide 19
Page 21
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Setting Up Your Computer
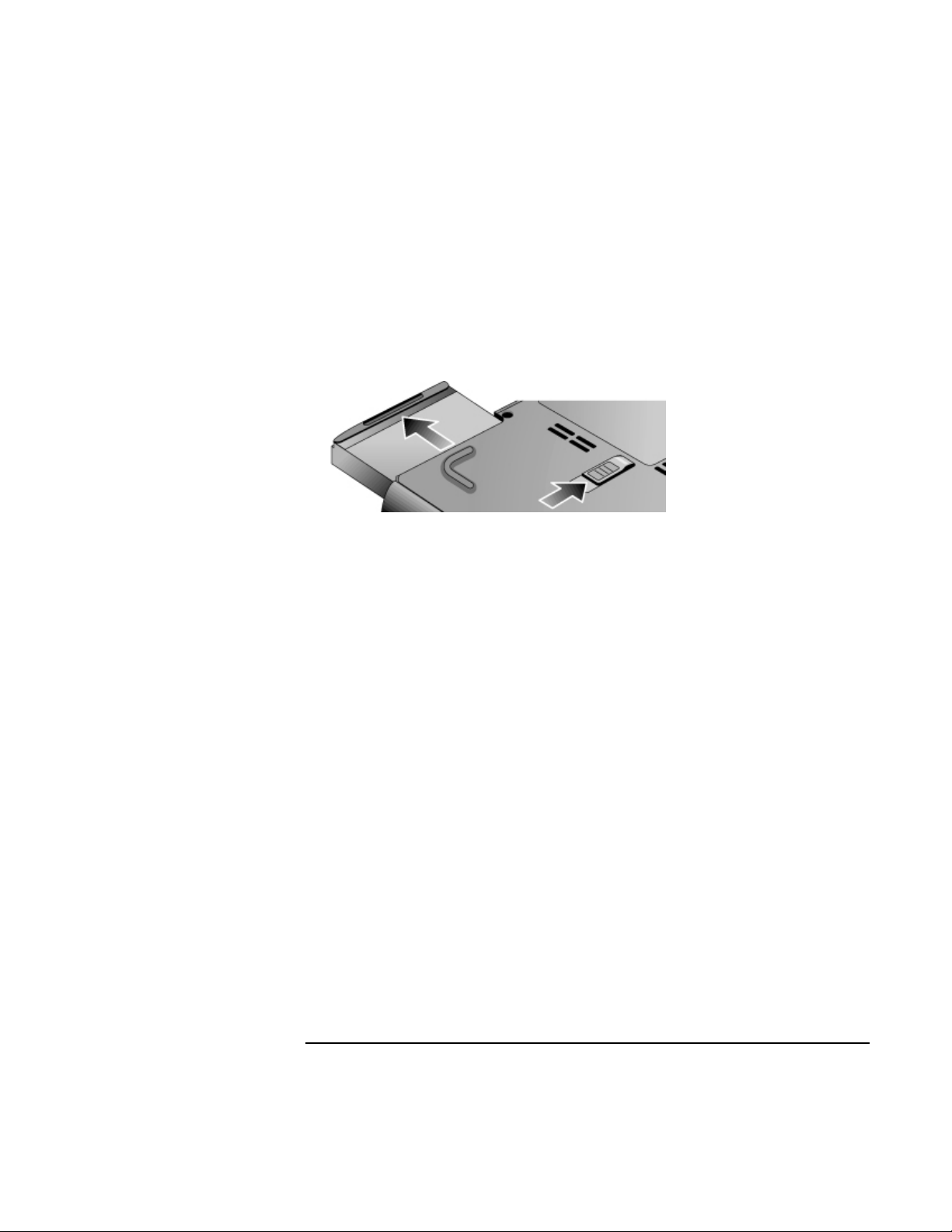
To remove the battery
1. Before removing the battery, do one of the following:
• Shut down the computer or put it into Hibernate mode, or
• Plug in the AC adapter.
2. Slide the battery’s release latch, and then slide the battery out of its compartment.
20 Reference Guide
Page 22
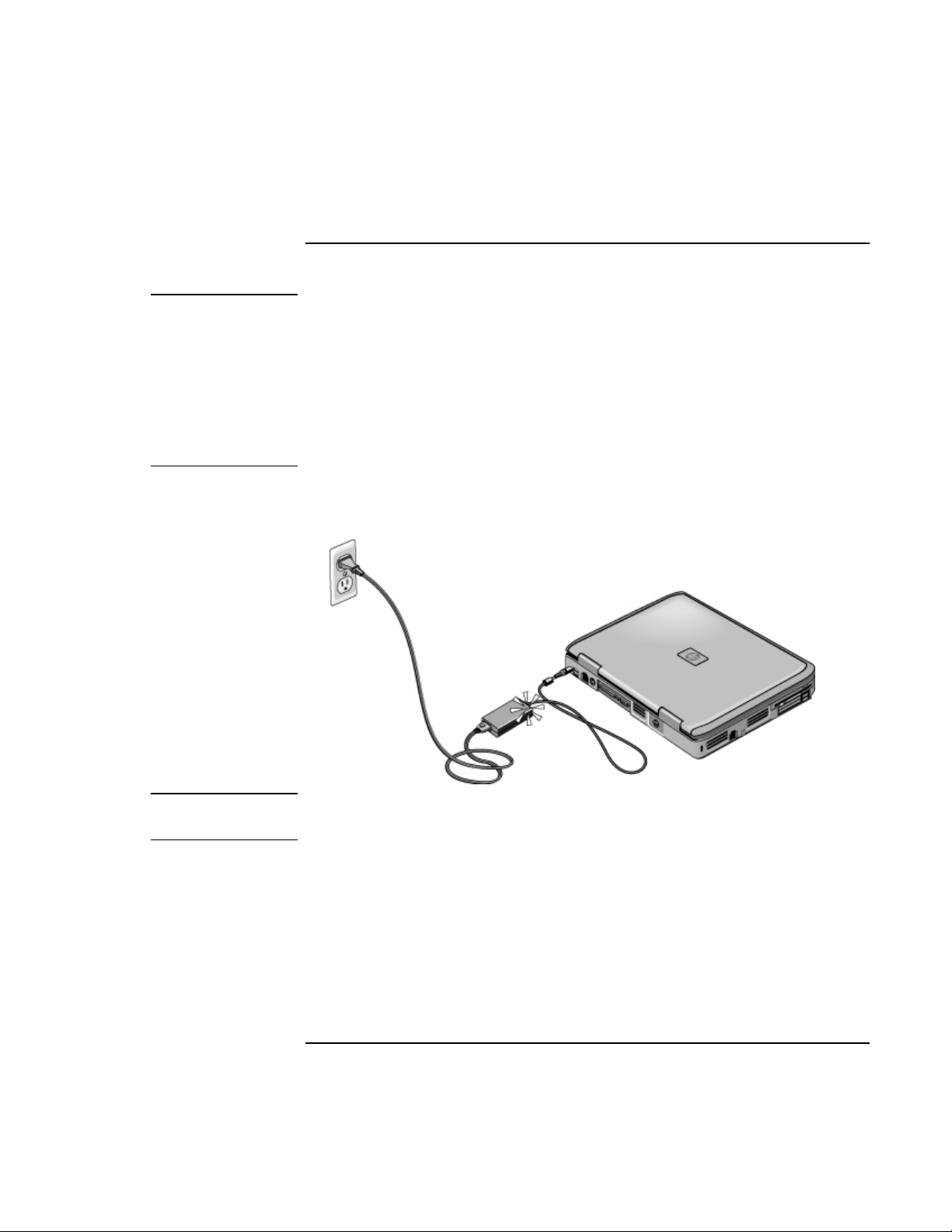
Step 2: Connect AC power
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Setting Up Your Computer
CAUTION
Use only the 90-watt HP AC adapter included with your computer (or other
approved adapter that meets the power requirements of the computer).
If “90W” is printed below the AC adapter socket, do not use a 60- or 75-watt
adapter, such as HP F1454A, F1781A, F4600, or F4814, and do not use DC adapter
accessories F1455A and F2297A.
Using the wrong AC adapter could damage the computer or adapter and may void
your warranty (see “Hewlett-Packard Limited Warranty Statement” on page 133).
• Plug the AC adapter into the computer and connect the power cord to the AC adapter,
then plug the power cord into a wall outlet. The computer’s battery then starts
charging.
Important
When unplugging the power cord, unplug it from the outlet before unplugging it from
the AC adapter.
While the battery is charging, you can continue with step 3.
Reference Guide 21
Page 23

Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Setting Up Your Computer
Step 3: Connect a phone line
You can use the built-in modem, or, if you prefer, you can connect to a PC Card modem
or an external modem.
1. Make sure the telephone line is an analog line, sometimes called a data line. (You
must not use a digital line.)
2. Connect the telephone cord into a telephone jack. If the plug on the phone cord
doesn’t fit the jack, you may need to use an adapter.
3. Plug the other end of the phone cord into the built-in modem.
For details about using the modem, see “Using the Modem” on page 60.
22 Reference Guide
Page 24

Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Setting Up Your Computer
Step 4: Turn on the computer
• Press the power button above the left side of the keyboard. The computer then boots
up, and Windows starts automatically.
Hint
If your computer does not turn on when operating on battery power, the battery may be
out of power. Plug in the AC adapter and press the power button again. Leave the AC
adapter plugged in for at least an hour—or 3–4 hours to charge the battery fully.
Reference Guide 23
Page 25
Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Setting Up Your Computer
Step 5: Set up Windows
Your notebook computer has Microsoft Windows preinstalled on its hard disk drive. The
first time you turn on your computer, the Windows Setup program runs automatically so
you can customize your setup.
1. Follow the Setup program’s instructions as they appear on the screen. If the program
prompts you to enter the Product ID code, you will find this code on the bottom of the
computer.
2. If you connected the modem, check the modem’s country or region settings:
• Windows XP: click Start, Control Panel, Printers and Other Hardware, Phone and
Modem Options, and then click Edit on the Dialing Rules tab.
• Windows 2000: click Start, Settings, Control Panel, double-click Phone and
Modem Options, and then click Edit on the Dialing Rules tab.
Step 6: Register your notebook
Be sure to register your computer. Registering is free and fast, and ensures you will
receive quicker, more personalized support. The information you provide during
registration allows us to provide you with better products and services.
Registering your computer does the following:
• Records your ownership of the computer with Hewlett-Packard and provides access
to service, support, and information.
• Records your ownership of the Windows XP operating system with Microsoft. If you
have Windows 2000, please contact Microsoft separately to register the operating
system.
If you decide not to register during Windows setup, choose the option to print the
registration form, and then fax it to HP at the fax number on the form. Or you can register
by calling HP Customer Care—see “To contact HP for support or service”on page 128 to
find the phone number.
24 Reference Guide
Page 26

Getting Started with Your HP Notebook
Setting Up Your Computer
To connect to the Internet
If you are connected to a wired or wireless LAN with Internet access or your computer
has a modem (built-in, PC Card, or external), you can connect to the Internet. For details,
see “Using the Modem” on page 60, “Connecting to a LAN” on page 68, or “Making
Wireless Connections” on page 69.
What to do next
• If you’re not familiar with the version of Windows installed on your computer, click
Start, Tour Windows XP or Start, Help (Windows 2000), or check the Windows
manual to discover what’s new.
• See the online Reference Guide to learn more about using and maintaining your
computer—click Start, Help and Support, HP Library (Windows XP) or Start,
Programs, Hewlett-Packard, Notebook, HP Library (Windows 2000).
Reference Guide 25
Page 27

Page 28

Basic Operation
Reference Guide 27
Page 29
Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
Operating Your Computer
You can start and stop your computer using its power button. However, at certain times
you may want to use other methods to start or stop the computer—depending on power
considerations, types of active connections, and start-up time.
To turn the computer on and off
Power mode To enter this mode
On mode
Power mode status light is on.
Standby mode
Saves significant power.
Turns off the display and other components.
Maintains current session in RAM.
Restarts quickly.
Restores network connections.
Power mode status light is blinking.
Hibernate mode
Saves maximum power.
Saves current session to disk, then shuts down.
Restores network connections.
Power mode status light is off.
Shut down (off)
Saves maximum power.
Turns off without saving current session.
At startup, resets everything, starts a new
session, and restores network connections.
Power mode status light is off.
To turn on: Press the power button to restart, or to resume your session from Standby or Hibernate mode.
You can also customize the way these power modes work. See “How the computer
manages power automatically” on page 52.
Press the power button.
Press the power button
–or–
click Start, Turn Off Computer, Stand By (Windows XP)
–or–
click Start, Shut Down, Standby (Windows 2000)
–or–
allow timeout.
Press Fn+F12
–or–
click Start, Shut Down, Hibernate (Windows 2000)
–or–
allow timeout.
Click Start, Turn Off Computer, Turn Off (Windows XP)
–or–
click Start, Shut Down, Shut down (Windows 2000)
–or–
press the power button for 4 seconds (only if the Start
menu procedure doesn’t work).
28 Reference Guide
Page 30
Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
To reset the computer
Occasionally, you may find that Windows or the computer has stopped responding, and
will not let you turn the computer off. If this happens, try the following in the order listed.
• If possible, shut down Windows:
Windows XP: press CTRL+ALT+DEL, and then click Shut Down, Restart.
Windows 2000: press CTRL+ALT+DEL, click Shut Down, and press the power
button to restart.
–or, if this fails–
• Press the power button for 4 seconds until the display shuts down, and then press the
power button again to restart.
–or, if this fails–
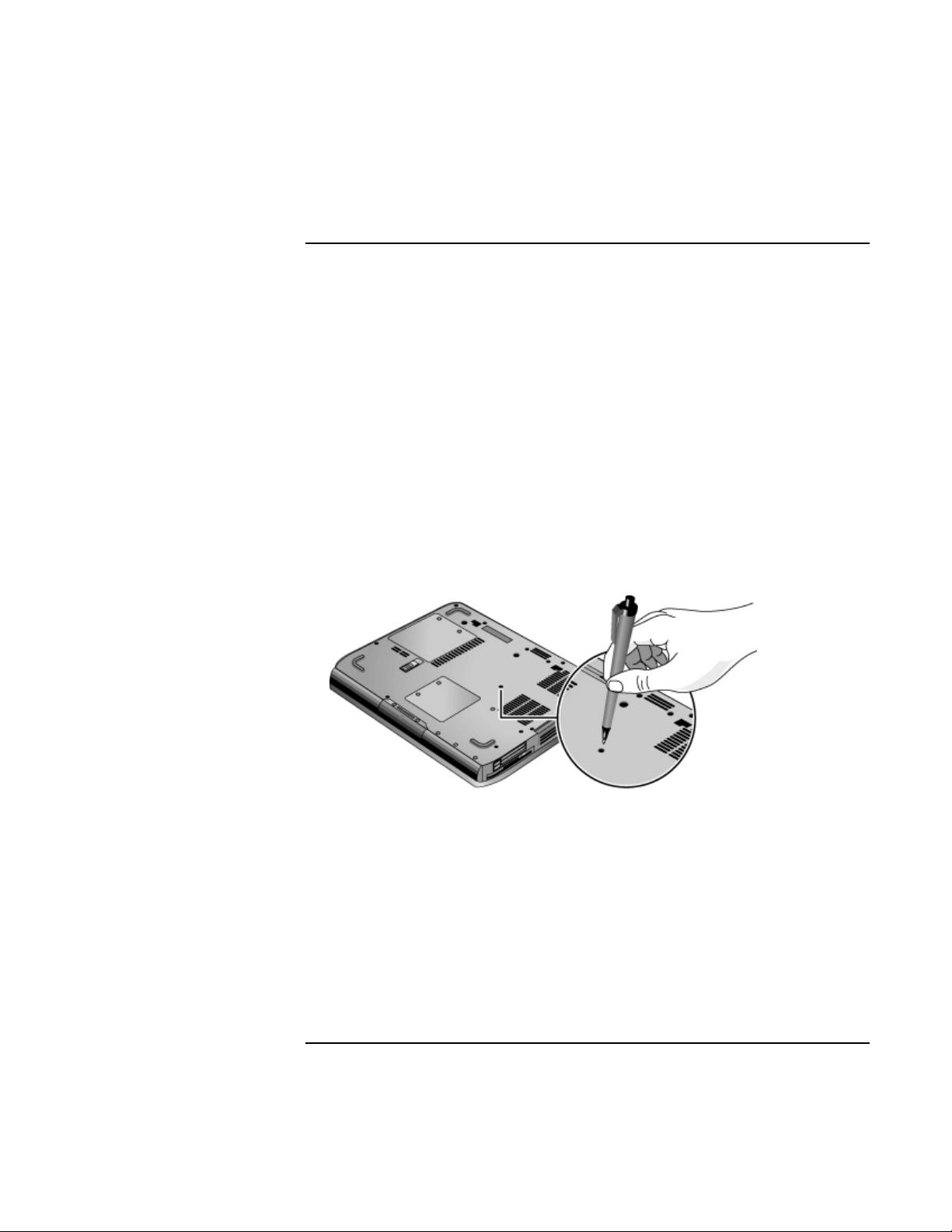
• Insert the tip of a ballpoint pen into the reset button on the bottom of the computer,
and then press the power button to restart.
To reset the computer while it’s docked in a port replicator, you can press the reset button
on the left side of the port replicator.
Reference Guide 29
Page 31

Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
To change the boot device
The computer normally boots from its internal hard disk. You can also boot the computer
from a floppy disk drive, a CD-ROM drive, or an internal network interface card.
1. Click Start, Turn Off Computer (or Shut Down), Restart.
2. When the HP logo appears, press ESC to display the Boot menu.
3. Use the arrow keys to select the boot device, and press ENTER.
If you want to boot from a specific device whenever it is present, change the boot order
using the BIOS Setup utility—see “To run the BIOS Setup utility” on page 118.
30 Reference Guide
Page 32

Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
To use the touch pad
The touch pad includes an on-off button so you can turn off the touch pad to avoid
moving the pointer accidentally, such as by touching the pad while typing. The indicator
light turns off when you turn off the touch pad.
1. Click buttons. The click buttons work like the left and right buttons on a standard
mouse.
2. Touch pad (touch-sensitive pointing device).
3. Touch pad on-off button and indicator light.
4. Scroll pad. The scroll pad scrolls the contents of the active window.
Reference Guide 31
Page 33

Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
Moving and selecting
1. Place your hands in a normal typing position.
2. Move a thumb or finger across the touch pad in the direction you want the pointer to
move.
3. Use the left and right click buttons, which function like the left and right buttons on a
mouse, to make your selection:
• To open an application, move the pointer over the icon and double-click the left
button.
• To make menu selections, move the pointer to the menu item and click the left
button.
• To open the shortcut menu for an item, move the pointer over the item and click
the right button.
• To drag an item, move the pointer over the item. Then press and hold the left
button while you move the pointer to the new location, and release the button.
In addition, you can tap the touch pad to select items and use other advanced touch pad
features. For more information, double-click the touch pad icon in the taskbar, and then
click Help in the tab for a particular feature.
You can use Mouse in Control Panel or the touch pad icon in the taskbar to customize the
operation of your computer’s pointing devices (touch pad and external mouse): you can
change the left, right, and scroll pad actions, double-click speed, pointer speed, and more.
Scrolling with the scroll pad
• Move your finger down the scroll pad to scroll down through the contents of a
window. Move your finger up the scroll pad to scroll up.
32 Reference Guide
Page 34

Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
To use the Fn hot keys
The combination of the Fn key plus another key creates a hot key—a shortcut key
sequence—for various system controls. To use a hot key, press and hold Fn, press the
appropriate second key, and then release both keys.
This hot key Does this
Fn+F1 Decreases the display brightness.
Fn+F2 Increases the display brightness.
Fn+F5
Fn+F8 Toggles the built-in keypad on and off. Does not affect an external keyboard. If Num
Fn+F12 Enters Hibernate mode.
Fn+NumLock Toggles Scroll Lock on and off.
Fn+Page Up Increases the audio volume and cancels the mute setting.
Fn+Page Down Decreases the audio volume.
Fn+Backspace Mutes the audio output.
Toggles among the built-in display, an external display, and simultaneous display on
both.
Lock is on, then the numeric functions are active; otherwise, cursor control is active
(as marked on an external keyboard).
Reference Guide 33
Page 35

Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
To use the One-Touch buttons
Your computer includes five One-Touch buttons that can start any application or open a
document or Web site with a single press.
• Press the One-Touch button to open the corresponding application, document, or
Web site.
Your computer is preconfigured to access the following services:
1. Microsoft Outlook Express e-mail software.
2. HP TV Now—see “To use a TV set as a monitor” on page 84.
–or–
HP Presentation Ready—see “To change computer settings for a presentation” on
page 39.
3. Microsoft Internet Explorer.
4. HP Quick Lock—see “To lock your computer” on page 43.
5. Online notebook information.
34 Reference Guide
Page 36

Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
To reprogram a One-Touch button
1. Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Hewlett-Packard, Notebook, HP One-Touch,
HP One-Touch Configuration.
2. On the One-Touch tab, click the button you want to reprogram.
3. Type a label for the button, and then select the application, document, folder, or Web
site you want the button to open.
4. If you want a label to appear onscreen when you press a One-Touch button, select that
option on the Onscreen Display tab.
To use the Windows and Applications keys
The Windows key brings up the Windows Start menu. This is the same as clicking the
Start button on the taskbar.
The Applications key brings up the shortcut menu for the current application. This is the
same menu that appears when you right-click while pointing at the application.
This key combination Does this
Windows key+E Runs Windows Explorer.
Windows key+F1 Runs Windows Help.
Windows key+F Runs Windows Find: Search (Windows XP) or File or Folders (Windows 2000).
Windows key+M Minimizes all displayed windows.
Shift+Windows key+M Returns all minimized windows to original size.
Windows key+R Runs the Windows Run dialog box.
Reference Guide 35
Page 37

Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
To use the embedded keypad
Your computer’s built-in keyboard includes an embedded keypad you can use to type
numbers and arithmetic operators. The keys in this keypad are marked using light blue
characters.
• Press Fn+F8 to turn on the embedded keypad.
• Hold Fn while typing a key to turn the embedded keypad on temporarily.
When the embedded keypad is active, you can use Num Lock to change how the keypad
functions:
• Num Lock on: the keys enter the numbers and arithmetic operators printed in light
gold on the keyboard.
• Num Lock off: the keys act as cursor control keys, as marked on an external
keyboard.
To use the ALT GR key
Non-U.S. keyboards have an ALT GR key to the right of the spacebar. This is a shift key
that provides access to certain special keyboard characters.
• For a character in the lower-right corner of a key, press and hold ALT GR to type the
character.
1. Shifted.
2. Unshifted.
3. ALT GR.
36 Reference Guide
Page 38

Hint
Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
To adjust the display
Changing the brightness
• Press Fn+F1 or Fn+F2 to decrease or increase (respectively) the display’s brightness.
–or–
• Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Hewlett-Packard, Notebook, HP Display
Settings. You have the option of adding a display settings icon in the taskbar for quick
access.
To maximize your battery operating time, set the brightness to the lowest level you can
view comfortably.
Changing display settings
You can customize a number of display settings for your computer, such as color depth
and screen area.
1. Click Start, Control Panel, Appearance and Themes, Display (Windows XP), or click
Start, Settings, Control Panel, and then double-click Display (Windows 2000).
2. Click the Settings tab, and then choose the settings you want.
The computer has an LCD display, which behaves differently from a normal computer
monitor. If you change the display resolution, the desktop changes size, but the objects on
it do not. You normally won’t change the resolution except to use an external monitor.
Changing icon and label sizes
If the icons and labels on your screen seem too small, you can enlarge them using
HP Desktop Zoom.
• Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Hewlett-Packard, HP Desktop Zoom,
HP Desktop Zoom.
Using an external monitor
If you want, you can attach an external monitor to your notebook computer. See “To use
an external monitor” on page 82.
Reference Guide 37
Page 39

Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
To adjust the volume
To increase or decrease the volume
• Press Fn+PageUp or Fn+PageDown.
• Press the back or front half of the volume control on the right side of the computer.
• Click the speaker icon in the taskbar (if not present, see Windows Help), and drag the
volume control bar up or down.
To mute the audio
You can mute the audio output without changing the volume setting. This feature is
handy when you want to block all speaker output regardless of what your computer is
doing.
• Press Fn+Backspace.
• Press the audio mute button on the right side of the computer. The button lights when
audio is muted.
• Click the speaker icon in the taskbar (if not present, see Windows Help), and click
Mute.
38 Reference Guide
Page 40

Basic Operation
Operating Your Computer
To change computer settings for a presentation
When you show a presentation to an audience, you’ll often want to adjust some of your
video and power settings for the show. You can easily do this with HP Presentation
Ready, an application that automatically adjusts your computer for slide shows and
similar presentations, and also opens the presentation itself. Once the presentation is
through, HP Presentation Ready automatically returns your computer to its normal
settings.
To prepare for the presentation
1. Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Hewlett-Packard, HP Presentation Ready,
Configure.
–or–
Click the HP Presentation Ready icon in the taskbar (if present), and then click
Configure.
2. Select the presentation you want to show. If you don’t select one, you can choose one
when you start the show.
3. If you want to change the video or power settings for the show, click Settings.
To show the presentation
• If a One-Touch button is assigned to HP Presentation Ready, press that button.
–or–
Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Hewlett-Packard, HP Presentation Ready,
Start Presentation.
–or–
Click the HP Presentation Ready icon in the taskbar (if present), and then click Start
Presentation.
To adjust settings during the presentation, press the One-Touch button or click the
taskbar icon and choose Configure.
To end the presentation and restore the computer’s normal settings, close the presentation
application or click the taskbar icon and choose Stop Presentation.
Reference Guide 39
Page 41

Basic Operation
Using CDs or DVDs
Using CDs or DVDs
To insert or remove a CD or DVD
CAUTION
Do not remove a CD or DVD while the computer is reading it. Otherwise, the
computer could stop responding and you could lose data.
Be sure to press the CD or DVD onto the spindle. You can damage the disk or
drive if you just lay it on the tray.
1. Press the button on the face of the CD-ROM or DVD drive. If you are using this drive
for the first time, be sure to remove the cardboard packing insert.
2. Place the CD or DVD into the drive (label facing up) and gently press down to seat it
on the spindle.
–or–
Remove the CD or DVD.
3. Slide the tray back into the module to close it.
If your computer loses power, you can manually open the drive to remove a CD. Insert a
straightened paper clip into the recessed hole on the front of the drive to open it.
40 Reference Guide
Page 42

Hint
Basic Operation
Using CDs or DVDs
To play DVD movies
If your computer came with a DVD drive, it also includes DVD player software that lets
you play DVD movies.
• Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Multimedia, DVD Player, InterVideo
WinDVD.
For Windows XP, you can also use Windows Media Player to play DVD movies.
To play DVD movies on a TV, see “To use a TV set as a monitor” on page 84.
For best performance while playing movies on battery power, set the Control Panel
power scheme to Portable/Laptop (Windows XP). See “How the computer manages
power automatically” on page 52.
Important
DVDs can have regional codes embedded in the disc data. These codes prevent DVD
movies from being played outside the region of the world in which they are sold. If you
get a region code error, you are trying to play a DVD intended for a different region.
Most DVD drives let you change the region code only a limited number of times
(usually no more than four). When you reach this limit, your last change to the region
code will be hard-coded on the DVD drive, and will be permanent. Your HP warranty
does not cover the expense of correcting this situation. Refer to the help for your DVD
player software for details about setting region codes.
To create or copy CDs
If your computer came with a CD-RW drive, it also includes software that lets you copy
or create CDs.
• Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Multimedia, CD Writer, RecordNow,
RecordNow.
For Windows XP, you can use Windows Media Player to create audio CDs, and
Windows Explorer to create data CDs using a CD-RW drive.
Refer to the software’s help for details about creating or copying CDs. HP recommends
using HP C4403A (CD-R) or C4404A (CD-RW) media—read and write quality may
vary for other media.
Reference Guide 41
Page 43

Basic Operation
Securing Your Computer
Securing Your Computer
To set up password protection
You can protect your computer from access by another user when you set up password
protection, which is available through Windows and through the BIOS Setup utility. For
complete protection, set passwords in Windows as well as through BIOS Setup.
To cancel password protection, set an empty password.
BIOS Setup Utility
1. Click Start, Turn Off Computer (or Shut Down), Restart.
2. When the HP logo appears, press F2 to enter BIOS Setup.
3. From the Security menu, enter or modify the Administrator Password or User
Password as needed. See “Security Menu” on page 120.
4. Press F10 to save and exit BIOS Setup.
Windows XP
1. Click Start, Control Panel, User Accounts, and then select your account.
2. Click Create a Password, and then set the password.
3. Click Start, Control Panel, Performance and Maintenance, Power Options.
4. On the Advanced tab, select the option to prompt for a password when the computer
leaves Standby mode.
Windows 2000
1. Press CTRL+ALT+DEL, and then select Change Password to change the password.
2. Create or modify your Windows password.
3. Click Start, Settings, Control Panel, and then double-click Power Options.
4. On the Advanced tab, select the option to prompt for a password when the computer
leaves Standby mode.
To protect your computer when you’re not using it, see “To lock your computer” below.
42 Reference Guide
Page 44

Basic Operation
Securing Your Computer
To lock your computer
To protect against unauthorized access while your computer is running, lock the
computer before leaving it unattended, or set up a screen saver with a password in
Control Panel Display. You can lock the computer these ways:
• Press the HP Quick Lock button—the five One-Touch buttons are located above the
keyboard.
–or–
• Press CTRL+ALT+DEL and click Lock Computer. This option may not be available
in all configurations.
To unlock the computer, follow your normal logon steps.
To attach a security cable
Your computer includes a built-in connector you can use to secure the computer with a
cable and a lock (such as the Kensington MicroSaver lock system, available at many
computer stores).
1. Wrap the cable around a secure object, such as a table leg.
2. Loop the cable to create a slip knot around the stationary object, and make sure it
can’t slip off.
3. Insert the lock into the security connector on the left side of the computer and release
the key. Store the key in a safe place away from the computer.
Reference Guide 43
Page 45

Basic Operation
Securing Your Computer
To protect against viruses
Virus-protection software can help protect the integrity of your data. This is especially
important if you use the Web.
Your computer comes equipped with Norton AntiVirus software. You can get detailed
instructions from the software’s online Help.
44 Reference Guide
Page 46

Working in Comfort with a Notebook PC
Working in Comfort with a Notebook PC
Basic Operation
WARNING
Note
Improper use of keyboards and other input devices has been associated with
ergonomic injury. For more information about reducing your risk, visit our
ergonomics Web site at www.hp.com/ergo—or see Working in Comfort in the
online HP Library.
You can use your HP notebook computer virtually anywhere, anytime. The following
recommendations should help you work more comfortably.
If you are using your portable computer as your primary computer, or using it for
extended periods, you should use it with a full-size keyboard, monitor, and mouse. This
will give your portable computer the adjustability and comfort features of a desktop
unit. HP docking accessories offer quick, easy connections to these devices. More
information on how to prepare your workspace environment and set up your HP
equipment is available in Working in Comfort, which is preloaded on the hard disk in
the HP Library and available on the Windows 2000 Recovery CD or DVD in
\hp\library—as well as at www.hp.com/ergo.
Your Mobile Work Environment
• Use a chair that provides good support for your lower back. If an adjustable chair is
not available, you can use a pillow or rolled-up towel to provide lower back support.
• Try to keep your thighs parallel to the floor and your feet flat on the floor. In a mobile
environment, you can do this by using a phone book or briefcase to support your feet.
• Adjust the height of either your work surface or chair to keep your arms in a neutral
position. Your arms should be relaxed and loose, elbows at your sides, with the
forearms and hands parallel with the floor.
• Position your notebook computer display to minimize glare and reflection. For
example, on an airplane, lower the window shade, or in a hotel room, draw the
curtains. You also should maintain a comfortable viewing distance–approximately 40
to 60 cm (16 to 24 inches). Adjust the angle of your display to help keep your head
angled slightly downward in a comfortable position.
Reference Guide 45
Page 47

Basic Operation
Working in Comfort with a Notebook PC
Using Your Mobile Computer
• Position the computer so your wrists and hands are in a neutral position. Your wrists
should be as straight as possible and should not have to bend sideways or more than
10 degrees up or down. If your notebook computer does not have a built-in palm rest,
you can use a rolled-up towel.
• Try to type as lightly as possible. The notebook keyboard requires little force to
activate.
• Take frequent, short rest breaks–this is especially important in a mobile computing
environment.
• Portable computers weigh between approximately 1.4 and 3.7 kilos (3 and 8 pounds).
When traveling, be sure to carry your computer properly to minimize strain on your
body. Shift the bag containing your notebook equipment frequently between your left
and right hands and shoulders.
46 Reference Guide
Page 48

Taking Care of Your Computer
Use the following recommendations to maintain your computer during everyday use and
prevent potential physical damage or data loss.
To protect your hard disk drive
Hard disk drives, as well as other internal components, are not indestructible and can be
damaged by inappropriate handling and operation.
• Avoid bumps or jolts.
• Do not operate the computer while traveling over bumpy terrain.
• Suspend or shut down the computer before transporting it. This turns off the hard
drive. A drop of a few inches onto a rigid surface while the hard drive is operating
could destroy data or damage the drive.
Basic Operation
Taking Care of Your Computer
• Carry the computer in a padded case to protect against bumps and jolts.
• Set down the computer gently.
To maintain your computer
• Provide adequate ventilation around the computer. Always set the computer on a flat
surface, so that air can flow freely around and underneath it.
• Always shut down the computer or put it in Hibernate mode before putting it in a
carrying case or other enclosed space.
• Do not pick up or carry the computer by its display.
• Observe the temperature limits and other specifications listed in “Hardware
Specifications” on page 136. Do not use the computer outside in the rain or snow
(inclement weather). If the computer is cold, warm it gradually to avoid condensation.
• Maintain your battery for best performance—see “To get the most from your
batteries” on page 56.
Reference Guide 47
Page 49
Basic Operation
Taking Care of Your Computer
To safeguard your data
• Do not use a pointing device or activate any other device that interrupts operation
while the system is starting or stopping.
• Back up your work regularly. Copy files to floppy, CD-RW, or network drives.
• Use a virus-scanning program (such as the Norton AntiVirus program included with
your computer) to check the integrity of your files and operating system. Since new
viruses appear frequently, you will also want to update the program’s virus definitions
from time to time; updates are on the Web at www.symantec.com for Norton
AntiVirus.
• Check your disk using the Tools tab in the disk’s Properties window.
To extend the life of the display
• Set the display brightness to the lowest comfortable level (Fn+F1).
• When working at your desk, connect an external monitor and turn off the internal
display (Fn+F5).
• If you are not using an external monitor, set the Turn off monitor timeouts (for both
AC and battery operation) to the shortest comfortable interval.
• Avoid using a screen saver or other software that prevents the computer from
changing to Display-off or Standby mode after a timeout period. If you use a screen
saver, enable the option to shut off the display after a time delay.
• Do not disable Display-off or Standby timeouts.
• If you are using AC power and have no external monitor attached, put the computer in
Standby mode when not in use.
48 Reference Guide
Page 50

Basic Operation
Taking Care of Your Computer
To clean your computer
• You can clean the computer with a soft cloth dampened with clean water or with
water containing a mild detergent. Do not use an excessively wet cloth, and take care
to keep water out of the case.
• Do not use abrasive cleaners, especially on the display. Do not apply any cleaner
directly to the display. Instead, apply the cleaner to a soft cloth and then gently wipe
the display.
• You can clean the keyboard with a vacuum cleaner to remove accumulated dust.
Reference Guide 49
Page 51

Page 52

Batteries and Power Management
Reference Guide 51
Page 53

Batteries and Power Management
Managing Power Consumption
Managing Power Consumption
When you’re running your computer on battery power, you will want to maximize
operating time without compromising performance. Your computer is designed to help
you reduce power consumption and extend battery life without needing to turn it off.
• During idle periods, the computer automatically enters power-saving modes after
specified timeout periods. You can adjust these timeouts to suit your working habits.
• You can manually send the computer into a power-saving mode at any time by
pressing the appropriate key—see “To manage power manually” on page 54.
How the computer manages power automatically
Your computer automatically enters Hibernate mode and Standby mode, and turns off the
hard disk and display based on values set in Power Options in Control Panel.
Automatic action Occurs after… To resume…
Turns off hard disk.
Turns off the hard disk drive. This is usually
set to occur shortly after the display is turned
off.
Turns off display.
Turns off the display to conserve battery
power and extend the life of the display.
Enters Standby mode.
Maintains your current session in RAM, and
turns off the display and other components
to conserve battery power.
Enters Hibernate mode.
Saves your current session to the hard disk,
and then turns off the computer.
The hard disk is not accessed
for the specified interval.
No keyboard, pointing device,
or other input activity occurs for
the specified interval.
No pointing devices are used,
no disk drive is accessed, and
no port (serial, parallel, or IR) is
active for the specified interval.
The computer stays in Standby
mode for the specified interval.
Begin using the computer:
the hard disk turns on
when needed.
Press any key or move a
pointing device to turn on
the display.
Press the power button to
return to your current
session.
Press the power button to
restore your previous
session.
52 Reference Guide
Page 54

Batteries and Power Management
Managing Power Consumption
CAUTION
CAUTION
Make a habit of saving your work before allowing your computer to enter Standby
mode. If power is interrupted while the computer is in Standby mode, any
information that was not saved will be lost.
The computer can also enter Hibernate mode if battery power reaches a critically low
level. (See “To respond to a low-battery warning” on page 56.) If this happens, you will
find on resuming that all your data has been saved, but some functions may be disabled.
To resume normal operation, restore power by connecting an AC adapter or installing a
charged battery, and then shut the computer off and restart it.
Changing timeout settings and creating power schemes
You can adjust the periods of non-use after which your computer automatically shuts
down components or enters a power-saving mode. You can also save these settings as a
power scheme.
1. Open Power Options in Control Panel:
• Windows XP: click Start, Control Panel, Performance and Maintenance, Power
Options.
• Windows 2000: click Start, Settings, Control Panel, and then double-click Power
Options.
2. Click the Power Schemes tab, and enter the settings you want. If you don’t want a
particular timeout to occur, set the value to Never. See Windows Help for details.
If you want to save the settings as a power scheme, click Save As and enter a name
for the scheme.
Do not disable Hibernate support in the Power settings, or you will lose any
unsaved data if the computer’s battery runs down completely.
Managing CPU power
To conserve battery power, the computer automatically runs the processor at a slower
speed when the AC adapter is unplugged. To run with maximum performance, plug in the
AC adapter. For Windows XP, you can control the processor speed and power in Control
Panel Power Options—on the Power Schemes tab, select the power scheme you want.
Reference Guide 53
Page 55

Batteries and Power Management
Managing Power Consumption
To manage power manually
In addition to allowing the computer to enter its power-saving modes automatically, you
can also put it into any of the following three modes whenever you need to.
Power mode Does this… Use when… To enter this mode…
Standby Maintains your current
session in RAM, and turns off
the display and other
components.
Hibernate Saves the current session to
disk, and then shuts down.
Provides maximum power
savings while still allowing
you to recover the current
session.
Off
Turns off your computer,
providing maximum power
savings. The current session
will not be saved, and any
unsaved data will be lost.
You will be away
from your computer
for up to several
hours.
You will be away
from your computer
for a day or more,
but want to continue
your session.
You’re done with
your work.
Press the power button
–or–
click Start, Turn Off Computer,
Stand By (Windows XP)
–or–
click Start, Shut Down,
Standby (Windows 2000)
Press Fn+F12
–or–
click Start, Shut Down,
Hibernate (Windows 2000).
Click Start, Turn Off
Computer, Turn Off
(Windows XP)
–or–
click Start, Shut Down, Shut
down (Windows 2000)
–or–
press the power button (only if
the Start menu procedure
doesn’t work).
You can also turn off the display by closing the lid.
54 Reference Guide
Page 56

Using Battery Power
To check battery status
From the battery status light
You computer has a battery status light—see “Status Lights” on page 17.
From the Windows taskbar
The Windows taskbar can display a power icon that provides detailed battery status
information (see Windows Help for details). The icon looks like a battery when AC is not
connected.
• Place the pointer over the power icon to display the remaining battery charge. This
value is shown as either a percentage of charge remaining, or as time remaining.
Batteries and Power Management
Using Battery Power
• Double-click the power icon to open the Battery Meter window.
From the Windows Control Panel
• Windows XP: click Start, Control Panel, Performance and Maintenance, Power
Options, and then click the Power Meter tab to see the battery status. The Alarms and
Advanced tabs provide additional Windows’ power-information options.
• Windows 2000: click Start, Settings, Control Panel, and then double-click Power
Options. This provides access to all of Windows’ power-information options.
On the battery
1. Remove the battery from the computer—see “Step 1: Install the battery” on page 19.
2. Press the contact pad on the side of the battery. The number of lights that turn on
indicates the remaining charge (each light represents 20% of a full charge).
Reference Guide 55
Page 57

Note
Batteries and Power Management
Using Battery Power
To respond to a low-battery warning
The computer automatically alerts you when the battery power drops to a critically low
level. The computer first emits a high-pitched beep or displays a warning message. Then,
if you do not restore power within a short time, the computer goes into Hibernate mode.
Once the computer enters Hibernate mode in this way, you won’t be able to turn it on
again until you restore power by doing one of the following:
• Replace the battery with a charged one. See “Step 1: Install the battery” on page 19.
• Plug in the AC adapter. See “Step 2: Connect AC power” on page 21.
If you plug in the AC adapter, you can continue to work while your battery recharges.
To recharge the battery
CAUTION
The AC adapter is normally warm whenever plugged into an AC outlet. The
computer is normally warm while recharging. Don’t recharge the computer in a
briefcase or other confined space, or its battery could overheat.
• Plug the AC adapter into the computer.
To get the longest operating time, wait until the battery’s charge is below 50% before
recharging, and then charge it fully (100%). Charging can take up to approximately
3 hours. If you continue working while the battery charges, the charging time may
increase to 4 hours.
A fully charged battery can operate the computer for up to 3 hours, depending on your
computer’s model, power management settings, and level of use.
To get the most from your batteries
Follow these suggestions to make your battery’s power last as long as possible.
• Plug in the AC adapter, especially when using a CD-ROM or DVD drive, or any
external connections such as a PC Card or a modem.
• Set the display brightness to the lowest comfortable level (Fn+F1).
• Put the computer in Standby mode whenever you are not using it for a short while:
press the power button, or click Start, Turn Off Computer (or Shut Down), Standby.
56 Reference Guide
Page 58

Batteries and Power Management
Using Battery Power
• Put the computer in Hibernate mode whenever you want to save your current session,
but will not be using the computer for a day or more: press Fn+F12.
• Set the automatic timeout settings to emphasize saving power—see “How the
computer manages power automatically” on page 52.
• If your computer has a wireless on-off button, turn off the wireless function when
you’re not using it. Press the wireless on-off button so the light turns off.
• Check that the display is using the Powerplay option. In Control Panel Display, on the
Settings tab click Advanced, and then on the Powerplay tab check whether Powerplay
is enabled. This allows the computer to save power when it’s not needed by the
display.
• If you have an I/O PC Card—that is, a PC Card having an external connection, such
as a network card—remove it when you’re not using it. Some I/O cards use
significant power even while they’re inactive.
• If you work with an application that uses an I/O PC Card, exit the application when
you finish using it.
In addition, follow these suggestions to extend the life of your batteries.
• Do not leave batteries unused for long periods. If you have more than one, rotate
them.
• If you normally use AC power, make a practice of using the battery as your power
source at least once a week.
• Unplug the AC adapter when the computer is not in use.
• To preserve the life of a battery, be sure to charge it regularly.
• For long-term storage, the battery must be charged 20–50% to minimize capacity loss
by self-discharge and to avoid deterioration of battery performance.
• To maintain maximum battery capacity and accuracy of the battery gauge, perform
this calibration procedure every few months:
1. Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Hewlett-Packard, Notebook, HP Battery
Optimizer.
2. Follow the displayed instructions to test and condition your battery. The process
could take 4–6 hours or more per battery. You can use the computer during the
process. If you interrupt the process, the battery might be left with a low charge.
Reference Guide 57
Page 59

Page 60

Modem and Network Connections
Reference Guide 59
Page 61

Modem and Network Connections
Using the Modem
Using the Modem
You can connect your modem to a telephone line and communicate with other computers
throughout the world. You can explore the Internet, send and receive e-mail messages,
and use your PC to send and receive faxes. Your computer contains several software
programs that work with your modem:
• Internet Explorer, for browsing the World Wide Web
• Outlook Express, for sending and receiving e-mail messages
• Windows XP Fax Console or Windows 2000 fax software for sending and receiving
faxes
The modem is a high-speed 56-Kbps modem. For best performance, you can connect to
any Internet Service Provider (ISP) or modem network that has V.90 or V.92
interoperable modems. Check with your ISP for a list of telephone numbers that support
V.90 or V.92.
The maximum speed for faxing is 14.4 Kbps. Even though the modem is capable of
downloading at 56 Kbps, your ISP or modem network may not operate at this speed or
support this technology. Please check with your service provider for information on its
capabilities. Furthermore, download transmission rates depend on the condition of the
telephone line.
60 Reference Guide
Page 62

To connect the modem
Modem and Network Connections
Using the Modem
CAUTION
To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunications line
cord to connect the modem to the telephone wall jack.
1. Check that the telephone line is an analog line, sometimes called a data line. (You
must not use a digital line.)
2. Connect a telephone cord with an RJ-11 plug into a telephone jack. If the plug on the
phone cord doesn’t fit the jack, you may need to use an adapter.
3. Plug the other end of the phone cord into the built-in modem.
4. Check your modem’s country or region settings:
• Windows XP: click Start, Control Panel, Printers and Other Hardware, Phone and
Modem Options.
CAUTION
• Windows 2000: click Start, Settings, Control Panel, double-click Phone and
Modem Options, and then click Edit on the Dialing Rules tab.
Your built-in modem may not work with multiple phone lines or a private branch
exchange (PBX), cannot be connected to a coin-operated telephone, and does not
work with party lines. Some of these connections may result in excess electrical
voltage and could cause a malfunction in the internal modem. Check your
telephone line type prior to connecting your phone line.
Reference Guide 61
Page 63

Modem and Network Connections
Using the Modem
Special restrictions in certain countries
• Many countries impose a blackout period after a modem repeatedly fails to connect to
a service provider. The number of failed attempts and the period you must wait before
trying again differ from country to country: check with your telephone company.
For example, if you are dialing from Italy and fail to connect to your server or cancel
the connection, you must wait one minute before dialing that number again. If you
dial before then, you will get an error message that says “delay.” After the fourth
failed connection, you must wait one hour before trying the number again. If you dial
before the hour is up, you will get a message that says “black list.”
• When using a modem in the Republic of South Africa, an external surge protector
may be necessary in order to prevent computer damage by lightning or other electrical
surges. Connect any approved surge protector to the modem cable whenever you are
using the modem.
To connect to the Internet
Signing up with an Internet Service Provider
Before you can connect to the Internet, you need to set up an account with an Internet
Service Provider (ISP). For some countries and models, Hewlett-Packard provides easy
Internet signup so that you can connect quickly to an ISP.
1. Connect your built-in modem—see the previous topic. (If you prefer, you can use a
PC Card modem or an external modem.)
2. If available, double-click the Connect to the Internet or Easy Internet Signup icon on
the desktop. This launches the Internet Connection or New Connection wizard, which
helps you locate an ISP in your area, transfer an existing Internet account to this
computer, or set up an Internet connection manually.
–or–
If available, click Start, Programs, Online Services (Windows XP or 2000) or Start,
All Programs, Easy Internet Signup (Windows XP), and select one of the listed ISPs.
This begins the registration process for the ISP you choose.
62 Reference Guide
Page 64

Modem and Network Connections
Using the Modem
Connecting to the Internet
1. Double-click the Internet Explorer icon on the desktop. For your first connection,
you’ll be prompted for information about your connection.
2. Click the Connect button in the Dial-up Connection or Network Connections window.
For Windows XP, to display an icon for your connection, open Network Connections in
Control Panel, right-click the connection, select Properties, and select the icon option. For
Windows 2000, when you are successfully connected to the Internet, you’ll see a connect
icon (two connected computers) in the taskbar.
To disconnect from the Internet
You remain connected to the Internet until you shut down the computer, disconnect the
phone line from the computer, or give a command to hang up the connection.
• For Windows XP, click Start, Control Panel, Network and Internet Connections,
Network Connections, and then right-click the connection and select Disconnect.
–or–
Double-click the connect icon in the taskbar, and click Disconnect. (For
Windows XP, you can enable this icon as described in “To connect to the Internet,”
above.)
To dial in to a network
You can use the modem to dial in to a LAN (local area network) that supports dial-in
connections. This gives you access to network resources from a remote location.
• See Windows Help for information about setting up and using dial-in network
connections—click Start, Help and Support (or Help).
Reference Guide 63
Page 65

Modem and Network Connections
Using the Modem
To change your modem settings
The modem is already set up to be compatible with telephone systems and modems in
most areas. However, in some situations, you may have to change modem settings to
match local conditions. If you have questions about local requirements, contact your
telephone company.
• Control Panel. Open Phone and Modem Options in Control Panel to change many
modem settings. On the Modems tab, click Properties to set connection speeds, or on
the Dialing Rules tab click Edit to set dialing options.
• Communications software. Many communications applications provide options for
controlling modem settings. See the help for your software.
• AT commands. You can control many aspects of modem operation using modem AT
commands. AT commands are special strings of characters sent to the modem to set
up specific conditions. Those command strings normally start with “AT”. For a list of
AT commands for the built-in modem, see “Modem Reference Information” on
page 139.
Open Phone and Modem Options in Control Panel. On the Modems tab, click
Properties. You can type AT commands on the Advanced tab in the space for extra
settings.
For example, to force a built-in modem to turn off its speaker, you can use the M0
command as shown in table of AT commands—type ATM0 in the space for extra
settings.
64 Reference Guide
Page 66

Modem and Network Connections
Using the Modem
To send and receive e-mail
Sending and receiving e-mail requires an e-mail account with an Internet Service
Provider or with your company’s communications system. If you are using AOL, e-mail
services are part of your AOL service. For another ISP, you can use Outlook Express
(included with your computer) or an e-mail system of your choice. This topic includes
instructions for using Outlook Express.
To start Outlook Express
1. Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Outlook Express, or double-click Outlook
Express on the desktop (if available).
2. If you are not currently connected to the Internet, the Dial-up Connection window
appears. Choose Connect to connect to the Internet.
To send an e-mail message
1. In Outlook Express, click the New Mail or Create Mail tool on the toolbar.
2. Fill in the information in the New Message window.
3. When you’re finished, click the Send button.
To receive e-mail messages
1. In Outlook Express, click the Send/Recv tool on the toolbar to have Outlook deliver
new messages.
2. Click the Inbox folder to view the list of messages. Unread messages appear bold on
the screen.
3. To view a message, click it once. (Or double-click to view the message in its own
window.)
Reference Guide 65
Page 67

Modem and Network Connections
Using the Modem
To send and receive faxes (Windows XP)
Sending and receiving faxes requires just a telephone connection—you don’t need an
Internet connection. You can use the modem and fax software to send and receive faxes
on your computer. Fax Console fax software is included with Windows XP.
To set up Fax Console
Before you can use Fax Console, you need to install it.
1. Click Start, Control Panel, Add or Remove Programs.
2. Click Add/Remove Windows Components, select Fax Services, and follow the
instructions on the screen. If prompted for the Windows CD, point instead to the
c:\i386 directory.
To start Fax Console
• Click Start, All Programs, Accessories, Communications, Fax, Fax Console.
The first time you start Fax Console, the Fax Configuration Wizard steps you through the
process of setting options and customizing the program for your personal use. Follow the
onscreen instructions. If you’re not sure which setting to choose, accept the default
choice.
To send a fax
• Click Start, All Programs, Accessories, Communications, Fax, Send a Fax, and then
follow the instructions that appear on the screen.
If instead you want to send a document as a fax, open the document in its application
window, and then open the Print dialog box. Change the selected printer to Fax, and then
print it.
To receive faxes
Faxes are automatically received when Fax Console is running in an open or minimized
window. New faxes are indicated in the status box in the Fax Console window. To
receive a fax manually:
• When a fax call is coming in, click Receive now on the Fax Console menu bar.
To view and print a fax
1. In the Fax Console tree, click Inbox, and then double-click the fax you want to view.
2. Click the printer icon to print the fax.
66 Reference Guide
Page 68

Modem and Network Connections
Using the Modem
To send and receive faxes (Windows 2000)
Sending and receiving faxes requires just a telephone connection—you don’t need an
Internet connection. You can use the modem and fax software to send and receive faxes
on your computer. Fax software is built into Windows 2000.
To set up for faxing
1. Click Start, Settings, Control Panel, Fax. Enter your fax information.
2. On the Advanced Options tab, add a fax printer.
If you do not want to receive faxes, stop here.
3. On the Advanced Options tab, open the Fax Service Management window.
4. In the list under Fax, click Devices, and then right-click the modem and click
Properties.
5. On the General tab, enable the modem to receive faxes.
6. On the Received Faxes tab, select the option to save faxes in a folder.
To send a fax
• Click Start, Programs, Accessories, Communications, Fax, Send Cover Page Fax.
Follow the instructions to create and send the fax.
If instead you want to send a document as a fax, open the document in its application
window, and then open the Print dialog box. Change the selected printer to the fax
printer, and then print it.
To receive, view, and print faxes
If you enabled the modem to receive faxes, they are automatically received.
1. Click Start, Programs, Accessories, Communications, Fax, My Faxes.
2. In the Received Faxes folder, double-click the fax.
3. To print, click File, Print.
Reference Guide 67
Page 69

Modem and Network Connections
Connecting to a LAN
Connecting to a LAN
You can connect to local area networks (LANs), which give you access to network
resources, such as printers and file servers on your corporate network, and possibly to the
Internet.
To connect to a LAN
1. Check that the existing LAN supports Ethernet 10Base-T (10 Mbps) or 100Base-TX
(100 Mbps) connections.
2. Plug the LAN cable (not supplied) into the built-in LAN port. The cable must have an
RJ-45 connector.
3. Windows automatically detects and sets up a LAN connection. To edit settings, open
Network and Dial-up Connections in Control Panel.
See Windows Help for information about setting up and using LAN connections—click
Start, Help and Support (or Help). Contact your network administrator for network
information.
Two lights next to the LAN port indicate the status of the connection:
• The yellow light indicates network activity.
• The green light indicates a 100 MB per second link.
68 Reference Guide
Page 70

Making Wireless Connections
If your computer includes a wireless on-off button—located on the right side of the front
of the computer—you can connect by radio to a wireless local area network (LAN) and
access computers and other resources on the network.
A wireless network provides all the functions of a typical “wired” network, but also
provides for “roaming.” Since your computer connects to the network by radio rather
than through cables, you can move from place to place within the network—from your
office to a conference room, for example—and remain on the network the entire time.
To prepare for connections (Windows XP)
Before you can connect your computer to a particular 802.11 wireless network, you have
to configure the computer for the specific wireless connection.
Connecting to an Existing Wireless Network
Modem and Network Connections
Making Wireless Connections
You can connect to an access point that gives you access to a local area network, or you
can connect directly to other computers in an “adhoc” network.
1. Right-click the wireless network connection icon in the taskbar, and then select View
Available Wireless Networks from the pop-up menu.
2. A list of available networks appears. Select the network you want, enter the
encryption key if required, and click Connect.
If the network you want is not on the list, click Advanced, Configure, and enter the
required network parameters. If the network is not using 802.1x authentication
protocol, clear the automatic key option.
3. On the General tab, edit network settings as needed for your local network. See your
network administrator. You can also display an icon in the taskbar when connected to
a network.
4. On the Wireless Networks tab, view the wireless networks available within range.
Each network SSID is listed. Click the network you want and click Configure.
Reference Guide 69
Page 71

Modem and Network Connections
Making Wireless Connections
5. If the wireless network uses standard encrypted communication, uncheck the
automatic key option, and then select the following parameters—see your network
administrator for the required settings:
• Key: ASCII passphrase or hexadecimal key string.
• Key format: ASCII for passphrase, hexadecimal for key string.
• Key length: smaller number for 64-bit encryption, larger number for 128-bit.
6. Click OK to save the configuration. This network is added to your list of preferred
networks.
The computer automatically connects to the first preferred network that’s within range if
wireless communication is turned on—see “To turn wireless communication on and off”
on page 73.
Creating a New Computer-to-Computer Network (AdHoc)
You can set up a new network available to other local computers.
1. Click Start, Control Panel, Network and Internet Connections, Network Connections.
2. Double-click the wireless connection to show its status, and then click Properties.
3. On the Wireless Networks tab, click Add to create a new network.
4. Type a name for the new network.
5. If you want to use encrypted communication, uncheck the automatic key option, and
then select the following parameters:
• Key: ASCII passphrase or hexadecimal key string.
• Key format: ASCII for passphrase, hexadecimal for key string.
• Key length: smaller number for 64-bit encryption, larger number for 128-bit.
6. Mark the option to make this a computer-to-computer (adhoc) network.
7. Click OK to save the configuration. This network is added to your list of preferred
networks and becomes available to other computers.
70 Reference Guide
Page 72

Modem and Network Connections
Making Wireless Connections
To prepare for connections (Windows 2000)
Before you can connect your computer to a particular 802.11 wireless network, you have
to configure the computer for the specific type of connection: “AdHoc” or
“Infrastructure.”
Computer-to-Computer Connection (AdHoc)
An AdHoc network provides a wireless connection from your computer directly to one or
more computers with wireless capabilities, even if they aren’t connected to a LAN. You
can then share resources such as shared files, printers, and Internet connections with the
other computers.
1. Click the wireless link icon in the taskbar.
2. On the Configuration tab, set these parameters:
Mode: AdHoc.
ESSID: any name; must be identical for all computers connecting to each other. Do
not use a name that is used by a nearby access point.
AdHoc Channel: must be identical for all computers connecting to each other. For
best performance, do not use a channel that is the same as or adjacent to a channel
already being used by a nearby access point.
3. If the computers use encrypted communication, use the Encryption tab to set the
following parameters, which must be identical for all computers that will connect to
each other:
Encryption: 64-bit or 128-bit.
Key: see the hint below.
The computers automatically connect whenever they’re within range of each other and
wireless communication is turned on—see “To turn wireless communication on and off,”
below.
Reference Guide 71
Page 73

Modem and Network Connections
Making Wireless Connections
LAN Connection (Infrastructure)
In an infrastructure network, your computer connects to a LAN (local area network)
through a wireless access point. This gives you access to the resources on the network,
such as printers, file servers, and possibly the Internet. Your network administrator can
provide the settings you’ll need to connect to the wireless access point, as well as the
additional settings you’ll need for the network itself.
1. Set up your computer for your local network:
Windows automatically detects and sets up a LAN connection. To edit settings, open
Network and Dial-up Connections in Control Panel.
2. Click the wireless link icon in the taskbar.
3. On the Configuration tab, set these parameters:
Mode: Infrastructure.
ESSID: the ID used by the access point. “ANY” connects to the access point with the
strongest signal, regardless of its ESSID.
4. If your wireless network uses encrypted communication, use the Encryption tab to set
these parameters—see the network administrator for the required settings:
Hint
Encryption: 64-bit or 128-bit.
Key: see the hint below.
The computer automatically connects to the infrastructure network whenever it’s within
range of an access point and wireless communication is turned on—see “To turn wireless
communication on and off,” below.
If the wireless network uses shared authentication, open Windows Device Manager,
expand the network devices, and double-click the 802.11 device. On the Advanced tab,
set the authentication algorithm.
If you are connecting to an access point or computer that is using Lucent/Agere-based
software, you must set up compatible encryption on your computer. You can enter the
encryption key manually. If you know only the Lucent/Agere passphrase, see
c:\hp\drivers\wireless\readme.txt.
72 Reference Guide
Page 74

Modem and Network Connections
Making Wireless Connections
To turn wireless communication on and off
Important
Wireless networks and cellular modems are examples of devices that use wireless
communication. Such devices may be restricted in some situations or environments,
such as when traveling in an airplane. If in doubt, be sure to ask for authorization before
turning on your computer’s wireless networking.
In Italy, Singapore, and possibly other countries, you may be required to ask the
responsible authority for a license paid for by you before using the wireless function.
Turning on communication and making a connection
1. If the computer isn’t on, turn it on.
2. The wireless indicator light is lit whenever the wireless function is on. If the indicator
isn’t lit, do one of the following:
Press the wireless on-off button.
–or–
Windows XP: Click Start, Control Panel, Network and Internet Connections,
Network Connections, and then double-click the wireless network connection icon.
–or–
Windows 2000: Click the wireless icon in the taskbar, and then click Radio On/Off.
Reference Guide 73
Page 75

Modem and Network Connections
Making Wireless Connections
If you’re within range of your wireless network, your computer automatically connects.
To check the status of your wireless connection, open Network Connections in Control
Panel and double-click the connection (Windows XP), or click the wireless link icon in
the taskbar and click the Link tab (Windows 2000).
Turning off communication and ending a connection
1. Important: close any files that reside on other network computers.
2. To turn off the wireless function without turning off the computer, do one of the
following:
Press the wireless on-off button.
–or–
Windows XP: Right-click the wireless network connection icon in the taskbar and
select Disable.
–or–
Windows 2000: Click the wireless icon in the taskbar, and then click Radio On/Off.
Suspending or shutting down the computer also turns off the wireless function.
74 Reference Guide
Page 76

Add-On Devices
Reference Guide 75
Page 77
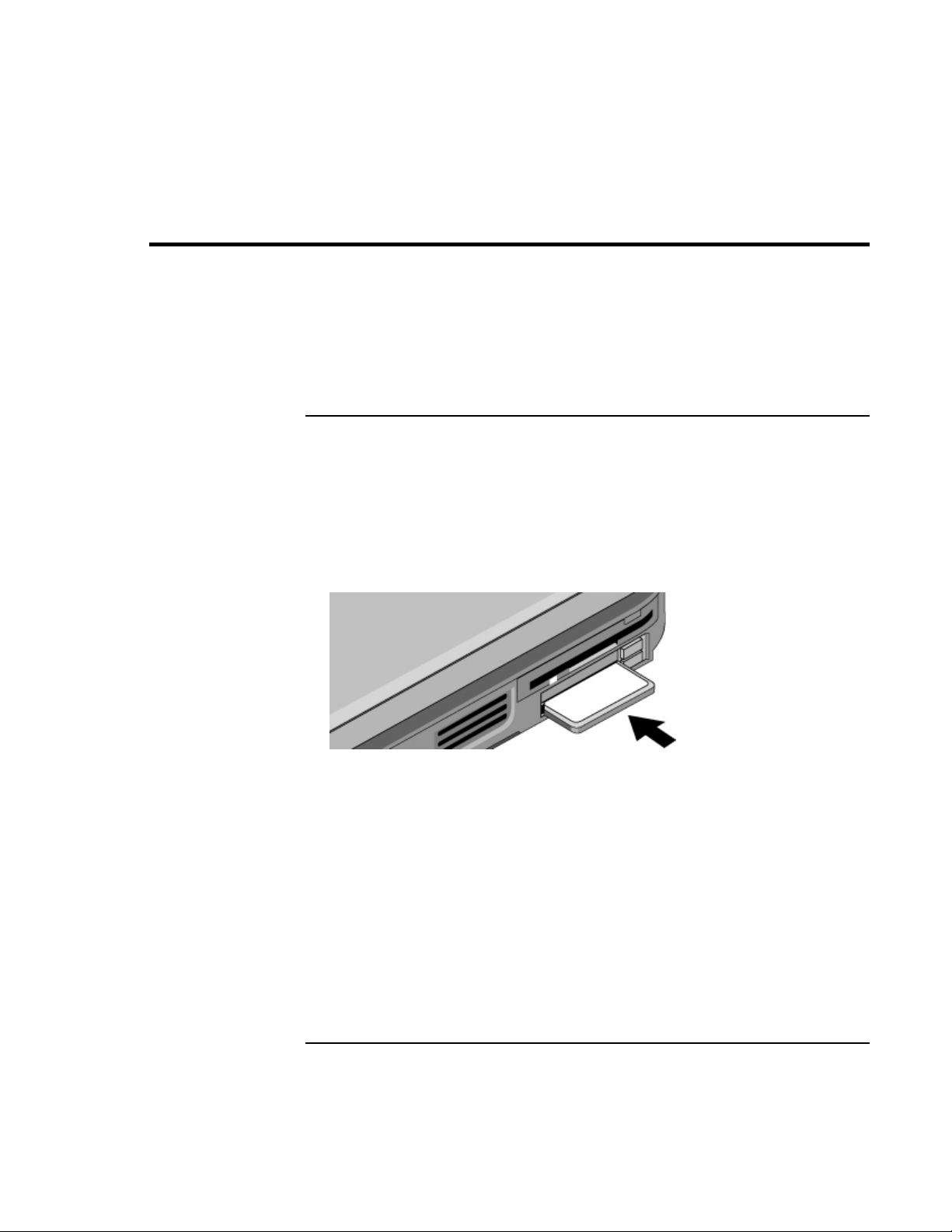
Add-On Devices
Connecting PC Cards
Connecting PC Cards
The computer’s PC Card slots are available for storing data and expanding the
communication capabilities of the computer. The computer supports standard Type II and
III PC Cards (PCMCIA and CardBus).You can insert two Type II cards or one Type III
card.
To insert or remove a PC Card
Inserting a PC Card
1. Hold the PC Card with its face up and its connector holes toward the card slot.
2. Slide the PC Card all the way into the slot. Most cards are properly seated when the
outer edge is flush with the casing of the computer, but some cards are designed to
protrude from the case.
76 Reference Guide
Page 78

CAUTION
Add-On Devices
Connecting PC Cards
Removing a PC Card
Before removing a PC Card, you must use the Eject Hardware or Safely Remove
Hardware icon in the taskbar, or shut down the computer. Otherwise, you could
lose data.
1. Before removing the card, click the Eject Hardware or Safely Remove Hardware icon
in the taskbar, and then click the card you want to remove. This protects your data and
helps avoid unexpected problems.
If needed, you can restart the card by removing and then reinserting it.
2. Flip out the eject button, then press it in to eject the PC Card.
Reference Guide 77
Page 79

Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
Connecting External Devices
To identify connectors for external devices
The diagrams below show your computer’s connectors for external devices and for the
port replicator.
Locating connectors on the computer
1. Universal serial bus (USB) port.
2. AC adapter jack.
3. Two USB ports.
4. LAN port.
5. PS/2 keyboard or PS/2 mouse port.
6. Parallel port (LPT1). Use this port for a parallel printer or other parallel device.
7. External monitor port.
8. S-video port.
78 Reference Guide
Page 80

Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
9. Audio jacks (left to right): audio out (headphones), external microphone.
10. Modem port.
11. IEEE 1394 port (on certain models).
12. Infrared port.
Locating connectors on the port replicator
1. AC adapter jack.
2. PS/2 keyboard and PS/2 mouse ports.
3. USB ports.
4. External monitor port.
5. Parallel port.
6. Serial port.
7. LAN port.
8. Digital audio port (SPDIF).
9. S-video port.
10. Audio ports (microphone, headphone, line-in).
11. USB port.
Reference Guide 79
Page 81

Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
Note
Before you connect any device, check its documentation to see if you need to make any
settings or adjustments to the equipment before using it. This might include setting
switches to configure the equipment so that it will operate properly with your computer
and the software you plan to use.
To connect a printer or other parallel device
The computer’s parallel port uses a standard 25-pin connector, most commonly used for
connecting dot-matrix, ink-jet, and laser printers. You can also use it to connect a parallel
Zip drive.
• Connect the cable from the parallel printer or other parallel device to the computer’s
parallel port.
To connect an external keyboard or mouse
• Plug a USB mouse or keyboard into a USB port.
–or–
• Plug a PS/2 mouse or keyboard into a PS/2 port.
The pointing stick and touch pad are normally disabled while an external PS/2 mouse is
connected.
To connect a PS/2 mouse and keyboard at the same time, use the HP F1469A Y adapter.
To connect a USB device
Your computer’s universal serial bus (USB) provides a bi-directional serial interface for
adding peripheral devices such as game controllers, serial and parallel ports, and scanners
on a single bus.
• Attach the device’s USB cable to one of the USB ports. Windows automatically
recognizes the USB device. Some USB devices can be connected to the computer in
series—this is called a daisy-chain connection.
80 Reference Guide
Page 82

Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
Note
CAUTION
If you have problems making this connection, contact the device manufacturer and the
HP Business Support Web site (www.hp.com/go/bizsupport) for the latest version of the
driver for the device.
To connect an audio device
You can plug in an external microphone, external speakers, or headphones. In addition, if
you connect your computer to the port replicator, you can plug in a stereo source (such as
a CD player) or a device that accepts digital audio (such as a digital audio recorder).
The headphone and line-in jacks are three-terminal stereo jacks. They are not
compatible with two-terminal mono plugs. Connecting a mono plug into either of
these jacks may damage the computer.
• Attach the audio cable to the corresponding audio port on the computer or port
replicator.
Note
1. Audio out (headphones).
2. External microphone.
When you plug a device into the headphone port, the built-in speakers automatically
turn off. When you plug a device into either audio port on the computer, any device
connected to the corresponding port on the port replicator is ignored.
Reference Guide 81
Page 83

Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
To use an external monitor
Connecting an external monitor
1. Click Start, Turn Off Computer, Turn Off (Windows XP) or Start, Shut Down, Shut
down (Windows 2000).
2. Connect the monitor cable from the monitor to the monitor port on the back of the
computer.
3. Connect the monitor to a power source and turn it on.
4. Press the power button to turn on the computer.
Switching the display to the external monitor
• Press Fn+F5 to cycle through the display options: notebook display, external monitor,
both.
–or–
Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Hewlett-Packard, Notebook, HP Display
Settings.
You can also add a display settings icon in the taskbar for quick access.
• If you need to use both displays at once, press Fn+F5 repeatedly until the image
shows on both displays. With the default display settings, the external monitor uses
the same settings as the internal display. The external monitor displays the same
image as the internal display, regardless of the screen area, colors, and other settings,
and the refresh rate is the same for as the internal display (60 Hz). If you use only the
external monitor, you can select different settings that aren’t limited by the internal
display.
Adjusting monitor resolution and other settings
1. Click Start, Control Panel, Appearance and Themes, Display (Windows XP), or click
Start, Settings, Control Panel, and then double-click Display (Windows 2000).
2. On the Settings tab, adjust the Screen area. Other settings are also available.
For high-resolution external monitors, see “Hardware Specifications” on page 136 for the
maximum supported resolutions, colors, and refresh rates. The capabilities of external
monitors vary greatly, and the display quality of your monitor may not be optimal at
higher settings.
82 Reference Guide
Page 84

Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
If you need to increase the refresh rate on the external monitor, you can switch to only the
external monitor. An alternative is to make one display a “secondary” display so you can
select independent refresh rates:
1. Click Start, Control Panel, Appearance and Themes, Display (Windows XP), or click
Start, Settings, Control Panel, and then double-click Display (Windows 2000).
2. On the Settings tab, click the Advanced button, and then the Displays or Monitor tab.
Set the refresh rate on the Monitor tab.
Using dual display mode (Windows XP)
You can extend your desktop by connecting an external monitor to your computer.
1. Click Start, Control Panel, Appearance and Themes, Display.
2. Click the Settings tab.
3. Click the second display, and then select the option to extend the desktop.
You can set different resolutions and numbers of colors for each display. However, using
the Extended Desktop requires video memory for each display. For this reason, higher
resolutions and higher numbers of colors may cause unexpected behavior on the displays.
Try starting with 1024 × 768 resolution on the external display and 64 K colors (16-bit)
on both displays. You can then try higher settings to see whether they work for your
applications. In addition, certain operations such as playing DVDs and running 3D
graphics require extra video memory, so you may have to adjust display settings.
If you’re playing a DVD movie, the movie will show only on the primary display. To
change the primary display, go to the Settings tab of Display Properties (see the steps
above), right-click the display you want, and select Primary.
Reference Guide 83
Page 85

Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
To use a TV set as a monitor
You can connect a television set or other video device to your computer to use as a
display.
To connect a TV set
1. Connect the TV set to the S-video port using a standard S-video cable, or a
composite-video adapter with a standard RCA-type video cable.
2. Optional: connect an audio cable from the computer’s headphone output jack to the
TV audio input. The S-video port doesn’t include audio output.
To activate the TV display
HP TV Now automatically adjusts your computer for using a TV. For example, the
display timeout is disabled to prevent the screen from turning off, and the resolution is
optimized for TV viewing.
• If a One-Touch button is assigned to HP TV Now, press that button. (The five One-
Touch buttons are located above the keyboard.)
–or–
• Click Start, All Programs (or Programs), Hewlett-Packard, Notebook, HP TV Now.
To adjust the HP TV Now options, click Start, All Programs (or Programs),
Hewlett-Packard, Notebook, HP TV Now Options.
To return the display to its normal settings, run HP TV Now again. Normal display
settings are also restored if the computer suspends or turns off.
If the image on the TV is bad, the format used for TV output may be incorrect for your
TV. In North America, the normal setting is NTSC. In Europe, Asia, and Africa, the
normal setting is PAL. To change the TV format, connect a TV to the S-video port, open
Control Panel Display, on the Settings tab click Advanced, on the Displays tab click the
TV button, and then set the format on the Format tab.
To play DVD movies on the TV
The movie shows only on the main display. If the movie doesn’t appear on the TV, open
Display in Control Panel, click the Settings tab, then click Advanced and make the TV a
“primary” display.
For more information, see “To play DVD movies” on page 41.
84 Reference Guide
Page 86

Note
Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
To connect an IEEE 1394 device
If your computer has an IEEE 1394 port (located on the computer’s left side), you can
use it to connect devices such as audio and video equipment, disk drives, printers, and
other computers.
• Attach the device’s cable to the IEEE 1394 port. Windows automatically recognizes
the device.
The IEEE 1394 port is a 4-pin port. If you want to connect a device that has a 6-pin plug,
you should buy a simple adapter if the device is unpowered, or a hub if the device
requires power.
If you have problems making this connection, contact the device manufacturer and the
HP Business Support Web site (www.hp.com/go/bizsupport) for the latest version of the
driver for the device.
To connect a serial device
The port replicator includes a standard 9-pin serial port that you can use to connect
devices such as external modems and fax modems.
• Connect the device’s serial cable to the port replicator’s serial port.
To connect an infrared device
The infrared port, which is located on the front of the computer, provides wireless, serial
communication between the computer and other infrared devices such as printers or other
computers.
By default, the infrared port is not enabled, so you must enable it before you can use it.
1. Click Start, Control Panel, Performance and Maintenance, System (Windows XP) or
Start, Settings, Control Panel, System (Windows 2000).
2. On the Hardware tab, click Device Manager and expand the infrared devices. Double-
click the infrared port and select the option to enable the device.
Reference Guide 85
Page 87

Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
Using the infrared port
• Make sure the infrared ports of your computer and the other device lie in as straight a
line as possible. The two ports should be no more than 1 meter apart, with no
obstructions in between. Noise from nearby equipment can cause transmission errors.
• To check the status of communications, open Wireless Link in Control Panel.
Disabling the infrared port
You should generally disable infrared communication when you aren’t using it.
1. Close any applications that are using infrared, and any folders on an infrared link.
2. Click Start, Control Panel, Performance and Maintenance, System (Windows XP) or
Start, Settings, Control Panel, System (Windows 2000).
3. On the Hardware tab, click Device Manager and expand the infrared devices. Double-
click the infrared port and select the option to disable the device.
Printing to an infrared printer
• Install your printer and assign it to the computer’s infrared port. You can then print
from your applications as you would to any other printer.
CAUTION
Transferring files through an infrared connection
You can use your computer’s infrared port to transfer files by using Wireless Link. See
the Windows online help for instructions on using Wireless Link.
To use a port replicator
A port replicator provides your computer with external connections that you can leave in
place whenever you remove the computer from your desk. Instead of disconnecting and
reconnecting peripheral devices, you can simply undock and dock the computer.
Use only the 90-watt HP AC adapter included with your computer (or other
approved adapter that meets the power requirements of the computer).
If “90W” is printed below the AC adapter socket, do not use a 60- or 75-watt
adapter, such as HP F1454A, F1781A, F4600, or F4814, and do not use DC adapter
accessories F1455A and F2297A.
Using the wrong AC adapter could damage the computer or adapter and may void
your warranty (see “Hewlett-Packard Limited Warranty Statement” on page 133).
86 Reference Guide
Page 88

Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
You can dock or undock the computer in any power state: on, off, standby, or
hibernation. Make sure, however, that the computer is not entering into or resuming from
standby or hibernation when you dock or undock, or the computer could lock up.
To dock to the port replicator
1. Plug in the AC adapter, and then connect it to the back of the port replicator. You can
also operate the port replicator using power from the computer battery.
2. Remove the rubber cover from the docking connector on the bottom of the computer.
3. Align the computer with the locator posts on the port replicator.
Note
4. Press the computer down until both sides click into place.
5. If the computer is off, open the computer and press the power button to turn it on. The
lights on the port replicator turn on.
When the computer is docked, you can use the computer’s security connector to secure
the computer. To secure both the computer and port replicator, install the Kensington
lock in the security connector next to the undock button—this locks the undock button.
If a device is connected to an audio port on the computer, any device connected to the
corresponding port on the port replicator is ignored.
Reference Guide 87
Page 89

Add-On Devices
Connecting External Devices
To undock from the port replicator
1. Press down the undock button on the right side of the port replicator.
2. Lift the computer out of the port replicator.
88 Reference Guide
Page 90

Installing Additional RAM
The computer has no memory (RAM) built in but has two slots that hold two RAM
modules. At least one slot contains a RAM module installed at the factory. You can use
both slots to expand your RAM.
To install a RAM expansion module
Use HP PC2100 DDR-266 or higher RAM only.
You’ll need a small Phillips screwdriver for these steps.
CAUTION
Your computer’s chips are extremely sensitive to static electricity, and can be
permanently damaged by it. Handle the RAM module only by its edges. Before
installing the memory module, discharge your body’s static electricity by touching
the metal shielding around the connectors on the back of the computer.
1. Click Start, Turn Off Computer, Turn Off (Windows XP) or Start, Shut Down, Shut
down (Windows 2000).
Add-On Devices
Installing Additional RAM
2. Important: unplug the AC adapter, if present, and remove the battery.
3. Turn the unit bottom-side up, loosen the screws holding the RAM cover, and remove
the cover.
Reference Guide 89
Page 91

Add-On Devices
Installing Additional RAM
4. Insert the RAM board into the connector at about a 30° angle until it is fully inserted.
Then press down at both sides until both latches snap closed.
5. Replace the cover.
CAUTION
6. Insert the battery.
To remove a RAM expansion module
You may want to remove a RAM module so you can install a larger one. You’ll need a
small Phillips screwdriver for these steps.
Your computer’s chips are extremely sensitive to static electricity, and can be
permanently damaged by it. Handle the RAM module only by its edges. Before
installing the memory module, discharge your body’s static electricity by touching
the metal shielding around the connectors on the back of the computer.
1. Click Start, Turn Off Computer, Turn Off (Windows XP) or Start, Shut Down, Shut
down (Windows 2000).
2. Important: unplug the AC adapter, if present, and remove the battery.
3. Turn the unit bottom-side up, loosen the screws holding the RAM cover, and remove
the cover.
90 Reference Guide
Page 92

Add-On Devices
Installing Additional RAM
4. Release the two latches at the sides of the RAM board, so the free edge of the board
pops up.
5. Pull the board out of the connector.
6. Replace the cover.
7. Insert the battery.
Reference Guide 91
Page 93

Add-On Devices
Replacing the Hard Disk Drive
Replacing the Hard Disk Drive
To replace the hard disk drive
You’ll need a small Phillips screwdriver for this procedure.
1. Unplug the AC adapter if you’re using one, and remove the battery.
2. Turn the unit bottom side up.
3. Use a pointed tool to remove the plug from the center screw hole, and then remove
the three screws.
4. Gently pull the hard drive out of the computer.
Important
5. Gently slide the new drive into the hard drive compartment. Press firmly to make sure
the connector seats properly.
6. Reinstall the hard drive screws and plug.
If you are installing a new hard disk drive, you should create a Utility partition on the
drive before loading any software. See “To recover the factory installation of your hard
disk” on page 122.
92 Reference Guide
Page 94

Add-On Devices
Replacing the Hard Disk Drive
To replace the hard disk drive holder
If you are installing a new hard drive that does not have a holder, you can remove the
holder parts from the old hard drive. You’ll need a small Phillips screwdriver for this
procedure.
1. Remove the four screws from the sides of the holder and drive case, and then slide the
drive out of the holder.
2. Notice that the hard drive has a pin connector attachment at one end. Carefully
remove this connector from the end of the drive. Work alternately at each end so that
the connector slides off evenly without bending the connector pins.
3. Carefully put the pin connector attachment back onto the pins on the end of the new
hard drive. Work alternately at each end so that the connector slides on evenly
without bending the connector pins.
4. Insert the drive into the holder.
5. Reinstall the screws into the holder and drive case.
Reference Guide 93
Page 95

Add-On Devices
Replacing the Hard Disk Drive
To prepare a new hard disk drive
When you install a new hard disk drive, you also need to prepare it to be able to work
with your computer.
• If you want to restore the Windows software and operating system that were
originally installed on your computer, you can do so using the Recovery CD or DVD
that also came with your computer. See “To recover the factory installation of your
hard disk” on page 122.
• If you want to use the hard disk with other than the original software and operating
system, prepare the hard disk as described in the Corporate Evaluator’s Guide,
available at the HP Business Support Web site (www.hp.com/go/bizsupport).
94 Reference Guide
Page 96

Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Reference Guide 95
Page 97

Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Troubleshooting Your Computer
Troubleshooting Your Computer
This section contains solutions to a many types of problems you might have with your
computer. Try the solutions one at a time, in the order in which they are presented.
Here are some other sources of information for troubleshooting:
• Open the HP Web-based troubleshooting tool: click Start, All Programs, HP Instant
Support (Windows XP), or double-click the HP Instant Support icon on the Windows
desktop (Windows 2000). Search or browse the troubleshooting database for the
information related to your problem.
• Click Start, Help and Support, Fixing a Problem (Windows XP) or Start, Help
(Windows 2000), and use the Windows troubleshooters.
• See the Microsoft Windows manual shipped with the computer.
• See the HP Notes in the online HP Library for updated information.
• Find technical tips and software updates for the computer at the HP Business Support
Web site (www.hp.com/go/bizsupport).
• Test your computer by running the e-Diagtools test program. See “Testing the
Hardware” on page 116.
• Contact your dealer or Hewlett-Packard—see “To contact HP for support or service”
on page 128. Please have your computer with you when you call.
Audio Problems
If no sound is audible
• Press the back end of the volume control several times.
• Click the speaker icon on the taskbar (if present), and make sure that Mute is not
checked and the Volume Control slider is not set to the bottom. Or, press the audio
mute button so the indicator light goes off.
• When you are operating your computer in MS-DOS mode (for example, when
running MS-DOS games), you may find that the sound does not operate properly. Use
Windows applications for full use of sound capabilities.
96 Reference Guide
Page 98

Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Troubleshooting Your Computer
If sound does not record
• Plug in an external microphone. The computer does not have a built-in microphone.
• Check the software controls for recording sound: click Start, All Programs (or
Programs), Accessories, Multimedia (or Entertainment), Sound Recorder.
• In Volume Control, click Options, Properties, and make sure the microphone is
enabled in the recording controls.
• Test the audio with the e-Diagtools diagnostics. See “Testing the Hardware” on
page 116.
If you hear a loud high-pitched whine (feedback) from the speakers
• In the Volume Control, try reducing the Master volume: double-click the speaker icon
in the taskbar.
• In Volume Control, click Options, Properties, and select the microphone option for
the playback settings. Then in Volume Control, make sure the microphone is muted.
CD-ROM and DVD Problems
If you can’t boot from a CD or DVD in the CD/DVD drive
• Make sure the CD or DVD is bootable, such as the Recovery CD or DVD.
• Make sure the CD-ROM/DVD drive is selected as the boot device—see “To change
the boot device” on page 30.
• Restart the computer: click Start, Turn Off Computer (or Shut Down), Restart.
• Test the DVD drive with the e-Diagtools diagnostics. See “Testing the Hardware” on
page 116.
If a DVD plays erratically
• Dirt or smudges can cause a disc to skip. Clean the disc with a soft cloth. If the disc is
badly scratched, it will probably have to be replaced.
• If you’re playing the DVD on battery power, try changing the power scheme. See the
hint under “To play DVD movies” on page 41.
Reference Guide 97
Page 99

Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Troubleshooting Your Computer
If a DVD movie stops playing in the middle
• The DVD may be double-sided. Open the DVD tray, and read the text near the center
hole of the disc. If it says Side A, flip the disc over, close the tray, and press the Play
button to continue playing the movie.
• You may have accidentally paused the DVD movie. Press the Play button to resume.
If you get a Region Code error when playing a DVD movie
• DVDs can have regional codes embedded in the disc data. These codes prevent DVD
movies from being played outside the region of the world in which they are sold. If
you get a Region Code error, you are trying to play a DVD intended for a different
region.
If the computer cannot read a CD or DVD
• For a single-sided CD or DVD, make sure the disc is placed in the drive with the label
facing up.
• Clean the disc.
• Wait 5 to 10 seconds after closing the tray to give the computer time to recognize the
disc.
• Restart the system: remove the disc from the drive, and click Start, Turn Off
Computer (or Shut Down), Restart.
• If you created the CD on a CD-RW-type drive, try using a different media brand, such
as the recommended HP C4403A (CD-R) or C4404A (CD-RW) media. Read and
write quality may vary for other media.
If a DVD movie doesn’t fill the screen
• Each side of a double-sided DVD has a different format (standard or widescreen). In
widescreen format, black bands appear at the top and bottom of the screen. To view
the standard format, flip the disc over and play the other side.
If a DVD doesn’t play with two displays
• For Windows XP, if you’re using the Extended Desktop (dual displays), move the
player window to the display selected as primary. If you’re not using Extended
Desktop and both displays are active, press Fn+F5 to switch to one display.
• For Windows 2000, if both displays are active, press Fn+F5 to switch to one display.
98 Reference Guide
Page 100

Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Troubleshooting Your Computer
If the computer can’t find Wordpad.exe after inserting a CD
• The system is trying to open a .doc file in WordPad, but cannot find the Wordpad.exe
program file. Type C:\Program Files\Accessories in the error message box.
Display Problems
If the computer is on, but the screen is blank
• Move the mouse or tap the touch pad. This will wake the display if it is in Display-off
mode.
• Press Fn+F5 in case the internal display was disabled. (Do this three times to return to
the state you started from.)
• If the computer is cold, allow it to warm up.
If the screen is difficult to read
• Try setting the display resolution to its default setting of 1024×768 or higher,
depending on your model: click Start, Control Panel, Appearance and Themes,
Display (Windows XP) or Start, Settings, Control Panel, Display, Settings
(Windows 2000).
• Try adjusting the size of the desktop icons and labels—see “To adjust the display” on
page 37.
If an external display does not work
• Check the connections.
• Press Fn+F5 in case the external monitor was disabled. (Do this three times to return
to the state you started from.)
• The external monitor may not be detected. In the BIOS Setup utility, try setting Video
Display Device to Both in the System Devices menu.
• If you’re using a TV connected to the S-video port, you must activate the TV—see
“To use a TV set as a monitor” on page 84.
• Test the display with the e-Diagtools diagnostics. See “Testing the Hardware” on
page 116.
Reference Guide 99
 Loading...
Loading...