Page 1

Using PCI 1000Base-T and HSC/PCI 1000Base-SX
(Gigabit Ethernet)
Manufacturing Part Number : J5683-90002
E0602
U.S.A.
© Copyright 2002, Hewlett-Packard Company.
Page 2

Legal Notices
The information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Hewlett-Packard makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this manual, including,
but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular
purpose. Hewlett-Packard shall not be held liable for errors contained herein or direct,
indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing,
performance, or use of this material.
Warranty. A copy of the specific warranty terms applicable to your Hewlett-Packard
product and replacement parts can be obtained from your local Sales and Service Office.
Restricted Rights Legend. Use, duplication or disclosure by the U.S. Government is
subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph (c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical
Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013 for DOD agencies, and
subparagraphs (c) (1) and (c) (2) of the Commercial Computer Software RestrictedRights
clause at FAR 52.227-19 for other agencies.
HEWLETT-PACKARD COMPANY
3000 Hanover Street
Palo Alto, California 94304
U.S.A.
Use of this manual and flexible disk(s) or tape cartridge(s) supplied for this pack is
restricted to this product only. Additional copies of the programs may be made for
security and back-up purposes only. Resale of the programs in their present form or with
alterations, is expressly prohibited.
Copyright Notices. ©copyright 1983-2002 Hewlett-Packard Company, all rights
reserved.
Reproduction, adaptation, or translation of this document without prior written
permission is prohibited, except as allowed under the copyright laws.
©copyright 1979, 1980, 1983, 1985-93 Regents of the University of California
This software is based in part on the Fourth Berkeley Software Distribution under
license from the Regents of the University of California.
©copyright 1980, 1984, 1986 Novell, Inc.
©copyright 1986-1992 Sun Microsystems, Inc.
©copyright 1985-86, 1988 Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
©copyright 1989-93 The Open Software Foundation, Inc.
©copyright 1986 Digital Equipment Corporation.
©copyright 1990 Motorola, Inc.
©copyright 1990, 1991, 1992 Cornell University
©copyright 1989-1991 The University of Maryland
©copyright 1988 Carnegie Mellon University
Trademark Notices UNIX is a registered trademark of The Open Group.
Itanium is a trademark of Intel Corp.
X Window System is a trademark of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
MS-DOS and Microsoft are U.S. registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
2
Page 3

OSF/Motif is a trademark of the Open Software Foundation, Inc. in the U.S. and other
countries.
3
Page 4

4
Page 5

Preface
The information in this manual is intended for network managers who administer
Gigabit Ethernet networks. It is assumed that the Gigabit Ethernet hardware and
software have been installed and configured. For instructions on how to install and
configure Gigabit Ethernet hardwareandsoftware,refertotheQuick Installation Guide,
available in the /opt/networkdocs directory on your system and on the web (see “Manuals
Available for Gigabit Ethernet” in Chapter 3).
This manual is organized as follows:
Chapter 1 Chapter 1, "Introduction," provides an overview of Gigabit Ethernet
and lists its features.
Chapter 2 Chapter 2, "Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Parameters," describes how
to configure Gigabit Ethernet parameters using the lanadmin(1M)
command line interface.
Chapter 3 Chapter 3, "Gigabit Ethernet Resources," provides references to other
useful tools for installing, configuring, and maintaining Gigabit
Ethernet.
Chapter 4 Chapter 4, "Troubleshooting," provides flowcharts to help diagnose
Gigabit Ethernet hardware and software problems.
Appendix A Appendix A, "Gigabit Ethernet lanadmin Display," defines the terms
listed in the lanadmin(1M) command display.
Appendix B Appendix B, "Gigabit Ethernet Card Statistics," gives an explanation
of the card statistics.
Appendix C Appendix C, "Hardware Reference Information," provides information
about the card LEDs, cabling requirements, and card specifications.
Appendix D Appendix D, "Hardware Regulatory Statements," includes regulatory
statements for the United States, Canada, Australia/New Zealand,
Japan, and the European community.
Glossary Provides definitions of terms used in the manual.
3
Page 6

4
Page 7

1 Introduction
This chapter gives an overview of the Gigabit Ethernet products and lists its features.
Chapter 1
5
Page 8

Introduction
Product Overview
Product Overview
Gigabit Ethernet is a high-performance Ethernet networking solution for HP servers
and workstations.
The LAN adapters are data link adapters that support the IEEE 802.3z standard for
1000Base-SX operation over multimode fiber, and the IEEE 802.3ab standard for
1000Base-T operation over 4-pair Cat-5 or Cat-5E UTP copper wiring.
The Gigabit Ethernet intelligent adapters are designed to maximize host CPU efficiency
by performing functions such as TCP/IP checksum, interrupt coalescing, and byte
swapping.Bulk data transfers can be optimized with the use of Jumbo Frames; the large
9000 byte maximum transfer unit (MTU) improves system efficiency.
1000Base-T brings high bandwidth with 10, 100, and 1000 Mbps speeds, whch makes
more processing power available for applications. The tri-speed adapter supports
autonegotiation and autosensing. It operates in full-duplex mode at 10, 100, and 1000
Mbps or in half-duplex mode at 10 and 100 Mbps.
1000Base-SX supports full-duplex point-to-point or back-to-back (via switch to adapter
or adapter to adapter) operations only. The adapters do not support half-duplex and do
not speed negotiate (1000 Mbps operation only), but do perform autonegotiation for other
link parameters.
A6847A supports PCI only. Older 1000Base-SX adapters support HSC/PCI. 1000Base-T
supports PCI only.
The PCI adapters require a single slot in the host system and support all PCI bus
configurations: 32-bit, 33/66 MHz and 64-bit, 33/66 MHz. (Note: A6794A, A6847A, and
A6825A support 64-bit only.)
Features
Features of Gigabit Ethernet include:
• 1000Base-T features:
— Triple speed 10/100/1000 Mbps
— Full duplex operation at 10/100/1000 Mbps and half-duplex operation at 10/100
Mbps (no half-duplex support for 1000 Mbps)
— Autonegotiation and autosensing to the highest available link speed
• 1000Base-SX features:
— 1000 Mbps
— Full-duplex operation
• Supports IEEE 802.1Q VLAN tagging and IEEE 802.1p Priority Queuing (HP-UX
11i)
• Minimized host CPU utilization
— Protocol offloading through on-board TCP, UDP, and IP checksum calculations
— Adaptive interrupt coalescence based on traffic load
6
Chapter 1
Page 9

Introduction
Product Overview
• Jumbo Frame support
— Large 9000 byte maximum transfer unit (MTU) for improved efficiency and
performance with bulk data transfer
— Supported only at 1000Mbps interface (link partner must also support Jumbo
Frames)
• SNMP (MIB-II) support
• MC/ServiceGuard and Auto-Port Aggregation (APA) support for high availability
Note: MC/ServiceGuard is not supported on HP-UX 11iv1.5. APA is not supported on
HP-UX 11i v1.5 and 11i v1.6.
• Configuration support through SAM
• Promiscuous mode (link and SAP) inbound and outbound support
• Supports TCP/IP, NFS, and DLPI applications. Ethernet and SNAP encapsulations
are supported.
• Supports OLA/R (Online Addition and Replacement) (HP-UX 11i, PCI only)
Note that SX and T cards are not considered to be like cards for OLA/R, that is, you
cannot replace an SX card with a T card, and vice versa.
HP does not support OLA/R on A6794A although HP-UX tools will allow the device
to be suspended and resumed.
Performance on A6794A, A6847A, and A6825A
TCP performance is improved with better throughput on inbound and bidirectional
traffic and better request/response rate.
Differences Between gelan and igelan
The differences between gelan and igelan are:
• Supported platforms - see Table 1-1, “List of Gigabit Ethernet Products”.
• LED behavior - see Table C-1, “LED Description and Status for 1000Base-SX” and
Table C-2, “LED Description and Status for 1000Base-T”.
Chapter 1
7
Page 10
Introduction
About this Manual
About this Manual
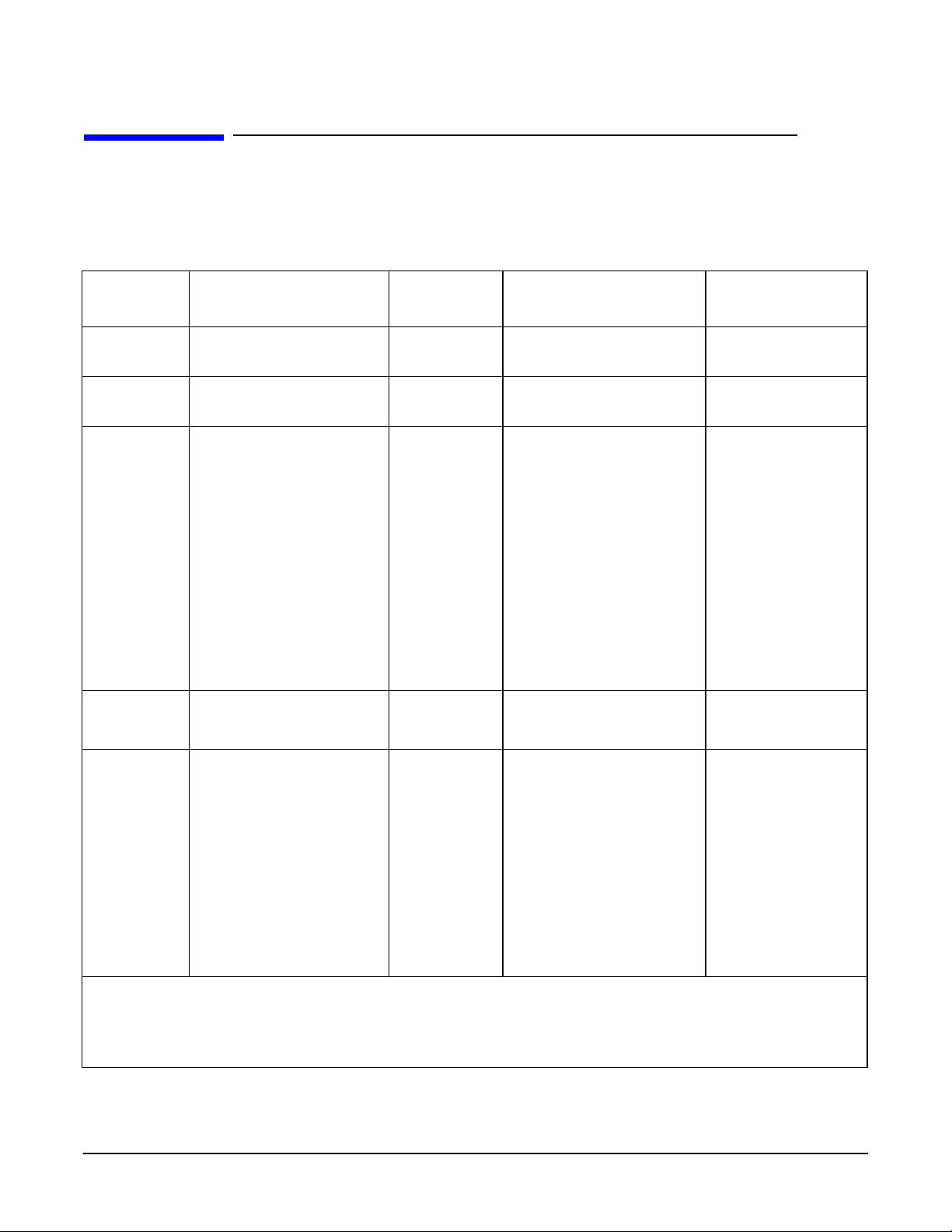
The information in this manual applies to the following Gigabit Ethernet products:
Table 1-1 List of Gigabit Ethernet Products
Product Description
A4924A HSC 1000Base-SX for
K-Class
A4925A HSC 1000Base-SX for
D/R-Class
A4926A
A4929A
A6794A 1000Base-T/SCSI igelan rp7410 server core I/O
PCI 1000Base-SX
PCI 1000Base-T
Driver
Name
gelan K-Class server 10.20, 11.0, and 11i
gelan D350 and above, R380
gelan B-Class except B180L
Supported Systems
and R390 servers
andbelow,C-Classexcept
C1xx, J2240 and above
workstations and rp2400
(A-Class) server
rp5400 series (L-Class),
rp7400 (N-Class), and
V-Class servers
SD (Superdome), rp7410,
and rp8400 servers
rx4610 and rx9610
servers
See Note
Operating
System
10.20, 11.0, and 11i
10.20, 11.0, and 11i
11.0 and 11i
11i
11i v1.5, 11i v1.6
11i, 64-bit only
11i v1.6
A6847A
A6825A
Note: For information on IPF (ItaniumTM Processor Family) platforms supported on HP-UX 11i v1.6, see
the Gigabit Ethernet support web page. Log on to itrc.hp.com and click on “navigate knowledge trees and
response center FAQs” under “maintenance and support” to go to the Knowledge Tree area, then navigate
to Networks/hp-ux networking/lan/gigabit ethernet/technical support.
8
PCI 1000Base-SX
PCI 1000Base-T
igelan B1000and higher, C3000
and higher, and J5000
and higher workstations
rp5400 series (L-Class),
rp7400 (N-Class), and
rp2400 series (A400 and
higher) servers
SD (Superdome), rp7410,
and rp8400 servers
See Note
11.0 and 11i, 64-bit
only
11.0 and 11i, 64-bit
only
11i, 64-bit only
11i v1.6
Chapter 1
Page 11

Introduction
About this Manual
This manual does not include step-by-step instructions on how to install and configure
the Gigabit Ethernet hardware and software. Those instructions are provided in the
Quick Installation Guide, which is available in the /opt/networkdocs directory on your
system and on the web (see “Manuals Available for Gigabit Ethernet” on page 21).
Chapter 1
9
Page 12

Introduction
About this Manual
10
Chapter 1
Page 13

2 Configuring Gigabit Ethernet
Parameters
This chapter describes how to configure the Gigabit Ethernet parameters using the
lanadmin(1M) command line interface.
Chapter 2
11
Page 14

Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
Understanding the Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
Understanding the Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
Several parameters can be configured using either the lanadmin(1M) command line
interface or the graphical user interface provided by the System Administration
Manager (SAM). Refer to the next section, “Using the lanadmin Tool with Gigabit
Ethernet” for details on the use of the lanadmin(1M) command. The following
parameters can be configured:
Generic Parameters
• Ethernet Station Address
The Gigabit Ethernet cards come preprogrammed with an Ethernet Station Address
in the read-only memory. This cannot be modified. However, the station address
actually used by the card for sending and receiving network packets, also known as
the MAC Address, can be set via lanadmin or SAM.
• Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU)
The MTU can be either the regular Ethernet MTU (1500 bytes) or the Jumbo Frame
MTU (9000 bytes). For 1000Base-T, jumbo frames can be configured only when the
link speed is 1000 Mbps.
Link Parameters
• Speed, Duplexity, and Autonegotiation
While 1000Base-SX operates only at 1000 Mbps in full-duplex mode, 1000Base-T
operates at 10 or 100 Mbps in either half-duplex or full-duplex mode and also at 1000
Mbps in full-duplex mode.
The speed and duplexity of 1000Base-SX cannot be modified, but its ability to
autonegotiate can be turned on and off for other link parameters. Thus,
autonegotiation has no effect on the speed or duplexity of 1000Base-SX.
1000Base-T can be manually set to 10 or 100 Mbps but not 1000 Mbps. To achieve
gigabit speed, it must be allowed to autonegotiate with its link partner,and provided
the partner can autonegotiate,1000Base-Twilloperateatthehighestcommonspeed
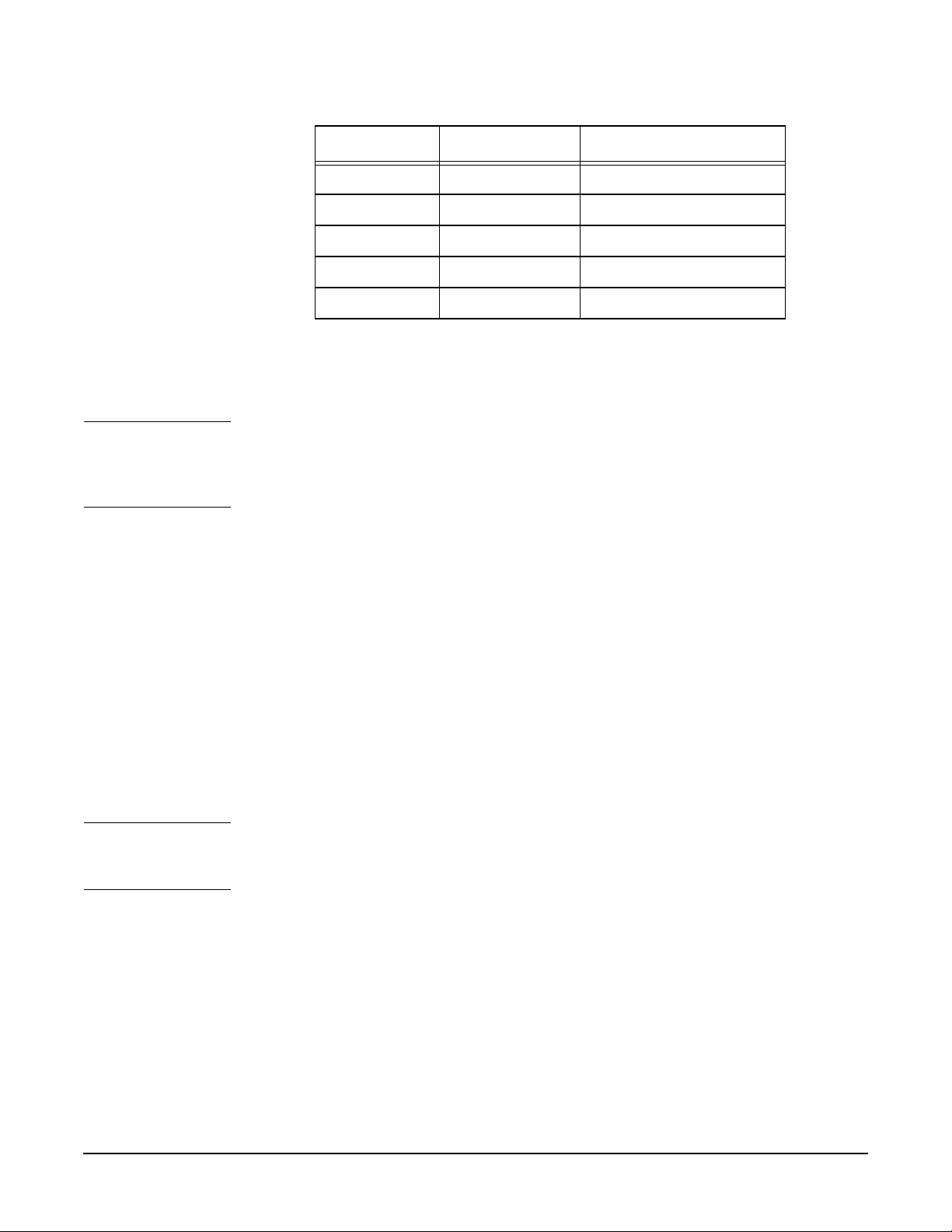
and duplexity. The following table summarizes the valid settings for 1000Base-T:
12
Chapter 2
Page 15
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
Understanding the Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
Speed Duplexity Autonegotiation
10 Half Off
10 Full Off
100 Half Off
100 Full Off
1000* N/A* On
*When autonegotiation is on, 1000Base-T will autonegotiate with its link partner;
then, if its partner also autonegotiates and can attain a speed of 1000 Mbps,
1000Base-T will operate at 1000 Mpbs full-duplex (it is not designed to operate at
1000 Mbps half-duplex).
NOTE Partners on a link must be configured to have the same setting, that is, either both
must autonegotiate or both must be set to the same manual setting. For example, if
the card is set to 100 Mbps full-duplex, the link partner must also be set to 100 Mbps
full-duplex. This will help ensure operation without degraded performance.
• Receive flow control
Flow control allows use of flow control negotiation and sending and receiving of
pause frames. When the flow control parameter is on, the card receives and manages
pause frames sent by the link partner. When the flow control parameter is off, the
card will silently discard these pause frames. The card cannot be configured to send
pause frames.
Performance Tuning Parameters
• Send Buffer Coalescing Threshold
• Receive Buffer Coalescing Threshold
• Send Interrupt Coalescing Ticks
• Receive Interrupt Coalescing Ticks
CAUTION These features are for advanced users. If you set these parameters and you do not
understand what they do, you may have unpredictable results. It is recommended to use
the default settings.
When the card transmits or receives a frame, the system must be notified of the event. If
the card interrupts the system for each transmitted and received frame, the result is a
high degree of processor overhead. To prevent that, Gigabit Ethernet provides a feature
called Interrupt Coalescence. Effective use of this feature can reduce system overhead
and improve performance.
Chapter 2
Interrupt Coalescence essentially means that the card interrupts the system after
sending or receiving a few frames. The number of frames after which the card interrupts
the processor can be tuned independently for both send and receive. The tuning can be
specified via two parameters each for send and receive, so that there are four parameters
13
Page 16
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
Understanding the Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
in all. One of the two parameters specifies the number of data buffers that the card must
transmit (or receive) before interrupting and the other specifies the number of system
clock ticks that must elapse before interrupting.
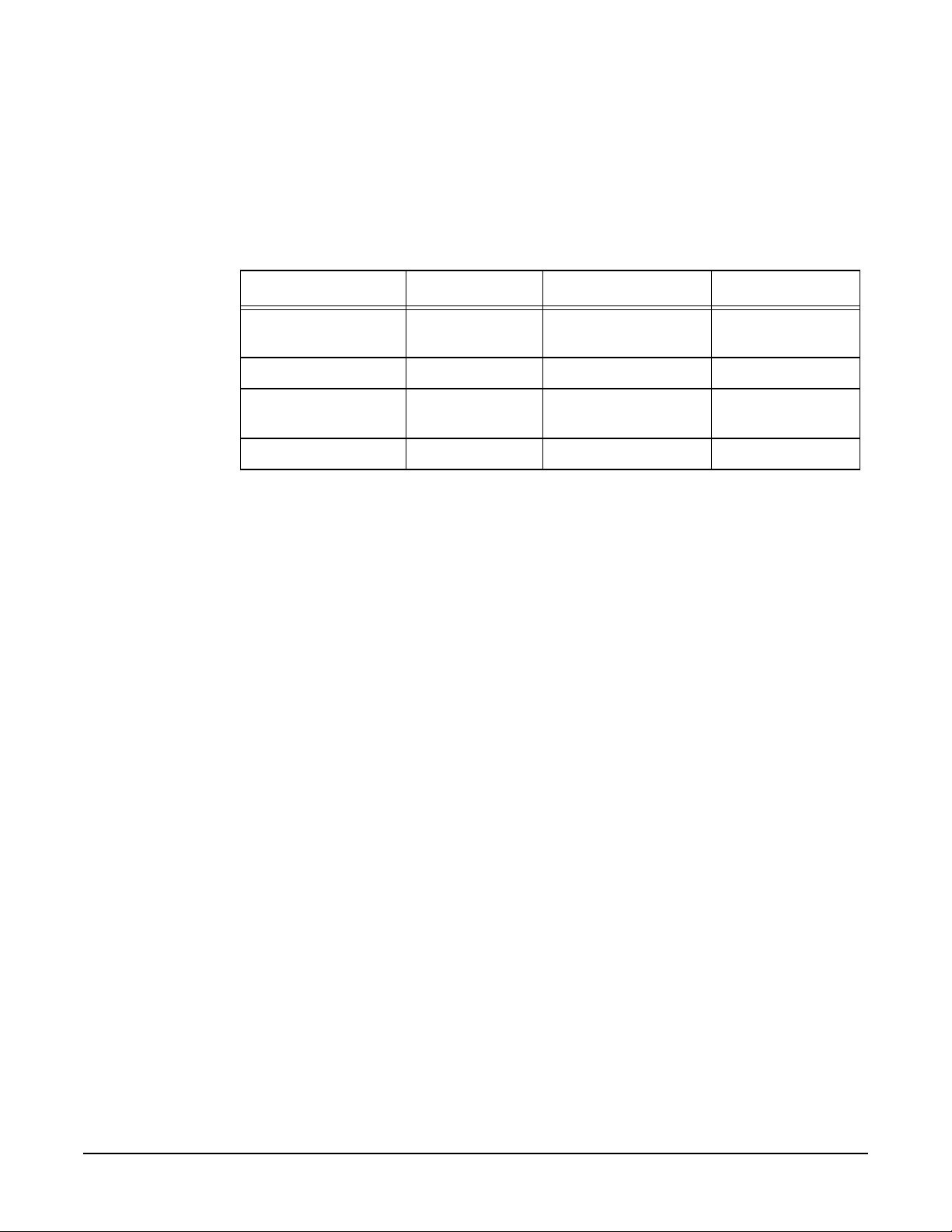
The four tuning parameters are summarized in the following table.
Table 2-1 Performance Tuning Parameters
Name Range Default Units
send_max_bufs 1 – 128 16 (for gelan)
10 (for igelan)
recv_max_bufs 1 – 256 1 # of buffers
send_coal_ticks 0 – 10000000 1000 (for gelan)
150 (for igelan)
recv_coal_ticks 0 – 10000000 0 microseconds
A send interrupt is generated by the card to the host when either:
• the number of buffers sent by the card since the previous send interrupt equals
send_max_bufs
or
• the time that has elapsed since the previous send interrupt equals send_coal_ticks (a
value of zero disables timer-based interrupt coalescing),
whichever occurs first.
A receive interrupt is generated by the card to the host when either:
• the number of frames received by the card since the previous receive interrupt
equals recv_max_bufs
or
# of buffers
microseconds
14
• the time that has elapsed since the previous receive interrupt equals recv_coal_ticks
(a value of zero disables timer-based interrupt coalescing),
whichever occurs first.
Chapter 2
Page 17

Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
Using the lanadmin Tool with Gigabit Ethernet
Using the lanadmin Tool with Gigabit Ethernet
This section explains the options available in lanadmin to support the Gigabit Ethernet
driver and how to use them. The lanadmin(1M) tool is used to display and set
parameters, as specified by the following commands:
NOTE When your system is rebooted, settings that were made via the lanadmin(1M) command
will be lost. To retain configuration settings permanently in the configuration file
(/etc/rc.config.d/hpgelanconf or /etc/rc.config.d/hpigelanconf), use the SAM
utility or manually edit the configuration file.
To display the card’s station address, execute:
$ lanadmin -a
To set the card’s station address, execute:
$ lanadmin -A
where nmid is the Network Management Identifier (NMID) (for HP-UX 10.20) and ppa
is the Card Instance Number (also known as physical point of attachment or PPA) (for
HP-UX 11.0 and later). Both the NMID and PPAmaybeobtained from the lanscan(1M)
output.
To display the MTU, execute:
$ lanadmin -m
To set the MTU, execute:
$ lanadmin -M
On HP-UX 10.20, the setting of the MTU should be followed by configuring the interface
with the appropriate IP address using ifconfig(1M). See the ifconfig man page for
details. The change in MTU should be verified, on all HP-UX operating systems, by
executing:
$ netstat -rn
To display link parameters, execute:
nmid/ppa
station_addr nmid/ppa
nmid/ppa
mtu_size nmid/ppa
Chapter 2
$ lanadmin -x
To set link parameters, execute:
$ lanadmin -X
where
option
option nmid/ppa
option nmid/ppa
specifies the operation to be carried out.
15
Page 18
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
Using the lanadmin Tool with Gigabit Ethernet
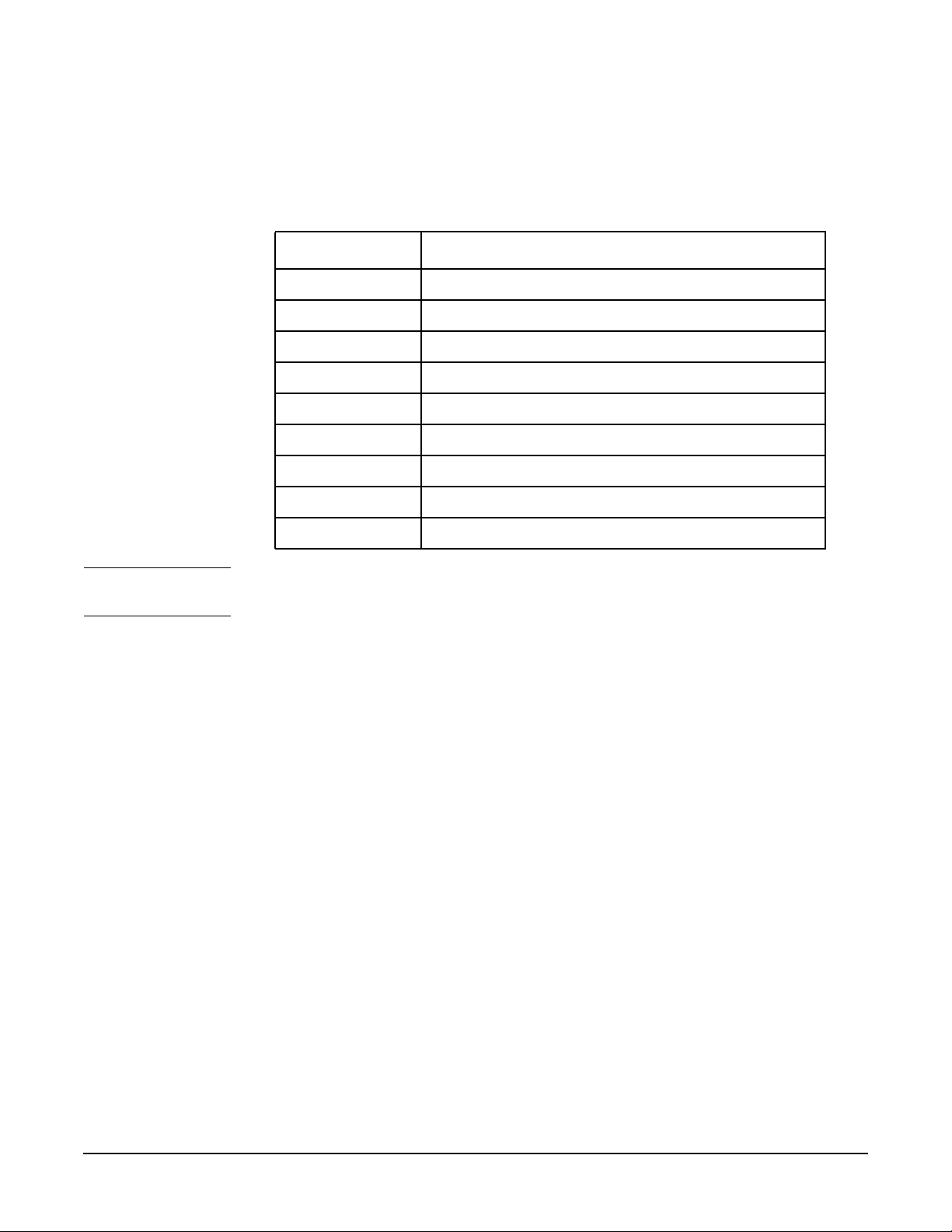
Displaying Values
The command $ lanadmin -x (or -X) help
used to display values.
Option Display
help List of -x or -X options
speed Speed and duplexity of the link
fctrl Whether Receive Flow Control is enabled or not
send_max_bufs Value of send buffer coalescing threshold
recv_max_bufs Value of receive buffer coalescing threshold
send_coal_ticks Value of send interrupt coalescing ticks
recv_coal_ticks Value of receive interrupt coalescing ticks
stats drv Driver and adapter statistics
card_info Adapter and driver revision and settings
NOTE If option is not specified, then the speed, duplexity, and autonegotiation settings are
displayed.
nmid/ppa
displays a list of valid options
Examples
Card Information To display the card information, execute:
$ lanadmin -x card_info
*********** Version Information ***********
Driver version: B.10.20.11
Firmware version: 12.4.5
Chip version: 0x6
PCI Sub-System ID: 0x106f (1000Base-SX)
PCI Sub-Vendor ID: 0x103c
Board revision: C
Software Key: 6
Engineering Date Code: B-3845
*********** Card Setting ***********
Driver State: GELAN_ONLINE
Auto Negotiation: On
Flow Control: On
Send Max Buf Descriptors: 16
Recv Max Buf Descriptors: 1
Send Coalesced Ticks: 1000
Recv Coalesced Ticks: 0
nmid/ppa
16
Chapter 2
Page 19
Using the lanadmin Tool with Gigabit Ethernet
Card Statistics To display the card statistics, execute:
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
$ lanadmin -x stats drv
NOTE See Appendix B for a sample output and explanation of the card statistics.
Send Buffer Coalescing To display the send buffer coalescing threshold, execute:
$ lanadmin -x send_max_bufs
Send buffer coalescing threshold = 16
Receive Interrupt Coalescing To display the receive interrupt coalescing ticks,
execute:
$ lanadmin -x recv_coal_ticks
Receive interrupt coalescing ticks = 0
Flow Control To display the flow control setting, execute:
$ lanadmin -x fctrl
Flow control is enabled
nmid/ppa
nmid/ppa
nmid/ppa
nmid/ppa
Setting Values
The command $ lanadmin -X (or -x) help
used to set values.
Option Setting
help Lists -X or -x options
auto_on Turns on auto-negotiation mode
auto_off Turns off autonegotiation mode for a 1000Base-SX
fctrl on Turns on receive flow control
fctrl off Turns off receive flow control
10hd Sets speed of a 1000Base-T to 10 Mbps half-duplex
10fd Sets speed of a 1000Base-T to 10 Mbps full-duplex
100hd Sets speed of a 1000Base-T to 100 Mbps half-duplex
100fd Sets speed of a 1000Base-T to 100 Mbps full-duplex
send_max_bufs* Sets send buffer coalescing threshold [1 – 128]
recv_max_bufs* Sets receive buffer coalescing threshold [1 – 256]
nmid/ppa
displays a list of valid options
Chapter 2
send_coal_ticks* Sets send interrupt coalescing ticks [0 – 10000000]
17
Page 20

Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Parameters
Using the lanadmin Tool with Gigabit Ethernet
Option Setting
recv_coal_ticks* Sets receive interrupt coalescing ticks [0 – 10000000]
stats clear Clears all driver and adapter statistics
* These options require the desired value to be specified after the option name.
Examples
Speed To set the speed to 100 Mbps full-duplex on 1000Base-T, execute:
$ lanadmin -X 100fd
NOTE The lanadmin -S option to set the speed is not supported on Gigabit Ethernet.
Stats Clear To clear all driver and card statistics, execute:
$ lanadmin -X stats clear
Buffer Coalescing Threshold To set the send buffer coalescing threshold, execute:
$ lanadmin -X send_max_bufs 32
Note that the tuning option send_max_bufs requires the additional option 32 (the
coalescing threshold).
Interrupt Coalescing Ticks To set the send interrupt coalescing ticks, execute:
$ lanadmin -X send_coal_ticks 2000
Note that the tuning option send_coal_ticks requires the additional option 2000 (the
number of coalescing ticks).
nmid/ppa
nmid/ppa
nmid/ppa
nmid/ppa
18
Chapter 2
Page 21

3 Gigabit Ethernet Resources
This chapter provides references to other useful tools for installing, configuring, and
maintaining Gigabit Ethernet.
Chapter 3
19
Page 22

Gigabit Ethernet Resources
HP-UX Manual Reference Pages
HP-UX Manual Reference Pages
While installing, configuring, or troubleshooting Gigabit Ethernet, you may need to refer
to any of the following online manual reference pages (man pages) for useful HP-UX
operating system or Gigabit Ethernet commands. To display a man page, type the
following at the system prompt: man command name. For example, man arp.
• arp(1M) displays and modifies the Internet-to-station address mapping tables used
by the Address Resolution Protocol.
• hosts(4) is a database that contains a single line entry for each host name entry.
• ifconfig(1M) assigns an address to a network interface and configures and displays
network parameters.
• ioscan(1M) scans system hardware, usable I/O system devices, or kernel I/O system
data structures as appropriate, and lists the results.
• lanadmin(1M) resets or reports the status of the LAN card.
• lanconfig(1M) in HP-UX 10.20 sets/resets the packet encapsulation method for a
network interface.
• lanscan(1M) displays information about LAN cards that are successfully bound to
the system.
• linkloop(1M) verifies network connectivity through the Data Link Layer (OSI
Layer 2).
• netfmt(1M) formats common tracing and logging binary files.
• netstat(1) provides network statistics and information about network connections.
• nettl(1M) logs network events and traces packets as they enter and exit the Gigabit
Ethernet driver.
• ping(1M) verifies network connectivity through the Network Layer (OSI Layer 3)
and reports the round-trip time of communications between the local and remote
hosts.
• rad(1M) in HP-UX 11i performs OLA/R functions without any comprehensive
checks.
• route(1M) adds and deletes entries to the network routing table.
• sam(1M) configures networking software.
• swinstall(1M)loads software filesets.
• swverify(1M)verifies software installation.
20
Chapter 3
Page 23

Gigabit Ethernet Resources
Manuals Available for Gigabit Ethernet
Manuals Available for Gigabit Ethernet
Refer to the following Quick Install Guide for step-by-step instructions on how to install
and configure Gigabit Ethernet hardware and software. This guide is available on the
web at http://docs.hp.com under “Networking and Communications ” and in the
/opt/networkdocs directory on your system.
• For A4924A, A4925A, A4926A, and A4929A:
PCI 1000Base-T and HSC/PCI 1000Base-SX/9000 Quick Installation
• For A6794A, A6847A and A6825A:
PCI 1000Base-T and 1000Base-SX Quick Installation and Configuration Guide
NOTE Forcompletecomponentinstallationinstructions, refer to the Service Guide HP 9000
Server manual for your server or the appropriate Owner’s Guide for your
workstation.
Other Useful Manuals
The following manuals also provide useful information. They are available on the web at
http://docs.hp.com.
• Installing and Administering LAN/9000 Software
Provides information on installing and administering the LAN product. It also
includes information on configuring other HP-UX link products.
• Configuring HP-UX For Peripherals
Provides detailed information on using OLA/R (Online Addition and Replacement).
Chapter 3
21
Page 24

Gigabit Ethernet Resources
Error Messages
Error Messages
Gigabit Ethernet comes with an online message catalog that is used to report
networking problems. You must use the nettl logging and tracing utility to display the
probable cause and action for a message.
Logging Messages
Gigabit Ethernet uses the nettl(1M) logging and tracing facility supplied with HP-UX.
You may access the logging and tracing utility using either the graphical user interface
(GUI) version or the command line interface.
Features of the GUI version, which are now a part of your HP 9000 system, include:
• An interface which guides you through logging and tracing tasks.
• An interface which allows you to create and format reports.
• The capability to collect logging and tracing subsystem-specific information.
• Report screens which are updated instantaneously with current logging and tracing
information by the subsystem.
• Context-sensitive on-line help.
To access the GUI version of the logging and tracing utility, execute:
nettladm
See the nettladm(1M) man page for information on using the GUI version, or the
nettl(1M) man page for information on using the command line interface.
Listed below are some example commands using the command line interface.
• To examine the log file with cause and action descriptions, execute:
netfmt -v -f /var/adm/nettl.LOG00 | more
netfmt -v -f /var/adm/nettl.LOG000 | more (for HP-UX 11i and later)
The -v option enables the reporting of available cause and action descriptions for
each log message. A sample log message using the -v option is shown below.
***********Gigabit Ethernet LAN/9000 Networking***********
Timestamp : Mon Aug 3 PDT 1998 18:37:16.175754
Process ID : [ICS] Subsystem:GELAN
User ID ( UID ) : -1 Log Class:DISASTER
Device ID : 3 Path ID: 0
Connection ID : 0 Log Instance: 0
22
• To examine just the log messages in the log file, execute:
netfmt -f /var/adm/nettl.LOG00
netfmt -f /var/adm/nettl.LOG000 (for HP-UX 11i and later)
• To check network logging and tracing status, execute:
Chapter 3
Page 25

Gigabit Ethernet Resources
Logging Messages
nettl -status
• To start Gigabit Ethernet tracing to the file /tmp/tracefile.TRC0, execute:
nettl -traceon all -entity gelan -file /tmp/tracefile
or
nettl -traceon all -entity igelan -file /tmp/tracefile
Note: nettl(1m) adds the .TRC0 postfix for you.
• To stop Gigabit Ethernet tracing, execute:
nettl -traceoff -entity gelan
or
nettl -traceoff -entity igelan
• To format the Gigabit Ethernet trace file into the file /tmp/traceout, execute:
netfmt -f /tmp/tracefile.TRC0 > /tmp/traceout
Refer to the netfmt(1M)man page for further information on how to create a filter for
trace formatting.
Chapter 3
23
Page 26

Gigabit Ethernet Resources
Contacting Your HP Representative
Contacting Your HP Representative
If you have no service contract with HP, you may follow the procedure described below,
but you will be billed accordingly for time and materials.
If you have a service contract with HP, document the problem as a Service Request (SR)
and forward it to your HP representative. Include the following information where
applicable:
• A characterization of the problem. Describe the events leading up to and including
the problem. Attempt to describe the source and symptoms of the problem.
Your characterization should include: HP-UX commands; communication subsystem
commands; job streams; result codes and messages; and data that can reproduce the
problem. You should also provide a network map with the host name, IP/Internet
address, and station address of each system connected with the HP system.
Illustrate as clearly as possible the context of any message(s). Prepare copies of
information displayed at the system console and user terminal.
• Obtain the version, update, and fix information for all software. For example, to
check the version number, execute:
what /stand/vmunix | grep gelan or the swlist command and look for
GigEther-00 (for gelan on HP-UX 11i and later)
or
what /stand/vmunix | grep igelan or the swlist command and look for
GigEther-01 (for igelan on HP-UX 11i and later).
To check the version of your kernel, execute uname -r.
This allows HP to determine if the problem is already known and if the correct
software is installed at your site.
• Prepare copies of the /etc/hosts, /etc/rc.config.d/hpgelanconf (or
hpigelanconf), and /etc/rc.config.d/netconf files.
• Execute the dmesg command and record messages about the status of the card.
• Execute the lanscan -v command and record the output.
• Execute the display command of the lanadmin diagnostic on the Gigabit Ethernet
interface and record the output.
• Record the troubleshooting flowchart number where you are unable to resolve the
problem.
• Record all error messages and numbers that appear at the user terminal and the
system console.
• Save all network log files:
24
/var/adm/nettl.LOG00 and nettl. LOG01
/var/adm/nettl.LOG000 and nettl. LOG001 (for HP-UX 11i and later)
Chapter 3
Page 27

Gigabit Ethernet Resources
Contacting Your HP Representative
Make sure that ERROR and DISASTER log classes are enabled when log files are
collected.
Prepare the formatted output and a copy of the log file for your HP representative to
further analyze.
• Prepare a listing of the HP-UX I/O configuration you are using for your HP
representative to further analyze.Use the ioscan(1M) command to help collect this
information
• Try to determine the general area within the software where you think the problem
exists. Refer to the appropriate reference manual and follow the guidelines on
gathering information for that product.
• Document your interim, or “workaround,” solution. The cause of the problem can
sometimes be found by comparing the circumstances in which it occurs with the
circumstances in which it does not occur.
• Create copies of any Internet or Gigabit Ethernet link trace files that were active
when the problem occurred for your HP representative to further analyze.
• In the event of a system failure, a full memory dump must be taken. Use the
HP-UX utility savecore(1M) to save a core dump. Send the output to your HP
representative.
• Run the lanadmin command to collect card configuration and statistics. Examples:
For HP-UX 10.20, execute:
lanadmin -x card_info
lanadmin -x stats drv
For HP-UX 11.0 and later, execute:
lanadmin -x card_info
lanadmin -x stats drv
nmid
nmid
ppa
ppa
Chapter 3
25
Page 28

Gigabit Ethernet Resources
Contacting Your HP Representative
26
Chapter 3
Page 29

4 Troubleshooting
This chapter provides flowcharts that will help diagnose Gigabit Ethernet hardwareand
software problems.
Chapter 4
27
Page 30

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting Overview
Troubleshooting Overview
As with any troubleshooting, a systematic approach is helpful. The following table and
flowcharts provide a logical sequence of steps to follow when troubleshooting Gigabit
Ethernet. Using the diagnostic flowcharts, identify whether the problem is with Gigabit
Ethernet or any of the connections to the switch, or whether it is in some other part of
the network, verify your assumptions and, if it is limited to Gigabit Ethernet software or
hardware, correct the problem.
NOTE To help ensure operation without degraded performance, make sure that both link
partners are set to autonegotiate, or, if using manual settings, that each side is set to the
same speed and duplexity.
If you cannot solve the problem on your own, call your HP representative. Use the
guidelines at the end of Chapter 3 to help you effectively communicate what is wrong.
The Gigabit Ethernet products use diagnostic tools compatible with the HP LAN Link
product.
28
Chapter 4
Page 31

Table 4-1
Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Diagnostic Flowcharts
The following table summarizes the types of network tests in the diagnostic flowcharts.
Chart Type of Test Purpose
1 Cable and LED
Test
2 Link Level Test Checks communication between link levels on source and
3 Network Level
Tests
3a ARP Test Verifies that an entry exists for the remote host in your
3b ping Test Checks communicationbetweennetworklayerson the source
4 Transport Level
Test
5 Bridge/Gateway
Loopback Test
6 Configuration
Tests
6a ioscanandlanscan
Test
Checks that hardware, cables, and connectors between your
system and card are operational.
target host using linkloop(1M).
Validates arp(1M) entries and remote host availability.
Checks communication between network layers on source
and target host using ping(1M).
system's ARP cache.
and target host.
Checks communication between transport layers on source
and target host using telnet and ftp sessions.
Checks general network connections through a gateway.
Verifies configuration of network interface on a host using
ioscan(1M), lanscan(1M), netfmt(1M), lanadmin(1M), and
ifconfig(1M).
Verifies configuration of network interface on a host.
Chapter 4
6b netfmt and
lanadmin Test
6c ifconfig Test Verifies configuration of network interface on a host.
Verifies configuration of network interface on a host.
29
Page 32

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 1: Cable and LED Test
Checks that hardware, cables, and connectors between your system and card are
operational.
Figure 4-1 Flowchart 1
Cable
and LED
Test
Does
dmesg/syslog show
error message
for gelan/igelan?
NO
YES
Check card
installation, reset
and/or reseat card
1000Base-SX Link
LED = OFF
or
For gelan driver:
1000Base-T
All speed LEDS = ON
?
NO
1000Base-T
All speed LEDS = OFF
or
For gelan driver:
1000Base-SX
Link LED = Flashing
?
YES
Check for incorrect/faulty network
cable or connector. Ensure settings for
switch and card are the same.
YES
NO
Link Level Test
Configuration
Tests
30
Chapter 4
Page 33

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 1 Procedures
• Check dmesg/syslog output and look for error messages pertaining to gelan/igelan.
Also, check nettl log messages. If errors, check card installation and reset and/or
reseat card.
• Verify LEDs. If 1000Base-SX link LED = OFF or for gelan, 1000Base-T all speed
LEDs = ON, check card installation and reset and/or reseat card. If LEDs are then
displayed correctly, continue to Link Level Test.
• If 1000Base-T all speed LEDs = OFF or for gelan, 1000Base-SX Link LED =
Flashing, check for incorrect or faulty network cable or connector. Ensure that
switch is capable of 1000 Mbps operation. Ensure that the switch (or immediate link
partner) and card are set to same autonegotiation settings. Then go to Configuration
Tests. Otherwise, if 1000Base-SX link LED or one of 1000Base-T speed LEDs is on,
continue to Link Level Test.
NOTE Refer to Table C-1, “LED Description and Status for 1000Base-SX” and Table C-2, “LED
Description and Status for 1000Base-T” for LED status.
On a 1000Base-SX card, if both Link and Activity LEDs are on and there is no network
connectivity, it could mean that the I/O cage is not seated well. Remove and reseat the
entire PCI I/O cage and reboot.
Chapter 4
31
Page 34

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 2: Link Level Test
Checks communications between link levels on source and target host using
linkloop(1M).
Figure 4-2 Flowchart 2
Link Level
Test
Execute
linkloop to
remote host
Loopback FAILED:
Address has bad
format or
Not an individual
address
Correct the link
address parameter
Repeat
Link Level
Test
Linkloop
successful?
NO
Loopback FAILED:
Remote host fails
to respond
Re-check remote
host address or
choose a different
remote host and
re-execute linkloop
Linkloop
successful?
YES
Network
Level
Tests
YES
Network Level
NO
Configuration
Tests
Tests
32
Chapter 4
Page 35

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 2 Procedures
• Execute linkloop(1M) to remote host. If linkloop is successful, continue to Network
Level Tests. Otherwise, note which error was returned.
• If loopback failed error = “Address has bad format” or “Not an individual address,”
correct link level address with proper station address format/value and repeat Link
Level Test.
• Otherwise, loopback failed because remote host did not respond. Double check
remote host address or choose another remote host and re-execute linkloop(1M).If
linkloop is successful, continue to Network Level Tests. Youmay also want to call the
node manager of the remote host that did not respond (if this was the case). If
linkloop fails, go to Configuration Tests.
Chapter 4
33
Page 36

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 3: Network Level Tests
Validates arp(1M) entries and remote host availability. Checks communication between
network layers on source and target host using ping(1M).
Figure 4-3 Flowchart 3
Network
Level
Tests
ARP Test
ping Test
Flowchart 3 Procedures
• See Flowchart 3a to validate arp(1M) entries and remote host availability.
• See Flowchart 3b to check communication between network layers on source and
target host using ping(1M).
34
Chapter 4
Page 37

Flowchart 3a: ARP Test
Validates arp(1M) entries and remote host availability.
Figure 4-4 Flowchart 3a
ARP Test
Execute
ping <remotehost> 2000 -n 1
Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Is remote host
NO
entry in ARP
cache?
YES
Is the ARP
entry correct
NO
and complete
?
YES
ping Test
Flowchart 3a Procedures
Remote
host up?
NO
Bring up
remote host
Use ARP to
correct and
complete the
entry
YES
Chapter 4
• Execute ping(1M) to remote host so that ARP entry is added. Whether or not ping is
successful, proceed to the next step.
• Use arp(1M) to verify that an entry exists for the remote host in your system's ARP
cache, executing arp hostname.
• If there is no ARP entry for the remote host, check to see if the remote host is up. If
not, bring up remote host and continue to ping Test.
• If the ARP entry is correct or complete, continue to ping Test. Otherwise, use
arp(1M) to enter the correct station address of the remote system and continue to
ping Test.
35
Page 38

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 3b: ping Test
Checks communication between network layers on source and target host using
ping(1M).
Figure 4-5 Flowchart 3b
ping Test
Execute
ping <remotehost> 2000
YES
Successful?
Transport
Level
Test
NO
Is speed
1000 Mbps?
(1000Base-T only)
Ensure speed is 1000 Mbps on
local and remote hosts
by executing
lanadmin -x speed <nmid./ppa>
YES
NO
Execute
netstat -in.
Are MTUs same on
local and remote
hosts?
YES
Are you
using jumbo
frames?
Ensure MTUs are same
on local and remote hosts
by executing
lanadmin -M <new mtu>
NO
<nmid/ppa>
Repeat
ping Test
YES
NO
Validate network,
remote host, and
configuration
settings
continued
36
Repeat
ping Test
Chapter 4
Page 39

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 3b Procedures
• Execute ping(1M) to remote host. If ping is successful, continue to Transport Level
Test.
• If ping is not successful, execute netstat -in to verify MTU size. Ensure MTU size
is the same on both local and remote hosts (9000 for jumbo frames and 1500 for
standard frames) by executing lanadmin -M
Test.
• If ping is still not successful and you are either (1) not using jumbo frames or (2)
using jumbo frames with the correct speed setting, continue to next flowchart to
validate network, remote host, and configuration settings.
new_mtu nmid/ppa
, and repeat ping
• If link speed is not 1000 Mbps, set it with lanadmin -x
repeat ping Test.
speed nmid/ppa
,and
Chapter 4
37
Page 40

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 3b (continued)
Figure 4-6 Flowchart 3b (continued)
ping not
successful
Network
unreachable?
error?
NO
No response
from ping?
NO
Unknown host
error?
NO
No route to
host error?
YES
Configuration
YES
YES
YES
Tests
YES
Are you using
jumbo frames?
NO
Correct BIND, YP,
or /etc/hosts
configuration
Add route
table entry
Do switches in
the path support
jumbo frames?
YES
Cable and
LED Test
Repeat
ping
Test
NO
Reconfigure
network
Repeat
ping
Test
38
NO
Call HP
Chapter 4
Page 41

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 3b (continued) Procedures
• If network unreachable error, go to Configuration Tests.
• If there is no response from ping, and using jumbo frames, validate that switches in
the path support jumbo frames, making sure path MTU is 9000 from source host to
destination host. Otherwise, reconfigure network path and repeat ping Test. If not
using jumbo frames, or switches and path MTU are set for jumbo frames (9000
bytes), go to Cable and LED Test.
• If you receive an unknown host error, add missing host name and repeat ping Test.
• If you receive “error=SendTo: No route to host,” use route(1M) to add route table
entry for missing host and repeat ping Test. Otherwise, call your HP representative.
Chapter 4
39
Page 42

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 4: Transport Level Test
Checks communications between transport layers on source and target host using telnet
and ftp sessions.
Figure 4-7 Flowchart 4
Transport
Execute telnet to
remote host
Level
Test
telnet
successful?
NO
Execute ftp to
remote host
ftp
successful?
NO
Is
TCP configured
on local or
remote host
?
YES
Network
congested
?
YES
YES
YES
NO
NO
Stop
Call HP
Configure TCP
Call HP
Repeat
Transport
Level Test
40
Call HP
Chapter 4
Page 43

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 4 Procedures
• Execute telnet(1M) to a remote host. If successful, stop.
• If not successful, try to establish an ftp to a remote host. Unlike telnet, ftp does not
use a pseudoterminal (pty) driver on your system. This will determine if pty is why
telnet failed. If ftp is successful, call your HP representative to determine why you
have a problem with pty.
• If ftp fails, check to see if TCP is configured on both hosts by verifying the
/etc/protocols file. Telnetand ftp work at transport layerand require TCP. If TCP
is not configured, configure now and repeat Transport Level Test.
• If TCP is installed on both hosts, telnet to another host and/or use netstat(1M)to
check for lost packets. If network is congested, you may need to reconfigure network.
If network congestion is not the cause, more detailed network diagnostics are
required. In either case, call your HP representative.
Chapter 4
41
Page 44

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 5: Bridge/Gateway Loopback Test
Checks general network connections through a gateway.
Figure 4-8 Flowchart 5
Gateway
Execute ping from a
known good host through
a gateway to another
known good host
Bridge/
Test
Successful?
YES
NO
Examine gateway
YES
Refer to non-HP
documentation or if HP,
execute ifconfig on gateway
Network
YES
interface
up?
NO
Configure interface up
Repeat/
Bridge/
Gateway
Test
Check route table
on problem host
and all hosts in
path and correct
if necessary
Network
Level
Tests
Configuration
Tests
YES
42
Chapter 4
Page 45

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 5 Procedures
• Execute ping(1M) from a known good host through a gateway to another known
good host. This will test connectivity through bridge/gateway level. If successful,
execute netstat -r and examine route table on problem host and all hosts in path.
If necessary, correct routing table and go to Network Level Tests.
• If ping fails, examine gateway to see if HP 9000 or non-HP. If non-HP, refer to
networking documentation for that product. If HP 9000, execute ifconfig(1M) for
all interfaces on gateway or host (see Configuration Tests for more details on
ifconfig).
• If ifconfig does not show parameter as UP in output for gateway, execute netstat -i
to check status of network interfaces. An asterisk (*) indicates interface is down. If
network interface is down, configure interface up and repeat Bridge/GatewayTest. If
all interfaces are up, continue to Configuration Tests and test all interfaces on
gateway.
Chapter 4
43
Page 46

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 6: Configuration Tests
Verifies configuration of network interface on a host using ioscan(1M), lanscan(1M),
netfmt(1M), lanadmin(1M), and ifconfig(1M).
Figure 4-9 Flowchart 6
ioscan and lanscan
Configuration
Tests
Test
netfmt and lanadmin
Test
ifconfig Test
44
Chapter 4
Page 47

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 6 Procedures
• Verify configuration of network interface on a host using ioscan(1M), lanscan(1M),
netfmt(1M), lanadmin(1M), and ifconfig(1M).
Chapter 4
45
Page 48

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 6a: ioscan and lanscan Test
Verifies configuration of network interface on a host using ioscan(1M) and
lanscan(1M).
Figure 4-10 Flowchart 6a
ioscan
and
lanscan
Test
Is the card
claimed by the
system as shown
by executing
ioscan?
NO
what /stand/vmunix
Does
display the
gelan/igelan
driver?
Install driver using
swinstall(1M) and verify
or edit /stand/system
to add driver keyword
gelan/igelan. Regenerate
kernel and reboot
system.
Repeat
ioscan and
lanscan
Test
NO
YES
YES
lanscan show
Does
dmesg/syslog
show error message
for gelan/igelan
?
NO
Call HP
Does
Execute
Hardware UP
for your
interface?
NO
netfmt
and
lanadmin
Test
YES
YES
Cable
and LED
Test
Check card
installation, reset
and/or reseat card
Repeat
ioscan
lanscan
Test
46
Chapter 4
Page 49

Flowchart 6a Procedures
• Execute ioscan(1M) as follows:
Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
ioscan -kfd
Table 1-1, “List of Gigabit Ethernet Products”).
Verify output from ioscan shows card “CLAIMED” by the system.
• If card is claimed, execute lanscan(1M) and check if the hardware state display
shows “UP.” If so, go to Cable and LED Test.If not, continue to netfmt and lanadmin
Test.
• If card is not claimed, execute what /stand/vmunix | grep
drivername
documented in the Release Notes for your Gigabit Ethernet product. Use the name of
the running kernel image file in place of “/stand/vmunix” as appropriate.
• If driver is displayed, check if dmesg/syslog output shows error messages pertaining
to gelan/igelan. Also, check nettl log messages. If errors, check card installation and
reset and/or reseat card, then repeat ioscan and lanscan Test. Otherwise, call your
HP representative.
• If driver is not displayed, install driver using swinstall(1M) and verify or edit
/stand/system to contain gelan or igelan keyword. (See Chapter 3 of Installing and
Administering LAN/9000 Software for instructions on how to edit /stand/system
and create a new kernel.) Reboot system and repeat ioscan and lanscan Test.
drivername,
is as mentioned above. Verify if the output is similar to the output
where
drivername
is either gelan or igelan (refer to
drivername,
where
Chapter 4
47
Page 50

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 6b: netfmt and lanadmin Test
Verifies configuration of network interface on a host using netfmt(1M) and
lanadmin(1M).
Figure 4-11 Flowchart 6b
netfmt
and
lanadmin
Test
Execute netfmt.
Check causes and
actions in the log
output
Problem
solved?
NO
Reset card
YES
Reset
successful?
NO
Reset
card once
more; if still
not successful,
call HP.
YES
ifconfig Test
YES
Link Level Test
48
Chapter 4
Page 51

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 6b Procedures
• Execute netfmt(1M) and view error and disaster log messages.
Example: netfmt -vf /var/adm/nettl.LOG00
It will help to use the time stamp to find proper logs. Ensure you are looking at
1000Base-SX/T information.
• If problem is solved, continue to ifconfig Test.
• If problem persists, run lanadmin(1M) to reset card.
• If reset is successful, go to Link Level Test. Otherwise, reset the card once more; if
still not successful, call your HP representative.
Chapter 4
49
Page 52

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 6c: ifconfig Test
Verifies configuration of network interface on a host using ifconfig(1M).
Figure 4-12 Flowchart 6c
ifconfig
Test
Execute
ifconfig <interface>
<IP address>
netmask <netmask> up.
Execute
ifconfig <interface>
ifconfig
successful
?
YES
ifconfig entry in
/etc/rc.config.d/netconf
?
NO
Add network config
for card to
/etc/rc.config.d/netconf
Network
Level
Tests
NO
YES
Are flags
correct?
YES
Any error
messages
returned?
YES
Correct problem
according to
message received
NO
NO
Correct ifconfig
flag settings
Call HP
Repeat
ifconfig
Test
50
Chapter 4
Page 53

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 6c Procedures
• Execute ifconfig(1M) on the interface you want to configure to ensure that
interface is enabled. Example:
ifconfig lan1 192.6.1.17 netmask 255.255.255.0 up
Next, execute ifconfig
IP address is displayed. Example:
ifconfig lan1
<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST,CKO>
• If IP and flags are correct, verify there is an entry for card interface in
/etc/rc.config.d/netconf. If so, go to Network Level Tests. Otherwise, add
correct interface parameters to /etc/rc.config.d/netconf file and reboot. If
flags are incorrect, correct them with ifconfig and repeat ifconfig Test. Otherwise,
if ifconfig is not successful and error messages appear, correct them accordingly
and repeat ifconfig Test.
• If you cannot correct errors, call your HP representative.
interface
to test and verify flag setting is UP and correct
Chapter 4
51
Page 54

Troubleshooting
Diagnostic Flowcharts
52
Chapter 4
Page 55

A Gigabit Ethernet lanadmin Display
This appendix defines the terms listed in the lanadmin(1M) command display.
Appendix A
53
Page 56

Gigabit Ethernet lanadmin Display
LAN Interface Status Display
LAN Interface Status Display
The following is a sample of a lanadmin(1M) command display. The fields are defined in
the section that follows.
HP-UX 10.20 lanadmin output:
Network Management ID = 5
Description = lan3 HP 1000Base-SX Adapter HW Rev A-3814
Type (value) = ethernet-csmacd(6)
MTU Size = 1500
Speed = 1000000000
Station Address = 0x60b0c41121
Administration Status (value) = up(1)
Operation Status (value) = up(1)
Last Change = 1
Inbound Octets = 0
Inbound Unicast Packets = 0
Inbound Non-Unicast Packets = 0
Inbound Discards = 0
Inbound Errors = 0
Inbound Unknown Protocols = 0
Outbound Octets = 0
Outbound Unicast Packets = 0
Outbound Non-Unicast Packets = 0
Outbound Discards = 0
Outbound Errors = 0
Outbound Queue Length = 0
Specific = 655367
LAN INTERFACE STATUS DISPLAY
Sun, Jun 21,1998 14:39:36
54
Ethernet-like Statistics Group
Index = 5
Alignment Errors = 0
FCS Errors = 0
Single Collision Frames = 0
Multiple Collision Frames = 0
Deferred Transmissions = 0
Late Collisions = 0
Excessive Collisions = 0
Internal MAC Transmit Errors = 0
Carrier Sense Errors = 0
Frames Too Long = 0
Internal MAC Receive Errors = 0
Appendix A
Page 57

Gigabit Ethernet lanadmin Display
LAN Interface Status Display
HP-UX 11.0 lanadmin output:
LAN INTERFACE STATUS DISPLAY
Sun, Jun 21,1998 14:49:43
PPA Number = 3
Description = lan3 HP 1000Base-SX Adapter HW Rev
A-3814
Type (value) = ethernet-csmacd(6)
MTU Size = 1500
Speed = 1000000000
Station Address = 0x60b0c401d4
Administration Status (value) = up(1)
Operation Status (value) = up(1)
Last Change = 14
Inbound Octets = 2220359858
Inbound Unicast Packets = 87658661
Inbound Non-Unicast Packets = 577
Inbound Discards = 0
Inbound Errors = 0
Inbound Unknown Protocols = 0
Outbound Octets = 2729643634
Outbound Unicast Packets = 107383997
Outbound Non-Unicast Packets = 285158
Outbound Discards = 0
Outbound Errors = 0
Outbound Queue Length = 0
Specific = 655367
Ethernet-like Statistics Group
Index = 9
Alignment Errors = 0
FCS Errors = 0
Single Collision Frames = 0
Multiple Collision Frames = 0
Deferred Transmissions = 0
Late Collisions = 0
Excessive Collisions = 0
Internal MAC Transmit Errors = 0
Carrier Sense Errors = 0
Frames Too Long = 0
Internal MAC Receive Errors = 0
Appendix A
55
Page 58

Gigabit Ethernet lanadmin Display
RFC 1213 MIB II
RFC 1213 MIB II
Followingare descriptions of the statistics fields in the lanadmin(1M) command display.
For more detailed information about the fields, refer to RFC 1213.
Field Description
Network Management ID A unique ID assigned by the system for the network
PPA Number A unique number assigned to each network interface,
Description A textual string containing information about the
Type (value) The type of interface, distinguished according to the
management of each network interface.
distinct from NMID.
interface.
physical/link protocols, immediately below the
network layer in the protocol stack.
Gigabit Ethernet can have one of the following
values: ethernet or IEEE 802.3.
MTU Size The size of the largest datagram which can be
sent/received on the interface specified in octets. This
value can be 1500 or 9000.
Speed in bits per second The speed of the card — 1000 Mbps for 1000Base-SX
and 10, 100, or 1000 Mbps for 1000Base-T.
Station Address The interface address at the protocol layer
immediately below the network layer in the protocol
stack. For interfaces which do not have such an
address, such as serial line, this object contains an
octet string of zero length.
Administration Status The status of the card. This parameter is set to up(1)
and is not configurable. It will have one of the
following values:
up(1) Ready to pass packets
down(2) Not operative
testing(3) In test mode
Operation Status The status of the link. This value is the same as the
administration status. If the value is up, the link is
operational.
56
Last Change The value of SysUpTime at the time the interface
entered its current operational state. If the current
state was entered prior to the last reinitialization of
the local network management subsystem, then this
object contains a zero value.
Appendix A
Page 59

Gigabit Ethernet lanadmin Display
RFC 1213 MIB II
Inbound Octets The total number of octets received on the interface,
including framing characters.
Inbound Unicast Packets The number of subnetwork-unicast packets delivered
to a high-layer protocol.
Inbound Non-Unicast Packets The number of non-unicast (subnetwork-broadcast or
subnetwork-multicast) packets delivered to a
higher-layer protocol.
Inbound Discards The number of inbound packets that were discarded
even though no errors had been detected, preventing
them from being delivered to a higher-layerprotocol.
One possible reason for discarding such a packet
could be out of receive buffers.
Inbound Errors The number of inbound packets that contained
errors, preventing them from being deliverable to a
higher-layer protocol.
Inbound Unknown Protocols The number of packets received via the interface that
were discarded because of an unknown or
unsupported protocol.
Outbound Octets The total number of octets transmitted out of the
interface, including framing characters.
Outbound Unicast Packets The total number of packets that higher-level
protocols requested be transmitted to a
subnetwork-unicast address, including those that
were discarded or not sent.
Outbound Non-Unicast Packets The total number of packets that higher-level
protocols requested be transmitted to a non-unicast
(a subnetwork-broadcast or subnetwork-multicast)
address, including those that were discarded or not
sent.
Outbound Discards The number of outbound packets that were discarded
even though no errors had been detected to prevent
them from being transmitted. One possible reason for
discarding such a packet could be out of transmit
buffers.
Outbound Errors The number of outbound packets that could not be
transmitted because of errors.
Outbound Queue Length The length of the output packet queue (in packets).
Appendix A
57
Page 60

Gigabit Ethernet lanadmin Display
RFC 1284 Ethernet-Like Interface Statistics
RFC 1284 Ethernet-Like Interface Statistics
Following are descriptions of the Ethernet-like statistics fields in the lanadmin(1M)
command display.
Field Description
Index A value that uniquely identifies an interface to an
Alignment Errors A count of frames received on a particular interface
FCS Errors A count of frames received on a particular interface
Single Collision Frames A count of successfully transmitted frames on a
802.3 medium.
that are not an integral number of octets in length
and do not pass the FCS check.
that are not an integral number of octets in length
and do not pass the FCS check.
particular interface for which transmission is
inhibited by exactly one collision.
Multiple Collision Frames A count of successfully transmitted frames on a
particular interface for which transmission is
inhibited by more than one collision.
Deferred Transmissions A count of frames for which the first transmission
attempt on a particular interface is delayed because
the medium is busy. The count represented by an
instance of this object does not include frames
involved in collisions.
Late Collisions The number of times that a collision is detected on a
particular interface later than 512 bit-times into the
transmission of a packet.
Excessive Collisions A couple of frames for which transmission on a
particular interface fails due to excessive collisions or
packets dropped.
Internal MAC Transmit Errors A count of frames for which transmission on a
particular interface fails due to an internal MAC
sublayer transmit error.
Carrier Sense Errors The number of times that the carrier sense condition
was lost or never asserted when attempting to
transmit a frame on a particular interface.
Frames Too Long A count of frames received on a particular interface
that exceed the maximum permitted frame size.
58
Internal MAC Receive Errors Acount of frames for which reception on a particular
interface fails due to an internal MAC sublayer
receive error.
Appendix A
Page 61

B Gigabit Ethernet Card Statistics
This appendix defines the card statistics that are output from the lanadmin(1M)
command.
Appendix B
59
Page 62

Gigabit Ethernet Card Statistics
Card Statistics Output
Card Statistics Output
The following is a sample card statistics output. An explanation of the statistics is in the
section that follows.
****** Driver Statistics ******
In Packet Error 0
Out Packet Error 0
Loopback packets 0
Link down events 0
****** Host Command Statistics ******
nicCmdsDelMCastAddr 0
nicCmdsSetMACAddr 0
nicCmdsSetMulticastMode 0
micCmdsClearStats 0
****** NIC Events Statistics ******
nicEventsFirmwareOperational 1
nicEventsStatsUpdated 362765
nicEventsLinkStateChanged 1
nicEventsMCastListUpdated 1
****** Interface Statistics ******
ifIndex 4
ifType 6
ifMtu 1514
ifSpeed 1000000000
ifAdminStatus 1
ifOperStatus 1
ifLastChange 12
ifInDiscards 0
ifInErrors 0
ifInUnknownProtos 0
ifOutDiscards 0
ifOutErrors 0
ifOutQLen 0
ifInOctets_low 26719576
ifInOctets_high 0
ifInUcastPkts_low 0
ifInUcastPkts_high 0
ifInMulticastPkts_low 0
ifInMulticastPkts_high 0
ifInBroadcastPkts_low 382146
ifInBroadcastPkts_high 0
ifOutOctets_low 0
ifOutOctets_high 0
ifOutUcastPkts_low 0
ifOutUcastPkts_high 0
ifOutMulticastPkts_low 0
ifOutMulticastPkts_high 0
ifOutBroadcastPkts_low 0
ifOutBroadcastPkts_high 0
60
Appendix B
Page 63

Gigabit Ethernet Card Statistics
Explanation of Card Statistics
Explanation of Card Statistics
Following are descriptions of the card statistics that are output from the lanadmin(1M)
command.
Field Description
Driver Statistics
In Packet Error Number of inbound packets discarded because they
were received when the driver was not operational or
the packet length was incorrect.
Out Packet Error Number of outbound packets discarded because the
driver was not operational or the driver had
insufficient resources (Memory) to transmit the
packet.
Loopback packets Number of packets looped back to the upper layers by
the driver.
Link Down events Number of link down events, i.e., cable disconnects
processed by the driver.
Host Command Statistics
nicCmdsDelMCastAddr Number of times the driver has issued a command to
the NIC to delete a multicast MAC address.
nicCmdsSetPromiscMode Number of times the NIC received a command to
enable or disable promiscuous mode.
nicCmdsSetMACAddr Number of times the NIC received a command to set
the current MAC address.
nicCmdsClearStats Number of times the NIC received a command to
clear the card statistics maintained by the card.
NIC Events Statistics
nicEventsFirmwareOperational The number of events the driver has received from
the NIC indicating that the firmware on theNIC is in
the operational state.
nicEventsStatsUpdated The number of times the NIC has updated the MIB
interface statistics.
nicEventsLinkStateChanged The number of events the driver has processed
indicating that the status of the link has changed.
Appendix B
nicEventsMCastListUpdated The number of times the NIC generated an event to
report the addition or deletion of a multicast MAC
address.
Interface Statistics
These are the MIB statistics collected by the card as documented in RFC1066.
61
Page 64

Gigabit Ethernet Card Statistics
Explanation of Card Statistics
62
Appendix B
Page 65

C Hardware Reference Information
This appendix contains information about the card LEDs, cabling requirements, and
card specifications.
Appendix C
63
Page 66

Hardware Reference Information
The Meaning of the LEDs
The Meaning of the LEDs
The Link LED indicates the card’s status and must be on for the card to function
properly. Note that there is no Link LED on the 1000Base-T card. In its place are three
LEDs which indicate what speed (10, 100, or 1000 Mbps) the link has been established.
The following tables show the LED description and status.
Table C-1 LED Description and Status for 1000Base-SX
LED Description
and Color
Link - Green Good connection between
card and network at 1000
Mbps.
ACT (Activity) - Amber Data detected Data detected No data detected
On (Steady) Flashing Off
Port disabled by software, connection failed,
or card trying to
establish connection.
Note: A6847A is not
programmed to flash
the Link LED.
No connection
between card and
network
Table C-2 LED Description and Status for 1000Base-T
LED Description
and Color
1000 - Green
100 - Green
10 - Green
Note: Only one speed
LED should be on at
any given time.
Good connection between
card and network at either
10, 100, or 1000 Mbps as
indicated by LED.
Note: For A4929A, if all
Link speed LEDs are on
steady, the driver is disabled
or not installed.
On (Steady) Flashing Off
N/A No connection between
card and network.
ACT (Activity) - Amber
(Green on A6794A)
64
Data detected Data detected No data detected
Appendix C
Page 67

Hardware Reference Information
Cabling Requirements
Cabling Requirements
Connectors on LAN cards adhere to appropriate standards agreed upon by various
standards bodies and are widely available. The 1000Base-SX port is compatible with the
IEEE 802.3z standard and uses a single duplex SC connector. The 1000Base-T port is
compatible with the IEEE 802.3ab standard and uses an RJ-45 connector.
Incorrectly wired or installed cabling is the most common cause of communications
problems for local area networks. HP recommends that you work with a qualified cable
installer for assistance in your cabling requirements. The following tables summarize
cabling requirements:
Table C-3 Cabling Requirements for 1000Base-SX
Description
(850nm short-wave laser)
62.5 micron MMF
(multimode fibre)
50 micron MMF
(multimode fibre)
Modal Bandwidth Operating Distance
160 (MHz * km) 2 to 220 meters
200 (MHz * km) 2 to 275 meters
400 (MHz * km) 2 to 500 meters
500 (MHz * km) 2 to 550 meters
Table C-4 Cabling Requirements for 1000Base-T
Description Bandwidth Operating Distance
Cat 5 or Cat 5E UTP 100 MHz Up to 100 meters
Back-to-Back Connection
When running 1000Base-T back-to-back at either 10 or 100 Mbps, you must use a
crossover cable configuration. At 1000 Mbps, you can use either a crossover or
straight-through cable.
Appendix C
65
Page 68

Hardware Reference Information
Card Specifications
Card Specifications
For compliance to European directives and related specifications, see the Declaration of
Conformity statement in Appendix D.
A4924A/A4925A/A4926A
Physical
Dimensions (HSC for K):
Dimensions (HSC for D/R):
Dimensions (PCI):
Electrical
Power requirement (HSC):
Power requirement (PCI):
Environmental
Temperature
Degrees F = (1.8 x Degrees C) + 32
Operating Temperature:
Storage Temperature:
Humidity
Operating Relative Humidity
Range
5.625 in by 3.25 in
13.375 in by 4.875 in
6.73 in by 4.75 in
+15 watts max
+14 watts max
0o C to 55o C
-40o C to 70oC
5 to 85% non-condensing
40o C: 16 hour dwells at extremes
66
Non-operating/Storage
Humidity:
Altitude
Operating: 10,000 ft (3.1km)
Non-operating: 35,000 ft
Electromagnetic Compatibility
FCC Class A USA
CISPR-22/EN55022 Class A
EN55082-1
5 to 95% non-condensing
10o C/hour
International and Europe
Europe
Appendix C
Page 69

VCCI Class A (PCI card only) Japan
A4929A
Physical
Dimensions: 6.73 in by 4.75 in
Electrical
Power requirement: +14 watts max
Environmental
Temperature
Degrees F = (1.8 x Degrees C) + 32
Hardware Reference Information
Card Specifications
Operating Temperature:
Storage Temperature:
Humidity
Operating Relative Humidity
Range
Non-operating/Storage
Humidity:
Altitude
Operating: 10,000 ft (3.1km)
Non-operating: 35,000 ft
Electromagnetic Compatibility
FCC Class A USA
CISPR-22/EN55022 Class A
0o C to 45o C
-40o C to 70oC
15 to 80% non-condensing
40o C: 16 hour dwells at extremes
5 to 95% non-condensing
10o C/hour
International and Europe
Appendix C
EN55082-1
VCCI Class A Japan
Europe
67
Page 70

Hardware Reference Information
Card Specifications
A6825A/A6847A
Physical
Dimensions: 6.6 in by 2.5 in
Electrical
Power requirement: +8 watts max
Environmental
Temperature
Degrees F = (1.8 x Degrees C) + 32
Operating Temperature:
Storage Temperature:
Humidity
Operating Relative humidity
range
Non-operating/storage
humidity:
Altitude
Operating: 10,000 ft (3.1km)
Non-operating: 35,000 ft
Electromagnetic Compatibility
FCC Class A USA
CISPR-22/EN55022 Class A
0o C to 50o C
-40o C to 60oC
5 to 95% non-condensing
(40o C: 16 hour dwells at extremes)
5 to 95% non-condensing
20o C/hour
International and Europe
68
CISPR-24
VCCI Class A Japan
Europe
Appendix C
Page 71

D Hardware Regulatory Statements
This appendix contains regulatory statements for the United States, Canada,
Australia/New Zealand, Japan, and the European community.
Appendix D
71
Page 72

Hardware Regulatory Statements
FCC Statement (For U.S.A.)
FCC Statement (For U.S.A.)
Federal Communications Commission Radio Frequency Interference
Statement
WARNING This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC rules. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
(1) This device may not cause harmful interference and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference
that might cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when
the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy, and, if not installed
and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
interference, in which case the user at his own expense will be required to
take whatever measures may be required to correct the interference.
Hewlett-Packard’s system certification tests were conducted with
HP-supported peripheral devices and cables, such as those received with your
system. Changes or modifications to this equipment not expressly approved by
Hewlett-Packard could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Canada
Warning: This Class A digital apparatus meets all requirements of the Canadian
Interference-Causing Equipment Regulations.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A respecte toutes les exigences du règlement sur le
matériel brouilleur du Canada.
72
Appendix D
Page 73

Hardware Regulatory Statements
EMI (Australia and New Zealand)
EMI (Australia and New Zealand)
This product meets the applicable requirements of the Australia and New Zealand EMC
Framework.
VCCI (Japan) (PCI Card Only)
This equipment complies with the Class A category for information technology
equipment based on the rules of Voluntary Control Council for Interference by
Information Technology Equipment. When used in a residential area, radio interference
may be caused. In this case, the user may be required to take appropriate corrective
actions.
Figure D-1 VCCI Regulatory Statement
EMI Statement (European Community)
NOTE This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case you may be required to take adequate measures.
Appendix D
73
Page 74

Hardware Regulatory Statements
Laser Safety Statements
Laser Safety Statements
Laser Safety Statements - U.S. FDA/CDRH - Optical (laser) Transceiver
CAUTION The optical transceiver provided on the network interface card contains a laser system
and is classified as a “Class-I Laser Product” under a U.S. Department of Health and
Human Services (DHHS) Radiation Performance standard according to the Radiation
Control for Health and Safety Act of 1968. The Class I label and compliance statement
are located on the optical transceiver.
To ensure proper use of this product, please read this instruction manual carefully and
retain for future reference. Should the unit ever require maintenance, contact an
authorized service location.
CAUTION Use of controls, adjustments or the performance procedures other than those specified
herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure. To prevent direct exposure to laser
beam, do not try to open the enclosure.
Laser Safety - European Union - Optical Transceiver Only
CAUTION The optical transceiver provided on the network interface card contains a laser system
and is classified as a “Class 1 Laser Product” per EN 60825-1, Safety of Laser products.
Class 1 laser products are considered safe and do not pose a biological hazard if used
within the data sheet limits and instructions.
To ensure proper use of this product, please read this instruction manual carefully and
retain for future reference. Should the unit ever require maintenance, contact an
authorized service location.
CAUTION Use of controls, adjustments or the performance procedures other than those specified
herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure. To prevent direct exposure to laser
beam, do not try to open the enclosure.
There are no user serviceable parts nor any maintenance required for the optical
transceiver. All adjustments are made at the factory before shipment to customers.
Tampering with or any attempt to modify the optical transceiver will result in voided
product warranty. It may also result in improper operation of the network card circuitry
and possible overstress of the laser source. Device degradation or product failure may
result.
74
Appendix D
Page 75

Hardware Regulatory Statements
Laser Safety Statements
Appendix D
75
Page 76

Hardware Regulatory Statements
Laser Safety Statements
76
Appendix D
Page 77

Hardware Regulatory Statements
Laser Safety Statements
Appendix D
77
Page 78

Hardware Regulatory Statements
Laser Safety Statements
78
Appendix D
Page 79

Glossary
Numerics
1000Base-SX: A specific implementation of
1000Mbps operating over two multimode fiber
cables, as specified in Standard IEEE
802.3z/D.50-1998.
1000Base-T: A specific implementation of 1000
Mbps operating over four-pair Cat-5 or Cat-5e UTP
cables, as specified in IEEE 802.3ab standards.
A
Alias: Name of the interface that corresponds to a
given Internet address on a system.
Autonegotiation: A mechanism defined in IEEE
802.3u-1995 whereby devices sharing a link segment
can exchange data and automatically configure
themselves to operate at the highest capability mode
shared between them. This is also used for link
configuration per IEEE 802.3z and IEEE 802.3ab
standards of duplex and flow control configuration
between two 1000Base-SX/T links.
C
Card Instance Number: A number that uniquely
identifies a device within a class. A class of devices is
a logical grouping of similar devices.
D
Destination Address: A field in the message
packet format identifying the end node(s) to which
the packet is being sent.
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
DLPI: Data Link Provider Interface. An
industry-standard definition for message
communications to STREAMS-based network
interface drivers.
E
F
Fast Ethernet: A commonly used name applied to
100Base-T.
Full-Duplex Mode: A mode of media utilization
whereby data can flow in both directions
simultaneously across the multiple wire pairs of a
physical link. While full-duplex operation is not
defined per se in the IEEE 802.3u-1995 specification,
the specification does define a mechanism for this
mode to be autonegotiated between devices on each
end of a link. Full-duplex mode is typically found on
switches.
H
HSC: High-speed connect bus.
Half-Duplex Mode: The media utilization mode of
IEEE 802.3u-1995 networks whereby data can flow
in only one direction at a time across the multiple
wire pairs of a physical link.
Hardware Path: An identifier assigned by the
system according to the physical location (slot) of the
card in the hardware backplane. On HP servers, the
I/O subsystem identifies each LAN card by its
hardware path.
Hostname: Name of system on the network.
Hub: A network interconnection device that allows
multiple devices to share a single logical link
segment.
I
IEEE: The Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers. A national association, whose activities
include publishing standards applicable to various
electronic technologies. The IEEE technical
committees are numbered and grouped by area. The
802.3 committee produced the standard for LAN
networks.
Ethernet: A 10 Mbps LAN, developed by Digital
Equipment Corporation, Intel, and Xerox
Corporation, upon which the IEEE 802.3 network is
based.
Glossary
IEEE 802.3u-1995 network: A 10 or 100 Mbps
LAN, specified in the IEEE 802.3u-1995 Standard
for Local Area Networks. It uses the Carrier Sense
Multiple Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
network access method to give every node equal
access to the network.
79
Page 80

Glossary
Internet Address: The network address of a
computer node. This address identifies both which
network the host is on and which host it is. Refer to
the Installing and Administering LAN/9000
Software manual for detailed information about
network addressing.
IP Address: See Internet Address.
L
LAN: See Local Area Network.
Local Area Network (LAN): A data
communications system that allows a number of
independent devices to communicate with each
other.
Local Network: The network to which a node is
directly attached.
M
Major Number: Unique value that identifies an
individual hardware device.
Node: Any point in a network where services are
provided or communications channels are
interconnected. A node could be a workstation or a
server processor.
O
Online Addition/Replacement (OLA/R): The
ability of a PCI I/O card to be added or replaced
without the need to shut down or reboot the system.
For instructions on how to perform OLA/R, refer to
Configuring HP-UX For Peripherals.
P
PCI: Peripheral Component Interconnect.
Packet: A sequence of binary digits that is
transmitted as a unit in a computer network. A
packet usually contains control information plus
data.
Physical Point of Attachment: A unique number
assigned to each network interface, distinct from
NMID.
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU): Largest
amount of data that can be transmitted through that
interface. This value does not include the LLC or
MAC headers.
Mbps: Megabits per second
MBps: Megabytes per second
MTU: See Maximum Transmission Unit
N
Network Interface: A communication path
through which messages can be sent and received. A
hardware network interface has a hardware device
associated with it, such as a LAN or FDDI card. A
software network interface does not include a
hardware device, for example, the loopback
interface. For every IP address instance, there must
be one network interface configured.
Network Management Identifier (NMID): A
unique ID assigned by the system for the network
management of each network interface.
NMID: See Network Management Identifier
PMTU: Path MTU
PPA: See Physical Point of Attachment
Protocol: A specification for coding messages
exchanged between two communications processes.
R
RJ-45: The name for the connector type used with
UTP cabling.
S
Subnetwork: Small discrete physical networks
connected via gateways which share the same
network address space. Refer to Installing and
Administering LAN/9000 Software for detailed
information about subnetworks and subnet
addressing.
Subnet mask: A 32-bit mask which, when AND'd
with an internet address, determines a subnetwork
address. When the internet address is AND'd with
the subnet mask, the ones in the host portion of the
subnet mask will “overwrite” the corresponding bits
of the host portion of the internet address, resulting
8080
Glossary
Page 81

in the subnet address. Refer to Installing and
Administering LAN/9000 Software for detailed
information about subnet masks.
Switch: A network interconnection device that
allows multiple connected senders and receivers to
communicate simultaneously in contrast to a hub
(repeater) where only one device can send at a time.
Some switches have fixed port speeds (10 or 100
Mbps) while others allow port speeds to be
configured or autonegotiated.
T
Topology: The physical and logical geometry
governing placement of nodes in a computer
network. Also, the layout of the transmission
medium for a network.
U
Glossary
Unshielded Twisted Pair: A data cable type
consisting of pairs of wires twisted together without
an electrically shielding jacket.
UTP: See Unshielded Twisted Pair
Glossary
81
 Loading...
Loading...