Page 1

HP Hub & Switch Management for OV -UX
User Guide
Page 2

© Copyright 1998 Hewlett-Packard Company
All Rights Reserved.
This document contains information which is protected by
copyright. Reproduction, adaptation, or translation without
prior permission is prohibited, except as allowed under the
copyright laws.
Publication Number
Edition 1
September 1998
Applicable Product
HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-UX
J3250M
Disclaimer
The information contained in this document is subject to
change without notice.
HEWLETT-P ACKARD COMPANY MAKES NO WARANTY
OF ANY KIND WITH REGARD TO THIS MATERIAL,
INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Hewlett-Packard shall not
be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental or
consequential damages in connection with the furnishing,
performance, or use of this material.
Hewlett-Packard assumes no responsibility for the use or
reliability of its software on equipment that is not furnished
by Hewlett-Packard.
Warranty
A copy of the specific warranty terms applicable to your
Hewlett-Packard products and replacement parts can be
obtained from your HP Sales and Service Office or authorized dealer.
Hewlett-Packard Company
8000 Foothills Boulevard, m /s 5551
Roseville, California 95747-5551
http://www.hp.com/go/network_city
Page 3

Contents
1 Information About HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-
UX
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Features of HP Hub & Switch Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
HP Proactive Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Support for New Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Technical Product Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
2 Before Installing HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-
UX
Support Informati on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Management Station Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Required Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Required Patches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Before Installing HP H ub & Switch Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Removing HP Hub & Switch Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
3 Introduction to HP Hub & Switch Management
HP Hub & Switch Management Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
HP OpenView Network Management Platform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Definitions, Processes, and Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
SNMP Manager and Agents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Community Names for Manager and Agent Interaction . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
What HP Devices Can Be Managed . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
HP ProCurve Family of Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
4 Running HP Hub & Switch Management
Starting the Manager Application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
i
Page 4

Starting HP OpenView . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Verifying Installatio n of the Manager Product Set . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Stopping and Restarting the Manager Applicat i on . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Stopping the Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Restarting the Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
5 Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
HP Proactive Networking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-1
Uptime . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Performance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Interpreting the Alert Log - Find/Fix/Inform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
6 Accessing Hub Features
More Information on Device Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-1
Accessing the Device View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Viewing Device Identity Info rmation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Interpreting Device Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
Reading the Performance Gauges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Status - Global Counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-4
Status - Po rt Counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
Configuring Your Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-5
Configuration - Fault Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-6
Configuration - System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-7
Configuring IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-8
Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-9
Configuration - Backup Links . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-9
Configuring Load Balancing - Sw itching Hu bs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-11
Configuration - Support URL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-11
7 Managing Switches
Switch Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
Status - Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
ii
Page 5

Status - Po rt Counters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
Status - Po rt Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-4
Identity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
Device View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
Configuration - Fault Detection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
Configuration - System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
Configuration - IP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
Configuration - Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
Configuration - Assigning a Monitoring Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-10
Configuration - Device Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
Automatic Broadcast Control (ABC) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-12
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-14
The Spanning Tree Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-15
Configuration - Support/Mgmt URLs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-16
8 Setting Up Security for a Device
Device Passwords . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-1
Manager/Operator Password Combinations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-2
The Function of Community Names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-3
Port Security (hubs only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
Address Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-4
Authorized Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-5
Eavesdrop Prevention . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-5
Send Alarm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-5
Disable Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-6
Set Security Policy fo r Selected Ports (hubs only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-7
The Intrusion Log (hubs only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8-7
9 Performing Diagnostics
Performing a Ping/Link Test . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-1
Rebooting a Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-2
Resetting a Hub to Factory Default Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
iii
Page 6

Producing a Configuration Report . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-3
10 HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
Starting HP Hub & Switch Management Admin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-5
HP Admin Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-5
Network Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-6
User Interface Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-7
Graph Options Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-9
Printer Configuration Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-10
OpenView Configuration Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10-11
11 Management for Non-Browserable Devices
About Closeup Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-1
Displaying the Closeup View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-2
Closeup View Areas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-3
Overview of Toolbar Functio ns . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-4
Configuration Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11-8
Appendix A
iv
Agent Firmware Versions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Verifying Device Agent Versions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Preparing Network Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
Device Network Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
Globally Assigned IP Network Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
Configuring IP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-3
Page 7

Information About HP Hub & Switch
Management for OV-UX
This chapter includes:
■ Introduction
■ Features of HP Hub & Switch Management
■ Technical Product Support
Introduction
This guide will help you use HP Hub & Switch Management for basic man agement of HP network devices.
1
Switch Management for OV-
Information About HP Hub &
We assume that you are a knowledgeable HP-UX system and network administrator ,andhave supervisory access toyour network system and devices. For
example, you should know the following:
■ how to update your HP-UX system with new software
■ how to kill processes
■ how to write scripts
■ how to modify X Window/Motif resources
■ how to view, search, and edit files
You should understand the functio ns and correct operation of your network
devices, such as hubs, bridges, routers, and switches. Your system should be
set up to support the use of the HP OpenView platform and HP Hub & Switch
Management. You should already have the appropriate network sof t w are
running and know how to use your network utilities.
1-1
Page 8

Information About HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-UX
Features of HP Hub & Switch Management
Features of HP Hub & Switch
Management
This section presents some of the features that are included in this version of
HP Hub & Switch Management.
Information About HP Hub &
Switch Management for OV-
HP Proactive Networking
HP Proactive Networking offers the comb ined benefits of outstanding products and effective, easy-to-use network management that provide you with the
control, uptime and performance your network needs.
Control
■ Increases visibility into the network by monitoring all segments and
displaying network performanc e information
■ Provides Anywhere Management with an easy-to-use Web browser inter-
face
■ Is compatible with other vendor’s products
Uptime
■ Finds and fixes common network proble ms, th en informs the network
administrator
■ Provides high availability and high performance
• Switch meshing for switching
®
• Cisco Fast EtherChannel
■ Standards-based products
■ Lifetime warranty (for as long as you own the product) and free end-user
telephone support
for servers
1-2
Performance
■ Award winning products
■ Large capacity “pipes” (up to 20 Gbps) between switches
■ Provides high availability and high performance
• Switch meshing for switching
®
• Cisco Fast EtherChannel
for servers
Page 9

Information About HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-UX
Features of HP Hub & Switch Management
■ Scalable solutions from 10 Mbps t o Gig ab it Et hernet
■ Blocks unwanted traffic with Protocol Filtering
HP Proactive Networking produc t s save time, money and increase productivity. The agent-enabled, web-based management component of Proactive
Networking is embedded in newly introduced HP managed hubs and switches.
It consists of a Java-based W eb agent and an embedded webserver.In the past,
if you wanted to see a graphical representation of your network or get devicespecific information, you had to first load management software on a specific
station and then be at that station to view the screens.
Y ou can now use most W eb browsers that supports Java and frames. There is
no need to learn a new application. Y ou see th e same interface wi th the same
look and feel —Java is operating-system independent. You can use a Web
browser on any networked computer, day or night, to configure, control, and
monitor networkingdevices (managedhubs andswitches), andto query faults
from any of these devices. You will immediately see the reduced cost of
ownership, since the devices can be managed with minimal effort anytime,
anywhere, and with any platform.
Using your Web browser, you can now perform network management functions for several HP devices.
Note: The device must have an IP address in order to be managed with
a browser. The management station must also have an IP address.
Switch Management for OV-
Information About HP Hub &
Support for New Switches
Several new switches are supported, as described below.
■ HP ProCurve Switch 8000M (J4110A) — a 10/100/Gigabit Ethernet
modular backbone switch that providesscalable, high portdensity 10/100/
Gigabit switching with HP Proactive Networking. Features include:
• 10/100 auto-sensing ports (up to 80 ports)
• Multiple Gigabit connectivity
®
• Fast EtherChannel
• 100Base-FX fiber-optic port connectivity
• Automatic Broadcast Control
• Switch meshing
■ HP ProCurve Switch 1600M (J4120A) — a 10/100/Gigabit server farm
connectivity switch that provides 10/100/Gigabit switching w ith HP Proactive Networking. Features include :
• Sixteen 10/100 auto-sensing ports optimized f or Ethernet
to servers
1-3
Page 10

Information About HP Hub &
Information About HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-UX
Technical Product Support
• An expansion slot for Gigabit connectivity
• Gigabit Fiber Optic port or 8 10/100 auto-sensing ports
• Layer 3 switching
• Fast EtherChannel
• Switch meshing
HP ProCurve Switch 4000M (J4121A) — a 10/100/Gigabit Ethernet modular
desktop switch that provides scalable/expandable, low-cost migration 10/100/
Gigabit switching to the desktop with HP Proactive Networking. Features
Switch Management for OV-
include:
• Forty 10/100Base-T desktop switch auto-sensing ports
• Five open slots for additional modules
• Can support up to 80 10/100 auto-sensing ports
HP ProCurveSwitch 2400M(J4122A)—a 10/100 desktop switch, idealfor lowcost migration to desktop switching.
HP ProCurve Switch 212M (J3298A) and HP ProCur ve Switch 224M (J3299A)
— 10 Mbps desktop switches that provide 12 or24ports ofdedicated switching
to the desktop withtwo 10/100 Mbps “fat” pipes and HP Proactive Networking.
®
to servers
1-4
Technical Product Support
Product support is available on the World Wide Web. The URL is:
http://www.hp.com/go/network_city
Click on Support. The information available at this site includes:
■ HP network device MIBs
■ HP network device firmware
■ HP Hub & Switch Management frequently asked questions
In addition, you can call your HP Authorize d Dealer or the nearest HP Sa les
and Support Office.
Page 11

Before Installing HP Hub & Switch
Management for OV-UX
This chapter includes:
■ Support Information
■ Management Station Requirements
■ Hardware Requireme nts
■ Software Requirements
■ Required Network Configuration
■ Before Installing HP Hub & Switch Mana gement
■ Removing HP Hub & Switch Management
It is assumed that your network devices are properly set up.
2
Switch Management for OV-
Before Installing HP Hu b &
Support Information
If you have difficulty installing or using this product, call your HP Authorized
Dealer or the nearest HP Sales and Support Office. You can also obtain
information by accessing the HP World Wide Web pages at the following
URL:
http://www.hp.com/go/network_city
2-1
Page 12

Before Installing HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-UX
Management Station Requirements
Management Station Requirements
Hardware
The following table shows the recommendations for HP 9000 hardware.
HP 9000 Systems with HP-UX 10.20 or 11.00
Models all (except 705 with Series 700)
Before Installing HP Hu b &
Memory
(minimum megabytes)
Disk Space
(minimum megabytes**)
Monitor Color with at least 1280 x 1024 resolution
Color planes 8
Mouse Yes
Switch Management for OV-
* The larger your IP network or the more HP OpenView Windows (ovw) sessions you run,
the more memory you will need. A good guideline is 10 megabytes for every additional 500
nodes, or 25 megabyte s of memory fo r every ad ditio nal ovw session that you expect to run.
**Includes HP OpenView Network Node Manager.
64 MB*
150 MB
Software
The following table shows the software that must be installed, configured,
and verified to run properly prior to installing HP Hub & Switch
Management. These prerequisites assume that you are running a single
HP OpenView Windows (ovw) session.
HP 9000 Systems
2-2
OS version HP-UX 10.20 and 11.00
OS configured swap space
(minimum megabytes)
Type of window software X Window with OSF/Motif/CDE
LAN software LAN/Link for HP 9000 & ARPA Services/9000
120 MB*
Page 13

Before Installing HP Hub & Switch Mana geme nt for OV-U X
Required Network Configuration
* The more OpenView Windows (ovw) sessions you run, the more OS configured swap
space will be necessary. A good guideline is to configure 25 megabytes of swap space for
each additional ovw session t hat you expect to run.
Required Network Configuration
The installation starts the automatic discovery and layout of the network
map, based on your internetwork’s IP addressing scheme. This depends on
the following:
■ Correct IP addressing. The IP addresses and subnet masks must be
correctly configur ed on the manager station, and on all rou t ers and
gatewayhosts that supportSNMP . Otherwise, the automaticallygenerated
map could contain incorrect networks with nodes from outsidethe administrative domain.
■ Network design that aids isolation of network faults and traffic, by doing
the following:
• Logically subdividing an internetwork into manag eable-sized
networks and subnetworks, using routers, gateway hosts and IP
subnet addressing.
• Physically subdividing networks and subnetworks into manageablesized segments using hubs, bridges, and gateway hosts. HP recommends that the segments have no more than 200 nodes each.
■ SNMP-based, MIB-I (RFC 1156) or MIB-II (RFC 1213) compliant agents
running on management stations, routers, and gateway hosts at a
minimum, and running on bridge s and hubs for manageable segments.
This ensures speed and accuracy of map generation.
■ All HP 9000 Systems (manager stations or hosts) that a re running HP-UX
version 10.20 or HP-UX ve rsion 11.00 should also be running the HP
OpenView SNMP Agent software as part of their ne tworking software.
■ All managed HP devices should contain a supported version of ag en t
firmware.
Switch Management for OV-
Before Installing HP Hu b &
2-3
Page 14
Before Installing HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-UX
Required Patches
Required Patches
The following patches must be installed before installing HP Hub & Switch
Management for OV-UX. Contact your HP Authorized Dealer or the neare s t
HP Sales and Support Office, or do wnload the patches from the HP
Electronic Support Center. The URL is:
http://us-support2.external.hp.com
The two patches are:
■ For HP-UX 10.20 — PHSS_15043 S700_800 10.x HP aC++ runtime library
components (A.01.15)
■ For HP-UX 11.00 — S700_800 11.00 HP aC++ runtime library components
(A.03.10)
Before Installing HP Hu b &
Switch Management for OV-
Before Installing HP Hub & Switch Management
Before you can begin installing HP Hub & Switch Management, you must
have successfully completed installing y our Network Node Manager
product. See the HP OpenView Network Node Manager Products
Installation Guide for instructions on installing the HP Network Node
Manager and obtaining your software license.
You may set up multiple manager sta ti ons on y our network. Each manager
on which you install the manager produc t set does its own p olling, so the
manager traffic on your network will increase in proportion to the number of
managers.
Note: This applies only if you buy multiple copies. Your license only
entitles you to instal l one copy.
If you are installing this product set on a workstation with an existing
application, be sure you first exit any ovw sessions currently running, then
stop all HP OpenView processes using the ovstop command (available to
root user).
2-4
Page 15

Before Installing HP Hub & Switch Mana geme nt for OV-U X
Removing HP Hub & Switch Mana gement
Note: It is also a good practice to make a backup of your curr ent
OpenView application (especially your network map) before
proceeding with the installation of new applications.
Installation Directories
The HP Hub & Switch Management pr oduct is installed in the following
directories:
• /var/opt/HPASA
• /opt/HPASA
In compliance with the OSF standards, the /opt/HPASA directories hold the
read-only files, which include a ll th e executables, libraries, release notes,
and Device Model Files. The /var/opt/HPASA directories contain the
writeable directories such as product data directories. Be sure you have the
required amount of free disk space before you install the products. You can
make one of the following arra ngements for the required space:
• having the requi r ed amount of disk space in /opt and /var
• mounting a dedicated volume for /var/opt/HPASA and
/opt/HPASA
• making /var/opt/HPASA and /opt/HPASA symbolic links to a
file system with enough disk space.
The management system must have b oth manager and agent software
installed.
Make sure the drive that you will be loading from is connected to the
workstation and that your workstation is configured to recognize the CDROM drive.
Consult the README file on the HP Hub & Switch Management CD for
installation procedures.
Switch Management for OV-
Before Installing HP Hu b &
Removing HP Hub & Switch
Management
If necessary, you can remove product s th at you installed by using the
command that is appropriate for your operating system. Y ou must be logged
on as root and you must remove them in the reverse order that you installed
2-5
Page 16

Before Installing HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-UX
Removing HP Hub & Switch Management
them, that is, remove Hub & Switch Management first, th en remove Network
Node Manager and/or the SNM P Management Platform.
Instructions are given here f or removing the Hub & Switch Management
product. If you want to remove Network Node Manager, see the HP
OpenView Network Node Manager Products Installation Guide.
To remove products for HP-UX 10.20 or 11.00, use the HP System
Administration Manager.
Before Installing HP Hu b &
1. Select
2. Select
3. Select
Software Management
Remove Software
Remove Local Host Software
4. Highlight the program you want to remove and pick the appropriate action
from the Actions menu.
If you used the “install” command to install the software, you can also use
this method for removing it:
1. Mount the Hub & Switch Management product CD in your CD-ROM drive.
Switch Management for OV-
2. Type in the command:
./remove
This command will remove the Hub & Switch Management files and its
directories. The swinstall command only removes the program files.
Note: The remove command only works with current Hub & Switch
Management products.
2-6
Page 17

Introduction toHP Hub & Switch Management
This chapter introduces HP Hub & Switch Management and includes the
following topics:
■ HP Hub & Switch Management Overview
■ HP OpenView Network Management Platform
■ Definitions, Processes, and Files
■ What Devices Can Be Managed
HP Hub & Switch Management Overview
HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-UX is a network management
application that allows you to manage and control Hewlett-Packard (HP)
hubs, bridges, and switches on a TCP/IP network. HP Hub & Switch
Management runs on the HP OpenView pla t form, which allows multivendor
enterprise-wide network man age me nt. For communications with managed
devices, Hub & Switch Ma nagement uses the Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP)—an industry standar d ne twork management
communications protocol.
3
Introduction to HP Hub &
Switch Managemen t
HP Hub & Switch Management is integrated with HP OpenView Network
Node Manager applications.
When using Hub & Switch Manag e me nt, you can do the following:
■ use HP OpenView functions to automatically discover and display the IP
map (and submaps). HP hubs, bridges, and sw it ches that are set up for
SNMP/IP operation will be displayed as appropriate “connector” devices.
■ use your Web browser to launch Device Views for Proactive networ k
management
■ manage HP hub and switch security features
■ run network tests to troubleshoot network or device problems
3-1
Page 18

Introduction to HP Hub & Switc h Management
HP OpenView Network Management Platform
HP OpenView Network Management
Platform
HP OpenView is a “platform” for network management applications. As a
platform, it allows multiple network management applications that are
OpenView compliant—such as HP Hub & Swit ch Management—to share
platform functionality and a common display.
Using the HP OpenView, Network Node Manager provides many shared
management functions, which include:
■ automatic discovery and mapping of IP networks and objects
■ dynamic submap creation
■ map navigation Tool Bar
■ Quick Navigator
■ a map zoom viewer
■ device polling to monitor de vices on an OpenView map
■ an event notification and logging system
■ generic SNMP device m a nagement
■ graphing and logging of traffic
■ client/server architecture enabling processes to be run on other worksta-
tions
Introduction to HP Hub &
For more information on HP OpenView platform operation and functions,
refer to the HP OpenView Network Node Manager documentation.
Switch Management
Definitions, Processes, and Files
The basic concepts and processes of management for networks are
described briefly in the following paragraphs.
3-2
Page 19

Introduction to HP Hub & Switch Management
Definitions, Processes, and Files
SNMP Manager and Agents
HP Hub & Switch Management uses SNMP (Simple Network Management
Protocol) to communicate with managed devices. SNMP commands are
transmitted and received on the network using the Internet Protocol (IP).
The network management station used to run Hub & Switch Manage ment is
referred to as an SNMP manager system. HP devices with SNMP agents ar e
called agent systems . Each network management operation requested by
the manager system is executed by one or more agent systems.
The manager system communicates with HP devices to retrieve or modify
management information. The devices contain Network Management SNMP
Agent software to support this communication.
Note: For Hub & Switch Management operation, you must set up HP
network devices for SNMP/IP operation. See
Appendix A for more
information.
Community Names for Manager and Agent Interaction
Most SNMP exchanges involve a community name, which can be thought
of as a password for a managed device or group of devices.
Depending on the device, SNMP get requests for information from a device
agent may require the manager to supply a community name that is
configured on the device.
Introduction to HP Hub &
Switch Managemen t
If a password has been specifically configured on a device, then password
authentication is required to perform any SNMP set operations that alter the
configuration or invoke self-test or reset on that device. The manager system
automatically asks you fo r t he password, then puts the encrypted password
in the community name field of subsequent set operations.
Configuring a password on HP devices is recommended but not required. As
described later in this manual, you can use Hub & Switch Management to set
a device password.
3-3
Page 20
Introduction to HP Hub & Switc h Management
What HP Devices Can Be Managed
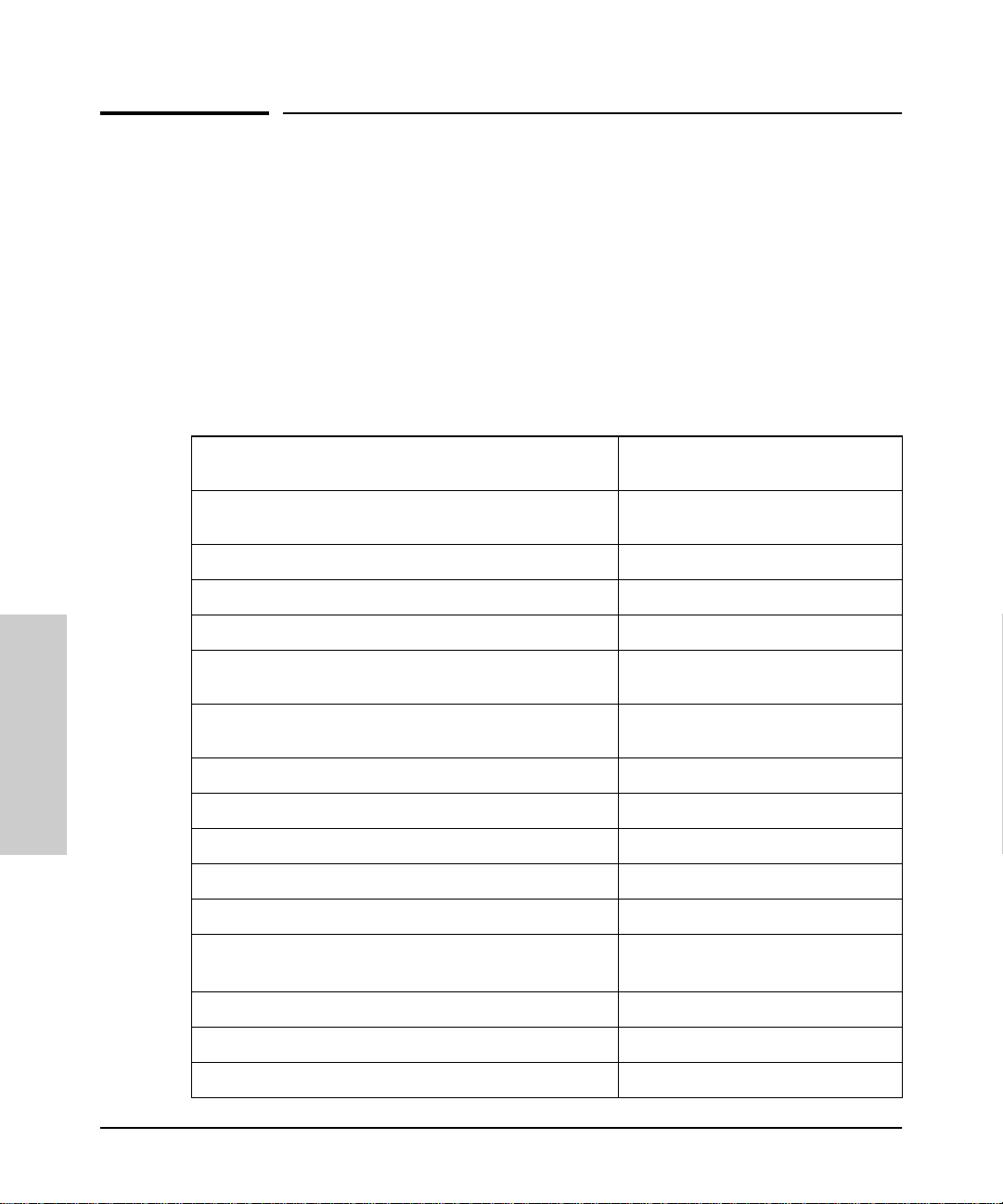
What HP Devices Can Be Managed
For device management, HP Hub & Switch Management provides a Device
View for most managed HP devices.
Y ou can display a Device View using your browser if th is feature is supported
for the device. The devices that support this feature are noted in the table
below.
Table 3-1. HP Devices That Can be Managed
HP AdvanceStack Family of Hubs and Switches HP EtherTwist Family of Hubs and
HP J2410A AdvanceStack 100 VG Hub-15
HP J2413A AdvanceStack 100VG Hub-7M
HP J2415A AdvanceStack 100VG Hub-14
HP J2600A AdvanceStack 10Base-T Hub-12
Note 1
Note 1
Note 1
Note 2
Bridges
HP 28688A/B EtherTwist Hub Plus (12 port)
HP 28699A EtherTwist Hub Plus/48
HP J2355A EtherTwist Hub Plus/24S
HP 28682A Fiber-Optic Hub Plus
Introduction to HP Hub &
HP J2601A/B AdvanceStack 10Base-T
Note 2
Hub-24
HP J2602A/B AdvanceStack 10Base-T
Note 2
Hub-48
HP J2610A/B 10Base-T Hub-8U
Switch Management
HP J2611A/B 10Base-T Hub-16U
HP J2631A 10Base-T Hub-24 (SNMP bundle)
HP J2632A 10Base-T Hub-48 (SNMP bundle)
HP J2980A AdvanceStack 10/100 LAN Switch-16
Note 3
Note3
Note2
Note2
Note4
HP 28692A ThinLAN Hub Plus
HP 28674B Remote Bridge RB
HP 28673A 10:10 LAN Bridge
HP J3100A/B AdvanceStack Switch 2000
HP J3100B is browser-manageable (firmware B.04.xx)
HP J3101A AdvanceStack Switch 2000 Bundle
HP J3125A AdvanceStack Switch 200
HP J3126A AdvanceStack Switch 100
Note 5
Note 5
3-4
Page 21
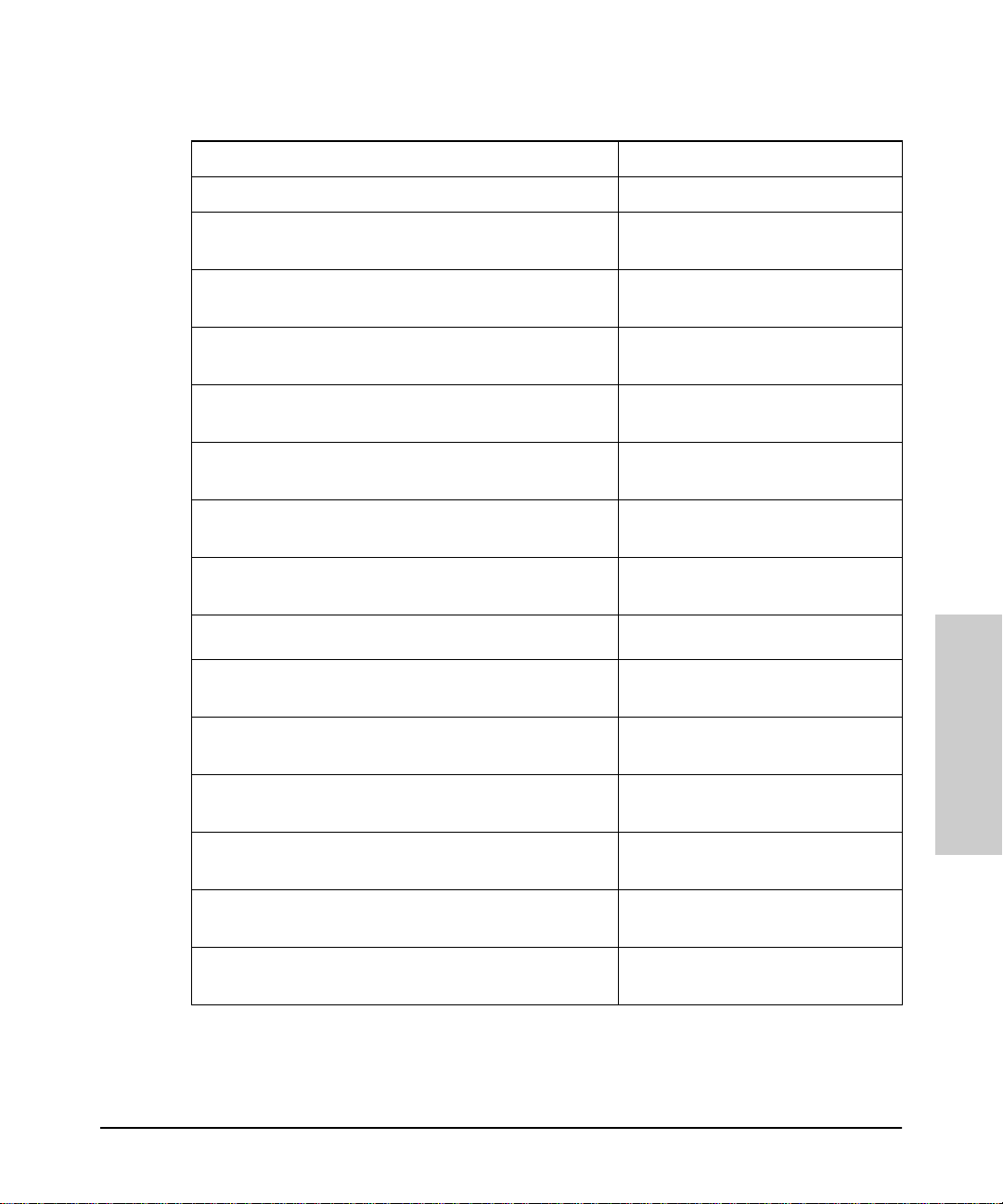
Table 3-1. HP Devices That Can be Managed
Introduction to HP Hub & Switch Management
What HP Devices Can Be Managed
HP J3174A AdvanceStack Switch 208T
HP J3177A AdvanceStack Switch 224T
HP J3200A AdvanceStack 10Base-T Switchi ng Hub-12R
Note 6
Note 6
Note 7
Browser-manageable (firmw are A.0 3 .xx)
HP J3202A AdvanceStack 10Base-T Switchi ng Hub-24R
Note 7
Browser-manageable (firmw are A.0 3 .xx)
HP J3204A AdvanceStack 10Base-T Swit ch ing Hub-24T
Note 7
Browser-manageable (firmw are A.0 3 .xx)
HP J3222A AdvanceStack 100Base -T H ub-12TXM
Note 8
Browser-manageable
HP J3245A AdvanceStack Switch 800T
Browser-manageable (firmw are B.0 4 .xx)
HP J3301A AdvanceStack 10Base-T Hub 12M
Browser-manageable (firmw are A.0 1 .xx)
HP J3303A AdvanceStack 10Base-T Hub 24M
Browser-manageable (firmw are A.0 1 .xx)
HP ProCurve Family of Switches
HP J3298A HP Procurve Switch 212M
Browser-manageable
Introduction to HP Hub &
Switch Managemen t
HP J3299A HP ProCurve Switch 224M
Browser-manageable
HP J4110A HP ProCurve Switch 8000
Browser-manageable
HP J4210A HP ProCurve Switch 1600
Browser-manageable
HP J4121A HP ProCurve Switch 4000M
Browser-manageable
HP J4122A HP ProCurve Switch 2400M
Browser-manageable
3-5
Page 22

Introduction to HP Hub & Switc h Management
What HP Devices Can Be Managed
Table 3-1. HP Devices That Can be Managed
Note 1
Optional SNMP module for HP 100 VG hubs is J2414A or J2414B
Note 2
Optional SNMP module for 10Base-T hubs is J2603A/B. HP AdvanceStack 10Base-T hubs provided�
with SNMP module preinstalled include: HP J2630A (12-port), HP J2631A/B (24-port), HP J2632A/B (48-�
port).�
Note 3
SNMP module J3133A available for J2610B and J2611B. �
Note 4
HP J2980A 10/100 LAN Switch-16 is not supported on IPX networks. To discover this device on an �
IP network, the SNMP community name “public” must be configured on the device.100VGmodule J2981A
and 100BaseTX module J2984A available for HP J2980A.
Note 5
No IPX Network Management support.
Note 6
Requires Management Module J3178A.
Note 7
Requires Management Module J3210A.
Note 8
No Closeup View provided. Use telnet.
Note: HP AdvanceStack hubs can be chained together on a nonnetwork connection called a Distributed Management Chain. For Hub
& Switch Management to access a chain of AdvanceStack hubs, at least
one hub in the chain must contain an SNMP module. Chained hubs
must be of the same media type (100VG or 10Base-T). For more
information, refer to the device’s installation and reference manual.
Introduction to HP Hub &
For general management of generic SNMP devices (from HP and other
vendors), use the HP OpenView Network Node M an ager functions (such as
SNMP Configuration and SNMP MIB Browser).
Switch Management
3-6
Page 23
Running HP Hub & Switch Management
This chapter describes how to start and stop HP Hub & Switch Management.
It includes the following topics:
■ Starting the Manager Application
■ Verifying Installation of the Manager Product Set
■ Stopping and Restarting the Manager Application
Note: Before you begin, yo u should ensure that the network devices ar e
properly set up for IP operation. For information on setting up HP
network devices, see
Starting the Manager Application
Appendix A
.
4
The entire product set that you have installed is started as one application,
“the manager”, on your management stat ion. In other words, HP Hub &
Switch Management starts along w it h Ne twork Node Manager.
Starting HP OpenView
Do the following steps to start your product.
1. Add /opt/OV/bin to your path using one of the commands below. Note
that you only need to do this the first time you start the HP OpenView
manager software.
For These Shells Use These Commands
/bin/ksh or /bin/
sh
/bin/csh� setenv PATH “$PATH:/opt/OV/bin:/usr/
PATH=$PATH:/opt/OV/bin:/usr/sbin
export PATH
sbin”
4-1
Running HP Hub & Switch
Management
Page 24

Running HP Hub & Switch Management
Starting the Mana ger Application
2. Optionally, execute the /opt/OV/bin/ovstatus command to verify
that the trapd, ovwdb, ovtopmd , and netmo n background processes are
running. If the background processes are not running, execute the
/opt/OV/bin/ovstart command. If you are surprised that a background process is not running, run ovstart -v, whic h gi ve s you more
information. The ovstart command starts the background proc esses.
(You must be root to perform this step.)
3. If you are not running X Windows (X Windows, HP VUE or HP CDE for
HP-UX systems), start it.
4. Optionally, if you want to redirect your X Windows displa y to a system
other than the management system:
a. Set your X Windows
management system using one of the commands below. Replace
hostname with the host name of the sy stem to w hich you are
redirecting the display.
For these shells Use these commands
DISPLAY
variable onthe HP OpenView network
Running HP Hub & Switch
Management
/bin/ksh or /bin/
sh
/bin/csh setenv DISPLAY hostname:0.0
DISPLAY=hostname:0.0
export DISPLAY
5. Make sure that the management system has permission to display
windows on hostname. If the management system does not have permission, and if the hostname is using the host-based authorization, use the
xhost command to add the management system to the xhost table on the
hostname system. To do so, on hostname type:
xhost + <managementsystem name>
where managementsystem name is the host name of the management
system. If the hostname is using the MIT-MAGIC-COOKIE-1
authorization, please refer to the xauth man pages to set up the
.Xauthority file.
6. Start the graphical network map (user interface) by typing:
ovw
ovw is executable by anyone.
Alternatively, you can run ovw in the background to free up the ter minal
window for other uses. In some cases, ovw prints error messages to
standard output and stand ar d error. To capture these messages and to
4-2
Page 25
Verifying Installation of the Mana ger Product Set
Running HP Hub & Switch Management
prevent jobs from stopping, you may want to redirect messages to a
temporary file. To run ovw in the background and to redirect error
messages to a temporary file, type
ovw > /tmp/ovw.log 2>&1 &
This starts up the entire product set y ou have installed. The graphical
network map will be generated in a window, w it h the H P Hu b & Switch
Management menu items availa ble in the pull-down menus from the
menu bar.
For more information, ref er to t he HP OpenView Network Node
Manager Reference and the various man pages on the processes.
Verifying Installation of the Manager
Product Set
If the products are installed properly, you should find the menu items
associated with HP hubs, bridges, and sw it ches under the “Options” and
“Monitor” menus. The Menu items that H ub & Sw itch Management adds to
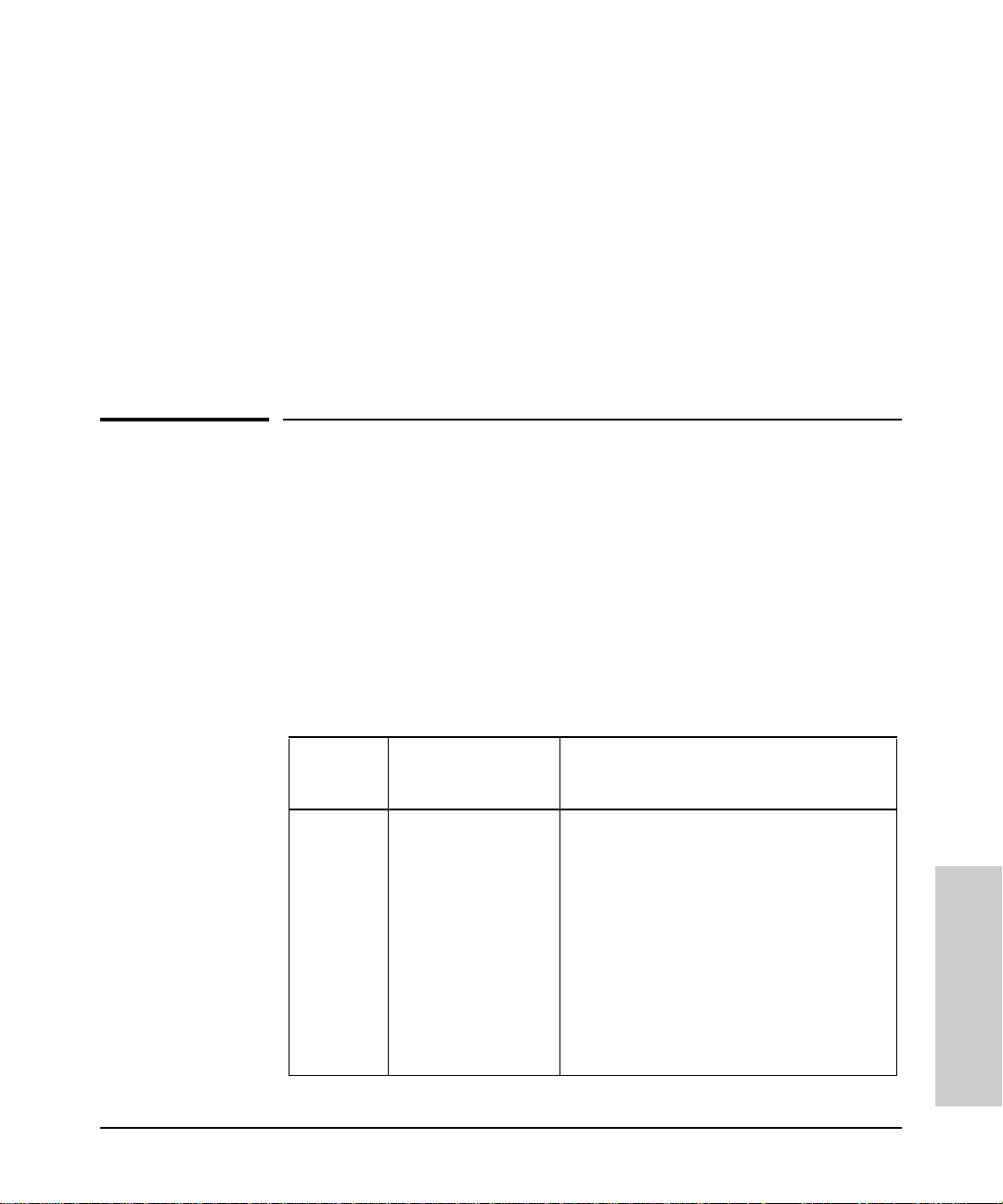
Network Node Manager are shown in the following table.
Tabl e 4-1. OpenView Menu Items
OpenView
Menu
Monitor HP Hu b/Switch Monitor HP Hub/Switch: Displays a graphical
Menu Item added by
HP Hub & Switch
Management
Description
control panel (Closeup View) of a selected (IPaddressed) HP hub , brid ge, or switch.
SNMP Configuration: Allows you to configure
the following on the devices that can be
managed with a browser:
Thresholds
Tra p Re ceivers
Community Names
Authorized Managers
Running HP Hub & Switch
Management
4-3
Page 26
Running HP Hub & Switch Management
Stopping and Restarting the Manager Application
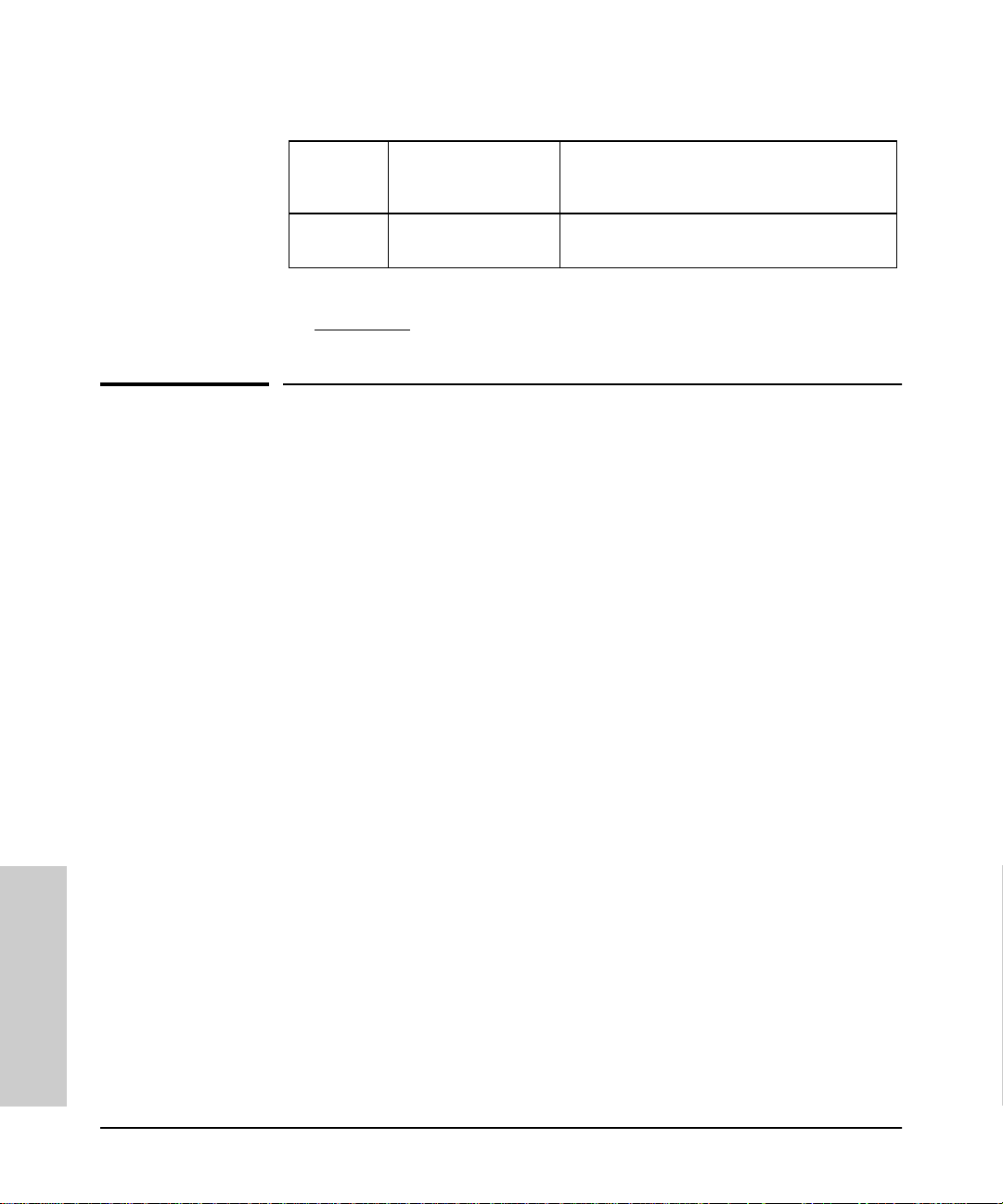
Table 4-1. OpenView Menu Items
OpenView
Menu
Options HP Hub & Switch
Menu Item added by
HP Hub & Switch
Management
Admin
Description
Runs the HP Admin utility for setting Hub &
Switch Management parameters.
Note: For information on setting up network devices for IP operation,
see
Appendix A.
Stopping and Restarting the Manager
Application
Stopping the Manager
Stopping the manager consists of:
1. Exiting the manager’s graphical network map and user interface, and
2. Optionally stopping the manager’s background processes.
To exit from the network map and interfa ce (ovw), select Exit in the map’s
File menu.
Running HP Hub & Switch
If you want the manager to continuously collect data and monitor changes
even when the map and interface are not up (that is, even if you exit from
ovw), do step 1 and not step 2. The background pr ocesses—netmon, trapd,
ovwdb, ovtopmd, and snmpCollect—w ill continue to run and you need only
run /opt/OV/bin/ovw to return to the map and in terface. For more
information on these background processes, refer to the HP OpenView
Network Node Manager Reference manual or read the man page for the
process.
If you want to stop the background processes, use the command /opt/OV/
bin/ovstop. Using ovstop without arguments stops all of the
processes—netmon, trapd, ovwdb, ovtopmd, a nd snmpCollect—in the
correct order.
Management
4-4
Page 27

Stopping and Restarting the Manager Application
Running HP Hub & Switch Management
Restarting the Manager
If you have stopped the background processes and you want to restart them,
use the command /opt/OV/bin/ovstart.
4-5
Running HP Hub & Switch
Management
Page 28

Running HP Hub & Switch Management
Stopping and Restarting the Manager Application
Running HP Hub & Switch
Management
4-6
Page 29

Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
HP Proactive Networking
Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
This chapter contains information on:
■ HP Proactive Networking
■ Interpreting the Alert Log
HP Proactive Networking
HP Proactive Networking offers the comb ined benefits of outstanding products and effective, easy-to-use network management that provide you with the
control, uptime and performance your network needs.
Note: Devices that are manageable with your Web browser featur e HP
Proactive Networking. For older HP devices, read the chapter
“Management for Non-Browserable Devices” or see the online help.
5
Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
Control
Control with Management. Improve c ontrol of your network with:
■ Increased visibility into the network by monitoring all segments and
displaying network performanc e information
■ Compatibility with other vendor’s products
Control with Technologies. For your future network, you will need to rely
on emerging technologies. Two principal emerging technologies that HP
provides are:
■ Gigabit Ethernet. This technology i s the natu ral evolut io n of 10Base -T
and 100Base-T. It is the high-performance network of the future.
5-1
Page 30

Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
HP Proactive Networking
■ Advanced Switching. New switching techniques like meshing, VLAN
tagging, and voice and data handling provide high performance
networking for the future.
Control of Costs. HP provides Tot al Cost of Ownership benefits by
focusing on “out-of-the-box” manageability based on a combination of HP Top
Tools for Hubs & Switches and management-enabled hardware.
Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
Uptime
Find, Fix, Inform. The Find/Fix/Inform feature of HP Proactive
Networking discovers, corr ects, and reports on problems that occur on the
network. The three parts are:
■ Hardware Agent. The hardware agent monitors the network continu-
ously, automatically balancingtrafficand finding and fixingmost common
network problems.
■ Management Software. The Web browser-based user interface provides
a consistent, friendly environment fo r monitoring your network.
■ Network Manager. HP Hub and Switch Management for OV-UX helps
you achieve maximum control, uptime, and performance by lett ing you
manage the network anytime, anywhere.
Quality and Reliability. High quality, reliable HP products will help keep
your network running into the next century. HP’s Quality of Service provides
service-level guarantees for mission critical applications and multimedia
communication applications.
Best Warranty and Support. HP products are backed by a lifetime
warranty (for as long as you own the product) and free end-user telephone
support. Every HP Proactive Ne t w orking product is Year 2000 ready.
5-2
Performance
Bandwidth Performance. Video and multimedia applications require large
amounts of bandwidth. HP has these solutions to meet your bandwidth needs:
■ A line of high-speed hubs and switches that deliver extensive bandwidth
to the desktop. HP hubs and switches use industry-standard Ethernet
technology with its low cost and scalability from 10 Mbps to 1,000 Mbps.
■ Protocols and product software that co ntrol bandwidth utilization and
improve information delivery
■ Backbones that are fast, reliable and robust
Page 31

Interpreting the Alert Log - Find/Fix/Inform
■ Switch meshing for switching
■ Cisco Fast EtherChannel
HP Proactive Networking produc t s save time, money and increase productivity.
®
for servers
Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
Interpreting the Alert Log - Find/Fix/
Inform
The Alert Log is displayed in the lower area o f the device’ s Status -Overview
page. Its “Find/Fix/ Inform” (patent pending) capability helps you proactively
manage your network by displaying network traps and problem conditions in
one easily accessible browser page. It displays messages about events that
have occurred on the device, such as loss of link, a problem cable , or a
broadcast storm. Select Open Event or double-click on an alert to display
more information.
Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
Figure 5-1. Find/Fix/Inform — Notify and provide possible solutions
5-3
Page 32

Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
Interpreting the Alert Log - Find/Fix/Inform
The dialog box displays more infor ma tion about the alert as well as some
suggestions for fixing the problem. When you have reviewed an alert, the
“New” icon is nolonger displayed. Closingan alert indicates that it is no longer
a problem.
The following table shows the common faults and how they are indicated.
Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
Table 5-1. Find/Fix/Inform Faults
Problem How the Problem is In di cated
Fault 1: Problem Driver or Network
Interface Card (NIC)
Fault 2: Problem XCVR or NIC Indicated by long packets with bad CRCs.
Fault 3: Problem Cable Indicated by normal size packets with CRC
Fault 4. Cable Length/Repeater Hops Indicated by late collisions.
Fault 5: Over Bandwidth Indicated by a high collision rate.
Fault 6: Broadcast Storm Indicated by a high rate of broadcast packets.
Fault 7: Auto Partition (hubs only) Indicated by a port repeatedly partitioning and
Fault 8: Misconfigured SQE (hub only) Indicates a misconfigured transceiver detected
Fault 9: Polarity reversal (hub only) Indicates a mis-wired cable detected by internal
Fault 10: Network Loops Indicated by a high traffic level in correlation
Indicated by long or short packets with good
CRCs.
errors.
healing due to a network loop or problem cable.
by internal hardware.
hardware.
with duplicate traffic on the network.
5-4
Fault 11: Link Loss Lost link beat to a cascade port.
The Find/Fix/Inform function runs continuously in the background at a sensitivity threshold level that you select. Sensitivity threshold settings control the
severity of the alerts that are displayed. The settings internally adjust the
counter thresholds automatically.
Page 33

Interpreting the Alert Log - Find/Fix/Inform
Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
Sensitivity settings are selected in the Configuration page for the device. Select
the Fault Detection button. For hubs, you can set the sensit ivity for logging
network problems and disabling ports. Switches only have a sensitivity setting
for logging network problems. Switches are more capa ble of isolating problems occurring on a single port than h ubs are.
The sensitivity settings are:
■ High Sensitivity: the device will act when a network problem of any
severity occurs. Network problems are automatically detected and
entered into the Alert Log (located unde r the Status Tab).
■ Medium Sensitivity: the device will act when serious network problems
occur.
■ Low Sensitivity: the devicewill act only when severe ne twork problems
occur. These are problems that may bring the network down.
■ Never: The device will never take any actio ns regardless of the severity
of the problem.
Only serious and persistent problems that impact other users on the network
will cause a hub to disable a port. These problems include:
■ A problem XCVR or NIC
■ A broadcast storm
■ Excessive Auto Partitions
■ A network loop
Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
A warning is entered in the Alert Log shortly before the port is disabled.
Another entry is made indicating that the port has been disabled.
Acknowledging Events. Click on the Acknowledge Selected Events
button to indicate that you have seen the alert. Acknowledging an alert
changes its st a te from new to open.
Closing Events. To close an alert and remove it from the Alert Log, select
the alert and click on t he Close Events button.
Sorting Events. Double-click on the column head to sort the alerts
according to severity, the name of the alert, the address of the device, or the
date and time of the alert.
Deleting Events. Click on the Delete Selected Events button to remove
these alerts from the Alert Log.
5-5
Page 34

Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
Interpreting the Alert Log - Find/Fix/Inform
First Time Installation Information. There will be an entry in the Alert
Log for first time installation information for the device.
5-6
Page 35

Accessing Hub Features
HP Hub & Switch Management lets you manage your HP devices with your
browser from anywhere in your network. Several features provide
information about the status of your device, alert you to problems in your
network, and give you the ability to configure settings for proactive network
management.
Note: For older HP devices that cannot be managed with a Web
browser , read the chapter “ Management for Non-Browser able Devices”
or see the online help.
This section includes information on:
■ Accessing the Device View
■ Viewing Device Identity Information
■ Interpreting Device Status
■ Reading the Performance Gauges
■ Status - Global Counters
■ Configuring Your Device
■ Fault Detection
■ Load Balancing
■ Support
More Information on Device Features
Accessing Hub Fe atures
6
Accessing Hub Features
More Information on Device Features
See Setting Up Security for a Device for information about device security .
See Performing Diagnostics
performing Link and Ping tests.
for information about resetting d evic es and
6-1
Page 36

Accessing Hub Feature s
Accessing the Device View
Accessing the Device View
To launch the Device View, double-click on a device symbol in the HP
Network Node Manager map or right-mouse-click on the device symbol and
select Monitor HP Hub/Switch. The Status -Overview page for the device
displays. Select the Configuration tab and click on Device View to display
the port view of the device.
Viewing Device Identity Information
Y o u can view some basic information about the device by selecting the
Identity tab. Y ou ca n change the information by selecting th e Configuration
tab and clicking on the System Informa tion button.
Accessing Hub Features
See the online help for information about setting or changing these values.
6-2
Interpreting Device Status
The Status - Overview page for the hubs displays the Performance Gauges
and any alerts that have occurred. For switching hubs, the Status - Overview
page displays gauges by segment inst ead of by attribute.
Page 37

Figure 6-1. Hub Status Overview Page
Accessing Hub Fe atures
Interpreting Device Status
Accessing Hub Features
Reading the Performance Gauges
The performance gauges display statistical information abo ut the selected
device. By looking at the gauges, you can q uickly determine if there are
problems with the network utilization, collisions, the numb er of broadcasts
per second, or the number of error packets. The gauges are refreshed every
five seconds.
The information shown for hubs is for all ports on the device. You can obtain
information for each port by selecting the Performance Gauges button, then
selecting an individual port from the drop down list. If you want to monitor a
different attribute for that port, just select the desired attribute from the
drop down list below the port number.
The following table explains the attributes and gives their threshold settings
on a per port basis for hubs. These settings cannot be changed. You can view
an attribute value for all the ports of a device by selecting All Ports from the
drop down list above the attribu te. For the switching hubs, you can also
select a segment from the drop down list.
6-3
Page 38

Accessing Hub Feature s
Interpreting Device Status
Table 6-1. Gauge Attributes for Hubs
Attribute Description Severity Values
Utilization% Represents the traffic on the port as a
percentage of the port’s bandwidth.
Collisions% Represents the number of collisions that have
occurred expressed as a percentage of the
packets transmitted through the port.
Broadcasts/sec Represents the number of broadcast packets
being transmitted throug h the port pe r second.
Errors% Represents the number of errors that have
occurred expressed as a percentage of the
total number of packets received through the
port.
Multicasts/sec Represents the number of multicast packets
being transmitted throug h the po rt per second.
Warning: 40%
Critical: 75%
Warning: 30%
Critical: 50%
Warning: 150/sec
Critical: 400/sec
Warning: 0%-1%
Critical: 1%
Warning: 1500/
sec
Critical: 4000/sec
Accessing Hub Features
Status - Global Counters
Hub Global Counters
Selecting the Global Counters button displays a page listing eight counters
and their values since the last device reset. The counters are totals for the
device. To view counters by port, select the Port Cou nters tab.
6-4
Switching Hub Global Counters
The switching hubs display the count ers described in the following table.
Tabl e 6-2. Switching Hub Global Counters
Counter Description
T otal Packets T otal number of packets (including bad pa ckets, broadc ast
packets, and multicast packets) received.
Page 39

T able 6-2. Switching Hub Global Counters
Counter Description
Accessing Hub Fe atures
Configuring Your Device
To tal Octets Total number of octets of data (including bad packets)
received on the network. This object can be used to
estimate Ethernet utilization.
Broadcast Packets Messages sent to all users on the network.
Multicast Packets Multicast packets are delivered to a subset of users on the
network, as opposed to Broadcast packets, which are sent
to all users.
Collisions When two or more devices attempt to transmit a message
on a cable at the same time, i nterferin g with on e anoth er’s
transmissions. The number of coll isions should be
proportional to the number of p ackets transmitted over ti me
and the number of nodes operating on the network.
CRC/Alignment Errors The Cyclic Redund ancy Check (CRC) is a code typically
placed at the end of the frame or packet to ensure the
integrity of the data within the frame.
Alignment Errors are the number of instances where the
CRC method was used to correct a packet whose bits were
misaligned because of timi ng e rrors.
Fragments Total number of packets received that were less than 64
octets in length and had a bad Frame Check Sequence
(FCS).
Jabbers Total number of packets received th at were longer than
1518 octets and had a bad Frame Check Sequence (FCS).
High levels indicate too many packet transmissions.
Accessing Hub Features
Status - Port Counters
The Port Counters button displays a pa ge with information about important
counters for each port. See the online help for information on each counter.
Configuring Your Device
When you select the Configuration tab the Device View (formerly a Closeup
View) is displayed in the page. The other buttons in this page provide access
to various configuration f e at ures for that device.
6-5
Page 40

Accessing Hub Feature s
Configuring Your Device
If the device you sel ected is not manageable by browser, you can only
manage it from the management workstation.
Accessing Hub Features
Figure 6-2. 10Base-T Hub-12M Device View
Y ou can enable and disable individual ports (click on the port to select it), or
click on the Select All Ports button to enable or disable all the ports of a
device in one step.
For the switching hub, select a hu b or card from the stack using the drop
down list at the top. The Closeup View for that hub or card will d isplay.
To move selected ports to a particular segment:
1. Select the Move Selected Ports to Segment button.
2. Select a hub from the drop down list, then select t he seg ment th at y ou
want to move the port to.
3. Click on Apply Settings.
Click on the link “meaning behind the po rt icons” to view the port indicator
legend.
Configuration - Fault Detection
The automatic fault detection feature protects your network from failing
because of problems such as network loops, defective cables, transce iv er s
6-6
Page 41

Accessing Hub Fe atures
Configuring Your Device
and faulty network interface cards. The Fault Detection page lets you set the
sensitivity and actions that occur when a fault is detected on a port in your
network. For hubs, you can set the sensitivity for l ogging network problems
and disabling ports. The sensitivity settings are:
High Sensitivity: the device will act when a ne twork problem of any
severity occurs. Network problems are automatically detected and entered
into the Alert Log.
Medium Sensitivity: the dev ice w ill act when serious network problems
occur.
Low Sensitivity: the device will act only when severe network problems
occur. These are problems that may bring the network dow n.
Never: The device will never take any actio ns regardless of the severity of
the problem.
Accessing Hub Features
Figure 6-3. Fault Detection Sensitivity Settings
Configuration - System Information
The System Information page lets you enter a system name for the device,
the location of the device, and whom to contact in the event of a proble m.
6-7
Page 42

Accessing Hub Feature s
Configuring Your Device
Configuring IP
Select the way that you want IP add resses configured for your net w ork:
■ Manual - Set the IP address throu gh th e console.
■ Disabled -IP is disabled, there is no access to management or telnet. Not
Recommended.
■ Use Bootp - The Bootp prot ocol sets the IP address automatically.
Hub IP Configuration
If you select Manual, you must then enter an IP Address, Subnet Mask,
Default Gateway, and Time to Live for the device. If you select Bootp/DHCP,
the IP address will be assigned automatically.
Switching Hub IP Configuration
For the switching hubs, you must select a segment to configure before you
select Manual or Bootp/DHCP. If you select Manual, you must then enter an
IP Address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, and Time to Live for the device.
Accessing Hub Features
If you select Bootp/DHCP, the IP address will be assigned automatically.
Characteristics of Bootp and DCHP. The Bootp protocol is designed for
a network in which each host has a permanent network connection. It is not
adaptable to a mobile computing environment.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Prot ocol (DHCP) manages the alloca tion
of TCP/IP configuration information by automatically assigning IP
addresses.When a device connects to the network, it requests an address
from the DHCP server. In dynamic mode, the address is used by the device
for a specified period of time. The time period depends on the situation; one
device may only need the address for an hour, while another device may use
the same address for several days . DHCP is more suitable in environments
where the number of IP addresses needed exceeds the number available. It
also allows a device to obtain its configuration information, such a s the IP
Address and Subnet Mask, in one me ssage, reducing the demand on the
network.
A static IP address is a unique address that is assigned to one client only.
Static addresses are used for an extended time period.
6-8
Page 43

Accessing Hub Fe atures
Configuring Your Device
Port Configuration
The Port Configuration page displa ys information about the hub ports. To
enable a port, select the port number in the page, then click Enable
Selected Port s. Use the Disable Selected Ports button to disable a port
or group of ports.
The information displayed is described in the table.
Ta ble 6-3. Hub Port Configuration
Setting Description
Port The port number.
State The port can be on or off.
Connected Yes: A device is connected to this port.
No: There is nothing conn ected to this port.
Partitioned: The no de i s disconnected from
the network and the traffic that the p ort
generates is lost.
Polarity Reversed: Some signals in the cable
are reversed due to a miswired cable.
Segment For switching hubs, the segment that the port
is on.
Last Source Address The address of the last device that sent
packets through this port.
Security Violation States whether there is a security violation
or no violation.
Configuration - Backup Links
A backup link (hubs only) configures two ports on one hub to create a
redundant connection to another device. This provides a connection with
fault-tolerant capability for highly reliable networking. One port is
designated the primary port; the second port is the backup port. The backup
port becomes active only if the primary port becomes i noperativ e. Any of the
network ports (twisted-pair, ThinLAN, or AUI/Xcvr) can be used as the
primary port or backup po rt.
Accessing Hub Features
6-9
Page 44

Accessing Hub Feature s
Configuring Your Device
Figure 6-4. Setting Backup Links
Accessing Hub Features
You can create one or more backup links by selecting the Backup Links
button and clicking on the Add New Backup Link... button at the bottom of
that page. The parameters are descr ibed in the table.
Table 6-4. Backup Link Parameters
Parameter Description
Status Displays which port is currently b eing used, a primary
port or a backup port.
Primary Port A port that you can use as a primary port, or the port
Backup Port The backup port to be used if there is a failure on the
MAC Address The MAC address of the device that the primary and
Test Time The interval in seconds between test packets sent
that will be used during standard connecti on of a hub
and the connected device.
primary port.
backup ports are connecte d to.
between the primary port and the receiving device.This
checks the integrity o f the link to determin e whether to
initiate a backup link.
6-10
Page 45

Table 6-4. Backup Link Parameters
Parameter Description
Accessing Hub Fe atures
Configuring Your Device
Retries The maximum number of times the primary port can fail
before the backup port becomes active.
Configuring Load Balancing - Switching Hubs
Only the switching hubs provide a load balancing feature to automatically
distribute the switching hub ports among the four segments to optimize
performance. This feature req uires a switch module. To access this feature,
select the Load Balancing button. Click on the Perform Automatic Load
Balancing button. If you wa nt to undo t he load balancing, select the Undo
Last Load Balancing button.
Configuration - Support URL
You can obtain support information by going t o the HP Support site on the
World Wide Web. The URL is:
http://www.hp.com/go/network_city
Select Support.
Accessing Hub Features
Figure 6-5. Support URL
6-11
Page 46

Accessing Hub Feature s
Configuring Your Device
If you want to change the URL that is accessed when the Support tab is
selected, type in the new address and click on the Apply Changes button.
For example, you could change the URL to launch your site home page.
Accessing Hub Features
6-12
Page 47

Managing Switches
This chapter has information on:
■ Switch Status
■ Switch Identity
■ Configuration
■ Using VLANs
■ Support/Mgmt URL
Managing Switches
Switch Status
7
Switch Status
Status - Overview
T o la unch the Status - Overview page for a switch that is manageable by
browser, double-click on the switch symbol in the HP Network Node
Manager map or right-mouse -c lick on the symbol and select Monitor HP
Hub/Switch.
Note: If the devic e is no t manageable by browser you will see the
Closeup View in a separate window (you must launch the Closeup View
from the management station). Read the chapter “Management for
Non-Browserable Devices” or see the online help for more information.
The Status - Overview page is divi de d into two ar ea s, t he Gra ph area and the
Alert Log area.
Managing Switches
7-1
Page 48

Managing Switches
Switch Status
Figure 7-1. Switch Status Overview Page
Graph Area
The bar graph gives a quick overview of the performance of the switch. Each
bar shows the highest percentage of transmitted (TX) or received (RX)
traffic utilization for that port in the last five seconds.
The graph area proport ionally depicts three attributes for each por t:
Managing Switches
■ Unicast packets - The percent utilization for packet s that were not
addressed to a multicast or broa dcast address.
■ Non-Unicast packets -The percent utilization of received non-unicast
packets (bothbroadcast andmulticast). If there is abroadcast storm,only
the portreceiving these packets shows high utilization, letting you quickly
pinpoint the problem.
■ Errors - The percent utilization for error packets received. A high
percentage may indicate possible network problems.
Place the cursor over a bar in t he graph to display the exact percentages for
each attribute and the speed of that port. The above graph displays a high
percentage of non-unicast packets on port 2 (a 10 Mbps port) becau se this
port is running video. Port 5 is indicating some errors.
7-2
Page 49

Managing Switches
Switch Status
The graph only scales to 40% utilization. Network utilization above this level
indicates serious performa nce problems.
The graph also shows you if a port is active, dis a bled, or not connected.
Alert Log Area - Find/Fix/Inform
The “Find/Fix/Inform” capability of a device helps you proactively manage
your network by displaying netw ork traps and problem conditions in one
easily accessible browser page. The device itself monitors counte rs, in ternal
hardware information, and network t ra f f ic. When a problem is discovered,
such as loss of link, a problem cable, or a broadcast storm, the Alert Log
displays clear messages about the problem. When you double -c lick on an
alert in the Alert Log (or select the alert and click on the Open Event button),
the Alerts page displays more information about the alert as well as some
suggestions for fixing the problem.
For example, the Alert Log may display the alert “Cable Length”. The
following information is available:
Description:
Packet loss detected on port 4. This may be due to an overextended LAN
topology or faulty hardware . The loss was detected on this port, but the
actual problem can be occurring elsewhere on this segment.
Solution:
Managing Switches
■ Verify the ne twork topo logy is within IEEE 802.3 topology standards. All
ThinLan coaxial cabling must be 185 meters or shorter. No more than 4
repeaters are allowed between any two stations in the network.
■ Insertbridges or switches between repeaters to extendnetwork topology
if needed.
■ Also, check for faulty cablin g, transceivers, and NICs.
Using the Find/Fix/Inform capability, the device can isolate a problem that
occurs on one port, preventing it from affecting the entire network.
See Alerts - Find/Fix/Inform
for information on reading and acknowledging
alerts.
Status - Port Counters
The Port Counters information for switches displays specific network
conditions or traffic. See the online help for more information a bout each
counter.
7-3
Page 50

Managing Switches
Switch Status
Status - Port Status
The Port Status page (switches only) d ispla ys the operational status of each
switch port. The settings can be changed in the Configuration -Port
Configuration page.
The Port Status settings are describe d in t he fo llow ing table.
Ta bl e 7-1. Port Status Settings
Setting D es c ription
Port The port number.
Port Type The network type of each switch port, for example, 100TX.
Enabled Whether the port is enabled or disabled.
Link Status The port’ s current operational status. Up means the port is working
correctly. Down m eans the port is disabled.
Current Mode The operational mode of the port.
• 10/100 Base TX -Can be 10 Mbits half or full duplex or 100 Mbits
half or full dupl ex.
• 100 Base FX - Can be 1 00/f ull dupl ex o r 100/half duplex.
• Gigabit - Can only be 1000 full duplex.
Flow Control Indicates the current state of flow control for this port.
• 10/100TX, 10 FL, 100 FX:
– On - Flow control is enabled.
– Off - Flow control is disabled (default).
• Gigabit:
Managing Switches
Bcast Limit (not
available on
the HP J3298 A or HP
J3299A)
– On (TX, RX) - Flow control is enabled on transmit and
receive.
– On (RX) - Flow control on receive only.
– Off (default) - Flow control is di sabled.
The Broadcast Limit, expressed as a percentage of broadcast
packets relative to the theoretical limit. Any broadcast or multicast
traffic exceeding this limit will be dropped. A value of zero
indicates that no l imit i s to be applied. Values range from 0- 99.
7-4
Page 51
Managing Switches
Identity
Identity
The Identity tab displays the following information about the switch:.
■ System Name ■ Product Number and Name
■ System Location ■ Firmware Version
■ System Contact ■ IP Address
■ System Up-Time ■ Management Server
The Management Server field di splays the a ddress (URL) of th e management
station where HP Hub & Switch Management was insta lled. This can be
changed by selecting the Configuration tab a nd displaying the Support/
Mgmt URLs page. Enter the URL in the Management Server URL field.
Online help can be displayed at any clie nt when this URL is set correctly.
Configuration
The Configuration page lets you configure many device features, for
example, the sens itivity levels for Fault Detec ti on.
Device View
There is a Device View for every managed HP switch. The Device View for
the HP ProCurve Switch 8000M looks like the following graphic. Use the
online help to obtain information a bout specific switch modules.
Managing Switches
7-5
Page 52

Managing Switches
Configuration
Figure 7-2. HP ProCurve Switch 8000M Device View
Configuration - Fault Detection
The automatic fault detection feature protects your network from failing
because of problems such as network loops, defective cables, transce iv er s
and faulty network interface cards. Network problems are automatica lly
detected and entered in the Alert Log. The Fault Detection page lets you set
the sensitivity levels for the actions to be taken wh en a fau lt is d etect ed on a
port in your network. Switches only have a sensitivity setting for logging
Managing Switches
7-6
network problems. The sensitivity se tting s are:
High Sensitivity: The device will make an entry in the Alert Log (located in
the Status tab) when a network problem of any severity occu rs.
Medium Sensitivity: The device will make an entry in the Alert Log when
serious network problems occur.
Low Sensitivity: The device will make an entry in the Alert Log only wh en
severe network problems occur. These are problems that may bring the
network down.
Never: The device will never make any entries in th e A lert Log re gar dless of
the severity of the problem.
Page 53

Managing Switches
Configuration
Configuration - System Information
The System Information page lets you enter a system name for the device,
the location of the device, and whom to contact in the event of a proble m.
Configuration - IP Configuration
Select the way that you want IP add resses configured for your net w ork:
■ Manual - Set the IP address throu gh th e console.
■ Disabled -IP is disabled, there is no access to management or telnet. Not
Recommended.
■ Use Bootp - The Bootp ( or DHCP) protocol sets the IP address automat-
ically.
If you select Manual configurat ion, you can change the IP address, a subnet
mask, and a default ga t eway for the device.
Some switches let you configure an IP address for every VLAN you hav e
created.
Figure 7-3. Switch IP Configuration
Managing Switches
7-7
Page 54

Managing Switches
Configuration
Characteristics of Bootp and DHCP. The Bootp protocol is designed for
a network in which each host has a permane nt network location. It is not
adaptable to a mobile computing environme nt.
The Dynamic Host Configuration Prot ocol (DHCP) manages the alloca tion
of TCP/IP configuration information by automatically assigning IP
addresses.When a device connects to the network, it requests an address
from the DHCP server. In dynamic mode, the address is used by the device
for a specified period of time. The time period depends on the situation; one
device may only need the address for an hour, while another device may use
the same address for several days . DHCP is more suitable in environments
where the number of IP addresses needed exceeds the number available. It
also allows a device to obtain its configuration information, such a s the IP
Address and Subnet Mask, in one me ssage, reducing the demand on the
network.
A static IP address is a unique address that is assigned to one client only.
Static addresses are used for an extended time period.
Configuration - Port Configuration
The Port Configuration page displays information about the switch ports.
The settings are explained in the following table. To modify a port setting,
click on a port then select the Modify Selected Ports button. Modify
multiple ports at one time by using Ctrl-Click to select the desired ports.
Note: Some switches support trunking. For information on trunking,
see the online help for that device.
Managing Switches
7-8
Page 55

Modify port settings
Managing Switches
Configuration
Figure 7-4. Switch Port Configuration
Ta ble 7-2. Switch Port Configuration Settings
Setting Description
Port The port number. The port may be appended with one of the
following:
• Trkx -The port trunk to which this port belongs
• Mesh - The port has been assigned to a switch mesh domain
• MP - The port is a Monitor Port
Port Type The MAC layer type, for example, 100VG or FDDI.
Enabled Whether the port is enabled or disabled.
Config Mode The speed and duplexing fo r the port. Auto mode will negotiate
with the device on that port to determine the mode.
Click on Modify Selected Ports to ch an ge t he mode.
Managing Switches
7-9
Page 56

Managing Switches
Configuration
Ta ble 7-2. Switch Port Configuration Settings
Setting Description
Flow Control Indicates the current state of flow control for this port. When
Bcast Limit The Broadcast Lim it, expressed as a percentage of broadcast
disabled, the port does not generate flow cont rol packets and
drops any flow control packets it receives.
• 10/100TX, 10FL, 100FX:
– On - Flow control is enabled.
– Off - Flow control is disabled (default).
• Gigabit:
– On (TX, RX) - Flo w control is enabled on transmit and
receive.
– On (RX) - Flow control on receive only.
– Off (default) - Flow control is disabled.
packets relative to the theoretical limi t. Any broadcast or multicast
traffic exceeding this limit will be dropped. A value of zero
indicates that no limit is to be applied.Values range from 0-99.
Configuration - Assigning a Monitoring Port
The Monitor Port tab (only found on switches) lets you select a “Monitoring
Port” that you can use with a network analyzer to monitor other ports on the
switch. For the HP J3298A and HP J3299A you can only choose the
Monitoring port and the port to be monitored. For other switches you ca n
choose to have all the ports for one VLAN monitored, or you can select
individual ports to be monitored . See th e online help for information on
specific switches.
Managing Switches
7-10
Page 57

Figure 7-5. Selecting a Monitoring Port on a Switch
Managing Switches
Configuration
Using VLANS
Virtual LANs, or VLANs, are generally defined as broadcast domains created
with software rather than being a funct ion of t he hardware. They can be
viewed as a group of end nodes, possibly on different physical LAN
segments, that can commu nicate with each other.
As networks expand, more routers are needed to separate users into
broadcast domains. Latency degrades network performance, and is a special
problem for multimedia applications. Switches using VLANS create the same
division of the network into broad cast domains, but do not have the latency
problems of a router. Switches are also a more cost-effective solution. You
can create virtual LANs by assigning selected ports of your HP switch to a
VLAN.
The benefits of VLANs include:
■ Grouping users into logical networks for increased performance
■ Providing an easy, flexible, less costly way to modify logical groups in
changing environments
■ Preserving current investment in equipment and cabling
■ Allowing administrators to “fine tune” the network
■ Providing independence from the physical topology of the network
Managing Switches
7-11
Page 58

Managing Switches
Configuration
VLANs make large networks more manageable. You can group users
according to some shared characteristic, such as a common business
function or a common protocol. A single switch may have several
independent VLANs within it.
Note: VLANs must be created with the device console.
Configuration - Device Features
The Device Features page (only found on sw itches) lets you set some or all
of these features:
■ Automatic Broadcast Control (ABC)
■ Multicast Filtering (IGMP)
■ Spanning Tree
Automatic Broadcast Control (ABC)
Automatic Broadcast Control (ABC) is a feature that controls broadcasts
through IP/IPX Broadcast Reduction. IP /I PX Broadcast Reductio n reduces
the number of broadcas ts propagated through the network.
Using ABC, the switch acts as a proxy server, replying to Address Resolution
Protocol (ARP) requests, Nearest Server Query (NSQ) requests, and
GetLocalTarget requests on behalf of the destination node. An ARP cache
(learned address table) is created for each subnet allowing the swit ch to
proxy reply with the resolved MA C address instead of forwarding the
requests out all ports. This limits the broadcasts within the switching
domain. The Service Advertising Prot ocol (SAP) table performs the same
function in an IPX network. By using these tables, the switch can resolve
Managing Switches
addresses for any node in the network that it already knows about.
Routing Information Protocol. The switch also intercepts Routing
Information Protocol (RIP) and SAP broadcasts and forwards these only to
ports where routers and servers have been detected. This also reduces the
number of broadcasts on t he network.
For example, if User A sends out a broadcast message to connect to its
server, the request is sent out of all ports on the switch. When th e s e rver
responds to User A, the switch intercepts the response and learns that the
server is on that port. When User B sends a request to the same server, the
switch already knows which port that server is on and sends that
information to User B, just as if the server had responded to the request.
User B’s request is not broadcast out any of the switch ports.
7-12
Page 59

Managing Switches
Configuration
Enabling Broadcast Control for IP
The IP protocol uses Address Resolution Protoc ol (ARP) packets to find the
MAC address of a node that corresponds to the network layer address. When
Broadcast Control is enabled, the switch intercepts the ARP packet on its
way to the destination node. If this destination is unknown to the switch, the
switch floods the ARP request to all ports. When the destination port
responds, the switch stores information about the source and destinat ion
MAC addresses and layer 3 addresses in its ARP cache. This information
allows the switch to proxy a reply containing the MAC address of a
destination to the source of an ARP request. The source can then send a
unicast packet directly to the destination. The amount of broadcast traffic
has been decreased.
Automatic IP RIP Control. To further reduce broadcast traffic, you can
check Automatic IP RIP Control. IP RIP packets are sent out periodically
(every 30 seconds) to distribute routing information. By enabling Automatic
IP RIP Control, the switch will only forw a rd R I P packet s out the ports on
which RIP packets have been received. Since routers are the only devices
that generate RIP packets, this ensu res that RIP packets are only sent out
ports with routers attached to t hem. When this featu re is not enabled, IP RIP
packets are forwarded to all ports.
Enabling Broadcast Control for IPX
The IPX protocol broadcasts all of its kno wn routes and services every
minute by using IPX, RIP and Service Adv e rtising Protocol (SAP) packets.
When servers are booted u p, they advertise their services using SAP. These
frames must be forwarded by routers, which maintain a database of this
information, allowing clients on the netw ork to obtain the internetwork
addresses of the servers where they can access services.
Automatic IPX RIP/SAP Control. To further reduce network traffic, you
can check the Automatic IPX RIP/SAP Control check box. The switch will
intercept RIPs and SAPs, broadcasting them only to ports where IPX routers
or servers have been detected, or to ports that have been configured to
transmit RIPs or SAPs. When this feature is not enabled, IPX RIP/SAP
packets are forwarded to all ports.
Automatic IP Gateway Configuration
When Automatic IP Gateway Configuration is ena bled, the switch will
modify replies from the DHCP server so that the Default Gateway IP address
of client becomes the client’s own IP address. This is useful in a multinetted
7-13
Managing Switches
Page 60

Managing Switches
Configuration
environment (where more than one I P network is configured in a single
broadcast domain).
See Routing Information Protocol.
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
Multimedia and email applic ations need the ability to communicate to
multiple destinations efficiently. IP multicasting allows hosts to dynamically
register for sending or receiving multicast traffic.
The Internet Group Management Prot ocol is a method for automatically
controlling multicast traffic through the ne twork. Using multicasting,
applications can send one copy of a packet addressed to a g roup of
computers that wish to receive it. This method is more efficient than sending
a separate copy to each node. Other advantages of multicasting includ e:
■ information delivered in a timely, synchronized manner because all desti-
nation nodes receive the sam e pa c ke t
■ information can be sent to destinations whose addresses are unknown
■ reduces the number of packets on the network because only one multicast
packet is sent.
IGMP uses multicast queriers and hosts that support IGMP to manage
multicast traffic on the network. It specifies how the host informs the
network that it is a member of a multicast group. A set of queriers and hosts
that send and receive data from the same set of sources is a multicast group.
The HP switches have a standards-based IGMP implementation. The
switches process IGMP packets by learning which of the switch’s interfaces
are linked to hosts that are members of multicast groups and multicast
routers. It limits multicast traffic by monitoring the IGMP traffic to learn
Managing Switches
which hosts are in which multicast groups, then allowing IP multicast traffic
to be sent only to ports with valid host gro up members.
When a switch receives an IGMP packet, it updates the internal IP multicast
forwarding table with the IGMP me mbership read from that packet. The
switch then sends the packet to the ports with members of the destination
multicast group.
Special multicast routers/queriers com municate b y using three message
types - query, report, and leave group. The query message, sent by a querier,
is used to discover which network interfaces belong to a multicast gr oup.
Each host responds to the query message with a repor t message that tell s the
querier the host is a member of the multicast group. The host also can send a
report message to join a group or a leave message to leave a group.
7-14
Page 61

Managing Switches
Configuration
Note: Using the console you can designate specific ports to always or
never forward multicast packets.
Forward with High Priority
When “Forward with High Priority” is checked, any IGMP packets received
by the switch will be forwar ded in a prioritized manner, preceding packets
with normal priority.
The Spanning Tree Protocol
The Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1d) maintains a loop-free topology in
networks with redundant bridges or switches. The spanning tree devices
determine which devices will be active and which will be backups so that no
two nodes in a network have more than one active path between them at any
time. The Spanning Tree Protocol uses the most efficien t path be t w een
segments. If a bridge or switch fails, the other bridges and switches
reconfigure the network automatically. When the problem is repaired, the
bridges and switches automatically return to t he original network
configuration.
Figure 7-6. Switch Device Features — ABC, IGMP and STP
Managing Switches
7-15
Page 62

Managing Switches
Configuration
If you have configured VLANs for the switch (you must do this with the
device console), se lect a VLAN for which the fea ture s will apply.
Configuration - Support/Mgmt URLs
Support URL
To go directly to the HP Support Site on the World Wide Web, click on the
Support tab. You will launch the site indicated by the URL that has been
entered in the Configure - Support/Mgmt URLs page. By default this is the HP
Network City support site. The Network City site has info rmation about HP
devices, FAQs, firmware upgrades, white papers on current technologies,
and much more. This URL is:
http://www. hp.com/go/network _cit y
If you want to change the URL that is accessed when the Support tab is
selected, type in the new address and click on the Apply Changes button.
For example, you could change the URL to launch your site home page.
Managing Switches
Figure 7-7. Setting URLs for Support and the Management Station
7-16
Page 63

Managing Switches
Configuration
Management Server URL
Enter the URL for your management server. This will let you display the
online help at any client in the network.
Note: This field will contain the address for the HP Network City web
site by default. If you do not change it, the online help will be loaded
from the HP Network City site.
7-17
Managing Switches
Page 64

Managing Switches
Configuration
Managing Switches
7-18
Page 65

Setting Up Security for a Device
It is advisable to set up security for your devices to prevent unauthorized
access to the device or the network. You can configure device security to
prevent unauthorized use of certain parts of the network by certain node s,
and to keep unwanted traffic out of certain parts of the network.
Note: For older HP devices that cannot be managed with a Web
browser , read the chapter “ Management for Non-Browser able Devices”
or see the online help.
This chapter contains information on:
■ Device Passwords
■ The Function of Community Names
■ Port Security
■ Address Selection
■ Eavesdrop Prevention
■ Setting Security Policy
■ The Intrusion Log
Setting Up Security for a Device
Device Passwords
8
Device Passwords
Assigning passwords to devices helps limit access to authorized persons. In
the Security page, sele ct the
for the device.
Device Passwords
button to assign passwords
8-1
Setting Up Security for a
Device
Page 66

Setting Up Security for a Device
Device Passwords
Setting Up Security for a
Figure 8-1. Assign Passwords to a Device
There are two categories of passwords:
■ Operator (Read only): The Operator can vi ew allpages except the Security
pages. For switches, this password is the sam e as th e console password.
■ Manager (Full Read and Write permissions): The M ana g er can view all
pages and make any chang es in any page. The Manager name and passwordare the same as the name and password used in accessingthe device
through theconsole or a telnet session. If you change the passwordin this
page, the console password is overwritt en and becomes this password.
Enter the desired names and passwords. The minimum recommended setup
is to have one Manager password. Click on the
want to clear these changes select the
Clear Changes
Apply Changes
button. This will not
button. If you
clear any changes that you have alre ady applied to the device.
Manager/Operator Password Combinations
Device
The level of protection and the access granted to the device depends on
what passwords are set at what levels. The table below describes the
settings and their consequences.
8-2
Page 67

Table 8-1. Manager/Operator Password Combinations
Setting Up Security for a Device
Device Passwords
Passwords Read
Manager password set
Operator password not set
Manager password set
Operator password set
Manager password not set
Operator password set
Manager password not set
Operator password not set
Protected
N/A Yes Anyone can get Read Access, but only the
Yes Yes Both the Manager and the Operator have
Yes Yes The Operator has both Read and Write
N/A N/A Anyone can get Read and Write Access to
See the online help for information a bout non-browserable devices.
The Function of Community Names
A community defines authentication and access control between an SNMP
agent and a management station. The community name functions as a
password in that management stations must use the community name for all
Get and Set operations. This is different and separate from the Operator and
Manager passwords, whic h protect access to the browser interface and
console settin gs.
Write
Protected
Results
Manager can read and write to the device.
Recommended minimum setting.
Read Access, but only the Manager has
Write Access. Everyone else is shut out of
the device. Recommended setting.
Access because Write Access has not
been reserved for the Manager.
the device. Not recommended.
T o set a Community Name for a device:
1. Right mouse click on a device symbol and sele ct
SNMP Configure HP
Hub/Switch
2. Enter the passwords in the Set SNMP Passwords (Communities) page.
Setting Up Security for a
Device
8-3
Page 68

Setting Up Security for a Device
Port Security (hubs only)
Port Security (hubs only)
Y ou can assign security levels on hubs port by port. Select the Port Security
button to view the current settings for each port. This fe ature is not a vailable
for switches.
Setting Up Security for a
Figure 8-2. View the Secu rity Set tings for Ea ch Po rt.
Address Selectio n
Address Selection refers to how the authorized address for a port is
discovered. The three settings are explained in the table.
Ta ble 8-2. Address Selection
Setting Description
Continuous The device learns the address of the device attached to the port and
Device
8-4
makes it the authorized MAC address. If a different device is later
attached to the port, the new address is learned and becomes the
authorized addres s.
Page 69

Ta ble 8-2. Address Selection
Setting Description
Setting Up Security for a Device
Port Security (hubs only)
First Heard
Assigned Enter the address of the device that is authorized to be attached to
To set the Address Selection :
1. Click on the Set Security Policy for Selected Ports button.
2. Select a setting from the Address Selection drop down list.
3. Click on Apply Settings.
The device learns the address of the device attached to the port and
makes it the authorized MAC address. If a different device is later
attached to the port, the new address is registered as an “intruder
address”; a security violation has occurred and the port is
automatically disabled.
the port. If a different de vice is atta ched to the port, t he new address
is registered as an “intruder address”; a security violati on has
occurred and the port is disabled.
Authorized Address
The Authorized Address field contains the M AC ad dress of the device that is
authorized to be attached to the port.
Eavesdrop Prevention
Eavesdrop Prevention is a feature of several HP devices that stops a
computer or other device from seeing network traffic that is not intended for
that port. When Eaves dr op P revention is configured on a port, the port’s
authorized MAC address is compared with the destination address of any
outbound packets.
Set the Eavesdrop Prevention param ete r f or a port or group of ports by
clicking on the
“yes” from the Prevent Eavesdropping drop down list.
Set Security Policy for Selected Ports
button and selecting
Send Alarm
If you set the Send Alarm parameter to “yes”, a trap will be sen t to the
management station when an unrecognized address is received. Set the Send
Alarm parameter for a port or group of ports by clicking on the Set Security
Policy for Selected Ports button and selecting “yes” from the Send Alarm
drop down list.
8-5
Setting Up Security for a
Device
Page 70

Setting Up Security for a Device
Port Security (hubs only)
Note: In order for traps to function, you must also set the trap in the
Thresholds dialog box, as follows:
1. Using the right mouse button, click on the device symbol in the HP
Network Node Manager map.
2. Select
3. Select the Thresholds tab and set the thresholds for the traps you are
4. Select the Trap Receivers tab and set the management stations that can
5. Select the Authorized Managers tab and set the management stations that
SNMP Configuration
interested in receiving.
capture traps.
can send and receive SNMP requests for the device.
.
Setting Up Security for a
Figure 8-3. Set Trap Receiver Thresholds
Disable Port
Device
8-6
If the Disable Port parameter displays “yes”, the port may be disabled when
an unrecognized address is r ecei ved. Disabling the port depends on the
Address Selection parameter that you have chosen. The settings First Heard
and Assigned will disable the port if a new address is heard on that port. The
Page 71

Set Security Policy for Selected Ports (hubs only)
port will not be disabled when a new address is learned if the setting is
Continuous
.
Setting Up Security for a Device
Set Security Policy for Selected Ports
(hubs only)
You can set the security policy port by port, or by selecting a group of ports.
Select one port by clicking on the e nt ry in the Port Security page. To select
more than one port, you can C trl-click on each port you want to incl ude, or
to select a range of cont igu ous ports, click on the first port in the range, then
shift-click on the last port to be included. Click the
Selected Ports
button. Select the parameters that you want to assign.
Set Security Policy for
Figure 8-4. Setting Security Policy for Several Ports
The Intrusion Log (hubs only)
The Intrusion Log page lets you view security intrusions (violations) of a
device. The information displayed includes:
■ Port - The ports that have detected attempts of unaut horized access.
Setting Up Security for a
Device
8-7
Page 72

Setting Up Security for a Device
The Intrusion Log (hubs only)
■ Intruder Address - Address of the intruder. The IP address is displayed for
■ Date/Time - Date and time the security intrusion occurred.
SNMP agent violations. The MAC address is displayed for port violations.
The port violation must be cleared before another port violation will
display.
Setting Up Security for a
Device
8-8
Page 73

Performing Diagnostics
Performing a Ping/Link Test
Performing Diagnostics
Using HP Hub & Switch Management, you can hel p isola t e faults by running
device self-tests, Link tests, and Ping tests (IP networks).
Note: For older HP devices that cannot be managed with a Web
browser , read the chapter “ Management for Non-Browser able Devices”
or see the online help.
This chapter includes information on:
■ Performing a Ping/Link Test
■ Rebooting a Device
■ Resetting a Hub to Factory Default Settings
■ Producing a Configuration Report
9
Performing Diagnostics
Performing a Ping/Link Test
You can isolate faults by running Link tests or Ping tests (IP netw orks).
Select the Diagnostics tab and clic k on the Ping/Link Test button. Choose
a test for sending test packets to, or through, a de v ice in order to verify the
path between two network devices . In the Destination MAC/IP Address
field enter the IP address or MAC address of the device for which you want
to test the connection. Specify the nu mber of packets to send and the
timeout (in seconds) for each test. Click on the
Click on the
button to stop the test.
Stop
button to start the test.
Start
9-1
Page 74

Performing Diagnostics
Rebooting a Device
Performing Diagnostics
Figure 9-1. Ping/Link Test
9-2
The number of successes or failure s of the t est packets reaching the
Destination IP or MAC Address are displayed at the top of the page. A failure
means that either the device at the de s tin ation address did not respond
within the timeout specified, or the dat a retur ne d from the device indicated
an error.
The Defaults button will reset the Number of Packets to Send and the
Timeout value to the default values of 10 packets and 1 second, respectively.
Rebooting a Device
Rebooting the device is the same as power ing off the device. Network
operation will be interrupted while the device initializes.
Page 75

Resetting a Hub to Factory Default Settings
Performing Diagnostics
Resetting a Hub to Factory Default
Settings
Resetting the hub to the factory default settings removes any con figuration
changes that you have made since installing the device, and restores the
factory defaults. The IP address is also removed; you must enter an IP
address before the device will operate on y our network, unless you have
Bootp or DHCP.
Producing a Configuration Report
The Configuration Report displays in format ion ab out the curren t settings on
your device. You can use your browser’s capabilities to print a copy of the
report or save it to a file. See the online help for a more detailed explanation
of this report.
Performing Diagnostics
9-3
Page 76

Performing Diagnostics
Producing a Confi guration Report
Performing Diagnostics
9-4
Page 77

HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
HP Hub & Switch Management Admin is an administration utility that allows
you to set specified configuration and control parameters used by HP Hub &
Switch Management for OV-UX. HP Admin is automatically installed when you
install HP Hub & Switch Management for OV-UX.
This chapter includes the following topics:
■ Starting HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
■ HP Admin Parameters
Starting HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
10
Management Admin
HP Hub & Switch
You can start HP Admin in the following ways:
■ Enter /opt/HPASA/bin/admin at the command line prompt.
■ In an OpenView submap, display the Options menu and select HP Hub
& Switch Admin.
HP Admin Parameters
The parameters that you can set in HP Admin are grouped into these categories:
■ Network parameters
■ User Interface parameters
■ Graph options parameters
■ Printer Configuration parameters
■ OpenView Configuration options
10-5
Page 78

HP Hub & Switch
Management Admin
HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
HP Admin Parameters
The parameters are briefly described below . For more information, see t he HP
Admin online help.
Network Parameters
Network parameters enable you to setvalues and behavior for network device
communication and Closeup View activity. The parameters for network device
communication are described in the following table.
10-6
Figure 10-1. Setting Network Parameters
Table 10-1. Network Parameters
Parameter Description
SNMP Max Retries Specifies the number of times will retry an SNMP request to
get a response. The range is 1-5 times. The default is 3.
SNMP Timeout Specifies the time (in seconds) that HP Hub & Swi tch
Management will wait for a reply on each request. The range
is 1-6 seconds. The default is 5.
HP OpenView Device Symbols
There are two states for an OpenView device symbol on an OpenView map,
explodable and executable. When the device symbol is in the explodable
state(no box appears around it) and you double-click on it, a submap showing
Page 79

HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
HP Admin Parameters
the attached devices appears. When the device symbol is in the executable
state (a box appears around the symbol) and you double-click on it, a Closeup
View of the device appears.
HP Admin gives you two check boxes in th e Make Device Symbols Execut-
able at OpenView Startup section that allow you to change the state of the
device symbols the next time OpenView is started. If the check box for Hubs/
Bridges/Switches is enabled (box is darker), the next time that OpenView is
started the associated device symbols will be executable. If the check box is
not enabled, the next time that OpenView is started the state of the symbols
will not have changed. If the symbols were in the executable state when you
exited OpenView , theywill remain inthe executable state.If the symbols were
in the explodable state when you exited OpenView, they will remain in the
explodable state.
Note: When an HP Admin check box is disabled, no change in the
existing device symb ol st ate occurs when Op e nView is restarted.
Note: If you enable a Hub/Bridge/Switch check box while OpenView is
running, the change in symbol state to executable will not occur until
OpenView is restarted. OpenView checks these parameters at startup.
Management Admin
HP Hub & Switch
User Interface Parameters
User Interface parameters enable you toset the visual environment and object
attributes in the HP Hub & Switch Management Device Views.
10-7
Page 80

HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
HP Admin Parameters
Table 10-2. User Interface Parameters
Parameter Description
HP Hub & Switch
Management Admin
User Level • This parameter controls HP Hub & Switch Management
messages to the user. There are 3 user-level
parameters:
• Beginner (User Level 1, default): Message boxes will
notify the user when device parameter modifications
have completed. Also, the user will be warned abou t
changes that are about to be made to a device or to a
local file. The user will be allowed to cancel the change.
• Intermediate (User Level 2): The user will be warned
about changes that are about to be made to a device or
to a local file. The user will be allowed to cancel the
change.
• Advanced (User Level 3): There will be no notificat i on
or confirmation messages.
Port Statistics Interval This parameter is set by a sliding bar and specifies the
sampling interval (in seconds) for the port statistics
graphical displays. The default is 5 seconds.
Show Tool Bar Banner This parameter specifies whether the title of each T oolbar
button is displayed in the graphical control panels
(Closeup Views) as the mouse cursor is passed ov er the
button. The default is for button titles to be displayed.
Closeup Status Interval This parameter is set by a sliding bar and specifies the
sampling interval (in seconds) for port status in the
graphical control panels (Closeup Views). The default is 10
seconds.
10-8
Closeup Gauge Interval This parameter is set by a sliding bar and specifies the
sampling interval (in seco nds) for the “LAN Activity%” an d
the “Collision%” gauges in the graphical control panels
(Closeup Views). The default is 5 seconds.
Thresholds: Activity% Sliding bars are used to specify the levels at which the
Thresholds: Collisi on%; Hig h
Priority
“LAN Activity%” gauges in graphical control panels
(Closeup Views) change color fr om gr ee n to ye llow, and
from yellow to red. The de fau lt le vels are 30% an d 5 0%,
respectively.
Sliding Bars are used to specify the levels at which the
“Collision%” gauges in graphical control panels (Closeup
Views) change color from green to yellow, and from yellow
to red. The default levels are 30% and 50%, respectiv e ly.
Page 81

HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
HP Admin Parameters
Graph Options Parameters
HP Admin graph options parameters enable you to control different aspects
of the graphing feature. The parameters are described in the following table.
Table 10-3. Graph Option Parameters
Parameter Description
Graph Log Format This parameter allows you to choose the format of the
Graph Digits to Display This parameter is set by a sliding bar and specifies the
Graph Interval This parameter is set by a sliding bar and specifies the default
Graph Log File The parameters set in this section specifies the file name for
Enable Graph Sensitive
Scaling
information logged to a graph log file from the Graph Counters
function.
• T ext: Data will be logged to the log file as straigh t ASCII text.
The default is “Text”.
• Spreadsheet-T ab: Data will be logge d to the log file as ASCII
text separated by tabs for ease of exporting the data to
spreadsheets that use tabs.
• Spreadsheet-Comma: Data will be logged to the file a s ASCII
text separated by commas for ease of exporting the data to
spreadsheets that use commas.
maximum number of digits displayed for a counter value before
displaying the value in scientific notation. The default is 4.
sampling time interval (hh:mm:ss) for graphing. The minimum
setting is 1 second. The maximum value is 9999:59:59. The
default is 20 seconds.
the graph log file and the size of the log file.
Default log file name is “graphs.log”
Default log file size is 128000 bytes. The minimum log file size is
10000 bytes. The maximum is 2
This parameter controls the scalin g of gr ap hs. The default is
“disabled”.
If enabled, the “Y-axis” graphing scale will automatically adjust
to display only the range of values needed. A more detailed
view of the graph will be displayed.
If disabled, the “Y-axis” graphing scale will start at zero. The
upper limit will automatically adjust to the power of 10 as
needed.
32
-1 bytes.
Management Admin
HP Hub & Switch
10-9
Page 82

HP Hub & Switch
Management Admin
HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
HP Admin Parameters
Printer Configuration Parameters
Network management applicat ions that implement printer support on X
Window systems can use the Print Configuration dialog box to configure
printer configurati on parameters.
Figure 10-2. Printer Configuration
10-10
Table 10-4. Printer Configuration Parameters
Parameter Description
Default Printer Displays the current default printer name. This printer will be used if
the choice of printers is not overridden.
Installed Printers Provides a sorted list of all currently configur ed p rin t ers. The
currently displayed printer updates the “lp command” and “Out p ut
Format” boxes.
lp command Shows the device name and port for the currently select ed printer,
and the lp command string. The lp command is used to redirect the
output to a specific device—printed output is “piped” into the
command specified by the lp command text. Your can modify the lp
command string to meet your printer requirements. See your HP-UX
man pages for more information on the lp command.
Output Format Identifies the driver type of the pri nter that is currentl y select ed. T he
lp command string must be compa tible with the format identified in
this box. You may need to edit the lp command string or choose
another printer.
Page 83

Table 10-4. Printer Configuration Parameters
Parameter Description
HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
HP Admin Parameters
Set As Default Sets the printer selected in the “Install ed Printers” box as the default
printer .
Remove Removes a selected printer from the “Installed Printers” list.
Add Displays a list of supported printers that you can select and add to
the “Installed Printers” list.
Test Print Prints a sample test file to a selected printer if the printer
configuration has been saved (see the OK button) .
OK Saves the configurat ion and returns to the main HP Admin dialo g box.
Cancel Returns to the main HP Admin dialog box without saving
configuration ch anges.
Help Acces ses th e HP Admin online help system.
OpenView Configuration Options
Y o u can change the way that OpenView and HP Hub & Switch Management
interact by setting these options:
■ ForceMapUpdates
■ NoMapWalk
■ Trace
■ Distributed Console
Management Admin
HP Hub & Switch
These options provide advanced tuning capabilities for knowledgeable users
of OpenView. You do not need to use them to run the applic a ti on.
Any changes that you make will not take effect until the next time that
OpenView (ovw) is run.
10-11
Page 84

HP Hub & Switch
Management Admin
HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
HP Admin Parameters
Figure 10-3. OpenView Configuration Options
The options are described in more detail here.
ForceMapUpdates. If the attributes (na me of icon, application name) of a
symbol are changed, for example, during an update, the symbol must be reregistered with OpenView for the changes to take effect. Selecti ng this option
will update the symbol the next time that the master copy of OpenView (ovw)
is run. If this option is not set, symbols that are already executable are not
updated with the new information.
10-12
NoMapWalk. When you start HP Hub & Sw itch Management, it can take a
long time toscan (“walk”) a large OpenView map to get the information ne eded
to provide full functionality. When the NoMapWalk option is selected, HP Hub
& Switch Management start up tim e is gre a tly decreased.
When NoMapWalk is enabled, the symbols of newly discovered devices will
not be executable with a double-mouse-click. Y ou must click on th e device in
the OpenView map, then use the Monit or menu (select HP Hub/Bridge) t o
display the device's Closeup View. You also will lose the ability to perform
batch security settings.
Trace. This option is provided to assist support personnel in tracking down
problems related to OpenView integration with HP Hub & Switch Management. Do not set this option unless you are told to do so by support personnel.
Page 85

HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
Distributed Console. HP Hub & Switch Management is started remotely
when you use Network Node Manager’s Distributed Console feature from a
client station. The program “ovexec” displays a pop-up window in which you
enter a password for the remote system. If you do not want this pop-up to be
displayed, that is, you do not wish to enter a password, select the “remsh”
option to start HP Hub & Switch Management remotely.
HP Admin Parameters
Note: If you selec t “
/etc/hosts.equiv
in the
remsh
”, the name of your client machine must be
file or the
$HOME/.rhosts
file on the
remote system. Refer to these man pages for more information on these
files:
man hosts.equiv
man rhosts
Browser Launch. You can enter the full path name for the browser that will
launch when you click on a devic e that is manageable with a browser, for
example:
/opt/netscape/netscape
Management Admin
HP Hub & Switch
10-13
Page 86

HP Hub & Switch
Management Admin
HP Hub & Switch Management Admin
HP Admin Parameters
10-14
Page 87

Management for Non-Browserable Devices
This chapter provides a summary of hub, bridge, and switch management
functions fordevices that cannot be managed with the Web browserinterface.
It includes the following topics:
■ About Closeup Views
■ Overview of Toolbar Functions
Use the online help for more information about specific device functions.
About Closeup Views
HP Hub & Switch Management provides direct access to HP hub, bridge, and
switch management for d evices that are not manageable with a Web browser
through graphical control panels, or Closeup Views. If you have switching
hubs, you can also use the Closeup View to create and modify segments in
your network.
11
Browserable Devices
Management for Non-
A Closeup View is an interactive, visual display of a device. You can use the
Closeup View to obtain device status, and run Hub & Switch Management
command functions through push-button icons and menus. There is a Closeup
View for most HP managed devices.
There will be differences in the availabl e function icons depending on the
device type. Icons for functions that are not available for some devices will
either not be selectable (gray ed out) or will not appear. Also, menu options
launched from icons that are not available for some devices eith er will not
appear, or if they appear, they will not be selectable. For information on device
management functions for any particular device, refer to the online help in the
Closeup View.
ForHP AdvanceStack hubs, CloseupViews are available for managing allhubs
on a Distributed Mana gement Chain. Closeu p Views for chaine d hubs that are
without SNMP modules are accessed through the appropriate SNMP-based
hub’s Closeup View. Functions that are not available for chained hubs will not
be selectable.
11-1
Page 88

Management for Non-Browserable Devices
About Closeup Views
Displaying the Closeup View
You can display a Closeup View in several ways, including the following:
■ From an HP OpenView map, use the left mouse button and double-click
on a hub, bridge, or switch symbol.
■ On an HP OpenView map, select a hub, bridge, or switch symbol. Then
display the Monitor menu and select HP Hub/Switch.
■ From a Closeup View of an SNMP-based Advan ceSt a ck hub, display the
list of chained hubs by clicking on the Chained Devices button. The list
displayed identifies each chained hub by MAC address and hub type .
Select the MAC address for t he desired hub.
■ Right-mouse-click on a device symbol and select Monitor HP Hub/
Switch.
Browserable Devices
Management for Non-
Figure 11-1. Switching Hub Closeup View
11-2
Page 89

Management for Non-Browserable Devices
The number of Closeup Views that you can display at one time depends on
your free system resources available (such as available memory).
If the HP device can be managed with your browser, the menu option SNMP
Configure HP Hub/Switch will also display when you right-mouse-click on
a device symbol. Selecting this feature allows you to configure community
names and authorized m an age rs f or the device. See the online help for
configuration instructions.
About Closeup Views
Closeup View Areas
The regions of the Closeup View are discussed below.
Title Bar
At the top of the Closeup V iew is a title bar that displays th e de vi ce t ype and
its network address.
Message Bar
The Message Bar is along the bottom of the Closeup View . It is primarily used
to identify, or describe the purpose of, various items in the view. Simply place
the cursor on an item and read the appropriate box in the Message Bar.
If a port is selected, the center box in the Message Ba r identifies the selected
port (for example, “Port A9”).
Toolbar
The Toolbar contains buttons to perform H ub & Switch Management
commands and functions. If you place the cursor over a Toolbar button,
message bar text is displayed that identifies the command or function. (See
the online help for a descript ion of the Toolbar icons.)
Activity Gauges
Two lin ear bar charts, or “gauges”, are displaye d on most Closeup Views.
These gauges provide indications of LAN traffic sampled by the device. The
gauges are:
■ Activity%—Represents the total LAN activity viewed by all segments
attached to the device as a p ercent of the total bandwidth ofthe segments.
■ Collisions%—Shows the total collisions viewed by all segments attached
to the device as a percentage of total packets seen by these segments.
11-3
Browserable Devices
Management for Non-
Page 90

Management for Non-Browserable Devices
Overview of Too lbar Functions
Hub LAN Ports
TheCloseup View allows youto view each hub portand determine portstatus.
Port status can be determined by the port icon symbol and colors displayed.
Y ou can individually select any port on a Closeup View by clicking on the port
itself. The port number will be displayed in the message bar. If you select a
port, you can perform management functions through the applicable Toolbar
button. (If passwords are used, you must be logged onto the hub to change a
port’s configuration.)
Overview of Toolbar Functions
HP Hub & Switch Management device functions in the Closeup Views allow
you to configure, monitor and manage HP hubs, bridges, and switches.
The following table summarizes the Toolbar menu functions in the Closeup
Views. For specific information about how to use a part icular device function
or menu dialog box, click on the Help button in the dia log box.
Table 11-1. Summary of Toolbar Functions
Icon Toolbar Button Description
Device ID Display s iden tifi ca tion information for an HP hub,
bridge or switch. For example, you can determine
the device type, firmware version, and MA C
address.
Browserable Devices
Management for Non-
Graph Counters Display s the Graph Counters - Graph window for
graphing various counters and statistical formulas
on a device. The default graph is the LAN Activity%
statistics. If you positi on th e cu rs or ov er th e
graphing area and press the right mouse button, a
pop-up menu is displayed. Select “Options” to
modify the counters and devices for graphing, and
to configure other graphi ng opti ons.
11-4
Page 91

Table 11-1. Summary of Toolbar Functions
Icon Toolbar Button Description
Management for Non-Browserable Devices
Overview of Toolba r Func tio ns
Port Statistics Displays gauges for viewing statis tical counters f or
Port Statistics
Summary
Logon Displays a Logon dialog box. If a hub, bridge or
a segment and selected por t s on the segment.
• Hubs: gauges for LAN Activity, Error Packets,
and Broadcast Packets are displayed.
• Bridges: gauges for Broadcast Packets, Packets
Forwarded, Packets Filter e d, an d Error Packets
are displayed.
• Switches: gauges for LAN Activity, Packets
Forwarded, Packets Filtered, Broadca sts
Received, Collisions, and Errors Received are
displayed.
Display s an informa tion window that li sts important
statistics and counte r values for each port on the
device. The displayed counters will differ
depending on the device type (for example, 10BaseT hub, 100VG hub, 10/100 switch, or bridge).
switch has a password, you must first log on to it
before you can change configuration or security
features, or run diagno stic tests. Logo n password s
are set up using the Configur ation button (select Set
Administration). If you forget a password, you may
need to go to the device to clear th e password (see
your device manual s) .
Browserable Devices
Management for Non-
Configuration Displays a tabbed dialog box for device
configuration (The tabs displayed depend on the
device):
• Administration
• IP Config
• Thresholds
• Port Conf i gurat i on
• Backup Links
• Upload
• Downloa d
• Monitor P ort
• Address Table
• Wild Character Filter
• Spanning Tree
• Bridge Co nfiguration
11-5
Page 92

Management for Non-Browserable Devices
Overview of Too lbar Functions
Table 11-1. Summary of Toolbar Functions
Icon Toolbar Button Description
Diagnose Displays a pop-up menu list of device or network
Security Display s a tabbed dialog box for configuring
Enable Port Enabl es a selected hub port. If a password is
test functions. The tests that can be performed
depend on the type of device.
security:
• Authorized Managers: The network
management stations that can send and receive
SNMP requests for this device.
• Community Names: Names that are valid for
SNMP requests to the device or stac k of hubs. A
read and write level are specified for each
community name.
• Security Policy: Set global security for all
devices of the same type on your netw o rk.
• Port Security: Configure Intruder Detection and
Eavesdrop Prevention for each port.
• Intrusion Log: View security intrusions for a
device.
assigned to the hub, you must log on to the hub
before you can change the state of a port.
Disable Port Disables a selected hub port. If a password i s
Browserable Devices
Management for Non-
Logoff Displays a Logoff dialog box. If a hub or b ridge has
VLAN
Configuration
assigned to the hub, you must log on to the hub
before you can change the state of a port.
a password, you can log off the device to prevent
configuration changes .
Displays the VLAN Configuration window.
11-6
Page 93

Table 11-1. Summary of Toolbar Functions
Icon Toolbar Button Description
Management for Non-Browserable Devices
Overview of Toolba r Func tio ns
Properties Displ ays a dialog box that allows you to view or
Large icons Displays ports as large icons.
Small icons Displays ports as small icons.
List Lists all port icons in rows.
Details List information with each port:
change information about a selected VLAN or
segment:
• Port number
• Name of VLAN
• Connected status
• Enabled/Disabled status
• Active status
• Protocol type
• Port number
• Segment to which the port belongs
• Connected status:
currently connected to a de vice
• Status: the port is enabled or disabled.
indicates whether the po rt is
Browserable Devices
Management for Non-
Help Runs the Hub & Switch Management online help
system.
11-7
Page 94

Management for Non-Browserable Devices
Overview of Too lbar Functions
Configuration Functions
items displayed depend on the type of device.
See the online help for details about the C onfiguration menu items.
Setting the Configuration Parameters
When you select the Configuration icon, the Configuration tabbed dialog box
displays. Byclickingon the appropriate tab, you can configure parameters for
your devices as well as performing software uploads to and downloads from
a configuration file. See the online help to obtain instructions for configuring
a specific function.
The Configurat ion button displays a menu that allows you
to perform configuration functions for the device. The menu
Browserable Devices
Management for Non-
11-8
Page 95

Appendix A
Appendix A contains the following topics:
■ Agent Firmware Versions
■ Preparing Network Devices
■ Globally Assigned IP Network A ddresses
■ Configuring IP Parameters
Agent Firmware Versions
Agent Firmware Versions
Appendix A
A
HP Hub & Switch Management communica t es wit h network devices using
SNMP (Simple Network Manage ment Protocol).To access device features,
each network device must contain a compatible version of agen t software or
firmware.
Note: The latest firmware agents can be obtained from the Support
section of the HP networking Web page. The URL is:
http://www .hp.com/go/network_city
Verifying Device Agent Versions
Y o u can check the agent version on an HP device using one of the following
methods:
■ Use the device’s console port interface (a non-network connection).
Y ou can connect a terminal or computer directly to the device or through
a modem. Refer to the device’s Installation and Reference Guide for use
of the device’s RS-232 console port.
• For HP devices, you can use an ASCI I terminal or computer with
VT 100 terminal emulation.
■ Use an available network application (a network connection).
Appendix A
A-1
Page 96

Appendix A
Preparing Network Device s
For HP devices, use an existing version of HP Hub & Swit ch Management
or other device management utility.
Update the device’s software or firmware to the current supported version.
Note: HP Hub & Switch Management may be able to discover devices
that have previous versions of device agent firmware. However, the use
of some functions may be limited.
Preparing Network Devices
For HP Hub & Switch Management to communicate with devices on your
network, the network devices must :
■ have SNMP agent firmware that is compatible with this version of HP Hub
& Switch Management.
■ for IP networks, have a uniq ue IP network address.
Note: Hubs and bridges shipped prior to July 1992 must be upgraded.
Appendix A
Basic hub management features are available for chained AdvanceStack hubs
if they are connected to an SNMP-based hub of the same media type (10BaseT or 100VG) over a Distributed Management chain.
Device Network Addresses
Onan IP network,each managed devicemust have an IP address. If you intend
to run HP Hub & Switch Management on an IP netwo rk, you must configure
the IP address for each device you want to manage.
IP addresses are normally configured when the device is installed. For
HP hubs, bridges, and switches, IP addresses are configured using the console
port interface. For more details on console port connection and available
commands, see the device’s Installation and Reference Guide.
Note: You can use HP Hub & Switch Management to change an IP
address on a hub after it has been assigned, but not on a switch or a
A-2
Page 97

Configuring IP Parameters
Appendix A
bridge.
Globally Assigned IP Network Addresses
If you intend to connect your network to other networks that use globally
administered IP addresses, Hewlett-Packard strongly recommends that you
use IP addresses that have be en assigned to you. There is a formal process for
assigning unique IP addresses to networks worldwide. Contact one of the
following companies:
United States and coun- Network Solutions, Inc.
tries not in Europe or
Asia/Pacific
Europe RIPE NCC
Asia/Pacific Attention: IN-ADDR.ARPA Registration
Attn: InterNIC Registration Service
505 Huntmar Park Drive
Herndon, VA 22070
Kruislaan 409NL-1098 SJ
Amsterdam
The Netherlands
Asia Pacific Network Information Center
c/o Internet Initiative Japan, Inc.
Sanbancho Annex Bldg. 1-4
Sanban-cho, Chiyod a- ku
Tokyo 102, Japan
For more information, refer to Internetworking with TCP/IP: Principles,
Protocols and Architecture by Douglas E. Comer (Prentice-Hall, Inc.,
publisher).
1-703-742-4777
questions@internic.net
http://rs.internic.net
+31 20 592 5065
ncc@ripe.net
http://www.ripe.net
domreg@apnic.net
http://www.apnic.net
Configuring IP Parameters
T o run HP Hub and Switch Management on an IP network, you mustconfigure
the management station and all managed devices for IP.
A-3
Appendix A
Page 98

Appendix A
Configuring IP Parameters
The network management station is configured for IP using the TCP/IP stack
utilities. To configure a device for IP, you typically connect to the device’s
console port and use the console port interface. (Refer to the device’s installation manual for more information.)
Before you configure the network management statio n and manageable
devices for IP , make a list of all the devices on the network and what their IP
addresses will be.
Note: Make sure that every device has a unique IP address. Make sure
that all devices on a given IP network number have the same subnet
mask.
The IP configuration parameters are desc ribed below.
IP Address . The IP address of the hub, bridge, or switch is written in the
format X.X.X.X, where each X is a decimal number between 1 and 254. Every
IP address on a network must be unique.
The default value, 0. 0.0.0, disa bles IP communications. Use the default va lue
only if you are not going to manage the device with HP Hub & Switch
Management and you want to d isable IP communications for that device.
Appendix A
Subnet Mask. The bit mask defines which portion of the IP address is the
subnet address and is written in the format X.X.X.X. The default value is
automatically generat ed and depends on the class of IP addre ss th at you
entered. See your network administ rator for the subnet mask address. All
devices on a given IP network number must use the same subnet mask
address.
Primary Default Router . The routing IP address of the nearest router in
your network. The default is 0.0.0.0.
Backup Default Router. The IP address of the router to use when the
primary default router is inaccessible. The default value is 0.0.0.0. If there is
no backup router and no primary default router, use the default.
Time To Live . The number of IP routers a packet is allowed to cross before
the packet is discarded. The default value is 32. Increase this value if the hub,
bridge, or switch is managed from a network management station that is more
than 32 routers away. The maximum allowable v a lue i s 255.
Note: For selected devices, such as the HP J2980A AdvanceStack 10/
100 LAN Switch-16, you must preconfigure the SNMP community
A-4
Page 99

Configuring IP Parameters
Appendix A
name “public” on the device to allow the device to be discovered and
managed by HP Hub and Switch Management. Typically, the
community name on HP hubs and bridges will automatically default to
“public”.
T o configure a device for IP networks, use the device ’s console port interface.
Refer to the device’s Installation and Reference Guide for use of the device’s
RS-232 console port.
Note: For HP hubs, HP Hub & Switch Management can be used to
change IP addresses after they have been initially assigned during
installation.
Network Bootp Server
HP EtherTwist Hub Plus/24S and HP AdvanceStack 10Base-T hubs (with
SNMP modules installed) support the use of Bootp (Bootstrap Protocol) to
automatically retrieve their IP configuration from a server on the network. A
device’s IP configu ra tion must be configured in a file on the Bootp server.
When the device is powe red on, Bootp is used to automatically download the
IP configuration to the device.
■ Each device that supports Bootp must have Bootp enabled to retrieve its
IP configuration from the server. The factory default setting is for Bootp
operation to be enabled. You can enable or disable Bootp operation
through the device’s console port, or from a network m an age me nt application (such as HP Hub & Switch Management).
■ For more information on IP configurat ion using Bootp, refer to your
device’s Installation and Reference Guide.
A-5
Appendix A
Page 100

Appendix A
Configuring IP Parameters
Appendix A
A-6
 Loading...
Loading...